Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips

How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, what is your plagiarism score.

Argument and Persuasion: Structuring and Writing an Argument Essay
- Find Articles
- Structuring and Writing an Argument Essay
Page Overview
This page deals with the process of writing the argument: planning, structuring, strategies, writing, revision.
Pre-Writing Considerations
There are things that should be given some attention before you begin writing your argument. Thoughtful planning in the pre-writing stage increases the chances of your argument successfully convincing your audience. A well-executed piece of writing should be unified, coherent, and complete.
unified = the paper presents only a single idea or, if more than one idea, one point is made the principal one and the others are subordinated to it
coherent = the discussion flows smoothly and logically and is easy for the reader to follow; trying to make sense of the writing does not become an ordeal
complete = everything that should be said, has been said; no questions are left in the mind of the reader
Achieving a coherent, complete, unified piece of Argumentative Writing
1. Clearly state the argument/proposition of your essay.
2. Analyze the proposition. First, jot down points of conflict between your view and the opposing view. Second, think over your jottings and try to decide which points are the issues on which your argument should hinge. Third, arrange your jottings in order to give unity and coherence to your essay.
3. Write a paragraph (or more if necessary) on each point of conflict. (This step will have some variation, depending on whether you are using the block or point pattern of organization.)
4. Analyze and evaluate what you have written to see whether (a) the evidence seems reliable and (b) the reasoning free of fallacies.
5. Establish effective transitions between the discussions of the various points ( coherence ), keeping in mind that your objective is to connect each point to the main contention of your theme, the main proposition.
6. Think of your introduction. What makes the topic worth arguing about now (purpose)? (NOTE: Your topic should be broad enough to interest a large number of people, yet narrow enough that you can focus and manage the discussion.) What kind of people are you writing for (audience)? Can you depend on an interested and sympathetic hearing, or must you strive to gain attention and win people over? If you have to gain attention, how will you go about it? After you have thought about these things and written a first draft of your introduction, do you think it necessary to go back and revise the discussion in the body of your essay to make it better adapted to your audience?
7. Treat your conclusion as the last impression you will leave on your readers. Do you return here to your key point (your thesis), showing how your whole argument essay bears on and supports it? Do you leave your readers with a positive impression of your effort, even if you cannot be sure of having totally convinced them by reason?
Outlines for an Argument Essay
Pattern Outlines for an Argument Essay
(Based on https://apps.spokane.edu/.../Summary%20Response%20Essay%20Assignment.pdf
In the context of argument, "pro" means agree/support, and "con" means disagree/oppose. Whether you structure your argument to follow the block style or point-by-point pattern, the three principal components of presentation, support, and refutation must be included. A point-by-point structure probably will be easier to follow, as the block style creates some separation between the "pro" and "con" sides of an argument which may require readers to do some up-and-down "scrolling" of the text.
Breaking it Down in Detail
- Argument Deconstructed Source: Mesa Community College. Provides multiple links to cover argument in-depth and from many aspects. Includes argument essay charts, outlines, and worksheets.
Defining Arguments: defines what argument is and is not while providing some insights on laying the groundwork before the writing begins
How To Create an Argument: covers the stages of pre-writng, writing, and revising an argument
Argument at a Glance: P.A.P.A.: a blank page with no content
Argument Claims: discusses types of claims and perspectives from which to launch your argument; includes links to sample readings
Argument Outline: provides outlines for various argument structures and types and also contains worksheets for preparing an argument
Rogerian Argument: explains an alternative approach to the "traditional" argumentative style
Ethos, Logos, and Pathos: offers tips on how to interact with the audience in an argumentative context
Fallacies: a glossary of things to avoid
Sample Essays: a selection of seven argumentative essays written by students
Argument on the Web
The Purdue OWL: The OWL is the Online Writing Laboratory maintained by Purdue University. It is a comprehensive, encyclopedic online reference source for nearly all aspects of research and writing, from topic selection to citation styles and source evaluation. Every serious researcher should bookmark the OWL.
For information regarding writing argumentative papers, either type "Purdue OWL" argument into an internet search box. The first page of results provides links to more specific aspects of writing argument. Or, you can type the word argument into the "Search the OWL" box (https://owl.purdue.edu/search.html). Once you have landed on any OWL screen, it is good to scan the left pane for other pages which you may find useful.
CAVEAT: Purdue OWL has merged with Chegg, a for-profit company who has created a citation machine service for citation management. This partnership has resulted in pop-up advertisements appearing on OWL screens as well as permitting Chegg influence on OWL's citation help pages. Those using the OWL may wish to keep these things in mind.
Useful options besides the Purdue OWL are
- Excelsior College Online Writing Lab ( https://owl.excelsior.edu/ )
- Massey University OWLL ( http://owll.massey.ac.nz/index.php )
To locate information on the internet on argument, in the search box type argument along with a modifying term such as writing or structure.
To locate additional LibGuides on argument on the internet, in the search box type argument libguide.
- << Previous: Find Books
- Last Updated: Nov 8, 2023 1:49 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jsu.edu/argument

What this handout is about
This handout will define what an argument is and explain why you need one in most of your academic essays.
Arguments are everywhere
You may be surprised to hear that the word “argument” does not have to be written anywhere in your assignment for it to be an important part of your task. In fact, making an argument—expressing a point of view on a subject and supporting it with evidence—is often the aim of academic writing. Your instructors may assume that you know this and thus may not explain the importance of arguments in class.
Most material you learn in college is or has been debated by someone, somewhere, at some time. Even when the material you read or hear is presented as a simple fact, it may actually be one person’s interpretation of a set of information. Instructors may call on you to examine that interpretation and defend it, refute it, or offer some new view of your own. In writing assignments, you will almost always need to do more than just summarize information that you have gathered or regurgitate facts that have been discussed in class. You will need to develop a point of view on or interpretation of that material and provide evidence for your position.
Consider an example. For nearly 2000 years, educated people in many Western cultures believed that bloodletting—deliberately causing a sick person to lose blood—was the most effective treatment for a variety of illnesses. The claim that bloodletting is beneficial to human health was not widely questioned until the 1800s, and some physicians continued to recommend bloodletting as late as the 1920s. Medical practices have now changed because some people began to doubt the effectiveness of bloodletting; these people argued against it and provided convincing evidence. Human knowledge grows out of such differences of opinion, and scholars like your instructors spend their lives engaged in debate over what claims may be counted as accurate in their fields. In their courses, they want you to engage in similar kinds of critical thinking and debate.
Argumentation is not just what your instructors do. We all use argumentation on a daily basis, and you probably already have some skill at crafting an argument. The more you improve your skills in this area, the better you will be at thinking critically, reasoning, making choices, and weighing evidence.
Making a claim
What is an argument? In academic writing, an argument is usually a main idea, often called a “claim” or “thesis statement,” backed up with evidence that supports the idea. In the majority of college papers, you will need to make some sort of claim and use evidence to support it, and your ability to do this well will separate your papers from those of students who see assignments as mere accumulations of fact and detail. In other words, gone are the happy days of being given a “topic” about which you can write anything. It is time to stake out a position and prove why it is a good position for a thinking person to hold. See our handout on thesis statements .
Claims can be as simple as “Protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged,” with evidence such as, “In this experiment, protons and electrons acted in such and such a way.” Claims can also be as complex as “Genre is the most important element to the contract of expectations between filmmaker and audience,” using reasoning and evidence such as, “defying genre expectations can create a complete apocalypse of story form and content, leaving us stranded in a sort of genre-less abyss.” In either case, the rest of your paper will detail the reasoning and evidence that have led you to believe that your position is best.
When beginning to write a paper, ask yourself, “What is my point?” For example, the point of this handout is to help you become a better writer, and we are arguing that an important step in the process of writing effective arguments is understanding the concept of argumentation. If your papers do not have a main point, they cannot be arguing for anything. Asking yourself what your point is can help you avoid a mere “information dump.” Consider this: your instructors probably know a lot more than you do about your subject matter. Why, then, would you want to provide them with material they already know? Instructors are usually looking for two things:
- Proof that you understand the material
- A demonstration of your ability to use or apply the material in ways that go beyond what you have read or heard.
This second part can be done in many ways: you can critique the material, apply it to something else, or even just explain it in a different way. In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue.
Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as “Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.” Such a statement might capture your initial impressions of Wright as you have studied him in class; however, you need to look deeper and express specifically what caused that “greatness.” Your instructor will probably expect something more complicated, such as “Frank Lloyd Wright’s architecture combines elements of European modernism, Asian aesthetic form, and locally found materials to create a unique new style,” or “There are many strong similarities between Wright’s building designs and those of his mother, which suggests that he may have borrowed some of her ideas.” To develop your argument, you would then define your terms and prove your claim with evidence from Wright’s drawings and buildings and those of the other architects you mentioned.
Do not stop with having a point. You have to back up your point with evidence. The strength of your evidence, and your use of it, can make or break your argument. See our handout on evidence . You already have the natural inclination for this type of thinking, if not in an academic setting. Think about how you talked your parents into letting you borrow the family car. Did you present them with lots of instances of your past trustworthiness? Did you make them feel guilty because your friends’ parents all let them drive? Did you whine until they just wanted you to shut up? Did you look up statistics on teen driving and use them to show how you didn’t fit the dangerous-driver profile? These are all types of argumentation, and they exist in academia in similar forms.
Every field has slightly different requirements for acceptable evidence, so familiarize yourself with some arguments from within that field instead of just applying whatever evidence you like best. Pay attention to your textbooks and your instructor’s lectures. What types of argument and evidence are they using? The type of evidence that sways an English instructor may not work to convince a sociology instructor. Find out what counts as proof that something is true in that field. Is it statistics, a logical development of points, something from the object being discussed (art work, text, culture, or atom), the way something works, or some combination of more than one of these things?
Be consistent with your evidence. Unlike negotiating for the use of your parents’ car, a college paper is not the place for an all-out blitz of every type of argument. You can often use more than one type of evidence within a paper, but make sure that within each section you are providing the reader with evidence appropriate to each claim. So, if you start a paragraph or section with a statement like “Putting the student seating area closer to the basketball court will raise player performance,” do not follow with your evidence on how much more money the university could raise by letting more students go to games for free. Information about how fan support raises player morale, which then results in better play, would be a better follow-up. Your next section could offer clear reasons why undergraduates have as much or more right to attend an undergraduate event as wealthy alumni—but this information would not go in the same section as the fan support stuff. You cannot convince a confused person, so keep things tidy and ordered.
Counterargument
One way to strengthen your argument and show that you have a deep understanding of the issue you are discussing is to anticipate and address counterarguments or objections. By considering what someone who disagrees with your position might have to say about your argument, you show that you have thought things through, and you dispose of some of the reasons your audience might have for not accepting your argument. Recall our discussion of student seating in the Dean Dome. To make the most effective argument possible, you should consider not only what students would say about seating but also what alumni who have paid a lot to get good seats might say.
You can generate counterarguments by asking yourself how someone who disagrees with you might respond to each of the points you’ve made or your position as a whole. If you can’t immediately imagine another position, here are some strategies to try:
- Do some research. It may seem to you that no one could possibly disagree with the position you are arguing, but someone probably has. For example, some people argue that a hotdog is a sandwich. If you are making an argument concerning, for example, the characteristics of an exceptional sandwich, you might want to see what some of these people have to say.
- Talk with a friend or with your teacher. Another person may be able to imagine counterarguments that haven’t occurred to you.
- Consider your conclusion or claim and the premises of your argument and imagine someone who denies each of them. For example, if you argued, “Cats make the best pets. This is because they are clean and independent,” you might imagine someone saying, “Cats do not make the best pets. They are dirty and needy.”
Once you have thought up some counterarguments, consider how you will respond to them—will you concede that your opponent has a point but explain why your audience should nonetheless accept your argument? Will you reject the counterargument and explain why it is mistaken? Either way, you will want to leave your reader with a sense that your argument is stronger than opposing arguments.
When you are summarizing opposing arguments, be charitable. Present each argument fairly and objectively, rather than trying to make it look foolish. You want to show that you have considered the many sides of the issue. If you simply attack or caricature your opponent (also referred to as presenting a “straw man”), you suggest that your argument is only capable of defeating an extremely weak adversary, which may undermine your argument rather than enhance it.
It is usually better to consider one or two serious counterarguments in some depth, rather than to give a long but superficial list of many different counterarguments and replies.
Be sure that your reply is consistent with your original argument. If considering a counterargument changes your position, you will need to go back and revise your original argument accordingly.
Audience is a very important consideration in argument. Take a look at our handout on audience . A lifetime of dealing with your family members has helped you figure out which arguments work best to persuade each of them. Maybe whining works with one parent, but the other will only accept cold, hard statistics. Your kid brother may listen only to the sound of money in his palm. It’s usually wise to think of your audience in an academic setting as someone who is perfectly smart but who doesn’t necessarily agree with you. You are not just expressing your opinion in an argument (“It’s true because I said so”), and in most cases your audience will know something about the subject at hand—so you will need sturdy proof. At the same time, do not think of your audience as capable of reading your mind. You have to come out and state both your claim and your evidence clearly. Do not assume that because the instructor knows the material, he or she understands what part of it you are using, what you think about it, and why you have taken the position you’ve chosen.
Critical reading
Critical reading is a big part of understanding argument. Although some of the material you read will be very persuasive, do not fall under the spell of the printed word as authority. Very few of your instructors think of the texts they assign as the last word on the subject. Remember that the author of every text has an agenda, something that he or she wants you to believe. This is OK—everything is written from someone’s perspective—but it’s a good thing to be aware of. For more information on objectivity and bias and on reading sources carefully, read our handouts on evaluating print sources and reading to write .
Take notes either in the margins of your source (if you are using a photocopy or your own book) or on a separate sheet as you read. Put away that highlighter! Simply highlighting a text is good for memorizing the main ideas in that text—it does not encourage critical reading. Part of your goal as a reader should be to put the author’s ideas in your own words. Then you can stop thinking of these ideas as facts and start thinking of them as arguments.
When you read, ask yourself questions like “What is the author trying to prove?” and “What is the author assuming I will agree with?” Do you agree with the author? Does the author adequately defend her argument? What kind of proof does she use? Is there something she leaves out that you would put in? Does putting it in hurt her argument? As you get used to reading critically, you will start to see the sometimes hidden agendas of other writers, and you can use this skill to improve your own ability to craft effective arguments.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Booth, Wayne C., Gregory G. Colomb, Joseph M. Williams, Joseph Bizup, and William T. FitzGerald. 2016. The Craft of Research , 4th ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Ede, Lisa. 2004. Work in Progress: A Guide to Academic Writing and Revising , 6th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Gage, John T. 2005. The Shape of Reason: Argumentative Writing in College , 4th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A., and John J. Ruszkiewicz. 2016. Everything’s an Argument , 7th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Kirsten DeVries
At school, at work, and in everyday life, argument is one of main ways we exchange ideas with one another. Academics, business people, scientists, and other professionals all make arguments to determine what to do or think, or to solve a problem by enlisting others to do or believe something they otherwise would not. Not surprisingly, then, argument dominates writing, and training in argument writing is essential for all college students.
This chapter will explore how to define argument and how to talk about arguments.
1. What Is Argument?
2. What Are the Components and Vocabulary of Argument?
1. What Is Argument?
All people, including you, make arguments on a regular basis. When you make a claim and then support the claim with reasons, you are making an argument. Consider the following:
- If, as a teenager, you ever made a case for borrowing your parents’ car using reasonable support—a track record of responsibility in other areas of your life, a good rating from your driving instructor, and promises to follow rules of driving conduct laid out by your parents—you have made an argument.
- If, as an employee, you ever persuaded your boss to give you a raise using concrete evidence—records of sales increases in your sector, a work calendar with no missed days, and personal testimonials from satisfied customers—you have made an argument.
- If, as a gardener, you ever shared your crops at a farmer’s market, declaring that your produce is better than others using relevant support—because you used the most appropriate soil, water level, and growing time for each crop—you’ve made an argument.
- If, as a literature student, you ever wrote an essay on your interpretation of a poem—defending your ideas with examples from the text and logical explanations for how those examples demonstrate your interpretation—you have made an argument.
The two main models of argument desired in college courses as part of the training for academic or professional life are rhetorical argument and academic argument . If rhetoric is the study of the craft of writing and speaking, particularly writing or speaking designed to convince and persuade, the student studying rhetorical argument focuses on how to create an argument that convinces and persuades effectively. To that end, the student must understand how to think broadly about argument, the particular vocabulary of argument, and the logic of argument. The close sibling of rhetorical argument is academic argument, argument used to discuss and evaluate ideas, usually within a professional field of study, and to convince others of those ideas. In academic argument , interpretation and research play the central roles.
However, it would be incorrect to say that academic argument and rhetorical argument do not overlap. Indeed, they do, and often. A psychologist not only wishes to prove an important idea with research, but she will also wish to do so in the most effective way possible. A politician will want to make the most persuasive case for his side, but he should also be mindful of data that may support his points. Thus, throughout this chapter, when you see the term argument , it refers to a broad category including both rhetorical and academic argument .
Before moving to the specific parts and vocabulary of argument, it will be helpful to consider some further ideas about what argument is and what it is not.
Argument vs. Controversy or Fight
Consumers of written texts are often tempted to divide writing into two categories: argumentative and non-argumentative. According to this view, to be argumentative, writing must have the following qualities: It has to defend a position in a debate between two or more opposing sides, it must be on a controversial topic, and the goal of such writing must be to prove the correctness of one point of view over another.
A related definition of argument implies a confrontation, a clash of opinions and personalities, or just a plain verbal fight. It implies a winner and a loser, a right side and a wrong one. Because of this understanding of the word “argument,” many students think the only type of argument writing is the debate-like position paper, in which the author defends his or her point of view against other, usually opposing, points of view.
These two characteristics of argument—as controversial and as a fight—limit the definition because arguments come in different disguises, from hidden to subtle to commanding. It is useful to look at the term “argument” in a new way. What if we think of argument as an opportunity for conversation, for sharing with others our point of view on an issue, for showing others our perspective of the world? What if we think of argument as an opportunity to connect with the points of view of others rather than defeating those points of view?
One community that values argument as a type of communication and exchange is the community of scholars. They advance their arguments to share research and new ways of thinking about topics. Biologists, for example, do not gather data and write up analyses of the results because they wish to fight with other biologists, even if they disagree with the ideas of other biologists. They wish to share their discoveries and get feedback on their ideas. When historians put forth an argument, they do so often while building on the arguments of other historians who came before them. Literature scholars publish their interpretations of different works of literature to enhance understanding and share new views, not necessarily to have one interpretation replace all others. There may be debates within any field of study, but those debates can be healthy and constructive if they mean even more scholars come together to explore the ideas involved in those debates. Thus, be prepared for your college professors to have a much broader view of argument than a mere fight over a controversial topic or two.
Argument vs. Opinion
Argument is often confused with opinion. Indeed, arguments and opinions sound alike. Someone with an opinion asserts a claim that he thinks is true. Someone with an argument asserts a claim that she thinks is true. Although arguments and opinions do sound the same, there are two important differences:
- Arguments have rules; opinions do not . In other words, to form an argument, you must consider whether the argument is reasonable. Is it worth making? Is it valid? Is it sound? Do all of its parts fit together logically? Opinions, on the other hand, have no rules, and anyone asserting an opinion need not think it through for it to count as one; however, it will not count as an argument.
- Arguments have support; opinions do not . If you make a claim and then stop, as if the claim itself were enough to demonstrate its truthfulness, you have asserted an opinion only. An argument must be supported, and the support of an argument has its own rules. The support must also be reasonable, relevant, and sufficient.
Figure 3.1 “Opinion vs Argument”

Argument vs. Thesis
Another point of confusion is the difference between an argument and an essay’s thesis . For college essays, there is no essential difference between an argument and a thesis; most professors use these terms interchangeably. An argument is a claim that you must then support. The main claim of an essay is the point of the essay and provides the purpose for the essay. Thus, the main claim of an essay is also the thesis. For more on the thesis, see Chapter 4, “ The Writing Process.”
Consider this as well: Most formal essays center upon one main claim (the thesis) but then support that main claim with supporting evidence and arguments. The topic sentence of a body paragraph can be another type of argument, though a supporting one, and, hence, a narrower one. Try not to be confused when professors call both the thesis and topic sentences arguments. They are not wrong because arguments come in different forms; some claims are broad enough to be broken down into a number of supporting arguments. Many longer essays are structured by the smaller arguments that are a part of and support the main argument. Sometimes professors, when they say supporting points or supporting arguments, mean the reasons ( premises ) for the main claim ( conclusion ) you make in an essay. If a claim has a number of reasons, those reasons will form the support structure for the essay, and each reason will be the basis for the topic sentence of its body paragraph.
Argument vs. Fact
Arguments are also commonly mistaken for statements of fact. This comes about because often people privilege facts over opinions, even as they defend the right to have opinions. In other words, facts are “good,” and opinions are “bad,” or if not exactly bad, then fuzzy and thus easy to reject. However, remember the important distinction between an argument and an opinion stated above: While argument may sound like an opinion, the two are not the same. An opinion is an assertion, but it is left to stand alone with little to no reasoning or support. An argument is much stronger because it includes and demonstrates reasons and support for its claim.
As for mistaking a fact for an argument, keep this important distinction in mind: An argument must be arguable . In everyday life, arguable is often a synonym for doubtful. For an argument, though, arguable means that it is worth arguing, that it has a range of possible answers, angles, or perspectives: It is an answer, angle, or perspective with which a reasonable person might disagree. Facts, by virtue of being facts, are not arguable. Facts are statements that can be definitely proven using objective data. The statement that is a fact is absolutely valid. In other words, the statement can be pronounced as definitively true or definitively false. For example, 2 + 2 = 4. This expression identifies a verifiably true statement, or a fact, because it can be proved with objective data. When a fact is established, there is no other side, and there should be no disagreement.
The misunderstanding about facts (being inherently good) and argument (being inherently problematic because it is not a fact) leads to the mistaken belief that facts have no place in an argument. This could not be farther from the truth. First of all, most arguments are formed by analyzing facts. Second, facts provide one type of support for an argument. Thus, do not think of facts and arguments as enemies; rather, they work closely together.
Explicit vs. Implicit Arguments
Arguments can be both explicit and implicit. Explicit arguments contain prominent and definable thesis statements and multiple specific proofs to support them. This is common in academic writing from scholars of all fields. Implicit arguments , on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement. Implicit arguments involve evidence of many different kinds to build and convey their point of view to their audience. Both types use rhetoric, logic, and support to create effective arguments.
Argument and Rhetoric
An argument in written form involves making choices, and knowing the principles of rhetoric allows a writer to make informed choices about various aspects of the writing process. Every act of writing takes place in a specific rhetorical situation. The most basic and important components of a rhetorical situation are
- Author of the text.
- Purpose of the text.
- Intended audience (i.e., those the author imagines will be reading the text).
- Form or type of text.
These components give readers a way to analyze a text on first encounter. These factors also help writers select their topics, arrange their material, and make other important decisions about the argument they will make and the support they will need. For more on rhetoric, see Chapter 2, “Rhetorical Analysis.”
Key Takeaways: What is an Argument?
With this brief introduction, you can see what rhetorical or academic argument is not :
- An argument need not be controversial or about a controversy.
- An argument is not a mere fight.
- An argument does not have a single winner or loser.
- An argument is not a mere opinion.
- An argument is not a statement of fact.
Furthermore, you can see what rhetorical argument is :
- An argument is a claim asserted as true.
- An argument is arguable.
- An argument must be reasonable.
- An argument must be supported.
- An argument in a formal essay is called a thesis. Supporting arguments can be called topic sentences.
- An argument can be explicit or implicit.
- An argument must be adapted to its rhetorical situation.
2. What Are the Components and Vocabulary of Argument?
Questions are at the core of arguments. What matters is not just that you believe that what you have to say is true, but that you give others viable reasons to believe it as well—and also show them that you have considered the issue from multiple angles. To do that, build your argument out of the answers to the five questions a rational reader will expect answers to. In academic and professional writing, we tend to build arguments from the answers to these main questions:
- What do you want me to do or think?
- Why should I do or think that?
- How do I know that what you say is true?
- Why should I accept the reasons that support your claim?
- What about this other idea, fact, or consideration?
- How should you present your argument?
When you ask people to do or think something they otherwise would not, they quite naturally want to know why they should do so. In fact, people tend to ask the same questions. As you make a reasonable argument, you anticipate and respond to readers’ questions with a particular part of argument:
1. The answer to What do you want me to do or think? is your conclusion : “I conclude that you should do or think X.”
2. The answer to Why should I do or think that? states your premise : “You should do or think X because . . .”
3. The answer to How do I know that what you say is true? presents your support : “You can believe my reasons because they are supported by these facts . . .”
4. The answer to Why should I accept that your reasons support your claim? states your general principle of reasoning, called a warrant : “My specific reason supports my specific claim because whenever this general condition is true, we can generally draw a conclusion like mine.”
5. The answer to What about this other idea, fact, or conclusion? acknowledges that your readers might see things differently and then responds to their counterarguments .
6. The answer to How should you present your argument? leads to the point of view , organization , and tone that you should use when making your arguments.
As you have noticed, the answers to these questions involve knowing the particular vocabulary about argument because these terms refer to specific parts of an argument. The remainder of this section will cover the terms referred to in the questions listed above as well as others that will help you better understand the building blocks of argument.
What Is a Conclusion, and What Is a Premise?
The root notion of an argument is that it convinces us that something is true. What we are being convinced of is the conclusion . An example would be this claim:
Littering is harmful.
A reason for this conclusion is called the premise . Typically, a conclusion will be supported by two or more premises . Both premises and conclusions are statements . Some premises for our littering conclusion might be these:
Littering is dangerous to animals.
Littering is dangerous to humans.
Thus, to be clear, understand that an argument asserts that the writer’s claim is true in two main parts: the premises of the argument exist to show that the conclusion is true.
Be aware of the other words to indicate a conclusion– claim , assertion , point –and other ways to talk about the premise– reason , factor , the why . Also, do not confuse this use of the word conclusion with a conclusion paragraph for an essay.
What Is a Statement?
A statement is a type of sentence that can be true or false and corresponds to the grammatical category of a declarative sentence . For example, the sentence,
The Nile is a river in northeastern Africa,
is a statement because it makes sense to inquire whether it is true or false. (In this case, it happens to be true.) However, a sentence is still a statement, even if it is false. For example, the sentence,
The Yangtze is a river in Japan,
is still a statement; it is just a false statement (the Yangtze River is in China). In contrast, none of the following sentences are statements:
Please help yourself to more casserole.
Don’t tell your mother about the surprise.
Do you like Vietnamese pho?
None of these sentences are statements because it does not make sense to ask whether those sentences are true or false; rather, they are a request, a command, and a question, respectively. Make sure to remember the difference between sentences that are declarative statements and sentences that are not because arguments depend on declarative statements .
A question cannot be an argument, yet students will often pose a question at the end of an introduction to an essay, thinking they have declared their thesis. They have not. If, however, they answer that question ( conclusion ) and give some reasons for that answer ( premises ), they then have the components necessary for both an argument and a declarative statement of that argument ( thesis ).
To reiterate: All arguments are composed of premises and conclusions, both of which are types of statements. The premises of the argument provide reasons for thinking that the conclusion is true. Arguments typically involve more than one premise.
What Is Standard Argument Form?
A standard way of capturing the structure of an argument, or diagramming it, is by numbering the premises and conclusion. For example, the following represents another way to arrange the littering argument:
- Littering is harmful
- Litter is dangerous to animals
- Litter is dangerous to humans
This numbered list represents an argument that has been put into standard argument form . A more precise definition of an argument now emerges, employing the vocabulary that is specific to academic and rhetorical arguments. An argument is a set of statements , some of which (the premises : statements 2 and 3 above) attempt to provide a reason for thinking that some other statement (the conclusion : statement 1) is true.
Diagramming an argument can be helpful when trying to figure out your essay’s thesis. Because a thesis is an argument, putting the parts of an argument into standard form can help sort ideas. You can transform the numbered ideas into a cohesive sentence or two for your thesis once you are more certain what your argument parts are.
Figure 3.2 “Argument Diagram”

Recognizing arguments is essential to analysis and critical thinking; if you cannot distinguish between the details (the support) of a piece of writing and what those details are there to support (the argument), you will likely misunderstand what you are reading. Additionally, studying how others make arguments can help you learn how to effectively create your own.
What Are Argument Indicators?
While mapping an argument in standard argument form can be a good way to figure out and formulate a thesis, identifying arguments by other writers is also important. The best way to identify an argument is to ask whether a claim exists (in statement form) that a writer justifies by reasons (also in statement form). Other identifying markers of arguments are key words or phrases that are premise indicators or conclusion indicators. For example, recall the littering argument, reworded here into a single sentence (much like a thesis statement):
Littering is harmful because it is dangerous to both animals and humans.
The word “because” here is a premise indicator . That is, “because” indicates that what follows is a reason for thinking that littering is bad. Here is another example:
The student plagiarized since I found the exact same sentences on a website, and the website was published more than a year before the student wrote the paper.
In this example, the word “since” is a premise indicator because what follows is a statement that is clearly intended to be a reason for thinking that the student plagiarized (i.e., a premise). Notice that in these two cases, the premise indicators “because” and “since” are interchangeable: “because” could be used in place of “since” or “since” in the place of “because,” and the meaning of the sentences would have been the same.
Figure 3.3 “Common Premise Indicators”

In addition to premise indicators, there are also conclusion indicators . Conclusion indicators mark that what follows is the conclusion of an argument. For example,
Bob-the-arsonist has been dead for a year, so Bob-the-arsonist didn’t set the fire at the East Lansing Starbucks last week.
In this example, the word “so” is a conclusion indicator because what follows it is a statement that someone is trying to establish as true (i.e., a conclusion). Here is another example of a conclusion indicator:
A poll administered by Gallup (a respected polling company) showed candidate X to be substantially behind candidate Y with only a week left before the vote; therefore , candidate Y will probably not win the election.
In this example, the word “therefore” is a conclusion indicator because what follows it is a statement that someone is trying to establish as true (i.e., a conclusion). As before, in both of these cases, the conclusion indicators “so” and “therefore” are interchangeable: “So” could be used in place of “therefore” or “therefore” in the place of “so,” and the meaning of the sentences would have been the same.
Figure 3.4 “Common Conclusion Indicators”

Which of the following are arguments? If it is an argument, identify the conclusion (claim) of the argument. If it is not an argument, explain why not. Remember to look for the qualifying features of an argument: (1) It is a statement or series of statements, (2) it states a claim (a conclusion), and (3) it has at least one premise (reason for the claim).
- The woman with the hat is not a witch since witches have long noses, and she doesn’t have a long nose.
- I have been wrangling cattle since before you were old enough to tie your own shoes.
- Albert is angry with me, so he probably won’t be willing to help me wash the dishes.
- First, I washed the dishes, and then I dried them.
- If the road weren’t icy, the car wouldn’t have slid off the turn.
- Marvin isn’t a fireman and isn’t a fisherman, either.
- Are you seeing the rhinoceros over there? It’s huge!
- Obesity has become a problem in the US because obesity rates have risen over the past four decades.
- Bob showed me a graph with rising obesity rates, and I was very surprised to see how much they had risen.
- Marvin isn’t a fireman because Marvin is a Greyhound, which is a type of dog, and dogs can’t be firemen.
- What Susie told you is not the actual reason she missed her flight to Denver.
- Carol likely forgot to lock her door this morning because she was distracted by a clown riding a unicycle while singing Lynyrd Skynyrd’s “Simple Man.”
- No one who has ever gotten frostbite while climbing K2 has survived to tell about it; therefore, no one ever will.
What Constitutes Support?
To ensure that your argument is sound—that the premises for your conclusion are true—you must establish support . The burden of proof, to borrow language from law, is on the one making an argument, not on the recipient of an argument. If you wish to assert a claim, you must then also support it, and this support must be relevant, logical, and sufficient.
It is important to use the right kind of evidence, to use it effectively, and to have an appropriate amount of it.
- If, for example, your philosophy professor did not like that you used a survey of public opinion as your primary evidence in an ethics paper, you most likely used material that was not relevant to your topic. Rather, you should find out what philosophers count as good evidence. Different fields of study involve types of evidence based on relevance to those fields.
- If your professor has put question marks by your thesis or has written, “It does not follow,” you likely have problems with logic . Make sure it is clear how the parts of your argument logically fit together.
- If your instructor has told you that you need more analysis, suggested that you are “just listing” points or giving a “laundry list,” you likely have not included enough explanation for how a point connects to and supports your argument, which is another problem with logic , this time related to the warrants of your argument. You need to fully incorporate evidence into your argument. (See more on warrants immediately below.)
- If you see comments like “for example?,” “proof?,” “go deeper,” or “expand,” you may need more evidence. In other words, the evidence you have is not yet sufficient . One or two pieces of evidence will not be enough to prove your argument. Similarly, multiple pieces of evidence that aren’t developed thoroughly would also be flawed, also insufficient. Would a lawyer go to trial with only one piece of evidence? No, the lawyer would want to have as much evidence as possible from a variety of sources to make a viable case. Similarly, a lawyer would fully develop evidence for a claim using explanation, facts, statistics, stories, experiences, research, details, and the like.
You will find more information about the different types of evidence, how to find them, and what makes them credible in Chapter 6, “Research.” Logic will be covered later on in this chapter.
What Is the Warrant?
Above all, connect the evidence to the argument. This connection is the warrant . Evidence is not self-evident. In other words, after introducing evidence into your writing, you must demonstrate why and how this evidence supports your argument. You must explain the significance of the evidence and its function in your paper. What turns a fact or piece of information into evidence is the connection it has with a larger claim or argument: Evidence is always evidence for or against something, and you have to make that link clear.
Student writers sometimes assume that readers already know the information being written about; students may be wary of elaborating too much because they think their points are obvious. But remember, readers are not mind readers: Although they may be familiar with many of the ideas discussed, they don’t know what writers want to do with those ideas unless they indicate that through explanations, organization, and transitions. Thus, when you write, be sure to explain the connections you made in your mind when you chose your evidence, decided where to place it in your paper, and drew conclusions based on it.
What Is a Counterargument?
Remember that arguments are multi-sided. As you brainstorm and prepare to present your idea and your support for it, consider other sides of the issue. These other sides are counterarguments . Make a list of counterarguments as you work through the writing process, and use them to build your case – to widen your idea to include a valid counterargument, to explain how a counterargument might be defeated, to illustrate how a counterargument may not withstand the scrutiny your research has uncovered, and/or to show that you are aware of and have taken into account other possibilities.
For example, you might choose the issue of declawing cats and set up your search with the question should I have my indoor cat declawed? Your research, interviews, surveys, personal experiences might yield several angles on this question: Yes, it will save your furniture and your arms and ankles. No, it causes psychological issues for the cat. No, if the cat should get outside, he will be without defense. As a writer, be prepared to address alternate arguments and to include them to the extent that it will illustrate your reasoning.
Almost anything claimed in a paper can be refuted or challenged. Opposing points of view and arguments exist in every debate. It is smart to anticipate possible objections to your arguments – and to do so will make your arguments stronger. Another term for a counterargument is antithesis (i.e., the opposition to a thesis). To find possible counterarguments (and keep in mind there can be many counterpoints to one claim), ask the following questions:
- Could someone draw a different conclusion from the facts or examples you present?
- Could a reader question any of your assumptions or claims?
- Could a reader offer a different explanation of an issue?
- Is there any evidence out there that could weaken your position?
If the answer to any of these questions is yes, the next set of questions can help you respond to these potential objections:
Is it possible to concede the point of the opposition, but then challenge that point’s importance/usefulness?
- Can you offer an explanation of why a reader should question a piece of evidence or consider a different point of view?
- Can you explain how your position responds to any contradicting evidence?
- Can you put forward a different interpretation of evidence?
It may not seem likely at first, but clearly recognizing and addressing different sides of the argument, the ones that are not your own, can make your argument and paper stronger. By addressing the antithesis of your argument essay, you are showing your readers that you have carefully considered the issue and accept that there are often other ways to view the same thing.
You can use signal phrases in your paper to alert readers that you are about to present an objection. Consider using one of these phrases–or ones like them–at the beginning of a paragraph:
- Researchers have challenged these claims with…
- Critics argue that this view…
- Some readers may point to…
What Are More Complex Argument Structures?
So far you have seen that an argument consists of a conclusion and a premise (typically more than one). However, often arguments and explanations have a more complex structure than just a few premises that directly support the conclusion. For example, consider the following argument:
No one living in Pompeii could have survived the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius. The reason is simple: The lava was flowing too fast, and there was nowhere to go to escape it in time. Therefore, this account of the eruption, which claims to have been written by an eyewitness living in Pompeii, was not actually written by an eyewitness.
The main conclusion of this argument—the statement that depends on other statements as evidence but doesn’t itself provide any evidence for other statements—is
A. This account of the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius was not actually written by an eyewitness.
However, the argument’s structure is more complex than simply having a couple of premises that provide evidence directly for the conclusion. Rather, some statements provide evidence directly for the main conclusion, but some premise statements support other premise statements which then support the conclusion.
To determine the structure of an argument, you must determine which statements support which, using premise and conclusion indicators to help. For example, the passage above contains the phrase, “the reason is…” which is a premise indicator, and it also contains the conclusion indicator, “therefore.” That conclusion indicator helps identify the main conclusion, but the more important element to see is that statement A does not itself provide evidence or support for any of the other statements in the argument, which is the clearest reason statement A is the main conclusion of the argument. The next questions to answer are these: Which statement most directly supports A? What most directly supports A is
B. No one living in Pompeii could have survived the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius.
However, there is also a reason offered in support of B. That reason is the following:
C. The lava from Mt. Vesuvius was flowing too fast, and there was nowhere for someone living in Pompeii to go to escape it in time.
So the main conclusion (A) is directly supported by B, and B is supported by C. Since B acts as a premise for the main conclusion but is also itself the conclusion of further premises, B is classified as an intermediate conclusion . What you should recognize here is that one and the same statement can act as both a premise and a conclusion . Statement B is a premise that supports the main conclusion (A), but it is also itself a conclusion that follows from C. Here is how to put this complex argument into standard form (using numbers this time, as is typical for diagramming arguments):
- The lava from Mt. Vesuvius was flowing too fast, and there was nowhere for someone living in Pompeii to go to escape it in time.
- Therefore, no one living in Pompeii could have survived the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius. (from 1)
- Therefore, this account of the eruption of Mt. Vesuvius was not actually written by an eyewitness. (from 2)
Notice that at the end of statement 2 is a written indicator in parentheses (from 1), and, likewise, at the end of statement 3 is another indicator (from 2). From 1 is a shorthand way of saying, “this statement follows logically from statement 1.” Use this convention as a way to keep track of an argument’s structure. It may also help to think about the structure of an argument spatially, as the figure below shows:
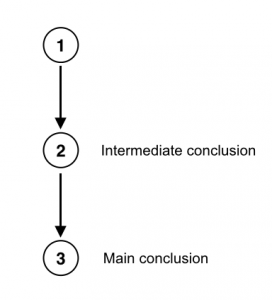
The main argument here (from 2 to 3) contains a subargument , in this case, the argument from 1 (a premise) to 2 (the intermediate conclusion). A subargument, as the term suggests, is a part of an argument that provides indirect support for the main argument. The main argument is simply the argument whose conclusion is the main conclusion.
Another type of structure that arguments can have is when two or more premises provide direct but independent support for the conclusion. Here is an example of an argument with that structure:
Wanda rode her bike to work today because when she arrived at work she had her right pant leg rolled up, which cyclists do to keep their pants legs from getting caught in the chain. Moreover, our co-worker, Bob, who works in accounting, saw her riding towards work at 7:45 a.m.
The conclusion of this argument is “Wanda rode her bike to work today”; two premises provide independent support for it: the fact that Wanda had her pant leg cuffed and the fact that Bob saw her riding her bike. Here is the argument in standard form:
- Wanda arrived at work with her right pant leg rolled up.
- Cyclists often roll up their right pant leg.
- Bob saw Wanda riding her bike towards work at 7:45.
- Therefore, Wanda rode her bike to work today. (from 1-2, 3 independently)
Again, notice that next to statement 4 of the argument is an indicator of how each part of the argument relates to the main conclusion. In this case, to avoid any ambiguity, you can see that the support for the conclusion comes independently from statements 1 and 2, on the one hand, and from statement 3, on the other hand. It is important to point out that an argument or subargumen t can be supported by one or more premises, the case in this argument because the main conclusion (4) is supported jointly by 1 and 2, and singly by 3. As before, we can represent the structure of this argument spatially, as the figure below shows:
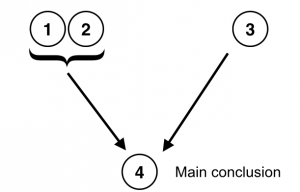
There are endless argument structures that can be generated from a few simple patterns. At this point, it is important to understand that arguments can have different structures and that some arguments will be more complex than others. Determining the structure of complex arguments is a skill that takes some time to master, rather like simplifying equations in math. Even so, it may help to remember that any argument structure ultimately traces back to some combination of premises, intermediate arguments, and a main conclusion.
Write the following arguments in standard form. If any arguments are complex, show how each complex argument is structured using a diagram like those shown just above.
1. There is nothing wrong with prostitution because there is nothing wrong with consensual sexual and economic interactions between adults. Moreover, there is no difference between a man who goes on a blind date with a woman, buys her dinner and then has sex with her and a man who simply pays a woman for sex, which is another reason there is nothing wrong with prostitution.
2. Prostitution is wrong because it involves women who have typically been sexually abused as children. Proof that these women have been abused comes from multiple surveys done with female prostitutes that show a high percentage of self-reported sexual abuse as children.
3. Someone was in this cabin recently because warm water was in the tea kettle and wood was still smoldering in the fireplace. However, the person couldn’t have been Tim because Tim has been with me the whole time. Therefore, someone else must be in these woods.
4. Someone can be blind and yet run in the Olympic Games since Marla Runyan did it at the 2000 Sydney Olympics.
5. The train was late because it had to take a longer, alternate route seeing as the bridge was out.
6. Israel is not safe if Iran gets nuclear missiles because Iran has threatened multiple times to destroy Israel, and if Iran had nuclear missiles, it would be able to carry out this threat. Furthermore, since Iran has been developing enriched uranium, it has the key component needed for nuclear weapons; every other part of the process of building a nuclear weapon is simple compared to that. Therefore, Israel is not safe.
7. Since all professional hockey players are missing front teeth, and Martin is a professional hockey player, it follows that Martin is missing front teeth. Because almost all professional athletes who are missing their front teeth have false teeth, it follows that Martin probably has false teeth.
8. Anyone who eats the crab rangoon at China Food restaurant will probably have stomach troubles afterward. It has happened to me every time; thus, it will probably happen to other people as well. Since Bob ate the crab rangoon at China Food restaurant, he will probably have stomach troubles afterward.
9. Lucky and Caroline like to go for runs in the afternoon in Hyde Park. Because Lucky never runs alone, any time Albert is running, Caroline must also be running. Albert looks like he has just run (since he is panting hard), so it follows that Caroline must have run, too.
10. Just because Linda’s prints were on the gun that killed Terry and the gun was registered to Linda, it doesn’t mean that Linda killed Terry since Linda’s prints would certainly be on her own gun, and someone else could have stolen her gun and used it to kill Terry.

Key Takeaways: Components of Vocabulary and Argument
- Conclusion —a claim that is asserted as true. One part of an argument.
- Premise —a reason behind a conclusion. The other part of an argument. Most conclusions have more than one premise.
- Statement —a declarative sentence that can be evaluated as true or false. The parts of an argument, premises and the conclusion, should be statements.
- Standard Argument Form —a numbered breakdown of the parts of an argument (conclusion and all premises).
- Premise Indicators —terms that signal that a premise, or reason, is coming.
- Conclusion Indicator —terms that signal that a conclusion, or claim, is coming.
- Support —anything used as proof or reasoning for an argument. This includes evidence, experience, and logic.
- Warrant —the connection made between the support and the reasons of an argument.
- Counterargument —an opposing argument to the one you make. An argument can have multiple counterarguments.
- Complex Arguments –these are formed by more than individual premises that point to a conclusion. Complex arguments may have layers to them, including an intermediate argument that may act as both a conclusion (with its own premises) and a premise (for the main conclusion).
CC Licensed Content, Shared Previously
About Writing: A Guide, Robin Jeffrey, CC-BY.
A Concise Introduction to Logic, Craig DeLancey, CC-BY-NC-SA.
English 112: College Composition II , Lumen Learning, CC-BY-SA.
English Composition 1 , Lumen Learning, CC-BY-SA.
Frameworks for Academic Writing , Stephen Poulter, CC-BY-NC-SA.
Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking, Matthew J. Van Cleave, CC-BY.
Methods of Discovery, Pavel Zemilanski, CC-BY-NC-SA.
Writing for Success , CC-BY-NC-SA.
Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence , Amy Guptill, CC-BY-NC-SA.
Image Credits
Figure 3.1 “Opinion vs Argument,” by Kalyca Schultz, Virginia Western Community College, derivative image from original by ijmaki, pixabay, CC-0.
Figure 3.2 “Argument Diagram,” Virginia Western Community College, derivative image using “ Thin Brace Down ,” by pathoschild, Wikimedia, CC-BY-SA 3.0.
Figure 3.3 “Common Premise Indicators,” by Kalyca Schultz, Virginia Western Community College, CC-0.
Figure 3.4 “Common Conclusion Indicators,” by Kalyca Schultz, Virginia Western Community College, CC-0.
Figure 3.5 Untitled, by Matthew Van Cleave, from Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking , CC-BY.
Figure 3.6 Untitled, by Matthew Van Cleave, from Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking , CC-BY.
Argument Copyright © 2021 by Kirsten DeVries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Module 9: Academic Argument
The argumentative essay, learning objectives.
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Figure 1 . When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- You write about how something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the increase of industrial pollution and the resulting decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean.
Evaluation Arguments
- You can write an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you also need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your Introduction to Educational Theory class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- With this type of writing, you need to propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a removal of parking fines on students who use the parking deck on campus.
Narrative Arguments
- For this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your negative experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past. For this type of writing assignment, you have to explain what you are refuting first, and then you can expand on your new ideas or perspectives.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
Essay Examples
- You can read more about an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/ . License : Other . License Terms : https://pixabay.com/service/terms/#license


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.1: What is Argument?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 107778
All people, including you, make arguments on a regular basis. When you make a claim and then support the claim with reasons, you are making an argument. Consider the following:
The two main models of argument desired in college courses as part of the training for academic or professional life are rhetorical argument and academic argument . If rhetoric is the study of the craft of writing and speaking, particularly writing or speaking designed to convince and persuade, the student studying rhetorical argument focuses on how to create an argument that convinces and persuades effectively. To that end, the student must understand how to think broadly about argument, the particular vocabulary of argument, and the logic of argument. The close sibling of rhetorical argument is academic argument, argument used to discuss and evaluate ideas, usually within a professional field of study, and to convince others of those ideas. In academic argument , interpretation and research play the central roles.
However, it would be incorrect to say that academic argument and rhetorical argument do not overlap. Indeed, they do, and often. A psychologist not only wishes to prove an important idea with research, but she will also wish to do so in the most effective way possible. A politician will want to make the most persuasive case for his side, but he should also be mindful of data that may support his points. Thus, throughout this chapter, when you see the term argument , it refers to a broad category including both rhetorical and academic argument .
Before moving to the specific parts and vocabulary of argument, it will be helpful to consider some further ideas about what argument is and what it is not.
Argument vs. Controversy or Fight
Consumers of written texts are often tempted to divide writing into two categories: argumentative and non-argumentative. According to this view, to be argumentative, writing must have the following qualities: It has to defend a position in a debate between two or more opposing sides, it must be on a controversial topic, and the goal of such writing must be to prove the correctness of one point of view over another.
A related definition of argument implies a confrontation, a clash of opinions and personalities, or just a plain verbal fight. It implies a winner and a loser, a right side and a wrong one. Because of this understanding of the word “argument,” many students think the only type of argument writing is the debate-like position paper, in which the author defends his or her point of view against other, usually opposing, points of view.
These two characteristics of argument—as controversial and as a fight—limit the definition because arguments come in different disguises, from hidden to subtle to commanding. It is useful to look at the term “argument” in a new way. What if we think of argument as an opportunity for conversation, for sharing with others our point of view on an issue, for showing others our perspective of the world? What if we think of argument as an opportunity to connect with the points of view of others rather than defeating those points of view?
One community that values argument as a type of communication and exchange is the community of scholars. They advance their arguments to share research and new ways of thinking about topics. Biologists, for example, do not gather data and write up analyses of the results because they wish to fight with other biologists, even if they disagree with the ideas of other biologists. They wish to share their discoveries and get feedback on their ideas. When historians put forth an argument, they do so often while building on the arguments of other historians who came before them. Literature scholars publish their interpretations of different works of literature to enhance understanding and share new views, not necessarily to have one interpretation replace all others. There may be debates within any field of study, but those debates can be healthy and constructive if they mean even more scholars come together to explore the ideas involved in those debates. Thus, be prepared for your college professors to have a much broader view of argument than a mere fight over a controversial topic or two.
Argument vs. Opinion
Argument is often confused with opinion. Indeed, arguments and opinions sound alike. Someone with an opinion asserts a claim that he thinks is true. Someone with an argument asserts a claim that she thinks is true. Although arguments and opinions do sound the same, there are key distinctions between them.
- Arguments have rules; opinions do not . In other words, to form an argument, you must consider whether the argument is reasonable. Is it worth making? Is it valid? Is it sound? Do all of its parts fit together logically? Opinions, on the other hand, have no rules, and anyone asserting an opinion need not think it through for it to count as one; however, it will not count as an argument.
- Arguments have support; opinions do not . If you make a claim and then stop, as if the claim itself were enough to demonstrate its truthfulness, you have asserted an opinion only. An argument must be supported, and the support of an argument has its own rules. The support must also be reasonable, relevant, and sufficient.

Argument vs. Thesis
Another point of confusion is the difference between an argument and an essay’s thesis . For college essays, there is no essential difference between an argument and a thesis; most professors use these terms interchangeably. An argument is a claim that you must then support. The main claim of an essay is the point of the essay and provides the purpose for the essay. Thus, the main claim of an essay is also the thesis.
Consider this as well: Most formal essays center upon one main claim (the thesis) but then support that main claim with supporting evidence and arguments. The topic sentence of a body paragraph can be another type of argument, though a supporting one, and, hence, a narrower one. Try not to be confused when professors call both the thesis and topic sentences arguments. They are not wrong because arguments come in different forms; some claims are broad enough to be broken down into a number of supporting arguments. Many longer essays are structured by the smaller arguments that are a part of and support the main argument. Sometimes professors, when they say supporting points or supporting arguments, mean the reasons ( premises ) for the main claim ( conclusion ) you make in an essay. If a claim has a number of reasons, those reasons will form the support structure for the essay, and each reason will be the basis for the topic sentence of its body paragraph.
Argument vs. Fact
Arguments are also commonly mistaken for statements of fact. This comes about because often people privilege facts over opinions, even as they defend the right to have opinions. In other words, facts are “good,” and opinions are “bad,” or if not exactly bad, then fuzzy and thus easy to reject. However, remember the important distinction between an argument and an opinion stated above: While argument may sound like an opinion, the two are not the same. An opinion is an assertion, but it is left to stand alone with little to no reasoning or support. An argument is much stronger because it includes and demonstrates reasons and support for its claim.
As for mistaking a fact for an argument, keep this important distinction in mind: An argument must be arguable . In everyday life, arguable is often a synonym for doubtful. For an argument, though, arguable means that it is worth arguing, that it has a range of possible answers, angles, or perspectives: It is an answer, angle, or perspective with which a reasonable person might disagree. Facts, by virtue of being facts, are not arguable. Facts are statements that can be definitely proven using objective data. The statement that is a fact is absolutely valid. In other words, the statement can be pronounced as definitively true or definitively false. For example, 2 + 2 = 4. This expression identifies a verifiably true statement, or a fact, because it can be proved with objective data. When a fact is established, there is no other side, and there should be no disagreement.
The misunderstanding about facts (being inherently good) and argument (being inherently problematic because it is not a fact) leads to the mistaken belief that facts have no place in an argument. This could not be farther from the truth. First of all, most arguments are formed by analyzing facts. Second, facts provide one type of support for an argument. Thus, do not think of facts and arguments as enemies; rather, they work closely together.
Explicit vs. Implicit Arguments
Arguments can be both explicit and implicit. Explicit arguments contain prominent and definable thesis statements and multiple specific proofs to support them. This is common in academic writing from scholars of all fields. Implicit arguments , on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement. Implicit arguments involve evidence of many different kinds to build and convey their point of view to their audience. Both types use rhetoric, logic, and support to create effective arguments.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Go on a hunt for an implicit argument in the essay, “ 37 Who Saw Murder Didn’t Call the Police ” ( https://tinyurl.com/yc35o25x ) by Martin Gansberg.
- Read the article, and take notes on it–either using a notebook or by annotating a printed copy of the text itself. Mark or write down all the important details you find.
- After you are finished reading, look over your notes or annotations. What do all the details add up to? Use the details you have read about to figure out what Gansberg’s implicit argument is in his essay. Write it in your own words.
- Discuss your results with a partner or a group. Did you come up with the same argument? Have everyone explain the reasoning for his or her results.
Contributors and Attributions
Adapted from Let's Get Writing (Browning, DeVries, Boylan, Kurtz and Burton) . Sourced from LibreTexts , licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Rogerian Argument

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Rogerian argument (or Rogerian rhetoric) is a form of argumentative reasoning that aims to establish a middle ground between parties with opposing viewpoints or goals. Developed by psychotherapist Carl Rogers and adapted to rhetoric by writing scholars Young, Becker, and Pike, the speaker seeks compromise, acknowledging positive aspects of each party’s argument to arrive at a mutually-beneficial solution to an issue.
You may already use Rogerian argument in your everyday life to negotiate with your friends, family, and/or romantic partners. For example, if you wanted to watch a comedy and your friend wanted to watch a romance, you might compromise by offering to watch a rom-com, as this offers each of you a bit of what you are looking for in that particular moment. Note, however, that this style of argument is decidedly less common in academic settings, where various empirical or theoretical notions of truth are often prized above the practical advantages of the Rogerian method.
While Aristotelian styles of argument are often seen as eristic (concerned primarily with winning), the Rogerian argument can be viewed as more dialectic in nature (a conversation between two or more parties with the goal of arriving at some mutually-satisfying solution). Thus, practicing the Rogerian argument will enhance your ability to understand the complex relations of opposing viewpoints and provide tools for addressing such discrepancies sympathetically. It’s also great for day-to-day conflict resolution at home or in the workplace.
However, Rogerian argument does come with disadvantages. For example, because Rogerian argument relies on compromise between opposing parties, it may not work well when your opponents are unwilling or unable to compromise, or if they are arguing in bad faith (e.g., they care only about winning). It may also lead to sub-optimal solutions if your opponent’s position is demonstrably wrong, since in this case you may nevertheless be forced to sacrifice some of your (ostensibly superior) goals order to accommodate your opponent’s (inferior) ones.
In “Rhetoric: Discovery and Change” (1970), Young, Becker, and Pike describe the primary aims of the Rogerian argument as follows:
- to convey to the reader that he is understood,
- to delineate the area within which he believes the reader's position to be valid, and
- to induce him to believe that he and the writer share similar moral qualities (honesty, integrity, and good will) and aspirations (the desire to discover a mutually acceptable solution).
The first aim shows the reader that you understand the complexities of the argument and that you have listened sympathetically to what it is they have to say. This is important, because the success of the Rogerian arguments relies on cooperation and collaboration. The second aim puts this understanding into practice by seeking a symbiotic solution. The third aim builds ethos and rapport between the parties. If audiences believe they share a value system with a speaker or writer, they are more likely to agree to the terms of whatever solution is presented.
While each of these aims is important, Young, Becker, and Pike stress that they are just that: aims, not steps. You should not necessarily view these aims as occurring in a linear, step-by-step process. The authors present a synthesized discussion of what a successful Rogerian argument should contain, but they eschew any formalized structure. The structure of the argument should instead be determined by the speaker, and it should be modified and adapted according to the rhetorical situation at hand.
Again, there is no formalized structure for the Rogerian argument, though the following example provides a foundation for considering how you might structure your own argument.
A successful Rogerian argument will likely include the following:
- Introduction (addressing the topic to be discussed and/or the problem to be solved)
- Opposing position (showing that you understand your opposition’s viewpoints/goals)
- Context for opposing position (showing that you understand the situations in which their viewpoint is valid)
- Your position (introducing/addressing your viewpoint as it differs from the reader’s)
- Context for your position (objectively showing the reader the context(s) under which your position is valid)
- Benefits (appeal to the opposition by showing how they would benefit by adopting elements of your position)
Below, we’ve provided an example Rogerian argument that follows the formula above. In this example, we will take the position that technology (e.g., laptops and tablets) should be allowed in writing classes while also considering the opinion of the opposition, who argue that such technology is more of a distraction than a helpful tool. In so doing, we should be able to arrive at a solution that considers both arguments and develops a solution that benefits both parties while still achieving our goal of allowing technology in the classroom.
Introduction
Here, we would introduce the topic and briefly discuss why it is a matter of contention. We would lay out the differing perspectives, briefly mention the merits of each argument, and discuss the implications closely considering all perspectives to arrive at a solution that works for everyone.
Opposing position
Here, we would introduce the opposing position that digital technology should not be allowed in the writing classroom. We would also list and discuss their objections to the proposition of technology in the classroom. These might include the notions that it’s distracting for the individual, the class, and the instructor, and is often used to avoid the lesson and instead play games or go on social media.
Context for opposing position
Here we might provide specific details that lend merit to their argument. We want to show that we are fully considering their claims and not just giving lip service, in the hope that that they will give similar value to our opinions. We could include statistics, testimony from instructors and students, or even examples from media that support their theory that digital technology can indeed be a distraction during instruction.
Your Position
Here, we would introduce our claim that digital technology should be allowed in the writing classroom. We would still want to speak as objectively as possible in order to establish our ethos as concerned but unbiased speaker. We might even qualify our position by acknowledging that there are, of course, situations in which technology should be put away, but reiterate that, generally speaking, the presence of digital technology is a positive.
Context for your position
Here, we can provide examples that run contrary to the ones we used for the context of our opposition’s position. For example, we could gather testimony from students who claim that using these technologies in class has been beneficial. We could include research and scholarship that supports our position and even quote instructors who have developed pedagogy around these technologies. We might even subtly demonstrate that our opposition has failed to account for all possibilities by choosing our examples carefully. For instance, we could easily include accounts of students with learning disabilities who might otherwise have a difficult time succeeding in class without the help of assistive technologies.
Here, we would use the points we’ve established throughout the argument to appeal to our opposition and find some productive middle ground that benefits both parties. We would acknowledge that some instructors do not want digital technologies present in the classroom, as they believe they distract from paying attention during lectures. We would maintain, however, that these technologies can indeed be productive tools for learning—in some cases, they can even be a virtual requirement for learning. We could then offer a solution: that these digital technologies should be kept aside during lecture portions of a lesson except in the case of students with documented disabilities. This way, students will likely be paying attention, taking notes by hand which they can transcribe later if they so wish. However, once a class moves from lecture to activity (whether group or individual), students should be allowed to access these technologies to more effectively engage with the activity, organize their thoughts, and access information. Now that the instructor is no longer lecturing, it should be easier to monitor student progress and engagement and the use of technology for these activities will lead to more developed and better organized results from the students.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the 7 elements of the Rogerian argument. - know your audience. - establish common ground. - introduce premises that underline your position. - explain shared premises. - introduce and develop position. - consider possible objections. - find places of agreement, comprimise, contingency.
Sentence 2: Provide relevant background knowledge, answer the prompt. Sentence 3: Thesis that lists three points of interest. How to write an body paragraph for an argumentative essay? Topic sentence: A sentence that introduces the contents of the paragraph, one point of your thesis. Evidence: Relevant quotation from the text.
Argumentative Essay. Writing that presents an opinion or idea and supports it with evidence. designed to convince the audience to agree with the writers opinion. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Hook, Introduction, Thesis statement and more.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like - It is a piece of writing that _____ on an issue. - A writer attempts to _____ to understand and support their point of view about an issue by stating their _____ and providing _____ to support it., 6 Elements of an argumentative essay, _____ is an idea about which the opinions of people are different. and more.
Beatriz is writing an argument to support her claim that Bob Dylan deserved to win the Nobel Prize in Literature. Read this paragraph from her argumentative essay. (1) Dylan's poetry has commented insightfully on politics, society, and the human condition. (2) He spoke out against war when the United States was fighting in Vietnam.
Choose matching term. Identify the 3 arrangements for the argumentative essay. Identify the 5 steps of the inductive argument. Identify the 6 parts of the Six-Part Oration model. Identify the 6 steps of the Toulmin argument.
a : the representing of one thing or person as similar to or like another. b : an examination of two or more items to establish similarities and dissimilarities. conclusion. : the last part of something: as. a : result, outcome. b plural : trial of strength or skill. c : a final summation.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
Sample Essays: a selection of seven argumentative essays written by students. Argument on the Web. The Purdue OWL: The OWL is the Online Writing Laboratory maintained by Purdue University. It is a comprehensive, encyclopedic online reference source for nearly all aspects of research and writing, from topic selection to citation styles and ...
An academic argument asserts a claim and supports that claim with evidence. The goal of an argument is to convince readers that the writer's position is reasonable, valid, and worthy of consideration. Therefore, an argumentative thesis statement needs to be not only clear and focused, but also debatable, assertive, and reasoned. Additionally ...
In order to succeed at this second step, though, you must have a particular point to argue. Arguments in academic writing are usually complex and take time to develop. Your argument will need to be more than a simple or obvious statement such as "Frank Lloyd Wright was a great architect.". Such a statement might capture your initial ...
This section will help you determine the purpose and structure of an argumentative essay. The Purpose of Argument in Writing. The idea of an argument often conjures up images of two people yelling and screaming in anger. In writing, however, an argument is very different. An argument is a reasoned opinion supported and explained by evidence.
Another point of confusion is the difference between an argument and an essay's thesis. For college essays, there is no essential difference between an argument and a thesis; most professors use these terms interchangeably. An argument is a claim that you must then support. The main claim of an essay is the point of the essay and provides the ...
The argumentative essay is commonly assigned as a capstone or final project in first year writing or advanced composition courses and involves lengthy, detailed research. Expository essays involve less research and are shorter in length. Expository essays are often used for in-class writing exercises or tests, such as the GED or GRE.
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
Another point of confusion is the difference between an argument and an essay's thesis. For college essays, there is no essential difference between an argument and a thesis; most professors use these terms interchangeably. An argument is a claim that you must then support. The main claim of an essay is the point of the essay and provides the ...
When preparing to compose a good argumentative essay, utilize the following steps: Step 1: Select a topic. Step 2: Identify a position. Step 3: Locate appropriate resources. Step 4: Identify evidence supporting the position.(NOTE: If there is little evidence in support of the claim, consider re-examining the main argument.)Steps to write an argumentative essay
Step 1: Analyze the Prompt. The Argument Essay question format is relatively straightforward, and the language will largely be the same for all Argument Essay prompts except for two parts: the topic and the short list of relevant foundational documents. With this in mind, analyzing the prompt for this question type is easy!
Drafting Tips. Introduction: Engage the reader with a hook and state the claim. Reason 1: the first reason, support it with evidence, and. explain the connections. Reason 1: Explain the first , support it with , and explain the connections. Rebuttal: Use reasons and evidence to fairly point out limitations of the.
Rogerian Argument. The Rogerian argument (or Rogerian rhetoric) is a form of argumentative reasoning that aims to establish a middle ground between parties with opposing viewpoints or goals. Developed by psychotherapist Carl Rogers and adapted to rhetoric by writing scholars Young, Becker, and Pike, the speaker seeks compromise, acknowledging ...
Download free-response questions from past exams along with scoring guidelines, sample responses from exam takers, and scoring distributions. If you are using assistive technology and need help accessing these PDFs in another format, contact Services for Students with Disabilities at 212-713-8333 or by email at [email protected].
AP® English Language and Composition 2022 Scoring Guidelines. Argument Essay 6 points. Colin Powell, a four-star general and former United States secretary of state, wrote in his 1995 autobiography: "[W]e do not have the luxury of collecting information indefinitely. At some point, before we can have every possible fact in hand, we have to ...