To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, restaurant and foodservice research: a critical reflection behind and an optimistic look ahead.
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management
ISSN : 0959-6119
Article publication date: 10 April 2017
The purpose of this paper is to present a review of the foodservice and restaurant literature that has been published over the past 10 years in the top hospitality and tourism journals. This information will be used to identify the key trends and topics studied over the past decade, and help to identify the gaps that appear in the research to identify opportunities for advancing future research in the area of foodservice and restaurant management.

Design/methodology/approach
This paper takes the form of a critical review of the extant literature that has been done in the foodservice and restaurant industries. Literature from the past 10 years will be qualitatively assessed to determine trends and gaps in the research to help guide the direction for future research.
The findings show that the past 10 years have seen an increase in the number of and the quality of foodservice and restaurant management research articles. The topics have been diverse and the findings have explored the changing and evolving segments of the foodservice industry, restaurant operations, service quality in foodservice, restaurant finance, foodservice marketing, food safety and healthfulness and the increased role of technology in the industry.
Research limitations/implications
Given the number of research papers done over the past 10 years in the area of foodservice, it is possible that some research has been missed and that some specific topics within the breadth and depth of the foodservice industry could have lacked sufficient coverage in this one paper. The implications from this paper are that it can be used to inform academics and practitioners where there is room for more research, it could provide ideas for more in-depth discussion of a specific topic and it is a detailed start into assessing the research done of late.
Originality/value
This paper helps foodservice researchers in determining where past research has gone and gives future direction for meaningful research to be done in the foodservice area moving forward to inform academicians and practitioners in the industry.
- Hospitality management
- Restaurants
- Food and beverage
- Foodservice research
DiPietro, R. (2017), "Restaurant and foodservice research: A critical reflection behind and an optimistic look ahead", International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management , Vol. 29 No. 4, pp. 1203-1234. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-01-2016-0046
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2017, Emerald Publishing Limited
Related articles
All feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
Approaches for restaurant revenue management
- Research Article
- Published: 23 February 2021
- Volume 21 , pages 17–35, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Mohit Tyagi 1 &
- Nomesh B. Bolia 1
1446 Accesses
10 Citations
Explore all metrics
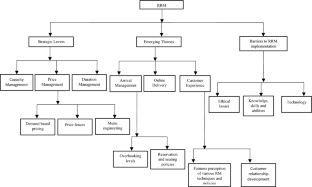
Revenue management (RM) helps predict customer demand to optimize inventory availability and price so that revenue growth can be maximized. The main aim of revenue management is to sell the right product at the right time and for the right price to the right consumer. Over the past two decades, revenue management techniques for restaurant industries have started to appear in the literature. This paper aims to thoroughly review this literature and identify emerging issues. The paper is mainly structured around strategic levers of restaurant revenue management, barriers to the implementation of revenue management strategies in restaurants, and emerging themes in restaurant revenue management. The paper concludes with a summary of key findings and carefully identified directions for future research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
A decision framework for restaurant revenue management

Lost opportunities in restaurant revenue management

Can restaurant revenue management work with menu analysis?
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Aburto, Luis, and Richard Weber. 2007. A Sequential Hybrid Forecasting System for Demand Prediction. In International Workshop on Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition , 518–32. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Alexandrov, Alexei, and Martin A. Lariviere. 2011. Are Reservations Recommended?”. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management 14 (2): 218–30. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.1110.0360 .
Article Google Scholar
Alon, Ilan, Min Qi, and Robert J. Sadowski. 2001. Forecasting Aggregate Retail Sales: A Comparison of Artifcial Neural Networks and Traditional Methods. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 8 (3): 147–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-6989(00)00011-4 .
Anderson, Chris K., and Xiaoqing Xie. 2010. Improving Hospitality Industry Sales: Twenty-Five Years of Revenue Management. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 51 (1): 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965509354697 .
Barz, Christiane, and Karl-Heinz Waldmann. 2006. An Application of Markov Decision Processes to the Seat Inventory Control Problem. In Perspectives on Operations Research , 113–28. DUV.
Bayou, Mohamed E., and Lee B. Bennett. 1992. Profitability Analysis for Table-Service Restaurants. The Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 33 (2): 49–55. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203910016.ch13 .
Bertsimas, Dimitris, and Romy Shioda. 2003. Restaurant Revenue Management. Operations Research 51 (3): 472–86. https://doi.org/10.1287/opre.51.3.472.14956 .
Box, George E.P.., Gwilym M. Jenkins, Gregory C. Reinsel, and Greta M. Ljung. 2015. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control . San Francisco: John Wiley & Sons.
Google Scholar
Çavuşoğlu, Mehmet. 2012. Electronic Commerce and Turkish Patterns of Online Food Delivery System. Journal of Internet Applications & Management/İnternet Uygulamaları ve Yönetimi Dergisi 3 (1): 45–62.
Cetin, Gurel, Tevfik Demirciftci, and Anil Bilgihan. 2016. Meeting Revenue Management Challenges: Knowledge, Skills and Abilities. International Journal of Hospitality Management 57: 132–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2016.06.008 .
Chen, Pin-Chang., Chih-Yao. Lo, Hung-Teng. Chang, and Yu. Locho. 2011. A Study of Applying Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm in Sales Forecasting Model. Journal of Convergence Information Technology 6 (9): 352–62.
Chiang, Wen Chyuan, Jason C.H.. Chen, and Xu. Xiaojing. 2007. An Overview of Research on Revenue Management: Current Issues and Future Research. International Journal of Revenue Management 1 (1): 97–128. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJRM.2007.011196 .
Choi, Sunmee, and Anna S. Mattila. 2005. Impact of Information on Customer Fairness Perceptions of Hotel Revenue Management. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 46 (4): 444–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880404270032 .
Choi, Sunmee, and Anna S. Mattila. 2004. Hotel Revenue Management and Its Impact on Customers’ Perceptions of Fairness. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 2 (4): 303–14. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rpm.5170079 .
Cohen, E., R. Mesika, and Z. Schwartz. 1998. Multidimensional Approach to Menu Sales Mix Analysis. Praxis 2 (1): 130–44.
Coxe, Stefany, Stephen G. West, and Leona S. Aiken. 2009. The Analysis of Count Data: A Gentle Introduction to Poisson Regression and Its Alternatives. Journal of Personality Assessment 91 (2): 121–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223890802634175 .
Cranage, David A., and William P. Andrew. 1992. A Comparison of Time Series and Econometric Models for Forecasting Restaurant Sales. International Journal of Hospitality Management 11 (2): 129–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4319(92)90006-H .
Cravy. 2018. The Restaurant Industry—A Global Perspective. 2018. https://medium.com/@CravyHQ/the-restaurant-industry-a-global-perspective-26cea1b91701 .
Cross, Robert G. 1997. Launching the Revenue Rocket: How Revenue Management Can Work for Your Business. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 38 (2): 32–43.
Cui, Yao, Izak Duenyas, and Ozge Sahin. 2018. Unbundling of Ancillary Service: How Does Price Discrimination of Main Service Matter?”. Manufacturing and Service Operations Management 20 (3): 455–66. https://doi.org/10.1287/msom.2017.0646 .
De Vries, Jelle, Debjit Roy, and René De Koster. 2018. Worth the Wait? How Restaurant Waiting Time Influences Customer Behavior and Revenue. Journal of Operations Management 63: 59–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2018.05.001 .
Desiraju, Ramarao, and Steven M. Shugan. 1999. Strategic Yield Service And. Journal of Marketing 63 (1): 44–56.
Dickson, Duncan, Robert C. Ford, and Bruce Laval. 2005. Managing Real and Virtual Waits in Hospitality and Service Organizations. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 46 (1): 52–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880404271560 .
Doan Ngoc, Ha. 2013. Demand Creation of Online Services for B2B and Consumer Market-Food Delivery in Vietnam .
Dodds, William B., Kent B. Monroe, and Dhruv Grewal. 1991. Effect of Price, Brand, and Store Information Buyers ’ Evaluations. Journal of Marketing Research 28 (3): 307–19.
Escobari, Diego, Nicholas G. Rupp, and Joseph Meskey. 2018. Dynamic Price Discrimination in Airlines. 88078.
Etemad-Sajadi, Reza. 2018. Are Customers Ready to Accept Revenue Management Practices in the Restaurant Industry?”. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management 35 (4): 846–56.
Fard, Farzad Alavi, Malick Sy, and Dmitry Ivanov. 2019. Optimal Overbooking Strategies in the Airlines Using Dynamic Programming Approach in Continuous Time. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 128: 384–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2019.07.001 .
Fischer, John W. 2005. At Your Service: A Hands-On Guide to the Professional Dining Room . New York: John Wiley & Sons Incorporated.
Forst, Frank G. 1992. Forecasting Restaurant Sales Using Multiple Regression And Box-Jenkins Analysis. Journal of Applied Business Research (JABR) 8 (2): 15. https://doi.org/10.19030/jabr.v8i2.6157 .
Fukui, Hideki, and Koki Nagata. 2020. How Do Passengers React to Airlines’ Overbooking Strategies? Evidence from the US Airlines. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice 132: 242–55.
Gregorash, Bill J. 2016. Restaurant Revenue Management: Apply Reservation Management?”. Information Technology and Tourism 16 (4): 331–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40558-016-0065-0 .
Grewal, Dhruv, Kent B. Monroe, and R. Krishnan. 1998. The Effects of Price-Comparison Advertising on Buyers’ Perceptions of Acquisition Value, Transaction Value, and Behavioral Intentions. Journal of Marketing 62 (2): 46–59. https://doi.org/10.2307/1252160 .
Guerriero, Francesca, Giovanna Miglionico, and Filomena Olivito. 2014. Strategic and Operational Decisions in Restaurant Revenue Management. European Journal of Operational Research 237 (3): 1119–32.
Guillet, Basak Denizci. 2020. An Evolutionary Analysis of Revenue Management Research in Hospitality and Tourism: Is There a Paradigm Shift?”. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 32 (2): 560–87. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-06-2019-0515 .
Guillet, Basak Denizci, Yuanyuan Guo, and Rob Law. 2015. Segmenting Hotel Customers Based on Rate Fences through Conjoint and Cluster Analysis. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing 32 (7): 835–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10548408.2015.1063825 .
Guillet, Basak Denizci, Rob Law, and Deniz Kucukusta. 2018. How Do Restaurant Customers Make Trade-Offs among Rate Fences? Journal of Foodservice Business Research 21 (4): 359–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/15378020.2017.1401896 .
Guillet, Basak Denizci, and Ibrahim Mohammed. 2015. Revenue Management Research in Hospitality and Tourism. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 27 (4): 526–60. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM-06-2014-0295 .
Guo, Xiaolong, and Xiabing Zheng. 2017. Examination of Restaurants Online Pricing Strategies: A Game Analytical Approach. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management 26 (6): 659–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2017.1272085 .
Hayes, David K., and Lynn Huffman. 1985. Menu Analysis: A Better Way. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 25 (4): 64–70.
Heide, Morten, Camilla White, Kjell Grønhaug, and Terje M. Østrem. 2008. Pricing Strategies in the Restaurant Industry. Scandinavian Journal of Hospitality and Tourism ISSN 8 (3): 251–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/15022250802451065 .
Heo, Cindy Y. 2013. Restaurant Revenue Management. Revenue Management for Hospitality and Tourism , 118–29.
Heo, Cindy Yoonjoung. 2016. Exploring Group-Buying Platforms for Restaurant Revenue Management. International Journal of Hospitality Management 52: 154–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2015.07.009 .
Heo, Cindy Yoonjoung. 2017. International Journal of Hospitality Management New Performance Indicators for Restaurant Revenue Management: ProPASH and ProPASM. International Journal of Hospitality Management 61: 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2016.10.005 .
Heo, Cindy Yoonjoung, and Seoki Lee. 2011. Influences of Consumer Characteristics on Fairness Perceptions of Revenue Management Pricing in the Hotel Industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management 30 (2): 243–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2010.07.002 .
Heo, Cindy Yoonjoung, Seoki Lee, Anna Mattila, and Hu. Clark. 2013. Restaurant Revenue Management: Do Perceived Capacity Scarcity and Price Differences Matter?”. International Journal of Hospitality Management 35: 316–26.
Hoang, Phi. 2007. The Future of Revenue Management and Pricing Science. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 6 (2): 151–53. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rpm.5160069 .
Horton, Brett W. 2001. Labor and Menu Category: Effects on Analysis. Hospitality Review 19 (2): 35–46.
Hossain, Ferdaus, and Adesoji O. Adelaja. 2000. Consumers ’ Interest in Alternative Food Delivery Systems: Results from a Consumer Survey in New Jersey. Journal of Food Distribution Research 31: 49–67.
Hu, Clark, Ming Chen, and Shiang-Lih Chen. McCain. 2004. Forecasting in Short-Term Planning and Management for a Casino Buffet Restaurant Clark. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing 16 (2–3): 79–98. https://doi.org/10.1300/J073v16n02 .
Ishigaki, Tsukasa, Takeshi Takenaka, and Yoichi Motomura. 2010. Customer-Item Category Based Knowledge Discovery Support System and Its Application to Department Store Service. In 2010 IEEE Asia-Pacific Services Computing Conference , 371–77. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSCC.2010.69 .
Kansara, Darshini, and Mradul Mishra. 2019. Indian Restaurant & Food Service Industry—Structure & Prospects .
Kasavana, Michael L. 2001. EMarketing: Restaurant Websites That Click. Journal of Hospitality & Leisure Marketing 9 (3–4): 161–78. https://doi.org/10.1300/J150v09n03 .
Kasavana, Michael L., and Donald I. Smith. 1982. Menu Engineering: A Practical Guide to Menu Analysis . Hospitality Publications.
Khan, Mahmood A. 2020. Technological Disruptions in Restaurant Services: Impact of Innovations and Delivery Services. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research 20 (10): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348020908636 .
Kim, Kwangji, Mi.-jung Kim, and Jae-kyoon Jun. 2020. Small Queuing Restaurant Sustainable Revenue Management. Sustainability 12 (8): 3477.
Kim, Woo Gon, Jun Justin Li, and Robert A. Brymer. 2016. The Impact of Social Media Reviews on Restaurant Performance: The Moderating Role of Excellence Certificate. International Journal of Hospitality Management 55: 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2016.03.001 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 1989. The Basics of Yield Management. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 30 (3): 14–19.
Kimes, Sheryl E. 1994. Perceived Fairness of Yield Management: Applying Yield-Management Principles to Rate Structures Is Complicated by What Consumers Perceive as Unfair Practices. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 35 (1): 22–29.
Kimes, Sheryl E. 1999. Implementing Restaurant Revenue Management: A Five-Step Approach. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 40 (3): 16–21.
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2002. Perceived Fairness of Yield Management. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 43 (1): 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8804(02)80005-2 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2004. Restaurant Revenue Management: Implementation at Chevys Arrowhead. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 45 (1): 52–67. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880403260107 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2005. Restaurant Revenue Management: Could It Work?”. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 4 (1): 95–97. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rpm.5170132 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2008. The Role of Technology in Restaurant Revenue Management. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 49 (3): 297–309. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965508322768 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2011. Customer Attitudes towards Restaurant Reservations Policies. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 10 (3): 244–60. https://doi.org/10.1057/rpm.2009.24 .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2011b. Customer Perceptions of Electronic Food Ordering. Cornell Hospitality Report 11 (10): 6–15. https://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/chrpubs .
Kimes, Sheryl E. 2011. The Future of Distribution Management in the Restaurant Industry. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 10 (2): 189–94. https://doi.org/10.1057/rpm.2011.1 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., Deborah I. Barrash, and John E. Alexander. 1999. Developing a Restaurant Revenue-Management Strategy. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 40 (5): 18–29. https://doi.org/10.1177/001088049904000505 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jonathan Beard. 2013. The Future of Restaurant Revenue Management. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 12 (5): 464–69. https://doi.org/10.1057/rpm.2013.22 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., Richard B. Chase, Sunmee Choi, Philip Y. Lee, and Elizabeth N. Ngonzi. 1998. Restaurant Revenue Management: Applying Yield Management to the Restaurant Industry. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 39 (3): 32–39.
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jeannette Ho. 2019. Implementing Revenue Management in Your Restaurants: A Case Study with Fairmont Raffles Hotels International. Cornell Hospitality Report . Vol. 19.
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Leo M. Renaghan. 2011. The Role of Space in Revenue Management. In Revenue Management , 17–28. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Chapter Google Scholar
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Stephani K A. Robson. 2004. The Impact of Restaurant Table Characteristics on Meal Duration and Spending. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 45 (4): 333–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880404270063 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Gary M. Thompson. 2004. Restaurant Revenue Management at Chevys: Determining the Best Table Mix. Decision Sciences 35 (3): 371–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0011-7315.2004.02531.x .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Gary M. Thompson. 2005. An Evaluation of Heuristic Methods for Determining the Best Table Mix in Full-Service Restaurants. Journal of Operations Management 23 (6): 599–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2004.07.010 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jochen Wirtz. 2002. Perceived Fairness of Demand-Based Pricing for Restaurants. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 43 (1): 31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-8804(02)80006-4 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jochen Wirtz. 2003. Has Revenue Management Become Acceptable?: Findings From an International Study on the Perceived Fairness of Rate Fences. Journal of Service Research 6 (2): 125–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670503257038 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jochen Wirtz. 2007. Customer Satisfaction with Seating Policies in Casual-Dining Restaurants. Cornell Hospitality Report . Vol. 7. https://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/chrpubs/63 .
Kimes, Sheryl E., and Jochen Wirtz. 2016. Revenue Management in Restaurants: Unbundling Pricing for Reservations from the Core Service. Cornell Hospitality Report . Vol. 16.
Kisilevich, Slava, Daniel Keim, and Lior Rokach. 2013. A GIS-Based Decision Support System for Hotel Room Rate Estimation and Temporal Price Prediction: The Hotel Brokers’ Context. Decision Support Systems 54 (2): 1119–33.
Kivela, Jaksa, Robert Inbakaran, and John Reece. 1999. Consumer Research in the Restaurant Environment, Part 1: A Conceptual Model of Dining Satisfaction and Return Patronage. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 11 (5): 205–22.
Koshiba, Hitoshi, Takeshi Takenaka, and Yoichi Motomura. 2012. Service Management System Based on Computational Customer Models Using Large-Scale Log Data of Chain Stores. In Th International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics , 57–64.
Koshiba, Hitoshi, Takeshi Takenaka, and Yoichi Motomura. 2013. A Service Demand Forecasting Method Using a Customer Classification Model. In The Philosopher’s Stone for Sustainability , 281–85. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
Kuo, R.J. 2001. A Sales Forecasting System Based on Fuzzy Neural Network with Initial Weights Generated by Genetic Algorithm. European Journal of Operational Research 129 (3): 496–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00463-4 .
Kwon, SoYeon, and SooCheong Shawn. Jang. 2011. Price Bundling Presentation and Consumer’s Bundle Choice: The Role of Quality Certainty. International Journal of Hospitality Management 30 (2): 337–44.
Lai, Hao Bin, Shahrim Karim Jack, Steven E. Krauss, and Farah A. C. Ishak. 2019. Can Restaurant Revenue Management Work with Menu Analysis ?”. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 18 (3): 204–12. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-019-00194-6 .
Lasek, Agnieszka, Nick Cercone, and Jim Saunders. 2016. Restaurant Sales and Customer Demand Forecasting: Literature Survey and Categorization of Methods. In Smart City 360° , 479–91. Cham: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33681-7 .
LeBruto, Stephen M., William J. Quain, and Robert A. Ashley. 1995. Menu Engineering: A Model Including Labor. Hospitality Review 13 (1): 41–49. http://digitalcommons.fiu.edu/hospitalityreview/vol13/iss1/5/?utm_source=digitalcommons.fiu.edu/hospitalityreview/vol13/iss1/5&utm_medium=PDF&utm_campaign=PDFCoverPages .
Liu, Lon-Mu., Siddhartha Bhattacharyya, Stanley L. Sclove, Rong Chen, and William J. Lattyak. 2001. Data Mining on Time Series: An Illustration Using Fast-Food Restaurant Franchise Data. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 37 (4): 455–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-9473(01)00014-7 .
Luca, Michael. 2016. Reviews, Reputation, and Revenue: The Case of Yelp.Com. Harvard Business School NOM Unit Working Paper .
Martin-Consuegea, David, Angel Millan, Estrella Diaz, and Eunju Ko. 2010. The Effects of Price Salience on Consumer Perception and Purchase Intentions. Journal of Global Academy of Marketing Science 20 (2): 149–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/12297119.2010.9730187 .
Mathe-Soulek, Kimberly, Matt Krawczyk, Robert J. Harrington, and Michael Ottenbacher. 2016. The Impact of Price-Based and New Product Promotions on Fast Food Restaurant Sales and Stock Prices. Journal of Food Products Marketing 22 (1): 100–117. https://doi.org/10.1080/10454446.2014.949996 .
Mathies, Christine, and Siegfried Gudergan. 2007. Revenue Management and Customer Centric Marketing—How Do They Influence Travellers’ Choices?”. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 6 (4): 331–46. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.rpm.5160109 .
Mcguire, Kelly A., and Sheryl E. Kimes. 2006. The Perceived Fairness of Waitlist-Management Techniques for Restaurants. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 47 (2): 121–34. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880405284212 .
Miao, Qing, Yihua Li, and Xiubin B. Wang. 2018. Restaurant Reservation Management Considering Table Combination. Pesquisa Operacional 38 (1): 73–86. https://doi.org/10.1590/0101-7438.2018.038.01.0073 .
Miller, Jack E. 1992. Menu Pricing and Strategy . Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Miller, James J., Cynthia S. McCahon, and Judy L. Miller. 1991. Foodservice Forecasting Using Simple Mathematical Models. Hospitality Research Journal 15 (1): 43–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/109634809101500105 .
Miller, James J., Cynthia S. McCahon, and Judy L. Miller. 1993. Foodservice Forecasting: Differences in Selection of Simple Mathematical Models Based on Short-Term and Long-Term Data Sets. Hospitality Research Journal 16 (2): 93–102.
Milliman, Ronald E. 1986. The Influence of Background Music on the Behavior of Restaurant Patrons. Journal of Consumer Research 13 (2): 286–89. https://doi.org/10.1086/209068 .
Morgan, Michael S., and Pradeep K. Chintagunta. 1997. Forecasting Restaurant Sales Using Self-Selectivity Models. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 4 (2): 117–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-6989(96)00035-5 .
Mudie, P., and A. Pirrie. 2006. Services Marketing Management . New York: Elsevier.
Muller, Christopher. 2018. Restaurant Delivery: Are the ‘ODP’ the Industry’s ‘OTA’? Part I & II. Boston Hospitality Review .
Nazlan, Nadia Hanin, Sarah Tanford, Carola Raab, and Choongbeom (CB) Choi. . 2018. The Influence of Scarcity Cues and Price Bundling on Menu Item Selection. Journal of Foodservice Business Research 21 (4): 420–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/15378020.2018.1440129 .
Nemeschansky, Ben. 2020. Listen to Your Customer - How to Manage Your Restaurant More Effectively. Journal of Foodservice Business Research 23 (1): 17–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/15378020.2019.1671119 .
Noone, Breffni M., Sheryl E. Kimes, Anna S. Mattila, and Jochen Wirtz. 2007. The Effect of Meal Pace on Customer Satisfaction. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 48 (3): 231–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880407304020 .
Noone, Breffni M., Sheryl E. Kimes, Anna S. Mattila, and Jochen Wirtz. 2009. Perceived Service Encounter Pace and Customer Satisfaction An Empirical Study of Restaurant Experiences. Journal of Service Management 20 (4): 380–403. https://doi.org/10.1108/09564230910978494 .
Noone, Breffni M., and Chung Hun Lee. 2011. Hotel Overbooking: The Effect of Overcompensation on Customers’ Reactions to Denied Service. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research 35 (3): 334–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348010382238 .
Noone, Breffni M., and Kelly A. McGuire. 2014. Effects of Price and User-Generated Content on Consumers’ Prepurchase Evaluations of Variably Priced Services. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Research 38 (4): 562–81. https://doi.org/10.1177/1096348012461551 .
Norvell, Tim, and Alisha Horky. 2017. A Framework and Model to Evaluate Promotions: A Restaurant Cross-Promotion in-Market Study. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 16 (4): 345–56. https://doi.org/10.1057/rpm.2016.14 .
NRAI. 2019. I ndian Restaurant Industry Employed 7.3 Million People in 2018-19: NRAI . SNS Web. 2019. https://www.thestatesman.com/business/indian-restaurant-industry-employed-7-3-million-people-2018-19-nrai-1502753854.html .
Pavesic, David V. 1983. Cost/Margin Analysis: A Third Approach to Menu Pricing and Design. International Journal of Hospitality Management 2 (3): 127–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4319(83)90033-6 .
Pimentel, Victor, Aishajiang Aizezikali, and Tim Baker. 2019. Hotel Revenue Management: Benefits of Simultaneous Overbooking and Allocation Problem Formulation in Price Optimization. Computers and Industrial Engineering 137: 106073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.106073 .
Raman, Arun, and Debjit Roy. 2015. An Analytical Modeling Framework for Determining the Optimal Table Mix in Restaurants. IFAC-PapersOnLine 48 (3): 225–30.
Rao, Akshay R., and Kent B. Monroe. 1989. The Effect of Price, Brand Name, and Store Name on Buyers’ Perceptions of Product Quality: An Integrative Review. Journal of Marketing Research 26 (3): 351–57. https://doi.org/10.2307/3172907 .
Raul, Nataasha, Yash Shah, and Mehul Devganiya. 2016. Restaurant Revenue Prediction Using Machine Learning. International Journal of Engineering And Science 6 (4): 91–94.
Reynolds, Dennis, Imran Rahman, and William Balinbin. 2013. Econometric Modeling of the U.S. Restaurant Industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management 34: 317–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2013.04.003 .
Riasi, Arash, Zvi Schwartz, and Srikanth Beldona. 2019. Hotel Overbooking Taxonomy: Who and How?”. International Journal of Hospitality Management 82: 1–4.
Rowson, Bill, Wouter van Poppel, and Sjoerd Gehrels. 2016. Wasted Millions: Revenue Management in Dutch Culinary Restaurants. Research in Hospitality Management 6 (2): 127–33. https://doi.org/10.1080/22243534.2016.1253278 .
Ryu, Kisang, and Alfonso Sanchez. 2003. The Evaluation of Forecasting Methods at an Institutional Foodservice Dining Facility. The Journal of Hospitality Financial Management 11 (1): 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/10913211.2003.10653769 .
Saito, Taiga, Akihiko Takahashi, and Noriaki Koide. 2017. Optimal Overbooking Strategy in Online Hotel Booking Systems . CIRJE, Faculty of Economics. 2017. http://www.cirje.e.u-tokyo.ac.jp/research/03research02dp.html .
See-Kwong, Goh, N.G. Soo-Ryue, Wong Shiun-Yi, and Chong Lily. 2017. Outsourcing to Online Food Delivery Services: Perspective of F&B Business Owners. The Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce 22 (2): 1–18.
Sellers, Kimberly F., and Galit Shmueli. 2010. A Flexible Regression Model for Count Data. The Annals of Applied Statistics 4 (2): 943–61. https://doi.org/10.1214/09-AOAS306 .
Shaw, Mary. 2014. Loyalty Program Attributed to Starbucks Sales Success . 2014. https://www.customerinsightgroup.com/loyaltyblog/loyalty-program-attributed-to-starbucks-sales-success/ .
Sill, Brian, and Robert Decker. 1999. Applying Capacity-Management Science: The Case of Browns Restaurants. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 40 (3): 22–30.
Song, Boqian, and Michael Z.F.. Li. 2018. Dynamic Pricing with Service Unbundling. Production and Operations Management 27 (7): 1334–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/poms.12871 .
Susskind, Alex M. 2010. Guest Service Management and Processes in Restaurants: What We Have Learned in Fifty Years. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 51 (4): 479–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965510375028 .
Susskind, Alex M., Dennis Reynolds, and Eriko Tsuchiya. 2004. An Evaluation of Guests’ Preferred Incentives to Shift Time-Variable Demand in Restaurant. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 45 (1): 68–84. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880403260108 .
Tan, Tom Fangyun, and Serguei Netessine. 2019. At Your Service on the Table: Impact of Tabletop Technology on Restaurant Performance. Management Science 66: 4496–4515.
Tang, Jason, Toni Repetti, and Carola Raab. 2019. Perceived Fairness of Revenue Management Practices in Casual and Fine-Dining Restaurants. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights 2 (1): 92–108. https://doi.org/10.1108/JHTI-10-2018-0063 .
Thompson, Gary. 2015. Restaurant Reservations Optimization Tool. Cornell Hospitality Tool 6 (4): 3–10. http://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/chrtools .
Thompson, Gary M. 2002. Optimizing a Restaurant’s Seating Capacity. Cornell Hotel and Restaurant Administration Quarterly 43 (4): 48–57. https://doi.org/10.1177/0010880402434005 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2007. Restaurant Capacity Effectiveness: Leaving Money on the Tables . https://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/chrpubs/143 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2009. (Mythical) Revenue Benefits of Reducing Dining Duration in Restaurants. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 50 (1): 96–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965508328422 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2010. Restaurant Profitability Management: The Evolution of Restaurant Revenue Management. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 51 (3): 308–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965510368653 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2011. Cherry-Picking Customers by Party Size in Restaurants. Journal of Service Research 14 (2): 201–13. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670511401367 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2011. Inaccuracy of the ‘Naïve Table Mix’ Calculations. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 52 (3): 241–52. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965511398261 .
Thompson, Gary M., and Gary M. Thompson. 2015. An Evaluation of Integer Programming Models for Restaurant Reservations. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 14 (5): 305–20. https://doi.org/10.1057/rpm.2015.17 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2019. The Value of Timing Flexibility in Restaurant Reservations. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly 60 (4): 378–88. https://doi.org/10.1177/1938965518805685 .
Thompson, Gary M., and Robert J. Kwortnik. 2008. Pooling Restaurant Reservations to Increase Service Efficiency. Journal of Service Research 10 (4): 335–46. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670508314267 .
Thompson, Gary M. 2003. Dedicated or Combinable? A Simulation to Determine Optimal Dedicated or Combinable? https://scholarship.sha.cornell.edu/chrpubs .
Tse, Tony S.M.., and Yiu-Tung. Poon. 2017. Modeling No-Shows, Cancellations, Overbooking, and Walk-Ins in Restaurant Revenue Management. Journal of Foodservice Business Research 20 (2): 127–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/15378020.2016.1198626 .
Upadhyay, Amit, and Nomesh B. Bolia. 2014. An Optimization Based Decision Support System for Integrated Planning and Scheduling on Dedicated Freight Corridors. International Journal of Production Research 52 (24): 7416–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2014.932463 .
Vinod, B. 2019. Hotel Retailing with Attribute-Based Room Pricing and Inventory Control. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 18 (6): 429–33. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-019-00207-4 .
Wang, Jiana-Fu., Yi-Chiun. Lin, Chen-Feng. Kuo, and Shao-Jen. Weng. 2017. Cherry-Picking Restaurant Reservation Customers. Asia Pacific Management Review 22 (3): 113–21.
Whelan-Ryan, Fiona. 2000. Yield Management and the Restaurant Industry. In Yield Management: Strategies for the Service Industries , 271–88.
Wulu, J.T., Jr., K.P. Singh, F. Famoye, T.N. Thomas, and G. McGwin. 2002. Regression Analysis of Count Data. Journal of the Indian Society of Agricultural Statistics 55 (2): 220–31. https://doi.org/10.2307/2670019 .
Xu, Jingmei, Hu. Li, Xiaolong Guo, and Xia Yan. 2020. Online Cooperation Mechanism: Game Analysis between a Restaurant and a Third-Party Website. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management 19 (1): 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-018-00181-3 .
Zhang, Peter G. 2003. Time Series Forecasting Using a Hybrid ARIMA and Neural Network Model. Neurocomputing 50: 159–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(01)00702-0 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, India
Mohit Tyagi & Nomesh B. Bolia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mohit Tyagi .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tyagi, M., Bolia, N.B. Approaches for restaurant revenue management. J Revenue Pricing Manag 21 , 17–35 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-021-00288-0
Download citation
Received : 20 November 2020
Accepted : 19 January 2021
Published : 23 February 2021
Issue Date : February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41272-021-00288-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Restaurant revenue management (RRM)
- Arrival management
- Price management
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Access through your organization
- Purchase PDF
Article preview
Introduction, section snippets, references (127), cited by (114).

International Journal of Hospitality Management
A review of restaurant research in the last two decades: a bibliometric analysis.
- • Two periods are identified in restaurant research in hospitality field.
- • Interest is directed from service to the customer’s perceptions and emotions.
- • Currently, satisfaction as consequence of diverse attributes is the motor theme.
- • The future of research is the health, CBBE and technology innovativeness.
Background to restaurant research
Bibliometric analysis in hospitality and tourism, bibliometric analysis: data sets, scientific performance, main conclusions, implications for academic research, acknowledgements, consumer responses to interactive restaurant self-service technology (irsst): the role of gadget-loving propensity, int. j. hosp. manage., changes in the structures and directions of destination management and marketing research: a bibliometric mapping study, 2005–2016, j. destin. mark. manage., my destination in your brain: a novel neuromarketing approach for evaluating the effectiveness of destination marketing, explicating restaurant performance: the nature and foundations of sustainable service and organizational environment, maturity and development of high-quality restaurant websites: a comparison of michelin-starred restaurants in france, italy and spain, vicious advice: analyzing the impact of tripadvisor on the quality of restaurants as part of the cultural heritage of venice, tour. manage., the intellectual structure of research in hospitality management: a literature review using bibliometric methods of the journal international journal of hospitality management, perceived values, satisfaction, and behavioral intentions: the role of familiarity in korean restaurants, influencing factors on restaurant customers’ revisit intention: the roles of emotions and switching barriers, impact of hotel-restaurant image and quality of physical-environment, service, and food on satisfaction and intention, consumer-based chain restaurant brand equity, brand reputation, and brand trust, professional conceptions of creativity in restaurant space planning, structural effects of cognitive and affective responses to web advertisements, website and brand attitudes, and purchase intentions: the case of casual-dining restaurants, creating a model of customer equity for chain restaurant brand formation, restaurant experiences triggering positive electronic word-of-mouth (ewom) motivations, the effects of health value on healthful food selection intention at restaurants: considering the role of attitudes toward taste and healthfulness of healthful foods, the relationship between brand equity and firms’ performance in luxury hotels and chain restaurants, measuring customer perceptions of restaurant innovativeness: developing and validating a scale, triangulation in tourism research: a bibliometric study of top three tourism journals, tourism manage. perspect., bibliometric studies in tourism, ann. tour. res., what we know and do not know about authenticity in dining experiences: a systematic literature review, how nutrition information frame affects parents’ perceptions of restaurants: the moderating role of information credibility, knowledge mapping of hospitality research − a visual analysis using citespace, hospitality marketing research: recent trends and future directions, authenticity perceptions, brand equity and brand choice intention: the case of ethnic restaurants, which bundles of corporate governance provisions lead to high firm performance among restaurant firms, who’s on the tourists’ menu exploring the social significance of restaurant experiences for tourists, tour. manag., a netnographic examination of constructive authenticity in victoria falls tourist (restaurant) experiences, sparking interest in restaurant dishes cognitive and affective processes underlying dish design and ecological origin. an fmri study, physiol. behav., psychological factors influencing customers’ acceptance of smartphone diet apps when ordering food at restaurants, food and gastronomy research in tourism and hospitality: a bibliometric analysis, tourism and statistics: bibliometric study 1998–2002, managing brand equity: capitalizing on the value of a brand name, intelligent agent technology: what affects its adoption in hotel food supply chain management, j. hosp. tour. technol., foreign tourists’ motivation and information source(s) influencing their preference for eating out at ethnic restaurants in bangkok, int. j. hosp. tour. adm., analysis of the scientific production international indigenous tourism 1990 to 2013: a bibliometric study and proposal of a research agenda, pasos rev. tur. patrim. cult., restaurant assessment of local food and the global sustainable tourism criteria, eur. j. tour. res., technological disruptions in services: lessons from tourism and hospitality, j. serv. manage., classifying restaurants to improve usability of restaurant research, int. j. contemp. hosp. manage., bibliometric analysis of the scientific production of judo as a combat sport, revista de artes marciales asiáticas, i ate, i enjoyed and i posted: tripadvisor and marvelous experiences in restaurants, rosa dos ventos-turismo e hospitalidade, the effects of luxury restaurant environments on diners’ emotions and loyalty: incorporating diner expectations into an extended mehrabian-russell model, a tri-method approach to a review of adventure tourism literature: bibliometric analysis, content analysis, and a quantitative systematic literature review, j. hosp. tour. res., examining consumers’ intentions to dine at luxury restaurants while traveling, sport management: a bibliometric study on central themes and trends, eur. sport. manag. q., scimat: a new science mapping analysis software tool, j. am. soc. inf. sci. technol., the intellectual development of management information systems, 1972–1982: a co-citation analysis, manage. sci., taking the local food movement one step further: an exploratory case study of hyper-local restaurants, tour. hosp. res., state of the art of research in the sector of thermalism, thalassotherapy and spa: a bibliometric analysis, restaurant and foodservice research, a review of three decades of academic research on brand equity: a bibliometric approach using co-word analysis and bibliographic coupling.
Bibliometric analysis has been applied in many disciplines in recent years to raise awareness of their value, describe their evolution, and identify the predominant themes over time, while providing academics and professionals with a better understanding of the state of the art of the discipline in question. Examples of this type of study can be found in diverse fields such as consumer research (Jia, Zhou, and Allaway, 2018; Zuschke, 2020), financial marketing (Muñoz-Leiva, Sánchez-Fernández, Liébana-Cabanillas, and Martínez-Fiestas, 2013), business-to-business marketing (Kumar, Sharma, and Salo, 2019; Möller and Halinen, 2018), management information systems (Culnan, 1986), integrated marketing communications (Muñoz-Leiva et al., 2015), comparative advertising (Del Barrio-García, Muñoz-Leiva, and Golden, 2020), brand personality (Radler, 2018), strategic management (Vogel and Güttel, 2013), business capabilities (Kouropalatis, Giudici, and Acar, 2019), socially-responsible consumer behavior (Nova-Reyes, Muñoz-Leiva, and Luque-Martinez, 2020), restaurant tourism (Rodríguez-López, Alcántara-Pilar, Del Barrio-García, and Muñoz-Leiva, 2020), medical tourism (De la Hoz-Correa, Muñoz-Leiva, and Bakucz, 2018), qualitative research in marketing (Murgado-Armenteros et al., 2015), service research (Donthu, Gremler, Kumar, and Pattnaik, 2020a), and strategic marketing (Donthu, Kumar, Paul, Pattnaik, and Strong, 2020b). In the specific field of branding scholarship, there are some bibliometric studies on collateral aspects such as brand positioning (Sciasci, Garcia, and Galli, 2012), place branding (Ma, Schraven, de Bruijne, De Jong, and Lu, 2019), brand personality (Lara-Rodríguez, Rojas-Contreras, and Oliva, 2019), or brand experience (Zha, Melewar, Foroudi, and Jin, 2020).
Two decades of customer experience research in hospitality and tourism: A bibliometric analysis and thematic content analysis
A bibliometric review of research on covid-19 and tourism: reflections for moving forward, big social data and customer decision making in vegetarian restaurants: a combined machine learning method.
The current study highlights the importance of online review analysis for managing restaurant marketing. This issue has been highlighted in the existing literature that emphasized the strength of eWOM and online reviews in restaurant industry to identify dining behaviour of customers (DiPietro, 2017; Kim and Tanford, 2019; Rodríguez-López et al., 2019; Zhang and Hanks, 2018). The current study significantly shows the application of online reviews for market segmentation in restaurant industry contrasted with traditional market segmentation through survey.
The rise of online food delivery culture during the COVID-19 pandemic: an analysis of intention and its associated risk
Measuring gastronomic image online.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW

It is a literature review for restaurant management system
Related papers
International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
American Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation (AJMRI) ISSN: 2158-8155 (Online), 2832-4854 (Print), 2022
The study was conducted to determine the pros and cons of using Restaurant Management System (RMS) based on the views of restaurant staff in the context of Bangladesh. The effectiveness of RMS use in terms of business features was examined and differences were sought. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire. Participants working in restaurants where RMS was used were of the view that RMS simplified operations, increased sales, and improved product / service quality, while those working in restaurants where RMS was not used had higher scores in expressions of difficulty using the system. In addition, RMS has a more positive impact on sales growth and product / service quality delivery according to the chain restaurant staff (p <0.05). Again, restaurant employees with a minimum score of 10 or fewer employees are included in relation to the positive impact of using RMS in terms of operations management and sales growth. Therefore, there is a relationship between business size and RMS usage requirements.
Advances in Hospitality, Tourism, and the Services Industry, 2019
Customers expect a high standard and fast service from enterprises. In addition, competition among enterprises necessitates that enterprises renew themselves, meet customer expectations at maximum level, and raise the standard of products and services. Traditional restaurant management is inadequate to provide all this. This situation led to search, and restaurant management systems (RMS) have been developed. RMS, which emerged in the 1970s, are now much more developed, facilitating both the operation and management process and offering a professional management opportunity. RMS has made it possible for the restaurants to institutionalize and establish chain enterprises. Moreover, income and expense control can be made more effective via RMS. This chapter explains RMS and the operation of RMS via a sample program.
International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET), 2022
The Restaurant Management System provides necessary services for the typical fast food restaurant to manage all the day-today activities. The restaurant management system is there to help communication between all teams within a restaurant by minimizing the probability of human error and getting more efficient and effective information. This system has a built-in POS system with order management solutions and kitchen management to handle all the food production efficiently to get the orders to the customer
Existing restaurant systems are partially automated. We have developed a fully automated restaurant management and communication system. This paper covers the partial automation that exists and focuses the details regarding how we have implemented full automation in management and communication for restaurants. It also covers technical aspects of web based application and android application and how they are clubbed together with their advantages and disadvantages. It also lights the future work that can be added on regarding android application to make it more user friendly.
International Journal For Reseacrh In Applied Science And Engineering Technology, 2020
Catering Service for food/Online Cafe (OC) is the software designed to order food online for Customers. The prime objective of the project is to provide smart and effective service to the end-users. It is a web-based application that is built using JAVA with a user-friendly interface for customers to browse the catalogue and order the food online. The shop keepers can include as many products as possible and also categorize them as they prioritize, manage orders and process the payments. The clients have to make their own choice and choose their preferred mode of payment and wait for the delivery of their food items. The OC system processes all sorts of information related to the order type options. It facilitates an end to end solution in online food ordering. By adopting this new approach, the information can be accessed with just a single click. The study focuses on a web application in JAVA for online food ordering system and provides an option for the restaurant owners to update their food menu as well. This study also focuses on establishing effective connectivity between the front end (shopkeeper and customer) and back-end (admin) using JAVA database connectivity with MySQL. Keywords: catering, customer, food order, online cafe, shopkeeper I. INTRODUCTION The technological innovations and advancements in information and communication technology have undergone a paradigm change in the last decade. Ever-rapidly evolving strategies that adapt itself to the ever-changing human practices are the need of the hour. Despite innovations happening very rapidly across various industries, Food industry had always been lagging in terms of innovations, novelty and modernization. With online presence being felt across all industries, the food industry has undergone a revolutionary change in practice in the last five years. Food systems these days have undergone a massive shift from being supply-driven to demand-driven [1]. In the past, the food industry traditionally lagged behind other industries in adapting itself to innovations and newer technologies. Recent advances in the field of computer technology and ever-increasing expectations from the end-users (consumers) have made it mandatory for the food industry to bring in a full-fledged automated process that enabled complete transparency in the food sale and distribution process [2]. Another motivation can be considered as the increasing use of smartphones by the customers so that any users of this system get all service of the system. The system will be designed to avoid users doing fatal errors where users can change their profile also where users can track their food items through GPS and where users can provide feedback and recommendations to Restaurants/Mess service providers. There's a need for the system due to lack of a full-fledge application that can fulfil the customer requirements by providing him food from restaurants/mess service. For the students studying in different cities, our system will be very helpful. The flexibility to the Customers/Users to order from either Restaurants or Mess is provided by our system. A recommendation to the customers is also provided from the restaurants/mess owners which are updated daily. There will be no limitation on the amount of order the customer wants by ordering food from our system. As a Startup Business for the developers, the same system application can be used. Real-time customer's feedback ratings are provided by our system with the comments to the restaurants/mess owner. It gives appropriate feedbacks to users, so if there is any error happened, and then there will be a feedback dialogue toward users. To avoid users doing fatal errors and inappropriate action our system application is designed. Input will be taken by the user from the graphical user interface. The major attributes such as name, address, and email-Id, mobile no, other personal related values will give input to the dataset. The User/Customer's Order, Bill, Feedback and Recommendation will provide the output. For the initial implementation of the system, we have considered 2 restaurants and 2 mess services in 5 areas. Khairunnisa proposed a project that presented an in-depth technical operation of the Wireless Ordering System (WOS) that included systems architecture, their function, various limitations and possible recommendations [3]. Our research project aims to design and develop a fully automated wireless food ordering system facility for the customers ordering food from a restaurant.
SISFORMA, 2021
Indonesia is one of the largest culinary attractions in Southeast Asia. The culinary diversity in Indonesia encourages stakeholders to create restaurant businesses with effective and efficient business processes. One of the efforts to make the restaurant business process effective and efficient is to build a restaurant management information system. By using a system, business actors will be able to control and evaluate their business with appropriate reports. For this reason, the purpose of this study is to build a restaurant management information system using the RAD (Rapid Application Development) method, because building this application requires a systematic, structured, and object-oriented process. The RAD method emphasizes a high quality systems, fast development and delivery and low costs development process [1] so that this process requires a serious role from business actors to build a restaurant management information system. The results of this system design can make ...
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
NOVATEUR PUBLICATION, 2020
Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research, 2021
JELAJAH: Journal of Tourism and Hospitality
IRJET, 2022
World Academy of Research in Science and Engineering, 2020
International Journal for Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology, 2023
International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 2007
Ekonomika poljoprivrede
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 27 September 2024
The dental needs of children with Epidermolysis Bullosa and service delivery: a scoping review
- Z. Smith ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5575-1165 1 ,
- S. Nath ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8714-7264 2 ,
- M. Javanmard ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3675-9871 1 &
- Y. Salamon ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1710-8056 1
BMC Oral Health volume 24 , Article number: 1131 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) is a genetic condition with fragility of the skin and oral mucosal lining requiring appropriate care and management by dental health professionals. The objective of this scoping review was to comprehensively examine the specialised dental needs of children with Epidermolysis Bullosa and map evidence towards the type, availability, and accessibility of specialised dental care services within various health care systems.
This scoping review was conducted using the JBI Methodology framework for scoping reviews. Five databases were used to source relevant literature: MEDLINE, Embase, Dentistry & Oral Sciences Source, Scopus, and Web of Science during the period 1963–2022.
Thirty three published case reports were identified reporting on 45 participants encompassing the dental care and management of children diagnosed with EB aged between 0–12 years of age from an Australian and international health care context. The findings reveal the need for greater awareness amongst health professionals in the management and specialised dental care needs of children and the need for further research, and care pathways for children with EB.
There is a dearth of evidence which examines the dental needs of children, in particular referral pathways and timely access to dental health services and professionals. Dentists play an important role in monitoring and providing individualised and specialised oral care and treatment to the child with EB. It is vital that dentists as well as the wider multidisciplinary team have knowledge and understanding of the EB condition in meeting the specialised needs and management of these children.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) is a rare inherited disease affecting the skin and mucosal membranes in response to minor trauma. The condition has thirty reported sub types across four main classifications of the disease based on the blister formations noted as: EB Simplex (EBS), Junctional EB (JEB), Dystrophic EB (DEB) and Kindler EB (KEB) [ 1 ]. The type of EB can range from mild to severe in nature impacting an estimated 500,000 people globally [ 1 ]. The condition is incurable and affects people from birth with chronic fragility of the skin, blistering, ulcerations, and trauma to the skin and mucosal membranes from minor injury, trauma, rubbing, friction, and heat [ 2 , 3 ]. Babies born with this condition are commonly referred to as ‘butterfly children’ due to the thin, fragile, and translucent nature of their skin similar to that of a delicate butterfly’s wings [ 1 ]. Children with EB have been reported to experience traumatic stress reactions from not only their medical treatments but interactions with health professionals providing painful treatments [ 4 , 5 ]. Similarly, continued daily EB treatments and management of their condition has also reported to impact and cause strain on the individuals, their family and those providing care [ 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Dependent on the type of EB, the eyes, nails, and hair can also be affected in addition to the mouth, gums, throat and esophagus, stomach, and bladder [ 1 ]. For children, blistering and trauma to the oral mucosa can impact their ability to eat and maintain healthy weight, nutrition, growth, and wound healing [ 7 ]. Of the four types of EB all patients experienced some degree of mouth ulceration. EBS is identified as having milder oral cavity ulceration [ 1 ]. However, JEB, DEB and KEB have additional health issues of tooth enamel decay, tooth decay, overcrowding or misalignment of teeth, and oesophageal blistering [ 1 ]. The sub type KEB also has additional oral cavity complications of gingivitis, tooth decay, loss of teeth and gingival enlargement ( growth of the gum around the teeth ) [ 8 ]. For the EB child general oral health care is complex with a focus on preventative care, the management of oral hygiene, dental caries, and necessary tooth extractions [ 5 , 9 ]. Similarly, dental sensitivity, pain and oral care in general are areas often overlooked for children with this condition. Several authors report children as reluctant to conduct daily cleaning, thereby being noncompliant with ongoing recommended treatment/care when visiting dentists thereby increasing the incidence of ongoing dental treatment issues such as infection, teeth cavities and inflammation of the gums and overall poor oral health [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. For children with EB regular in the chair dental treatment can be painful and traumatic with further trauma and complications experienced to the oral mucosa, with many children refusing treatment based on fear, pain, and previous negative dental experiences [ 13 ].
Children with EB may undergo numerous invasive procedures with their condition further compromised in the regular dental environment due to non-compliance, pain, trauma, and further complications to the oral mucosa. Dental care for EB children is often required to be undertaken in the operating room setting under general anaesthetic where specialised care and management can be fulfilled in a safe and controlled environment. Little is currently understood of the current arrangement of dental services, accessibility, and the availability of healthcare services for EB children.
Current guidelines on dental care for EB patients focus on prevention and management with a shared care approach with the multidisciplinary team providing care [ 8 ]. Referrals to specialist dental services are often required for the management of painful extractions or dental treatments which are unable to be performed in a regular dental clinic. For many children, dental treatment is best undertaken within the perioperative setting with experienced anaesthetic staff familiar with the EB condition as anaesthetic management can be hazardous with issues such as difficultly establishing an airway during intubation and trauma to the airway [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Many children with EB have had successful surgical procedures conducted under a general anaesthetic, with new techniques to manage the airway successfully intraoperatively in a controlled environment to improve their long-term oral EB rehabilitation to delimit exacerbating further oral, skin trauma and integrity during the perioperative period [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ].
Globally, there is extensive literature of challenging and complex dental EB cases and the necessity for individualised dental care and management across the lifespan [ 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ]. It is imperative that health services and schemes are available to assist patients with ongoing care requirements across the lifespan. In the Australian context, there is support by the National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) for children and adults with significant physical impairment for the severe types of EB whilst those with milder forms of EB are unsupported in meeting their specific care requirements [ 25 ]. Therefore, there is a need for greater attention on the dental needs and care requirement for the EB child in line with their developmental oral health needs. Dental guidelines in managing EB patients have emphasised the need for early access to dental services with regular prevention and monitoring by a local dentist [ 8 , 26 ]. In effect, the local dentist is a primary conduit for a shared care approach and referral to specialised dentistry services should sedation or general anesthesia be required to aid in the child’s ongoing management and improve the quality of oral health outcomes across the lifespan [ 21 ]. Access to regular and specialised dental services may not always be readily available. This may impact how children and families who may require individualised preventative care, access treatment and care to manage their condition and their long-term oral health. Improving dental care and services for children with EB is an area often overlooked and in need of highlighting for the whole multidisciplinary health team. As treatment is often required early it is important for all health professionals to have an awareness of EB and the potential impact on the child’s developmental phases, nutrition, healthy weight, growth, wound healing, speech, and oral health. The purpose of this scoping review is to provide insight into the best evidence base of specialised dental care and management for children with EB during their pivotal developmental ages between 0–12 years and map evidence towards the type, availability, and accessibility of specialised dental care services within various health care systems from the extant literature.
Scoping review questions
The following questions guided the scoping review:
What are the specialised dental needs of children with EB?
What is the availability and accessibility of specialised dental care services currently available for children impacted with EB?
Given the rare nature of EB and the dearth of literature specifically exploring the dental care of children it was decided that a scoping review was the best approach and suitable in nature to address the research topic and questions from an international perspective. To guide the review process, the scoping review was conducted in accordance with the JBI methodology framework for scoping reviews and reported using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) [ 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ] to broadly explore and map current evidence from the extant literature.
Inclusion criteria
Participants.
In line with the review questions, we included children 0–12 years of age, both male and female, of any ethnicity diagnosed with any type and form of EB ( e.g., EB Simplex (EBS), Junctional EB (JEB), Dystrophic EB (DEB) and Kindler EB (KEB ).
Included were studies which examined EB dental treatments for paediatric patients requiring specialised dental care, treatment, or specialised services from various health care settings ( e.g., dental clinic, hospital setting, hospital clinic, operating room ) inclusive of care provided by the multidisciplinary health care professionals ( e.g., dentists, dental nurse, dental surgeons & anesthetists ).
Studies from any geographical location, setting which reported on children 0–12 years of age with EB requiring specialised dental care or treatment or services were considered for inclusion within this review. Studies which addressed aspects of ‘ dental services ’, ‘ referral processes ’ and ‘ management of the paediatric EB patient ’ were included within this review.

Types of sources
This review considered all forms of primary studies; experimental and quasi-experimental study designs including randomized controlled trials, non-randomized controlled trials, before and after studies, interrupted time-series studies, qualitative studies, and text and opinion papers published in English language.
Exclusion criteria
The following exclusion criteria were applied during the abstract, title and full-text review stages:
▪ Ineligible phenomena of interest or health condition
▪ Conference posters
▪ Ineligible age population e.g. studies focused on children more than 12 years.
▪ Studies published in another language without an English translation were excluded due to lack of time and cost of translation.
Search strategy
The search strategy aimed to locate both published and unpublished primary studies. An initial search of MEDLINE, Embase, Dentistry & Oral Sciences Source (DOSS), Scopus, Web of Science was undertaken with a librarian to identify the relevant text words, and index terms to identify and source relevant articles on the topic during October 2022. The keyword search terms used for MEDLINE were: Exp epidermolysis bullosa OR epidermolysis bullosa.ti,ab OR EB.ti,ab OR bullous epidermolysis.ti,ab OR epidermoid bullosa.ti,ab Dental care.sh OR dental care for children.sh OR oral health.sh OR exp Surgery, Oral OR exp Oral Surgical Procedures OR exp Dentistry, Operative OR dentistry.sh OR exp "Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons" OR exp tooth extraction OR exp dental clinics OR oral hygiene.sh OR dental*.ti,ab OR ((teeth OR tooth OR dental) adj2 (extraction* OR excision OR removal)).ti,ab OR oral health.ti,ab OR dental surg*.ti,ab OR dentist*.ti,ab OR teeth.ti,ab OR tooth.ti,ab OR oral maxillofacial.ti,ab OR ((hospital outpatient OR program*) adj3 (dental* OR oral OR dentist* OR teeth OR tooth OR extraction*)).ti,ab Exp child OR exp infant OR child*.ti,ab OR preschool*.ti,ab OR pediatric.ti,ab OR paediatric.ti,ab OR minor*.ti,ab OR infant*.ti,ab OR toddler*.ti,ab Exp Australia OR Australia*.ti,ab. These search terms and strings were further used to develop a full search strategy, including all identified keywords and index terms, to ensure they were applied, and adapted accordingly for each included database and information source. The databases searched included JBI Evidence Synthesis, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, MEDLINE, Embase, Dentistry & Oral Sciences Source (DOSS), Scopus, Web of Science. Sources of unpublished studies/gray literature were also searched including Google Scholar and Open Grey. Studies published in any language were included if also available in English. Studies were not limited by a specific date range apart from the inclusion of all published papers up until September 2022.
Study selection
Following the search, all identified citations were collated and uploaded into Endnote 20 ( Clarivate Analytics, PA, USA) [ 31 ], with duplicates removed prior to import into the JBI System for the Unified Management, Assessment and Review of Information (JBI SUMARI) (JBI, Adelaide, Australia) [ 32 ]. Following a pilot test, titles and abstracts were screened by three independent reviewers (ZS, MJ, YS) for assessment against the inclusion criteria filtering ineligible studies and those irrelevant to the review question. Studies put forward for full text review were assessed in detail by two independent reviewers (ZS, YS) against the inclusion criteria and where consensus could not be reached a third reviewer (MJ) was consulted. Studies excluded were recorded and reported noting the reasons for exclusion.
Data extraction, analysis & presentation
Data was extracted from the papers by reviewers (SN, ZS) using a data extraction tool developed by the reviewers and checked for accuracy and completeness of information extracted by (ZS). Extracted data included specific details about the participants, concept, context, setting, study methods, and key findings relevant to the review question/s is presented (Table 1 ). The data collected from each of the included studies was analysed by (ZS, SN) and has been presented graphically and in tabular format with a narrative summary of the tabulated results related to the reviews objective and questions exploring the types of EB, care, and management of specialised dental services for children impacted with EB.
The literature search resulted in 789 articles sourced, and after removing duplicates and removing articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria, 33 publications were considered for full-text review. After reviewing the full-text articles, data extraction was carried out for these articles. All the reported literature were either case reports or case reviews published from 1963 to 2022. The PRISMA-ScR flow diagram describes the study selection process (Fig. 1 ).

Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) [ 30 ]
Population characteristics
The total number of patients reported was 45, which included 23 males and 22 females. The geographic distribution and proportion of EB cases were predominantly reported from the United States ( n = 10 ) [ 33 , 36 , 38 , 42 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 51 , 63 , 64 ], followed by Brazil in second place with six case reports [ 44 , 50 , 52 , 55 , 58 , 60 ]. Other countries reporting on EB were India [ 39 , 56 ], Iran [ 22 , 57 ], Turkey [ 54 , 59 ], and Taiwan [ 37 , 47 ], having 2 case reports each. All the other reports were from European countries: France [ 35 ], Germany [ 34 ], Italy [ 40 , 48 ], Russia [ 62 ], and the United Kingdom [ 49 ]. Australia had two publications on EB [ 41 , 53 ]. The ages ranged from newborns to age 12 (Fig. 2 ). All the studies reported on children 0–12 years of age, except for two studies who reported on not only a child but an adult patient within their reported case reviews ( highlighted in Table 1 ) [ 40 , 61 ].

Patients per age
Oral manifestation of EB
According to the literature, there are four major manifestations of Epidermolysis bullosa: EB simplex, junctional EB, Dystrophic EB, and Kindler syndrome [ 65 ]. For this review, we found EB simplex was described in seven case reports [ 37 , 41 , 42 , 47 , 58 , 59 , 62 ]. The Koebner subtype [ 37 ], and herpetiformis (Dowling Meara type) [ 47 ] type were the reported subtypes for EB simplex. Dystrophic EB was the most commonly reported type of EB, having 23 case reports [ 33 , 34 , 36 , 38 , 22 , 39 , 40 , 44 , 46 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 60 , 61 , 63 , 64 ]. The Dystrophic form has two main subtypes, dominant and recessive subtypes. The recessive type was more commonly reported ( n = 10 ), with two cases of the Haliopeau-Siemens subtype [ 34 , 40 ], and one of the Touraine subtype [ 45 ]. Only one case was found on the mixed EB: the Kindler subtypes [ 35 ]. There were no reported oral manifestations of Junctional EB from our literature search.
The oral manifestation can significantly decrease the quality of life. The most common intraoral features in all the reports were multiple bullae, erosions and/or vesicles on the oral mucosa, including sites such as the tongue, hard palate, gingiva, and buccal mucosa. Most patients experienced limited mouth opening or microstomia due to repeated blistering and healing, leading to scarring and contractures around the lips and mouth [ 34 , 36 , 39 , 44 , 46 , 50 , 53 , 54 , 61 ]. The absence of upper and lower frenum [ 39 ], and lingual papillae (ankyloglossia) [ 34 , 40 , 44 , 52 ] was also observed. Few patients had obliteration of the buccal and lingual vestibule [ 39 , 40 , 46 , 54 , 61 ]. The tongue showed a denuded appearance without papillae [ 44 , 57 , 60 ], and rugae were absent from the palate [ 54 , 61 ]. White lesions were observed on the tongue, gingiva, and buccal mucosa [ 37 , 39 , 47 , 52 , 54 ]. Pigmentation of lips and angular cheilitis were also reported [ 35 ].
The EB had affected both the primary and permanent dentition. Maintaining proper oral hygiene is essential for overall health, and children with EB may struggle due to pain and limited mouth opening, leading to a higher risk for dental caries and periodontal disease. The dental findings included enamel hypoplasia [ 35 , 40 ] and enamel pitting [ 59 ], which progressed to carious teeth [ 33 , 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 40 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 48 , 50 , 53 , 54 ] and, in severe cases, led to dentoalveolar abscess formation [ 22 , 46 , 51 , 56 , 63 , 64 ]. The rapid progression of caries resulted in the deterioration of teeth, leaving only remnants of root fragments [ 37 ]. There was delayed eruption of permanent teeth. Features of Class II malocclusion were also observed, showing signs of severe crowding, protrusion of incisors, and anterior open or deep bite [ 22 , 41 , 45 , 61 , 62 ]. The periodontal tissues were also affected, showing gingival inflammation or hyperplasia [ 59 ] and ulceration [ 60 ], causing gingivitis [ 34 , 45 , 48 ], and eventually progressing to periodontitis [ 35 ].
Healthcare treatment context & specialised treatment
The dental treatment for EB were predominantly managed in a hospital setting ( n = 18, 55% ) [ 33 , 22 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 54 , 56 , 63 , 64 ], and a dental hospital ( n = 14, 42% ), [ 9 , 34 , 39 , 44 , 48 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 55 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 62 ] with ( n = 1, 3%) reporting orthodontic treatment provided in the dental clinic setting.63 Children requiring specialised treatment or interventions were reported within the general hospital and dental hospitals where ( n = 12 ) required a general anaesthetic [ 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 43 , 45 , 46 , 49 , 50 , 56 , 63 , 64 ], a local anaesthetic ( n = 5 ) [ 9 , 35 , 39 , 57 , 60 ] with one case requiring a local and a general anaesthetic [ 22 ] and ( n = 2 ) patients had dental care provided with IV Ketamine [ 33 , 51 ], another required topical local anaesthetic [ 52 ] and one report noted a combination of treatments such as nitrous oxide, regional anaesthesia, IV sedation with ketamine [ 53 ]. Whilst ( n = 11 ) were not reported to require anaesthesia for specialised treatment [ 40 , 41 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 48 , 54 , 55 , 58 , 59 , 62 ]. Therefore, children within this review received a variety of anaesthetic approaches to ensure optimal care and outcomes.
Dental treatment outcomes
A number of dental treatments were reported from preventative, diagnostic and restorative (Fig. 3 ). Dental extraction under local or general anaesthesia was the most common treatment for severely decayed teeth [ 35 , 36 , 45 , 46 , 49 , 51 ], or even full mouth extraction [ 33 , 50 ]. For mild to moderate dental caries, the teeth were restored with GIC [ 22 , 55 ] composite [ 38 , 64 ], silver amalgam [ 34 , 38 , 53 , 59 , 63 ], and pulp therapy [ 37 , 45 , 64 ], or root canal treatment, [ 44 , 53 ]was performed in severe cases. Five authors suggested using stainless steel crowns for restoring primary molars [ 38 , 45 , 46 , 63 , 64 ]. Galeotti et al. [ 40 ] reported using lasers to remove caries. In adjunctive to therapeutic and surgical treatment, oral hygiene therapy was performed [ 35 , 38 , 44 , 53 , 55 , 57 , 60 ], Fluoride gels [ 53 ], fluoride varnish [ 39 , 52 , 55 , 59 ] and fissure sealants [ 34 , 57 ] were used for the preventative strategies. Two authors suggested removing or fixing partial dentures to rehabilitate missing dentition for permanent dentition [ 37 , 52 ], Rochette bridge, [ 53 ] and space maintainers of primary teeth [ 36 ]. Marini et al. [ 48 ] suggested home care methods such as topical application of Sucralfate on the blisters, and Scheidt et al. 47 recommended using aloe vera gel. Three authors performed removal and fixed orthodontic treatment for treating malocclusion [ 35 , 41 , 62 ].

Types of treatment
This scoping review focussed on studies primarily on children with EB exploring their dental needs and specialised treatments received. Due to the rarity of this disease and limited focus on the dental care needs of children, this scoping review comprehensively maps the evidence highlighting the complex dental and specialised care needs of forty five case reviews of children with EB informing this scoping review.
Individualised care & follow up
The need for individualised care was emphasised throughout all the case reviews presented. A number of authors reported the need for dentists to provide continuous dental examinations from birth throughout the lifespan to monitor, recognise and address dental issues as early as possible. Therefore, predominant care in the early stages is focussed on preventative measures commencing from birth [ 45 ]. The study by Camm et al. [ 36 ] recommends triannual dental examinations, whilst other authors reported follow up monthly [ 35 , 44 ] and every six months [ 22 ].
Dental compliance & health professional trust
This review has highlighted the complexity of dental care for children and the need for routine care to manage dental symptoms prior to the eruption of their first tooth and ongoing follow up care to manage their overall oral health development milestones. As recognised within this review, children requiring dental care may undergo numerous invasive procedures as a result of various dental ailments where they were unable to be managed in the regular dental environment due to complexity of care, non-compliance, pain, trauma, and further complications to their oral mucosa.
Dental compliance for any child can be difficult even more so for the child with EB where daily dental preventative treatment as simple as brushing their teeth can cause painful intraoral blistering with limited mouth opening [ 36 , 56 ]. Preventative care is also related to parental knowledge, understanding of diet impacting oral health and compliance in monitoring dental hygience at home. The study by Eswara [ 39 ] highlighted this aspect reporting the experience of parents avoiding brushing their child’s teeth up until aged seven years of age to avoid pain and not to cause further intra oral blistering. Therefore, parents play a pivotal role in the oral health of their child, encouraging regular oral hygiene, the use of soft toothbrushes, puree diets and supplements as required [ 52 ]. This is further supported by Torres et al. [ 60 ] who recommends diet counselling as a preventative measure to reduce potential oral health issues.
The need for timely access to dental services was also identified amongst the case reviews. The earlier study by Hochberg et al. [ 42 ] also confirmed that many patients were not brought to the dentist until they required actual care to resolve a dental issue. This was the case for a child who although from birth was diagnosed with EB was not seen by a dentist until 11 years of age until he was flagged by the dermatologist as requiring urgent dental treatment [ 53 ]. Whilst other children were seen from birth and followed through for alternate specialised care such as orthodontic treatment [ 41 ] or new innovative treatments such as sucralfate for pain and blisters [ 48 ].
For children with EB developing trust in health professionals is important particularly when undergoing painful procedures. As such for the EB child requiring specialised care, meeting new dentists, oral surgeons, and other health professionals, as well as visiting new places such as an operating room or an outpatient clinic can be a difficult and traumatic experience. Interestingly, to build trust and continuity of care with patients a few of the dentists within this review reported providing ongoing dental care across the lifespan for the child [ 35 , 54 ]. This may not always be possible with specialised care and referral required elsewhere dependant on the needs of the child and compliance with treatment. This was the case when earlier authors reported issues with limited cooperation by some children with dental therapy in the chair, [ 33 , 58 ] and the preference for dental therapy to involve procedures under anaesthesia [ 35 , 36 , 45 , 46 , 49 , 51 ].
Specialised care & treatment in the operating room
Several authors (dentists) have discussed the need to monitor and minimise trauma to their patients when providing any form of treatment to delimit fragility of the oral tissue causing blistering [ 33 , 48 , 58 ] with less invasive procedures producing the best effects [ 40 ], as well as a focus on overall safety and patient benefits of procedures in the operating setting [ 46 , 50 ]. Several of the case reviews reported the need for uncooperative children with EB requiring dental treatment in the operating room setting where specialised care and management could be fulfilled in a safe and controlled environment [ 45 , 54 , 63 ]. The risks of care under general anaesthesia was reported as primarily inflicting only minor trauma to the airway, and minor post operative complications as well as general trauma to the skin when inserting intravenous lines as well as the use of various tapes [ 36 ]. The type of treatments for EB primarily in the operating setting were reported as dental extractions and this continues to be the main surgery type. This was confirmed by Hubbert and Adams [ 43 ] earlier report noting dental and reconstructive surgery of the hands and fingers as prominent surgeries for EB within the operating room setting. Overall, access to specialised care and treatment via surgical intervention was effective in managing the child’s condition with minimal trauma and pain experienced.
Other minor forms of treatment were provided in the hospital or dental clinics with clinicians preferring treatment in outpatient settings to decrease the risk of patients developing secondary infections [ 42 ]. An important aspect of EB is the need to monitor oral infections and blistering on a regular basis. Authors Yoon and Ohkawa [ 64 ], recommend the use of topical antibiotics and oral antiseptics to assist in resolving secondary infections. Whilst Hochberg et al. [ 42 ] reported the use of antibiotics pre and post dental treatment.
Dental services, individualised care, continuity of care & referral processes
Little is currently understood of the current arrangements or dental care pathways for patients with EB. As evidenced with the reports each patient has had a unique journey through the health system in receiving care at varied ages. There is a dearth of information on the nature of dental services, accessibility, and the availability of healthcare services for EB children nor how the team provides initial referral in amongst the multidisciplinary team. From the case reviews examined both internationally and within the Australian context the process of referral is an unexplored phenomenon. The case review by Lindemeyer et al. [ 46 ] reported the need for an international referral from Saudi Arabia of two siblings aged four and eight years of age for treatment in the United States encompassing anaesthetic management during surgery.
Many authors emphasise the need for patients diagnosed with EB necessitating a comprehensive dental care plan in conjunction with a conservative dental treatment plan, with a multidisciplinary care team approach to improve the quality of life for these children [ 44 , 57 , 58 ]. Surprisingly none of the case reviews explored and outlined aspects of referral processes or care pathways for these children. Several authors however do emphasise the need for managing the complex conditions of each patient, accessibility to care in some reports, the decision making processes in providing the best available care via intraoperative management, and safe and effective treatments across the lifespan [ 9 , 60 , 62 , 63 , 64 ]. Continuity of care is an area which requires further exploration as some children had not seen a dentist for some time, and this certainly can restrict timely care towards correcting oral health issues.
Across the studies, accessibility to dental care was not reported as a dominant issue although there are differences and perhaps disparities in health services and accessibility to dental care services globally. Interestingly from an Australian context only two papers were identified exploring the dental management of EB patients [ 41 , 53 ]. A report outlining data from the EB national registry on the distribution of EB patients described a large number of people residing predominantly outside the major metropolitan areas with many living in rural and remote regions with limited access to health professionals and treatment [ 66 ].
Implications for practice & research
Many health professionals are unfamiliar with EB as a condition as well the complexity in managing and treating patients. Several of the studies reviewed commented on the need for the multidisciplinary team to work together in providing comprehensive care to EB patients. This multidisciplinary team involves, paediatricians, geneticists, dermatologists, gastroenterologist, paediatric dentists, oral surgeons, anaesthetists, mental health teams, dieticians, physiotherapists, speech, and language therapists across various settings [ 9 ]. Interestingly, nurses play a pivotal role in providing care within the hospital, the perioperative setting and community setting for EB patients however there is little literature on the specific aspects of oral and dental care provided for these patients by nurses. From a dentistry perspective, care can be complex and challenging. It is important to raise awareness of the dental needs of children with EB in amongst the multidisciplinary team to ensure early referral, management, and specialised treatment. Dentists also need to have an awareness and understanding of the EB condition, treatment and provide appropriate and timely referral to enhance the patients’ oral outcomes and quality of life across the lifespan [ 6 , 44 , 57 , 58 ]. Whilst there are international practice guidelines [ 10 ], further research on the efficacy of services and accessibility to specialised dental services is an area worth exploring further to establish care pathways and accessible services for children from birth across their lifespan.
Limitations of the review
It is acknowledged that this review was limited based on the focus of children and the absence of research articles which met the review inclusion criteria. Unfortunately, there were limited research papers with a focus on EB and dentistry limited to children zero to 12 years of age from an international context. Similarly, this review excluded papers not published in English which can be regarded as a limitation of this scoping review. Another significant limitations to this review is the number of case reviews and reports included within the review which limit the generalisability of these papers as they are predominantly case specific. On the other hand, a strength of this review was the ability to focus solely on children and capture the data as reported via the individual case reviews from an International perspective. Overall, this review, provides an insight towards the type of care provided to children, the context of this care, the treatment received and treatment outcomes as well as the types of specialised dental care services accessed across the different health care systems as well as highlighting the importance of continuity of care and best practice towards optimal oral health.
EB is a condition which can affect the quality of life for children with this condition. The overall findings confirm that children with EB require ongoing dental monitoring and specialised care. Therefore, as identified through the case reports most of the children with this condition from newborn with ongoing needs and care requirements across their lifespan. The scoping review provides an insight into the need for further research. Greater attention is required on the dental needs of children, in particular referral and timely access to dental health professionals and services. The review raises awareness of EB, and the importance of health professionals and dentists working together to meet the specialised dental care needs of these children to ensure they thrive and have a quality of life.
Data availability
Data is provided within the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published manuscript and its supplementary files.
DEBRA International. Austria. [cited 2022 October 2, 2022]. Available from: https://www.debra-international.org
Boeira VLSY, Souza ES, Rocha BO, et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Clinical and therapeutic aspects: Epidermólise bolhosa hereditária: Aspectos clínicos e terapêuticos. An Bras Dermatol. 2013;88:185–98.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Has C, Bauer J, Bodemer C, et al. Consensus reclassification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa and other disorders with skin fragility. Br J Dermatol. 2020;183:614–27.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Bodán RC. Reframing the Care of Children With Epidermolysis Bullosa Through the Lens of Medical Trauma. Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association. 2020;12:16–23.
Article Google Scholar
Korolenkova M, Poberezhnaya A, Starikova N, Udalova N, Dmitrieva N. Complex dental rehabilitation in children with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100:65–6.
Google Scholar
Kearney S, Donohoe A, McAuliffe E. Living with epidermolysis bullosa: Daily challenges and health-care needs. Health Expect. 2020;23:368–76.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kramer S. Chapter 1: General information on epidermolysis bullosa for the oral health care professional. Spec Care Dentist. 2020;40:9–12.
Krämer S, Lucas J, Gamboa F, et al. Clinical practice guidelines: Oral health care for children and adults living with epidermolysis bullosa. Spec Care Dentist. 2020;40:3–81.
Veliz S, Huber H, Yubero MJ, Fuentes I, Alsayer F, Kramer SM. Early teeth extraction in patients with generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: A case series. Special care in dentistry : official publication of the American Association of Hospital Dentists, the Academy of Dentistry for the Handicapped, and the American Society for Geriatric Dentistry. 2020;40:561–5.
Kramer SM, Serrano MC, Zillmann G, et al. Oral Health Care for Patients with Epidermolysis Bullosa - Best Clinical Practice Guidelines. Int J Pediatr Dent. 2012;22:1–35.
Dag C, Bezgin T, Ozalp N. Dental management of patients with epidermolysis bullosa. Oral health and dental management. 2014;13:623–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
Kosmidou A, Liversidge HM, Hector MP. Tooth formation in children with Epidermolysis Bullosa. J Dent Res. 2001;80:1165–1165.
Kramer S, Lucas J, Gamboa F, et al. CHAPTER 3: Oral health care and dental treatment for children and adults living with epidermolysis bullosa-Clinical practice guidelines. Spec Care Dentist. 2020;40:32–53.
Blazquez Gomez E, Garces Aleta A, Monclus Diaz E, Manen Berga F, Garcia-Aparicio L, Ontanilla LA. Anaesthetic management in a paediatric patient with a difficult airway due to epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2015;62:280–4.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Iohom G, Lyons B. Anaesthesia for children with epidermolysis bullosa: A review of 20 years’ experience. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2001;18:745–54.
Griffin RP, Mayou BJ. The anaesthetic management of patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: A review of 44 patients over a 10 year period. Anaesthesia. 1993;48:810–5.
Korolenkova MV. Dental treatment in children with dystrophic form of epidermolysis bullosa. Stomatologiia. 2015;94:34–6.
Stevens P, Hustig A. 5-year review of airway management in children with Epidermolysis Bullosa at a tertiary paediatric centre. Trends in Anaesthesia and Critical Care. 2020;30: e156.
Lin Y-C, Golianu B. Anesthesia and pain management for pediatric patients with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Anesth. 2006;18:268–71.
Wai C, Raghavendra T. Anaesthetic non-touch technique for butterfly children. Anaesthesia. 2014;69:120.
Colovic A, Jovicic O, Stevanovic R, Ivanovic M. Oral health status in children with inherited dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2017;74:644–51.
Esfahanizade K, Mahdavi AR, Ansari G, Fallahinejad Ghajari M, Esfahanizadeh A. Epidermolysis bullosa, dental and anesthetic management: a case report. Journal of dentistry (Shiraz, Iran). 2014;15:147–52.
Agustin-Panadero R, Gomar-Vercher S, Penarrocha-Oltra D, Guzman-Letelier M, Penarrocha-Diago M. Fixed full-arch implant-supported prostheses in a patient with epidermolysis bullosa: a clinical case history report. Int J Prosthodont. 2015;28:33–6.
Baican A, Chiriac G, Torio-Padron N, Sitaru C. Childhood epidermolysis bullosa acquisita associated with severe dental alterations: A case presentation. J Dermatol. 2013;40:410–1.
DEBRA International. National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) and Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB). https://www.debra.org.au/ndis/ .
Ogonowska A, Zadroga E. Dental needs and health behaviors in patients with epidermolysis bullosa - A survey. Dental and Medical Problems. 2016;53:103–10.
Peters MD, Marnie C, Tricco AC, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI evidence synthesis. 2020;18:2119–26.
Pollock D, Tricco AC, Peters MDJ, et al. Methodological quality, guidance, and tools in scoping reviews: a scoping review protocol. JBI Evidence Synthesis. 2022;20:1098–105.
Peters MD, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Baldini Soares C, Khalil H, Parker D. Scoping reviews. Joanna Briggs Institute reviewer’s manual. 2017;2015:1–24.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
The EndNote Team. EndNote. EndNote 20 edn. Philadelphia: Clarivate; 2013.
Munn Z, Aromataris E, Tufanaru C, et al. The development of software to support multiple systematic review types: the Joanna Briggs Institute System for the Unified Management, Assessment and Review of Information (JBI SUMARI). JBI Evidence Implementation. 2019;17:36–43.
Album MM, Gaisin A, Lee KW, Buck BE, Sharrar WG, Gill FM. Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica polydysplastica. A case of anesthetic management in oral surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1977;43:859–72.
Azrak B, Kaevel K, Hofmann L, Gleissner C, Willershausen B. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: oral findings and problems. Spec Care Dentist. 2006;26:111–5.
Blanchet I, Tardieu C, Casazza E. Oral Care in Kindler Syndrome: 7-Year Follow-up of 2 Brothers. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021;45:41–7.
Camm JH, Gray SE, Mayes TC. Combined medical-dental treatment of an epidermolysis bullosa patient. Spec Care Dentist. 1991;11:148–50.
Chuang LC, Hsu CL, Lin SY. A fixed denture for a child with epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2015;16:315–8.
Endruschat AJ, Keenen DA. Anesthetic and dental management of a child with epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973;36:667–71.
Eswara U. Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa in a child. Contemp Clin Dent. 2012;3:90–2.
Galeotti A, D’Antò V, Gentile T, et al. Er:YAG Laser Dental Treatment of Patients Affected by Epidermolysis Bullosa. Case Rep Dent. 2014;2014: 421783.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Goldschmied F. Orthodontic management of a patient with epidermolysis bullosa. Aust Orthod J. 1999;15:302–7.
Hochberg MS, Vazquez-Santiago IA, Sher M. Epidermolysis bullosa. A case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993;75:54–7.
Hubbert CH, Adams JG. Anesthetic management of patients with epidermolysis bullosa. South Med J. 1977;70:1375–7.
Kummer TR, Nagano HC, Tavares SS, Santos BZ, Miranda C. Oral manifestations and challenges in dental treatment of epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. J Dent Child (Chic). 2013;80:97–100.
Lanier PA, Posnick WR, Donly KJ. Epidermolysis bullosa–dental management and anesthetic considerations: case report. Pediatr Dent. 1990;12:246–9.
Lindemeyer R, Wadenya R, Maxwell L. Dental and anaesthetic management of children with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2009;19:127–34.
Liu HH, Chen CJ, Miles DA. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: review and report of case. ASDC J Dent Child. 1998;65:349–53.
Marini I, Vecchiet F. Sucralfate: a help during oral management in patients with epidermolysis bullosa. J Periodontol. 2001;72:691–5.
Marshall BE. A comment on epidermolysis bullosa and its anaesthetic management for dental operations. Br J Anaesth. 1963;35:724–7.
Mello BZ, Neto NL, Kobayashi TY, et al. General anesthesia for dental care management of a patient with epidermolysis bullosa: 24-month follow-up. Spec Care Dentist. 2016;36:237–40.
Morgan WC. Dental anesthetic management of epidermolysis bullosa: a new approach. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1975;40:732–5.
Oliveira TM, Sakai VT, Candido LA, Silva SM, Machado MA. Clinical management for epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica. J Appl Oral Sci. 2008;16:81–5.
Olsen CB, Bourke LF. Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Two case reports with 20-year follow-up. Aust Dent J. 1997;42:1–7.
Pekiner FN, Yücelten D, Ozbayrak S, Sezen EC. Oral-clinical findings and management of epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2005;30:59–65.
Silva LC, Cruz RA, Abou-Id LR, Brini LN, Moreira LS. Clinical evaluation of patients with epidermolysis bullosa: review of the literature and case reports. Spec Care Dentist. 2004;24:22–7.
Prabhu VR, Rekka P, Swathi S. Dental and anesthetic management of a child with epidermolysis bullosa. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2011;29:155–60.
Sanjari K, Bayani M, Zadeh HE. Conservative dental management of a patient with Epidermolysis bullosa. A case report Pediatric Dental Journal. 2020;30:245–50.
Scheidt L, Sanabe ME, Diniz MB. Oral Manifestations and Dental Management of Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2015;8:239–41.
Sipahier M. Epidermolysis bullosa: a case report. Quintessence Int. 1994;25:839–43.
Torres CP, Gomes-Silva JM, Mellara TS, Carvalho LP, Borsatto MC. Dental care management in a child with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Braz Dent J. 2011;22:511–6.
Véliz S, Huber H, Yubero MJ, Fuentes I, Alsayer F, Krämer SM. Early teeth extraction in patients with generalized recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: A case series. Spec Care Dentist. 2020;40:561–5.
Volovikov O, Velichko E, Razumova S, Said OB. The First Case Report about Noninvasive Impression Taking in Orthodontic Patient with Epidermolysis Bullosa. Journal of International Dental and Medical Research. 2021;14:1587–91.
Wright JT. Epidermolysis bullosa: dental and anesthetic management of two cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;57:155–7.
Yoon RK, Ohkawa S. Management of a pediatric patient with epidermolysis bullosa receiving comprehensive dental treatment under general anesthesia. Pediatr Dent. 2012;34:251–3.
Fine J-D, Eady RA, Bauer EA, et al. The classification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa (EB): Report of the Third International Consensus Meeting on Diagnosis and Classification of EB. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:931–50.
Harris AG, Todes-Taylor NR, Petrović N, Murrell DF. The distribution of epidermolysis bullosa in Australia with a focus on rural and remote areas. Australas J Dermatol. 2017;58:122–5.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Vikki Langdon, Faculty Librarian, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, The University of Adelaide for contribution to the initial database search strategy.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no potential sources of conflict of interest towards this project.
Publication Funded by Adelaide Nursing School, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, The University of Adelaide.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Adelaide Nursing School, Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Z. Smith, M. Javanmard & Y. Salamon
Australian Research Centre for Population Oral Health, School of Dentistry, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ZS conceived and designed the scoping review, search strategy and project administration. ZS, MJ & YS contributed to article screening. SN and ZS contributed to data extraction and analysis and write up of results. ZS contributed to the write up of the manuscript and development of figures with SN, MJ & YS providing editorial review and approval of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Z. Smith .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Smith, Z., Nath, S., Javanmard, M. et al. The dental needs of children with Epidermolysis Bullosa and service delivery: a scoping review. BMC Oral Health 24 , 1131 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-024-04861-y
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 04 September 2024
Published : 27 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-024-04861-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Epidermolysis bullosa
- Specialist dental service
- Health services
BMC Oral Health
ISSN: 1472-6831
- General enquiries: [email protected]
A systematic literature review on requirement prioritization techniques and their empirical evaluation
- November 2019
- Computer Standards & Interfaces 69(13):103389

- University of Twente

- Eindhoven University of Technology
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
No full-text available
To read the full-text of this research, you can request a copy directly from the authors.

- Waleed Helmy
- Habib Un Nisa

- Rahila Anwar
- Muhammad Bilal Bashir

- Michelle Binder
- Annika Vogt
- Adrian Bajraktari

- Soheil Afraz

- Mohammad Faisal
- Anupama Mishra
- Rakesh Kumar
- Muhammad Asim Siddique

- Noraini Ibrahim

- Evangelia Latsa

- Rami Bahsoon

- Dimitrios Tzimos
- Jeyaganesh Kumar Kailasam
- Rajkumar Nalliah
- Saravanakumar Nallagoundanpalayam Muthusamy

- EXPERT SYST APPL

- Gonca Canan Oztekin

- Zongsheng Wang

- Ayomide Bakare

- Giancarlo Succi

- Sukiswo Dirdjosuparto
- EMPIR SOFTW ENG

- Lynne Blair

- Pedro G. Campos

- Rebecca Lee

- Sabine N van der Veer

- Eliad Amsalem

- Riftika Rizawanti
- Terry Woodings
- Intan Ermahani A. Jalil
- CMC-COMPUT MATER CON

- Muhammad Ibrahim Khalil

- ADV ENG INFORM

- COMPUT IND ENG
- Wenqiang Li

- Chuanxiao Li
- Syeda S. Tanveer

- Karthikeyan R
- J SYST SOFTWARE

- Sezi Cevik Onar

- Mohan Kumar Palanichamy
- Selvam Lakshmanan
- Arokia Renjith Jerald
- Le Hoang Son

- Apostolos Martinis
- Kiran Ilyas
- Taila Jabeen
- Ghulam Mustafa

- Oswaldo Kenan Zohoun

- Pavol Budaj

- Chetna Gupta

- Iyas Ibriwesh

- Maya Daneva

- A. Vinaya Babu

- J INTELL MANUF

- LEE Sai Peck

- Izaz Ur Rehman
- Yawar Hayat Khan
- Salman Rashid

- Chuie-Hong Tan

- R. Vijay Anand
- M. Dinakaran
- Khadija Sania Ahmad
- Nazia Ahmad
- Shaista Khan
- Yash Veer Singh

- Jitendra Kumar

- Heena Ahuja

- Vaibhav Sachdeva

- Nikita Garg

- Norbert Seyff

- M. Svahnberg
- Aimable Karasira
- Thomas Bebensee

- Rao Muzamal Liaqat

- Susana Prozil Rodrigues

- Norman Riegel

- M. Goransson
- Alexander Felfernig

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This conceptual study specifically aims at reviewing the critical managerial issues of menu, and demonstrating the conceptual structure of menu management. Based on the conceptual and empirical findings of menu literature, the major menu management issues are menu planning, menu pricing, menu designing, menu operating and menu development.
LITERATURE REVIEW ON RESTAURANT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM M. Faizan Khandwani*1, Pratik Lanke*2, Pratik Harne*3, Anuj Sapkal*4, Adesh Adhao*5
Based on the conceptual and empirical findings of menu literature, the major menu management issues are menu planning, menu pricing, menu designing, menu operating and menu development.
The current literature on restaurant menus, mainly within the domain of hospitality management, focuses on two key themes: (a) menu design, dealing with topics such as the layout of menu display, item labels and descriptions, and position of menu items within a category; and (b) menu analysis, focusing on systematically evaluating menu item ...
This paper takes the form of a critical review of the extant literature that has been done in the foodservice and restaurant industries. Literature from the past 10 years will be qualitatively assessed to determine trends and gaps in the research to help guide the direction for future research.
Implications - From a theoretical point of view, the reinterpretation of TheFork as a smart service system can contribute to service science and restaurant management advancements.
Abstract This research was conducted to determine the positive and negative aspects of using Restaurant Management System (RMS) in restaurants based on the perspectives of restaurant staff.
Menu analysis and revenue management approaches contribute to improving a restaurant's profitability. Yet, both approaches are often implemented independently with constraints. This paper explores the potential of integrating both approaches to improve strategy formulation. Hence, this paper identified the extent of applicability and synergies among both approaches. Findings highlighted that ...
Demand forecasting is one of the important inputs for a successful restaurant yield and revenue management system. Sales forecasting is crucial for an independent restaurant and for restaurant chains as well. In the paper a comprehensive literature review and...
Demand forecasting is one of the important inputs for a suc-cessful restaurant yield and revenue management system. Sales forecast-ing is crucial for an independent restaurant and for restaurant chains as well. In the paper a comprehensive literature review and classification of restaurant sales and consumer demand techniques are presented.
In contrast to prior reviews, this study provides a review of research contexts, research designs, and theories used in restaurants' business performance research. It also identifies measures and antecedents of restaurants' business performance. Additionally, this systematic review highlights gaps for future research on restaurants' business performance. A total of 148 articles were ...
The main aim of revenue management is to sell the right product at the right time and for the right price to the right consumer. Over the past two decades, revenue management techniques for restaurant industries have started to appear in the literature. This paper aims to thoroughly review this literature and identify emerging issues.
The current study was conducted to design and implement computerized restaurant menu system, to analyze the requirement for the proposed system, to design and develop computerized restaurant menu system and to test and implement the system.
The present paper presents the results of a bibliometric analysis of published academic research dealing with restaurants in the fields of hospitality…
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW Introduction This chapter will contain or provide general understanding about the related review of literature of the beach house restaurant management system and any other articles that explains the meaning of it in detail; also this system will discuss the conceptual and theoretical development of mailing system which means the previous works and comparing between ...
The current literature on restaurant menus, mainly within the domain of hospitality management, focuses on two key themes: (a) menu design, dealing with topics such as the layout of menu display, item labels and descriptions, and position of menu items within a category; and (b) menu analysis, focusing on sys-tematically evaluating menu item ...
Abstract and Figures The body of innovation management literature grew considerably over the last 35 years. This led to an increasing amount of different models of innovation processes. This paper ...
The system can also recommend hotels and food based on user ratings. Payment options include online payment or pay-on-delivery, with separate accounts for each user, which ensures secure ordering through individual IDs and passwords. Keywords: Food Ordering System, Dynamic Database Management, Smart Phone.
This paper aims to provide practical pointers to scholars, students, and practitioners about applying Porter's Five Forces analysis, a longstanding, comprehensive, and practical framework in strategic analysis. The paper combines two methodologies: a review of prior studies and the inductive methodology. The latter involved drawing on examples from different industries and contexts ...
Background Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) is a genetic condition with fragility of the skin and oral mucosal lining requiring appropriate care and management by dental health professionals. The objective of this scoping review was to comprehensively examine the specialised dental needs of children with Epidermolysis Bullosa and map evidence towards the type, availability, and accessibility of ...
In recent years, some researchers have presented SLRs (systematic literature review) on techniques and challenges of prioritizing requirements [9, 10].
This paper presents the results of a systematic literature review showing how the literature on quality management (QM) in higher education (HE) has evolved. As a first contribution, this work presents a systematic breakdown of research in the field of HE quality management.