
100+ Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature
With the Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature, you can easily make your research perfect. PhD in English Literature is a pursuit that requires both passion and precision.
English Literature serves as a lens through which societal changes, cultural shifts, and human experiences are analyzed, critiqued, and understood. These research topics not only foster intellectual curiosity but also encourage critical thinking, enabling scholars to push the boundaries of conventional scholarship and contribute significantly to the ongoing discourse in the field.
In this article, we delve into the vibrant realm of English Literature, presenting an extensive array of the latest research topics tailored for aspiring PhD candidates. These topics encompass a wide spectrum of themes, genres, and methodologies, catering to the diverse interests and scholarly inclinations within the discipline.
Let’s now delve into the comprehensive compilation of 100+ of the latest research topics designed to inspire and guide scholars on their doctoral journey in English Literature.
Also Read: Benefits of Content Writing for Businesses PDF
Table of Contents
What Is A Good Research Topic For Literature?
A good research topic for literature is both relevant and engaging and contributes to the existing scholarly discourse. It should encompass a specific area within literature that holds significance in terms of cultural, historical, social, or theoretical implications. A strong research topic in literature often addresses unexplored territories. It offers innovative perspectives or re-examines existing narratives through a fresh lens.
Additionally, an effective research topic should be well-defined, allowing for focused inquiry and enabling the researcher to delve deeply into the subject matter. It should be feasible within available resources and time constraints while providing ample scope for critical analysis, interpretation, and argumentation.
Moreover, a good research topic should generate interest and provoke discussion among scholars, contributing new insights, interpretations, or methodologies to the field. Whether exploring themes, genres, historical contexts, theoretical frameworks, or cultural perspectives, a compelling research topic in literature can expand knowledge, challenge assumptions, and offer nuanced understandings of literary texts or trends.
How Do You Choose A Topic For Research In English Literature?
Following are the steps for choosing the Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature.
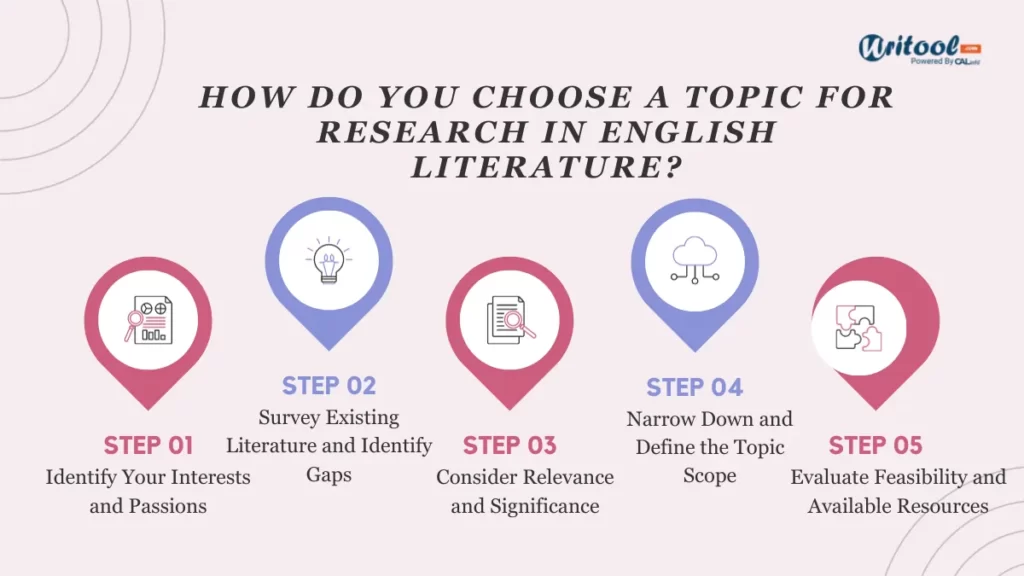
List of 100+ Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature
Here are the best and Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature.
Literary Theory and Criticism
- New Materialism and its Implications for Literary Analysis
- Ecofeminist Literary Criticism: Redefining Nature and Gender Relations
- Reception Theory: Understanding Reader Responses in Literary Texts
- Posthumanist Perspectives in Science Fiction Literature
- Queer Temporalities in Literature: Rethinking Chronology and Narrative
- Postcolonial Feminism: Intersectional Approaches in Literary Criticism
- Aestheticism and Decadence in 19th-century Literature: Relevance Today
- Formalist Criticism in Contemporary Literary Analysis
- Cognitive Literary Studies: Exploring the Mind and Imagination in Reading
- Critical Animal Studies: Ethics and Representation in Literature
- Hermeneutics and the Art of Interpretation in Literary Texts
- Structuralism and Semiotics: Analyzing Signs and Symbols in Literature
- Reception Aesthetics: Examining Reader Response in Literary Reception
- Marxist Literary Criticism and Socioeconomic Analyses in Texts
- Ecocritical Hermeneutics: Environmental Interpretation in Literature
Historical Contexts and Literary Movements
- Gothic Revival in Contemporary Literature and Culture
- Post-War Literature and the Reconstruction of Identity
- Harlem Renaissance: Exploring Socio-cultural Transformation through Literature
- Literary Responses to Colonialism in the Caribbean
- Decolonizing the Literary Canon: Perspectives from Global South Writers
- Literature of the Roaring Twenties: Cultural Shifts and Literary Expression
- Modernism and Postmodernism in Contemporary Literature: Parallels and Divergence
- The Harlem Renaissance and Jazz Culture: Intersections in Literature
- Post-War Trauma in Holocaust Literature: Representing Unimaginable Experiences
- The Literature of Revolution: Voices of Change and Rebellion
- Literature of the Jazz Age: Cultural Shifts and Literary Contributions
- The Lost Generation Writers: Their Impact on Modern Literature
- Literature of the Cold War Era: Politics, Paranoia, and Cultural Reflection
- The Prague School and its Influence on Literary Theory and Analysis
- The Postcolonial Literary Boom: Emergence, Evolution, and Influence
Genre Studies Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature
- Cyberpunk Literature and the Technological Imagination
- Evolution of the Bildungsroman in Modern Literature
- Steampunk as a Subgenre: Victorian Aesthetics in Contemporary Works
- Literary Journalism in the Digital Age: Challenges and Innovations
- Satire and Political Commentary in Modern Literary Forms
- Speculative Fiction and Social Commentary: Critiquing the Present through Future Worlds
- Indigenous Science Fiction and Futurism: Reimagining Traditions and Technology
- Evolution of the Detective Genre: Contemporary Perspectives and Innovations
- Non-binary Identities in Poetry: Challenging Gender Norms and Language
- Transmedia Storytelling: Literature in Conjunction with Multiple Media Forms
Cultural Studies and Identity in Literature
- Disability Narratives in Graphic Novels and Comics
- Representations of Masculinity in Post-Millennial Literature
- Indigenous Perspectives in Eco-Literature and Environmental Activism
- Muslim Identity in Contemporary Western Literature
- Post-9/11 Literature: Shifting Paradigms in Cultural Representation
- Diasporic Literature and Identity Politics: Negotiating Belonging
- Post-Modern Feminist Narratives in Literature: Reclaiming Agency and Voice
- Disability in Young Adult Literature: Empowerment and Representation
- Multiculturalism in Contemporary Picture Books: Reflecting Diversity
- Transcultural Narratives in a Globalized World: Literature as a Bridge
Environmental and Ecocritical Perspectives
- Animal Studies in Literature: Ethics and Representations
- Urban Ecology and the Cityscape in Literature
- Climate Fiction (Cli-Fi): Imagining Environmental Futures in Literature
- Environmental Justice in Indigenous Literature
- Eco-Poetics: Nature, Language, and Poetry
- Indigenous Ecocriticism: Land, Spirituality, and Survival Narratives
- Urban Wastelands in Literature: Representing Environmental Degradation
- Ecofeminist Poetry and the Connection Between Women and Nature
- Environmental Apocalypse in Literature: Fear, Hope, and Activism
- Rewilding in Literature: Reconnecting Humanity with the Natural World
Technology and Literature Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature
- Virtual Reality Narratives: Immersive Storytelling in Literature
- AI and Ethics: Dystopian and Utopian Visions in Science Fiction
- Literature in the Age of Data Mining and Surveillance
- Transhumanism in Speculative Fiction and its Cultural Implications
- Digital Narratives: Exploring Interactive and Hypertextual Literature
- Augmented Reality in Literature: Blurring the Lines Between Real and Imaginary
- Blockchain Technology and its Potential in Preserving Literary Works
- Literature in the Age of Gaming: Interactive Storytelling and Narrative Structures
- Surveillance Culture in Dystopian Literature: Reflections on Privacy and Control
- AI-Penned Literature: Exploring Machine-Generated Creative Writing
Global and Comparative Literature
- Border Literature: Identity, Migration, and Cultural Hybridity
- Postcolonial Diasporic Literature: Negotiating Home and Belonging
- Comparative Study of Mythologies in Global Literary Traditions
- Literature of Exile and Displacement: Narratives of Refugees
- Cultural Translation and Adaptation in Global Literary Contexts
- Borderlands Literature: Narratives of Conflict and Coexistence
- Comparative Analysis of Folktales from Different Cultures
- Diaspora Writing: Literature as a Cultural and Emotional Space
- The Global Impact of Translated Literature: Understanding Cross-Cultural Influences
- Literature of Protest Movements: Worldwide Expressions of Dissent
Psychological and Medical Perspectives in Literature
- Trauma and Memory in Post-Conflict Narratives
- Representations of Mental Health in Young Adult Literature
- Psychoanalysis and Character Development in Literary Texts
- Disability Studies and Chronic Illness Narratives in Literature
- Existentialism in Literature: Navigating Meaning and Absurdity
- Neurodiversity in Contemporary Fiction: Depicting Cognitive Diversity
- Psychoanalysis and Trauma Narratives: Healing Through Storytelling
- Illness and Healing in Indigenous Literature: Cultural Perspectives
- Existential Crisis in Young Adult Literature: Coming-of-Age in Uncertain Times
- Madness and Sanity in Literature: Representation and Interpretation
Performance and Adaptation Studies
- Shakespearean Adaptations in Different Cultural Contexts
- Film and TV Adaptations: Impact on Literary Interpretation
- Oral Tradition and Folklore: Preservation and Adaptation in Writing
- Theatre of the Oppressed: Social Change through Performance
- Literary Festivals and Cultural Exchange: Engaging Global Audiences
- Adaptation and Appropriation in Theatre: Transforming Literary Works
- The Influence of Manga and Anime on Contemporary Literature
- Digital Storytelling and Social Change: Engaging Audiences in New Media
- Indigenous Oral Traditions and Their Transition into Written Literature
- Literary Tourism: Exploring the Impact of Literature on Travel and Place
So, these are the most amazing Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature.
Conclusion – Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature
These are all about the Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature. We give the latest research topics presented for a PhD in English Literature that embodies the dynamic and evolving nature of the field. These topics span diverse thematic areas, encompassing contemporary societal concerns, technological advancements, cultural shifts, and interdisciplinary intersections. They beckon aspiring scholars to embark on nuanced inquiries that transcend traditional boundaries, offering opportunities to explore uncharted territories within literary studies.
The curated list encapsulates the multifaceted dimensions of literature, inviting critical engagement with global perspectives, marginalized narratives, environmental concerns, technological impacts, and identity explorations. These research avenues not only stimulate intellectual curiosity but also encourage scholars to contribute significantly to the ongoing discourse by presenting innovative interpretations, challenging conventions, and providing fresh insights into the ever-expanding realm of English Literature.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- How it works
Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Literature Dissertation Topics
Published by Carmen Troy at January 9th, 2023 , Revised On February 7, 2023
Introduction
A literature dissertation aims to contextualise themes, ideas, and interests that have grabbed a reader’s interest and attention, giving them a more profound meaning through the movement of time within and outside cultures.
Literature is a comprehensive knowledge of other writers’ views, and to understand them, a student must perform extensive reading and research. A writer coveys their thoughts and ideas through their literary works, including the views and opinions of writers ranging from topics on philosophy , religious preferences, sociology , academics, and psychology .
To help you get started with brainstorming for literature topic ideas, we have developed a list of the latest topics that can be used for writing your literature dissertation.
These topics have been developed by PhD qualified writers of our team , so you can trust to use these topics for drafting your dissertation.
You may also want to start your dissertation by requesting a brief research proposal from our writers on any of these topics, which includes an introduction to the topic, research question , aim and objectives , literature review along with the proposed methodology of research to be conducted. Let us know if you need any help in getting started.
Check our dissertation examples to get an idea of how to structure your dissertation .
Review the full list of dissertation topics for 2022 here.
2022 Literature Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: impact of the second language barrier on the social integration of immigrants- a case of chinese nationals migrating to the uk.
Research Aim: This research purposes an analysis to show the impact of the second language barrier on the social integration of Chinese immigrants in the UK. It will analyze how this barrier affects various segments of their lives by limiting their social interactions. Moreover, it will identify ways (language courses, communal support, financial support, etc.) through which government and civil society help these immigrants to overcome this barrier to make them feel inclusive in the UK and play a part in the economy.
Topic 2: The Power of the Writer’s Imagination- A Study Finding the Role of Writer Imagination in the Social Revolution in 19th-Century Europe
Research Aim: This study intends to identify the role of the writer’s imagination in the social revolution in 19 th century Europe. It will show how writers’ imagination is reflected in their writings and how it affects ordinary individuals’ mindsets. It will assess the writings of various authors during the 19 th -century social revolution when Europe replaced the monarchy with democracy. It will show the language used by the authors and its effect on the individuals’ will to achieve democracy.
Topic 3: How does an Accent Develop? An Exploratory Analysis Finding Factors Shaped Various English Accents in the World- A Case of America, Australia, and India
Research Aim: This research will analyze how an accent develops when a language is imported from one region to the other. It will identify how various factors such as culture, norms, politics, religion, etc., affect accent development. And to show this effect, this research will show how the English accent changed when it came to America, Australia, and India. Moreover, it will indicate whether social resistance in these areas affected the accent or was readily accepted.
Topic 4: “Gender Pronouns and their Usage” a New Debate in the Social Linguistics Literature- A Systematic Review of the Past and Present Debates
Research Aim: This study sheds light on a relatively new debate in politics, sociology, and linguistics, which is how to correctly use gender pronouns in all of these contexts. Therefore, this study will explore these areas, but the main focus will be on linguistics. It will review various theories and frameworks in linguistics to show multiple old and new debates on the subject matter. Moreover, a systematic review will determine the correct usage of gender pronouns.
Topic 5: Are Men Portrayed Better in the English Literature? A Feminist Critique of the Old English Literature
Research Aim: This research will analyze whether men are portrayed better in English literature through a feminist lens. It will assess a different kind of English literature, such as poems, essays, novels, etc., to show whether men are portrayed better than women in various contexts. Moreover, it will analyze multiple classical and modern-day writers to see how they use different male and female characters in their literature. Lastly, it will add a feminist perspective on the subject matter by introducing the feminist theory and its portrayal of men and women.
Covid-19 Literature Research Topics
Topic 1: the scientific literature of coronavirus pandemic.
Research Aim: This study will review the scientific literature of Coronavirus pandemic
Topic 2: Literature and the future world after Coronavirus.
Research Aim: This study will reveal the world’s literature predictions after the pandemic.
Topic 3: Coronavirus is a trending topic among the media, writers, and publishers
Research Aim: Covid-19 has disrupted every sector’s health care system and economy. Apart from this, the topic of the Coronavirus has become trending everywhere. This study will highlight whether the information provided about COVID-19 by all the sources is authentic? What kind of misleading information is presented?
Literature Dissertation Topics for 2021
Topic 1: dependence of humans on computers.
Research Aim: This research aims to study the dependence of humans on the computer, its advantages and disadvantages.
Topic 2: Whether or not the death penalty is effective in the current era?
Research Aim: This research aims to identify whether the death penalty is effective in the current era.
Topic 3: Fashion Industry and its impact on people's upward and downward social perception
Research Aim: This research aims to identify the impact on people’s upward and downward social perception
Topic 4: Communication gaps in families due to the emergence of social media
Research Aim: This research aims to address the communication gaps in families due to the emergence of social media and suggest possible ways to overcome them.
Topic 5: Employment and overtime working hours- a comparative study
Research Aim: This research aims to measure the disadvantages of overtime working hours of employees.
Topic 6: Machine translators Vs. human translators
Research Aim: This research aims to conduct a comparative study of machine translators and human translators
Topic 7: Freelancing Vs 9 to 5 jobs- a comparative study
Research Aim: This research aims to compare freelancing jobs with 9 to 5 jobs.
Literature Dissertation Topics for 2020
Topic 1: the effects of everyday use of digital media on youth in the uk..
Research Aim: Digital media is a normal part of a person’s life. In this research, the aim is to examine and analyse; how young people between the ages of 15-25 in the UK engage with digital media. The study includes the amount of time interaction occurs and the role of time-space, time elasticities, and online/offline intersections.
Topic 2: Critical analysis of the teenager protagonist in “The Room on the Roof” written by Ruskin Bond.
Research Aim: Many Indian writers and children’s book authors regard Ruskin Bond as an icon. This research will systematically study the alienated teenage protagonist in Ruskin’s “The Room on the Roof” and how Ruskin evolved the character gradually throughout the novel. The way Ruskin used this protagonist to reflect his feelings and convey them to the reader.
Topic 3: Promotion of women empowerment through mass media in Nepal.
Research Aim: The primary purpose of this study is to analyse the role of mass media, including audio, print, and audio-visual, in the empowerment of women in the Nepal region. It also discusses the development of mass media in Nepal and spreading awareness of women’s empowerment.
How Can ResearchProspect Help?
ResearchProspect writers can send several custom topic ideas to your email address. Once you have chosen a topic that suits your needs and interests, you can order for our dissertation outline service , which will include a brief introduction to the topic, research questions , literature review , methodology , expected results , and conclusion . The dissertation outline will enable you to review the quality of our work before placing the order for our full dissertation writing service !
Seventeenth and Eighteenth-Century Literature Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: eighteenth-century british literature..
Research Aim: This study aims to study the evolution of modern British literature compared to eighteenth-century literature. This research will focus on the genre of comedy only. The research will discuss the causes of laughter in the eighteenth century compared to things that cause laughter in modern times.
Topic 5: A systematic study of Chaucer’s Miller’s tale.
Research Aim: This research aims to take a closer look at Chaucer’s heavily censored story, “The Miller’s Tale.” It seeks to look at why “The Miller’s Tale” is criticised and categorised as obscene and unfit for a general read. The study will analyse the writer’s writing style, language, and method for the research paper.
Topic 3: Understanding 17th-century English culture using a model of Francis Bacon’s idea.
Research Aim: This research aims to take a more in-depth look into Francis Bacon’s idea of modern economic development. To conduct the study, machine learning processes will be implemented to examine Francis’s ideas and their implementations in contemporary times.
Topic 4: The relation between early 18th-century English plays and The emerging financial market.
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse the relationship between eighteenth-century plays and a flourishing financial market. Most theatrical plays were written and performed in the middle of the 1720s, but writing carried out contributed to the financial market.
Topic 5: Issues of climate change used in early English literature: Shakespeare’s View of the sky.
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse climate change’s impact on early English writings. Climatic issues were faced even in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, providing writers with another topic to add to their published work. This research will focus on the work of Shakespeare, in which he included the specifics of climate change.
Also Read: Medicine and Nursing Dissertation Topics Free
Nineteenth-Century Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: impact of nineteenth-century gothic vampire literature on female members of the gothic subculture..
Research Aim: This research will look at the introduction of gothic vampire literature and its impact on female members of the gothic subculture. It includes a complete analysis of writing style and the impression it left of the female readers’.
Topic 2: Women theatre managers and the theatre in the late nineteenth century.
Research Aim: This research aims to view the impact on theatres under the management of women theatre managers. The improvement to theatre shows, along with the hardships faced by some managers, is discussed. The proposed study analyses the categories of theatre plays.
Topic 3: The history of American literature.
Research Aim: This research aims to give a brief history of American literature’s development and evolution throughout the centuries. The timeline begins from the early 15th century to the late 19th century. Word variations, sentence structures, grammar, and written impressions will be analysed.
Topic 4: “New women” concept in the novels of Victorian age English writers.
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse women’s position in the early nineteenth and how later Victorian writers used their work to give women a new identity. The method employed by these writers who wrote from a feminist point of view will also be discussed.
Topic 5: Discussing the role of the writer in their own story.
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse the form in which the writer reveals their presence to the reader. The methods can be achieved directly or use the characters to replace themselves in the narrative. The study observes the phrases, vocabulary, and situations the writer uses to narrate.
“Complete this short online form and provide as much information as possible to receive instant quotes from our writers specialising in your area of research.”
Order a Proposal
Worried about your dissertation proposal? Not sure where to start?
- Choose any deadline
- Plagiarism free
- Unlimited free amendments
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Completed to match exact requirements
Twentieth Century Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: effect of gender association in modern literature..
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse the issue of gender association in twentieth-century literature. Currently, male characters are described in a more masculine term than before in comparison to female counterparts. This research will also explore the possible approach of the possible characterisation of the two genders.
Topic 2: Feminism and literature.
Research Aim: This research aims to analyse the impacts of feminism on modern English literature quality. The study will look into the ideology of feminism and how feminist thoughts impact the readers’ view.
Topic 3: Modern literature based on climate change and eco-themes.
Research Aim: This research will study the various works of writers who tackled climate change and other eco-themes in their work. The study discusses the way they portrayed the item along with their views on preventing climate change. Modern work is compared to the work of previous writers who wrote about climate change.
Topic 4: How are fathers portrayed in modern literature?
Research Aim: This research will study the role of fathers in modern literature. The way the father character is portrayed in recent times has changed compared to writing in the early centuries. This research will look into the evolution of the father figure over time.
Topic 5: Literature for Asian American children.
Research Aim: This research will examine the fusion of classic American literature and Asian literature for children. The different genera’s that are produced and the style of writing will be analysed.
Also Read: Free Law Dissertation Topics
Children’s Literature Dissertation Topics
Topic 1: the influence of the intersection of race and bullying in children’s books..
Research Aim: This research will analyse the literature made for children from 2015 to 2019 in which the intersection between race and bullying is made. The study will evaluate the impact of literature read by a child in which there is bullying. Various picture books are analysed to observe the influence of racism on bullying.
Topic 2: Diversity of culture in children’s literature.
Research Aim: This research will observe the influence of the various cultural aspects of children’s books. The study will analyse the impact of mixed cultures on literature in a community and how it affects children’s mindsets from a young age.
Topic 3: The use of literature to shape a child's mind.
Research Aim: This research will analyse the effects of literature on a child’s mind. Behaviour, intelligence, and interactions between children and their age fellows are to be observed. A child’s behaviour with adults will also be analysed.
Topic 4: Evolution of children's literature.
Research Aim: This research will explore the change in children’s literature trends. This research will compare the literary work from the mid-nineteen century with modern-day children’s books. Differences in vocabulary, sentence structure, and mode of storytelling will be examined.
Topic 5: Racial discrimination in “the cat in the hat” impacts children’s racial views.
Research Aim: This research will take an in-depth analysis of the children’s story, “The Cat in the Hat,” to observe if it has any racial remarks which cause an increase in racism among children. The words used and the pictures found on the page will be thoroughly analysed, and their impact on the children reading it.
Topic 6: Measuring the nature of a child’s early composing.
Research Aim: This research will analyse the development of a child’s writing skills based on the type of books they read. The book’s genera, vocabulary, and the writing style of the child’s preferred book will be considered.
Topic 7: Use of a classroom to incorporate multicultural children’s literature.
Research Aim: This research will reflect on the potential use of a school classroom to promote multicultural literature for children. Since a classroom is filled with children of different cultural backgrounds, it becomes easier to introduce multicultural literature. The difficulties and the advantages to society in the incorporation of multicultural literature in classrooms are discussed.
Important Notes:
As literature looking to get good grades, it is essential to develop new ideas and experiment with existing literature theories – i.e., to add value and interest to your research topic.
The literature field is vast and interrelated to many other academic disciplines like linguistics , English literature and more. That is why creating a literature dissertation topic that is particular, sound, and actually solves a practical problem that may be rampant in the field is imperative.
We can’t stress how important it is to develop a logical research topic based on your entire research. There are several significant downfalls to getting your topic wrong; your supervisor may not be interested in working on it, the topic has no academic creditability, the research may not make logical sense, and there is a possibility that the study is not viable.
This impacts your time and efforts in writing your dissertation , as you may end up in the cycle of rejection at the initial stage of the dissertation. That is why we recommend reviewing existing research to develop a topic, taking advice from your supervisor, and even asking for help in this particular stage of your dissertation.
While developing a research topic, keeping our advice in mind will allow you to pick one of the best literature dissertation topics that fulfil your requirement of writing a research paper and add to the body of knowledge.
Therefore, it is recommended that when finalizing your dissertation topic, you read recently published literature to identify gaps in the research that you may help fill.
Remember- dissertation topics need to be unique, solve an identified problem, be logical, and be practically implemented. Please look at some of our sample literature dissertation topics to get an idea for your own dissertation.
How to Structure your Literature Dissertation
A well-structured dissertation can help students to achieve a high overall academic grade.
- A Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Declaration
- Abstract: A summary of the research completed
- Table of Contents
- Introduction : This chapter includes the project rationale, research background, key research aims and objectives, and the research problems. An outline of the structure of a dissertation can also be added to this chapter.
- Literature Review : This chapter presents relevant theories and frameworks by analysing published and unpublished literature on the chosen research topic to address research questions . The purpose is to highlight and discuss the selected research area’s relative weaknesses and strengths whilst identifying any research gaps. Break down the topic and key terms that can positively impact your dissertation and your tutor.
- Methodology : The data collection and analysis methods and techniques employed by the researcher are presented in the Methodology chapter, which usually includes research design , research philosophy, research limitations, code of conduct, ethical consideration, data collection methods, and data analysis strategy .
- Findings and Analysis : Findings of the research are analysed in detail under the Findings and Analysis chapter. All key findings/results are outlined in this chapter without interpreting the data or drawing any conclusions. It can be useful to include graphs, charts, and tables in this chapter to identify meaningful trends and relationships.
- Discussion and Conclusion : The researcher presents his interpretation of results in this chapter and states whether the research hypothesis has been verified or not. An essential aspect of this section of the paper is to link the results and evidence from the literature. Recommendations with regards to implications of the findings and directions for the future may also be provided. Finally, a summary of the overall research, along with final judgments, opinions, and comments, must be included in the form of suggestions for improvement.
- References : Your University’s requirements should complete this
- Bibliography
- Appendices : Any additional information, diagrams, and graphs used to complete the dissertation but not part of the dissertation should be included in the Appendices chapter. Essentially, the purpose is to expand the information/data.
About ResearchProspect Ltd
ResearchProspect is a UK based academic writing service that provides help with Dissertation Proposal Writing , PhD. Proposal Writing , Dissertation Writing , Dissertation Editing, and Improvement .
Our team of writers is highly qualified. They are experts in their respective fields. They have been working for us for a long time. Thus, they are well aware of the issues and the trends of the subject they specialize in.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
You May Also Like
Can’t find a topic for your radiology dissertation? Pick from our top radiology research topics to prepare your dissertation or radiology publication.
Need interesting and manageable Islamic Finance dissertation topics? Here are the trending Islamic Finance dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
It is a famous saying by henry ford that the only foundation of a business is service. It is very true and is followed by businesses of all scales.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
From admission to dissertation. Tips on making the PhD journey happy, productive and successful

How to Choose a PhD Research Topic in English Literature
To pick a right topic for research in English Literature during PhD is something a huge task. There are many topics out there for a good research. Here are my tips on how to rightly choose a PhD research topic in English Literature
- Choose the right poet or author that interests your topic.
- Ask PhD. supervisor the relevance of the poet to research.
- Search for some areas of research taken in the past.
- Choose a new topic that was not researched in the past.
- Check if sufficient Primary Sources are available or not.
- Try to take help from professors around you.
- Buy some books that are relevant to English Literature.
- Read for some days about the research topic.
- Read more literary theories and apply them to your PhD topic.
The proven way to choose a research topic in English Literature is to ask your professor on what they have researched upon while they had been doing their Ph.D. After this, you have to search for new trending topics at the present time. If someone has got an award or Nobel prize, Take that person and it is always best. Every year there are awards given to the authors who contributed well to English Literature. Choose a topic from them.
First, choose the right author to research
You’re about to choose an author to research for your Ph.D. in English literature. This is important and so you should take your time doing. You want to ensure the author is someone who is interesting and intriguing for everyone in the literary academic world. The words of the author need to be words that will make you think, question and analyze.
Start off broadly, looking at a number of authors. Slowly narrow down your search. You need to connect to the author – how is his or her work significant, why does it appeal to you, will it appeal to academics, is there enough to write on, and is he or she relevant. Look at how much work he or she has written and made quite sure you can get your hands on the books.
Relevance is important. We live in a time where gender is a top priority, as is history, politics, art, feminism, sexism, the way stories are told and who tells them. Your Ph.D. is going to be based on this author. His or her words need to be relevant, perhaps controversial and significant. This author needs to be engaging and someone whose work you can engage with.
Learn more about the books of the author
As an academic, reading and research are the two most important thing you are going to do. You need to read as much as you possibly can, not just on the author of your choice, but all the books written by the author of your choice. Reading is something that you learn from but also something that stimulates you and gives you your own writing style.
The more you can learn about the author, the better you can come up with a research topic in English literature. Read as many of his or books as possible, but also, read books or articles that have been written about the author. After a while, you will start to feel like you know and understand the author. This is what you want. The more you read, the more knowledgeable you become, in every aspect.
If you cannot find the books – some may be obscure – spend time in libraries. Libraries are in fact very conducive to writing a Ph.D. – something about the bookshelves, space, the solitude and of course, the history. Remember, you want to find angles or information on the author that is new. Look online, look in libraries and don’t feel shy to ask your lecturers if they have books for you to borrow.
Learn more about the author’s personal life
You may already know that what an author writes about does not have to reflect his or her personal life. Which means when you are researching an author, you do not only want to learn about his or her written words? These words are important. But so are their personal words. Personal lives give you a good insight into the author too. If he or she had children, did they work alone, how did they die?
When we say personal words, we also mean personal life. Because the written word is different to the ‘living word’, an author can have many personas. Perhaps they write about sexuality in a very open way yet in real life, are deeply conservative. This makes for an interesting Ph.D. Knowing how the author lived out her personal life is very important.
You are going to have to delve into realms of information to learn about an author’s personal life. This is going to be interesting for you, and for your reader. In today’s world of fake news, you also need to be very careful. Double check your sources, always, to ensure you are getting and then choosing out the correct information. Read, and then read some more.
Read thoroughly all the novels for ten days
This may seem extreme to you, but we have already said that a successful Ph.D in English Literature is about reading and research. You’ve chosen your author and you’ve written out a list of his or her books. Now, you are going to curl up in a corner somewhere, or at your desk, and read. We’ve already said it but the more you read, the more you learn.
Spend the next ten days reading. This way you are immersing yourself in the author’s words, subjects, feelings, emotions, history, religion, characters, sexuality, gender and more. The more you read, the more you will start to understand your chosen author and to feel and think the way the author did or does. Remember, reading not only educates you, but it also inspires you.
Make notes as you read. Choose a pen or highlighter and highlight those passages that make you really think. Cross-reference paragraphs, characters, emotions or metaphors. Take note of anything you find important or astonishing or unusual or surprising. Go back to your notes. Your very Ph.D. may relate to your first few notes. Keep all your reading material too; one day you are going to need it. All Ph.D. students seem to buy new bookshelves!
Write down the summaries on your own
The best way to understand something, and to remember something, is to write. The more you write, the easier things will stick in your head. Read a book, or a few chapters, and then write your own summaries. Chances are your time is limited, which is why summaries are good. Also, when you write a summary, things start becoming clearer and you may have an epiphany.
If the book you are reading has 15 chapters, perhaps summarize after every chapter. This is a personal choice – and of course, it depends on the books – but more summaries are better than less. Summarize in your own words and you will find that through summaries, you find your own style too. Cross-reference your summaries to the books you are reading.
When we say write, you may enjoy writing and you may enjoy typing. This is personal. Academics can generally be seen in front of their computers, hammering away at their keyboards. Type if you like, but sometimes writing with a pen and paper can actually get your creative juices flowing in a different way. Writing makes you think and gives you the ability to see things in a fresh way too. Always write, as much as you can.
Take a course on literary theories
There are many online literary theory courses that you can choose and we would suggest you sign up for one. The literary theory may seem academic and overwhelming but once you understand it, you’re on your way to writing a successful and highly revered Ph.D. Take a look and see how many prestigious universities offer courses on literary theory. That way you will see how important it is to do one.
A literary theory course will change the way you think about language, literature, society, and identity. A course will help you hone your critical reading skills and to understand theoretical terms such as postcolonialism, deconstruction, and Marxist criticism. A literary theory course will arm you with all the skills that you will need to dissect, criticize, analyze and understand your author, subject or topic you are researching.
There are many literary theory courses and you need to find one that will help you with your subject. A literary theory course will help you understand how you should approach literature, criticism verse theory, structure, analysis, and psycho-analysis of the subject and the author. You can choose to do one literary theory course and do it in your own time. There are many online courses; do one for a successful Ph.D.
Learn to relate those theories to each other
You’re writing a Ph.D. which is a huge step. You are going to bring in various literary theories which means not only do you need to understand the various literary theories, but you need to know how they all relate to one another. For a Ph.D. to be successful, you need to discuss, analyze, criticize and be open for debate. You also need to be open to criticism.
Take a look at the various literary theories. There are traditional literary theories and also formalism and new criticism. There are Marxism and critical theory and then there’s structuralism and post-structuralism. You are likely comfortable with some theories, and others not so much. Remember, fellow academics are going to question your theories and criticize you. Criticism is not always bad. It is academic criticism and it is there for a reason. Your research needs to be complete.
Again, a literary theory course can help you. Depending on your subject and author of choice, depends on which theories you will need to bring in. There are others – including new historicity and cultural materialism, ethnic studies and post-colonialism criticism. You need to relate them to one another. A course may help you to pick a good topic for PhD English literature.
Now think about how the author followed theories in novels
It’s important to note that in the academic world there are often many complex perspectives regarding literary theories. You need to read about your chosen author and have a look at how he or she followed literary theories in their books. Was there consistency? Was there a specific literary theory that was followed?
Sometimes the theories are simple and easy to follow. Sometimes there is a single theory or theme in a book. Sometimes theories are mixed, or many sides are given. You need to be able to read, review, analyze and understand the theories your author chose to follow. And your research needs to be so good, that fellow academics can analyze too and have brainwave moments from your writing.
Reading needs to be engaging, no matter the kind of reading. It also needs to make you think. Reading should stimulate. Sometimes, more than one theory is applied so that there are conflicting views, ideas, debate, and discussion. Take a look carefully at the author you are researching, their books, and the ideas that are put forward. Do they follow the theories you have been learning about? If so, which one or which ones. Do you have any theories of your own?
Choose one theory that pins your interest
You may find some literary theories more exciting than others. Perhaps post-colonialism is your thing, or Marxist criticism excites you. The trick is not to get too tied down to one theory, too soon. Read, read again, make notes, summarize and review. And look at various literary theories. You are going to find that some theories absolutely fascinate you and others you find irrelevant. Make notes and slowly you will be lead towards the theories that are right for you.
The more you read and make notes, the more one particular theory is going to leap out at you. It may be a slow process and in fact, the slower the better. This means your thinking is going to be clearer, and more critical. Once you find yourself honing in on a certain theory, you will find your direction.
Let’s say poststructuralism has caught your interest. You will now start thinking in a different light. You will find yourself coming up with your own theories, perhaps relating theories together, perhaps finding clarity in just the one. Make notes – you may not use them all, but you will find them useful when you start tying everything together. And always, always, theorize.
Jot down what others are researching
If you have not yet decided on your topic, make sure you know what other students are researching, or thinking of researching. You do not want to suddenly find out you are doing the same thing. And you do not want to waste your time. Jot down other people’s topics. Jot down any ideas you have and at some point, you will find it all comes together. Wake up and make notes. Sit with fellow researchers and make notes.
The thing about choosing a PhD research topic in English literature is that you constantly need to listen, read, listen to some more, research and keep reading. You also need to open yourself up to the conversation, with other researchers, Ph.D. students, and lecturers. Talk to others, even if your literary topics are different. Or even to make sure that they are different.
The academic world is constantly bouncing ideas off one another. It’s important to talk about your ideas, to get feedback on your ideas, and to listen to other people’s ideas. Keep a notebook with you at all times and jot down what and how other people are doing their research. You are not going to copy anyone, but you are going to find inspiration and you are going to inspire others.
Don’t take already beaten topics
You need to put effort into finding the right PhD topic. This can take time and be agonizing. It may seem like each topic you are choosing has already been taken. Take your time and find a topic that appeals to you, will challenge you and will exit you. Find a topic where you can give new and exciting information too.
Choosing a topic for your PhD in English literature may depend on the literature available, how much time it is going to take you, and also, it the topic worthy of research and investigation. You are going to have to immerse yourself totally in all the literature available on the topic – choose wisely.
Only choose a topic already done if you are going to look at new angles and find different analyses to the ones out there already. Only choose a topic that you are pretty sure will become clear to you, as you research, and therefore clear to others too. You can choose a topic that is interesting to you, and been done before, as long as you have a new and exciting way from which to write.
Be creative and choose at least 5 topics randomly
Most students will look at up to 5 topics before making a decision. It’s quite normal to pick a topic, change your mind, pick another one, do some research, put it away, look at a third topic, and so on. This is a good process. You need to be proactive in your decision which means you need to spend time thinking of what you are going to write, and how you are going to write it.
The reason you choose at least 5 research topics in English literature is that you can really find that topic that excites and challenges you. Look at why you would study the topic and what your research would mean to you, and to others. Take your topics to fellow researchers or academics. Ask them for advice. Listen to what people have to say about your topic choices.
You may choose the first topic and have your heart set on it. Perhaps you find little information on it, or even worse, you find too much. The topic may have been over-researched. It is time to move on to your next topic until you settle on the one that is right for you. Don’t be hasty in making a choice.
Sit with a literature expert for review of topics
Once you have your list of possible topics for your Ph.D., ask a literature expert to spend some time with you. This could be a professor, lecturer, fellow researcher, or author. Put forward your ideas and ensure you have the correct information on your ideas. Ask for feedback. When you ask for feedback, listen without getting defensive. You have asked for a review of your topics. Listen to the feedback.
A literature expert can be someone you know but it doesn’t have to be. If you know about a specialist in your area of interest, ask for a meeting. And remember, you can also approach a professional organization and ask to chat. Fellow academics are generally happy to help. You can find fellow academics at your university but you are also free to chat with academics at other learning institutions.
Finally, use the Internet. You can find a variety of sources online that will answer any questions you may have regarding your proposed topic. You will be able to get ideas online about your proposed topics, and if they can work, if they have been done, if you are on the right path, and if there is interest.
Consult 5 English teachers and show the topics
You are choosing a PhD research topic in English literature and so it makes sense for you to discuss your various topics with an English teacher. You are taking to the very people who are going to have an interest in your ideas and you will find good English teachers are eager to talk to you. You will find teachers at your own place of learning, but you can also ask for meetings with teachers you don’t know but are expert in their field.
Tell them about your ideas. Ask them for feedback, what they think and if they would advise you to do the proposed topic. Ask if they think your topic has good potential and if it could become a dissertation. Ask them what they know about the topic and if they feel it would be significant. Listen carefully to the advice you are given.
You want your topic to uncover new information. You might think you have new information, but experienced English teachers may know differently. Chat with them, listen to them more important, and ask for their honest opinions. The academic world is an inclusive one and experts are going, to be honest with you. Listen to them.
Get the topic automatically suggested by your teachers
Choosing a Ph.D. topic in English literature is no easy task. Your research needs to be significant and helpful to future researchers. It has to be groundbreaking. It has to shed light on topics, or at least offer controversial opinions. It can be really hard to choose a topic, for these reasons. You may find that some of your teachers actually give out topics and this is an easy way to make a choice.
You can go for the topic that is automatically suggested by your teachers. This way you know that the topic is one that is significant and has not been over-researched or over analyzed. Chat with your teacher and ask why they are suggesting the topic. Get their advice.
When you choose a topic for your research, you want to get feedback from people who are ‘in the know.’ Don’t go with the first topic that comes along. Go with a topic that excites you and that you know will be hard work but interesting, creative and challenging too. Go with a topic that is going to have the academic world thinking and questioning, in a good way!
Do not reveal your topic to your friends before joining your PhD
You may think this is not something that should be up for debate but the truth is the academic world is a competitive one. If your idea is fantastic and food for thought and we hope it is, you don’t want a fellow student to follow your idea. Rather keep your research topic to yourself until you join your PhD. You don’t want your idea stolen, but you also don’t want to lose confidence in your idea, especially if you are convinced by it.
The other reason not to reveal your topic in advance is in case of friends brush off your idea. You may think your topic is worthy but somebody may take away your confidence. As long as you have done your research in advance and you feel strongly about your topic, keep it. Always listen to advice given by academics, but be a little more guarded with your friends. Do initially only.
Confidence is necessary when doing a Ph.D. You can drive yourself literally made when you question and the second question what you are doing. Don’t let friends or academics second guess you, unless you are asking their opinions. Otherwise, as long as you feel sure, keep going.
Attend various interviews taking the topic
This is a good tip for you when you are deciding about your research topic, but also once you have chosen your research topic. Universities are always having special interest lectures, interviews, workshops and more, and you will find all of these on your topic of interest. When we say interview, we mean an interview, a meeting, and a lecture.
Attend as many interviews as you can. This means you should try and go to all public lecturers or book readings or similar when you have chosen your topic. And if you are still choosing your topic, ask as many experts on the subject as possible to interview and talk to you. Remember; interview a wide range of people before settling on a topic. People are interesting and have interesting ideas – one person will give you something nobody else will have thought of.
One on one interviews or meetings can be the most beneficial thing. You, as the researcher, need to do a lot of listening. An interviewer will guide you in every single way and make you think. If an interviewer can make you think, imagine how one day you are going to make your readers think.
Try to buy novels
Have you ever seen an academic’s bookshelves? They are always jam-packed, floor to ceiling, with books. And academics have many bookshelves, not just one. Your research topic is going to be with you for a long time. It’s your Ph.D., you are going to read, research, write and defend. It’s yours and will be forever.
Buy all the novels and books you need. You are the expert on your subject, the expert on your topic. You need to read everything you can lay your hands on. And print is so much better than online. Take the books with you to bed, to the bath, to your coffee shop. Do more reading
It’s also an excellent idea to make a note of all the books you read. You will have a Ph.D. English literature file. Have an index and one of the chapters should include all the books by the author, and all the books you have read on the author. Summarize and make notes on the books. Make notes in the book. Read the book a second time if it really appeals to you.
Do not read novels on the computer
This is a contentious issue because academia is changing. There are two schools of thought – read novels in print or read novels on the computer. Don’t do both. The truth is you can do whatever works for you. If you prefer to read online, it is better than not reading at all.
The reason academia says ‘do not read novels on the computer’ is that they feel you may not retain as much. When you read in print you can make notes easily, highlight certain sentences or chapters, dog ear pages so you remember what to go back to, and also, read at any time.
Books are fantastic, especially in print. You always have them, you don’t have to go online to find them, they are real treasures and should be treated as such. And to have a whole range of novels or books on the subject of your thesis is something incredibly special.
Use time properly with some interest
It is very easy, especially in this world with the internet, to be distracted. When you are writing a Ph.D. the one thing you cannot afford is a distraction. You need to use your time properly and be incredibly disciplined. Many academics say when they write a Ph.D., they eat, drink and sleep it.
Let’s get back to discipline. Your thesis is going to take you a long time. When you undertake your research topic, think about the time frame that you have. You will need to manage your time well. You need to be well disciplined in giving yourself time to collect data and go through it.
Everyone needs to take a break sometimes. Do things that you enjoy in your free time. But when you are working on your Ph.D. work. Use your time smartly and always be reading, researching or writing. Do this and you will not have any last minute chaos in meeting your deadline.
Make a point to take short notes of ideas
The one thing you always need to have in your bag is a pen and pencil. Otherwise, have a mobile device where you can take notes. Ideas come to people at the strangest of times – when you’re taking a walk, sipping coffee, waiting for a friend on the corner. Always write them down.
Likewise, when you attend an interview or a lecture, have your pen and paper handy. Make notes so that you can refer to them and read them. Once you have got home, take your notebook and transfer anything relevant to your PhD folder.
Be aware of the interview or lecture, or meeting that you are in. It may come across as rude if you scribble down every little thing. Be discerning with your notes. Yes, write things down, definitely. But don’t write down an entire lecture. Listen, jot down short notes, and always – go over everything afterward.
Do some literary survey what others are interested
Before you choose your literary Ph.D. topic, do a lot of research. Your idea may be an extraordinary one, but what if nobody has any interest in reading it? You want to choose a topic that is interesting and excited and where the academic world will be talking about it.
Ask your lecturers what they think of your topic. Make notes and surveys. You could choose five topics – as suggested earlier – and run a literary survey. Ask lecturers, fellow academics and other students what they think of your topics. Put it in a survey form and see which topic comes out tops.
Look carefully at the results of your survey. If everyone is choosing one topic for a reason, they are probably right. It does not mean they are definitely right though. You can take your survey one step further and find out why they find that particular topic interesting. Then make a decision based on how you feel.
Do not take foolish and irrelevant topics
This is an obvious one, isn’t it? Nobody is going to read a PhD, or take it seriously when your top is foolish or irrelevant. We are living in a world where relevance is everything. Whether it does to with gender, feminism, sexism, history, climate change, politics or art – you must be relevant.
Remember, a PhD is something that everyone in the academic world takes seriously. Your research is going to be read by your peers and by peers who you hold in high esteem. You want them to read your work and be wowed by your work. If you are foolish, you lose your chance of being held in high esteem too.
You are going to be spending a long time on your PhD, maybe a year and maybe more. You also want to be interested in what you are doing and not find it a chore. Your research is important, not just for others but for you too. Take the whole thing seriously. PhD studies are serious – you need to be serious too.
Do lots of reading about other areas
You need to read as much as possible when you are writing a PhD. To be honest, you need to read as much as possible at all times. When you read other work, ideas come to you. You learn about style and content by reading. Read anything you can get your hands on. You are going to be writing your PhD. A good writer reads a lot, it is the only way they become a good writer.
When we say you should do a lot of reading, it does not mean you have to only read about matters connected to your particular research. You should read everything you can. Read academic papers, read transcribed interviews, read the newspaper, read novels and read magazines. The more you read, the better you write. Any writer will tell you that.
As a researcher, books are going to become the most important thing in your life. All books are going to become important to you. Keep a book in your bag. Read when you’re on the bus, on the train and at home in front of the television. Reading gets our own creative juices flowing, whether academic, fiction or non-fiction. Reading makes you think.
Keep all the collected notes and reading in hand
When you write a PhD you are going to have a ton of material that you need to go through. The first thing you need to do, even before you have chosen a topic, is to open up a PhD file. Get yourself a good one, it’s going to be with you for a long time. Make different sections.
Your collected notes are going to be the most important part of your Ph.D.; you are going to refer to them for a very long time. Make sure you have your notes in one section and as you can, cross-references them to your summaries or to chapters or books you are reading. Always go over your notes. You will suddenly read something and go ‘oh that makes sense.’
The same goes with all your reading. Keep your reading close by. Wake up in the morning, read. When you go to bed at night, read. The more reading you do, the better. Make notes of all the books you have, and of all the books you still plan to get. Tick them off as you read them. And mostly, always have a copy of your PhD notes and research as you go along. You do not want to lose it.
Popular posts that others are reading now::
- How many words per page in apa style format
- How to Finish PhD Quickly
- 19 Simple steps to Write a Research Paper
- Top 20 Scopus Indexed Journals in ELT 2021 List (English Language Teaching)
- Scopus Indexed Journals in English Literature
Syam Prasad Reddy T
Hello, My name is Syam, Asst. Professor of English and Mentor for Ph.D. students worldwide. I have worked years to give you these amazing tips to complete your Ph.D. successfully. Having put a lot of efforts means to make your Ph.D. journey easier. Thank you for visiting my Ph.D. blog.

You May Also Like

Top 29 Benefits and Advantages of doing PhD in Australia

What is the Eligibility for PhD in English

Age Limit For PhD in New Zealand

English Language and Literature MPhil/PhD
London, Bloomsbury
One of the highest-ranking English departments in the UK ( The Guardian University Guide 2023 - English ), UCL English provides excellent opportunities for PhD students to study in the heart of literary London, with access to vast quantities of resources and research materials, and a high number of academic staff working on a diverse range of specialist research topics.
UK tuition fees (2024/25)
Overseas tuition fees (2024/25), programme starts, applications accepted.
- Entry requirements
An undergraduate degree in English Literature or a related subject is a pre-requisite for this programme, and a UK Master's degree in a relevant discipline, or an overseas qualification of an equivalent standard will normally be required. Research degree students are expected to start in September, but may request to start in January if there are exceptional reasons to do so. Applicants who wish to be considered for AHRC/ LAHP funding must have submitted a complete application by 5 January 2024.
The English language level for this programme is: Level 2
UCL Pre-Master's and Pre-sessional English courses are for international students who are aiming to study for a postgraduate degree at UCL. The courses will develop your academic English and academic skills required to succeed at postgraduate level.
Further information can be found on our English language requirements page.
Equivalent qualifications
Country-specific information, including details of when UCL representatives are visiting your part of the world, can be obtained from the International Students website .
International applicants can find out the equivalent qualification for their country by selecting from the list below. Please note that the equivalency will correspond to the broad UK degree classification stated on this page (e.g. upper second-class). Where a specific overall percentage is required in the UK qualification, the international equivalency will be higher than that stated below. Please contact Graduate Admissions should you require further advice.
About this degree
With access to vast collections of research materials and supervision from world-leading experts* in a wide range of literary periods and topics, UCL provides an exceptionally strong environment in which to study for an English PhD. UCL English Department has specialists in every period of English and American literature, as well as English language, with an outstanding record of internationally recognised scholarship and publications. A PhD in English at UCL will allow you to pursue original research and make a significant contribution to your field.
Students accepted for admission are given a principal supervisor with whom they will work closely during the course of the degree. A subsidiary supervisor is also appointed to provide additional advice. Great importance is attached to matching student and supervisor, and ensuring that students' progress is well monitored. Students meet either one or other supervisor approximately ten times during the academic year.
Graduate students initially register for the MPhil degree, but usually upgrade to full PhD student status in the second year, if progress is satisfactory. (The English Department does not offer a standalone research Master's programme, nor is it possible to be admitted as a PhD student directly.) In addition to the upgrade review in the second year, progress is also reviewed at the end of each year. Students who are making good progress will usually be offered opportunities to gain teaching experience from the second year onwards.
There are normally about 45 students undertaking research degrees in the department. They form a diverse, friendly, and vibrant intellectual community. There is a full programme of departmental research seminars at which papers are given by invited speakers and graduate students, and students also have access to a wide range of seminars and research events across UCL and the University of London. Research skills training is provided both within and beyond the department.
PhD students at UCL have access to an incomparable range of libraries, including the British Library and Senate House Library (the library of the University of London). They can also apply to spend a period as a visiting scholar at Yale as part of the UCL-Yale Collaborative Partnership.
Who this course is for
This programme is suitable for applicants with a strong interest or background in a wide range of literary periods or in English Linguistics, and who want to do complete research alongside specialists in literature in English and linguistics of the English language. The programme is suitable for both recent Masters graduates as well as early or mid-career professionals who have achieved the stated entry requirements.
What this course will give you
As one of the most respected academic institutions in the world ( QS World University Rankings 2023 ), UCL is an excellent place to study for a PhD in English. Our PhD students benefit from specialist supervision by world-leading researchers* as well as access to the outstanding range of research resources available to them in London.
The clear structure of the PhD programme, with regular progress reviews, supports successful completion, while the training courses offered by the department and UCL enable the development of both specific research skills and the professional skills needed for an academic career.
The relatively small department also offers many opportunities for formal and informal intellectual exchanges and collaborations, supported by our programme of research seminars. Many of our students also make the most of UCL’s partnership with Yale to spend a period of study there.
PhD students in English at UCL acquire advanced skills of the highest calibre as researchers, writers, and presenters of their work. They will also usually gain experience of teaching (both tutorials and seminars).
*UCL English has an outstanding research record, with 94% of our research outputs being graded as 4* 'world leading' or 3* 'internationally excellent' in the REF 2021.
The foundation of your career
The English Department is proud of its PhD alumni and values its ongoing relationship with them. We welcome alumni to departmental events, and encourage them to keep in touch with us at [email protected] . For more information on UCL’s wider alumni community, please see our website .
Employability
Our PhD graduates have an excellent record of securing employment in institutions of higher education and have progressed to academic positions here at UCL, at Oxford and Cambridge, in the wider University of London, at other universities across the UK, and in international destinations including the United States, Canada, and New Zealand. They are also well placed to pursue careers outside academia, as the skills in research, analysis, writing, and communication obtained during the PhD transfer easily to high-level work in many sectors.
Networking both among students and with academic staff and visiting speakers is facilitated by our lively programme of departmental research seminars, as well as our various reading groups and events. Beyond the department, extensive opportunities to meet fellow specialists and exchange knowledge and ideas are offered by the events programmes of the UCL Institute for Advanced Studies, the University of London Institute of English Studies, and numerous other research institutions near UCL and across London.
Teaching and learning
The MPhil/PhD degree programme primarily consists of independent research and self-directed study, and the central work of defining a thesis topic, and planning the stages of research and writing, is undertaken in close consultation with the primary supervisor. You will also undertake skills training that may take the form of seminars, workshops, and conferences.
Graduate students initially register for the MPhil degree, but upgrade to full PhD student status at the start of the second year, if progress is satisfactory.
In addition to the upgrade review at the start of the second year, progress is also reviewed at the end of the first year, in the first-year review, where the student submits a portfolio to their supervisory team, and at the Higher Degrees Sub Committee (HDSC) in their third year, where a submitted portfolio is assessed by a panel of senior academics in the department. A successful performance at the HDSC normally means the student will achieve Completing Research Student (CRS) status. Students who are making good progress will usually be offered opportunities to gain teaching experience from the second year onwards.
The MPhil/PhD degree programme consists of independent research and self-directed study. There are no set contact hours for the programme, but it is expected that your hours of study will mirror that of staff engagement as closely as possible (and this should be pro-rata for part-time study). If you have external funding, you should also ensure that you meet the Terms & Conditions of your funder in this regard. You will typically meet with your supervisory team up to ten times per academic year, and you will also undertake skills training that may take the form of seminars, workshops, and conferences.
Research areas and structure
We offer expertise in a wide range of topics within the field of English literature and language. Some areas in which the department would particularly welcome applications are:
- Old and Middle English literature and manuscript studies
- Relations between English and insular and continental French writings from the thirteenth to the fifteenth centuries
- Post-medieval bibliography and palaeography
- History of the book, textual and editorial theory and practice in all periods
- Shakespeare studies, including Shakespeare’s London
- The literature of the Elizabethan court
- Women writers of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries
- Classicism in seventeenth and eighteenth-century literary culture
- Literature and science in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries
- Revolutionary Writings in the Romantic period
- Homosexuality and literary history
- Literature and technology in late nineteenth and early twentieth-century literature
- Victorian and Edwardian writings on sexuality and adolescence
- Contemporary poetry
- Postmodern fiction
- London in literature/urban literature
- English grammar
- English language
- The history of the English language
- Corpus linguistics
You can read about our staff research interests on our website .
Research environment
UCL English has, throughout its history, been a pioneer in the study of English language and English literature, from Old English to contemporary texts. The department comprises a dynamic community of scholars with a breadth of expertise across literary periods and topics, as well as in language and linguistics. The comparatively small size of the department creates a friendly, inclusive research environment, with close contact between staff and students and many opportunities for intellectual exchange and collaboration.
Members of the English department have expertise in a wide range of approaches to English literature and language. Many of our literary research activities are organised around the key themes of The City, Editions, and Intercultural Exchanges, while our research in English Language is co-ordinated by the renowned Survey of English Usage. The department hosts regular research seminars at which PhD students, members of staff, and visiting speakers present their work; these include a themed strand of seminars on Race, Power, and Poetics. There are also many more seminars, reading groups and research events, both within the department, at the UCL Institute of Advanced Studies, and at the University of London’s Institute of English Studies. The department’s PhD students organise an annual Graduate Conference, where UCL speakers are joined by others from across the UK and beyond to share their research. They also publish Moveable Type, a peer-reviewed journal of academic articles, poetry and prose fiction.
UCL Library has outstanding physical and digital collections for literary research, as well as specialist materials in its excellent Special Collections department. Among these are the George Orwell Archive; Little Magazines; the Routledge and Kegan Paul Archives (publishing history); the Brougham Papers and papers of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge (19th-century liberalism); and the Chadwick Papers (19th-century sanitary reform). UCL Library also has superb holdings in London history. We enjoy unrivalled proximity to the British Library, with its vast collections, and Senate House Library (the library of the University of London), as well as other rich research resources including the Institute of Historical Research, the Warburg Institute, and the Wellcome Collection.
The period of registration for the MPhil/PhD degree programme is 3 years for full-time study. You are required to register initially for the MPhil degree with the expectation of transfer to PhD after successful completion of an upgrade review 9-18 months after initial registration.
Throughout your period of registration, you will meet regularly with your supervisory team, receiving feedback on work-in-progress. Regular completion of an online research log will help you and your supervisors to assess your specific training needs. The English Department provides a course in PhD Skills Training; many further training opportunities are also offered by the UCL Doctoral Skills Development Programme and LAHP (the London Arts and Humanities Partnership).
To ensure timely and successful completion of the thesis, the English Department formally reviews each student’s progress at regular intervals (usually the end of each year) by requiring submission of a dossier of work which is discussed in an interview. The most important of these reviews falls during your second year (9-18 months from registration) and will assess your readiness to transfer from MPhil to full PhD student status.
Upon successful completion of your approved period of registration, you may apply for a further period of 1 year as a Completing Research Student (CRS) to prepare your thesis for submission. The final degree assessment takes the form of an oral examination based on the thesis and is conducted by two examiners, usually one internal and one external.
The period of registration for the MPhil/PhD degree programme is 5 years for part-time study. You are required to register initially for the MPhil degree with the expectation of transfer to PhD after successful completion of an upgrade review 15-30 months after initial registration for part-time study. Throughout your period of registration, you will meet regularly with your supervisory team, receiving feedback on work-in-progress. Regular completion of an online research log will help you and your supervisors to assess your specific training needs. The English Department provides a course in PhD Skills Training; many further training opportunities are also offered by the UCL Doctoral Skills Development Programme and LAHP (the London Arts and Humanities Partnership). To ensure timely and successful completion of the thesis, the English Department formally reviews each student’s progress at regular intervals (usually the end of each year) by requiring submission of a dossier of work which is discussed in an interview. The most important of these reviews falls during your second or third year (15-30 months from registration) for part-time study, and will assess your readiness to transfer from MPhil to full PhD student status. Upon successful completion of your approved period of registration, you may apply for a further period of 2 years (for part-time students) as a Completing Research Student (CRS) to prepare your thesis for submission. The final degree assessment takes the form of an oral examination based on the thesis and is conducted by two examiners, usually one internal and one external.

Accessibility
Details of the accessibility of UCL buildings can be obtained from AccessAble accessable.co.uk . Further information can also be obtained from the UCL Student Support and Wellbeing team .
Fees and funding
Fees for this course.
The tuition fees shown are for the year indicated above. Fees for subsequent years may increase or otherwise vary. Where the programme is offered on a flexible/modular basis, fees are charged pro-rata to the appropriate full-time Master's fee taken in an academic session. Further information on fee status, fee increases and the fee schedule can be viewed on the UCL Students website: ucl.ac.uk/students/fees .
Additional costs
Additional costs may include expenses such as books, stationery, printing or photocopying, and conference registration fees.
The Department has some funds which can be applied for, to help offset the cost of travel to conferences or archives in the UK or overseas.
For more information on additional costs for prospective students please go to our estimated cost of essential expenditure at Accommodation and living costs .
Funding your studies
AHRC grants are available for UK/EU English PhD applicants who are applying to start a research degree in 2024. Applications are made directly to the London Arts and Humanities Partnership, who administer the awarding of AHRC funding at UCL. AHRC funding covers all fees, as well as providing a stipend for living expenses, for three years. If you have any questions about the application process please contact [email protected] .
UCL's Research Excellence Scholarships are available for UK/EU/Overseas applicants starting in 2024 and provides full funding including a stipend for living allowance for the length of the programme.
For a comprehensive list of the funding opportunities available at UCL, including funding relevant to your nationality, please visit the Scholarships and Funding website .
Quirk PhD Scholarship
Deadline: 26 January 2024 Value: Fees and maintenance (3yrs) Criteria Based on both academic merit and financial need Eligibility: UK
We recommend that applicants look at our list of staff on the UCL English website before submitting an application. Whilst potential supervisors are unable to accept a PhD student without a formal application form, we attach great importance to the match between supervisors and students, so please check that we have a member of teaching staff who could potentially supervise your project before applying. Applicants who are interested in applying for AHRC funding via the London Arts and Humanities Partnership (LAHP) must submit completed applications (including references) by 5 January 2024 (you will also need to complete a LAHP application form: see the LAHP website for details).
Please note that you may submit applications for a maximum of two graduate programmes (or one application for the Law LLM) in any application cycle.
Choose your programme
Please read the Application Guidance before proceeding with your application.
Year of entry: 2024-2025
Year of entry: 2023-2024, got questions get in touch.

English Language and Literature
UCL is regulated by the Office for Students .
Prospective Students Graduate
- Graduate degrees
- Taught degrees
- Taught Degrees
- Applying for Graduate Taught Study at UCL
- Research degrees
- Research Degrees
- Funded Research Opportunities
- Doctoral School
- Funded Doctoral Training Programmes
- Applying for Graduate Research Study at UCL
- Teacher training
- Teacher Training
- Early Years PGCE programmes
- Primary PGCE programmes
- Secondary PGCE programmes
- Further Education PGCE programme
- How to apply
- The IOE approach
- Teacher training in the heart of London
- Why choose UCL?
- Entrepreneurship
- Inspiring facilities and resources
- Careers and employability
- Your global alumni community
- Your wellbeing
- Postgraduate Students' Association
- Your life in London
- Accommodation
Department of English and Related Literature
PhD in English and Related Literature
Work in an intellectually invigorating environment and be supported by supervisors who are experts in their field.
Be inspired to reach your research ambitions in an intellectual and supportive community at the forefront of English research.
Your research
The diversity of our staff’s research interests means that we are well-positioned to supervise research in any field of literature, from the Middle Ages to the present day, including literature in languages other than English, and literary works in translation.
We also have distinctive expertise in practice-led teaching and research, including archival work and printing. The PhD in English and Related Literature is available on a full-time or part-time basis.
Under the guidance of your supervisor, you'll complete a thesis of up to 80,000 words. A typical semester will involve a great deal of independent research, punctuated by meetings with your supervisor who will be able to suggest direction and address concerns throughout the writing process. You'll be encouraged to undertake periods of research at archives and potentially internationally, depending on your research thesis.
Throughout your degree, you'll have the opportunity to attend a wide range of research training sessions in order to learn archival and research skills, and a range of research seminars organised by the research schools, which bring speakers from around the world for research talks and networking. There is also internal funding available if you wish to propose research events and symposia/conferences.
[email protected] +44 (0) 1904 323366
Related links
- How to apply
- Research degree funding
- Accommodation
- International students
- Life at York
You also have the option of enrolling in a PhD in English by distance learning, where you will have the flexibility to work from anywhere in the world. You will attend the Research Training Programme online in your first year and have supervision and progression meetings online.
You must attend a five-day induction programme in York at the beginning of your first year. You will also visit York in your second and third years (every other year for part-time students).
Apply for PhD in English and Related Literature (distance learning)
Top ten department
We're a top ten research department according to the Times Higher Education’s ranking of the latest REF results (2021).
35th in the world
for English Language and Literature in the QS World University Rankings by Subject, 2023.
Athena Swan Bronze
We're proud to hold an Athena Swan Bronze award in recognition of the work we do to support gender equality in English.

Explore funding for postgraduate researchers in the Department of English and Related Literature.

Supervision
Explore the expertise of our staff and identify a potential supervisor.
Research training
You'll receive training in research methods and skills appropriate to the stage you've reached and the nature of your work. In addition to regular supervisory meetings to discuss planning, researching and writing the thesis, we offer sessions on bibliographic and archival resources (digital, print and manuscript). You'll receive guidance in applying to and presenting at professional conferences, preparing and submitting material for publication and applying for jobs. We meet other training needs in handling research data, various modern languages, palaeography and bibliography. Classical and medieval Latin are also available.
We also offer training in teaching skills for students who wish to pursue teaching posts following their degree. This includes sessions on the delivery and content of seminars and workshops to undergraduates, a structured shadowing programme, teaching inductions and comprehensive guidance and resources for our graduate teaching assistants. Our teacher training is directed by a dedicated staff member.
You'll also benefit from the rich array of research and training sessions at the Humanities Research Centre .

Course location
This course is run by the Department of English and Related Literature.
You'll be based on Campus West , though your research may take you further afield.
We also have a distance learning option available for this course.
Entry requirements
For doctoral research, applicants should hold or be predicted to achieve a first-class or high upper second-class undergraduate degree with honours (or equivalent international qualification) and a Masters degree with distinction.
The undergraduate and Masters degrees should be in literature, or in a related subject that is closely tied to the proposed research project.
Other relevant experience and expertise may also be considered:
- Evidence of training in research techniques may be an advantage.
- It is expected that postgraduate applicants would be familiar with the recent published work of their proposed supervisor.
- Publications are not required and we don't expect applicants to have been published before they start their research degrees.
Supervisors interview prospective research students to ensure good supervisory match and to help with funding applications.
The core deciding factor for admission is the quality of the research proposal, though your whole academic profile will be taken into account. We are committed to ensuring that no prospective or existing student is treated less favourably. See our admissions policy for more information.
Apply for the PhD in English and Related Literature
Have a look at the supporting documents you may need for your application.
Before applying, we advise you to identify potential supervisors in the department. Preliminary enquiries are welcomed and should be made as early as possible. However, a scattershot approach – emailing all staff members regardless of the relationship between their research interests and yours – is unlikely to produce positive results.
If it's not clear which member of staff is appropriate, you should email the Graduate Chair .
Students embarking on a PhD programme are initially enrolled provisionally for that qualification. Confirmation of PhD registration is dependent upon the submission of a satisfactory proposal that meets the standards required for the degree, usually in the second year of study.
Find out more about how to apply .
English language requirements
You'll need to provide evidence of your proficiency in English if it's not your first language.
Check your English language requirements
Research proposals
In order to apply for a PhD, we ask that you submit a research proposal as part of your application.
When making your application, you're advised to make your research proposals as specific and clear as possible. Please indicate the member(s) of staff that you'd wish to work with.
Your research proposal should:
- Identify the precise topic of your topic and communicate the main aim of your research.
- Provide a rigorous and thorough description of your proposed research, including the contributions you will make to current scholarly conversations and debates.
- Describe any previous work you have done in this area, with reference to relevant literature you have read so far.
- Communicate the central sources that the project will address and engage.
- Offer an outline of the argument’s main claims and contributions. Give a clear indication of the authors and texts that your project will address.
- Include the academic factors, such as university facilities, libraries resources, centres, other resources, and / or staff, which have specifically led you to apply to York.
What we look for:
- How you place your topic in conversation with the scholarly landscape: what has been accomplished and what you plan to achieve. This is your chance to show that you have a good understanding of the relevant work on your topic and that you have identified a new way or research question to approach the topic.
- Your voice as a scholar and critical thinker. In clean, clear prose, show those who will assess your application how your proposal demonstrates your original thinking and the potential of your research.
- Your fit with York, including the reasons for working with your supervisor and relevant research schools and centres.
- Above all, remember that there isn’t one uniform way to structure and arrange your research proposal, and that your approach will necessarily reflect your chosen topic.
Careers and skills
- You'll receive support in applying to and presenting at professional conferences, preparing and submitting material for publication and applying for jobs.
- You'll benefit from training in handling research data, various modern languages, palaeography and bibliography. Classical and medieval Latin are also available. The Humanities Research Centre also offers a rich array of valuable training sessions.
- We also offer training in teaching skills if you wish to pursue a teaching post following your degree. This includes sessions on the delivery and content of seminars and workshops to undergraduates, a structured shadowing programme, teaching inductions and comprehensive guidance and resources for our graduate teaching assistants.
- You'll have the opportunity to further your training by taking courses accredited by Advance HE: York Learning and Teaching Award (YLTA) and the York Professional and Academic Development scheme (YPAD) .
Find out more about careers

Discover York

We offer a range of campus accommodation to suit you and your budget, from economy to deluxe.

Discover more about our researchers, facilities and why York is the perfect choice for your research degree.

Graduate Research School
Connect with researchers across all disciplines to get the most out of your research project.
Find a supervisor
Explore our staff expertise
Find out all you need to know about applying to York
Find funding to support your studies
We use cookies to help our site work, to understand how it is used, and to tailor ads that are more relevant to you and your interests.
By accepting, you agree to cookies being stored on your device. You can view details and manage settings at any time on our cookies policy page.

English Literature PhD
Key information, full-time - 4 years, part-time - 8 years.
Research brochure
Register for updates
Webinars and events
Why choose this programme
We perform innovative and world-leading research across literature, writing and linguistics.
We’re part of the interdisciplinary School of Literature and Languages, which has research-active staff who are at the forefront of knowledge in English literature, creative writing, film studies, translation studies, theoretical and applied linguistics, and literary and cultural studies.
Our research concentrates on a range of periods, themes and subjects, including:
- Medieval literature
- Shakespeare and the Renaissance
- Romanticism
- Victorian and 19th-century literature
- Modern and contemporary literature
- Creative writing
- Film studies.
Our diverse mix of subject specialities mean that we are a vibrant and imaginative community with lots of opportunity for intellectual exchange.
We’re part of TECHNE , an Arts and Humanities Research Council (AHRC)-funded doctoral training partnership, which provides access to comprehensive academic and professional training programmes, as well as the possibility of funding for your studies.
The Research Excellence Framework (REF) 2021 ranked the School of Literature and Languages 10th for research impact in the UK, with 75% of our case studies rated as having outstanding impacts, in terms of reach and significance (4*). Our submission to REF included contributions from the Guildford School of Acting (GSA).

Frequently asked questions about doing a PhD
What you will study
Our English Literature PhD will train you in critical and analytical skills, research methods, and knowledge that will equip you for your professional or academic career. It normally takes around three or four years to complete our full-time PhD.
You’ll be assigned a primary and secondary supervisor, who will meet with you regularly to read and discuss your work and progress. For us, writing is essential for understanding and developing new perspectives, so you’ll be submitting written work right from the start of your course.
In the first year of your PhD, you’ll refine your research proposal and plan the structure of your work with the guidance and support of your supervisors. As you go into your second and third year, you’ll gradually learn to work more independently, and your supervisors will guide you on how to present at conferences and get your work published.
After 12-15 months, you’ll submit a substantial piece of work for a confirmation examination. The confirmation examination will be conducted by two internal members of staff not on your supervisory team and will give you the opportunity to gain additional guidance on your research-to-date. The final two years of your PhD will be devoted to expanding and refining your work ready for submission of the final thesis.
As a doctoral student in the School of Literature and Languages, you’ll receive a structured training programme covering the practical aspects of being a researcher, including grant-writing, publishing in journals, and applying for academic jobs.
Your final assessment will be based on the presentation of your research in a written thesis, which will be discussed in a viva examination with at least two examiners. You have the option of preparing your thesis as a monograph (one large volume in chapter form) or in publication format (including chapters written for publication), subject to the approval of your supervisors.
Research support
The professional development of postgraduate researchers is supported by the Doctoral College , which provides training in essential skills through its Researcher Development Programme of workshops, mentoring and coaching. A dedicated postgraduate careers and employability team will help you prepare for a successful career after the completion of your PhD.

Research themes
- Women's writing (especially medieval women's writing, early modern women's drama and Victorian women writers)
- Medieval romance
- Romanticism
- Victorian studies
- Modernism and modernity
- Travel and mobility
- Western and global esotericisms
- Sexuality and queer theory
- Postmodern and post-postmodern writing
- Contemporary fiction
- Transnational literature.
Our academic staff
See a full list of all our academic staff within the School of Literature and Languages.
Research areas
Research facilities.
You’ll be allocated shared office space within the School of Literature and Languages and have full access to our library and online resources. Our close proximity to London also means that the British Library and many other important archives are within easy reach.
In addition to a number of excellent training opportunities offered by the University, our PhD students can take additional subject-specific training and take part in the School’s research seminars and events. These provide a valuable opportunity to meet visiting scholars whose work connects with our own research strengths across literature, theory, and creative writing.

Edwin Gilson
A real highlight for me was having an article published in a well-known journal in my field. This came out of a chapter I wasn’t expecting to write at the start of the thesis, on a novel I read during the PhD.

Entry requirements
Applicants are expected to hold a good first-class UK degree (a minimum 2:1 or equivalent) and an MA in a relevant topic.
International entry requirements by country
English language requirements.
IELTS Academic: 7.0 or above with a minimum of 6.5 in each component (or equivalent).
Application requirements
Applicants are advised to contact potential supervisors before they submit an application via the website. Please refer to section two of our application guidance .
After registration
Students are initially registered for a PhD with probationary status and, subject to satisfactory progress, subsequently confirmed as having PhD status.
Selection process
Selection is based on applicants:
- Meeting the expected entry requirements
- Being shortlisted through the application screening process
- Completing a successful interview
- Providing suitable references.
Student life
At Surrey we offer the best of both worlds – a friendly campus university, set in beautiful countryside with the convenience and social life of Guildford on your doorstep.
Start date: July 2024
Start date: October 2024
Start date: January 2025
Start date: April 2025
- Annual fees will increase by 4% for each year of study, rounded up to the nearest £100 (subject to legal requirements).
- Any start date other than September will attract a pro-rata fee for that year of entry (75 per cent for January, 50 per cent for April and 25 per cent for July).
View the list of fees for all postgraduate research courses.
Additional costs
There are additional costs that you can expect to incur when studying at Surrey.
A Postgraduate Doctoral Loan can help with course fees and living costs while you study a postgraduate doctoral course.
Apply online
If you are applying for a studentship to work on a particular project, please provide details of the project instead of a research proposal.
Read our application guidance for further information on applying.
To apply online first select the course you'd like to apply for then log in.
1. Select your course
Select the course you wish to apply for.
To apply online sign in or create an account.
Code of practice for research degrees
Surrey’s postgraduate research code of practice sets out the University's policy and procedural framework relating to research degrees. The code defines a set of standard procedures and specific responsibilities covering the academic supervision, administration and assessment of research degrees for all faculties within the University.
Download the code of practice for research degrees (PDF) .
Terms and conditions
When you accept an offer to study at the University of Surrey, you are agreeing to follow our policies and procedures , student regulations , and terms and conditions .
We provide these terms and conditions in two stages:
- First when we make an offer.
- Second when students accept their offer and register to study with us (registration terms and conditions will vary depending on your course and academic year).
View our generic registration terms and conditions (PDF) for the 2023/24 academic year, as a guide on what to expect.
This online prospectus has been published in advance of the academic year to which it applies.
Whilst we have done everything possible to ensure this information is accurate, some changes may happen between publishing and the start of the course.
It is important to check this website for any updates before you apply for a course with us. Read our full disclaimer .
Course location and contact details
Campus location
Stag Hill is the University's main campus and where the majority of our courses are taught.
University of Surrey Admissions
University of Surrey Guildford Surrey GU2 7XH
- Hirsh Health Sciences
- Webster Veterinary
English Literature: Resources for Graduate Research
Find articles in jumbosearch, search for articles on topics in english in these databases, database search strategies, need more articles, link tufts resources to google scholar.
- Books on Literary History, Theory, Criticism & More
- Novels, Poems & Other Primary Texts
- Literature Reviews
- Historic Newspapers & More
- Reviews, Essays & More
- English & the Digital Humanities
- How to Find Cited Material
- Citing Your Sources This link opens in a new window
- Getting Items that Tufts Doesn't Own
- Copyright & Publication This link opens in a new window
Developing Search Terms
The first step in picking a topic is to brainstorm by asking yourself a few questions. What do you already know about this topic from your course readings? Are there similar ideas you might want to explore? What are the key concepts that you're interested in pursuing?
Once you've spent a bit of time answering these questions, you can take the concepts you've identified and use the keywords and phrases to start searching for information. Keep in mind that you'll need to build a base of knowledge before you can write effectively.
See the Database Search Strategies box on this page for more help with keyword searching!
Want to discover everything that Tisch Library has on your topic? Try searching for your topic in JumboSearch, which simultaneously searches across all of the library's resources, including journal articles in databases, online, and in print.
Search by Keyword, Title, Subject, or Creator
Below is a selection of online resources that include a vast number of articles on topics in English, including literary criticism. The resources on this page include articles from both scholarly and popular sources, so be sure to evaluate your sources to make sure that they are appropriate for your project.
- MLA International Bibliography This database is a classified listing and subject index of scholarly books and articles on modern languages, literatures, folklore and linguistics which has been compiled by the Modern Language Association of America since 1921. The electronic version includes the Bibliography's entire print run and currently contains more than 2 million records.
- JSTOR JSTOR includes scholarship published in more than 1,400 of the highest-quality academic journals across the humanities, social sciences, and sciences, as well as monographs and other materials valuable for academic work.
- Project MUSE Provides electronic access to the full text of Johns Hopkins University Press's scholarly publications in the humanities, social sciences, and mathematics.
- Academic OneFile Academic OneFile has over 8,000 peer-reviewed journals, the majority in full-text, from the world's leading journals and reference sources.
- Academic Search Premier This multi-disciplinary database provides full text for more than 4,600 journals, including full text for nearly 3,900 peer-reviewed titles.
- Gale Literature Resource Center Find up-to-date biographical information, overviews, full-text literary criticism and reviews on more than 130,000 writers in all disciplines, from all time periods and from around the world.
Databases respond best to keyword searching. To search efficiently, turn your research question into a keyword search:
Research Question : How does Gish Jen address issues of American identity?
Search One : (Search with keywords connected by “and”): Gish Jen and American and identity
Search Two : (Truncate some of the keywords using *): Gish Jen and America* and ident*
Search Three : (Add alternate words into the search with “(or)”): Gish Jen and (America* or United States) and (ident* or belong*)
Truncate keywords where applicable. Truncation uses the asterisk ( * ) to end a word at its core, allowing you to retrieve many more documents containing variations of the search term. Truncation can also be used to find the singular and plural forms of a term. Example: educat* will find educate, educates, education, educators, educating and more.
Looking for more articles? Search Google Scholar to find more information on your topic.

If you're off campus, you can link Tufts resources to your Google Scholar results. Linking Google Scholar to the Tufts libraries lets Google show you which full-text articles we have access to through the library's subscriptions. Once you link them, Google Scholar will automatically check to see if Tufts provides access to full-text articles. If we do, you'll be able to access the articles directly from Google Scholar, which is especially helpful if you're off campus. Follow these instructions to link Tufts to Google Scholar:
- Open Google Scholar .
- Click on the Parallel Bars icon (hamburger stack) on the upper left side of the Google Scholar page.
- Scroll down and click on Settings. On the Google Scholar Settings page, click Library Links in the left sidebar.
- Enter Tufts University into the search bar and click search.
- When prompted, check the box next to Tufts University – Get this Item at Tufts
- Click Save at the bottom of the screen.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Books on Literary History, Theory, Criticism & More >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 3:34 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/EnglishGraduateResources

- Schools & departments

English Literature PhD
Awards: PhD
Study modes: Full-time, Part-time
Funding opportunities
Programme website: English Literature
Discovery Day
Join us online on 18th April to learn more about postgraduate study at Edinburgh
View sessions and register
Research profile
Doctorate-level study is an opportunity to expand upon your interests and expertise in a community that really values research; and to make an original, positive contribution to learning in literature and related fields.
As the oldest department of English Literature in the UK, based in one of the largest and most diverse Schools in the University of Edinburgh, we are the ideal place for PhD study.
Our interdisciplinary environment brings together specialists in all periods and genres of literature and literary analysis.
Research excellence
Based on our performance in the latest Research Excellence Framework (REF), over 90 per cent of our research and impact is classed as world-leading and internationally excellent by Research Professional. 69 per cent is graded at the world-leading level – the highest of REF’s four categories.
In Times Higher Education's REF analysis, English at Edinburgh is ranked fifth in the UK (out of more than 90 institutions) for:
- the overall quality of our publications and other outputs
- the impact of our research on people’s lives
- our supportive research environment
Given the breadth and depth of our expertise, we are able to support students wishing to develop research projects in any field of Anglophone literary studies. These include American studies, literary and critical theory, the history of the book, gender and sexuality studies, and global Anglophone literatures - where our specialisms include Pacific, African, South Asian, and African-American writing.
We have particular strengths in each of the main periods of English and Scottish Literature:
- Renaissance/early modern
- Enlightenment
- 21st century
- Contemporary
Emergent research themes in the department include the digital humanities, the economic humanities, the environmental humanities and literature and medicine.
- Explore our range of research centres, networks and projects in English and Scottish Literature
Working with colleagues elsewhere in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures, and across the wider University, we are able to support PhD theses crossing boundaries between disciplines and/or languages.
- Be inspired by the range of PhD research in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures
Over the course of your PhD, you’ll be expected to complete an original body of work under the expert guidance of your supervisors leading to a dissertation of usually between 80,000 and 100,000 words.
You will be awarded your doctorate if your thesis is judged to be of an appropriate standard, and your research makes a definite contribution to knowledge.
- Read our pre-application guidance on writing a PhD research proposal
Go beyond the books
Beyond the Books is a podcast from the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures (LLC) that gives you a behind-the-scenes look at research and the people who make it happen.
Listen to a mix of PhD, early career and established researchers talk about their journey to and through academia and about their current and recent research.
- Browse Beyond the Books episodes and hear our research community talk about their work
Training and support
Between the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures (LLC), the Careers Service, and the Institute for Academic Development (IAD), you’ll find a range of programmes and resources to help you develop your postgraduate skills.
You will also have access to the University’s fantastic libraries, collections and worldwide strategic partnerships.
Part of a community
As part of our research community, you will be immersed in a world of knowledge exchange, with lots of opportunities to share ideas, learning and creative work.
Activities range from talks by visiting speakers and work-in-progress seminars, to reading groups, conferences, workshops, performances, online journals and forums, many of which are led by PhD candidates.
Highlights include student reading for the James Tait Black Prizes, Britain's oldest literary awards which typically involve reading submissions across fiction and biography and advising the judges on the shortlists.
- Read an interview with 2022 James Tait Black reader, Céleste Callen
Our graduates tell us that they value the friendliness of the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures (LLC), the connections they make here and the in-depth guidance they receive from our staff, who are published experts in their field.
A UNESCO World City of Literature, Edinburgh is a remarkable place to study, write, publish, discuss and perform prose, poetry and drama.
Take a PhD with us and you will be based in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures (LLC) in the historic centre of this world-leading festival city.
You will have access to the University’s many literary treasures. These include the libraries of:
- William Drummond
- Lewis Grassic Gibbon
- Hugh MacDiarmid
- Norman MacCaig
The Centre for Research Collections holds the W.H. Auden collection; the Corson Collection of works by and about Sir Walter Scott; and the Ramage collection of poetry pamphlets.
It also holds a truly exceptional collection of early Shakespeare quartos and other early modern printed plays put together by the 19th century Shakespearean James Halliwell-Phillipps, the correspondence of Thomas and Jane Welsh Carlyle (the focus of one of the major editorial projects in Victorian studies of the last half-century), and the extensive Laing collection of medieval and early modern manuscripts, as well as letters and papers by - and relating to - authors including:
- Christopher Isherwood
- Rudyard Kipling
- John Middleton Murry
- Walter de la Mare
- George Mackay Brown
- Compton Mackenzie
Many of the University's Special Collections are digitised and available online from our excellent Resource Centre, Computing Labs, and dedicated PhD study space in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures (LLC).
Look inside the PhD study space in LLC
In the city
Our buildings are close to the National Library of Scotland (where collections include the Bute Collection of early modern English drama and the John Murray Archive), Edinburgh Central Library, Scottish Poetry Library, Scottish Storytelling Centre, Writers’ Museum and a fantastic range of publishing houses, bookshops, and theatres.
We have strong links with the Edinburgh International Book Festival, which annually welcomes around 1,000 authors to our literary city.
Entry requirements
These entry requirements are for the 2024/25 academic year and requirements for future academic years may differ. Entry requirements for the 2025/26 academic year will be published on 1 Oct 2024.
A UK masters, or its international equivalent, with a mark of at least 65% in your English literature dissertation of at least 10,000 words.
If your masters programme did not include a dissertation or included a dissertation that was unmarked or less than 10,000 words, you will be expected to produce an exceptional research proposal and personal statement to show your ability to undertake research at the level required by this programme.
International qualifications
Check whether your international qualifications meet our general entry requirements:
- Entry requirements by country
- English language requirements
Regardless of your nationality or country of residence, you must demonstrate a level of English language competency at a level that will enable you to succeed in your studies.
English language tests
We accept the following English language qualifications at the grades specified:
- IELTS Academic: total 7.0 with at least 6.5 in each component. We do not accept IELTS One Skill Retake to meet our English language requirements.
- TOEFL-iBT (including Home Edition): total 100 with at least 23 in each component. We do not accept TOEFL MyBest Score to meet our English language requirements.
- C1 Advanced ( CAE ) / C2 Proficiency ( CPE ): total 185 with at least 176 in each component.
- Trinity ISE : ISE III with passes in all four components.
- PTE Academic: total 70 with at least 62 in each component.
Your English language qualification must be no more than three and a half years old from the start date of the programme you are applying to study, unless you are using IELTS , TOEFL, Trinity ISE or PTE , in which case it must be no more than two years old.
Degrees taught and assessed in English
We also accept an undergraduate or postgraduate degree that has been taught and assessed in English in a majority English speaking country, as defined by UK Visas and Immigration:
- UKVI list of majority English speaking countries
We also accept a degree that has been taught and assessed in English from a university on our list of approved universities in non-majority English speaking countries (non-MESC).
- Approved universities in non-MESC
If you are not a national of a majority English speaking country, then your degree must be no more than five years old* at the beginning of your programme of study. (*Revised 05 March 2024 to extend degree validity to five years.)
Find out more about our language requirements:
Fees and costs
Scholarships and funding, featured funding.
There are a number of scholarship schemes available to eligible candidates on this PhD programme, including awards from the Arts and Humanities Research Council.
Please be advised that many scholarships have more than one application stage, and early deadlines.
- Find out more about scholarships in literatures, languages and cultures
Other funding opportunities
Search for scholarships and funding opportunities:
- Search for funding
Further information
- Phone: +44 (0)131 650 4086
- Contact: [email protected]
- School of Literatures, Languages & Cultures
- 50 George Square
- Central Campus
- Programme: English Literature
- School: Literatures, Languages & Cultures
- College: Arts, Humanities & Social Sciences
Select your programme and preferred start date to begin your application.
PhD English Literature - 3 Years (Full-time)
Phd english literature - 6 years (part-time), application deadlines.
Due to high demand, the school operates a number of selection deadlines. We will make a small number of offers to the most outstanding candidates on an ongoing basis, but hold the majority of applications until the next published selection deadline when we will offer a proportion of the places available to applicants selected through a competitive process.
Deadlines for applicants applying to study in 2024/25:
- How to apply
You must submit two references with your application.
The online application process involves the completion of a web form and the submission of supporting documents.
For a PhD programme, you should include:
- a sample of written work of about 3,000 words (this can be a previous piece of work from an undergraduate or masters degree)
- a research proposal - a detailed description of what you hope to achieve and how
- Pre-application guidance
Before you formally apply for this PhD, you should look at the pre-application information and guidance on the programme website.
This will help you decide if this programme is right for you, and help us gain a clearer picture of what you hope to achieve.
The guidance will also give you practical advice for writing your research proposal – one of the most important parts of your application.
Find out more about the general application process for postgraduate programmes:
Share this page
The graduate program in English provides you with a broad knowledge in the discipline, including critical and cultural theory and literary history. This solid foundation enables you to choose your own path based on the wide variety of areas of concentration. Our flexible program allows you to take courses outside the department to further explore your chosen field(s). Our program emphasizes excellence in writing, innovative scholarship, and eloquent presentations—important skills you will need in your future profession. The program and its faculty are committed both to diversity in its student body and in the diversity of thought and scholarship.
Examples of student theses and dissertations include “The Write to Stay Home: Southern Black Literature from the Great Depression to Early Twenty-first Century,” “Profaning Theater: The Drama of Religion on the Modernists Stage,” and “Sentimental Borders: Genre and Geography in the Literature of Civil War and Reconstruction.”
Graduates have secured faculty positions at institutions such as Brown University, Columbia University, and University of California, Los Angeles. Others have begun their careers with leading organizations such as Google and McKinsey & Company.
Additional information on the graduate program is available from the Department of English and requirements for the degree are detailed in Policies .
Areas of Study
Unspecified | Medieval | Renaissance/Early Modern | 18th Century/Enlightenment | 19th Century British/Romantics/Victorian | Early American (to 1900) | 20th Century British | 20th Century American | Criticism and Theory | The English Language | Transnational Anglophone/Postcolonial | African American Literature | Drama | Poetry
Admissions Requirements
Please review admissions requirements and other information before applying. You can find degree program-specific admissions requirements below and access additional guidance on applying from the Department of English .
Writing Sample
The writing samples (one primary and one secondary) are highly significant parts of the application. Applicants should submit 2 double-spaced, 15-page papers of no more than 5,000 words each, in 12-point type with 1-inch margins. The writing samples must be examples of critical writing (rather than creative writing) on subjects directly related to English. Applicants should not send longer papers with instructions to read an excerpt or excerpts but should edit the samples themselves so that they submit only 15 pages for each paper. Applicants who know the field in which they expect to specialize should, when possible, submit a primary writing sample related to that field.
Statement of Purpose
The statement of purpose is not a personal statement and should not be heavily weighted down with autobiographical anecdotes. It should be no longer than 1,000 words. It should give the admissions committee a clear sense of applicants’ individual interests and strengths. Applicants need not indicate a precise field of specialization if they do not know, but it is helpful to know something about a candidate’s professional aspirations and sense of their own skills, as well as how the Harvard Department of English might help in attaining their goals. Those who already have a research topic in mind should outline it in detail, giving a sense of how they plan their progress through the program. Those who do not should at least attempt to define the questions and interests they foresee driving their work over the next few years.
Standardized Tests
GRE: Not Accepted
While there are no specific prerequisites for admission, a strong language background helps to strengthen the application, and students who lack it should be aware that they will need to address these gaps during their first two years of graduate study.
While a candidate's overall GPA is important, it is more important to have an average of no lower than A- in literature (and related) courses. In addition, while we encourage applications from candidates in programs other than English, they must have both the requisite critical skills and a foundation in English literature for graduate work in English. Most of our successful candidates have some knowledge of all the major fields of English literary study and advanced knowledge of the field in which they intend to study.
Theses & Dissertations
Theses & Dissertations for English
See list of English faculty
APPLICATION DEADLINE
Questions about the program.
Department of English

You are here
Ph.d. in literature.

Our PhD students are involved in a range of interdisciplinary and public initiatives. For example, some affiliate with interdisciplinary Designated Emphases ; others have received grants to create podcasts , convene interdisciplinary working groups , or organize and annual graduate student conferences . Each year one student participates in a year-long exchange program with the Obama Institute for Transnational American Studies in Mainz, Germany; some have worked as Graduate Assistants and researchers for research centers such as the Medieval and Early Modern Studies Program , the experimental media Modlab , and the university’s Datalab .
Students graduate with the qualitative and quantitative skills necessary for professional research and teaching in English, as well as extensive pedagogical training and a range of teaching experience that includes writing and composition, as well as designing and teaching Introduction to Literature courses. Our Alumni Directory includes titles of recent dissertations, as well as information about the diverse careers for which the PhD has helped prepare our graduates. There is an option to complete an MA in literature , but it is not a stand-alone program.
Questions? Contact:
Aaron Barstow Graduate Program Coordinator, Ph.D. Program in Literature [email protected] (530) 752-2738 Pronouns: he/they
Admissions / Online Application
Degree requirements for the Ph.D. program (links to more details) include 50 units of coursework with at least 44 units taken for a letter grade, proficiency in one foreign language proficiency before degree conferral, preliminary and qualifying examinations, and a dissertation. In addition, there are also opportunities for students to pursue a Designated Emphasis and gain teaching experience.
Coursework Requirements
2 Core Courses (8 units)
- English 200: Introduction to Graduate Studies (taken as Satisfactory/Unsatisfactory)
- One survey course in literary theory (Critical Theory 200A or 200C taken for a grade).
1 Workshop (2 units)
- English 288: Prospectus Workshop (taken as Satisfactory/Unsatisfactory); students may petition to complete this course independently with a Prospectus Adviser.
10 Graduate-level Seminars (40 units)
- All courses must be taken for a grade.
- Five courses must satisfy the breadth requirement (see below).
- Five courses will be comprised of electives (see below).
- Students may count one undergraduate 100-level course as one of their ten required courses.
- Aside from ENL 200, no course graded Satisfactory-Unsatisfactory may count as one of the twelve required seminars. Independent and group studies may not be taken for a grade.
13 Total Graduate Courses (50 units; 44 units taken for a grade) Additionally, students who enter the Ph.D. program without a MA degree can earn one en route to the Ph.D. degree.
The English Ph.D. requires a reading knowledge of one foreign language before completing the degree; it is not an admissions requirement. This could be satisfied through previous or current coursework or an exam. Any of the following demonstrates proficiency:
Completion within the past eight years of 3 semester-length, or 4 quarter-length courses in a foreign language at the undergraduate level. Students must earn a passing grade, but courses may be taken on a Pass/No Pass basis.
Students may take the Placement Test offered by the UC Davis Language Center , testing out of the language at the intermediate level.
A Pass in the language exam offered in the English Department at the beginning of Fall or Spring quarter each year.
The breadth requirements must be fulfilled by coursework in the Department of English or coursework taught by English Department faculty. Five courses (of the total 40 units above) will satisfy this requirement. Students must complete two Earlier Period courses, and two Later Period courses, and one Focus course.
Earlier Period Courses Pre-1800; or Pre-1865 if the course focus is on American literature
Later Period Courses post-1800; or post-1865 if the course focus is on American literature
Focus Course Interdisciplinary, Identity, Genre, Other National, Method, Theory
Faculty and/or the Graduate Advisor may choose to designate a course as fulfilling more than one category, but students may use the course to fulfill only one requirement. For instance, a student could use a course on women in Early Modern literature to satisfy the Earlier Period requirement, or the Focus (Identity) requirement, but not both. A student could use a course on Cold War Drama to satisfy the Later Period requirement or the Focus (Genre) requirement, but not both.
The electives requirement can be fulfilled by actual offered seminars inside or outside the English Department. Five elective courses will satisfy degree requirements. UWP 390 is acceptable as one of the electives. Also, be aware 299s are ungraded but still count towards overall units. With the approval of the Graduate Adviser, students may also enroll in a graduate class at another University of California campus through the Intercampus Exchange Program .
Students who enter the Ph.D. program with MA coursework from another institution may petition the Graduate Adviser for a Course Waiver up to three of the twelve required seminars; each approved petition will reduce the number of required courses by one. Students may not reduce their coursework to fewer than nine seminars.
Students holding an MA may also petition the Graduate Adviser for course relief for up to five of the breadth requirements; each approved petition allows the student to substitute elective courses. ENL 200 may not be waived or relieved.
For each waiver or relief request, students must submit to the English Graduate Office a Course Waiver or Relief Request form (available in the office) along with the syllabus from the course and the student's seminar paper.
Graduate students may participate in a Designated Emphasis (DE) , a specialization that might include a new method of inquiry or an important field of application which is related to two or more existing Ph.D. programs. The DE is awarded in conjunction with the Ph.D. degree and is signified by a transcript notation; for example, “Ph.D. in Literature with a Designated Emphasis in Native American Studies.” More information .
In the Spring Quarter of the second year or Fall Quarter of the third year of graduate study, students take a Preliminary Examination in two historical fields and one focus field. Three faculty members conduct the oral examination, each representing one of the fields. Prior to taking the Preliminary Examination, students must have completed the following:
Introduction to Graduate Studies (ENL200)
Survey of Literary Theory (CRI200A or CRI200C)
Four of five Breadth Requirements
Four of five Elective Requirements
Additionally, students select one focus field. A student may devise her/his own focus list in collaboration with two faculty members or, as is more common, choose one from among the following:
Black Studies
Critical Theory
Disability Studies
Ecocriticism and Environmental Humanities
Film Studies
Media Technologies
Performance Studies
Postcolonial Theory
Psychoanalysis
Queer Feminisms
Queer Theories
Race and Ethnicity Studies
Science and Literature
Science Fiction
English 299 (Independent Study) is ordinarily used the quarters before the Preliminary Examination to prepare for the oral examination and is graded Satisfactory-Unsatisfactory. Students may register for ENL 299 under the Graduate Advisor or a faculty member in the field of their exam for the quarter(s) they intend to study.
In the event that the student does not pass the exam, the exam chair will report the decision to the Graduate Adviser, who will work with the committee to decide whether the student should be given a chance to retake the exam (no less than six months later) or whether the student should be dismissed from the program. The Graduate Adviser will report this final decision to the student within 72 hours of the exam’s conclusion.
Any remaining requirements after taking the Preliminary Examination must be completed before scheduling the Qualifying Examination.
Students will select two historical fields from among the following list. Students who would like to do non-consecutive historical fields need to get prior approval from the Graduate Adviser. These lists and additional helpful documents can be accessed via our box folder "Preliminary Exam" in the English Graduate Program file.
The Qualifying Examination happens as early as the spring of the third year and should be taken no later than the spring of the fourth year . The reading list for this exam, which is conducted orally, is constructed by the student in consultation with his or her three-person dissertation committee. When making their lists, students may consult the standard lists for preliminary exams available on the department's Box site. If the student has elected a designated emphasis (DE), materials from that field should also be incorporated into the Qualifying Exam reading list.
Graduate Studies requires the Qualifying Examination Application (GS319) to be submitted at least 30 days prior the the scheduled exam date.
Qualifying Examination Committee The student, in consultation with their Prospectus Adviser and, if needed, the Graduate Adviser, nominates four faculty to serve on the Qualifying Examination Committee:
- The three proposed Dissertation Committee members
- One member must be from outside the English graduate program (this may be a member of the Dissertation Committee).
The QE Committee is responsible for administering the exam. Neither the “Prospectus Adviser” nor the Dissertation Director (in many, though not all, cases these will be same) may be the chair of the QE Committee. Students with a designated emphasis (DE) must include one faculty member affiliated with the DE on both their qualifying and dissertation committee. DE paperwork must be approved before the QE application is submitted. The exam will focus on the Prospectus and the Qualifying Exam reading list. The bibliography of the prospectus will normally overlap substantially with the Qualifying Exam reading list.
The Qualifying Exam Report (GS343) must be submitted withing 72 hours of the exam. Upon successful completion, students receive the Candidacy for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy, Plan B (GS321) .
If you are disabled, you are entitled to accommodations for all requirements of the program you’re enrolled in, a process formally handled by the Student Disability Center . We recommend starting the process of coordinating with the SDC early in your graduate school journey, as it can take time for the Center to process information. We must work with the SDC to implement your accommodations for your exams. Please indicate your need for accommodations to us as soon as possible, so we can include the Center in our exam scheduling process. Please notify us by the fourth week of the quarter in which you intend to sit the exam.
The dissertation must be an original work of scholarship and/or interpretation. It may be critical, bibliographical, historical, or biographical in its subject. Students work with a dissertation director and consult with two official readers as well as with other faculty knowledgeable about the project. A dditional details .

PhD Program in English Language and Literature
The department enrolls an average of ten PhD students each year. Our small size allows us to offer a generous financial support package. We also offer a large and diverse graduate faculty with competence in a wide range of literary, theoretical and cultural fields. Each student chooses a special committee that works closely along side the student to design a course of study within the very broad framework established by the department. The program is extremely flexible in regard to course selection, the design of examinations and the election of minor subjects of concentration outside the department. English PhD students pursuing interdisciplinary research may include on their special committees faculty members from related fields such as comparative literature, medieval studies, Romance studies, German studies, history, classics, women’s studies, linguistics, theatre and performing arts, government, philosophy, and film and video studies.
The PhD candidate is normally expected to complete six or seven one-semester courses for credit in the first year of residence and a total of six or seven more in the second and third years. The program of any doctoral candidate’s formal and informal study, whatever his or her particular interests, should be comprehensive enough to ensure familiarity with:
- The authors and works that have been the most influential in determining the course of English, American, and related literatures
- The theory and criticism of literature, and the relations between literature and other disciplines
- Concerns and tools of literary and cultural history such as textual criticism, study of genre, source, and influence as well as wider issues of cultural production and historical and social contexts that bear on literature
Areas in which students may have major or minor concentrations include African-American literature, American literature to 1865, American literature after 1865, American studies (a joint program with the field of history), colonial and postcolonial literatures, cultural studies, dramatic literature, English poetry, the English Renaissance to 1660, lesbian, bisexual and gay literary studies, literary criticism and theory, the nineteenth century, Old and Middle English, prose fiction, the Restoration and the eighteenth century, the twentieth century, and women's literature.
By the time a doctoral candidate enters the fourth semester of graduate study, the special committee must decide whether he or she is qualified to proceed toward the PhD. Students are required to pass their Advancement to Candidacy Examination before their fourth year of study, prior to the dissertation.
PhD Program specifics can be viewed here: PhD Timeline PhD Procedural Guide
Special Committee
Every graduate student selects a special committee of faculty advisors who work intensively with the student in selecting courses and preparing and revising the dissertation. The committee is comprised of at least three Cornell faculty members: a chair, and typically two minor members usually from the English department, but very often representing an interdisciplinary field. The university system of special committees allows students to design their own courses of study within a broad framework established by the department, and it encourages a close working relationship between professors and students, promoting freedom and flexibility in the pursuit of the graduate degree. The special committee for each student guides and supervises all academic work and assesses progress in a series of meetings with the students.
At Cornell, teaching is considered an integral part of training in academia. The field requires a carefully supervised teaching experience of at least one year for every doctoral candidate as part of the program requirements. The Department of English, in conjunction with the John S. Knight Institute for Writing in the Disciplines, offers excellent training for beginning teachers and varied and interesting teaching in the university-wide First-Year Writing Program. The courses are writing-intensive and may fall under such general rubrics as “Portraits of the Self,” “American Literature and Culture,” “Shakespeare,” and “Cultural Studies,” among others. A graduate student may also serve as a teaching assistant for an undergraduate lecture course taught by a member of the Department of English faculty.
Language Requirements
Each student and special committee will decide what work in foreign language is most appropriate for a student’s graduate program and scholarly interests. Some students’ doctoral programs require extensive knowledge of a single foreign language and literature; others require reading ability in two or more foreign languages. A student may be asked to demonstrate competence in foreign languages by presenting the undergraduate record, taking additional courses in foreign languages and literature, or translating and discussing documents related to the student’s work. Students are also normally expected to provide evidence of having studied the English language through courses in Old English, the history of the English language, grammatical analysis or the application of linguistic study to metrics or to literary criticism. Several departments at Cornell offer pertinent courses in such subjects as descriptive linguistics, psycholinguistics and the philosophy of language.
All PhD degree candidates are guaranteed five years of funding (including a stipend , a full tuition fellowship and student health insurance):
- A first-year non-teaching fellowship
- Two years of teaching assistantships
- A fourth-year non-teaching fellowship for the dissertation writing year
- A fifth-year teaching assistantship
- Summer support for four years, including a first-year summer teaching assistantship, linked to a teachers’ training program at the Knight Institute. Summer residency in Ithaca is required.
Students have also successfully competed for Buttrick-Crippen Fellowship, Society for the Humanities Fellowships, American Council of Learned Societies (ACLS), Shin Yong-Jin Graduate Fellowships, Provost’s Diversity Fellowships, fellowships in recognition of excellence in teaching, and grants from the Graduate School to help with the cost of travel to scholarly conferences and research collections.
Admission & Application Procedures
The application for Fall 2024 admission will open on September 15, 2023 and close at 11:59pm EST on December 1, 2023.
Our application process reflects the field’s commitment to considering the whole person and their potential to contribute to our scholarly community. Applicants will be evaluated on the basis of academic preparation (e.g., performance in relevant courses, completion of substantive, independent research project). An applicant’s critical and creative potential will be considered: applicants should demonstrate interest in extensive research and writing and include a writing sample that reveals a capacity to argue persuasively, demonstrate the ability to synthesize a broad range of materials, as well as offer fresh insights into a problem or text. The committee will also consider whether an applicant demonstrates a commitment to inclusion, equity, and diversity and offers a substantive explanation for why study at Cornell is especially compelling (e.g., a discussion of faculty research and foci). Admissions committees will consider the entire application carefully, including statements and critical writing, as well as transcripts, letters of recommendation, and a resume/cv (if provided). Please view the requirements and procedures listed below, if you are interested in being considered for our PhD in English Language and Literature program.
Eligibility: Applicants must currently have, or expect to have, at least a BA or BS (or the equivalent) in any field before matriculation. International students, please verify degree equivalency here . Applicants are not required to meet a specified GPA minimum.
To Apply: All applications and supplemental materials must be submitted online through the Graduate School application system . While completing your application, you may save and edit your data. Once you click submit, your application will be closed for changes. Please proofread your materials carefully. Once you pay and click submit, you will not be able to make any changes or revisions.
Deadline: December 1st, 11:59pm EST. This deadline is firm. No applications, additional materials, or revisions will be accepted after the deadline.
PhD Program Application Requirements Checklist
- Academic Statement of Purpose Please describe (within 1000 words) in detail the substantive research questions you are interested in pursuing during your graduate studies and why they are significant. Additionally, make sure to include information about any training or research experience that you believe has prepared you for our program. You should also identify specific faculty members whose research interests align with your own specific questions. Note that the identification of faculty is important; you would be well advised to read selected faculty’s recent scholarship so that you can explain why you wish to study with them. Do not rely on the courses they teach. Please refrain from contacting individual faculty prior to receiving an offer of admission.
- Personal Statement Please describe (within 1000 words) how your personal background and experiences influenced your decision to pursue a graduate degree and the research you wish to conduct. Explain, for example the meaning and purpose of the PhD in the context of your personal history and future aspirations. Please note that we will pay additional attention to candidates who identify substantial reasons to obtain a PhD beyond the pursuit of an academic position. Additionally, provide insight into your potential to contribute to a community of inclusion, belonging, and respect where scholars representing diverse backgrounds, perspectives, abilities, and experiences can learn (productively and positively) together.
- Critical Writing Sample Your academic writing sample must be between 3,000 and 7,500 words (12-30 pages), typed and double-spaced. We accept excerpts from longer works, or a combination of shorter works.
- Three Letters of Recommendation We require 3 letters of recommendation. At the time of application, you will be allowed to enter up to 4 recommenders in the system. Your application will be considered “Complete” when we have received at least 3 letters of recommendation. Letters of recommendation are due December 1 . Please select three people who best know you and your work. Submitting additional letters will not enhance your application. In the recommendation section of the application, you must include the email address of each recommender. After you save the information (and before you pay/submit), the application system will automatically generate a recommendation request email to your recommender with instructions for submitting the letter electronically. If your letters are stored with a credential service such as Interfolio, please use their Online Application Delivery feature and input the email address assigned to your stored document, rather than that of your recommender’s. The electronic files will be attached to your application when they are received and will not require the letter of recommendation cover page.
- Transcripts Scan transcripts from each institution you have attended, or are currently attending, and upload into the academic information section of the application. Be sure to remove your social security number from all documents prior to scanning. Please do not send paper copies of your transcripts. If you are subsequently admitted and accept, the Graduate School will require an official paper transcript from your degree-awarding institution prior to matriculation.
- English Language Proficiency Requirement All applicants must provide proof of English language proficiency. For more information, please view the Graduate School’s English Language Requirement .
- GRE General Test and GRE Subject Test are NO LONGER REQUIRED, effective starting with the 2019 application In March 2019, the faculty of English voted overwhelmingly to eliminate all GRE requirements (both general and subject test) for application to the PhD program in English. GRE scores are not good predictors of success or failure in a PhD program in English, and the uncertain predictive value of the GRE exam is far outweighed by the toll it takes on student diversity. For many applicants the cost of preparing for and taking the exam is prohibitively expensive, and the exam is not globally accessible. Requiring the exam narrows our applicant pool at precisely the moment we should be creating bigger pipelines into higher education. We need the strength of a diverse community in order to pursue the English Department’s larger mission: to direct the force of language toward large and small acts of learning, alliance, imagination, and justice.
General Information for All Applicants
Application Fee: Visit the Graduate School for information regarding application fees, payment options, and fee waivers .
Document Identification: Please do not put your social security number on any documents.
Status Inquiries: Once you submit your application, you will receive a confirmation email. You will also be able to check the completion status of your application in your account. If vital sections of your application are missing, we will notify you via email after the Dec. 1 deadline and allow you ample time to provide the missing materials. Please do not inquire about the status of your application.
Credential/Application Assessments: The Admission Review Committee members are unable to review application materials or applicant credentials prior to official application submission. Once the committee has reviewed applications and made admissions decisions, they will not discuss the results or make any recommendations for improving the strength of an applicant’s credentials. Applicants looking for feedback are advised to consult with their undergraduate advisor or someone else who knows them and their work.
Review Process: Application review begins after the submission deadline. Notification of admissions decisions will be made by email by the end of February.
Connecting with Faculty and/or Students: Unfortunately, due to the volume of inquiries we receive, faculty and current students are not available to correspond with potential applicants prior to an offer of admission. Applicants who are offered admission will have the opportunity to meet faculty and students to have their questions answered prior to accepting. Staff and faculty are also not able to pre-assess potential applicant’s work outside of the formal application process. Please email [email protected] instead, if you have questions.
Visiting: The department does not offer pre-admission visits or interviews. Admitted applicants will be invited to visit the department, attend graduate seminars and meet with faculty and students before making the decision to enroll.
Transfer Credits: Students matriculating with an MA degree may, at the discretion of the Director of Graduate Studies, receive credit for up to two courses once they begin our program.
For Further Information
Contact [email protected]
Ph.D. Program
Click here for the Handbook for Graduate Study in English . This document includes departmental policies and procedures concerned with graduate study.
The Berkeley English Department offers a wide-ranging Ph.D. program, engaging in all historical periods of British and American literature, Anglophone literature, and critical and cultural theory. The program aims to assure that students gain a broad knowledge of literature in English as well as the highly-developed skills in scholarship and criticism necessary to do solid and innovative work in their chosen specialized fields.
Please note that the department does not offer a Master’s Degree program or a degree program in Creative Writing. Students can, however, petition for an M.A. in English with an emphasis in Creative Writing upon completion of the Ph.D. course requirements (one of which must be a graduate writing workshop) and submission of a body of creative work.
Students interested in combining a Ph.D. in English with studies in another discipline may pursue Designated Emphases or Concurrent Degrees in a number of different fields
Normative time to complete the program is six years. The first two years are devoted to fulfilling the course and language requirements. The third year is spent preparing for and taking the Ph.D. oral qualifying examination. The fourth through sixth years are devoted to researching and writing the prospectus and dissertation.
The general goal of the first two years is to assure that the students have a broad and varied knowledge of the fields of British and American literature in their historical dimensions, and are also familiar with a wide range of literary forms, critical approaches, and scholarly methods. Students will complete twelve courses distributed as follows:
- 1) English 200, “Problems in the Study of Literature”
- 2) Medieval through 16 th -Century
- 3) 17 th - through 18 th -Century
- 4) 19 th -Century
- 5) 20 th -Century
- 6) a course organized in terms other than chronological coverage.
- 7-12) Elective courses.
(A thirteenth required course in pedagogy can be taken later.) Students who have done prior graduate course work may transfer up to three courses for credit toward the 12-course requirement. Up to five of the 12 courses may be taken in other departments.
Students must demonstrate either proficiency in two foreign languages or advanced knowledge in one foreign language before the qualifying examination. There are no "canonical languages" in the department. Rather, each specifies which languages are to count, how they relate to the student's intellectual interests, and on which level knowledge is to be demonstrated. "Proficiency" is understood as the ability to translate (with a dictionary) a passage of about 300 words into idiomatic English prose in ninety minutes. The proficiency requirement may also be satisfied by completing one upper-division or graduate literature course in a foreign language. The advanced knowledge requirement is satisfied by completing two or three literature courses in the language with a grade of "B" or better.
At the end of the second year each student’s record is reviewed in its entirety to determine whether or not he or she is able and ready to proceed to the qualifying exam and the more specialized phase of the program.
The Qualifying Examination
Students are expected to take the qualifying examination within one year after completing course and language requirements. The qualifying exam is oral and is conducted by a committee of five faculty members. The exam lasts approximately two hours and consists of three parts: two comprehensive historical fields and a third field which explores a topic in preparation for the dissertation. The exam is meant both as a culmination of course work and as a test of readiness for the dissertation.
The Prospectus and Dissertation
The prospectus consists of an essay and bibliography setting forth the nature of the research project, its relation to existing scholarship and criticism on the subject, and its anticipated value. Each candidate must have a prospectus conference with the members of their committee and the Graduate Chair to discuss the issues outlined in the proposal and to give final approval to the project. The prospectus should be approved within one or two semesters following the qualifying exam.
The dissertation is the culmination of the student's graduate career and is expected to be a substantial and original work of scholarship or criticism. Students within normative time complete the dissertation in their fourth through sixth years.
English (Literature), PHD
On this page:.
At a Glance: program details
- Location: Tempe campus
- Second Language Requirement: No
Program Description
Degree Awarded: PHD English (Literature)
The PhD program in English with a concentration in literature trains students in various methodologies, pedagogies and areas of inquiry that constitute literary and cultural studies.
With a diverse and distinguished faculty, the program offers opportunities for specialization in traditional areas of literary criticism, cultural analysis and theory, as well as various fields of interdisciplinary study.
A doctorate in literature equips students with a range of highly sought-after skills and competencies: research and analysis of complex material, communication in written and oral modes, collaboration, independence and self-motivation, creativity and adaptability.
The PhD in English (literature) at ASU is a premier graduate program in the U.S. with strong interdisciplinary ties and faculty links to research centers on campus and in the state, including the Arizona Center for Medieval and Renaissance Studies, the Center for the Study of Race and Democracy, the Institute for Humanities Research, and the Virginia G. Piper Center for Creative Writing. With these resources and a strong mentorship program at their fingertips, our graduates are prepared for a wide array of professional opportunities including careers in college teaching, research, writing, editing, higher education, and humanities-related organizations.
Lee Bebout , Director
Sheila Luna , Program Manager
Faculty in Literature
Doctoral Examinations
Doctoral Procedures and Timeline
Teaching Assistantships
Degree Requirements
84 credit hours, a foreign language exam, a written comprehensive exam, an oral comprehensive exam, a prospectus and a dissertation
A student with an appropriate master's degree must complete a minimum of 54 credit hours of approved graduate work, which includes 12 credit hours of dissertation, provided the student's master's degree is accepted by the supervisory committee and the academic unit. Research hours may be used toward coursework in consultation with the advisor.
A student without an appropriate master's degree must complete 84 credit hours of work at ASU. At the advisor's discretion, students may include up to 12 credit hours of appropriate, graduate-level coursework undertaken at another university and not previously counted toward any other degree.
Specifically required are six credit hours in theory courses and ENG 501 Approaches to Research. Students must complete eight graduate courses in any of the following categories:
- cultural studies
- ethnic studies
- gender studies
- history and structure of the English language
- literature 1500--1660
- literature 1660--1900
- literature since 1900
- literature to 1500
- postcolonial or anglophone literatures
Students must take at least five graduate seminars at the 600 level en route to the doctorate, at least three of which must be taken in the doctoral program. Up to 12 credit hours taken outside the department may be counted toward the degree. Students should consult with their supervisory committees when choosing electives.
Admission Requirements
Applicants must fulfill the requirements of both the Graduate College and The College of Liberal Arts and Sciences.
Applicants are eligible to apply to the program if they have earned a bachelor's or master's degree from a regionally accredited institution.
Applicants must have a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.00 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in the last 60 hours of their first bachelor's degree program, or a minimum cumulative GPA of 3.50 (scale is 4.00 = "A") in an applicable master's degree program.
All applicants must submit:
- graduate admission application and application fee
- official transcripts
- statement of purpose
- resume or curriculum vitae
- three letters of recommendation
- academic writing sample relevant to the field
- proof of English proficiency
Additional Application Information An applicant whose native language is not English and has not graduated from an institution of higher learning in the United States must provide proof of English proficiency, regardless of current residency. Applicants can find more information about English proficiency requirements on the school website . Please note that official scores must be sent to ASU in order for the application to be processed.
The well-considered, one- to two-page, single-spaced statement of purpose should explain the applicant's scholarly background and training, career goals, proposed research specialization, any secondary field of interest and why the applicant wishes to pursue a PhD in English (Literature) at Arizona State University. Applicants applying for funding must also submit a statement of teaching philosophy.
Courses and Electives
Approaches to Research (3 credits / one class) : Students must take the core class ENG 501 Approaches to Research.
Theory (6 credits / two courses): Appropriate courses for filling this requirement must be in the area of the history of criticism, literary theory, rhetorical theory, linguistic theory or cultural theory. Examples of courses which meet this requirement, if the specific topic is appropriate, include the following: ENG 502, 503, 504, 550, 551, 552, 554, 556, 602, 604, 651, LIN 510, 516, 517; however, an equivalent or more advanced course in linguistic, rhetorical or literary theory would also be acceptable.
Additional Required Courses (24 credits / 8 classes): Students must complete eight graduate courses in any of the following categories: cultural studies, ethnic studies, gender studies, genre, history and structure of the English language, literature to 1500, literature 1500-1660, literature 1660-1900, literature since 1900, postcolonial or anglophone literatures.
A minimum of five courses counted toward the PhD, which may include those listed above, must be taken at the 600-level (three of which must be taken in the doctoral program at ASU). Students wishing to take courses outside of the department may count up to 12 credit hours toward the degree. These courses may also fulfill some of the above degree requirements. Students should consult with an advisor or their committee chair when choosing electives.
Other Requirements
Language Requirement : PhD students must demonstrate evidence of a competent knowledge of a natural language other than modern English, to be selected by the student, subject to the approval of the chair of the dissertation committee. The language requirement must be completed before the student is eligible to take the doctoral exams. This requirement may be met by
- Earning a “B” (3.00) or higher in a 400- or 500-level course in an appropriate (approved) language.
- Demonstrating comparable proficiency by taking a language examination, administered by the School of International Letters and Cultures, in a language approved by the student’s supervisory committee.
- Demonstrating native-speaker proficiency, as determined by the School of International Letters and Cultures, in a language approved by the student’s supervisory committee.
- Earning a “B” (3.00) or higher in both ENG 530 Old English and ENG 531 Old English Literature or their equivalent.
- Holding a bachelor’s degree in an approved foreign language.
- Having fulfilled a foreign language requirement towards a previously awarded master’s degree that has been completed within five years of the semester for which the student has been admitted to the doctoral program. This foreign language must be in a language approved by the student’s doctoral supervisory committee.
- For languages which the School of International Letters and Cultures does not offer or does not offer above the 200 level, two years (4 semesters) of successfully completed college level coursework at least at the 100 and 200 level with a C or better would fulfill the requirement. The coursework must have been successfully completed no more than six years prior to admission to the degree program.
PhD Examinations : Essay, oral exam, colloquy on the dissertation prospectus.
Dissertation : Students must take 12 credit hours of ENG 799.
Miscellaneous : Students may take research (ENG 792) for the purpose of working independently in preparation for the doctoral examination. This is an alternative to be elected by the student at the discretion and with the approval of the advisor and supervisory committee and can count towards course work. Satisfactory completion of ENG 792 is indicated by the grade of "Y." Individual interim segments of ENG 792 will be graded "Z" (course in progress), and changed to "Y" (successful completion) after the dissertation defense. No conventional letter grades are awarded for ENG 792 or 799.
The Graduate College also requires that students be enrolled every semester, excluding summer sessions, until they have completed all requirements for the degree. Continuous enrollment may be satisfied by registration for one hour of ENG 799, or, in cases where dissertation or other credit hours are not needed, Continuous Registration (ENG 595 or 795). If students wish to interrupt their programs of study for one or more semesters, they may apply for a leave of absence, not to exceed one year. Failure to enroll or obtain leave status for the semesters in which they are not enrolled will result in dismissal from the program.
Doctoral Supervisory Committee
The doctoral supervisory committee consists of a minimum of three members from the graduate faculty selected at the time the student files a program of study. In consultation with the director of the Ph.D. program, the student will select the committee chair, who also serves as the student's advisor. Once a graduate faculty member has agreed to serve as the student's chair, the student and chair will then consult before recommending two other members to the director of the doctoral program. Ideally another member of the supervisory committee in addition to the chair should be in the area of specialization. It is the responsibility of each student to form a supervisory committee very early in the program so that the chair and members of the committee may be involved in shaping the course of study, for example, in determining such matters as the choice of foreign language(s) and in specifying courses that will be required for the student's particular area of concentration.
Important Notice to Current International Students
In order for international students to maintain good standing for their VISAs, they must take a minimum of 9 credit hours per semester (i.e., 3 classes), 6 credits (2 classes) should be face-to-face classes.
Next Steps to attend ASU
Learn about our programs, apply to a program, visit our campus, application deadlines, learning outcomes.
- Identify and evaluate various disciplinary arguments, trends, traditions and debates within the knowledge community of literary and cultural studies scholars.
- Demonstrate the ability to produce written work of publishable quality.
- Demonstrate research skills necessary to bring a project of literary or cultural analysis to fruition, including the ability to evaluate disciplinary debates and developments; and the ability to produce research on historical and cultural meanings of texts and related cultural productions.
Career Opportunities
Graduates are prepared for careers in higher education and other fields that value this expertise. Sectors employing high numbers of arts and humanities graduates include information and communication, financial and insurance, public administration and defense, arts and entertainment, and education.
Career examples include:
- art director
- criminal investigator or special agent
- intelligence analyst
- market research analyst
- museum curator, educator or exhibit designer
- political analyst
- public relations specialist or manager
- technical writer
Global Opportunities
Global experience.
With over 250 programs in more than 65 countries (ranging from one week to one year), study abroad is possible for all ASU students wishing to gain global skills and knowledge in preparation for a 21st-century career. Students earn ASU credit for completed courses, while staying on track for graduation, and may apply financial aid and scholarships toward program costs. https://mystudyabroad.asu.edu
Program Contact Information
If you have questions related to admission, please click here to request information and an admission specialist will reach out to you directly. For questions regarding faculty or courses, please use the contact information below.
- [email protected]
- 480/965-3194
Research Topics For PHD in English Literature
Research Topics For Ph.D. in English Literature - Are you looking to do a Ph.D. in English? Have you decided on your thesis topic yet? If no then you are in the right place. I have listed some of the best topics for you. You can choose one of the topics or you can replicate one of them.
Choosing a Ph.D . thesis is tough unless you have a good guide and passion for a particular area. If you are interested in one particular area like British poetry or Tribal literature. Before choosing the Ph.D. thesis topic you must have a conversation with your guide or mentor.

Research Topics For Ph.D. in English Literature
- Sons and Lovers As The Poetry of Love In Fiction: A Study
- Method of Teaching English Literature
- Dancing through English Literature
- MODERN INDIAN LITERATURE IN ENGLISH TRANSLATION
- Women Writers and the Survey of English Literature: A Proposal and Annotated Bibliography for Teachers
- Seventeenth-Century English Literature on Painting
- The Influence of the Bible on English Literature
- The Influence of the Classics on English Literature
- The Neoclassical Period in English Literature: A Psychological Definition
- The Scope of English Literature in Education
- John Ruskin: Master of English Literature
- The Influence of Darwin on Literature
- Medieval English Literature and the Idea of the Anthology
- Islam in Medieval and Early Modern English Literature: A Select Bibliography
- Canonizing the Canonized: A Short History of The Norton Anthology of English Literature
- English Literary Studies, Women’s Studies and Feminism in India
- The Return to Nature in English Poetry of the Eighteenth Century
- English Literature Becomes a University Subject: King’s College, London as Pioneer
- The Development of English Prose from Elizabeth to Victoria
- Colonialist Nationalism in the Critical Practice of Indian Writing in English: A Critique
- Three Women’s Texts and a Critique of Imperialism
- Dancing through the Minefield: Some Observations on the Theory, Practice and Politics of a Feminist Literary Criticism
- FUNCTION OF LITERARY CRITICISM IN INDIA
- A Survey of Jungian Literary Criticism in English
- Some Notes on Defining a “Feminist Literary Criticism”
- Stylistics and the Theory of Literature
- METAFOLKLORE AND ORAL-LITERARY CRITICISM
- Dialogics as an Art of Discourse in Literary Criticism
- Romantic Criticism and the Meanings of the French Revolution
- Navigating the Wide Sargasso Sea: Colonial History, English Fiction, and British Empire
- Angela Carter’s “The Bloody Chamber” and the Decolonization of Feminine Sexuality
- Unaccommodated Woman and the Poetics of Property in Jane Eyre
- Medieval Feminism in Middle English Studies: A Retrospective
- Charlotte Brontë’s Haunted Text
- FEMINISM AND MODERN INDIAN LITERATURE
- Where are the Mothers in Shakespeare? Options for Gender Representation in the English Renaissance
- “Mirror, Mirror on the Wall”: Readers’ Reflections on Literature through Literary Theories
- Writing the Discipline: A Generic History of English Studies
- Constructing an Interdisciplinary Course on Literature and Environmental Feminism
- What Has Never Been: An Overview of Lesbian Feminist Literary Criticism
- Expanding the Archives of Global Feminisms: Narratives of Feminism and Activism
- A Map for Rereading: Or, Gender and the Interpretation of Literary Texts
- SHAKESPEARE’S “ROMEO AND JULIET”, AND MALE MELODRAMA
- Reading the House: A Literary Perspective
- Comparatist Trends within Literary Studies (1914–1950)
- English in North America: Accounting for its Evolution
- American Indian Literature and a Legacy of Misappropriation
- Tribal Strengths and American Indian Students
- LANGUAGE, TRIBE AND THE CONCEPT OF ‘ONE ZAMBIA, ONE NATION’
- Literary Representation: Partition in Indian and Pakistani Novels in English
- NISSIM EZEKIEL: The Father of Contemporary Indian English Poetry
- WOMEN IN INDIAN-ENGLISH LITERATURE: THE QUESTION OF INDIVIDUATION
- Anglo-Indian English: A Nativized Variety of Indian English
- THE CONCEPT OF ‘INDIANNESS’ IN INDIAN FICTION IN ENGLISH
- The Perversion of Manliness in Macbeth
- Glimpsing a “Lesbian” Poetics in “Twelfth Night”
- Women and Migration: The Social Consequences of Gender
- Unfallen Marriage and the Fallen Imagination in Paradise Lost
- Recent Studies in the English Renaissance
How to Choose Topics For Ph.D. in English
Choosing a Ph.D. topic is tough, especially when it comes to the English language and literature. It is not easy to select a Ph.D. thesis topic, it needs lots of hard work and mental work to get to a point when you think is ready.
one of the hardest parts is choosing your thesis topics. Some spending months even years this research projects because they did not know; how to choose a great topics? Choosing a great dissertation or thesis topic is a difficult decision to make.
Tips to choose Ph.D. topics
- Broaden Your Thinking
- Choose the topic that you are interested
- Be realistic by choosing topics
- Pic a topic that is related to your field
- Select topics that your advisor finds interesting and is knowledgeable about
- Find a topic that you already have some expertise
- Select unique topics
- Choose manageable topics
- Read everything you can relate to the topics
- Find documents that support your topics
- Take advantage available in the locality
- Consult your mentor
- Find available data

Seminar Topics For MA, MPHIL, PHD PDF Download
Share this:
Let your curiosity lead the way:
Apply Today
- Arts & Sciences
- Graduate Studies in A&S
Topics in Literature:
English literature 3525.
Jump to navigation
Inaugural International Symposium on Social Justice and the Teaching of World Literature
The English Department at the University of the Incarnate Word welcomes presentation proposals for its inaugural international interdisciplinary symposium on “Social Justice and the Teaching of World Literature.” The study and teaching of global texts actively allows for an inclusive representation of diverse voices and perspectives. This symposium seeks to explore more deeply the intersection between teaching world literature and social justice issues as they emerge in the 21st century.
Taking Survey of The Survey of English Literature
Permanent Session: English Literature Pre 1800 I
Panel Topic: Taking Survey of The Survey of English Literature
This Permanent Section of the MMLA invites papers, which reflect on the significance of the survey course, past present and future.
Adaptations Area: Midwest Popular Culture Association/Midwest American Culture Association Annual Conference
CALL FOR PAPERS, ABSTRACTS, AND PANEL PROPOSALS
Midwest Popular Culture Association/Midwest American Culture Association Annual Conference: Adaptations Area
Friday-Sunday, 4-6 October 2024
DePaul University—Loop Campus, Chicago, IL
Address: DePaul Center, 1 E. Jackson Blvd. Chicago, IL 60604 Phone: (312) 362-8000
Extended and Revised Call for Chapters on FX Channel Original TV Series Edited Collection
The FX Reader
Extended and revised call for chapters on select FX Channel original TV series are sought for an edited book collection. In a similar vein as The Essential HBO Reader (2008) , this scholarly collection will serve as a valuable resource for TV scholars and educators on FX’s history and its most critically acclaimed, noteworthy series.
Each chapter is expected to focus on each series’ creation and production history, its overall aesthetics and key performances, core themes, its association with genre conventions, and relevance to the FX Channel. We still need chapter proposals on the following series:
Call for Chapters: Qualitative Research Methods for Dissertation Research
Katherine Mansfield: Spaces, Places, Traces - Extended Deadline
Katherine Mansfield: Spaces, Places, Traces
IADT Dún Laoghaire, Dublin
June 14th–16th 2024
An international conference organised by the Katherine Mansfield Society
Hosted by the Institute of Art, Design and Technology, Dún Laoghaire
Navigating The Many Parts of Graduate School
While it takes copious research to get into a graduate program, it is also impossible to fully encompass the experience of being within a graduate program from the outside looking in. Given that so much of graduate school can often be a mystery, and given that there are also many ways one can be a graduate student, those who are newer to the experience of graduate school may find themselves wondering what to do when faced with handbooks, seminar syllabi, or even teaching for the first time. While these resources from your program will always be helpful, there remain aspects of graduate education that can seem rather opaque and mysterious to the point of being intimidating.
Illinois Global Institute
Russian, East European, and Eurasian Center
- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
Fall 2024 Courses with Russia, East Europe, and Eurasian Content
- Current Courses
- Area Studies Courses Catalog
- FLAS Fellowships
- Language Courses Catalog
- Courses in the REES Rubric
- Funding Opportunities
- Study Abroad
- Administration & Staff
- Student Staff
- Executive Committee
- Faculty Affiliates
- REEES Students
- FLAS Fellows
- Regional Affiliates & Research Associates
- Visiting Scholars
- REEEC Events Calendar
- Public Lecture Series
- Conferences and Workshops
- Events Archive
- K-12 and Community Outreach
- Open Research Laboratory
- Summer Research Laboratory
- For Students
- For Faculty
- For Researchers
- Professional and Employment Opportunities
- Education and Humanitarian Resources on Nagorno-Karabakh
- Russia's War on Ukraine: Educational and Humanitarian Resources
- Multimedia Library
- Get Involved
- Mission and History
- REEEC at Illinois
Note: The courses listed below are not an exhaustive list of courses being offered on the REEE region. Please see course explorer for additional classes.
*Check with Advisor or FLAS Coordinator whether the course will fulfill area studies course requirements
Area Studies
BCS 115: South Slavic Cultures Peter Wright 12:30PM – 01:50PM, TTR, Location TBD
Exploration of South Slavic cultures in the historically rich and complex region sometimes referred to as "the Balkans," focusing particularly on those groups found within the successor states of the former Yugoslavia. Critical look at the traditional view of the region as the crossroads or the bridge between East and West, and at the term Balkanization which has become a pejorative term used to characterize fragmented, and self-defeating social systems.
HIST 168: A History of Judaism* Instructor TBD 12:30PM-1:50PM, TTR, Location TBD
Examines the social, political, economic, and intellectual history of the Jews from Abraham to the present-day, with particular attention to Jewish thought and society.
HIST 274: US Foreign Relations, 1917-* Prof. Kristin Hoganson 12:00PM - 12:50PM, MWF, 223 Gregory Hall
Over the course of the twentieth century the United States rose to superpower status, in the process profoundly shaping world affairs. Students will study the connections between U.S. and global history in this pivotal period. Explores the impact of the United States on world affairs from roughly 1917 through the end of the Cold War. Attention given to the perspectives of people affected by U.S. policies and the limits of U.S. power in the face of developments such as anticolonial nationalism and great power rivalries.
HIST 353: European History 1918 to 1939* Peter Fritzsche 11:00AM-12:20PM, TTR, 393 Bevier Hall
Survey of European society from 1918 to 1939, with emphasis on the impact of World War I, the Russian Revolution, fascism, and the intellectual trends of the twenties and thirties. This course examines the political and cultural environment of Europe from the demise of the continental empires after World War I to the dawn of the thousand-year Reich at the start of World War II. This Age of Extremes saw the rise of liberal democracies, the flourishing of new artistic movements, and the birth of new technologies such as film. At the same time, this period was also marked by the ascension of dictators, crises in colonial empires, and one of the largest economic crisis in history. Perhaps more famous (or infamous) than these events are the individuals we will cover, which includes the likes of Neville Chamberlain, Francisco Franco, Adolf Hitler, and Joseph Stalin. We will explore the period through a variety of sources, including speeches, contemporary films, and a novel concerned with an even greater threat: newts.
LAW 657: International Human Rights Law* Francis Boyle 03:00PM - 04:30PM, MT, Online
Based primarily on a series of contemporary “real world” problems, the course introduces the student to the established and developing legal rules and procedures governing the protection of international human rights. Its thesis is that there exists a substantial body of substantive and procedural International Human Rights Law, and that lawyers, government officials, and concerned citizens should be familiar with the policies underlying this law and its enforcement, as well as with the potential it offers for improving the basic lot of human beings everywhere. Additionally, the course presupposes that the meaning of “human rights” is undergoing fundamental expansion, and therefore explores Marxist and Third World conceptions of human rights as well as those derived from the liberal West.
Sequence and Prerequisites: None
Evaluation: Paper
Categories: International and Comparative / Upper-Level
MUSC 449: Balkanalia Donna Buchanan 6:00PM - 8:50PM, T, 0061A Music Building
Instruction and experience in the performance of various non-Western and vernacular music traditions such as African mbira, Andean panpipes, North American string band, Gamelan Kebyar, European and South American traditional music, etc. Topics vary according to available instructors. Course Information: 1 undergraduate hour. 1 graduate hour. May be repeated to a maximum of 3 hours in the same term if topics vary for a total of 16 undergraduate hours, 12 graduate hours in separate terms. Prerequisite: Consent of instructor.
REES 200: Intro to Russia and Eurasia TBD 9:30AM - 10:50PM, TTR, G24 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics
Eurasia, geographically between the “East” and the “West,” encompasses 11 time zones and over 100 different ethnic groups. Its multicultural complexity and political diversity over recent centuries have made it a rich source for the study of political, economic, and social change. This interdisciplinary course introduces students to key issues and themes that cross disciplines and are important for understanding the contemporary socio-politics of the region. As a class we will draw out these themes by examining major texts, novels, poems, film, and music that were not only impactful within their own genre, but whose influence has rippled throughout disciplines to become interdisciplinary. Major themes to be investigated include: regional interactions/geopolitics, socioeconomics, political action, subjectivity and alterity, identity, gender, and ethnicity & race.
REES 495/ 550: Seminar in REEE Studies Maureen Marshall 3:00PM - 4:50PM, TR, Room 1110 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics Interdisciplinary seminar involving faculty in a number of disciplines. The course examines Russia, Eastern Europe, and Eurasia and the methodologies of its study through questions of identities, cultural values, and change.
RUSS 1 15: Intro to Russian Culture David Cooper 2:00PM - 2:50PM, MWF, TBD
Introduction to the culture of Russia and the USSR. Course addresses two central themes. First, the very distinctiveness of Russian culture, and the functions of that notion within Russia and for outsiders; Second, Russia as a cultural space between East and West. We will explore Russian culture through the following, the language(s); foundational narratives of collective memory going back to the medieval times; the cultural impact of colonial subjugation both by and of peoples to the East, South, and West; Russian Orthodoxy's connection with the political and cultural spheres; peak achievements in literature, music, architecture and visual arts. Course Information: Same as REES 116.
RUSS 220: Golden Age of Russian Lit David Cooper 12:30PM-1:50PM, TTR, 1136 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics
Survey of Russian literature in the long 19th century; romanticism, realism, nationalism, orientalism, empire; writers may include Pushkin, Gogol, Lermontov, Pavlova, Turgenev, Dostoevsky, Tolstoy, Chekhov, and others; reading and discussion in English. Course Information: Same as CWL 227.
RUSS 514: Russian Literature After 1956 Richard Tempest 12:00PM-1:50PM, M, Location TBD
Graduate-level survey of Russian literature of the second half of the twentieth century. Course focuses on the questions of the Soviet "before" and "after," considering specifically the development of socialist realism after its High Stalinist period, its late-socialist manifestations, and theories of post-modernism as applied to late and post-Soviet Russian Literature and culture. Novels, films, and theoretical texts (focusing on the periods of the 1960s, stagnation, collapse, and "after") will provide a common base for thinking about late and post-Soviet culture. Course Information: 4 graduate hours. No professional credit. Prerequisite: Ability to read in Russian or consent of instructor.
SLAV 117: Russ & Euro Science Fiction Richard Tempest 3:00PM-4:50PM, MWF, Location TBD
Survey of the science fiction writing of Russia and the countries of Eastern Europe since 1750, with particular emphasis on the post-World War II period. The role of the Science Fiction tradition in the respective national cultures. The influence on Russian and East European Science Fiction of Anglo-American Science Fiction. All readings are in English. Course Information: Same as CWL 117.
SLAV 452/CWL 453: Slavic Cultural Studies “Kyiv: A Biography of a City” Instructor: Prof. Valeria Sobol 2:00PM - 3:20PM, TTR, Location TBD
This course traces the historical, social, and artistic development of Kyiv as a city and as an idea from the medieval period to the present day. As we read a variety of literary works and watch several films in which Kyiv figures prominently, we will think about what makes up this city’s “text” and pay special attention to its frequently competing Ukrainian, Russian, Polish, and Jewish versions. The course is conducted in English, and all the texts will be available in English translations.
SLAV 452: Polish Cinema Instructor: Prof. George Gasyna 11:00AM - 12:20PM, TTR, Location TBD
Selected topics in the literatures of Russia and Eastern Europe. Topics covered will range from in-depth studies of specific authors, time periods, and thematic discussions of specific genre and literary traditions. Readings in English unless specified. Course Information: Same as CWL 453. 3 undergraduate hours. 4 graduate hours. May be repeated to a maximum of 6 undergraduate hours or 8 graduate hours in same term; or 9 undergraduate hours or 12 graduate hours in separate terms. Prerequisite: Two years of literature, preferably Russian or East European; or consent of instructor
TURK 270/ANTH 272/GLBL 272/SAME 272: Languages and Culture in Turkey Ayse Ozcan 11:00AM – 12:20PM, TTR, 3038 Campus Instructional Facility
As a country located at the crossroads of Asia, Europe and Africa, Turkey has always been under the spotlight. In this course, we will study the dynamic relationship between language and culture in Ottoman and modern Turkey through a timely analysis of its transition from a long-lasting empire to a young "secular" nation-state. We will examine the complexities of Turkish modernity from a holistic perspective to better comprehend how central Asian and Middle Eastern cultural influences, continuities, and transformations gave birth to modern Turkish language. The course should help you not only in developing an understanding of the Turkish language within a cultural framework, but also in gaining insight into Turkey's history, politics, literature, and media. No former knowledge of Turkey or the Turkish language is required.
UKRA 113: Ukrainian Culture Prof. Valeria Sobol 3:30AM-4:50AM, TTR, G24 Literatures, Cultures, and Linguistics
Course situates Ukrainian culture in the broad context of Slavic nations. Acquaints students with Ukrainian culture from the origins of Kievan Rus' in the Middle Ages to the present. Includes highlights of historical-cultural events, an overview of literature and of the arts, as well as an outline of Ukrainian folklore. No knowledge of Ukrainian required.
“The goal of this course is to acquaint students with Ukrainian culture from the origins of Kyivan Rus in the Middle Ages to the present. The course will examine the many facets that make up culture: history, politics, language, literature, folklore, religion, music, art, cinema, education, etc. It will also place Ukrainian culture in the broader context of the Slavic nations and peoples. Topics in contemporary Ukrainian culture will be given special emphasis. Lectures and readings will all be in English.”
For other languages and courses available through the BTAA contact [email protected]
Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian
BCS 10 1 : First Year Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian I
MTWR 09:00AM - 09:50AM, 1020 Lincoln Hall
BCS 20 1 : Second Year Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian I
MTWR 10:00AM - 10:50AM, 1030 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics
BCS 301 : Third Year Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian I
MWF 10:00AM-10:50AM, Location TBD
CZCH 102 : Elementary Czech I
MTWTR: 09:00AM - 9:50PM, Online
POL 1 01 : Elementary Polish I
MWTR 10:00-10:50, 1126 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics
POL 20 1 : Second Yr Polish I
MTWTR 11:00-11:50, 1038 Literatures, Cultures, & Linguistics
RUSS 10 1 : First-Year Russian I
MTWR 10:00-10:50, 316S Mumford Hall
MTWR 11:00-11:50, 241 Armory
RUSS 20 1 : Second-Year Russian I
MTWR 11:00-11:50, 134 Armory
RUSS 30 1 : Third Year Russian I
MWF 11:00-11:50, 1040 Literatures, Cultures, and Linguistics
RUSS 40 1 : Fourth Year Russian I
MWF 12:00-12:50, 1020 Lincoln Hall
RUSS 50 1 : Russian for Grad Students I
TTR 01:00-2:20, 1018 Literatures, Cultures, and Linguistics
TURK 20 1 : Elementary Turkish I
MTWRF 09:00-09:50, 1126 Literatures, Cultures, and Linguistics
TURK 40 3 : Advanced Turkish I
MTWTR 10:00 AM - 10:50 AM, Location TBD
UKRA 10 1 : Basic Ukrainian I
MTWR 10:00-10:50, 241 Armory
UKRA 20 1 : Second-Year Ukrainian I
MTWR 10:00-10:50, 241 Armory

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recent PhD Dissertations. Terekhov, Jessica (September 2022) -- "On Wit in Relation to Self-Division". Selinger, Liora (September 2022) -- "Romanticism, Childhood, and the Poetics of Explanation". Lockhart, Isabel (September 2022) -- "Storytelling and the Subsurface: Indigenous Fiction, Extraction, and the Energetic Present".
Genre Studies Latest Research Topics For PhD In English Literature. Cyberpunk Literature and the Technological Imagination. Evolution of the Bildungsroman in Modern Literature. Steampunk as a Subgenre: Victorian Aesthetics in Contemporary Works. Literary Journalism in the Digital Age: Challenges and Innovations.
Children's Literature Dissertation Topics. Topic 1: The influence of the intersection of race and bullying in children's books. Topic 2: Diversity of culture in children's literature. Topic 3: The use of literature to shape a child's mind. Topic 4: Evolution of children's literature.
Ideas for Writing English Papers. Research topics on English literature initially start off broad and then narrow down and you come up with your thesis. Using any of the research topics listed (gender, comparisons, historical background, politics, and religion) can take you almost anywhere. Choose your general topic based on the literature ...
There are many topics out there for a good research. Here are my tips on how to rightly choose a PhD research topic in English Literature. Choose the right poet or author that interests your topic. Ask PhD. supervisor the relevance of the poet to research. Search for some areas of research taken in the past.
Take your time in composing your research proposal, carefully considering the requirements outlined below. Your proposal should not be more than 2,000 words. PhD degrees are awarded on the basis of a thesis of up to 100,000 words. The 'Summary of roles and responsibilities' in the University's Code of Practice for Supervisors and Research ...
About this degree. With access to vast collections of research materials and supervision from world-leading experts* in a wide range of literary periods and topics, UCL provides an exceptionally strong environment in which to study for an English PhD. UCL English Department has specialists in every period of English and American literature, as well as English language, with an outstanding ...
The PhD in English and Related Literature is available on a full-time or part-time basis. Under the guidance of your supervisor, you'll complete a thesis of up to 80,000 words. A typical semester will involve a great deal of independent research, punctuated by meetings with your supervisor who will be able to suggest direction and address ...
Applicants are expected to hold a good first-class UK degree (a minimum 2:1 or equivalent) and an MA in a relevant topic. ... English Literature PhD. Full-time, April 2025: Applications open. Closing date: Friday 28 February 2025. Apply. English Literature PhD. Part-time, April 2025:
Below is a selection of online resources that include a vast number of articles on topics in English, including literary criticism. The resources on this page include articles from both scholarly and popular sources, so be sure to evaluate your sources to make sure that they are appropriate for your project.
Are you an aspiring English Literature scholar embarking on the exciting journey of a PhD? Look no further, as we've got your back! 📚🎓In this comprehensive...
Be inspired by the range of PhD research in the School of Literatures, Languages and Cultures. Over the course of your PhD, you'll be expected to complete an original body of work under the expert guidance of your supervisors leading to a dissertation of usually between 80,000 and 100,000 words. You will be awarded your doctorate if your ...
Examples of student theses and dissertations include "The Write to Stay Home: Southern Black Literature from the Great Depression to Early Twenty-first Century," "Profaning Theater: The Drama of Religion on the Modernists Stage," and "Sentimental Borders: Genre and Geography in the Literature of Civil War and Reconstruction."
Faculty of Arts Postgraduate Research Admissions. +44 (0) 117 428 2296. [email protected]. Faculty of Arts. School of Humanities. Department of English. Find out about the University of Bristol's PhD in English Literature, including entry requirements, supervisors and research groups.
Students in our PhD program gain advanced knowledge of literature from the British Middle Ages and colonial America to global/postcolonial and U.S. contemporary, as well as knowledge of literary theory, literary analysis, and interdisciplinary methods. The course of study balances coverage of national literary traditions with innovative methods and topics such as literature and science ...
English PhD students pursuing interdisciplinary research may include on their special committees faculty members from related fields such as comparative literature, medieval studies, Romance studies, German studies, history, classics, women's studies, linguistics, theatre and performing arts, government, philosophy, and film and video studies.
The Berkeley English Department offers a wide-ranging Ph.D. program, engaging in all historical periods of British and American literature, Anglophone literature, and critical and cultural theory. The program aims to assure that students gain a broad knowledge of literature in English as well as the highly-developed skills in scholarship and ...
Here are 16 potential research topics for a PhD in English Literature, along with brief explanations: With the Latest Research Topics For a PhD In English Literature, you can easily make your ...
The PhD in English (literature) at ASU is a premier graduate program in the U.S. with strong interdisciplinary ties and faculty links to research centers on campus and in the state, including the Arizona Center for Medieval and Renaissance Studies, the Center for the Study of Race and Democracy, the Institute for Humanities Research, and the Virginia G. Piper Center for Creative Writing.
University of Dundee School of Humanities. The primary objective of this PhD project is to research the interaction in literature of love and relationships with themes of disabilities, ill-health or neurodivergence. Read more. Supervisor: Prof M Gratzke. 30 June 2024 PhD Research Project Self-Funded PhD Students Only.
Research Topics For Ph.D. in English Literature. Sons and Lovers As The Poetry of Love In Fiction: A Study. Method of Teaching English Literature. Dancing through English Literature. MODERN INDIAN LITERATURE IN ENGLISH TRANSLATION.
University of Sheffield School of English. As a PhD student in the School of English, you will be studying and researching in one of the largest and the most successful English departments in the UK. Read more. Funded PhD Programme (Students Worldwide) Arts Research Programme. More Details.
This course grapples with a range of global Anglophone literatures to explore the dark underside of globalization, minding the unevenness and violences of its histories and structures. Particularly, we will work through a set of literary and theoretical texts to investigate the role of literature and literary criticism in reproducing ...
Permanent Session: English Literature Pre 1800 I. Panel Topic: Taking Survey of The Survey of English Literature ... While it takes copious research to get into a graduate program, it is also impossible to fully encompass the experience of being within a graduate program from the outside looking in. Given that so much of graduate school can ...
Topics covered will range from in-depth studies of specific authors, time periods, and thematic discussions of specific genre and literary traditions. Readings in English unless specified. Course Information: Same as CWL 453. 3 undergraduate hours. 4 graduate hours.