Digestive System of Human Body Essay
In order to study the digestive system of the human body thoroughly, it is necessary to understand where each part of the system is located. To begin with, the organs that participate in the process of digestion can be divided into two large groups. The first group unites body parts that form the alimentary tract that is a long canal.
Speaking about the parts of the given tract, it is necessary to list the mouth that is regarded as the beginning of the track, the throat (which is located in the front part of the neck), the esophagus that can be also called a food pipe (which is located between the throat and the stomach), the stomach (which is located in the abdominal region and below the diaphragm). Apart from that, the alimentary tract includes the small intestine or intestinum tenue that is located in the lower central part of the abdominal region and the large intestine located in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. In the end, there are the rectum and the anus at the end of the alimentary tract that is located in the lesser pelvis.
The second group of organs that allow the human body to process alimentary products and maintain the appropriate level of energy unites so-called accessory organs (“Accessory organs,” n.d.). These organs are supposed to fulfil important functions that make it possible for the human body to digest the food but they differ from the organs belonging to the first group as the food being digested does not pass through them. Thus, accessory organs include the teeth (there are two rows located in upper and lower jawbones), the tongue (in the lower part of the mouth). Apart from that, these organs include the parotid salivary glands (it is the organ that is located below the concha of the auricle) which is the largest out of three types of glands, the submandibular glands (the organ located below the lower jaw), and the Rivinus glands (the smallest out of three glands) located in the floor of the mouth cavity (Husney & Thompson, 2015).
Also, speaking about the organs whose activity is strictly interconnected with the process of food digestion, it is necessary to mention liver that is located in the right part of the abdominal region near the stomach. The next part of the digestive system of the human body is the cholecystis or the gall bladder – this term is used in order to denote the organ which is located in the right lower part of the abdominal region, it is a little bit lower than the liver. In the end, this group of organs related to the process of digestion includes pancreas that can be also called the pancreatic gland; the latter is the organ that is located in the left part of the abdominal region and it is very close to the stomach.
There is no doubt that the construction of the digestive system of the human body remains an extremely significant topic when it comes to different subjects. Digestion belongs to the number of processes of vital importance, and it is critical to understand the way that the digestive system works, the particular functions that digestive organs fulfil, and their location relative to each other.
Considering the importance of a clear understanding of food digestion in the human body, it may be necessary to develop an effective technique that would allow anyone to memorize the location of the parts mentioned. In order to retain the information of where each body part related to the process of food digestion is located, I will apply the combination of a few techniques as I believe that those studying methods that encourage the human brain to work with different kinds of information simultaneously can be called the most effective due to the fact that they help a person to see the aggregate picture of certain phenomenon or process.
To begin with, nowadays, it is widely accepted that there are different learning styles and it can be regarded as an extremely important practice if a person tries to pay increased attention to his or her distinctive features while processing and memorizing certain information. In order to better understand the work of the digestive system of the human body and memorize the location of the organs responsible for processing alimentary products, I decided to utilize my knowledge in the sphere of learning techniques as well.
First, I suppose that learning the information presented with the help of visual means can be regarded as the best way for me to memorize something. To fulfil this task using eidetic memory, I can perform the following actions: have a look at every single organ presented in the picture (one by one), have a look at the whole picture, close my eyes, and then try to process the information and see everything as a system (“The visual (spatial) learning style,” 2017). What is more, it needs to be mentioned that this method of memorizing information can be used in succession many times and it can improve the result and make it easier to memorize the organs and their location. In general, I suppose that my skills related to visual memory are quite strong, and this is why I am going to rely on this method most of the time.
Apart from those who put an increased focus on visual information while learning, there are people who cannot memorize a great volume of information if they do not see the logical connection between the particular facts or objects. Consequently, those people who feel that they need to see the links between objects or concepts and the ways that they can influence each other can easily restore the information using this knowledge. In fact, I suppose that it is extremely important for me to use the elements related to the analytic learning style because I seem to demonstrate very good results when I try to see into a matter while learning new information.
In order to be able to memorize the location of those organs responsible for food digestion, I would apply the method allowing me to synthesize the information. To apply it, I will need to have a look at the picture where the digestive system of the human body is presented and consider each element that needs to be memorized. As for the first technique that I decided to use, it requires me to memorize the location of every single element of the digestive system. Applying the second one, I will have to pay the acute attention to the links that exist between the organs located in the same anatomical regions. For instance, in order to memorize the location of salivary glands, I will have to explain to myself that they are responsible for producing saliva that allows mammals to process a food bolus with the help of jaws, and it means that the glands are located near the mouth cavity.
Therefore, using this method, I will have to draw the links between each part of the digestive system and other parts located nearby. In fact, it is necessary to assume that the implementation of this approach may involve certain time expenditures. At the same time, this way to process the information on the digestive system is much better when there is a need to understand the process instead of memorizing separate facts.
The mouth cavity remains an extremely important part of the digestive system as there are many important processes that the organs located in this area are involved in. These processes include propulsion (the teeth and the tongue help to move the food bolus along) and mechanical digestion (the teeth are used to reduce the food to fragments). Apart from that, the organs located in the mouth such as salivary glands also initiate chemical digestion as the parotid fluid makes the food softer and, therefore, prepares it for further processing.
As for the esophagus and digestive processes associated with this part of the digestive apparatus, it is necessary to mention propulsion. With the help of the esophagus, the food bolus can be delivered to the stomach where it will be processed.
The stomach is the organ that is responsible for the process of chemical digestion (the food is mixed with gastric juice). Also, there are the processes of mechanical digestion and propulsion. Plain muscles located in the stomach process the food and prevent it from returning back to the esophagus – instead, they allow the food bolus to reach the small intestines. Importantly, when the food bolus is in the stomach, the nutrients are absorbed and one has a sense of fullness.
The next part of the digestive tract represented by the small intestines fulfils the following functions: propulsion (the myenteron propels the food to the large intestines), absorption (water, vitamins, and other nutrients are absorbed there), and chemical digestion.
In reference to the large intestines, this part of the digestive tract participates in such processes as propulsion (the body has to make away with the food that has already lost all its nutrients), chemical digestion (the breakage of dietary fibre), and mechanical digestion (represented by peristalsis).
Propulsion is the process that involves propelling the food bolus from one part of the digestive tract to another (“Peristalsis creates propulsion,” n.d.). Due to it, the food can reach the organs where it will be processed.
Absorption is the mechanism that takes place when the nutrients extracted from the food enter the blood. This process remains extremely important as it is strictly interconnected with the final goal of the digestion process.
Chemical digestion is the mechanism involving processing the food bolus with the help of different substances produced by the human body such as saliva or digestive juices (Martinez, 2014). Due to chemical digestion, the organism manages to extract the nutrients that need to be absorbed.
Mechanical digestion is the process that involves breaking the food into small pieces in order to make it easier to extract useful substances (“Mechanical and chemical digestion,” n.d.). Apart from that, it is easier for the muscle coat to propel the food that has been mechanically processed.
Accessory organs: Glands and organs that facilitate the process of digestion . (n.d.)
Husney, A. & Thompson, G. (2015). Salivary glands .
Martinez, J. (2014). What is chemical digestion ?
Mechanical and chemical digestion . (n.d.)
Peristalsis creates propulsion: How food moves through the alimentary canal . (n.d.)
The visual (spatial) learning style . (2017).
- Nutrition During Pregnancy and Childbirth
- Prevention and Detection of Obesity
- Origin of Digestive System Terminologies
- Human Digestion
- Electrical Assignment - Economic Operation of Propulsion Transformer
- Chocolate and Lumosity Performance Index
- The Obesity Problem and Proposed Interventions
- The Harmful Effects of Sugar on the Human Body
- Health, Safety and Nutrition for the Young Child
- Nutritional Support for Patients with Hypertension
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, September 10). Digestive System of Human Body. https://ivypanda.com/essays/digestive-system/
"Digestive System of Human Body." IvyPanda , 10 Sept. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/digestive-system/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Digestive System of Human Body'. 10 September.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Digestive System of Human Body." September 10, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/digestive-system/.
1. IvyPanda . "Digestive System of Human Body." September 10, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/digestive-system/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Digestive System of Human Body." September 10, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/digestive-system/.
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
- Biology Article

Human Digestive System
Digestive system of humans.
The digestive tract of humans starts with the mouth and ends with the anus. It includes different structures such as the mouth, oesophagus, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gall bladder, and anus.
Table of Contents
Introduction Structure Parts
- Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Accessory organs, digestion process.
- Mixing and Movement
Disorders Functions Notes
The Human Digestive System
The digestive system of the human body comprises a group of organs working together to convert food into energy for the body. Anatomically, the digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract, along with accessory organs such as the liver, pancreas and gallbladder. The hollow organs that make up the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) include the mouth, stomach, oesophagus, small intestine and large intestine that contains the rectum and anus.
Human Digestive System and Nutrition involve the intake of food by an organism and its utilization for energy. This is a vital process which helps living beings to obtain their energy from various sources. The food which we eat undergoes much processing before the nutrients present in them are utilized to generate energy. This processing is known as digestion. Humans and other animals have specialized organs and systems for this process.
The digestion process involves the alimentary canal along with various accessory organs and organ systems. In humans, the process is quite simple due to our monogastric nature. This means that we have a one-chambered stomach, unlike other animals such as cows, which have four chambers.
Some parts of nervous and circulatory systems also play a significant role in the digestion process. A combination of nerves, bacteria, hormones, blood and other organs of the digestive system completes the task of digestion.
Let us have a detailed look at the human digestive system, its parts and functions. Also provided at the end of the chapter are digestive system notes.
Also Read: Alimentary Canal
Diagram Of The Human Digestive System
The diagram given below represents different parts of the human digestive system that convert food into essential nutrients absorbed by the body.
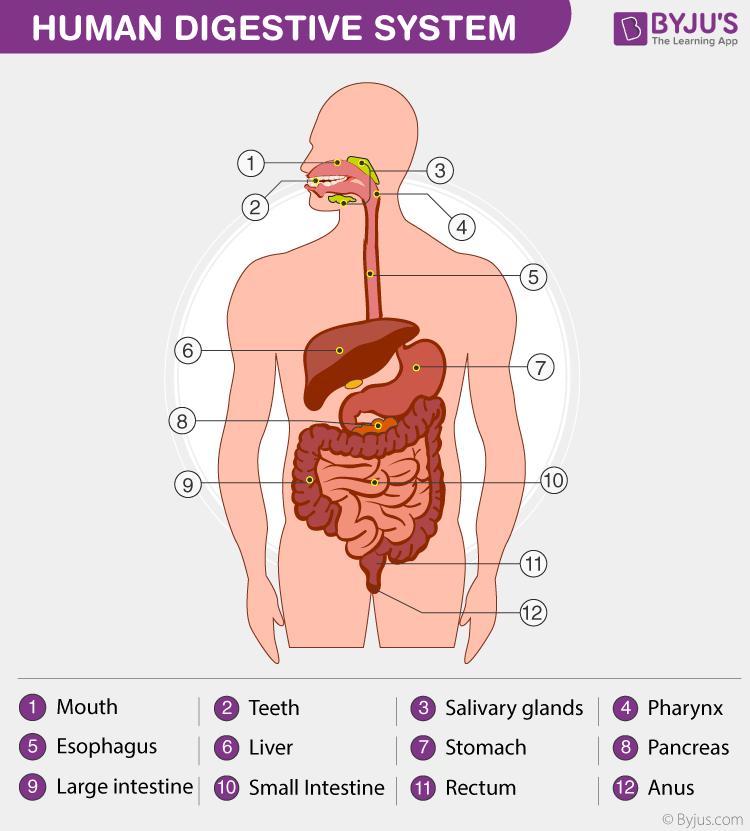
Parts of the Human Digestive System
The digestive system of the human body comprises a group of organs that work together in converting food into energy and other basic nutrients to power the body. The food we take in is digested and utilized by our body, and the unused parts of the food are defecated.
The digestive system of the human body is the sum of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT; also called alimentary canal) and accessory organs (tongue, liver, pancreas, etc.). These two parts together help in the digestion process.
The alimentary canal is the long tube through which the food that we eat is passed. It begins at the mouth (buccal or oral cavity), passes through the pharynx, oesophagus or food pipe, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, rectum and finally ends at the anus. The food particles gradually get digested as they travel through various compartments of the alimentary canal.
Accessory organs are organs which participate in the digestion process but are not actually a part of GIT. They stimulate the digestion by releasing certain enzymes that help in breaking down the food.
Let us have a detailed look at the digestive system of the human body, along with its parts and functions:
Food starts its journey from the mouth or the oral cavity. There are many other organs that contribute to the digestion process, including teeth, salivary glands, and tongue. Teeth are designed for grinding food particles into small pieces and are moistened with saliva before the tongue pushes the food into the pharynx.
A fibromuscular y-shaped tube attached to the terminal end of the mouth. It is mainly involved in the passage of chewed/crushed food from the mouth through the oesophagus. It also has a major part in the respiratory system, as air travels through the pharynx from the nasal cavity on its way to the lungs.
This is a muscular tube that connects the pharynx, which is a part of an upper section of the gastrointestinal tract. It supplies swallowed food along with its length.
Also Read: Food Pipe
It serves as a muscular bag which is situated towards the left side of the abdominal cavity, beneath the diaphragm. This vital organ acts as a storage for the food and provides enough time to digest meals. The stomach also produces digestive enzymes and hydrochloric acid that maintains the process of digestion.
Mucous : It is an aqueous secretion produced by the mucous membranes. It functions by protecting the stomach lining and gastric pits from the acid, which is produced by the glands to destroy the bacteria that entered along with the food particles.
Digestive enzymes : They are the group of enzymes which functions by breaking down polymeric macromolecules like biopolymers into their smaller and simpler substances.
Hydrochloric acid : It is the digestive fluid formed by the stomach during the process of digestion. It functions by destroying harmful microorganisms present in the food particles.
The small intestine is a thin, long tube of about 10 feet long and a part of the lower gastrointestinal tract. It is present just behind the stomach and acquires a maximum area of the abdominal cavity. The complete small intestine is coiled and the inner surface consists of folds and ridges.
This is a thick, long tube measuring around 5 feet in length. It is present just beneath the stomach and wraps over the superior and lateral edges of the small intestine. It absorbs water and consists of bacteria (symbiotic) that support the breakdown of wastes to fetch small nutrients.
Also Read: Large Intestine
Waste products are passed into the end of the large intestine called the rectum and eliminated out of the body as a solid matter called stool. It is stored in the rectum as semi-solid faeces which later exits from the body through the anal canal through the process of defecation.
It is a large gland present just behind the stomach. It is short with its anterior connected to the duodenum and posterior pointing towards the left part of the abdominal cavity. The pancreas releases digestive enzymes to complete the process of chemical digestion.
Read More: Pancreas
The liver is a roughly triangular, reddish-brown accessory organ of the digestive system located to the right of the stomach. It produces bile , which helps in the digestion of fat in the small intestine. The bile is stored and recycled in the gallbladder. It is a small, pear-shaped organ which is located just next to the liver.
Also Read: Cellulose in Digestion
The process of digestion begins from the mouth and ends in the small intestine – the large intestines’ main function is to absorb the remaining water from the undigested food and enable bacterial fermentation of materials that can no longer be digested.
The alimentary canal or the gastrointestinal tract is a series of hollow organs and tubes that begins from the mouth cavity and continues into the pharynx, through the stomach, small intestines, large intestines, and finally ending at the anus. Food particles gradually get digested as they travel through various compartments of the gastrointestinal tract.
The digestion process takes place in the following steps.
The very first step involves mastication (chewing). The salivary glands, along with the tongue, helps to moisten and lubricate food, before being pushed down into the food pipe.
It involves the process of lubricating and manipulating food and pushing it down the food through the food pipe (using peristalsis ), and into the stomach.
The stomach, small intestine, liver, and pancreas secrete enzymes and acids to aid the process of digestion. It functions by breaking down food particles into simple components and easily absorbable components.
Also Read: What is Liver
The process of converting complex food particles into simpler substances in the presence of enzymes and acids secreted by different digestive organs.
Read more: What are digestive juices?
This process begins in the small intestine where most of the nutrients and minerals are absorbed. The excess water in the indigestible matter is absorbed by the large intestines.
The process of removing indigestible substances and waste by-products from the body through the process of defecation.
In a nutshell, the digestion process consists of the six following steps:
Ingestion ⇒ Mixing and Movement ⇒ Secretion ⇒ Digestion ⇒ Absorption ⇒ Excretion
Also Read: Gastrointestinal Tract
Disorders of the Human Digestive System
Vomiting : It is the ejection of stomach contents through the mouth.
Diarrhoea : It is the abnormal watery bowel movement. Prolonged diarrhoea eventually leads to dehydration.
Constipation : A condition in which the faeces are clutched within the rectum due to an irregular bowel movement.
Indigestion : A pain or discomfort in the stomach which is caused when food is not digested properly, resulting in the feeling of fullness. Indigestion is mainly caused due to inadequate enzyme secretion, food poisoning, anxiety, overeating and eating spicy foods.
Also Read: Difference between trachea and oesophagus
Functions of the Human Digestive System
Digestion and absorption are the two main functions of the digestive system.
Digestion is necessary for breaking down food particles into nutrients that are used by the body as an energy source, cell repair and growth.
Food and drink need to be converted into smaller molecules of nutrients before it is absorbed by the blood and carried to the cells throughout the body. The body breaks the nutrients present in the drinks and food into carbohydrates, vitamins, fats and proteins.

Human Digestive System Notes
- The human digestive system breaks down food to release energy essential for the body to carry out its activities.
- The process of digestion takes place in 6 major steps.
- The food is ingested by the alimentary canal and is propelled through the body for further processing.
- The autonomous nervous system controls the peristalsis, contraction and relaxation of muscles within the alimentary canal wall.
- The food is passed to the small intestine where it is digested, and the nutrients are absorbed.
- Water, electrolytes and vitamins are absorbed by the large intestine and the waste is defecated.
Also Read: Mouth and Buccal Cavity
To learn more about the human digestive system parts and functions, as well as related topics such as the digestion process and disorders of the digestive system, keep visiting BYJU’S Biology or download the BYJU’S app, for further reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
Deduce the function of the human digestive system..
The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and the accessory organs. Their main function is to break down the ingested food into its components and produce vital nutrients and energy required to sustain life.
What are accessory organs?
Accessory organs are organs which are not part of the digestive system; however, they aid in the digestion process by performing many secondary functions. The main accessory organs of the digestive system are the tongue, liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
Outline the process of digestion, step by step.
The process of digestion involves the following steps, namely:
List out the parts of the digestive system.
- Mouth & Buccal Cavity
Explain the role of the tongue as an accessory organ.
The tongue is not a part of the digestive system, but it provides support functions such as moving and manipulating the food within the buccal cavity. Furthermore, moistening food also helps to swallow and pass through the oesophagus without much resistance.
Register at BYJU’S to explore digestive system notes and more.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Excellent notes
its good thing for learning
Its very good article and for learning
It is important for everybody because after knowing it anybody could become able to care of his or her health.
Thanks a lot. It really helped me
Year it really helped I passed my exam
Thank you byjus it really help me a lot
Notes are very good 👍👌
Thank u so much for your help! Byjus is really doing great work.
Thanks a lot for helping me with my biology project
Thanks for your help.
Thank you for helping students especially for those who want to write the exam
It helps me a lot. Awesome notes. Very good
Helpful 👍🏻👍🏻👍🏻👍🏻
Thanks a lot, very good
Thanks for your help great😊
Thank you for your help👍👍👍
Thank you BYJUS because of you only I got full marks in my exams and trust me because each and every single thing is described so nicely and in so simple language. (VERY HELPFUL MUST DOWNLOAD BYJUS TO GET GOOD AND EVEN EXTRA MARKS : ) ^_^ )
Thanks for this brief notes which help me to cover my digestion topics
Thanks a lot for this such an informative notes It’s really helpful for me👍keep growing
Thank you so much sir. It’s such an informative note great efforts.
I understood the digestion process more nicely.
Thanks for these brief notes which help me to cover my digestion topics
It helps us in study
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Digestion means simplification of complex foods. It is the process of breaking various foodstuff into simple products. The complex foods like carbohydrates, proteins and fats are converted into glucose, amino acids and fatly acids respectively by the action of digestive enzymes.
The digestive system includes the following: the oral cavity with organs located in it and the adjacent large salivary glands; pharynx; esophagus; stomach; small and large intestine; liver; pancreas (Rogers 15).
Digestion belongs to the number of processes of vital importance, and it is critical to understand the way that the digestive system works, the particular functions that digestive organs fulfil, and their location relative to …
The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms that can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
The human digestive system is responsible for the intake, breakdown, absorption and finally removal of nutrients and energy needed for the functioning of the human body.
The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food, breaking it down into usable energy and nutrients. The system plays a crucial …
The digestive system of the human body is the sum of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT; also called alimentary canal) and accessory organs (tongue, liver, pancreas, etc.). These two parts together help in the digestion process.