You can turn a subject into a central idea by focusing. Begin by reviewing what you know about your subject or by looking over notes you have made about it through listing, brainstorming, clustering, freewriting, or other prewriting activities.
With these details fresh in your mind, ask yourself:
What is my purpose in writing about this topic? What main point do I want to make about the topic?
WHAT IS MY PURPOSE?
Let's say you decide to write about high school. You might tell a story about your history class, compare two schools you attended, or argue that high schools should require foreign-language study.
If you want to compare the two high schools you attended, you can include details about their academic programs, athletic teams, students, or teachers. But you probably wouldn't argue that high schools should stay open in summer because doing so would take you outside your declared purpose.
WHAT IS MY MAIN POINT?
The next step in focusing is to decide what to say about your subject. What is the most interesting or important point you want to make about the schools you are comparing? The answer will be your main point, which ties all the details of the essay together.
Again, you turn an abstract subject into a central idea by stating a main point about that subject. If your main point is that entering a new school improved your attitude about education, your central idea might read:
Changing high schools made me a more serious student.
MAKING A POINT ABOUT A SUBJECT
In the box below, main points have been added to subjects to form working topic sentences or thesis statements.
Back to Top
CHECK YOUR WORKING CENTRAL IDEA
After writing a working central idea, check it for qualities that will make it effective as the basis of a paragraph or essay. Ask yourself:
Is my central idea expressed in a complete thought? Is it specific? Does it express an idea that is worth developing in a full-length paragraph or essay? Is it limited enough to discuss in a short piece of writing?
Never confuse a central idea with a simple subject. Central ideas are expressed in complete sentences; subjects are words or phrases. Take these subjects:
The city zoo. Professional athletes. Majoring in foreign languages.
Can you write a paragraph or essay on one of these subjects? Only if you decide on the main point you want to make about it. Try these as working central ideas:
The city zoo is in great need of repairs. Professional athletes are overpaid. Studying foreign languages leads to many career choices.
A CENTRAL IDEA IS SPECIFIC
Make your central idea specific. The key to this step is to focus your main point as precisely as you can. That will give you a clear direction to follow as you develop an essay or paragraph. Take this central idea:
Jogging isn't for everybody.
It is correct, but it leaves questions unanswered. For example, what kind of people should not jog? What ill effects might jogging cause them? Now, try this:
Jogging can be harmful to people who suffer from heart, back, or joint problems.
A CENTRAL IDEA CONTAINS A MAIN POINT THAT IS WORTH DEVELOPING
Make sure your main point is an idea-not just a fact-that is worth developing in a full-length paragraph or essay. Read these two sentences:
The War Memorial is in Ottawa. The War Memorial has been severely vandalized.
The first sentence is a statement of fact; it does not call for discussion. The second lends itself to discussion. For example, you might describe what the vandals did, explain how much repairs will cost, or discuss ways to prevent future problems.
A CENTRAL IDEA IS LIMITED
Essays that beginning college or university students write usually contain approximately five to seven paragraphs of about 50 to 100 words. Therefore, you should limit your working topic sentence or thesis, making it as specific as you can. Otherwise, you won't be able to make your point clearly and completely.
LIMIT THE DISCUSSION TO A MANAGEABLE LENGTH
Let's say you want to convince someone to stop smoking. You might limit yourself to three reasons to stop smoking: the health risks, the costs, and its effects on others.
Here's your working thesis:
Break the habit: otherwise, it will ruin your health, empty your wallet, and annoy your friends.
Your working topic sentences, which will control the three body paragraphs, could be as follows:
Smoking causes cancer, emphysema, and heart disease. You can save hundreds or even thousands of dollars a year by quitting. Smoking is offensive to friends and family.
LIMITING YOUR CENTRAL IDEA FURTHER
You begin a rough draft by discussing illnesses caused by smoking. However, you soon realize that you can't cover all three reasons for quitting and still keep the essay short. So you limit yourself to the issue of health risks.
Your thesis statement becomes:
Break the habit: smoking causes heart disease, emphysema, and cancer.
Your topic sentences become:
Smoking weakens the heart and impairs circulation. Smoking is a major cause of emphysema. Smoking has been linked directly to cancer of the mouth and the esophagus.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A TOPIC SENTENCE AND A THESIS
A topic sentence is the sentence that expresses the central idea of a paragraph. A thesis statement is a sentence that expresses the central idea of an essay.
It's a good idea to decide the topic sentence of a paragraph after writing the working version of an essay's thesis. A topic sentence explains one aspect or point in the thesis and, therefore, should always be more specific and limited than a thesis.
REVISE AND REFINE THE CENTRAL IDEA AS YOU WORK
You can revise a central idea whenever you need to. The working version of a topic sentence or thesis statement provides only a starting point and a sense of direction. Don't be afraid to look back to your central ideas and rewrite them often. As a matter of fact, focusing is something you should do throughout the writing process.


Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

Thesis Statements

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
A strong component of academic writing that all writers must understand is the difference between subject, topic, and thesis. Knowing the difference between these three terms will help you create a strong argument for your paper. This handout is designed to help inform you about these three distinct introductory elements, and it will also help you transition from deciding on a subject you are writing about, to the essay’s topic, and finally to your overall thesis.
The subject of your paper is a broad idea that stands alone. At this point, there is no detailed information associated with it or any kind of argumentation. It serves, in essence, as a launching pad for you to form an idea, or argument, which will eventually become the purpose of your paper.
Example: Women
The topic of your paper is an evolved, narrower version of your subject. Here is where you add a detailed, more conclusive area of focus for your paper so that you can eradicate vagueness.
Example: Women in late 1990s television
The thesis acts as the final idea on which the entirety of your paper will focus. It is the central message that ties the whole paper together into one definitive purpose that prepares readers for what you are arguing.
Example : Although people may argue that television in the late 1990s helped portray women in a more honest and intrepid light, programs including Buffy the Vampire Slayer, Charmed , and Sex and the City failed to illustrate the depth and truth of womanhood, choosing to focus heavily on clichéd romantic entanglements, unbecoming pathetic quarrels, and thin temptresses adorned with fashionable costumes and bare midriffs.
Subject to Topic
The following are some suggestions to help you shift from a broad subject area to a narrow, focused topic.
Seek out narrow topics
Inappropriate.
Subject: Women
Topic: Women in history
Note: In this case, the topic is too large to create a complex thesis statement worthy of a paper. The broader the topic, the more difficulty you will have narrowing your argument enough to affect readers.
Appropriate
Topic: Famous women aviators of WWII
Note: Here the topic as narrowed down the subject by focusing on women belonging to a specific profession in a particular historical period. It is thorough enough to discover a thesis statement.
Choose arguable topics
Subject: Toni Morrison
Topic: Biography
Note: This idea does not allow for speculation or disagreement, which gives it an underdeveloped quality.
Topic: Literary merits of the novel Tar Baby
Note: This idea allows for speculation or disagreement, which gives it a strong, developed quality.
Choose topics within your comfort zone
Subject: Linguistics
Topic: OE Northumbrian dialects
Note: Unless you have studied OE Northumbrian dialects at length, it perhaps poses too high of a research challenge to pursue.
Subject: College Freshmen
Topic: The Freshman Fifteen
Note: This topic is narrow enough and familiar enough to most college students to purse as a topic.
Rules for Thesis Statements
- Needs to correspond to the assignment’s expectations
- Usually, but not always, one sentence
- Typically appears that the end of the introduction
- More often than not, it is explicitly stated
- Establishes an argument
- Establishes the criteria for scrutiny of the topic (previews the structure of the paper)
- Write for an audience. Your paper should be catchy enough to retain readers’ attention.
Determine a "Research Question"
Determining a research question is a crucial aspect of your writing. In order to stay focused on the assignment, you must form a clear and concise argument. Choose one major idea you want to concentrate on, and expand from there.
When your instructor assigns a paper, try and find some angle that makes you inspired to fulfill the assignment to the best of your abilities. For example, if your history professor assigns you to write about a historical figure who changed the world for the better, write about an individual whose work you can relate to. If you are interested in the supernatural, you could write about Joan of Arc, who became a crusader because of the visions she claimed to have had from God.
Next, ask yourself a series of questions to help form your research question. Try to avoid questions you can answer with “yes” or “no” because these will not allow you to explore your topic as thoroughly or as easily as questions that begin with “who,” “what,” “why,” or “how.”
- When did Joan rise to prominence?
- Did she develop a strong following that her enemies felt threatened by?
- How did her gender play a part in her tragic demise?
- What does Joan’s execution say about female leaders of the 15th century?
Once you have developed a series of questions, consider which questions allow you to form an argument that is not too broad that you cannot write a sufficient paper, but not too narrow that it prevents you from crafting an interesting and compelling piece of writing. Decide which question represents this criteria, then you can start researching. In this case, from the above examples, you may select “How did Joan’s gender play a part in her tragic demise?” This question will allow you to develop a complex thesis with argumentative points to pose to readers. Below is a way to develop a thesis statement from the simply worded question that was just brainstormed.
The answer to your research question can become the core of your thesis statement.
Research Question:
How did Joan of Arc’s gender play a part in her tragic demise?
Thesis Statement:
Joan of Arc’s gender played a significant role in her tragic demise because of the laws and social customs concerning women during France’s 15th century, which included social ideals that perceived women as secular citizens; political standards that favored men to hold positions of power over women; as well as religious ideals that perceived Joan’s alleged clairvoyant gifts as a natural trait of witchcraft, a crime of heresy also associated with women.
Note: Beginning writers are taught to write theses that list and outline the main points of the paper. As college students, professors might expect more descriptive theses. Doing this will illustrate two points: 1) Readers will be able to isolate your argument, which will keep them more inclined to focus on your points and whether or not they agree with you. They may find themselves questioning their own thoughts about your case. 2) A descriptive thesis serves as a way to show your understanding of the topic by providing a substantial claim.
Troubleshooting your Thesis Statement
The following are some suggestions to help you scrutinize your working draft of your thesis statement to develop it through further revisions.
Specify your details
Example: In today’s society, beauty advertisements are not mere pictures that promote vanity in the public, but instead, they inspire people to make changes so that they can lead better lifestyles.
- Uses cliché phrases like “In today’s society.”
- What kind of beauty advertisements are you referring to? All of them? Or specific kinds?
Note: Who is this targeting? Women? Men? Adolescents? Being more specific with the targeted audience is going to strengthen your paper.
Example: Makeup, clothing, and dieting advertisements endorse American ideals of female beauty and show the public that women should possess full ownership of their bodies and fight the stigma of physical and sexual repression which has been placed upon them.
- Identifies specific forms of beauty advertisements for the sake of clearly expressing a strong argument.
- Uses descriptive language.
Note: By signifying that women’s beauty is the main topic being argued in the paper, this author clearly identifies their main, targeted audience.
Make arguable claims
Undeveloped.
Example: Social media is not conducive to people’s personal growth because of the distractions, self-doubt, and social anxiety it can cause to its users.
- “Social media” and “personal growth” both encompass a large span of topics and so they leave the reader confused about the particular focus of this paper.
Note: The thesis is too broad to form a well-constructed argument. It lacks details and specificity about the paper’s points.
Example: Although Facebook allows people to network personally and professionally, the procrastination and distraction from one’s demanding responsibilities can lead people to invest more time in narcissistic trivialities, resulting in severe cases of anxiety and low self-esteem.
- It alludes to some kind of counterargument in the opening dependent clause.
- The thesis specifies several points that makes a thesis credible. The argument connects all the points (distractions, self-doubt, and social anxiety) together into one linear train of thought, relating the ideas to one another.
Note: The thesis is more focused. It concentrates on the idea that social media plays up on a person’s self-worth.
Preview the paper’s structure
Example: College is a crucial stage in one’s life that will help them become more sophisticated individuals upon entering the harsh world as an adult.
Note: Not only does this statement lack specificity and excitement, but it fails to present an idea of what the paper will look like, and how the argument is set up. As readers, we know this writer believes college is an imperative part of one’s life, but we have no idea how they are going to go about arguing that claim.
Example: College is a crucial stage in a young adult’s life because it is the time in which they begin to transition from childhood to adulthood, learn to live away from their parents, budget their own finances, and take responsibility for their successes and failures, which will force them to make more responsible decisions about their lives.
Note: The thesis points to different aspects of college life that help students ease into adulthood, which shows the reader the points the writer will explore throughout the body of the paper.
- transition from childhood to adulthood
- learn to live away from their parents
- budget their own finances
- take responsibility for their successes and failures
Final Thoughts
When you are asked to write a paper in college, there may not be as many detailed descriptions telling you what subject or argument to write about. Remember, the best way to pick your subject is to write about something that interests you. That way, the assignment will be more promising and passionate for you and may help you feel more in control of your writing.
As you venture closer to crafting your thesis, make sure your subject is narrowed down to a specific enough topic so that you can stay focused on the task. If your topic is specific enough, you will be able to create an argument that is concentrated enough for you to provide sufficient argumentative points and commentary.
Thesis vs. Topic
As you begin to formulate a thesis for your essay, think about the following distinction between topic and thesis. A topic is a general area of inquiry; derived from the Greek topos (place), "topic" designates the general subject of your essay. For instance, "Munro Leaf's The Story of Ferdinand (1936) and Dr. Seuss's And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street (1937) both respond to the rise of fascism" would be a weak thesis but a good a topic for an essay. From a topic, many specific theses can be extracted and developed. A thesis is more specific and delimited; it exists "within" your topic. In your essay, you need to use an argumentative thesis.
In argumentative writing, the writer takes a stance and offers reasons in support of it. Crucial to any piece of argumentative writing is its thesis. The thesis arises from the topic, or subject, on which the writing focuses, and may be defined as follows:
A thesis is an idea, stated as an assertion, which represents a reasoned response to a question at issue and which will serve as the central idea of a unified composition.
If we've selected as a topic the notion that these books show the power of unions we need to ask, "So what?" Do both stories make exactly the same argument in exactly the same way? How do they differ? How are they similar? In each tale, what are the workers' demands? With what degree of sympathy are those demands presented? In sum, what does focusing on this theme tells about what the books might mean? One possible thesis is:
If Munro Leaf's The Story of Ferdinand (1936) and Dr. Seuss's And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street (1937) both respond to the rise of fascism, neither clearly articulates a political position on the subject: Although Leaf's book offers more allusions to European fascism than Seuss's does, both can be read as critical of fascism, indifferent to it, or proposing another political strategy entirely.
When you compose a thesis statement, think about how it satisfies the following tests:
1. Is it an idea? Does it state, in a complete sentence, an assertion? 2. Does it make a claim that is truly contestable and therefore engaging? (Yes, because one could also argue for a greater difference between these two tales, or that one or both more clearly advances a particular political ideology.) 3. Are the terms you are using precise and clear? (Key terms here seem to be: "fascism," "articulates," "political position," and "critical.") 4. Has the thesis developed out of a process of reasoning?
Once these questions have been satisfactorily answered, use the resulting thesis to organize your evidence and begin the actual writing. As you do so, bear in mind the following questions:
1. What is my purpose in writing? What do I want to prove? (Notice the explicit purpose in the thesis statement: it does not merely point out that both books show the power of organizing. Instead, the thesis takes a position on this topic, and then answers the question "So what?") 2. What question(s) does my writing answer? 3. Why do I think this question is important? Will other people think it equally important? 4. What are my specific reasons, my pieces of evidence? Does each piece of evidence support the claim I make in my thesis? 5. Where does my reasoning weaken or even stop? Am I merely offering opinions without reasoned evidence? 6. How can I best persuade my reader?

How to Start Your Research
- Choose a Topic
- Search Library Databases
- Search the Library Catalog
- Search Google
- Stay Organized
Your Librarian

In This Section
In this section, you'll find advice on.
- Choosing a topic
- Doing some background reading
- The difference between a topic, thesis, and research question
Start With What You Know
What are you curious about.
- What do you still have questions about?
- This might seem obvious, but your topic should interest you!
How can you contribute to the conversation?
- Are there gaps in existing research?
- Can you approach a topic from a new angle or perspective?
Picking a topic is research, too!
This video (3 minutes) describes the process of choosing and testing out a topic. See more tips below the video, too!
Do Some Background Reading
Reference sources are a great place to start when you're trying to choose or narrow a topic..
They'll help you learn the language of the topic you're interested in, and help you gather:
- basic facts or established information on your topic
- key concepts, terms, and people
- related topics and, often, suggested resources for learning more
Try these general reference sources to get started, and check out our Research Guides for subject-specific reference works.
A reference source summarizes key facts, important figures, and major concepts of a topic and provides useful background information. Reference sources include dictionaries and encyclopedias and can be in print or online.
Topic vs. Thesis vs. Research Question
What's the difference between a topic, a thesis, and a research question.
- << Previous: Start Here
- Next: Find Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 12, 2023 10:57 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uj.edu/research
Difference Between Topic Sentence Vs. Thesis Statement

After being introduced during the K-12 years of a student's education, academic writing is a mainstay in college and higher education. With proper format and technique being a major aspect of academic writing, it is essential for students to understand the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis statement.
Explore this article
- Essay Format
- Topic Sentences
- Thesis Statement
- Differences
1 Essay Format
Before delving into the differences between topic sentences and thesis statements, it is important to first establish the general format for a written essay. For K-12 students, written essays can commonly require the five-paragraph format, which consist of an introduction, three paragraphs that make up the body of the paper and the final paragraph as the conclusion. By understanding this general format of academic writing, it is easier to understand where topic sentences and thesis statements fit into place.
2 Topic Sentences
Topic sentences are used in each major paragraph of an essay paper. The purposes of these sentences are to develop and state the key idea of each paragraph in an effort to define the point of the paragraph. For example, when writing an essay paper on the effects of the Gettysburg Address, one of the paragraphs in the body of the paper could discuss how the audience received President Lincoln's famous speech. The topic sentence for this paragraph could be, "With the brief yet poignant nature of the Gettysburg Address, President Lincoln reminded his audience why the country was fighting so desperately to conserve the Union."
3 Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a single sentence that is used to define the purpose of your paper. Thesis statements inform readers as to the purpose of your paper. After reading your thesis statement, anyone reviewing your paper should be able to determine what your paper is going to prove or argue. For example, a thesis statement for a paper about William Shakespeare's famous play "Romeo and Juliet" could be as follows: "The play 'Romeo and Juliet' demonstrates the incredible power and impatient nature of young love, as the star-crossed lovers' inability to exercise patience or control their passion for one another results in their deaths."
4 Differences
With the purposes of both topic sentences and thesis statements established, the differences between the two are clear. Thesis statements need to be more broad and leave room to expand on further points to support the paper's argument. With the thesis statement in the previous section, a writer could continue explaining his argument about Romeo and Juliet by providing sub-points, demonstrating instances where the pair made hasty choices that had fatal consequences. Topic sentences are more specific in their purpose. For example, with the topic sentence in section two, it is clear that the next paragraph will discuss how President Lincoln used the Gettysburg Address to remind his countrymen about the purpose of the Civil War.
- 1 Indiana University: Paragraphs and Topic Sentences
Related Articles

The Similarities and Differences Between a Paragraph...

Paragraph Writing Skills for Beginners

How to Write a Hook for an Essay

How to Write an Introductory Paragraph in Elementary...

5 Ways to Develop a Paragraph

How to Write a Persuasive Essay

What Is a Narrative Response?

What Is a Lead-in Statement?

How to Build a Thesis for a College Essay

Important Elements in Writing Argument Essays

Abolitionists & the Moral Argument Regarding Slavery

What is a Clincher Statement?

Three Types of History Sources

How to Write an Introduction to a History Essay

How to Write an Introduction Paragraph With Thesis...

How Did Hearst & Pulitzer Use Newspapers to Provoke...

How Did John Jay Interpret the Constitution?

Major Parts of a Term Paper

How to Write a Composition on the Figurative Language...
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10.2: Topic Sentences
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 225938

WHAT IS A TOPIC SENTENCE?
The PIE paragraph strategy begins with a topic sentence, and knowing how to build a strong topic sentence is the foundation of writing a convincing paragraph.
WHAT’S THE PURPOSE OF A TOPIC SENTENCE?
The main point (claim) of a paragraph is often indicated in a single sentence called the topic sentence. A topic sentence is like a thesis in that you can also ask yourself: Can I disagree? You want to be able to answer YES to show that there is an arguable claim that needs to be proven. While it is true that in published writing you’ll sometimes find topic sentences in the middle or even at the end of a paragraph, placing your topic sentences at the beginning of each of your paragraphs is useful because:
- A strong topic sentence can help you, the writer, to focus each paragraph on one main point.
- A strong topic sentence can help your reader to see where you are headed with your ideas in a particular paragraph; topic sentences help your reader form a mental map of your essay.
WHY USE TOPIC SENTENCES?
A strong topic sentence connects back to your overall thesis and connects forward to the specific supporting point you are making in the paragraph to prove and illustrate your thesis and this makes the paragraph focused and unified. Here is a visual:

HOW CAN I WRITE STRONG TOPIC SENTENCES?
What differentiates a strong topic sentence from a weak one.
The chart below points out some of the main differences between a topic sentence that is genuinely helpful to you and your readers, and one which is not:
SOME GUIDELINES FOR WRITING STRONG TOPIC SENTENCES:
A topic sentence must predict or promise what follows, so it cannot be a question. To orient the reader, you may use a question as the first sentence, with the topic sentence as the answer to that question.
Weak: Should schools provide free computers for their students?
Strong: Schools must provide free computers for their students to assist them in their studies and prepare them for their future careers.
Phrases such as “I think” or “in my opinion” may muddle or weaken topic sentences. Your writing is always your opinion, so you don’t need these phrases unless they are central to the idea that you are trying to convey.
Weak: I think that it is important for every woman to carry pepper spray.
Strong: As violent criminals take over the city streets, women must carry pepper spray to protect themselves.
The topic sentence should provide clear relationships among all of its elements so that it can provide a framework for understanding the rest of the paragraph.
Weak: Historians record only dry statistics; we should read novels.
Strong: Accurate historical novels give us a deeper understanding of the past than do the dry collections of facts and statistics that pass for history texts.
A topic sentence needs to be clear and specific, so that it can predict and summarize the rest of the paragraph for the reader.
Weak: Public transit is terrible.
Strong: Incapable of providing reliable, comfortable service, the San Francisco Municipal Transit System is failing its ridership.
Practice: Choosing the topic sentence that fits
The topic sentence of the paragraphs below has been removed. Read them carefully and then choose the best topic sentence among the four choices below. Be prepared to explain your choice.
Paragraph 1: _________________________________________________________________________________________.
This belief is especially common among weight lifters who often consume large quantities of high protein foods and dietary supplements, thinking it will improve their athletic performance. Like weightlifters, football players consume too much protein, expecting it to produce additional muscle energy. Although it is true that muscles contain more protein than other tissues, there is no evidence that a high protein diet actually constructs more muscle tissue than a normal diet. Nutritionists point out that muscle cells grow not from excess protein but from exercise: when a muscle is used, it pulls in protein for its consumption. This is how a muscle grows and strengthens. If athletes want to increase their muscle mass, then they must exercise in addition to following a well-balanced, normal diet.
- Many athletes have false ideas regarding proper nutrition.
- My brother, a weightlifter, is an example of someone who consumes a lot of protein because he thinks it will make him bulky.
- Many athletes falsely believe that protein improves athletic performance by increasing muscle mass.
- The public is often confused by the seemingly conflicting advice nutritionists give us about our health.
Paragraph 2: _________________________________________________________________________________________.
Lately parents and critics across the country have been making a bigger fuss about the number and content of commercials aimed at children, and it seems as though the media has become a scapegoat for adults who have set questionable health guidelines for their children. It is both logical and factual to state that parents are the number one authority for most everything in their child’s life, which of course includes food choices. Recent studies from the Institute of Medicine found that the easiest and most reliable measure of understanding a child’s health and diet is to look at the health and diet of the parents. It is very likely that a child’s obesity did not come from the media, but from behaviors within the family. Even if advertisements became restricted or more limited, if parents do not enforce healthy diets or teach nutrition, the children will have learned nothing. Timothy J. Muris of The Wall Street Journal realizes that without addressing the issues of parental control, the ban on child food advertisements are “appealing on the surface, but ultimately useless.”
- Despite increasing rates of childhood obesity, we should not ban junk food ads aimed at children.
- According to Andrew Martin of the Chicago Tribune , “… the rates of obesity among 6 to 11-year-olds more than tripling during the last three decades, doubling for children ages 2 to 5 and increasing even more for adolescents 12 to 19 years old.”
- The staggering figures regarding childhood obesity alone are alarming enough to generate a stir.
- Although junk food advertisements are being blamed for children’s poor dietary habits, regulating these ads would not address the real source of the problem: lack of parental guidance.
Paragraph 1: 3. Many athletes falsely believe that protein improves athletic performance by increasing muscle mass.
Paragraph 2:
4. Although junk food advertisements are being blamed for children’s poor dietary habits, regulating these ads would not address the real source of the problem: lack of parental guidance.
Practice: Creating a topic sentence that fits
Now try creating your own topic sentences for the following paragraphs: 1) _______________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________
Famous inventor Thomas Edison, for instance, did so poorly in his first years of school that his teachers warned his parents that he'd never be a success at anything. Similarly, Henry Ford, the father of the auto industry, had trouble in school with both reading and writing. But perhaps the best example is Albert Einstein, whose parents and teachers suspected that he was mentally disabled because he responded to questions so slowly and in a stuttering voice. Einstein's high school record was poor in everything but math, and he failed his college entrance exams the first time. Even out of school the man had trouble holding a job-until he announced the theory of relativity.
2) Eating disorders afflict as many as ten million women and one million men in the Unites States. But why? _____ _____________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________
Young girls not only play with Barbie dolls that display impossible, even comical, proportions, but they are also bombarded with images of supermodels. These images leave an indelible mental imprint of what society believes a female body should look like. Carri Kirby, a University of Nebraska mental health counselor, adds that there is a halo effect to body image as well: “We immediately identify physical attractiveness to mean success and happiness.”
3) From Deborah Blum’s “What’s the Difference between Boys and Girls?” _____ _____________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________
Boys tend to gather in large, competitive groups. They play games that have clear winners and losers and bluster through them, boasting about their skill. Girls, early on, gather in small groups, playing theatrical games that don’t feature hierarchy or winners. One study of children aged three to four found they were already resolving conflict in separate ways—boys resorting to threats, girls negotiating verbally and often reaching a compromise.
1) On inventors: Doing well in school does not always demonstrate intelligence or future success. 2) On eating disorders: The images of beauty we are surrounded by are unrealistic and impossible to attain and make many women feel unattractive and deeply unhappy with themselves. 3) On Deborah Blum’s article: The female approach to interacting with one another is more harmonious and democratic.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
Published on July 21, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 5, 2023.
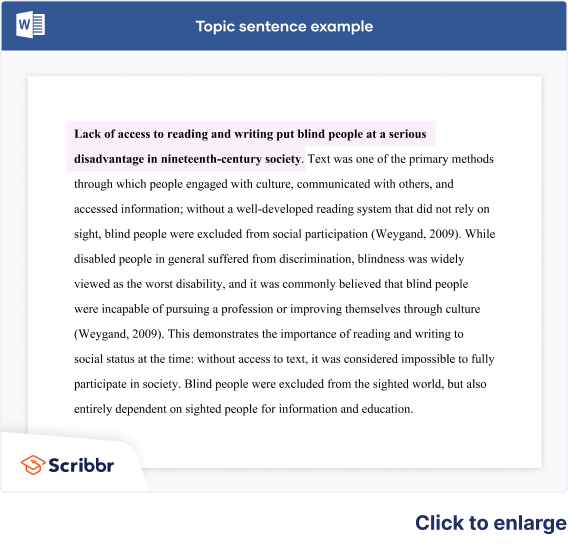
Every paragraph in your paper needs a topic sentence . The topic sentence expresses what the paragraph is about. It should include two key things:
- The topic of the paragraph
- The central point of the paragraph.
After the topic sentence, you expand on the point zwith evidence and examples.
To build a well-structured argument, you can also use your topic sentences to transition smoothly between paragraphs and show the connections between your points.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Writing strong topic sentences, topic sentences as transitions between paragraphs, topic sentences that introduce more than one paragraph, where does the topic sentence go, frequently asked questions about topic sentences.
Topic sentences aren’t the first or the last thing you write—you’ll develop them throughout the writing process. To make sure every topic sentence and paragraph serves your argument, follow these steps.
Step 1: Write a thesis statement
The first step to developing your topic sentences is to make sure you have a strong thesis statement . The thesis statement sums up the purpose and argument of the whole paper.
Thesis statement example
Food is an increasingly urgent environmental issue, and to reduce humans’ impact on the planet, it is necessary to change global patterns of food production and consumption.
Step 2: Make an essay outline and draft topic sentences
Next, you should make an outline of your essay’s structure , planning what you want to say in each paragraph and what evidence you’ll use.
At this stage, you can draft a topic sentence that sums up the main point you want to make in each paragraph. The topic sentences should be more specific than the thesis statement, but always clearly related to it.
Topic sentence example
Research has consistently shown that the meat industry has a significant environmental impact .
Step 3: Expand with evidence
The rest of the paragraph should flow logically from the topic sentence, expanding on the point with evidence, examples, or argumentation. This helps keep your paragraphs focused: everything you write should relate to the central idea expressed in the topic sentence.
In our example, you might mention specific research studies and statistics that support your point about the overall impact of the meat industry.
Step 4: Refine your topic sentences
Topic sentences usually start out as simple statements. But it’s important to revise them as you write, making sure they match the content of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence is specific enough to give a clear sense of what to expect from the paragraph, but general enough that it doesn’t give everything away. You can think of it like a signpost: it should tell the reader which direction your argument is going in.
To make your writing stronger and ensure the connections between your paragraphs are clear and logical, you can also use topic sentences to create smooth transitions. To improve sentence flow even more, you can also utilize the paraphrase tool .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you write each topic sentence, ask yourself: how does this point relate to what you wrote in the preceding paragraph? It’s often helpful to use transition words in your topic sentences to show the connections between your ideas.
Emphasize and expand
If the paragraph goes into more detail or gives another example to make the same point, the topic sentence can use words that imply emphasis or similarity (for example, furthermore , indeed , in fact , also ).
Indeed , cattle farming alone is responsible for a large proportion of greenhouse gas emissions.
Summarize and anticipate
If the paragraph turns to a different aspect of the same subject, the topic sentence can briefly sum up the previous paragraph and anticipate the new information that will appear in this one.
While beef clearly has the most dramatic footprint, other animal products also have serious impacts in terms of emissions, water and land use.
Compare and contrast
If the paragraph makes a comparison or introduces contrasting information, the topic sentence can use words that highlight difference or conflict (for example, in contrast , however , yet , on the other hand ).
However , the environmental costs of dietary choices are not always clear-cut; in some cases, small-scale livestock farming is more sustainable than plant-based food production.
You can also imply contrast or complicate your argument by formulating the topic sentence as a question.
Is veganism the only solution, or are there more sustainable ways of producing meat and dairy?
Sometimes you can use a topic sentence to introduce several paragraphs at once.
All of the examples above address the environmental impact of meat-eating versus veganism. Together, they make up one coherent part of a larger argument, so the first paragraph could use a topic sentence to introduce the whole section.
In countries with high levels of meat consumption, a move towards plant-based diets is the most obvious route to making food more sustainable. Research has consistently shown that the meat industry has significant environmental impacts.
The topic sentence usually goes at the very start of a paragraph, but sometimes it can come later to indicate a change of direction in the paragraph’s argument.
Given this evidence of the meat industry’s impact on the planet, veganism seems like the only environmentally responsible option for consumers. However, the environmental costs of dietary choices are not always clear-cut; in some cases, small-scale livestock farming is more sustainable than plant-based food production.
In this example, the first sentence summarizes the main point that has been made so far. Then the topic sentence indicates that this paragraph will address evidence that complicates or contradicts that point.
In more advanced or creative forms of academic writing , you can play with the placement of topic sentences to build suspense and give your arguments more force. But if in doubt, to keep your research paper clear and focused, the easiest method is to place the topic sentence at the start of the paragraph.
View topic sentences in an example essay
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
Topic sentences help keep your writing focused and guide the reader through your argument.
In an essay or paper , each paragraph should focus on a single idea. By stating the main idea in the topic sentence, you clarify what the paragraph is about for both yourself and your reader.
The topic sentence usually comes at the very start of the paragraph .
However, sometimes you might start with a transition sentence to summarize what was discussed in previous paragraphs, followed by the topic sentence that expresses the focus of the current paragraph.
Let’s say you’re writing a five-paragraph essay about the environmental impacts of dietary choices. Here are three examples of topic sentences you could use for each of the three body paragraphs :
- Research has shown that the meat industry has severe environmental impacts.
- However, many plant-based foods are also produced in environmentally damaging ways.
- It’s important to consider not only what type of diet we eat, but where our food comes from and how it is produced.
Each of these sentences expresses one main idea – by listing them in order, we can see the overall structure of the essay at a glance. Each paragraph will expand on the topic sentence with relevant detail, evidence, and arguments.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 05). How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose. Scribbr. Retrieved April 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/topic-sentences/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, example of a great essay | explanations, tips & tricks, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, transition words & phrases | list & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

What Is The Difference Between Thesis And Topic Sentence
Writing academic papers can be a daunting task, and one of the most important steps is understanding the difference between a thesis and a topic sentence. A thesis is a statement that conveys the main idea of an entire paper, while a topic sentence is a statement that conveys the main idea of a single paragraph.
In this blog post, we’ll explore these concepts in greater detail, examining how to craft effective thesis and topic sentences, when to use them, and the different purposes they serve in a paper.

The difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is that a thesis is a statement that expresses the main idea of an essay or research paper, while a topic sentence is a sentence that introduces a new idea or concept in a paragraph. A thesis is usually more specific and takes more research to create than a topic sentence, which is generally more general.
A thesis statement is used to provide the reader with an overview of the paper and to help the writer stay focused on their argument, while a topic sentence provides a bridge between the ideas in the current paragraph to the ideas in the next paragraph. In short, a thesis serves as the central point of an essay, while a topic sentence helps guide the reader through the essay by connecting different ideas and concepts.
A topic sentence

The main difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is that a thesis serves as the main argument or claim of an entire piece of writing, while a topic sentence serves as a stepping stone to the main argument and helps to introduce the main idea in the body of the paper. A thesis is a statement that expresses the main point, idea, or argument of a paper, while a topic sentence is a sentence that introduces the main idea in a paragraph. The thesis should be specific and focus on one main idea, while the topic sentence should be supported by evidence and explain the main idea of the paragraph.
In short, the thesis is the backbone of an essay, and the topic sentence is its supporting structure.
The role of thesis and topic sentences in an essay

The difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is often confusing. A thesis statement is a statement that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay. It is usually found at the end of the first paragraph of an essay.
It is usually found at the end of the first paragraph of an essay. On the other hand, a topic sentence is a sentence that states the main idea of a paragraph. The topic sentence usually appears at the beginning of a paragraph and is followed by evidence and analysis that support the main idea.
In short, a thesis is a statement that sums up the overall main point of an essay, while a topic sentence is a statement that introduces and summarizes a single paragraph within the essay.
How to write a thesis and topic sentence

Writing a thesis and topic sentence can be a challenging task, and understanding the difference between them is key to crafting an effective essay. The thesis is the main point of your essay, and it should be stated in your introduction. It is the central argument you will be discussing and defending throughout the paper.
On the other hand, a topic sentence is a sentence that introduces the main idea of a paragraph. It should provide a clear indication of what the paragraph is about and be supported by the rest of the sentences in the paragraph.
Knowing the difference between a thesis and a topic sentence can help you effectively organize your essay and ensure that your argument is clearly expressed.
Examples of thesis vs. topic sentences

The difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is often confusing. A thesis is a statement that expresses the main idea of an essay or other written piece.
It concisely summarizes the main point or claim of the essay. A topic sentence, on the other hand, is a sentence that expresses the main idea of a paragraph or section within a piece of writing. It is typically found at the beginning of the paragraph and helps to introduce the main point of the paragraph.
While both a thesis and a topic sentence are important elements of an essay or other written work, the main difference is that a thesis conveys the main point of the entire piece, while a topic sentence conveys the main point of a single paragraph within the piece.
In conclusion, the main difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is that a thesis serves as the main argument or claim of an essay, while a topic sentence serves as a summary of the main point of a paragraph. Thesis statements are specific, while topic sentences are more general. A thesis should be supported by evidence and research, while a topic sentence should only be supported by the rest of the paragraph.
A thesis should be supported by evidence and research, while a topic sentence should only be supported by the rest of the paragraph. Knowing the difference between a thesis and a topic sentence can help writers create more effective and organized essays.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Thesis Statement or Topic Sentence?
- High School

Occasionally at IEW our customer service team will receive questions about the differences between topic sentences and thesis statements. Hopefully this blog post will dispel any confusion between the two and empower you to help your students assail the essay in style!
Thesis statements summarize the central position of an entire essay and typically appear at the end of the introductory paragraph. Think of them as guideposts for the entire essay. They provide the reader of the essay an idea of the direction it will take. While beginning essay writers will typically write a single-sentence thesis statement, the thesis can be more than one sentence.
Depending upon the type of essay being written, a thesis statement’s emphasis will vary. In an expository essay, an essay that explains or informs, the thesis will narrow what is being explained. Thesis statements in narrative essays, which are essays that relate a story, paint an overall picture of the story that is being described and as such tend to be more personal in nature. Another type of essay, the argumentative essay, features thesis statements that underscore the writer’s opinion. In contrast, persuasive essays employ a somewhat different approach. In a persuasive essay, the thesis statement is oftentimes replaced with a question. This question serves to entice the reader to continue reading the essay in order to learn the writer’s position.
While you can think of thesis statements as guideposts for an entire essay, think of topic sentences as guideposts for individual paragraphs. Topic sentences appear in the body of the essay and are the first sentence in the paragraph. Not only do topic sentences focus the content in the paragraph, they also support the thesis statement made in the introduction.
So what might thesis statements and topic sentences look in a real-life example? Let’s consider a narrative essay prompt that asks the writer to describe someone who challenged him or her to work hard. A thesis statement might look something like this: “My gym teacher, Mr. Hernandez, never stopped encouraging me to do ‘hard things’ in high school.” This thesis statement helps the reader prepare to read some of the ways that Mr. Hernandez encouraged the writer. The topic sentences would support the thesis. Consider the following potential topic sentences:
- Mr. Hernandez encouraged me to enroll in an honors English class my senior year in high school.
- When he learned of an opportunity to help a family who had fallen on hard times, Mr. Hernandez reached out to me to help organize a clothing drive.
- Once I began to apply to colleges, Mr. Hernandez encouraged me to apply to a selective college and even offered to write a reference letter on my behalf.
These topic sentences all support the thesis of the paper by showing how Mr. Hernandez supported the writer of the essay. In the conclusion of the essay, the writer would reiterate the topics one more time before finishing the paper by emphasizing the most important point that underscores the thesis. That point might be something like this:
Mr. Hernandez saw something in me that I didn’t recognize in myself. He helped me to grow in confidence and take on challenges I would never have considered on my own. I’m excited to say that this next fall I’ll be attending ____________ University as an honors student majoring in English. And I even received an academic scholarship thanks in part to his letter of recommendation. I am so thankful he took the time to help me on my path!
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Dissertation vs Thesis: Understanding the Key Differences

Table of Contents
Undergraduate and graduate students often find themselves navigating the intricacies of higher education, including the requirement to complete a research project as part of their academic journey.
This can be a source of confusion, particularly when it comes to distinguishing between a dissertation and a thesis. While both terms are used interchangeably in some educational institutions, they actually have distinct meanings and purposes. Let's delve into the world of dissertations and theses, exploring their differences, purposes, and unique attributes.
Defining the Terms: Dissertation and Thesis
What is a dissertation.
A dissertation is a research project that marks the culmination of a doctoral program. It requires students to conduct original research and contribute new knowledge to their field of study. Dissertations are typically longer and more comprehensive than theses, as they delve deep into a specific topic, often spanning several chapters.
When embarking on a dissertation, students are expected to choose a research topic that is both relevant and original. This topic should contribute to the existing body of knowledge in their field and address a gap in current research. To accomplish this, students must thoroughly review the existing literature and identify areas that require further investigation.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis, on the other hand, is usually associated with a master's degree program. It is a research project that allows students to explore a particular topic in depth. Theses are generally shorter than dissertations, spanning fewer chapters. While they also require original research, the depth and scope may be narrower compared to a dissertation.
Similar to a dissertation, a thesis requires students to select a research topic and conduct a thorough literature review. However, due to the shorter length of a thesis, the literature review may not be as extensive as that of a dissertation. Nevertheless, it is still important for students to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the existing knowledge on their chosen topic.
Key Differences Between Dissertation and Thesis
Purpose and structure.
The primary difference between a dissertation and a thesis lies in their purpose and structure. A dissertation aims to contribute new knowledge to a specific field of study and is typically a more extensive and comprehensive project. It involves an in-depth exploration of a research problem or question, often requiring the collection and analysis of primary data. The structure of a dissertation usually includes multiple chapters, such as an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Furthermore, a dissertation often requires the student to engage in critical thinking, originality, and creativity to develop a unique contribution to the field. It may involve the development of new theories, models, or frameworks that can advance the understanding of a particular subject area.
Length and Depth of Research
Dissertations are known for their length and the depth of research they require. Doctoral candidates spend years conducting original research, analyzing data, and crafting comprehensive arguments. The research conducted for a dissertation is typically more extensive and rigorous compared to that of a thesis.
In addition, a dissertation often involves a thorough review of existing literature to establish a theoretical framework and identify research gaps. This review helps situate the research within the broader academic context and provides a foundation for the research design and methodology. The depth of research in a dissertation allows for a more comprehensive analysis and interpretation of the findings.
Degree Level and Requirements
Another key difference between dissertations and theses is the level of education for which they are typically required. Dissertations are a common requirement for doctoral degrees, such as Ph.D. programs, while theses are more commonly associated with master's degree programs. The specific requirements for each project may vary across institutions and academic disciplines.
Doctoral candidates are expected to demonstrate a high level of expertise and mastery in their field of study. They are often required to defend their dissertation orally in front of a committee of experts in the field. This defense allows for a rigorous examination of the research, ensuring its validity and contribution to the field.
On the other hand, theses for master's degrees are usually shorter in length and may not require the same level of originality and depth of research as a dissertation. However, they still require students to demonstrate their ability to critically analyze existing literature, conduct research, and present their findings in a coherent and scholarly manner.
Choosing Between a Dissertation and a Thesis
Factors to consider.
When deciding between a dissertation and a thesis, several factors should be taken into account. Firstly, consider your academic goals and the requirements of your degree program. If you aim to pursue a doctoral degree or a research career, a dissertation may be the most appropriate choice. However, if your goals are more focused on professional advancement or further specialization within your field, a thesis may suit your needs.
Understanding Your Academic Goals
Reflect on your academic interests and aspirations, as well as the amount of time and resources you are willing to invest in your research project. Each option comes with its own set of challenges and expectations, so it is important to choose the path that aligns with your academic and career goals.
The Process: From Proposal to Defense
The dissertation process.
The dissertation process involves multiple stages, starting with the development of a research proposal. Doctoral candidates must conduct a literature review, outline their research methodology, collect and analyze data, and present their findings in a comprehensive written document. The final step typically involves defending the dissertation orally, where candidates must respond to questions and critique from a committee of experts in the field.
The Thesis Process
The thesis process follows a similar trajectory but on a smaller scale. Students will still need to develop a research proposal, conduct a literature review, collect and analyze data, and present their findings in a written document. The defense process for a thesis may involve an oral presentation or an examination by a committee, depending on the institution's requirements.
The Role of Advisors in Dissertations and Theses
Guidance and support in the dissertation journey.
Dissertation advisors play a crucial role in guiding students through the research process. They provide valuable mentorship, offer insights into the field, and help refine research questions and methodologies. Advisor-advisee relationships are essential for the successful completion of a dissertation, as advisors provide ongoing feedback and support during the entire research journey.
Mentorship in the Thesis Process
Similarly, thesis advisors offer mentorship and guidance to students pursuing a master's degree. They help students refine their research topic, provide feedback on drafts, and ensure that the research project meets the required standards. Working closely with a knowledgeable advisor can significantly enhance a student's thesis experience and contribute to the overall success of the project.
Understanding the differences between dissertations and theses is essential for students embarking on their research journey. By considering their academic goals and evaluating the resources available, students can make an informed decision when choosing between a dissertation and a thesis. Additionally, the guidance and support provided by advisors throughout the process are invaluable and contribute to the successful completion of these significant research endeavors.
You might also like

AI for Meta-Analysis — A Comprehensive Guide

Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Safeguarding Students and Faculty Data

How To Write An Argumentative Essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The thesis is a specific argument that will be involved in every paragraph of the paper whether one is introducing it, defending it, or reinforcing it. It is the sole reason for the paper's existence and should be one written as a well-constructed sentence that acts as a map for how the paper will unfold. Here are a few examples of topics and ...
Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences A thesis driven essay is comprised of an initial thesis statement that establishes a claim or argument, and ensuing topic sentences that support and develop that claim. Ideally, a reader would be able to read only the thesis statement and topic sentences of your text, and still be able to understand the ...
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Exercise #1: Writing topic sentences first, and then using the topic sentences to create your thesis While writing a first draft, many writers write their introduction and thesis statement first. But in this exercise, write your body paragraphs with topic sentences first, before you write your thesis. This drafting style is useful because your ...
A thesis statement is written to state the main purpose or argument of your writing. That means that your thesis statement will be supported through all of the body paragraphs that make up your essay. A topic sentence is the first sentence of a body paragraph. This sentence indicates for your reader how the paragraph will support your thesis.
A strong set of topic sentences will work together to support a thesis. A . thesis statement (the main point of a whole essay) is usually found at the . end of an introduction. A . topic sentence (the main point of a paragraph) is usually at the . beginning of a paragraph. Thesis statements and topic sentences are similar in some ways: − They are
Your thesis statement becomes: Break the habit: smoking causes heart disease, emphysema, and cancer. Your topic sentences become: Smoking weakens the heart and impairs circulation. Smoking is a major cause of emphysema. Smoking has been linked directly to cancer of the mouth and the esophagus. DIFFERENCES BETWEEN A TOPIC SENTENCE AND A THESIS
Topic + Stance + Reasons. Adding reasons to your stance makes your point stronger from the start. You might know all the reasons right away, but you can add them as you go. By being clear from the start, your planning process and your essay itself will be clearer. (Topic + Stance) We should not allow the military to recruit in high schools.
This video explains the difference between the Thesis Statement and the Topic Sentence. After you watch this, you will clearly understand what each one is. H...
Thesis Statements. A strong component of academic writing that all writers must understand is the difference between subject, topic, and thesis. Knowing the difference between these three terms will help you create a strong argument for your paper. This handout is designed to help inform you about these three distinct introductory elements, and ...
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
As you begin to formulate a thesis for your essay, think about the following distinction between topic and thesis. A topic is a general area of inquiry; derived from the Greek topos (place), "topic" designates the general subject of your essay. For instance, "Munro Leaf's The Story of Ferdinand (1936) and Dr. Seuss's And to Think That I Saw It on Mulberry Street (1937) both respond to the rise ...
Reference sources are a great place to start when you're trying to choose or narrow a topic. They'll help you learn the language of the topic you're interested in, and help you gather: basic facts or established information on your topic. key concepts, terms, and people. related topics and, often, suggested resources for learning more.
After being introduced during the K-12 years of a student's education, academic writing is a mainstay in college and higher education. With proper format and technique being a major aspect of academic writing, it is essential for students to understand the differences between a topic sentence and a thesis ...
This video explains how to understand the differences between a topic, a theme, and a thesis statement, and the need to have a solid thesis statement as the ...
The chart below points out some of the main differences between a topic sentence that is genuinely helpful to you and your readers, and one which is not: ... Helps your reader see how this paragraph relates to and advances/supports your thesis; SOME GUIDELINES FOR WRITING STRONG TOPIC SENTENCES: A topic sentence must predict or promise what ...
Step 2: Make an essay outline and draft topic sentences. Next, you should make an outline of your essay's structure, planning what you want to say in each paragraph and what evidence you'll use. At this stage, you can draft a topic sentence that sums up the main point you want to make in each paragraph. The topic sentences should be more ...
A thesis. The difference between a thesis and a topic sentence is that a thesis is a statement that expresses the main idea of an essay or research paper, while a topic sentence is a sentence that introduces a new idea or concept in a paragraph. A thesis is usually more specific and takes more research to create than a topic sentence, which is ...
Thesis statements summarize the central position of an entire essay and typically appear at the end of the introductory paragraph. Think of them as guideposts for the entire essay. They provide the reader of the essay an idea of the direction it will take. While beginning essay writers will typically write a single-sentence thesis statement ...
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools. A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be…
thesis and topic sentences are related and support each other. How does this tool applies to the big picture of writing? It is essential in every essay because without the connection between the thesis and the topic sentences , the essay will be incorrect.
As nouns the difference between thesis and topic is that thesis is a statement supported by arguments while topic is subject; theme; a category or general area of interest. As an adjective topic is (l). thesis . English. Noun (theses) A statement supported by arguments.
The primary difference between a dissertation and a thesis lies in their purpose and structure. A dissertation aims to contribute new knowledge to a specific field of study and is typically a more extensive and comprehensive project. It involves an in-depth exploration of a research problem or question, often requiring the collection and ...