Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay
- Introduction
- Thesis Statement

Background study
- Impacts of online education
Introduction to Online Education
Online learning is one of the new innovative study methods that have been introduced in the pedagogy field. In the last few years, there has been a great shift in the training methods. Students can now learn remotely using the internet and computers.
Online learning comes in many forms and has been developing with the introduction of new technologies. Most universities, high schools, and other institutions in the world have all instituted this form of learning, and the student population in the online class is increasing fast. There has been a lot of research on the impacts of online education as compared to ordinary classroom education.
If the goal is to draw a conclusion of online education, considerable differences between the online learning environment and classroom environment should be acknowledged. In the former, teachers and students don’t meet physically as opposed to the latter, where they interact face to face. In this essay, the challenges and impact of online classes on students, teachers, and institutions involved were examined.
Thesis Statement about Online Classes
Thus, the thesis statement about online classes will be as follows:
Online learning has a positive impact on the learners, teachers, and the institution offering these courses.
Online learning or E learning is a term used to describe various learning environments that are conducted and supported by the use of computers and the internet. There are a number of definitions and terminologies that are used to describe online learning.
These include E learning, distance learning, and computer learning, among others (Anon, 2001). Distant learning is one of the terminologies used in E learning and encompasses all learning methods that are used to train students that are geographically away from the training school. Online learning, on the other hand, is used to describe all the learning methods that are supported by the Internet (Moore et al., 2011).
Another terminology that is used is E learning which most authors have described as a learning method that is supported by the use of computers, web-enabled communication, and the use of new technological tools that enhance communication (Spector, 2008). Other terminologies that are used to describe this form of online learning are virtual learning, collaborative learning, web-based learning, and computer-supported collaborative learning (Conrad, 2006).
Impacts of Online Classes on Students
Various studies and articles document the merits, demerits, and challenges of online studies. These studies show that online study is far beneficial to the students, teachers, and the institution in general and that the current challenges can be overcome through technological advancement and increasing efficiency of the learning process.
One of the key advantages of online learning is the ability of students to study in their own comfort. For a long time, students had to leave their comfort areas and attend lectures. This change in environment causes a lack of concentration in students. In contrast, E-learning enables the students to choose the best environment for study, and this promotes their ability to understand. As a result, students enjoy the learning process as compared to conventional classroom learning.
Another benefit is time and cost savings. Online students are able to study at home, and this saves them travel and accommodation costs. This is in contrast with the classroom environment, where learners have to pay for transport and accommodation costs as well as any other costs associated with the learning process.
Online study has been found to reduce the workload on the tutors. Most of the online notes and books are availed to the students, and this reduces the teacher’s workload. Due to the availability of teaching materials online, tutors are not required to search for materials. Teachers usually prepare lessons, and this reduces the task of training students over and over again.
Accessibility to learning materials is another benefit of online learning. Students participating in online study have unlimited access to learning materials, which gives them the ability to study effectively and efficiently. On the other hand, students in the classroom environment have to take notes as the lecture progress, and these notes may not be accurate as compared to the materials uploaded on the websites.
Unlimited resources are another advantage of online study. Traditionally, learning institutions were limited in the number of students that could study in the classroom environment. The limitations of facilities such as lecture theaters and teachers limited student enrollment in schools (Burgess & Russell, 2003).
However, with the advent of online studies, physical limitations imposed by classrooms, tutors, and other resources have been eliminated. A vast number of students can now study in the same institution and be able to access the learning materials online. The use of online media for training enables a vast number of students to access materials online, and this promotes the learning process.
Promoting online study has been found by most researchers to open the students to vast resources that are found on the internet. Most of the students in the classroom environment rely on the tutors’ notes and explanations for them to understand a given concept.
However, students using the web to study most of the time are likely to be exposed to the vast online educational resources that are available. This results in the students gaining a better understanding of the concept as opposed to those in the classroom environment (Berge & Giles, 2008).
An online study environment allows tutors to update their notes and other materials much faster as compared to the classroom environment. This ensures that the students receive up-to-date information on a given study area.
One of the main benefits of E-learning to institutions is the ability to provide training to a large number of students located in any corner of the world. These students are charged training fees, and this increases the money available to the institution. This extra income can be used to develop new educational facilities, and these will promote education further (Gilli et al., 2002).
Despite the many advantages that online study has in transforming the learning process, there are some challenges imposed by the method. One of the challenges is the technological limitations of the current computers, which affect the quality of the learning materials and the learning process in general.
Low download speed and slow internet connectivity affect the availability of learning materials. This problem is, however, been reduced through the application of new software and hardware elements that have high access speeds. This makes it easier to download learning materials and applications. As computing power increases, better and faster computers are being unveiled, and these will enable better access to online study facilities.
Another disadvantage of online learning as compared to the classroom environment is the lack of feedback from the students. In the classroom environment, students listen to the lecture and ask the tutors questions and clarifications any issues they didn’t understand. In the online environment, the response by the teacher may not be immediate, and students who don’t understand a given concept may find it hard to liaise with the teachers.
The problem is, however, been circumvented by the use of simple explanation methods, slideshows, and encouraging discussion forums between the teachers and students. In the discussion forums, students who don’t understand a concept can leave a comment or question, which will be answered by the tutor later.
Like any other form of learning, online studies have a number of benefits and challenges. It is, therefore, not logical to discredit online learning due to the negative impacts of this training method. Furthermore, the benefits of e-learning far outweigh the challenges.
Conclusion about Online Education
In culmination, a comparative study between classroom study and online study was carried out. The study was done by examining the findings recorded in books and journals on the applicability of online learning to students. The study revealed that online learning has many benefits as compared to conventional learning in the classroom environment.
Though online learning has several challenges, such as a lack of feedback from students and a lack of the proper technology to effectively conduct online learning, these limitations can be overcome by upgrading the E-Leaning systems and the use of online discussion forums and new web-based software.
In conclusion, online learning is beneficial to the students, tutors, and the institution offering these courses. I would therefore recommend that online learning be implemented in all learning institutions, and research on how to improve this learning process should be carried out.
Anon, C. (2001). E-learning is taking off in Europe. Industrial and Commercial Training , 33 (7), 280-282.
Berge, Z., & Giles, L. (2008). Implementing and sustaining e-learning in the workplace. International Journal of Web-Based Learning and Teaching Technologies , 3(3), 44-53.
Burgess, J. & Russell, J. (2003).The effectiveness of distance learning initiatives in organizations. Journal of Vocational Behaviour , 63 (2),289-303.
Conrad, D. (2006). E-Learning and social change, Perspectives on higher education in the digital age . New York: Nova Science Publishers.
Gilli, R., Pulcini, M., Tonchia, S. & Zavagno, M. (2002), E-learning: A strategic Instrument. International Journal of Business Performance Management , 4 (1), 2-4.
Moore, J. L., Camille, D. & Galyen, K. (2011). E-Learning, online learning and distance learning environments: Are they the same? Internet and Higher Education, 14(1), 129-135.
Spector, J., Merrill, M., Merrienboer, J. & Driscoll, M. P. (2008). Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (3rd ed.), New York: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 28). Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/
"Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." IvyPanda , 28 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay'. 28 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay." October 28, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/impact-of-online-courses-on-education/.
- The Concept of Medical Terminology
- Healthcare Terminologies and Classification Systems
- Medical terminology
- Medical terminology errors
- Research Process and Terminology: Criminal Justice
- Medical Terminology as a Communication Barrier
- The Impact of Standardized Nursing Terminology
- Students With Children and Teachers’ High Expectations
- Medical Terminology Abbreviations
- Nursing Terminologies: NANDA International
- Strategies for Motivating Students
- Importance of Sexual Education in School
- New School Program in Seattle
- General Education Courses
- E-learning as an Integral Part of Education System

Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
Students are often asked to write an essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
Introduction.
Online classes during lockdown have become a new normal. Schools shut down, but learning never stopped, thanks to technology.
Online classes provide flexibility and convenience. Students can learn from the safety of their homes, reducing the risk of virus spread.
However, it’s not all rosy. Some students face issues with internet access and distractions at home.
Despite challenges, online classes have ensured uninterrupted learning. They are a testament to human adaptability in crisis times.
250 Words Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
The COVID-19 pandemic has necessitated a dramatic shift in the educational landscape, with online classes becoming the new norm. This abrupt transition has brought both challenges and opportunities for students and educators alike.
Benefits of Online Learning
Online classes have enabled uninterrupted learning during lockdown. With the ability to access course materials anytime and anywhere, students have the flexibility to learn at their own pace. This self-paced learning can enhance understanding and retention. Furthermore, online platforms facilitate the use of multimedia content, making learning interactive and engaging.
Challenges and Solutions
However, online learning is not without its challenges. Issues such as lack of access to technology, internet connectivity, and a suitable learning environment can hinder students’ progress. To mitigate these, institutions can provide technological support, while governments can invest in improving internet infrastructure.
Moreover, the lack of face-to-face interaction can lead to feelings of isolation. To counter this, educators can foster a sense of community through discussion forums, group projects, and regular video conferencing.
In conclusion, while online classes during lockdown have presented a unique set of challenges, they have also opened up new avenues for learning. As we navigate this new normal, it is crucial to address the challenges and leverage the opportunities to ensure quality education for all. The pandemic has underscored the importance of adaptability and resilience, qualities that will serve students well in their future endeavors.
500 Words Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically reshaped the education sector worldwide. As lockdowns and social distancing measures were implemented, traditional classroom-based education was abruptly disrupted. In response, online classes emerged as a lifeline, ensuring the continuity of learning during lockdown.
The Transition to Online Learning
The shift from physical classrooms to digital platforms was sudden and unprecedented. Schools, colleges, and universities were compelled to adopt online teaching methods, utilizing various digital platforms like Zoom, Google Classroom, and Microsoft Teams. This transition was not without its challenges. It required a significant adaptation from both educators and students, who had to become familiar with new technologies and methodologies.
The Advantages of Online Classes
Despite the challenges, online classes have presented several advantages. First, they have allowed learning to continue in the face of a global crisis. Second, they have provided a flexible learning environment, where students can learn at their own pace and according to their own schedules. Third, online classes have broadened access to education, allowing students from remote or disadvantaged backgrounds to participate in learning activities that would otherwise be inaccessible.
The Challenges of Online Learning
However, online learning has also exposed several issues. The digital divide has become more apparent, with students from lower socio-economic backgrounds struggling to access the necessary technology and stable internet connections. Additionally, online learning requires a high level of self-discipline and motivation, which can be challenging for many students. There is also the issue of reduced social interaction, which can impact students’ mental health and sense of community.
The Role of Instructors in Online Learning
Instructors have had to adapt their teaching methodologies for the online environment. This has involved learning how to use new technologies, creating engaging online content, and developing strategies to monitor and assess student progress remotely. The role of the instructor has expanded to include not only teaching but also providing emotional support and encouragement to students navigating this new learning landscape.
The Future of Online Learning
The experience of online classes during lockdown has highlighted the potential of digital learning. It has shown that education can be made more accessible, flexible, and adaptable through the use of technology. However, it has also underscored the need for strategies to address the challenges that online learning presents. As we move forward, the lessons learned during this period can inform the development of more effective and inclusive online learning systems.
In conclusion, online classes during lockdown have been a crucial response to an unprecedented global crisis. They have ensured the continuity of education while also revealing both the potential and the challenges of online learning. As we emerge from the pandemic, these insights can guide us in creating a more resilient and inclusive educational system for the future.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Yoga Fitness for Humanity
- Essay on Service to Humanity is Service to God
- Essay on Humanity
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
COVID-19: A Framework for Effective Delivering of Online Classes During Lockdown
- Arena of Pandemic
- Published: 30 January 2021
- Volume 5 , pages 322–336, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Digvijay Pandey ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0353-174X 1 ,
- Gabriel A. Ogunmola 2 ,
- Wegayehu Enbeyle 3 ,
- Marzuk Abdullahi 4 ,
- Binay Kumar Pandey 5 &
- Sabyasachi Pramanik 6
18k Accesses
24 Citations
Explore all metrics
A Correction to this article was published on 12 May 2021
This article has been updated
The world as we know it has changed over a short period of time, with the rise and spread of the deadly novel Corona virus known as COVID-19, the world will never be the same again. This study explores the devastating effects of the novel virus pandemic, the resulting lockdown, thus the need to transform the offline classroom into an online classroom. It explores and describes the numerous online teaching platforms, study materials, techniques, and technologies’ being used to ensure that educating the students does not stop. Furthermore, it identifies the platforms, technologies which can be used to conduct online examination in a safe environment devoid of cheating. Additionally, it explores the challenges facing the deployment of online teaching methods. On the basis of literature review, a framework was proposed to deliver superior online class room experience for the students, so that online classroom is as effective as or even better than offline classrooms. The identified variables were empirically tested with the aid of a structured questionnaire; there were 487(according to Craitier and Morgan)150 number of respondents who were purposefully sampled. The results indicate that students prefer the multimedia means of studies. As a result of binary logistic regression, poor internet connection, awareness on COVID-19, enough sources of materials, recommends massive open online course, favourite online methods, and satisfaction with online study are significant in the model or attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic at 5% level of significance. The study recommends online teaching methods, but finally, the study concludes that satisfaction with online study is significant in the model or attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic at 5% level of significance.
Similar content being viewed by others

COVID-19: Creating a Paradigm Shift in Indian Education System

Covid-19: Study of Online Teaching, Availability and Use of Technological Resources

Challenges Faced by the University Students During COVID-19 Pandemic in Poland
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The Corona virus pandemic is a strange viral infection that is highly transmittable especially from person to person. The COVID-19 infectivity that is caused by a completely unique mental strain of corona virus was first detected in Wuhan, China, in the last week of December 2019 and acknowledged a world health emergency of international concern by the World Health Organization on January 30, 2020. The World Health Organization has confirmed the fast-moving coronavirus outbreak in China, a “world health emergency of worldwide concern” ( https://doi.org/10.1021/cen-09805-buscon4 ). Eventually, the disease continues to spread across the globe, killing many, and collapsing the various economic, educational, and social activities across the globe.
Death rate ranges between 2 and 3%. It is drastically less severe than 2003 SARS (MR 10%) or 2012 MERS (MR 35%) outbreaks. Threat of decease is merely high in older people (above an age of ~ 60 years) and other people with pre-active health conditions, and approximately 80% of individuals have gentle symptoms and get over the sickness in 2 weeks. The majority of the symptoms are often treated on time medication (John Hopkins Center for System Science and Engineering (Live dashboard), as reported on March 11, 2020).
In view of the forgoing, all institutions of learning across the globe are subjected to an imminent and unavoidable indefinite break. This is an attempt to stop the virus from affecting the students or the teachers. This however has brought about lackadaisical attitudes among the students at home because they are idle and thus thinking nothing but evil.
Most countries across in the world including my country, Nigeria, have developed a way of engaging this students at home, and in some developed countries like the USA, students have resume back to school facelessly (via online). In Nigeria; a platform was developed online for educational used by students and any other researcher (academia.nitda.gov.ng). This is a laudable initiative but hampered by resources like electricity, internet, and to some awareness.
Consequently, all hands are now on desk, reviewing academic online platforms and updating it to meet up with the peculiarities of our day-to-day challenges while making it easy for studies and evaluations of student’s academic performance. This is the quest for this research work. Research problem: the global method of teaching is physical dialogue, whereby students and teachers will meet on a scheduled venue and physically interact. With the advent of these pandemic, public gatherings are prohibited; this makes it impossible for teaching to continue, so long as there is going to be person-to-person contact.
Hence, the need for a platform that will substitute the obsolete means of teaching in an effective and efficient method with the capability of evaluating students academic performance is imminent. Research gap: there are no academic researches on this topic; researches are yet to study online classes platforms, etc.
Objectives: The study explores and describes the present state of online classes, opportunities, and challenges. It is a novel research on the techniques and method adopted by teachers to bring the offline classroom online. The key goal of the learning is to assess socio-demographic and related factors on the attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic in India.
Literature Review
The approach of online-learning as an aspect of the synergistic study worldwide incorporates Web 2.0 advances, which are in the main used by our understudies and are presently enhancing into the homeroom. Teachers state that these innovative advances extremely help increments to their DE homerooms as they will upgrade learning among our technically knowledgeable understudies, reflecting the usage of those advances in their day-by-day lives. Web 2.0 main advances incorporate wikis, sites, broadcasts, informal communities, and online video-sharing destinations like YouTube. Teachers and scientists can foresee that new advances will in any case be presented, which can require transformation by the two understudies and educators, upheld by examination by analysts on their viability. It is essential to appear for “hints on how e-learning advances can turn out to be ground-breaking impetuses for change additionally as devices for updating our education and instructional frameworks” (Shroff & Vogel, 2009 , p.60).
The developing of instructional stages, likewise referenced as Knowledge Management Systems (KMS), is another advancement in ongoing DE history. Saadé & Kira ( 2009 ) depict Learning Management Systems (LMS) as a structure that has educator instruments, learning measure apparatuses, and a store of information. Tests of KMS stages incorporate WebCT, Blackboard, and DesireToLearn, which have risen on the grounds that the best three LMS are unavoidable in the present DE condition. Last Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment (Moodle) has developed as a substitution to LMS open-source framework, a free option to the previously mentioned stages (Unal & Unal, 2011 ). It is fundamental that the devices executed help the course tasks, exercises, and substance (Singh et al. 2010 ; Smart & Cappel, 2006 ). “Unmistakably, innovation upheld learning conditions can possibly flexibly instruments and structure to modify training” (Shroff & Vogel, 2009 , p. 60). The researchers used in this investigation are presented to Blackboard LMS through which understudies partake in conversation gatherings, online diaries, Wikis, Web-based testing and practice tests, virtual groups, YouTube, and other intelligent devices.
The idea of online-learning and hence the plan to utilize Moodle in college option came after a progression of global temporary jobs we were included and after a progression of on-line classes and stage setup for improving instructing ventures. There are numerous advantages of utilizing online instruction together with correspondence, collaboration between understudies, bunch improvement, and a superior admittance to information. Regardless of those advantages, numerous Romanian colleges regularly consent to stay in customary instructing without extra help. Moodle might be a learning stage initially planned by Martin Dougiamas (first form of Moodle was delivered on August 20, 2002). Moodle, as a solid open-source e-learning stage, was utilized and created by worldwide cooperative exertion of global network. Moodle is implied and proceed with improved to flexibly instructors, directors, and students with one vigorous, secure, and incorporated framework to make customized learning conditions. Presently, on March 27, 2014, Moodle 2.6.2 was launched. We consider Moodle a Web-based versatile community-oriented learning condition that contains all parts portrayed by Wang et al. ( 2004 ): conversation gathering and one-on-one companion help client model, collective methodology model, and versatile segment. A few creators were likewise inquisitive about cooperation and human correspondence on a Web-based collaborative learning environment (Zhang et al. 2004 ), while different creators call these virtual learning situations (Knight & Halkett, 2010 ). Comparative encounters of utilizing intelligent e-learning instruments as Moodle were portrayed by different creators (Beatty & Ulasewicz, 2006 ). They all pointed in their papers (Shen et al., 2006 ) that utilizing Moodle can build up understudies’ psychological blueprint, help to develop their insight, advance understudies’ uplifting mentalities towards talking about and helping out companions, and increment understudies’ aptitudes to embrace deep-rooted learning by utilizing the information innovation. Options as far as Web-based collaborative learning are given by Pfahl et al. ( 2001 ). During this adaptable online network for learning, understudies collaborate with course assets and are prepared to grow new abilities and to structure their own learning direction. Applying this e-learning stage, we exploited understudy’s spare time and their accessibility to spend and structure their activities (Arbaugh et al. 2009 ) in order to submit schoolwork regarding a firm cutoff time.
Massive open online courses (MOOCs) and open education research (OER) MOOCs are online courses that by and large permit anybody to enrol and complete without any extra fee (at any rate for the fundamental course). Cormier and Siemens [8] contend that they are a possible result of “open educating and study.” The degree of receptiveness in MOOCs varies from course to course and if the course is realistic on a MOOC stage, relying on the stage. While numerous cMOOCs offered its substance utilizing open authorizing, other MOOC suppliers just give the substance to privately utilize it as it were. For example, Coursera, single among the main xMOOC stages (Kibaru, 2018 ), expresses that the texture is “just for your very own, non-business use. you'll not in any case duplicate, imitate, retransmit, disseminate, distribute, monetarily abuse or in any case move any material, nor may you alter or make subsidiaries mechanism of the material” ( Rabe-Hemp et al., 2009 ). In this manner, yet a “by item” of the open education development, MOOCs appear to be less open than OERs, uninhibitedly available instructive substance, which are for the most part delivered with open authorizing.
E-learning Tools for Distance Education
With the growing concerns over COVID-19, many school districts have moved classroom instruction online for the foreseeable future. We understand that this change can present challenges on many levels for educators, administrators, students, and families. The following recommended tools may be helpful in making the transition to digital learning during this difficult time. These resources include general e-learning tools for educators, subject-based tools for students, and extensions to assist students with learning differences. Almost all of these resources are free, with the exception of a few inexpensive tools/available free trials (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). 2020.)
SOURCE: United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), 2020
Descriptive Analysis of Tools of Online Class MOOC
Impartus : This is the main video proposal for OER and training. Around 130 higher institutions in India are currently using this platform ( http://www.impartus.com ).
Webex : Webex is an online tool that allows you to virtually hold meetings without leaving your homes or offices. It only requires a computer with an internet access and a separate phone line. This is a product of Cisco Company and is capable giving access to up to 100 clients at a time. It is free to sign up but requires $49/month subscription ( http://www.webex.com ).
Zoom : This is another online livestreaming tool but it is a mobile app. It is available on Android and iOS. While online, you can record sessions, collaborate on projects, and share or annotate one another’s screen. It cost $14.99/month, and it allows meetings recording on the cloud. It has unlimited number of participants, but the meetings can only last for 40 min ( https://zoom.us ).
Google Classroom : This is an open source Web service provided by Google for education and training with the sole aspire of online evaluation of test and assignment in a paperless way. However, organizations must register their corporate account on G-Suit before they can use this service. The students only need a valid email account to get connected to the class. This is linked to Google Drive, Google Docs, and Gmail for efficient sharing of resources ( https://classroom.google.com ).
Microsoft Teams : This is designed by Microsoft as an all-round collaborative platform offering: chats, voice, and calling features. It allows instant messaging with inbuilt office 365 for manipulating documents with live stream. All you need to do is to subscribe to the Microsoft 365 business essentials package; however, this package cost $5/month and per single user ( https://support.office.com ).
Descriptive Tools for Online Classes
Internet learning content is available through various types (text, pictures, sounds, and curios) (Moore & Kearsley, 2012 ) and kinds of media (versatile, intelligent, account, profitable) (Laurillard, 2002 ). The educated client can utilize different Web-based learning assets to make a learning domain that suits his own adapting needs (for example, learning styles, singular openness needs, inspiration); moreover, to the information on different kinds of ICT, it is critical to know somebody’s very own adapting needs (Grant et al., 2009 ).
There are many online tools that are already in use to achieve online classes. It depends on the resources available for the organization to subscribe to such online services. Each of these tools has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of security, cost, and regional peculiarities. The below table can assist in analyzing some selected tools based on their cost and security.
Descriptive Analysis of Tools of Online Examination
For a complete online classroom, there is a need for an equivalent system/platform in place for an online examination evaluation. Many of such platforms are readily available online. It is left for organizations to analyse the available systems and choose the best that suits their requirements considering the cost and security of the model. Below are some selected tools fitted for that purpose;
TCexam : This is an open source system for electronic exam. It is also known as computer-based assessment (CBA) and computer-based test (CBT). It is free and does not require additional hardware to run.
Virtualx : This is a free online exam management information system. It is cloud-based, and it is an open source. It is user friendly and scalable to user requirements.
Moodle : This is a learning platform or course management system that is aimed at online automation of examinations. It gives the opportunity for lecturers to create their own personal websites. It is free and open source.
FlexiQuiz : This is a main online test producer that will work without human intervention and mark and grade your quizzes. It is an open source and free. And it is secured with SSL encryption technology.
EdBase : This is a powerful and flexible tool for online examinations and grading. It is cloud-based and free. It has the feature of creating question bank and autograding. It is easier in generating portable reports in different formats and is secured with SSL encryption technology.
Tabular comparison of online examination tools
Challenges of online classes.
Nowadays, smart KMS (Knowledge Management Systems) and LMS (Learning Management Systems) with technology inbuilt are in demand for increasing the need of self directness. Evidence have shown that students tend to understand better if multimedia (Adnan, 2018 ) tools are integrated into their teaching. Despite efforts by institutions to adapt the use of internet and ICT in teaching, most especially in the present condition of lockdowns, certain challenges are curtailing these efforts. Viz;
Lack of internet in most developing countries, like Africa: this proposed framework is purely online, and as such, reliable internet network is the backbone of its emergence. Most developing countries like Africa do not have sufficient internet network for their citizens, and this is a major setback for e-learning.
Security: The major challenge of anything online is security. This is because of the fair of cyber-attacks by hackers. Such a proposed framework will be handling students’ records and examination results. Any possible breach of access can result to serious information mismanagement. Hence, the need to put a serious security in place.
Lack of infrastructures like computers and ICT gadgets due to the level of poverty in some regions like Africa: for a successful online classroom, there must be resources to be sufficiently made available. These resources include network hardware, system hardware/software, and human resources, but due to economic factors of some countries, such provisions are relatively impossible and thus, a big challenge for e-learning.
Lack of power supply in many regions, like Africa: there cannot be technology without electricity and the issue of electricity is a regional challenge to Africans. Most universities in Nigeria were operating strictly on generators because there is no sufficient power supply. This makes it impossible for the students to gain access online as expected because they may not have the means of power supply while out of campus.
Lack of political will due to corruption in Africa: democracy is now a global rule of law. Though, every region or Country has its way of politics; in Africa corruption has pose major challenge in the development of the region and this makes it unfavourable for developmental trends like; ICT, Power etc.
Lack of scalable policies by government: In some countries, there are strict policies on the use of ICT; this might be due to the prevailing cybercrimes over the cyberspace and the process of adhering to such policies; it poses a great challenge in the development of educational technologies and other ICT-related platforms.
Lack of ICT knowledge/awareness among students and lecturers: In some countries and institutions, the knowledge of ICT is very scarce. In fact, some are resisting to accept technology as a modern science. They view the concept of ICT as an attempt to scam and hence, posing a very big challenge in the implementation of any ICT framework to such categories of Institutions/people.
Advantages of Online Classes
Easily accessible: you can log in anywhere you are, so long as you are online and you are registered on the platform. Unlike the traditional classroom where you to be at a scheduled venue, to receive lectures physically.
Unlimited access to resources: Most online-learning platforms are connected to an unlimited number of e-libraries from various academic institutions. Once you have access, you will gain access to unlimited e-books, journals, etc.
Flexibility in learning: Online-learning platforms simplify the methods of teaching, in the sense that lecturers can leave offline materials and assignments and each student can log in at his/her free time to download and act accordingly.
Sharing of resources is easier: Resources are easily shared via emails or direct download from the platform. Students do not need to go for photocopies or any physical stress.
Academic collaborations are enhanced: With the use of online teaching platforms, students collaborate far more than physically been in class. Such collaborations will assist them in group research and efficient time management for academic attainments.
Very portable and comfortable: Students can log in at their comfort zones. You can be in bed and still connect to the class and situation where you have travelled or lost your computer; all you need to do is to fine another one, connect to the internet, and log in to your classroom to continue your classes.
Possible Solutions to the Challenges of Online Classes
Nowadays, smart KMS (Knowledge Management Systems) and LMS (Learning Management Systems) with technology inbuilt is in demand for increasing the need of self directness (Gibson et al., 2008 ). Below are some proposed solutions to the aforementioned challenges;
Reliable internet network: The government should provide internet networks across the country at a subsidize rate. It is recommended that students been given free access to the internet while other citizens should pay either monthly or annually as proposed.
Sufficient power supply: Government should make available electricity to its citizens at a subsidise rate. This will bring about Industrialisations and thus, providing job opportunities among graduates.
Fighting corruption: The government should establish strong institutions for fighting corruption. These institutions should be independent and should have members from European, African Union (EAU), United Nations (UN), and any other intentional agency that is capable of checkmating the international affairs of a country.
Flexible government policies: Government should make their policies very favourable to their citizens. Government should be reviewing their policies routinely to curtail the shortcomings in their policies.
Strong ICT awareness: Students and the teachers should be train on ICT trends. The immediate societies should also be given awareness on the positive impacts of ICT in their environments.
Methodology
The study area will conduct in India and other country. The study populations are all populations who are delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19. A total of 150 respondents were included.
Study Design
A cross-sectional study design would be carried out. Cross-sectional survey design is mainly used for the collection of information on and related socio-demographic factors at a given point in time to attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown. The learning design for this learning was a traverse sectional survey conducted using population based representative sample. Variables are collected for several sample units at the same points in time (one time shoot), just the data collected from the respondents directly in a particular time. Cross-sectional surveys are used to gather information (Brecht & Ogilby, 2008 ) on a population at a single point in time. An example of a cross-sectional survey would be a questionnaire that collects data on peoples’ experiences of a particular initiative or event.
Source of Data
Primary data were collected from a community-based, cross-sectional survey. Primary data collection is the process of gathering data through surveys, interviews, or experiments. A typical aims for this study for data collection was primary data is online surveys by conducting well-done questions in India for 150 respondents. Online surveys were effective and therefore require computational logic and branching technologies for exponentially more accurate survey data collection versus any other traditional means of surveying. They are straightforward in their implementation and take a minimum time of the respondents (150). The investment required for survey data collection using online surveys is also negligible in comparison to the other methods. The results are collected in real-time for researchers to analyse and decide corrective measures.
Sampling Techniques
It is an inspecting method during which the choice of individuals for an example relies upon the possibility of comfort, individual decision or intrigue. For this examination we utilized judgment sampling. During this case, the individual taking the example has immediate or backhanded power over which things are chosen for the example.
Study Variables
The variables measured in this learning are taken based on previous studies at the global and national level. Those factors considered during this examination are delegated as: reliant and logical factors. The outcome variable is for the study attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19, which is dichotomous. The response variable for each respondent is given by:
The independent variables are measured from structural questionnaires. In this learning, the possible determinant factors estimated to be a significant effect on are included as variables. Poor internet connection, source of info about COVID-19, awareness on COVID-19, recommends MOOC, satisfaction with online study, materials and information sent, enough sources of materials, presently enrolled course, and favourite online methods were included for this study.
Methods of Data Analysis
In this study, frequency distribution, cross-tabulation, and percentage were applied to see the prevalence of the dependent variable. Binary logistic regression was applied to identify the factors for the outcome variable.
Binary Logistic Regression
Binary logistic regression is a prognostic model that is fitted where there is a dichotomous-/binary-dependent variable like in this instance where the researcher is interested in whether there was positive or negative. Usually, the categories are coded as “0” and “1” as it results is a straightforward interpretation. Binary logistic regression is the sort of regression used in our study (attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19). The model is given by
\(ln\left(\frac{{\pi }_{i}}{1-{\pi }_{i}}\right)={\beta }_{0} + {\beta }_{1}{X}_{1i}+{{\beta }_{2}X}_{2i}+ \dots \dots ..{\beta }_{k}{X}_{ki}\dots \dots \dots \dots \dots \dots \dots \dots ..\) (1 \()\) .
\(\frac{{\pi }_{i}}{1-{\pi }_{i}}= exp\left({\beta }_{0} + {\beta }_{1}{X}_{1i}+{{\beta }_{2}X}_{2i}+ \dots \dots ..{\beta }_{k}{X}_{ki}\right)\) ……… (2).
where: \({\pi }_{i}\) is the probability of success, \(1-{\pi }_{i}\) is the probability of failure \(,{\beta }_{0}\) is the constant term, \(\beta\) the regression coefficients, and \({X}_{i}\) are the independent variables. Logistic regression quantifies the relationship between the dichotomous dependent variable and the predictors using odds ratios. Odds ratio is the probability that an event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not happen. In this study, the odds ratio is the probability that attitudes towards delivering of online classes being negative divided by the probability that the attitudes towards delivering of online classes being positive. Method of maximum likelihood estimation yields to estimate values for the unknown parameters which maximize the probability of obtaining the observed set of knowledge. For logistic regression, the model coefficients are estimated by the utmost likelihood method and therefore the likelihood equations are non-linear explicit function of unknown parameters. For statistical analysis SAS version 9.4 software will be used at 5% level of significance.
Results and Discussion
Socio-economic variables are categorical. For our study the dependent variable might be “positive” or “negative.” In this case we would carry out a binary logistic regression analysis.
Table 1 depicted that poor internet connection, awareness on COVID-19, enough sources of materials; recommends MOOC, favourite online methods, and satisfaction with online study are significant in the model. The positive parameter estimates indicated that there is a positive relationship between the dependent variable and associated independent variables whereas the negative coefficients parameters indicated that there is a negative relationship between a dependent variable and independent variables. Where, X 1 is poor internet connection (No), X 2 is favourite online methods(E-books), X 3 is favourite online methods(Videos), X 4 is enough sources of materials(Yes), X 5 is satisfaction with online study (Very satisfied), X 6 is satisfaction with online study(Satisfied), X 7 is recommends MOOC (No), and X 8 is awareness on COVID-19 (No). Fitted model is given by
The poor internet connection (lack of internet access) had statistically significant effect to the attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic. The odds ratio of the poor internet connection (no) equals exp (0.178) = 1.081(95% CI 1.320, 0.476) (adjusted for the other variables are constant); the results show that those students who had not good connection in the study area are 0.081 times more likely to be negative attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic compared with that of students who had good connection. Sufficient internet network for their students is a major problem setback for e-learning or online class. Without good way of connection with respect to internet, academic collaborations were not enhanced; without the use of online teaching platforms, students cannot collaborate far more than physically been in class. Such collaborations will not assist them in group research and efficient time management for academic attainments.
Awareness on COVID-19 had also statistically significant effect on delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic. This implies that will help to locate out the data and information gaps among the students regarding the COVID-19 and the misconceptions and credulous beliefs popular in the society about it. It will also provide expressive data which may be useful for the concerned authority and planning institutions that prepare plans of programs to tackle the COVID-19 disease. Students who had awareness about COVID-19 pandemic odds ratio = exp (− 0.303) = 0.739 (95% CI 0.634, 0.861) times less likely to be negative attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic compared students who had not awareness about COVID-19 pandemic.
Many of such platforms are readily available online; it is left for organizations to analyse the available systems and choose the best that suits their requirements considering the online methods of learning and teaching. Even though, favourite online methods had an important factor for attitudes towards delivering. The odds ratio of the favourite online methods exp (0.830) = 2.293 and exp (0.585) = 1.795 for e-books and videos respectively (adjusted other variables). This implies students whose favourite online methods e-books = 2.293 (95% CI 1.421, 3.701) times more likely to be negative attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic compared all. Although students whose favourite videos, online methods of learning = 1.795 times more likely to be negative attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic compared all. Overall, e-books and videos significantly affect than all on attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown.
The key objective of the study is to assess the socio-demographic and related factors on the attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic in India. Primary data were collected from a community-based, cross-sectional survey. Just the data collected from the respondents directly in a particular time. For this examination we utilized judgment sampling. We have used a sample of 150 participants. Accordingly, descriptive analysis (frequency distribution, cross-tabulation, and percentage) and binary logistic regression were used. Binary logistic regression was found to be the model that could be applied for the study to such a variable as the dependent could meet the assumptions that should be satisfied for methods to be fitted. The backward stepwise logistic regression started with a model with all the variables and excluded the variables with insignificant coefficients until the model was at its best predictive power. As a result of binary logistic regression, poor internet connection, awareness on COVID-19, enough sources of materials, recommends MOOC, favourite online methods, and satisfaction with online study are significant in the model or attitudes towards delivering of online classes during lockdown COVID-19 pandemic at 5% level of significance. The analysis of the significance of the logistic coefficients was done using likelihood ratio and Wald test. The model was considered to be valid since both the model fitting and the validation sample produced almost the same classification accuracy.
Change history
12 may 2021.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-021-00196-0
Adnan, M. (2018). Professional development in the transition to online teaching: the voice of entrant online instructors. ReCALL, 30 (1), 88–111. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0958344017000106 .
Article Google Scholar
Arbaugh, J. B., Godfrey, M. R., Johnson, M., Pollack, B. L., Niendorf, B., & Wresch, W. (2009). Research in online and blended learning in the business disciplines: key findings and possible future directions. Internet and Higher Education, 12, 71–87
Beatty, B., & Ulasewicz, C. (2006). Faculty perception on movingfrom blackboard to the Moodle learning management system, TechTrends: Linking Research and Practice to Improve Learning, 50 (4), 36-45
Brecht, H., & Ogilby, S. M. (2008). Enabling a comprehensive teaching strategy: video lectures. Journal of Information Technology Education, 7 , IIP71-IIP86. Retrieved from https://www.jite.org/documents/Vol7/JITEV7IIP071-086Brecht371.pdf .
Gibson, S., Harris, M., & Colaric, S. (2008). Technology acceptance in an academic context: faculty acceptance of online education. Journal of Education for Business, 83 (6), 355–359
Grant, D. M., Malloy, A. D., & Murphy, M. C. (2009). A comparison of student perceptions of their computer skills and their actual abilities. Journal of Information Technology Education: 8 , 141–160. Retrieved from https://www.jite.org/documents/Vol8/JITEv8p141-160Grant428.pdf .
Kibaru, F. (2018).Supporting faculty to face challenges in design and delivery of quality courses in virtual learning environments. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 19 (4), 176–197. https://doi.org/10.17718/tojde.471915 .
Knight, S. A. & Halkett, G. K. B. (2010). Living systems, complexity & information systems science. Paper presented at the Australasian Conference in Information Systems (ACIS-2010), Brisbane, Australia
Laurillard, D. (2002). Rethinking University Teaching . London: Routledge, https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315012940 .
Moore, M., & Kearsley, G. (2012). Distance education: A systems view of online learning . Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Google Scholar
Pfahl, D., Angkasaputra, N., Differding, C., & Ruhe, G. (2001): CORONET-Train: A methodology for web-based collaborative learning in software Organizations. In: Althoff, K.-D., Feldmann, R.L., & Müller, W. (eds.) LSO 2001. LNCS, vol. 2176, p. 37. Springer, Heidelberg
Rabe-Hemp, C., Woollen, S., & Humiston, G. (2009).A comparative analysis of student engagement, learning, and satisfaction in lecture hall and online learning settings. Quarterly Review of Distance Education, 10 (2), 207–218
Saadé, G. R., & Kira, D. (2009). The e-motional factor of e-learning. Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks, 13 (4), 57-72
Shen, D., Laffey, J., Lin, Y. & Huang, X. (2006). Social influence for perceived usefulness and ease-of-use of course delivery systems. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, vol. 5, No. 3 , Winter. Retrieved [May 12, 2010] from https://www.ncolr.org/jiol/issues/PDF/5.3.4.pdf . In press
Shroff, R., & Vogel, D. (2009). Assessing the factors deemed to support individual student Intrinsic motivation in technology supported onlineand face-to-face discussions. Retrieved 7 December 2020, from https://doi.org/10.28945/160 .
Singh, A., Mangalaraj, G., & Taneja, A. (2010). "Bolstering teaching through online tools," Journal of Information Systems Education: Vol. 21 : Iss. 3 , 299-312. Available at: https://aisel.aisnet.org/jise/vol21/iss3/4
Smart, K.L. & Cappel, J.J. (2006). Students’ perceptions of online learning: A comparative study. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 5 (1), 201-219. Informing Science Institute. Retrieved December 7, 2020 from https://www.learntechlib.org/p/111541/ .
Unal, Z., & Unal, A. (2011). Evaluating and comparing the usability of web-based course management systems. Journal Of Information Technology Education: Research, 10, 019-038. https://doi.org/10.28945/1358 .
Wang, Y., Li, X. & Gu, R. (2004). Web-Based Adaptive Collaborative Learning Environment Designing, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, LNCS 3143, 163168
Zhang, X., Luo, N., Jiang, D. X., Liu, H., & Zhang, W. (2004). Web-based collaborative learning focused on the Study of Interaction and Human Communication. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, LNCS, 3143, 113–119
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Technical Education, IET, Dr A.P.J Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow, India
Digvijay Pandey
Faculty of Management, Sharda University, Andijan, Uzbekistan
Gabriel A. Ogunmola
Department of Statistics, Mizan-Tepi University, Tepi, Ethiopia
Wegayehu Enbeyle
Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Sule Lamido University, Jigawa State, Kafin Hausa, Nigeria
Marzuk Abdullahi
Department of IT, COT, Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Uttarakhand, Pantnagar, India
Binay Kumar Pandey
Haldia Institute of Technology, Haldia, India
Sabyasachi Pramanik
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Digvijay Pandey .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article unfortunately contained mistake. The affiliation address of Wegayehu Enbeyle should be changed to Department of Statistics, Mizan-Tepi University, Tepi, Ethiopia
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Pandey, D., Ogunmola, G.A., Enbeyle, W. et al. COVID-19: A Framework for Effective Delivering of Online Classes During Lockdown. Hu Arenas 5 , 322–336 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-020-00175-x
Download citation
Received : 28 September 2020
Revised : 25 November 2020
Accepted : 01 December 2020
Published : 30 January 2021
Issue Date : June 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42087-020-00175-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- E-learning tools
- Online learning
- Binary logistic regression
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 25 January 2021
Online education in the post-COVID era
- Barbara B. Lockee 1
Nature Electronics volume 4 , pages 5–6 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
138k Accesses
204 Citations
337 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The coronavirus pandemic has forced students and educators across all levels of education to rapidly adapt to online learning. The impact of this — and the developments required to make it work — could permanently change how education is delivered.
The COVID-19 pandemic has forced the world to engage in the ubiquitous use of virtual learning. And while online and distance learning has been used before to maintain continuity in education, such as in the aftermath of earthquakes 1 , the scale of the current crisis is unprecedented. Speculation has now also begun about what the lasting effects of this will be and what education may look like in the post-COVID era. For some, an immediate retreat to the traditions of the physical classroom is required. But for others, the forced shift to online education is a moment of change and a time to reimagine how education could be delivered 2 .

Looking back
Online education has traditionally been viewed as an alternative pathway, one that is particularly well suited to adult learners seeking higher education opportunities. However, the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has required educators and students across all levels of education to adapt quickly to virtual courses. (The term ‘emergency remote teaching’ was coined in the early stages of the pandemic to describe the temporary nature of this transition 3 .) In some cases, instruction shifted online, then returned to the physical classroom, and then shifted back online due to further surges in the rate of infection. In other cases, instruction was offered using a combination of remote delivery and face-to-face: that is, students can attend online or in person (referred to as the HyFlex model 4 ). In either case, instructors just had to figure out how to make it work, considering the affordances and constraints of the specific learning environment to create learning experiences that were feasible and effective.
The use of varied delivery modes does, in fact, have a long history in education. Mechanical (and then later electronic) teaching machines have provided individualized learning programmes since the 1950s and the work of B. F. Skinner 5 , who proposed using technology to walk individual learners through carefully designed sequences of instruction with immediate feedback indicating the accuracy of their response. Skinner’s notions formed the first formalized representations of programmed learning, or ‘designed’ learning experiences. Then, in the 1960s, Fred Keller developed a personalized system of instruction 6 , in which students first read assigned course materials on their own, followed by one-on-one assessment sessions with a tutor, gaining permission to move ahead only after demonstrating mastery of the instructional material. Occasional class meetings were held to discuss concepts, answer questions and provide opportunities for social interaction. A personalized system of instruction was designed on the premise that initial engagement with content could be done independently, then discussed and applied in the social context of a classroom.
These predecessors to contemporary online education leveraged key principles of instructional design — the systematic process of applying psychological principles of human learning to the creation of effective instructional solutions — to consider which methods (and their corresponding learning environments) would effectively engage students to attain the targeted learning outcomes. In other words, they considered what choices about the planning and implementation of the learning experience can lead to student success. Such early educational innovations laid the groundwork for contemporary virtual learning, which itself incorporates a variety of instructional approaches and combinations of delivery modes.
Online learning and the pandemic
Fast forward to 2020, and various further educational innovations have occurred to make the universal adoption of remote learning a possibility. One key challenge is access. Here, extensive problems remain, including the lack of Internet connectivity in some locations, especially rural ones, and the competing needs among family members for the use of home technology. However, creative solutions have emerged to provide students and families with the facilities and resources needed to engage in and successfully complete coursework 7 . For example, school buses have been used to provide mobile hotspots, and class packets have been sent by mail and instructional presentations aired on local public broadcasting stations. The year 2020 has also seen increased availability and adoption of electronic resources and activities that can now be integrated into online learning experiences. Synchronous online conferencing systems, such as Zoom and Google Meet, have allowed experts from anywhere in the world to join online classrooms 8 and have allowed presentations to be recorded for individual learners to watch at a time most convenient for them. Furthermore, the importance of hands-on, experiential learning has led to innovations such as virtual field trips and virtual labs 9 . A capacity to serve learners of all ages has thus now been effectively established, and the next generation of online education can move from an enterprise that largely serves adult learners and higher education to one that increasingly serves younger learners, in primary and secondary education and from ages 5 to 18.
The COVID-19 pandemic is also likely to have a lasting effect on lesson design. The constraints of the pandemic provided an opportunity for educators to consider new strategies to teach targeted concepts. Though rethinking of instructional approaches was forced and hurried, the experience has served as a rare chance to reconsider strategies that best facilitate learning within the affordances and constraints of the online context. In particular, greater variance in teaching and learning activities will continue to question the importance of ‘seat time’ as the standard on which educational credits are based 10 — lengthy Zoom sessions are seldom instructionally necessary and are not aligned with the psychological principles of how humans learn. Interaction is important for learning but forced interactions among students for the sake of interaction is neither motivating nor beneficial.
While the blurring of the lines between traditional and distance education has been noted for several decades 11 , the pandemic has quickly advanced the erasure of these boundaries. Less single mode, more multi-mode (and thus more educator choices) is becoming the norm due to enhanced infrastructure and developed skill sets that allow people to move across different delivery systems 12 . The well-established best practices of hybrid or blended teaching and learning 13 have served as a guide for new combinations of instructional delivery that have developed in response to the shift to virtual learning. The use of multiple delivery modes is likely to remain, and will be a feature employed with learners of all ages 14 , 15 . Future iterations of online education will no longer be bound to the traditions of single teaching modes, as educators can support pedagogical approaches from a menu of instructional delivery options, a mix that has been supported by previous generations of online educators 16 .
Also significant are the changes to how learning outcomes are determined in online settings. Many educators have altered the ways in which student achievement is measured, eliminating assignments and changing assessment strategies altogether 17 . Such alterations include determining learning through strategies that leverage the online delivery mode, such as interactive discussions, student-led teaching and the use of games to increase motivation and attention. Specific changes that are likely to continue include flexible or extended deadlines for assignment completion 18 , more student choice regarding measures of learning, and more authentic experiences that involve the meaningful application of newly learned skills and knowledge 19 , for example, team-based projects that involve multiple creative and social media tools in support of collaborative problem solving.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, technological and administrative systems for implementing online learning, and the infrastructure that supports its access and delivery, had to adapt quickly. While access remains a significant issue for many, extensive resources have been allocated and processes developed to connect learners with course activities and materials, to facilitate communication between instructors and students, and to manage the administration of online learning. Paths for greater access and opportunities to online education have now been forged, and there is a clear route for the next generation of adopters of online education.
Before the pandemic, the primary purpose of distance and online education was providing access to instruction for those otherwise unable to participate in a traditional, place-based academic programme. As its purpose has shifted to supporting continuity of instruction, its audience, as well as the wider learning ecosystem, has changed. It will be interesting to see which aspects of emergency remote teaching remain in the next generation of education, when the threat of COVID-19 is no longer a factor. But online education will undoubtedly find new audiences. And the flexibility and learning possibilities that have emerged from necessity are likely to shift the expectations of students and educators, diminishing further the line between classroom-based instruction and virtual learning.
Mackey, J., Gilmore, F., Dabner, N., Breeze, D. & Buckley, P. J. Online Learn. Teach. 8 , 35–48 (2012).
Google Scholar
Sands, T. & Shushok, F. The COVID-19 higher education shove. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/3o2vHbX (16 October 2020).
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T. & Bond, M. A. The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/38084Lh (27 March 2020).
Beatty, B. J. (ed.) Hybrid-Flexible Course Design Ch. 1.4 https://go.nature.com/3o6Sjb2 (EdTech Books, 2019).
Skinner, B. F. Science 128 , 969–977 (1958).
Article Google Scholar
Keller, F. S. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 1 , 79–89 (1968).
Darling-Hammond, L. et al. Restarting and Reinventing School: Learning in the Time of COVID and Beyond (Learning Policy Institute, 2020).
Fulton, C. Information Learn. Sci . 121 , 579–585 (2020).
Pennisi, E. Science 369 , 239–240 (2020).
Silva, E. & White, T. Change The Magazine Higher Learn. 47 , 68–72 (2015).
McIsaac, M. S. & Gunawardena, C. N. in Handbook of Research for Educational Communications and Technology (ed. Jonassen, D. H.) Ch. 13 (Simon & Schuster Macmillan, 1996).
Irvine, V. The landscape of merging modalities. Educause Review https://go.nature.com/2MjiBc9 (26 October 2020).
Stein, J. & Graham, C. Essentials for Blended Learning Ch. 1 (Routledge, 2020).
Maloy, R. W., Trust, T. & Edwards, S. A. Variety is the spice of remote learning. Medium https://go.nature.com/34Y1NxI (24 August 2020).
Lockee, B. J. Appl. Instructional Des . https://go.nature.com/3b0ddoC (2020).
Dunlap, J. & Lowenthal, P. Open Praxis 10 , 79–89 (2018).
Johnson, N., Veletsianos, G. & Seaman, J. Online Learn. 24 , 6–21 (2020).
Vaughan, N. D., Cleveland-Innes, M. & Garrison, D. R. Assessment in Teaching in Blended Learning Environments: Creating and Sustaining Communities of Inquiry (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2013).
Conrad, D. & Openo, J. Assessment Strategies for Online Learning: Engagement and Authenticity (Athabasca Univ. Press, 2018).
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA, USA
Barbara B. Lockee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Barbara B. Lockee .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The author declares no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Lockee, B.B. Online education in the post-COVID era. Nat Electron 4 , 5–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Download citation
Published : 25 January 2021
Issue Date : January 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-020-00534-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
A comparative study on the effectiveness of online and in-class team-based learning on student performance and perceptions in virtual simulation experiments.
BMC Medical Education (2024)
Leveraging privacy profiles to empower users in the digital society
- Davide Di Ruscio
- Paola Inverardi
- Phuong T. Nguyen
Automated Software Engineering (2024)
Growth mindset and social comparison effects in a peer virtual learning environment
- Pamela Sheffler
- Cecilia S. Cheung
Social Psychology of Education (2024)
Nursing students’ learning flow, self-efficacy and satisfaction in virtual clinical simulation and clinical case seminar
- Sunghee H. Tak
BMC Nursing (2023)
Online learning for WHO priority diseases with pandemic potential: evidence from existing courses and preparing for Disease X
- Heini Utunen
- Corentin Piroux
Archives of Public Health (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how

With schools shut across the world, millions of children have had to adapt to new types of learning. Image: REUTERS/Gonzalo Fuentes
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Cathy Li
Farah lalani.
.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Education, Gender and Work is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, education, gender and work.
- The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom.
- As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms.
- Research suggests that online learning has been shown to increase retention of information, and take less time, meaning the changes coronavirus have caused might be here to stay.
While countries are at different points in their COVID-19 infection rates, worldwide there are currently more than 1.2 billion children in 186 countries affected by school closures due to the pandemic. In Denmark, children up to the age of 11 are returning to nurseries and schools after initially closing on 12 March , but in South Korea students are responding to roll calls from their teachers online .
With this sudden shift away from the classroom in many parts of the globe, some are wondering whether the adoption of online learning will continue to persist post-pandemic, and how such a shift would impact the worldwide education market.

Even before COVID-19, there was already high growth and adoption in education technology, with global edtech investments reaching US$18.66 billion in 2019 and the overall market for online education projected to reach $350 Billion by 2025 . Whether it is language apps , virtual tutoring , video conferencing tools, or online learning software , there has been a significant surge in usage since COVID-19.
How is the education sector responding to COVID-19?
In response to significant demand, many online learning platforms are offering free access to their services, including platforms like BYJU’S , a Bangalore-based educational technology and online tutoring firm founded in 2011, which is now the world’s most highly valued edtech company . Since announcing free live classes on its Think and Learn app, BYJU’s has seen a 200% increase in the number of new students using its product, according to Mrinal Mohit, the company's Chief Operating Officer.
Tencent classroom, meanwhile, has been used extensively since mid-February after the Chinese government instructed a quarter of a billion full-time students to resume their studies through online platforms. This resulted in the largest “online movement” in the history of education with approximately 730,000 , or 81% of K-12 students, attending classes via the Tencent K-12 Online School in Wuhan.
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023.
Other companies are bolstering capabilities to provide a one-stop shop for teachers and students. For example, Lark, a Singapore-based collaboration suite initially developed by ByteDance as an internal tool to meet its own exponential growth, began offering teachers and students unlimited video conferencing time, auto-translation capabilities, real-time co-editing of project work, and smart calendar scheduling, amongst other features. To do so quickly and in a time of crisis, Lark ramped up its global server infrastructure and engineering capabilities to ensure reliable connectivity.
Alibaba’s distance learning solution, DingTalk, had to prepare for a similar influx: “To support large-scale remote work, the platform tapped Alibaba Cloud to deploy more than 100,000 new cloud servers in just two hours last month – setting a new record for rapid capacity expansion,” according to DingTalk CEO, Chen Hang.
Some school districts are forming unique partnerships, like the one between The Los Angeles Unified School District and PBS SoCal/KCET to offer local educational broadcasts, with separate channels focused on different ages, and a range of digital options. Media organizations such as the BBC are also powering virtual learning; Bitesize Daily , launched on 20 April, is offering 14 weeks of curriculum-based learning for kids across the UK with celebrities like Manchester City footballer Sergio Aguero teaching some of the content.
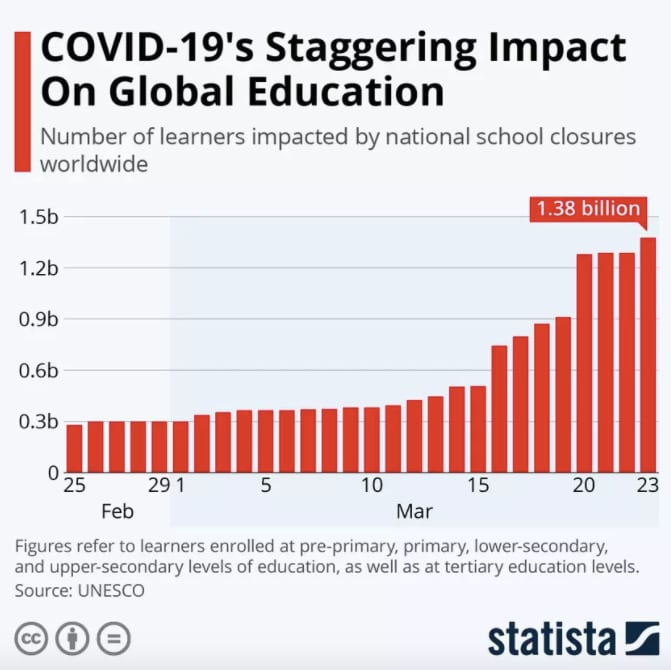
What does this mean for the future of learning?
While some believe that the unplanned and rapid move to online learning – with no training, insufficient bandwidth, and little preparation – will result in a poor user experience that is unconducive to sustained growth, others believe that a new hybrid model of education will emerge, with significant benefits. “I believe that the integration of information technology in education will be further accelerated and that online education will eventually become an integral component of school education,“ says Wang Tao, Vice President of Tencent Cloud and Vice President of Tencent Education.
There have already been successful transitions amongst many universities. For example, Zhejiang University managed to get more than 5,000 courses online just two weeks into the transition using “DingTalk ZJU”. The Imperial College London started offering a course on the science of coronavirus, which is now the most enrolled class launched in 2020 on Coursera .
Many are already touting the benefits: Dr Amjad, a Professor at The University of Jordan who has been using Lark to teach his students says, “It has changed the way of teaching. It enables me to reach out to my students more efficiently and effectively through chat groups, video meetings, voting and also document sharing, especially during this pandemic. My students also find it is easier to communicate on Lark. I will stick to Lark even after coronavirus, I believe traditional offline learning and e-learning can go hand by hand."
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning
The challenges of online learning.
There are, however, challenges to overcome. Some students without reliable internet access and/or technology struggle to participate in digital learning; this gap is seen across countries and between income brackets within countries. For example, whilst 95% of students in Switzerland, Norway, and Austria have a computer to use for their schoolwork, only 34% in Indonesia do, according to OECD data .
In the US, there is a significant gap between those from privileged and disadvantaged backgrounds: whilst virtually all 15-year-olds from a privileged background said they had a computer to work on, nearly 25% of those from disadvantaged backgrounds did not. While some schools and governments have been providing digital equipment to students in need, such as in New South Wales , Australia, many are still concerned that the pandemic will widenthe digital divide .

Is learning online as effective?
For those who do have access to the right technology, there is evidence that learning online can be more effective in a number of ways. Some research shows that on average, students retain 25-60% more material when learning online compared to only 8-10% in a classroom. This is mostly due to the students being able to learn faster online; e-learning requires 40-60% less time to learn than in a traditional classroom setting because students can learn at their own pace, going back and re-reading, skipping, or accelerating through concepts as they choose.
Nevertheless, the effectiveness of online learning varies amongst age groups. The general consensus on children, especially younger ones, is that a structured environment is required , because kids are more easily distracted. To get the full benefit of online learning, there needs to be a concerted effort to provide this structure and go beyond replicating a physical class/lecture through video capabilities, instead, using a range of collaboration tools and engagement methods that promote “inclusion, personalization and intelligence”, according to Dowson Tong, Senior Executive Vice President of Tencent and President of its Cloud and Smart Industries Group.
Since studies have shown that children extensively use their senses to learn, making learning fun and effective through use of technology is crucial, according to BYJU's Mrinal Mohit. “Over a period, we have observed that clever integration of games has demonstrated higher engagement and increased motivation towards learning especially among younger students, making them truly fall in love with learning”, he says.
A changing education imperative
It is clear that this pandemic has utterly disrupted an education system that many assert was already losing its relevance . In his book, 21 Lessons for the 21st Century , scholar Yuval Noah Harari outlines how schools continue to focus on traditional academic skills and rote learning , rather than on skills such as critical thinking and adaptability, which will be more important for success in the future. Could the move to online learning be the catalyst to create a new, more effective method of educating students? While some worry that the hasty nature of the transition online may have hindered this goal, others plan to make e-learning part of their ‘new normal’ after experiencing the benefits first-hand.
The importance of disseminating knowledge is highlighted through COVID-19
Major world events are often an inflection point for rapid innovation – a clear example is the rise of e-commerce post-SARS . While we have yet to see whether this will apply to e-learning post-COVID-19, it is one of the few sectors where investment has not dried up . What has been made clear through this pandemic is the importance of disseminating knowledge across borders, companies, and all parts of society. If online learning technology can play a role here, it is incumbent upon all of us to explore its full potential.
Our education system is losing relevance. Here's how to unleash its potential
3 ways the coronavirus pandemic could reshape education, celebrities are helping the uk's schoolchildren learn during lockdown, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-17xejub{-webkit-flex:1;-ms-flex:1;flex:1;justify-self:stretch;-webkit-align-self:stretch;-ms-flex-item-align:stretch;align-self:stretch;} .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Bird flu spread a ‘great concern’, plus other top health stories
Shyam Bishen
April 24, 2024

This Earth Day we consider the impact of climate change on human health
Shyam Bishen and Annika Green
April 22, 2024

Scientists have invented a method to break down 'forever chemicals' in our drinking water. Here’s how
Johnny Wood
April 17, 2024

Young people are becoming unhappier, a new report finds

Promoting healthy habit formation is key to improving public health. Here's why
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024

What's 'biophilic design' and how can it benefit neurodivergent people?
Fatemeh Aminpour, Ilan Katz and Jennifer Skattebol
Essays About Online Class: Top 5 Examples and 7 Prompts
Essays about online class tell many stories. If you need to write about e-learning, discover the top examples and prompts for the subject in our guide.
With over 5.8 million American students attending in 2021, online classes are now one of the education sector’s most popular and modern learning methods. Although it became prevalent because of the pandemic, it’s believed that the concept of distance learning began in the late 1800s .
Online classes pose many benefits that many still take advantage of even after the pandemic. However, not everyone adjusts well to this technology-centered learning due to no face-to-face contact and difficulty learning without the back-and-forth of lesson question time.
1. My Experience as an Online Student by Debra Sicard
2. how to succeed in online classes essay by anonymous on ivypanda.com, 3. essay on advantages and disadvantages of online classes by anonymous on selfstudymantra.com, 4. online school vs. traditional school essay by anonymous on gradesfixer.com, 5. short essay on online classes by anonymous on byjus.com, 7 helpful prompts on essays about online class, 1. online classes: defined, 2. my experience with online classes during lockdown, 3. how does online class work, 4. the best sites for online class, 5. the pros and cons of enrolling in online class, 6. review of a book about online class, 7. should online classes be the norm.
“I am not a traditional student, so I have non-traditional needs… online classes fit my lifestyle.”
Sicard shares her positive experience with online classes, primarily centering her essay on convenience. She says that with online courses, she can fit more lessons into her schedule, save her money on gas, and have more time with her family. In addition, she mentions she can work and do other things besides taking her credits.
To have a proper perspective of the topic, Sicard also includes the disadvantages of virtual learning, such as devices catching viruses and missing in-real-life interactions with her professors and classmates. But, she believes that an online student can learn as much or even more than what students learn in traditional classes.
“In an online class, a student can only achieve success if he is committed to time management, balancing personal obligations, finding an ideal study environment, asking questions, and applying more effort to completing the course requirements.”
This essay contains steps a non-traditional student can take to avoid failing online classes. The author says that students, especially multitaskers, must know how to manage and balance their time to avoid losing focus. In addition, having a dedicated study spot is necessary to avoid distractions.
“Online classes or online method of learning presents an easy and comfortable method to achieve knowledge. Online classes have now become a great alternative to traditional classes.”
The writer delves into the benefits and drawbacks of online versus traditional learning. Virtual classes offer students freedom regarding their schedules and whereabouts. Some schools also allow students to learn for free. E-learning effectively trains individuals to be responsible and disciplined.
However, individuals who are not computer literate will find online classes frustrating. Plus, electronic devices can be bad for health, and a lack of personal interaction can hinder personality development.
“[Online course] will also help you become more self-motivated, a trait that will make you stand out in the workplace and beyond.”
By listing the similarities and differences between online and traditional schools, the author demonstrates what classes a student should pick. The writer concludes that while traditional schools prepare students for the real world by interacting with diverse people, online schools help students become more self-motivated to stand out.
“The advantages of online classes take over their disadvantages. If students want to learn, then they have immense opportunities to learn from online classes.”
The author defines online classes as a type of education system where students use electronic devices with an internet connection to learn. However, while online learning improves the quality of education, it can also make the student lazy and cultivates a sense of isolation. Ultimately, they believe that to have the best education system, school teachers and officials must learn how to combine the two methods.
If the topic you’re thinking of is still confusing and you don’t know where to start, here are seven easy writing prompts to inspire you:

Explain the topic to your reader and give a brief history of the origins of online classes. Then briefly compare it to the traditional class to make the differences clear. Finally, point out the distinct features of online classes that conventional learning doesn’t offer, such as face-to-face interaction and question-and-answer debates. You can also discuss various online classes schools offer, such as hybrid learning, interactive online courses, etc.
Tell your story if you’re a student with experience with online classes. Narrate how your school switched to virtual classrooms. Relay the challenges you encountered, including how you adapted. Finish your essay by stating your current preference and why.
For example, you favor e-learning because it cuts your transportation expenses, helps you be more responsible for managing your time, and lets you sleep in the mornings.
Relate your experience when your school moved online. Discuss any equipment or devices you need to buy before enrolling in your online class. Explain how your school handles online courses and what it does when there are technical difficulties. Add how these challenges (such as unstable internet connection and sudden power outage), such as attendance and participation, impact a class.
To make your essay more intriguing, add the average price of your online classes and if you think it’s fair. For instance, you can argue that since schools don’t provide computers and save expenses on cleaning and utilities when physical classrooms are unused, they should cut their laboratory or miscellaneous fees. You may also be interested in these articles about back to school .

Zoom, Google Classroom, and Microsoft Team are just three of the most popular online teaching software for online classes. In this prompt, look for the most useful and efficient software sites teachers or schools should incorporate into e-learning. Find examples or reliable data that show the number of students or schools that use them. Finally, ensure the details you add are accurate to make your essay credible.
Do you want to write about technology instead? Check out our essays about technology .
Discussing online classes’ positive and negative effects is a usual essay topic. To make your essay stand out, pick the most impactful points on everyone involved. Don’t just explore the students’ perspectives. Include how virtual learning influences teachers, parents, and businesses.
To give you an idea, you can look into businesses near the campus that closed down when the school shifted to virtual classrooms.
This prompt requires you to search for publications about online classes and share your opinion on them.
For example, John F. Lyons’s book, How to Succeed in an Online Class , published in 2011, introduced technology students encounter in online classes. Suppose you read this book. First, enumerate Lyons’ advice, tips, and learning techniques to prevent a student from failing their online course. Then, briefly explain them individually and include examples or proof that his advice helped.
Online schooling has been around for a long time but has only become widespread because of the pandemic. Use this prompt to write your opinion on whether schools should make virtual learning a permanent option for students. Whatever your answer is, explain your reason to your readers.If you’re interested in learning more about essays, check out our essay writing tips !

Maria Caballero is a freelance writer who has been writing since high school. She believes that to be a writer doesn't only refer to excellent syntax and semantics but also knowing how to weave words together to communicate to any reader effectively.
View all posts

Essay on Online Education During The COVID – 19 for Students
Essay on online education during the covid – 19.
The COVID-19 pandemic has wreaked havoc on daily life, including school closures. It has affected over 240 million school-aged children in the country. Extended school closures may cause huge learning losses. This meant that schools needed to not only remodel and reimagine how they taught and learned, but also implement a suitable method of teaching and learning that combined home and school-based education. Students who are mature, self-disciplined, motivated, well-organised, and possess a high degree of time management skills have found online education to be an extremely effective alternative method of education. But it is an ineffective learning environment for more dependent learners who struggle to assume the responsibilities required by online education.
Online education, or digital education, has a number of advantages over traditional classroom instruction. It is one of the most effective methods for ensuring school education continuity. While online or digital education cannot completely replace face-to-face instruction, it does have some advantages. It enables adaptive and personalised learning at the learner’s pace, and content can be enhanced and expanded continuously through digital means. Rapid internet adoption and various government initiatives, such as the Digital India campaign, have facilitated the transition to digital education.
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted schools. Students face a unique situation with no clear future. Disruptions in academic space are alarming. Unfavorable circumstances forced undergraduate and graduate students to drop out. The pandemic situation evoked exclusion, highlighting academic inequity. As a result, online education can help instructors and students learn more effectively and efficiently while reducing stress. While online and classroom education produce similar learning outcomes, online education is perceived as less interactive.
Online education offers increased flexibility and learning opportunities: easy access to experts, exposure to educational environments, a wide range of course types, and joining student communities. Online education has several disadvantages, such as internet browsing issues, computer compatibility issues, and technical issues.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, students had to adjust their daily routines to an environment of isolation. Those studying abroad had to return home, but many were unable to do so due to airport and border closures. The lack of socialisation harmed students’ social-emotional balance, especially those with pre-existing issues. Anxiety and depression were cited as main effects of isolation .
Online education is a rapidly evolving field concerned primarily with the process of teaching and learning via digital media. This has progressed from activities such as sharing text resources and submitting online assignments to the availability of various types of content such as audio, video, and multimedia resources. The continuous advancement of information and communication technology (ICT) and the internet has made multiple modes of digital education possible.
The process of preparing teachers for digital education is twofold. The first is the requirement for teacher preparation in order for them to teach students effectively using digital technology. The second is to utilise digital media to stay current on educational developments in order to further their professional development. Teachers must be prepared to take advantage of digital technology’s potential to stay current professionally. The instructor may:
• Investigate digital technologies e.g., LMSs, apps, web portals, and digital labs, as well as a repository of Open Educational Resources on a National/State/Global Scale.
• Attend webinars, online training programmes, and online courses on a variety of topics related to ICT, pedagogy, and content integration.
• Connect with peers and learn about how other countries approach digital education by participating in forums, interest groups, and online communities.
• Acquaint yourself with both copylefted and open-source (FOSS) electronic content as well as educational tools. Teachers can be educated on the value of open resources, as not everything on the Internet is freely downloadable or shareable.
Transitioning to digital modes of education is fraught with difficulties in a country like India, which is characterised by a wealth of diversity and resource constraints (ICT infrastructure, electricity, budget, and skilled manpower). Local, decentralised planning and implementation are required, and various State/UT-level organisations such as SCERTs, School Boards, DIETs, BIETs, CTEs, and IASEs, as well as national-level organisations such as NCERT, CBSE, NIOS, KVS, and NVS, must collaborate to ensure that the change is sustainable post-COVID-19. This type of collaboration will enable us to continuously improve the quality of education and skill development for our large student population and will position us to benefit from the demographic dividend in the coming years.
Discover more from Smart English Notes
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown for Students
Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown: Get well-researched online classes during lockdown essay in 500, 300, 250, 200 and 150 words in simple words. In recent years, online classes have gained significant popularity as a convenient and accessible mode of education. However, their importance skyrocketed during the global pandemic-induced lockdowns.
With schools and universities shut down, educators and students alike turned to online platforms to continue their academic pursuits. In this essay on online classes during lockdown, we will explore the impact, benefits, challenges, and prospects of remote learning. Let’s delve into this transformative educational experience. Read a comprehensive essay on online classes during lockdown on different word counts.
Table of Contents
Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
During the lockdown, online classes became the go-to solution for educational institutions worldwide. Schools and universities rapidly adopted digital platforms, allowing students to learn from the safety and comfort of their homes. The sudden surge in demand for online education led to the development of innovative tools and technologies to enhance the learning experience.
Benefits of Online Classes During Lockdown
Online classes during lockdown offered numerous advantages to both students and educators. Let’s explore some of the key benefits:
Flexibility and Convenience
One of the primary advantages of online classes is the flexibility they offer. Students can access course materials, attend lectures, and complete assignments independently. This flexibility is especially beneficial for individuals with other commitments, such as part-time jobs or family responsibilities. Moreover, eliminating commuting time allowed students to optimize their schedules efficiently.
Access to a Wide Range of Courses
Online classes provide students with access to a diverse range of courses and programs. Regardless of location, learners could enroll in prestigious institutions and learn from renowned professors. This global reach broadened educational opportunities and facilitated cross-cultural learning experiences.
Enhanced Learning Experience
Digital platforms enable educators to employ interactive and engaging teaching methods. Through multimedia resources, virtual simulations, and real-time discussions, online classes fostered active learning and a deeper understanding of the subjects. Furthermore, students had easy access to recorded lectures, enabling them to revisit the material and reinforce their knowledge.
Personalized Attention and Individualized Learning
Instructors can provide personalized attention to each student in a virtual classroom setting. With smaller class sizes and the ability to interact one-on-one, educators can effectively address individual queries and concerns. This individualized approach enhanced the learning experience and allowed students to progress independently.
Improved Technological Skills
The transition to online classes necessitated the acquisition of digital skills. Students were able to enhance their technological proficiency, a valuable asset in today’s digital age. By familiarizing themselves with online platforms, collaboration tools, and multimedia resources, learners developed highly relevant skills in professional settings.
Challenges Faced During Online Classes
While online classes present numerous benefits, they also come with their fair share of challenges. It is essential to acknowledge these difficulties to understand the complete picture. Let’s explore some of the common challenges faced during online classes during lockdown:
Technical Issues
Technical glitches and connectivity problems were frequent obstacles in the online learning environment. Students with limited access to high-speed internet or outdated devices face difficulties attending live sessions and accessing online resources. These challenges often hindered the seamless flow of learning.
Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction
In traditional classrooms, face-to-face interaction allows students to engage in lively discussions and build interpersonal relationships. However, the virtual nature of online classes limited the social aspect of education. Students miss out on spontaneous exchanges and collaborative activities that foster a sense of community and camaraderie.
Self-Motivation and Discipline
With the absence of physical classrooms and fixed schedules, self-motivation and discipline became crucial factors in successful online learning. The freedom to manage one’s own time requires students to cultivate self-discipline and stay motivated to complete assignments and study independently.
Increased Screen Time
Online classes led to a significant increase in screen time for students. Extended periods of staring at screens can cause eye strain, fatigue, and other health issues. Balancing screen time with physical activities and adequate breaks became essential to maintain overall well-being.
Limited Practical Learning Opportunities
Certain subjects, such as science experiments, arts and crafts, or physical education , heavily rely on hands-on practical learning experiences. The virtual environment of online classes limited such opportunities, and students missed out on valuable practical knowledge and skills.
The advent of online classes during the lockdown revolutionized the field of education. Despite the challenges, the benefits of remote learning must be noticed. Online classes offer flexibility, access to diverse courses, enhanced learning experiences, and personalized attention.
While technical issues and limited practical learning opportunities posed challenges, educators and students adapted to the new normal and continued their educational journeys. As we progress, online classes will likely continue to be an integral part of the education system, providing opportunities for individuals worldwide to expand their knowledge and skills.
FAQs About Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown
How effective are online classes during lockdown.
Answer: Online classes during lockdown have proven effective, with students completing their courses and achieving learning outcomes. The key lies in the adaptability and commitment of both educators and learners.
Are online degrees valued the same as traditional degrees?
Answer: Online degrees are increasingly gaining recognition and acceptance in the job market. Employers value the skills and competencies acquired during online programs, primarily if they are obtained from reputable institutions.
Can online classes provide personalized attention to students?
Answer: Yes, online classes can provide personalized attention to students. Educators can interact with students individually, address their queries, and offer guidance through virtual platforms.
How can students stay motivated during online classes?
Answer: Students can stay motivated during online classes by creating a dedicated study space, setting goals, establishing a routine, seeking support from peers and instructors, and celebrating small achievements.
What steps can educational institutions take to improve the online learning experience?
Answer: Educational institutions can invest in robust technology infrastructure, provide training for educators on effective online teaching strategies, and create interactive and engaging learning materials to improve the online learning experience.
Will online classes continue to be relevant after the pandemic?
Answer: The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of online classes, and they will likely continue to be a significant component of education. Online learning offers flexibility, accessibility, and opportunities for lifelong learning.
Visit Homepage: EssayTome
- Short Essay On Online Classes
Short Essay on Online Classes
500+ words short essay on online classes.
Online classes and learning have emerged as a new method of teaching nowadays, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Online classes have gained immense popularity due to the many advantages like time flexibility, affordability etc. The traditional teaching method includes face-to-face interaction between the teacher and the students. However, in online learning, the interaction takes place in a digital platform in the form of videos, audio, graphics etc. Also, there are hybrid means of studying which combine face-to-face meetings with an online component. In this essay on online classes, we will be covering the topic of online classes and online learning. We have also compiled a list of CBSE Essays on different topics which students can practise to boost their writing skills. It will also help them to participate in different essay writing competitions conducted at the school level.
Online Classes
Online Classes are a type of education system that is delivered via the Internet to students using computers, laptops, mobile phones, tablets etc., in the comfort of their homes. During the last decade, online courses and classes have become popular. Especially during the COVID pandemic, most schools have opted for online classes, and the teachers deliver the lectures remotely through digital platforms.
Online classes are not just the use of technology in the education system, but it is a medium to transmit knowledge, values and skills to younger generations. In many fields, online education and e-learning have become the default way to conduct training or provide education. The online classes consist of four basic elements. The first element is to teach what learners need to learn. The second is to define clear learning objectives. The third is to build knowledge on the right objectives, and the final is in the power of delivering the lectures using technology.
Benefits of Online Classes
Online education has brought a positive impact on the lives of students and working professionals. It has given them an opportunity to take up additional courses along with their studies or job at their convenience. Online classes have also helped the faculty in the institutions to ask students to refer to/study some parts of the syllabus online, which do not require much classroom teaching. Thus, faculty can save time and utilise it to interact with the students more. The quality of education has improved through online classes. Students can easily refer to the content at their time and convenience. Online classes liberate students from planning their schedule of attending classes, driving to school, and being physically present. Online classes work as a lifeline to those people who face physical disabilities and geographical distances. In the era of digitalisation, the scope of online classes has increased even more.
The advantages of online classes take over their disadvantages. If students want to learn, then they have immense opportunities to learn from online classes. In conclusion, we can say that a combination of online and traditional learning methods will be the best for students. Because there are few things which are easier to understand by visualisation where online classes will help, and there are some topics which can be explained better in the physical presence of a teacher. So, combining both online and offline together will make the best education system.
Students must have found the “Essay on Online Classes” essay useful for improving their essay writing skills. They can get the study material and the latest updates on CBSE/ICSE/State Board/Competitive Exams at BYJU’S.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling
Essay on Fest
Search this blog, essay on online education during lockdown, essay on online education during lockdown .
Teaching has gone online because of Covid-19. All schools across the globe have closed and over 1.2 billion children are out of school. Online education takes place over the internet. It is also called e-learning.
Here the students access online study materials, join virtual lectures, post questions to teachers, chat with fellow students, give virtual exams and do much more things. Online classes provide good quality of education to students in the comfort of their homes and also help in controlling virus spread.
There is no barrier to time. They can study at their convenience. Another positive effect of online education is students have become more tech-savvy. They got to know more about various apps and programs. All the study material is safely stored in an online database.
If students need further explanations, they can easily view these records and resolve doubts instantly. Students have a lot of options to choose an online education program. They can select subjects and topics of their interest very easily.
But there are some drawbacks of online education. There is no face-to-face conversation between teachers and students. This puts a barrier in communication skills and personality development.
Internet connectivity is also a big issue in some areas. Internet prices are also increasing and everyone cannot afford online education. Online education provides freedom to students which are not good for them as it lacks discipline. Azure AZ-900 Practice Test
In online education, everything is scripted. It lacks emotions like laughter, excitement, or anger. Thus, there are both advantages and disadvantages of online education but in this lockdown time, this is truly helpful in providing continuous and uninterrupted learning.
Essay on online classes during lockdown in India
The COVID-19 has resulted in educational institutions shut all across the world. As a result, education has changed dramatically, while some institutions moved their classes to online and distance education platforms, many others struggled.
Online education is conducted in two ways. The first is through the use of recorded classes, which, when opened out to the public, are referred to as Massive Open Online Course (MOOCs). The second one is via live online classes conducted as webinars or zoom sessions.
Educational institutions require high-speed internet and education delivery platforms, and faculty members who are comfortable teaching online. Some students without reliable internet access or technology struggle to participate in digital learning.
* Allows innovative methods of teaching with the help of technology and online tools.
* Allows reaching out to a large number of students across geographies.
* Especially useful for distance learning.
* The ability to learn using different online tools and methods.
* No disruption in learning because of the pandemic.
* Listening to recorded and live conversations and working at their own speed.
Disadvantages
* Online teaching takes time and practice.
* Students can't be evaluated in a fair manner.
* Inability to have a face-to-face connection with students and facilitate free conversations, discussions, and mentoring.
* Inability to reach all students because of technological limitations.
* No disruption in learning because of the pandemic.
CONCLUSION:
It is unfair to expect the same level of concentration and involvement as in the classroom. There is a pressing need to innovate and implement alternative educational and assessment strategies. All of this can strengthen the future education system in a country.
An Online Class is a method of education that takes place over the internet. Due to the covid-19 pandemic, most of the governments around the world have imposed a lockdown and temporarily closed educational institutions.
These online classes are really helpful for the students, especially during this lockdown period. This is helping the teachers too as they get to communicate with their students and share knowledge.
These classes provide good quality of education to students in the comfort of their homes and also help in controlling the virus spread. Not only studies but various other extra-curricular activities are possible through these courses.
But there are some drawbacks. Only some educational institutions could adopt online teaching methods while many others have struggled. Moreover, there are some issues related to proper internet connectivity in some areas.
Thus, there are both advantages and disadvantages of online classes but in these lockdown times, these are truly helpful in providing continuous and uninterrupted learning.
Post a Comment
Popular posts from this blog, my vision for india in 2047 postcard, essay on my vision for india in 2047 in 150,300,400 words, education should be free for everyone essay.

Paragraph Writing on Online Classes during Lockdown in English Online Learning/Education
ONLINE CLASSES DURING LOCKDOWN
An online class is a method of education that takes place over the internet. Due to Covid-19 pandemic, most of the governments around the world have imposed lockdown and temporarily closed educational institutions. These online classes are really helpful for the students especially during this lockdown period. This is helping the teachers too as they get to communicate with their students and share knowledge. These classes provide good quality education to students in the comfort of their homes and also help in controlling the virus spread. Not only studies but various extra-curricular activities are possible through these courses. But there are some drawbacks. Only some educational institutions could adopt online teaching method while many others have struggled. Moreover, there are some issues related to poor internet connectivity in some areas. Thus, there are both advantages and disadvantages of online classes but in these lockdown times these are truly helpful in providing continuous and uninterrupted learning.
Click here to Download
PARAGRAPH WRITING
Discipline in Student's Life My Mother Health is Wealth
it help me lot

Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English
👀 This essay written on “Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English ” essay can be used for your school or college project and also you can practice this essay topic for you companies essay writing round. You will find latest essays on various other topics on our website, which you can read and practice on all the topics.
The sudden breakdown of the COVID 19 pandemic affected the world in a very crucial way and changed the way things worked. It was new to everyone, and every prevention method was adopted. One of them was lockdowns, which were imposed all over the globe as the world switched to the online way of conducting things, from working to solving every issue.
At this crucial time, schools and colleges, apart from offices, also turned to virtual classes for rescue. Learning has now become online for most of the time, and in lockdown, it has started spreading to everyone. Teachers and students started getting involved in the tech field as they adapted to the new changes of talking to devices, explaining things over the camera, making groups, inviting for video calls etc.
Online classes during lockdown have affected the educational style in many ways be it good or bad. There has been a decrease in syllabus allowing people to adapt to new changes as the teachers tried creating a curriculum that could be executed in online classes. Regular assignments and tests were taken on the groups where all the notes were reaching the students at right time. Learning this way is beyond the normal way of teaching. Online classes have always been part of education until now when every resource and way of learning is in front of you and is your only option. The internet is just like a treasure chest with all the resources available and gems hidden and ready to be used. The education that has been limiting teachers from teaching the same things in class has also gone to students choosing their skills and learning new things from the internet.
Apart from all the pros, there are challenges faced because of being new to online classes/education. The teaching, apart from delivery, is also about eye contact and actions. The teachers cannot keep track of how many of the students are understanding or if they need to change delivery. School students are expected to grasp basic education, and it is not able to reach everyone. Apart from theoretical knowledge, the practicals, which were previously done in labs, are also being conducted via online means. This has brought great disadvantages to students.
Apart from being at a basic level, college students are also facing large disadvantages. The college has always been about exposure, practical learning, interaction and networking with skills development. But the online education in lockdown has subsided it into only the ‘education’, which is not even half of what is taught in college. Students who are in college were not able to experience the advantages others had, though everyone is trying to thrive more with all the possibilities.
It would be right to say that the online education in Lockdown has affected many people, many positive and many negatively. Some has been focusing more on different skills to upgrade, interact, apply for opportunities, and study via different means and methods, day by day. Some have also limited themselves to being distracted by social media and websites showcasing different videos. On the economic level, online classes were not able to reach every household, which had made it limited to people who are financially well off. This is unfair by all means. Online education can be made more efficient with proper measures, making it more interesting with videos or animations.
👉 If you like this essay on “Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English Sample 1” then share this essay with friends to help them.
More Latest Essay Writing Topics
Humble request:.
Thus “Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English ” ends here. We have tried our best to avoid any kind of error in this “ Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English ” Still if you fi nd any error in this essay then you can give your valuable suggestion by email. So that we can present you articles consistently without any errors.
If you have any suggestion regarding this essay ( Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English ) or you want that something else should be added to it, then you can write your suggestions in the comment section below. With these suggestions / ideas, we will get a chance to learn something and improve something.
🔗 If you liked this article “Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown in English “, you got to learn something from it, then to show your happiness and eagerness, please use this post on the social networks link given below. Can share (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, Whatsapp, Telegram etc.).
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Impact of online classes on the satisfaction and performance of students during the pandemic period of COVID 19
1 Chitkara College of Hospitality Management, Chitkara University, Chandigarh, Punjab India
Varsha Singh
Arun aggarwal.
2 Chitkara Business School, Chitkara University, Chandigarh, Punjab India
The aim of the study is to identify the factors affecting students’ satisfaction and performance regarding online classes during the pandemic period of COVID–19 and to establish the relationship between these variables. The study is quantitative in nature, and the data were collected from 544 respondents through online survey who were studying the business management (B.B.A or M.B.A) or hotel management courses in Indian universities. Structural equation modeling was used to analyze the proposed hypotheses. The results show that four independent factors used in the study viz. quality of instructor, course design, prompt feedback, and expectation of students positively impact students’ satisfaction and further student’s satisfaction positively impact students’ performance. For educational management, these four factors are essential to have a high level of satisfaction and performance for online courses. This study is being conducted during the epidemic period of COVID- 19 to check the effect of online teaching on students’ performance.
Introduction
Coronavirus is a group of viruses that is the main root of diseases like cough, cold, sneezing, fever, and some respiratory symptoms (WHO, 2019 ). Coronavirus is a contagious disease, which is spreading very fast amongst the human beings. COVID-19 is a new sprain which was originated in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Coronavirus circulates in animals, but some of these viruses can transmit between animals and humans (Perlman & Mclntosh, 2020 ). As of March 282,020, according to the MoHFW, a total of 909 confirmed COVID-19 cases (862 Indians and 47 foreign nationals) had been reported in India (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020 ). Officially, no vaccine or medicine is evaluated to cure the spread of COVID-19 (Yu et al., 2020 ). The influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the education system leads to schools and colleges’ widespread closures worldwide. On March 24, India declared a country-wide lockdown of schools and colleges (NDTV, 2020 ) for preventing the transmission of the coronavirus amongst the students (Bayham & Fenichel, 2020 ). School closures in response to the COVID-19 pandemic have shed light on several issues affecting access to education. COVID-19 is soaring due to which the huge number of children, adults, and youths cannot attend schools and colleges (UNESCO, 2020 ). Lah and Botelho ( 2012 ) contended that the effect of school closing on students’ performance is hazy.
Similarly, school closing may also affect students because of disruption of teacher and students’ networks, leading to poor performance. Bridge ( 2020 ) reported that schools and colleges are moving towards educational technologies for student learning to avoid a strain during the pandemic season. Hence, the present study’s objective is to develop and test a conceptual model of student’s satisfaction pertaining to online teaching during COVID-19, where both students and teachers have no other option than to use the online platform uninterrupted learning and teaching.
UNESCO recommends distance learning programs and open educational applications during school closure caused by COVID-19 so that schools and teachers use to teach their pupils and bound the interruption of education. Therefore, many institutes go for the online classes (Shehzadi et al., 2020 ).
As a versatile platform for learning and teaching processes, the E-learning framework has been increasingly used (Salloum & Shaalan, 2018 ). E-learning is defined as a new paradigm of online learning based on information technology (Moore et al., 2011 ). In contrast to traditional learning academics, educators, and other practitioners are eager to know how e-learning can produce better outcomes and academic achievements. Only by analyzing student satisfaction and their performance can the answer be sought.
Many comparative studies have been carried out to prove the point to explore whether face-to-face or traditional teaching methods are more productive or whether online or hybrid learning is better (Lockman & Schirmer, 2020 ; Pei & Wu, 2019 ; González-Gómez et al., 2016 ; González-Gómez et al., 2016 ). Results of the studies show that the students perform much better in online learning than in traditional learning. Henriksen et al. ( 2020 ) highlighted the problems faced by educators while shifting from offline to online mode of teaching. In the past, several research studies had been carried out on online learning to explore student satisfaction, acceptance of e-learning, distance learning success factors, and learning efficiency (Sher, 2009 ; Lee, 2014 ; Yen et al., 2018 ). However, scant amount of literature is available on the factors that affect the students’ satisfaction and performance in online classes during the pandemic of Covid-19 (Rajabalee & Santally, 2020 ). In the present study, the authors proposed that course design, quality of the instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations are the four prominent determinants of learning outcome and satisfaction of the students during online classes (Lee, 2014 ).
The Course Design refers to curriculum knowledge, program organization, instructional goals, and course structure (Wright, 2003 ). If well planned, course design increasing the satisfaction of pupils with the system (Almaiah & Alyoussef, 2019 ). Mtebe and Raisamo ( 2014 ) proposed that effective course design will help in improving the performance through learners knowledge and skills (Khan & Yildiz, 2020 ; Mohammed et al., 2020 ). However, if the course is not designed effectively then it might lead to low usage of e-learning platforms by the teachers and students (Almaiah & Almulhem, 2018 ). On the other hand, if the course is designed effectively then it will lead to higher acceptance of e-learning system by the students and their performance also increases (Mtebe & Raisamo, 2014 ). Hence, to prepare these courses for online learning, many instructors who are teaching blended courses for the first time are likely to require a complete overhaul of their courses (Bersin, 2004 ; Ho et al., 2006 ).
The second-factor, Instructor Quality, plays an essential role in affecting the students’ satisfaction in online classes. Instructor quality refers to a professional who understands the students’ educational needs, has unique teaching skills, and understands how to meet the students’ learning needs (Luekens et al., 2004 ). Marsh ( 1987 ) developed five instruments for measuring the instructor’s quality, in which the main method was Students’ Evaluation of Educational Quality (SEEQ), which delineated the instructor’s quality. SEEQ is considered one of the methods most commonly used and embraced unanimously (Grammatikopoulos et al., 2014 ). SEEQ was a very useful method of feedback by students to measure the instructor’s quality (Marsh, 1987 ).
The third factor that improves the student’s satisfaction level is prompt feedback (Kinicki et al., 2004 ). Feedback is defined as information given by lecturers and tutors about the performance of students. Within this context, feedback is a “consequence of performance” (Hattie & Timperley, 2007 , p. 81). In education, “prompt feedback can be described as knowing what you know and what you do not related to learning” (Simsek et al., 2017 , p.334). Christensen ( 2014 ) studied linking feedback to performance and introduced the positivity ratio concept, which is a mechanism that plays an important role in finding out the performance through feedback. It has been found that prompt feedback helps in developing a strong linkage between faculty and students which ultimately leads to better learning outcomes (Simsek et al., 2017 ; Chang, 2011 ).
The fourth factor is students’ expectation . Appleton-Knapp and Krentler ( 2006 ) measured the impact of student’s expectations on their performance. They pin pointed that the student expectation is important. When the expectations of the students are achieved then it lead to the higher satisfaction level of the student (Bates & Kaye, 2014 ). These findings were backed by previous research model “Student Satisfaction Index Model” (Zhang et al., 2008 ). However, when the expectations are students is not fulfilled then it might lead to lower leaning and satisfaction with the course. Student satisfaction is defined as students’ ability to compare the desired benefit with the observed effect of a particular product or service (Budur et al., 2019 ). Students’ whose grade expectation is high will show high satisfaction instead of those facing lower grade expectations.
The scrutiny of the literature show that although different researchers have examined the factors affecting student satisfaction but none of the study has examined the effect of course design, quality of the instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations on students’ satisfaction with online classes during the pandemic period of Covid-19. Therefore, this study tries to explore the factors that affect students’ satisfaction and performance regarding online classes during the pandemic period of COVID–19. As the pandemic compelled educational institutions to move online with which they were not acquainted, including teachers and learners. The students were not mentally prepared for such a shift. Therefore, this research will be examined to understand what factors affect students and how students perceived these changes which are reflected through their satisfaction level.
This paper is structured as follows: The second section provides a description of theoretical framework and the linkage among different research variables and accordingly different research hypotheses were framed. The third section deals with the research methodology of the paper as per APA guideline. The outcomes and corresponding results of the empirical analysis are then discussed. Lastly, the paper concludes with a discussion and proposes implications for future studies.
Theoretical framework
Achievement goal theory (AGT) is commonly used to understand the student’s performance, and it is proposed by four scholars Carole Ames, Carol Dweck, Martin Maehr, and John Nicholls in the late 1970s (Elliot, 2005 ). Elliott & Dweck ( 1988 , p11) define that “an achievement goal involves a program of cognitive processes that have cognitive, affective and behavioral consequence”. This theory suggests that students’ motivation and achievement-related behaviors can be easily understood by the purpose and the reasons they adopted while they are engaged in the learning activities (Dweck & Leggett, 1988 ; Ames, 1992 ; Urdan, 1997 ). Some of the studies believe that there are four approaches to achieve a goal, i.e., mastery-approach, mastery avoidance, performance approach, and performance-avoidance (Pintrich, 1999 ; Elliot & McGregor, 2001 ; Schwinger & Stiensmeier-Pelster, 2011 , Hansen & Ringdal, 2018 ; Mouratidis et al., 2018 ). The environment also affects the performance of students (Ames & Archer, 1988 ). Traditionally, classroom teaching is an effective method to achieve the goal (Ames & Archer, 1988 ; Ames, 1992 ; Clayton et al., 2010 ) however in the modern era, the internet-based teaching is also one of the effective tools to deliver lectures, and web-based applications are becoming modern classrooms (Azlan et al., 2020 ). Hence, following section discuss about the relationship between different independent variables and dependent variables (Fig. (Fig.1 1 ).

Proposed Model
Hypotheses development
Quality of the instructor and satisfaction of the students.
Quality of instructor with high fanaticism on student’s learning has a positive impact on their satisfaction. Quality of instructor is one of the most critical measures for student satisfaction, leading to the education process’s outcome (Munteanu et al., 2010 ; Arambewela & Hall, 2009 ; Ramsden, 1991 ). Suppose the teacher delivers the course effectively and influence the students to do better in their studies. In that case, this process leads to student satisfaction and enhances the learning process (Ladyshewsky, 2013 ). Furthermore, understanding the need of learner by the instructor also ensures student satisfaction (Kauffman, 2015 ). Hence the hypothesis that the quality of instructor significantly affects the satisfaction of the students was included in this study.
- H1: The quality of the instructor positively affects the satisfaction of the students.
Course design and satisfaction of students
The course’s technological design is highly persuading the students’ learning and satisfaction through their course expectations (Liaw, 2008 ; Lin et al., 2008 ). Active course design indicates the students’ effective outcomes compared to the traditional design (Black & Kassaye, 2014 ). Learning style is essential for effective course design (Wooldridge, 1995 ). While creating an online course design, it is essential to keep in mind that we generate an experience for students with different learning styles. Similarly, (Jenkins, 2015 ) highlighted that the course design attributes could be developed and employed to enhance student success. Hence the hypothesis that the course design significantly affects students’ satisfaction was included in this study.
- H2: Course design positively affects the satisfaction of students.
Prompt feedback and satisfaction of students
The emphasis in this study is to understand the influence of prompt feedback on satisfaction. Feedback gives the information about the students’ effective performance (Chang, 2011 ; Grebennikov & Shah, 2013 ; Simsek et al., 2017 ). Prompt feedback enhances student learning experience (Brownlee et al., 2009 ) and boosts satisfaction (O'donovan, 2017 ). Prompt feedback is the self-evaluation tool for the students (Rogers, 1992 ) by which they can improve their performance. Eraut ( 2006 ) highlighted the impact of feedback on future practice and student learning development. Good feedback practice is beneficial for student learning and teachers to improve students’ learning experience (Yorke, 2003 ). Hence the hypothesis that prompt feedback significantly affects satisfaction was included in this study.
- H3: Prompt feedback of the students positively affects the satisfaction.
Expectations and satisfaction of students
Expectation is a crucial factor that directly influences the satisfaction of the student. Expectation Disconfirmation Theory (EDT) (Oliver, 1980 ) was utilized to determine the level of satisfaction based on their expectations (Schwarz & Zhu, 2015 ). Student’s expectation is the best way to improve their satisfaction (Brown et al., 2014 ). It is possible to recognize student expectations to progress satisfaction level (ICSB, 2015 ). Finally, the positive approach used in many online learning classes has been shown to place a high expectation on learners (Gold, 2011 ) and has led to successful outcomes. Hence the hypothesis that expectations of the student significantly affect the satisfaction was included in this study.
- H4: Expectations of the students positively affects the satisfaction.
Satisfaction and performance of the students
Zeithaml ( 1988 ) describes that satisfaction is the outcome result of the performance of any educational institute. According to Kotler and Clarke ( 1986 ), satisfaction is the desired outcome of any aim that amuses any individual’s admiration. Quality interactions between instructor and students lead to student satisfaction (Malik et al., 2010 ; Martínez-Argüelles et al., 2016 ). Teaching quality and course material enhances the student satisfaction by successful outcomes (Sanderson, 1995 ). Satisfaction relates to the student performance in terms of motivation, learning, assurance, and retention (Biner et al., 1996 ). Mensink and King ( 2020 ) described that performance is the conclusion of student-teacher efforts, and it shows the interest of students in the studies. The critical element in education is students’ academic performance (Rono, 2013 ). Therefore, it is considered as center pole, and the entire education system rotates around the student’s performance. Narad and Abdullah ( 2016 ) concluded that the students’ academic performance determines academic institutions’ success and failure.
Singh et al. ( 2016 ) asserted that the student academic performance directly influences the country’s socio-economic development. Farooq et al. ( 2011 ) highlights the students’ academic performance is the primary concern of all faculties. Additionally, the main foundation of knowledge gaining and improvement of skills is student’s academic performance. According to Narad and Abdullah ( 2016 ), regular evaluation or examinations is essential over a specific period of time in assessing students’ academic performance for better outcomes. Hence the hypothesis that satisfaction significantly affects the performance of the students was included in this study.
- H5: Students’ satisfaction positively affects the performance of the students.
Satisfaction as mediator
Sibanda et al. ( 2015 ) applied the goal theory to examine the factors persuading students’ academic performance that enlightens students’ significance connected to their satisfaction and academic achievement. According to this theory, students perform well if they know about factors that impact on their performance. Regarding the above variables, institutional factors that influence student satisfaction through performance include course design and quality of the instructor (DeBourgh, 2003 ; Lado et al., 2003 ), prompt feedback, and expectation (Fredericksen et al., 2000 ). Hence the hypothesis that quality of the instructor, course design, prompts feedback, and student expectations significantly affect the students’ performance through satisfaction was included in this study.
- H6: Quality of the instructor, course design, prompt feedback, and student’ expectations affect the students’ performance through satisfaction.
- H6a: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between quality of the instructor and student’s performance.
- H6b: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between course design and student’s performance.
- H6c: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between prompt feedback and student’s performance.
- H6d: Students’ satisfaction mediates the relationship between student’ expectations and student’s performance.
Participants
In this cross-sectional study, the data were collected from 544 respondents who were studying the management (B.B.A or M.B.A) and hotel management courses. The purposive sampling technique was used to collect the data. Descriptive statistics shows that 48.35% of the respondents were either MBA or BBA and rests of the respondents were hotel management students. The percentages of male students were (71%) and female students were (29%). The percentage of male students is almost double in comparison to females. The ages of the students varied from 18 to 35. The dominant group was those aged from 18 to 22, and which was the under graduation student group and their ratio was (94%), and another set of students were from the post-graduation course, which was (6%) only.
The research instrument consists of two sections. The first section is related to demographical variables such as discipline, gender, age group, and education level (under-graduate or post-graduate). The second section measures the six factors viz. instructor’s quality, course design, prompt feedback, student expectations, satisfaction, and performance. These attributes were taken from previous studies (Yin & Wang, 2015 ; Bangert, 2004 ; Chickering & Gamson, 1987 ; Wilson et al., 1997 ). The “instructor quality” was measured through the scale developed by Bangert ( 2004 ). The scale consists of seven items. The “course design” and “prompt feedback” items were adapted from the research work of Bangert ( 2004 ). The “course design” scale consists of six items. The “prompt feedback” scale consists of five items. The “students’ expectation” scale consists of five items. Four items were adapted from Bangert, 2004 and one item was taken from Wilson et al. ( 1997 ). Students’ satisfaction was measure with six items taken from Bangert ( 2004 ); Wilson et al. ( 1997 ); Yin and Wang ( 2015 ). The “students’ performance” was measured through the scale developed by Wilson et al. ( 1997 ). The scale consists of six items. These variables were accessed on a five-point likert scale, ranging from 1(strongly disagree) to 5(strongly agree). Only the students from India have taken part in the survey. A total of thirty-four questions were asked in the study to check the effect of the first four variables on students’ satisfaction and performance. For full details of the questionnaire, kindly refer Appendix Tables Tables6 6 .
The study used a descriptive research design. The factors “instructor quality, course design, prompt feedback and students’ expectation” were independent variables. The students’ satisfaction was mediator and students’ performance was the dependent variable in the current study.
In this cross-sectional research the respondents were selected through judgment sampling. They were informed about the objective of the study and information gathering process. They were assured about the confidentiality of the data and no incentive was given to then for participating in this study. The information utilizes for this study was gathered through an online survey. The questionnaire was built through Google forms, and then it was circulated through the mails. Students’ were also asked to write the name of their college, and fifteen colleges across India have taken part to fill the data. The data were collected in the pandemic period of COVID-19 during the total lockdown in India. This was the best time to collect the data related to the current research topic because all the colleges across India were involved in online classes. Therefore, students have enough time to understand the instrument and respondent to the questionnaire in an effective manner. A total of 615 questionnaires were circulated, out of which the students returned 574. Thirty responses were not included due to the unengaged responses. Finally, 544 questionnaires were utilized in the present investigation. Male and female students both have taken part to fill the survey, different age groups, and various courses, i.e., under graduation and post-graduation students of management and hotel management students were the part of the sample.
Exploratory factor analysis (EFA)
To analyze the data, SPSS and AMOS software were used. First, to extract the distinct factors, an exploratory factor analysis (EFA) was performed using VARIMAX rotation on a sample of 544. Results of the exploratory analysis rendered six distinct factors. Factor one was named as the quality of instructor, and some of the items were “The instructor communicated effectively”, “The instructor was enthusiastic about online teaching” and “The instructor was concerned about student learning” etc. Factor two was labeled as course design, and the items were “The course was well organized”, “The course was designed to allow assignments to be completed across different learning environments.” and “The instructor facilitated the course effectively” etc. Factor three was labeled as prompt feedback of students, and some of the items were “The instructor responded promptly to my questions about the use of Webinar”, “The instructor responded promptly to my questions about general course requirements” etc. The fourth factor was Student’s Expectations, and the items were “The instructor provided models that clearly communicated expectations for weekly group assignments”, “The instructor used good examples to explain statistical concepts” etc. The fifth factor was students’ satisfaction, and the items were “The online classes were valuable”, “Overall, I am satisfied with the quality of this course” etc. The sixth factor was performance of the student, and the items were “The online classes has sharpened my analytic skills”, “Online classes really tries to get the best out of all its students” etc. These six factors explained 67.784% of the total variance. To validate the factors extracted through EFA, the researcher performed confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) through AMOS. Finally, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to test the hypothesized relationships.
Measurement model
The results of Table Table1 1 summarize the findings of EFA and CFA. Results of the table showed that EFA renders six distinct factors, and CFA validated these factors. Table Table2 2 shows that the proposed measurement model achieved good convergent validity (Aggarwal et al., 2018a , b ). Results of the confirmatory factor analysis showed that the values of standardized factor loadings were statistically significant at the 0.05 level. Further, the results of the measurement model also showed acceptable model fit indices such that CMIN = 710.709; df = 480; CMIN/df = 1.481 p < .000; Incremental Fit Index (IFI) = 0.979; Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) = 0.976; Goodness of Fit index (GFI) = 0.928; Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index (AGFI) = 0.916; Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.978; Root Mean Square Residual (RMR) = 0.042; Root Mean Squared Error of Approximation (RMSEA) = 0.030 is satisfactory.
Factor Analysis
Author’s Compilation
Validity analysis of measurement model
Author’s compilation
AVE is the Average Variance Extracted, CR is Composite Reliability
The bold diagonal value represents the square root of AVE
The Average Variance Explained (AVE) according to the acceptable index should be higher than the value of squared correlations between the latent variables and all other variables. The discriminant validity is confirmed (Table (Table2) 2 ) as the value of AVE’s square root is greater than the inter-construct correlations coefficient (Hair et al., 2006 ). Additionally, the discriminant validity existed when there was a low correlation between each variable measurement indicator with all other variables except with the one with which it must be theoretically associated (Aggarwal et al., 2018a , b ; Aggarwal et al., 2020 ). The results of Table Table2 2 show that the measurement model achieved good discriminate validity.
Structural model
To test the proposed hypothesis, the researcher used the structural equation modeling technique. This is a multivariate statistical analysis technique, and it includes the amalgamation of factor analysis and multiple regression analysis. It is used to analyze the structural relationship between measured variables and latent constructs.
Table 3 represents the structural model’s model fitness indices where all variables put together when CMIN/DF is 2.479, and all the model fit values are within the particular range. That means the model has attained a good model fit. Furthermore, other fit indices as GFI = .982 and AGFI = 0.956 be all so supportive (Schumacker & Lomax, 1996 ; Marsh & Grayson, 1995 ; Kline, 2005 ).
Criterion for model fit
Hence, the model fitted the data successfully. All co-variances among the variables and regression weights were statistically significant ( p < 0.001).
Table Table4 4 represents the relationship between exogenous, mediator and endogenous variables viz—quality of instructor, prompt feedback, course design, students’ expectation, students’ satisfaction and students’ performance. The first four factors have a positive relationship with satisfaction, which further leads to students’ performance positively. Results show that the instructor’s quality has a positive relationship with the satisfaction of students for online classes (SE = 0.706, t-value = 24.196; p < 0.05). Hence, H1 was supported. The second factor is course design, which has a positive relationship with students’ satisfaction of students (SE = 0.064, t-value = 2.395; p < 0.05). Hence, H2 was supported. The third factor is Prompt feedback, and results show that feedback has a positive relationship with the satisfaction of the students (SE = 0.067, t-value = 2.520; p < 0.05). Hence, H3 was supported. The fourth factor is students’ expectations. The results show a positive relationship between students’ expectation and students’ satisfaction with online classes (SE = 0.149, t-value = 5.127; p < 0.05). Hence, H4 was supported. The results of SEM show that out of quality of instructor, prompt feedback, course design, and students’ expectation, the most influencing factor that affect the students’ satisfaction was instructor’s quality (SE = 0.706) followed by students’ expectation (SE =5.127), prompt feedback (SE = 2.520). The factor that least affects the students’ satisfaction was course design (2.395). The results of Table Table4 4 finally depicts that students’ satisfaction has positive effect on students’ performance ((SE = 0.186, t-value = 2.800; p < 0.05). Hence H5 was supported.
Structural analysis
Table Table5 5 shows that students’ satisfaction partially mediates the positive relationship between the instructor’s quality and student performance. Hence, H6(a) was supported. Further, the mediation analysis results showed that satisfaction again partially mediates the positive relationship between course design and student’s performance. Hence, H6(b) was supported However, the mediation analysis results showed that satisfaction fully mediates the positive relationship between prompt feedback and student performance. Hence, H6(c) was supported. Finally, the results of the Table Table5 5 showed that satisfaction partially mediates the positive relationship between expectations of the students and student’s performance. Hence, H6(d) was supported.
Mediation Analysis
In the present study, the authors evaluated the different factors directly linked with students’ satisfaction and performance with online classes during Covid-19. Due to the pandemic situation globally, all the colleges and universities were shifted to online mode by their respective governments. No one has the information that how long this pandemic will remain, and hence the teaching method was shifted to online mode. Even though some of the educators were not tech-savvy, they updated themselves to battle the unexpected circumstance (Pillai et al., 2021 ). The present study results will help the educators increase the student’s satisfaction and performance in online classes. The current research assists educators in understanding the different factors that are required for online teaching.
Comparing the current research with past studies, the past studies have examined the factors affecting the student’s satisfaction in the conventional schooling framework. However, the present study was conducted during India’s lockdown period to identify the prominent factors that derive the student’s satisfaction with online classes. The study also explored the direct linkage between student’s satisfaction and their performance. The present study’s findings indicated that instructor’s quality is the most prominent factor that affects the student’s satisfaction during online classes. This means that the instructor needs to be very efficient during the lectures. He needs to understand students’ psychology to deliver the course content prominently. If the teacher can deliver the course content properly, it affects the student’s satisfaction and performance. The teachers’ perspective is critical because their enthusiasm leads to a better online learning process quality.
The present study highlighted that the second most prominent factor affecting students’ satisfaction during online classes is the student’s expectations. Students might have some expectations during the classes. If the instructor understands that expectation and customizes his/her course design following the student’s expectations, then it is expected that the students will perform better in the examinations. The third factor that affects the student’s satisfaction is feedback. After delivering the course, appropriate feedback should be taken by the instructors to plan future courses. It also helps to make the future strategies (Tawafak et al., 2019 ). There must be a proper feedback system for improvement because feedback is the course content’s real image. The last factor that affects the student’s satisfaction is design. The course content needs to be designed in an effective manner so that students should easily understand it. If the instructor plans the course, so the students understand the content without any problems it effectively leads to satisfaction, and the student can perform better in the exams. In some situations, the course content is difficult to deliver in online teaching like the practical part i.e. recipes of dishes or practical demonstration in the lab. In such a situation, the instructor needs to be more creative in designing and delivering the course content so that it positively impacts the students’ overall satisfaction with online classes.
Overall, the students agreed that online teaching was valuable for them even though the online mode of classes was the first experience during the pandemic period of Covid-19 (Agarwal & Kaushik, 2020 ; Rajabalee & Santally, 2020 ). Some of the previous studies suggest that the technology-supported courses have a positive relationship with students’ performance (Cho & Schelzer, 2000 ; Harasim, 2000 ; Sigala, 2002 ). On the other hand, the demographic characteristic also plays a vital role in understanding the online course performance. According to APA Work Group of the Board of Educational Affairs ( 1997 ), the learner-centered principles suggest that students must be willing to invest the time required to complete individual course assignments. Online instructors must be enthusiastic about developing genuine instructional resources that actively connect learners and encourage them toward proficient performances. For better performance in studies, both teachers and students have equal responsibility. When the learner faces any problem to understand the concepts, he needs to make inquiries for the instructor’s solutions (Bangert, 2004 ). Thus, we can conclude that “instructor quality, student’s expectation, prompt feedback, and effective course design” significantly impact students’ online learning process.
Implications of the study
The results of this study have numerous significant practical implications for educators, students and researchers. It also contributes to the literature by demonstrating that multiple factors are responsible for student satisfaction and performance in the context of online classes during the period of the COVID-19 pandemic. This study was different from the previous studies (Baber, 2020 ; Ikhsan et al., 2019 ; Eom & Ashill, 2016 ). None of the studies had examined the effect of students’ satisfaction on their perceived academic performance. The previous empirical findings have highlighted the importance of examining the factors affecting student satisfaction (Maqableh & Jaradat, 2021 ; Yunusa & Umar, 2021 ). Still, none of the studies has examined the effect of course design, quality of instructor, prompt feedback, and students’ expectations on students’ satisfaction all together with online classes during the pandemic period. The present study tries to fill this research gap.
The first essential contribution of this study was the instructor’s facilitating role, and the competence he/she possesses affects the level of satisfaction of the students (Gray & DiLoreto, 2016 ). There was an extra obligation for instructors who taught online courses during the pandemic. They would have to adapt to a changing climate, polish their technical skills throughout the process, and foster new students’ technical knowledge in this environment. The present study’s findings indicate that instructor quality is a significant determinant of student satisfaction during online classes amid a pandemic. In higher education, the teacher’s standard referred to the instructor’s specific individual characteristics before entering the class (Darling-Hammond, 2010 ). These attributes include factors such as instructor content knowledge, pedagogical knowledge, inclination, and experience. More significantly, at that level, the amount of understanding could be given by those who have a significant amount of technical expertise in the areas they are teaching (Martin, 2021 ). Secondly, the present study results contribute to the profession of education by illustrating a realistic approach that can be used to recognize students’ expectations in their class effectively. The primary expectation of most students before joining a university is employment. Instructors have agreed that they should do more to fulfill students’ employment expectations (Gorgodze et al., 2020 ). The instructor can then use that to balance expectations to improve student satisfaction. Study results can be used to continually improve and build courses, as well as to make policy decisions to improve education programs. Thirdly, from result outcomes, online course design and instructors will delve deeper into how to structure online courses more efficiently, including design features that minimize adversely and maximize optimistic emotion, contributing to greater student satisfaction (Martin et al., 2018 ). The findings suggest that the course design has a substantial positive influence on the online class’s student performance. The findings indicate that the course design of online classes need to provide essential details like course content, educational goals, course structure, and course output in a consistent manner so that students would find the e-learning system beneficial for them; this situation will enable students to use the system and that leads to student performance (Almaiah & Alyoussef, 2019 ). Lastly, the results indicate that instructors respond to questions promptly and provide timely feedback on assignments to facilitate techniques that help students in online courses improve instructor participation, instructor interaction, understanding, and participation (Martin et al., 2018 ). Feedback can be beneficial for students to focus on the performance that enhances their learning.
Limitations and future scope of the study
The data collected in this study was cross-sectional in nature due to which it is difficult to establish the causal relationship between the variables. The future research can use a longitudinal study to handle this limitation. Further, the data was collected from one type of respondents only, that is, the students. Therefore, the results of the study cannot be generalized to other samples. The future research can also include the perspectives of teachers and policy makers to have more generalization of the results. The current research is only limited to theory classes; therefore, it can be implemented to check students’ performance in practical classes. The study is done on the Indian students only; thus, if the data is collected from various countries, it can give better comparative results to understand the student’s perspective. This study is limited to check the performance of students, so in the future, the performance of teachers can be checked with similar kinds of conditions. There may be some issues and problems faced by the students, like the limited access to the internet or disturbance due to low signals. Some of the students may face the home environment issues such as disturbance due to family members, which may lead to negative performance. The above-mentioned points can be inculcated in the future research.
Declarations
Not applicable.
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Ram Gopal, Email: [email protected] .
Varsha Singh, Email: [email protected] .
Arun Aggarwal, Email: [email protected] .
- Agarwal S, Kaushik JS. Student’s perception of online learning during COVID pandemic. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2020; 87 :554–554. doi: 10.1007/s12098-020-03327-7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aggarwal A, Dhaliwal RS, Nobi K. Impact of structural empowerment on organizational commitment: The mediating role of women's psychological empowerment. Vision. 2018; 22 (3):284–294. doi: 10.1177/0972262918786049. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aggarwal A, Goyal J, Nobi K. Examining the impact of leader-member exchange on perceptions of organizational justice: The mediating role of perceptions of organizational politics. Theoretical Economics Letters. 2018; 8 (11):2308–2329. doi: 10.4236/tel.2018.811150. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aggarwal A, Chand PA, Jhamb D, Mittal A. Leader-member exchange, work engagement and psychological withdrawal behaviour: The mediating role of psychological empowerment. Frontiers in Psychology. 2020; 11 :1–17. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00423. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Almaiah MA, Almulhem A. A conceptual framework for determining the success factors of e-learning system implementation using Delphi technique. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology. 2018; 96 (17):5962–5976. [ Google Scholar ]
- Almaiah MA, Alyoussef IY. Analysis of the effect of course design, course content support, course assessment and instructor characteristics on the actual use of E-learning system. Ieee Access. 2019; 7 :171907–171922. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956349. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ames C. Classrooms: Goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology. 1992; 84 :261–271. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.84.3.261. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ames C, Archer J. Achievement goals in the classroom: Student's learning strategies and motivational processes. Journal of Educational Psychology. 1988; 80 :260–267. doi: 10.1037/0022-0663.80.3.260. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- APA Work Group of the Board of Educational Affairs . Learner-centered psychological principles: A framework for school reform and redesign. American Psychological Association; 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- Appleton-Knapp S, Krentler KA. Measuring student expectations and their effects on satisfaction: The importance of managing student expectations. Journal of Marketing Education. 2006; 28 (3):254–264. doi: 10.1177/0273475306293359. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arambewela R, Hall J. An empirical model of international student satisfaction. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics. 2009; 21 (4):555–569. doi: 10.1108/13555850910997599. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Azlan AA, Hamzah MR, Sern TJ, Ayub SH, Mohamad E. Public knowledge, attitudes and practices towards COVID-19: A cross-sectional study in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2020; 15 (5):e0233668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233668. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baber H. Determinants of Students' perceived outcome and satisfaction in online learning during the pandemic of COVID-19. Journal of Education and e-Learning Research. 2020; 7 (3):285–292. doi: 10.20448/journal.509.2020.73.285.292. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bangert AW. The seven principles of good practice: A framework for evaluating on- line teaching. The Internet and Higher Education. 2004; 7 (3):217–232. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2004.06.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bates EA, Kaye LK. “I’d be expecting caviar in lectures”: The impact of the new fee regime on undergraduate students’ expectations of higher education. Higher Education. 2014; 67 (5):655–673. doi: 10.1007/s10734-013-9671-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bayham, J., & Fenichel, E.P. (2020). The impact of school closure for COVID-19 on the US healthcare workforce and the net mortality effects. Available at SSRN: 10.2139/ssrn.3555259.
- Bersin J. The blended learning book: Best practices, proven methodologies and lessons learned. Pfeiffer Publishing; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Biner PM, Summers M, Dean RS, Bink ML, Anderson JL, Gelder BC. Student satisfaction with interactive telecourses as a function of demographic variables and prior telecourse experience. Distance Education. 1996; 17 (11):33–43. doi: 10.1080/0158791960170104. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Black GS, Kassaye WW. Do students learning styles impact student outcomes in marketing classes? Academy of Educational Leadership Journal. 2014; 18 (4):149–162. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bridge, S. (2020). Opinion: How edtech will keep our students on track during covid-19. Arabian business. Com Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/docview/2377556452?accountid=147490 . Accessed 12 Oct 2020.
- Brown SA, Venkatesh V, Goyal S. Expectation confirmation in information systems research: A test of six competing models. MIS Quarterly. 2014; 38 (3):729–756. doi: 10.25300/MISQ/2014/38.3.05. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brownlee J, Walker S, Lennox S, Exley B, Pearce S. The first year university experience: Using personal epistemology to understsnd effective learning and teaching in higher education. Higher Education. 2009; 58 (5):599–618. doi: 10.1007/s10734-009-9212-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Budur T, Faraj KM, Karim LA. Benchmarking operations strategies via hybrid model: A case study of café-restaurant sector. Amozonia Investiga. 2019; 8 :842–854. [ Google Scholar ]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Reducing stigma. Retrieved November 26, 2020, from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/about/related-stigma.html .
- Chang N. Pre-service Teachers' views: How did E-feedback through assessment facilitate their learning? Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 2011; 11 (2):16–33. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chickering AW, Gamson ZF. Seven principles for good practice in undergraduate education. AAHE Bulletin. 1987; 39 (7):3–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cho W, Schelzer C. Just in-time education: Tools for hospitality managers of the future? International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management. 2000; 12 (1):31–36. doi: 10.1108/09596110010305000. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Christensen AL. Feedback, affect, and creative behavior: A multi-level model linking feedback to performance. Arizona State University; 2014. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clayton K, Blumberg F, Auld DP. The relationship between motivation, learning strategies and choice of environment whether traditional or including an online component. British Journal of Educational Technology. 2010; 41 (3):349–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.00993.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Darling-Hammond, L. (2010). Evaluating teacher effectiveness: How teacher performance assessments can measure and improve teaching . Washington, DC: Center for American Progress
- DeBourgh GA. Predictors of student satisfaction in distance-delivered graduate nursing courses: What matters most? Journal of Professional Nursing. 2003; 19 :149–163. doi: 10.1016/S8755-7223(03)00072-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dweck C, Leggett E. A social–cognitive approach to motivation and personality. Psychological Review. 1988; 95 :256–273. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.95.2.256. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot AJ. A conceptual history of the achievement goal construct. In: Elliot A, Dweck C, editors. Handbook of competence and motivation. Guilford Press; 2005. pp. 52–72. [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliot A, McGregor H. A 2 _ 2 achievement goal framework. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2001; 80 :501–519. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.80.3.501. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Elliott ES, Dweck CS. Goals: An approach to motivation and achievement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1988; 54 (1):5. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.1.5. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eom SB, Ashill N. The determinants of students' perceived learning outcomes and satisfaction in university online education: An update. Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education. 2016; 14 (2):185–215. doi: 10.1111/dsji.12097. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eraut, M., (2006). Feedback. Learning in Health and Social Care. Volume-5, issue-3. Pg 111–118. Retrieved from https://edservices.wiley.com/how-student-feedback-creates-better-online- learning/ . Accessed 23 Oct 2020.
- Farooq MS, Chaudhry AH, Shafiq M, Berhanu G. Factors affecting students' quality of academic performance: A case of secondary school level. Journal of Quality and Technology Management. 2011; 7 :1–14. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fredericksen E, Shea P, Pickett A. Factors influencing student and faculty satisfaction in the SUNY learning network. State University of New York; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gold, S. (2011). A constructivist approach to online training for online teachers. Journal of Aysnchronous Learning Networks, 5 (1), 35–57.
- González-Gómez D, Jeong JS, Rodríguez DA. Performance and perception in the flipped learning model: An initial approach to evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching methodology in a general science classroom. Journal of Science Education and Technology. 2016; 25 (3):450–459. doi: 10.1007/s10956-016-9605-9. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gorgodze S, Macharashvili L, Kamladze A. Learning for earning: Student expectations and perceptions of university. International Education Studies. 2020; 13 (1):42–53. doi: 10.5539/ies.v13n1p42. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Grammatikopoulos, V., Linardakis, M., Gregoriadis, A., & Oikonomidis, V. (2014). Assessing the Students' evaluations of educational quality (SEEQ) questionnaire in Greek higher education. Higher Education., 70 (3).
- Gray JA, DiLoreto M. The effects of student engagement, student satisfaction, and perceived learning in online learning environments. International Journal of Educational Leadership Preparation. 2016; 11 (1):n1. [ Google Scholar ]
- Grebennikov L, Shah S. Monitoring trends in student satisfaction. Tertiary Education and Management. 2013; 19 (4):301–322. doi: 10.1080/13583883.2013.804114. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair JF, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE, Tatham RL. Multivariate data analysis 6th edition. Pearson Prentice Hall. New Jersey. Humans: Critique and reformulation. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 2006; 87 :49–74. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hansen G, Ringdal R. Formative assessment as a future step in maintaining the mastery-approach and performance-avoidance goal stability. Studies in Educational Evaluation. 2018; 56 :59–70. doi: 10.1016/j.stueduc.2017.11.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harasim L. Shift happens: Online education as a new paradigm in learning. The Internet and Higher Education. 2000; 3 (1):41–61. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7516(00)00032-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hattie J, Timperley H. The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research. 2007; 77 (1):81–112. doi: 10.3102/003465430298487. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henriksen D, Creely E, Henderson M. Folk pedagogies for teacher transitions: Approaches to synchronous online learning in the wake of COVID-19. Journal of Technology and Teacher Education. 2020; 28 (2):201–209. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ho A, Lu L, Thurmaier K. Testing the reluctant Professor's hypothesis: Evaluating a blended-learning approach to distance education. Journal of Public Affairs Education. 2006; 12 (1):81–102. doi: 10.1080/15236803.2006.12001414. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- ICSB (2015). Addressing undergraduate entrepreneurship student expectations: An exploratory study. International Council for Small Business (ICSB). Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/docview/1826918813?accountid=147490 . Accessed 20 Oct 2020.
- Ikhsan, R. B., Saraswati, L. A., Muchardie, B. G., & Susilo, A. (2019). The determinants of students' perceived learning outcomes and satisfaction in BINUS online learning. Paper presented at the 2019 5th International Conference on New Media Studies (CONMEDIA). IEEE.
- Jenkins, D. M. (2015). Integrated course design: A facelift for college courses. Journal of Management Education, 39 (3), 427–432.
- Kauffman, H. (2015). A review of predictive factors of student success in and satisfaction with online learning. Research in Learning Technology, 23 .
- Khan NUS, Yildiz Y. Impact of intangible characteristics of universities on student satisfaction. Amazonia Investiga. 2020; 9 (26):105–116. doi: 10.34069/AI/2020.26.02.12. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kinicki AJ, Prussia GE, Wu BJ, McKee-Ryan FM. A covariance structure analysis of employees' response to performance feedback. Journal of Applied Psychology. 2004; 89 (6):1057–1069. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.89.6.1057. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 2. The Guilford Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kotler, P., & Clarke, R. N. (1986). Marketing for health care organizations . Prentice Hall.
- Lado N, Cardone-Riportella C, Rivera-Torres P. Measurement and effects of teaching quality: An empirical model applied to masters programs. Journal of Business Education. 2003; 4 :28–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ladyshewsky RK. Instructor presence in online courses and student satisfaction. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning. 2013; 7 :1. doi: 10.20429/ijsotl.2013.070113. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lah, K., & G. Botelho. (2012). Union Opts to Continue Chicago Teachers Strike; Mayor Takes Fight to Court. http://articles.cnn.com/2012-09-16/us/us_illinois-chicago-teachersstrike_1_chicago-teachers-union-union-president-karen-lewis-union-delegates .
- Lee J. An exploratory study of effective online learning: Assessing satisfaction levels of graduate students of mathematics education associated with human and design factors of an online course. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning. 2014; 15 (1):111–132. doi: 10.19173/irrodl.v15i1.1638. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liaw S-S. Investigating students' perceived satisfaction, behavioral intention, and effectiveness of e-learning: A case study of the blackboard system. Computers & Education. 2008; 51 (2):864–873. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2007.09.005. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin Y, Lin G, Laffey JM. Building a social and motivational framework for understanding satisfaction in online learning. Journal of Educational Computing Research. 2008; 38 (1):1–27. doi: 10.2190/EC.38.1.a. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lockman AS, Schirmer BR. Online instruction in higher education: Promising, research-based, and evidence-based practices. Journal of Education and e-Learning Research. 2020; 7 (2):130–152. doi: 10.20448/journal.509.2020.72.130.152. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luekens, M.T., Lyter, D.M., and Fox, E.E. (2004). Teacher attrition and mobility: Results from the teacher follow-up survey, 2000–01 (NCES 2004–301). National Center for Education Statistics, U.S. Department of Education . Washington, DC. https://nces.ed.gov/pubsearch/pubsinfo.asp?pubid=2004301 .
- Malik, M. E., Danish, R. Q., & Usman, A. (2010). The impact of service quality on students’ satisfaction in higher education institutes of Punjab. Journal of Management Research, 2 (2), 1–11.
- Maqableh, M., & Jaradat, M. (2021). Exploring the determinants of students’ academic performance at university level: The mediating role of internet usage continuance intention. Education and Information Technologies . 10.1007/s10639-021-10453-y. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Marsh HW. Students' evaluations of university teaching: Research findings, methodological issues, and directions for future research. International Journal of Educational Research. 1987; 11 :253–388. doi: 10.1016/0883-0355(87)90001-2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marsh, H. W., & Grayson, D. (1995). Latent variable models of multitrait-multimethod data.Marsh, H. W., & Grayson, D. (1995). Latent variable models of multitrait-multimethod data. In R. H. Hoyle (Ed.), Structural equation modeling: Concepts, issues, and applications (p. 177–198). Sage Publications, Inc.
- Martin, A. M. (2021). Instructor qualities and student success in higher education online courses. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 37 (1), 65–80.
- Martínez-Argüelles, M. J., & Batalla-Busquets, J. M. (2016). Perceived service quality and student loyalty in an online university. International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 17 (4), 264–279.
- Martin F, Wang C, Sadaf A. Student perception of helpfulness of facilitation strategies that enhance instructor presence, connectedness, engagement, and learning in online courses. The Internet and Higher Education. 2018; 37 :52–65. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2018.01.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mensink PJ, King K. Student access of online feedback is modified by the availability of assessment marks, gender and academic performance. British Journal of Educational Technology. 2020; 51 (1):10–22. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12752. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohammed SS, Suleyman C, Taylan B. Burnout determinants and consequences among university lecturers. Amazonia Investiga. 2020; 9 (27):13–24. doi: 10.34069/AI/2020.27.03.2. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Moore JL, Dickson-Deane C, Galyen K. E-learning, online learning, and distance learning environments: Are they the same? Internet Higher Educ. 2011; 14 (2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.iheduc.2010.10.001. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mouratidis, A., Michou, A., Demircioğlu, A. N., & Sayil, M. (2018). Different goals, different pathways to success: Performance-approach goals as direct and mastery-approach goals as indirect predictors of grades in mathematics. Learning and Individual Differences, 61 , 127–135.
- Mtebe JS, Raisamo R. A model for assessing learning management system success in higher education in sub-Saharan countries. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries. 2014; 61 (1):1–17. doi: 10.1002/j.1681-4835.2014.tb00436.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Munteanu C, Ceobanu C, Bobâlca C, Anton O. An analysis of customer satisfaction in a higher education context. The International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2010; 23 (2):124. doi: 10.1108/09513551011022483. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Narad A, Abdullah B. Academic performance of senior secondary school students: Influence of parental encouragement and school environment. Rupkatha Journal on Interdisciplinary Studies in Humanities. 2016; 8 (2):12–19. doi: 10.21659/rupkatha.v8n2.02. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- NDTV (2020). Schools Closed, Travel To Be Avoided, Says Centre On Coronavirus: 10 Points. NDTV.com. Retrieved March 18, 2020.
- O'donovan B. How student beliefs about knowledge and knowing influence their satisfaction with assessment and feedback. Higher Education. 2017; 74 (4):617–633. doi: 10.1007/s10734-016-0068-y. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oliver RL. A congitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. JMR, Journal of Marketing Research (Pre-1986) 1980; 17 (000004):460. doi: 10.1177/002224378001700405. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pei L, Wu H. Does online learning work better than offline learning in undergraduate medical education? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medical Education Online. 2019; 24 (1):1666538. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2019.1666538. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Perlman S, & Mclntosh K. (2020). Coronaviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). In: J.E Benett, R. Dolin, M. J. Blaser (Eds.), Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious diseases. 9th ed . Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier: chap 155.
- Pillai, K. R., Upadhyaya, P., Prakash, A. V., Ramaprasad, B. S., Mukesh, H. V., & Pai, Y. (2021). End-user satisfaction of technology-enabled assessment in higher education: A coping theory perspective. Education and Information Technologies . 10.1007/s10639-020-10401-2.
- Pintrich P. The role of motivation in promoting and sustaining self-regulated learning. International Journal of Educational Research. 1999; 31 :459–470. doi: 10.1016/S0883-0355(99)00015-4. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rajabalee, Y. B., & Santally, M. I. (2020). Learner satisfaction, engagement and performances in an online module: Implications for institutional e-learning policy. Education and Information Technologies . 10.1007/s10639-020-10375-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Ramsden PA. Performance indicator of teaching quality in higher education: The course experience questionnaire. Studies in Higher Education. 1991; 16 (2):129–150. doi: 10.1080/03075079112331382944. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rogers J. Adults learning. 3. Open University Press; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rono, R. (2013). Factors affecting pupils' performance in public primary schools at Kenya certificate of primary education examination (Kcpe) in Emgwen Division, Nandi District, Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi) .
- Salloum, S. A. and Shaalan, K. (2018). Investigating students' acceptance of e-learning system in higher educational environments in the UAE: Applying the extended technology acceptance model (TAM), Ph.D. dissertation, Brit. Univ. Dubai, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2018.
- Sanderson G. Objectives and evaluation. In: Truelove S, editor. Handbook of training and development. 2. Blackwell; 1995. pp. 113–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schumacker RE, Lomax RG. A beginner's guide to structural equation modeling. L. L. Erlbaum Associates; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwarz C, Zhu Z. The impact of student expectations in using instructional tools on student engagement: A look through the expectation disconfirmation theory lens. Journal of Information Systems Education. 2015; 26 (1):47–58. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwinger M, Stiensmeier-Pelster J. Performance-approach and performance-avoidance classroom goals and the adoption of personal achievement goals. British Journal of Educational Psychology. 2011; 81 (4):680–699. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8279.2010.02012.x. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sher, A. (2009). Assessing the relationship of student-instructor and student-student interaction to student learning and satisfaction in web-based online learning environment. Journal of Interactive Online Learning, 8 (2).
- Sibanda L, Iwu CG, Benedict OH. Factors influencing academic performance оf university students. Демографія та соціальна економіка 2015; 2 :103–115. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sigala M. The evolution of internet pedagogy: Benefits for tourism and hospitality education. Journal of Hospitality, Leisure Sport and Tourism Education. 2002; 1 (2):29–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Simsek, U., Turan, I., & Simsek, U. (2017). Social studies teachers‟ and teacher candidates” perceptions on prompt feedback and communicate high expectations. PEOPLE: International Journal of Social Sciences, 3 (1), 332, 345.
- Singh, S. P., Malik, S., & Singh, P. (2016). Factors affecting academic performance of students. Paripex-Indian Journal of Research, 5 (4), 176–178.
- Shehzadi, S., Nisar, Q. A., Hussain, M. S., Basheer, M. F., Hameed, W. U., & Chaudhry, N. I. (2020). The role of digital learning toward students' satisfaction and university brand image at educational institutes of Pakistan: a post-effect of COVID-19. Asian Education and Development Studies, 10 (2), 276–294.
- Tawafak RM, Romli AB, Alsinani M. E-learning system of UCOM for improving student assessment feedback in Oman higher education. Education and Information Technologies. 2019; 24 (2):1311–1335. doi: 10.1007/s10639-018-9833-0. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO (2020). United nations educational, scientific and cultural organization. COVID19 educational disruption and response. UNESCO, Paris, France. https://en.unesco.org/themes/education-emergencies/coronavirus-school-closures . Accessed 17 Nov 2020.
- Urdan, T. (1997). Achievement goal theory: Past results, future directions. Advances in Motivation and Achievement, 10 , 99–141.
- Wilson KL, Lizzio A, Ramsden P. The development, validation and application of the course experience questionnaire. Studies in Higher Education. 1997; 22 (1):33–53. doi: 10.1080/03075079712331381121. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wooldridge, B. (1995). Increasing the effectiveness of university/college instruction: Integrating the results of learning style research into course design and delivery. In R. R. Simms and S. J. Simms (Eds.), the Importance of Learning Styles. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 49–67.
- World Health Organization (2019). https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1 , Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- Wright CR. Criteria for evaluating the quality of online courses. Alberta distance Educ. Training Assoc. 2003; 16 (2):185–200. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yen SC, Lo Y, Lee A, Enriquez J. Learning online, offline, and in-between: Comparing student academic outcomes and course satisfaction in face-to-face, online, and blended teaching modalities. Education and Information Technologies. 2018; 23 (5):2141–2153. doi: 10.1007/s10639-018-9707-5. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin H, Wang W. Assessing and improving the quality of undergraduate teaching in China: The course experience questionnaire. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. 2015; 40 (8):1032–1049. doi: 10.1080/02602938.2014.963837. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yorke M. Formative assessment in higher education: Moves towards theory and the enhancement of pedagogic practice. Higher Education. 2003; 45 (4):477–501. doi: 10.1023/A:1023967026413. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yu F, Du L, Ojcius DM, Pan C, Jiang S. Measures for diagnosing and treating infections by a novel coronavirus responsible for a pneumonia outbreak originating in Wuhan, China. Microbes and Infection. 2020; 22 (2):74–79. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.01.003. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yunusa AA, Umar IN. A scoping review of critical predictive factors (CPFs) of satisfaction and perceived learning outcomes in E-learning environments. Education and Information Technologies. 2021; 26 (1):1223–1270. doi: 10.1007/s10639-020-10286-1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zeithaml VA. Consumer perceptions of price, quality, and value: A means-end model and synthesis of evidence. Journal of Marketing. 1988; 52 (3):2–22. doi: 10.1177/002224298805200302. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhang L, Han Z, Gao Q. Empirical study on the student satisfaction index in higher education. International Journal of Business and Management. 2008; 3 (9):46–51. [ Google Scholar ]
"Advertisement"
Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown | Online Classes Essay

Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown
Hello Friends, In this post “ Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown | Online Classes Essay “, We will read about Online Classes During Lockdown as an Essay In detail with Benefits, Advantages, And Disadvantages , etc. So…
Let’s Start…
Today, hiring an online essay writer has become an essential part of students’ life. As this became a central issue, young learners even have to dedicate their papers to it.
If you don’t feel comfortable writing on such a point, find a professional custom writing service, like CustomWritings, and ask for some help. Who knows this field better than the company that represents it?
For the first time ever schools in India have moved as online classes .
Educational institutions had to adjust their teaching practices through online mode.
All my teachers are trying their best to clear all my doubts.
After explaining the lesson, our teachers provide us with notes of the chapter and assign us online homework .
The people of our country, our school’s students, and children and their parents had felt the impact of shutdowns schools and educational institutions .
Online classes via Skype, Zoom, Youtube, Google blog , etc are really helpful for everyone in society especially children as they are benefited from the same purpose and learning.
This is helping the teachers too as they get to communicate with their students and share knowledge .
Adjusting learning into the existing schedule is one of the best advantages of online classes .
In my opinion, a physical classroom is much more effective than online learning .
But these classes have helped me to keep up with my studies and disciplined me towards learning.
This has also inspired me to explore new digital learning tools. So I find my experience of online classes helpful.
The exams are held online. A couple of times, there are some issues relating to the poor quality of internet connection.
I really miss the traditional classes and interacting with my teachers and classmates.
Short And Long Essay On Online Classes
Write a Letter To Your Friend Telling Him About Online Classes
Dialogue Between Two Friends About Covid-19
Short Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown In 200+ Words
Online classes during lockdown are very much necessary in today’s “ Corona ” time.
The students are now being taught through this online mode only.
Teachers are trying so much to motivate students and involve them in online classes.
During this lockdown period , the teachers and students interacting as it happened earlier in a traditional classroom are not possible now.
the student also misses their classmates, friends very much.
First of all, the teachers are making a group of students on WhatsApp then send a link to join the various online meeting apps such as zoom, Jio meets, Google meets, etc .
The teacher then shares the screen with students of various topics. it can be audio as well as video.
They also, explain different chapters on various subjects. the teachers are really giving time which is appreciable.
They are trying to clarify the doubts of students even though this is live chatting.
To make every student indulge in online classes is really a work of patience.
The teachers tolerate every kind of indiscipline occurred due to students.
As the duration of the online classes is increasing, it has become a hectic schedule for both teachers and students.
due to this, the side effects of headaches and eye problems are prevalent.
Still, the teachers are putting tremendous effort and working hard to guide students.
Dialogue Between A Doctor And A Patient About Covid-19
Essay On The Best Thing I Learned During lockdown In 150+ Words
Essay On Experience Of Online Classes During the Lockdown

Due to this pandemic lockdown implemented all over the world.
During the lockdown , everything is closed. all schools and colleges are closed regarding safety purposes.
It is my first experience when I am staying at a home long time.
In starting days I felt very happy because I did not have to go to school but after few days my online classes started and I attend them regularly and my studies go on very well.
Online classes are like live classes where all students ask their queries and the teacher resolves them at same as traditional classes .
Online classes are amazing at it give us an opportunity to study like before without worrying about our safety.
We definitely enjoy our classes going and also appreciated the efforts made by our teachers and staff in arranging it.
These online classes also have their extra activity session where we get to interact with personalities having talents in various fields and they motivate and encourage us all.
We often play games online like GK quiz, and trick maths puzzles, etc . which are really funny and interesting.
These online classes are also in shorter duration as compared to traditional classes .
that provide extra time to improve me on the other skills that I am interested in.
If you have any questions related to “Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown | Online Classes Essay”, comment.
Finally, Thank you For Reading “Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown | Online Classes Essay”.
Write a Letter to Your Sister Congratulating her on Success in the Examination
Essay On How I Spent My Lockdown Days For all Class Students
Frequently Asked Questions & Answer:
There are many ways by which online classes help students during lockdown such as: It is available easily across the country. time-flexibility as well as money-saving. students can select the best tutors according to their choice etc.
My experience of online classes is so much good as well as funny. I’ve shared everything about my experience in this post, you can read it.
there are many advantages and disadvantages of online classes. but if we read in short, here are some main advantages as well as disadvantages of online classes: Advantages: The flexibility of time Easy to access A large number of students can join it at a time. Disadvantages: Poor internet connection in rural areas. Technical issues. Lack of discipline among students etc.
Online classes are not effective in India because most of the regions of India are rural areas. so, there is no proper internet connection, and rural people are not able to effort expensive devices such as mobiles, laptops, computers, etc.
You can read this post, But in short if we talk about it. then definitely online classes are good for students. but at this time a mixture of online as well as offline classes is more effective.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Digital Education
CDE Portal for Students & Teachers
Essay on Lockdown in English for Students and Children

This long essay on lockdown in English is suitable for students of classes 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10, 11, 12, and also for competitive exam aspirants. All important information related to how to write an amazing essay about Lockdown.
- 1.1 Definition
- 1.2 Introduction
- 1.3 Online Education During Lockdown
- 1.4 Advantages of Lockdown
- 1.5 Disadvantage of Lockdown
- 1.6 Lockdown 2021
- 1.7 Conclusion
Long Essay on Lockdown in English 800 Words
Lockdown essay in English – Lockdown is a term that exploded collectively around the world in the year 2020. With the widespread attack of an invisible virus, known as the Novel Coronavirus , the entire world was devastated by the Pandemic of this virus. It occurs during a wide variety of emergencies and it disrupts normal life.
Many words became popular after the arrival of Coronavirus, the term “lockdown” being one of them. A lockdown is a period of time when people have to stay home and are only allowed to travel in an emergency. During this period everything is closed except for some essential services like hospitals, grocery stores, medical stores, etc.
Introduction
Coronavirus has been considered the most contagious virus ever in the history of mankind. Its effects have become catastrophic within a short time. To prevent the spread of this Coronavirus in the country, our government has taken some drastic steps.
One of the most important measures implemented is a lockdown, where all businesses have been closed, all people have been confined to their homes and almost all professional, personal, and economic activities have come to a standstill.
The lockdown was announced and enforced on the 25 th of March, 2020. It has been extended, in phases, to continue till mid-June. The government has issued advisories to all citizens to practice social distancing and stay at home. The purpose of the lockdown is to prevent community transmission of this deadly virus so that the chain of transmission can be broken.
Each and every person faced many difficulties during this period but for the daily wagers, it was much more difficult. Work from home, online education , and online business were some of the options during this period, and the Indian government also helped the people a lot.
Online Education During Lockdown
For the first time, schools in India have moved to online classes. It is a struggle for the teacher as well as the students. School students, children, and their parents felt the impact to close schools and educational institutions.
The lockdown situation prompted people to learn and use digital technology and as a result, increased digital literacy.
The teaching material is easily shared among the students and the doubt questions are solved on Telegram, WhatsApp, E-mail, and various social media. Students need to learn digital skills for their own sake and improve the quality of education as well as changes in syllabus, textbooks, teacher training, and examination systems, but at the very least, the quality of online education must also improve needed.
Advantages of Lockdown
Due to the lockdown, on the one hand, while people have been forced to remain imprisoned in the house, on the other hand, many big benefits are also being seen. Some important benefits of essay on lockdown:-
- The rapidly spreading Coronavirus has been controlled by applying Lockdown.
- Due to the lockdown, the movement of vehicles has been reduced very much, factories have been closed, and the air of the cities has started to clear due to the rein in such activities.
- The impact of the lockdown is also being seen on global warming. In early April, scientists showed a hole of 1,000,000 square kilometers in the ozone layer above the North Pole. According to NASA, it has started filling these holes now.
- Earth’s vibration has been reduced by 30 to 50 percent due to less traffic, machines, and noise pollution.
- Due to Coronavirus, there has been a change in the cleanliness habits of the people. People are being more vigilant. Due to the lockdown, more time is also available for cleaning the house.
- People are learning to live with limited resources and insist on being self-sufficient (or Aatmnirbhar ) in the future so that they can produce themselves.
- During this lockdown period, we have got a lot of time for self-development and self-awareness.
- Most people in Lockdown are cooking at home and eating the same. Health will also be good due to good food.
Disadvantage of Lockdown
Some important disadvantages of the essay on Lockdown:-
- Many migrant laborers got trapped in different cities and they could not return to their homes due to which they had to face many difficulties.
- Many industries like agriculture, education, and entertainment are suffering. It has negatively impacted the world economy.
- Unemployment has increased rapidly due to the lockdown. Because of this many people have lost their jobs.
- All schools and colleges were closed due to the lockdown, due to which the students were not able to study well.
Lockdown 2021
The lockdown was imposed due to Coronavirus in March 2020 last year. The same situation is being seen again. Again in April 2021, Coronavirus is spreading rapidly due to which lockdown is being imposed in all the states one by one.
In view of this spreading Coronavirus, the CBSE board canceled the class 10 examination and postponed the class 12 examination.
Lockdown is something that affects people from all backgrounds and especially the daily wagers. Some of the main problems during a lockdown are employment, poverty, and starvation.
Overall, we should keep in mind that lockdowns are only imposed for our welfare, so it is always our duty to follow the rules of lockdown.
Related Article –
- Essay on New Education Policy 2020
- Essay on Article 370
- Essay on Farm Bill 2020
- Essay on Narendra Modi
- Essay on Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- Essay on Independence Day 2021
I hope you like this post “ Essay on Lockdown in English “. If you want to give any suggestions then comment below. Share this essay with your friends.
My Name is Mukesh Kumar. I am a Teacher, Blogger, Educational Content Writer, and Founder of CBSE Digital Education.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This change in environment causes a lack of concentration in students. In contrast, E-learning enables the students to choose the best environment for study, and this promotes their ability to understand. As a result, students enjoy the learning process as compared to conventional classroom learning.
In conclusion, we identified across‐year differences between primary and secondary school students' online learning experience during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Several recommendations were made for the future practice and research of online learning in the K‐12 student population.
Descriptive analyses indicated that about half of the students reported that the quality of the online classes received during the pandemic was bad or very bad (T1 = 54.1%, T2 = 46.2%), and more than a half thought that their academic development worsened during online classes compared to face-to-face classes (T1 = 66.4%, T2 = 68.9%).
Similarly, a survey of around 1,300 parents in the Netherlands found that during lockdown, children from working-class families had fewer computers at home and less room to study than upper/middle ...
What benefits did online classes bring to students during the lockdown period? 2. What challenges did students encounter with the online experience? 3. What are students beliefs, attitudes, and overall evaluation of online classes especially when compared ... (Goodyear and Zenios, 2007). Online classes during the pandemic may offer a fun and ...
14. I resist and/or am confused when getting appropriate help during online classes. 2.19: 1.52: 15. I have poor understanding of directions and expectations during online learning. 2.16: 1.56: 16. I perceive technology as a barrier to getting help from others during online classes. 2.47: 1.43: Student isolation challenges (SIC) 2.77: 1.34: 17.
Conclusion. In conclusion, online classes during lockdown have been a crucial response to an unprecedented global crisis. They have ensured the continuity of education while also revealing both the potential and the challenges of online learning. As we emerge from the pandemic, these insights can guide us in creating a more resilient and ...
The world as we know it has changed over a short period of time, with the rise and spread of the deadly novel Corona virus known as COVID-19, the world will never be the same again. This study explores the devastating effects of the novel virus pandemic, the resulting lockdown, thus the need to transform the offline classroom into an online classroom. It explores and describes the numerous ...
In this paper, we critically reflect on our experience of teaching urban design research methods online during the early COVID-19 lockdown in the UK. This is an exploratory case study with a qualitative approach with an aim to inform resilient practices of teaching in the face of public health emergencies.
Online education has traditionally been viewed as an alternative pathway, one that is particularly well suited to adult learners seeking higher education opportunities. However, the emergence of ...
The COVID-19 has resulted in schools shut all across the world. Globally, over 1.2 billion children are out of the classroom. As a result, education has changed dramatically, with the distinctive rise of e-learning, whereby teaching is undertaken remotely and on digital platforms. Research suggests that online learning has been shown to ...
Finally, point out the distinct features of online classes that conventional learning doesn't offer, such as face-to-face interaction and question-and-answer debates. You can also discuss various online classes schools offer, such as hybrid learning, interactive online courses, etc. 2. My Experience with Online Classes During Lockdown
The university suspended regular classes from 13th March 2020 and later a nationwide lockdown began in India on 25th March 2020. The academic programs of the university are based on intense classroom- and laboratory-based activities. ... 6 CONCLUSION. Online education has been on the fringe for a long time. The COVID-19 pandemic made it the ...
Online education has several disadvantages, such as internet browsing issues, computer compatibility issues, and technical issues. During the COVID-19 pandemic, students had to adjust their daily routines to an environment of isolation. Those studying abroad had to return home, but many were unable to do so due to airport and border closures.
Essay on Online Classes During Lockdown: Get well-researched online classes during lockdown essay in 500, 300, 250, 200 and 150 words in simple words. In recent years, online classes have gained significant popularity as a convenient and accessible mode of education. However, their importance skyrocketed during the global pandemic-induced ...
Overall, the students reported coping well during lockdown but indicated that lecturers were challenged by distance teaching, which created some stress for the students. ... The overall conclusion is that the majority of students would like to see a return to face-to-face classes. ... & Miller, S. F. (2013). Higher education: The online ...
Online Classes. Online Classes are a type of education system that is delivered via the Internet to students using computers, laptops, mobile phones, tablets etc., in the comfort of their homes. During the last decade, online courses and classes have become popular. Especially during the COVID pandemic, most schools have opted for online ...
An Online Class is a method of education that takes place over the internet. Due to the covid-19 pandemic, most of the governments around the world have imposed a lockdown and temporarily closed educational institutions. These online classes are really helpful for the students, especially during this lockdown period.
ONLINE CLASSES DURING LOCKDOWN. An online class is a method of education that takes place over the internet. Due to Covid-19 pandemic, most of the governments around the world have imposed lockdown and temporarily closed educational institutions. These online classes are really helpful for the students especially during this lockdown period.
Online classes during lockdown have affected the educational style in many ways be it good or bad. There has been a decrease in syllabus allowing people to adapt to new changes as the teachers tried creating a curriculum that could be executed in online classes. Regular assignments and tests were taken on the groups where all the notes were ...
The online classes has sharpened my analytic skills: 3.08: 0.82: 0.815: An online class really tries to get the best out of all its students: 3.38: 0.79: 0.734: 18.385: This course has helped me develop the ability to plan my own work: 3.18: 0.83: 2.52: 11.50: 0.804: 20.654: 0.891: Online classes has encouraged me to develop my own academic ...
Short Essay On Online Classes During Lockdown In 200+ Words. Online classes during lockdown are very much necessary in today's "Corona" time. The students are now being taught through this online mode only. Teachers are trying so much to motivate students and involve them in online classes. During this lockdown period, the teachers and ...
Definition. Lockdown essay in English - Lockdown is a term that exploded collectively around the world in the year 2020. With the widespread attack of an invisible virus, known as the Novel Coronavirus, the entire world was devastated by the Pandemic of this virus. It occurs during a wide variety of emergencies and it disrupts normal life.