
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Appendix A: Case Studies
List of case studies, case study 1: handling roommate conflicts, case study 2: salary negotiation at college corp, case study 3: oecollaboration, case study 4: the ohio connection, case study 5: uber pays the price, case study 6: diverse teams hold court.
Chapter Reference: Section 2.2 Approaches to Conflict
Whether you have a roommate by choice, by necessity, or through the random selection process of your school’s housing office, it’s important to be able to get along with the person who shares your living space. While having a roommate offers many benefits such as making a new friend, having someone to experience a new situation like college life with, and having someone to split the cost on your own with, there are also challenges. Some common roommate conflicts involve neatness, noise, having guests, sharing possessions, value conflicts, money conflicts, and personality conflicts (Ball State University, 2001). Read the following scenarios and answer the following questions for each one:
- Which conflict management style, from the five discussed, would you use in this situation?
- What are the potential strengths of using this style?
- What are the potential weaknesses of using this style?
Scenario 1: Neatness. Your college dorm has bunk beds, and your roommate takes a lot of time making their bed (the bottom bunk) each morning. They have told you that they don’t want anyone sitting on or sleeping in the bed when they are not in the room. While your roommate is away for the weekend, your friend comes to visit and sits on the bottom bunk bed. You tell your friend what your roommate said, and you try to fix the bed back before your roommate returns to the dorm. When they return, your roommate notices that the bed has been disturbed and confronts you about it.
Scenario 2: Noise and having guests. Your roommate has a job waiting tables and gets home around midnight on Thursday nights. They often brings a couple friends from work home with them. They watch television, listen to music, or play video games and talk and laugh. You have an 8 a.m. class on Friday mornings and are usually asleep when they returns. Last Friday, you talked to your roommate and asked them to keep it down in the future. Tonight, their noise has woken you up and you can’t get back to sleep.
Scenario 3: Sharing possessions. When you go out to eat, you often bring back leftovers to have for lunch the next day during your short break between classes. You didn’t have time to eat breakfast, and you’re really excited about having your leftover pizza for lunch until you get home and see your roommate sitting on the couch eating the last slice.
Scenario 4: Money conflicts. Your roommate got mono and missed two weeks of work last month. Since they have a steady job and you have some savings, you cover their portion of the rent and agree that they will pay your portion next month. The next month comes around and your roommate informs you that they only have enough to pay their half of the rent.
Scenario 5: Value and personality conflicts. You like to go out to clubs and parties and have friends over, but your roommate is much more of an introvert. You’ve tried to get them to come out with you or join the party at your place, but they’d rather study. One day your roommate tells you that they want to break the lease so they can move out early to live with one of their friends. You both signed the lease, so you have to agree or they can’t do it. If you break the lease, you automatically lose your portion of the security deposit
Works Adapted
“ Conflict and Interpersonal Communication ” in Communication in the Real World by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Ball State University. (2001). Roommate conflicts. accessed June 16, 2001, from http://cms.bsu.edu/CampusLife/CounselingCenter/VirtualSelfHelpLibrary/RoommateIssues.asx.
Chapter Reference: Section 2.4 Negotiation
Janine just graduated college, she’s ready to head out on her own and get that first job, and she’s through her first interviews. She receives an offer of a $28,000 salary, including benefits from COLLEGE CORP, from an entry-level marketing position that seems like a perfect fit. She is thrown off by the salary they are offering and knows that it is lower than what she was hoping for. Instead of panicking, she takes the advice of her mentor and does a little research to know what the market range for the salary is for her area. She feels better after doing this, knowing that she was correct and the offer is low compared to the market rate. After understanding more about the offer and the rates, she goes back to the HR representative and asks for her preferred rate of $32,500, knowing the minimum that she would accept is $30,000. Instead of going in for her lowest amount, she started higher to be open to negotiations with the company. She also sent a note regarding her expertise that warranted why she asked for that salary. To her happy surprise, the company counter offered at $31,000—and she accepted.
- What key points of Janice’s negotiation led to her success?
- What could have Janice done better to get a better outcome for her salary?
“ Conflict and Negotiations ” in Organizational Behaviour by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
“Good & Bad Salary Negotiations,” Salary.com , April 19, 2018, https://www.salary.com/articles/good-bad-examples-of-salary-negotiations .
Herner, M. (n.d). 5 things HR wishes you knew about salary negotiation. Payscale.com, accessed October 21, 2018, https://www.payscale.com/salary-negotiation-guide/salary-negotiation-tips-from-hr .
Chapter Reference: Section 3.2 Creating, Maintaining, and Changing Culture
At OECollaboration, a technology company that develops virtual collaboration software for new companies, Mike Jones is a new manager. One of the biggest challenges he has faced is that the team that he is managing is well established and because he is an outsider, the team members haven’t yet developed trust in him.
Two weeks into his new employment, Mike held a meeting and discussed all of the changes to the remote work agreements as well as implementing new meeting requirements for each employee to have a biweekly meeting scheduled with him to discuss their projects. The team was outraged, they were not excited, and the following days he wasn’t greeted in a friendly way; in addition, his team seemed less engaged when asked to participate in team functions.
Tracy James is also a new manager at OECollaboration who started at the same time as Mike, in a similar situation where she is a new manager of an existing team. Tracy was able to hold a meeting the first day on the job to listen to her team and get to know them. During this meeting she also told the team about herself and her past experiences. Additionally, she held one-on-one meetings to listen to each of her team members to discuss what they were working on and their career goals. After observation and discussion with upper management, she aligned her own team goals closely with the skills and experiences of her new team. She met with the whole team to make changes to a few policies, explaining why they were being changed, and set the strategy for the team moving forward.
Because she got her team involved and learned about them before implementing her new strategy, this was well received. Her team still had questions and concerns, but they felt like they could trust her and that they were included in the changes that were being made.
- What challenges can a new manager encounter when starting to manage an existing team?
- What strategies can a new manager implement to ensure that their new team is engaged with them and open to change and growth?
Adapted Works
“ Organizational Power and Politics ” in Organizational Behaviour by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Giang, V. (2013, July 31). The 7 types of power that shape the workplace. Business Insider. https://www.businessinsider.com/the-7-types-of-power-that-shape-the-workplace-2013-7
Morin, A. (2018, June 25). How to prevent a workplace bully from taking your power. Inc. https://www.inc.com/amy-morin/how-to-prevent-a-workplace-bully-from-taking-your-power.html
Weinstein, B. (n.d.). 10 tips for dealing with a bully boss,” CIO , accessed October 13, 2018, https://www.cio.com.au/article/198499/10_tips_dealing_bully_boss/.
Chapter Reference: Section 4.1 Power
Janey worked as an executive assistant to a product manager at her company: Ohio Connection. Overall, she loved her job; she was happy to work with a company that provided great benefits, and she and found enjoyment in her day-to-day work. She had the same product manager boss for years, but last year, her manager left Ohio Connection and retired. Recently her new manager has been treating her unfairly and showcasing bullying behavior.
Yesterday, Janey came into work, and her boss decided to use their power as her manager and her “superior” to demand that she stay late to cover for him, correct reports that he had made mistakes on, and would not pay her overtime. She was going to be late to pick up her son from soccer practice if she stayed late; she told him this, and he was not happy.
Over subsequent days, her boss consistently would make comments about her performance, even though she had always had good remarks on reviews, and created a very negative work environment. The next time she was asked to stay late, she complied for fear of losing her job or having other negative impacts on her job. Janey’s situation was not ideal, but she didn’t feel she had a choice.
- What type of power did Janey’s boss employ to get her to do the things that he wanted her to do?
- What negative consequences are apparent in this situation and other situations where power is not balanced in the workplace?
- What steps should Janey take do to counteract the power struggle that is occurring with her new manager?
Chapter Reference: Section 5.1 Interpersonal Relationships at Work
Uber revolutionized the taxi industry and the way people commute. With the simple mission “to bring transportation—for everyone, everywhere,” today Uber has reached a valuation of around $70 billion and claimed a market share high of almost 90% in 2015. However, in June 2017 Uber experienced a series of bad press regarding an alleged culture of sexual harassment, which is what most experts believe caused their market share to fall to 75%.
In February of 2017 a former software engineer, Susan Fowler, wrote a lengthy post on her website regarding her experience of being harassed by a manager who was not disciplined by human resources for his behavior. In her post, Fowler wrote that Uber’s HR department and members of upper management told her that because it was the man’s first offense, they would only give him a warning. During her meeting with HR about the incident, Fowler was also advised that she should transfer to another department within the organization. According to Fowler, she was ultimately left no choice but to transfer to another department, despite having specific expertise in the department in which she had originally been working.
As her time at the company went on, she began meeting other women who worked for the company who relayed their own stories of harassment. To her surprise, many of the women reported being harassed by the same person who had harassed her. As she noted in her blog, “It became obvious that both HR and management had been lying about this being his ‘first offense.’” Fowler also reported a number of other instances that she identified as sexist and inappropriate within the organization and claims that she was disciplined severely for continuing to speak out. Fowler eventually left Uber after about two years of working for the company, noting that during her time at Uber the percentage of women working there had dropped to 6% of the workforce, down from 25% when she first started.
Following the fallout from Fowler’s lengthy description of the workplace on her website, Uber’s chief executive Travis Kalanick publicly condemned the behavior described by Fowler, calling it “abhorrent and against everything Uber stands for and believes in.” But later in March, Uber board member Arianna Huffington claimed that she believed “sexual harassment was not a systemic problem at the company.” Amid pressure from bad media attention and the company’s falling market share, Uber made some changes after an independent investigation resulted in 215 complaints. As a result, 20 employees were fired for reasons ranging from sexual harassment to bullying to retaliation to discrimination, and Kalanick announced that he would hire a chief operating officer to help manage the company. In an effort to provide the leadership team with more diversity, two senior female executives were hired to fill the positions of chief brand officer and senior vice president for leadership and strategy.
Critical Thinking Questions
- Based on Cox’s business case for diversity, what are some positive outcomes that may result in changes to Uber’s leadership team?
- If the case had occurred in Canada, what forms of legislation would have protected Fowler?
- What strategies should have been put in place to help prevent sexual harassment incidents like this from happening in the first place?
“ Diversity in Organizations ” in Organizational Behaviour by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Della Cava, M. (2017, June 13). Uber has lost market share to Lyft during crisis. USA Today. https://www.usatoday.com/story/tech/news/2017/06/13/uber-market-share-customer-image-hit-string-scandals/102795024/
Fowler, T. (2017, February 19). Reflecting on one very, very strange year at Uber. https://www.susanjfowler.com/blog/2017/2/19/reflecting-on-one-very-strange-year-at-uber.
Lien, T. (2017, June 6). Uber fires 20 workers after harassment investigation. Los Angeles Times. http://www.latimes.com/business/la-fi-tn-uber-sexual-harassment-20170606-story.html
Uber (2017, February). Company info. https://www.uber.com/newsroom/company-info/
Chapter Reference: Section 5.3 Collaboration, Decision-Making and Problem Solving in Groups
Diverse teams have been proven to be better at problem-solving and decision-making for a number of reasons. First, they bring many different perspectives to the table. Second, they rely more on facts and use those facts to substantiate their positions. What is even more interesting is that, according to the Scientific American article “How Diversity Makes Us Smarter,” simply “being around people who are different from us makes more creative, diligent, and harder-working.”
One case in point is the example of jury decision-making, where fact-finding and logical decision-making are of utmost importance. A 2006 study of jury decision-making, led by social psychologist Samuel Sommers of Tufts University, showed that racially diverse groups exchanged a wider range of information during deliberation of a case than all-White groups did. The researcher also conducted mock jury trials with a group of real jurors to show the impact of diversity on jury decision-making.
Interestingly enough, it was the mere presence of diversity on the jury that made jurors consider the facts more, and they had fewer errors recalling the relevant information. The groups even became more willing to discuss the role of race case, when they hadn’t before with an all-White jury. This wasn’t the case because the diverse jury members brought new information to the group—it happened because, according to the author, the mere presence of diversity made people more open-minded and diligent. Given what we discussed on the benefits of diversity, it makes sense. People are more likely to be prepared, to be diligent, and to think logically about something if they know that they will be pushed or tested on it. And who else would push you or test you on something, if not someone who is different from you in perspective, experience, or thinking. “Diversity jolts us into cognitive action in ways that homogeneity simply does not.”
So, the next time you are called for jury duty, or to serve on a board committee, or to make an important decision as part of a team, remember that one way to generate a great discussion and come up with a strong solution is to pull together a diverse team.
- If you don’t have a diverse group of people on your team, how can you ensure that you will have robust discussions and decision-making? What techniques can you use to generate conversations from different perspectives?
- Evaluate your own team at work. Is it a diverse team? How would you rate the quality of decisions generated from that group?
Sources: Adapted from Katherine W. Phillips, “How Diversity Makes Us Smarter,” Scientific American, October 2014, p. 7–8.
“ Critical Thinking Case ” in Organizational Behaviour by OpenStax is licenced under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Conflict Management Copyright © 2022 by Laura Westmaas, BA, MSc is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Our Pillars
Think fast, fluently and structurally
Communicate with confidence and charisma
Navigate workplace challenges with ease
- Comparative Analysis
- Success Stories

Negotiation and Conflict Management: Skills, Case Studies, and Techniques
- Conflict Management
- June 28, 2024

Have you ever found yourself in the middle of a heated argument or complex negotiation, wondering how it could be resolved peacefully and effectively? Whether it’s in the boardroom or at the family dinner table, negotiation and conflict management skills are crucial tools for navigating human relationships.
Negotiation and conflict management are two dynamic fields that, when blended, offer robust solutions to some of life’s most challenging situations. These practices involve more than just talking through disagreements; they require a deep understanding of human behaviour, strategic communication, and a knack for finding common ground. Mastering conflict management skills can lead to enhanced relationships, more productive workplaces, and even personal growth.
Effective negotiation and dispute resolution require considering the needs and perspectives of the other party and other stakeholders . By understanding different perspectives , one can navigate conflicts more effectively. Additionally, accessing resources like a free special report can provide valuable insights and strategies for successful negotiation and dispute resolution .
This blog will explore the relationship between negotiating and managing conflicts, providing you with the strategies and insights needed to handle disputes effectively in any area of your life. Join us as we dive into a comprehensive guide designed to empower you with practical skills for peaceful resolution and agreement-making.
Understanding Conflict Management
Conflict management is an essential skill in both personal and professional realms, involving the ability to navigate and mitigate disputes effectively. At its core, conflict management is not about avoiding disagreements but rather about addressing them in ways that prevent escalation and foster mutual respect. Here, we explore the foundational aspects of conflict management, offering a deeper understanding of why conflicts occur and how they can be managed constructively within an organization . By learning to negotiate and deal with conflicts through talks and collaborative effort , individuals and teams can build stronger relationships and a more harmonious environment.
Conflict arises from differences in values, goals, needs, or expectations. In the workplace, conflicts emerge from resource allocation, workload distributions, or varying work styles among team members. In personal settings, differences in beliefs and lifestyles can lead to disputes. Effective conflict management not only resolves these issues but also enhances relational dynamics, promoting a culture of cooperation and respect. Involving every person and participants in the conversations helps in reaching a consensus . In a company , ongoing research can provide insights into the best practices for managing conflicts constructively, ultimately fostering a more collaborative and respectful environment.
Common Causes of Conflicts

Explore the key factors that often lead to conflicts in various settings.
Resource constraints: Limited resources can lead to competition among team members, sparking conflicts.
Value and cultural differences: Diverse backgrounds lead to varied perspectives, which can clash without a mutual understanding.
Communication gaps: Misunderstandings and lack of effective communication often escalate into conflicts.
Personality clashes: Differences in personalities and working styles can create friction.
Types of Conflicts
Understand the various types of conflicts that can arise in different situations.

Interpersonal conflicts: Arise from personal disputes among individuals, such as disagreements between co-workers over work styles or between friends over personal values. Two team members argue over the best approach to a project, each believing their method is superior.
Intra-group conflicts: Occur within a group and affect its internal dynamics. These can stem from differing opinions on how a group project should be executed. A project team splinters into factions over the direction of the project, leading to reduced cooperation and strained relationships.
Inter-group conflicts: Involve disputes between different groups or teams, often due to competition for resources or conflicting objectives. Sales and marketing teams clash over resource allocation, each accusing the other of jeopardising the company’s goals.
Organisational conflicts: Stem from structural or operational issues, such as conflicting departmental goals or misaligned incentives. A company’s production and quality assurance departments conflict over production speed versus quality control standards.
Psychological And Emotional Considerations
Emotions play a significant role in conflict scenarios. Stress, fear, and anger can exacerbate conflicts, making resolution more challenging. Emotional intelligence is crucial; it involves understanding and managing one’s own emotions and empathising with others. Training in emotional intelligence can help individuals recognise emotional responses to conflict and approach disputes with a level-headed, empathetic perspective. This emotional skill set is vital for de-escalating conflict and fostering an environment conducive to constructive resolution.
Result Of Effective Conflict Management
Discover the positive outcomes that effective conflict management can achieve.

Improved relationships: Constructive conflict resolution builds trust and understanding among parties, strengthening professional and personal relationships.
Enhanced problem-solving: Open, respectful communication during conflict resolution leads to innovative solutions that may not have been considered in a conflict-free environment.
Increased productivity: Effective conflict resolution removes obstacles that impede progress, leading to greater efficiency and satisfaction in work outcomes.
Greater organisational health: A culture that manages conflicts constructively experiences lower turnover rates, better employee morale, and a more cohesive work environment.
Effective conflict management not only resolves disputes but also transforms potential obstacles into opportunities for growth and collaboration. By embracing these principles and strategies, individuals and organisations can create a more positive, productive, and stable environment equipped to handle the complexities of human interactions.
Understanding Negotiation Skills
Negotiation is an indispensable skill in both professional and personal settings. It plays a critical role in conflict resolution and effective communication. Mastering negotiation skills enables individuals to reach agreements that benefit all parties involved, fostering collaboration and improving relationships. In this section, we explore the essentials of negotiation, including its definition, importance, and the critical skills required for successful outcomes.
Negotiation is when two or more parties with differing needs and goals discuss an issue to find a mutually acceptable solution. It is used across various contexts, from business transactions and labour agreements to resolving familial or interpersonal conflicts. Effective negotiation helps prevent misunderstandings, builds stronger relationships, and leads to better solutions that satisfy all involved parties.
Core Skills For Effective Negotiation
These skills equip individuals to manage disagreements constructively, create value in interactions, and achieve desired outcomes more efficiently.

Problem-solving: Negotiation is a problem-solving process. It requires creativity in finding solutions that are acceptable to all parties. This involves thinking outside the box and being willing to consider alternative solutions that may not have been initially apparent.
Decision-making: Effective negotiation requires timely and decisive decision-making. This involves analysing information, balancing risks and benefits, and making choices that move the negotiation toward a resolution.
Assertiveness: Being assertive means being able to firmly communicate your needs and rights without infringing on the rights of others. However, it’s equally important to remain flexible and open to compromise.
Like any skill, negotiation abilities improve with practice. Regular reflective practices, seeking feedback, and learning from each experience are essential for growth. Attending workshops, reading relevant literature, and getting coaching can also enhance one’s negotiation skills.
Understanding and mastering negotiation skills are essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of modern relationships and organisations effectively.
Core Principles Of Negotiation And Conflict Management
Negotiation and conflict management are different but interconnected disciplines with several core principles essential for effective resolution and agreement-making. These principles form the foundation of strategies designed to navigate disputes, enhance collaboration, and forge lasting agreements.

1. Preparation And Planning
Both negotiation and conflict management require meticulous preparation and planning. This involves understanding the context of the dispute or negotiation, identifying the interests and goals of all parties involved, and anticipating potential challenges. In conflict management, preparation might include gathering facts about the dispute and understanding the emotional landscape of the parties. In negotiation, it involves understanding the negotiation landscape, the stakes involved, and the other party’s objectives.
As Dwight D. Eisenhower famously said, “Plans are worthless, but planning is everything,” underscoring the importance of the planning process in any strategic scenario. Adequate preparation ensures that you enter negotiations or conflict resolutions with a clear strategy and objectives, improving the likelihood of a favourable outcome.
2. Clear Communication
At the heart of both fields is the necessity for clear, concise, and effective communication. This includes articulating your own needs and viewpoints clearly and listening actively to others. In conflict management, poor communication can escalate misunderstandings into full-blown disputes, while in negotiation, a failure to communicate effectively can result in missed opportunities for agreement.
A study by the American Management Association highlights that effective communication leads to a 50% reduction in conflict duration, emphasising the efficiency gains from precise interactions.
Techniques such as active listening, mutual understanding, and assertive communication are vital. These skills help prevent misinterpretations and foster an environment where all parties feel heard and understood, paving the way for effective problem-solving.
3. Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is crucial for managing one’s own emotions and understanding the feelings of others in both negotiating and managing conflicts. High emotional intelligence allows individuals to approach negotiations and disputes with empathy, manage stress effectively, and remain calm under pressure. This capability is essential for maintaining a constructive atmosphere during discussions, even when tensions rise. For instance, recognising when emotions might derail a conversation and addressing these emotions can prevent escalation and facilitate a more rational approach to problem-solving.
4. Focus on Interests Rather Than Positions
Both fields emphasise the importance of focusing on interests rather than positions. In conflict management, digging into the underlying interests helps reveal the real issues at stake beyond what is explicitly stated. Similarly, in negotiation, understanding the underlying motivations and needs of all parties allows for creating solutions that can satisfy deeper interests, leading to more durable and acceptable outcomes.
Nelson Mandela’s negotiations to end apartheid are prime real-life examples of focusing on interests over positions, where he looked beyond the immediate political disputes to the broader need for peace and reconciliation in South Africa. This approach encourages all involved to move beyond their initial demands (positions) to the reasons behind these demands (interests), facilitating a more flexible and creative problem-solving process.
5. Seeking Win-Win Outcomes
The aim in both negotiation and conflict management is often to achieve win-win outcomes where all parties feel they have gained something of value. This principle is about finding integrative solutions that do not merely compromise but optimise the outcomes for all involved. It involves identifying opportunities for synergy and mutual benefit. For example, in a workplace conflict over resource allocation, rather than dividing the resources equally (and perhaps suboptimally), identifying additional resources or alternate ways to enhance efficiency might satisfy all parties more effectively.
6. Respect And Fairness
Studies show that perceptions of fairness in negotiation contribute significantly to the durability of agreements, underscoring the importance of equitable processes. A commitment to respect and fairness is fundamental. This means treating all parties with dignity, ensuring that the process is transparent and the outcomes are fair.
In both negotiation and conflict resolution, perceived fairness in the process can significantly influence acceptance of the outcome. Ensuring that each party’s views are considered and that the final agreement respects their fundamental interests is crucial for maintaining ongoing relationships and trust.
Negotiators need a strong knowledge base and an understanding of the legal landscape and the other party’s interests. They can leverage the experience of their community, like colleagues or online forums, to refine their strategy. In some cases, government regulations influence the negotiation, requiring awareness of these frameworks.
7. Adaptability And Flexibility
Lastly, both negotiation and conflict management require adaptability and flexibility. Being open to changing one’s stance and adapting strategies in response to new information or shifting dynamics is critical. This flexibility can lead to more innovative solutions and improve the agreement’s or resolution’s resilience over time. This flexibility was notably demonstrated in the Cuban Missile Crisis negotiations, where President Kennedy’s ability to offer a reciprocal removal of U.S. missiles from Turkey helped resolve what could have escalated into a catastrophic conflict.
Negotiation vs. Conflict Management
In organisational behaviour and interpersonal dynamics, negotiation and conflict management are often discussed together. While they overlap and interact significantly, it’s crucial to understand their distinctions, as each plays a unique role in how businesses and individuals navigate dispute resolution and achieve objectives.

Negotiation: The negotiation process is used to resolve disputes by discussing the issues openly and aiming to reach an agreement that benefits all parties involved. It is a subset of conflict resolution focusing on direct communication and compromise to settle differences. Negotiation is often transactional and can be considered a tactical approach aimed at resolving a particular conflict or concluding a specific agreement.
Conflict Management: Conflict management is a broader term that encompasses a range of strategies and processes used to prevent, manage, and resolve conflicts. It includes not only negotiation but also other methods, such as avoidance, accommodation, or even competition, depending on the situation. Conflict management is more strategic and consists of the identification, analysis, and resolution of conflicts within a team or organisation over time.
Objective and Focus
Negotiation Goals: The primary goal of negotiation is to find a solution or reach an agreement that all parties can accept. Negotiators often seek a win-win scenario, where compromises are made to ensure that each party’s fundamental interests are addressed. The focus is on the issue at hand, and the process is generally confined to specific conflicts or deals.
Conflict Management Goals: Conflict management aims to improve interaction patterns and team dynamics to prevent the escalation of conflicts. It focuses not only on resolving disputes specifically but also on creating an environment that reduces the likelihood of conflicts arising in the first place. The ongoing health of relationships and organisational culture is a key concern.
Processes And Techniques
Negotiation Techniques: Negotiation involves techniques such as preparing a bargaining table, understanding the opponent’s needs, active listening, persuasive communication, and sometimes mediation by a third party. It often requires a deep understanding of negotiation tactics and the ability to apply them effectively to sway the outcome favourably.
Conflict Management Techniques: Conflict management may utilise a variety of techniques based on the conflict type and the organisational context. These include setting clear communication protocols, establishing norms for interaction, training team members in emotional intelligence, and designing feedback mechanisms. Conflict management is continuous and proactive, aiming to equip teams with the skills to handle disputes internally before they escalate.
Temporal Nature
Negotiation Duration: Negotiation is generally a shorter-term activity with a clear beginning and end. Once the parties reach an agreement, the negotiation is typically considered complete, although the implementation of agreements might be ongoing.
Conflict Management Duration: Conflict management is an ongoing process. It does not end with resolving a single issue but continues to evolve as the organisation or team grows. Effective conflict management adapts to new challenges and conflicts as they arise, making it a continuous aspect of organisational development.
Outcomes And Evaluation
Negotiation Outcomes: Successful negotiation is measured by the terms of the agreement reached and how well it is implemented. The immediate effectiveness is often visible and tangible, whether in contractual terms or resolved disputes.
Conflict Management Outcomes: The success of conflict management is evaluated over a more extended period and can be seen in the overall reduction in conflict occurrences, improved team cohesion, and enhanced productivity. It involves a more qualitative assessment of team and organisational health.
While negotiation can be an effective tool within conflict management, it does not encompass the entire scope of managing conflicts. Negotiation skills are a part of the toolkit for conflict management, which also requires understanding broader dynamics and developing systems to manage conflicts effectively across an organisation.
Combining Negotiation And Conflict Management
Negotiation and conflict management are complementary skills that, when used together effectively, can resolve disputes and foster a cooperative environment. Understanding when to use negotiation as part of a broader conflict management strategy is crucial for achieving lasting solutions, particularly in complex or sensitive situations. This section explores the strategic integration of negotiation within conflict management, illustrated with real-world case studies and strategies for negotiating with challenging personalities.
When To Use Negotiation To Manage Conflicts
Learn when negotiation is the best approach to resolving conflicts effectively.

Interests are alignable: When the conflicting parties have interests that can potentially be aligned or integrated, negotiation is a suitable method. It allows for the deep exploration of these interests and the discovery of creative solutions that satisfy both sides.
Direct Communication is possible: If the parties are willing to engage directly and openly, negotiation can lead to a more thorough understanding and more durable agreements.
The relationship is valuable: In situations where maintaining or improving the relationship is as important as resolving the conflict itself, negotiation offers a respectful and collaborative approach to conflict resolution.
Disney And Pixar Merger: A Case Study
The merger between Disney and Pixar in 2006 is a classic example of how effective negotiation and conflict management can lead to a successful integration of two companies, each with its own unique culture and creative philosophy. This merger not only combined two entertainment giants but also blended differing corporate cultures and artistic approaches, making the negotiation and subsequent management of potential conflicts crucial for success.

Background And Challenges
Disney, a long-established leader in animated films, was facing creative stagnation and needed a fresh infusion of innovation and creativity. Pixar, known for its cutting-edge animation technology and innovative storytelling, had been a vital partner, but the existing distribution agreement between the two parties was set to expire. The potential renewal of this agreement brought to light various underlying conflicts, including issues of content control, revenue sharing, and operational independence.
Negotiation Strategies Employed
Explore various strategies used to achieve successful negotiation outcomes.

Aligning interests: Central to the negotiation was the alignment of interests. Disney desired continued access to Pixar’s creative power and technological prowess, whereas Pixar sought to retain its artistic independence and control over its projects. Both companies recognised that a successful merger could provide mutual benefits: Disney could revitalise its animation studio with Pixar’s creative input, and Pixar could leverage Disney’s vast distribution network.
Preserving culture and independence: One of the most significant potential conflicts was the fear that Pixar’s unique culture and creative process would be stifled under Disney’s corporate structure. To manage this conflict, Disney negotiated terms that allowed Pixar to retain its independent identity, including its brand, creative process, and operational independence. This assurance was pivotal in mitigating concerns and fostering a cooperative atmosphere.
Leadership roles: Another significant aspect of the negotiation involved leadership roles. Ed Catmull and John Lasseter of Pixar were given control of Disney’s animation division, ensuring that the creative philosophies that had made Pixar successful would permeate Disney’s broader animation efforts. This move was critical in managing potential internal conflicts by aligning leadership goals across both organisations.
Conflict Management Post-Merger
Understand the essential techniques for managing conflicts following a merger.

Integration without assimilation: Post-merger, the challenge was to integrate the companies without diluting Pixar’s successful culture. Disney managed this potential conflict by allowing Pixar to operate as a separate entity, thus preventing the usual post-merger cultural clashes.
Regular communication and collaboration: To further manage conflicts and foster a positive relationship, Disney and Pixar established regular communication channels at all levels of both organisations. This openness prevented misunderstandings and ensured that minor disputes were resolved quickly before escalating.
Shared goals and vision: By continuously aligning on shared goals and reinforcing the vision of collaborative success, both companies managed potential conflicts about the direction of joint projects. They celebrated shared successes, which reinforced the many benefits of the merger and the value of combined efforts.
The Disney-Pixar merger is widely regarded as one of the most successful mergers in entertainment history, primarily due to the effective negotiation and conflict management strategies employed. The merger allowed Disney to reclaim its animation leadership while Pixar continued to produce critically acclaimed films under its own brand.
This case study exemplifies how combining negotiation with conflict management can address potential issues effectively, leading to a partnership that respects autonomy and enhances the strengths of both parties involved. The careful handling of cultural integration, leadership alignment, and preservation of creative independence were critical factors in the enduring success of the Disney-Pixar merger.
The strategic combination of negotiation and conflict management is pivotal in transforming potential adversities into opportunities for growth and collaboration. By prioritising clear communication, respecting cultural differences, and aligning interests, organisations can navigate complex negotiations and manage conflicts with finesse.
Whether dealing with corporate mergers, team dynamics, or personal relationships, the principles of negotiation and conflict management serve as fundamental tools for fostering a cooperative environment and achieving sustainable resolutions. This comprehensive exploration underscores their indispensable role in modern organisational and personal success, encouraging a proactive rather than reactive approach to conflict and negotiation.

Rishabh Bhandari
Rishabh Bhandari is the Content Strategist at Kapable. Rishabh likes to transform complex ideas into captivating narratives relatable to the target audience. He loves telling stories through his content. He believes that stories have the power to shift mindsets and move mountains. He has 3 years of experience in educational blog writing and copywriting.
Stress and Conflict Management: Managing Conflict and Stress in Contemporary Society
The importance of emotional intelligence: its need and impact in life, kapable updates.

July Cohort Orientation

Develop Must-Have Skills To Navigate Workplace Challenges And Build Executive Presence
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Gain insider access to expert strategies and solutions for leadership success
Explore Topics
- Presentation Skills (21)
- Stage Fear (3)
- Conflict Management (17)
- Emotional Intelligence (29)
- Articulation (2)
- Story Telling (1)
- Communication Skills (25)
- Public Speaking (12)
- Leadership (60)
- Persuasion (10)
- Self Confidence (17)
- Negotiation Skills (31)
Recent Posts

Self Confidence Swami Vivekananda Quotes: Wisdom and Inspiration
- 16 February 2024

200 Public Speaking Topics: Unique Speech Ideas for Students in English
- 22 January 2024

Inspiring Leadership Stories: Short Narratives with Moral Lessons
- 15 January 2024

Contingency Theory Of Leadership: Meaning, Approach, Models, and Examples
- 20 October 2023

Behavioral Theory of Leadership: Definition, Approach in Organisational Behavior
Begin your transformational journey, you can also check out.

10-Step Framework For Public Speaking Tips

How To Become A Public Speaker: 5-Step Process

Frequently Asked Questions
We train working professionals on enhancing the essential skills so that they become better thinkers, communicators, and leaders. Our comprehensive programs cover key aspects of leadership including strategic thinking, effective communication, and management capabilities.
Our programs are ideal for anyone looking to enhance their executive presence, lead teams effectively, and communicate with confidence and charisma to make a significant impact in their organisation.
- Your Journey
What Is Conflict Resolution?
Why are conflict resolution skills important, conflict resolution skills examples, conflict resolution skills at work: case studies, how to build conflict resolution skills, conflict resolution skills: the bottom line, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Table of Contents
No one likes conflict. When you disagree with a coworker, it can be awkward at best and lead to job dissatisfaction and even a threat to your position at worst. Conflict resolution skills are crucial to positive work relationships, success, and growth at work.
But what exactly are conflict resolution skills? How can you cultivate them, even without work experience? We’ll discuss everything you need to know about conflict resolution, why it’s essential, and how to build these critical soft skills — without stepping foot into an office.
Conflict resolution is the ability to end a dispute respectfully in a way that benefits all parties. More simply, it’s the ability to end a disagreement, argument, or even a fight politely and successfully.
In our everyday lives, this can range from something as simple as disagreeing with your friend on what to cook for dinner to something larger like addressing your friend’s feelings when they’re feeling left out of your friend group. In the workplace, conflict ranges from small to big, too; you might disagree with a coworker about how to phrase an email your company is sending, or you might have a more significant conflict about how they acted while working with you on a project.
Regardless of the situation, conflict resolution skills can help you work through challenges with others to get your work done more efficiently and stress-free. Conflict resolution skills can lead to:
- Better working relationships: Working with someone you find difficult is no fun. Conflict resolution skills can help you iron out issues so you can work together harmoniously.
- Getting work done more efficiently: When you can resolve conflict with others, work, especially collaborative projects, becomes much more manageable. You don’t need a coworker to be yet another blocker to hitting your team’s goals; instead, work becomes easier when you can collaborate and work together, not against each other.
- Happier work environment: It’s unpleasant to show up to work (in-person or virtually) when you have a conflict with someone. Addressing issues head-on can clear the air and make your work experience more enjoyable.
- Career growth: Conflict resolution skills are valuable soft skills. Being an effective mediator can help you become a more successful and personable employee, someone everyone wants to work with and have on their team.

Client Service
Practice de-escalating conflict as a customer service specialist. Record a call between you and your client and suggest a suitable path forward.
Avg. Time: 3-4 hours
Skills you’ll build: Triage, problem-solving, de-escalation, customer retention, composure
Conflict resolution requires various skills to effectively listen to others, empathize with them, and work together toward a solution.
Active Listening
Active listening is when you’re not only listening to someone but actively engaging with and processing what they’re saying. It might look like engaged body language (like nodding and eye contact) or asking follow-up questions to clarify or further explore what the other person was saying.
Active listening is vital to conflict resolution. It allows you to truly understand and process what the other person in the conflict is going through. Listening to their perspective and taking it seriously can help you know where they’re coming from and find a solution that considers their feelings, perspectives, and goals.
Negotiation
Resolving a conflict often means you’ll need to use negotiation skills to get the outcome you’re looking for. The goal is to find a solution that works for both or all parties, which means asking for what you want while trying to find a middle ground.
Many of us may shy away from conflict because it requires asserting ourselves in sometimes awkward or difficult situations. This is where leadership skills come in. The decision to resolve a conflict requires one person to step up to address the problem — taking ownership, considering multiple perspectives, and developing an action plan.
Decision-Making
Conflict resolution ends with a decision that benefits all parties. Good decision-making skills can help you assess the facts of the situation and come to a rational conclusion. These skills also come in handy when a conflict seems to drag on forever; people who are good decision-makers are biased toward action and focus on finding a solution rather than continuing to fight.
Communication
Unfortunately, even if you’re in a dispute with a person you really can’t stand, you’ll need to communicate with them to resolve a conflict. Using communication skills to speak or write confidently, clearly, and with empathy can help you find an agreeable solution more efficiently.
>>MORE: What Are Verbal Communication Skills?
Collaboration
When you’re in a conflict, it can feel like you’re going head-to-head with someone else; however, you must work together to resolve that conflict. Collaboration skills ensure you consider the other person’s perspective, communicate the right information, and work together to determine the best solution.
Now you know what conflict resolution skills are, but how are they actually applied at work?
Connecting on the Outcome
Peter Premenko, founder and president of Phronesis Group, a boutique consultancy focusing on leadership, management, and team culture development, shared a time he wanted to change a company process—but not everyone was on board.
“My team needed to change the way we executed new employee onboarding,” Premenko says. “Our director of recruiting was dead set against the change because our existing program was world-class, and his team relied on it as part of the pitch to come work for our company. My approach with him was to take things up a level to something we did agree on: having the best people doing their best work for our company. This way we were solving a problem we both cared about together, instead of trying to defend my priority and defeat his. It took a little longer than I might have liked, but he eventually saw why the change I wanted to make was important and agreed to it.”
Connecting on why Premenko wanted to make the change allowed the director of recruiting to understand his motivation and realize they shared the same goal.
Leading With Kindness
Stefan Chekanov, co-founder and CEO of Brosix, a secure instant messenger, shared a stressful moment when his team had been working hard to release new software features, include an AI integration, and redesign the company website.
“This churn caused a bit of extra tension to start brewing internally, and unproductive, heated discussions rarely lead to anything more than mutual frustration,” Chekanov says.
To resolve the conflict, Chekanov decided to lead with kindness.
“Whenever I noticed a team member (including myself) becoming increasingly agitated, I set up a private meeting for a genuine heart-to-heart,” he said. “At the end of the day, leading with empathy is how I gently nudge communication in a more constructive, positive direction. You don’t need work experience to be a decent human being, to put it simply.”
Providing Context
I had a conflict with a manager about an article I was working on about the “girlboss.” The main point of my article was that “girlboss” isn’t something to strive to be, but my manager disagreed and asked me to rewrite the piece. She took offense, thinking I wasn’t advocating for women’s advancement in the workplace; I took offense because she thought those were my views!
To resolve the conflict, I realized a vital piece of context was missing. As a Gen Zer, “girlboss” is a term my friends and I use sarcastically and jokingly; however, when the term first came into the cultural context, it was considered empowering.
>>MORE: Bye-Bye, ‘Bandwidth’ — 50 Examples of Gen Z Jargon at Work
I did more research to show my manager how the conversation around the term had changed and brought concrete examples of how people were using the term now. After providing that context, we were able to edit the piece to add that research and nuance. It led to one of my favorite pieces I’ve ever written — one that was much better than the first draft I’d handed in.
Listening to Everyone’s Ideas
Kimberly Best’s work directly involves conflict resolution; she’s a civil mediator, trained family mediator, certified arbitrator, and owner of Best Conflict Solutions. She worked closely with a health care system with 17 medical offices struggling with employees leaving — the system had an attrition rate of 33%.
With such a company-wide issue, Best sought to understand what leaders and employees had to say.
“First, I spoke with managers to hear what they experienced and what they proposed as resolutions,” she said. “I then formulated a statistically valid and reliable survey. I included a Likert scale and open-ended questions to get a full picture of management and team experience. Then I met with individuals and heard their stories and ideas. I asked teams to propose their needs and provide solutions.”
After listening to various people, Best used the data to meet with management and brainstorm what they could do differently.
“Ironically, one primary need was for conflict management training and an effective conflict management system,” she said. “I provided conflict management training to teams and managers.”
After Best both provided training and helped create a system for conflict management processes, attrition at the health care system was 18% the following year.
Soft skills can feel more challenging to build because they’re less tangible than hard skills . For example, it may seem easier to approach learning programming skills , where you can take a coding bootcamp , than to learn how to collaborate better. But that doesn’t mean you can’t learn soft skills — or that you need to be in the workplace to learn them! Here’s what conflict resolution experts recommend if you’re looking to build these soft skills before landing your first role.
Role-Playing
“Participate in role-playing exercises or simulations that mimic workplace conflicts,” says Beth Fries, an organizational leadership professional and doctoral candidate researching readiness skills in diverse corporate sectors. “This can be done in a classroom setting, with friends or mentors, or through online platforms.”
Forage job simulations can help you practice conflict resolution skills without needing a friend or even leaving your home.

Getting Ready to Join the Workforce
Practice using mediation skills to resolve an internal conflict on your team.
Avg. Time: 4-5 hours
Skills you’ll build: Emotional intelligence, prioritization, time management, self-reflection
Get Feedback
Fortunately (and unfortunately), conflict is often a part of our everyday lives, even if we might not realize it. The next time you argue with a friend or disagree with a family member, take a step back and reflect on how you approached the situation.
“Ask friends, family, or mentors for feedback on handling conflicts in everyday situations,” Fries says. “Use their input to improve your approach.”
Practice the Process
Kristyn Carmichael, professional mediator, family attorney, and certified divorce financial analyst, shares a three-step process for resolving conflict: listen, respond, resolve.
First, use active listening skills as the other person shares their perspective. Carmichael notes it’s essential to identify the “underlying issues rather than positions.”
A position is someone’s feelings about a situation, like “I don’t like working in a group with you.”
“An interest is the underlying why: the person fears you will overshadow their work or get credit; they’re nervous you won’t put in work due to past experience; they don’t like you because you stole their lunch once (even on accident),” Carmichael says. “We all have underlying interests for what we want. It is important to be an active listener and ask questions, not become defensive or shut the other person down by shifting the conversation to yourself.”
Next, it’s time to respond by addressing the issues the person raised and acknowledging their feelings, even if you disagree with them.
Using the same scenario of someone not wanting to work in a group with you, Carmichael offers an example response:
“Thank you for sharing with me that you don’t want to be on this project with me because you have heard negative things about my work ethic from others who have worked with me and you don’t think we will get along. I appreciate you sharing your thoughts and understand why you may be nervous to work with me.”
Ultimately, your goal is to find a resolution that benefits everyone. Carmichael recommends brainstorming solutions that work for both parties. Once you’ve decided on one, ensure you have a plan to implement and follow through on the resolution.
Conflict can be scary, and you might try to avoid it. Yet good conflict resolution skills can not only improve your working relationships, but can also lead to career growth and a happier work environment.
“Conflict is not bad; it’s a sign of a problem to solve,” Best says. “The most important thing in conflict resolution is building trust. This is done by listening well, empathy through genuine caring, and providing an environment that is safe to be honest. Safety is achieved through the above and through confidentiality and an environment without blame or judgment. When people feel heard, understood, and validated — the world makes sense through their eyes, and you demonstrate that you can see that — then creativity and problem-solving begin.”
Image credit: Canva

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, what is github uses and getting started, what is git definition and how to use it, upskill with forage.

Gain job skills you can talk about in interviews.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Must-Have Conflict Management Case Study Examples with Templates and Samples

Ananya Bhaduri
“Avoiding conflict doesn’t make it go away; it just goes away and sharpens its fangs.”- Amy Alkon.
Conflicts often emerge like untamed brushstrokes on a canvas in the vast tapestry of the modern workplace, where diverse personalities and ambitions intertwine. Like skilled artists, adept leaders know conflict management is critical to transforming these chaotic clashes into harmonious masterpieces. Picture a symphony conductor orchestrating a medley of differing notes, rhythmically merging dissonance into a harmonious melody. Workplace conflict management is akin to that conductor, delicately navigating the complexities of human interaction, listening to the various voices and perspectives, and conducting a harmonious resolution. It is the art of understanding, empathy, and communication, allowing teams to transcend discord and embark on a collective journey toward collaboration and success.
Importance of Conflict Management
Conflict management or conflict resolution is essential for fostering productive and harmonious relationships in both personal and professional contexts. It is pivotal in promoting understanding, resolving differences, and facilitating growth and innovation. Effective conflict management enables individuals and groups to navigate disagreements, negotiate compromises and maintain a positive and collaborative atmosphere.
By addressing conflicts constructively, conflicts can be transformed into opportunities for learning and development. Conflict management helps to prevent escalation and destructive outcomes, such as strained relationships, loss of trust, and decreased productivity. It promotes open communication, active listening, end empathy, allowing parties to express their concerns, interests, and needs.
Moreover, conflict management is crucial for promoting diversity and inclusivity. It encourages the exploration of various perspectives and fosters a culture of respect and acceptance. By acknowledging and valuing differences, conflicts can be seen as a means to challenge assumptions, foster creativity, and drive innovation.
In summary, conflict management is of utmost importance. It enables individuals and organizations to handle disagreements and differences constructively, improving relationships, increasing productivity, and creating a more inclusive and resilient environment.
Suppose you're willing to offer practical training for your team and colleagues regarding conflict management. In that case, you can check our training module, which focuses on workplace conflict and prevention techniques.
Template 1: A Case Study on Conflict Management at Workplace
Explore the following template that showcases a case study on workplace conflict management. Use this pre-designed template to outline the context of the conflict within your organization. This concise yet comprehensible template enables your workforce to effectively grasp the conflict's background. Get this template now!

Download now
Template 2: A case study on Conflict Management at the Workplace
Use this slide to highlight the decision regarding conflict management in your organization. This template describes the decision taken and the outcome of the decision. This ready-to-use template is column structured. One explains the decisions taken, and the other denotes the outcomes. This format easily attracts customers; you can edit the decisions and outcomes per your requirements.

Template 3: Recommended Conflict Management Solution Template
This content-ready template helps you showcase the recommendations regarding the conflict management solution. It states that the decisions should be based on facts, and there should be proper reasoning when making the decisions. On the other hand, it also mentions using external assessment firms for making such decisions. Lastly, you can formulate workplace behavior rules and regulations to control aggressive employee behavior. Since this template is customizable, you can add more recommendations according to your needs.

Template 4: Case Study on Employee Dispute at Workplace Template
This PPT Slide allows you to describe the background of the employee dispute in your workplace. Disputes or conflicts can be based on discrimination. In this template, you can highlight the conflict between the employees and what are the issues faced by them. Get this slide now to get started!

Template 5: Conflict with Manager Template
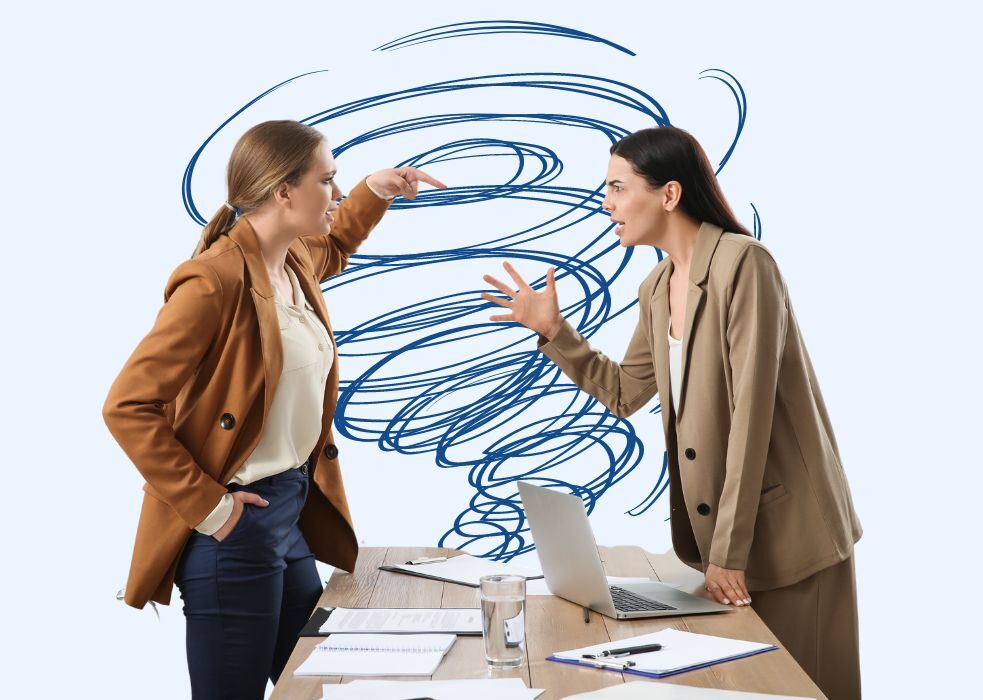
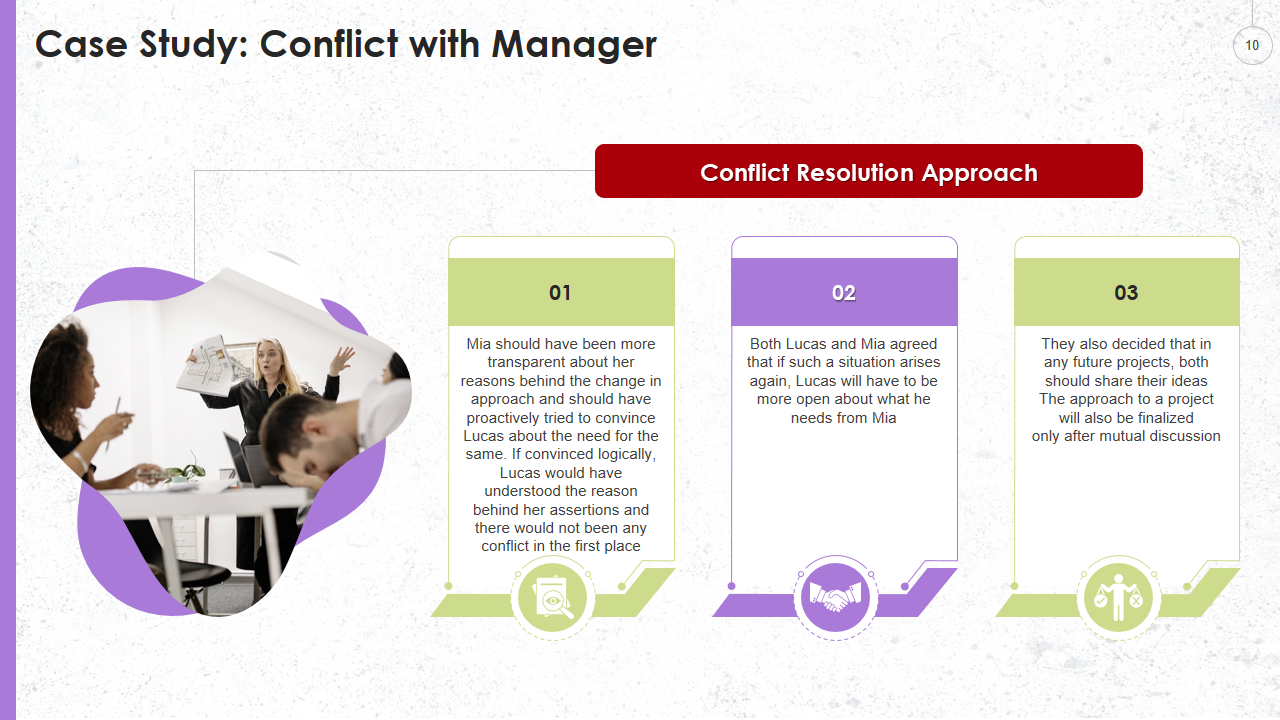
Use this slide to emphasize the background of the conflict involving the manager. This specific slide highlights the conflict stemming from divergent perspectives on a project. Our dedicated experts have designed these templates to be easily editable, enabling you to incorporate the conflict's background according to your specific needs. Access this template from the given link.

Template 6: Conflict Resolution Approach Template
Discover this PPT Template that showcases the conflict resolution approach adopted within your organization. Within this template, the initial resolution articulates a clear and rational rationale for the change in approach. The second resolution emphasizes the significance of mutual agreement through a constructive dialogue between the employee and the manager. You have the flexibility to customize the resolutions based on the conflict background prevalent in your company. The captivating structure and enriching content of this template will undoubtedly captivate your audience. Act now and seize this opportunity!
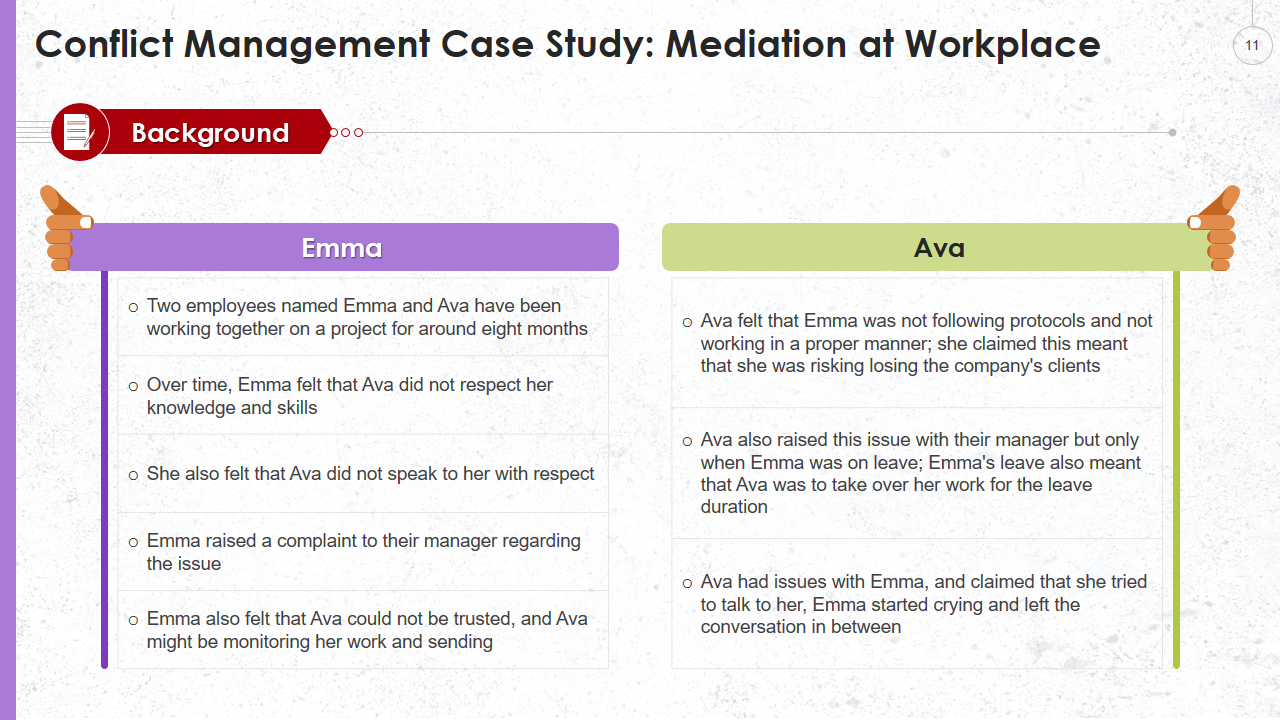
Template 7: Mediation at Workplace Template
Mediation holds utmost importance in resolving workplace conflicts among employees or teams. To address conflicts within your company, avail yourself of this downloadable template. It provides a platform to outline the background of the conflict comprehensively. The template emphasizes conducting a role play to effectively resolve the conflict, suggesting the involvement of three individuals as volunteers to portray the employees' roles. However, you have the liberty to customize the template to suit your specific requirements. Download this template right away.
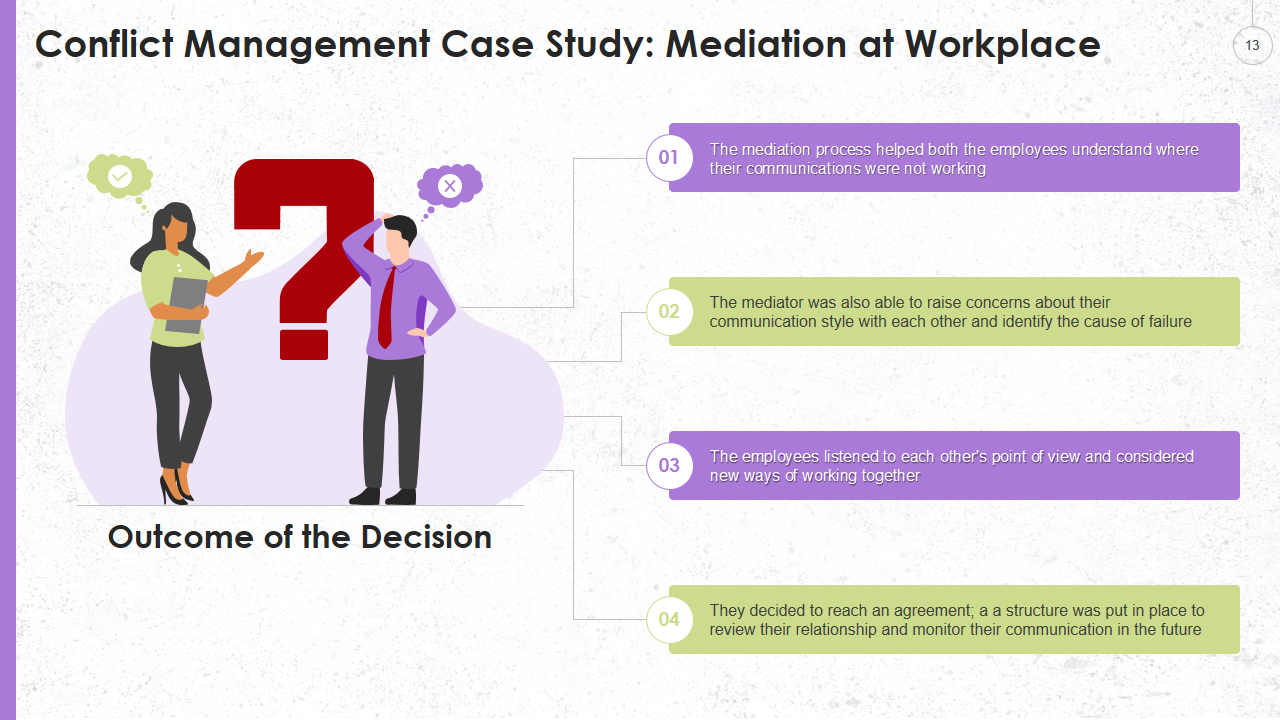
Template 8: Outcome of the Decision Template
This template allows you to focus on the Outcome of the decision. It states that the mediation process helps when communication doesn't work. With this template, you can identify the cause of failure and find new ways of working together. Grab this template now!
Template 9: Conflict Resolution Template
Use this PPT Slide to define your actions regarding the resolution of conflict when both of them were part of your team. With the background of the incident, you can act to resolve the conflict. The colorful and rich content can easily attract your customers. Get this template from the given link!

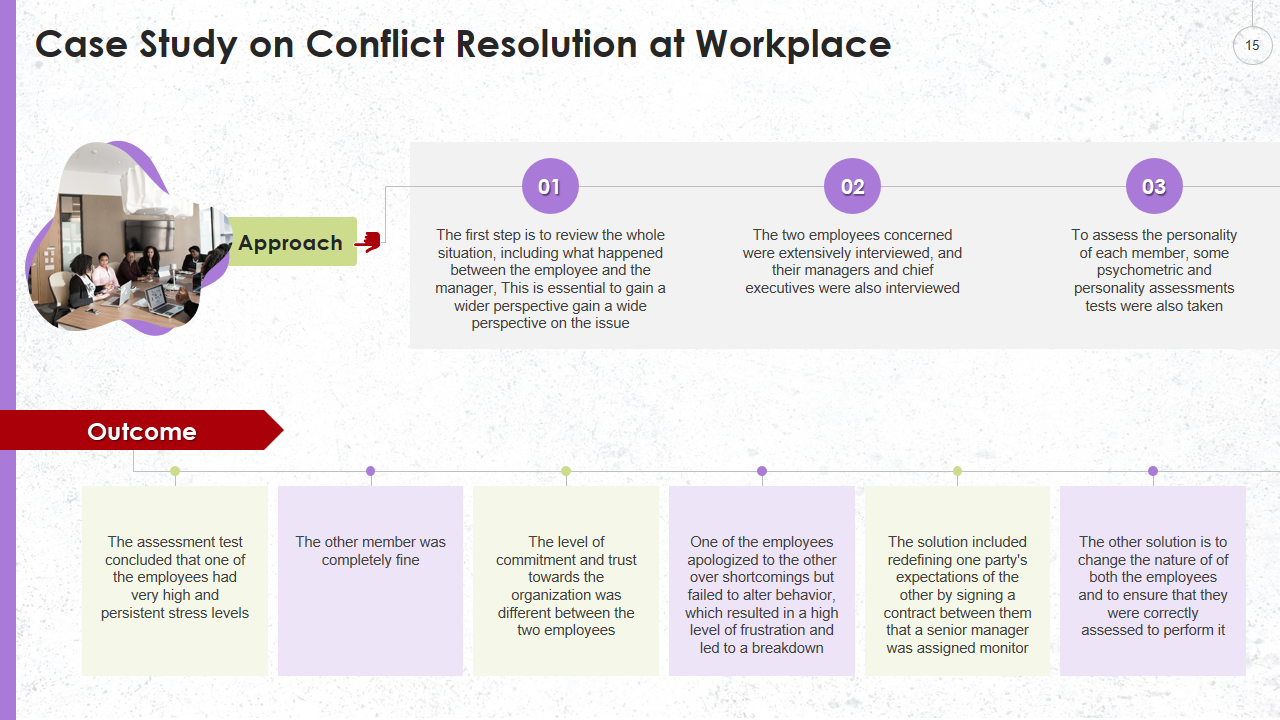
Template 10: Approach and Outcome Template
This template helps you to find the approach and outcomes of conflict resolution in the workplace. It states to review the entire situation first, then the concerned employees and the managers should be interviewed, and lastly, there should be some psychometric tests to assess the personality. This will lead to understanding the persistent stress level of the employees.
Wrapping up
The above ten templates related to workplace conflict management will help you point out, avoid and mitigate workplace conflicts. Do you know these templates are easily customizable? Also, you can use and save these powerpoint graphics in the format of your choice.
FAQs on Conflict Management
What is a good example of conflict management.
X manages a customer service team. She oversees 16 employees, and it's her first leadership role. She has one team member, Y, with a low customer satisfaction score. In a previous meeting, she told Y she would like her to raise the score, but it's been a month without improvement.
In such cases, X could work to develop her leadership and communication skills by conducting a training session.
What is an example of a conflict case?
X is an accountant for a software production company. He requires all the sales figures each month to create his reports. One of his colleagues on the sales team, Mr. Y, always gives him the figures late, which affects X's report.
What are the five types of conflict management?
Five types of Conflict management includes-accommodating is the situation when the issue is not essential to you as it is to the other person; avoiding involves simply ignoring the issue; compromising is the opportunity to find a middle-ground solution; collaborating is beyond finding the middle ground to finding a solution and competing that involves sticking to your argument.
What are the 5 Cs of conflict management with examples?
The five C's include- carefully listening, considering the situation, having a calm discussion, conscientiously looking at the facts, and cooperatively working together.
Related posts:
- Top 7 Conflict Management Templates With Samples And Examples!
- The Ultimate Guide to Conflict Management and Resolution in the Workplace (Best PowerPoint Templates Included)
- [Updated 2023] Top 10 Winning Case Study Competition Presentations [and 10 Vexing Business Issues They Can Help You Solve]
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 PowerPoint Templates to Devise a Systematic Research Methodology
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Must-Have Construction Change Order Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 5 Daily Appointment Templates with Samples and Examples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

--> Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

--> Sales funnel results presentation layouts
--> 3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

--> Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Future plan powerpoint template slide

--> Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

--> Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

--> Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market


--> Agenda powerpoint slide show

--> Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

--> Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

--> Meet our team representing in circular format

University of California Institute on Global Conflict and Cooperation
Conflict Case Studies
- Conference Proceedings
- Newsletters
- Old Archived Documents
- Other Recent Work
- Policy Briefs
- Policy Papers
- Research Papers
- SITC Research Briefs
- Working Papers
Case Study #4: Empathy: Effective Response with Escalating Aggression
- Erbe, Nancy
This is the fourth case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
Introduction to Conflict Case Studies
Case Study #1: Neutral Fact-Finding and Empowerment Within Conflicted Systems
Case Study #2: Intrapersonal Approaches to Conflict: Cognitive and Perceptual Biases
Case Study #3: Negative Intergroup Influence
Case Study #5: Assessing Covert Bad Faith and Power Abuse
Case Study #6: Cultural Competence: Ethical and Empowered Response With Discrimination
Case Study #7: Empowered Process---Skilled Leadership: Diffusion, Party Capacity and Speaking Truth to Power
Case Series #8: Empowered Process: Multicultural Collaboration
This series, Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action, presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying this introduction. Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided here is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
Case Study #7: Empowered Process---Skilled Leadership: Diffusion, Party Capacity & Speaking Truth to Power
This is the seventh case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
Case Study #5: Assessing Covert Bad Faith & Power Abuse
This is the fifth case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
This is the third case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
This is the sixth case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
Case Study #2: Intrapersonal Approaches to Conflict: Cognitive & Perceptual Biases
This is the second case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
This is the first case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
Case Study #8: Empowered Process: Multicultural Collaboration
This is the eighth case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction. (See Introduction to Conflict Case Studies, Nancy D. Erbe). Because the case study format is intentionally unique, written in an interactive and non-linear workbook style, unlike many introductions, the information provided there is required for understanding the case studies. Readers are encouraged to send comments and critiques directly to the author. Because of the deliberate one-of-a-kind format of the text, detailed page-by-page comments and questions are welcome. A list of the entire series is included below.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Business Education
- Business Law
- Business Policy and Strategy
- Entrepreneurship
- Human Resource Management
- Information Systems
- International Business
- Negotiations and Bargaining
- Operations Management
- Organization Theory
- Organizational Behavior
- Problem Solving and Creativity
- Research Methods
- Social Issues
- Technology and Innovation Management
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Managing conflict for effective leadership and organizations.
- Dean Tjosvold , Dean Tjosvold Department of Management, Lingnan University
- Alfred S. H. Wong Alfred S. H. Wong Department of Management, Lingnan University
- and Nancy Yi Feng Chen Nancy Yi Feng Chen Department of Management, Lingnan University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190224851.013.240
- Published online: 28 August 2019
Leaders and employees deal with conflict as they collaborate in the everyday life of organizations and as they confront crises. Depending how they manage conflict, they can frustrate employees and provoke customer complaints but also stimulate their relationships and decision-making. The possibilities of constructive conflict are significant and documented, but the challenges to making conflict constructive are significant too. The practice of defining conflict as a win-lose battle has obscured ways of managing conflict constructively. Fortunately, researchers have developed concepts and findings that can help managers and employees manage conflict. A first step is developing a useful, unconfounded definition of conflict. Deutsch proposed that conflict occurs when there are incompatible activities. Team members are in conflict as they argue for different options for a decision.
Deutsch also theorized that how people believe their goals are related very much affects their interaction, specifically their conflict management. They can conclude that their goals are cooperative (positively related), competitive (negatively related), or independent. People with cooperative goals believe that as one of them moves toward attaining goals, that helps others achieve their goals. In competition, people conclude that their goals are negatively related and only one can succeed in the interaction. In independence, one person ‘s success neither benefits nor harms the others’ success. Researchers have found that the nature of the cooperative or competitive relationship between protagonists has a profound impact on their mutual motivation to discuss conflicts constructively. Cooperative and competitive methods of handling conflict have consistent, powerful effects on constructive conflict. Team members with cooperative goals engage in open-minded discussions where they develop and express their opposing positions, including the ideas, reasons, and knowledge they use to support their positions. They also work to understand each other’s perspectives. They are then in a position to combine the best of each other’s ideas and create effective resolutions of conflict that they are both committed to implement. Teams that rely on cooperative, mutual benefit interaction ways of managing conflict and avoid competitive, win-lose ways been found to use conflict to promote high quality decisions, to stimulate learning, and to strengthen their work relationships. What has an impact on constructive conflict is not so much the occurrence, amount, or type of conflict but how leaders and employees approach and handle their conflicts, specifically, the extent to which their discussions are cooperative and open-minded.
- incompatible activities
- mutual benefit conflict
- win–lose conflict
- constructive conflict
- open-minded discussions
Conflict is pervasive and greatly affects leadership and teamwork, the very drivers of organizations (Blake & Mouton, 1964 ; Jehn, 1995 ; Johnson, 2015 ). Conflict is part of the everyday life of organizations in making decisions, handling customer complaints, and managing performance; conflict is also part of dealing with dramatic events such as acquisitions, strikes, and bankruptcies. Conflicts have both constructive and destructive sides. Conflicts can sabotage alliances and relationships, but effectively managed conflict vitalizes partnerships and invigorates interpersonal bonds. Conflict challenges leaders and teammates and engages them in the full range of experiences that organizations offer.
Research on how to manage conflict is critical to understanding relationships and organizations as well as how to make them effective. Leaders and employees must learn to live with conflict; they have to deal with and resolve the many conflicts that threaten to divide them and frustrate joint progress.
We often blame conflict for our frustrations and give it power over us. We think that if we only had less conflict, our lives would be happy and productive. The goal is to be conflict-free, or at least to keep our conflicts minor and forgettable. However, how we approach and handle conflict greatly affects whether it is constructive or destructive. It’s not so much having conflict or how much conflict we have that matters, but what is critical is how we manage our conflict that affects whether it is constructive or destructive.
Constructive conflict occurs when protagonists conclude that the benefits of their conflict management outweigh the costs; they believe that their investments made in handling conflict will pay off (Deutsch, 1973 ). The costs and wasteful investments of destructive conflict are typically well recognized. Angry feelings leave relationships fragmented and joint work stalled; both people and productivity suffer (Averill, 1983 ).
However, conflicts can have very constructive effects, so useful that we may hesitate to call them conflicts. Through discussing opposing ideas in conflict, protagonists can deepen their understanding of their own ideas as they defend their views (Tjosvold, Wong, & Chen, 2014a ). They can also listen to and understand the views of their protagonists; they put themselves in each other’s shoes. They open the possibility of combining the best ideas to create new solutions. In addition to enriching their learning, they can appreciate each other’s feelings, motives, and commitments, making their joint life more personal and richer.
The possibilities of constructive conflict are significant and documented, but the challenges to making conflict constructive are significant too. Managing conflict constructively may sound straightforward, and it can be. But making conflict constructive often tests us intellectually, emotionally, and interpersonally. Managing conflict constructively gives a lot, but it takes a lot.
This article has six sections. Conflict has been defined in confounded ways so that popular stereotypes have interfered with practice and research. The first section defines conflict as incompatible activities that may or may not have opposing goals. Arguing that what has an impact on constructive conflict is not the occurrence or amount of conflict but how we approach and handle conflict, the second section proposes that open-minded discussion and cooperative goals are key conditions to making conflict constructive. The third section reviews research on task and relationship conflict that suggests that these types of conflict can be managed. The fourth section reviews how constructive conflict can strengthen leadership and thereby very much contribute to the relationship between employees and managers. Then research on how conflict can be managed across cultural boundaries is discussed. The sixth and final part suggests how training can strengthen constructive conflict, leadership, and organizations.
Understanding Conflict
Researchers typically have not considered defining conflict critical for understanding it; indeed, they have tended to define conflict by including several notions (Barki & Hartwick, 2004 ; Rahim, 1992 ). However, popular definitions have tended to define conflict in terms of opposing goals and interests. This definition of conflict has greatly frustrated research progress in identifying the many ways conflict can constructively contribute to individual learning and organizational performance. Defining conflict as incompatible actions, we propose, is a much more solid foundation for research than defining conflict as opposing interests.
Conflict as Opposing Interests
Traditionally, conflict is defined in terms of opposing interests involving scarce resources and goal divergence and frustration (e.g., Pondy, 1967 ). Defining conflict as opposing interests is consistent with the prevalent assumption that conflict involves not only differences but is win–lose and reinforces the popular thinking that conflict is typically dealt with harshly and competitively. For many people, conflict is a win–lose battle over goals that they want to win, not lose.
However, defining conflict as opposing interests frustrates effective operations and measures. Conflict is confused with win–lose ways to manage it. For example, the Interpersonal Conflict at Work Scale measures conflict with such items as “people do nasty things to me at work” (Spector & Bruk-Lee, 2008 ). This item measures a competitive, win–lose way to manage conflict, not conflict itself.
The popular assumption that conflict is competitive and a fight over opposing interests underscores the difficulties of measuring conflict with items including the term “conflict” in them. For example, research scales that measure types of conflict, such as task and relationship conflict, typically include the term “conflict.” Including the word conflict is likely to contribute to the common finding that both relationship and task conflicts contribute to team ineffectiveness (De Dreu & Weingart, 2003 ; DeChurch, Mesmer-Magnus, & Doty, 2013 ; Tjosvold, Law, & Sun, 2006 ). Conceptual and operational definitions of conflict should help us appreciate both the constructive as well as the destructive sides of conflict and should avoid confounding conflict with popular confusions and stereotypes.
Conflict as Opposing Activities
Deutsch ( 1973 ) proposes that conflict occurs when there are incompatible activities (Tjosvold et al., 2014a ). Team members are in conflict when they argue for different options for a team decision as they perform actions that interfere with each other’s actions. They express their various reasons for the joint action their team should take. Different parties arguing for their different positions are incompatible actions that block each person from getting their option accepted; they are in conflict.
They may express their views to reflect that they have cooperative goals as well as conflicting activities. They argue for their favored option as they put forth their reasons for this option. They may defend their preferred position vigorously and conduct additional research to support their option. They want team members to consider their proposed option seriously. Their goal with protagonists is a cooperative one, however: they want to make the best decision for the team as a whole.
Alternatively, team members may have opposing goals when they argue for different options; they are in competition as well as in conflict. They argue that their option must be accepted and other options should be rejected. They express their arguments for their favored option in win–lose ways. Only one option can be accepted and it should be theirs.
Expressing one’s view can be done both cooperatively and competitively. Studies indicate that these different ways of expressing one’s options often have dramatic effects on the dynamics and outcomes of conflict (Tjosvold et al., 2014a ).
Approaches to Conflict
This article argues that research on how team members manage and deal with their conflicts very much contributes to understanding and developing constructive conflict. It is not so much the frequency, amount, and type of conflict as it is how team members discuss and work out their conflicts. Cooperative and competitive methods of handling conflict have been found to have consistent, powerful effects on constructive conflict.
Researchers recognize the value of a contingency perspective that holds that managers and employees should have alternative ways to deal with a conflict so that they can select the one most useful and appropriate in their situation (Rahim, 1992 ; Thomas, 1976 ). Pretending that there is no conflict and avoiding discussing conflict are useful in some situations, but generally conflict avoidance is not useful, indeed is often destructive (De Dreu & Van Vianen, 2001 ; Friedman, Chi, & Liu, 2006 ; Liu, Fu, & Liu, 2009 ; Lovelace, Shapiro, & Weingart, 2001 ; Ohbuchi & Atsumi, 2010 ). Without direct discussion and action, conflicts seldom disappear by themselves; they can fester and intensify, becoming more complex and destructive (Bacon & Blyton, 2007 ; Eisenhardt, Kahwajy, & Bourgeois, 1997 ; Nemeth & Owens, 1996 ).
This section argues that studies conducted using different theoretical frameworks together indicate that open-minded discussion between protagonists results in constructive outcomes in many situations (Johnson, 2015 ; Tjosvold et al., 2014a ). In open-minded discussions, protagonists develop and express their opposing positions, including the ideas, reasons, and knowledge they use to support their positions. They also work to understand each other’s perspectives. They are then in a position to combine the best of each other’s ideas and create effective resolutions of conflict that they are both committed to implement.
This section further proposes that cooperative relationships, but not competitive ones, are an effective foundation for open-minded discussion and constructive conflict. These relationships orient protagonists to identify and express their own ideas and proposals. They trust that others will try to understand their ideas and positions accurately (Hempel, Zhang, & Tjosvold, 2009 ). They feel they can rely upon each other to use these views to promote each other’s benefit. Their concerns that others will use their ideas and positions against them are minimized. They recognize that they can all gain from the conflict as each protagonist’s goals are promoted.
Open-Minded Discussion
Open-mindedness is the willingness to actively search for evidence against one’s favored beliefs and ideas and to weigh such evidence impartially and fully (Baker & Sinkula, 1999 ; Cegarra-Navarro & Sánchez-Polo, 2011 ; Mitchell, Nicholas, & Boyle, 2009 ; Sinkula, Baker, & Noordewier, 1997 ). Open-minded discussion occurs when people together seek to understand each other’s ideas and positions, consider each other’s reasoning for these positions impartially, and work to integrate their ideas into mutually acceptable solutions.
In open-minded discussion, protagonists express their own views directly to each other, listen and try to understand each other’s positions and arguments, and work to combine their ideas into new agreements acceptable to all. They are open with their own views, open to those of others, and open to new solutions to resolve the conflict. Evidence indicates that these aspects of openness are reinforcing and together constitute open-minded discussion (Johnson, 2015 ; Tjosvold, 1990a ; Tjosvold, Dann, & Wong, 1992 ; Tjosvold & Halco, 1992 ).
Survey items to measure open-mindedness give a specific understanding of open-mindedness (Chen, Liu, & Tjosvold, 2005 ; Wong, Tjosvold, & Yu, 2005 ). These items include: (a) express our own views directly to each other, (b) listen carefully to each other’s opinions, (c) try to understand each other’s concerns, and (d) work to use each other’s ideas. These items are typically strongly correlated with each other and the scale has high reliability.
Open-mindedness in conflict is inherently interpersonal as people act and react to each other. It takes two to have a conflict and it takes two to manage conflict. One protagonist can make bold, persistent, and skilled actions that encourage an otherwise closed-minded protagonist to discuss conflict open-mindedly. Generally, though, open-mindedness by all protagonists is needed to make conflict constructive. Evidence also suggests that protagonists develop similar levels of open-mindedness; one protagonist’s open-mindedness encourages others to be open (Tjosvold, 1990a ; Tjosvold et al., 1992 ; Tjosvold & Halco, 1992 ). Conflicts are more likely to be constructively managed when protagonists discuss their views directly and integrate them into solutions.
Researchers have used various terms to characterize the nature of discussion that results in constructive outcomes. These terms have their own historical roots, emphasize difference aspects of interaction, and provide various ways to measure and operationalize the interaction. These concepts and their operations help us understand the nature of open-minded discussion.
Open-Mindedness Research
Research conclusions are more fully understood and deserve more confidence when various researchers using different operations and samples develop consistent findings. Conflict researchers have used a variety of terms and operations to investigate open-mindedness. We propose that, although these terms are not identical, their differences should not obscure the considerable agreement among conflict researchers that open-minded discussion contributes to resolving conflicts in many situations. The operations of these terms further suggest the similarity of the concepts to open-minded discussion.
Integrative negotiation research provides indirect support that open-minded discussion is a foundation for developing constructive conflict. This research has examined the conditions that develop the creative process by which bargainers discover superior new options for both parties than those currently under consideration (Follett, 1940 ). Walton and McKersie ( 1965 ) propose that this integration is more likely when protagonists consider several issues simultaneously, consider the issues as problems to be solved, freely exchange accurate and credible information about their interests, avoid win–lose behaviors, and argue their own position unless and until they are convinced otherwise.
Experimental integrative negotiation researchers have argued similarly that problem solving interaction characterized by full information exchange results in mutually beneficial solutions (Pruitt & Carnevale, 1993 ; Pruitt, Carnevale, Ben-Yoav, Nochajski, & Van Slyck, 1983 ; Pruitt & Lewis, 1975 ). The operations to measure this problem solving interaction include asking for valid information, requesting information about the other’s interests, giving truthful information, showing interest in the other bargainer’s welfare, and proposing mutual concessions. Integrated negotiators challenge each other’s original ideas, dig into these positions to identify each other’s underlying interests, endure the uncertainty of not finding a quick solution, and are only satisfied with solutions that promote the interests of all.
De Dreu and colleagues have drawn upon integrative negotiation research to develop the motivated information processing approach (De Dreu, 2007 ; De Dreu, Koole, & Steinel, 2000 ; De Dreu, Nijstad, & van Knippenberg, 2008 ). This research also proposes and measures constructive interaction in conflict in terms of problem solving and information exchange. The extent to which protagonists engage in thorough, systematic processing of information was found to induce them to question perceptions that one protagonist can achieve their interests only to the extent that others cannot achieve their own; challenging this trade-off in turn results in more accurate assessments and more integrative agreements (De Dreu et al., 2000 ).
Conflict management styles researchers propose five alternative approaches to dealing with conflict (Rahim, 1983 , 1995 ; Thomas, 1976 ; Van de Vliert & Kabanoff, 1990 ). Although arguing that all five can be useful in some circumstances, these researchers have concluded that the collaborative conflict management style, at times supplemented with other styles, is constructive under a wide range of conditions (Van de Vliert, Euwema, & Huismans, 1995 ; Van de Vliert, Nauta, Giebels, & Janssen, 1999 ). Research on collaborative conflict management styles and experiments on negotiation support that being open with one’s own views as well as being open to other ideas and integrating them contribute to constructive conflict (Pruitt & Carnevale, 1993 ).
Diverse researchers have found that open-minded discussion contributes to resolving conflicts within and between organizations (Johnson, Johnson, & Tjosvold, 2006 ; Tjosvold, 1985 ). Conflict involves incompatible actions, specifically the intellectual aspects of proposing and reconciling opposing ideas that temporarily disrupt reaching a resolution. Fortunately, research by various scholars supports that open-minded discussion very much contributes to effective conflict management.
Cooperative Relationships for Open-Minded Discussion
When do protagonists discuss their conflicts open-mindedly? Researchers have theorized that the nature of the relationship between protagonists has a profound impact on their mutual motivation to discuss conflicts open-mindedly. Open-minded discussions occur when both participants are motivated to work together to manage their conflicts constructively.
Theory of Cooperation and Competition
Deutsch ( 1948 , 1973 ) theorized that how people believe their goals are related very much affects their interaction and thereby their outcomes. They can conclude that their goals are cooperative (positively related), competitive (negatively related), or independent. People with cooperative goals believe that as one of them moves toward attaining goals, that helps others achieve their goals. In competition, people conclude that their goals are negatively related and only one can succeed in the interaction. In independence, one person’s success neither benefits nor harms the others’ success.
Deutsch ( 1973 ) further proposed that cooperative goals are a useful way to understand when protagonists are able to manage their conflicts constructively. Both survey and experimental studies confirm that with cooperative goals, managers and employees discuss their differences directly and open-mindedly (Alper, Tjosvold, & Law, 1998 ; Poon, Pike, & Tjosvold, 2001 ; Schei & Rognes, 2003 ; Tjosvold, 1988 ). Teams are considered cooperative to the extent that members rate that their goals go together (Alper et al., 1998 ); they are considered competitive to the extent that members rate that they favored their own goals over the goals of others (Alper et al., 1998 ); teams are considered independent to the extent that members rate that one member’s success is unrelated to the success of their teammates (Alper et al., 1998 ). Competitive and independent goals have been found to lead to conflict avoidance or to conflict escalation or both (Alper, Tjosvold, & Law, 2000 ; Tjosvold et al., 2001 ). Protagonists with cooperative goals promote each other’s benefit because doing so is to their own advantage.
Protagonists typically have mixed interdependencies as well as more “pure” cases. Galinsky and Schweitzer ( 2015 ) note that social relationships contain both competitive and cooperative aspects. This co-opetition has been thought to leave protagonists more flexibility in how they manage conflict (Landkammer & Sassenberg, 2016 ).
Antecedents to Open-Mindedness
A key dynamic of having positively related goals of cooperation is that by helping others reach their goals, one also reaches one’s own goals. In cooperation, people promote their own goals and others’ goals simultaneously. Researchers have used other theoretical frameworks to capture this idea of positively related goals where self-interests are mutual in that promoting one’s self-interest promotes the self-interest of the others. Researchers have used the dual concerns and pro-social motivation to capture positively related self-interests.
In dual concerns, theorists have proposed that conflict participants can be committed to promoting others’ interests as well as their own (Thomas, 1976 , 1992 ). Rahim and Bonoma ( 1979 ) and Rahim ( 1983 , 1992 ) built upon Blake and Mouton’s ( 1964 ) managerial grid. Concern for self describes the extent to which people attempt to satisfy their own interests. The second dimension describes the extent to which people want to satisfy the concerns of others (Rahim & Bonoma, 1979 ). High concern for self and high concern for others resemble cooperative goals. Dual concerns occur when protagonists are motivated by their own interests and outcomes: they are willing to assert themselves to get what they want and they are also motivated to promote their partners’ interests and outcomes.
Dean Pruitt and other integrative negotiation researchers have also developed the dual concerns model (Pruitt & Carnevale, 1993 ; Pruitt et al., 1983 ; Pruitt & Rubin, 1986 ). Here protagonists committed to the interests of the other as well as themselves discuss conflict open-mindedly where they are only satisfied with solutions that promote the interests of both.
Motivational and social value orientation theory (Kelley & Schenitzki, 1972 ; McClintock, 1977 ; Messick & McClintock, 1968 ; Van Lange & Kuhlman, 1994 ) also found that preference for both self and other promotes constructive conflict (De Dreu & Van Lange, 1995 ; De Dreu, Weingart, & Kwon, 2000 ). Social motives refer to preferences for outcomes to the self and other: pro-social, pro-self, and competitive negotiators differ in attaching a positive, zero, or negative weight to the other’s outcomes, respectively (De Dreu & Boles, 1998 ; De Dreu & McCusker, 1997 ; Van Lange, 1999 ).
Pro-social protagonists choose options that maximize joint outcomes; protagonists are pro-self if they select options where their own outcomes are higher than the other, and they are classified as competitive if they choose options that maximize the differences between the two, that is, their own outcomes are much better than the other’s outcomes. Pro-social motivation has been found to develop the open-minded exchange of information that results in constructive conflict (De Dreu, Weingart, et al., 2000 ; Nauta, De Dreu, & Van der Vaart, 2002 ).
Researchers have developed the dual concerns model, pro-social and pro-self social motivation, and cooperative goals as theoretical perspectives to understand relationships that promote constructive conflict (De Dreu, Weingart, et al., 2000 ; Deutsch, 1973 ; Pruitt & Rubin, 1986 ; Rahim & Bonoma, 1979 ). This section argues that these different terms obscure fundamental agreement that the commitment to promoting each other’s goals facilitates open-minded discussion.
Managers and employees of course do not always discuss their differences open-mindedly and, according to the contingency perspective, under certain conditions it would be inappropriate and dysfunctional to do so. Commitments to competitive and independent goals are apt to lead to closed-minded discussions with an emphasis on promoting one’s own interests without concern for the ideas and aspirations of the other. Indeed, with competitive goals they are apt to actively frustrate each other’s goals as they understand this is a way of promoting their own.
This article refers to cooperative relationships as underlying open-minded discussion. Previous research has directly tested whether cooperative relationships promote open-mindedness, providing both experimental and survey data (Deutsch, 1973 ). Research has demonstrated both the causal relationship that cooperative goals promote open-mindedness and survey evidence that supports that cooperative relationships support open-minded discussion in a wide variety of organizational situations (Tjosvold et al., 2014a ). In addition, many social psychologists and other social scientists have developed our understanding of cooperation and competition (Deutsch, 1973 ; Deutsch, Coleman, & Marcus, 2011 ).
Conflict Type Research
For more than two decades, organizational researchers have distinguished types of conflict and argued that the type of conflict determines how constructive the conflict is (Jehn, 1997 ; Jehn, Greer, Levine, & Szulanski, 2008 ). Whether the conflict is about getting tasks done or about the quality of relationships between protagonists, conflict type is thought to determine whether conflict is constructive or destructive. Theorizing on the role of conflict types has stimulated considerable research by many investigators.
Research findings on conflict types supports the traditional view that high levels of conflict disrupt teamwork, and refines this idea by indicating that this proposition is especially true when these conflicts are relationship-based. Relationship conflicts, as measured by such items as how much friction, tension, and personality conflict are in the team, have been found to make conflict destructive (Jehn, 1994 ; Jehn et al., 2008 ). Reviews of literature, including several meta-analyses, have consistently found that relationship conflicts correlate with low levels of team productivity (Choi & Sy, 2010 ; De Dreu & Weingart, 2003 ; DeChurch et al., 2013 ).
These results have straightforward practical implications for leaders and team members in reducing relationship conflict. Given the heavy reliance on correlational findings, it can be more cautiously concluded that relationship conflicts are signs of destructive conflict and are unlikely to contribute to constructive conflict. Researchers have, however, sought to identify boundary conditions that minimize the negative impact, and unlock the positive impact, of relationship conflict (Thiel, Harvey, Courtright, & Bradley, 2017 ).
Whereas relationship conflicts disrupt, it has been proposed that conflicts over tasks contribute to group performance (Jehn, 1997 ; Jehn et al., 2008 ). However, findings do not consistently support this theorizing that task conflict strengthens group performance (Choi & Sy, 2010 ; De Dreu & Weingart, 2003 ; DeChurch et al., 2013 ). The inconsistent effects of task conflict indicate that expressing diverse views can be useful but not consistently. It appears that expressing opposing views must be done skillfully to contribute to constructive conflict, but task conflict theory does not directly suggest the conditions under which expressing opposing views contributes to constructive conflict.
Managing Task and Relationship Conflict
Researchers have worked to document the conditions that determine whether task and relationship conflict are constructive or destructive. For example, some evidence suggests that task conflict is apt to be more productive when it is in moderate amounts, is not closely related to relationship conflict, and when the outcomes are financial performance and decision quality rather than overall performance (De Dreu, 2006 ; de Wit, Greer, & Jehn, 2012 ; Farh, Lee, & Farh, 2010 ; Mooney, Holahan, & Amason, 2007 ; Shaw et al., 2011 ).
Several studies show that relationship conflict can hinder teams from capitalizing on the potential positive value of task conflict (de Jong, Song, & Song, 2013 ; de Wit, Jehn, & Scheepers, 2013 ; Shaw et al., 2011 ). Research has found that relationship conflicts encourage a competitive approach to managing conflict by leading people to make forceful demands, overstate their position to get their way, and in other ways treat conflict as a win–lose contest (Tjosvold et al., 2006 ). In contrast, to the extent that protagonists had few relationship conflicts, they resolved their conflicts in ways that supported mutual benefit; specifically, they encouraged a “we are in it together” attitude, sought a solution useful for all members, combined their best ideas, and treated conflict as a mutual problem to solve (de Jong et al., 2013 ; de Wit et al., 2013 ; Shaw et al., 2011 ).
Research suggests that how task and relationship conflicts are discussed, not just the amount of them, affects their constructiveness (DeChurch et al., 2013 ; Maltarich, Kukenberger, Reilly, & Mathieu, 2018 ; Rispens, Greer, Jehn, & Thatcher, 2011 ; Tekleab, Quigley, & Tesluk, 2009 ; Todorova, Bear, & Weingart, 2014 ). Recent studies have found that task conflict can be constructive when discussed open-mindedly and skillfully (Bradley, Klotz, Postlethwaite, & Brown, 2013 ; Chun & Choi, 2014 ; Humphrey, Aime, Cushenbery, Hill, & Fairchild, 2017 ; Jiang, Zhang, & Tjosvold, 2012 ; Tekleab et al., 2009 ). Teams with members with high levels of openness as a personality characteristic were found to have constructive task conflict (Bradley et al., 2013 ; de Jong et al., 2013 ). Overall, evidence indicates that open-minded discussion contributes to making both relationship and task conflict constructive (Gibson & Callister, 2010 ; Lau & Cobb, 2010 ; Tjosvold, 2002 ; Tjosvold & Su, 2007 ; Weingart, Behfar, Bendersky, Todorova, & Jehn, 2015 ).
Conflict Management for Leadership
Leadership has long been considered a key contributor to effective organizations. Much of the power of organizations is that they motivate and coordinate the work of many people; for that to happen, managers must lead employees. Without leadership, employees may fail to face up to difficulties, allow problems to simmer, and just go through the motions. Research indicates that to have effective leadership, managers and employees must make conflict constructive (Chen et al., 2005 ; Chen & Tjosvold, 2007 , 2013 ; Chen, Tjosvold, Huang, & Xu, 2011 ; Hui, Wong, & Tjosvold, 2007 ).
Conflict management research is updating our understanding of what it takes to be an effective leader and how to develop it. Studies indicate that by developing constructive conflict, managers can improve the quality of their leader relationships with employees. Managers can then orient and train employees so that they discuss their various ideas and improve the quality of their decision-making and their overall teamwork. Researchers have demonstrated that leaders can be effective by adopting various leadership styles; recent studies show that constructive conflict is very much needed to make these leadership styles effective.
Conflict for Quality Leadership Relationships
Leadership has long been thought to be “situational” in that the actions effective leaders take depend upon the situation; they monitor the situations and decide upon effective actions in the situation (Stogdill, 1974 ). In addition, though, researchers have found that successful leaders are consistent across many situations in that they develop quality relationships. Considerable research has found that successful leaders have quality relationships (Graen & Uhl-Bien, 1995 ). It’s not so much that managers have the “right” personal skills and characteristics but that they have high quality relationships with employees that help them influence employees and increase their productivity. With these relationships, leaders are able to engage employees, strengthen their teamwork, and in other ways convince them to contribute effectively to the organization.
Less recognized is that leaders and employees cannot allow frustrations to brew; they need to manage their conflicts to develop quality relationships (Chen & Tjosvold, 2007 ; Chen, Tjosvold, & Su, 2005 ; Tjosvold, Poon, & Yu, 2005 ). An important reason why quality relationships are useful is because they promote constructive conflict that in turn results in employee involvement and performance (Chen & Tjosvold, 2013 ; Tjosvold, Hui, & Law, 1998 ). Otherwise, relationship conflicts are apt to undermine team productivity as they allow frustrations to fester (Chen et al., 2005 ; Chen & Tjosvold, 2007 ; Tjosvold et al., 2005 ). Leaders need to manage their conflicts to reduce relationship conflicts and develop and maintain quality relationships.
Conflict for Making Decisions
Leaders have traditionally been thought to make tough decisions and then use their power to implement them. But this is a misleading notion. Studies by diverse researchers have documented the contribution of conflict to making decisions (Amason, 1996 ; Anderson, 1983 ; Cosier, 1978 ; George, 1974 ; Gruenfeld, 1995 ; Mason & Mitroff, 1981 ; Mitchell et al., 2009 ; Peterson & Nemeth, 1996 ; Salas, Rosen, & DiazGranados, 2010 ; Schweiger, Sandberg, & Ragan, 1986 ; Somech, Desivilya, & Lidgoster, 2009 ; Tetlock, Armor, & Peterson, 1994 ; Tjosvold, Wedley, & Field, 1986 ; Wong, Ormiston, & Tetlock, 2011 ). Through conflict, conventional thinking is challenged, threats and opportunities identified, and new solutions forged. Discussing opposing views has been found to give teams the confidence to take calculated risks where they also are prepared to recover from their mistakes; with this preparation, they innovate (Tjosvold & Yu, 2007 ). Even in a crisis, leaders are typically more effective when they seek out diverse views (Tjosvold, 1984 , 1990b ). Rather than making tough decisions alone, effective leaders are oriented toward promoting the conditions and relationships for open-minded discussion of opposing views among colleagues and employees. They develop constructive conflict that helps employees make and implement decisions as a team.
Conflict to Implement Leadership Styles
Researchers have argued that managers can be effective by adopting leadership styles such as transformational, servant, and productivity and people values (Eisenbeiss, van Knippenberg, & Boerner, 2008 ; Xu & Thomas, 2011 ). Less appreciated is that these styles are effective by promoting constructive conflict. Recent studies have demonstrated that to be successful in applying these styles, leaders develop constructive conflict.
Transformational leaders are expected to stimulate superior performance by appealing to employees’ higher aspirations (Bass, 2006 ). For example, they were found highly motivated not by unilaterally directing employees but by helping them manage their conflicts cooperatively and constructively (Zhang, Cao, & Tjosvold, 2011 ). This constructive conflict in turn resulted in high team performance in a sample of independent business groups. In a related study, government officials who exercised transformational leadership promoted cooperative conflict management that in turn resulted in strong government–business partnerships (Wong, Wei, & Tjosvold, 2014 ).
Leaders who value people and productivity have long been thought to be effective leaders, but the dynamics by which these values have beneficial effects have only recently been documented. In a study of international joint ventures (Wong, Wei, Yang, & Tjosvold, 2017 ), results support the idea that productivity and participation values strengthen the partners’ beliefs that their goals are cooperatively related, which in turn reduces free riding and promotes performance; in contrast, competitive goals appear to promote free riding and obstruct joint performance. The results have practical implications by showing that developing cooperative goals can strengthen the benefits of productivity and participation values.
Working in diverse organizations in India, team leaders indicated their people and productivity values and team members rated their open-minded discussion and their effectiveness and performance (Bhatnagar & Tjosvold, 2012 ). Structural equation analysis suggested that productivity values promoted open-minded discussion and thereby team effectiveness and productivity. Productivity-oriented team leaders challenge their teams to make high quality decisions and induce them to discuss issues open-mindedly, which in turn helps teams be effective (Bhatnagar & Tjosvold, 2012 ).
Servant leaders, as they emphasize service to others, team consensus, and the personal development of individuals, have been thought to lay the groundwork for cooperative conflict management in customer service teams (Wong, Liu, & Tjosvold, 2015 ). This constructive conflict helps team members resolve issues and in other ways effectively coordinate with each other; this coordination in turn helps these teams serve their customers. Findings indicate that to the extent that they have servant leaders, teams are able to discuss their disagreements, frustrations, and difficulties directly and work out solutions for the benefit of the team and its customers. These results provide support that improving the capacity to discuss opposing views open-mindedly can be a useful means for servant leaders to enhance teamwork and customer service in China and perhaps in other countries as well.
Ethical leaders want to act justly themselves but they also want employees to be committed to ethical principles and to act morally (Eisenbeiss, 2012 ; Mayer, Aquino, Greenbaum, & Kuenzi, 2012 ). A recent study indicates that effective ethical leaders and their employees engage in open-minded, cooperative conflict management where they express their ideas, work to understand each other, integrate their ideas, and apply their resolutions. Through this constructive conflict management, they work out arrangements that help them act effectively and morally in their situation as they also develop trusting, high quality relationships with each other. Ethical leaders and their employees were found to avoid competitive conflict involving trying to impose one’s own ideas and resolutions on others. Results also confirm that effective leaders develop high quality relationships that help them influence employees as well as to be open and influenced by them (Graen & Uhl-Bien, 1995 ).
Researchers have identified a number of styles that have been shown to help leaders be effective. Although they are developed from diverse leadership theories, studies have found that constructive conflict, in particular cooperative open-minded discussion, is an important mediator of successful implementation of these leadership styles, whether they be transformational leadership, valuing people and productivity, servant, or ethical leadership. Managers can use different leadership styles to encourage constructive conflict that empowers them to lead effectively.
Cultural Differences
Theories of conflict management that can be applied in diverse cultures are increasingly relevant. In the global marketplace, many managers and employees must handle conflicts that cross cultural boundaries. Team members increasingly have diverse cultural backgrounds, even when all operations are in one country. Many managers have to work with suppliers and customers who are from other cultures and live in other countries. Research has shown that open-mindedness and cooperative relationships develop constructive conflict in organizations even when protagonists are from both Western and Eastern cultures (Chen, Tjosvold, & Pan, 2010 ; Tjosvold, Wu, & Chen, 2010 ; Tjosvold, Wong, & Chen, 2014a ).
Research on conflict management has developed our understanding of the impact of cultural values, in particular collectivism and individualism. Western cultures have traditionally been thought to support open discussion of conflict consistent with their emphasis on individuals with their rights and proclivity to express their views. Eastern cultures have been considered collectivist where there is deference to their groups and leaders. Some studies support this traditional thinking. People from the West have indicated more preference for open handling of conflict, whereas those from the East prefer reticence (Kirkbride, Tang, & Westwood, 1991 ).
However, research suggests that this reasoning needs updating. Recent studies indicate that collectivist values induce open-minded discussion whereas individualistic values promote conflict avoidance. Collectivist values have been found in experiments to strengthen cooperative relationships that in turn promote open-minded discussion between individuals from collectivist and individualistic cultures (Chen et al., 2010 ; Tjosvold, Wu, et al., 2010 ; Tjosvold, Wong, & Chen, 2014a ). Collectivist culture team members were found to believe their goals are cooperative and that they are expected to work effectively with each other, and they sought to and actually understood opposing arguments and combined ideas for integrated decisions.
Studies confirm that cooperative and competitive approaches to managing conflict, although developed from theory in the West, apply to organizations in collectivist China as well (Chen et al., 2011 ). Indeed, findings challenge stereotypes that Chinese culture and leadership are highly conflict-negative. Chinese people are not rigidly committed to conflict avoidance but have been found to manage conflict cooperatively and openly. Chinese collectivism, social face, and other values can be applied in ways that aid direct, open, cooperative conflict management (Tjosvold, Wong, & Chen, 2014b ).
Cooperative conflict management can also guide the strengthening of cross-cultural interaction. Bond ( 2003 ) and Smith ( 2003 ) argue that cross-cultural researchers, in addition to the tradition of documenting cultural value differences, should study the relationship and interaction between culturally diverse people to identify how they work together effectively. Recent studies show that diverse people can work together when they manage their conflicts cooperatively (Chen et al., 2010 ; Chen & Tjosvold, 2007 , 2008 ; Chen, Tjosvold, & Wu, 2008 ).
While the “genotype” (the underlying conceptual structure of the theory of cooperation and competition) appears to be similar, the “phenotypes” (how the theory is manifested in particular situations) often are not (Lewin, 1938 ). In particular, the actions that develop cooperative goals and communicate an attempt to discuss conflicts open-mindedly may be quite different in China than in North America, as may the general levels of cooperative goals and conflict. However, diverse people can use research to develop a common understanding and platform for how they can manage conflict cooperatively and productively (Tjosvold & Leung, 2003 ).
Training Teams
Employees, managers, and executives are more effective when they manage important conflicts open-mindedly and cooperatively. Research suggests that, when they study cooperative, open-minded conflict, plan how to approach their own conflicts, and reflect on their experiences, managers and employees are more effective at managing conflict and more productive (Lu, Tjosvold, & Shi, 2010 ; Tjosvold et al., 2014a ).
A software company in Beijing used a cooperative team workshop and two months of follow-up of team feedback and reflection to develop open-minded conflict management (Lu et al., 2010 ). More than 150 employees from all the teams in the company participated in the workshop and the follow-up activities.
They had already organized cooperative teams to work on projects and satisfy customers. At the workshop, these groups studied the theory and reviewed the research in order to appreciate the value for them and their organization of strengthening cooperative, open-minded approaches to managing their conflicts. They decided that they wanted to improve their conflict management. They met regularly to assess their current level of cooperative conflict and developed plans for managing their conflicts more constructively. They practiced in their teams, met regularly to assess their current level of cooperative conflict, and developed plans for managing their conflicts more constructively. They reflected on their experience managing conflict within and between teams with consultants, and developed concrete ways to improve their conflict management.
Findings confirmed that open-minded discussion and cooperative relationships are a valuable basis upon which teams can strengthen their conflict management, collaboration among teams, and contributions to their organization. The training was found to heighten cooperative goals, develop open-minded discussion of conflicts, foster creativity within and between cultures, and produce higher group confidence and productivity.
Human resource personnel can apply conflict management findings by initiating professional development teams for managers and employees (Tjosvold & Tjosvold, 2015 ). They realize that becoming more effective requires the encouragement, feedback, and support of others. In these teams, managers and employees study cooperative, open-minded conflict management, reflect on their current experiences, and develop concrete ways to strengthen and practice conflict management skills. They remember not to expect perfection but to focus on reflecting on their experiences to improve.
Managers and employees confront a great variety of conflicts. With persistent pressures for them to rely on each other’s resources and to work together as a team, they are likely to encounter increasingly difficult conflicts that spread across organizational and national boundaries. Yet they are expected to resolve them quickly. Theory and research such as that referred to in this article helps to focus our efforts to manage even our complex conflicts constructively. We have learned from research that we can profitably strengthen our cooperative relationships and discuss our conflicts open-mindedly. Our conflicts will not disappear, but we can engage our partners so that we manage our conflicts and work together to get things done.
- Alper, S. , Tjosvold, D. , & Law, K. S. (1998). Interdependence and controversy in group decision making: Antecedents to effective self-managing teams. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , 74 , 33–52.
- Alper, S. , Tjosvold, D. , & Law, K. S. (2000). Conflict management, efficacy, and performance in self-managing work teams. Personnel Psychology , 53 , 625–638.
- Amason, A. C. (1996). Distinguishing the effects of functional and dysfunctional conflict on strategic decision making: Resolving a paradox for top management teams. Academy of Management Journal , 39 , 123–148.
- Anderson, P. A. (1983). Decision making by objection and the Cuban missile crisis. Administrative Science Quarterly , 28 , 201–222.
- Averill, J. R. (1983). Studies on anger and aggression: Implications for theories of emotion. American Psychologist , 38 , 1145–1160.
- Bacon, N. , & Blyton, P. (2007). Conflict for mutual gains? Journal of Management Studies , 44 , 814–834.
- Baker, W. E. , & Sinkula, J. M. (1999). The synergistic effect of market orientation and learning orientation on organizational performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science , 27 , 411–427.
- Barki, H. , & Hartwick, J. (2004). Conceptualizing the construct of interpersonal conflict. International Journal of Conflict Management , 15 , 216–244.
- Bass, B. M. (2006). Transformational leadership . Riggio, R. E. 2nd ed. Mahwah, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates.
- Bhatnagar, D. , & Tjosvold, D. (2012). Leader values for constructive controversy and team effectiveness in India. International Journal of Human Resource Management , 23 , 109–125.
- Blake, R. , & Mouton, J. (1964). The managerial grid: The key to leadership excellence . Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing Company.
- Bond, M. H. (2003). Cross-cultural social psychology and the real world of culturally diverse teams and dyads. In D. Tjosvold & K. Leung (Eds.), Cross-cultural foundations: Traditions for managing in a cross-cultural world (pp. 43–58). Farnham, U.K.: Ashgate.
- Bradley, B. H. , Klotz, A. C. , Postlethwaite, B. E. , & Brown, K. G. (2013). Ready to rumble: How team personality composition and task conflicts interact to improve performance. Journal of Applied Psychology , 98 , 385–392.
- Cegarra-Navarro, J. G. , & Sánchez-Polo, M. T. (2011). Influence of the open-mindedness culture on organizational memory: An empirical investigation of Spanish SMEs. International Journal of Human Resource Management , 22 , 1–18.
- Chen, G. , Liu, C. , & Tjosvold, D. (2005). Conflict management for effective top management teams and innovation in China. Journal of Management Studies , 42 , 277–300.
- Chen, Y. F. , & Tjosvold, D. (2007). Cooperative conflict management: An approach to strengthen relationships between foreign managers and Chinese employees. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources , 45 , 271–294.
- Chen, Y. F. , & Tjosvold, D. (2008). Goal interdependence and leader–member relationships for cross-cultural leadership in foreign ventures in China. Leadership & Organization Development Journal , 29 , 144–166.
- Chen, Y. F. , & Tjosvold, D. (2013). Inside the leader relationship: Constructive controversy for team effectiveness in China. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 43 , 1827–1837.
- Chen, Y. F. , Tjosvold, D. , Huang, X. , & Xu, D. (2011). New manager socialization and conflict management in China: Effects of relationship and open conflict values. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 41 , 332–356.
- Chen, Y. F. , Tjosvold, D. , & Pan, Y. J. (2010). Collectivist team values for Korean–Chinese co-worker relationships and job performance. International Journal of Intercultural Relationships , 34 , 475–481.
- Chen, Y. F. , Tjosvold, D. , & Su, F. (2005). Working with foreign managers: Conflict management for effective leader relationships in China. International Journal of Conflict Management , 16 , 265–286.
- Chen, Y. F. , Tjosvold, D. , & Wu, P. G. (2008). Effects of relationship values and goal interdependence on guanxi between foreign managers and Chinese employees. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 38 , 2440–2486.
- Choi, J. N. , & Sy, T. (2010). Group-level organizational citizenship behavior: Effects of demographic faultlines and conflict in small work groups. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 31 , 1032–1054.
- Chun, J. S. , & Choi, J. N. (2014). Members’ needs, intragroup conflict, and group performance. Journal of Applied Psychology , 99 , 437–450.
- Cosier, R. A. (1978). The effects of three potential aids for making strategic decisions on prediction accuracy. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance , 22 , 295–306.
- De Dreu, C. K. (2006). When too little or too much hurts: Evidence for a curvilinear relationship between task conflict and innovation in teams. Journal of Management , 32 , 83–107.
- De Dreu, C. K. (2007). Cooperative outcome interdependence, task reflexivity, and team effectiveness: A motivated information processing perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology , 92 , 628–638.
- De Dreu, C. K. , & Boles, T. L. (1998). Share and share alike or winner take all? The influence of social value orientation upon choice and recall of negotiation heuristics. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , 76 , 253–276.
- De Dreu, C. K. , Koole, S. L. , & Steinel, W. (2000). Unfixing the fixed pie: A motivated information-processing approach to integrative negotiation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 79 , 975–987.
- De Dreu, C. K. , & McCusker, C. (1997). Gain–loss frames and cooperation in two-person social dilemmas: A transformational analysis. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 72 , 1093–1106.
- De Dreu, C. K. , Nijstad, B. A. , & van Knippenberg, D. (2008). Motivated information processing in group judgment and decision making. Personality and Social Psychology Review , 12 , 22–49.
- De Dreu, C. K. , & Van Lange, P. A. (1995). The impact of social value orientations on negotiator cognition and behavior. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 21 , 1178–1188.
- De Dreu, C. K. , & Van Vianen, A. E. (2001). Managing relationship conflict and the effectiveness of organizational teams. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 22 , 309–328.
- De Dreu, C. K. , & Weingart, L. R. (2003). Task versus relationship conflict, team performance, and team member satisfaction: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 , 741–749.
- De Dreu, C. K. , Weingart, L. R. , & Kwon, S. (2000). Influence of social motives on integrative negotiation: A meta-analytic review and test of two theories. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 78 , 889–905.
- De Jong, A. , Song, M. , & Song, L. Z. (2013). How lead founder personality affects new venture performance: The mediating role of team conflict. Journal of Management , 39 , 1825–1854.
- De Wit, F. R. , Greer, L. L. , & Jehn, K. A. (2012). The paradox of intragroup conflict: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology , 97 , 360–390.
- De Wit, F. R. , Jehn, K. A. , & Scheepers, D. (2013). Task conflict, information processing, and decision-making: The damaging effect of relationship conflict. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , 122 , 177–189.
- DeChurch, L. A. , Mesmer-Magnus, J. R. , & Doty, D. (2013). Moving beyond relationship and task conflict: Toward a process-state perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology , 98 , 559–578.
- Deutsch, M. (1948). The effects of cooperation and competition upon group process . Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
- Deutsch, M. (1973). The resolution of conflict . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Deutsch, M. , Coleman, P. T. , & Marcus, E. (2011). The handbook of conflict resolution: Theory and practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
- Eisenbeiss, S. A. (2012). Re-thinking ethical leadership: An interdisciplinary integrative approach. Leadership Quarterly , 23 , 791–808.
- Eisenbeiss, S. A. , van Knippenberg, D. , & Boerner, S. (2008). Transformational leadership and team innovation: Integrating team climate principles. Journal of Applied Psychology , 93 , 1438–1446.
- Eisenhardt, K. M. , Kahwajy, J. L. , & Bourgeois, L. J. (1997). How management teams can have a good fight. Harvard Business Review , 75 (4), 77–85.
- Farh, J. L. , Lee, C. , & Farh, C. I. (2010). Task conflict and team creativity: A question of how much and when. Journal of Applied Psychology , 95 , 1173–1180.
- Follett, M. P. (1940). Constructive conflict. In H. C. Metcalf & L. Urwick (Eds.), Dynamic administration: The collected papers of Mary Parker Follett (pp. 183–209). New York: Harper.
- Friedman, R. , Chi, S. C. , & Liu, L. A. (2006). An expectancy model of Chinese–American differences in conflict-avoiding. Journal of International Business Studies , 37 , 76–91.
- Galinsky, A. , & Schweitzer, M. (2015). Friend & foe: When to cooperate, when to compete, and how to succeed at both . New York: Crown Business.
- George, A. L. (1974). Adaptation to stress in political decision making: The individual, small group, and organizational contexts. In G. V. Coelho , D. A. Hamburg , & J. E. Adams (Eds.), Coping and adaptation (pp. 176–245). New York: Basic Books.
- Gibson, D. E. , & Callister, R. R. (2010). Anger in organizations: Review and integration. Journal of Management , 36 , 66–93.
- Graen, G. B. , & Uhl-Bien, M. (1995). Relationship-based approach to leadership: Development of leader–member exchange (LMX) theory of leadership over 25 years; Applying a multi-level multi-domain perspective. Leadership Quarterly , 6 , 219–247.
- Gruenfeld, D. H. (1995). Status, ideology, and integrative complexity on the US Supreme Court: Rethinking the politics of political decision making. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 68 , 5–20.
- Hempel, P. S. , Zhang, Z. X. , & Tjosvold, D. (2009). Conflict management between and within teams for trusting relationships and performance in China. Journal of Organization Behavior , 30 , 41–65.
- Hui, C. , Wong, A. , & Tjosvold, D. (2007). Turnover intention and performance in China: The role of positive affectivity, Chinese values, perceived organizational support and constructive controversy. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , 80 , 735–751.
- Humphrey, S. E. , Aime, F. , Cushenbery, L. , Hill, A. D. , & Fairchild, J. (2017). Team conflict dynamics: Implications of a dyadic view of conflict for team performance. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes , 142 , 58–70.
- Jehn, K. A. (1994). Enhancing effectiveness: An investigation of advantages and disadvantages of value-based intragroup conflict. International Journal of Conflict Management , 5 , 223–238.
- Jehn, K. A. (1995). A multimethod examination of the benefits and detriments of intragroup conflict. Administrative Science Quarterly , 40 , 256–282.
- Jehn, K. A. (1997). A qualitative analysis of conflict types and dimensions in organizational groups. Administrative Science Quarterly , 42 , 530–557.
- Jehn, K. A. , Greer, L. , Levine, S. , & Szulanski, G. (2008). The effects of conflict types, dimensions, and emergent states on group outcomes. Group Decision and Negotiation , 17 , 465–495.
- Jiang, J. Y. , Zhang, X. , & Tjosvold, D. (2012). Emotion regulation as a boundary condition of the relationship between team conflict and performance: A multi-level examination. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 34 , 714–734.
- Johnson, D. W. (2015). Constructive controversy: Theory, research, practice . Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press.
- Johnson, D. W. , Johnson, R. T. , & Tjosvold, D. (2006). Constructive controversy: The value of intellectual opposition. In M. Deutsch , P. T. Coleman , & E. Marcus (Eds.), The handbook of conflict resolution: Theory and practice (pp. 69–91). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
- Kelley, H. H. , & Schenitzki, D. P. (1972). Bargaining. In C. G. McClintock (Ed.), Experimental social psychology (pp. 298–337). New York: Holt.
- Kirkbride, P. S. , Tang, S. F. Y. , & Westwood, R. I. (1991). Chinese conflict preferences and negotiating behaviour: Cultural and psychological influences. Organization Studies , 12 , 365–386.
- Landkammer, F. , & Sassenberg, K. (2016). Competing while cooperating with the same others: The consequences of conflicting demands in co-opetition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 145 , 1670–1686.
- Lau, R. S. , & Cobb, A. T. (2010). Understanding the connections between relationship conflict and performance: The intervening roles of trust and exchange. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 31 , 898–917.
- Lewin, K. (1938). The conceptual representation and the measurement of psychological forces . Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
- Liu, J. , Fu, P. , & Liu, S. (2009). Conflicts in top management teams and team/firm outcomes: The moderating effects of conflict-handling approaches. International Journal of Conflict Management , 20 , 228–250.
- Lovelace, K. , Shapiro, D. L. , & Weingart, L. R. (2001). Maximizing cross-functional new product teams’ innovativeness and constraint adherence: A conflict communications perspective. Academy of Management Journal , 44 , 779–793.
- Lu, J. F. , Tjosvold, D. , & Shi, K. (2010). Team training in China: Testing and applying the theory of cooperation and competition. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 40 , 101–134.
- McClintock, C. (1977). Social motives in settings of outcome interdependence. In D. Druckman (Ed.), Negotiations: Social psychological perspective (pp. 49–77). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
- Maltarich, M. A. , Kukenberger, M. , Reilly, G. , & Mathieu, J. (2018). Conflict in teams: Modeling early and late conflict states and the interactive effects of conflict processes. Group & Organization Management , 43 , 6–37.
- Mason, R. O. , & Mitroff, I. I. (1981). Challenging strategic planning assumptions: Theory, cases, and techniques . New York: Wiley.
- Mayer, D. M. , Aquino, K. , Greenbaum, R. L. , & Kuenzi, M. (2012). Who displays ethical leadership, and why does it matter? An examination of antecedents and consequences of ethical leadership. Academy of Management Journal , 55 , 151–171.
- Messick, D. M , & McClintock, C. G. (1968). Motivational bases of choice in experimental games. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 4 , 1–25.
- Mitchell, R. , Nicholas, S. , & Boyle, B. (2009). The role of openness to cognitive diversity and group processes in knowledge creation. Small Group Research , 40 , 535–554.
- Mooney, A. C. , Holahan, P. J. , & Amason, A. C. (2007). Don’t take it personally: Exploring cognitive conflict as a mediator of affective conflict. Journal of Management Studies , 44 , 733–758.
- Nauta, A. , De Dreu, C. K. , & Van der Vaart, T. (2002). Social value orientation, organizational goal concerns and interdepartmental problem-solving behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 23 , 199–213.
- Nemeth, C. , & Owens, P. (1996). Making groups more effective: The value of minority dissent. In M. A. West (Ed.), Handbook of work group psychology (pp. 125–141). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley.
- Ohbuchi, K. I. , & Atsumi, E. (2010). Avoidance brings Japanese employees what they care about in conflict management: Its functionality and “good member” image. Negotiation and Conflict Management Research , 3 , 117–129.
- Peterson, R. S. , & Nemeth, C. J. (1996). Focus versus flexibility majority and minority influence can both improve performance. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 22 , 14–23.
- Pondy, L. R. (1967). Organizational conflict: Concepts and models. Administrative Science Quarterly , 12 , 296–320.
- Poon, M. , Pike, R. , & Tjosvold, D. (2001). Budget participation, goal interdependence and controversy: A study of a Chinese public utility. Management Accounting Research , 12 , 101–118.
- Pruitt, D. G. , & Carnevale, P. J. (1993). Negotiation in social conflict . Buckingham, U.K.: Open University Press.
- Pruitt, D. G. , Carnevale, P. J. , Ben-Yoav, O. R. L. Y. , Nochajski, T. H. , & Van Slyck, M. (1983). Incentives for cooperation in integrative bargaining. Aspiration Levels in Bargaining and Economic Decision Making , 213 , 22–34.
- Pruitt, D. G. , & Lewis, S. A. (1975). Development of integrative solutions in bilateral negotiation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 31 , 621–633.
- Pruitt, D. G. , & Rubin, J. (1986). Social conflict . New York: Random House.
- Rahim, M. A. (1983). A measure of styles of handling interpersonal conflict. Academy of Management Journal , 26 , 368–376.
- Rahim, M. A. (1992). Managing conflict in organizations . 2nd ed. New York: Praeger.
- Rahim, M. A. (1995). Confirmatory factor analysis of the styles of handling interpersonal conflict: First-order factor model and its invariance across groups. Journal of Applied Psychology , 80 , 122–132.
- Rahim, A. , & Bonoma, T. V. (1979). Managing organizational conflict: A model for diagnosis and intervention. Psychological Reports , 44 , 1323–1344.
- Rispens, S. , Greer, L. , Jehn, K. A. , & Thatcher, S. (2011). Not so bad after all: How relational closeness buffers the association between relationship conflict and helpful and deviant group behaviors. Negotiation and Conflict Management Research , 4 , 277–296.
- Salas, E. , Rosen, M. A. , & DiazGranados, D. (2010). Expertise-based intuition and decision making in organizations. Journal of Management , 36 , 941–973.
- Schei, V. , & Rognes, J. K. (2003). Knowing me, knowing you: Own orientation and information about the opponent’s orientation in negotiation. International Journal of Conflict Management , 14 , 43–59.
- Schweiger, D. M. , Sandberg, W. R. , & Ragan, J. W. (1986). Group approaches for improving strategic decision making: A comparative analysis of dialectical inquiry, devil’s advocacy, and consensus. Academy of Management Journal , 29 , 51–71.
- Shaw, J. D. , Zhu, J. , Duffy, M. K. , Scott, K. L. , Shih, H. A. , & Susanto, E. (2011). A contingency model of conflict and team effectiveness. Journal of Applied Psychology , 96 , 391–400.
- Sinkula, J. M. , Baker, W. E. , & Noordewier, T. (1997). A framework for market-based organizational learning: Linking values, knowledge, and behavior. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science , 25 , 305–318.
- Smith, P. B. (2003). Meeting the challenge of cultural difference. In D. Tjosvold & K. Leung (Eds.), Cross-cultural foundations: Traditions for managing in a cross-cultural world (pp. 59–71). Farnham, U.K.: Ashgate.
- Somech, A. , Desivilya, H. S. , & Lidgoster, H. (2009). Team conflict management and team effectiveness: The effects of task interdependence and team identification. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 30 , 359–378.
- Spector, P. E. , & Bruk-Lee, V. (2008). Conflict, health, and well-being. In C. K. W. De Dreu & M. J. Gelfand (Eds.), The psychology of conflict and conflict management in organizations (pp. 267–288). New York: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Stogdill, R. M. (1974). Handbook of leadership: A survey of theory and practice . New York: Free Press.
- Tekleab, A. G. , Quigley, N. R. , & Tesluk, P. E. (2009). A longitudinal study of team conflict, conflict management, cohesion, and team effectiveness. Group & Organization Management , 34 , 170–205.
- Tetlock, P. E. , Armor, D. , & Peterson, R. S. (1994). The slavery debate in antebellum America: Cognitive style, value conflict, and the limits of compromise. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 66 , 115–126.
- Thiel, C. E. , Harvey, J. , Courtright, S. , & Bradley, B. (2017). What doesn’t kill you makes you stronger: How teams rebound from early-stage relationship conflict . Journal of Management , 45 (4), 1623–1659.
- Thomas, K. W. (1976). Conflict and conflict management. In M. D. Dunnette (Ed.), Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology (pp. 889–935). Chicago, IL: Rand McNally.
- Thomas, K. W. (1992). Conflict and negotiation processes in organizations. In L. M. Hough & M. D. Dunnette (Eds.), Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology , 2nd ed., Vol. 3 (pp. 651–717). Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologists Press.
- Tjosvold, D. (1984). Effects of crisis orientation on managers’ approach to controversy in decision making. Academy of Management Journal , 27 , 130–138.
- Tjosvold, D. (1985). Implications of controversy research for management. Journal of Management , 11 , 19–35.
- Tjosvold, D. (1988). Effects of shared responsibility and goal interdependence on controversy and decision making between departments. Journal of Social Psychology , 128 , 7–18.
- Tjosvold, D. (1990a). The goal interdependence approach to communication in conflict: An organizational study. In M. A. Rahim (Ed.), Theory and research in conflict management (pp. 15–27). New York: Praeger.
- Tjosvold, D. (1990b). Flight crew collaboration to manage safety risks. Group and Organization Studies , 15 , 177–191.
- Tjosvold, D. (2002). Managing anger for teamwork in Hong Kong: Goal interdependence and open-mindedness. Asian Journal of Social Psychology , 5 , 107–123.
- Tjosvold, D. , Cho, Y. H. , Park, H. H. , Liu, C. , Liu, W. C. , & Sasaki, S. (2001). Interdependence and managing conflict with sub-contractors in the construction industry in East Asia. Asia Pacific Journal of Management , 18 , 295–313.
- Tjosvold, D. , Dann, V. , & Wong, C. L. (1992). Managing conflict between departments to serve customers. Human Relations , 45 , 1035–1054.
- Tjosvold, D. , & Halco, J. A. (1992). Performance appraisal of managers: Goal interdependence, ratings, and outcomes. Journal of Social Psychology , 132 , 629–639.
- Tjosvold, D. , Hui, C. , & Law, K. S. (1998). Empowerment in the manager–employee relationship in Hong Kong: Interdependence and controversy. Journal of Social Psychology , 138 , 624–636.
- Tjosvold, D. , Law, K. S. , & Sun, H. (2006). Conflict in Chinese teams: Conflict types and conflict management approaches. Management and Organization Review , 2 , 231–252.
- Tjosvold, D. , & Leung, K. (2003). Cross-cultural management: Foundations and future . Farnham, U.K.: Ashgate.
- Tjosvold, D. , Poon, M. , & Yu, Z. Y. (2005). Team effectiveness in China: Cooperative conflict for relationship building. Human Relations , 58 , 341–367.
- Tjosvold, D. , & Su, F. S. (2007). Managing anger and annoyance in organizations in China: The role of constructive controversy. Group & Organization Management , 32 , 260–289.
- Tjosvold, D. , & Tjosvold, M. (2015). Teamwork with customers. In Building the team organization (pp. 141–150). London: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Tjosvold, D. , Wedley, W. C. , & Field, R. H. (1986). Constructive controversy, the Vroom-Yetton model, and managerial decision-making. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 7 , 125–138.
- Tjosvold, D. , Wong, A. S. , & Chen, N. Y. (2014a). Constructively managing conflicts in organizations. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior , 1 , 545–568.
- Tjosvold, D. , Wong, A. S. H. , & Chen, N. Y. F. (2014b). Cooperative and competitive conflict management in organizations. In N. Ashkanasy , K. Jehn , & R. Ayoko (Eds.), Handbook of research in conflict management (pp. 33–50). Cheltenham, U.K.: Edward Elgar.
- Tjosvold, D. , Wu, P. , & Chen, Y. F. (2010). The effects of collectivistic and individualistic values on conflict and decision making: An experiment in China. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 40 , 2904–2926.
- Tjosvold, D. , & Yu, Z. (2007). Group risk taking: The constructive role of controversy in China. Group & Organization Management , 32 , 653–674.
- Todorova, G. , Bear, J. B. , & Weingart, L. R. (2014). Can conflict be energizing? A study of task conflict, positive emotions, and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Psychology , 99 , 451–467.
- Van de Vliert, E. , Euwema, M. C. , & Huismans, S. E. (1995). Managing conflict with a subordinate or a superior: Effectiveness of conglomerated behavior. Journal of Applied Psychology , 80 , 271–281.
- Van de Vliert, E. , & Kabanoff, B. (1990). Toward theory-based measures of conflict management. Academy of Management Journal , 33 , 199–209.
- Van de Vliert, E. , Nauta, A. , Giebels, E. , & Janssen, O. (1999). Constructive conflict at work. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 20 , 475–491.
- Van Lange, P. A. (1999). The pursuit of joint outcomes and equality in outcomes: An integrative model of social value orientation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 77 , 337–349.
- Van Lange, P. A. , & Kuhlman, D. M. (1994). Social value orientations and impressions of partner’s honesty and intelligence: a test of the might versus morality effect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 67 , 126–141.
- Walton, R. E , & McKersie, R. B. (1965). A behavioral theory of labor negotiations . New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Weingart, L. R. , Behfar, K. J. , Bendersky, C. , Todorova, G. , & Jehn, K. A. (2015). The directness and oppositional intensity of conflict expression. Academy of Management Review , 40 , 235–262.
- Wong, A. S. H. , Liu, Y. , & Tjosvold, D. (2015). Service leadership for adaptive selling and effective customer service teams. Industrial Marketing Management , 46 , 122–131.
- Wong, A. S. H. , Tjosvold, D. , & Yu, Z. Y. (2005). Organizational partnerships in China: Self-interest, goal interdependence, and opportunism. Journal of Applied Psychology , 90 , 782–791.
- Wong, A. S. H. , Wei, L. , & Tjosvold, D. (2014). Business and regulators partnerships: Government transformational leadership for constructive conflict management. Asia Pacific Journal of Management , 31 , 497–522.
- Wong, A. , Wei, L. , Yang, J. , & Tjosvold, D. (2017). Productivity and participation values for cooperative goals to limit free riding and promote performance in international joint ventures. Journal of World Business , 52 , 819–830.
- Wong, A. , Yang, J. , & Tjosvold, D. (2018). Ethical leaders manage conflict to develop trust. Manuscript, Lingnan University, Hong Kong.
- Wong, E. M. , Ormiston, M. E. , & Tetlock, P. E. (2011). The effects of top management team integrative complexity and decentralized decision making on corporate social performance. Academy of Management Journal , 54 , 1207–1228.
- Xu, J. , & Thomas, H. C. (2011). How can leaders achieve high employee engagement? Leadership and Organization Development Journal , 32 , 339–416.
- Zhang, X. A. , Cao, Q. , & Tjosvold, D. (2011). Linking transformational leadership and team performance: A conflict management approach. Journal of Management Studies , 48 , 1586–1611.
Related Articles
- The Personality Underpinnings of Strategic Leadership: The CEO, TMT, and Board of Directors
- Managing Team Diversity in the Workplace
- Is There a Female Leadership Advantage?
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Business and Management. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 27 August 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.66.15.189]
- 185.66.15.189
Character limit 500 /500
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Managing conflicts
- Managing yourself
- Interpersonal skills
- Interpersonal communication
- Negotiating skills
Manny Ramirez and the Dilemma of the Badly Behaved Superstar
- John Baldoni
- August 04, 2008
Three Ways to Capitalize on Creative Tension
- Muriel Maignan Wilkins
- May 18, 2010
Defusing an Emotionally Charged Conversation with a Colleague
- Ron Friedman
- January 12, 2016
How to Repair a Damaged Professional Relationship
- Dorie Clark
- June 05, 2014
Quality of Work Life—Learning from Tarrytown
- Robert H. Guest
- From the July 1979 Issue
Racial Remarks in the Workplace: Humor or Harassment?
- Terry L. Leap
- Larry R. Smeltzer
- From the November 1984 Issue

Why People Lie at Work - and What to Do About It
- June 24, 2021
The Case of the Machinists’ Mutiny
- W. Bruce Chew
- From the November–December 1990 Issue

Disagreement Doesn’t Have to Be Divisive
- Francesca Gino
- November 16, 2020

When a Team Member Speaks Up - and It Doesn't Go Well
- Megan Reitz
- Amy C. Edmondson
- July 12, 2024
How to Fix Misunderstandings at Work and in Life
- Dan Pallotta
- December 21, 2010
8 Ways to Get a Difficult Conversation Back on Track
- Monique Valcour
- May 22, 2017

Why We Fight at Work
- Annie McKee
- June 13, 2014
Is Your Culture Too Nice?
- Ron Ashkenas
- August 24, 2010

How to Work with Someone Who Creates Unnecessary Conflict
- Amanda Ripley
- August 17, 2021

7 Steps to Repair a Damaged Business Partnership
- Rebecca Zucker
- Jonathan Becker
- January 19, 2024

What to Do When Stakeholders Have Competing Visions
- Karen Walker
- December 06, 2023
Managing Confrontation in Multicultural Teams
- April 06, 2012
Ending the War Between Sales and Marketing
- Philip Kotler
- Neil Rackham
- Suj Krishnaswamy
- From the July–August 2006 Issue
When an Argument Gets Too Heated, Here's What to Say
- Liane Davey
- March 03, 2016

Student Who Was Missing-in-Action
- Steven J. Spear
- June 04, 2001
THE POWERSCREEN PROBLEM - General Instructions
- Bruce Patton
- Mark Gordon
- Andrew Clarkson
- January 01, 1984
The International Committee of The Red Cross: Development of an Ethical Procurement Policy
- Remi Charpin
- Elodie Le Grand
- Marie-Eve Rancourt
- August 25, 2021
Arcelik: COVID-19 Fueled Omnichannel Growth (B)
- Ayelet Israeli
- Fares Khrais
- February 04, 2021
Endesa Chile: Raising the Ralco Dam (A)
- Paula J. Lashober
- Dina Pradel
- Kathleen L. McGinn
- April 14, 2006
Disability Accommodations and Promotions at Bunco
- Katherine E Breward
- January 15, 2010
World Trade Center Redevelopment Negotiation - Confidential Instructions for the City's Representative
- Lawrence Susskind
- Katherine Harvey
- David Kovick
- January 01, 2008
VCPE Strategy Vignettes II
- Josh Lerner
- G. Felda Hardymon
- Matthew Rhodes-Kropf
- Lisa Strope
- December 22, 2010
An Introduction to Business-to-Business Exchanges
- Phillip E. Pfeifer
- Richard Johnson
- March 12, 2001
PrimeGeo (B): Buying Share from an Angry Partner - Confidential Instructions for Thomas
- Horacio Falcao
- Rodrigo Gouveia
- May 29, 2017
Noah Fisher (MBA 2016)
- Leslie A. Perlow
- Matthew Preble
- September 10, 2019
Levendary Cafe: The China Challenge
- Christopher A. Bartlett
- October 24, 2011

HBR Guide to Navigating the Toxic Workplace
- Harvard Business Review
- January 16, 2024
Hewlett-Packard Co.: The War Within
- Krishna G. Palepu
- Jay W. Lorsch
- Eliot Sherman
- Carin-Isabel Knoop
- November 01, 2006
Sermo, Inc.
- Thomas R. Eisenmann
- Lars P. C. Nielsen
- April 10, 2009

Multigenerational Workplace: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business Review
- Megan W Gerhardt
- Paul Irving
- Sarita Gupta
- August 22, 2023
Errors in Social Judgment: Implications for Negotiation and Conflict Resolution, Part 2
- Robert J. Robinson
- February 06, 1997
Hilton HHonors Worldwide: Loyalty Wars
- John Deighton
- Stowe Shoemaker
- October 12, 2000
BAKRA BEVERAGE - Confidential Instructions for BebsiCo's Director of Middle East Operations
- Robert C. Bordone
- January 01, 2004

HBR's 10 Must Reads on Communication, Vol. 2 (with bonus article "Leadership Is a Conversation" by Boris Groysberg and Michael Slind)
- Heidi Grant
- Scott Berinato
- Tsedal Neeley
- March 30, 2021
Popular Topics
Partner center.
- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Volume 2024, Issue 8, August 2024 (In Progress)
- Volume 2024, Issue 7, July 2024
- Bariatric Surgery
- Breast Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Colorectal Surgery
- Colorectal Surgery, Upper GI Surgery
- Gynaecology
- Hepatobiliary Surgery
- Interventional Radiology
- Neurosurgery
- Ophthalmology
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Otorhinolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Plastic Surgery
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery
- Upper GI Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access
- Reasons to Submit
- About Journal of Surgical Case Reports
- Editorial Board
- Advertising and Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
- Self-Archiving Policy
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

Article Contents
Introduction, case report, acknowledgements, conflict of interest statement, consent for publication.
- < Previous
Challenges in diagnosis and management of invasive ductal carcinoma in axillary ectopic breast tissue: a case study
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
Alsadig Suliman, MagdAlden Osman, Siddig Ali, Sara Hussein, Reem Mohamed Osman, Enas Tageldin, Lobna E Ali, Challenges in diagnosis and management of invasive ductal carcinoma in axillary ectopic breast tissue: a case study, Journal of Surgical Case Reports , Volume 2024, Issue 8, August 2024, rjae531, https://doi.org/10.1093/jscr/rjae531
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Ectopic breast tissue (EBT) is breast tissue located outside the normal anatomic boundaries of the breasts, developing due to incomplete embryological regression of the mammary ridges. EBT can develop anywhere along the milk line, with the axilla being the most common site. While generally benign, EBT can undergo malignant transformation. This case report discusses a 24-year-old female with locally advanced invasive ductal carcinoma in the axillary EBT, highlighting its clinical presentation, diagnostic process, and management in a resource-limited setting. The patient underwent wide local excision and axillary lymph node dissection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy, achieving a favorable short-term outcome. This case underscores the importance of considering EBT in differential diagnosis of axillary masses and the need for tailored treatment strategies in such settings.
Ectopic breast tissue (EBT), also known as accessory breast tissue, refers to the presence of breast tissue located outside the normal anatomical boundaries of the breasts [ 1 ]. EBT develops due to incomplete embryological regression of the mammary ridges, which extend from the axilla to the vulva [ 2 , 3 ]. It is present in 2%–6% of the population and, like normal breast tissue, has the potential to develop malignancy [ 4 , 5 ]. Although malignancies in EBT are rare, they tend to have a progressive clinical course. The incidence of EBT carcinoma is 0.3%–0.6% of all breast cancers, with the axilla being the most common site [ 6 ]. We present a unique case of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) in the EBT of the axilla, highlighting the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges associated with this condition.
A 24-year-old female, unmarried and a nonsmoker, presented with a painless mass in her left axilla that had been developing for approximately six months. She also reported significant weight loss and fatigue but had no family history of breast cancer. On physical examination, both breasts and the right axilla were normal. However, the left axilla revealed a hard, mobile lump measuring 12.6 × 8.4 × 4.5 cm with hyperpigmented and ulcerated skin. In addition, palpable, painless left axillary lymph nodes (ALNs) were observed ( Fig. 1 ).

Beginning of surgery (WLE) at left axilla with ulcerated prominent ectopic breast tissue (indicated by an arrow).
An ultrasound of the left axilla revealed a mass measuring 12.6 × 8.4 × 4.5 cm, located near the anterior border of the latissimus dorsi muscle and inferior to the axillary vein. The mass exhibited heterogeneous echotexture and irregular margins, suggestive of malignancy. Additionally, three enlarged ALNs with irregular borders were identified. A core needle biopsy of the mass, guided by ultrasound, confirmed the presence of IDC ( Fig. 2 ). Furthermore, an ultrasound-guided biopsy of the suspicious ALNs confirmed malignancy.

H&E stain slide shows histopathological features of IDC.
Immunohistochemical analysis of the axillary mass biopsy revealed estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor positivity, while human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 was negative. Thoracoabdominal CT showed no secondary localizations, and whole-body bone scintigraphy detected no bone metastases. The overall stage was determined to be T4bN1M0 (Stage IIIB).
A multidisciplinary team determined the patient to be a candidate for neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) followed by surgical management and adjuvant chemotherapy (AC). However, due to the unavailability of chemotherapy at the time of diagnosis, surgical management proceeded after careful patient counseling. A wide local excision (WLE) of the mass with levels I and II axillary lymph node clearance (ALNC) was performed ( Fig. 3 ). Histopathology reported a Nottingham grade III IDC with infiltrative borders and dense marginal lymphatic infiltration. The tumor was totally excised with 10 out of 15 soft white lymph nodes showing extensive metastatic deposits. The patient did not suffer any complications postoperatively. Upon follow-up after three weeks, the patient was in good health. Postoperatively, she received four of the six planned cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy; the fourth cycle was canceled due to neutropenia. She also received hormonal therapy and radiotherapy as per the treatment plan.

Gross finding appearance of the EBT specimen showed a solid mass with clear margins. S : superficial margin; D : deep margin; M : medial margin; L : lateral margin.
EBT results from the failure of complete regression of the mammary ridges during embryological development. Axilla is the most common location for EBT, accounting for 58% of reported cases [ 6 ]. Other locations include the parasternal line, sub clavicular area, sub-mammary region, and vulvar region [ 7 ]. EBT may contain only glandular tissue or be associated with a nipple-areola complex [ 8 ]. Hormonal regulation influences its development, and it may become apparent during puberty and pregnancy, similar to normal breast tissue [ 9 ]. EBT is subject to the same pathologies, including pain, inflammation, fibroadenoma, and cancers [ 6 ]. However, the exact incidence of primary EBT carcinoma and the rate of malignant transformation remain unknown [ 2 ]. Accurate diagnosis of axillary EBT carcinoma is crucial as it provides precise staging information for patients with concurrent ipsilateral breast cancer [ 10 ]. IDC is the most frequently reported pathological type of EBT cancer, although other types such as medullary, lobular, and phyllodes have also been reported [ 6 ].
Managing EBT cancer is consistent with the guidelines for pectoral breast cancer, involving a multidisciplinary approach and standard triple therapy: surgery, systemic therapy, and radiation, depending on the staging and tumor biology [ 7 ]. Imaging studies like breast MRI, US, and mammography are vital for assessing EBT cancer [ 6 ]. Fine-needle aspiration cytology can aid in diagnosing malignancy, but distinguishing between EBT cancer and lymph node metastasis from occult primary lesions can be challenging. Histologically, the presence of adjacent normal breast tissue (ducts and lobules) and lack of lymphoid tissue confirm the diagnosis of EBT cancer and exclude metastatic lymph nodes [ 11 ]. According to lymph node guidelines, using ultrasound-guided biopsy of suspicious ALNs is essential in confirming malignancy before undertaking ALNC [ 12 ].
This case involves a young patient with locally advanced IDC of axillary EBT. Despite resource limitations, WLE with ALNC followed by AC and radiotherapy contributed to a favorable short-term outcome. The choice of treatment modalities was guided by the aggressive nature of the tumor, ALNs involvement, and the need to achieve optimal disease control.
In modern breast surgery, NAC would have been the gold standard prior to surgery for a premenopausal patient with metastatic ALNs. NAC is significant in reducing tumor volume to increase the breast-conserving rate. It is crucial for downgrading locally advanced inoperable patients to provide surgical opportunities [ 13 ]. On the other hand, AC was initiated to target potential micrometastases and systemic spread, aligning with recommendations for cases with adverse prognostic features. The patient's response highlights the critical role of surgical intervention in such cases [ 14 ]. Adjuvant radiotherapy was administered to enhance local control and reduce the risk of recurrence, in accordance with recommendations despite existing controversies regarding its use in ipsilateral disease-free pectoral breast [ 7 ].
Ectopic breast tissue pathologies are rarely reported, leading to a lack of awareness among clinicians regarding their presentation, diagnosis, and management. The absence of specific clinical guidelines for EBT cancer can result in misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment, leading to poor prognosis. Clinicians should include EBT in breast examinations and consider its inclusion in screening procedures.
Our appreciation extends to the medical, surgical, and healthcare teams for their expertise and dedication in managing this case.
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
This case report did not receive any specific funding.
An informed consent was signed by the patient.
Sperduto W , McCullough A , Northfelt D , et al. Implications of a supernumerary nipple breast cancer in a BReast CAncer sequence variation carrier: a case report . Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes 2023 ; 7 : 437 – 42 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2023.08.006 .
Google Scholar
Ectopic Breast Cancer Arising within an Axillary Lymph Node - Okayama University Scientific Achievement Repository [Internet] . [ cited 30 May 2024 ] https://ousar.lib.okayama-u.ac.jp/en/66676 .
Aksu E , Kayali A , Spasova V , et al. Primary ectopic breast cancer of the vulva: a case report with a short literature review . Chir . 2024 ; 37 : 45 – 7 . https://doi.org/10.23736/S0394-9508.23.05555-9 .
Özdamar MY , Özdamar MY . Developmental anomalies of the breast in the pediatric population . J Compr Surg 2024 ; 2 : 12 – 4 . https://doi.org/10.51271/JOCS-0026 .
Mansouri G , Alkatout I , Iranpour M . et al. Unexpected presentation of accessory breast: vulvar accessory breast tissue: a case report . J Med Case Reports 2023 ; 17 : 189 – 4 . https://link.springer.com/articles/10.1186/s13256-023-03930-0 .
Park SY , Lee J , Park JY , et al. Primary invasive ductal carcinoma arising in axillary accessory breast: a case report . J Korean Soc Radiol . 2024 ; 85 : 421 .
Remmert N , Moin N , Daniele K , et al. Accessory breast cancer: a case series . J Surg Res 6 : 217 – 20 . https://doi.org/10.26502/jsr.10020299 .
Assoni AS , Silva BBA DA , Assoni AS , Sampaio FMS . Primary ductal carcinoma of ectopic breast . An Bras Dermatol . 2023 ; 98 : 257 .
Ishiguro A , Tosa M , Sakatani T , Ohashi R , Ogawa R . A case of axillary Fibroadenoma that grew rapidly from axillary accessory breast tissue over 40 days . Plast Reconstr Surg - Glob Open . 2023 ; 11 :e5420. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000005420 .
Zhang S, Yu YH, Qu W, Zhang Y, Li J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Accessory Breast Cancer in 11 Patients. New York: Spandidos Publications. [Internet] . [cited 31 May 2024] . https://www.spandidospublications.com/ol/10/3/1783 .
Iacuzzo C , Pellitteri C , Di BC , et al. Axillary ectopic breast tissue primary cancer: a rare presentation of a common disease: axillary ectopic breast cancer . Arch Breast Cancer 2022 ; 9 : 411 – 5 . https://doi.org/10.32768/abc.202293411-415 .
Zheng H , Zhao R , Wang W , et al. The accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy in diagnosing axillary lymph nodes in women with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Front Oncol 2023 ; 13 : 1166035 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1166035 .
Chen Y , Qi Y , Wang K . Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: an evaluation of its efficacy and research progress . Front Oncol 2023 ; 13 : 1169010 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1169010 .
Yang F , Xie X , Liu J , et al. Accessory breast cancer of the right axillary region: a case report and review of management . Int J Biol Life Sci 2023 ; 3 : 15 – 8 . https://doi.org/10.54097/ijbls.v3i3.03 .
Email alerts
Citing articles via, affiliations.
- Online ISSN 2042-8812
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Browse Topics
- Executive Committee
- Affiliated Faculty
- Harvard Negotiation Project
- Great Negotiator
- American Secretaries of State Project
- Awards, Grants, and Fellowships
- Negotiation Programs
- Mediation Programs
- One-Day Programs
- In-House Training – Inquiry Form
- In-Person Programs
- Online Programs
- Advanced Materials Search
- Contact Information
- The Teaching Negotiation Resource Center Policies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Negotiation Journal
- Harvard Negotiation Law Review
- Working Conference on AI, Technology, and Negotiation
- 40th Anniversary Symposium
- Free Reports and Program Guides
Free Videos
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Event Series
- Our Mission
- Keyword Index
PON – Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - https://www.pon.harvard.edu
Team-Building Strategies: Building a Winning Team for Your Organization

Discover how to build a winning team and boost your business negotiation results in this free special report, Team Building Strategies for Your Organization, from Harvard Law School.
New Conflict Management Skills: Understand How to Resolve “Hot Conflicts”
Three specific conflict resolution skills you can use in conflict management.
By PON Staff — on November 5th, 2020 / Business Negotiations
Negotiating effectively with colleagues can be more challenging than dealing with outsiders. Conventional wisdom advises addressing team conflict by staying focused on tasks and avoiding relationship issues. Yet a case study of conflict management by Harvard Business School professor Amy Edmondson and Diana McLain Smith of The Monitory Group concludes that this approach to dispute resolution works only when the issues are “cool” ones that can be resolved through objective analysis.
The researchers found three common symptoms of “hot conflicts,” which are usually prompted by differences in underlying belief systems, interests, and values:
- Team members persist in arguing the same points.
- When the team reaches impasses, talks get personal. Accusations may be spoken out loud, and members may speculate privately about one another’s motives.
- Once negative attributions take hold, emotions flare and progress halts.

Claim your FREE copy: Business Negotiation Strategies: How to Negotiate Better Business Deals
Discover step-by-step techniques for avoiding common business negotiation pitfalls when you download a copy of the FREE special report, Business Negotiation Strategies: How to Negotiate Better Business Deals , from the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School.
Resolving Conflict Using 3 Specific Dispute Resolution Skills
The authors discovered that management teams can resolve hot conflicts by integrating three specific skills.
First , engage in individual self-management, or “the ability to examine and transform the thoughts and feelings that hijack one’s ability to reason calmly when conflicts heat up.” (See also, A Case Study of Conflict Management: Family Conflict Resolution Lessons from the Home ).
Second , mutually manage conversations so that taboo topics and feelings can be raised without fear of emotional eruptions. That requires deft framing and a willingness to find the concern beneath seemingly irrational comments. (For more negotiation tips on how to frame the conversation, see also International Negotiations and Agenda Setting ).
The first two practices support a third skill : managing team relationships for the long term, which requires trust building and investing in the key individual relationships, specifically those that lie on “organizational fault lines” where intrafirm conflicts occur. (See also, Negotiation Examples and Negotiation Techniques: Six Strategies for Building Trust in Negotiations ).
It also requires shared appreciation of the dynamic quality of relationships: how “ what I say affects what you think , which affects what you say and then what I think next , and so on.” Without that kind of insight, each teammate will feel blameless for the problems that plague the group.
How have conflict management skills helped you in a negotiation? Let us know in the comments.
Related Business Negotiations Article: Best Negotiation Examples – Negotiating Conflicts of Interest
Adapted from “Resolve Hot Topics with Cooler Heads,” first published in the Negotiation newsletter, May 2007.
Originally published in 2011.
Related Posts
- 10 Great Examples of Negotiation in Business
- Top 10 Notable Negotiations of 2022
- Negotiation Preparation Strategies
- Contingency Contracts in Business Negotiations
- Right of First Refusal: A Potentially Win-Win Negotiation Tool
No Responses to “New Conflict Management Skills: Understand How to Resolve “Hot Conflicts””
One response to “new conflict management skills: understand how to resolve “hot conflicts””.
Thank you for yet another great insight. I do believe that managing relations between co-workers is one of the most important topics today.
Click here to cancel reply.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Negotiation and Leadership
- Download Program Guide: Fall 2024
- Register Online: Fall 2024
- Learn More about Negotiation and Leadership

NEGOTIATION MASTER CLASS
- Download Program Guide: November 2024
- Register Online: November 2024
- Learn More about Harvard Negotiation Master Class

Negotiation Essentials Online
- Download Program Guide: December 2024 and June 2025
- Register Online: December 2024 June 2025
- Learn More about Negotiation Essentials Online

Beyond the Back Table: Working with People and Organizations to Get to Yes
- Learn More about Beyond the Back Table

Select Your Free Special Report
- Negotiation Essentials Online (NEO) December 2024 and June 2025 Program Guide
- Negotiation Essentials In-House Program Guide
- Negotiation Master Class November 2024 Program Guide
- Beyond the Back Table February 2025 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Fall 2024 Program Guide
- Make the Most of Online Negotiations
- Managing Multiparty Negotiations
- Getting the Deal Done
- Salary Negotiation: How to Negotiate Salary: Learn the Best Techniques to Help You Manage the Most Difficult Salary Negotiations and What You Need to Know When Asking for a Raise
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiation: Cross Cultural Communication Techniques and Negotiation Skills From International Business and Diplomacy
Teaching Negotiation Resource Center
- Teaching Materials and Publications
Stay Connected to PON
Preparing for negotiation.
Understanding how to arrange the meeting space is a key aspect of preparing for negotiation. In this video, Professor Guhan Subramanian discusses a real world example of how seating arrangements can influence a negotiator’s success. This discussion was held at the 3 day executive education workshop for senior executives at the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School.
Guhan Subramanian is the Professor of Law and Business at the Harvard Law School and Professor of Business Law at the Harvard Business School.
Articles & Insights
- BATNA and Other Sources of Power at the Negotiation Table
- Michael Scott, Negotiation Genius? Lessons from TV Negotiations
- BATNA Strategy: Should You Reveal Your BATNA?
- Take your BATNA to the Next Level
- Taylor Swift: Negotiation Mastermind?
- What is Conflict Resolution, and How Does It Work?
- How to Manage Conflict at Work
- Conflicts of Interest: How to Avoid and Manage Them
- Cognitive Biases in Negotiation and Conflict Resolution – Common Negotiation Mistakes
- The Pitfalls of Negotiations Over Email
- Crisis Negotiation Lessons: The U.S.-Russia Prisoner Swap
- What is Crisis Management in Negotiation?
- Famous Negotiations Cases – NBA and the Power of Deadlines at the Bargaining Table
- Crisis Communication Examples: What’s So Funny?
- AI Negotiation in the News
- Trust and Honesty in Negotiations: Dealing with Dishonest Negotiators
- Bargaining in Bad Faith: Dealing with “False Negotiators”
- How to Renegotiate a Bad Deal
- Consensus-Building Techniques
- How to Manage Difficult Staff: Gen Z Edition
- What Leads to Renegotiation?
- Does Your Negotiation Process Need Improvement?
- 5 Dealmaking Tips for Closing the Deal
- Trump’s Negotiating Style as President-Elect
- Understanding Exclusive Negotiation Periods in Business Negotiations
- Using Principled Negotiation to Resolve Disagreements
- Dear Negotiation Coach: Responding (Or Not) to an Ultimatum in Negotiation
- What is Alternative Dispute Resolution?
- What Is an Umbrella Agreement?
- Cultural Barriers and Conflict Negotiation Strategies: Apple’s Apology in China
- The Pros and Cons of Back-Channel Negotiations
- The Negotiation Process in China
- How to Solve Intercultural Conflict
- Managing Cultural Differences in Negotiation
- Best Negotiators in History: Nelson Mandela and His Negotiation Style
- Directive Leadership: When It Does—and Doesn’t—Work
- Counteracting Negotiation Biases Like Race and Gender in the Workplace
- What Is Collective Leadership?
- The Trait Theory of Leadership
- Charismatic Leadership: Weighing the Pros and Cons
- Why is Negotiation Important: Mediation in Transactional Negotiations
- How Mediation Can Help Resolve Pro Sports Disputes
- The Mediation Process and Dispute Resolution
- What Makes a Good Mediator?
- AI Mediation: Using AI to Help Mediate Disputes
- A Difficult but Well-Fought Negotiation Campaign
- 10 Negotiation Failures
- When Not to Show Your Hand in Negotiations
- Four Negotiation Examples in the Workplace That Sought Greater Equity and Diversity
- Value Claiming in Negotiation
- 10 Negotiation Training Skills Every Organization Needs
- 3-D Negotiation Strategy
- Use a Negotiation Preparation Worksheet for Continuous Improvement
- The Importance of a Relationship in Negotiation
- Collaborative Negotiation Examples: Tenants and Landlords
- Salary Negotiation: How to Ask for a Higher Salary
- How to Counter a Job Offer: Avoid Common Mistakes
- Renegotiate Salary to Your Advantage
- Are Salary Negotiation Skills Different for Men and Women?
- How to Ask for a Salary Increase
- Learn from the Best with the Great Negotiator Case Studies
- The Best New Simulations
- Negotiation Journal Now Open Access, New Issue Just Released!
- Check Out the Three-Party Coalition All-In-One Curriculum Package
- Camp Lemonnier: Negotiating a Lease Agreement for a Key Military Base in Africa
- Streaming Toward Win-Win Negotiation: Spotify Upgrades Its Negotiating Strategy
- What is a Win-Win Negotiation?
- How to Negotiate Mutually Beneficial Noncompete Agreements
- Labor Negotiation Strategies
- How to Use Tradeoffs to Create Value in Your Negotiations
PON Publications
- Negotiation Data Repository (NDR)
- New Frontiers, New Roleplays: Next Generation Teaching and Training
- Negotiating Transboundary Water Agreements
- Learning from Practice to Teach for Practice—Reflections From a Novel Training Series for International Climate Negotiators
- Insights From PON’s Great Negotiators and the American Secretaries of State Program
- Gender and Privilege in Negotiation
Remember Me This setting should only be used on your home or work computer.
Lost your password? Create a new password of your choice.
Copyright © 2024 Negotiation Daily. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Here is a case study of conflict management emphasizing the importance of hearing all sides in a dispute. Keep reading to learn more.
In this fictional case, the CEO of a sports apparel manufacturer is faced with an ongoing conflict between two of his top executives. Specifically, the head of sales and the CFO are at each other ...
Case Study 1: Handling Roommate Conflicts Chapter Reference: Section 2.2 Approaches to Conflict Whether you have a roommate by choice, by necessity, or through the random selection process of your school's housing office, it's important to be able to get along with the person who shares your living space.
In this case study of conflict management, the Program on Negotiation offers advice drawn from negotiation research about forming negotiating teams.
Conflict resolution is the process of resolving a dispute or a conflict by meeting at least some of each side's needs and addressing their interests. Conflict resolution sometimes requires both a power-based and an interest-based approach, such as the simultaneous pursuit of litigation (the use of legal power) and negotiation (attempts to ...
Conflict and Resolution New research on conflict and resolution from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including conflict management, navigating conflicts of interest, and dealing with the "irrational" negotiator.
When Agreeing to Disagree Is a Good Beginning. by Clea Simon, Harvard Gazette. When conflict stems from honest and open listening, disagreement can be a good thing, say Francesca Gino and Julia Minson. But developing those skills requires patience and discipline.
This section explores the strategic integration of negotiation within conflict management, illustrated with real-world case studies and strategies for negotiating with challenging personalities.
This study examines how an organization-wide self-managed interpersonal conflict resolution system is experienced from the point of view of permanent and seasonal employees. Twenty semi-structured interviews and observations at a single agricultural organization were used to assess the alternative dispute resolution (ADR) system.
Conflict resolution skills are the skills you use to end a dispute respectfully. Here's how to build them on your own.
Discover our Conflict Resolution Case Study Template, designed to help you analyze and resolve workplace conflicts, featuring structured approach.
This is the seventh case study in the series Holding These Truths: Empowerment and Recognition in Action. This series presents case studies for a future conflict resolution textbook. It has been successfully piloted with several international classes. Those, who benefit most, stress the importance of carefully studying the introduction.
In these teams, managers and employees study cooperative, open-minded conflict management, reflect on their current experiences, and develop concrete ways to strengthen and practice conflict management skills.
Case Study: When Two Leaders on the Senior Team Hate Each Other Managing conflicts Magazine Article Boris Groysberg Katherine Connolly Baden
This part contains case studies of industries, including Mayer Manufacturing and Telestar International, to illustrate project conflict management. Abstract Conflicts can occur anywhere in the project and with anyone. Some conflicts are severe while others are easily solvable. In the past, project managers avoided conflicts when possible.
Conflict Management in the Workplace: A Case Study in a TVET College in Mpumalanga Province, presented to obtain a Master of Education at UNISA, is my own work and that no one has presented it before to any other institutions of higher learning. All sources cited in my research study are displayed and acknowledged in
A program conflict management model is developed for the effective management of program conflicts. The model provides a systematic view of the learning cycle of program conflict management, including conflict identification, resolution, feedback, and prevention, of which many patterns are found distinct from project conflict management.
The purpose of our study is to enhance the understanding of relationships between conflict management style, team coordination, and performance in multicultural project team contexts. We investigat...
The purpose of the study is to emphasize the impact of conflict management for university employees. The research method of this study used the second-hand data listed in different databases of books, research papers and related articles on conflict management on the Internet.
Case Study of Conflict Management: To Resolve Disputes and Manage Conflicts, Assume a Neutral 3rd Party Role Posted May 13th, 2024 by PON Staff & filed under Conflict Resolution.
Our appreciation extends to the medical, surgical, and healthcare teams for their expertise and dedication in managing this case. Conflict of interest statement. All authors declare no conflicts of interest. Funding. This case report did not receive any specific funding. Consent for publication. An informed consent was signed by the patient ...
A case study of conflict management by Harvard Business School professors dispute a popular dispute resolution approach you might not know.