An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.15(3); 2023 Mar
- PMC10065366


Symptoms, Mechanisms, and Treatments of Video Game Addiction
Shabina mohammad.
1 Department of Anatomy, Taibah University, Madinah, SAU
Raghad A Jan
2 Collage of Medicine, Taibah University, Madinah, SAU
Saba L Alsaedi
Video game addiction is defined as the steady and repetitive use of the Internet to play games frequently with different gamers, potentially leading to negative consequences in many aspects of life. As recent technological development has given easy access to gaming on many devices, video game addiction has become a serious public health issue with increased prevalence. Many studies have shown that video game addiction leads to changes in the brain that are similar to those that occur in substance addiction and gambling. Evidence has also shown that there is an association between video game addiction and depression, as well as other psychological and social problems. In light of these issues, our review article aims to increase awareness of video game addiction in society. The main objectives of this review are as follows: to describe the mechanism of addiction, to consider whether video game addiction is a real addiction, and to highlight the signs and symptoms of addiction. In addition, we identify the consequences of video game addiction and possible treatments for addicts. The information was extracted from high-quality research papers and reliable websites like PubMed and ScienceDirect.
Introduction and background
Video game addiction falls into the category of Internet gaming disorders (IGDs), which have been strongly correlated with motivational control issues and are regularly compared with gambling [ 1 ]. Many studies have suggested that behavioral addiction can result from compulsive use of the internet [ 2 - 4 ]. Although the spectrum of internet addiction includes video gaming, online shopping, gambling, and social networking, video game addiction seems to be its most studied form [ 5 ]. Currently, according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), video game addiction is defined as the steady and repetitive use of the Internet to play games frequently with different gamers, which leads to clinically significant distress and psychological changes as demonstrated by five or more criteria in a year [ 1 , 6 ].
Evidence has shown that addiction can cause changes in some areas of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex (PFC), the ventral striatum (VS), and the dorsal striatum (DS) [ 5 ]. In 1999, neuroimaging evidence showed that increases in dopamine (DA) levels in the brain are associated with pleasure and euphoria [ 7 , 8 ].
Cross-sectional studies revealed that those with IGD played video games longer, usually missed classes in school, had lower grades, reported more sleep problems, and showed more addiction to video games than those without IGD [ 1 ]. Yee suggested that gamers are generally more youthful and may have low self-esteem or emotional disturbances, and those with emotional disturbances might be more vulnerable to addiction to gaming [ 9 ]. In video games, gamers can explore different sides of themself. They can be increasingly vocal and experience assuming the role of a leader, among others. Unfortunately, problems can arise when these youthful gamers become dependent upon the personalities they create in online games - blurring the line between reality and the game [ 10 ]. The rapid development of technology has given young gamers further access to games, such as advanced mobile phones, tablets, and personal computers (PCs). These online video games usually have tasks and achievements. As an achievement in video games occurs quickly, they are especially alluring for youthful gamers as a method for experiencing fun. Games depend on such feelings, as they often delight the individual and give them satisfaction in their accomplishment. Moreover, the use of a microphone or text chat is enabled in many games, allowing gamers to satisfy their need for relatedness by speaking with others [ 11 ]. Gamers regularly experience difficulty with social connections and feel forlorn-lacking a sense of belonging. This inclination can be particularly strong among kids and youths who have never felt like they belong to a place in reality, and most likely their only friends are also gamers [ 10 ].
Video game addiction may have both short and long-term impacts on gamers, including various emotional, psychological, and neurological effects. A few studies have demonstrated that anxiety and depression are common among individuals who are dependent on video games [ 6 , 12 ]. In the new generation of children, physical activity time is less and shorter in duration when compared with the parent's generation because children’s activities moved toward indoor more than outdoor play. There is a negative relationship between the time spent on online gaming and exercise and that leads to a sedentary lifestyle which is a risk factor for many medical health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and coronary artery disease [ 13 ]. According to the American Medical Association, approximately 90% of young Americans play computer games. Furthermore, 15% of these gamers (i.e., over five million children) could be considered addicted [ 10 ]. Issues arising from gaming have become so serious that the first detox center for video game addiction opened in 2006 in the Netherlands [ 14 ]. As described by Keith Bakker, director of Amsterdam-based Smith and Jones Addiction Consultants and their treatment center, although video games may look innocent, they can be as addictive as gambling or drugs and just as difficult of a habit to break [ 11 ]. A study in an international school in Buraidah, Saudi Arabia showed that 16% of the 276 students were addicted to video games, and the data showed a strong relationship between video game addiction and psychological distress [ 6 ]. In light of these issues, our review article aims to increase awareness of video game addiction in society.
Mechanism of addiction
Researchers have demonstrated that at the initial phases of the intentional use of any substance, the choice to utilize it is made by the brain, specifically the PFC and the VS, as habituation to utilize and compulsion begins. In the DS, brain activity changes and become progressively activated through dopaminergic innervation [ 15 ]. There are also changes in the dopaminergic pathways of the brain, particularly those of the anterior cingulate (AC), the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), and the nucleus accumbens (NAc), due to the repetitive long-term use of the substance, which may result in a decreased response to natural reward and diminished control over seeking and using the substance [ 12 , 16 ]. The long-term use of substances decreases synaptic activity [ 17 ], and the brain becomes progressively responsive by craving substance cues like accessibility [ 18 , 19 ]. In the case of video game addiction, seeing the game or the controller can lead to cravings. Cravings for substance use involve complicated interactions between various brain regions [ 20 ]. The OFC plays a significant role in such stimulation-affecting behavior, as does the amygdala (AMG) and the hippocampus (Hipp) [ 21 ]. Eventually, an increase in the amount of substance is required to create the desired impact, and the brain’s natural reward system becomes inadequate, prompting the activation of an anti-reward system that diminishes the ability of the addicted to finding biological reinforcers pleasurable [ 22 ]. Withdrawal symptoms can also develop, which are due to the absence of DA in the mesocorticolimbic pathways [ 21 ]. Research has demonstrated that changes in brain activity generally occur in substance addiction after a compulsive commitment to use [ 23 ], which suggests that there may be similar changes associated with video game addiction. However, as mentioned previously, increases in DA levels occur by various mechanisms. In this way, the DA theory of addiction explains the powerful activation of mesolimbic DA, which is a strong feature of every addictive substance. However, although the increase in DA may clarify the intense fortifying impacts of addictive substances, it does not clarify associated long-term behavioral anomalies such as desiring and relapsing, which are obvious features even when DA levels return to normal after the clearance of the substance [ 24 ]. Therefore, changes in DA levels cannot be the reason for the adaptive behavior that presents long after the substance has been cleared from the brain [ 25 , 26 ]. Accordingly, it has been proposed that the changes induced by a substance in specific neurotransmission circuits of the mesocorticolimbic area play a role in the pathological behavior of addictive patients [ 27 ].
Whether it is real addiction or not
Numerous governments see the compulsive playing of online video games as a serious general medical problem and have set up treatment facilities, particularly in China and South Korea [ 28 ]. However, whether video games can lead to a real addiction is still hotly debated, and the question arises as to whether a game can be considered an intoxicant. The neurological proof suggests that video games might act as substances, with convincing similarities between their impacts on brain chemistry [ 5 ]. Professor Nancy Petry of the American Psychiatric Association committee considered adding video game addiction to the most recent diagnostic manual but ultimately chose to wait for further consideration [ 28 ]. In recent years, the concept of becoming addicted to behavior has grown in popularity, especially with growing neuroimaging evidence of the brain’s response to such behavior. For example, gambling has been shown to activate the brain’s reward system in a way that is similar to that of a substance [ 28 ]. In 2011, a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study on 154 participating 14-year-olds by Simone Kühn of Ghent University in Belgium found that frequent gamers had increased grey matter in the left VS - a change that may result from increased DA discharge and also appears in those addicted to gambling [ 29 ]. According to the WHO, adding video game addiction to the ICD-11 depends on evidence and agreement among specialists from various countries that are associated with the procedures of specialized consultations. The inclusion of video game addiction in the ICD-11 follows the improvement of treatment programs for individuals with similar conditions in many countries, which will bring more attention to the dangers of this addiction among health professionals, as well as to available avoidance and treatment measures. For gaming addiction to be diagnosed, the signs and symptoms must be of adequate seriousness to bring impairment in different aspects of the person’s life, with the effects normally being obvious for at least one year [ 30 ].
Sign and symptoms
It is important to be able to identify the signs and symptoms of video game addiction, and the sooner one looks for help, the better the outcome. As video games are still a relatively new technology, therapists may disregard the signs of video game addiction. To be able to make informed choices and act successfully in navigating addiction, the following signs can be used as a guide [ 10 ].
Preoccupation with Gaming
Video game addiction starts when gamers become preoccupied with video games, where they will think and fantasize about the game when they are not playing it when they should be focusing on other things, such as schoolwork [ 10 ].
Lying or Hiding Gaming Use
Gamers may play games for uncountable numbers of hours and days, leading to a lack of eating, resting, or personal hygiene. They may also lie to loved ones about what they are truly doing for hours in their rooms. Gamers may tell their parents that they are getting their work done, say that they are using their PC for work, or make up many reasons why they cannot go out and socialize [ 10 ].
Loss of Interest in Other Activities
As video game addiction increases, the person’s interest in daily activities they used to enjoy decreases [ 31 ]. For example, one gamer’s mother said that her child cherished baseball and played varsity on his secondary school team until he discovered Xbox Live, which led to declining grades [ 32 ]. However, she only realized that there was a problem when he stopped playing baseball, as he cherished the sport to an extreme.
Social Withdrawal
One’s character might also change as the addiction increases. For example, social people may remove themselves from their loved ones to invest more time in play. Otherwise normal and happy children may be inclined to simply make friendships in the game, which can become more important than those in real life [ 10 ].
Psychological Withdrawal
Gaming addicts may experience loss when they cannot play a game, as they miss it and feel the need to play it. This inclination can become intense to the point that they become emotionally unstable when compelled to abandon the game. As a result, they cannot focus on anything else except playing [ 10 ].
Defensiveness and Anger
When gaming addicts need to play or when they are compelled to stop playing, they can become defensive and furious. Guardians attempting to set time limits for the game have reported that their children can become angry, unreasonable, and even brutal in response [ 10 ].
Gaming Addicts Use the Game World as a Psychological Escape
Video games, as an easy way to mitigate upsetting emotions, can turn into a safe space that is removed from real-world issues [ 10 ]. Those who feel shy or alienated from their peers can feel more confident while gaming and this fictional life can become more fulfilling than their real life [ 32 ].
Continued Use Despite Its Consequences
Frequently, gamers have the urge to be the best in the game. Therefore, the more they develop and progress in the game, the more they have to play it. This progress is found particularly in journey-type games, where gamers join each other and complete missions in the game together [ 10 ]. Ultimately, gaming addicts may continue game use despite its negative effect on their lives. Although young gamers may drop out of school and disregard their hygiene and self-care just to play, and adults may lose their jobs or relationships, they often continue to play [ 32 ].
Consequences
Video game addiction can lead to a number of serious consequences. Gamers can forget that they need to sleep and eat, or even how to communicate with people in the real world. Gamers may play for 10, 15, or even 20 hours in a single gaming session. Only a couple more minutes can turn into hours as the gamer progresses to the next challenge. They may also endure various medical issues resulting from back strain, eye strain, and carpel tunnel syndrome. For example, one addicted gamer said that he stopped washing himself, ate very little food, and experienced weight loss [ 10 ]. The gamer’s appearance had deteriorated so much that his mom said that he looked like a heroin addict. Although gamers make friends in the game, their friendships or relations in real life can end up being damaged. Furthermore, often it is not only the gamer that suffers the consequences of their addiction. In South Korea, parents were arrested because their four-month-old daughter died due to suffocation after they left her alone in the house for many hours while they played World of Warcraft at a nearby café [ 33 ]. In another similar story, parents from Reno were playing video games so obsessively that they forgot about their children - a two-year-old boy and a girl who was almost one year old - who were seriously malnourished and near death when doctors saw them. The parents pleaded guilty to child neglect and faced a 12-year jail sentence. According to the Associated Press, authorities said the parents were so distracted by video games, mainly the fantasy role-playing Dungeons and Dragons series, that they forgot to take care of their children [ 34 ].
Research on video game addiction treatment is ongoing, only a few clinical trials have been conducted. Some therapists have suggested cognitive behavior therapy (CBT) [ 35 ]. As a prevention strategy for IGD, exercises, and physical activities have been recommended. Particularly, outdoor activities and sports [ 36 ].
Based on the peer-reviewed literature, CBT seems to be the most common treatment for video game addiction and IGD [ 37 , 38 ]. Specifically, substance abuse treatment is often applied, including stimulus control, learning proper adapting reactions, self-monitoring strategies, cognitive rebuilding, addiction-related critical thinking, and withdrawal regulation methods with exposure [ 37 , 39 ]. One systematic review and meta‐analysis suggested that this treatment option is effective for IGD as a short‐term intervention for reducing IGD and symptoms of depression. However, the effectiveness of CBT in reducing the amount of time that is spent on games was unclear. Therefore, there is a need for more studies to determine the long‐term benefits of CBT for IGD [ 40 ].
Programa Individualizado Psicoterapéutico para la Adicción a las Tecnologías de la Información y la Comunicación (PIPATIC) has been used to treat addiction to technology. PIPATIC is an individualized psychotherapy program that is available for people aged 12 to 18 years who have IGD and is designed to integrate several areas of intervention. PIPATIC comprises six modules: psychoeducational, treatment as usual, intra-personal, interpersonal, family intervention, and development of a new lifestyle [ 39 ]. The program uses many psychotherapeutic strategies, one of them is CBT [ 41 ]. It was suggested that the use of many psychotherapeutic strategies is more effective than one (Dong and Potenza 2014; Orzack et al. 2006; Sheketal 2009; Therien et al. 2014). The goals of the program are to reduce the symptoms of video game addiction and to improve the well-being of adolescents, and its initial findings have been encouraging [ 39 ]. The program has a duration of six months and involves 22 to 45-minute sessions each week for video game addicts and their families. The PIPATIC intervention is a person-to-person approach that involves a qualified clinical psychologist [ 41 ], with therapeutic homework to strengthen the establishment that is related to the therapeutic changes required to help change everyday behavior. In the PIPATIC program, the family collaborates to achieve treatment progress, and it is usually them who ask for therapeutic care or psychological treatment [ 42 ]. Although the PIPATIC program appears promising, there are some limitations. First, it was designed to focus on only one specific population, adolescents. Second, it must commit to specific methodological standards for the application and evaluation of the intervention, and it is difficult for addicts to adapt to these particular needs. However, results have suggested that the treatment is effective, as data from 17 video-game addicts that went through the program showed a decrease in time spent playing video games and improvement in many important daily life activities (e.g., family and educational or occupational functioning) [ 41 ].
Pharmacotherapy
The medications trial that has been done were on drugs usually used to treat depression or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Bupropion is one of the medications used for depression. It has been investigated as a treatment for IGD in randomized clinical trials [ 43 , 44 ]. The drug was superior to the control group with no medication [ 43 ]. Also, superior compared to the placebo group in decreasing the symptoms of IGD that were maintained for four weeks after the treatment [ 44 ]. Another antidepressant is escitalopram. Compared to bupropion it was inferior in reducing the symptoms [ 43 ].
Conclusions
Many studies suggest that the changes that occur in video game addicts are similar to those that occur in other addictions, such as substance-related addiction and gambling. The WHO has added video game addiction to the ICD-11, with adolescents being the most susceptible. Video game addiction can lead to many serious consequences for gamers and the people close to them. Although research on video game addiction treatment is ongoing, only a few clinical trials have been conducted on the efficacy of the treatment options, for example, CBT, PIPATIC, and pharmacotherapy.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Personal Excellence Pathway (PEP) committee at Taibah University in Madinah, Saudi Arabia, for giving us the chance to write this review article.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
The association between video gaming and psychological functioning.

- 1 Department of Psychology, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Mainz, Germany
- 2 Department of Psychosomatic Medicine, University Medical Center, Mainz, Germany
Video gaming is an extremely popular leisure-time activity with more than two billion users worldwide ( Newzoo, 2017 ). However, the media as well as professionals have underscored the potential dangers of excessive video gaming. With the present research, we aimed to shed light on the relation between video gaming and gamers’ psychological functioning. Questionnaires on personality and psychological health as well as video gaming habits were administered to 2,734 individuals (2,377 male, 357 female, M age = 23.06, SD age = 5.91). Results revealed a medium-sized negative correlation between problematic video gaming and psychological functioning with regard to psychological symptoms, affectivity, coping, and self-esteem. Moreover, gamers’ reasons for playing and their preferred game genres were differentially related to psychological functioning with the most notable findings for distraction-motivated players as well as action game players. Future studies are needed to examine whether these psychological health risks reflect the causes or consequences of video gaming.
Introduction
Video gaming is a very popular leisure activity among adults ( Pew Research Center, 2018 ). The amount of time spent playing video games has increased steadily, from 5.1 h/week in 2011 to 6.5 h/week in 2017 ( The Nielsen Company, 2017 ). Video gaming is known to have some benefits such as improving focus, multitasking, and working memory, but it may also come with costs when it is used heavily. By spending a predominant part of the day gaming, excessive video gamers are at risk of showing lower educational and career attainment, problems with peers, and lower social skills ( Mihara and Higuchi, 2017 ). On the one hand, video game use is widespread, and it may come with certain precursors as well as consequences. On the other hand, little is known about the relations between various video gaming habits and psychological functioning. This study aims to shed light on these important relations using a large sample.
A video game is defined as “a game which we play thanks to an audiovisual apparatus and which can be based on a story” ( Esposito, 2005 ). In the last few years, the amount of scientific research devoted to video game playing has increased (e.g., Ferguson, 2015 ; Calvert et al., 2017 ; Hamari and Keronen, 2017 ). Most scientific studies in this area of research have focused on the extent of video game play and its diverse correlates. While some researchers have emphasized the benefits of game playing and even suggested a therapeutic use of video games ( Primack et al., 2012 ; Granic et al., 2014 ; Colder Carras et al., 2018 ), others have been intrigued by its potential dangers ( Anderson et al., 2010 ; Müller and Wölfling, 2017 ).
Parents and professionals may be worried about their excessively playing children being “addicted.” However, problematic and potentially addictive video game use goes beyond the extent of playing (in hours per week; Skoric et al., 2009 ). It also includes such issues as craving, loss of control, and negative consequences of excessive gaming. While it is still a matter of debate whether problematic video game play should be considered a behavioral addiction , its status as a mental disorder has been clarified since the release of the DSM-5 in 2013. In the DSM-5, the American Psychiatric Association (2013) defined Internet Gaming Disorder with diagnostic criteria closely related to Gambling Disorder. Generally, this decision has been supported by many researchers (e.g., Petry et al., 2014 ) but has also caused controversies. Researchers have criticized the selection of diagnostic criteria and the vague definition of the Internet Gaming Disorder construct, which excludes offline games from being related to addictive use (e.g., Griffiths et al., 2016 ; Bean et al., 2017 ).
Several studies, literature reviews, and meta-analyses have focused on the correlates of problematic video gaming, usually assessed as a continuum with addiction marking the upper end of the scale (e.g., Ferguson et al., 2011 ; Kuss and Griffiths, 2012 ). The degree of addictive video game use has been found to be related to personality traits such as low self-esteem ( Ko et al., 2005 ) and low self-efficacy ( Jeong and Kim, 2011 ), anxiety, and aggression ( Mehroof and Griffiths, 2010 ), and even to clinical symptoms of depression and anxiety disorders ( Wang et al., 2018 ). Potential consequences of video game use have been identified as well, such as a lack of real-life friends ( Kowert et al., 2014a ), stress and maladaptive coping ( Milani et al., 2018 ), lower psychosocial well-being and loneliness ( Lemmens et al., 2011 ), psychosomatic problems ( Müller et al., 2015 ; Milani et al., 2018 ), and decreased academic achievement ( Chiu et al., 2004 ; Gentile, 2009 ). Effect sizes have varied widely across studies ( Ferguson et al., 2011 ). There seem to be sex and age differences with regard to video gaming behavior: potentially problematic video gaming was found to be more likely among males than females (e.g., Greenberg et al., 2010 ; Estévez et al., 2017 ), and among younger gamers ( Rehbein et al., 2016 ).
In addition to looking at problematic video game use and its relation to psychological functioning, it is relevant to also focus on why individuals play video games. Players use video games for very different reasons ( Ryan et al., 2006 ; Yee, 2006 ) such as to distract themselves from daily hassles or because they enjoy the social relationships they have developed in the virtual world. Potentially problematic video gaming has been found to be related to various reasons for playing such as coping and escape ( Hussain and Griffiths, 2009 ; Schneider et al., 2018 ), socialization ( Laconi et al., 2017 ), and personal satisfaction ( Ng and Wiemer-Hastings, 2005 ). Coping ( Laconi et al., 2017 ), social interaction, and competition were among the main reasons for gaming among males but not among females ( Lucas and Sherry, 2004 ). Mixed results emerged concerning age differences ( Greenberg et al., 2010 ), but especially younger gamers seemed to be motivated for video gaming by social interactions ( Hilgard et al., 2013 ). However, so far it remains unclear to what extent people’s various reasons for playing video games are differentially related to their psychological functioning.
Besides investigating the links between potentially problematic video game use and psychological functioning as well as between reasons for playing video games and psychological functioning, it is relevant to also look at which game genres individuals prefer. Correlates of preferences for certain game genres (e.g., simulation, strategy, action, role-playing) are cognitive enhancement ( Dobrowolski et al., 2015 ; Bediou et al., 2018 ), but also the amount of time spent playing ( Lemmens and Hendriks, 2016 ; Rehbein et al., 2016 ) and psychopathological symptoms ( Laconi et al., 2017 ). Males were shown to prefer action and strategy games, whereas females showed a preference for games of skill ( Scharkow et al., 2015 ; Rehbein et al., 2016 ). Younger gamers seemed to prefer action games, older players more so games of skill ( Scharkow et al., 2015 ). However, it is not yet understood to what extent preferences for certain video game genres are differentially related to psychological functioning.
Typically, research has focused merely on violent video games (e.g., Anderson and Bushman, 2001 ; Elson and Ferguson, 2014 ) or one specific game within one specific game genre (frequently World of Warcraft; Graham and Gosling, 2013 ; Visser et al., 2013 ; Herodotou et al., 2014 ), thereby neglecting the variety of possible gaming habits across various game genres.
In the present study, our objective was to examine the relation between video gaming and psychological functioning in a fine-grained manner. For this purpose, we examined psychological functioning by employing various variables such as psychological symptoms, coping strategies, and social support. Likewise, we assessed video gaming in a similarly detailed way, ranging from (a) problematic video game use, (b) the reasons for playing, to (c) the preferred game genres. This strategy prevented us from making potentially invalid generalizations about video gaming in general and allowed us to examine the spectrum of gaming habits and the respective relations between such habits and a diverse set of variables representing psychological functioning.
Playing video games excessively should be appealing to individuals with poor psychological functioning because games allow people to avoid their everyday problems and instead immerse themselves in another environment ( Taquet et al., 2017 ). Moreover, video games offer people a chance to connect with other people socially despite any more or less evident psychological problems they may have ( Kowert et al., 2014b ; Mazurek et al., 2015 ). On the other hand, potentially problematic video game use may also lead to psychological problems because it reduces the amount of time and the number of opportunities gamers have to practice real-life behavior ( Gentile, 2009 ). Thus, we expected to find a negative correlation between problematic video gaming and variables representing psychological functioning such that we expected more potentially problematic video game use to be related to dysfunctional coping strategies ( Wood and Griffith, 2007 ), negative affectivity ( Mathiak et al., 2011 ), and poor school performance ( Mihara and Higuchi, 2017 ). Moreover, we expected to find differential correlates of people’s reasons for playing video games and their psychological functioning: Playing for escape-oriented reasons such as distraction should go along with diverse indices of poor psychological functioning ( Király et al., 2015 ), whereas playing for gain-oriented reasons such as the storyline or the social connections in the game should be related to adequate psychological functioning ( Longman et al., 2009 ). Also, we expected to find people’s preferred game genres (e.g., strategy, action) to be differentially related to their psychological functioning ( Park et al., 2016 ). Finally, we aimed to shed light on the unique contribution of each measure of psychological functioning to the prediction of problematic video game use.
Materials and Methods
Participants 1.
A total of N = 2,891 individuals (2,421 male, 470 female) with a mean age of 23.17 years ( SD = 5.99, Range: 13–65) participated in our study. Of these participants, N = 2,734 (95%) confirmed their use of video games and were thus included in further analyses (2,377 male, 357 female, with a mean age of 23.06 years; SD = 5.91, Range: 13–65). The distribution of participants with regard to sex and age mirrors the findings of past research with males and younger individuals being more likely to play video games (e.g., Griffiths et al., 2004 ). Participants’ place of residence was Germany.
Procedure and Instruments 2
We posted links to our online questionnaire on various online forums as well as on popular online game sites. To achieve heterogeneity of the sample, no exclusion criteria other than having access to the Internet and understanding German were specified. As an incentive to participate in the study, four vouchers of 50€ were raffled.
Video Gaming
Potentially problematic video game use.
The AICA-S, the Scale for the Assessment of Internet and Computer game Addiction ( Wölfling et al., 2016 ), was used to assess participants’ gaming behavior with regard to potential problematic use. Based on the DSM criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder (tolerance, craving, loss of control, emotion regulation, withdrawal, and unsuccessful attempts to cut back), this standardized self-report scale consists of 15 items usually with a five-point scale ranging from 1 ( never ) to 5 ( very often ). The final score (Min = 0, Max = 27 points) is computed using weighted scoring (items with an item-total correlation > 0.55 in the norm sample are weighted double; Wölfling et al., 2011 ). The AICA-S score can be used to differentiate between regular (0–6.5 points) and problematic use of video games (7–13 points: abuse; 13.5–27 points: addiction). In our sample, N = 2,265 (83%) were identified as regular gamers, and N = 469 (17%) as problematic gamers. We used the AICA-S as a continuous variable for all further analyses ( M = 3.98, SD = 3.22, Range: 0–24). The instrument has been validated for different age groups in the general population and in clinical samples ( Müller et al., 2014a , 2019 , but note small sample size; Müller et al., 2014b ). Cronbach’s alpha was α = 0.70. As expected, the AICA-S score was correlated with male sex ( r = 0.17 ∗∗∗ ) and age ( r = –0.15 ∗∗∗ ). On average, participants played video games for M = 4.09 hours per weekday ( SD = 4.44, Range: 0–24), and M = 4.21 h per day at the weekend ( SD = 2.99, Range: 0–24).
Reasons for playing
Gamers indicated how often they played video games for certain reasons. They rated each of 10 reasons separately on Likert scales ranging from 1 ( never ) to 4 ( very often ). The most prevalent reasons were relaxation ( M = 2.96, SD = 0.91), amusement ( M = 2.94, SD = 0.85), and because of the storyline ( M = 2.67, SD = 1.10).
Game genres
Gamers were asked how often they usually played various video game subgenres such as first-person shooter, round-based strategy, massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs), life simulations, and others. Ratings were made on Likert scales ranging from 1 ( never ) to 4 ( very often ). Using Apperley’s (2006) classification of game genres, we categorized the subgenres into the main genres action ( M = 2.54, SD = 0.84), strategy ( M = 2.13, SD = 0.80), role-playing ( M = 2.01, SD = 0.73), and simulation ( M = 1.58, SD = 0.44). A cluster for unclassified subgenres ( M = 1.54, SD = 0.39) was added to additionally account for such subgenres as jump’n’runs and games of skill. Descriptive statistics and intercorrelations for all measures (including sex and age) are presented in Supplementary Tables S1–S4 .
Psychological Functioning
Participants provided ratings of their psychological functioning on the following constructs:

General psychopathology
The SCL-K-9 ( Klaghofer and Brähler, 2001 ), a short version of the SCL-90-R ( Derogatis, 1975 ), was administered to assess participants’ subjective impairment regarding psychological symptoms (somatization, obsessive-compulsive, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, paranoid ideation, and psychoticism). The SCL-K-9 score is strongly correlated with the original score of the SCL-90-R ( r = 0.93). The 9 items were answered on 5-point Likert-type scales ranging from 1 ( do not agree at all ) to 5 ( agree completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was satisfactory (α = 0.77).
We assessed 10 coping strategies with the Brief COPE ( Carver, 1997 ; German version by Knoll et al., 2005 ), which is the shorter version of the COPE ( Carver et al., 1989 ): self-distraction, denial, substance use, venting, self-blame, behavioral disengagement, acceptance, active coping, planning, and positive reframing. The two items per subscale were administered on 5-point Likert-type scales ranging from 1 ( never ) to 5 ( very often ). Intercorrelations of the two items per subscale ranged from r = 0.32, p < 0.001 for positive reframing to r = 0.78, p < 0.001 for substance use (with one exception: r = -0.05, p = 0.01 for self-distraction).
We measured general affect as a trait and affect during video gaming as a state using the German version ( Krohne et al., 1996 ) of the Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS; Watson et al., 1988 ). On a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 5 ( completely ), participants rated the intensity of 20 adjectives. Cronbach’s alpha was α = 0.78 for general positive affect, α = 0.83 for general negative affect, α = 0.85 for positive affect while playing, and α = 0.83 for negative affect while playing.
The measure for the assessment of shyness in adults ( Asendorpf, 1997 ) consists of 5 items that were answered on a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 5 ( completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was excellent (α = 0.86).
We administered the German version ( Elbing, 1991 ) of the NYU Loneliness Scale ( Rubenstein and Shaver, 1982 ). The 4 items were answered on 5- to 6-point Likert-type scales. Cronbach’s alpha was satisfactory (α = 0.79).
Preference for solitude
A 10-item measure of preference for solitude ( Nestler et al., 2011 ) was answered on a 6-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 6 ( completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was excellent (α = 0.86).
Life satisfaction
Participants answered a one-item life satisfaction measure on a 4-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 4 ( completely ).
Self-esteem
We administered the German version ( von Collani and Herzberg, 2003 ) of the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES; Rosenberg, 1979 ). The 10 items were answered on a 4-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 4 ( completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was excellent (α = 0.88).
Self-efficacy
We administered a 10-item generalized self-efficacy scale ( Schwarzer and Jerusalem, 1995 ), which was answered on a 4-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 4 ( completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was excellent (α = 0.86).
Social support and friends
We administered the perceived available social support subscale from the Berlin Social Support Scales (BSSS; Schwarzer and Schulz, 2003 ). The 8 items were answered on a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 ( not at all ) to 5 ( completely ). Cronbach’s alpha was excellent (α = 0.94). Participants indicated how many offline friends and offline acquaintances they had ( r = 0.44, p < 0.001) as well as how many online friends and online acquaintances they had ( r = 0.33, p < 0.001). Due to left-skewed distributions, we logarithmized the data before aggregation.
Participants reported their grade point average. German grades are assessed on a scale that ranges from 1 ( excellent ) to 6 ( insufficient ). Thus, higher scores indicate worse grades.
Participants further reported their sex and age. Both were used as control variables in further analyses.
In a first step, we computed zero-order correlations between the video gaming variables and the measures of psychological functioning. In a second step, we computed partial correlations in which we controlled for sex and age because past research has repeatedly shown that sex and age are correlated with both video gaming ( Homer et al., 2012 ; Mihara and Higuchi, 2017 ) and psychological functioning ( Kessler et al., 2007 ; Nolen-Hoeksema, 2012 ). Finally, we explored the unique contribution of each measure of psychological functioning to the prediction of potentially problematic video gaming. Therefore, we computed regressions with potentially problematic video gaming as the dependent variable and sex, age, and the measures of psychological functioning as predictors (entered simultaneously into the regression equation). By employing this procedure, we were able to determine the effect that each variable had over and above the other ones. For instance, we could identify whether general psychopathology was predictive of potentially problematic video game use when the influence of all other variables (e.g., shyness, loneliness, and others) was held constant.
Additionally, we included analyses regarding sex and age differences in the link between video gaming and psychological functioning. Since we collected a self-selected sample where different sexes and age groups were not represented equally, our findings are only preliminary, but may stimulate future research.
Potentially Problematic Video Game Use and Psychological Functioning
First, we examined whether potentially problematic video game use was related to various psychological functioning variables. As can be seen in Table 1 , the results for the zero-order correlations were similar to those for the partial correlations in which we controlled for sex and age. A medium-sized positive relation to the potentially problematic use of video games emerged for the presence of psychological symptoms including depression, anxiety, and hostility. Furthermore, several coping strategies were differentially associated with the potentially problematic use of video games: Self-blame and behavioral disengagement showed the strongest positive relations to potentially problematic video game use, followed by denial, acceptance, substance use, self-distraction, and venting. Planning, active coping, and, to a lesser extent, positive reframing were negatively associated with the potentially problematic use of video games. Moreover, the association with potentially problematic video game use was negative for general positive affect and positive and larger in size for general negative affect. However, potentially problematic video game use was clearly positively associated with the experience of both positive and negative affect while playing. Further, a preference for solitude, shyness, and loneliness were positively correlated with the potentially problematic use of video games. Lower self-esteem, lower life satisfaction, and, to a lesser extent, poorer perceived social support and lower self-efficacy went along with potentially problematic video game use. There was an association between fewer offline friends and acquaintances but more online connections with potentially problematic video gaming. Finally, poorer performance in school (i.e., higher grades) was related to the potentially problematic use of video games. These results suggest that potentially problematic video gaming goes along with poor psychological functioning and vice versa.
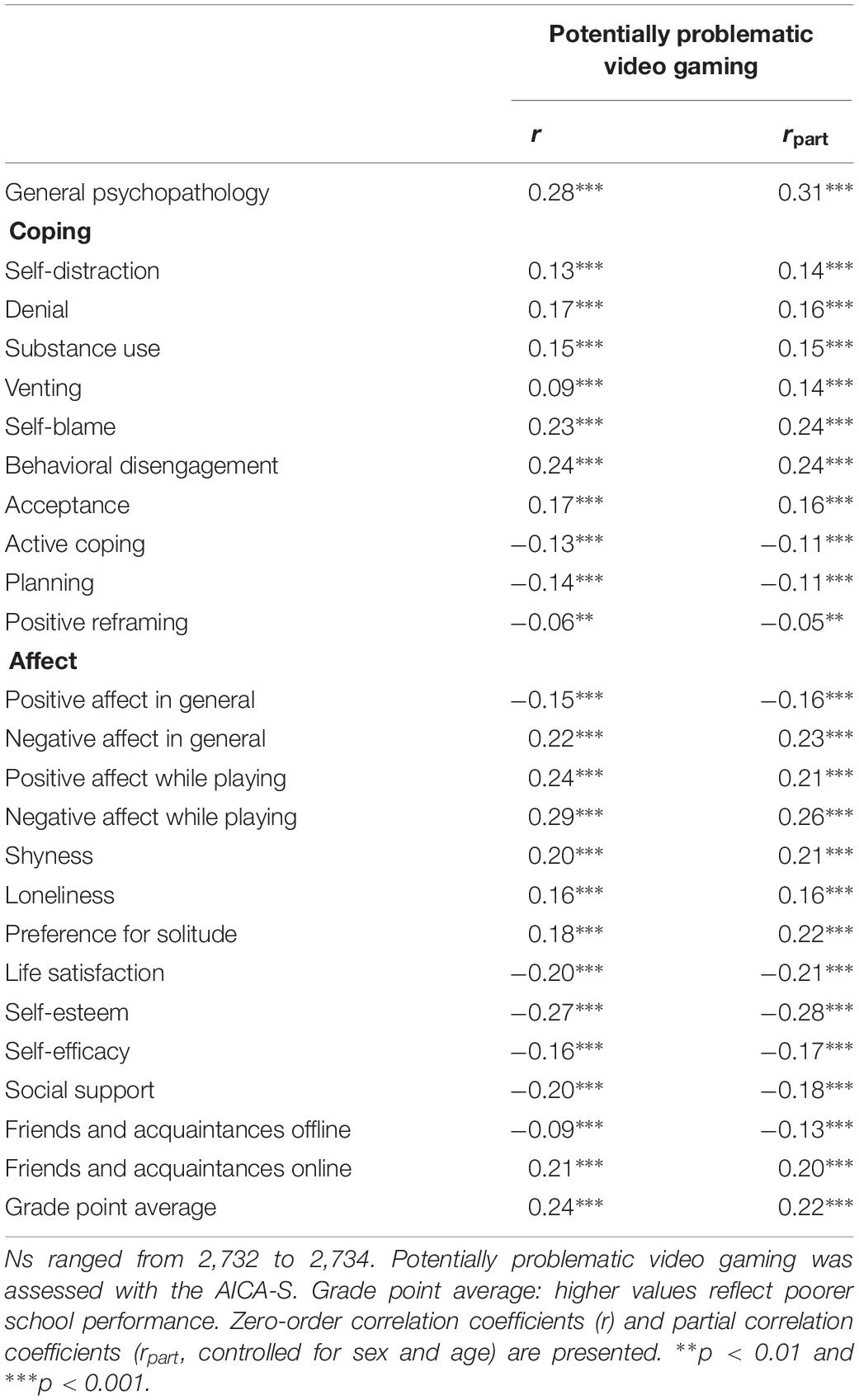
Table 1. Associations between potentially problematic video gaming and psychological functioning.
Reasons for Playing Video Games and Psychological Functioning
Second, we investigated whether players’ reasons for playing video games were differentially related to the psychological functioning variables. Table 2 presents the partial correlations, controlling for sex and age. Using video games to distract oneself from stress was clearly connected to a high level of psychological symptoms. Distraction-motivated gamers preferred coping strategies such as self-blame, behavioral disengagement, self-distraction, denial, substance use, venting, and acceptance, but they neglected active coping and planning. They showed less general positive affect and more negative affect both in general and while playing as well as more positive affect while playing. These gamers further reported low self-esteem and low life satisfaction, loneliness, a preference for solitude, shyness, a lack of self-efficacy and social support, and poor achievement in school. A similar but somewhat less extreme picture was revealed for gamers who played video games in order to have something to talk about . However, these gamers reported more online connections. Gamers who played video games to improve their real-life abilities also reported more online connections. In addition, these gamers showed higher levels of general positive affect. The strongest association with online friends and acquaintances emerged, as expected, for gamers who played because of the social relations in the virtual world. Although all reasons for playing video games were related to positive affect while playing, the strongest associations emerged for gamers who played because of the social relations , to stimulate their imagination , and for curiosity . It is interesting that, for gamers who played video games because of the storyline and for relaxation , there was a relation only to positive but not to negative affect while playing. Reasons for playing were only weakly related to sex and age (see Supplementary Table S2 ). In sum, several reasons for playing video games were differentially associated with psychological functioning.
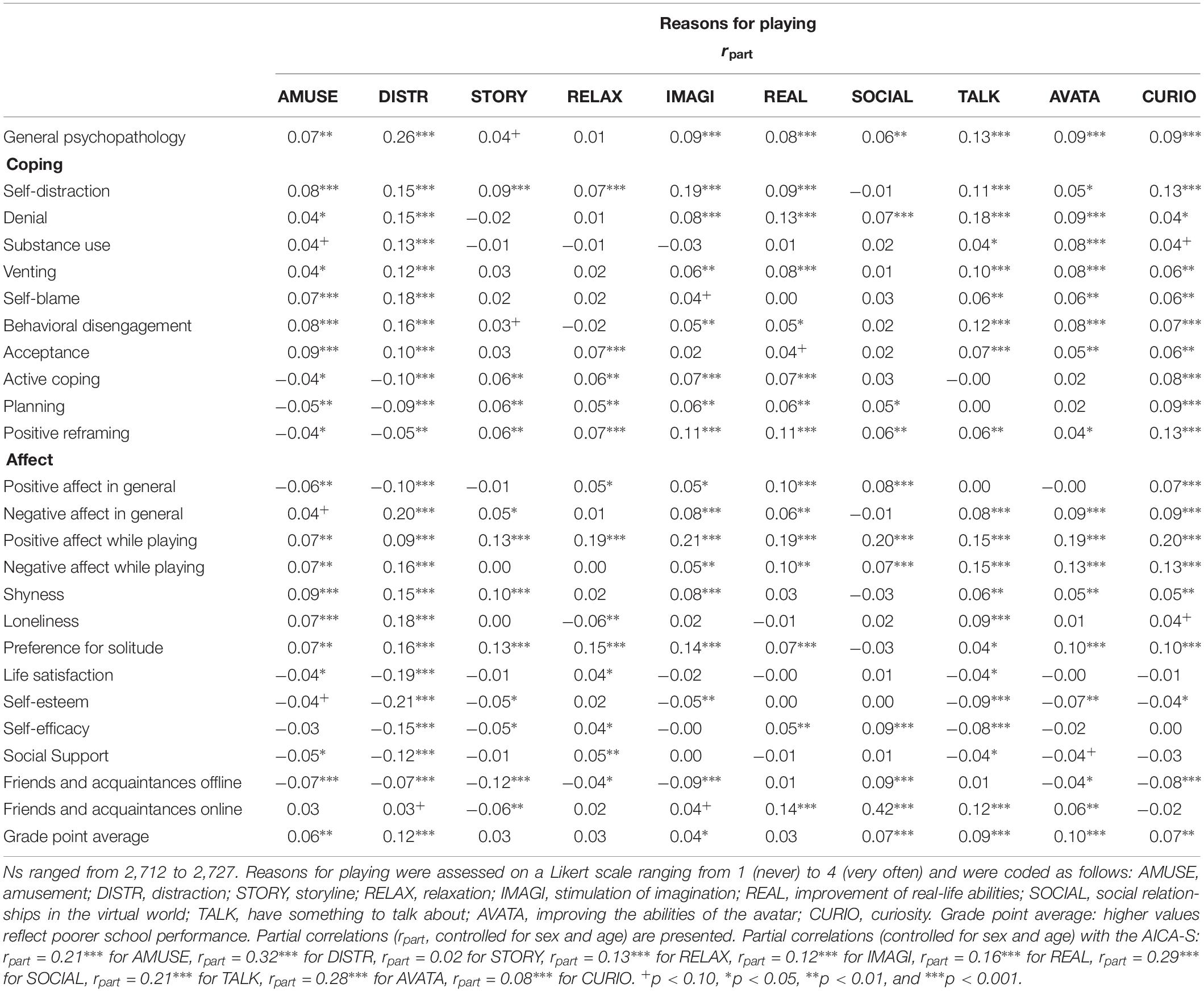
Table 2. Associations between reasons for playing video games and psychological functioning.
Video Game Genre and Psychological Functioning
Third, we examined whether players’ preferences for different video game genres were differentially associated with the measures of psychological functioning. Table 3 shows the partial correlations in which we controlled for sex and age. There was a weak connection between general psychological symptoms and all of the video game genres we investigated except strategy. A preference for action games had the strongest association with affect while playing. Thus, action games seem to be both rewarding and a source of frustration. A preference for action games went along with poorer school performance. Gamers who preferred role-playing games scored higher on shyness and a preference for solitude and lower on self-esteem; they also reported fewer offline connections. By contrast, preferences for games of the unclassified category on average went along with a larger number of offline friends and more positive affect, both while playing and in general. Two game genres (i.e., role-playing and unclassified games) were related to the coping strategy of self-distraction. Because preferred game genre was related to participants’ sex (see Supplementary Table S3 ), we had a more detailed look at the correlations between preferred game genre and psychological functioning separately for both sexes: For males ( n = 2,377), the strongest correlation between general psychopathology and game genre emerged for action ( r = 0.08, p < 0.001), followed by role playing ( r = 0.07, p < 0.01), and unclassified ( r = 0.07, p < 0.01). For females ( n = 357), the strongest relation between general psychopathology and game genre emerged for simulation ( r = 0.17, p < 0.01). Differences were also found regarding the strength of the relation between number of friends online and the genre action: r = 0.06, p < 0.01 for males, and r = 0.27, p < 0.001 for females. Similarly, preferred game genre was related to participants’ age (see Supplementary Table S3 ). However, there were merely differences with regard to the relation of psychological functioning and game genre, when analyzed separately for different age groups (<19 years, n = 557; 19–30 years, n = 1916; >31 years, n = 261). In sum, our results speak to the idea that individuals with different levels of psychological functioning differ in their choices of game genres and vice versa.
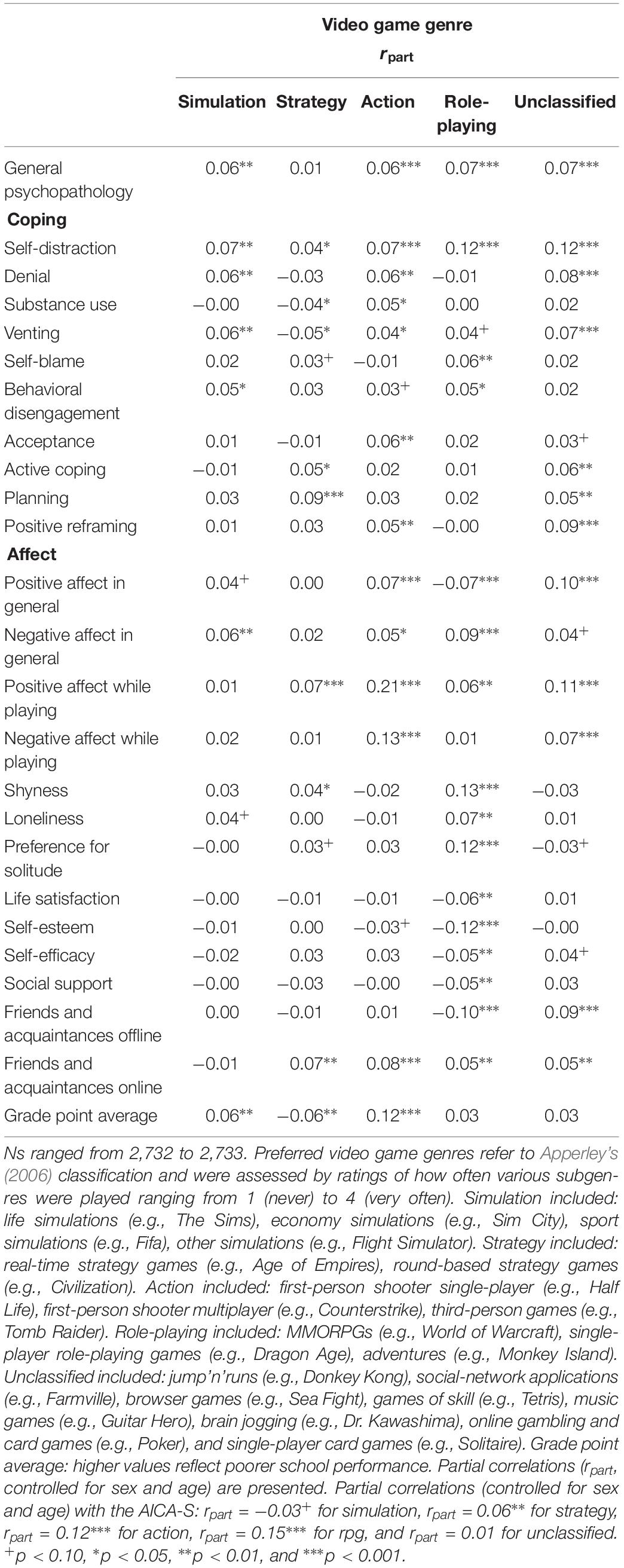
Table 3. Associations between preferred video game genre and psychological functioning.
Predicting Potentially Problematic Video Game Use by Psychological Functioning Variables
In a final step, we entered all of the investigated psychological functioning variables as well as sex and age as predictors of the potentially problematic use of video games. By employing this procedure, we were able to determine the unique contribution of each psychological functioning variable when the influence of all other variables was held constant. As Table 4 shows, the number of online friends and acquaintances as well as positive affect while playing were most predictive of potentially problematic video game use over and above all other variables. General psychopathology, a lack of offline connections, and poor school performance were weaker but still relevant predictors of potentially problematic video game use.
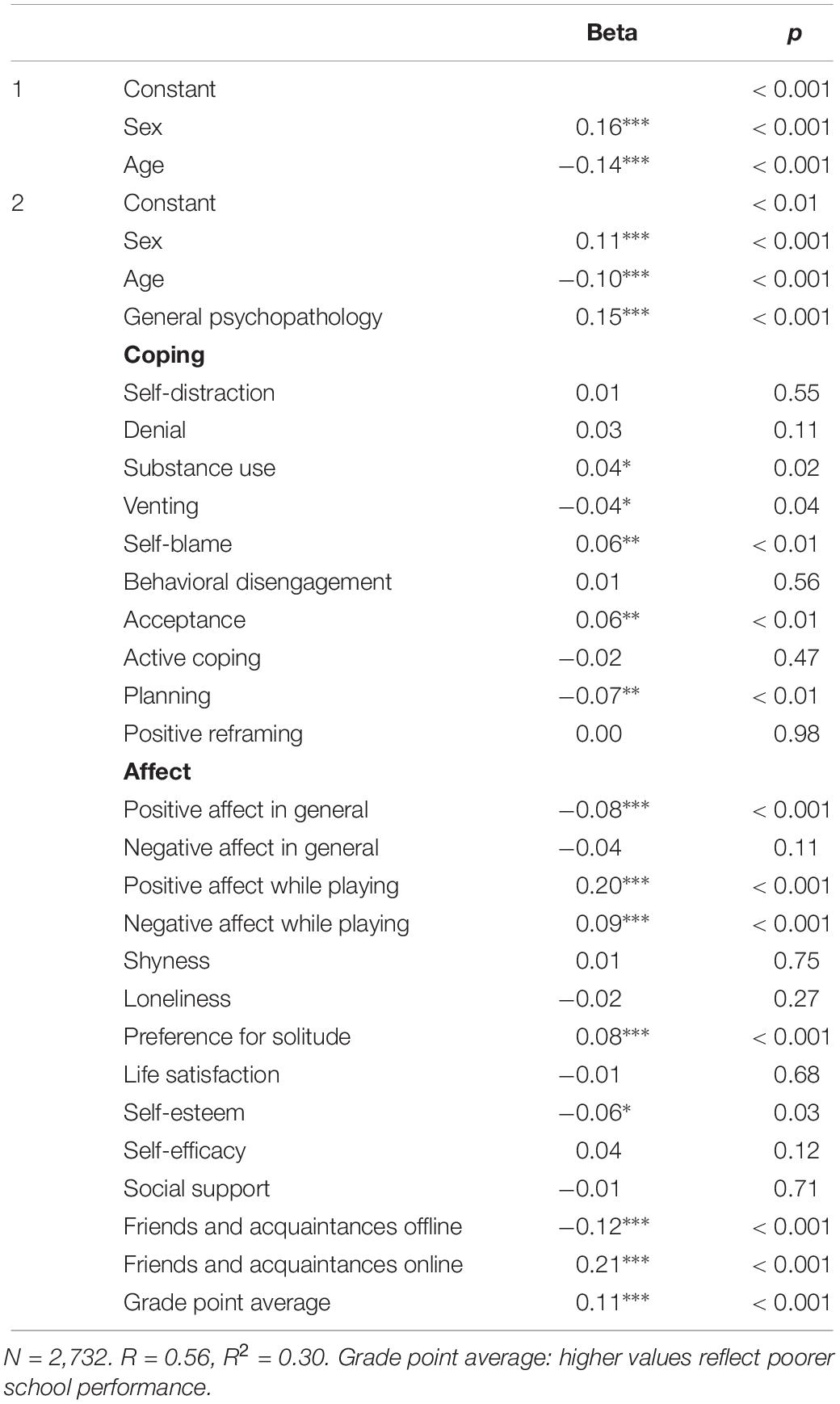
Table 4. Prediction of potentially problematic video game use by psychological functioning variables.
With this study, we aimed to shed light on the association of diverse video gaming habits with gamers’ psychological functioning. Drawing on a large sample, our results revealed a medium-sized relation between potentially problematic video game use and poor psychological functioning with regard to general psychological symptoms, maladaptive coping strategies, negative affectivity, low self-esteem, and a preference for solitude as well as poor school performance. These findings are in line with those of prior work (e.g., Kuss and Griffiths, 2012 ; Milani et al., 2018 ). Also, reasons for playing video games were differentially related to psychological functioning with the most pronounced findings for escape-oriented in contrast to gain-oriented motives. Specifically, distraction-motivated gaming went along with higher symptom ratings, lower self-esteem, and more negative affectivity, whereas playing to establish social relationships in the virtual world was related to a larger number of online connections and more positive affect while playing. Furthermore, there were only weak relations between the preferred game genres and psychological functioning. The action games genre was associated with the strongest ratings of affect while playing. These results on reasons and genres may help to explain conflicting findings of former studies, because in our work we examined various reasons for playing, several game genres, and various aspects of psychological functioning simultaneously. Finally, positive affect while playing and a larger number of online friends were the strongest unique predictors of potentially problematic video game use, followed by psychological symptoms, a lack of offline connections, and poor school performance. These findings suggest that, on the one hand, independent of one’s psychological conditions, enjoying oneself during gaming (i.e., experiencing positive affect, connecting with online friends) may go along with potentially problematic use of video games. On the other hand, poor psychological functioning seems to be a unique risk factor for potentially problematic video gaming.
The presented results are generally in line with previous work that has identified a connection between video gaming and psychological health, academic problems, and social problems ( Ferguson et al., 2011 ; Müller et al., 2015 ). However, our study moved beyond prior research by providing in-depth analyses of both video gaming habits (including potentially problematic use, reasons for playing, and preferred game genre) and psychological functioning (including psychological symptoms, coping styles, affectivity, as well as variables that are related to individuals and their social environments). In addition, we identified unique predictors of potentially problematic video game use.
How can the findings on differential relations between video gaming and various indices of psychological functioning – ranging from beneficial results ( Latham et al., 2013 ) to unfavorable results ( Barlett et al., 2009 ; Möller and Krahé, 2009 ; Anderson et al., 2010 ) – be integrated? According to Kanfer and Phillips (1970) , problematic behavior (e.g., excessive video gaming) can be understood as a function of the situation (e.g., being rejected by a peer); the organism (e.g., low self-esteem); the person’s thoughts, physical reactions, and feelings (e.g., sadness, anger); and finally, the short- as well as long-term consequences of the behavior (termed SORKC model). In the short run, according to our results, playing video games may be a way to distract oneself from everyday hassles and may lead to positive affect while playing and a feeling of being connected to like-minded people, all of which are factors that have an immediate reinforcing value. In the long run, however, spending many hours per day in front of a computer screen may prevent a person from (a) developing and practicing functional coping strategies, (b) finding friends and support in the social environment, and (c) showing proper school achievement, factors that are potentially harmful to the person. Thus, differentiating between short- and long-term perspectives may help us understanding the differential correlates of intensive video gaming.
When is it appropriate to speak of video game addiction? More and more researchers have suggested a continuum between engagement ( Charlton and Danforth, 2007 ; Skoric et al., 2009 ) and pathological gaming/addiction, instead of a categorical perspective. In part, this recommendation has also been followed in the DSM-5 ( American Psychiatric Association, 2013 ) where Internet Gaming Disorder is classified with different degrees of severity, ranging from mild to moderate to severe, according to the functional impairment associated with it. The AICA-S also allows for a differential perspective on gaming behavior by providing ways to assess both the time spent playing video games and the main DSM criteria that indicate Internet Gaming Disorder. However, in our study we did not aim at making a diagnosis, but at having a closer look at potentially problematic gaming behavior and its correlates in a non-clinical sample.
In sum, it seems relevant to assess not only the extent of video game use but also the reasons behind this behavior (e.g., distraction) and the concrete rewards that come from playing (e.g., the experience of strong affect while playing action games) to fully understand the relation between video gaming and psychological functioning.
Limitations and Future Directions
With the present study, we aimed to uncover the association between video gaming and psychological functioning. Our approach was cross-sectional and warrants interpretative caution because correlations cannot determine the direction of causation. It remains unclear whether potentially problematic gaming is a factor that contributes to the development of psychological dysfunction or whether psychological dysfunction contributes to potentially problematic gaming. Also, a third factor (e.g., preexisting mental difficulties) may produce both psychological dysfunction and potentially problematic gaming. Thus, longitudinal studies that are designed to identify the causal pathway may provide a promising avenue for future research. Future studies may also answer the question whether the link between video gaming and psychological functioning is moderated by sex, age, the reasons for playing, or the preferred game genre. In addition, it is important not to forget that the present results are based on a self-selected sample in which potentially problematic video gamers were overrepresented (e.g., Festl et al., 2013 , for a representative sample). Thus, future research should replicate our findings in a representative sample. Further, we relied on self-reported data, which is a plausible method for assessing inner affairs such as people’s reasons for their behaviors, but it would be helpful to back up our findings with evidence derived from sources such as peers, caregivers, and health specialists. Our work reflects only a first approach to the topic, and future work may additionally collect in-game behavioral data from the players ( McCreery et al., 2012 ; Billieux et al., 2013 ) to objectively and more specifically investigate diverse patterns of use. Furthermore, one must not forget that the used taxonomy to classify video game genres is only one of various possible options and one should “think of each individual game as belonging to several genres at once” ( Apperley, 2006 , p. 19). Finally, some of the effects reported in our paper were rather modest in size. This is not surprising considering the complexity and multiple determinants of human behavior. In our analyses, we thoroughly controlled for the influence of sex and age and still found evidence that video gaming was differentially related to measures of psychological functioning.
The current study adds to the knowledge on gaming by uncovering the specific relations between video gaming and distinct measures of psychological functioning. Potentially problematic video gaming was found to be associated with positive affect and social relationships while playing but also with psychological symptoms, maladaptive coping strategies, negative affectivity, low self-esteem, a preference for solitude, and poor school performance. Including gamers’ reasons for playing video games and their preferred game genres helped deepen the understanding of the specific and differential associations between video gaming and psychological health. This knowledge might help developing adequate interventions that are applied prior to the occurrence of psychological impairments that may go along with potentially problematic video gaming.
Ethics Statement
In our online survey, participants were given information on voluntary participation, risks, confidentiality/anonymity, and right to withdraw. Whilst participants were not signing a separate consent form, consent was obtained by virtue of completion. We implemented agreed procedures to maintain the confidentiality of participant data.
Author Contributions
BB, BE, JH, and KM conceived and designed the study. BB, JH, and KM collected and prepared the data. JH analyzed the data. BE and JH wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01731/full#supplementary-material
- ^ The data were gathered as part of a larger project ( Stopfer et al., 2015 ; Braun et al., 2016 ). However, the analyses in the present article do not overlap with analyses from previous work.
- ^ Other measures were administered, but they were not relevant to the present research questions and are thus not mentioned in this paper. The data set and analysis script supporting the conclusions of this manuscript can be retrieved from https://osf.io/emrpw/?view_only=856491775efe4f99b407e258c2f2fa8d .
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5 , 5th Edn. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Google Scholar
Anderson, C. A., and Bushman, B. J. (2001). Effects of violent video games on aggressive behavior, aggressive cognition, aggressive affect, physiological arousal, and prosocial behavior: a meta-analytic review of the scientific literature. Psychol. Sci. 12, 353–359. doi: 10.1111/1467-9280.00366
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anderson, C. A., Shibuya, A., Ihori, N., Swing, E. L., Bushman, B. J., Sakamoto, A., et al. (2010). Violent video game effects on aggression, empathy, and prosocial behavior in eastern and western countries: a meta-analytic review. Psychol. Bull. 136, 151–173. doi: 10.1037/a0018251
Apperley, T. H. (2006). Genre and game studies: toward a critical approach to video game genres. Simul. Gaming 37, 6–23. doi: 10.1177/1046878105282278
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Asendorpf, J. B. (1997). SGSE-Schüchternheits- und Geselligkeitsskalen für Erwachsene [Scales on shyness and sociality for adults ]. Berlin: Humboldt-Universität.
Barlett, C. P., Anderson, C. A., and Swing, E. L. (2009). Video game effects—Confirmed, suspected, and speculative: a review of the evidence. Simul. Gaming 40, 377–403. doi: 10.1177/1046878108327539
Bean, A. M., Nielsen, R. K. L., van Rooij, A. J., and Ferguson, C. J. (2017). Video game addiction: the push to pathologize video games. Prof. Psychol. Res. Pr. 48, 378–389. doi: 10.1037/pro0000150
Bediou, B., Adams, D. M., Mayer, R. E., Tipton, E., Green, C. S., and Bavelier, D. (2018). Meta-analysis of action video game impact on perceptual, attentional, and cognitive skills. Psychol. Bull. 144, 77–110. doi: 10.1037/bul0000130
Billieux, J., Van der Linden, M., Achab, S., Khazaal, Y., Paraskevopoulos, L., Zullino, D., et al. (2013). Why do you play World of Warcraft? An in-depth exploration of self-reported motivations to play online and in-game behaviours in the virtual world of Azeroth. Comput. Hum. Behav. 29, 103–109. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2012.07.021
Braun, B., Stopfer, J. M., Müller, K. W., Beutel, M. E., and Egloff, B. (2016). Personality and video gaming: comparing regular gamers, non-gamers, and gaming addicts and differentiating between game genres. Comput. Hum. Behav. 55, 406–412. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.041
Calvert, S. L., Appelbaum, M., Dodge, K. A., Graham, S., Nagayama Hall, G. C., Hamby, S., et al. (2017). The american psychological association task force assessment of violent video games: science in the service of public interest. Am. Psychol. 72, 126–143. doi: 10.1037/a0040413
Carver, C. S. (1997). You want to measure coping but your protocol’s too long: consider the brief cope. Int. J. Behav. Med. 4, 92–100. doi: 10.1207/s15327558ijbm0401_6
Carver, C. S., Scheier, M. F., and Weintraub, J. K. (1989). Assessing coping strategies: a theoretically based approach. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 56, 267–283. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.56.2.267
Charlton, J. P., and Danforth, I. D. (2007). Distinguishing addiction and high engagement in the context of online game playing. Comput. Hum. Behav. 23, 1531–1548. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2005.07.002
Chiu, S. I., Lee, J. Z., and Huang, D. H. (2004). Video game addiction in children and teenagers in Taiwan. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 7, 571–581. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2004.7.571
Colder Carras, M., Van Rooij, A. J., Spruijit-Metz, D., Kvedar, J., Griffiths, M. D., Carabas, Y., et al. (2018). Commercial video games as therapy: a new research agenda to unlock the potential of a global pastime. Front. Psychiatry 8:300. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00300
Derogatis, L. R. (1975). SCL-90-R: Symptom Checklist-90-R: Administration, Scoring, and Procedures Manual. London: NCS Pearson.
Dobrowolski, P., Hanusz, K., Sobczyk, B., Skorko, M., and Wiatrow, A. (2015). Cognitive enhancement in video game players: the role of video game genre. Comput. Hum. Behav. 44, 59–63. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.051
Elbing, E. (1991). Einsamkeit: Psychologische Konzepte, Forschungsbefunde und Treatmentansätze [Loneliness: Psychological Concepts, Research Findings, and Treatments]. Göttingen: Hogrefe.
Elson, M., and Ferguson, C. J. (2014). Twenty-five years of research on violence in digital games and aggression: empirical evidence, perspectives, and a debate gone astray. Eur. Psychol. 19, 33–46. doi: 10.1027/1016-9040/a000147
Esposito, N. (2005). “A short and simple definition of what a videogame is,” in Proceedings of the DiGRA (Digital Games Research Association) Conference: Changing Views-Worlds in Play , (British Columbia: University of Vancouver).
Estévez, A., Jáuregui, P., Sánchez-Marcos, I., López-González, H., and Griffiths, M. D. (2017). Attachment and emotion regulation in substance addictions and behavioral addictions. J. Behav. Addict. 6, 534–544. doi: 10.1556/2006.6.2017.086
Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do angry birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10, 646–666. doi: 10.1177/1745691615592234
Ferguson, C. J., Coulson, M., and Barnett, J. (2011). A meta-analysis of pathological gaming prevalence and comorbidity with mental health, academic and social problems. J. Psychiatr. Res. 45, 1573–1578. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.09.005
Festl, R., Scharkow, M., and Quandt, T. (2013). Problematic computer game use among adolescents, younger and older adults. Addiction 108, 592–599. doi: 10.1111/add.12016
Gentile, D. (2009). Pathological video-game use among youth ages 8 to 18: a national study. Psychol. Sci. 20, 594–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2009.02340.x
Graham, L. T., and Gosling, S. D. (2013). Personality profiles associated with different motivations for playing World of Warcraft. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 16, 189–193. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2012.0090
Granic, I., Lobel, A., and Engels, R. C. (2014). The benefits of playing video games. Am. Psychol. 69, 66–78. doi: 10.1037/a0034857
Greenberg, B. S., Sherry, J., Lachlan, K., Lucas, K., and Holmstrom, A. (2010). Orientations to video games among gender and age groups. Simul. Gaming 41, 238–259. doi: 10.1177/1046878108319930
Griffiths, M., Van Rooij, A. J., Kardefeldt-Winther, D., Starcevic, V., Király, O., Pallesen, S., et al. (2016). Working towards an international consensus on criteria for assessing internet gaming disorder: a critical commentary on Petry et al. (2014). Addiction 111, 167–175. doi: 10.1111/add.13057
Griffiths, M. D., Davies, M. N., and Chappell, D. (2004). Demographic factors and playing variables in online computer gaming. CyberPsychol. Behav. 7, 479–487. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2004.7.479
Hamari, J., and Keronen, L. (2017). Why do people play games? A meta-analysis. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 37, 125–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2017.01.006
Herodotou, C., Kambouri, M., and Winters, N. (2014). Dispelling the myth of the socio-emotionally dissatisfied gamer. Comput. Hum. Behav. 32, 23–31. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.10.054
Hilgard, J., Engelhardt, C. R., and Bartholow, B. D. (2013). Individual differences in motives, preferences, and pathology in video games: the gaming attitudes, motives, and experiences scales (GAMES). Front. Psychol. 4:608. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00608
Homer, B. D., Hayward, E. O., Frye, J., and Plass, J. L. (2012). Gender and player characteristics in video game play of preadolescents. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28, 1782–1789. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2012.04.018
Hussain, Z., and Griffiths, M. D. (2009). Excessive use of massively multi-player online role-playing games: a pilot study. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 7:563. doi: 10.1007/s11469-009-9202-8
Jeong, E. J., and Kim, D. H. (2011). Social activities, self-efficacy, game attitudes, and game addiction. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 14, 213–221. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2009.0289
Kanfer, F. H., and Phillips, J. (1970). Learning Foundations of Behavior Therapy. New York, NY: Wiley.
Kessler, R. C., Amminger, G. P., Aguilar-Gaxiola, S., Alonso, J., Lee, S., and Ustun, T. B. (2007). Age of onset of mental disorders: a review of recent literature. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 20, 359–364. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0b013e32816ebc8c
Király, O., Urbán, R., Griffith, M. D., Ágoston, C., Nagygyörgy, K., Kökönyei, G., et al. (2015). The mediating effect of gaming motivation between psychiatric symptoms and problematic online gaming: an online survey. J. Med. Int. Res. 17:e88. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3515
Klaghofer, R., and Brähler, E. (2001). Konstruktion und teststatistische Prüfung einer Kurzform der SCL-90-R [Construction and statistical evaluation of a short version of the SCL-90-R]. Z. Klin. Psychol. Psychiatr. Psychother. 49, 115–124.
Knoll, N., Rieckmann, N., and Schwarzer, R. (2005). Coping as a mediator between personality and stress outcomes: a longitudinal study with cataract surgery patients. Eur. J. Personal. 19, 229–247. doi: 10.1002/per.546
Ko, C. H., Yen, J. Y., Chen, C. C., Chen, S. H., and Yen, C. F. (2005). Gender differences and related factors affecting online gaming addiction among Taiwanese adolescents. J. Nervous Mental Dis. 193, 273–277. doi: 10.1097/01.nmd.0000158373.85150.57
Kowert, R., Domahidi, E., Festl, R., and Quandt, T. (2014a). Social gaming, lonely life? The impact of digital game play on adolescents’ social circles. Comput. Hum. Behav. 36, 385–390. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.04.003
Kowert, R., Domahidi, E., and Quandt, T. (2014b). The relationship between online video game involvement and gaming-related friendships among emotionally sensitive individuals. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 17, 447–453. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2013.0656
Krohne, H. W., Egloff, B., Kohlmann, C. W., and Tausch, A. (1996). Untersuchungen mit einer deutschen version der positive and negative affect schedule (PANAS) [Investigations with a German version of the PANAS]. Diagnostica 42, 139–156.
Kuss, D. J., and Griffiths, M. D. (2012). Internet gaming addiction: a systematic review of empirical research. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 10, 278–296. doi: 10.1007/s11469-011-9318-5
Laconi, S., Pirès, S., and Chabrol, H. (2017). Internet gaming disorder, motives, game genres, and psychopathology. Comput. Hum. Behav. 75, 652–659. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.012
Latham, A. J., Patston, L. L., and Tippett, L. J. (2013). The virtual brain: 30 years of video-game play and cognitive abilities. Front. Psychol. 4:629. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00629
Lemmens, J. S., and Hendriks, S. J. F. (2016). Addictive online games: examining the relationship between game genres and internet gaming disorder. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 19, 270–276. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2015.0415
Lemmens, J. S., Valkenburg, P. M., and Peter, J. (2011). Psychosocial causes and consequences of pathological gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 27, 144–152. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2010.07.015
Longman, H., O’Connor, E., and Obst, P. (2009). The effect of social support derived from World of Warcraft on negative psychological symptoms. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 12, 563–566. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2009.0001
Lucas, K., and Sherry, J. L. (2004). Sex differences in video game play: a communication-based explanation. Commun. Res. 31, 499–523. doi: 10.1177/0093650204267930
Mathiak, K. A., Klasen, M., Weber, R., Ackermann, H., Shergill, S. S., and Mathiak, K. (2011). Reward system and temporal pole contributions to affective evaluation during a first person shooter video game. BMC Neurosci. 12:66. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-66
Mazurek, M. O., Engelhardt, C. R., and Clark, K. E. (2015). Video games from the perspective of adults with autism spectrum disorder. Comput. Hum. Behav. 51, 122–130. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.04.062
McCreery, M. P., Krach, S. K., Schrader, P. G., and Boone, R. (2012). Defining the virtual self: personality, behavior, and the psychology of embodiment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 28, 976–983. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2011.12.019
Mehroof, M., and Griffiths, M. D. (2010). Online gaming addiction: the role of sensation seeking, self-control, neuroticism, aggression, state anxiety, and trait anxiety. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 13, 313–316. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2009.0229
Mihara, S., and Higuchi, S. (2017). Cross-sectional and longitudinal epidemiological studies of Internet gaming disorder: a systematic review of the literature. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 71, 425–444. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12532
Milani, L., La Torre, G., Fiore, M., Grumi, S., Gentile, D. A., Ferrante, M., et al. (2018). Internet gaming addiction in adolescence: risk factors and maladjustment correlates. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 16, 888–904. doi: 10.1007/s11469-017-9750-2
Möller, I., and Krahé, B. (2009). Exposure to violent video games and aggression in German adolescents: a longitudinal analysis. Aggress. Behav. 35, 75–89. doi: 10.1002/ab.20290
Müller, K. W., Beutel, M. E., Dreier, M., and Wölfling, K. (2019). A clinical evaluation of the DSM-5 criteria for internet gaming disorder and a pilot study on their applicability to further Internet-related disorders. J. Behav. Addict. 8, 16–24. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.140
Müller, K. W., Beutel, M. E., and Wölfling, K. (2014a). A contribution to the clinical characterization of internet addiction in a sample of treatment seekers: validity of assessment, severity of psychopathology and type of co-morbidity. Compr. Psychiatry 55, 770–777. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2014.01.010
Müller, K. W., Glaesmer, H., Brähler, E., Wölfling, K., and Beutel, M. E. (2014b). Prevalence of internet addiction in the general population: results from a German population-based survey. Behav. Inform. Technol. 33, 757–766. doi: 10.1080/0144929X.2013.810778
Müller, K. W., Janikian, M., Dreier, M., Wölfling, K., Beutel, M. E., Tzavara, C., et al. (2015). Regular gaming behavior and internet gaming disorder in European adolescents: results from a cross-national representative survey of prevalence, predictors and psychopathological correlates. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 24, 565–574. doi: 10.1007/s00787-014-0611-2
Müller, K. W., and Wölfling, K. (2017). Both sides of the story: addiction is not a pastime activity: commentary on: scholars’ open debate paper on the World Health Organization ICD-11 Gaming Disorder proposal (Aarseth et al.). J. Behav. Addict. 6, 118–120. doi: 10.1556/2006.6.2017.038
Nestler, S., Back, M. D., and Egloff, B. (2011). Psychometrische Eigenschaften zweier Skalen zur Erfassung interindividueller Unterschiede in der Präferenz zum Alleinsein [Psychometric properties of two scales for the assessment of interindividual differences in preference for solitude]. Diagnostica 57, 57–67. doi: 10.1026/0012-1924/a000032
Newzoo (2017). 2017 Global Games Market Report: Trends, Insights, and Projections Toward 2020. Available at: http://progamedev.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/06/Newzoo_Global_Games_Market_Report_2017_Light.pdf (accessed February 16, 2018).
Ng, B. D., and Wiemer-Hastings, P. (2005). Addiction to the internet and online gaming. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 8, 110–113. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2005.8.110
Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2012). Emotion regulation and psychopathology: the role of gender. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 8, 161–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143109
Park, J. H., Han, D. H., Kim, B. N., Cheong, J. H., and Lee, Y. S. (2016). Correlations among social anxiety, self-esteem, impulsivity, and game genre in patients with problematic online game playing. Psychiatry Investig. 13, 297–304. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.3.297
Petry, N. M., Rehbein, F., Gentile, D. A., Lemmens, J. S., Rumpf, H. J., Mossle, T., et al. (2014). An international consensus for assessing internet gaming disorder using the new DSM-5 approach. Addiction 109, 1399–1406. doi: 10.1111/add.12457
Pew Research Center (2018). 5 Facts About Americans and Video Games. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center.
Primack, B. A., Carroll, M. V., McNamara, M., Klem, M. L., King, B., Rich, M. O., et al. (2012). Role of video games in improving health-related outcomes: a systematic review. Am. J. Prevent. Med. 42, 630–638. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2012.02.023
Rehbein, F., Staudt, A., Hanslmaier, M., and Kliem, S. (2016). Video game playing in the general adult population of Germany: can higher gaming time of males be explained by gender specific genre preferences? Comput. Hum. Behav. 55, 729–735. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.10.016
Rosenberg, M. (1979). Conceiving the Self. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Rubenstein, C., and Shaver, P. R. (1982). “The experience of loneliness,” in Loneliness: A Sourcebook of Current Theory, Research, and Therapy , eds L. A. Peplau and D. Perlman (New York, NY: Wiley-Interscience), 206–223.
Ryan, R. M., Rigby, C. S., and Przybylski, A. (2006). The motivational pull of video games: a self-determination theory approach. Motiv. Emot. 30, 344–360. doi: 10.1007/s11031-006-9051-8
Scharkow, M., Festl, R., Vogelgesang, J., and Quandt, T. (2015). Beyond the “core-gamer”: genre preferences and gratifications in computer games. Comput. Hum. Behav. 44, 293–298. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.11.020
Schneider, L. A., King, D. L., and Delfabbro, P. H. (2018). Maladaptive coping styles in adolescents with Internet gaming disorder symptoms. Int. J. Mental Health Addict. 16, 905–916. doi: 10.1007/s11469-017-9756-9
Schwarzer, R., and Jerusalem, M. (1995). “Generalized self-efficacy scale,” in Measures in Health Psychology: A User’s Portfolio. Causal and Control Beliefs , eds J. Weinman, S. Wright, and M. Johnston (Windsor: NFER-NELSON), 35–37.
Schwarzer, R., and Schulz, U. (2003). Soziale Unterstützung bei der Krankheitsbewältigung: die Berliner Social Support Skalen (BSSS) [Social support in coping with illness: the Berlin social support scales]. Diagnostica 49, 73–82. doi: 10.1026//0012-1924.49.2.73
Skoric, M. M., Teo, L. L. C., and Neo, R. L. (2009). Children and video games: addiction, engagement, and scholastic achievement. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 12, 567–572. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2009.0079
Stopfer, J. M., Braun, B., Müller, K. W., and Egloff, B. (2015). Narcissus plays video games. Personal. Individ. Differ. 87, 212–218. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2015.08.011
Taquet, P., Romo, L., Cottencin, O., Ortiz, D., and Hautekeete, M. (2017). Video game addiction: cognitive, emotional, and behavioral determinants for CBT treatment. J. Thér. Comportementale Cogn. 27, 118–128. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcc.2017.06.005
The Nielsen Company (2017). Games 360 U.S. Report. New York, NY: The Nielsen Company.
Visser, M., Antheunis, M. L., and Schouten, A. P. (2013). Online communication and social well-being: how playing World of Warcraft affects players’ social competence and loneliness. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 43, 1508–1517. doi: 10.1111/jasp.12144
von Collani, G., and Herzberg, P. Y. (2003). Eine revidierte Fassung der deutschsprachigen Skala zum Selbstwertgefühl von Rosenberg [A revised German version of Rosenberg‘s self-esteem scale]. Z. Differ. Diagn. Psychol. 24, 3–7. doi: 10.1026/0012-1924/a000032
Wang, H. R., Cho, H., and Kim, D.-J. (2018). Prevalence and correlates of comorbid depression in a nonclinical online sample with DSM-5 internet gaming disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 226, 1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.005
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., and Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 54, 1063–1070. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.54.6.1063
Wölfling, K., Beutel, M. E., and Müller, K. W. (2016). “OSV-S – skala zum onlinesuchtverhalten [AICA-S – Scale for the assessment of internet and computer game addiction],” in Diagnostische Verfahren in der Psychotherapie [Diagnostic Measures in Psychotherapy] , eds K. Geue, B. Strauß, and E. Brähler (Göttingen: Hogrefe), 362–366.
Wölfling, K., Müller, K. W., and Beutel, M. (2011). Reliabilität und Validität der Skala zum Computerspielverhalten [Reliability and validity of the scale for the assessment of pathological computer-gaming]. Psychother. Psychosom. Med. Psychol. 61, 216–224. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1263145
Wood, R. T., and Griffith, M. D. (2007). A qualitative investigation of problem gambling as an escape-based coping strategy. Psychol. Psychother. 80, 107–125. doi: 10.1348/147608306X107881
Yee, N. (2006). Motivations for play in online games. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 9, 772–775. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2006.9.772
Keywords : computer games, video gaming behavior, game genres, coping, psychological health
Citation: von der Heiden JM, Braun B, Müller KW and Egloff B (2019) The Association Between Video Gaming and Psychological Functioning. Front. Psychol. 10:1731. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01731
Received: 14 September 2018; Accepted: 11 July 2019; Published: 26 July 2019.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2019 von der Heiden, Braun, Müller and Egloff. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juliane M. von der Heiden, [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.

IMAGES
VIDEO