
- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.


10.1: Introduction to Polynomials
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 118993
Study Guides > College Algebra
Introduction to polynomials, learning objectives.
- Identify the degree and leading coefficient of polynomials.
- Add and subtract polynomials.
- Multiply polynomials.
- Use FOIL to multiply binomials.
- Perform operations with polynomials of several variables.
Licenses & Attributions
Cc licensed content, specific attribution.
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/ [email protected] :1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution .
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Introduction to Polynomials
A series of free, online Intermediate Algebra Lessons or Algebra II lessons, with videos, examples, and solutions. In these lessons, we will learn
- what are polynomials
- about polynomial functions
Related Pages More Lessons for Intermediate Algebra More Lessons for Algebra Math Worksheets
The following diagrams show the types of polynomial according to the number of terms: monomials, binomials, trinomials, polynomials and the degree of a polynomial. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on how to define polynomial functions.
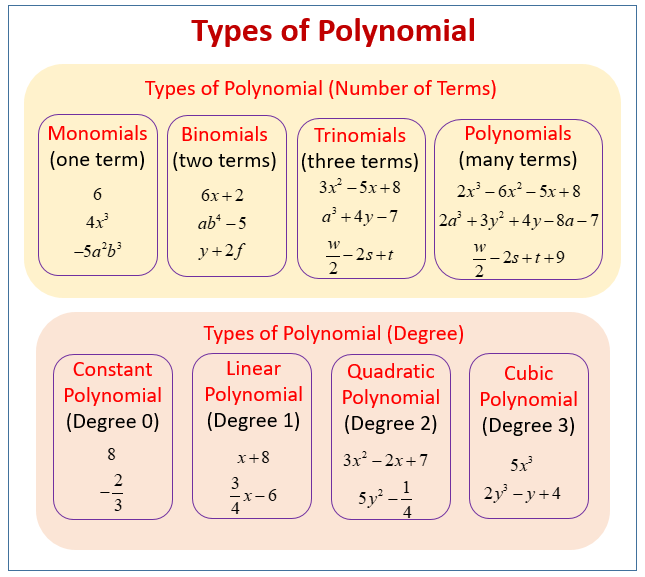
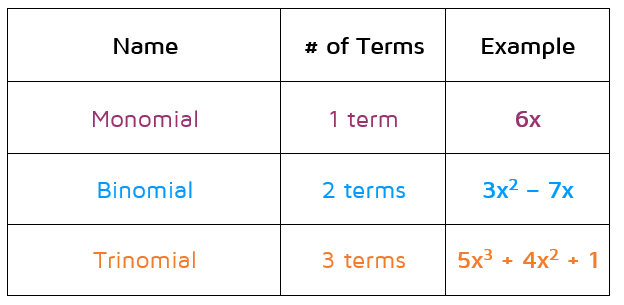
Before adding and subtracting polynomials or multiplying polynomials, it is important to have an introduction to polynomials with a definition of a polynomial and polynomial vocabulary. Important polynomial definitions include terms, monomial, the degree of a monomial, polynomial degree and standard form.
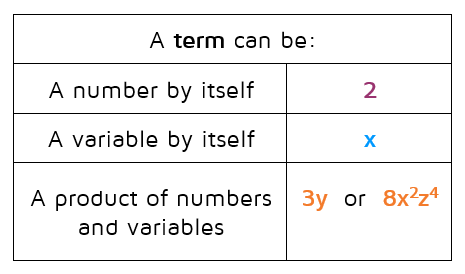
What is a term? A term can be a number, a variable, a product of numbers and/or variables, or a quotient of numbers and/or variables.
What is a monomial? A monomial is a real number and/or the product of variables with non-negative exponents.
What is a polynomial? A polynomial is a monomial or a sum of monomials. Remember that subtraction can be rewritten as addition.
What is the degree of a term? The degree of a term is the number of variable factors in the term. You can also say the degree of a term is the sum of the exponents on the variables.
What is the degree of a polynomial? The leading term of a polynomial is the term of highest degree. The degree of a polynomial is the same as the degree of the leading term.
How to talk about polynomials?
Polynomial Functions
A polynomial function is a function comprised of more than one power function where the coefficients are assumed to not equal zero. The term with the highest degree of the variable in polynomial functions is called the leading term. All subsequent terms in a polynomial function have exponents that decrease in value by one.
How to evaluate a polynomial in function notation.
How we define polynomial functions, and identify their leading coefficient and degree? Polynomial Fundamentals (Identifying Polynomials and the Degree) We look at the definition of a polynomial. We the practice identifying whether a function is a polynomial and if so what its degree is using 8 different examples.

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
- Pre-Algebra

Introduction to Polynomials
what are terms.
Polynomials
Names of Polynomials
Degrees of Polynomials
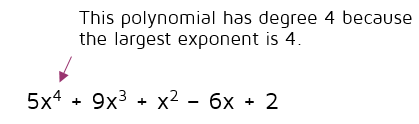
Introduction to Polynomial and Rational Functions
Chapter outline.
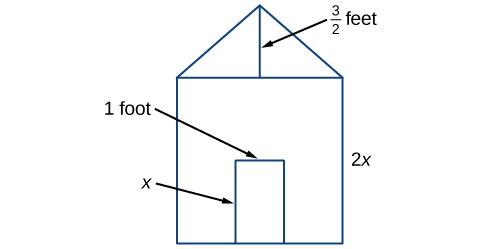
You don't need to dive very deep to feel the effects of pressure. As a person in their neighborhood pool moves eight, ten, twelve feet down, they often feel pain in their ears as a result of water and air pressure differentials. Pressure plays a much greater role at ocean diving depths.
Scuba and free divers are constantly negotiating the effects of pressure in order to experience enjoyable, safe, and productive dives. Gases in a person's respiratory system and diving apparatus interact according to certain physical properties, which upon discovery and evaluation are collectively known as the gas laws. Some are conceptually simple, such as the inverse relationship regarding pressure and volume, and others are more complex. While their formulas seem more straightforward than many you will encounter in this chapter, the gas laws are generally polynomial expressions.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/precalculus-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-functions
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Precalculus 2e
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus-2e/pages/1-introduction-to-functions
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus-2e/pages/3-introduction-to-polynomial-and-rational-functions
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. 4. Marcus states that the polynomial expression 3x3 - 4x2y + y3 + 2 is in standard form. Ariel states that it should be y3 - 4x2y + 3x3 +2. Explain which student is correct and why. They are both correct because there is more than one way to write a multivariable polynomial in standard form. Marcus has the exponents on the x variable in ...
Ignite Christian Academy/Alpha Omega Academy (ICA/AOA) Edgenuity 04.14.2023 Assignment Algebra I B v.1 Good Luck:)
A polynomial is a special algebraic expression with terms that consist of real number coefficients and variable factors with whole number exponents. Examplesofpolynomials: 3x2 7xy + 5 3 2x3 + 3x2 − 1 2x + 1 6x2y − 4xy3 − 4xy3 + 7. Polynomials do not have variables in the denominator of any term. Examplesthatarenotpolynomials:
A polynomial is a finite expression constructed from variables and constants, using the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and taking non-negative integer powers. A polynomial can be written as the sum of a finite number of terms. Each term consists of the product of a constant (called the coefficient of the term) and a finite ...
Transcript. This introduction to polynomials covers common terminology like terms, degree, standard form, monomial, binomial and trinomial. Polynomials are sums of terms of the form k⋅xⁿ, where k is any number and n is a positive integer. For example, 3x+2x-5 is a polynomial. Created by 1.
10.1 Add and Subtract Polynomials. 10.2 Use Multiplication Properties of Exponents. 10.3 Multiply Polynomials. 10.4 Divide Monomials. 10.5 Integer Exponents and Scientific Notation. 10.6 Introduction to Factoring Polynomials. Expressions known as polynomials are used widely in algebra. Applications of these expressions are essential to many ...
Learn how to identify, add, subtract, multiply and perform operations with polynomials of one or more variables. See examples, definitions and applications of polynomials in algebra and geometry.
Learn how to add, subtract, multiply, and factor polynomials, and how to solve polynomial equations and graph polynomial functions. This unit covers the basics of polynomials, including monomials, binomials, trinomials, and quadratics.
Learn. Zeros of polynomials introduction. Zeros of polynomials: plotting zeros. Zeros of polynomials: matching equation to zeros. Zeros of polynomials: matching equation to graph. Zeros of polynomials (with factoring): grouping. Zeros of polynomials (with factoring): common factor.
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. Help. OpenStax. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
Learn the definition, vocabulary and examples of polynomials and polynomial functions with videos and activities. Find out how to identify the degree, leading term and standard form of polynomials.
The nomial in polynomial has to do with "terms." So you can think of a polynomial as "many terms." Whenever you add or subtract terms together, you form a polynomial. . There are a few rules about polynomials. There are certain restrictions on what you can and can't have in a polynomial. Here are a few things that are allowed in a polynomial: .
In this lesson we learn about the standard form of a polynomial, how polynomials are similar to integers, and how to add and subtract polynomials. You can a...
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Introduction to Polynomial and Rational Functions; 3.1 Complex Numbers; 3.2 Quadratic Functions; 3.3 Power Functions and Polynomial Functions; 3.4 Graphs of Polynomial Functions; 3.5 Dividing Polynomials; 3.6 Zeros of Polynomial Functions; 3.7 Rational Functions; 3.8 Inverses and Radical Functions; 3.9 Modeling Using Variation
a single number, variable, or number with a variable. Coefficient. a number that is multiplied by a variable (the number in front of the variable) Polynomial. A mathematical expression that is the sum of a number of terms. Degree. of a term is the sum of the exponent of the variables that appear in it. Expression (Algebriac Expression)
Fill in this table as you work through the lesson. You may also use the glossary to help you. polynomial. an expression involving a sum of powers in one or more variables multiplied by coefficients, where the powers must be whole numbers. degree of a polynomial. the highest exponent or sum of exponents on any variable term powers.
a Polynomial What is the number of terms and the degree of each polynomial? a) 4x2 2+ 3 b) 7a2 - 2ab + b c) 5x + z - 6 d) 7 Solution a) 2The polynomial 4x + 3 has two terms. The term with the highest degree is 4x2. Its degree is 2. The degree of the polynomial is 2. b) The polynomial 7a2 - 2ab + b2 has three terms. Each of the three terms has a ...
Which algebraic expressions are polynomials? Check all that apply. (1)A. 2x^3 - 1/x (2)B. x^3y - 3x^2 + 6x (3)C. y^2 + 5y - sqrt3 (4)D. 2 - sqrt4x
Algebra. Introduction to Polynomials. Alina fully simplifies this polynomial and then writes it in standard form. xy2 - 2x2y + 3y3 - 6x2y + 4xy2. If Alina wrote the last term as 3y3, which must be the first term of her polynomial in standard form? Click the card to flip 👆. -8x2y. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 6.