

Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Students are often asked to write an essay on Examination Stress on Students in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Understanding examination stress.
Examination stress is a common issue among students. It refers to the anxiety and nervousness students feel before and during exams.
Causes of Examination Stress
The main causes of exam stress include high expectations from parents, fear of failure, and lack of preparation.
Effects on Students
Examination stress can lead to health problems like headaches, sleep issues, and even depression. It also affects a student’s concentration and performance.
In conclusion, it’s vital to manage exam stress for overall well-being and academic success.
250 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Introduction.
Examinations are an integral part of the academic system, designed to assess students’ understanding and knowledge of subjects. However, they often induce a significant amount of stress among students, which can adversely affect their performance and overall well-being.
The Origin of Examination Stress
Examination stress primarily originates from the pressure to perform well. This pressure can stem from various sources such as high personal expectations, fear of failure, or societal and parental expectations. The competitive nature of the academic system, along with the perception that success in examinations equates to success in life, further exacerbates this stress.
Impacts of Examination Stress
Examination stress can have profound psychological and physiological impacts on students. It can lead to anxiety, depression, sleep disorders, and even physical health problems like headaches and fatigue. Moreover, it can impair students’ cognitive functions, thus negatively affecting their academic performance.
Managing Examination Stress
Effective stress management strategies are crucial for students to navigate through examination stress. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet can help maintain physical health and reduce stress levels. Psychological strategies such as mindfulness, positive affirmations, and relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
While examinations are necessary for academic evaluation, it’s essential to address the stress they cause. A balanced approach, focusing on both academic excellence and mental well-being, can help students manage examination stress effectively, thus leading to a healthier and more productive academic life.
500 Words Essay on Examination Stress on Students
Examinations are an integral part of the educational system, designed to evaluate a student’s understanding and knowledge of the subjects studied. However, they often bring with them a significant amount of stress, causing a negative impact on the mental and physical health of students. This essay delves into the phenomenon of examination stress, its causes, effects, and possible solutions.
Examination stress is a psychological condition in which students experience extreme distress and anxiety in the period leading up to, during, and even after examinations. It is characterized by feelings of fear, self-doubt, and apprehension about one’s performance in the exams. While a certain level of stress can be motivational, excessive stress can hinder performance and well-being.
The causes of examination stress are multifaceted. The pressure to perform well, high expectations from parents and teachers, competition amongst peers, and fear of failure are common triggers. Additionally, the lack of effective study habits, poor time management, and the absence of relaxation or recreational activities can exacerbate the stress. The modern educational system, with its emphasis on grades and rankings, often overlooks the individual learning pace and capabilities of students, further contributing to this stress.
Effects of Examination Stress
Examination stress can have severe implications on a student’s mental and physical health. It can lead to anxiety disorders, depression, and in extreme cases, suicidal thoughts. Physically, it can cause headaches, sleep disorders, loss of appetite, and a weakened immune system. Moreover, it can negatively impact a student’s academic performance and hinder the learning process, creating a vicious cycle of stress and poor performance.
Addressing Examination Stress
Addressing examination stress necessitates a multi-pronged approach. Firstly, a change in perspective towards examinations is required. They should be perceived as a part of the learning process rather than a do-or-die situation. Secondly, students should be encouraged to adopt effective study habits and time management techniques, which can reduce last-minute cramming and associated stress.
Moreover, the importance of physical exercise and recreational activities in maintaining mental health should be emphasized. Regular breaks, balanced diet, and adequate sleep are crucial for stress management. Counseling services should also be made available in educational institutions to help students cope with stress.
In conclusion, examination stress is a prevalent and severe issue faced by students. It is crucial to address this problem to ensure the holistic development of students and foster a healthy learning environment. By altering our perspectives, improving study habits, and prioritizing mental health, we can mitigate the effects of examination stress and transform the educational experience into a more enjoyable and less stressful journey.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Telephone for Students
- Essay on Student Politics
- Essay on My Strength as a Student
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Partnerships
Exams as a source of stress: How assessments may affect learning, through stress

Emotions and learning / Effective lifelong learning / Quality, equity, and relevance of education and learning
Executive Summary
- Assessment and examination methods have a profound impact on how students study, what they learn and the way they subsequently use new knowledge, ranging from mostly factual knowledge to abilities and skills, and from surface learning to deep learning.
- Traditional exams and evaluations can exert a stressful pressure on students which may affect both the learning process and memory formation in different ways. However, responses to stress depend on the temperament of each individual, among other factors.
- The effects of stress on memory depend on the particular memory phase, for example, encoding, consolidation or retrieval, as well as on the temporality of the stress with respect to the learning activity or memory stage.
- Usually, the temporality of exams with respect to memory phase or learning activity, makes the stress that such evaluations may generate detrimental to memory consolidation, thus making the overall learning process less effective.
- When examination is coupled with the acquisition of new learning and knowledge perceived as relevant to the situation, or when learning and testing take place in the same context, recall is spared from the damaging effects of stress. These methods may contribute to consolidating memory, making for a more efficient learning process.
Introduction
One of the major ongoing questions in education is the role of exams, i.e. what purpose do they serve. Assessments are used to verify whether a student is qualified, although they can be used for other reasons as well, for example progress monitoring and as an educational tool to influence the learning process including memory consolidation, for example through feedback with students. Exam qualifications may be used as selection criteria to determine students’ access to particular high schools or university studies through a numerical classification that can be interpreted by some as an educational “end point”, if a sufficient rating is not achieved, although for others, it can serve as a stimulus to further progress. Temperamental disposition towards stress and anxiety may contribute to these different responses 1 , but the examination method used, as well as the so-called testing effect, may also play a part 2,3 .
The examination method and question typology used to test students’ knowledge on any given subject may also have a considerable impact on how and when students study, what they learn and the way they subsequently use new knowledge 4 . Moreover, official examinations, which depend on the educational policy and legislation of each country or region, such as those allowing access to higher studies (i.e., entry into university), can influence the way teachers teach 5 and, consequently, the way students study and learn. Put simply, if an assessment is mainly a test of factual knowledge, students will be expected to learn, memorize and recall facts and details. Where an assessment requires the ability to interpret, give examples, summarize, compare, explain, apply, analyse, evaluate or synthesize the students will have to focus more on skills. Of course, even if the assessment is mainly of factual knowledge, students can still learn how to interpret, compare, apply, analyse and so on, but the tendency will be to focus more on facts and details to get the best qualification. Conversely, if the assessment is mainly of abilities and skills, students still have to learn facts and details (otherwise they will not have sufficient material to apply their skills to), but they will tend to focus more on these abilities. The same can be said for other kinds of assessment, including those that combine different examination systems. The use of any specific method or combination of different methods, i.e. fact-based or skill-based exams, as well as the precise form in which they are designed (essay, multiple choice test, open-books exam, etcetera; see below for discussion on examination methods) depends on diverse factors such as educational policies, education centres and teaching systems, and it varies worldwide.
Alongside these considerations, exams and evaluations may exert a stressful pressure on students. In fact, stressful events are quite common in educational settings, for both students and teachers. Stress, however, can have a critical adverse impact on learning and memory processes 6,7 and, taken to an extreme where it becomes chronic, it may also contribute to some brain disorders such as major depressive disorder or post-traumatic stress disorder 8 . Many studies have been conducted to clarify the effects of stress on learning and memory, both in humans and using animal modelling systems. The effects of stress are complex, producing both enhancements and impairments to memory and learning as well as to the control of executive functions such as the attentional systems, working memory, inhibition (emotional management) and cognitive flexibility, among others 9,10 , depending on the specific cognitive process, the student’s developmental stage (from childhood to adulthood) and temperament, etcetera 6,11 (se below for discussion on these issues).
Thus, although assessment is crucial to monitor the effectiveness of both teaching and learning and to verify whether a student is qualified, at the same time, assessment methods shape how students approach learning, how much they learn and what (i.e., the content) they learn 12,13 . In this context, the stress generated by examination and evaluations may affect the learning process from “inside”, that is, from neural mechanisms linking stress responses and learning. Consequently, teachers, students, testers, curriculum designers, policy makers, institutions and administrations are all, in some way, affected by testing and examination methods.
In this brief, the effects of exams and evaluations on stress responses and consequently on learning will be discussed. It is not intended to be a review of current evaluation systems or educational policies around the world, which differ substantially depending on national and regional policies 14 , educational traditions, available technical resources, etcetera, but to provide ideas and hypotheses that may help in rethinking the role exams may play and which kind of exams can best fulfill this function, to inform educational policies and teaching practices, and to guide future research in educational neuroscience towards development and progress in this area. To reach this goal, this brief will first summarize how the typology of exams may influence learning and, from there, it will consider the effects of stress on memory consolidation and executive functions in different scenarios.
How the typology of exams may influence learning: an overview
Memory retrieval, which is a crucial cognitive activity during examination, is an active process that can alter the content and accessibility of stored memories. Although this testing effect often becomes visible only over time 2,3 , it is of potential relevance for educational practice, as it has been shown that memory retrieval fosters better retention than mere studying 3 (e.g. the use flashcards to study, which depend on retrieval). However, stress, a physiological response to potential threat, that is quite common during examinations as well as during the process of preparing for examinations, may also affect the learning process and memory formation in different ways 6,7 , which, in turn, may mean that assessments can produce contradictory effects on these processes.
Various forms of examination and assessment are traditionally used, each of which has specific characteristics which may influence teaching and learning in different ways 15 :
– Written exams, which may include short-answer and essay questions. Short-answer questions are mainly used to test how students recall specific facts (although they don’t have to be, as for example it is quite easy to have a short answer question that asks students to compare and contrast two things). Conversely, essay questions may give a better assessment of how students have understood a subject and their ability to apply their knowledge and perform analysis, comparison, evaluation and synthesis (see the annex for an example).
– Multiple-choice tests, which are mainly used to focus on detailed factual knowledge.
– Open-book exams, in which students are allowed to use textbooks and other materials. This can be helpful to test students’ understanding and ability to apply knowledge and select relevant information.
– Computer-based assessment, which can be formed of multiple-choice questions, but may also include interactive problems students have to elaborate on using the software, thus combining factual knowledge and skills.
– Take-home exams, in which the tasks are used to test students’ understanding and ability to apply knowledge and select and synthesize relevant information, possibly decreasing the pressure of having a very limited time to solve them.
– Oral examination, which is useful to test the students’ knowledge and understanding of a topic in a dynamic and interactive way, including their skills of application, analysis, integration, argument and synthesis of information. Moreover, the direct feedback in oral examination provides opportunities for students to learn immediately from the examination, and it has also been shown that presenting knowledge aloud contributes to its consolidation 16 . However, some temperaments may impair students’ performance when facing oral examination.
– Report writing and oral or poster presentations of tasks performed, in which the ability of students to perform tasks and apply knowledge to unfamiliar situations, including analysis and synthesis, as well as to write and present the outcomes, is tested.
The first work on the effect of written examinations on learning and on retention of learning dates back to 1938 17 . One of the main conclusions of this seminal work is that “the use of examinations stimulates achievement to a significant degree, […] but there is as yet no evidence to show that the greater achievement […] persists after six weeks to three months”. Much more recently, several works have analysed the effects of exam typology on how and what students learn. For example, comparing an end-of-course essay assignment to a multiple-choice examination among second-year education students from the University of Sydney 4 , it was reported that students were more likely to employ surface learning approaches in the multiple-choice examination context and to perceive multiple-choice examinations as assessing knowledge-based intellectual processing. In contrast, students were more likely to employ deep learning approaches when preparing their essay assignments, which they perceived as assessing higher levels of cognitive processing. Poorer performance in the essay assignment was associated with the employment of surface learning strategies, and poorer performance in the multiple-choice task was associated with the employment of deep learning strategies. Surface learning strategies may be defined as memorizing solely what is needed for an exam 18 . It is said that students engaged in surface learning tend to be more passive learners and to see learning as coping with tasks so that they can pass the assessment 18 . Conversely, students adopting a deep learning approach seek to understand meaning, are more likely to have a genuine curiosity about the subject, and its connections with other subjects, building on their current learning 18 . It is said that these students may enjoy social learning, including discussing different points of view 19 . It has also been shown that active learning increases student performance in science, engineering and mathematics 20 , and that problem-based learning improves deep learning 21 .
In another work, focused on the effects of tests on language studies 22 , the positive effects or influences were summarized in the following points: (1) Tests induce teachers to cover their subjects more thoroughly; (2) Tests motivate students to work harder to gain a sense of accomplishment and thus enhance learning [although mainly factual learning], and (3) Good tests can be utilized and designed as beneficial teaching-learning activities so as to encourage positive teaching-learning processes. In the same way, the following negative effects were reported: (1) Tests encourage teachers to narrow the curriculum and lose instructional time, leading to “teaching to the test”; (2) Tests induce anxiety in both teachers and students and distort their performance [see discussion about stress and learning, below]; (3) Students may not be able to learn real-life knowledge, but instead learn the discrete points of knowledge that are tested, and (4) Cramming will lead students to have a negative association with tests and will accordingly alter their learning motivation.
One way to take advantage of the positive effects of different examination methods and decrease the incidence of the negative ones is to use a combination of the different examination methods to conduct assessments. Although, currently, most pedagogical strategies and educational policies do utilize this idea, the author feels it is important to emphasize these aspects as this brief is intended for use worldwide. It is also worth noting that examination methods focused on testing the ability to apply knowledge to particular situations and to perform analysis, comparison and evaluation can be applied not only individually but also to groups of students, thus testing their capacity for working collaboratively 23-25 . This may also be useful for assessing teaching practice where this strategy (collaborative work) has been used during teaching. However, the common denominator of all exams is that for some or even many students they generate stress, which may have contradictory effects.
Finally, it is important to note that the use of the above-reported variety of examination methods depends not only on educational policies and traditions, but also on the availability of the materials and instruments needed, such as textbooks for open-book exams, computers and internet connectivity for computer-based assessments, appropriate spaces and proper parental or caregiving support for take-home exams, etcetera. These factors, in turn, are also, but not solely, influenced by regional differences and socioeconomic status 26 .
Memory retrieval and memory consolidation
As stated above, memory retrieval, which is a crucial cognitive activity during examinations, contributes to memory consolidation. Memory consolidation refers to the process by which a temporary, labile memory is transformed into a more stable, long-lasting form (Figure 1). It was first proposed in 1900 27 to account for the phenomenon by which learned material remains vulnerable to interference for a period of time after learning. During memory consolidation, that is, the gradual reorganization of the brain systems that support memory 28,29 , the hippocampus guides the reorganization of the information stored in the neocortex 30 . The hippocampus is part of the limbic system and plays an important role in the consolidation of information from short-term to long-term memory and in spatial memory that enables navigation. In turn, the neocortex is part of the human brain’s cerebral cortex where higher cognitive functioning, including executive functions, is thought to originate from. In other words, memory consolidation refers to. Moreover, under some conditions, long-term memory can transiently return to a labile state and then gradually stabilize again, a phenomenon termed reconsolidation 31-33 . It is worth noting that the dynamic nature of long-term memory 34 makes it reconstructive every time it is evoked or used, but also vulnerable to error, as in, for example, false memories 35 . Although much of this effect is not to the extent of false memories, what is important is that the act itself of recalling the memory changes the memory.
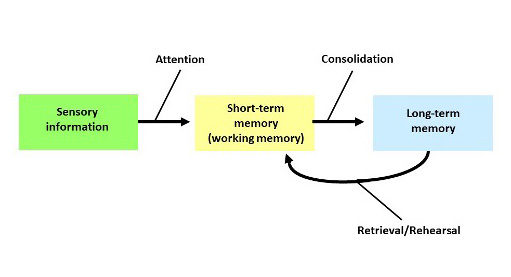
Figure 1. From sensory memory to long-term memory: the role of memory retrieval in memory consolidation.
This point highlights the importance of evaluation methods that do not disrupt previous learning, but instead contribute to its growth and consolidation, as in, for example, when students must analyse novel information relevant to the examination and apply knowledge to a novel situation. It is worth noting, however, that the putative disruption effect may be used to induce conceptual changes when needed.
In this schema, retrieving newly learned information from memory is an active process that consolidates information, and thus it decreases the incidence of forgetting 36,37 . This effect is specially relevant when combined with spacing between learning and successive retrievals 38,39 . The question of forgetting curves was first examined at the end of the nineteenth century 40 . Since then, several works have demonstrated that spacing retrieval has powerful effects on retention over substantial time periods, enhancing initial learning and slowing forgetting in several different situations 41-44 (Figure 2). To summarize the main results, repeatedly rehearsing material in the same study session will not have abiding effects and may even impair learning. Conversely, retrieving the same material on different days and in different ways will produce long-term results. Moreover, as practice increases, the information will remain accessible through longer gaps and subsequent repetitions will take much less effort. Thus, once the information is acquired, it should be revisited with increasing intervals, starting with days and weeks, and then spreading out to months and, ideally, years 45 (which is the idea behind spiral curricula).
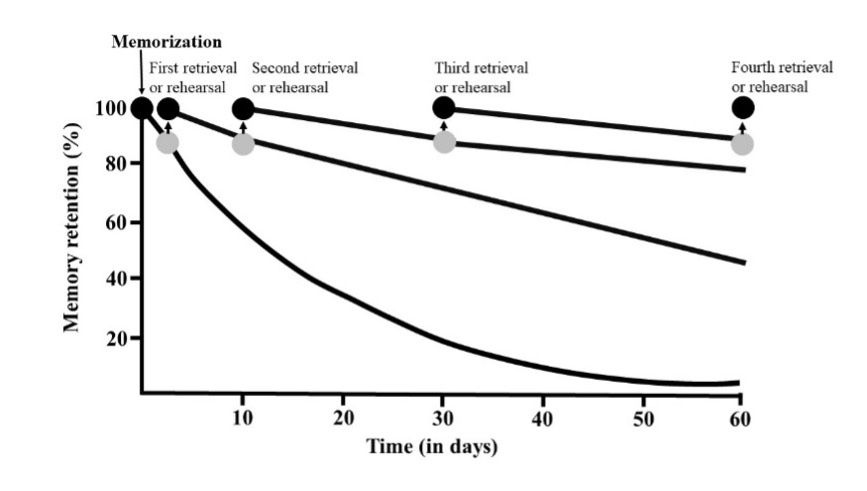
Figure 2. Idealization of the effect of spacing knowledge retrieval to slow and decrease forgetting. Modified from [40].
Effects of stress on memory and learning: the role of exams
If a situation is appraised as stressful, a well-described cascade of physiological and endocrine changes is set in motion in order to re-establish homoeostasis and to promote long-term well-being 47 . Although the stress response is very complex, with numerous mediators involved, two major stress systems appear to be critical for the modulation of learning and memory processes, the rapid autonomic nervous system and the slower hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis. Within seconds, the autonomic nervous system is activated, leading to the release of catecholamines such as noradrenaline, both from the adrenal medulla and the locus coeruleus in the brain 47 . Catecholamines prepare the body for ”fight-or-flight” responses and rapidly affect neural functioning in several brain regions critical for learning and memory, such as the hippocampus, amygdala and prefrontal cortex 48,49 .
A second system is also activated in response to stress, the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis, about 10 seconds later than the autonomic nervous system, resulting in the release of corticosteroids such as cortisol from the adrenal cortex 47 (the adrenal cortex comprises the outer layers of the adrenal glands, which are found above the kidneys). In this context, it has been shown that glucocorticoids such as cortisol can induce memory enhancement or conversely impair memory function, depending largely on the temporal proximity between the stressful event and the memory process investigated 50,51 . For instance, stress experienced just before memory retrieval, when catecholamine levels are still high and cortisol levels are not yet elevated, may have very different effects from stress experienced 90 min before retrieval, when catecholamine levels have returned to baseline and cortisol actions are at work 51-54 . In this regard, declarative memory, i.e. the memory for facts, events and word meaning, which is the most studied type of memory on which glucocorticoids exert an influence, may be both positively affected through consolidation and negatively affected through impairment by cortisol. These contradictory effects may depend on the cortisol receptor type, dose, time of exposure, memory component and the salience of stimuli, retrieval being generally affected and storage being facilitated, especially for emotionally relevant events. Interestingly, glucocorticoids also induce hippocampal atrophy, specially under acute chronic stress conditions, which may impair long-term memory storage.
Similarly, distinct memory stages such as encoding, consolidation or retrieval may be differently affected by these time-dependent physiological changes after a stressful encounter, also in anticipation of a stressful encounter 51,55 . In this respect, it has been shown that exposure to mild or moderate punctual stress (see discussion below on the ambiguity of the word stress ) may result in better memory performance during the consolidation phase but conversely reduces memory performance during retrieval, which it is important to note is the case during most examinations. Acute stressors impair both consolidation as well as retrieval. These memory-enhancing and memory-impairing effects are strongly related to stress-induced cortisol and sympathetic activity 55 .
The word stress may be, somewhat, ambiguous. One way to reduced ambiguity is by classifying stress in three categories, namely good stress, tolerable stress, and toxic stress 56 . “Good stress” refers to the experience of rising to a challenge, taking a risk, and feeling rewarded by an often-positive outcome. Even adverse outcomes can function as growth experiences for individuals with healthy self-esteem and good impulse control and decision-making capability, which are part of the so-called executive functions. “Tolerable stress”, in turn, refers to situations where negative events occur, but the individual with healthy brain architecture is able to cope, often with the aid of family, friends, and other individuals who provide support. Finally, “toxic stress” refers to situations in which negative events, adversity or traumas are experienced by an individual who usually has limited support and may also have brain architecture that reflects the effects of adverse early life events that have impaired the development of impulse control and adequate self-esteem 57 . In other words, good or even tolerable stressors generating mild to moderate punctual stress may contribute to memory consolidation during the consolidation phase but may reduce memory performance during retrieval, and toxic (acute) stress impairs both processes, which it is worth noting during most examinations.
Despite this general information, it is also worth noting the existence of individual differences in temperamental characteristics which are relevant for the onset of stress in early childhood and adolescence 1,58,59 . Thus, for example, the presentation of more shy-inhibited behaviours such as fearful withdrawal from unfamiliar people, displays of shyness, etcetera, and associated behavioural inhibition, i.e., withdrawal and fear in novel and/or unfamiliar situations, are consistently related to more severe anxiety in later childhood, particularly social anxiety 60,61 . Associations between shy-inhibited temperament and later internalizing behaviours have also been established 59,62 . Similarly, it has been suggested that negative reactivity characteristics such as anger, distress at limitations, moodiness or irritability, during toddlerhood are strongly associated with the later development of broader internalizing behaviours and less so with later anxiety symptoms 63,64 . Moreover, individual resilient capacity to manage both anxiety and stress it is also crucial for interindividual differences, and in this way examinations may also be used to reinforcing this influential process allowing for positive adaptation in a context of significant adversity (resilience will be addressed in another brief).
Beyond the specific neural, physiological and molecular aspects of the effects of stress on learning and memory, what is most significant for this brief is the effect of stressful situations that may occur during examinations on learning and memory performance. Thus, it has been shown that stress at around the time of learning enhances memory, but stress long before learning or in a distinctly different context does not promote new learning and can even hinder successful encoding of new information 65 (Figure 3). For example, while moderate stress immediately before learning enhances later recognition memory, memory is impaired if stress was experienced between 1 hour and 30 min before learning 66-68 . At the molecular and cellular level, this impairment to learning has been associated with a decrease in neural excitability in the hippocampus long after cortisol release, as it has been shown in animal modelling 69 . Similarly, stress shortly after learning also improves memory consolidation, an effect which is more marked when emotionality is concomitant, thus highlighting the important influence of emotions on learning 55,70,71 .
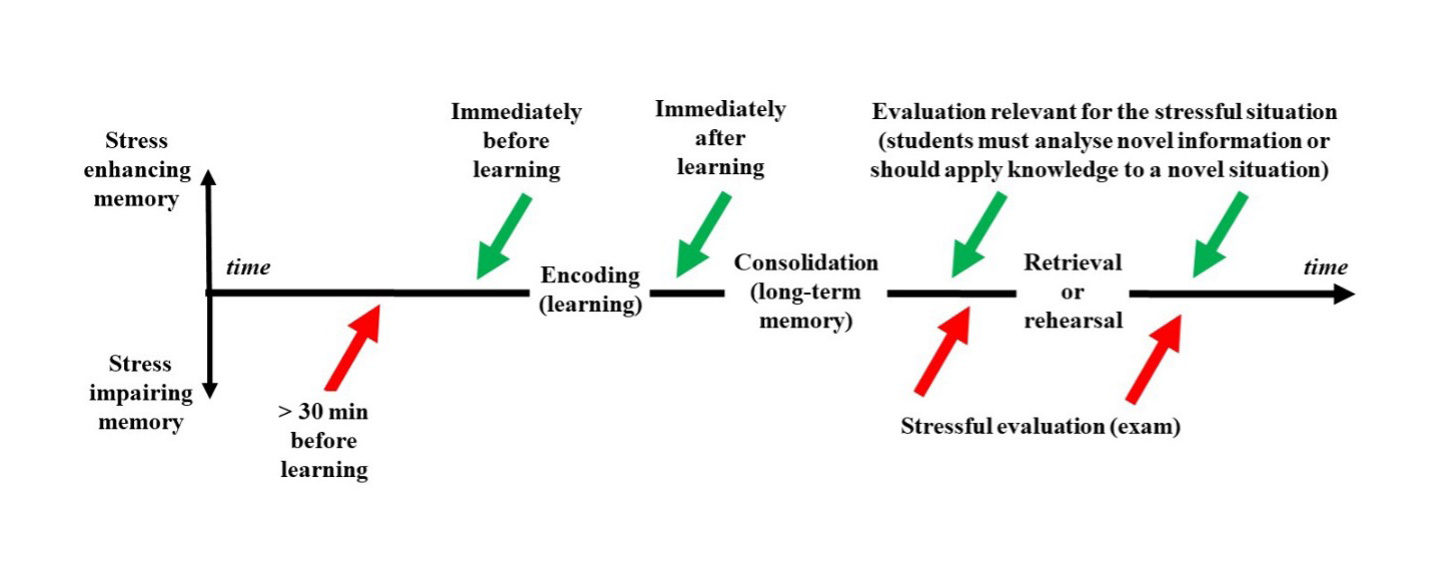
Figure 3. The effects of stress on memory, depending on temporal proximity and on specific memory process. Modified from [51].
As stated above, the effects of stress on memory extend to memory retrieval, which includes exams. Many studies have demonstrated that acute stress (or toxic stress according to the distinction above) impairs memory retrieval after a stressful encounter 72-76 . Interestingly for the focus of this brief, this retrieval deficit after stress has been found both in adults and in children, highlighting the relevance of these findings for educational settings 73 . Moreover, disruptive effects of stress on retrieval are stronger in emotional contexts, for example, after psychosocial stress 77,78 . Psychosocial stress is the result of a cognitive appraisal of what is at stake and what can be done about it, and can be defined as an imbalance between demands placed on us and our ability to manage them. However, crucial to the issue addressed in this brief, if the retrieval test, i.e., the exam or evaluation, is relevant for the stressful situation or a context is used to memory retrieval, i.e. there is context serving as a retrieval cue, recall is spared from the damaging effects of stress 53,79 . It is worth noting that in this regard the “context” do no refer to context-dependent learning, but to transfer knowledge to a new contextual situation. This point emphasizes the importance of evaluation methods that do not disrupt previous learning but instead contribute to its growth and consolidation, such as when students must analyse novel information relevant to the examination and apply knowledge to a novel situation (Figure 3; see the annex for an example). From an educational point of view, this can be achieved more easily with some forms of examination than others, for example, by means of essays in written exams, open-book exams, take-home exams, oral examination, report writing, etcetera.
Integrating new information into existing memories is a key process in education, which often involves some disruption. Furthermore, there is evidence that consolidated memories return to a labile state when they are reactivated, as occurs during an examination, which requires the subsequent re-stabilization of those memories in a process called reconsolidation 52,80,81 . During reconsolidation, a process involving the hippocampus 52 and the prefrontal cortex 82 , the reactivated memory can be weakened, strengthened or altered 52 . Several studies support the hypothesis that stress can affect memory reconsolidation and memory updating, but the specific conditions leading to either impairing or enhancing effects of stress on reconsolidation are still under investigation 83-85 .
Regarding the quality of learning, experiments, mostly using rodents, indicate that under stress more rigid stimulus–response associations are learned rather than complex representations of the environment 86-88 . In this way, it has been suggested that stress can affect not only how much information is learned but may also have considerable consequences for the nature and flexibility of memories and goal-directed behaviours 51, which are at the core of executive functions. Executive functions are a set of cognitive processes that are necessary for the cognitive control of behavior, i.e. selecting and successfully monitoring behaviors that facilitate the attainment of chosen goals, which in turn must be an essential component in the education systems.
Core executive functions such as working memory, inhibition and cognitive flexibility are integral to daily life and to goal-directed behaviours. A growing body of research has suggested that stress may also impair core executive functions, which are also crucial for learning as well as for goal-directed learning. For example, it has been reported that stress impairs working memory and cognitive flexibility 9,51 , which are central to some other abilities and skills that are crucial in education, such as decision-making, planning and imagination 89 , depending on how these functions mature during childhood and adolescence 10 . In this regard, it can be hypothesised that exams’ type and the way they are perceived by students may play a critical role in contributing to the development of this relevant functions.
Conclusions
Assessment is inseparable from teaching practice and affects both the way students learn and the way teachers teach. In consequence, it has been considered that to improve learning, examination and evaluation have to be critically analised 90 . Beyond factual knowledge, to favour cognitive processes such as those involved in executive functions, exams must allow for the mobilization of cognitive processes such as comprehension, description, representation, resolution, reasoning, reflection and communication 91 . This includes strengthening the feedback character of the examination 92 . Moreover, stressful situations, which are quite common during examination as well as during exam preparation, may also affect the learning process and memory formation, disrupting some aspects of memory retrieval and consolidation. However, when examination is coupled to the acquisition of new learning and knowledge which are perceived as relevant for the stressful situation, for example, when learning and testing take place in the same context, recall is spared from the damaging effects of stress 53,79 and may contribute to consolidating memory and developing executive functions, making the process of learning more efficient.
Taken together, data mentioned in this brief emphasize the importance of evaluation methods that do not disrupt previous learning, but instead, contribute to its growth and consolidation. Thus, from an educational point of view, methodologies used during examination have to be selected carefully to fulfil both the major roles of evaluations, that is, to serve as verification that a student is qualified and also as an educational tool to improve the learning process. To this end, novel approaches and both educational and scientific neuroscience research are needed to bring these ideas closer to the educational needs of each community, taking into account their resources.
Example of two distinct biology exams that use different methodologies. One of them (Example 1) is mostly focused on factual knowledge, while the other (Example 2) targets abilities and skills. They have been taken from the University Access Examination from different Autonomous Communities within Spain. Both are open access, and they were used in June/July 2020. Current educational policy in Spain allows decentralization of University Access Examinations, which are prepared by different tester teams. The author of this brief has been the coordinator of the biology examination for University Access in Catalonia for the last 14 years. Both examples are presented in their original version and language as well as translated into English. Despite there being no scientific studies on the effects on learning or memory of these two specific different methodologies, they can be speculatively deduced from general data given in this brief.

Example 1. Written exam, short-answer questions designed mostly to evaluate factual knowledge. It also includes the interpretation of an image. Original language: Spanish.
English translation:
b) What are the asymmetric carbons in a D-glucose molecule? Which carbon determines the D and L configurations when there is more than one asymmetric carbon? (0.6)
- Observe the following image:
a) What type of structure does it represent? What are its functions? (1.0)
b) Name each of the components marked with a number. (0.5)
c) Explain what exocytosis and endocytosis are. (0.5)

Example 2. Written exam, an essay question which provides novel information to students, designed mostly to evaluate abilities and skills and to take advantage of the stressful situation to consolidate learning (i.e., the context served as a retrieval cue and gives previously unknown information to students). Original language: Catalan.
In the early nineteenth century, all attempts to bring the smallpox vaccine to America had failed. The trip was too long, and the smallpox vaccine arrived useless. A doctor, Francesc Xavier Balmis, made a surprising proposal: to transport the vaccine via inoculated people. On November 30, 1803, the corvette Maria Pita sailed from A Coruña [Galicia, Spain] with 22 children from orphanages. They were known as the “vaccinating children” of the Royal Philanthropic Expedition of the Vaccine (1803-1806).
Figure legend: Plates by Francesc Xavier Balmis, in which the pus vesicles produced by the vaccine can be seen. Source: https://culturacientifica.com/2014/02/24/el-caso-de-los-ninos-vacuniferos.
- The procedure consisted of passing the vaccine from one child to another, step by step, until the end of the trip. The first child in the chain was inoculated with the content from the vesicles developed in cows that had the smallpox disease. This disease of cows, when it affects humans, only causes a few vesicles. It did not endanger life but provided protection against human smallpox.
Write a text similar to the one in the above paragraph using the following five terms: antigens, antibodies, immunization, cowpox virus, and human smallpox virus . [1 p]
- Eight days after inoculation with the contents of the vesicles, the first vaccinated child developed vesicles full of the virus, which were then used to vaccinate the next child in the chain, and so on. [1 p]
a) In relation to the immune response of the children in whom the vesicles fluid was injected, complete the following table:
Type of immunization: active / passive
Justification
b) In relation to the origin of the antigens, complete the following table:
Type of immunization: natural / artificial
Justification:
- When selecting the children, Balmis imposed the condition that they must not have suffered smallpox or previously been vaccinated. From the point of view of the primary or secondary immune response, would the transmission of the vaccine have worked if this condition had not been fulfilled by any of the children? Justify the answer by referring to these two types of immune response. [1 p]
- McLean M.A., Cobham V.E., Simcock G., Kildea S., & King S. (2019). Toddler temperament mediates the effect of prenatal maternal stress on childhood anxiety symptomatology: The QF2011 Queensland Flood Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 16(11): 1998.
- van den Broek, Segers, E., G., Takashima, A., & Verhoeven, L. (2014). Do testing effects change over time? Insights from immediate and delayed retrieval speed. Memory 22(7): 803-812.
- van den Broek, G., Takashima, A., Wiklund-Hörnqvist, C., Wirebring, L.K., Segers, E., Verhoeven, L., & Nybergbde, L. (2016). Neurocognitive mechanisms of the “testing effect”: A review. Trends in Neuroscience and Education 5(2): 52-66.
- Scouller, K. (1998). The influence of assessment method on students’ learning approaches: Multiple choice question examination versus assignment essay. Higher Education 35: 453–472.
- Prieto-Barrio, M.I., Cobo-Escamilla, A., González-García, M.N., Moreno-Fernández, E., & de la Rosa-García, P. (2015). Influence of Assessment in the Teaching-learning Process in the Higher Education. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences 176: 458-465.
- Joëls M., Pu Z., Wiegert O., Oitzl M.S., & Krugers H.J. (2006). Learning under stress: how does it work? Trends Cogn. Sci. 10(4): 15215-8.
- Schwabe L., Joëls M., Roozendaal B., Wolf O.T., & Oitzl M.S. (2012). Stress effects on memory: an update and integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36(7): 1740-1749
- Pitman R.K., Rasmusson A.M., Koenen K.C., Shin L.M., Orr S.P., Gilbertson M.W., Milad M.R., & Liberzon I. (2012). Biological studies of post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 13(11): 769-787.
- Shields G.S., Sazma M.A., & Yonelinas A.P. (2016). The effects of acute stress on core executive functions: A meta-analysis and comparison with cortisol. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 68: 651-668.
- Igazság B., Demetrovics Z., & Cserjési R. (2019). The developmental trajectory of executive functions and their stress sensitivity in adolescence. Psychiatr. Hung.;34(3):300-310.
- Joëls M., Fernandez G., & Roozendaal B. (2011). Stress and emotional memory: a matter of timing. Trends Cogn. Sci. 15(6): 280-288.
- Scouller, K.M., & Prosser, M. (1994). Students’ experiences in studying for multiple choice question examinations. Studies in Higher Education 19: 267–279.
- Boud, D. (1998). Assessment and Learning: Contradictory or Complementary?. In: Assessment for Learning in Higher Education , pp 35-48. London: Routledge Falmer.
- UNESCO (2020). Profiles Enhancing Educational Reviews (PEER). http://education-profiles.org/
- Wyse, D., Hayward, L., & Pandya, J. (Ed.). (2016). The SAGE Handbook of Curriculum, Pedagogy and Assessment . Los Angeles: SAGE Publishing.
- Bird, C.M., Keidel, J.L., Ing, L.P., Horner, A.J., & Burgess, N. (2015). Consolidation of complex events via reinstatement in posterior cingulate cortex. J. Neurosci. 35(43): 14426-14434.
- Johnson, B.E. (1938). The Effect of Written Examinations on Learning and on the Retention of Learning. The Journal of Experimental Education 7(1): 55-62.
- Haggis, T. (2003) Constructing images of ourselves? A critical investigation into ‘Approaches to learning’ research in higher education. British Educational Research Journal , 29(1): 89-104.
- Biggs, J.B., & Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for quality learning at university (4th ed.). Berkshire: Open University Press.
- Freeman S., Eddy S.L., McDonough M., Smith M.K., Okoroafor N., Jordt H., & Wenderoth M.P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111(23): 8410-8415.
- Dolmans, D.H.J.M., Loyens, S.M.M., Marcq, H., & Gijbels, D. (2016). Deep and surface learning in problem-based learning: a review of the literature. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. Theory Pract . 21(5): 1087-1112.
- Pan, Y. (2009). A review of washback and its pedagogical implications. VNU Journal of Science, Foreign Languages , 25: 257-263.
- Lusk, M., & Conklin, L. (2003). Collaborative testing to promote learning. J. Nurs. Educ. 42(3): 121-124.
- Shen, J., Hiltz, S.R., & Bieber, M. (2007). Collaborative online examinations: Impacts on interaction, learning, and student satisfaction. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics – Part A: Systems and Humans 36(6): 1045-1053.
- Cantwell, E.R., Sousou, J., Jadotte, Y.T., Pierce, J., & Akioyamen, L.E. (2017). Collaborative testing for improving student learning outcomes and test‐taking performance in higher education: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews 13(1): 1-18
- Global Education Monitoring Report Team. (2020). Global education monitoring report, 2020: Inclusion and education: all means all . Paris: UNESCO.
- Lechner H.A., Squire L.R., & Byrne J.H. (1999). 100 years of consolidation—Remembering Müller and Pilzecker. Learn. Mem. 2: 77–87.
- Dudai Y. (2012). The restless engram: Consolidations never end. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 35: 227–247.
- Squire, L.R., Genzel, L., Wixted, J.T., & and Morris, R.G. (2015). Memory Consolidation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 7(8): a021766.
- Dudai Y., & Morris R.G.M. (2000). To consolidate or not to consolidate: What are the questions? In: Brain, perception, memory advances in cognitive sciences (ed. Bulhuis J.J.), pp. 149–162. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Nader K., Schafe G.E., & Le Doux J.E. (2000). Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval. Nature 406: 722–726.
- Sara S.J. (2000). Retrieval and reconsolidation: Toward a neurobiology of remembering. Learn. Mem. 7: 73–84.
- Alberini C.M. (2005). Mechanisms of memory stabilization: Are consolidation and reconsolidation similar or distinct processes? Trends Neurosci. 28: 51–56.
- Dudai Y., Morris R.G.M. (2013). Memorable trends. Neuron 80: 742–750.
- Schacter D.L., & Dodson C.S. (2001). Misattribution, false recognition and the sins of memory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. B Bio.l Sci. 356: 1385–1393.
- Rowland, C.A. (2014). The effect of testing versus restudy on retention: a meta-analytic review of the testing effect. Psychol. Bull. 140(6): 1432-1463.
- Adesope, O.O., Trevisan, D.A., & Sundararajan, N. (2017). Rethinking the Use of Tests: A Meta-Analysis of Practice Testing. Review of Educational Research 87(3): 659-701.
- Latimier, A., Peyre, H., & Ramus, F. (2020). A meta-analytic review of the benefit of spacing out retrieval practice episodes on retention. PsyArXiv: kzy7u.
- Latimier, A., Rierget, A., Ly, S., & Ramus, F. (2020). Retrieval practice promotes long-term retention irrespective of the placement. PsyArXiv: dk63q.
- Ebbinghaus, H. (1885). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology. New York: Dover.
- Newble, D.I., & Jaeger, K. (1983). The effect of assessments and examinations on the learning of medical students . Med. Educ. 17(3): 165-171.
- Loftus, G. R. (1985). Evaluating forgetting curves. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition 11(2): 397–406.
- Pashler, H., Rohrer, D., Cepeda, N.J., & Carpenter, S.K. (2007). Enhancing learning and retarding forgetting: choices and consequences. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 14(2): 187-193.
- Cepeda, N.J., Vul, E., Rohrer, D., Wixted, J.T., & Pashler, H. (2008). Spacing effects in learning: a temporal ridgeline of optimal retention. Psychol. Sci. 19(11): 1095-1102.
- Brown, P.C., Roediger, H.L., & McDaniel, M.A. (2014). Make It Stick. The Science of Successful Learning . Harvard: Harvard University Press.
- Reisberg, D. (ed.). (2013). The Oxford Handbook of Cognitive Psychology . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Joëls, M., & Baram, T.Z. (2009). The neuro-symphony of stress. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10: 459–466.
- Katsuki, H., Izumi, Y., & Zorumski, C.F. (1997). Noradrenergic regulation of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 region. J. Neurophysiol. 77: 3013–3020.
- Arnsten, A.F.T. (2009). Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10: 410–422.
- Roozendaal, B. (2002). Stress and memory: opposing effects of glucocorticoids on memory consolidation and memory retrieval. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 78(3): 578-595.
- Vogel, S., & Schwabe, L. (2016). Learning and memory under stress: implications for the classroom. NPJ Sci Learn. 1: 16011.
- Schwabe, L., Nader, K., & Pruessner, J. C. (2014). Reconsolidation of human memory: brain mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biol. Psychiatry 76: 274–280.
- Schönfeld, P., Ackermann, K., & Schwabe, L. (2014). Remembering under stress: different roles of autonomic arousal and glucocorticoids in memory retrieval. Psychoneuroendocrinology 39: 249–256.
- Wang, B., & Bukuan, S. (2015). Timing matters: negative emotion elicited 5 min but not 30 min or 45 min after learning enhances consolidation of internal-monitoring source memory . Acta Psychol. 157: 56-64.
- Smeets, T., Otgaar, H., Candel, I., & Wolf, O.T. (2008) True or false? Memory is differentially affected by stress-induced cortisol elevations and sympathetic activity at consolidation and retrieval . Psychoneuroendocrinology 33(10): 1378-1386.
- McEwan, B.S. (2016). In pursuit of resilience: stress, epigenetics, and brain plasticity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1373: 56–64.
- Lazarus, R.S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal and Coping . New York: Springer-Verlag
- Forbes M.K., Rapee R.M., Camberis A.-L., McMahon C.A. (2017). Unique associations between childhood temperament characteristics and subsequent psychopathology symptom trajectories from childhood to early adolescence. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 45: 1221–1233.
- Bayer J.K., Morgan A., Prendergast L.A., Beatson R., Gilbertson T., Bretherton L., Hiscock H., & Rapee R.M. (2019). Predicting Temperamentally Inhibited Young Children’s Clinical-Level Anxiety and Internalizing Problems from Parenting and Parent Wellbeing: A Population Study. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 47: 1165–1181
- Edwards S.L., Rapee R.M., Kennedy S. (2010). Prediction of anxiety symptoms in preschool-aged children: Examination of maternal and paternal perspectives. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry. 51:313–321.
- Clauss J.A., Blackford J.U. (2012). Behavioral inhibition and risk for developing social anxiety disorder: A meta-analytic study . J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 51: 1066–1075.
- Abulizi X., Pryor L., Michel G., Melchior M., & van der Waerden J. (2017). Temperament in infancy and behavioral and emotional problems at age 5.5: The EDEN mother-child cohort. PLoS ONE . 12:e0171971.
- Savage J., Verhulst B., Copeland W., Althoff R.R., Lichtenstein P., & Roberson-Nay R. (2015). A genetically informed study of the longitudinal relation between irritability and anxious/depressed symptoms. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 54: 377–384.
- Humphreys K.L., Schouboe S.N.F., Kircanski K., Leibenluft E., Stringaris A., & Gotlib I.H. (2018). Irritability, Externalizing, and Internalizing Psychopathology in Adolescence: Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Associations and Moderation by Sex. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol .: 1–9.
- de Quervain, D.J.F., Roozendaal, B., Nitsch, R.M., McGaugh, J.L., & Hock, C. (2000). Acute cortisone administration impairs retrieval of long-term declarative memory in humans. Nat. Neurosci. 3: 313–314.
- Henckens, M., van Wingen, G.A., Joëls, M., & Fernandez, G. (2010). Time-dependent effects of corticosteroids on human amygdala processing. J. Neurosci. 30: 12725–12732.
- Zoladz, P.R., Clark, B., Warnecke, A., Smith, L., Tabar, J., & Talbot, J.N. (2011). Pre-learning stress differentially affects long-term memory for emotional words, depending on temporal proximity to the learning experience. Physiol. Behav. 103: 467–476.
- Henckens, M.J., Pu, Z., Hermans, E.J., van Wingen, G.A., Joëls, M., & Fernández, G. (2012). Dynamically changing effects of corticosteroids on human hippocampal and prefrontal processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 33: 2885–2897.
- Wiegert, O., Joëls, M., & Krugers, H. (2006). Timing is essential for rapid effects of corticosterone on synaptic potentiation in the mouse hippocampus. Learn. Mem. 13: 110–113.
- Cahill, L., Gorski, L., & Le, K. (2003). Enhanced human memory consolidation with postlearning stress: Interaction with the degree of arousal at encoding. Learn. Mem . 10: 270–274.
- Beckner, V.E., Tucker, D.M., Delville, Y., & Mohr, D.C. (2006). Stress facilitates consolidation of verbal memory for a film but does not affect retrieval. Behav. Neurosci. 120: 518–527.
- Buchanan, T.W., Tranel, D., & Adolphs, R. (2006). Impaired memory retrieval correlates with individual differences in cortisol response but not autonomic response. Learn. Mem. 13: 382–387.
- Quesada, A.A., Wiemers, U.S., Schoofs, D., & Wolf, O.T. (2012). Psychosocial stress exposure impairs memory retrieval in children. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37: 125–136.
- Hupbach, A., & Fieman, R. (2012). Moderate stress enhances immediate and delayed retrieval of educationally relevant material in healthy young men. Behav. Neurosci. 126: 819–825.
- Quaedflieg, C.W., Schwabe, L., Meyer, T., & Smeets, T. (2013). Time dependent effects of stress prior to encoding on event-related potentials and 24 h delayed retrieval. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38: 3057–3069.
- Schwabe, L., & Wolf, O. (2014). Timing matters: temporal dynamics of stress effects on memory retrieval. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 14: 1041–1048
- Kuhlmann, S., Piel, M., & Wolf, O.T. (2005). Impaired memory retrieval after psychosocial stress in healthy young men. J. Neurosci. 25: 2977–2982.
- Smeets, T., Giesbrecht, T., Jelicic, M., Merckelbach, H. (2007). Context-dependent enhancement of declarative memory performance following acute psychosocial stress. Biol. Psychol. 76(1-2): 116-23.
- Schwabe, L., & Wolf, O. T. (2009). The context counts: congruent learning and testing environments prevent memory retrieval impairment following stress. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 9: 229–236.
- Nader, K., & Hardt, O. (2009). A single standard for memory: the case for reconsolidation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10: 224–234.
- Dudai, Y. (2012). The restless engram: consolidations never end. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 35: 227–247.
- Sandrini, M., Censor, N., Mishoe, J., & Cohen, L. (2013). Causal role of prefrontal cortex in strengthening of episodic memories through reconsolidation. Curr. Biol. 23: 2181–2184.
- Schwabe, L. & Wolf, O.T. (2010). Stress impairs the reconsolidation of autobiographical memories. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 94: 153–157.
- Coccoz, V., Maldonado, H., & Delorenzi, A. (2011). The enhancement of reconsolidation with a naturalistic mild stressor improves the expression of a declarative memory in humans. Neuroscience 185: 61–72.
- Bos, M.G., Schuijer, J., Lodestijn, F., Beckers, T., & Kindt, M. (2014). Stress enhances reconsolidation of declarative memory. Psychoneuroendocrinology 46: 102–113.
- Packard, M.G., & Teather, L.A. (1998). Amygdala modulation of multiple memory systems: hippocampus and caudate-putamen. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 69: 163–203
- Packard, M.G. & Wingard, J.C. (2004). Amygdala and ‘emotional’ modulation of the relative use of multiple memory systems. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 82: 243–252.
- Wingard, J.C. & Packard, M.G. (2008). The amygdala and emotional modulation of competition between cognitive and habit memory. Behav. Brain Res. 193: 126–131.
- [89] Joo, H.R., & Frank, L.M. (2018). The hippocampal sharp wave–ripple in memory retrieval for immediate use and consolidation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 19: 744–757.
- McDonald, R. (2006). The use of evaluation to improve practice in learning and teaching. Innovations in Education and Teaching International 43(1): 3-13.
- Gulikers, J., Bastiaens, T.J., & Kirschner, P. (2004) The five-dimensional framework for authentic assessment. Educational Technology Research and Development 52(3): 67-86.
- Nicol, D.J., & Macfarlane‐Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self‐regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education 31(2): 199-218.
How to deal with exam stress
Exam season can bring on levels of stress and burnout that can hinder your studies. here are some handy tips on how to manage your anxiety.
- Student life
Seeta Bhardwa
Exam stress affects most students in varying ways. It is important to manage this stress and find little ways of helping to eliminate the risk of burnout.
For some students, exams can be a breeze; revision is second nature to them and they could ace an exam with their eyes closed. But for others, sweaty palms and heart palpitations are just a part of the territory, and it seems that nothing is more impossible than sitting down and revising. Here are some handy tips that can help to dissipate stress and make sure you can get through exam season.

Discover the University of Liverpools' online postgraduate courses
1. take regular breaks and schedule in fun things to look forward to.
Even the most intense exam timetables will allow a little time for a study break. This can include 20-minute breaks during your revision day, and longer activities that you can look forward to. Go out for dinner with friends, go to the cinema, attend a gig, anything that you like doing in your spare time that will take your mind off exams. Spending a little time away from the books will leave you feeling more refreshed and relaxed the next time you revise.
2. Exercise and get outdoors
Easily one of the most frustrating things about exam season is that it seems to occur just as the weather brightens up. Use this to your advantage and go out for a walk, or a run, or head to the gym or swimming pool. As well as keeping you healthy, exercise is known to boost your mood and can help to make you more productive while revising.
Video: 10 common Exam Results Day questions - answered How to deal with stress over exam results How to survive A-level Results Day How to deal with pressure at university
3. Don’t (always) listen to others
As the old saying goes: "comparison is the thief of joy". While it is helpful to discuss topics with fellow students and often to revise together, try not to compare other peoples' revision to your own. Chances are you’re doing just fine, and listening to other people talk about what they’ve learnt will only stress you out and may make you feel like you aren't progressing as well as them. Plus, if they themselves are stressed this can rub off on to you and other people’s stress is not what you need right now.
4. Speak to someone
If the stress gets to a point where it is overwhelming, and is affecting your day-to-day life, try and speak to someone about it. Your university or school should have a service where you can speak to people about your concerns, and will be able to offer more advice on how to manage it. If that seems like too big a step, open up to a family member or a friend about the pressure you feel. You’ll be amazed to know that you aren’t alone in feeling like this.
10 quick ways to help eliminate exam stress
- Watch a film, a TV show or listen to a podcast or comedian that makes you laugh.
- Drink some herbal tea or a hot chocolate. It’s a well known fact that hot drinks are known to soothe the soul (avoid too much caffeine though!).
- A shower or a bath can help to relieve stress.
- Cook or bake something. Just the thought of having something delicious to eat can bring you joy. As a bonus side note, try and cook something healthy too. You can’t feed your mind well, if you don’t feed your body well.
- Get some sleep. The virtues of a good night’s sleep during exam season should not be underestimated.
- Keep things in perspective. Yes, exams are important. But you are so much more than your exam results.
- Avoid other stressed people. You know the ones I mean. The ones with cue cards outside of the exam hall, frantically trying to remember key dates and equations. They will do nothing for your stress levels.
- Avoid the exam "post-mortem”. You don’t need to know how other people fared in the exam. You’ve done your best, you can’t go back and change your answers so the second you step out of the exam hall, focus on your next exam.
- Be flexible. While having a revision time table is one of the best tools in your arsenal for exam success, don’t be too hard on yourself if you don’t stick to it. If you accidentally oversleep, don’t write the day off.
- Write down everything you feel like you need to do and try and tick one thing off. Just the act of feeling like you are in control of your revision can help.
Discover the University of Liverpools' online postgraduate courses
You may also like.

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} How to deal with stress over exam results

5 revision techniques to help you ace exam season (plus 7 more unusual approaches)

How to stop procrastinating – from a procrastination psychologist
Nick Wignall
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
Exams might be stressful, but they improve learning
Senior Lecturer in Educational Psychology, Macquarie University
Senior Lecturer in Educational Assessment, Macquarie University
Disclosure statement
Penny Van Bergen has previously received funding from the Australian Research Council.
Rod Lane does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Macquarie University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners

In recent weeks, students across high school and university classrooms have been breathing sighs of relief. Exams are officially over, and celebrations have begun.
For many students, exams seem a necessary evil. Time-consuming yet inevitable. But are exams really necessary? And are they evil?
In 2011, Macquarie University was the first Australian university to debate the abolition of exams . No exams in any subject, at any year level. At the time it was suggested that exams fail to develop “questioning, self sufficient learners”. Critics also often argue that exams promote a superficial understanding of topics, and that they are inauthentic : that is, they fail to represent the kinds of things students will be asked to do “in the real world”.
However, this is taking a narrow view of the benefits of exams. Exams include many of the aspects we want from assessment.
What do we want from assessment?
Good assessment programs aim to provide a balanced, fair evaluation of each student. They achieve this in two ways. First, they use of a variety of strategies and tasks. This gives students multiple opportunities, in varying contexts, to demonstrate what they know and can do . It also enables teachers to be confident in the accuracy of their judgements about each student.
Second, tasks must be “fit for purpose” . Assuming a subject has a number of goals (knowledge to learn, skills to acquire), each task should be appropriate to the specific goal or goals it is assessing. This means that a task assessing base knowledge will look different to one assessing creativity.
Rather than abolishing exams, we should instead be asking what mix of assessment tasks is most appropriate for each subject. Where might exams fit? And what are their benefits?
Exams focus on breadth
In most disciplines, there are specific bodies of knowledge that students are expected to learn. Physics students might learn about thermodynamics, while history students might learn about the cold war. Exams enable us to accurately test students’ breadth of understanding of these topics.
Critics of exams often instead promote “deep”, “rich”, and “authentic” assessment tasks. These are typically project-based tasks that draw on students’ creativity and interest. For example, history students might be asked to choose and research a historical character in depth. Business studies students might be asked to design the pitch for a new business seeking venture capital.
These tasks develop several important higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and decision-making. However, they’re not alternatives to exams. They do different things. And this is exactly what we want: multiple, different tasks to maximise students’ opportunities to demonstrate what they know and can do.
We also want fit-for-purpose. Where breadth of knowledge is important, we want assessment tasks that target this breadth. We want our future doctors to know of the entire human body. We want our future teachers to know a full repertoire of teaching and learning approaches. Exams can help achieve this.
Exams are harder to cheat on
Exams are also useful for a very different reason: they are harder than essays to cheat on. In light of the recent “MyMaster” ghost-writing scandal , it is clear that plagiarism is a serious problem for universities.
Drawing on our characteristics of good assessment, it is impossible to provide a balanced, fair evaluation of a student’s performance if the student has paid someone else to complete their work for them.
Are we being defeatist in suggesting exams as a solution to plagiarism? Perhaps. We would like our schools and universities to be about discovery and exploration: not compliance. To date, however, essay mills have consistently remained one step ahead of academia.
While creative tasks may be one alternative solution, ghostwriter Dave Tomar writes in his book, The Shadow Scholar , that all sorts of tasks are ghost-written. More difficult tasks simply cost more. Tasks that cannot be purchased or copy-and-pasted must be integrated into the mix.
Exams do enhance learning
Finally, and on a more positive note, there is evidence that both studying for and sitting exams deepens learning.
Studying is like exercising. When one exercises, the muscles in use grow stronger. Likewise, the process of searching through ones memory and retrieving the relevant information strengthens that memory pathway for future uses. This means that when newly qualified teachers, doctors, lawyers, or accountants come to retrieve information they need, it is – as a consequence of having been practised previously – now easier to access.
So, how can we best make use of this “practice effect” for memory? Research tells us that learning is particularly strong when students self-test . Rather than passively reading and remembering by rote, we want our students to study by forming appropriate questions, searching memory for relevant responses, and knitting this information together into an appropriate answer.
We think this third benefit of exams is the most exciting. Exams don’t just provide a targeted, fit-for-purpose opportunity for students to demonstrate what they know: they also have the power to enhance what students know.

Faculty of Law - Academic Appointment Opportunities

Operations Manager

Senior Education Technologist

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)
Exam Stress: Effective Management Report
Executive summary.
Exam period is always a time that every student wishes to phase out. According to Hemmings (2014), this period of anxiety could be a tough time for students because of the expectations required of them. The article also identifies the importance of parents’ participation in a child’s education, especially during the examination period, and presents ten ways for students to handle stress effectively. Some of the outlined ways are being prepared, exercising, concentrating on success and managing expectations.
The anxiety experienced during exam time affects most students, and this influences their overall performance. Hemmings (2014) presents ten ways/steps for students to manage stress effectively during the exam period. The first way is being prepared. Consistent with Hemmings (2014), early preparation lessens the likelihood of anxiety during the exam period.
By ensuring that a student has a proper study plan, exam period will be smooth and free from bouts of anxiety. The second way is avoiding overdoing things. A student should study with zeal in phases. This means that studying for a few minutes is better and efficient than reading for many hours. This assists a child in studying efficiently and reducing anxiety. The third way is exercise. According to Hemmings (2014), fresh air and exercise help a student in clarifying his/her mind and maintaining excellent health. Parents should encourage their children to participate in such endeavors.
The fourth way is breaking information down. This is one of the best ways of ensuring proper and efficient extraction of information while studying with minimal anxiety. Breaking down of information makes it easy for the student in terms of learning and understanding a subject or topic. This facilitates a high chance of understanding an issue or subject matter before an exam thus preventing anxiety prior to and in the course of the examination.
The fifth way is having sufficient sleep. It is important for a child to get enough rest for the relaxation of the mind and body. This helps in reducing mind-clog that is associated with tiredness. Getting sufficient sleep ensures relaxation of the brain for high performance the next day.
The sixth way is having open communication. In line with Hemmings (2014), it is important for parents to analyze the mood of a child who is sitting for an exam to understand the situation and assist in calming down the student in case of signs of anxiety. This helps a child by talking out the problems that he/she might be facing and the parents should assist the children by addressing their nervousness before it gets out of hand. The seventh way is taking healthy brain food. The author suggests that parents should provide food that is healthy and that will boost the function of their children’s brain. This means that food with high volumes of sugars should be avoided as it facilitates mental fogginess, which ultimately leads to brain lockdown.
The eighth way is mentorship from older siblings. When a child is sitting for an examination, the anxiety gets the best of him/her. It is, therefore, important for a parent to ensure that the child is ready for the exam in proper time. One of the ways is through advice from the child’s older brothers or sisters who have encountered such conditions before. This boosts a child’s morale through encouragement from an experienced person.
The ninth way is concentrating on success. A student should focus on the positive side of success and parents should ensure that regardless of the outcome, the child is awarded for efforts in his/her studies. The tenth way is managing expectations. Parents want their children to perform excellently and this generates expectations. A child will feel pressured to meet the anticipations of the parents, which leads to anxiety, and may hinder the student from performing well in subsequent exams. Parents should show their support to children who do not meet such high expectations.
Hemmings, R. (2014). 10 ways to manage exam stress effectively . Gulf News.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 25). Exam Stress: Effective Management. https://ivypanda.com/essays/exam-stress-effective-management/
"Exam Stress: Effective Management." IvyPanda , 25 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/exam-stress-effective-management/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Exam Stress: Effective Management'. 25 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Exam Stress: Effective Management." January 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/exam-stress-effective-management/.
1. IvyPanda . "Exam Stress: Effective Management." January 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/exam-stress-effective-management/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Exam Stress: Effective Management." January 25, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/exam-stress-effective-management/.
- Thomas Jefferson on Civil Rights, Slavery, Racism
- Music as a Relaxation Technique
- Anxiety and Difficulty Concentrating Treatment
- “Effectiveness of Relaxation for Postoperative Pain and Anxiety” by Seers
- Exam Anxiety: A Descriptive Statistics Study
- Exam Anxiety as Psychological Disorder
- Strategies to Ace Your Exam
- Yoga Relaxation Exercises
- How Can College Students Cope With Stress
- The Effectiveness of Progressive Muscle Relaxation
- Mental Illness in the Creative Mind
- The Silence of the Lambs Psychological Analysis
- Psychoanalytic Study of Hamlet by Ernest Jones (Critical Writing)
- To Better Cope With Stress, Listen to Your Body
- Impoverished and Excessive Dreaming
- All Academics
- Mathematics Blogs
- Science Blogs
- General Knowledge Base
- Social studies blogs

Table of Contents
Introduction
Exams can be a source of immense stress and anxiety for many individuals. Whether you’re a student preparing for final exams, a professional studying for a certification test, or anyone facing a high-pressure examination, it’s essential to equip yourself with effective strategies to deal with exam stress. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore in-depth techniques, valuable insights, and practical advice that will help you conquer exam stress and perform at your best.
Understanding Exam Stress
To effectively manage and overcome exam stress, it’s important to first understand its underlying causes and effects. Exam stress occurs when the pressure to perform well in exams leads to feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and tension. This stress can manifest in various ways, including difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, lack of motivation, and physical symptoms like headaches or stomachaches.
One of the key factors contributing to exam stress is the fear of failure. Students often experience immense pressure to achieve high grades or meet academic expectations, leading to heightened stress levels. Additionally, time constraints, extensive syllabi, and the competitive nature of exams can further exacerbate stress.
Recognizing the Signs

To effectively address exam stress, it’s crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms associated with it. By identifying these indicators, you can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate stress. The following are some common symptoms of Practicing Self-Care and Mindfulness:
Feeling overwhelmed and constantly worried about exams
The anticipation of exams can lead to persistent feelings of worry and apprehension. You may find yourself constantly thinking about upcoming exams, which can negatively impact your ability to focus on studying.
Difficulty concentrating and racing thoughts
High levels of stress can make it challenging to focus and retain information. You may experience a racing mind, jumping from one thought to another, making it difficult to concentrate on studying effectively.
Effects on hunger, sleep, and energy levels
Exam stress can disrupt eating habits, sleep schedules, and overall energy levels. Some individuals may experience a loss of appetite, while others may turn to comfort eating. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns, are also common during periods of exam stress.
Increased irritability and mood swings
Stress can lead to heightened irritability, mood swings, and emotional instability. You may find yourself becoming easily frustrated, snapping at others, or experiencing frequent mood fluctuations.
Procrastination and avoidance
The fear and anxiety associated with exams can sometimes lead to procrastination and avoidance of study materials. You may find yourself engaging in activities unrelated to studying or finding excuses to delay your preparation, which can further intensify stress levels.
Coping Strategies for Exam Stress

Effective Time Management
Developing a well-structured study schedule is essential to effectively manage exam stress. Divide your study material into digestible bits and set out a time for each subject or topic. Prioritize tasks based on their importance and create a realistic timeline that accounts for both study time and breaks. By organizing your study sessions, you can reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed and ensure you cover all necessary material.
Consider using time management techniques such as the Pomodoro Technique, where you work in focused intervals followed by short breaks. This method can enhance productivity and prevent burnout. Experiment with different study schedules and find the one that works best for you.
Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your daily routine can significantly reduce exam stress. Being totally present at the moment, without judgment, is what mindfulness entails. It allows you to observe your thoughts and emotions without becoming overwhelmed by them.
Start by practicing deep breathing exercises to calm your mind and relax your body. Take calm, deep breaths through your nose and out through your mouth. You can also explore meditation and yoga, both of which promote relaxation, improve focus, and reduce anxiety. Set aside dedicated time each day for these practices to create a sense of calm and balance in your life.
Prioritize Self-Care

Taking care of your physical and mental well-being is vital during the exam preparation period. Neglecting self-care can amplify stress and hinder your ability to perform at your best. Consider the following self-care practices:
- Sleep : Ensure you get enough sleep to support optimal brain function and memory consolidation. Create a consistent sleep schedule and aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a bedtime routine that promotes relaxation, such as reading a book or listening to soothing music.
- Nutrition: Maintain a balanced diet with nutritious meals to fuel your body and mind. Avoid excessive caffeine and sugar, as they can contribute to energy crashes and hinder focus. Incorporate foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to support cognitive function.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Dehydration can cause lethargy, drowsiness, and headaches. Keep a water bottle available and make it a habit to drink water on a regular basis.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity to release endorphins, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Choose activities you enjoy, such as walking, jogging, dancing, or practicing a sport. Even short bursts of exercise can have positive effects on mood and cognition.
- Breaks and Recreation: Schedule breaks during your study sessions to relax, rejuvenate, and engage in activities you enjoy. Take a walk outdoors, listen to music, practice a hobby, or spend time with loved ones. Allow yourself moments of leisure to recharge your mind and prevent burnout.
Also, watch:
- Top Classic Kids Movies You Can Watch with Your Kids
- 20 Best 90s Cartoons: The Golden Era of Iconic Cartoons
Utilize Effective Study Techniques

Experiment with various study approaches to see what works best for you. Active learning, where you engage with the material through discussions, quizzes, or practical applications, can enhance understanding and retention. Consider the following study techniques:
- Note-taking: Take organized and concise notes during lectures and while reading textbooks. Summarize key points, highlight important information, and use visual aids like diagrams or mind maps to enhance comprehension.
- Mnemonic Devices: Create mnemonic devices or acronyms to help you remember complex information. Associating new concepts with familiar objects or memorable phrases can make the material more accessible and easier to recall during exams.
- Flashcards: Use flashcards to review and memorize key facts, definitions, or formulas. Write the question or term on one side and the answer on the other. Quiz yourself regularly using flashcards to reinforce your knowledge.
- Teach Others: Explaining concepts to someone else is an excellent way to solidify your understanding while reinforcing key concepts. Find a study partner or join a study group where you can take turns teaching and discussing topics.
- Practice Past Papers: Familiarize yourself with the exam format and types of questions by practicing past papers or sample exams. This will not only help you become comfortable with the exam structure but also identify areas where you need further revision.
Seek Support
When you need help, don’t be afraid to ask for it. Surround yourself with friends, family members, or classmates who can offer encouragement, understanding, and assistance. Join study groups to collaborate with peers, share knowledge, and discuss challenging topics. Explaining concepts to others can deepen your own understanding and provide a fresh perspective.
If exam stress becomes overwhelming or starts interfering with your daily life, consider speaking with a counselor or seeking professional help. They can offer advice, coping skills, and a safe venue for you to share your worries. Remember, seeking support is a sign of strength, and you don’t have to face exam stress alone.
Stay Positive and Visualize Success
Maintaining a positive mindset is crucial when dealing with exam stress. Negative thoughts and self-doubt can hinder your performance and increase anxiety. Instead, focus on positive affirmations and visualize yourself succeeding in your exams. Replace negative thoughts with statements like “I am prepared,” “I am capable,” and “I will do my best.”
Surround yourself with supportive and motivating individuals who believe in you and your capabilities. Engage in positive self-talk and remind yourself of past accomplishments and challenges you have overcome. Embrace the power of positive thinking to boost your confidence and reduce anxiety.
Exams may induce stress, but by implementing these comprehensive strategies, you can effectively manage and overcome exam-related anxieties. Remember that exams are just one aspect of your academic or professional journey, and your worth extends far beyond a test score. Prioritize your well-being, adopt healthy study habits, seek support when needed, and believe in your abilities. With a proactive mindset, diligent preparation, and the utilization of effective coping techniques, you can navigate exam stress with confidence and achieve the success you deserve.
Suggested Blogs:
- How to Avoid Procrastination and Achieve Optimal Productivity
- Time Management tips for students
Frequently Asked Questions
Effective time management is crucial during exam preparation. Break down your study material into manageable chunks, create a study schedule, and prioritize tasks based on their importance. Consider using techniques like the Pomodoro Technique, which involves working in focused intervals followed by short breaks. Experiment with different study schedules to find what works best for you.
Exam stress can be considerably reduced by incorporating relaxation practices into your routine. Practice deep breathing exercises, meditation, and yoga to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. Set aside dedicated time each day for these practices to create a sense of calm and balance in your life.
Self-care is essential during exam preparation as it supports your physical and mental well-being. Get enough sleep, maintain a balanced diet, stay hydrated, engage in regular physical activity, and take breaks to relax and rejuvenate. Prioritizing self-care helps reduce stress levels and improves your ability to perform at your best.
Different study techniques work for different individuals. Consider active learning methods such as note-taking, mnemonic devices, flashcards, teaching others, and practicing past papers. Experiment with these techniques to identify which ones enhance your understanding and retention of the material.
Seeking support is essential when dealing with exam stress. Surround yourself with supportive friends, family members, or classmates who can offer encouragement and assistance. Join study groups to collaborate with peers and discuss challenging topics. If needed, don’t hesitate to reach out to a counselor or seek professional help. They can offer advice, coping skills, and a safe venue for you to share your worries.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Most Popular
Recent comments, editor picks, popular posts, popular category.
- General Knowledge 44
- Mathematics Blogs 6
- Social studies 2
- Science Blogs 1
- Technology 0


2 thoughts on “Examination Stress on Students Essay in English”
- Pingback: Importance of Prayer Essay in English for Students | EssayTome
- Pingback: Short Essay on Garbage in English for Students | EssayTome
Comments are closed.
- Study resources
- Calendar - Graduate
- Calendar - Undergraduate
- Class schedules
- Class cancellations
- Course registration
- Important academic dates
- More academic resources
- Campus services
- IT services
- Job opportunities
- Safety & prevention
- Mental health support
- Student Service Centre (Birks)
- All campus services
- Calendar of events
- Latest news
- Media Relations
- Faculties, Schools & Colleges
- Arts and Science
- Gina Cody School of Engineering and Computer Science
- John Molson School of Business
- School of Graduate Studies
- All Schools, Colleges & Departments.
- Directories
- Future students
- Current students
- Alumni & friends
- Faculty & staff
- Arts & culture
- In the community
- Sports & wellness
- Student life
- University affairs
- Publications & reports
- Find an expert
- Our award winners
- Filming on campus
Exam stress
On this page:, signs and symptoms of exam stress, causes of exam stress, strategies that can help, additional resources.

Exam stress is the feeling of tension and worry that comes from test-taking situations. It is normal to feel some stress about upcoming tests, exams, papers or presentations. Indeed, a small amount of stress can challenge you and stimulate you to work harder. Exam stress becomes problematic when it interferes with your ability to perform and achieve your academic and learning goals.
Below are some signs that indicate you may be experiencing exam stress:
- Physical signs include a fast heartbeat, tense muscles, headache, sweating, upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea, dry mouth and difficulty sleeping.
- Behavioural signs include fidgeting, nail biting, and increased smoking, drinking or eating.
- Mental and emotional signs include difficulty concentrating, racing thoughts, "going blank," worry, and uncontrolled feelings of fear, dread or helplessness.
Exam stress can develop for many different reasons. Knowing the reason(s) for your stress helps you identify strategies to manage it. Causes can be placed into four main categories:
1. Lifestyle issues
- Inadequate sleep
- Poor nutrition
- Stimulant use (e.g., caffeine, energy drinks)
- Insufficient exercise
- Not scheduling available time
- Not prioritizing commitments
2. Information needs
- Lack of exam-taking strategies
- Lack of academic information (e.g., course requirements, lecturers' expectations, exam dates and exam location)
- Lack of knowledge of how to apply stress reduction techniques while studying, before an exam and during an exam
3. Poor studying styles
- Inefficient studying (e.g., inconsistent content coverage, trying to memorize the textbook, binge studying, all-night studying)
- Ineffective studying (e.g., reading without understanding, cannot recall the material, not making study/review notes, not studying/reviewing)
4. Psychological factors
- Feeling little or no control over the exam situation
- "I am not smart enough."
- "I’ll get a terrible grade."
- "I won’t pass this exam."
- "I can't do this."
- Irrational thinking about exams and outcomes
- "If I don’t pass, my family/boyfriend/girlfriend/friends will lose respect for me."
- "I will never get a degree."
- "I have to get at least an A or I am worthless."
- "I’ll fail no matter what I do — there’s no point."
The most effective way to reduce exam stress combines skill-focused approaches (e.g., building your study skills) with behaviour or cognitive approaches (e.g., learning stress management strategies).
When you have identified the cause of your exam stress, you need to ask additional questions to help you decide what intervention will be most helpful. For example, if you recognize that you were not sufficiently prepared, ask yourself:
- Why was I not prepared? Was it because I did not have enough time to study? Did I not understand the material?
- If I did not have sufficient time, why not? Because of other course work, family responsibilities, a job, watching television?
You can see how critical it is to thoroughly examine the causes of your experience! How you address your experience of exam stress will be very different, depending upon what you discover. Some ways to reduce exam stress include:
Improve your study and exam-taking skills
Effective preparation for an exam requires going beyond reading the material several times and making notes. There are numerous study and exam-taking skills you can develop and use to help you succeed. Concordia's Student Learning Services offers a great deal of support that includes:
- skill-building workshops
- individual, tailored counselling with Learning Specialists
- helpful information on the Student Learning Services website
Change negative thinking patterns
Some people see exams as a threat and thoughts about them are predominantly negative ones. These include thoughts like:
- "I don't understand this stuff."
- "I'm sure to fail this stupid exam."
- "What was I thinking when I took this course?"
These negative thoughts can lead to stress. Switching to a positive frame of mind can help to reduce stress. Pay close attention to your thoughts. When you hear yourself thinking negatively before or during an exam, stop and actively take a new perspective.
A technique called cognitive restructuring can be helpful in changing ineffective thinking. Learn more about cognitive restructuring here.
Learn to relax
Stress can affect you physically by creating tension in your body. Many people find that applying relaxation techniques is beneficial. The simplest of these techniques is deep breathing. One technique is to slowly and deeply inhale through your nose for a count of four, hold the breath for a count of seven and then exhale slowly though pursed lips for a count of eight. Do this four times in a row. With each exhalation, imagine your worries leaving your body. Do this a couple of times while studying, as well as before and during your exam to release tension.
Other relaxation techniques include progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, yoga and Tai-chi. Learn more about relaxation techniques here.
Talk things out with a professional
Some people find it difficult to identify the root of their stress and could benefit by speaking with a mental health professional. At Concordia, Counselling and Psychological Services offers appointments with professionals where students can explore the factors related to their exam stress and find ways to overcome them.
Engage in healthy behaviours
Eating healthfully , engaging in regular physical activity , avoiding tobacco and other positive health behaviours contribute to better health, which helps to buffer against the effects of stress.
For more information, explore the variety of health topics on the Health Services website or speak to a Health Promotion Specialist .
- Information from Concordia University to help with exam stress: The Exams page has "all the information you need to ace your exams". Set yourself up for success by getting familiar with scheduling, rules and study tools.
- Exam Anxiety Workshop is a video that provides a comprehensive look at exam stress and strategies to manage it
- Crash Course Study Skills is a YouTube playlist with 11 videos about study skills such as note taking, studying for exams and test anxiety
- Mastering Exam Anxiety resources from Athabasca University
© Concordia University
Would you like to explore a topic?
- LEARNING OUTSIDE OF SCHOOL
Or read some of our popular articles?
Free downloadable english gcse past papers with mark scheme.
- 19 May 2022
How Will GCSE Grade Boundaries Affect My Child’s Results?
- Akshat Biyani
- 13 December 2021
The Best Free Homeschooling Resources UK Parents Need to Start Using Today
- Joseph McCrossan
- 18 February 2022
Tips for Coping With Exam Anxiety
- January 25, 2022

Be sure to get enough sleep
Eat well before an exam, do practice exams, talk about their nerves, try teaching others, request extra time, when to seek professional help for exam anxiety .
Most students will experience anxiety around exams at some point. In fact, according to a study published by the British Psychological Society , 80% of young people have felt that exam pressure negatively impacted their mental health. Exam anxiety can feel like an unavoidable part of schooling, impacting students from primary school all the way up to A-Levels.
There are many reasons students can have exam anxiety, such as fear of failure , not understanding the material, or overwhelming pressure to perform. Though exam anxiety may feel unrelenting, there are many ways to help alleviate that anxiety. We’re here to show you some of our best tips for getting rid of pre-test nerves and setting your student up for confidence and success.

As you likely know all too well, everything feels so much worse when you’re overtired! Lack of sleep can often make negative emotions like anxiety feel insurmountable. More than that, lack of sleep significantly impacts cognitive function, making it much harder to recall information and focus on a task at hand. In short, not getting enough sleep is bad for your anxiety and your test-taking abilities.
It’s important that students get enough sleep the night before an exam. Whether it’s a basic spelling test or GCSE’s, adequate rest is essential. How many hours does your child need to be well-rested, though?
The amount of sleep needed varies from age to age. Primary school students (ages 6-12) need 9-12 hours of sleep per night. Once your child reaches their teenage years, their sleep needs don’t change too much, still requiring 8-10 hours a night–yet studies have found that 90% of British teens don’t get adequate rest every night!
However, there are things you can do to ensure your child gets adequate rest the night before a big exam. Limit your child’s screen time as best you can. If you have a teen who’s very attached to their phone, encourage them to leave it in the living room or kitchen a night before an exam.
Anxiety can make it difficult to get shut-eye. If your child’s worries are keeping them up the night before a big test, do what you can to help quiet their mind so they can rest. Younger kids may want to sleep in your bed with you or have a special toy with them to feel safe. To help your teen, encourage them to practice breathwork or meditation to help quiet their minds.
There are few things more distracting than a tummy grumbling from hunger! Eating well before an exam is an essential part of ensuring success. Your student’s body needs fuel to focus and help their brain work as best it can.
If you’re seeking an extra jolt of brainpower for your student, these foods that are proven to have brain-boosting abilities :
- Whole grains provide the kind of complex carbohydrates needed for ideal brain function.
- Omega - 3 is a complex fatty acid that helps increase brain function as well. You can find it in foods like salmon, olive oil, soybeans, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- Berries are rich in gallic acid, an important antioxidant. Strawberries, blueberries, raspberries–really any kind of berry gives you a great gallic acid boost!
- Eating your veggies is important for exam prep, too! Leafy greens like spinach and kale are full of Vitamin K, which helps the brain’s neuropathways thrive.
- Dark chocolate is a yummy treat that also packs an antioxidant punch.
These are some of the best foods to improve brain function. However, it’s most important to just eat something before an exam. Anxiety can make it difficult to stomach food. If your child is really anxious, encourage them to have small bites of bread or crackers, and to try a cup of hot tea. While caffeine can help your child stay alert, encourage them to limit their coffee or energy drink intake the morning of an exam. Too much caffeine can only exacerbate anxiety.
Practice makes perfect, and that often applies to exams, too! For many students, it’s not knowing what will be on an exam that makes it so stressful. This is particularly true for standardised tests like GCSEs or A-Levels.
Practice tests are a great way to help students feel more comfortable going into an exam. Rather than just simply studying and memorising, which is often a passive activity, practice tests force students to actively engage with the material and see where the gaps in their knowledge are. Practice tests also help familarise students with a test format, which can help them f eel more prepared and in turn reduce nerves.
Your child’s school may offer practice tests before big exams like GCSEs, and teachers can be a great resource to direct your child to further practice exam opportunities. Test-prep books with practice exams can also be found at many bookstores and online. However, if your child is seeking more individualised help for a practice exam, a tutor can provide customised support to help your student feel more secure in their ability to do well on an exam.
GoStudent’s world-class tutors utilise our innovative online learning platform to help students ace their practice exams and feel more prepared for the real thing.
Your child may be so anxious and overwhelmed about their upcoming exam that they don’t want to talk about it. However, talking about it is one of the most important (and easiest!) ways to cope with anxiety.
Start a conversation with your child about their exam anxiety. If they’re concerned about GCSE’s or A-Levels, they likely feel the pressure of performing well to be set up for a good future. This is a lot for a teenager to bear! When talking with your child about their exam anxiety, let them know that you are there to support them no matter what. Come up with an action plan together to help alleviate some of their test anxiety, such as tutoring, practice exams, and a study schedule.
You can also encourage your student to speak with someone else about their exam worries. An older sibling, cousin, or friend who has recently been through the same exams can help provide some perspective. Peers and classmates can also be helpful to talk to–knowing they aren’t alone in their anxieties is a great relief.
Though your student’s exam anxiety may be all they can think about, it can be helpful to remember that they’ve made it through school this far! Even if your child feels like they don’t know enough to do well on their exam, they have plenty of knowledge they can pass on to others. Becoming a tutor can be an enriching, motivating, and empowering activity. It can also help your child gain perspective, and realise that they are smart and knowledgeable, giving them the confidence they need to do well on their exam. GoStudent is always looking for passionate new tutors to join the team–why not check it out?
If your student is worried they won’t have enough time to complete their exam, requesting extra time can be a solution. Some teachers and schools will grant extra time to students upon request if they are anxious about finishing an exam in time. Extra time is mandated for students with certain learning disabilities, such as dyslexia , dysgraphia , and ADHD. However, tests administered by the government, including GSCEs, may require specific documentation to allow students to have extra time.
At the beginning of the school year, speak with your child’s teachers and other school officials to ensure all the proper documentation is on file so that when test time comes around, your student will get the accommodations they need.
Exam anxiety is normal, and something most students encounter at least once throughout their schooling. However, persistent, all-encompassing anxiety requires extra care.
If your child’s anxiety extends outside just schooling or isn’t alleviated by any of the methods outlined above, enlisting professional help can be crucial. How can you tell if your child’s anxiety is normal or requires treatment, though?
Signs of an anxiety disorder, such as general anxiety disorder, can include:
- Irritability
- Trouble concentrating
- Extreme self-consciousness or sensitivity to criticism
- Withdrawl from socialising with friends
- Frequent stomachs or headaches
- Changes in appetite
- Difficulty sleeping
- Repeated reassurance-seeking
- Substance abuse
- Sudden fits of rage
If your child is frequently exhibiting any of these signs, they may be living with an anxiety disorder. If you suspect that’s the case, start by talking with your child. Let them know you can tell they are feeling stressed and anxious, and that you want to help them. They may not even realise that how they feel is abnormal or something that can be fixed.
Your child may be apprehensive to get professional help, but remind them that getting help is what they need to feel better. If you’re unsure where to go, your child’s school counsellor or GP can help put you in touch with a qualified professional. Treatment can include talk therapy, cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), or in some cases, medication.
Exam anxiety is normal. However, it’s something that can be alleviated. With a little preparation, focus, and help, your child can feel ready to take on the world–or at least their GCSEs.

Popular posts

- By Guy Doza

- By Akshat Biyani

- By Joseph McCrossan
- In LEARNING TRENDS

4 Surprising Disadvantages of Homeschooling
- By Andrea Butler
The 12 Best GCSE Revision Apps to Supercharge Your Revision
More great reads:.

Advice From a Teacher: How Can I Help My Child If They Fail Their Mock Exams?
- By Natalie Lever
- January 9, 2024

What Are Mock Exams and Why Are They Important?
- January 8, 2024

SQA Results Day 2023: Important Information About How to Get Scottish Exam Results
- By Sharlene Matharu
- August 3, 2023
Book a free trial session
Sign up for your free tutoring lesson..

How to Write Good Essays in Exams (And Avoid Stress)
Blog , Pedagogy July 18, 2023
An essay is a piece of writing that presents a focused argument or explores a specific topic in a structured and coherent manner. Students often write essays in exams to assess their understanding of a subject matter, their ability to analyze and interpret information, and their skills in constructing coherent arguments. However, writing good work in exams requires careful planning, effective time management, and strong writing skills. Therefore, here is a step-by-step guide to help students write good essays for exams (and avoid stress).

Write Good Essays in Exams: A Step-By-Step Guide
Writing in exams can be challenging and stressful for many students. The step-by-step guide below will help you write good essays for exams, avoid stress and achieve better results.
Read the Instructions Carefully
Check you understand any restrictions or limitations mentioned in the instructions, such as word count, time limit, and how many questions to answer.
Read the Questions Carefully
Read through the exam paper once and then re-read each question. You might think a topic you’ve revised hasn’t come up when it is there, but the wording is unusual. Alternatively, the question might be obtuse, and you do not understand it.
Choose Your Questions Carefully
Mark any questions you might answer, and then check that you fully understand them. Do you have relevant knowledge, ideas, and evidence for the essays you plan to write?
Understand the Questions
Before you start writing, take time to read and understand the question. Underline or highlight the key points and requirements. And make sure you know what is asked of you.
Look for any keywords or phrases that indicate what you need to do, such as “explain,” “compare,” “contrast,” “define,” or “justify.”
Decide the Order You Plan to Answer Questions
Some people like to start with the topic they know best to give them a good start. Others prefer to answer their best question second because, with one essay written, they can relax, expand on their best ideas and gain a higher grade.
Plan Your Response to Write Good Essays in Exams
The stress of writing essays for exams can make all your preparation disappear. And it is essential to get your ideas across clearly and concisely in exams. So, take a few minutes to brainstorm and organize your thoughts.
Identify the main topic and discussion areas. Choose a few points or arguments about which you can write.
Make a mini-plan that puts your points/arguments in order before you start writing. This plan will serve as a roadmap for your writing and help you stay focused.
Manage Your Time
Good time management is necessary when writing essays under timed conditions. Ensure you allocate enough time for each essay section and stick to the time limit.
Divide your time according to the number of essays or sections to write.
Allocate time for each essay section, including planning, writing, and proofreading. Stick to this schedule to ensure enough time for all the necessary tasks.
Good Essays in Exams Are Clear and Concise
When writing time-constrained essays, express your ideas clearly and concisely. Avoid long, rambling sentences and focus on making your points clearly and concisely.
Write in clear and concise sentences. Avoid using overly complex language or jargon that might confuse the reader. Use specific and descriptive language to convey your ideas effectively.
Proofread and Edit
Take a few minutes at the end to review your essay. Check for any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors. Ensure you present ideas clearly and logically. If time permits, read your work aloud to identify any awkward phrasing or unclear sentences.
Once you have finished writing, take a few minutes to edit your work. Check for spelling and grammar mistakes, and make sure your essay flows logically.
Stay Calm and Focused
Stay relaxed and focused during the exam. Read the instructions carefully, manage your time wisely, and answer the questions to the best of your ability.
Write Good Essays in Exams: Structure Your Essay
A well-structured essay will make it easier for the reader to follow your arguments and understand the ideas presented.
Therefore, students should follow some basic guidelines to ensure their answers are concise and effectively convey their knowledge and understanding of the material.
Here are some tips to help you structure your exam essay.
- Start with a Strong Introduction : To write good essays in exams, begin your essay with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader’s attention. Clearly state your thesis or main argument. And provide a brief overview of the points you will discuss. This information shows the assessor how you understand the question and how you will answer it.
- Develop Coherent Body Paragraphs : Each body paragraph should focus on a single main idea that supports your thesis. Start each section with a topic sentence that introduces the main point and provides evidence or examples to support it. Use clear and logical transitions between paragraphs to maintain a smooth flow of ideas. Moreover, develop your story!
- Provide Evidence : Support your claims with relevant evidence such as examples, statistics, or references to authoritative sources. Make sure your evidence is accurate and supports your arguments effectively. This strategy will make your essay more convincing and help you score higher marks.
- Address Counterarguments : Acknowledge and address counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. This strategy demonstrates that you have considered different perspectives and strengthens your argument. Refute counterarguments with logical reasoning and evidence.
- Conclude Effectively : Summarize your main points in the conclusion and restate your thesis. Avoid introducing new information at this stage. End with a strong closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
What to Do if Your Mind Goes Blank
Most students fear this happening.
If it does—put your pen down, take a deep breath, sit back, and relax for a moment.
If you’re in the middle of an answer, read through what you have written so far—what happens next?
Lastly, if you can’t progress with your writing, then leave a gap! Your thoughts will probably return once you are less anxious.
What to Do if You Are Running Out of Time
Don’t panic.
Look at the questions left to answer (or essay sections left to write) and divide your remaining time to cover all the parts.
Or, perhaps you are halfway through writing an essay with 30 minutes to finish. Remember, give yourself 15 minutes to complete (or upload) your work because you may encounter technical problems!
Write economically—make your point, support it with evidence, and then move on to the next point.
If you can’t finish on time, briefly list the points you wanted to make—they could pick you up a few marks.
Referencing in Exams
Refer by name to the theorists and researchers in your subject area, also giving the year of their major works—the best you can given the time you have.
Citing a few up-to-date references in your essay demonstrates current knowledge and understanding.
For open-book exams, provide a reference list (i.e., evidence of your reading) at the end of your essay.
A reference list is not necessary for in-person exams, which are typically shorter in duration than open-book assessments. This requirement helps students focus on writing when time is at a premium.
Note. The reference section (if you require one) does not usually count towards the word limit. Moreover, there is no penalty for minor formatting deviations.
Write Good Essays in Exams: Marking Criteria
The marking criteria for written exams have a reduced emphasis on stylistic elements (e.g., APA formatting) to allow students to write good essays in exams.
However, being mindful of your marker’s needs is essential when writing good essays. For instance, understanding what they will be looking for can help you tailor your writing to meet their expectations. Plus, this will improve your chances of receiving a good grade.
Here are some things to consider when thinking about your marker’s needs (and to achieve better grades!):
- Knowledge & Understanding : Ensure you show thorough, up-to-date knowledge and comprehension of the topic by including evidence of reading beyond the key texts.
- Analysis : Ensure you examine ideas and principles beyond those introduced in the module resourcefully and imaginatively. Synthese ideas from diverse sources. Additionally, show independence of thought with critical evaluation.
- Reading & Referencing : Show clear evidence of extensive and relevant reading.
- Essay structure : Ensure your essay structure is logical, easy to follow, addresses the title, and enhances your argument and discussion.
- Use correct language : Use excellent standard written English.
Remember, writing essays for exams can be stressful, but you can succeed with careful planning and a clear strategy. So, stay calm, stay focused, and do your best.
However, a clear strategy is not enough when writing good essays for exams. Students should also be able to analyze, interpret, and synthesize the information they have learned, thus demonstrating their understanding of the subject matter.
Good luck with your exams!
Want to get the most out of your degree? Then check out my other pedagogy articles!
Did you find this student guide helpful? Spread the word.
Tags: Student Guide
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
My Instagram
@popesphotos

Images & Text © 2023 Paul Pope. Photographer & Educator. Privacy Policy
Essay on Stress Management
500 words essay on stress management.
Stress is a very complex phenomenon that we can define in several ways. However, if you put them together, it is basically the wear and tear of daily life. Stress management refers to a wide spectrum of techniques and psychotherapies for controlling a person’s stress level, especially chronic stress . If there is effective stress management, we can help one another break the hold of stress on our lives. The essay on stress management will throw light on the very same thing.

Identifying the Source of Stress
The first step of stress management is identifying the source of stress in your life. It is not as easy as that but it is essential. The true source of stress may not always be evident as we tend to overlook our own stress-inducing thoughts and feelings.
For instance, you might constantly worry about meeting your deadline. But, in reality, maybe your procrastination is what leads to this stress than the actual deadline. In order to identify the source of stress, we must look closely within ourselves.
If you explain away stress as temporary, then it may be a problem. Like if you yourself don’t take a breather from time to time, what is the point? On the other hand, is stress an integral part of your work and you acknowledging it like that?
If you make it a part of your personality, like you label things as crazy or nervous energy, you need to look further. Most importantly, do you blame the stress on people around you or the events surrounding you?
It is essential to take responsibility for the role one plays in creating or maintaining stress. Your stress will remain outside your control if you do not do it.
Strategies for Stress Management
It is obvious that we cannot avoid all kinds of stress but there are many stressors in your life which you can definitely eliminate. It is important to learn how to say no and stick to them. Try to avoid people who stress you out.
Further, if you cannot avoid a stressful situation, try altering it. Express your feelings don’t bottle them up and manage your time better. Moreover, you can also adapt to the stressor if you can’t change it.
Reframe problems and look at the big picture. Similarly, adjust your standards and focus on the positive side. Never try to control the uncontrollable. Most importantly, make time for having fun and relaxing.
Spend some time with nature, go for a walk or call a friend, whatever pleases you. You can also try working out, listening to music and more. As long as it makes you happy, never give up.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conclusion of the Essay on Stress Management
All in all, we can control our stress levels with relaxation techniques that evoke the relaxation response of our body. It is the state of restfulness that is the opposite of the stress response. Thus, when you practice these techniques regularly, you can build your resilience and heal yourself.
FAQ of Essay on Stress Management
Question 1: What is the importance of stress management?
Answer 1: Stress management is very efficient as it helps in breaking the hold which stress has on our lives. Moreover, you can also become happy, healthy and more productive because of it. The ultimate goal should be to live a balanced life and have the resilience to hold up under pressure.
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques.
Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Ask a Psychologist
Helping students thrive now.
Angela Duckworth and other behavioral-science experts offer advice to teachers based on scientific research. To submit questions, use this form or #helpstudentsthrive. Read more from this blog.
Tests Often Stress Students. These Tips Can Calm Their Nerves

- Share article
What can students do to help with stress before a test?
Rituals are a common choice to help calm the nerves. Here’s something I wrote about the topic for Character Lab as a Tip of the Week:
A professor at Harvard Business School I’ve known for many years always does the exact same thing before class. Because the school uses the case method, an open-ended discussion that can go in any direction at any time, class can be very unpredictable—and stressful. This professor paces back and forth in his office 30 minutes before class starts, running the discussion plan through his mind. He then writes down that plan on a pad of paper (that must be yellow) in a black-leather binder his father gave him 25 years ago, which he’s used every single day he’s taught at the school.
This person, of course, is me. What was I up to in my pacing and scribbling?
In times of stress and uncertainty, people often turn to rituals. And these rituals can be helpful in how we end up viewing our performance. In one study , researchers asked people to complete this ritual every day for a week:
Bring your fists together at your chest, slowly raise them above your head, and as you do, draw in a large inhale through your nose. Return your fists to your chest while drawing out an exhale through your mouth. Repeat this three times.
People then had to complete a series of difficult tasks that they were bound to make mistakes on. The researchers measured a pattern of brain activity that tracks the feelings that emerge in response to how well we did versus how well we thought we would do—basically, an “uh-oh” reaction to errors. They found that rituals decreased people’s negative response to their mistakes, suggesting that rituals help us move past our inevitable mistakes whenever we perform.
Here are two steps to help you explore the potential of performance rituals. First, take an audit of your existing ones. The next time you’re gearing up for a presentation, notice the little things you do to get yourself “ready to go.” Second, consider honing your existing rituals and even trying new ones in moments where you haven’t before. The stuff you need is already around you. Pacing, yellow paper, and black binders do it for me, and you know best what might resonate for you.
Don’t be embarrassed if you use rituals to try to calm your nerves.
Do experiment with using rituals to prepare yourself before performing, whether it’s taking a test or competing in a sport, and help young people do the same. Even small acts can provide comfort if and when you make a mistake so you feel ready to face what’s to come.
The opinions expressed in Ask a Psychologist: Helping Students Thrive Now are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for The Savvy Principal
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Speech on Exam Stress
- Updated on
- Feb 26, 2023

Do you know which factor helps students in giving their best in exams as well as getting the best result? It is the ability to manage exam stress. A little bit of stress is positive as it pushes the student to give their best in the exam but excessive stress makes the situation worse as the student despite hard work underperforms in the exam. Speech on exam stress is an important ASL topic and given below, are two samples of speech on exam stress.

Sample Speech on Exam Stress [200 – 300 Words]
Good morning everyone! I am ABC and today I stand before you to present an insightful and eye-opening speech on exam stress. Notes, resources, and study material for cracking an exam are easily available yet the most prevalent issue is the inability to tackle exam stress. Be it board exam students, UPSC aspirants, CAT aspirants, JEE aspirants, all of them do face anxiety and exam stress at a certain point. This speaks volumes louder, how important it is to inculcate the skill of emotional intelligence and stress management in students as it is the ability to manage the stress that sets us apart from the rest. Various factors lead to an increase in stress among students. Those factors are poor time management skills, low-self esteem, spending too much time on the phone, bad company, negative comparisons by teachers and parents, and procrastination. The most important factor according to me is procrastination because most of the students wait for some sort of motivation or spark to get them started. But the truth is waiting for motivation is useless because you won’t get motivated unless you start working. The journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step and it is just about that one step which the student needs to take and that is start studying daily instead of piling up at the last moment. There are various ways of managing stress which will ensure optimal performance in the exam. Some of the ways are doing exercises and meditation, practising deep breathing techniques, practising affirmations, having a positive company and environment, and proper time management. Always remember that apart from testing knowledge, what exams actually test is the ability to stay calm and handle pressure. Thus, along with mastering your syllabus don’t forget to master the art of stress management.
Also Read: 10 Stress Management Techniques for Students
Sample on Exam Stress [400 – 500 Words]
Good morning everyone! I am ABC and today I stand before you to present an insightful and eye-opening speech on exam stress. I would like to begin by quoting the lines by Hans Selye which says “Adopting the right attitude can convert a negative stress into a positive one.” Handling stress can either be a make-or-break situation depending upon how one handles it. Schools and colleges do ensure that they have taught concepts mentioned in the textbook with utmost clarity but at times they forget that the most important thing to be taught to students is managing stress. Stress management is that one skill that sets the best standout from the rest and helps in meeting life challenges. A common thing in board exam toppers, apart from their sky-high scores, is the ability to manage exam stress effectively. The never-ending rat race to score the highest in examinations, constant pressure from parents, and unhealthy competition from peers may lead to the development of psychological disorders in students such as depression, anxiety, etc. As per statistics, one student in every one hour commits suicide in our country. This grave situation speaks volumes louder about the need to instill the skill of emotional intelligence and stress management in students. There are various underlying causes behind the stress which students face at the time of examinations. Some of those causes are having low self-esteem, spending too much time on social media, chronic procrastination, inconsistency, poor time management skills, negative peers, and unhealthy comparisons by parents. The most crucial cause I believe is poor time management skills as the topper as well as underperformer has the same twenty-four hours. The one who can effectively manage time faces less stress as compared to the student who is not able to manage time. Students should have a habit of maintaining daily to-do lists as that reduces the load to remember tasks and helps in the breakdown of a huge chunk of the syllabus to be covered. Important techniques of stress management are proper time management skills, having command over the syllabus, doing yoga and meditation to calm the mind, and having a growth mindset. It is the mindset of an individual along with proper time management skills that help them crack all sorts of exams in a stress-free manner. Always remember, “The bad news is time flies. The good news is you’re the pilot.” Thank you so much! Everyone for being patient listeners.
Best Speech for ASL in English
- Speech on Dependence on Technology
- Speech on Importance of Social Media
- Speech on Child Labour
- Speech on Save Water
- Speech on Fear
- Speech on Corruption
- Global Warming Speech
- India of My Dreams Speech for ASL
- Speech on Indian Education System
- How to Write a Speech on Discipline?
This was all about the speech on exam stress. Hope you all found the speech to be riveting and insightful. For more blogs like these and regular abroad education updates, stay tuned to Leverage Edu!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
you just made my day thanks i got 10/10 on my asl exam however i need to make some ammendments.
Very nice article!! its all based on exam stress. I have always taken ashwagandha in capsule form; however, the gummies version is fresh and healthful. for stress free life and for good sleep and to be healthy .without any stress to write an exam .
Thank you so much for your appreciation of the article. We are glad that you have found your way to deal with exam stress. Please also check out our article on stress management tips for students and let us know your thoughts on it.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Elite College Admissions Have Turned Students Into Brands

By Sarah Bernstein
Ms. Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist in Brooklyn.
“I just can’t think of anything,” my student said.
After 10 years of teaching college essay writing, I was familiar with this reply. For some reason, when you’re asked to recount an important experience from your life, it is common to forget everything that has ever happened to you. It’s a long-form version of the anxiety that takes hold at a corporate retreat when you’re invited to say “one interesting thing about yourself,” and you suddenly believe that you are the most boring person in the entire world. Once during a version of this icebreaker, a man volunteered that he had only one kidney, and I remember feeling incredibly jealous of him.
I tried to jog this student’s memory. What about his love of music? Or his experience learning English? Or that time on a summer camping trip when he and his friends had nearly drowned? “I don’t know,” he said with a sigh. “That all seems kind of cliché.”
Applying to college has always been about standing out. When I teach college essay workshops and coach applicants one on one, I see my role as helping students to capture their voice and their way of processing the world, things that are, by definition, unique to each individual. Still, many of my students (and their parents) worry that as getting into college becomes increasingly competitive, this won’t be enough to set them apart.
Their anxiety is understandable. On Thursday, in a tradition known as “Ivy Day,” all eight Ivy League schools released their regular admission decisions. Top colleges often issue statements about how impressive (and competitive) their applicant pools were this cycle. The intention is to flatter accepted students and assuage rejected ones, but for those who have not yet applied to college, these statements reinforce the fear that there is an ever-expanding cohort of applicants with straight A’s and perfect SATs and harrowing camping trip stories all competing with one another for a vanishingly small number of spots.
This scarcity has led to a boom in the college consulting industry, now estimated to be a $2.9 billion business. In recent years, many of these advisers and companies have begun to promote the idea of personal branding — a way for teenagers to distinguish themselves by becoming as clear and memorable as a good tagline.
While this approach often leads to a strong application, students who brand themselves too early or too definitively risk missing out on the kind of exploration that will prepare them for adult life.
Like a corporate brand, the personal brand is meant to distill everything you stand for (honesty, integrity, high quality, low prices) into a cohesive identity that can be grasped at a glance. On its website, a college prep and advising company called Dallas Admissions explains the benefits of branding this way: “Each person is complex, yet admissions officers only have a small amount of time to spend learning about each prospective student. The smart student boils down key aspects of himself or herself into their personal ‘brand’ and sells that to the college admissions officer.”
Identifying the key aspects of yourself may seem like a lifelong project, but unfortunately, college applicants don’t have that kind of time. Online, there are dozens of lesson plans and seminars promising to walk students through the process of branding themselves in five to 10 easy steps. The majority begin with questions I would have found panic-inducing as a teenager, such as, “What is the story you want people to tell about you when you’re not in the room?”
Where I hoped others would describe me as “normal” or, in my wildest dreams, “cool,” today’s teenagers are expected to leave this exercise with labels like, Committed Athlete and Compassionate Leader or Environmentally Conscious Musician. Once students have a draft of their ideal self, they’re offered instructions for manifesting it (or at least, the appearance of it) in person and online. These range from common-sense tips (not posting illegal activity on social media) to more drastic recommendations (getting different friends).
It’s not just that these courses cut corners on self-discovery; it’s that they get the process backward. A personal brand is effective only if you can support it with action, so instead of finding their passion and values through experience, students are encouraged to select a passion as early as possible and then rack up the experience to substantiate it. Many college consultants suggest beginning to align your activities with your college ambitions by ninth grade, while the National Institute of Certified College Planners recommends students “talk with parents, guardians, and/or an academic adviser to create a clear plan for your education and career-related goals” in junior high.
The idea of a group of middle schoolers soberly mapping out their careers is both comical and depressing, but when I read student essays today, I can see that this advice is getting through. Over the past few years, I have been struck by how many high school seniors already have defined career goals as well as a C.V. of relevant extracurriculars to go with them. This widens the gap between wealthy students and those who lack the resources to secure a fancy research gig or start their own small business. (A shocking number of college applicants claim to have started a small business.) It also puts pressure on all students to define themselves at a moment when they are anxious to fit in and yet changing all the time.
In the world of branding, a word that appears again and again is “consistency.” If you are Charmin, that makes sense. People opening a roll of toilet paper do not want to be surprised. If you are a teenage human being, however, that is an unreasonable expectation. Changing one’s interests, opinions and presentation is a natural part of adolescence and an instructive one. I find that my students with scattershot résumés are often the most confident. They’re not afraid to push back against suggestions that ring false and will insist on revising their essay until it actually “feels like me.” On the other hand, many of my most accomplished students are so quick to accept feedback that I am wary of offering it, lest I become one more adult trying to shape them into an admission-worthy ideal.
I understand that for parents, prioritizing exploration can feel like a risky bet. Self-insight is hard to quantify and to communicate in a college application. When it comes to building a life, however, this kind of knowledge has more value than any accolade, and it cannot be generated through a brainstorming exercise in a six-step personal branding course online. To equip kids for the world, we need to provide them not just with opportunities for achievement, but with opportunities to fail, to learn, to wander and to change their minds.
In some ways, the college essay is a microcosm of modern adolescence. Depending on how you look at it, it’s either a forum for self-discovery or a high-stakes test you need to ace. I try to assure my students that it is the former. I tell them that it’s a chance to take stock of everything you’ve experienced and learned over the past 18 years and everything you have to offer as a result.
That can be a profound process. But to embark on it, students have to believe that colleges really want to see the person behind the brand. And they have to have the chance to know who that person is.
Sarah Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Political typology quiz.
Notice: Beginning April 18th community groups will be temporarily unavailable for extended maintenance. Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
Where do you fit in the political typology?
Are you a faith and flag conservative progressive left or somewhere in between.

Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That’s OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if it isn’t exactly right.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500 Words Essay on Exam Stress Introduction to Exam Stress. Exam stress is a prevalent issue among college students worldwide. It is a psychological condition in which students experience severe distress and anxiety in the face of upcoming examinations. This stress can manifest in various forms, such as insomnia, loss of appetite, irritability ...
Examination stress is a psychological condition in which students experience extreme distress and anxiety in the period leading up to, during, and even after examinations. It is characterized by feelings of fear, self-doubt, and apprehension about one's performance in the exams. While a certain level of stress can be motivational, excessive ...
Example 2. Written exam, an essay question which provides novel information to students, designed mostly to evaluate abilities and skills and to take advantage of the stressful situation to consolidate learning (i.e., the context served as a retrieval cue and gives previously unknown information to students). Original language: Catalan.
10 quick ways to help eliminate exam stress. Watch a film, a TV show or listen to a podcast or comedian that makes you laugh. Drink some herbal tea or a hot chocolate. It's a well known fact that hot drinks are known to soothe the soul (avoid too much caffeine though!). A shower or a bath can help to relieve stress.
Exams are also useful for a very different reason: they are harder than essays to cheat on. In light of the recent "MyMaster" ghost-writing scandal , it is clear that plagiarism is a serious ...
Prioritise your time when revising. Prioritising your time, subjects and workload can make a big difference and help to reduce your anxiety levels. You'll be able to ensure that the really important stuff is covered - and at the right time. Make a table with the dates of each exam and how many topics need to be covered for each.
Hemmings (2014) presents ten ways/steps for students to manage stress effectively during the exam period. The first way is being prepared. Consistent with Hemmings (2014), early preparation lessens the likelihood of anxiety during the exam period. By ensuring that a student has a proper study plan, exam period will be smooth and free from bouts ...
Coping with exam stress. Exam season is, for many students, the most stressful time of the academic year. Increasing numbers of students are seeking help for study related mental health issues. Despite what many people believe, being a student isn't all about drinking and partying. It is a time of high workloads and a lot of pressure coming ...
During midterm and finals seasons, every student feels at least a little bit of stress due to looming projects, essays, and exams. However, stress is never helpful when it comes to performing your best on important assessments. Everyone has their own ways of dealing with stress, but we could all use some additional inspiration on how to keep ...
Exam stress occurs when the pressure to perform well in exams leads to feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and tension. This stress can manifest in various ways, including difficulty concentrating, sleep disturbances, lack of motivation, and physical symptoms like headaches or stomachaches. One of the key factors contributing to exam stress is ...
This Exam Stress essay in English, helps to improve higher grades in exam. Examinations are an integral part of a student's academic journey, testing their knowledge and understanding of various subjects. However, the pressure and anxiety associated with exams can lead to significant stress among students. This essay explores the causes and ...
Exam stress is the feeling of tension and worry that comes from test-taking situations. It is normal to feel some stress about upcoming tests, exams, papers or presentations. Indeed, a small amount of stress can challenge you and stimulate you to work harder. Exam stress becomes problematic when it interferes with your ability to perform and ...
Another study undertaken at Kathmandu University in 2005-2006. among 407 clinical sciences students has identified that the five most common coping strategies adopted by. the students during the ...
Continue Reading to discover strategies to manage stress during exams below. 10 Pointers to Write Exam Stress Management Strategies During COVID-19 Essay in English . Managing exam stress is often a difficult job for school students. When the pandemic struck, everything was shut and so were the schools.
12. "Go to bed early and drink lots of water.". At the end of the day, keeping things in perspective is one of the most powerful ways of keeping your stress levels under control: Molly: 13. "Focus on you and don't worry about anyone else. Remember your best is good enough!". Jade: 14.
847 Words4 Pages. Overcoming Exam Stress. Exam stress is easier to deal with when you have prepared correctly and taken control of you study sessions. Organising your study sessions in the months leading up your exams requires that you prepare a study schedule and stick with it. The study schedule should have school, social, travel, sport and ...
Exam anxiety can feel like an unavoidable part of schooling, impacting students from primary school all the way up to A-Levels. There are many reasons students can have exam anxiety, such as fear of failure, not understanding the material, or overwhelming pressure to perform. Though exam anxiety may feel unrelenting, there are many ways to help ...
The stress of writing essays for exams can make all your preparation disappear. And it is essential to get your ideas across clearly and concisely in exams. So, take a few minutes to brainstorm and organize your thoughts. Identify the main topic and discussion areas. Choose a few points or arguments about which you can write.
Question 2: Give some stress management techniques. Answer 2: There are many stress management techniques through which one can reduce stress in their lives. One can change their situation or their reaction to it. We can try by altering the situation. If not, we can change our attitudes towards it. Remember, accept things that you cannot change.
What can students do to help with stress before a test? Rituals are a common choice to help calm the nerves. Here's something I wrote about the topic for Character Lab as a Tip of the Week:. A ...
Sample on Exam Stress [400 - 500 Words] Good morning everyone! I am ABC and today I stand before you to present an insightful and eye-opening speech on exam stress. I would like to begin by quoting the lines by Hans Selye which says "Adopting the right attitude can convert a negative stress into a positive one.".
Ms. Bernstein is a playwright, a writing coach and an essayist in Brooklyn. "I just can't think of anything," my student said. After 10 years of teaching college essay writing, I was ...
Where do you fit in the political typology? Are you a Faith and Flag Conservative? Progressive Left? Or somewhere in between? Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center.
Teachers are turning to AI tools and platforms — such as ChatGPT, Writable, Grammarly and EssayGrader — to assist with grading papers, writing feedback, developing lesson plans and creating ...