- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Analysis

What Is Business Forecasting? Definition, Methods, and Model
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/andy__andrew_beattie-5bfc262946e0fb005143d642.jpg)
What Is Business Forecasting?
Business forecasting involves making informed guesses about certain business metrics, regardless of whether they reflect the specifics of a business, such as sales growth, or predictions for the economy as a whole. Financial and operational decisions are made based on economic conditions and how the future looks, albeit uncertain.
Key Takeaways:
- Forecasting is valuable to businesses so that they can make informed business decisions.
- Financial forecasts are fundamentally informed guesses, and there are risks involved in relying on past data and methods that cannot include certain variables.
- Forecasting approaches include qualitative models and quantitative models.
Understanding Business Forecasting
Companies use forecasting to help them develop business strategies. Past data is collected and analyzed so that patterns can be found. Today, big data and artificial intelligence has transformed business forecasting methods. There are several different methods by which a business forecast is made. All the methods fall into one of two overarching approaches: qualitative and quantitative .
While there might be large variations on a practical level when it comes to business forecasting, on a conceptual level, most forecasts follow the same process:
- A problem or data point is chosen. This can be something like "will people buy a high-end coffee maker?" or "what will our sales be in March next year?"
- Theoretical variables and an ideal data set are chosen. This is where the forecaster identifies the relevant variables that need to be considered and decides how to collect the data.
- Assumption time. To cut down the time and data needed to make a forecast, the forecaster makes some explicit assumptions to simplify the process.
- A model is chosen. The forecaster picks the model that fits the dataset, selected variables, and assumptions.
- Analysis. Using the model, the data is analyzed, and a forecast is made from the analysis.
- Verification. The forecast is compared to what actually happens to identify problems, tweak some variables, or, in the rare case of an accurate forecast, pat themselves on the back.
Once the analysis has been verified, it must be condensed into an appropriate format to easily convey the results to stakeholders or decision-makers. Data visualization and presentation skills are helpful here.
Types of Business Forecasting
There are two key types of models used in business forecasting—qualitative and quantitative models.
Qualitative Models
Qualitative models have typically been successful with short-term predictions, where the scope of the forecast was limited. Qualitative forecasts can be thought of as expert-driven, in that they depend on market mavens or the market as a whole to weigh in with an informed consensus.
Qualitative models can be useful in predicting the short-term success of companies, products, and services, but they have limitations due to their reliance on opinion over measurable data. Qualitative models include:
- Market research : Polling a large number of people on a specific product or service to predict how many people will buy or use it once launched.
- Delphi method : Asking field experts for general opinions and then compiling them into a forecast.
Quantitative Models
Quantitative models discount the expert factor and try to remove the human element from the analysis. These approaches are concerned solely with data and avoid the fickleness of the people underlying the numbers. These approaches also try to predict where variables such as sales, gross domestic product , housing prices, and so on, will be in the long term, measured in months or years. Quantitative models include:
- The indicator approach : The indicator approach depends on the relationship between certain indicators, for example, GDP and the unemployment rate remaining relatively unchanged over time. By following the relationships and then following leading indicators, you can estimate the performance of the lagging indicators by using the leading indicator data.
- Econometric modeling : This is a more mathematically rigorous version of the indicator approach. Instead of assuming that relationships stay the same, econometric modeling tests the internal consistency of datasets over time and the significance or strength of the relationship between datasets. Econometric modeling is applied to create custom indicators for a more targeted approach. However, econometric models are more often used in academic fields to evaluate economic policies.
- Time series methods : Time series use past data to predict future events. The difference between the time series methodologies lies in the fine details, for example, giving more recent data more weight or discounting certain outlier points. By tracking what happened in the past, the forecaster hopes to get at least a better than average view of the future. This is one of the most common types of business forecasting because it is inexpensive and no better or worse than other methods.
Criticism of Forecasting
Forecasting can be dangerous. Forecasts become a focus for companies and governments mentally limiting their range of actions by presenting the short to long-term future as pre-determined. Moreover, forecasts can easily break down due to random elements that cannot be incorporated into a model, or they can be just plain wrong from the start.
But business forecasting is vital for businesses because it allows them to plan production, financing, and other strategies. However, there are three problems with relying on forecasts:
- The data is always going to be old. Historical data is all we have to go on, and there is no guarantee that the conditions in the past will continue in the future.
- It is impossible to factor in unique or unexpected events, or externalities . Assumptions are dangerous, such as the assumption that banks were properly screening borrowers prior to the subprime meltdown . Black swan events have become more common as our reliance on forecasts has grown.
- Forecasts cannot integrate their own impact. By having forecasts, accurate or inaccurate, the actions of businesses are influenced by a factor that cannot be included as a variable. This is a conceptual knot. In a worst-case scenario, management becomes a slave to historical data and trends rather than worrying about what the business is doing now.
Negatives aside, business forecasting is here to stay. Appropriately used, forecasting allows businesses to plan ahead for their needs, raising their chances of staying competitive in the markets. That's one function of business forecasting that all investors can appreciate.
Kesh, Someswar and Raja, M.K. "Development of a Qualitative Reasoning Model for Financial Forecasting." Information Management & Computer Security, vol. 13, no. 2, 2005, pp. 167-179.
Infiniti Research. " Business Forecasting: The Challenges in Knowing the Unknown ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-699097865-5914251597ff43a1b2e59a0c3cecc660.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
7 Financial Forecasting Methods to Predict Business Performance

- 21 Jun 2022
Much of accounting involves evaluating past performance. Financial results demonstrate business success to both shareholders and the public. Planning and preparing for the future, however, is just as important.
Shareholders must be reassured that a business has been, and will continue to be, successful. This requires financial forecasting.
Here's an overview of how to use pro forma statements to conduct financial forecasting, along with seven methods you can leverage to predict a business's future performance.
What Is Financial Forecasting?
Financial forecasting is predicting a company’s financial future by examining historical performance data, such as revenue, cash flow, expenses, or sales. This involves guesswork and assumptions, as many unforeseen factors can influence business performance.
Financial forecasting is important because it informs business decision-making regarding hiring, budgeting, predicting revenue, and strategic planning . It also helps you maintain a forward-focused mindset.
Each financial forecast plays a major role in determining how much attention is given to individual expense items. For example, if you forecast high-level trends for general planning purposes, you can rely more on broad assumptions than specific details. However, if your forecast is concerned with a business’s future, such as a pending merger or acquisition, it's important to be thorough and detailed.
Access your free e-book today.
Forecasting with Pro Forma Statements
A common type of forecasting in financial accounting involves using pro forma statements . Pro forma statements focus on a business's future reports, which are highly dependent on assumptions made during preparation, such as expected market conditions.
Because the term "pro forma" refers to projections or forecasts, pro forma statements apply to any financial document, including:
- Income statements
- Balance sheets
- Cash flow statements
These statements serve both internal and external purposes. Internally, you can use them for strategic planning. Identifying future revenues and expenses can greatly impact business decisions related to hiring and budgeting. Pro forma statements can also inform endeavors by creating multiple statements and interchanging variables to conduct side-by-side comparisons of potential outcomes.
Externally, pro forma statements can demonstrate the risk of investing in a business. While this is an effective form of forecasting, investors should know that pro forma statements don't typically comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) . This is because pro forma statements don't include one-time expenses—such as equipment purchases or company relocations—which allows for greater accuracy because those expenses don't reflect a company’s ongoing operations.
7 Financial Forecasting Methods
Pro forma statements are incredibly valuable when forecasting revenue, expenses, and sales. These findings are often further supported by one of seven financial forecasting methods that determine future income and growth rates.
There are two primary categories of forecasting: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative Methods
When producing accurate forecasts, business leaders typically turn to quantitative forecasts , or assumptions about the future based on historical data.
1. Percent of Sales
Internal pro forma statements are often created using percent of sales forecasting . This method calculates future metrics of financial line items as a percentage of sales. For example, the cost of goods sold is likely to increase proportionally with sales; therefore, it’s logical to apply the same growth rate estimate to each.
To forecast the percent of sales, examine the percentage of each account’s historical profits related to sales. To calculate this, divide each account by its sales, assuming the numbers will remain steady. For example, if the cost of goods sold has historically been 30 percent of sales, assume that trend will continue.
2. Straight Line
The straight-line method assumes a company's historical growth rate will remain constant. Forecasting future revenue involves multiplying a company’s previous year's revenue by its growth rate. For example, if the previous year's growth rate was 12 percent, straight-line forecasting assumes it'll continue to grow by 12 percent next year.
Although straight-line forecasting is an excellent starting point, it doesn't account for market fluctuations or supply chain issues.
3. Moving Average
Moving average involves taking the average—or weighted average—of previous periods to forecast the future. This method involves more closely examining a business’s high or low demands, so it’s often beneficial for short-term forecasting. For example, you can use it to forecast next month’s sales by averaging the previous quarter.
Moving average forecasting can help estimate several metrics. While it’s most commonly applied to future stock prices, it’s also used to estimate future revenue.
To calculate a moving average, use the following formula:
A1 + A2 + A3 … / N
Formula breakdown:
A = Average for a period
N = Total number of periods
Using weighted averages to emphasize recent periods can increase the accuracy of moving average forecasts.
4. Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression forecasts metrics based on a relationship between two variables: dependent and independent. The dependent variable represents the forecasted amount, while the independent variable is the factor that influences the dependent variable.
The equation for simple linear regression is:
Y = Dependent variable (the forecasted number)
B = Regression line's slope
X = Independent variable
A = Y-intercept
5. Multiple Linear Regression
If two or more variables directly impact a company's performance, business leaders might turn to multiple linear regression . This allows for a more accurate forecast, as it accounts for several variables that ultimately influence performance.
To forecast using multiple linear regression, a linear relationship must exist between the dependent and independent variables. Additionally, the independent variables can’t be so closely correlated that it’s impossible to tell which impacts the dependent variable.

Qualitative Methods
When it comes to forecasting, numbers don't always tell the whole story. There are additional factors that influence performance and can't be quantified. Qualitative forecasting relies on experts’ knowledge and experience to predict performance rather than historical numerical data.
These forecasting methods are often called into question, as they're more subjective than quantitative methods. Yet, they can provide valuable insight into forecasts and account for factors that can’t be predicted using historical data.
6. Delphi Method
The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance.
A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge. The facilitator then compiles their analyses and sends them to other experts for comments. The goal is to continue circulating them until a consensus is reached.
7. Market Research
Market research is essential for organizational planning. It helps business leaders obtain a holistic market view based on competition, fluctuating conditions, and consumer patterns. It’s also critical for startups when historical data isn’t available. New businesses can benefit from financial forecasting because it’s essential for recruiting investors and budgeting during the first few months of operation.
When conducting market research, begin with a hypothesis and determine what methods are needed. Sending out consumer surveys is an excellent way to better understand consumer behavior when you don’t have numerical data to inform decisions.

Improve Your Forecasting Skills
Financial forecasting is never a guarantee, but it’s critical for decision-making. Regardless of your business’s industry or stage, it’s important to maintain a forward-thinking mindset—learning from past patterns is an excellent way to plan for the future.
If you’re interested in further exploring financial forecasting and its role in business, consider taking an online course, such as Financial Accounting , to discover how to use it alongside other financial tools to shape your business.
Do you want to take your financial accounting skills to the next level? Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting —one of three courses comprising our Credential of Readiness (CORe) program —to learn how to use financial principles to inform business decisions. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
Planning, budgeting and forecasting is typically a three-step process for determining and mapping out an organization’s short- and long-term financial goals.
- Planning provides a framework for a business’ financial objectives — typically for the next three to five years.
- Budgeting details how the plan will be carried out month to month and covers items such as revenue, expenses, potential cash flow and debt reduction. Traditionally, a company will designate a fiscal year and create a budget for the year. It may adjust the budget depending on actual revenues or compare actual financial statements to determine how close they are to meeting or exceeding the budget.
- Forecasting takes historical data and current market conditions and then makes predictions as to how much revenue an organization can expect to bring in over the next few months or years. Forecasts are usually adjusted as new information becomes available.
The process is usually managed by a chief financial officer (CFO) and the finance department. However, the definition can be expanded to include all areas of organizational planning including: financial planning and analysis , supply chain planning , sales planning , workforce planning and marketing planning .
Discover the power of integrating a data lakehouse strategy into your data architecture, including enhancements to scale AI and cost optimization opportunities.
Register for the ebook on generative AI
Basic business accounting practices date as far back as the 1400s, when Venetian investors kept track of their Asian trade expeditions using double-entry bookkeeping, income statements and balance sheets. The word “budget” is from the old French word “bougette,” meaning “small purse.” The British government began to use the phrase “open the budget” in the mid-1700s, when the chancellor presented the annual financial statements. Businesses began to regularly use the term “budget” for their finances by the late 1800s.
Modern business forecasting began in response to the economic devastation of the Great Depression of the 1930s. New types of statistics and statistical analyses were developed that could help business better predict the future. Consulting firms emerged to help companies use these new prediction tools.
Accounting and forecasting were difficult in the early 20th century because they depended on laborious hand-written equations, ledgers and spreadsheets. The emergence of mainframe computers in the 1960s and personal computers in the 1980s sped up the process. Software applications such as Microsoft Excel became widely popular for financial reporting. However, Excel programs and spreadsheets were prone to input errors and cumbersome when various departments or individuals needed to collaborate on a report.
By the start of the 2000s, companies gained access to ever-growing operational data sources, as well as information outside corporate transaction systems — such as weather, social sentiment and econometric data. The vast amounts of available data for forecasting created a need for more sophisticated software tools to process it.
Numerous planning software packages emerged to handle this data complexity, making planning, budgeting and forecasting faster and easier — both for processing and collaboration. With predictive insights drawn automatically from data, companies could identify evolving trends and guide decision making with foresight, not just hindsight.
Today, cloud-based systems are becoming the standard, providing more flexibility, security and cost savings — helping organizations generate accurate predictions and budgets with fewer errors.
But despite these advancements, businesses are still quite dependent on traditional spreadsheets. 1 Seventy percent of businesses say they rely heavily on spreadsheet reporting, with only 16 percent using on-premise specialist software — and only ten percent using cloud software for planning.
Many businesses still base their strategy on annual plans and budgets, which is a management technique developed over a century ago. But in today’s more competitive environment, organizations are realizing that plans, budgets and forecasts need to reflect current reality — not the reality of two, three or more quarters ago. Continuous planning and rolling forecasts are becoming widely used methodologies to update plans, budgets and forecasts frequently throughout the year, on a quarterly or even monthly basis. These approaches help managers spot trends before their competitors — helping them make better informed, more agile decisions about pricing, product mix, capital allocations and even staffing levels.
Creating and implementing a sound planning, budgeting and forecasting process helps organizations establish more accurate financial report and analytics — potentially leading to more accurate forecasting and ultimately revenue growth. Its importance is even more relevant in today’s business environment where disruptive competitors are entering even the most tradition-bound industries.
When companies embrace data and analytics in conjunction with well-established planning and forecasting best practices, they enhance strategic decision making and can be rewarded with more accurate plans and more timely forecasts. Overall, these tools and practices can save time, reduce errors, promote collaboration and foster a more disciplined management culture that delivers a true competitive advantage.
Specifically, companies are able to:
- Quickly update plans and forecasts in response to new threats and opportunities, identifying risk areas early enough to rectify issues before they are serious.
- Identify and analyze the impact of changes as they occur.
- Strengthen the links between operational and financial plans.
- Better plan and predict cash flows.
- Improve communication and collaboration among plan contributors.
- Consistently deliver timely, reliable plans and forecasts, plus contingency plans, for a range of possible events.
- Analyze variances and deviations from plans and promptly take corrective action.
- Create a budget specifically for growth and having confidence in how much can be spent.
- More accurately manage sales pipelines while tracking performance against targets.
- Make more confident strategic decisions based on hard data, instead of hopes or guesswork.
- Provide evidence of an organization’s future trajectory to potential investors and lending institutions based on multiple data sources and sophisticated analysis.
Budgeting, planning and forecasting software can be purchased as an off-the-shelf solution or as part of a larger integrated corporate performance management (CPM) solution.
Advanced software solutions enable organizations to:
- Measure and monitor performance through interactive, self-service dashboards and visualizations.
- Examine root-causes with high-fidelity analysis of dimensionally rich data.
- Evaluate trends and make predictions automatically from internal or external data.
- Perform rapid what-if scenario modelling and create timely, reliable plans and forecasts.
Planning is easier and more effective when practitioners follow well-established best practices. Software solutions that support these practices can enhance the timeliness and reliability of information and increase participation by key people throughout the organization; especially those at the front lines.
Leading companies have moved to solutions that address the full planning cycle — data collection, modeling, analytics and reporting — on a common planning platform with lean infrastructure requirements. Such platforms can handle a diverse range of business functions, from budget-focused finance tasks to, for example, supply chain-focused planning for retail environments with thousands of SKUs (stock keeping units).
Companies like IBM offer holistic, integrated software solutions to streamline the planning, budgeting and forecasting process. The logic is that to adapt to today's quickly changing business conditions, an organization needs one solution that creates a single source of truth and visibility into all its data. These solutions can extend well beyond the financial aspects of the business, becoming a powerful forecasting engine across the enterprise. With these agile planning and exploratory analytics software solutions — whether in the cloud or on-premises — companies can perform planning, budgeting and forecasting with greater speed, agility and foresight.
Evaluating and selecting planning, budgeting and forecasting software is a complex task. It requires careful consideration of the software’s functionality, its value to the planning process and its ability to support planning best practices. There are also factors such as vendor reliability and support, user community connections and commitment to customer success once the sale is complete.
IBM Analytics recently published a guide to help organizations evaluate planning, budgeting and forecasting software — identifying key qualities to look for:
- Adaptive . Can you rapidly change models and re-forecast frequently, based on input from business units? Can you update plans as often as necessary?
- Timely . Is your information always current because users contribute directly to a central planning database? Are your consolidations and rollups done automatically to easily meet deadlines?
- Integrated . Do your planning, analysis, workflow and reporting functions reside on one common platform, reducing the need to maintain “shadow” planning systems?
- Collaborative . Is your solution web-based? Does it enable participation anytime, from anywhere with a secure connection?
- Self-service . Are users able to access data and perform complex analysis without the assistance of IT? Are you able to use a familiar spreadsheet interface for faster user adoption and accelerate time to value?
- Enterprise-scale data capacity . Is your solution capable of handling very large data volumes without limiting cube size? Some solutions do not handle “data sparsity” well — forcing data to be split into multiple cubes for analysis, causing version control issues.
- Efficient . Are your managers able to spend less time managing data and more time managing the business?
- Relevant . Do you have the ability to customize views for different user roles, to help increase adoption and process ownership? Do you have formula capabilities that enable modeling of all relevant business drivers?
- Accurate . Do your plans contain errors because of broken links, stale data, improper rollups and missing components?
The key is not just evaluating product features and capabilities, but also evaluating how those features will be implemented by different users within the organization. It’s important to test any planning solution that will be used by a large variety of stakeholders such as finance, operations, HR and sales.
Discover how one of the largest operators of parking facilities in the Middle East used IBM Planning Analytics to deliver better automation and multidimensional analytical power along with cost advantages.
Learn how the real estate developer enhanced its core planning, forecasting and project management capabilities with IBM technology to drive even greater profitability.
Find out how the company used IBM planning analytics to provide monthly and weekly reporting for engineering, marketing, sales and operations.
IBM Planning Analytics provides a single solution to automate planning, budgeting and forecasting for your enterprise.
Gain the autonomy you crave to find, explore and share insights in the governed, trusted environment you need, with IBM Cognos Analytics.
A comprehensive solution that provides power and flexibility for streamlined, best-practice financial consolidation and reporting.
Transform your marketing organization across people, process and platforms to remove complexity, unlock efficiency, and drive growth.
Learn how companies are delivering dependable business forecasts and optimizing the allocation of resources.
Learn the five common drawbacks to spreadsheets as planning tools
Discover the benefits of embracing data and analytics in conjunction with well-established planning and forecasting best practices.
See how you can synthesize information, uncover trends and deliver insights to improve decision making throughout the enterprise.
Request a live, 10-minute demo and get hands-on experience with IBM Planning Analytics by building a revenue plan.
See how headcount planning is done with IBM Planning Analytics in a quick, click-through demo.
1 The Future of Planning, Budgeting and Forecasting Global Survey, Workday and FSN, 2017 (link resides outside ibm.com)
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
What Is Business Forecasting? Why It Matters
April 25, 2021 - 10 min read
Companies conduct business forecasts to determine their goals, targets, and project plans for each new period, whether quarterly, annually, or even 2–5 year planning.
Forecasting helps managers guide strategy and make informed decisions about critical business operations such as sales, expenses, revenue, and resource allocation . When done right, forecasting adds a competitive advantage and can be the difference between successful and unsuccessful companies.
In this guide to business forecasting, we'll cover:
- What is business forecasting?
- What are the best forecasting techniques?
- Why forecasting in management is important
- How to conduct business forecasts
- A few forecasting examples for businesses
An introduction to business forecasting
What is business forecasting? Business forecasting is a projection of future developments of a business or industry based on trends and patterns of past and present data.
This business practice helps determine how to allocate resources and plan strategically for upcoming projects, activities, and costs. Forecasting enables organizations to manage resources , align their goals with present trends, and increase their chances of surviving and staying competitive.
The purpose of forecasts is to develop better strategies and project plans using available, relevant data from the past and present to secure your business's future . Good business forecasting allows organizations to gain unique, proprietary insights into likely future events, leverage their resources, set product team OKR , and become market leaders.
Managers conduct careful and detailed business forecasts to guarantee sound decision-making based on data and logic, not emotions or gut feelings.
What are important business forecasting methods?
There are several business forecasting methods. They fall into two main approaches:
- Quantitative forecasting
Qualitative forecasting
Quantitative and qualitative forecasting techniques use and provide different sets of data and are needed at different stages of a product's life cycle.
Note that significant changes in a company, such as new product focus, new competitors or competitive strategies, or changing compliance requirements diminish the connection between past and future trends. This makes choosing the right forecasting method even more important.
Quantitative business forecasting
Use quantitative forecasting when there is accurate past data available to analyze patterns and predict the probability of future events in your business or industry.
Quantitative forecasting extracts trends from existing data to determine the more probable results. It connects and analyzes different variables to establish cause and effect between events, elements, and outcomes. An example of data used in quantitative forecasting is past sales numbers.
Quantitative models work with data, numbers, and formulas. There is little human interference in quantitative analysis. Examples of quantitative models in business forecasting include:
- The indicator approach : This approach depends on the relationship between specific indicators being stable over time, e.g., GDP and the unemployment rate. By following the relationship between these two factors, forecasters can estimate a business's performance.
- The average approach : This approach infers that the predictions of future values are equal to the average of the past data. It is best to use this approach only when assuming that the future will resemble the past.
- Econometric modeling : Econometric modeling is a mathematically rigorous approach to forecasting. Forecasters assume the relationships between indicators stay the same and test the consistency and strength of the relationship between datasets.
- Time-series methods : Time-series methods use historical data to predict future outcomes. By tracking what happened in the past, forecasters expect to get a near-accurate view of the future.
Qualitative business forecasting is predictions and projections based on experts' and customers' opinions. This method is best when there is insufficient past data to analyze to reach a quantitative forecast. In these cases, industry experts and forecasters piece together available data to make qualitative predictions.
Qualitative models are most successful with short-term projections. They are expert-driven, bringing up contrasting opinions and reliance on judgment over calculable data. Examples of qualitative models in business forecasting include:
- Market research : This involves polling people – experts, customers, employees – to get their preferences, opinions, and feedback on a product or service.
- Delphi method : The Delphi method relies on asking a panel of experts for their opinions and recommendations and compiling them into a forecast.
How do you choose the right business forecasting technique?
- Choosing the right business forecasting technique depends on many factors. Some of these are:
- Context of the forecast
- Availability and relevance of past data
- Degree of accuracy required
- Allocated time to conduct the forecast
- Period to be forecast
- Costs and benefits of the forecast
- Stage of the product or business needing the forecast
Managers and forecasters must consider the stage of the product or business as this influences the availability of data and how you establish relationships between variables. A new startup with no previous revenue data would be unable to use quantitative methods in its forecast.
The more you understand the use, capabilities, and impact of different forecasting techniques, the more likely you will succeed in business forecasting.
Why is business forecasting important?
Any insight into the future puts your organization at an advantage. Forecasting helps you predict potential issues, make better decisions, and measure the impact of those decisions.
By combining quantitative and qualitative techniques, statistical and econometric models , and objectivity, forecasting becomes a formidable tool for your company.
Business forecasting helps managers develop the best strategies for current and future trends and events. Today, artificial intelligence, forecasting software, and big data make business forecasting easier, more accurate, and personalized to each organization.
Forecasting does not promise an accurate picture of the future or how your business will evolve, but it points in a direction informed by data, logic, and experiential reasoning.
What are the integral elements of business forecasting?
While there are different forecasting techniques and methods, all forecasts follow the same process on a conceptual level. Standard elements of business forecasting include:
- Prepare the stage : Before you begin, develop a system to investigate the current state of business.
- Choose a data point : An example for any business could be "What is our sales projection for next quarter?"
- Choose indicators and data sets : Identify the relevant indicators and data sets you need and decide how to collect the data.
- Make initial assumptions : To kickstart the forecasting process, forecasters may make some assumptions to measure against variables and indicators.
- Select forecasting technique : Pick the technique that fits your forecast best.
- Analyze data : Analyze available data using your selected forecasting technique.
- Estimate forecasts : Estimate future conditions based on data you've gathered to reach data-backed estimates.
- Verify forecasts : Compare your forecast to the eventual results. This helps you identify any problems, tweak errant variables, correct deviations, and continue to improve your forecasting technique.
- Review forecasting process : Review any deviations between your forecasts and actual performance data.
How do you do business forecasting?
Successful business forecasting begins with a collaboration between the manager and forecaster. They work together to answer the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the forecast? How will it be used?
- What are the components and dynamics of the system the forecast is focused on?
- How relevant is past data in estimating the future?
Once these answers are clear, choose the best forecasting methods based on the stage of the product or business life cycle, availability of past data, and skills of the forecasters and managers leading the project.
With the right forecasting method, you can develop your process using the integral elements of business forecasting mentioned above.
How do you get data for business forecasting?
A forecast is only as good as the data supplied. Before collecting data, ask:
- Why do you need it?
- What kind of data do you need?
- When will you collect it?
- Where will you gather it?
- Who is in charge of collecting it?
- How will you collect it?
- How will you analyze it?
When you have these answers, you can start collecting data from two main sources:
- Primary sources : These sources are gathered first-hand using reporting tools — you or members of your team source data through interviews, surveys, research, or observations.
- Secondary sources : Secondary sources are second-hand information or data that others have collected. Examples include government reports, publications, financial statements, competitors' annual reports, journals, and other periodicals.
Business forecasting examples
Some forecasting examples for business include:
- Calculating cash flow forecasts, i.e., predicting your financial needs within a timeframe
- Estimating the threat of new entrants into your market
- Measuring the opportunity of developing a new product or service
- Estimating the costs of recurring bills
- Predicting future sales growth based on past sales performance
- Analyzing relationships between variables, e.g., Facebook ads and potential revenue
- Budgeting contingencies and efficient allocation of resources
- Comparing customer acquisition costs and customer lifetime value over time
What are the limits of business forecasting?
You can follow the rules, use the right methods, and still get your business forecast wrong. It is, after all, an attempt to predict the future. Some limits to business forecasting include:
- Biases and errors by the forecasters or managers
- Incorrect information from employees, experts, or customers
- Inaccurate past numbers
- Sudden change in market conditions
- New industry regulations
How Wrike helps with business forecasting
The more accurate your business forecasting, the more effective your strategies and plans can be. While many things in business are out of your control, having an informed forecast of what lies ahead makes you prepared and confident about the future.
Wrike helps gather data in one central platform, extract insights, and communicate findings with forecasters and managers. Other benefits of Wrike include real-time data, integrations with other forecasting software, streamlined collaboration, and visibility into every business forecasting project.
Are you ready to make projections for your business, allocate your resources for the best results, and improve your business forecasting process? Get started with a two-week free trial of Wrike today.
Kelechi Udoagwu
Kelechi is a freelance writer and founder of Week of Saturdays, a platform for digital freelancers and remote workers living in Africa.
Related articles

Strengthen and Optimize Agency Resource Management
Improve your agency’s resource management processes and learn how Wrike boosts performance across the board with our robust project management software.

Release Management: Definition, Phases, and Benefits
What is release management and how can it improve software development strategy? In this guide, we talk about release management processes and their benefits.

The Definitive Guide to Data-Driven Marketing
Wondering what data-driven marketing is and how to reap its benefits for your business? Find out how to create your own data-driven strategy with our guide.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.

- Group Training
- Individual Training

- Individual Certification
- Corporate Certification
- Companies Certified
- Testimonial
- Companies w/ Certification
- Levels of Certification
- Certification Details
- Sample Exams
- Recertification
- Preparation Materials
- Exam Schedule
- CPF Prep/Review

- Research Reports
- Virtual Conference Recordings

- Cancellation Policy
- Refund Policy for Events
- Ambassador Program
- Member Companies
- Partnership
- Apply to Speak
- Subscription
- S&OP Self-Assessment
- Sponsored Content
- Become a Sponsor
- Exhibit at IBF Events

What Is Business Forecasting?
What exactly is business forecasting? To help answer this question, consider this. Whether you realize it or not, virtually every business decision and process is based on a forecast. Anything you plan is generally based on an assumption of something happening in the future which, by definition, is a forecast. Not all forecasts are derived from sophisticated methods, but an educated guess about the future is more valuable for the purposes of planning than no forecast at all.
It does not matter which industry you are in, whether your company manufactures products or offers services, or whether your company is small or large, you must have forecasts to plan effectively. Of course, the more accurate the forecasts, the better the plan. It stands to reason that if we know what happened in the past and why, or have insight into what may occur next, we can then predict what is likely to happen in the future. With this information, we can potentially alter the future to the company’s advantage.
Business Forecasting Drives Better Decision Making
Business Forecasting is the process of using analytics, data, insights, and experience to make predictions and respond to various business needs. The insight gained by Business Forecasting enables companies to automate and optimize their business processes. A Forecaster’s goal is to go beyond knowing what has happened and provide the best assessment of what will happen in the future to drive better decision making.
Many people think of a Business Forecast as how many of something we will sell next week. That is part of it, but Business Forecasting can encompass anything that identifies the likelihood of a future outcome, provides comparative information using analytics, or drives data-driven business decisions.
What Is Business Forecasting Used For?
Business Forecasting can be used for:
- Strategic planning and decision-making (long-term planning)
- Finance and accounting (budgets and cost controls)
- Marketing (consumer behavior, life cycle management, pricing)
- Operations and supply chain (resource planning, production, logistics, inventory)
Business Forecasting Techniques
At the heart of business process decision making is the forecast, which involves techniques including:
- Qualitative Forecasting : Refers to the use of opinion or educated guesses in developing forecasts.
- Quantitative Forecasting : Used to develop a future forecast using past data and, often, statistical or mathematical models.
These techniques, along with analyzing data and the use of statistical algorithms, can also be the foundation and input into a Demand Plan. For some companies, the forecast may be considered the Baseline Demand Forecast and is more statistically driven, and is a critical part of Demand Planning.

Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
What Business Forecasting Is and Why It Matters
As a business leader, you already understand that every decision you make impacts the overall success of the company. With this much at stake, it’s imperative that you make decisions with the most up-to-date facts and data possible. This step can be difficult when it comes to predicting future business statistics, such as sales data, inventory control, and budgetary figures. To help with this issue, many companies rely on business forecasting to make future projections based on high-level assumptions and historical data.
It’s crucial for your company to understand what business or demand forecasting is, why it matters and what methods to use to make these projections. This article defines these terms and delves into the types of forecast models you can use to learn more about your business and predict future trends.
“Business forecasting” is a part of our Project Management Glossary — check out the full list of terms and definitions!
What is business forecasting?
Business forecasting is a common practice companies of all sizes use frequently.
Business forecasting is the process of collecting and analyzing historical company data as well as marketing insights and trends to make projections regarding future business outcomes.
While the practice of business forecasting has been around for centuries, the combination of big data and advanced technologies, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, makes today’s predictions more accurate than ever before. Business leaders use this planning technique to predict everything from financial outcomes to future sales numbers. It’s important to note that there are numerous business forecasting methods you can use depending on the type of projections you need.
Types of business forecast methods
Business forecast methods typically fit into two primary categories: qualitative and quantitative.
Qualitative forecasting relies heavily on expert opinions and high-level assumptions. It’s an ideal planning tool for companies with less than three years of historic internal data or for when you’re forecasting during times of significant disruptions in the market. Quantitative forecasting, on the other hand, relies primarily on facts and numbers. These methods analyze current and past data to predict future outcomes.
Within these two categories, there are numerous types of business forecasting methods. Here’s a look at the top four.
- Delphi method : The Delphi method is a qualitative type of business forecasting that relies on expert opinions. Generally, project managers poll a panel of industry and field experts regarding relevant information, such as market trends and insights. Managers then compile and analyze this information to deliver data-driven forecasting results.
- Market research : The market research method involves polling users regarding specific products or features. This qualitative approach allows teams to obtain a general consensus as to the success or failures of these products and to determine future sales projections.
- Time-series method : The time-series method is a quantitative approach that relies heavily on the company’s past data points. This method uses the company’s historical data and advanced technology to analyze information and build models and other visuals that predict future outcomes.
- Econometric modeling : Econometric models use a mathematical approach that evaluates the company’s current and previous data to make strong projections regarding the company’s future. As a quantitative approach, it uses statistical analysis to predict future outcomes.
How to you know which of the forecasting techniques to use? It depends on several factors, including:
- Scope : The size of the project may limit the effectiveness of some forecasting methods. For example, the market research method may be difficult to complete for larger projects with many different steps and stages. In these cases, a quantitative approach, such as the time-series method may work better.
- Years in business : If your business is relatively new, a quantitative approach may not be possible. Typically, these methods require at least three years of hard data to deliver accurate results.
- Forecasting goals : The type of forecasting goals also determines the type of method you want to use. For instance, if you’re trying to identify shifts in the market, taking a quantitative approach that utilizes historical company data may not provide the results you need.
No matter which forecasting method you utilize, it plays a vital role in the project management process.
The role of business forecasting in project management
Accurate forecasting can help project managers set realistic goals and objectives, predict future outcomes, and conduct accurate risk assessments. These projections can help increase the project’s overall success and allow the team to meet tight deadlines.
Fortunately, advanced technology can help project managers track and manage company data to make business forecasting quick, easy, and effective. For example, monday.com allows project managers to store and view company data in one easy-to-use software. Our platform integrates with popular business platforms , such as Salesforce, Excel, Stripe, Zapier, and DropBox, which makes it easy to track business data, such as sales reports and financial information.
With the help of these digital tools, your company can reap the many benefits of business forecasting in project management.
Benefits of business forecasting in project management
Business forecasting offers organizations a variety of benefits, including those summarized below.
Gain valuable insights
Forecasting gives business leaders insights regarding the anticipated success of the company. While forecasting is not always 100% accurate, it does provide enough information to help companies with everything from managing cash flow to predicting inventory needs and setting realistic goals.
Make improvements
The business forecasting method, especially quantitative approaches, provides insights into the company’s past performance as well as future predictions. This visual representation can help your company identify problem areas, learn from past mistakes, and improve business operations.
Identify market shifts
Given today’s fast-paced market, it’s crucial for businesses to prepare for future changes. Forecasting — especially via qualitative methods — can help you understand future trends in the market, upcoming supply chain challenges, and changes in customer expectations. Having this knowledge in hand can help your organization prepare for the future and minimize the impact of any changes or shifts in the market.
Increase profits
The business forecasting process can improve your company’s long-term profitability in several ways:
- It allows your business leaders to develop budgets based on data-driven sales predictions .
- Accurate forecasting can help your organization secure the funding necessary to grow the business.
- Forecasting can help your company reduce waste by projecting shifts in the market.
The easiest way to understand the many benefits of business forecasting is to see this practice in action.
A few business forecasting examples and what they could mean for your team
To better understand how business forecasting can help your company prepare for the future, here’s a look at some forecasting examples and what they could mean for your team.
Sales forecasting
Suppose a shoe store wants to project next year’s sales numbers. Since this store has been in business for over five years, the time-series forecasting method is a good option. This method allows the business owner to use collected data to predict the future of the company. However, due to today’s fluctuating market, the shoe store owner may also want to take a qualitative approach, such as the Delphi method, to determine if any shifts in the market could impact future sales.
This forecasting data can help the shoe store owner with everything from planning next year’s budget to managing inventory to determining how many workers to hire.
Forecasting the success of a new product or service
Let’s look at a fashion design company that’s preparing for a new product launch. Knowing how much product to have on hand is crucial to the success of this launch. Too much inventory can impact profits, yet not enough inventory can affect customer satisfaction. In this case, the company can use market research to poll a number of potential customers to determine the likelihood of them making a purchase or referring this new product to others.
This forecasting data can help the company project future sales, set an appropriate price point, and have enough inventory in place to meet demand.
Frequently asked questions
What is forecasting in business.
Business forecasting is the process of analyzing big data, market insights, and expert opinions to make projections regarding future business outcomes. Business leaders use forecasting to set budgets, determine product offerings, oversee supply chain management, and manage projects.
How does forecasting help a business?
Forecasting is a critical tool for businesses of all sizes. While business planning is not 100% accurate every time, it does provide business leaders with data-driven insights. Leaders then use these insights to make informed decisions for the company, such as which products to sell, how many workers it needs, and how much inventory to secure.
What are the four basic forecasting methods?
There are dozens of business forecasting methods available, most of which are broken down into two categories, including qualitative and quantitative. The most popular qualitative methods are market research, which polls a panel of users to predict future outcomes, and the Delphi method, which involves gathering insights from industry experts. The most popular quantitative methods include the time-series method, which analyzes current and historical data to predict future outcomes, and econometric modeling, which uses mathematical models and statistical methods of analysis to make future projections.
Prepare for your company’s future with business forecasting
Don’t risk moving your company into the future without first understanding what to expect. Blindly leading your company into the upcoming weeks, months, and years can significantly impact the success of your business. Instead, rely on effective business forecasting techniques to help you project future outcomes, prepare for upcoming shifts and mitigate any possible risks.
monday.com’s seamless Work OS lets you gather data, work as a team to analyze it, and set goals and timelines so you can act on what you learn during forecasting.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.
What Is Business Forecasting? Predictions to Drive Success
November 29, 2021
by Alexandra Vazquez

In this post
Types of business forecasts, business forecasting methods, benefits of business forecasting, business forecasting challenges, business forecasting vs. scenario planning, business forecasting process, business forecasting examples.
It’s time to look inside your crystal ball and start forecasting. Forecasting gives you the tools you need to make reliable predictions about foreseeable events.
What is business forecasting?
Business forecasting is the process of analyzing data to predict future company needs and make insight-driven development decisions.
There’s really no downside to being prepared! Building a strong forecast prepares businesses for potential issues and identifies areas for profitable growth. Even if your predictions end up being inaccurate, you’ll have all the necessary data and information to get closer to the final forecast.
Some companies utilize predictive analytics software to collect and analyze the data necessary to make an accurate business forecast. Predictive analytics solutions give you the tools to store data, organize information into comprehensive datasets, develop predictive models to forecast business opportunities, adapt datasets to data changes, and allow import/export from other data channels.
Businesses can create various types of forecasts with business forecasting strategies. Because historical data and market trends affect so many aspects of business, comprehensive predictions can help prepare almost every element of your company.
- General business forecasting predicts overall market trends and external factors that affect your business’ success.
- Accounting forecasting creates projections of future business costs .
- Budget forecasting makes predictions for allocating the budget needed for future projects or addressing potential issues. Budgeting and forecasting software is an indispensable tool if you’re looking to forecast for budgeting your business activities.
- Financial forecasting projects a company’s monetary value as a whole. You can use the current assets and liabilities from your balance sheet to help you make a prediction.
- Demand forecasting predicts the future needs of your target customer base.
- Supply forecasting works with demand forecasting to allocate the necessary resources for fulfilling upcoming customer demands.
- Sales forecasting predicts the expected success of the company offerings and how it’ll affect future sales and cash flow.
- Capital forecasting makes predictions about a company’s future assets and liabilities.
There are two main types of business forecasting methods: quantitative and qualitative. While both have unique approaches, they’re similar in their goals and the information used to make predictions – company data and market knowledge.
Quantitative forecasting
The quantitative forecasting method relies on historical data to predict future needs and trends. The data can be from your own company, market activity, or both. It focuses on cold, hard numbers that can show clear courses of change and action. This method is beneficial for companies that have an extensive amount of data at their disposal.
There are four quantitative forecasting methods:
- Trend series method: Also referred to as time series analysis, this is the most common forecasting method. Trend series collects as much historical data as possible to identify common shifts over time. This method is useful if your company has a lot of past data that already shows reliable trends.
- The average approach: This method is also based on repetitive trends. The average approach assumes that the average of past metrics will predict future events. Companies most commonly use the average approach for inventory forecasting.
- Indicator approach: This approach follows different sets of indicator data that help predict potential influences on the general economic conditions, specific target markets, and supply chain. Some examples of indicators include changes in Gross Domestic Product (GDP), unemployment rate, and Consumer Price Index (CPI). By monitoring the applicable indicators, companies can easily predict how these changes may affect their own business needs and profitability by observing how they interact with each other. This approach would be the most effective for companies whose sales are heavily affected by specific economic factors.
- Econometric modeling: This method takes a mathematical approach using regression analysis to measure the consistency in company data over time. Regression analysis uses statistical equations to predict how variables of interest interact and affect a company. The data used in this analysis can be internal datasets or external factors that can affect a business, such as market trends, weather, GDP growth, political changes, and more. Econometric modeling observes the consistency in those datasets and factors to identify the potential for repeat scenarios in the future.
Qualitative forecasting
The qualitative forecasting method relies on the input of those who influence your company’s success. This includes your target customer base and even your leadership team. This method is beneficial for companies that don’t have enough complex data to conduct a quantitative forecast.
There are two approaches to qualitative forecasting:
- Market research: The process of collecting data points through direct correspondence with the market community. This includes conducting surveys, polls, and focus groups to gather real-time feedback and opinions from the target market. Market research looks at competitors to see how they adjust to market fluctuations and adapt to changing supply and demand . Companies commonly utilize market research to forecast expected sales for new product launches.
- Delphi method: This method collects forecasting data from company professionals. The company’s foreseeable needs are presented to a panel of experts, who then work together to forecast the expectations and business decisions that can be made with the derived insights. This method is used to create long-term business predictions and can also be applied to sales forecasts.
There are several benefits to making effective forecasts for your business. You gain valuable insights into its different aspects and the future of its success.
- Foresee upcoming changes with a heads up on potential market changes that can affect your business. With the right prediction, you can strategize the decisions to succeed in the face of the challenges ahead before they become costly surprises.
- Decrease the cost of unexpected demand by preparing ahead of time. Business forecasting is a great starting point for demand planning . If you plan to incorporate demand forecasting into your business processes, you’ll be prepared for upcoming market demands and avoid the extra costs associated with an influx of demand that you weren’t ready for.
- Increase customer satisfaction by giving them what they want, when they want it. Demand planning doesn’t just benefit you. With the right business forecast, your company can offer products or services to the target industry and meet their expectations. A company ready to serve its market is always met with customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Set long- and short-term goals by tracking your progress. Business forecasting tools help you outline your future company objectives. Continuous predictions allow you to track the progress of your proposed goals as those future expectations become the present reality.
- Learn from the past by analyzing it. Forecasting enables you to collect and study extensive historical company data. Keeping a close eye on this data can help you identify where things may have gone wrong in the past. With this new information, your company can make the necessary adjustments to avoid similar mistakes in the future.
While the benefits of business forecasting highlight all of the amazing advantages it has to offer, it’s not a surefire way to prepare for the future. Companies who plan to forecast should also keep the challenges in mind and make sure that forecasting has more pros than cons for their business. Below are some of the notable challenges of business forecasting.
- You can’t always expect the unexpected. While old data can help you gain insights into company processes and learn from mistakes, history doesn’t always repeat itself. Business forecasting isn’t a perfect process, and although helpful, it may not precisely predict future trends or business matters using old company data alone. It operates on the assumption that what happened will most likely happen again. Unfortunately, this is not always the case, and the hard work put into preparing for a forecasted event may never come to fruition.
- It takes time to create an accurate forecast. Forecasting can be a lengthy process when started from scratch. Some companies find it challenging to gather the resources needed to begin predicting and allocate the time to do it correctly.
- Historical data will always be outdated. There’s no way to know what’ll happen next. Although historical information is very valuable, it’s forever considered “old”. Forecasts are never based on the present and, therefore, are only as accurate as the data you already collected.
Business forecasting is often confused with scenario planning because of their shared goal of preparing for the future. Both rely on learning from past mistakes and reflecting on what decisions must be made to drive success. However, business forecasting and scenario planning differ in the preparation process.
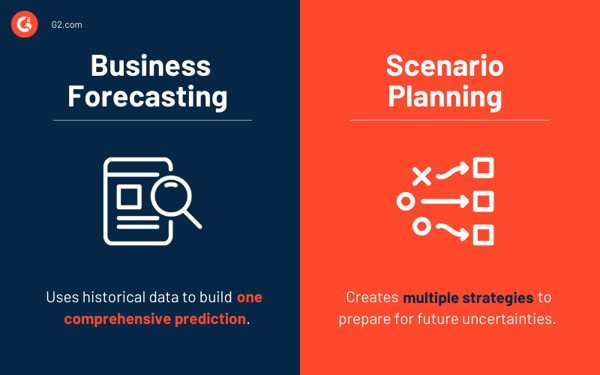
Business forecasting focuses on a problem at hand and uses historical data to predict what might happen next. It emphasizes predictive analytics and the need to eliminate existing uncertainties. The problem can be as broad as the actual performance of the entire company, or as specific as how a single product might sell in the future based on past market trends.
While built on tangible data, forecasting is essentially a guess of the future and you need to make assumptions ahead of time to prepare for any predicted issues. Forecasting is an all-hands-on-deck approach that involves many departments, including analysts, economists, managers, and more.
Scenario planning creates multiple scenarios to help prepare for the future. With these scenarios in mind, a company can begin planning a course of action to achieve the desired outcome. This includes creating step-by-step strategies and timelines for achieving objectives.
While business forecasting focuses on past information, scenario planning takes the past, present, and future into consideration with learnings from the past, understanding the capabilities of the present, and aspiring for future success. Although a team’s input is important in scenario planning, company’s primary decision-makers carry out the bulk of the process.
The way a company forecasts is always unique to its needs and resources, but the primary forecasting process can be summed up in five steps. These steps outline how business forecasting starts with a problem and ends with not only a solution but valuable learnings.
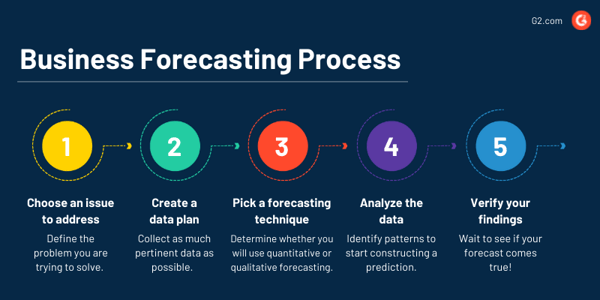
1. Choose an issue to address
The first step in predicting the future is choosing the problem you’re trying to solve or the question you’re trying to answer. This can be as simple as determining whether your audience will be interested in a new product your company is developing. Because this step doesn’t yet involve any data, it relies on internal considerations and decisions to define the problem at hand.
2. Create a data plan
The next step in forecasting is to collect as much data as possible and decide how to use it. This may require digging up some extensive historical company data and examining the past and present market trends. Suppose your company is trying to launch a new product. In this case, the gathered data can be a culmination of the performance of your previous product and the current performance of similar competing products in the target market.
3. Pick a forecasting technique
After collecting the necessary data, it’s time to choose a business forecasting technique that works with the available resources and the type of prediction. All the forecasting models are effective and get you on the right track, but one may be more favorable than others in creating a unique, comprehensive forecast.
For example, if you have extensive data on hand, quantitative forecasting is ideal for interpretation. Qualitative forecasting is best if you have less hard data available and are willing to invest in extensive market research.
4. Analyze the data
Once the ball starts rolling, you can begin identifying patterns in the past and predict the probability of their repetition. This information will help your company’s decision-makers determine what to do beforehand to prepare for the predicted scenarios.
5. Verify your findings
The end of business forecasting is simple. You wait to see if what you predicted actually happens. This step is especially important in determining not only the success of your forecast but also the effectiveness of the entire process. Having done some forecasting, you can compare the present experience with these forecasts to identify potential areas for growth.
When in doubt, never throw away “old” data. The final information of one forecasting process can also be used as the past data for another forecast. It’s like a life cycle of business development predictions.
With the different types of business forecasting come different potential use cases. A company may choose to utilize several elements of business forecasting to prepare for various situations. Here are some real-life examples where business forecasting would be valuable.
The seasoned veteran
Suppose you represent a company that has been in the market for a long time but has never tried business forecasting. Because of the long history of company data, you choose to try out quantitative business forecasting. Your aim is to make predictions using the most cost-effective and least time-consuming method. With those considerations, you may opt for the trend series method to manually identify common trends in old data, determine the likelihood of repeat instances, and forecast accordingly.
The new kid on the block
Imagine you are a new company that has entered the market to start selling your own brand of smartphones. You may think that business forecasting is impossible because you don’t have any historical company data to work off of. However, you can utilize qualitative business forecasting! Because the smartphone industry is a highly competitive one, you can use market research to take advantage of publicly available market data.
The one who wants the best of both worlds
Imagine you work for a recruiting company that has noticed that the country’s unemployment rate heavily affects company performance and has the data to prove it. As you have a clear indicator that directly impacts the potential for success, using the indicator approach to create long-term predictions would be the right call.
However, your company stresses the importance of integrating expert knowledge into the forecasting process. This extra note means that some qualitative forecasting can be used as well. You may choose to use the Delphi method to collect expert opinions and weigh that into the final forecasts as well.
What do the stars have in store for you?
Creating comprehensive predictions isn’t rocket science. With business forecasting, seeing the future is as easy as learning from the past. What you do with your findings is what will set you apart.
Want to start forecasting for your business? Learn more about business analytics and how it helps collect the necessary data and insights.

The future starts now
Automate business forecasting data analysis with predictive analytics software.

Alexandra Vazquez is a Senior Content Marketing Specialist at G2. She received her Business Administration degree from Florida International University and is a published playwright. Alexandra's expertise lies in writing for the Supply Chain and Commerce personas, with articles focusing on topics such as demand planning, inventory management, consumer behavior, and business forecasting. In her spare time, she enjoys collecting board games, playing karaoke, and watching trashy reality TV.
Recommended Articles

Contributor Network
A Guide to Choosing the Right Platform For Digital Business Cards
When was the last time you attended a business event and returned empty-handed? It's hard to...
by Mayuri Bangar

AI for Business Texting: Enhance Your Communication Strategy
AI's transformative impact has grown across all aspects of our lives. From anticipating retail...
by Jennifer Adler

5 Impactful Sustainable Business Practices
Sustainability is no longer a choice; it's a necessity.
by Lee Shields
Never miss a post.
Subscribe to keep your fingers on the tech pulse.
By submitting this form, you are agreeing to receive marketing communications from G2.
How Business Forecasting Works and Why You Should Use It

As you grow your small business, you need to plan and develop your long-term strategy. Well-run companies don’t just address things as they come up, they plan ahead. As a small business owner, it’s important to keep sight of the bigger picture through business forecasting.
With business forecasting, companies use different methods and data to predict market trends to help determine their short-term and long-term business outlook. This data is a vital part of helping companies grow, start new initiatives, and plan their finances for the quarter and year. It can also help you plan for potential seasonal dips in your cash flow or plan for future expansions.
Keep reading to find out more about the different types of and elements that make up business forecasting as well as why every small business should consider using forecasting methods.
What Is Business Forecasting?
Business forecasting is making informed predictions about business metrics. That can include specific aspects of a business, such as launching a new product, or cover the company as a whole. Often, financial, operational, and business decisions will be based on these forecasting techniques.
While no one can predict the future, business forecasting methods can help even small businesses develop strategies. With business forecasting, historical data is collected and analyzed to find potential patterns. Today, most forecasting includes some form of technology, such as artificial intelligence, to help develop models.
Why Should You Use Business Forecasting?
Business forecasts can be used for budgeting, expanding your business , figuring out where to allocate funding, making decisions about cash flow, and helping create timelines for business operations, such as new initiatives. It helps companies make decisions based on data rather than on intuition and opinion.
For example, forecasting can be used to figure out how much pressure competition will put on your business, measure the demand for a product, help allocate resources, and forecast earnings.
Small business owners can use business forecasting to identify weaknesses in their long-term plans, come up with a plan of action for the future growth of the company, and adapt to changes in the economy.
Types of Business Forecasting
There are a few methods to conduct business forecasting and planning. Most are either qualitative (which uses non-numerical data such as market reports and surveys) or quantitative (meaning they use mathematical and statistical modeling).
Qualitative Models
Qualitative forecasting models are usually used for short-term forecasting. They tend to rely more on opinions and trends rather than measurable data. This type of analysis is more expert-driven but can be limited to longer-term projections.
Some of the common qualitative models for business forecasting include:
Market research: Market research is a business forecasting technique that uses polling and surveying large numbers of prospective customers to collect information. This might be on the specific brand or product or about the company as a whole. Market research can be used to predict if customers will buy more or less of a specific product in the foreseeable future.
Delphi method: With the delphi method of analysis, experts are polled about specific topics. This usually includes a panel where the experts are presented with a questionnaire in a few rounds. After each round, the experts can adjust their responses based on the aggregate answers of all respondents. The opinions are then compiled to help forecast future trends.
Quantitative Models
Quantitative methods use hard data and avoid opinions or polls from people. Instead, these techniques focus solely on numbers. Quantitative models are used to predict long-term trends and variables, such as sales forecasts.
Some of the most common quantitative forecasting include:
Time series methods: This forecasting model, also called a time series analysis, uses past data points to predict the future, excluding deviations. It’s also the most common method used by companies. To use a time series method though, you need to have access to a lot of historical data that shows clear and stable trends, otherwise, your forecasting models will be inaccurate.
Indicator approach: This methodology uses the relations between different types of indicators — for example, looking at gross domestic product and the unemployment rate. It will look at the performance of the lagging indicators to try to measure the impact of business strategies.
Econometric modeling: With econometric modeling, you make several mathematical equations to test the consistency of datasets over time and measure the relationship between the different sets of data. This method is very math-heavy and can be used to predict changes in the economy and market conditions and the potential impact those changes could have on a company.
5 Steps of Business Forecasting
To get accurate forecasts in your business forecasting, you need to make sure the information you get is accurate. While each method uses different strategies, they generally each follow the same steps:
Identify your question or problem: First, you need to figure out what it is you want to know. What problem in your business are you trying to solve? For example, you might want to know if you can meet demand next quarter or calculate how much of a product you will sell over the year.
Gather data: Next, you need to figure out the data you have available to you. That can be anything from sales data, how long it takes you to produce products, demand forecasts, customer satisfaction forms, and more.
Choose your forecasting method: Once you have your data, you can decide which type of business forecasting analysis you want to use. The type of method you will choose will depend on what it is you’re trying to find out.
Make an estimate: Using the forecasting method chosen, you can start to make business predictions. This can help you estimate future business performance. Keep in mind that your forecasts are only as good as your data, so make sure you have the most accurate, updated data points.
Figure out any discrepancies: Look back at your predictions to determine if they were accurate. Keep track of your findings to help improve your forecasting models in the future. You can also consider using third-party business forecasting models and data to help create business predictions.
Grow Your Company With Accurate and Reliable Data
Business forecasting can help companies with their business planning and decision-making. Forecasting models help predict future trends and assist you in figuring out your operations and budgeting forecasts for the next year.
While there’s no crystal ball that can tell you exactly what will happen in the future, forecasting is the closest you can get to understanding the future. Of course, the more data you have, the easier it is to make accurate business forecasts.
If your financial models show that you might have a dip in your cash flow, make sure to plan ahead. With Backd, you can get access to a working capital advance of up to $2 million that can be used to bridge a seasonality gap or invest in equipment to expand your business.
You can also get a business line of credit so you have access to funds whenever you need them. Plus, you can apply in just minutes and your credit score won’t be affected.
Apply today and find out if you qualify in just 24 hours.
What would you do with the right amount of capital?
Working capital advance.
Easy payment structures offer amounts with fast turnaround, Simple and easy process to access working capital.
- Flexible - no collateral required
- Terms up to 16 months
- Automatic daily or weekly, or semi-monthly payments
Learn more...
Business Line of Credit
Get instant access to revolving credit with unlimited terms, and the best rates for your business.
- Draw funds anytime
- $10K - $750K
- Unlimited terms, incredible rates
- Soft credit pull that doesn't affect your credit score
More Articles
Working capital.
What is working capital? How do you ensure you’ve got the right amount? What do you do if you need an influx of it, fast?
Working Capital Ratio
Working capital ratios are delicate things. How do you determine the sweet spot for your business?
Working Capital Management
A breakdown of the components of working capital and the approaches to working capital management, as well as short-term business funding.
Working Capital Financing: What Are the Different Options?
Working capital financing helps you keep your business running when you need to cover a cash flow gap. Discover the funding available to you and how to choose.

1949 S I-35 Frontage Rd Austin, Texas 78741, USA
What is Business Forecasting? Definition, Methods, and Models
Gagan Singh July 10, 2023
- Business Forecasting
Business forecasting is a crucial aspect of strategic planning for organizations across various industries. It involves using historical data, market trends, and statistical techniques to predict future business outcomes. These forecasts help businesses make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and anticipate potential risks and opportunities. In this blog post, we will explore the definition, methods, and models used in business forecasting, highlighting the significance of accurate predictions for business success. Additionally, we will introduce WOWS Advisory Service' s expertise in business forecasting and the value they provide to organizations.
Definition of Business Forecasting
Business forecasting can be defined as the process of estimating future business conditions and outcomes based on historical data and analysis. It involves predicting metrics such as sales, revenue, market demand, customer behavior, and financial performance. Business forecasts can span different time horizons, from short-term forecasts covering the next few weeks or months to long-term forecasts that project years ahead. The goal is to minimize uncertainty, improve decision-making, and facilitate strategic planning.
Methods of Business Forecasting
- Qualitative Methods:
Qualitative forecasting methods rely on expert opinions, market research, and subjective judgment to predict future outcomes. These methods are commonly used when historical data is limited or unreliable. Examples of qualitative methods include market surveys, Delphi technique (collecting opinions from a panel of experts), and scenario analysis (assessing potential outcomes under different scenarios).
- Quantitative Methods:
Quantitative forecasting methods employ statistical models and historical data to generate predictions. These methods are widely used when sufficient historical data is available. Key quantitative methods include time series analysis, regression analysis, moving averages, exponential smoothing, and econometric modeling.
Time series analysis involves analyzing historical data to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. Various techniques, such as moving averages and exponential smoothing, help smooth out random fluctuations and highlight underlying trends. Regression analysis examines the relationship between a dependent variable and independent variables to predict future outcomes. Econometric modeling utilizes mathematical equations and statistical techniques to simulate complex economic systems and forecast variables based on economic theories.
- Judgmental Methods:
Judgmental forecasting methods combine qualitative and quantitative inputs, incorporating expert opinions and statistical models. This approach leverages the strengths of both methods to enhance forecast accuracy. Examples of judgmental methods include sales force composite, which aggregates salespeople's estimates, and market research surveys that combine statistical analysis with subjective insights.
Business Forecasting Models
- Time Series Models:
Time series models are based on the assumption that future patterns and trends can be derived from historical data. Common time series models include moving averages, exponential smoothing, and autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA). These models are suitable for forecasting metrics that exhibit patterns over time, such as sales, customer demand, and stock prices.
- Regression Models:
Regression models establish relationships between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. They are useful when forecasting outcomes influenced by various factors. For instance, a regression model could predict sales based on factors like advertising expenditure, product price, and market size. Multiple regression, logistic regression, and polynomial regression are examples of regression models used in business forecasting.
- Econometric Models:
Econometric models are employed when forecasting variables affected by economic factors, such as GDP, inflation, and interest rates. These models integrate economic theory with statistical techniques to predict outcomes in complex economic systems. Econometric models often require extensive historical data and expertise in economic analysis.
WOWS Global: Your Business Forecasting Partner
When it comes to accurate business forecasting, WOWS Global is a trusted partner. Our comprehensive suite of services includes a rolling 12-month forecast, budget vs. actual analysis, cash flow planning, and runway assessment. With our expertise, WOWS Advisory Services offers clients a less than one-week turnaround, ensuring timely and reliable forecasts.
- Rolling 12-Month Forecast:
We provide organizations with a rolling 12-month forecast, allowing businesses to anticipate and plan for future conditions. This forecast takes into account historical data, market trends, and industry insights to project key metrics, such as sales, revenue, and expenses. By providing a forward-looking view, businesses can make strategic decisions and allocate resources effectively.
- Budget vs. Actual Analysis:
To assess the accuracy and effectiveness of financial plans, WOWS Global conducts a budget vs. actual analysis. By comparing projected figures with actual performance, organizations can identify variances and understand the reasons behind them. This analysis provides valuable insights into areas of improvement, helps optimize resource allocation, and informs future forecasting processes.
- Cash Flow Planning and Runway Assessment:
Cash flow is crucial for the financial health and sustainability of a business. WOWS Global assists organizations in planning their cash flow by forecasting cash inflows and outflows. By accurately predicting future cash positions, businesses can manage liquidity effectively, avoid cash shortages, and plan for growth initiatives. Additionally, we perform runway assessments to determine the time frame within which a business can operate based on its cash reserves and projected cash flow.
- Less Than One-Week Turnaround:
We understand the importance of timely and up-to-date forecasts. With our commitment to providing forecasts within a week, organizations can rely on our expertise for quick decision-making. The efficient turnaround time ensures that businesses can adapt to market changes promptly, seize opportunities, and mitigate potential risks.
Business forecasting is a vital tool for organizations seeking to navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain business landscape. It involves utilizing historical data, market trends, and statistical techniques to predict future outcomes and make informed decisions. Qualitative, quantitative, and judgmental methods, along with various models such as time series, regression, and econometric models, are employed to generate accurate forecasts.
In this context, WOWS Advisory Service offers expert assistance in business forecasting, delivering a rolling 12-month forecast, budget vs. actual analysis, cash flow planning, and runway assessment. Our commitment to providing forecasts with a quick turnaround time enables businesses to stay agile and make data-driven decisions.
For more details and to leverage WOWS Advisory Service's expertise in business forecasting, you can contact them at [email protected] . By partnering with WOWS Global , organizations can enhance their forecasting capabilities, optimize resource allocation, and gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic business environment.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Business Forecasting: Why You Need It & How to Do It

Table of Contents
What is business forecasting, the importance of business forecasting, business forecasting process, business forecasting methods, elements of business forecasting, sources of data for forecasting, business forecasting only goes so far, how projectmanager helps business forecasting.
Well-run organizations don’t fly by the seat of their pants; they’re constantly working on business forecasting and business planning. Every decision and every process is based on data obtained from business forecasting, business intelligence tools, market research and scenario planning. Companies focus their energies on ways to predict market trends to help them set successful long-term strategies.
Some business forecasts are based on highly sophisticated statistical methods while others are based on experience and past data. Others simply follow a gut feeling. One thing remains constant: all industries rely on business forecasting.
Business forecasting refers to the process of predicting future market conditions by using business intelligence tools and forecasting methods to analyze historical data.
Business forecasting can be either qualitative or quantitative. Quantitative business forecasting relies on subject matter experts and market research while quantitative business forecasting focuses only on data analysis.
You can access historical data with project management tools such as ProjectManager , project management software that delivers real-time data for more insightful business forecasting. Our live dashboard requires no setup and automatically captures six project metrics which are displayed in easy-to-read graphs and charts. Get a high-level view of your project for better business planning. Get started with ProjectManager for free today.
Quantitative Forecasting
Quantitative forecasting is applicable when there is accurate past data available to predict the probability of future events. This method pulls patterns from the data that allow for more probable outcomes. The data used in quantitative forecasting can include in-house data such as sales numbers and professionally gathered data such as census statistics. Generally, quantitative forecasting seeks to connect different variables in order to establish cause and effect relationships that can be exploited to benefit the business.
Qualitative Forecasting
Qualitative forecasting is based on the opinion and judgment of consumers and experts. This business forecasting method is useful if you have insufficient historical data to make any statistically relevant conclusions. In such cases, an expert can help piece together the known bits of data you do have to try to make a qualitative prediction from that known information.
Qualitative business forecasting is also useful when little is known about the future in your industry. Relying on historical data is useless if that data is not relevant to the uncharted future you are approaching. This can be the case in innovative industries, or if there’s a new constraint entering the market that has never occurred before such as new tax law.
Business forecasting is critical for businesses whenever the future is uncertain or whenever an important strategic business decision is being made. The more the business can focus on the probable outcome, the more success the organization has as it moves forward.
Here are the steps that a business forecaster should typically follow:
- Define the question or problem you need to solve with your business forecasting efforts. For example, you might be interested in estimating whether your organization will be able to meet product demand for the next quarter.
- Identify the datasets and variables that need to be taken into consideration. In this case, datasets such as the sales records from the previous year and variables related to capacity, production and demand planning .
- Choose a business forecasting method that adjusts to your dataset and forecasting goals. That depends on whether your problem or question can be solved using a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach.
- Based on the analysis of historical data, you can proceed to estimate future business performance. Keep in mind that the accuracy of your business forecasting depends on the quality of your data.
- Determine the discrepancy between your business forecast and actual business performance. Document your findings and improve your business forecasting process.
As stated above, there are two main types of business forecasting methods, qualitative and quantitative. We’ve compiled some of the more common forecasting models from both sides below.
Delphi Method
This qualitative business forecasting method consists in gathering a panel of subject matter experts and getting their opinions on the same topic in a manner in which they can’t know each other’s thoughts. This is done to prevent bias , which makes it possible for a manager to objectively compare their opinions and see if there are patterns, consensus or division.
Market Research
There are many market research techniques that evaluate the behavior of customers and their response to a certain product or service. Some of those market research methods collect and analyze quantitative data, such as digital marketing metrics and others qualitative data, such as product testing, or customer interviews.
Time Series Analysis
Also referred to as “trend analysis method,” this business forecasting technique simply requires the forecaster to analyze historical data to identify trends. This data analysis process requires statistical analysis as outliers need to be removed. More recent data should be given more weight to better reflect the current state of the business.
The Average Approach
The average approach says that the predictions of all future values are equal to the mean of the past data. Past data is required to use this method, so it can be considered a type of quantitative forecasting. This approach is often used when you need to predict unknown values as it allows you to make calculations based on past averages, where one assumes that the future will closely resemble the past.
The Naïve Approach
The naïve approach is the most cost-effective and is often used as a benchmark to compare against more sophisticated methods. It’s only used for time series data where forecasts are made equal to the last observed value. This approach is useful in industries and sectors where past patterns are unlikely to be reproduced in the future. In such cases, the most recent observed value may prove to be the most informative.
- Develop the Basis: Before you can start forecasting, you must develop a system to investigate the current economic situation around you. That includes your industry and its present position as well as its popular products to better estimate sales and general business operations.
- Estimating Future Business Operations: Now comes the estimation of future conditions, such as the course that future events are likely to take in your industry. Again, this is based on collected data to help with quantitative estimates for the scale of operations in the future.
- Regulating Forecasts: Whatever your forecast is, it must be compared to actual results. This is the only way to find deviations from the norm. Then the reasons for those deviations must be figured out, so action can be taken to correct those deviations in the future.
- Reviewing Forecasting Process: By reviewing the deviations between forecasts and actual performance data, improvements are made in the process, allowing you to refine and review the information for accuracy.
Your forecast will only be as good as the data you put into it. Before collecting data, ask yourself these questions:
- Why collect data?
- What kind of data?
- When to collect it?
- Where to collect it?
- Who will collect it?
- How will it be collected?
These are the questions that will shape your plan for the collection of data, a crucial facet of business forecasting. Once you have your plan, you can collect data from a variety of sources.

Primary Sources
Primary sources contain first-hand data, often collected with reporting tools . These are the ones that you or the person assigned this task to collect personally. If primary data is not available, you must go out and source it through interviews, questionnaires or observations.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources contain published data or data that has been collected by others. This includes official reports from governments, publications, financial statements from banks or other financial institutions, annual reports of companies, journals, newspapers, magazines and other periodicals.
If business forecasting were a crystal ball, then everyone would be reaping the rewards of their foresight. While business forecasting is a tool to get a better view of what the future might have in store, there’s the argument that it’s wasting valuable time and resources on little return.
It’s true; you can follow the steps, use a variety of methodologies and still get it wrong. It is, after all, the future. There’s no way to ever manage all the variables that can impact future events. There are errors in calculations and the innate prejudices of the people managing the process, all of which add to the unpredictability of the results.
While you’re not going to have a clear, unobscured vision of the future by using business forecasting, it can provide you with insight into probable future trends to give your organization an advantage. Even a small step can be a great leap forward in the highly competitive world of business. By combining statistical and econometric models with experience, skill and objectivity, business forecasting is a formidable tool for any organization looking for a competitive advantage.
Clearly, business forecasting is a project unto itself. To manage a project and collect the data in a way that’s useful in the future, you need a project management tool that can help you plan your process and select the data that helps you decide on a way forward.
ProjectManager is award-winning software that organizes projects with features that address every phase. The first thing in forecasting is choosing how you’ll take action and make a plan. For example, if you’re going to interview customers to see where the market is likely headed, you’ll need to schedule those interviews. Our online Gantt chart places those interviews as tasks on a timeline so you can get everyone interviewed before your deadline.
Store All of Your Data in One Place
Those interviews will produce a lot of paperwork, and your data needs to be collected and stored somewhere easily accessible. You can attach notes to each task so the paperwork for each interviewee is saved with the notes that you took. You can also tag those tasks to make it easier to filter the project and locate the interview subjects for which you’re looking. If you’re worried that there’ll be too many documents and images attached to one task, don’t worry as we have unlimited file storage.
ProjectManager can’t predict the future, but it does provide you with the tools you need to take advantage of business forecasting. Our project management software collects data in real-time, and stores past data, allowing you to filter information and pull up the metrics you need to make the right decision. Try it today with this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.

- Enterprise Contact Center
- Integrations
- Customer Stories
- Zendesk Integration
Your Topics
- Conversational AI
- Customer service automation
- Telephony and channels
- Zendesk integration
- Salesforce integration
- babelforce platform
- Contact center management
Resources center
- Quick Guides
- On-demand webinars
What Is Business Forecasting? (and How to Increase Your Forecast Accuracy)
Forecasting is making predictions using past or live data. To increase forecasting accuracy, you have to study your customers, know industry trends, and assess the competition .
Forecasting is valuable to any organization to make informed business choices and plans. As such, it is crucial to make an almost accurate forecast to enhance business success short-term and long-term.
Do you want to start forecasting or improve forecasting techniques?
This article is for you!
We have listed the types of business forecasting, why forecasting is essential, and the best rate for forecast accuracy. You will also learn factors that affect forecasting and the best forecasting tools.
(Want more articles like this in your inbox? Click here to get our fortnightly CX newsletter.)
What types of business forecasting are there?
Types of business forecasting are dependent on what you want to predict about the future. Every business forecast focuses on a particular outcome or call center metric . They range from general (number of calls next month) to specific (number of calls after a product launch for the 2023 holiday season).
In addition, it’s incredibly helpful to present diagrams and visuals for your future business forecasts to make the situation easy to understand at a single glance.
Business forecasts are vital for all businesses. So, whether you’re starting a business or planning for an existing business, it’s important for you to understand the types of forecasts you’ll need and how to make each forecast as accurate as possible.
Here are the different types of business forecasting:
General business forecasting
Market trends and external conditions such as climate, community, politics, populations, national income, etc., affect every business.
General business forecasting will read these future conditions and predict any potential changes affecting the business. For instance, a business can forecast the effects of presidential elections on a country’s economy.
Sales forecasting
Sales forecasting is a prediction of future sales on sales data. Whether it’s about general sales or sales of a particular service or product, your company can make plans for resources, workforce, inventory, cash flow, and investment capital.
Sales forecasts can project revenue for the 2022 fiscal year to determine the number of salespeople to hire.

Capital forecasting
The capital forecast predicts liquid capital, cash flow, assets, and liability of a company.
Predicting future capital needs helps you plan for issues such as replacement, depreciation, reorganization, etc.
A company will also use its capital fully and get optimum investment returns. For instance, an organization can predict the coming year’s working capital to open a second branch.
Demand forecasting
Sales and demand forecasts are almost similar, except demand will predict what your customers will need or want in the future.
Demand forecasting determines customer or market demand for a service or good in the future. For example, an organization can predict demand for a new toy at Christmas.
Financial forecasting
You can get a clear picture of your company’s future with financial forecasting. It weights liabilities and assets, operating costs, accounts payable and accounts receivable, cash flow, capital structure, etc. Financial forecasting is crucial if you want your business to stay financially healthy.
Accounting forecasting
Accounting forecasting uses past and present company data to predict future costs your company will incur.
Your organization will predict how much it will use for inventory, raw materials, utilities, person-hours, rent, etc.
Call center forecasting
Forecasting for call centers entails estimating future workload and the staff capacity needed to handle the contact volume.
The law of supply and demand is crucial in call center forecasting, as in any other business field. Workload forecast accuracy is paramount for service providers, so that they can estimate changes in demand (inbound calls, messages, emails) and make proactive supply decisions (allocate the right number of advising agents).
Your call center performance is greatly dependent on the balance between customer satisfaction and the costs of employing the right number of agents.
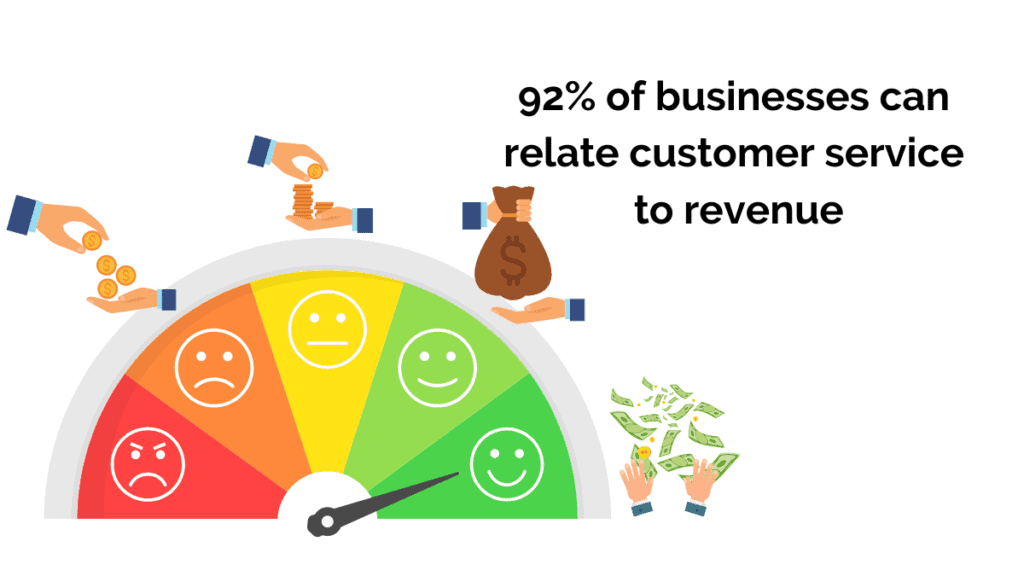
Why is business forecasting important?
Business forecasting helps you gain valuable insights into many aspects and future business success. Look at why it is crucial to do business forecasting:
- Increases chances of business success – Correct prediction determines the success of a business to a great extent. Knowing the future course of events can help you strategically plan for any challenges.
- Helps company formulate plans – You can’t plan a company’s future without forecasting since it helps in managerial planning. Let’s say you want to launch a product in the market. The best thing is demand or sales forecasting to see if there’s any market or demand for that product.
- Estimates the financial needs of a company – Companies that don’t have correct estimates of financial needs fall prey to less or excess capital. A company can plan for diversification, expansion, and improvement with financial forecasting.
- Improves customer satisfaction – Business forecasting helps give the market what it needs and wants at the right time. Your company can offer services or products to meet a target audience’s expectations, improving customer satisfaction and business sales.
What’s a reasonable rate of forecast accuracy
Unfortunately, you can’t know how accurate a forecast will become. Setting specific forecasting performance goals makes it impossible to achieve the goal since you can’t demand a certain level of accuracy. This is why:
- Forecasting can only help your company achieve other goals, such as improved customer satisfaction or reduced peak hour traffic.
- Forecasting is one aspect of achieving different goals. Other factors come to play, such as financial management.
What factors make forecasting more or less reliable
Let’s look at different factors that affect forecasting:
General conditions
General conditions that affect businesses include a country’s economy, wealth distribution, seasonal fluctuations, government policies, etc. A company can’t control all these factors, so they can drastically affect forecast accuracy.
Industry conditions
Factors with industry include products, competition, pricing policies, product line, competitor’s strategies, and policies. All these factors have to be considered during forecasting to avoid errors.
Internal enterprise factors
An enterprise’s internal factors like quality, price, plant capacity, resources, and advertisement policy, affect forecasting.
Let’s say your forecast shows that there will be peak hour traffic at the call center after a product launch. The company has to increase staff capacity but didn’t invest in job advertising and recruitment, so the forecast results are drastically wrong.
Tips to improve your forecast accuracy
Improving forecast accuracy leads to increased customer satisfaction and business success. Here’s how you can enhance your forecast accuracy:
Know industry trends
Study the industry insights and trends to serve your market. Always review the industry by analyzing old and new companies. How do they maintain success? Who are the winners and losers of your industry? Who’s worth looking out for competition? What are their plans?
Assess your competition
You can make valuable insights into your company by analyzing competitors first. Review the revenue potential by researching information on public companies online.
If private companies are your competitors, do online research and analysis of % market share, the number of employees, advertisement strategies, funding amounts.
Study your target audience
You need to understand the behavior of your customers. Look at their reaction to a new product or service. Does your customer cross-shop? What does your client do when products are out of stock? All the answers to this will help you gather essential data and increase forecast accuracy.
Best tools for reliable forecasting
- Forecasting software reports and insights help you stay organized, take action, and stay in control before problems arise. You need to choose software that is in line with your goals, budget, and business size. Some examples include Hubspot Forecasting Software, Anaplan , PipeDrive , etc.
- Resources that help you make forecasting efficient include cash flow statements, industry expert reports, internal assessment reports, organizational charts, performance indicators, etc.
Improve customer satisfaction with babelforce
There are different types of forecasting, including sales forecasting, financial forecasting, call-center forecasting, demand forecasting, etc. They all help an organization increase its success, formulate plans, estimate financial needs, and improve customer satisfaction .
To improve forecast accuracy, you need to study your customers, know industry trends, and assess the competition.
Are you looking to improve customer experience ?
babelforce is the most flexible platform for contact center service. We are a team combining contact center & telecoms veterans with developers & extreme sport experience designers.
Our cloud-based services and apps platform, on top of a multi-carrier telecoms network, guarantees you high-quality service. Use our suite of visual tools and pre-built elements to create any customer service process.
Book a demo with babelforce now!
Jack started as our #1 freelance writer back in 2016 and is now Head of Marketing. He’s starting to get the hang of blogging and reckons he can explain No-Code development to *anyone*.
Related Posts

Why do people hate call queues? Answers from psychology
Call queues are a universally dreaded aspect of calling customer service. No one likes to wait in line, whether it’s at the grocery store or

The stores swapping artificial for actual intelligence
A grocery chain has become the first in the UK to remove self-service checkouts from most of its stores following customer feedback. This is the
© 2024 babelforce GmbH.

Stay informed with news & updates .
Privacy overview.
spotSaaS Blog

Type and hit Enter to search
The importance of business forecasting in decision-making and planning (2023 guide).
Do you ever feel overwhelmed when it comes to making business decisions? If so, you’re not alone. In fact, the most successful companies rely on something called business forecasting to make informed strategic plans.
This article will guide you through the ins and outs of business forecasting, helping you leverage data for planning and decision-making like a pro.
Key Takeaways
- Business forecasting is essential for planning the future, making informed business decisions, and avoiding surprises in taxes.
- Effective business forecasting helps companies adapt to changing market conditions and align their strategies with their goals and objectives.
- By accurately predicting future trends and analyzing historical data, businesses can estimate financial projections, optimize operations, and drive growth.
What is Business Forecasting?
Business forecasting refers to the process of using historical data and predictive analysis to estimate future trends and make informed decisions for the business.
Business forecasting is a technique that combines past data, predictive analytics, and market research to estimate future trends. It’s mainly about predicting what might happen in the business environment.
This concept involves using statistical tools and techniques to predict future trends based on historical data and current market conditions. Business forecasts can span over short or long periods, depending on the nature of the business and its industry.
They help companies anticipate possible scenarios in sales, finances, demand, operations among other areas.
Methods (Quantitative and Qualitative)
Business forecasting utilizes two primary methods, quantitative and qualitative.
The Importance of Business Forecasting
Business forecasting is crucial for businesses as it helps in planning for the future, informing business decisions, and avoiding surprises in taxes.
Planning for the future
Business forecasting acts as a compass guiding firms into the future. It makes use of tools like predictive analysis and statistical methods to scan market trends, assess risks, and make financial projections.
These forecasts play an instrumental role in business planning by helping managers chart strategic paths for growth. Whether it’s managing inventory or optimizing production processes , efficient forward-looking strategies help businesses gain a competitive edge.
More than just educated guesses, these predictions are rooted in pragmatic data assessment enabling companies to adapt swiftly to changing environments while remaining aligned with their overall goals and objectives .
Thus, proactive forecast-based planning ensures that surprises are minimized and growth opportunities maximized.
Informing business decisions
Business forecasting plays a vital role in informing business decisions. By analyzing historical data and examining market conditions, businesses can make predictions about the future and use that information to guide their decision-making process.
This allows managers to develop strategies based on reliable forecasts, giving them confidence in their choices regarding sales, expenses, revenue, and more. With accurate forecasting insights at their disposal, businesses can navigate uncertainties with greater ease and make informed decisions that align with their goals and objectives.
Avoiding surprises in taxes
Business forecasting is a valuable tool for avoiding surprises in taxes. By accurately predicting future trends and analyzing historical data, businesses can estimate their financial projections and plan their budget accordingly.
This helps them anticipate any potential tax liabilities or changes in tax regulations, allowing them to make informed decisions and take necessary measures to minimize any unexpected tax burdens.
Through strategic forecasting and careful analysis of market conditions, businesses can better prepare themselves for tax season and ensure that they are complying with all necessary tax obligations without any last-minute surprises.
Types of Forecasting in Business
There are several types of forecasting in business, including general forecasting, financial forecasting, demand forecasting, sales forecasting, and capital forecasting.
Business forecasting is a vital tool for companies of all sizes and industries. It involves analyzing past data, market conditions, and future trends to make informed predictions about the future.
By leveraging historical information and utilizing statistical methods, businesses can develop accurate forecasts that support decision-making and strategic planning. Whether it’s projecting revenue, estimating growth, or identifying potential risks and opportunities, business forecasting provides valuable insights that help organizations stay ahead of the competition and achieve their goals.
Financial forecasting is a crucial aspect of business planning and decision-making. It involves predicting future financial outcomes based on historical data, market conditions, and various other factors.
By leveraging financial predictions, businesses can effectively budget their resources, estimate growth potential, and make informed decisions about investments and expenses. This enables them to stay ahead of the competition and adapt their strategies in an ever-changing marketplace.
Financial forecasts also help businesses avoid surprises when it comes to taxes and ensure they have a clear understanding of their financial health. With accurate financial projections, businesses can confidently navigate the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of business planning and decision-making. By accurately predicting future demand for products or services, businesses can align their production capabilities and inventory levels accordingly.
This allows them to avoid stockouts or overstocking, resulting in optimized operations and increased customer satisfaction. Demand forecasting also helps businesses anticipate market trends and adjust their marketing strategies to meet changing consumer needs.
Additionally, it enables effective resource allocation, ensuring that the right resources are allocated at the right time to meet customer demands efficiently. With accurate demand forecasting, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, promotions, product development, and supply chain management, ultimately driving growth and profitability.
In order to conduct demand forecasting effectively, businesses utilize various techniques such as statistical analysis based on historical data, market research surveys, expert opinions from industry professionals or consultants.
These methods help analyze factors that influence demand fluctuations such as seasonality patterns, economic conditions, competitor actions or new product launches in the market. By incorporating these insights into their decision-making processes and planning strategies proactively; businesses can stay ahead of competition by anticipating market dynamics swiftly and with minimum risks involved.
Sales forecasting is a crucial aspect of business planning and decision-making. By analyzing past sales data and market trends, businesses can project future sales figures and make informed decisions about production, inventory management, and resource allocation.
Sales forecasts help businesses set realistic targets, identify potential opportunities for growth, and plan marketing strategies to maximize revenue. This proactive approach enables businesses to stay ahead of the competition and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Accurate sales forecasting also helps in budgeting and financial planning by estimating expected revenues and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. Overall, sales forecasting plays a vital role in driving business success by providing valuable insights into customer demand and market conditions.
Forecasting capital requirements is a critical aspect of business planning. It involves estimating the funds needed to support various aspects of the business, such as purchasing new equipment, expanding operations, or investing in research and development.
By accurately forecasting capital needs, businesses can ensure they have the necessary financial resources available when opportunities arise. This allows them to make informed decisions about allocating funds and effectively manage their cash flow.
Additionally, accurate capital forecasting helps businesses avoid potential financial constraints or unexpected funding gaps that could hinder their growth and success.
How to Develop a Forecast
Developing a forecast involves projecting revenue, analyzing expenses, monitoring cash flow, and determining the desired time frame for the forecast.
Projecting revenue
Projecting revenue is a crucial aspect of business forecasting. It involves making educated estimations about the income a company expects to generate within a specific time frame.
By analyzing historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors, businesses can develop forecasts that help them plan for the future and make informed decisions. This information is valuable for budget planning, resource allocation, and setting financial goals.
Accurate revenue projections allow companies to anticipate cash flow fluctuations and adjust their strategies accordingly. Ultimately, projecting revenue enables businesses to have a clearer understanding of their financial health and make proactive choices to maximize profitability.
Forecasting Techniques
Statistical methods
Analyzing expenses
Analyzing expenses is a crucial step in business forecasting. By thoroughly examining and understanding expenses, businesses can develop accurate financial predictions and make informed decisions about budgeting and resource allocation.
Analyzing expenses allows businesses to identify areas where costs can be reduced or optimized, helping them maximize profitability. It also helps in identifying any unexpected or hidden costs that may impact the overall financial health of the organization.
Additionally, analyzing expenses provides valuable insights into spending patterns and trends, enabling businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly and maintain financial stability.
Monitoring cash flow
Monitoring cash flow is a crucial aspect of business forecasting. By keeping a close eye on the inflows and outflows of cash within an organization, businesses can effectively plan for future expenses and make informed decisions about their financial health.
With accurate cash flow monitoring, businesses can identify potential gaps or shortfalls in their finances, enabling them to take proactive measures to address any issues before they become problematic.
This allows businesses to maintain stability and ensure that they have enough working capital to cover operational expenses, invest in growth opportunities, and meet financial obligations when they arise.
Business forecasting involves predicting future trends and making informed decisions based on data analysis. When it comes to developing a forecast, it is essential to consider the time frame in which you are planning.
This allows businesses to align their strategies with specific goals or objectives. By considering factors such as market conditions, economic trends, and customer behavior within the chosen time frame, businesses can accurately estimate future demands and make necessary adjustments to their operations.
Time frame plays a crucial role in effective business planning as it ensures that forecasts are relevant and useful for taking proactive steps towards success.
Business forecasting plays a crucial role in decision-making and planning for businesses. By analyzing historical data and predicting future trends, businesses can make informed decisions about their operations, finances, and growth strategies.
With the help of forecasting techniques and market analysis, businesses can anticipate potential risks, identify opportunities, and develop data-driven strategies to stay ahead in the competitive marketplace.
Overall, business forecasting is an indispensable tool that empowers businesses to navigate uncertainty and achieve their goals efficiently.
1. Why is business forecasting important for decision-making and planning?
Business forecasting helps organizations anticipate future market trends, demand for products or services, and potential risks. This information enables informed decision-making and effective planning to maximize profitability.
2. How does business forecasting help in reducing uncertainty?
By analyzing past data and current market conditions, businesses can use forecasting techniques to make informed predictions about future outcomes. This reduces uncertainty by providing a clearer understanding of potential risks and opportunities.
3. What are the benefits of using business forecasting in financial planning?
Business forecasting allows companies to estimate expected revenues, expenses, cash flows, and profitability over a specific period. This helps in setting realistic financial goals, allocating resources effectively, and making sound investment decisions.
4. Can business forecasting be used across different industries?
Yes, business forecasting is applicable across various industries including retail, manufacturing, finance, healthcare etc., as it provides valuable insights into consumer behavior patterns and market dynamics that influence decision-making.
5. Are there any limitations or challenges associated with business forecasting?
While useful for decision-making and planning purposes, business forecasting involves some degree of uncertainty due to unpredictable factors such as economic fluctuations or changes in consumer preferences which may impact accuracy of the forecasts generated.
Share Article
Anisha Jain
Anisha Jain, a dynamic professional in the sports SaaS industry, transitioned from economics to digital marketing, driven by her passion for content writing. Her tenure at TBC Consulting culminated in her role as CEO, where she honed her skills in digital strategy, branding, copywriting, and team management. Anisha's expertise encompasses various aspects of digital marketing, including 360-degree marketing, digital growth consulting, client communication, and business development, making her a versatile asset in the SaaS domain.
The Importance of Streamlining Business Operations for Success (2023 Guide)
The complete guide to writing a business letter (2023 updated guide), related posts.

500+ Epic Team Names to use in 2024: Stand Out & Dominate

Resource Management Software: A detailed guide on how to use (2023)

Atlan Raises $105 Million in Series C Funding and Hits $750 Million Valuation

Stonal Secures up to €100 Million Investment from Aareon

SaaS Weekly Roundup #44 – SaaS Funding

LayerX Security Raises $26 Million in Series A Funding
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Business Forecasts Are Reliably Wrong — Yet Still Valuable
- Martin Reeves,
- Suvasini Ramaswamy,
- Annelies O’Dea

Six ways savvy leaders can use them to gain a competitive advantage.
Business forecasts are often wrong — and yet they can still be a powerful tool for savvy leaders if they view them in aggregate and ask the right questions. The authors offer six ways in which business leaders can gain competitive advantage from forecasts and offer their analysis of the themes revealed in 20 forecasts for 2022 and beyond by prominent commentators and thought leaders on business and society.
At the beginning of each year, while many individuals make New Year’s resolutions, organizations make forecasts about the year ahead. Both have high fallibility. Forecasts are predictions about what will happen in the future based on information currently available. As such, they are exercises of imagination, which studies have shown are rarely correct in their particulars.
- Martin Reeves is the chairman of Boston Consulting Group’s BCG Henderson Institute in San Francisco and a coauthor of The Imagination Machine (Harvard Business Review Press, 2021).
- SR Suvasini Ramaswamy is a project leader in the Los Angeles office of BCG. You may contact her by email at [email protected]
- AO Annelies O’Dea is a project leader in the Chicago office of BCG and a BCG Henderson Institute Ambassador. You may contact her by email at [email protected]
Partner Center
Case Studies
Resource Hub
Featured post
What is a Pitch Deck: The Definitive Guide for Entrepreneurs

Explore our latest posts
Innovative Revenue Models for Startups: Exploring New Ways to Monetize

Decoding the Lean Startup Methodology: A Practical Guide for Entrepreneurs

Leveraging Emotional Intelligence for Startup Leadership: Enhancing Team Dynamics and Decision-Making

The Financial Compass: Planning with Forecasts & Projections
Learn how to use financial forecasting and projections to plan for the future of your business. Discover the key components of a financial forecast, common mistakes to avoid, and best practices for presenting financial forecasts to stakeholders.
November 20, 2023
Do you know the difference between financial forecasts and financial projections? If not, don't worry. This guide will answer all your questions. There are many reasons why a company should use forecasting to plan for the future. Forecasting is simply predicting what will happen in the future based on past data. A company can forecast its sales, profitability, cash flow, and many other aspects of its business. Forecasts help businesses make decisions that might not be intuitive or easy to make.
What are Financial Forecasts and Projections?
Financial forecasting, also known as financial projection, is the process of predicting a company's financial position or a country's GDP in the future. The difference between forecasting and projecting is that forecasting deals with the past and present, while projection deals with the future. Forecasting can be used to predict market demand for certain products on a quarterly basis. For example, projecting can be used to predict a country's GDP for the next year based on current economic policies and other factors that may affect economic growth. Financial forecasts and projections are useful tools for capital suppliers and managers, who rely on firms' financial projections to set their own expectations of future cash flows for investing purposes.
There are two types of forecasts:
- Qualitative forecasts are based on the opinion of the analyst.
- Quantitative forecasts use statistical data and math.
Quantitative forecasts can be useful for decision-making, especially when used in conjunction with fundraising advisory services . These projections can help businesses understand the potential impact of their decisions on their financial future and make informed choices.
Why Use Financial Forecasting and Projection in Business?
Financial forecasting is an essential tool for businesses to plan ahead and avoid potential problems. Poor cash flow accounts for about 82% of small business failures, and forecasting can help identify and address these issues. It involves analyzing data and making informed estimates about future cash flows and revenues. In contrast, financial projections analyze past data to see if it matches expectations. Forecasting is forward-looking, while projection is backward-looking.
Forecasting is crucial for businesses because it allows them to stay on top of their finances and prepare for potential outcomes. By considering past trends and future possibilities, businesses can formulate action plans for different scenarios. While projections provide detailed information on past or future performance, forecasting gives an overview of the company's financial state.
Businesses with multiple lines of business or volatile cash flow streams that cannot be predicted accurately with financial projections alone should consider financial forecasting as a valuable tool in managing their finances.

How are Financial Forecasts Done?
The forecasting process can be a complicated task, especially when forecasting for a growing company. There are many aspects to take into account, and it may seem daunting. The forecast process starts with identifying the different scenarios that can happen within the company's industry and estimating their impact on the company's operations. Factors such as demand, prices, competitors, and new products should be considered when making forecasts. This section will explore two key aspects of forecasting that every company should consider when completing their forecast process.
What is Your Forecasting Horizon?
Before beginning the forecasting process, you must determine the length of time you plan to forecast. This is known as the forecasting horizon, or how far into the future you want to predict your expenses and revenues from contracts or other sources. There are generally three types of forecasting horizons:
- Short Term: This forecasting horizon is less than three months. It is used for job schedules, work tasks, client commitments, workforce and product levels in planning and purchasing.
- Medium Term: This forecast covers 3 months to a year, but can be up to 3 years. Management predicts aspects such as sales, production planning, and cash budgeting.
- Long term: This forecasting horizon is for more than three years. Management creates a long-term plan that may include installing new plants, factories, or outlets, and considers capital expenditures, factory locations, and other sectors.
Forecasting horizons are an integral part of planning and decision-making in any organization. This is why financial managers need to clearly define the horizon of their forecasts. From a financial perspective, horizon analysis examines the expected discounted returns of a security or investment portfolio's total returns over multiple periods.
How to Collect Data for Financial Forecasts?
Financial data can be collected by looking at historical data, analyzing trends, or estimating based on new forecasts made during the same period. For financial forecasting, quantitative data is collected within the organization. This data is measurable and can be expressed by numbers or figures that show a quantity. It includes any sort of data field that contains numbers that represent a value, such as prices, quantity, number of sales, time frame, etc. You can collect data from the production, sales, and marketing departments, as well as from the organization's filings, industrial data, and IT department.
In addition, qualitative data can also be used for financial analysis. Qualitative analysis is used to assess a company's performance, support organizations in making critical decisions, and advise investors on whether or not to invest. This data can be collected through surveys, focus groups, and interviews, which can help predict financial performance. For example, if a survey is taken at the pre-launch of a new product, the data collected can be analyzed to predict future sales.
Professional analyst research papers are another useful resource for improving the accuracy of your forecasting suggestions. However, it is impossible to predict the future with 100% accuracy. Forecasts require a lot of time and work, as well as business intelligence and creativity combined with experience. There are many tools that can forecast financials accurately, but not all of them are appropriate for every company or person doing forecasting. For best results, companies may consider seeking guidance from the best investors outreach agencies .

How are Financial Projections Made?
Financial projections are usually made in two ways:
Historical Data Analysis:
This method involves using past data to evaluate the future. By comparing financial statements over time, you can discover existing trends, analyze the findings, and build better strategies. This type of financial forecast is also a budgeting tool that estimates information based on historical and current facts. It aids in identifying future revenue and expenditure trends that could impact government policies, strategic goals, or community services in the short or long term. By studying what has worked successfully in the past, you can identify what needs to be changed in order to prevent any damage to the company.
Creative Forecasting:
This method involves using your imagination and creativity to create a projection without any knowledge of the past or future. You can predict the financial strength and outcomes that a business idea can give. You can forecast the number of sales the product can generate and predict revenue growth and capital expenditure. You will also have a better understanding of the company's overall growth structure. One can determine forecasts of cash inflows and outlays, income, and balance sheet. Additionally, if you are willing to seek funding, this is a great way to start. Projections need to be clear, concise, and easy to understand. It is essential for both project stakeholders and others who might want to know its progress. The projection should also be flexible enough to accommodate changes throughout the project timeline. It should be at a high enough level so that people can easily read it without too much detail but not too high a level to miss important information about how things are progressing at a higher level.

Key Components of a Financial Forecast/Projection
Creating a financial forecast or projection can be a complex process, but it's essential for businesses to plan for their future. Before creating a financial forecast or projection, there are several key components that you should consider. These include:
1. Revenue Projections
The revenue projection is one of the most important components of a financial forecast or projection. It estimates the amount of money that a company can expect to make over a given period, usually three to five years. Revenue projections should be based on realistic assumptions and supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends. It's important to consider how external factors such as economic conditions, changes in consumer behavior, and new regulations could impact revenue projections. Professional presentation design services can help businesses create visually appealing and informative presentations of their financial forecasts and projections.
2. Expense Projections
Expense projections estimate the costs associated with running the business over a given period. This includes all types of expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and supplies. It's essential to accurately estimate expenses to ensure that the business has enough cash flow to cover expenses. Underestimating expenses can lead to cash flow problems and ultimately, failure.
3. Cash Flow Projections
Cash flow projections estimate the amount of cash that a company will have on hand at any given time. It's important to accurately estimate cash flow to ensure that the business can cover its expenses and invest in growth opportunities. Cash flow projections should be based on realistic assumptions and supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends.
4. Profit and Loss Projections
Profit and loss projections estimate the amount of profit or loss that a company can expect to make over a given period. It takes into account revenue, expenses, and taxes. Profit and loss projections should be based on realistic assumptions and supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends.
5. Balance Sheet Projections
Balance sheet projections estimate the company's assets, liabilities, and equity over a given period. It provides a snapshot of the company's financial position at a specific point in time. Balance sheet projections should be based on realistic assumptions and supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends.
6. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis involves testing the financial forecast or projection against different scenarios to determine how it might perform under different conditions. This helps businesses to identify potential risks and opportunities and make more informed decisions. Sensitivity analysis should be based on realistic assumptions and supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends.
By considering these key components, businesses can create accurate and reliable financial forecasts and projections that can help them make informed decisions and plan for the future.

Common Mistakes to Avoid When Creating a Financial Forecast/Projection
Creating a financial forecast or projection is a complex process that requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a financial forecast or projection:
1. Failing to Consider External Factors
One of the biggest mistakes when creating a financial forecast or projection is failing to consider external factors that may impact the business. These external factors can include changes in the economy, new regulations, or shifts in consumer behavior. Failing to take these factors into account can lead to inaccurate projections and forecasts.
2. Overestimating Revenue
Overestimating revenue is a common mistake when creating a financial forecast or projection. It is important to base revenue projections on realistic assumptions and market research. Overestimating revenue can lead to overestimating profits and cash flow, which can lead to poor decision-making.
3. Underestimating Expenses
Another common mistake is underestimating expenses. It is important to accurately estimate expenses to ensure that the business has enough cash flow to cover expenses. Underestimating expenses can lead to cash flow problems and ultimately, failure.
4. Failing to Update Forecasts and Projections
Forecasts and projections need to be regularly updated and adjusted to ensure that they remain accurate and relevant. Failing to update forecasts and projections can lead to inaccurate projections and poor decision-making.
5. Using Inconsistent Methods
Using inconsistent methods when creating financial forecasts and projections can lead to inaccurate projections. It is important to use consistent methods and assumptions to ensure that projections are accurate and reliable.
6. Focusing Too Much on Short-Term Goals
Focusing too much on short-term goals can lead to neglecting long-term planning. While short-term goals are important, it is essential to also consider long-term goals when creating financial forecasts and projections.
By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can create accurate and reliable financial forecasts and projections that can help them make informed decisions and plan for the future.

Using Financial Forecasting to Secure Funding or Investments
Financial forecasting is an essential tool for businesses seeking funding or investment. Investors and lenders want to see a clear plan for how their money will be used and how it will generate returns. Financial forecasts provide this clarity by outlining the company's expected financial performance over a given period, usually three to five years.
To use financial forecasting to secure funding or investment, businesses should follow these steps:
- Determine the amount of funding required: The first step in securing funding or investment is to determine how much money the business needs. This should be based on the company's financial forecasts and the amount of capital required to achieve its strategic goals.
- Prepare a business plan: A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the company's strategy, goals, and financial projections. It should include a detailed description of the company's products or services, target market, competition, marketing strategy, management team, and financial projections.
- Develop financial forecasts: Financial forecasts should be based on realistic assumptions and should be supported by market research, historical data, and industry trends. They should include projected revenues, expenses, cash flow , and profitability.
- Prepare a funding proposal: A funding proposal should be a concise summary of the business plan and financial forecasts. It should include a description of the company, its products or services, target market, management team, and financial projections. It should also include details on how the funds will be used and how they will generate returns for the investor or lender.
- Present the proposal to potential investors or lenders: The final step in securing funding or investment is to present the funding proposal to potential investors or lenders. This can be done through in-person meetings, online platforms, or through referrals. The proposal should be clear, concise, and professional, and should include all relevant information needed for the investor or lender to make an informed decision.
In summary, financial forecasting is a crucial tool for businesses seeking funding or investment. By developing realistic financial forecasts and preparing a comprehensive funding proposal, businesses can increase their chances of securing the capital they need to achieve their strategic goals.

How to Update and Adjust Financial Forecasts/Projections as Your Business Evolves
As your business evolves, it is important to regularly update and adjust your financial forecasts and projections to ensure that they remain accurate and relevant. Here are some steps to follow when updating and adjusting your financial forecasts and projections:
- Review your financial assumptions: Start by revisiting your initial financial assumptions and consider how they may have changed over time. For example, if you projected a certain level of sales growth but have experienced slower than expected growth, you may need to adjust your projections accordingly.
- Analyze your financial data: Take a close look at your financial data, including your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Analyze trends and identify areas where you may need to make adjustments.
- Re-evaluate your business strategy: Consider how changes in your business strategy may impact your financial forecasts and projections. For example, if you are planning to launch a new product or expand into a new market, you may need to adjust your projections to account for the additional costs and potential revenue.
- Consider external factors: External factors such as changes in the economy, new regulations, or shifts in consumer behavior can also impact your financial forecasts and projections. Stay up-to-date on these external factors and adjust your projections accordingly.
- Use scenario planning: Scenario planning involves creating multiple versions of your financial forecasts and projections based on different scenarios. For example, you may create a best-case scenario, worst-case scenario, and a most-likely scenario. This can help you prepare for different outcomes and make more informed decisions.
- Monitor your progress: Finally, it is important to monitor your progress and regularly compare your actual financial results to your projections. This will help you identify areas where you may need to make adjustments and ensure that your projections remain accurate.
By regularly updating and adjusting your financial forecasts and projections, you can better prepare for the future and make more informed decisions about your business.

Best Practices for Presenting Financial Forecasts/Projections to Stakeholders
When presenting financial forecasts or projections to stakeholders, it is important to keep in mind that not everyone has a financial background. Here are some best practices to follow when presenting financial forecasts or projections to stakeholders:
- Keep it simple: Avoid using jargon or overly complex financial terminology. Use clear and concise language to explain the key concepts and numbers.
- Use visuals: Incorporate graphs, charts, and other visual aids to help stakeholders understand the information being presented. Visuals can help simplify complex data and make it more accessible to a wider audience.
- Provide context: Explain the assumptions and methodology used to arrive at the financial projections or forecasts. This helps stakeholders understand the reasoning behind the numbers and provides them with a basis for evaluating the accuracy and reliability of the projections.
- Be transparent: Be open and honest about the risks and uncertainties involved in the projections. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions and avoid surprises down the road.
- Focus on the big picture: While it is important to provide detailed financial information, it is equally important to focus on the big picture. Explain how the projections fit into the company's overall strategy and goals.
- Be prepared to answer questions: Stakeholders may have questions or concerns about the financial forecasts or projections. Be prepared to answer these questions and provide additional information as needed.
By following these best practices, you can help ensure that stakeholders understand and appreciate the financial forecasts or projections, and are better equipped to make informed decisions about the future of the company.

Financial forecasting and projections are critical tools that businesses can use to plan their future and avoid potential problems. Financial forecasting is forward-looking and involves analyzing data and making informed estimates about future cash flows and revenues. On the other hand, financial projections analyze past data to see if it matches expectations. While forecasting is crucial for businesses, projections provide detailed information on past or future performance. By considering past trends and future possibilities, businesses can formulate action plans for different scenarios. Financial forecasts and projections can help businesses make informed decisions and plan for their future.
Key Takeaways
Financial forecasting predicts a company's financial position in the future, while projection deals with the future.
Financial forecasts and projections are useful tools for capital suppliers and managers.
Financial forecasting is essential for businesses to plan ahead and avoid potential problems.
Financial projections are usually made in two ways: historical data analysis and creative forecasting.
Financial forecasts and projections can help businesses make informed decisions and plan for the future.
.webp)
Table Of Content
Explore Our Services

Explore our top-notch pitch deck service
We help discerning startups and growing businesses create powerful pitch decks that attract investors and secure big deals.

Subscribe to our newsletter and keep in touch with us
An error has occurred somewhere and it is not possible to submit the form. Please try again later.
Only available to newsletter subscribers!
Answers, To The Most Asked Questions
What is the difference between financial forecasting and projection, why is financial forecasting important for businesses, how are financial projections made, how can financial forecasting help secure funding or investment, how can businesses update and adjust their financial forecasts and projections as their business evolves, you may like.

10 Best Cyber Security Startup Ideas
Discover the most promising cybersecurity startup ideas for 2023. Drive innovation, meet market demands, and elevate digital safety. Start your journey now!
Read Article

10 Best Software Startup Ideas
Discover the hottest software startup ideas for 2023. Dive into trends, market potentials, and launch strategies to kickstart your entrepreneurial journey!

10 Pros and Cons of Venture Capital You Should Know
Explore the dynamics of venture capital. Dive into its benefits, potential pitfalls, and learn how it can shape startup trajectories. Make informed decisions with our guide.

10 Unique Clothing Business Ideas
Discover groundbreaking fashion business concepts for 2023! From sustainability to tech trends, master the art of differentiating your brand. Dive in now!
discover the menu
Get Ready For Funding
Pitch Deck Service
Pitch Training
Financial Modeling
Investor Outreach
Fundraising Consultant
We normally respond within 24 hours
View all our blog articles

Aug 6, 2023 12:30:00 PM | Business Forecasting and Planning: Ensuring Your Business is Ready for Tomorrow
In today's rapidly changing business world, it's vital for a company's survival and success to be good at predicting upcoming trends and making smart choices. Businesses need to stay one step ahead, aligning their strategies with market demands, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities.
This is where business forecasting and planning come into play. Let’s dive into the significance of business forecasting and planning and explore the techniques used to navigate the uncertainties of tomorrow's business landscape.

The Crucial Role of Business Forecasting and Planning
Business forecasting and planning play a crucial role in the success and sustainability of any business. Forecasting and planning is a structured process where you study past data, market shifts, and other important details to predict what's coming next . This helps you figure out the best way to use your resources, make smart decisions about creating new products, growing your market, setting prices, and running your operations efficiently.
Every business faces various risks, such as market fluctuations, economic uncertainties, changing consumer preferences, and competitive challenges. However, by analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can anticipate potential risks and take proactive measures to minimize their impact.
By forecasting and planning, companies can make backup plans, expand their product range, manage their stock effectively, and put in place measures to handle risks. During tough economic times or when their industry is shrinking, predicting what's ahead can help businesses spot potential problems and figure out ways to lessen the damage.
Forecasting: Seeing the Future Today
Forecasting is a vital process involving using historical data and market trends to predict future business performance. By analyzing past performance and external factors, businesses can gain insights into potential outcomes and make informed decisions in their planning efforts.

Here's a step-by-step list on how to start business forecasting and planning:
Define your goals
Make sure you spell out clearly what you hope to accomplish with your forecasting and planning. Pinpoint key areas to concentrate on, like increasing sales, hitting revenue goals, growing your market, cutting costs, or boosting profits. Having clear, quantifiable targets will steer your forecasting efforts in the right direction.
Collect relevant data
Collect and analyze relevant past data from your business operations, financial statements, sales records, customer data, and other information that provides information on previous performance. This data will serve as a foundation for understanding trends, patterns, and relationships that can build your forecasts.
Select Forecasting Methods
When it comes to forecasting methods, businesses have various options. Qualitative forecasting methods rely on subjective judgments and expert opinions, such as market surveys, the Delphi method, or scenario planning. Qualitative methods can be useful when historical data is limited or subjective factors play a significant role.
Meanwhile, quantitative forecasting methods use math models and past data analysis. Examples of these methods include time series forecasting, regression analysis, and econometric models. Quantitative methods are suitable when historical data is abundant, and patterns can be identified. The choice of method depends on factors like data availability, accuracy requirements, and the nature of the business. Consider using a combination of methods to improve accuracy.
Monitor External Factors
Keep a close eye on outside factors that might affect your business, like shifts in the market, changes in regulations, or advances in technology. Keep up with the latest news in your industry, economic signals, and changes in consumer behavior. Use this information to add depth to your forecasting process and tweak your plans and predictions as needed.
Getting your forecasts right can help improve your business planning by letting you allocate resources effectively, plan finances better, and manage risks. By taking advantage of these benefits, businesses can set themselves up for success.
Planning: Building a Roadmap for Success
Planning provides a roadmap for success by outlining the steps needed to achieve desired outcomes.

Here's a breakdown of the key aspects of planning:
Setting Goals
Planning begins by setting clear and specific goals that align with the vision and mission of the business. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART goals). These goals serve as a guide to help understand what goals are realistic and best for the business.
Outlining Strategies
Once goals are established, strategies must be developed to achieve them. Strategies are broad approaches or courses of action designed to address specific challenges or leverage opportunities. They outline the general direction and focus of the business, such as market expansion, product diversification, cost leadership, or customer segmentation.
Developing Action Plans
Action plans are the detailed steps and tasks required to implement the strategies and achieve the defined goals. They break down the strategies into actionable items, assign responsibilities, set timelines, and allocate resources. Action plans ensure everyone understands their role and contributes to the overall objectives.
Guiding Day-to-Day Operations
Planning provides structure for day-to-day operations. It helps prioritize tasks, allocate resources efficiently, and coordinate activities across different functions or departments. With a clear plan, businesses can streamline workflows, optimize productivity, and minimize inefficiencies.
Long-Term Strategies & Goals
Planning is used for both short-term and long-term goals. Long-term goals consist of considering market trends, competitive dynamics, and future opportunities. Long-term planning involves conducting market research, analyzing industry trends, and exploring potential growth avenues. It helps businesses anticipate changes and position themselves for long-term success.
Flexibility and Adaptability
An effective plan is flexible and adaptable to changing business environments. Regular reviews allow for evaluation, strategy assessment, and adjustments. Being responsive to changes enables businesses to seize opportunities and mitigate risks.
Integrating Forecasting and Planning for a Resilient Business
Forecasting and planning are like two sides of the same coin when it comes to running a business effectively.
Forecasting gives businesses helpful insights into what's likely to happen next in terms of trends, market situations, and performance measures. It helps predict what customers will want, spot possible risks, and expect changes in the market. This info becomes the foundation for making smart decisions during the planning process.
Planning establishes the framework and strategies for achieving business goals. It involves setting objectives, defining strategies, and outlining action plans. Planning takes into account the forecasts generated to determine the most appropriate course of action and allocate resources effectively.
The best practices for integrating these processes include:
- Aligning forecasts with strategic planning.
- Using forecasts to set realistic goals.
- Regularly reviewing and updating forecasts.
- Fostering cross-functional collaboration.
- Incorporating scenario planning.
- Monitoring performance against projections.

The Value of Your Banking Relationship in Forecasting and Planning
Forecasting and planning are important factors that allow businesses to see what’s to come. By leveraging their banking relationships, businesses can have access to resources, tools, and expertise that are needed in order for a business to navigate smoothly.
A strong banking relationship can bring significant value to your business. It provides access to financing options essential for growth, expansion, and managing cash flow . Maintaining a good relationship with your bank increases your chances of obtaining favorable loan terms, lower interest rates, and faster approval processes.
Banks can help provide insight into credit options available to businesses. They can help navigate different financing options, such as lines of credit, business loans, or equipment financing. Banks will also aid businesses in understanding the terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules associated with each option. This understanding of credit can assist businesses in aligning their forecasts and plans with the available financial resources.
Relationship-based lending has the potential to come into play when a business has a strong banking relationship. As your bank becomes more familiar with your business operations, they may consider your overall standing rather than relying solely on financial metrics. This is helpful during times of economic uncertainty or when you need additional support beyond traditional lending options.
Discover a New Way of Banking with Valliance Bank
While Valliance Bank doesn't offer financial advice, our expertise and insights can be a good source to enhance the forecasting and planning processes. We have experience working with businesses across various industries and can share industry-specific insights and best practices.
Valliance Bank is here to ensure your business is ready for tomorrow. Contact us today to learn more about our banking options for businesses like yours.
Written By: Valliance Bank
Newsletter signup.
Sign Up To Get Our Free Insights Delivered To Your Inbox
You May Also Like

Sep 28, 2022 12:05:33 PM | The Credit Gaps Facing Women Business Owners

Oct 20, 2022 8:01:13 AM | Small Business Loans and How They Work

Sep 28, 2022 12:05:13 PM | Are Banks in Favor of Giving Small Business Owners Access to Credit?
Outside USA: +1‑607‑330‑3200
Strategic Business Planning and Forecasting Cornell Course
Course overview.
As the saying goes, "A goal without a plan is just a wish." It's not enough to simply have a product or service worth buying; there are many factors you need to consider, such as: How many choices do customers have for a similar product? How many competitors do you have, and what are their strategies for competing with you? If you suddenly need a new supplier, will it interrupt production or force you to raise prices? How likely is it that new competitors enter your market? Answering these questions requires careful planning as well as a thorough understanding of your competition, your suppliers, and your customers.
In this course, you will identify the three major strategies that your company can select as it competes in the marketplace, and you will examine the characteristics of companies that pursue each strategy. You will also identify the various activities involved in supporting your chosen strategy alongside the complexity of acquiring raw materials and converting them into products for the end customer. Additionally, you will conduct an analysis to help assess your company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Finally, you will balance your planning against the often conflicting needs of a company's stakeholders, its shareholders, and the society in which it operates.
You are required to have completed the following courses or have equivalent experience before taking this course:
- Finance and Accounting Principles
- Marketing Fundamentals
Key Course Takeaways
- Define generic business strategies and position firms in their competitive environments
- Identify and describe the activities of the value chain
- Create a SWOT diagram for a firm
- Prioritize stakeholder and shareholder expectations
Download a Brochure
How it works, course authors.

- Certificates Authored
Pedro Pérez is Senior Lecturer of Applied Economics and Management at Cornell’s SC Johnson College of Business. He has taught large-format introductory courses to business management and entrepreneurship at Cornell since 2001. Dr. Pérez has degrees in chemical and industrial engineering, as well as an MBA and a Ph.D. in management.
- Investment Strategies
- Organizational Design
- Business Management Essentials

David Taylor, Ph.D., is an Associate Professor of Business Management/Marketing Communications at Kyoto University of Foreign Studies. His research focuses on consumer behavior and the marketing-leadership interface across cultures and has appeared in the Journal of Consumer Marketing and the Cornell Quarterly. He is a graduate of the Cornell Hotel School.
As a visiting professor, Dr. Taylor taught business management at Cornell University’s School of Continuing Education/Dyson School of Applied Economics and Management from 2000 to 2019 during the summer session. From 2015 to 2019, he also held a dual appointment as Director of Graduate Programs for the Hotel School and then Director of External Relations for the Cornell SC Johnson College of Business based at Cornell Tech in New York City.
Prior to becoming a professor, Taylor spent 15 years in industry working in or on over 25 markets in North America, Europe, Asia, and the Caribbean. While working for Hyatt International in Japan as the Director of Business Development/International Marketing, he and his marketing team were recipients of the Gold Key award as well as recognized by the prestigious Nikkei Business Weekly and the City of Osaka for success and creativity in advertising. He has also provided advisory and management search services to multinational companies operating in Japan.
Who Should Enroll
- Individual contributors interested in transitioning to leadership
- New managers
- Professionals who need to fill gaps in business fundamentals
- Professionals with work experience but no formal business training
- Professionals transitioning into roles within a corporate environment
- Small business owners and entrepreneurs
Stack To A Certificate
Request information now by completing the form below..
Enter your information to get access to a virtual open house with the eCornell team to get your questions answered live.

COMMENTS
Forecasting is valuable to businesses so that they can make informed business decisions. Financial forecasts are fundamentally informed guesses, and there are risks involved in relying on past ...
Mark Khavkin is the CFO of Pantheon Platform. A great forecast has five attributes. First, it includes projections of operating results and resource needs for the next 3-5 years. Firms typically ...
Bringing a real-world edge to forecasting. CFOs know what a "good" forecasting process should look like: it should be accurate and comprehensive but flexible enough to inform a range of critical business decisions—capital reallocation, hiring, strategy, sales, production, and more. But CFOs also recognize that there is no "typical ...
6. Delphi Method. The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance. A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge.
Planning, budgeting and forecasting is typically a three-step process for determining and mapping out an organization's short- and long-term financial goals. Planning provides a framework for a business' financial objectives — typically for the next three to five years. Budgeting details how the plan will be carried out month to month and ...
Why It Matters. Companies conduct business forecasts to determine their goals, targets, and project plans for each new period, whether quarterly, annually, or even 2-5 year planning. Forecasting helps managers guide strategy and make informed decisions about critical business operations such as sales, expenses, revenue, and resource allocation.
Now that you understand the basics of business forecasting, it's time to see how it works in practice. Read the following examples to better understand the different approaches to business forecasting. 1. A company forecasting its sales through the end of the year. Let's suppose a small greeting card company wants to forecast its sales ...
Business Forecasting is the process of using analytics, data, insights, and experience to make predictions and respond to various business needs. The insight gained by Business Forecasting enables companies to automate and optimize their business processes. A Forecaster's goal is to go beyond knowing what has happened and provide the best ...
Increase profits. The business forecasting process can improve your company's long-term profitability in several ways: It allows your business leaders to develop budgets based on data-driven sales predictions. Accurate forecasting can help your organization secure the funding necessary to grow the business.
General business forecasting predicts overall market trends and external factors that affect your business' success. Accounting forecasting creates projections of future business costs . Budget forecasting makes predictions for allocating the budget needed for future projects or addressing potential issues. Budgeting and forecasting software ...
With business forecasting, companies use different methods and data to predict market trends to help determine their short-term and long-term business outlook. This data is a vital part of helping companies grow, start new initiatives, and plan their finances for the quarter and year. It can also help you plan for potential seasonal dips in ...
Definition, Methods, and Models. Business forecasting is a crucial aspect of strategic planning for organizations across various industries. It involves using historical data, market trends, and statistical techniques to predict future business outcomes. These forecasts help businesses make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively ...
Clearly, business forecasting is a project unto itself. To manage a project and collect the data in a way that's useful in the future, you need a project management tool that can help you plan your process and select the data that helps you decide on a way forward. ProjectManager is award-winning software that organizes projects with features ...
planning and analysis (FP&A) teams spend most of their time looking at historical data to explain current outcomes. When they do get to look forward, they are likely focused on the budget, or on rolling up commitments from different business units into the overall business plan. Sometimes the business plan itself passes for the forecast.
Forecasting is making predictions using past or live data. To increase forecasting accuracy, you have to study your customers, know industry trends, and assess the competition. Forecasting is valuable to any organization to make informed business choices and plans. As such, it is crucial to make an almost accurate forecast to enhance business ...
Informing business decisions. Business forecasting plays a vital role in informing business decisions. By analyzing historical data and examining market conditions, businesses can make predictions about the future and use that information to guide their decision-making process. This allows managers to develop strategies based on reliable ...
Six Rules for Effective Forecasting. Summary. The primary goal of forecasting is to identify the full range of possibilities facing a company, society, or the world at large. In this article ...
March 08, 2022. Matthias Clamer/Getty Images. Summary. Business forecasts are often wrong — and yet they can still be a powerful tool for savvy leaders if they view them in aggregate and ask the ...
Forecasting horizons are an integral part of planning and decision-making in any organization. This is why financial managers need to clearly define the horizon of their forecasts. From a financial perspective, horizon analysis examines the expected discounted returns of a security or investment portfolio's total returns over multiple periods.
Business forecasting and planning play a crucial role in the success and sustainability of any business. Forecasting and planning is a structured process where you study past data, market shifts, and other important details to predict what's coming next. This helps you figure out the best way to use your resources, make smart decisions about ...
This section provides general guidance on important considerations in the practice of business forecasting, including: Recognition of uncertainty and the need for probabilistic forecasts. The essential elements of a useful forecast. Measurement of forecastability and bounds of forecast accuracy. Establishing appropriate benchmarks of forecast ...
You will also identify the various activities involved in supporting your chosen strategy alongside the complexity of acquiring raw materials and converting them into products for the end customer. Additionally, you will conduct an analysis to help assess your company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Strategic Planning and Forecasting Fundamentals Abstract Individuals and organizations have operated for hundreds of years by planning and forecasting in an intuitive manner. It was not until the 1950s that formal approaches became popular. Since then, such approaches have been used by business, government, and nonprofit organizations.