Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
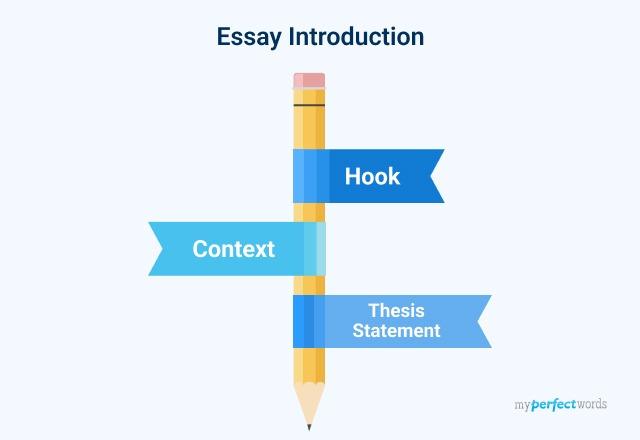
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college....

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an introduction paragraph in 3 steps.
General Education

It’s the roadmap to your essay, it’s the forecast for your argument, it’s...your introduction paragraph, and writing one can feel pretty intimidating. The introduction paragraph is a part of just about every kind of academic writing , from persuasive essays to research papers. But that doesn’t mean writing one is easy!
If trying to write an intro paragraph makes you feel like a Muggle trying to do magic, trust us: you aren’t alone. But there are some tips and tricks that can make the process easier—and that’s where we come in.
In this article, we’re going to explain how to write a captivating intro paragraph by covering the following info:
- A discussion of what an introduction paragraph is and its purpose in an essay
- An overview of the most effective introduction paragraph format, with explanations of the three main parts of an intro paragraph
- An analysis of real intro paragraph examples, with a discussion of what works and what doesn’t
- A list of four top tips on how to write an introduction paragraph
Are you ready? Let’s begin!

What Is an Introduction Paragraph?
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay , paper, or other type of academic writing. Argumentative essays , book reports, research papers, and even personal essays are common types of writing that require an introduction paragraph. Whether you’re writing a research paper for a science course or an argumentative essay for English class , you’re going to have to write an intro paragraph.
So what’s the purpose of an intro paragraph? As a reader’s first impression of your essay, the intro paragraph should introduce the topic of your paper.
Your introduction will also state any claims, questions, or issues that your paper will focus on. This is commonly known as your paper’s thesis . This condenses the overall point of your paper into one or two short sentences that your reader can come back and reference later.
But intro paragraphs need to do a bit more than just introduce your topic. An intro paragraph is also supposed to grab your reader’s attention. The intro paragraph is your chance to provide just enough info and intrigue to make your reader say, “Hey, this topic sounds interesting. I think I’ll keep reading this essay!” That can help your essay stand out from the crowd.
In most cases, an intro paragraph will be relatively short. A good intro will be clear, brief, purposeful, and focused. While there are some exceptions to this rule, it’s common for intro paragraphs to consist of three to five sentences .
Effectively introducing your essay’s topic, purpose, and getting your reader invested in your essay sounds like a lot to ask from one little paragraph, huh? In the next section, we’ll demystify the intro paragraph format by breaking it down into its core parts . When you learn how to approach each part of an intro, writing one won’t seem so scary!

Once you figure out the three parts of an intro paragraph, writing one will be a piece of cake!
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph
In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement . Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay.
Below, we’ll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an effective hook, providing context, and crafting a thesis statement. When you put these elements together, you’ll have an intro paragraph that does a great job of making a great first impression on your audience!
Intro Paragraph Part 1: The Hook
When it comes to how to start an introduction paragraph, o ne of the most common approaches is to start with something called a hook.
What does hook mean here, though? Think of it this way: it’s like when you start a new Netflix series: you look up a few hours (and a few episodes) later and you say, “Whoa. I guess I must be hooked on this show!”
That’s how the hook is supposed to work in an intro paragrap h: it should get your reader interested enough that they don’t want to press the proverbial “pause” button while they’re reading it . In other words, a hook is designed to grab your reader’s attention and keep them reading your essay!
This means that the hook comes first in the intro paragraph format—it’ll be the opening sentence of your intro.
It’s important to realize that there are many different ways to write a good hook. But generally speaking, hooks must include these two things: what your topic is, and the angle you’re taking on that topic in your essay.
One approach to writing a hook that works is starting with a general, but interesting, statement on your topic. In this type of hook, you’re trying to provide a broad introduction to your topic and your angle on the topic in an engaging way .
For example, if you’re writing an essay about the role of the government in the American healthcare system, your hook might look something like this:
There's a growing movement to require that the federal government provide affordable, effective healthcare for all Americans.
This hook introduces the essay topic in a broad way (government and healthcare) by presenting a general statement on the topic. But the assumption presented in the hook can also be seen as controversial, which gets readers interested in learning more about what the writer—and the essay—has to say.
In other words, the statement above fulfills the goals of a good hook: it’s intriguing and provides a general introduction to the essay topic.
Intro Paragraph Part 2: Context
Once you’ve provided an attention-grabbing hook, you’ll want to give more context about your essay topic. Context refers to additional details that reveal the specific focus of your paper. So, whereas the hook provides a general introduction to your topic, context starts helping readers understand what exactly you’re going to be writing about
You can include anywhere from one to several sentences of context in your intro, depending on your teacher’s expectations, the length of your paper, and complexity of your topic. In these context-providing sentences, you want to begin narrowing the focus of your intro. You can do this by describing a specific issue or question about your topic that you’ll address in your essay. It also helps readers start to understand why the topic you’re writing about matters and why they should read about it.
So, what counts as context for an intro paragraph? Context can be any important details or descriptions that provide background on existing perspectives, common cultural attitudes, or a specific situation or controversy relating to your essay topic. The context you include should acquaint your reader with the issues, questions, or events that motivated you to write an essay on your topic...and that your reader should know in order to understand your thesis.
For instance, if you’re writing an essay analyzing the consequences of sexism in Hollywood, the context you include after your hook might make reference to the #metoo and #timesup movements that have generated public support for victims of sexual harassment.
The key takeaway here is that context establishes why you’re addressing your topic and what makes it important. It also sets you up for success on the final piece of an intro paragraph: the thesis statement.
Elle Woods' statement offers a specific point of view on the topic of murder...which means it could serve as a pretty decent thesis statement!
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis
The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way . The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay. A good thesis statement will be clear, straightforward, and highlight the overall point you’re trying to make.
Some instructors also ask students to include an essay map as part of their thesis. An essay map is a section that outlines the major topics a paper will address. So for instance, say you’re writing a paper that argues for the importance of public transport in rural communities. Your thesis and essay map might look like this:
Having public transport in rural communities helps people improve their economic situation by giving them reliable transportation to their job, reducing the amount of money they spend on gas, and providing new and unionized work .
The underlined section is the essay map because it touches on the three big things the writer will talk about later. It literally maps out the rest of the essay!
So let’s review: Your thesis takes the idea you’ve introduced in your hook and context and wraps it up. Think of it like a television episode: the hook sets the scene by presenting a general statement and/or interesting idea that sucks you in. The context advances the plot by describing the topic in more detail and helping readers understand why the topic is important. And finally, the thesis statement provides the climax by telling the reader what you have to say about the topic.
The thesis statement is the most important part of the intro. Without it, your reader won’t know what the purpose of your essay is! And for a piece of writing to be effective, it needs to have a clear purpose. Your thesis statement conveys that purpose , so it’s important to put careful thought into writing a clear and compelling thesis statement.

How To Write an Introduction Paragraph: Example and Analysis
Now that we’ve provided an intro paragraph outline and have explained the three key parts of an intro paragraph, let’s take a look at an intro paragraph in action.
To show you how an intro paragraph works, we’ve included a sample introduction paragraph below, followed by an analysis of its strengths and weaknesses.
Example of Introduction Paragraph
While college students in the U.S. are struggling with how to pay for college, there is another surprising demographic that’s affected by the pressure to pay for college: families and parents. In the face of tuition price tags that total more than $100,000 (as a low estimate), families must make difficult decisions about how to save for their children’s college education. Charting a feasible path to saving for college is further complicated by the FAFSA’s estimates for an “Expected Family Contribution”—an amount of money that is rarely feasible for most American families. Due to these challenging financial circumstances and cultural pressure to give one’s children the best possible chance of success in adulthood, many families are going into serious debt to pay for their children’s college education. The U.S. government should move toward bearing more of the financial burden of college education.
Example of Introduction Paragraph: Analysis
Before we dive into analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of this example intro paragraph, let’s establish the essay topic. The sample intro indicates that t he essay topic will focus on one specific issue: who should cover the cost of college education in the U.S., and why. Both the hook and the context help us identify the topic, while the thesis in the last sentence tells us why this topic matters to the writer—they think the U.S. Government needs to help finance college education. This is also the writer’s argument, which they’ll cover in the body of their essay.
Now that we’ve identified the essay topic presented in the sample intro, let’s dig into some analysis. To pin down its strengths and weaknesses, we’re going to use the following three questions to guide our example of introduction paragraph analysis:
- Does this intro provide an attention-grabbing opening sentence that conveys the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide relevant, engaging context about the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide a thesis statement that establishes the writer’s point of view on the topic and what specific aspects of the issue the essay will address?
Now, let’s use the questions above to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of this sample intro paragraph.
Does the Intro Have a Good Hook?
First, the intro starts out with an attention-grabbing hook . The writer starts by presenting an assumption (that the U.S. federal government bears most of the financial burden of college education), which makes the topic relatable to a wide audience of readers. Also note that the hook relates to the general topic of the essay, which is the high cost of college education.
The hook then takes a surprising turn by presenting a counterclaim : that American families, rather than students, feel the true burden of paying for college. Some readers will have a strong emotional reaction to this provocative counterclaim, which will make them want to keep reading! As such, this intro provides an effective opening sentence that conveys the essay topic.
Does the Intro Give Context?
T he second, third, and fourth sentences of the intro provide contextual details that reveal the specific focus of the writer’s paper . Remember: the context helps readers start to zoom in on what the paper will focus on, and what aspect of the general topic (college costs) will be discussed later on.
The context in this intro reveals the intent and direction of the paper by explaining why the issue of families financing college is important. In other words, the context helps readers understand why this issue matters , and what aspects of this issue will be addressed in the paper.
To provide effective context, the writer refers to issues (the exorbitant cost of college and high levels of family debt) that have received a lot of recent scholarly and media attention. These sentences of context also elaborate on the interesting perspective included in the hook: that American families are most affected by college costs.
Does the Intro Have a Thesis?
Finally, this intro provides a thesis statement that conveys the writer’s point of view on the issue of financing college education. This writer believes that the U.S. government should do more to pay for students’ college educations.
However, the thesis statement doesn’t give us any details about why the writer has made this claim or why this will help American families . There isn’t an essay map that helps readers understand what points the writer will make in the essay.
To revise this thesis statement so that it establishes the specific aspects of the topic that the essay will address, the writer could add the following to the beginning of the thesis statement:
The U.S. government should take on more of the financial burden of college education because other countries have shown this can improve education rates while reducing levels of familial poverty.
Check out the new section in bold. Not only does it clarify that the writer is talking about the pressure put on families, it touches on the big topics the writer will address in the paper: improving education rates and reduction of poverty. So not only do we have a clearer argumentative statement in this thesis, we also have an essay map!
So, let’s recap our analysis. This sample intro paragraph does an effective job of providing an engaging hook and relatable, interesting context, but the thesis statement needs some work ! As you write your own intro paragraphs, you might consider using the questions above to evaluate and revise your work. Doing this will help ensure you’ve covered all of your bases and written an intro that your readers will find interesting!

4 Tips for How To Write an Introduction Paragraph
Now that we’ve gone over an example of introduction paragraph analysis, let’s talk about how to write an introduction paragraph of your own. Keep reading for four tips for writing a successful intro paragraph for any essay.
Tip 1: Analyze Your Essay Prompt
If you’re having trouble with how to start an introduction paragraph, analyze your essay prompt! Most teachers give you some kind of assignment sheet, formal instructions, or prompt to set the expectations for an essay they’ve assigned, right? Those instructions can help guide you as you write your intro paragraph!
Because they’ll be reading and responding to your essay, you want to make sure you meet your teacher’s expectations for an intro paragraph . For instance, if they’ve provided specific instructions about how long the intro should be or where the thesis statement should be located, be sure to follow them!
The type of paper you’re writing can give you clues as to how to approach your intro as well. If you’re writing a research paper, your professor might expect you to provide a research question or state a hypothesis in your intro. If you’re writing an argumentative essay, you’ll need to make sure your intro overviews the context surrounding your argument and your thesis statement includes a clear, defensible claim.
Using the parameters set out by your instructor and assignment sheet can put some easy-to-follow boundaries in place for things like your intro’s length, structure, and content. Following these guidelines can free you up to focus on other aspects of your intro... like coming up with an exciting hook and conveying your point of view on your topic!
Tip 2: Narrow Your Topic
You can’t write an intro paragraph without first identifying your topic. To make your intro as effective as possible, you need to define the parameters of your topic clearly—and you need to be specific.
For example, let’s say you want to write about college football. “NCAA football” is too broad of a topic for a paper. There is a lot to talk about in terms of college football! It would be tough to write an intro paragraph that’s focused, purposeful, and engaging on this topic. In fact, if you did try to address this whole topic, you’d probably end up writing a book!
Instead, you should narrow broad topics to identify a specific question, claim, or issue pertaining to some aspect of NCAA football for your intro to be effective. So, for instance, you could frame your topic as, “How can college professors better support NCAA football players in academics?” This focused topic pertaining to NCAA football would give you a more manageable angle to discuss in your paper.
So before you think about writing your intro, ask yourself: Is my essay topic specific, focused, and logical? Does it convey an issue or question that I can explore over the course of several pages? Once you’ve established a good topic, you’ll have the foundation you need to write an effective intro paragraph .

Once you've figured out your topic, it's time to hit the books!
Tip 3: Do Your Research
This tip is tightly intertwined with the one above, and it’s crucial to writing a good intro: do your research! And, guess what? This tip applies to all papers—even ones that aren’t technically research papers.
Here’s why you need to do some research: getting the lay of the land on what others have said about your topic—whether that’s scholars and researchers or the mass media— will help you narrow your topic, write an engaging hook, and provide relatable context.
You don't want to sit down to write your intro without a solid understanding of the different perspectives on your topic. Whether those are the perspectives of experts or the general public, these points of view will help you write your intro in a way that is intriguing and compelling for your audience of readers.
Tip 4: Write Multiple Drafts
Some say to write your intro first; others say write it last. The truth is, there isn’t a right or wrong time to write your intro—but you do need to have enough time to write multiple drafts .
Oftentimes, your professor will ask you to write multiple drafts of your paper, which gives you a built-in way to make sure you revise your intro. Another approach you could take is to write out a rough draft of your intro before you begin writing your essay, then revise it multiple times as you draft out your paper.
Here’s why this approach can work: as you write your paper, you’ll probably come up with new insights on your topic that you didn’t have right from the start. You can use these “light bulb” moments to reevaluate your intro and make revisions that keep it in line with your developing essay draft.
Once you’ve written your entire essay, consider going back and revising your intro again . You can ask yourself these questions as you evaluate your intro:
- Is my hook still relevant to the way I’ve approached the topic in my essay?
- Do I provide enough appropriate context to introduce my essay?
- Now that my essay is written, does my thesis statement still accurately reflect the point of view that I present in my essay?
Using these questions as a guide and putting your intro through multiple revisions will help ensure that you’ve written the best intro for the final draft of your essay. Also, revising your writing is always a good thing to do—and this applies to your intro, too!

What's Next?
Your college essays also need great intro paragraphs. Here’s a guide that focuses on how to write the perfect intro for your admissions essays.
Of course, the intro is just one part of your college essay . This article will teach you how to write a college essay that makes admissions counselors sit up and take notice.
Are you trying to write an analytical essay? Our step-by-step guide can help you knock it out of the park.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Essay Introduction
Last Updated: January 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,232,255 times.
The introduction of your essay serves two important purposes. First, it gets your reader interested in the topic and encourages them to read what you have to say about it. Second, it gives your reader a roadmap of what you're going to say and the overarching point you're going to make – your thesis statement. A powerful introduction grabs your reader's attention and keeps them reading.
Sample Essay Hooks & Introductions

Hooking Your Reader

- If you're writing a paper for a class, don't automatically assume your instructor is your audience. If you write directly to your instructor, you'll end up glossing over some information that is necessary to show that you properly understand the subject of your essay.
- It can be helpful to reverse-engineer your audience based on the subject matter of your essay. For example, if you're writing an essay about a women's health issue for a women's studies class, you might identify your audience as young women within the age range most affected by the issue.

- For this hook to be effective, your fact needs to be sufficiently surprising. If you're not sure, test it on a few friends. If they react by expressing shock or surprise, you know you've got something good.
- Use a fact or statistic that sets up your essay, not something you'll be using as evidence to prove your thesis statement. Facts or statistics that demonstrate why your topic is important (or should be important) to your audience typically make good hooks.

- For example, if you were writing an essay proposing a change to drunk driving laws, you might open with a story of how the life of a victim was changed forever after they were hit by a drunk driver.

- For example, if you're writing an essay about a public figure, you might include an anecdote about an odd personal habit that cleverly relates back to your thesis statement.
- Particularly with less formal papers or personal essays, humorous anecdotes can be particularly effective hooks.

- For example: "What would you do if you could play God for a day? That's exactly what the leaders of the tiny island nation of Guam tried to answer."
- If your essay prompt was a question, don't just repeat it in your paper. Make sure to come up with your own intriguing question.

- Broad, sweeping generalizations may ring false with some readers and alienate them from the start. For example, "everyone wants someone to love" would alienate someone who identified as aromantic or asexual.
Creating Your Context

- Use an appropriate transitional word or phrase, such as "however" or "similarly," to move from your specific anecdote back out to a broader scope.
- For example, if you related a story about one individual, but your essay isn't about them, you can relate the hook back to the larger topic with a sentence like "Tommy wasn't alone, however. There were more than 200,000 dockworkers affected by that union strike."

- For example, if your thesis relates to how blackface was used as a means of enforcing racial segregation, your introduction would describe what blackface performances were, and where and when they occurred.
- If you are writing an argumentative paper, make sure to explain both sides of the argument in a neutral or objective manner.

- Definitions would be particularly important if your essay is discussing a scientific topic, where some scientific terminology might not be understood by the average layperson.
- Definitions also come in handy in legal or political essays, where a term may have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used.

- If you're using 2 or 3 sentences to describe the context for your thesis, try to make each sentence a bit more specific than the one before it. Draw your reader in gradually.
- For example, if you're writing an essay about drunk driving fatalities, you might start with an anecdote about a particular victim. Then you could provide national statistics, then narrow it down further to statistics for a particular gender or age group.
Presenting Your Thesis

- For example, a thesis for an essay on blackface performance might be "Because of its humiliating and demoralizing effect on African American slaves, blackface was used less as a comedy routine and more as a way of enforcing racial segregation."
- Be assertive and confident in your writing. Avoid including fluff such as "In this essay, I will attempt to show...." Instead, dive right in and make your claim, bold and proud.
- Your outline should be specific, unique, and provable. Through your essay, you'll make points that will show that your thesis statement is true – or at least persuade your readers that it's most likely true.

- If you've created an outline for your essay, this sentence is essentially the main subjects of each paragraph of the body of your essay.
- For example, if you're writing an essay about the unification of Italy, you might list 3 obstacles to unification. In the body of your essay, you would discuss details about how each of those obstacles was addressed or overcome.
- Instead of just listing all of your supporting points, sum them up by stating "how" or "why" your thesis is true. For example, instead of saying, "Phones should be banned from classrooms because they distract students, promote cheating, and make too much noise," you might say "Phones should be banned from classrooms because they act as an obstacle to learning."

- To figure out if you need a transition sentence, read the introduction and the first paragraph out loud. If you find yourself pausing or stumbling between the paragraphs, work in a transition to make the move smoother.
- You can also have friends or family members read your easy. If they feel it's choppy or jumps from the introduction into the essay, see what you can do to smooth it out.
Bringing It All Together

- If you're writing your essay for a class assignment, ask your instructor for examples of well-written essays that you can look at. Take note of conventions that are commonly used by writers in that discipline.
- Make a brief outline of the essay based on the information presented in the introduction. Then look at that outline as you read the essay to see how the essay follows it to prove the writer's thesis statement.

- For shorter essays under 1,000 words, keep your introduction to 1 paragraph, between 100 and 200 words.
- Always follow your instructor's guidelines for length. These rules can vary at times based on genre or form of writing.

- As you write your essay, you may want to jot down things you want to include in your introduction. For example, you may realize that you're using a particular term that you need to define in your introduction.

- Delete any filler or unnecessary language. Given the shortness of the introduction, every sentence should be essential to your reader's understanding of your essay.

- The first sentence or two should be your hook, designed to grab your reader's attention and get them interested in reading your essay.
- The next couple of sentences create a bridge between your hook and the overall topic of the rest of your essay.
- End your introduction with your thesis statement and a list of the points you will make in your essay to support or prove your thesis statement.
Expert Q&A

- If you are answering or responding to an assigned question, make sure you've interpreted the question correctly. The quality of your writing is irrelevant if your essay doesn't answer the question. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 1
- Have friends or family members read your essay and provide you with feedback. If you're writing for a class, you might want to exchange essays with another classmate and give each other feedback on your work. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/audience/
- ↑ http://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/planning/intros-and-conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction/
- ↑ https://www.esu.edu/writing-studio/guides/hook.cfm
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/cliches/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185917
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/introductions-conclusions
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/planning/intros-and-conclusions/
About This Article

Start your introduction with a relevant story, fact, or quote that will engage readers. Then, add 2-3 sentences of background information to give your essay context, and include important dates, locations, or historical moments where applicable. Finally, include your thesis statement, which is a specific, arguable, and provable statement that answers a question about your essay topic. For example, your thesis might read: "In the modern age, online dating apps like Tinder provide a wider variety of romantic options than young people have ever had before." For more tips and examples on how to craft your thesis and put your introduction together, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 11, 2016
Did this article help you?
Jul 11, 2020
Teighan Vickrey
Mar 18, 2018
Apr 27, 2017
Arturo Rueda
Mar 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Most Popular
13 days ago
How to Write a Position Paper
How to reference a movie in an essay, is gen z actually lazy this admission consultant doesn’t think so, zoterobib review.
12 days ago
How to Write a Hypothesis
How to summarize an essay.

College and high school students (as well as maybe some middle schoolers) will often face the task of summarizing a book, article, video, or anything they’ve seen/read. Sometimes, you will have to create summaries for yourself, so that you understand the material better. Other times though, you will have to write summary essays, the main purpose of which is to give others an overview of the original source. In both cases, summaries look somewhat the same: they are concise, contain only the most crucial points, and pass on the key idea or essence of the initial material, be it a movie or a book. To serve that purpose, summaries need to be well-written and we will show you exactly how to summarize an essay in the most effective format.
The Key Parts of a Summary: Structure
As a student, you know that most writing tasks have guidelines. You also most probably know that, if you are asked to write a certain type of writing, it has a specific structure and format. See, that’s why you can’t write summaries at random too.
Thus, before starting the writing process, let’s first figure out what structure this type of writing has. This will allow you to create a summary essay outline that will make it easy for you to include all the essential information and will guide you throughout the writing process as well.
Here’s what you absolutely have to include in your essay summary:
- Introduction + thesis, which will provide readers with all the necessary details about the work (title, author, etc) and its key idea
- Body paragraphs that support the main point of the essay and therefore include all the necessary details that show how the author justifies their claims
- Conclusion paragraph, which is usually one sentence that may rephrase the main idea and which is called to tie everything together.
You can use our checklist below to help you track down whether you included all the necessary components:

Writing a Summary Essay: Detailed Guide
Before jumping straight to writing, let’s see what we now know about these special summaries:
- What is a summary essay? – Check✅ It’s a concise overview of the essay you’ve read that communicates the key ideas of the material.
- What parts does a summary essay have? – Another check✅ Introduction, with details about the essay + thesis statement; body, with the summary of the main points; conclusion, which wraps up the key idea of the essay.
- How to write a Summary? – ⚠️This one we will break down further in this paragraph.
One would think that the guide to writing a summary couldn’t be that complex: just read the text, sit down, and write. However, if you scroll through the writing guide below, you will see that there are nuances.
Read & Study
First things first, get to know what the essay is about. Read through it carefully. If it helps you, take notes as you read, marking the most important arguments and ideas that need mentioning in your essay. A good thing is you can get a feeling for the author’s style, tone, and mood, and try to identify the main claims they made.
Divide & Outline
After you are done reading, break down the essay into several sections. Breaking the text into several parts will make the material easier to grasp. With their help, you can also create a rough outline of what your summary will look like.
Identify Key Ideas
Read each part you divided the essay into once more. This time, highlight some of the key points. Mark areas you want to refer to in your summary, as well as those that shouldn’t be included in your essay. During this stage, you should also be able to identify the general message and the essence of the essay.
Create an Introduction
You now have all the necessary details to be able to begin summarizing. Start with an introduction with an opening line that includes the name of the author and the title of their essay. Follow that information with a rather broad overview of the content of the work you will be summarizing. Sometimes, if it is important to understand the essay, you may present here the author’s background as well. And don’t forget the thesis statement that transmits the purpose/point of the work.
Move on to the Body
In the main body paragraphs, state the ideas you’ve chosen while reading the text. Expand on them by including one or more examples from the original text. Don’t forget to include citations if you do that. Our citation generator can give a hand with that.
Quick Citations for Your Convenience
Also, in this part, you can mention any supportive points given in the original text. These could be examples, or stories (but brief or rephrased) that the author originally mentioned.
Finish with a Conclusion & References
Phew, we are at the finish line now. All that is left is to write a concluding paragraph, which is usually around 2-3 sentences tops. Here you need to basically rewrite the thesis statement, once again emphasizing the main purpose or claim of the original source. After that, don’t forget to include a properly formatted reference of the original source to acknowledge the writer. It is not always a requirement but it is especially needed if you include quotes in the text of your summary.
Review & Proofread
Okay, the hardest part is left behind. You can now read through what you’ve written. Make sure everything sounds logical and clear. Pay attention to grammatical and punctuation mistakes. Try reading it aloud or giving it to somebody else to read it for you. This will help you pinpoint places that need improvement and maybe throughout 1 or 2 unnecessary details.
Dos and Don’ts of Summary Essay Writing
Look at you, knowing all this about writing an essay summary. Good for you! And what’s more, you can basically complete any type of summary now, just switching up its content. However, we are not done with teaching you yet. We got the basics settled, so now it’s time to get to the advanced stuff. These are the dos and don’ts that will serve as boosters for your writing. Keeping these tips in mind will help you craft your summaries more quickly and will largely reduce the proofreading time.
Essay Summary Example for Inspiration
Here’s a simple example of a summary of an essay that can serve as a sample and inspiration for your work:

How do you write a summary of an essay?
If you want to create a good summary, start by carefully reading. You need to understand its main ideas and arguments. Then, in your own words, write a brief overview that captures the essay’s central theme and key points. Don’t forget to include the author’s thesis statement and the evidence they use to support their argument. Keep your summary short and focused, avoiding any personal opinions or unnecessary details.
How do I summarize my essay?
In case it’s your own essay you want to summarize, you should follow the same steps: identify your main argument, outline the supporting points, and then communicate this information in a short overview that gives a clear idea of your essay’s content.
What are the 5 parts of a summary?
Even though we mentioned only 3 major parts of the summary in our article, most summaries can be broken down into 5 aspects: introduction, thesis, body, conclusion, and references. Each of these is important for creating an all-inclusive summary.
What are the rules for summary essay?
Okay, let’s go over the basic summary rules once again. The summary should be short (around ¼ of the original) and concise (include only the most essential information without repetition). Additionally, this writing type should follow a logical structure, meaning you need to uncover the important facts in the same order as they are presented in the essay. Lastly, essay summaries should be independent. The readers chose to look through the summary because they didn’t want to read the whole text. Hence, they need to be able to learn everything important mentioned in the original.
What words should you start a summary essay with?
Usually, a summary of an essay starts with an introductory sentence that includes the name of the author, the title of the work, and the general idea of the text as you perceive it. Remember, you should describe everything in your own words, both to avoid plagiarism and to show your understanding of the material.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (2)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
In that, do we need to support the main idea?
More from Writing an Essay

Dec 11 2012
How to Write an Evaluation Essay
Nov 21 2012
Writing an Analysis Essay

Nov 16 2012
How to Write a Reflective Essay
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Narrative Essay
How to write a summary.
Proficient students understand that summarizing , identifying what is most important and restating the text (or other media) in your own words, is an important tool for college success.
After all, if you really know a subject, you will be able to summarize it. If you cannot summarize a subject, even if you have memorized all the facts about it, you can be absolutely sure that you have not learned it. And, if you truly learn the subject, you will still be able to summarize it months or years from now.
Proficient students may monitor their understanding of a text by summarizing as they read. They understand that if they can write a one- or two-sentence summary of each paragraph after reading it, then that is a good sign that they have correctly understood it. If they can not summarize the main idea of the paragraph, they know that comprehension has broken down and they need to use fix-up strategies to repair understanding.
Summary Writing Format
- When writing a summary, remember that it should be in the form of a paragraph.
- A summary begins with an introductory sentence that states the text’s title, author and main point of the text as you see it.
- A summary is written in your own words.
- A summary contains only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions, interpretations, deductions or comments into a summary.
- Identify in order the significant sub-claims the author uses to defend the main point.
- Copy word-for-word three separate passages from the essay that you think support and/or defend the main point of the essay as you see it.
- Cite each passage by first signaling the work and the author, put “quotation marks” around the passage you chose, and put the number of the paragraph where the passages can be found immediately after the passage.
- Using source material from the essay is important. Why? Because defending claims with source material is what you will be asked to do when writing papers for your college professors.
- Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
Example Summary Writing Format
In the essay Santa Ana , author Joan Didion’s main point is ( state main point ). According to Didion “… passage 1 …” (para.3). Didion also writes “… passage 2 …” (para.8). Finally, she states “… passage 3 …” (para. 12) Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Paul Powell. Provided by : Central Community College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Elisabeth Ellington and Ronda Dorsey Neugebauer. Provided by : Chadron State College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on 25 September 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 May 2023.
Summarising , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or analysing the source. You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, frequently asked questions.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarise an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyse or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarising is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organised into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.

Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarise this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying ‘an apple a day keeps the doctor away’.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or research paper, you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarising many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words.
Save yourself some time with the free summariser.
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarising, and on the purpose of the summary.
With the summariser tool you can easily adjust the length of your summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarise or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarising an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Reference the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarise the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarise a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 12). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 13 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/how-to-write-a-summary/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in harvard & apa, apa referencing (7th ed.) quick guide | in-text citations & references.

Introduction
Goals and Goal Setting
Goals Common to All RST Writers
Other Goals to Consider
Defining My Own Goals
Advice about Assignments
Getting Started: Listing Topics to Write about in the Tutorial
Narrative One: Personal Piece on a Significant Experience
Narrative Two: Academic Piece on a Significant Experience
Summary/Response One
Summary/Response Two
Tutorial Evaluation Postscript
On Using the Resources for Writers
Generating and Developing Ideas
Finding/Expressing Main Ideas
Showing v. Telling Sentences
Focusing Topic Sentences
Thesis Statements
Reading Strategies
Assessing Your Reading Strategies
Summarizing
Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays
Discourse Analysis Worksheet
Trade Magazines
Selecting Readings
A summary is a concise paraphrase of all the main ideas in an essay. It cites the author and the title (usually in the first sentence); it contains the essay's thesis and supporting ideas; it may use direct quotation of forceful or concise statements of the author's ideas; it will NOT usually cite the author's examples or supporting details unless they are central to the main idea. Most summaries present the major points in the order that the author made them and continually refer back to the article being summarized (i.e. "Damon argues that ..." or "Goodman also points out that ... "). The summary should take up no more than one-third the length of the work being summarized.
The Response:
A response is a critique or evaluation of the author's essay. Unlike the summary, it is composed of YOUR opinions in relation to the article being summarized. It examines ideas that you agree or disagree with and identifies the essay's strengths and weaknesses in reasoning and logic, in quality of supporting examples, and in organization and style. A good response is persuasive; therefore, it should cite facts, examples, and personal experience that either refutes or supports the article you're responding to, depending on your stance.
Two Typical Organizational Formats for Summary/Response Essays:
1. Present the summary in a block of paragraphs, followed by the response in a block:
Intro/thesis Summary (two to three paragraphs) Agreement (or disagreement) Disagreement (or agreement) Conclusion
Note: Some essays will incorporate both agreement and disagreement in a response, but this is not mandatory.
2. Introduce the essay with a short paragraph that includes your thesis. Then, each body paragraph summarizes one point and responds to it, and a conclusion wraps the essay up.
Intro/thesis Summary point one; agree/disagree Summary point two; agree/disagree Summary point three; agree/disagree Conclusion
Essay Writing Guide
Writing An Essay Introduction
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
15 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Essay introductions are the first impression that your reader will have of your paper.
You want to draw in your readers with an interesting opening that sets the tone for the rest of your work. So, it's important to make sure they're well-written and engaging.
In this blog, you will learn how to write an effective introduction to grab your reader’s attention from the very beginning. With the help of tips and examples below, you can craft an incredible essay introduction to set the tone for a powerful paper.
So let's begin!

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers
- 1. What is an Essay Introduction?
- 2. How To Write An Essay Introduction?
- 3. The Essay Introduction Structure
- 4. Essay Introduction Examples
- 5. Tips for Writing Better Essay Introductions
What is an Essay Introduction?
An essay introduction is the first paragraph of your It provides a roadmap for the rest of your paper and tells the reader what to expect from your work.
Purpose of the Essay Introduction
The main purpose of an essay introduction is to set the stage for what the reader can expect from your essay. It aims to catch the readers’ interest, provide necessary background information, and introduce them to the central argument.
How To Write An Essay Introduction?
Now that you know what an introduction is supposed to be, let’s move on to how to write an effective one.
There are four essential elements of an effective introduction:
- Engaging Hook
- Context and Background Information
- Overview of the Main Points and Essay Structure
- Thesis Statement
Let’s go over them step by step:
Step 1: Start With a Hook
Start your essay introduction with an interesting hook statement that grabs your readers’ attention. The goal of the hook is to make your reader interested in reading your essay and keep them engaged until the end.
Hooks can have several different forms; it can be a quote, an anecdote, or an interesting fact. Here are some types of hooks you can use:
- Anecdote: Share a relevant and interesting story or personal experience related to your topic.
- Rhetorical Question: Pose a thought-provoking question that encourages readers to think about the subject.
- Quotation: Begin with a compelling quote from a reputable source or a well-known figure.
- Surprising Fact or Statistic: Present a surprising or startling piece of information that relates to your topic.
- Vivid Description: Use descriptive language to paint a vivid picture that draws the reader into your essay.
The key to a successful hook is relevance. Ensure that your hook relates directly to the topic of your essay and sets the stage for what follows. You can also refer to other catchy hook examples for writing a captivating start.
Step 2: Discuss Context Background Information
After grabbing your reader's attention with a hook, it's crucial to provide context and background information about your topic.
This can include facts, definitions, and historical information. Knowing this information, your reader will be better equipped to understand the rest of your essay.
Depending on your topic, you can include these aspects to establish context:
- Historical Context: Explain the historical significance or evolution of the topic if relevant.
- Definitions: Provide a clear definition of key terms or concepts central to your essay.
- Explain Relevant Developments: Briefly mention important facts or developments related to your topic.
- Why It Matters: Explain why the topic is important or relevant to your readers or the society at large.
Here's an example:
Step 3: Overview of the Main Points and Essay Structure
Once you've engaged your reader and provided the necessary context, it's time to introduce the topic and overall argument. This part of the introduction serves as a preview of what to expect in the body of the essay.
You can achieve this by outlining the main points or arguments you will discuss and briefly mentioning the structure of the essay. This helps your reader navigate the content and understand the logical flow of your ideas.
Here's a demonstration of it.
Step 4: Write the Thesis Statement
The last part of the introduction is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the central point or argument of your essay. It conveys the main idea you will explore and defend in the following paragraphs.
A well-constructed thesis statement is specifically debatable and provides a road map for the entire essay. The thesis statement is written at the end of the introduction paragraph.
Here's a thesis statement example:
Now, if we put all these elements together step-by-step, we will have an excellent essay introduction. Here's an example of a strong introduction:
The Essay Introduction Structure
The structure of an essay introduction includes a hook, contextual information, and a thesis statement. In other words, the introduction moves from the general to the specific.

Check out these essay introduction samples that demonstrate the structure of an introduction.
Essay Introduction Outline
Essay Introduction Sample
Essay Introduction Examples
Here are some interesting introduction examples for different types of essays . Read these examples to understand what a powerful start looks like for various kinds of essays.
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing where the author takes a stance on a particular issue, presents arguments to support that stance, and aims to persuade the reader of the validity of their viewpoint.
To write an effective argumentative essay introduction, you should hook the reader's attention, provide context, present your thesis statement, and outline your main arguments.
Here is an example for you to understand how to write an argumentative essay introduction.
Persuasive Essay Introduction Example
A persuasive essay is a type of academic writing that seeks to convince the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. The writing process of a persuasive essay introduction is similar to what is described above.
Below is a perfect example of a persuasive essay introduction.
Compare and Contrast Essay Introduction Example
The compare and contrast essay analyzes the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. A compare and contrast essay introduction has to introduce two elements. Otherwise, it has a similar structure to introductions in general.
The following is a great introduction for a compare and contrast essay that you can refer to.
Synthesis Essay Introduction Example
A synthesis essay is a form of writing that challenges you to explore information from multiple sources to form a coherent and original perspective on a given topic.
Here is a good essay introduction example for a synthesis essay.
Narrative Essay Introduction Example
A narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that allows writers to share personal experiences, memories, or events in a creative and engaging way.
The content of narrative essay introductions is a bit different. They require you to set the scene, introduce the protagonist, and present the upcoming conflict. Here is an example:
Expository Essay Introduction Example
An expository essay is a common type of academic writing that aims to provide a clear and concise explanation or analysis of a specific topic, concept, or idea.
Here’s an example of how you can start an expository essay.
Abortion Essay Introduction Example
The abortion debate remains one of the most controversial topics in modern society.
Pro-choice and pro-life advocates have been debating this issue for decades, with no end in sight. Writing an essay on this topic requires thoughtful research and a clear understanding of both sides.
Here's an example of how to write an abortion essay introduction.
Tips for Writing Better Essay Introductions
Crafting an effective essay introduction is an art that can significantly influence how readers engage with your writing. Here are some valuable tips to help you create engaging and impactful introductions.
- Be Clear and Concise: Keep your introduction clear and concise. Avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language that might confuse your readers. Present your ideas in a straightforward way.
- State Your Thesis Clearly: Your thesis statement is the core of your introduction. Clearly state your main argument or the purpose of your essay. It should be specific and debatable, giving readers a roadmap of what to expect in the essay.
- Transition Smoothly: Ensure a smooth transition from your introduction to the body of the essay. Your introduction should provide a logical segue into the main points or arguments you will explore.
- Avoid Clichés and Overused Phrases: Try to avoid clichés or overused phrases in your introduction. Readers appreciate fresh and original language that piques their interest.
- Tailor the Introduction to the Essay Type: Consider the type of essay you're writing (e.g., persuasive, expository, narrative) and adapt your introduction accordingly. Each type may require a different approach to engage the reader effectively.
- Revise and Edit: Don't hesitate to revise and edit your introduction as needed. It's often helpful to write the introduction after completing the rest of the essay, as this allows you to better align it with the content.
- Consider the Audience: Think about your target audience and their expectations. Tailor your introduction to resonate with your specific readership.
- Seek Feedback: Before finalizing your introduction, seek feedback from peers, professors, or writing tutors. Fresh perspectives can help you refine your introduction for maximum impact.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Essay Introductions
Here are some common mistakes that you should avoid to write compelling introductions:
- Try to avoid writing a vague introduction of irrelevant details about the topic.
- Do not provide too much information and facts in the introduction. Simply present the topic with sufficient information for the reader’s understanding.
- Avoid using informal language or slang terms in the introduction. Essay introductions should be written in formal and academic language.
- Do not make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge of the topic. Provide only basic background information to fill any gaps in understanding.
- Finally, do not introduce any new information in the introduction. The introduction should only provide an overview of what will be discussed in the essay, not dive into details.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure that your essay introduction is clear and concise. It will help readers easily understand the topic and follow your argument throughout the paper.
Moreover, you can watch this video that introduces an easy method and helpful method for writing effective introductions.
To conclude,
By using the steps and tips discussed above, you can become a skilled essayist who leaves a lasting impression, one introduction at a time.
Just remember that writing is a process of constant refinement, and your introductions will evolve as your skills grow. So, the next time you sit down to write, take the time to craft it with care, for it holds the promise of what lies ahead.
However, if you are struggling to make your essay introduction engaging, don’t stress over it. MyPerfectWords.com is here to back you up!
You can get essay help online at our professional writing service. Our experienced and skilled writers can provide you with a perfect introduction and write a compelling story from start to finish!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
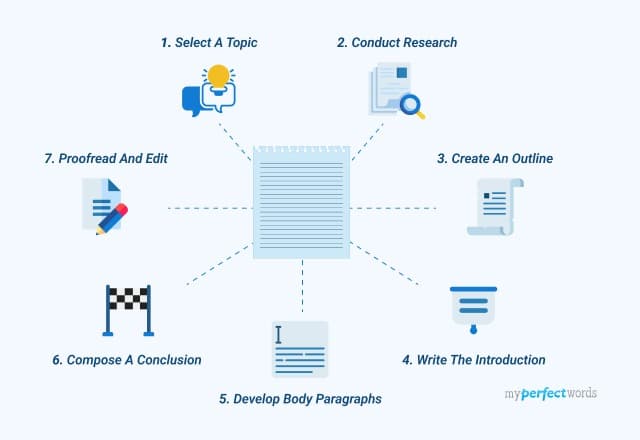
- How to Write a Summary
Proficient students understand that summarizing , identifying what is most important and restating the text (or other media) in your own words, is an important tool for college success.
After all, if you really know a subject, you will be able to summarize it. If you cannot summarize a subject, even if you have memorized all the facts about it, you can be absolutely sure that you have not learned it. And, if you truly learn the subject, you will still be able to summarize it months or years from now.
Proficient students may monitor their understanding of a text by summarizing as they read. They understand that if they can write a one- or two-sentence summary of each paragraph after reading it, then that is a good sign that they have correctly understood it. If they can not summarize the main idea of the paragraph, they know that comprehension has broken down and they need to use fix-up strategies to repair understanding.
Summary Writing Format
- When writing a summary, remember that it should be in the form of a paragraph.
- A summary begins with an introductory sentence that states the text’s title, author and main point of the text as you see it.
- A summary is written in your own words.
- A summary contains only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions, interpretations, deductions or comments into a summary.
- Identify in order the significant sub-claims the author uses to defend the main point.
- Copy word-for-word three separate passages from the essay that you think support and/or defend the main point of the essay as you see it.
- Cite each passage by first signaling the work and the author, put “quotation marks” around the passage you chose, and put the number of the paragraph where the passages can be found immediately after the passage.
- Using source material from the essay is important. Why? Because defending claims with source material is what you will be asked to do when writing papers for your college professors.
- Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
Example Summary Writing Format
In the essay Santa Ana , author Joan Didion’s main point is ( state main point ). According to Didion “… passage 1 …” (para.3). Didion also writes “… passage 2 …” (para.8). Finally, she states “… passage 3 …” (para. 12) Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Paul Powell. Provided by : Central Community College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Elisabeth Ellington and Ronda Dorsey Neugebauer. Provided by : Chadron State College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Peer Review Checklist
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Effective Thesis Statements
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Summary/Response Essays: Overview
A summary/response essay may, at first, seem like a simplistic exercise for a college course. But the truth is that most academic writing requires us to successfully accomplish at least two tasks: summarizing what others have said and presenting what you have to say. Because of this, summarizing and responding are core skills that every writer should possess.
Being able to write an effective summary helps us make sense of what others have to say about a topic and how they choose to say it. As writers, we all need to make an effort to recognize, understand, and consider various perspectives about different issues. One way to do this is to accurately summarize what someone else has written, but accomplishing this requires us to first be active and engaged readers.
Along with the other methods covered in the Reading Critically chapter , writing a good summary requires taking good notes about the text. Your notes should include factual information from the text, but your notes might also capture your reactions to the text—these reactions can help you build a thoughtful and in-depth response.
Responding to a text is a crucial part of entering into an academic conversation. An effective summary proves you understand the text; your response allows you to draw on your own experiences and prior knowledge so that you can talk back to the text.
As you read, make notes, and summarize a text, you’ll undoubtedly have immediate reactions. Perhaps you agree with almost everything or find yourself frustrated by what the author writes. Taking those reactions and putting them into a piece of academic writing can be challenging because our personal reactions are based on our history, culture, opinions, and prior knowledge of the topic. However, an academic audience will expect you to have good reasons for the ways you have responded to a text, so it’s your responsibility to critically reflect on how you have reacted and why.
The ability to recognize and distinguish between types of ideas is key to successful critical reading.
Types of Ideas You Will Encounter When Reading a Text
- Fact: an observable, verifiable idea or phenomenon
- Opinion: a judgment based on fact
- Belief: a conviction or judgment based on culture or values
- Prejudice: an opinion (judgment) based on logical fallacies or on incorrect, insufficient information
After you have encountered these types of ideas when reading a text, your next job will be to consider how to respond to what you’ve read.
Four Ways to Respond to a Text
- Reflection. Did the author teach you something new? Perhaps they made you look at something familiar in a different way.
- Agreement. Did the author write a convincing argument? Were their claims solid, and supported by credible evidence?
- Disagreement. Do you have personal experiences, opinions, or knowledge that lead you to different conclusions than the author? Do your opinions about the same facts differ?
- Note Omissions. If you have experience with or prior knowledge on the topic, you may be able to identify important points that the author failed to include or fully address.
You might also analyze how the author has organized the text and what the author’s purposes might be, topics covered in the Reading Critically chapter .
Key Features
A brief summary of the text.
Include Publication Information. An effective summary includes the author’s name, the text’s title, the place of publication, and the date of publication—usually in the opening lines.
Identify Main Idea and Supporting Ideas. The main idea includes both the topic of the text and the author’s argument, claim, or perspective. Supporting ideas help the author demonstrate why their argument or claim is true. Supporting ideas may also help the audience understand the topic better, or they may be used to persuade the audience to agree with the author’s viewpoints.
Make Connections Between Ideas. Remember that a summary is not a bullet-point list of the ideas in a text. In order to give your audience a complete idea of what the author intended to say, you need to explain how ideas in the text are related to one another. Consider using transition phrases.
Be Objective and Accurate. Along with being concise, a summary should be a description of a text, not an evaluation. While you may have strong feelings about what the author wrote, your goal in a summary is to objectively capture what was written. Additionally, a summary needs to accurately represent the ideas, opinions, facts, and judgments presented in a text. Don’t misrepresent or manipulate the author’s words.
Do Not Include Quotes. Summaries are short. The purpose of a summary is for you to describe a text in your own words . For this reason, you should focus on paraphrasing rather than including direct quotes from the text in your summary.
Thoughtful and Respectful Response to the Text
Consider Your Reactions. Your response will be built on your reactions to the text, so you need to carefully consider what reactions you had and how you can capture those reactions in writing.
Organize Your Reactions. Dumping all of your reactions onto the page might be useful to just get your ideas out, but it won’t be useful for a reader. You need to organize your reactions. For example, you might develop sections that focus on where you agree with the author, where you disagree, how the author uses rhetoric, and so on.
Create a Conversation. Avoid the trap of writing a response that is too much about your ideas and not enough about the author’s ideas. Your response should remain engaged with the author’s ideas. Keep the conversation alive by making sure you regularly reference the author’s key points as you talk back to the text.
Be Respectful. We live in an age when it’s very easy to anonymously air our grievances online, and we’ve seen how Reddit boards, YouTube comments, and Twitter threads can quickly devolve into disrespectful, toxic spaces. In a summary/response essay, as in other academic writing, you are not required to agree with everything an author writes—but you should state your objections and reactions respectfully. Imagine the author is standing in front of you, and write your response as if you value and respect their ideas as much as you would like them to value and respect yours.
Distinguish Between an Author’s Ideas and Your Own
Signal Phrases. A summary/response essay, especially your response, will include a mix of an author’s ideas and your ideas. It’s important that you clearly distinguish which ideas in your essay are yours, which are the author’s, and even others’ ideas that the author might be citing. Signal phrases are how you accomplish this. Remember to use the author’s last name and an accurate verb.
Examples of Signal Phrases
Poor Signal Phrases: “They say…” “The article states…” “The author says…”
Effective Signal Phrases: “Smith argues…” “Baez believes…” “Henning references Chan Wong’s research about…”
Drafting Checklists
These questions should help guide you through the stages of drafting your summary/response essay.
- Have you identified all the necessary publication information for the text that you will need for your summary?
- Have you identified the text’s main ideas and supporting ideas?
- What were your initial reactions to the text?
- What new perspectives do you have on the topic covered in the text?
- Do you ultimately agree or disagree with the author’s points? A little of both?
- Has the author omitted any points or ideas they should have covered?
- Has the author organized their text effectively for their purpose?
- Have they used rhetoric effectively for their audience?
- Have your reactions to the text changed since you first read it? Why or why not?
Writing and Revising
- Does your summary clearly tell your reader the author’s name, the text’s title, the place of publication, and the publication data?
- Has your summary effectively informed your reader about the text’s main ideas and supporting ideas? Have you made the connections between those ideas clear for your reader by using effective transition phrases?
- Would your reader think your summary is objective and accurate?
- You haven’t included any quotes in your summary, right?
- Does your response present your reactions to the text in an organized way that will make sense to your reader?
- Does your response create a conversation between you and the author by regularly referencing ideas from the text?
- Would your reader think that your response is respectful of the author’s ideas, opinions, and beliefs?
- Have you used signal phrases to help your reader recognize which ideas are the author’s and which ideas are yours?
- Have you carefully proofread your essay to correct any grammar, mechanics, punctuation, and spelling errors?
- Have you formatted your document appropriately and used citations when necessary?
Sources Used to Create this Chapter
Parts of this chapter were remixed from:
- First-Year Composition by Leslie Davis and Kiley Miller, which was published under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
Starting the Journey: An Intro to College Writing Copyright © by Leonard Owens III; Tim Bishop; and Scott Ortolano is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- College Application
College Essay Introduction Examples

Reading some college essay introduction examples is a great place to start if you’re struggling to begin writing your college essay. The college essay is a significant hurdle for many college applicants but reading sample college essays can help inspire your writing. Knowing how to write a killer introduction, though, is the first step, as the introduction of your essay can make or break your entire essay. In this blog, we’ll learn why the college essay introduction is so important, how to structure it and a step-by-step guide on how to write a killer essay introduction. We’ve also included some college essay introduction examples to guide you!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 7 min read
Why the college essay introduction is so important.
Your college essay can be vital to your admission to your top school, and the introduction of your college essay can make it or break it. The introduction of your college admissions essay, or common app essay , is often overlooked, but it is a crucial part of the overall essay. Why? Because your introduction is quite literally the first opportunity to introduce yourself to the admissions committee, and you need to make an impression. Getting into college requires more than high grades and good test scores nowadays. You need a well-rounded and impressive application. And to do this you need to know how to write a college essay . To write an essay that stands out from the crowd and makes you a memorable candidate for admission, you’ll need to know how to write an excellent college essay introduction.
The introduction of your college essay is so crucial because it is what first grabs your reader’s attention. Like any good piece of writing, if you don’t snag your reader’s interest in the first sentence, they won’t be inclined to read the rest of your essay. And you need them to be interested and engaged so you can make your point. A college essay counts for a significant portion of your overall candidacy as a college applicant. It can even be your secret to how to get into college with a low GPA . But writing essays is not easy, and introductions can be especially tricky for students to write. This is why plenty of college applicants hire college essay advisors to help them write their common app essays or supplemental college essays .
If you plan to apply to any of the schools which use the common app essay, you’ll be somewhat familiar with the required short essay format and structure. Your college essay will be around 250-650 words maximum, so your introduction needs to be fairly concise. It’s best to keep your introduction just a few sentences long, so you’ll need to be very wise with your words and make the most of each one. You may also want to add a title to your essay. This is not a requirement and should only be included if you think the title adds something significant. Otherwise, leave it out.
Here’s a list of what to include in your college essay introduction:
A college essay needs to have good flow, and this starts in the introduction. This means your \u201chook\u201d sentence needs to connect to the rest of your introduction, and then needs to connect seamlessly to your body paragraphs. Your writing should follow a clear path from your hook to your conclusion. One way to keep good flow is to use a strong transition sentence, but another way is to guide your reader. The second sentence, after your hook, shouldn\u2019t be unrelated or step away from your point, it should lead your reader to the reason why you are writing this essay. ","label":"Good flow","title":"Good flow"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
Before any writing can begin, we’ll need to start the brainstorming process. This is essentially gathering and writing down the key experiences, significant moments and important lessons you have learned throughout your life. Everyone’s experiences are unique, and the ideas you write down may vary depending on your situation. If you’re a non-traditional college applicant, you might write about the gap year you took after high school, or why you’re going back to college after years of working in your field. International students might write about their decision to study overseas or their experience with culture shock. First time college applicants may draw on their experiences with summer programs for high school students or the work experiences they’ve included in their high school resume .
Your choice of essay topic or the personal experiences you choose to highlight in your essay may also be influenced by the essay prompt or essay question, if the school provides one. If this is the case, you can reflect on which prompt or question resonates most with you or choose to write more than one essay if more than one prompt resonates. For schools that do not provide a question or essay prompt, you can reflect on your future career goals, personal goals or the reasons why you are applying to college.
Whatever your situation or your story, gather all of the personal experiences you can think of and jot them down. Brainstorming is an important process, but they key is to write down absolutely every idea you can think of to start.
Some personal experiences you might draw from for your brainstorming session could be:
- What sparked your interest in applying to college
- What life experiences sparked your interest in a particular field of study
- What made you interested in a career in this field of study
- What activities did you partake in growing up that grew your interest in this field
- What activities did you pursue during high school that grew your interest in this field
- What solidified your decision to apply to college
Your college essay is at heart a narrative that either answers the essay question or answers the question “why are you applying to this school?” Your essay should take the reader through each stage of your decision, but your introduction’s primary role is to grab the reader’s interest and set the stage. And just like an excellent stage play seizes the audience’s attention from the moment the lights turn on the stage, your essay needs to do the same. Be the narrator of your narrative and share with the audience what will be learned about you from reading your essay.
Want more tips for writing a college essay? Watch this video!
Here’s a quick guide to brainstorming and writing your college essay introduction
Once your essay is fully outlined, or even drafted, you might write your introduction last. This way you already know what your essay is about and just need to introduce it to the reader. "}]">
Once you’ve drafted your introduction, give it a read. Does the hook sentence grab you? Try reading it aloud and see how it flows into the body of your essay. If it doesn’t pique your own interest, it won’t hold your reader’s! Ask a friend, family member, college advisor or acquaintance to read it and give you feedback on your intro. Try a few different versions of your hook sentence or refine your transition sentence. Make sure your introduction is as strong as can be.
For our college essay introduction examples, we’ve used a few of the common app essay prompts you might see on your application. We’ve included sample introductions for essays from students of various different life experiences and situations to help you!
Prompt: Describe a topic, idea, or concept you find so engaging that it makes you lose all track of time. Why does it captivate you? What or who do you turn to when you want to learn more?
My love affair with painting started late in life. After 25 years of working as a science teacher, I never expected my hunt for a pre-retirement hobby to turn into a shift in career path. Painting has become a daily solace for me, and my involvement in my local arts community has opened up career opportunities I never dreamed of. And it has sparked a fascination with the arts and what it can add to my life. This fascination first started when I accepted an invitation from a friend to see her work on display at a local Art Walk.
Prompt: Discuss an accomplishment, event, or realization that sparked a period of personal growth and a new understanding of yourself or others.
I thought I would spend my gap year after high school laying on a beach and getting tan. Instead, I experienced a profound transformation within myself as I immersed myself in a new culture and a new people. A month after my graduation, I was on a plane on my way to Thailand, nothing on my mind except sun and sad. A year after, Thailand sent me home with an entirely new perspective and appreciation for life. When I left home, I was still unsure what I wanted from my life and whether I would apply for college. My wavering feelings were solidified after working with an amazing not-for-profit in some of Thailand’s remote villages, which also lead to the most impactful friendship of my life.
Prompt: The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure. How did it affect you, and what did you learn from the experience?
What I remember most from the night my entire life collapsed was the brightness of the stadium lights overhead. Not the chaos of the crowd or the faces staring down at me, talking over me. I was deaf to all that. The lights were so blinding, so distracting. And I kept thinking, over and over, ‘don’t take me out of the game’. Thoughts that would be strangely prophetic later, in the hospital, when they told me I wouldn’t be able to play the rest of the season, or maybe ever again. My entire life, my expected future, flew off a cliff. In those coming months, I would learn what it really means to start over, to pick yourself back up and keep playing the game.
To write a killer opening to your college essay, focus on the very first sentence, your “hook”. It should be unique, interesting and “hook” the reader’s attention. It’s the “big idea” or main lesson learned from your college essay. Play around with the sentence length and structure to see what works and try reading the introduction aloud to hear how it sounds to your ear.
Try not to start your college essay introduction with a cliché or a quote. Cliches have been read thousands of times by admissions officers, and they want to see something unique and interesting, not the same old things. And using a quote to start your essay isn’t a good idea, since it is meant to be written in your own words, not someone else’s.
Writing a good hook takes some work. Try to think of how you would summarize your essay or the personal experience you are highlighting. What was the key lesson you learned? What is at the centre of your motivations? Try writing this topic sentence a few different ways and read it aloud to see how it sounds.
The introduction of your essay needs to grab your reader’s attention right away. If it doesn’t, the admissions committee won’t want to read the rest of your essay and you’ll have lost them already. As the college essay counts for a significant part of your overall application, the introduction is crucial for your success.
It’s best not to do this, even if the quote is inspirational for you. College admission committees want to hear what you have to say, not someone else.
You can include a title if you choose, but it’s best to leave it out unless the title adds something important to your overall essay.
The introduction of a college essay needs to include a “hook” sentence, a transition sentence, an introduction of your essay content and good flow.
It’s advisable to keep your college essay introduction short and concise. It should make up about 10% of your essay’s word count, so in some cases this is quite short!
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your college applications stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into your dream college or university or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
English that goes straight to the heart
Summary Essay Examples
The summary essay is a brief account of the chief points of an essay. There’s no hard and fast rule about the length of the summary, but so much can be half of the original essay .
In this post, we have added the best 12+ Summary Essay Examples for you.
Daily Test - Attempt Now

Summary Essay Examples #1
ESSAY: When we survey our lives and efforts, we soon observe that almost the whole of our actions and desires are bound up with the existence of other human beings. We notice that the whole of nature resembles that of social animals. We eat food that others have produced, wear clothes that others have made, and live in houses that others have built. The greater part of our knowledge and beliefs has been passed on to us by other people through the medium of a language that others have created. Without language and mental capacities, we would have been poor indeed comparable to higher animals.
We have therefore to admit that we owe our principal knowledge over the least to the fact of living in human society. The individual if left alone from birth would remain primitive and beast-like in his thoughts and feelings to a degree that we can hardly imagine. The individual is what he is and has the significance that he has not much in virtue of individuality, but rather as a member of a great human community, which directs his material and spiritual existence from the cradle to the grave. (193 words)
Rough Draft
- Humans are social animals.
- They depend on each other for necessities and social needs.
- Humans use language to communicate with each other and further their mental development.
- Humans are superior to animals as they live in societies that guide their material and spiritual existence.
TITLE: Man and society
SUMMARY: Human beings have their actions and desires bound up with society as they are social animals. They depend on each other for food and clothes and share their knowledge and beliefs, and use language created by others to communicate, which helps in their mental development. They are superior to beasts because they live in human society. An individual left alone since birth would grow utterly beast-like. Human society guides man’s material and spiritual existence. (76 words)
Summary Essay Examples #2
If you will, believe me, you who are young, yours is the golden season of life. As you have heard it called, so it verily is the seed-time of life in which if you do not sow or if you sow tares instead of wheat, you will arrive at little. And in the course of years when you come to look back if you have not done what you have heard from your advisers and among many counsellors there is wisdom you will bitterly repent when it is too late.
The habit of studies acquired at universities is of the highest importance in the afterlife. At the season when you are young in years, the whole mind is, as it were, fluid, and is capable of forming itself into any shape that the owner of the mind pleases to allow it or constrain it, to form itself into. The mind is then in a plastic or fluid state but it hardens gradually to the consistency of rock or iron, and you can not alter the habits of an old man. (180 Words)
Title: The Golden Season of Life / The Importance of Sowing Good Seeds
Youth is the golden and fertile time of life. If one does not listen to and act upon the advice of his superiors, he must eventually repent. Youth is a fluid state of mind and any good habits now will stand you in good stead later in life. Then the mind becomes rigid and no good habits are formed. (58 Words)
The golden season of life is the seed-time of life in which if you do not sow or sow tares instead of wheat, you will arrive at little. The habit of studies acquired at universities is of the highest importance in the afterlife, as the mind is fluid but hardens gradually to the consistency of rock or iron. (58 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #3
Variety is the spice of life – is it not? We all practically live and strive for having better food, but food remains insipid without the addition of spices. The only difference between a good curry and a bad curry lies in the presence or absence of spices. The absence of variety makes life drab and monotonous. A man working six hours a week will have his rest on Sunday. A man wearing a coat for five days will like a shawl on the sixth day. If a man lives in Calcutta for six years, he will like to spend a month outside. We hear that Tagore could not live in the same house for a long time.
He used to change his residence pretty often, which shows a poet’s longing for novelty. Life is many stringed instruments and we must give proper attention to all the strings. Ever since creation man has gone on from progress to progress by responding to new circumstances. So, for the development of civilization, new circumstances and a new environment are necessary. (179 Words)
Title: The Need for Change and Variety / Variety: The Spice of Life
Variety is the spice of life, and without it, life is dull and monotonous. To develop civilization, new circumstances and a new environment are necessary. Tagore was a poet who changed his residence often, showing his longing for novelty. Life is many stringed instruments and we must give proper attention to all the strings. (54 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #4
Everyone has continual control during his life with the variety of experiences known as art. Their experience ranges from the craft level found in the design and execution of the practical things of life to the more imaginative because less material level is required for the enjoyment of music, painting, sculpture, and literature. In the fine arts, human creativity is no longer concerned with producing an object which will be required for use anyhow, whether it is beautiful or not, but with providing a stimulus for the satisfaction of human emotion in its various levels of manifestation.
The majority of human beings since they are culturally underprivileged, are satisfied if their emotions are roused easily and mechanically by the more simple emotional easily identified sentimentalities that easily assimilate emotional reflexes-by dance, and music, by the identified references of cinema organ sentimentalities, by the picture with a story or easily assimilated moral, and by the simple violent plots of the cheap magazine. The culturally privileged demand a more complicated satisfaction. They require because they are educated on the aesthetic aspects of the arts. (180 Words)
Title: The Power of Art / The Importance of Art Education
The most important idea is that art provides a stimulus for the satisfaction of human emotion and that the majority of people are satisfied with simple emotional sentimentalities, while the culturally privileged require a more complicated satisfaction due to their education in the aesthetic aspects of the arts. (48 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #5
The study of history depends more than any other branch of science or literature on the availability of many books. The history student nowadays is often discouraged or hampered by the lack of them, especially of those older standard works which have gone out of print. Even before the Second World War publishers were not willing to risk reprinting works often running into several big volumes for which the demand, was uncertain and the cost of production high. During the war air raids destroyed over a million books in one district of London alone, and reduced to ashes the entire stock of one firm which had specialized in historical works.
Since the war paper has been costly and scarce; the costs of printing and binding have risen sharply; and the demand, though greater, is still not large enough to make worthwhile the republication of many books which historians regard as essential. The main reason for this insufficient demand is the disappearance of the private library. Private libraries were common in Victorian Times but they no longer exist in modern small houses where there is no room for bookshelves. (190 Words)
Title: The Challenges of Historical Research in the Modern Era
The study of history is hindered by the lack of books, especially older standard works which have gone out of print due to the cost of printing and binding. The main reason is the disappearance of private libraries, which no longer exist in modern small houses. (46 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #6
Speech is a great blessing, but it can also be a great curse, for, while it helps us to make our intentions and desires known to our fellows, it can also, if we use it carelessly make our attitude completely misunderstood. A slip of the tongue. the use of an unusual or ambiguous word, and so on, may create an enemy where we had hoped to win a friend.
Again different classes of people use different vocabularies, and the ordinary speech of an educated man may strike an uneducated listener as showing pride; unwittingly we may use a word that bears a different meaning for our listener from what it does to men of our own class. Thus speech is not a gift to use lightly without thought, but one which demands careful handling. Only a fool will express himself alike to all kinds and conditions of men. (148 Words)
Title: The Blessing and Curse of Speech
Speech is a great gift, but it can also be a curse if used carelessly. Different classes of people use different vocabularies, and the ordinary speech of an educated man may strike an uneducated listener as pride. Careful handling of speech is essential, as only a fool will express himself alike to all people. (54 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #7
Man is the architect of his own fate. If he makes a proper division of his time and does his duties according he is sure to improve and prosper in life; but if he does otherwise, he is sure to repent, when it is too late and he will have dragged a miserable existence from day to day.
To kill time is as culpable as to commit suicide, but our life is nothing but the sum total of hours, days, and years. Youth is the golden season of life. In youth, the mind is pliable and soft and can be moulded in any form you like. If we lose the morning hours of life, we shall have to repent afterwards. It is called the ‘seed time of life’. If we sow good seeds, we shall reap a good harvest when we grow up. (142 Words)
Title: Youth: The Gloden Opportunity to shape your / Man is the Architect of his own Fate
Man is responsible for his own fate, and if he does not make proper use of his time, he will regret it. Youth is the golden season of life, and if we lose the morning hours of life, we will have to repent. (43 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #8
It is sometimes said that the pleasures of giving are peculiar to the rich, and no doubt the joy of giving is one of the greatest and purest that wealth can bestow. Still the poor also may be liberal and generous. The widow’s mite, so far as the widow is concerned, counts for as much as the rich man’s gold.
Moreover, as regards kindness and sympathy which are far more valuable than money, the poor can give as much as, perhaps even more than the rich. Money is not wealth. A proverb says: “A man’s true wealth is good that he does in the world”. When he dies, men will ask what property he has left behind, but Angels will inquire, “What good deeds hast thou sent before thee?” (130 Words)
Title: The Pleasure of Giving / Generosity Knows No Wealth
The poor can give as much as the rich, and kindness and sympathy are more valuable than money. A proverb states that a man’s true wealth is the good deeds he does in the world. (35 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #9
The lot of our Indian peasant is certainly a pitiable one. He labours under many disadvantages. In the first place, he is illiterate, and does not, therefore, care to know more than he has inherited from his ancestors. He laughs at his tiny piece of land from morning to evening and if the seasons favour him, earns what barely suffices to meet his daily demands. He does not grumble to pay his rent so much as he does for the loss of his plough cattle. He lives in debt over head and ears, yet he does not care to save anything for the morrow.
To ameliorate his condition, the supply of good plough cattle, the adoption of preventive measures to save the animals from diseases, and, last of all, primary education should engage the serious attention of the Indian Government. (138 Words)
Title: Illiteracy and its effect on Indian Peasant / The Pitiable Conditions of Indian Peasant
The Indian peasant is suffering from many disadvantages, such as illiteracy, poverty, and debt. To improve his situation, the supply of good plough cattle, preventive measures, and primary education should be addressed by the Indian Government. (36 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #10
The aim of culture and religion is the same. Men are all members of one great whole, and the sympathy which is in human nature will not allow one member to be different from the rest or to have perfect welfare independent of the rest. The expansion of our humanity to suit the idea of perfection that culture forms must be a general expansion. Perfection, as culture conceives it is not possible while the individual remains isolated. He must carry others along with him in his march towards perfection. Culture lays on us the same obligation as a religion which says that “to promote the kingdom of God is to increase and hasten one’s own happiness.
Culture is a harmonious expansion of all the powers which make the beauty and worth of human nature. Culture is not consistent with the over-development of any power at the expense of the rest. Here it goes beyond religion, as religion is generally conceived by us. (162 Words)
Title: Culture and Religion: The Two Sides of the Same Coin
Culture leading to perfection, like religion, complements rather than competes with the latter. Culture, like religion, demands perfection rather than the unification of everything. Culture means harmonious development of all faculties and not overdevelopment of any at the expense of others. Here it transcends religion in its emphasis on harmonious development. (50 Words)
The aim of culture and religion is the same: to expand humanity to suit the idea of perfection. Culture is a harmonious expansion of all the powers which make the beauty and worth of human nature, and is not consistent with the over-development of any power at the expense of the rest. It lays on us the same obligation as a religion to promote the kingdom of God is to increase and hasten one’s own happiness. (72 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #11
Perseverance is the very hinge of all virtues. On looking over the world, the cause of nine-tenths of the lamentable failures which occur in much of their history lies not in the want of talents, but in the manner of using them, in flying from object to object, in starting away at each little disgust, and thus applying the force which might conquer anyone difficulty to a series of difficulties so large that no human race can conquer them.
The smallest brook on earth by continuing to run has hollowed out for itself a considerable valley to flow in. Commend me, therefore, to the virtue of severance. Without it, all the rest are little better than fairy gold which glitters in your purse, but taken to the market proves to be state or cinders. (134 Words)
Title: The Importance of Perseverance / Perseverance: The Hinge of Virtues
Perseverance is the key to success, and severance is the virtue of severance. Without it, all the rest are a little better than fairy gold. (25 Words)
Perseverance is the key to all virtues and is the cause of many failures in history. It is the act of flying from object to object, starting away at each little disgust, and applying the force which might conquer anyone’s difficulty to a series of difficulties so large that no human race can conquer them. Without it, all the rest are little better than fairy gold which glitters in your purse, but when taken to the market proves to be state or cinders. (83 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #12
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially. The excitement of gangsterdom is permissible so long as the antisocial quality of gangsterdom is not held up as something desirable. Frivolous gaiety may be introduced, but it should not be presented as the be-all and end-all, of living. Life can be made exciting and romantic provided it is not permanently distorted.
For there can never be much human progress if we distort things by pretending the world is much better than it actually is. Thus the attitude of a film to the grimmer side of life can not be worthwhile if it glosses it over, since that only confirms our backwardness. Nothing bad should be treated approvingly. The introduction of gangsterdom, war, idle luxury; slums unemployment, poverty, and their accompanying misery, crime, and disease, should not leave the audience complacent, but should if anything inspire them with a determination to end them. (159 Words)
Title: Films -Entertainment or Distortion of Reality / The Impact of Films on Society
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially, and should not gloss over the grimmer side of life, such as gangsterdom, war, idle luxury, and poverty. (31 Words)
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially. Life can be made exciting and romantic, but it should not be permanently distorted. The introduction of gangsterdom, war, idle luxury, slums unemployment, poverty, and their accompanying misery, crime, and disease should not leave the audience complacent but should inspire them with a determination to end them. (60 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #13
A poor woman once came to the Buddha and begged him to revive her dead child. The holy man was touched by the woman’s great sorrow. Then he asked him to bring a handful of mustard seeds from a house where death had never entered. The sad mother started looking for mustard seeds from door to door. One said, our little child died last year. Another said I lost my father. The evening came.
He returned to Lord Buddha with a heavy heart and told him about the results of his search. Then the Buddha gently told him not to think of his own suffering, for suffering and death are common to all.
Title: The Buddha and the Grieving Mother / The Universal Experience of Suffering and Death
Summary: A poor woman came to the Buddha and begged him to revive her dead child. He asked her to bring a handful of mustard seeds from a house where death had never entered. The mother searched for mustard seeds from door to door and returned to Lord Buddha with a heavy heart. The Buddha gently reminded her that suffering and death are common to all. (65 Words)
You Asked, We Listened – Get Free Access to All Writing Lists 😍😍

10 Famous Moral Stories

Top 10 Short Stories for Kids
Daily reading comprehension test - attempt now, discover more from english luv.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Bar Exam Success Guide
Introduction.
- State Specific Bar Exam Resources
- Georgia Bar Exam
- Uniform Bar Examination (UBE)
- Multi-State Essay Exam (MEE)
- Georgia Essays
Instructions for Essay Answer - Georgia
Subjects tested, sample essays, georgia essays study aids.
- Next Gen Bar
- Financial Expectations
- Mindfulness
Most states' bar exams have an essay portion. Georgia has four essay questions prepared and graded by the Board of Bar Examiners. Applicants will be provided 45 minutes to answer each question.
- Assume that the questions arise under the laws of Georgia, unless otherwise indicated.
- Each answer should show: an understanding of the facts; a recognition of the issues involved; the principles of law applicable; and the reasoning by which you arrived at your conclusions. The value of an answer depends not so much upon the correctness of the conclusions as upon the presence and quality of the elements above-mentioned.
- Clearness and conciseness will count but make your answers complete. Do not volunteer irrelevant or immaterial information.
- Demonstrate not merely your memory, but your ability to think and analyze the issues.
- Read each question carefully and understand it before answering.
Essay questions prepared by the Board of Bar Examiners shall be drawn from the following list of subjects:
- Georgia Bar Exam Essays For exams February 2000 to July 2012 there are 4 questions, each with a corresponding page of sample answers.
- << Previous: Multi-State Essay Exam (MEE)
- Next: MPRE >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 10:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.law.gsu.edu/barexamsuccess
Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: a Summary of Roe V. Wade
This essay about the impact and controversies surrounding the Roe v. Wade Supreme Court decision discusses how it established a woman’s right to abortion under the privacy protections of the Fourteenth Amendment. It addresses both the legal challenges and societal divisions it has prompted over the years, including state-level restrictions and the significant political and cultural debates it has ignited. The essay also considers the broader implications for women’s reproductive rights and health, while acknowledging the persistent access issues and social stigma.
How it works
The decision in Roe v. Wade, made by the United States Supreme Court in 1973, has profoundly influenced both the legal framework and societal views on abortion and reproductive rights. The ruling established a woman’s right to make decisions about her own pregnancy, emphasizing this as a matter of privacy protected under the Due Process Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment. This significant judicial recognition shifted how reproductive rights are perceived, limiting the state’s ability to impose blanket prohibitions or severe constraints on abortions without a substantial justification.
Critics, however, have charged Roe v. Wade with judicial overreach, claiming the Court engaged in activism by creating law from the bench. This decision also sparked a vehement and ongoing controversy regarding the ethical and moral dimensions of abortion, leading to vehement opposition from religious and pro-life groups who view the ruling as a violation of life’s sanctity.
Over the years, the debates and disputes surrounding abortion have not waned, with numerous states attempting to erode the Roe decision through various restrictive measures. These include obligatory waiting periods and rigorous regulations for clinics, highlighting the ongoing tension between safeguarding women’s rights and protecting fetal interests.
The abortion issue has also become a significant element in American political and cultural divides, influencing elections and public policy discussions. Political candidates are often evaluated on their abortion stance, and the topic is a central issue in legislative sessions and judicial nominations.
Socially, Roe v. Wade has empowered women by broadening their control over reproductive choices, which has had ripple effects on family planning and women’s health. Access to safe, legal abortions is linked to lower maternal mortality rates and has allowed women more autonomy in managing their reproductive health.
Nevertheless, access to abortion services is uneven, often adversely affecting marginalized groups and deepening social inequities. Rural regions, in particular, suffer from a lack of adequate healthcare facilities, and economic hurdles can restrict access for low-income individuals.
Moreover, the stigma associated with abortion endures, creating a culture of silence and judgment that can affect women’s decisions about their pregnancies. Overcoming this stigma necessitates not only legal measures but also a shift in societal attitudes towards normalizing reproductive choices.
As we look to the future, the principles established in Roe v. Wade regarding personal autonomy and constitutional protections remain crucial in guiding ongoing debates about reproductive rights and justice. The evolving dynamics of the Supreme Court and the political landscape continue to make the future of abortion rights uncertain. However, the enduring principles from Roe v. Wade continue to underscore the broader quest for equality, dignity, and human rights in evolving societal contexts.
Cite this page
Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/
"Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/ [Accessed: 14 May. 2024]
"Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/
"Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/. [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Analyzing the Legal and Social Implications: A Summary of Roe v. Wade . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/analyzing-the-legal-and-social-implications-a-summary-of-roe-v-wade/ [Accessed: 14-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about summarizing.
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis. The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way. The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Make a brief outline of the essay based on the information presented in the introduction. Then look at that outline as you read the essay to see how the essay follows it to prove the writer's thesis statement. 2. Keep your introduction short and simple.
The introduction to an academic essay will generally present an analytical question or problem and then offer an answer to that question (the thesis). Your introduction is also your opportunity to explain to your readers what your essay is about and why they should be interested in reading it. You don't have to "hook" your
6) Try to grasp all of the ideas contained in the original text in your essay. Focus only on the most important points. Be objective, excluding your ideas, assumptions, judgments, or comments from the summary. Insert lengthy passages or quotes from the original material. Revise the summary after you've written it.
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
When writing a summary, remember that it should be in the form of a paragraph. A summary begins with an introductory sentence that states the text's title, author and main point of the text as you see it. A summary is written in your own words. A summary contains only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions ...
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Frequently asked questions.
Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays. The Summary: A summary is a concise paraphrase of all the main ideas in an essay. It cites the author and the title (usually in the first sentence); it contains the essay's thesis and supporting ideas; it may use direct quotation of forceful or concise statements of the author's ideas; it will NOT usually cite the author's examples or supporting ...
Step 4: Write the Thesis Statement. The last part of the introduction is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the central point or argument of your essay. It conveys the main idea you will explore and defend in the following paragraphs.
A summary contains only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions, interpretations, deductions or comments into a summary. Identify in order the significant sub-claims the author uses to defend the main point. Copy word-for-word three separate passages from the essay that you think support and/or defend the main ...
In your coursework, you may be asked to write a summary of an essay, book, film, video, or presentation. A summary is generally short, written objectively and in present tense. What is a summary? A summary is a short objective overview of the main ideas of a larger work. It includes only the broader points or purpose of a work rather than the ...
Summary Writing Steps. A summary is telling the main ideas of the article in your own words. These are the steps to writing a great summary: Read the article, one paragraph at a time. For each paragraph, underline the main idea sentence (topic sentence). If you can't underline the book, write that sentence on your computer or a piece of paper.
A summary/response essay may, at first, seem like a simplistic exercise for a college course. But the truth is that most academic writing requires us to successfully accomplish at least two tasks: summarizing what others have said and presenting what you have to say. Because of this, summarizing and responding are core skills that every writer ...
5. Write the summary. You can start your summary with the author's name and the title of the text. For example, you can use some variation of, "According to Martin Somers in 'The Child and the Wolf,'" to introduce your text. Then, include the thesis of the author in your first sentence.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Reading some college essay introduction examples is a great place to start if you're struggling to begin writing your college essay. The college essay is a significant hurdle for many college applicants but reading sample college essays can help inspire your writing. Knowing how to write a killer introduction, though, is the first step, as the introduction of your essay can make or break ...
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.. Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 4.95MB)
In general, your introductions should contain the following elements: Orienting Information. When you're writing an essay, it's helpful to think about what your reader needs to know in order to follow your argument. Your introduction should include enough information so that readers can understand the context for your thesis.
Summary Essay Examples #1. ESSAY: When we survey our lives and efforts, we soon observe that almost the whole of our actions and desires are bound up with the existence of other human beings. We notice that the whole of nature resembles that of social animals. We eat food that others have produced, wear clothes that others have made, and live ...
An essay outline is a way of planning the structure of your essay before you start writing. It involves writing quick summary sentences or phrases for every point you will cover in each paragraph, giving you a picture of how your argument will unfold. You'll sometimes be asked to submit an essay outline as a separate assignment before you ...
This essay about Ray Bradbury's "Fahrenheit 451" examines the dystopian future where books are outlawed and firemen burn any they find. It focuses on Guy Montag, a fireman whose encounters with his curious neighbor Clarisse and an old woman who chooses death over life without books lead him to question the society's book-burning policy.
We guide you through one with some examples. A compare and contrast essay is a type of analytical essay that explores the similarities and differences between two subjects. We guide you through one with some examples. ... A compare and contrast essay's introduction doesn't have much variance from intros in other essays, so don't skimp on ...
It highlights his introduction of the assembly line in 1913, which made cars widely accessible, and his progressive labor practices, including the introduction of a $5 daily wage in 1914. The essay also covers Ford's early environmental initiatives and his ventures in sustainable practices and urban planning, with a focus on the failed ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Introduction. Most states' bar exams have an essay portion. Georgia has four essay questions prepared and graded by the Board of Bar Examiners. Applicants will be provided 45 minutes to answer each question. ... Sample Essays. Georgia Bar Exam Essays. For exams February 2000 to July 2012 there are 4 questions, each with a corresponding page of ...
Essay Example: The decision in Roe v. Wade, made by the United States Supreme Court in 1973, has profoundly influenced both the legal framework and societal views on abortion and reproductive rights. The ruling established a woman's right to make decisions about her own pregnancy, emphasizing