

Qualitative Research Design: Start
Qualitative Research Design

What is Qualitative research design?
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much . It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Research Paradigms
- Positivist versus Post-Positivist
- Social Constructivist (this paradigm/ideology mostly birth qualitative studies)
Events Relating to the Qualitative Research and Community Engagement Workshops @ CMU Libraries
CMU Libraries is committed to helping members of our community become data experts. To that end, CMU is offering public facing workshops that discuss Qualitative Research, Coding, and Community Engagement best practices.
The following workshops are a part of a broader series on using data. Please follow the links to register for the events.
Qualitative Coding
Using Community Data to improve Outcome (Grant Writing)
Survey Design
Upcoming Event: March 21st, 2024 (12:00pm -1:00 pm)
Community Engagement and Collaboration Event
Join us for an event to improve, build on and expand the connections between Carnegie Mellon University resources and the Pittsburgh community. CMU resources such as the Libraries and Sustainability Initiative can be leveraged by users not affiliated with the university, but barriers can prevent them from fully engaging.
The conversation features representatives from CMU departments and local organizations about the community engagement efforts currently underway at CMU and opportunities to improve upon them. Speakers will highlight current and ongoing projects and share resources to support future collaboration.
Event Moderators:
Taiwo Lasisi, CLIR Postdoctoral Fellow in Community Data Literacy, Carnegie Mellon University Libraries
Emma Slayton, Data Curation, Visualization, & GIS Specialist, Carnegie Mellon University Libraries
Nicky Agate , Associate Dean for Academic Engagement, Carnegie Mellon University Libraries
Chelsea Cohen , The University’s Executive fellow for community engagement, Carnegie Mellon University
Sarah Ceurvorst , Academic Pathways Manager, Program Director, LEAP (Leadership, Excellence, Access, Persistence) Carnegie Mellon University
Julia Poeppibg , Associate Director of Partnership Development, Information Systems, Carnegie Mellon University
Scott Wolovich , Director of New Sun Rising, Pittsburgh
Additional workshops and events will be forthcoming. Watch this space for updates.
Workshop Organizer

Qualitative Research Methods
What are Qualitative Research methods?
Qualitative research adopts numerous methods or techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one-on-one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be participant observers to share the experiences of the subject or non-participant or detached observers.
What constitutes a good research question? Does the question drive research design choices?
According to Doody and Bailey (2014);
We can only develop a good research question by consulting relevant literature, colleagues, and supervisors experienced in the area of research. (inductive interactions).
Helps to have a directed research aim and objective.
Researchers should not be “ research trendy” and have enough evidence. This is why research objectives are important. It helps to take time, and resources into consideration.
Research questions can be developed from theoretical knowledge, previous research or experience, or a practical need at work (Parahoo 2014). They have numerous roles, such as identifying the importance of the research and providing clarity of purpose for the research, in terms of what the research intends to achieve in the end.
Qualitative Research Questions
What constitutes a good Qualitative research question?
A good qualitative question answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions and behavior.
Examples of good Qualitative Research Questions:
What are people's thoughts on the new library?
How does it feel to be a first-generation student attending college?
Difference example (between Qualitative and Quantitative research questions):
How many college students signed up for the new semester? (Quan)
How do college students feel about the new semester? What are their experiences so far? (Qual)
- Qualitative Research Design Workshop Powerpoint
Foley G, Timonen V. Using Grounded Theory Method to Capture and Analyze Health Care Experiences. Health Serv Res. 2015 Aug;50(4):1195-210. [ PMC free article: PMC4545354 ] [ PubMed: 25523315 ]
Devers KJ. How will we know "good" qualitative research when we see it? Beginning the dialogue in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999 Dec;34(5 Pt 2):1153-88. [ PMC free article: PMC1089058 ] [ PubMed: 10591278 ]
Huston P, Rowan M. Qualitative studies. Their role in medical research. Can Fam Physician. 1998 Nov;44:2453-8. [ PMC free article: PMC2277956 ] [ PubMed: 9839063 ]
Corner EJ, Murray EJ, Brett SJ. Qualitative, grounded theory exploration of patients' experience of early mobilisation, rehabilitation and recovery after critical illness. BMJ Open. 2019 Feb 24;9(2):e026348. [ PMC free article: PMC6443050 ] [ PubMed: 30804034 ]
Moser A, Korstjens I. Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 3: Sampling, data collection and analysis. Eur J Gen Pract. 2018 Dec;24(1):9-18. [ PMC free article: PMC5774281 ] [ PubMed: 29199486 ]
Houghton C, Murphy K, Meehan B, Thomas J, Brooker D, Casey D. From screening to synthesis: using nvivo to enhance transparency in qualitative evidence synthesis. J Clin Nurs. 2017 Mar;26(5-6):873-881. [ PubMed: 27324875 ]
Soratto J, Pires DEP, Friese S. Thematic content analysis using ATLAS.ti software: Potentialities for researchs in health. Rev Bras Enferm. 2020;73(3):e20190250. [ PubMed: 32321144 ]
Zamawe FC. The Implication of Using NVivo Software in Qualitative Data Analysis: Evidence-Based Reflections. Malawi Med J. 2015 Mar;27(1):13-5. [ PMC free article: PMC4478399 ] [ PubMed: 26137192 ]
Korstjens I, Moser A. Series: Practical guidance to qualitative research. Part 4: Trustworthiness and publishing. Eur J Gen Pract. 2018 Dec;24(1):120-124. [ PMC free article: PMC8816392 ] [ PubMed: 29202616 ]
Saldaña, J. (2021). The coding manual for qualitative researchers. The coding manual for qualitative researchers, 1-440.
O'Brien BC, Harris IB, Beckman TJ, Reed DA, Cook DA. Standards for reporting qualitative research: a synthesis of recommendations. Acad Med. 2014 Sep;89(9):1245-51. [ PubMed: 24979285 ]
Palermo C, King O, Brock T, Brown T, Crampton P, Hall H, Macaulay J, Morphet J, Mundy M, Oliaro L, Paynter S, Williams B, Wright C, E Rees C. Setting priorities for health education research: A mixed methods study. Med Teach. 2019 Sep;41(9):1029-1038. [ PubMed: 31141390 ]
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 4:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=1346006
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and application of qualitative research.
Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify and it is important to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore ‘compete’ against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each, qualitative and quantitative work are not necessarily opposites nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Examples of Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design has its origins in social and cultural anthropology, and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques with the aim of being able to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc. through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is the “generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior.” [5] As opposed to quantitative research which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and therefore lends itself to research that is aiming to study social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain for example how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is defined as the “study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular”. [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are quite similar, but upon careful examination, the differences can be seen. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the perspective of the individual. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the ‘lived experiences’ of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way, from their perspective . Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources whereas Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative Research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called ‘thick’ or ‘rich’ description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of ‘thick’ description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, in the hopes of creating a cohesive story, or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be “opportunities for innovation”. [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards that underpin different approaches to research. Essentially, research paradigms are the ‘worldview’ that inform research. [4] It is valuable for researchers, both qualitative and quantitative, to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontology and epistemologies . Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality” whereas epistemology is defined as the “assumptions about the nature of knowledge” that inform the work researchers do. [2] It is important to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a full understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, it is crucial that researchers understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist vs Postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we need to discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social as well as natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in its research which stems from positivist ontology that there is an objective reality that exists that is fully independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained but it could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world” and therefore postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are constructivist as well, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but rather that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. “Constructivism contends that individuals’ views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality”. [6] Essentially, Constructivist thought focuses on how ‘reality’ is not a fixed certainty and experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike in positivist views, that there is not necessarily an ‘objective’ reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and the world we live in are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have and can even change the role of the researcher themselves. [2] For example, is the researcher an ‘objective’ observer such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research itself, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the research undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research, as well as reflect on their own positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors at play. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale in terms of being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling-selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling-selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one on one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be a participant-observer to share the experiences of the subject or a non-participant or detached observer.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or in the environment of the participants, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed which may then be coded manually or with the use of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results also could be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
To standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes, the healthcare team can use two reporting standards. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a wider range of qualitative research. [13]
Examples of Application
Many times a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data for a better understanding of what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative methods can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research researchers can explore subjects that are poorly studied with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual's actions, and social science research.
A good qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure there are no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected which will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because many times, the information sought is not well compartmentalized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered “cool,” and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current non-smokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the results of the survey to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the major factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the major factor that contributed to teens to start smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into each of these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on how to keep teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and/or focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking first starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure of smoking. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and see that a shady, overgrown area of the park is where the smokers tend to hang out. The researcher notes the smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region of the park, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to the smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk population their perceptions of the changes, what factors are still at play, as well as quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community, the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or in combination with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation to not only help generate hypotheses which can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research provides researchers with a way to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many different ways, including the criteria for evaluating them. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. The correlating concepts in qualitative research are credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept is on the left, and the qualitative concept is on the right:
- Internal validity--- Credibility
- External validity---Transferability
- Reliability---Dependability
- Objectivity---Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid so should qualitative researchers ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple methods of data collection to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable by also interviewing the magician, back-stage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include using telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews as well as surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: Results can be reviewed by a peer to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
‘Thick’ or ‘rich’ description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research whereas using an indicator such as an audit trail might help with evaluating the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was carried out. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data themselves, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original records of information should also be kept (e.g., surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should take into consideration is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The Hawthorne effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. If a researcher was wanting to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tells the employees they are going to watch them to see what factors affect employee theft, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being watched.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens in an unconscious manner for the participant so it is important to eliminate or limit transmitting the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in artificial scenarios and/or with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative research by itself or combined with quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research does not exist as an island apart from quantitative research, but as an integral part of research methods to be used for the understanding of the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is important for all members of the health care team as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members including social works, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, health care team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Duong TVH, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [ 2014] Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics Peterson K, McCleery E. 2014 May
- Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. [Campbell Syst Rev. 2021] Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Mugellini G, Della Bella S, Colagrossi M, Isenring GL, Killias M. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun; 17(2):e1173. Epub 2021 May 24.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
- Types of qualitative research designs
Last updated
20 February 2023
Reviewed by
Jean Kaluza
Researchers often conduct these studies to gain a detailed understanding of a particular topic through a small, focused sample. Qualitative research methods delve into understanding why something is happening in a larger quantitative study.
To determine whether qualitative research is the best choice for your study, let’s look at the different types of qualitative research design.
Analyze all your qualitative research
Analyze qualitative data faster and surface more actionable insights
- What are qualitative research designs?
Qualitative research designs are research methods that collect and analyze non-numerical data. The research uncovers why or how a particular behavior or occurrence takes place. The information is usually subjective and in a written format instead of numerical.
Researchers may use interviews, focus groups , case studies , journaling, and open-ended questions to gather in-depth information. Qualitative research designs can determine users' concepts, develop a hypothesis , or add context to data from a quantitative study.
- Characteristics of qualitative research design
Most often, qualitative data answers how or why something occurs. Certain characteristics are usually present in all qualitative research designs to ensure accurate data.
The most common characteristics of qualitative research design include the following:
Natural environment
It’s best to collect qualitative research as close to the subject’s original environment as possible to encourage natural behavior and accurate insights.
Empathy is key
Qualitative researchers collect the best data when they’re in sync with their users’ concerns and motivations. They can play into natural human psychology by combining open-ended questioning and subtle cues.
They may mimic body language, adopt the users’ terminology, and use pauses or trailing sentences to encourage their participants to fill in the blanks. The more empathic the interviewer, the purer the data.
Participant selection
Qualitative research depends on the meaning obtained from participants instead of the meaning conveyed in similar research or studies. To increase research accuracy, you choose participants randomly from carefully chosen groups of potential participants.
Different research methods or multiple data sources
To gain in-depth knowledge, qualitative research designs often rely on multiple research methods within the same group.
Emergent design
Qualitative research constantly evolves, meaning the initial study plan might change after you collect data. This evolution might result in changes in research methods or the introduction of a new research problem.
Inductive reasoning
Since qualitative research seeks in-depth meaning, you need complex reasoning to get the right results. Qualitative researchers build categories, patterns, and themes from separate data sets to form a complete conclusion.
Interpretive data
Once you collect the data, you need to read between the lines rather than just noting what your participant said. Qualitative research is unique as we can attach actions to feedback.
If a user says they love the look of your design but haven’t completed any tasks, it’s up to you to interpret this as a failed test, even with their positive sentiments.
Holistic account
To paint a large picture of an issue and potential solutions, a qualitative researcher works to develop a complex description of the research problem. You can avoid a narrow cause-and-effect perspective by describing the problem’s wider perspectives.
- When to use qualitative research design
Qualitative research aims to get a detailed understanding of a particular topic. To accomplish this, you’ll typically use small focus groups to gather in-depth data from varied perspectives.
This approach is only effective for some types of study. For instance, a qualitative approach wouldn’t work for a study that seeks to understand a statistically relevant finding.
When determining if a qualitative research design is appropriate, remember the goal of qualitative research is understanding the “ why .”
Qualitative research design gathers in-depth information that stands on its own. It can also answer the “why” of a quantitative study or be a precursor to forming a hypothesis.
You can use qualitative research in these situations:
Developing a hypothesis for testing in a quantitative study
Identifying customer needs
Developing a new feature
Adding context to the results of a quantitative study
Understanding the motivations, values, and pain points that guide behavior
Difference between qualitative and quantitative research design
Qualitative and quantitative research designs gather data, but that's where the similarities end. Consider the difference between quality and quantity. Both are useful in different ways.
Qualitative research gathers in-depth information to answer how or why . It uses subjective data from detailed interviews, observations, and open-ended questions. Most often, qualitative data is thoughts, experiences, and concepts.
In contrast, quantitative research designs gather large amounts of objective data that you can quantify mathematically. You typically express quantitative data in numbers or graphs, and you use it to test or confirm hypotheses.
Qualitative research designs generally have the same goals. However, there are various ways to achieve these goals. Researchers may use one or more of these approaches in qualitative research.
Historical study
This is where you use extensive information about people and events in the past to draw conclusions about the present and future.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology investigates a phenomenon, activity, or event using data from participants' perspectives. Often, researchers use a combination of methods.
Grounded theory
Grounded theory uses interviews and existing data to build a theory inductively.
Ethnography
Researchers immerse themselves in the target participant's environments to understand goals, cultures, challenges, and themes with ethnography .
A case study is where you use multiple data sources to examine a person, group, community, or institution. Participants must share a connection to the research question you’re studying.
- Advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research
All qualitative research design types share the common goal of obtaining in-depth information. Achieving this goal generally requires extensive data collection methods that can be time-consuming. As such, qualitative research has advantages and disadvantages.
Natural settings
Since you can collect data closer to an authentic environment, it offers more accurate results.
The ability to paint a picture with data
Quantitative studies don't always reveal the full picture. With multiple data collection methods, you can expose the motivations and reasons behind data.
Flexibility
Analysis processes aren't set in stone, so you can adapt the process as ideas or patterns emerge.
Generation of new ideas
Using open-ended responses can uncover new opportunities or solutions that weren't part of your original research plan.
Small sample sizes
You can generate meaningful results with small groups.
Disadvantages
Potentially unreliable.
A natural setting can be a double-edged sword. The inability to attach findings to anything statistically relevant can make data more difficult to quantify.
Subjectivity
Since the researcher plays a vital role in collecting and interpreting data, qualitative research is subject to the researcher's skills. For example, they may miss a cue that changes some of the context of the quotes they collected.
Labor-intensive
You generally collect qualitative data through manual processes like extensive interviews, open-ended questions, and case studies.
Qualitative research designs allow researchers to provide an in-depth analysis of why specific behavior or events occur. It can offer fresh insights, generate new ideas, or add context to statistics from quantitative studies. Depending on your needs, qualitative data might be a great way to gain the information your organization needs to move forward.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Research Design 101
Everything You Need To Get Started (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | April 2023

Navigating the world of research can be daunting, especially if you’re a first-time researcher. One concept you’re bound to run into fairly early in your research journey is that of “ research design ”. Here, we’ll guide you through the basics using practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Research Design 101
What is research design.
- Research design types for quantitative studies
- Video explainer : quantitative research design
- Research design types for qualitative studies
- Video explainer : qualitative research design
- How to choose a research design
- Key takeaways
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project , from its conception to the final data analysis. A good research design serves as the blueprint for how you, as the researcher, will collect and analyse data while ensuring consistency, reliability and validity throughout your study.
Understanding different types of research designs is essential as helps ensure that your approach is suitable given your research aims, objectives and questions , as well as the resources you have available to you. Without a clear big-picture view of how you’ll design your research, you run the risk of potentially making misaligned choices in terms of your methodology – especially your sampling , data collection and data analysis decisions.
The problem with defining research design…
One of the reasons students struggle with a clear definition of research design is because the term is used very loosely across the internet, and even within academia.
Some sources claim that the three research design types are qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods , which isn’t quite accurate (these just refer to the type of data that you’ll collect and analyse). Other sources state that research design refers to the sum of all your design choices, suggesting it’s more like a research methodology . Others run off on other less common tangents. No wonder there’s confusion!
In this article, we’ll clear up the confusion. We’ll explain the most common research design types for both qualitative and quantitative research projects, whether that is for a full dissertation or thesis, or a smaller research paper or article.

Research Design: Quantitative Studies
Quantitative research involves collecting and analysing data in a numerical form. Broadly speaking, there are four types of quantitative research designs: descriptive , correlational , experimental , and quasi-experimental .
Descriptive Research Design
As the name suggests, descriptive research design focuses on describing existing conditions, behaviours, or characteristics by systematically gathering information without manipulating any variables. In other words, there is no intervention on the researcher’s part – only data collection.
For example, if you’re studying smartphone addiction among adolescents in your community, you could deploy a survey to a sample of teens asking them to rate their agreement with certain statements that relate to smartphone addiction. The collected data would then provide insight regarding how widespread the issue may be – in other words, it would describe the situation.
The key defining attribute of this type of research design is that it purely describes the situation . In other words, descriptive research design does not explore potential relationships between different variables or the causes that may underlie those relationships. Therefore, descriptive research is useful for generating insight into a research problem by describing its characteristics . By doing so, it can provide valuable insights and is often used as a precursor to other research design types.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational design is a popular choice for researchers aiming to identify and measure the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them . In other words, this type of research design is useful when you want to know whether a change in one thing tends to be accompanied by a change in another thing.
For example, if you wanted to explore the relationship between exercise frequency and overall health, you could use a correlational design to help you achieve this. In this case, you might gather data on participants’ exercise habits, as well as records of their health indicators like blood pressure, heart rate, or body mass index. Thereafter, you’d use a statistical test to assess whether there’s a relationship between the two variables (exercise frequency and health).
As you can see, correlational research design is useful when you want to explore potential relationships between variables that cannot be manipulated or controlled for ethical, practical, or logistical reasons. It is particularly helpful in terms of developing predictions , and given that it doesn’t involve the manipulation of variables, it can be implemented at a large scale more easily than experimental designs (which will look at next).
That said, it’s important to keep in mind that correlational research design has limitations – most notably that it cannot be used to establish causality . In other words, correlation does not equal causation . To establish causality, you’ll need to move into the realm of experimental design, coming up next…
Need a helping hand?
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to determine if there is a causal relationship between two or more variables . With this type of research design, you, as the researcher, manipulate one variable (the independent variable) while controlling others (dependent variables). Doing so allows you to observe the effect of the former on the latter and draw conclusions about potential causality.
For example, if you wanted to measure if/how different types of fertiliser affect plant growth, you could set up several groups of plants, with each group receiving a different type of fertiliser, as well as one with no fertiliser at all. You could then measure how much each plant group grew (on average) over time and compare the results from the different groups to see which fertiliser was most effective.
Overall, experimental research design provides researchers with a powerful way to identify and measure causal relationships (and the direction of causality) between variables. However, developing a rigorous experimental design can be challenging as it’s not always easy to control all the variables in a study. This often results in smaller sample sizes , which can reduce the statistical power and generalisability of the results.
Moreover, experimental research design requires random assignment . This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling ). Doing so helps reduce the potential for bias and confounding variables . This need for random assignment can lead to ethics-related issues . For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations.
Quasi-Experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used when the research aims involve identifying causal relations , but one cannot (or doesn’t want to) randomly assign participants to different groups (for practical or ethical reasons). Instead, with a quasi-experimental research design, the researcher relies on existing groups or pre-existing conditions to form groups for comparison.
For example, if you were studying the effects of a new teaching method on student achievement in a particular school district, you may be unable to randomly assign students to either group and instead have to choose classes or schools that already use different teaching methods. This way, you still achieve separate groups, without having to assign participants to specific groups yourself.
Naturally, quasi-experimental research designs have limitations when compared to experimental designs. Given that participant assignment is not random, it’s more difficult to confidently establish causality between variables, and, as a researcher, you have less control over other variables that may impact findings.
All that said, quasi-experimental designs can still be valuable in research contexts where random assignment is not possible and can often be undertaken on a much larger scale than experimental research, thus increasing the statistical power of the results. What’s important is that you, as the researcher, understand the limitations of the design and conduct your quasi-experiment as rigorously as possible, paying careful attention to any potential confounding variables .

Research Design: Qualitative Studies
There are many different research design types when it comes to qualitative studies, but here we’ll narrow our focus to explore the “Big 4”. Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design.
Phenomenological Research Design
Phenomenological design involves exploring the meaning of lived experiences and how they are perceived by individuals. This type of research design seeks to understand people’s perspectives , emotions, and behaviours in specific situations. Here, the aim for researchers is to uncover the essence of human experience without making any assumptions or imposing preconceived ideas on their subjects.
For example, you could adopt a phenomenological design to study why cancer survivors have such varied perceptions of their lives after overcoming their disease. This could be achieved by interviewing survivors and then analysing the data using a qualitative analysis method such as thematic analysis to identify commonalities and differences.
Phenomenological research design typically involves in-depth interviews or open-ended questionnaires to collect rich, detailed data about participants’ subjective experiences. This richness is one of the key strengths of phenomenological research design but, naturally, it also has limitations. These include potential biases in data collection and interpretation and the lack of generalisability of findings to broader populations.
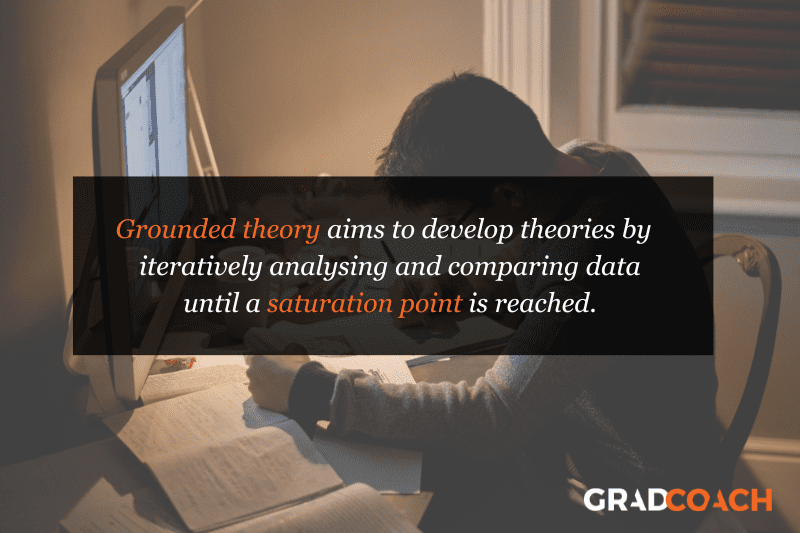
Grounded Theory Research Design
Grounded theory (also referred to as “GT”) aims to develop theories by continuously and iteratively analysing and comparing data collected from a relatively large number of participants in a study. It takes an inductive (bottom-up) approach, with a focus on letting the data “speak for itself”, without being influenced by preexisting theories or the researcher’s preconceptions.
As an example, let’s assume your research aims involved understanding how people cope with chronic pain from a specific medical condition, with a view to developing a theory around this. In this case, grounded theory design would allow you to explore this concept thoroughly without preconceptions about what coping mechanisms might exist. You may find that some patients prefer cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) while others prefer to rely on herbal remedies. Based on multiple, iterative rounds of analysis, you could then develop a theory in this regard, derived directly from the data (as opposed to other preexisting theories and models).
Grounded theory typically involves collecting data through interviews or observations and then analysing it to identify patterns and themes that emerge from the data. These emerging ideas are then validated by collecting more data until a saturation point is reached (i.e., no new information can be squeezed from the data). From that base, a theory can then be developed .
As you can see, grounded theory is ideally suited to studies where the research aims involve theory generation , especially in under-researched areas. Keep in mind though that this type of research design can be quite time-intensive , given the need for multiple rounds of data collection and analysis.
Ethnographic Research Design
Ethnographic design involves observing and studying a culture-sharing group of people in their natural setting to gain insight into their behaviours, beliefs, and values. The focus here is on observing participants in their natural environment (as opposed to a controlled environment). This typically involves the researcher spending an extended period of time with the participants in their environment, carefully observing and taking field notes .
All of this is not to say that ethnographic research design relies purely on observation. On the contrary, this design typically also involves in-depth interviews to explore participants’ views, beliefs, etc. However, unobtrusive observation is a core component of the ethnographic approach.
As an example, an ethnographer may study how different communities celebrate traditional festivals or how individuals from different generations interact with technology differently. This may involve a lengthy period of observation, combined with in-depth interviews to further explore specific areas of interest that emerge as a result of the observations that the researcher has made.
As you can probably imagine, ethnographic research design has the ability to provide rich, contextually embedded insights into the socio-cultural dynamics of human behaviour within a natural, uncontrived setting. Naturally, however, it does come with its own set of challenges, including researcher bias (since the researcher can become quite immersed in the group), participant confidentiality and, predictably, ethical complexities . All of these need to be carefully managed if you choose to adopt this type of research design.
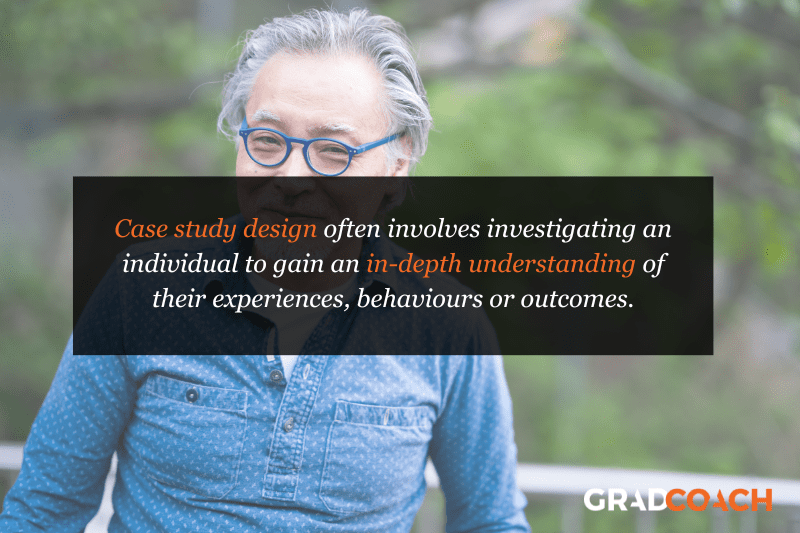
Case Study Design
With case study research design, you, as the researcher, investigate a single individual (or a single group of individuals) to gain an in-depth understanding of their experiences, behaviours or outcomes. Unlike other research designs that are aimed at larger sample sizes, case studies offer a deep dive into the specific circumstances surrounding a person, group of people, event or phenomenon, generally within a bounded setting or context .
As an example, a case study design could be used to explore the factors influencing the success of a specific small business. This would involve diving deeply into the organisation to explore and understand what makes it tick – from marketing to HR to finance. In terms of data collection, this could include interviews with staff and management, review of policy documents and financial statements, surveying customers, etc.
While the above example is focused squarely on one organisation, it’s worth noting that case study research designs can have different variation s, including single-case, multiple-case and longitudinal designs. As you can see in the example, a single-case design involves intensely examining a single entity to understand its unique characteristics and complexities. Conversely, in a multiple-case design , multiple cases are compared and contrasted to identify patterns and commonalities. Lastly, in a longitudinal case design , a single case or multiple cases are studied over an extended period of time to understand how factors develop over time.
As you can see, a case study research design is particularly useful where a deep and contextualised understanding of a specific phenomenon or issue is desired. However, this strength is also its weakness. In other words, you can’t generalise the findings from a case study to the broader population. So, keep this in mind if you’re considering going the case study route.
How To Choose A Research Design
Having worked through all of these potential research designs, you’d be forgiven for feeling a little overwhelmed and wondering, “ But how do I decide which research design to use? ”. While we could write an entire post covering that alone, here are a few factors to consider that will help you choose a suitable research design for your study.
Data type: The first determining factor is naturally the type of data you plan to be collecting – i.e., qualitative or quantitative. This may sound obvious, but we have to be clear about this – don’t try to use a quantitative research design on qualitative data (or vice versa)!
Research aim(s) and question(s): As with all methodological decisions, your research aim and research questions will heavily influence your research design. For example, if your research aims involve developing a theory from qualitative data, grounded theory would be a strong option. Similarly, if your research aims involve identifying and measuring relationships between variables, one of the experimental designs would likely be a better option.
Time: It’s essential that you consider any time constraints you have, as this will impact the type of research design you can choose. For example, if you’ve only got a month to complete your project, a lengthy design such as ethnography wouldn’t be a good fit.
Resources: Take into account the resources realistically available to you, as these need to factor into your research design choice. For example, if you require highly specialised lab equipment to execute an experimental design, you need to be sure that you’ll have access to that before you make a decision.
Keep in mind that when it comes to research, it’s important to manage your risks and play as conservatively as possible. If your entire project relies on you achieving a huge sample, having access to niche equipment or holding interviews with very difficult-to-reach participants, you’re creating risks that could kill your project. So, be sure to think through your choices carefully and make sure that you have backup plans for any existential risks. Remember that a relatively simple methodology executed well generally will typically earn better marks than a highly-complex methodology executed poorly.

Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. Let’s recap by looking at the key takeaways:
- Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data.
- Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive , correlational , experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs.
- Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological , grounded theory , ethnographic and case study designs.
- When choosing a research design, you need to consider a variety of factors, including the type of data you’ll be working with, your research aims and questions, your time and the resources available to you.
If you need a helping hand with your research design (or any other aspect of your research), check out our private coaching services .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Is there any blog article explaining more on Case study research design? Is there a Case study write-up template? Thank you.
Thanks this was quite valuable to clarify such an important concept.
Thanks for this simplified explanations. it is quite very helpful.
This was really helpful. thanks
Thank you for your explanation. I think case study research design and the use of secondary data in researches needs to be talked about more in your videos and articles because there a lot of case studies research design tailored projects out there.
Please is there any template for a case study research design whose data type is a secondary data on your repository?
This post is very clear, comprehensive and has been very helpful to me. It has cleared the confusion I had in regard to research design and methodology.
This post is helpful, easy to understand, and deconstructs what a research design is. Thanks
how to cite this page
Thank you very much for the post. It is wonderful and has cleared many worries in my mind regarding research designs. I really appreciate .
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Chapter 1. Introduction
“Science is in danger, and for that reason it is becoming dangerous” -Pierre Bourdieu, Science of Science and Reflexivity
Why an Open Access Textbook on Qualitative Research Methods?
I have been teaching qualitative research methods to both undergraduates and graduate students for many years. Although there are some excellent textbooks out there, they are often costly, and none of them, to my mind, properly introduces qualitative research methods to the beginning student (whether undergraduate or graduate student). In contrast, this open-access textbook is designed as a (free) true introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access more advanced instruction.
Textbooks are typically arranged in one of two ways: (1) by technique (each chapter covers one method used in qualitative research); or (2) by process (chapters advance from research design through publication). But both of these approaches are necessary for the beginner student. This textbook will have sections dedicated to the process as well as the techniques of qualitative research. This is a true “comprehensive” book for the beginning student. In addition to covering techniques of data collection and data analysis, it provides a road map of how to get started and how to keep going and where to go for advanced instruction. It covers aspects of research design and research communication as well as methods employed. Along the way, it includes examples from many different disciplines in the social sciences.
The primary goal has been to create a useful, accessible, engaging textbook for use across many disciplines. And, let’s face it. Textbooks can be boring. I hope readers find this to be a little different. I have tried to write in a practical and forthright manner, with many lively examples and references to good and intellectually creative qualitative research. Woven throughout the text are short textual asides (in colored textboxes) by professional (academic) qualitative researchers in various disciplines. These short accounts by practitioners should help inspire students. So, let’s begin!
What is Research?
When we use the word research , what exactly do we mean by that? This is one of those words that everyone thinks they understand, but it is worth beginning this textbook with a short explanation. We use the term to refer to “empirical research,” which is actually a historically specific approach to understanding the world around us. Think about how you know things about the world. [1] You might know your mother loves you because she’s told you she does. Or because that is what “mothers” do by tradition. Or you might know because you’ve looked for evidence that she does, like taking care of you when you are sick or reading to you in bed or working two jobs so you can have the things you need to do OK in life. Maybe it seems churlish to look for evidence; you just take it “on faith” that you are loved.
Only one of the above comes close to what we mean by research. Empirical research is research (investigation) based on evidence. Conclusions can then be drawn from observable data. This observable data can also be “tested” or checked. If the data cannot be tested, that is a good indication that we are not doing research. Note that we can never “prove” conclusively, through observable data, that our mothers love us. We might have some “disconfirming evidence” (that time she didn’t show up to your graduation, for example) that could push you to question an original hypothesis , but no amount of “confirming evidence” will ever allow us to say with 100% certainty, “my mother loves me.” Faith and tradition and authority work differently. Our knowledge can be 100% certain using each of those alternative methods of knowledge, but our certainty in those cases will not be based on facts or evidence.
For many periods of history, those in power have been nervous about “science” because it uses evidence and facts as the primary source of understanding the world, and facts can be at odds with what power or authority or tradition want you to believe. That is why I say that scientific empirical research is a historically specific approach to understand the world. You are in college or university now partly to learn how to engage in this historically specific approach.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries in Europe, there was a newfound respect for empirical research, some of which was seriously challenging to the established church. Using observations and testing them, scientists found that the earth was not at the center of the universe, for example, but rather that it was but one planet of many which circled the sun. [2] For the next two centuries, the science of astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry emerged and became disciplines taught in universities. All used the scientific method of observation and testing to advance knowledge. Knowledge about people , however, and social institutions, however, was still left to faith, tradition, and authority. Historians and philosophers and poets wrote about the human condition, but none of them used research to do so. [3]
It was not until the nineteenth century that “social science” really emerged, using the scientific method (empirical observation) to understand people and social institutions. New fields of sociology, economics, political science, and anthropology emerged. The first sociologists, people like Auguste Comte and Karl Marx, sought specifically to apply the scientific method of research to understand society, Engels famously claiming that Marx had done for the social world what Darwin did for the natural world, tracings its laws of development. Today we tend to take for granted the naturalness of science here, but it is actually a pretty recent and radical development.
To return to the question, “does your mother love you?” Well, this is actually not really how a researcher would frame the question, as it is too specific to your case. It doesn’t tell us much about the world at large, even if it does tell us something about you and your relationship with your mother. A social science researcher might ask, “do mothers love their children?” Or maybe they would be more interested in how this loving relationship might change over time (e.g., “do mothers love their children more now than they did in the 18th century when so many children died before reaching adulthood?”) or perhaps they might be interested in measuring quality of love across cultures or time periods, or even establishing “what love looks like” using the mother/child relationship as a site of exploration. All of these make good research questions because we can use observable data to answer them.
What is Qualitative Research?
“All we know is how to learn. How to study, how to listen, how to talk, how to tell. If we don’t tell the world, we don’t know the world. We’re lost in it, we die.” -Ursula LeGuin, The Telling
At its simplest, qualitative research is research about the social world that does not use numbers in its analyses. All those who fear statistics can breathe a sigh of relief – there are no mathematical formulae or regression models in this book! But this definition is less about what qualitative research can be and more about what it is not. To be honest, any simple statement will fail to capture the power and depth of qualitative research. One way of contrasting qualitative research to quantitative research is to note that the focus of qualitative research is less about explaining and predicting relationships between variables and more about understanding the social world. To use our mother love example, the question about “what love looks like” is a good question for the qualitative researcher while all questions measuring love or comparing incidences of love (both of which require measurement) are good questions for quantitative researchers. Patton writes,
Qualitative data describe. They take us, as readers, into the time and place of the observation so that we know what it was like to have been there. They capture and communicate someone else’s experience of the world in his or her own words. Qualitative data tell a story. ( Patton 2002:47 )
Qualitative researchers are asking different questions about the world than their quantitative colleagues. Even when researchers are employed in “mixed methods” research ( both quantitative and qualitative), they are using different methods to address different questions of the study. I do a lot of research about first-generation and working-college college students. Where a quantitative researcher might ask, how many first-generation college students graduate from college within four years? Or does first-generation college status predict high student debt loads? A qualitative researcher might ask, how does the college experience differ for first-generation college students? What is it like to carry a lot of debt, and how does this impact the ability to complete college on time? Both sets of questions are important, but they can only be answered using specific tools tailored to those questions. For the former, you need large numbers to make adequate comparisons. For the latter, you need to talk to people, find out what they are thinking and feeling, and try to inhabit their shoes for a little while so you can make sense of their experiences and beliefs.
Examples of Qualitative Research
You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research “in the field.” A good qualitative researcher will present the product of their hours of work in such a way that it seems natural, even obvious, to the reader. Because we are trying to convey what it is like answers, qualitative research is often presented as stories – stories about how people live their lives, go to work, raise their children, interact with one another. In some ways, this can seem like reading particularly insightful novels. But, unlike novels, there are very specific rules and guidelines that qualitative researchers follow to ensure that the “story” they are telling is accurate , a truthful rendition of what life is like for the people being studied. Most of this textbook will be spent conveying those rules and guidelines. Let’s take a look, first, however, at three examples of what the end product looks like. I have chosen these three examples to showcase very different approaches to qualitative research, and I will return to these five examples throughout the book. They were all published as whole books (not chapters or articles), and they are worth the long read, if you have the time. I will also provide some information on how these books came to be and the length of time it takes to get them into book version. It is important you know about this process, and the rest of this textbook will help explain why it takes so long to conduct good qualitative research!
Example 1 : The End Game (ethnography + interviews)
Corey Abramson is a sociologist who teaches at the University of Arizona. In 2015 he published The End Game: How Inequality Shapes our Final Years ( 2015 ). This book was based on the research he did for his dissertation at the University of California-Berkeley in 2012. Actually, the dissertation was completed in 2012 but the work that was produced that took several years. The dissertation was entitled, “This is How We Live, This is How We Die: Social Stratification, Aging, and Health in Urban America” ( 2012 ). You can see how the book version, which was written for a more general audience, has a more engaging sound to it, but that the dissertation version, which is what academic faculty read and evaluate, has a more descriptive title. You can read the title and know that this is a study about aging and health and that the focus is going to be inequality and that the context (place) is going to be “urban America.” It’s a study about “how” people do something – in this case, how they deal with aging and death. This is the very first sentence of the dissertation, “From our first breath in the hospital to the day we die, we live in a society characterized by unequal opportunities for maintaining health and taking care of ourselves when ill. These disparities reflect persistent racial, socio-economic, and gender-based inequalities and contribute to their persistence over time” ( 1 ). What follows is a truthful account of how that is so.
Cory Abramson spent three years conducting his research in four different urban neighborhoods. We call the type of research he conducted “comparative ethnographic” because he designed his study to compare groups of seniors as they went about their everyday business. It’s comparative because he is comparing different groups (based on race, class, gender) and ethnographic because he is studying the culture/way of life of a group. [4] He had an educated guess, rooted in what previous research had shown and what social theory would suggest, that people’s experiences of aging differ by race, class, and gender. So, he set up a research design that would allow him to observe differences. He chose two primarily middle-class (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly White) and two primarily poor neighborhoods (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly African American). He hung out in senior centers and other places seniors congregated, watched them as they took the bus to get prescriptions filled, sat in doctor’s offices with them, and listened to their conversations with each other. He also conducted more formal conversations, what we call in-depth interviews, with sixty seniors from each of the four neighborhoods. As with a lot of fieldwork , as he got closer to the people involved, he both expanded and deepened his reach –
By the end of the project, I expanded my pool of general observations to include various settings frequented by seniors: apartment building common rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, pharmacies, senior centers, bars, parks, corner stores, shopping centers, pool halls, hair salons, coffee shops, and discount stores. Over the course of the three years of fieldwork, I observed hundreds of elders, and developed close relationships with a number of them. ( 2012:10 )
When Abramson rewrote the dissertation for a general audience and published his book in 2015, it got a lot of attention. It is a beautifully written book and it provided insight into a common human experience that we surprisingly know very little about. It won the Outstanding Publication Award by the American Sociological Association Section on Aging and the Life Course and was featured in the New York Times . The book was about aging, and specifically how inequality shapes the aging process, but it was also about much more than that. It helped show how inequality affects people’s everyday lives. For example, by observing the difficulties the poor had in setting up appointments and getting to them using public transportation and then being made to wait to see a doctor, sometimes in standing-room-only situations, when they are unwell, and then being treated dismissively by hospital staff, Abramson allowed readers to feel the material reality of being poor in the US. Comparing these examples with seniors with adequate supplemental insurance who have the resources to hire car services or have others assist them in arranging care when they need it, jolts the reader to understand and appreciate the difference money makes in the lives and circumstances of us all, and in a way that is different than simply reading a statistic (“80% of the poor do not keep regular doctor’s appointments”) does. Qualitative research can reach into spaces and places that often go unexamined and then reports back to the rest of us what it is like in those spaces and places.
Example 2: Racing for Innocence (Interviews + Content Analysis + Fictional Stories)
Jennifer Pierce is a Professor of American Studies at the University of Minnesota. Trained as a sociologist, she has written a number of books about gender, race, and power. Her very first book, Gender Trials: Emotional Lives in Contemporary Law Firms, published in 1995, is a brilliant look at gender dynamics within two law firms. Pierce was a participant observer, working as a paralegal, and she observed how female lawyers and female paralegals struggled to obtain parity with their male colleagues.
Fifteen years later, she reexamined the context of the law firm to include an examination of racial dynamics, particularly how elite white men working in these spaces created and maintained a culture that made it difficult for both female attorneys and attorneys of color to thrive. Her book, Racing for Innocence: Whiteness, Gender, and the Backlash Against Affirmative Action , published in 2012, is an interesting and creative blending of interviews with attorneys, content analyses of popular films during this period, and fictional accounts of racial discrimination and sexual harassment. The law firm she chose to study had come under an affirmative action order and was in the process of implementing equitable policies and programs. She wanted to understand how recipients of white privilege (the elite white male attorneys) come to deny the role they play in reproducing inequality. Through interviews with attorneys who were present both before and during the affirmative action order, she creates a historical record of the “bad behavior” that necessitated new policies and procedures, but also, and more importantly , probed the participants ’ understanding of this behavior. It should come as no surprise that most (but not all) of the white male attorneys saw little need for change, and that almost everyone else had accounts that were different if not sometimes downright harrowing.
I’ve used Pierce’s book in my qualitative research methods courses as an example of an interesting blend of techniques and presentation styles. My students often have a very difficult time with the fictional accounts she includes. But they serve an important communicative purpose here. They are her attempts at presenting “both sides” to an objective reality – something happens (Pierce writes this something so it is very clear what it is), and the two participants to the thing that happened have very different understandings of what this means. By including these stories, Pierce presents one of her key findings – people remember things differently and these different memories tend to support their own ideological positions. I wonder what Pierce would have written had she studied the murder of George Floyd or the storming of the US Capitol on January 6 or any number of other historic events whose observers and participants record very different happenings.
This is not to say that qualitative researchers write fictional accounts. In fact, the use of fiction in our work remains controversial. When used, it must be clearly identified as a presentation device, as Pierce did. I include Racing for Innocence here as an example of the multiple uses of methods and techniques and the way that these work together to produce better understandings by us, the readers, of what Pierce studied. We readers come away with a better grasp of how and why advantaged people understate their own involvement in situations and structures that advantage them. This is normal human behavior , in other words. This case may have been about elite white men in law firms, but the general insights here can be transposed to other settings. Indeed, Pierce argues that more research needs to be done about the role elites play in the reproduction of inequality in the workplace in general.
Example 3: Amplified Advantage (Mixed Methods: Survey Interviews + Focus Groups + Archives)
The final example comes from my own work with college students, particularly the ways in which class background affects the experience of college and outcomes for graduates. I include it here as an example of mixed methods, and for the use of supplementary archival research. I’ve done a lot of research over the years on first-generation, low-income, and working-class college students. I am curious (and skeptical) about the possibility of social mobility today, particularly with the rising cost of college and growing inequality in general. As one of the few people in my family to go to college, I didn’t grow up with a lot of examples of what college was like or how to make the most of it. And when I entered graduate school, I realized with dismay that there were very few people like me there. I worried about becoming too different from my family and friends back home. And I wasn’t at all sure that I would ever be able to pay back the huge load of debt I was taking on. And so I wrote my dissertation and first two books about working-class college students. These books focused on experiences in college and the difficulties of navigating between family and school ( Hurst 2010a, 2012 ). But even after all that research, I kept coming back to wondering if working-class students who made it through college had an equal chance at finding good jobs and happy lives,
What happens to students after college? Do working-class students fare as well as their peers? I knew from my own experience that barriers continued through graduate school and beyond, and that my debtload was higher than that of my peers, constraining some of the choices I made when I graduated. To answer these questions, I designed a study of students attending small liberal arts colleges, the type of college that tried to equalize the experience of students by requiring all students to live on campus and offering small classes with lots of interaction with faculty. These private colleges tend to have more money and resources so they can provide financial aid to low-income students. They also attract some very wealthy students. Because they enroll students across the class spectrum, I would be able to draw comparisons. I ended up spending about four years collecting data, both a survey of more than 2000 students (which formed the basis for quantitative analyses) and qualitative data collection (interviews, focus groups, archival research, and participant observation). This is what we call a “mixed methods” approach because we use both quantitative and qualitative data. The survey gave me a large enough number of students that I could make comparisons of the how many kind, and to be able to say with some authority that there were in fact significant differences in experience and outcome by class (e.g., wealthier students earned more money and had little debt; working-class students often found jobs that were not in their chosen careers and were very affected by debt, upper-middle-class students were more likely to go to graduate school). But the survey analyses could not explain why these differences existed. For that, I needed to talk to people and ask them about their motivations and aspirations. I needed to understand their perceptions of the world, and it is very hard to do this through a survey.
By interviewing students and recent graduates, I was able to discern particular patterns and pathways through college and beyond. Specifically, I identified three versions of gameplay. Upper-middle-class students, whose parents were themselves professionals (academics, lawyers, managers of non-profits), saw college as the first stage of their education and took classes and declared majors that would prepare them for graduate school. They also spent a lot of time building their resumes, taking advantage of opportunities to help professors with their research, or study abroad. This helped them gain admission to highly-ranked graduate schools and interesting jobs in the public sector. In contrast, upper-class students, whose parents were wealthy and more likely to be engaged in business (as CEOs or other high-level directors), prioritized building social capital. They did this by joining fraternities and sororities and playing club sports. This helped them when they graduated as they called on friends and parents of friends to find them well-paying jobs. Finally, low-income, first-generation, and working-class students were often adrift. They took the classes that were recommended to them but without the knowledge of how to connect them to life beyond college. They spent time working and studying rather than partying or building their resumes. All three sets of students thought they were “doing college” the right way, the way that one was supposed to do college. But these three versions of gameplay led to distinct outcomes that advantaged some students over others. I titled my work “Amplified Advantage” to highlight this process.
These three examples, Cory Abramson’s The End Game , Jennifer Peirce’s Racing for Innocence, and my own Amplified Advantage, demonstrate the range of approaches and tools available to the qualitative researcher. They also help explain why qualitative research is so important. Numbers can tell us some things about the world, but they cannot get at the hearts and minds, motivations and beliefs of the people who make up the social worlds we inhabit. For that, we need tools that allow us to listen and make sense of what people tell us and show us. That is what good qualitative research offers us.
How Is This Book Organized?
This textbook is organized as a comprehensive introduction to the use of qualitative research methods. The first half covers general topics (e.g., approaches to qualitative research, ethics) and research design (necessary steps for building a successful qualitative research study). The second half reviews various data collection and data analysis techniques. Of course, building a successful qualitative research study requires some knowledge of data collection and data analysis so the chapters in the first half and the chapters in the second half should be read in conversation with each other. That said, each chapter can be read on its own for assistance with a particular narrow topic. In addition to the chapters, a helpful glossary can be found in the back of the book. Rummage around in the text as needed.
Chapter Descriptions
Chapter 2 provides an overview of the Research Design Process. How does one begin a study? What is an appropriate research question? How is the study to be done – with what methods ? Involving what people and sites? Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
Chapter 3 describes and explains various ways of knowing the (social) world. What is it possible for us to know about how other people think or why they behave the way they do? What does it mean to say something is a “fact” or that it is “well-known” and understood? Qualitative researchers are particularly interested in these questions because of the types of research questions we are interested in answering (the how questions rather than the how many questions of quantitative research). Qualitative researchers have adopted various epistemological approaches. Chapter 3 will explore these approaches, highlighting interpretivist approaches that acknowledge the subjective aspect of reality – in other words, reality and knowledge are not objective but rather influenced by (interpreted through) people.
Chapter 4 focuses on the practical matter of developing a research question and finding the right approach to data collection. In any given study (think of Cory Abramson’s study of aging, for example), there may be years of collected data, thousands of observations , hundreds of pages of notes to read and review and make sense of. If all you had was a general interest area (“aging”), it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to make sense of all of that data. The research question provides a helpful lens to refine and clarify (and simplify) everything you find and collect. For that reason, it is important to pull out that lens (articulate the research question) before you get started. In the case of the aging study, Cory Abramson was interested in how inequalities affected understandings and responses to aging. It is for this reason he designed a study that would allow him to compare different groups of seniors (some middle-class, some poor). Inevitably, he saw much more in the three years in the field than what made it into his book (or dissertation), but he was able to narrow down the complexity of the social world to provide us with this rich account linked to the original research question. Developing a good research question is thus crucial to effective design and a successful outcome. Chapter 4 will provide pointers on how to do this. Chapter 4 also provides an overview of general approaches taken to doing qualitative research and various “traditions of inquiry.”
Chapter 5 explores sampling . After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (Observations? Interviews?), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview , the sample should follow the research question and research design. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. Chapter 5 explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Chapter 6 addresses the importance of reflexivity in qualitative research. Related to epistemological issues of how we know anything about the social world, qualitative researchers understand that we the researchers can never be truly neutral or outside the study we are conducting. As observers, we see things that make sense to us and may entirely miss what is either too obvious to note or too different to comprehend. As interviewers, as much as we would like to ask questions neutrally and remain in the background, interviews are a form of conversation, and the persons we interview are responding to us . Therefore, it is important to reflect upon our social positions and the knowledges and expectations we bring to our work and to work through any blind spots that we may have. Chapter 6 provides some examples of reflexivity in practice and exercises for thinking through one’s own biases.
Chapter 7 is a very important chapter and should not be overlooked. As a practical matter, it should also be read closely with chapters 6 and 8. Because qualitative researchers deal with people and the social world, it is imperative they develop and adhere to a strong ethical code for conducting research in a way that does not harm. There are legal requirements and guidelines for doing so (see chapter 8), but these requirements should not be considered synonymous with the ethical code required of us. Each researcher must constantly interrogate every aspect of their research, from research question to design to sample through analysis and presentation, to ensure that a minimum of harm (ideally, zero harm) is caused. Because each research project is unique, the standards of care for each study are unique. Part of being a professional researcher is carrying this code in one’s heart, being constantly attentive to what is required under particular circumstances. Chapter 7 provides various research scenarios and asks readers to weigh in on the suitability and appropriateness of the research. If done in a class setting, it will become obvious fairly quickly that there are often no absolutely correct answers, as different people find different aspects of the scenarios of greatest importance. Minimizing the harm in one area may require possible harm in another. Being attentive to all the ethical aspects of one’s research and making the best judgments one can, clearly and consciously, is an integral part of being a good researcher.
Chapter 8 , best to be read in conjunction with chapter 7, explains the role and importance of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) . Under federal guidelines, an IRB is an appropriately constituted group that has been formally designated to review and monitor research involving human subjects . Every institution that receives funding from the federal government has an IRB. IRBs have the authority to approve, require modifications to (to secure approval), or disapprove research. This group review serves an important role in the protection of the rights and welfare of human research subjects. Chapter 8 reviews the history of IRBs and the work they do but also argues that IRBs’ review of qualitative research is often both over-inclusive and under-inclusive. Some aspects of qualitative research are not well understood by IRBs, given that they were developed to prevent abuses in biomedical research. Thus, it is important not to rely on IRBs to identify all the potential ethical issues that emerge in our research (see chapter 7).
Chapter 9 provides help for getting started on formulating a research question based on gaps in the pre-existing literature. Research is conducted as part of a community, even if particular studies are done by single individuals (or small teams). What any of us finds and reports back becomes part of a much larger body of knowledge. Thus, it is important that we look at the larger body of knowledge before we actually start our bit to see how we can best contribute. When I first began interviewing working-class college students, there was only one other similar study I could find, and it hadn’t been published (it was a dissertation of students from poor backgrounds). But there had been a lot published by professors who had grown up working class and made it through college despite the odds. These accounts by “working-class academics” became an important inspiration for my study and helped me frame the questions I asked the students I interviewed. Chapter 9 will provide some pointers on how to search for relevant literature and how to use this to refine your research question.
Chapter 10 serves as a bridge between the two parts of the textbook, by introducing techniques of data collection. Qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection – for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Techniques can be effectively combined, depending on the research question and the aims and goals of the study. Chapter 10 provides a general overview of all the various techniques and how they can be combined.
The second part of the textbook moves into the doing part of qualitative research once the research question has been articulated and the study designed. Chapters 11 through 17 cover various data collection techniques and approaches. Chapters 18 and 19 provide a very simple overview of basic data analysis. Chapter 20 covers communication of the data to various audiences, and in various formats.
Chapter 11 begins our overview of data collection techniques with a focus on interviewing , the true heart of qualitative research. This technique can serve as the primary and exclusive form of data collection, or it can be used to supplement other forms (observation, archival). An interview is distinct from a survey, where questions are asked in a specific order and often with a range of predetermined responses available. Interviews can be conversational and unstructured or, more conventionally, semistructured , where a general set of interview questions “guides” the conversation. Chapter 11 covers the basics of interviews: how to create interview guides, how many people to interview, where to conduct the interview, what to watch out for (how to prepare against things going wrong), and how to get the most out of your interviews.
Chapter 12 covers an important variant of interviewing, the focus group. Focus groups are semistructured interviews with a group of people moderated by a facilitator (the researcher or researcher’s assistant). Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are best used to collect data on a specific topic that is non-personal and shared among the group. For example, asking a group of college students about a common experience such as taking classes by remote delivery during the pandemic year of 2020. Chapter 12 covers the basics of focus groups: when to use them, how to create interview guides for them, and how to run them effectively.
Chapter 13 moves away from interviewing to the second major form of data collection unique to qualitative researchers – observation . Qualitative research that employs observation can best be understood as falling on a continuum of “fly on the wall” observation (e.g., observing how strangers interact in a doctor’s waiting room) to “participant” observation, where the researcher is also an active participant of the activity being observed. For example, an activist in the Black Lives Matter movement might want to study the movement, using her inside position to gain access to observe key meetings and interactions. Chapter 13 covers the basics of participant observation studies: advantages and disadvantages, gaining access, ethical concerns related to insider/outsider status and entanglement, and recording techniques.
Chapter 14 takes a closer look at “deep ethnography” – immersion in the field of a particularly long duration for the purpose of gaining a deeper understanding and appreciation of a particular culture or social world. Clifford Geertz called this “deep hanging out.” Whereas participant observation is often combined with semistructured interview techniques, deep ethnography’s commitment to “living the life” or experiencing the situation as it really is demands more conversational and natural interactions with people. These interactions and conversations may take place over months or even years. As can be expected, there are some costs to this technique, as well as some very large rewards when done competently. Chapter 14 provides some examples of deep ethnographies that will inspire some beginning researchers and intimidate others.
Chapter 15 moves in the opposite direction of deep ethnography, a technique that is the least positivist of all those discussed here, to mixed methods , a set of techniques that is arguably the most positivist . A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative data collection and quantitative data collection, commonly by combining a survey that is analyzed statistically (e.g., cross-tabs or regression analyses of large number probability samples) with semi-structured interviews. Although it is somewhat unconventional to discuss mixed methods in textbooks on qualitative research, I think it is important to recognize this often-employed approach here. There are several advantages and some disadvantages to taking this route. Chapter 16 will describe those advantages and disadvantages and provide some particular guidance on how to design a mixed methods study for maximum effectiveness.
Chapter 16 covers data collection that does not involve live human subjects at all – archival and historical research (chapter 17 will also cover data that does not involve interacting with human subjects). Sometimes people are unavailable to us, either because they do not wish to be interviewed or observed (as is the case with many “elites”) or because they are too far away, in both place and time. Fortunately, humans leave many traces and we can often answer questions we have by examining those traces. Special collections and archives can be goldmines for social science research. This chapter will explain how to access these places, for what purposes, and how to begin to make sense of what you find.
Chapter 17 covers another data collection area that does not involve face-to-face interaction with humans: content analysis . Although content analysis may be understood more properly as a data analysis technique, the term is often used for the entire approach, which will be the case here. Content analysis involves interpreting meaning from a body of text. This body of text might be something found in historical records (see chapter 16) or something collected by the researcher, as in the case of comment posts on a popular blog post. I once used the stories told by student loan debtors on the website studentloanjustice.org as the content I analyzed. Content analysis is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest. In other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis.
Where chapter 17 has pushed us towards data analysis, chapters 18 and 19 are all about what to do with the data collected, whether that data be in the form of interview transcripts or fieldnotes from observations. Chapter 18 introduces the basics of coding , the iterative process of assigning meaning to the data in order to both simplify and identify patterns. What is a code and how does it work? What are the different ways of coding data, and when should you use them? What is a codebook, and why do you need one? What does the process of data analysis look like?
Chapter 19 goes further into detail on codes and how to use them, particularly the later stages of coding in which our codes are refined, simplified, combined, and organized. These later rounds of coding are essential to getting the most out of the data we’ve collected. As students are often overwhelmed with the amount of data (a corpus of interview transcripts typically runs into the hundreds of pages; fieldnotes can easily top that), this chapter will also address time management and provide suggestions for dealing with chaos and reminders that feeling overwhelmed at the analysis stage is part of the process. By the end of the chapter, you should understand how “findings” are actually found.
The book concludes with a chapter dedicated to the effective presentation of data results. Chapter 20 covers the many ways that researchers communicate their studies to various audiences (academic, personal, political), what elements must be included in these various publications, and the hallmarks of excellent qualitative research that various audiences will be expecting. Because qualitative researchers are motivated by understanding and conveying meaning , effective communication is not only an essential skill but a fundamental facet of the entire research project. Ethnographers must be able to convey a certain sense of verisimilitude , the appearance of true reality. Those employing interviews must faithfully depict the key meanings of the people they interviewed in a way that rings true to those people, even if the end result surprises them. And all researchers must strive for clarity in their publications so that various audiences can understand what was found and why it is important.
The book concludes with a short chapter ( chapter 21 ) discussing the value of qualitative research. At the very end of this book, you will find a glossary of terms. I recommend you make frequent use of the glossary and add to each entry as you find examples. Although the entries are meant to be simple and clear, you may also want to paraphrase the definition—make it “make sense” to you, in other words. In addition to the standard reference list (all works cited here), you will find various recommendations for further reading at the end of many chapters. Some of these recommendations will be examples of excellent qualitative research, indicated with an asterisk (*) at the end of the entry. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. A good example of qualitative research can teach you more about conducting research than any textbook can (this one included). I highly recommend you select one to three examples from these lists and read them along with the textbook.
A final note on the choice of examples – you will note that many of the examples used in the text come from research on college students. This is for two reasons. First, as most of my research falls in this area, I am most familiar with this literature and have contacts with those who do research here and can call upon them to share their stories with you. Second, and more importantly, my hope is that this textbook reaches a wide audience of beginning researchers who study widely and deeply across the range of what can be known about the social world (from marine resources management to public policy to nursing to political science to sexuality studies and beyond). It is sometimes difficult to find examples that speak to all those research interests, however. A focus on college students is something that all readers can understand and, hopefully, appreciate, as we are all now or have been at some point a college student.
Recommended Reading: Other Qualitative Research Textbooks
I’ve included a brief list of some of my favorite qualitative research textbooks and guidebooks if you need more than what you will find in this introductory text. For each, I’ve also indicated if these are for “beginning” or “advanced” (graduate-level) readers. Many of these books have several editions that do not significantly vary; the edition recommended is merely the edition I have used in teaching and to whose page numbers any specific references made in the text agree.
Barbour, Rosaline. 2014. Introducing Qualitative Research: A Student’s Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A good introduction to qualitative research, with abundant examples (often from the discipline of health care) and clear definitions. Includes quick summaries at the ends of each chapter. However, some US students might find the British context distracting and can be a bit advanced in some places. Beginning .
Bloomberg, Linda Dale, and Marie F. Volpe. 2012. Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Specifically designed to guide graduate students through the research process. Advanced .
Creswell, John W., and Cheryl Poth. 2018 Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Traditions . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a classic and one of the go-to books I used myself as a graduate student. One of the best things about this text is its clear presentation of five distinct traditions in qualitative research. Despite the title, this reasonably sized book is about more than research design, including both data analysis and how to write about qualitative research. Advanced .
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. A readable and personal account of conducting qualitative research by an eminent sociologist, with a heavy emphasis on the kinds of participant-observation research conducted by the author. Despite its reader-friendliness, this is really a book targeted to graduate students learning the craft. Advanced .
Lune, Howard, and Bruce L. Berg. 2018. 9th edition. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences. Pearson . Although a good introduction to qualitative methods, the authors favor symbolic interactionist and dramaturgical approaches, which limits the appeal primarily to sociologists. Beginning .
Marshall, Catherine, and Gretchen B. Rossman. 2016. 6th edition. Designing Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Very readable and accessible guide to research design by two educational scholars. Although the presentation is sometimes fairly dry, personal vignettes and illustrations enliven the text. Beginning .
Maxwell, Joseph A. 2013. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced .
Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a comprehensive text that served as my “go-to” reference when I was a graduate student. It is particularly helpful for those involved in program evaluation and other forms of evaluation studies and uses examples from a wide range of disciplines. Advanced .
Rubin, Ashley T. 2021. Rocking Qualitative Social Science: An Irreverent Guide to Rigorous Research. Stanford : Stanford University Press. A delightful and personal read. Rubin uses rock climbing as an extended metaphor for learning how to conduct qualitative research. A bit slanted toward ethnographic and archival methods of data collection, with frequent examples from her own studies in criminology. Beginning .
Weis, Lois, and Michelle Fine. 2000. Speed Bumps: A Student-Friendly Guide to Qualitative Research . New York: Teachers College Press. Readable and accessibly written in a quasi-conversational style. Particularly strong in its discussion of ethical issues throughout the qualitative research process. Not comprehensive, however, and very much tied to ethnographic research. Although designed for graduate students, this is a recommended read for students of all levels. Beginning .
Patton’s Ten Suggestions for Doing Qualitative Research
The following ten suggestions were made by Michael Quinn Patton in his massive textbooks Qualitative Research and Evaluations Methods . This book is highly recommended for those of you who want more than an introduction to qualitative methods. It is the book I relied on heavily when I was a graduate student, although it is much easier to “dip into” when necessary than to read through as a whole. Patton is asked for “just one bit of advice” for a graduate student considering using qualitative research methods for their dissertation. Here are his top ten responses, in short form, heavily paraphrased, and with additional comments and emphases from me:
- Make sure that a qualitative approach fits the research question. The following are the kinds of questions that call out for qualitative methods or where qualitative methods are particularly appropriate: questions about people’s experiences or how they make sense of those experiences; studying a person in their natural environment; researching a phenomenon so unknown that it would be impossible to study it with standardized instruments or other forms of quantitative data collection.
- Study qualitative research by going to the original sources for the design and analysis appropriate to the particular approach you want to take (e.g., read Glaser and Straus if you are using grounded theory )
- Find a dissertation adviser who understands or at least who will support your use of qualitative research methods. You are asking for trouble if your entire committee is populated by quantitative researchers, even if they are all very knowledgeable about the subject or focus of your study (maybe even more so if they are!)
- Really work on design. Doing qualitative research effectively takes a lot of planning. Even if things are more flexible than in quantitative research, a good design is absolutely essential when starting out.
- Practice data collection techniques, particularly interviewing and observing. There is definitely a set of learned skills here! Do not expect your first interview to be perfect. You will continue to grow as a researcher the more interviews you conduct, and you will probably come to understand yourself a bit more in the process, too. This is not easy, despite what others who don’t work with qualitative methods may assume (and tell you!)
- Have a plan for analysis before you begin data collection. This is often a requirement in IRB protocols , although you can get away with writing something fairly simple. And even if you are taking an approach, such as grounded theory, that pushes you to remain fairly open-minded during the data collection process, you still want to know what you will be doing with all the data collected – creating a codebook? Writing analytical memos? Comparing cases? Having a plan in hand will also help prevent you from collecting too much extraneous data.
- Be prepared to confront controversies both within the qualitative research community and between qualitative research and quantitative research. Don’t be naïve about this – qualitative research, particularly some approaches, will be derided by many more “positivist” researchers and audiences. For example, is an “n” of 1 really sufficient? Yes! But not everyone will agree.
- Do not make the mistake of using qualitative research methods because someone told you it was easier, or because you are intimidated by the math required of statistical analyses. Qualitative research is difficult in its own way (and many would claim much more time-consuming than quantitative research). Do it because you are convinced it is right for your goals, aims, and research questions.
- Find a good support network. This could be a research mentor, or it could be a group of friends or colleagues who are also using qualitative research, or it could be just someone who will listen to you work through all of the issues you will confront out in the field and during the writing process. Even though qualitative research often involves human subjects, it can be pretty lonely. A lot of times you will feel like you are working without a net. You have to create one for yourself. Take care of yourself.
- And, finally, in the words of Patton, “Prepare to be changed. Looking deeply at other people’s lives will force you to look deeply at yourself.”
- We will actually spend an entire chapter ( chapter 3 ) looking at this question in much more detail! ↵
- Note that this might have been news to Europeans at the time, but many other societies around the world had also come to this conclusion through observation. There is often a tendency to equate “the scientific revolution” with the European world in which it took place, but this is somewhat misleading. ↵
- Historians are a special case here. Historians have scrupulously and rigorously investigated the social world, but not for the purpose of understanding general laws about how things work, which is the point of scientific empirical research. History is often referred to as an idiographic field of study, meaning that it studies things that happened or are happening in themselves and not for general observations or conclusions. ↵
- Don’t worry, we’ll spend more time later in this book unpacking the meaning of ethnography and other terms that are important here. Note the available glossary ↵
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
In contrast to methodology, methods are more simply the practices and tools used to collect and analyze data. Examples of common methods in qualitative research are interviews , observations , and documentary analysis . One’s methodology should connect to one’s choice of methods, of course, but they are distinguishable terms. See also methodology .
A proposed explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation. The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative research. Even when qualitative researchers offer possible explanations in advance of conducting research, they will tend to not use the word “hypothesis” as it conjures up the kind of positivist research they are not conducting.
The foundational question to be addressed by the research study. This will form the anchor of the research design, collection, and analysis. Note that in qualitative research, the research question may, and probably will, alter or develop during the course of the research.
An approach to research that collects and analyzes numerical data for the purpose of finding patterns and averages, making predictions, testing causal relationships, and generalizing results to wider populations. Contrast with qualitative research .
Data collection that takes place in real-world settings, referred to as “the field;” a key component of much Grounded Theory and ethnographic research. Patton ( 2002 ) calls fieldwork “the central activity of qualitative inquiry” where “‘going into the field’ means having direct and personal contact with people under study in their own environments – getting close to people and situations being studied to personally understand the realities of minutiae of daily life” (48).
The people who are the subjects of a qualitative study. In interview-based studies, they may be the respondents to the interviewer; for purposes of IRBs, they are often referred to as the human subjects of the research.
The branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. For researchers, it is important to recognize and adopt one of the many distinguishing epistemological perspectives as part of our understanding of what questions research can address or fully answer. See, e.g., constructivism , subjectivism, and objectivism .
An approach that refutes the possibility of neutrality in social science research. All research is “guided by a set of beliefs and feelings about the world and how it should be understood and studied” (Denzin and Lincoln 2005: 13). In contrast to positivism , interpretivism recognizes the social constructedness of reality, and researchers adopting this approach focus on capturing interpretations and understandings people have about the world rather than “the world” as it is (which is a chimera).
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Research based on data collected and analyzed by the research (in contrast to secondary “library” research).
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The practice of being conscious of and reflective upon one’s own social location and presence when conducting research. Because qualitative research often requires interaction with live humans, failing to take into account how one’s presence and prior expectations and social location affect the data collected and how analyzed may limit the reliability of the findings. This remains true even when dealing with historical archives and other content. Who we are matters when asking questions about how people experience the world because we, too, are a part of that world.
The science and practice of right conduct; in research, it is also the delineation of moral obligations towards research participants, communities to which we belong, and communities in which we conduct our research.
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Research, according to US federal guidelines, that involves “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research: (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or (2) Obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.”
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
A method of observational data collection taking place in a natural setting; a form of fieldwork . The term encompasses a continuum of relative participation by the researcher (from full participant to “fly-on-the-wall” observer). This is also sometimes referred to as ethnography , although the latter is characterized by a greater focus on the culture under observation.
A research design that employs both quantitative and qualitative methods, as in the case of a survey supplemented by interviews.
An epistemological perspective that posits the existence of reality through sensory experience similar to empiricism but goes further in denying any non-sensory basis of thought or consciousness. In the social sciences, the term has roots in the proto-sociologist August Comte, who believed he could discern “laws” of society similar to the laws of natural science (e.g., gravity). The term has come to mean the kinds of measurable and verifiable science conducted by quantitative researchers and is thus used pejoratively by some qualitative researchers interested in interpretation, consciousness, and human understanding. Calling someone a “positivist” is often intended as an insult. See also empiricism and objectivism.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
A word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data (Saldaña 2021:5).
Usually a verbatim written record of an interview or focus group discussion.
The primary form of data for fieldwork , participant observation , and ethnography . These notes, taken by the researcher either during the course of fieldwork or at day’s end, should include as many details as possible on what was observed and what was said. They should include clear identifiers of date, time, setting, and names (or identifying characteristics) of participants.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
A detailed description of any proposed research that involves human subjects for review by IRB. The protocol serves as the recipe for the conduct of the research activity. It includes the scientific rationale to justify the conduct of the study, the information necessary to conduct the study, the plan for managing and analyzing the data, and a discussion of the research ethical issues relevant to the research. Protocols for qualitative research often include interview guides, all documents related to recruitment, informed consent forms, very clear guidelines on the safekeeping of materials collected, and plans for de-identifying transcripts or other data that include personal identifying information.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari

Healthcare Simulation Research pp 73–78 Cite as
Key Concepts in Qualitative Research Design
- Margaret Bearman 6
- First Online: 14 November 2019
2801 Accesses
1 Citations
This chapter provides an outline of key concepts in qualitative research design for healthcare simulation. It explores three landmarks that provide orientation to researchers: (1) a defined purpose for the research; (2) an articulation of the researcher’s worldview; and (3) an overarching approach to research design. In practical terms, these translate to: writing the qualitative research question; articulating the relationship between the researcher and the research (reflexivity); and selecting an appropriate methodology. Three methodologies – grounded theory, phenomenology and qualitative description – are outlined and contrasted with a particular emphasis on different analysis traditions. The de facto use of methods as methodology is briefly explored and the importance of coherence across the three landmarks (as opposed to simple adherence to a particular tradition) will be emphasized. Finally, research credibility is introduced as a holistic, dynamic and tacit concept that is highly dependent on researchers and research context.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Oxford English Dictionary 2018.
Google Scholar
Boyer EL. Scholarship reconsidered: priorities of the professoriate. Lawrenceville: Princeton University Press; 1990.
Nestel D, Bearman M. Theory and simulation-based education: definitions, worldviews and applications. Clin Simul Nurs. 2015;11(8):349–54.
Article Google Scholar
Bunniss S, Kelly DR. Research paradigms in medical education research. Med Educ. 2010;44(4):358–66.
Pillow W. Confession, catharsis, or cure? Rethinking the uses of reflexivity as methodological power in qualitative research. Int J Qual Stud Educ. 2003;16(2):175–96.
Lingard L, Albert M, Levinson W. Grounded theory, mixed methods, and action research. BMJ. 2008;337(aug07_3):a567-a.
Watling CJ, Lingard L. Grounded theory in medical education research: AMEE guide no. 70. Med Teach. 2012;34(10):850–61.
Walton J, Chute E, Ball L. Negotiating the role of the professional nurse: the pedagogy of simulation: a grounded theory study. J Prof Nurs. 2011;27(5):299–310.
Tavakol M, Sandars J. Quantitative and qualitative methods in medical education research: AMEE guide no 90: part II. Med Teach. 2014;36(10):838–48.
Bearman M. Is virtual the same as real? Medical students’ experiences of a virtual patient. Acad Med. 2003;78(5):538–45.
Sandelowski M. Focus on research methods-whatever happened to qualitative description? Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(4):334–40.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Miles MB, Huberman AM, Huberman MA, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. Thousand Oaks: Sage; 1994.
Clarke V, Braun V. Thematic analysis. In: Teo T, editor. Encyclopedia of critical psychology. New York: Springer; 2014. p. 1947–52.
Chapter Google Scholar
Krogh K, Bearman M, Nestel D. Expert practice of video-assisted debriefing: an Australian qualitative study. Clin Simul Nurs. 2015;11(3):180–7.
Varpio L, Ajjawi R, Monrouxe LV, O’brien BC, Rees CE. Shedding the cobra effect: problematising thematic emergence, triangulation, saturation and member checking. Med Educ. 2017;51(1):40–50.
Additional Resources
Braun V, Clarke V. Successful qualitative research: a practical guide for beginners. London: Sage; 2013.
Cresswell JW. Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five traditions. Singapore: Sage; 1998.
Savin-Baden M, Major CH. Qualitative Research: The essential guide to theory and practice. London: Routledge; 2013.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Research in Assessment and Digital Learning (CRADLE), Deakin University, Docklands, VIC, Australia
Margaret Bearman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Margaret Bearman .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Monash Institute for Health and Clinical Education, Monash University, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Debra Nestel
Emergency Medicine, Kaiser Permanente, Los Angeles Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Department of Surgery, University of Maryland, Baltimore, Baltimore, MD, USA
Kevin Kunkler
Department of Psychology, Old Dominion University, Norfolk, VA, USA
Mark W. Scerbo
Department of Pediatrics, University of Louisville School of Medicine, Louisville, KY, USA
Aaron W. Calhoun
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Bearman, M. (2019). Key Concepts in Qualitative Research Design. In: Nestel, D., Hui, J., Kunkler, K., Scerbo, M., Calhoun, A. (eds) Healthcare Simulation Research. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26837-4_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-26837-4_10
Published : 14 November 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-26836-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-26837-4
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Design
Definition:
Research design refers to the overall strategy or plan for conducting a research study. It outlines the methods and procedures that will be used to collect and analyze data, as well as the goals and objectives of the study. Research design is important because it guides the entire research process and ensures that the study is conducted in a systematic and rigorous manner.
Types of Research Design
Types of Research Design are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
This type of research design is used to describe a phenomenon or situation. It involves collecting data through surveys, questionnaires, interviews, and observations. The aim of descriptive research is to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a particular group, event, or situation. It can be useful in identifying patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. This type of research design involves collecting data from participants and analyzing the relationship between the variables using statistical methods. The aim of correlational research is to identify the strength and direction of the relationship between the variables.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This type of research design involves manipulating one variable and measuring the effect on another variable. It usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups and manipulating an independent variable to determine its effect on a dependent variable. The aim of experimental research is to establish causality.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks one or more of the features of a true experiment. For example, there may not be random assignment to groups or a control group. This type of research design is used when it is not feasible or ethical to conduct a true experiment.
Case Study Research Design
Case study research design is used to investigate a single case or a small number of cases in depth. It involves collecting data through various methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. The aim of case study research is to provide an in-depth understanding of a particular case or situation.
Longitudinal Research Design
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
Structure of Research Design
The format of a research design typically includes the following sections:
- Introduction : This section provides an overview of the research problem, the research questions, and the importance of the study. It also includes a brief literature review that summarizes previous research on the topic and identifies gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: This section identifies the specific research questions or hypotheses that the study will address. These questions should be clear, specific, and testable.
- Research Methods : This section describes the methods that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes details about the study design, the sampling strategy, the data collection instruments, and the data analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This section describes how the data will be collected, including the sample size, data collection procedures, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: This section describes how the data will be analyzed, including the statistical techniques that will be used to test the research questions or hypotheses.
- Results : This section presents the findings of the study, including descriptive statistics and statistical tests.
- Discussion and Conclusion : This section summarizes the key findings of the study, interprets the results, and discusses the implications of the findings. It also includes recommendations for future research.
- References : This section lists the sources cited in the research design.

Example of Research Design
An Example of Research Design could be:
Research question: Does the use of social media affect the academic performance of high school students?
Research design:
- Research approach : The research approach will be quantitative as it involves collecting numerical data to test the hypothesis.
- Research design : The research design will be a quasi-experimental design, with a pretest-posttest control group design.
- Sample : The sample will be 200 high school students from two schools, with 100 students in the experimental group and 100 students in the control group.
- Data collection : The data will be collected through surveys administered to the students at the beginning and end of the academic year. The surveys will include questions about their social media usage and academic performance.
- Data analysis : The data collected will be analyzed using statistical software. The mean scores of the experimental and control groups will be compared to determine whether there is a significant difference in academic performance between the two groups.
- Limitations : The limitations of the study will be acknowledged, including the fact that social media usage can vary greatly among individuals, and the study only focuses on two schools, which may not be representative of the entire population.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations will be taken into account, such as obtaining informed consent from the participants and ensuring their anonymity and confidentiality.
How to Write Research Design
Writing a research design involves planning and outlining the methodology and approach that will be used to answer a research question or hypothesis. Here are some steps to help you write a research design:
- Define the research question or hypothesis : Before beginning your research design, you should clearly define your research question or hypothesis. This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods.
- Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
- Develop a sampling plan : If your research involves collecting data from a sample, you will need to develop a sampling plan. This should outline how you will select participants and how many participants you will include.
- Define variables: Clearly define the variables you will be measuring or manipulating in your study. This will help ensure that your results are meaningful and relevant to your research question.
- Choose data collection methods : Decide on the data collection methods you will use to gather information. This may include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data sources.
- Create a data analysis plan: Develop a plan for analyzing your data, including the statistical or qualitative techniques you will use.
- Consider ethical concerns : Finally, be sure to consider any ethical concerns related to your research, such as participant confidentiality or potential harm.
When to Write Research Design
Research design should be written before conducting any research study. It is an important planning phase that outlines the research methodology, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques that will be used to investigate a research question or problem. The research design helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and logical manner, and that the data collected is relevant and reliable.
Ideally, the research design should be developed as early as possible in the research process, before any data is collected. This allows the researcher to carefully consider the research question, identify the most appropriate research methodology, and plan the data collection and analysis procedures in advance. By doing so, the research can be conducted in a more efficient and effective manner, and the results are more likely to be valid and reliable.
Purpose of Research Design
The purpose of research design is to plan and structure a research study in a way that enables the researcher to achieve the desired research goals with accuracy, validity, and reliability. Research design is the blueprint or the framework for conducting a study that outlines the methods, procedures, techniques, and tools for data collection and analysis.
Some of the key purposes of research design include:
- Providing a clear and concise plan of action for the research study.
- Ensuring that the research is conducted ethically and with rigor.
- Maximizing the accuracy and reliability of the research findings.
- Minimizing the possibility of errors, biases, or confounding variables.
- Ensuring that the research is feasible, practical, and cost-effective.
- Determining the appropriate research methodology to answer the research question(s).
- Identifying the sample size, sampling method, and data collection techniques.
- Determining the data analysis method and statistical tests to be used.
- Facilitating the replication of the study by other researchers.
- Enhancing the validity and generalizability of the research findings.
Applications of Research Design
There are numerous applications of research design in various fields, some of which are:
- Social sciences: In fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, research design is used to investigate human behavior and social phenomena. Researchers use various research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and correlational designs, to study different aspects of social behavior.
- Education : Research design is essential in the field of education to investigate the effectiveness of different teaching methods and learning strategies. Researchers use various designs such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and case study designs to understand how students learn and how to improve teaching practices.
- Health sciences : In the health sciences, research design is used to investigate the causes, prevention, and treatment of diseases. Researchers use various designs, such as randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, and case-control studies, to study different aspects of health and healthcare.
- Business : Research design is used in the field of business to investigate consumer behavior, marketing strategies, and the impact of different business practices. Researchers use various designs, such as survey research, experimental research, and case studies, to study different aspects of the business world.
- Engineering : In the field of engineering, research design is used to investigate the development and implementation of new technologies. Researchers use various designs, such as experimental research and case studies, to study the effectiveness of new technologies and to identify areas for improvement.
Advantages of Research Design
Here are some advantages of research design:
- Systematic and organized approach : A well-designed research plan ensures that the research is conducted in a systematic and organized manner, which makes it easier to manage and analyze the data.
- Clear objectives: The research design helps to clarify the objectives of the study, which makes it easier to identify the variables that need to be measured, and the methods that need to be used to collect and analyze data.
- Minimizes bias: A well-designed research plan minimizes the chances of bias, by ensuring that the data is collected and analyzed objectively, and that the results are not influenced by the researcher’s personal biases or preferences.
- Efficient use of resources: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the resources (time, money, and personnel) are used efficiently and effectively, by focusing on the most important variables and methods.
- Replicability: A well-designed research plan makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study, which enhances the credibility and reliability of the findings.
- Validity: A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings are valid, by ensuring that the methods used to collect and analyze data are appropriate for the research question.
- Generalizability : A well-designed research plan helps to ensure that the findings can be generalized to other populations, settings, or situations, which increases the external validity of the study.
Research Design Vs Research Methodology
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...
Leave a comment x.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

6 Main Qualitative Questions Examples
Qualitative vs. quantitative research, the importance of qualitative questions, key elements of effective qualitative research questions, role in the research design, 6 types and examples of qualitative questions, how to choose qualitative research questions, start collecting qualitative data right now, fullsession pricing plans.
- FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research uncovers the details of human behavior, beliefs, and feelings. It gives us insights that numbers can’t always tell.
These research questions help us understand the “how” and “why” of things.
In this article, we’ll look at six examples of good qualitative questions. We aim to highlight how picking the right questions can improve your study.
It is important to understand the differences between qualitative and quantitative research.
Qualitative research questions aim to explore concepts, experiences, and perspectives. They offer the qualitative research expert an in-depth insight into the subject.
On the other hand, quantitative research questions focus on measurable aspects. They seek statistical comparisons to reach factual conclusions.
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have important roles in research. They serve unique purposes and provide different types of data.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative questions aren’t about numbers and statistical analysis. It’s about understanding the reason behind data from a focus group.
Why pick qualitative research? When conducting qualitative research, you want to know why someone does something, not just count how many times they do it.
You ask, and you listen. That’s the power of qualitative research. The right question is a key that unlocks valuable knowledge.
Effective qualitative research aims to unveil hidden truths. But how do you achieve it? With thought-provoking questions.
Here are the elements of the qualitative research questions for an in-depth exploration:
Open-ended and Exploratory
Qualitative research questions aim to understand the “how” and “why” of a topic. They invite people to share their views and stories.
Open-ended and exploratory questions help researchers grasp complex issues. These questions allow for diverse and detailed answers to a particular subject.
Clarity and Focus
Qualitative research questions need to be clear, focused, and brief. They help ensure the research meets its goals.
Being specific guides data collection and analysis, leading to valuable findings.
Relationships and Personal Experiences
Qualitative research questions examine how different factors relate to personal experiences and seek to understand why people act in certain ways.
They also explore how people respond to their surroundings, including culture and workplace rules.
Ethical Considerations
When creating qualitative research questions, it’s important to think about ethics. Questions need to respect participants’ dignity, privacy, and independence.
This makes sure that the research does not cause harm or distress. Ethics also matter when explaining and sharing results, as researchers must present data truthfully and with care.
The right qualitative research questions are crucial in the design of research projects for several reasons:
- Guidance on Research Methods: Directs the choice of qualitative research methods. Options include:
- Focus Groups: Small groups discuss topics with a moderator.
- In-Depth Interviews: Offers detailed insights from individual viewpoints.
- Qualitative Surveys: Gathers open-ended responses from a broad audience.
- Ensuring the Right Tools are Used: Matching objectives with the most suitable research tools. Enables thorough investigation and captures the complexity of experiences.
- Facilitating a Clear Understanding: Aims to uncover not just what is happening but why. Explores thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and the effects of various influences.
- Informing the Research Design: Influences all design aspects, including participant selection and analysis framework. Ensures ethical standards guide the research process.
Here are six types of qualitative questions with examples:
1. Descriptive
These questions are aimed at describing the characteristics or features of a product.
- Example 1: How do users describe their initial impressions when they first interact with our new software interface?
- Example 2: What are the specific colors and design elements that users notice about the new smartphone model when they see it for the first time?
2. Exploratory
Exploratory questions are designed to investigate how things work or how users interact with a product.
- Example 1: What strategies do users employ to navigate through the features of our newly launched app?
- Example 2: How do users attempt to solve problems when they encounter errors using our digital service platform?
3. Experiential
These questions focus on the user’s experiences and emotions related to the product.
- Example 1: Can you describe a memorable experience you had while using our product?
- Example 2: What emotions do you feel when using our product under stressful conditions?
4. Comparative
Comparative questions look at differences between products, user groups, or other variables.
- Example 1: How do new users’ experiences with our product compare to those of long-term users?
- Example 2: In what ways does our product perform better or worse than our main competitor’s product in similar conditions?
5. Process-oriented
These questions delve into the processes or sequences of actions related to using the product.
- Example 1: Can you walk me through the process you typically follow when setting up our product for the first time?
- Example 2: What steps do you take when you troubleshoot an issue with our product?
6. Theoretical
Theoretical questions aim to understand the underlying principles or theories that explain user behavior or product dynamics.
- Example 1: What theories can explain why users prefer our product’s design over traditional designs?
- Example 2: Based on your knowledge, what psychological principles might influence how users adapt to our product’s innovative features?
When selecting qualitative questions, the aim is to deeply understand user interactions, perceptions, and experiences with the product.
Here are some key considerations for choosing good qualitative research questions:
- Define Your Objectives
Start by clearly defining the research objective of your product testing. What specific aspects of the product are you looking to evaluate? Are you interested in usability, aesthetics, functionality, or user satisfaction? Your objectives will guide the types of questions you need to ask. For example, if user satisfaction is your focus, you might ask about the user’s emotional response to the product.
- Consider the Type of Qualitative Research
Different types of qualitative methods—such as ethnographic, narrative, phenomenological, or grounded theory—may influence the style and structure of your questions. For instance, narrative research focuses on stories and experiences, so your questions should encourage storytelling about product use.
- Ensure Questions are Open-Ended
Qualitative questions should be open-ended to allow for detailed responses that can reveal insights not anticipated by the researcher. Instead of asking, “Do you like our product?” which prompts a yes or no answer, ask, “How do you feel about our product?” to encourage a more detailed and nuanced response.
- Be Clear and Concise
While questions should allow for open-ended answers, they must also be clear and concise to avoid confusing the respondent. Ambiguity can lead to unreliable qualitative data , as different participants might interpret the questions differently.
- Sequence the Questions Logically
The order in which you ask questions can impact the flow of conversation and the quality of information gathered. Start with more general questions to make the respondent comfortable before moving to more specific or sensitive topics. This sequence helps build rapport and can lead to more honest and detailed responses later in the discussion.
- Consider the Participant
Tailor your questions to fit the background and experience level of your participants. Questions that are too technical or too basic can frustrate users or fail to elicit useful information. Understanding your audience allows you to frame questions that are appropriately challenging and engaging.
- Pilot Test Your Questions
Before finalizing your set of questions, conduct a pilot test with a small group of participants. This testing can reveal if any questions are confusing or ineffective at eliciting useful responses. Feedback from this phase can be invaluable in refining your questions.
- Be Prepared to Adapt
Finally, while it’s important to prepare your questions carefully, also be flexible during actual interactions. The conversation may reveal new paths of inquiry that are worth exploring. Being adaptive can help you capture deep insights that strictly adhering to a prepared list of questions might miss.
It takes less than 5 minutes to set up your first website or app feedback form, with FullSession , and it’s completely free!
After that, you will be able to collect high-quality feedback and avoid the guesswork.
The FullSession platform offers a 14-day free trial. It provides two paid plans—Basic and Business. Here are more details on each plan.
- The Basic plan costs $39/month and allows you to monitor up to 5,000 monthly sessions.
- The Business plan costs $149/month and helps you to track and analyze up to 25,000 monthly sessions.
- The Enterprise plan starts from 100,000 monthly sessions and has custom pricing.
If you need more information, you can get a demo.
FAQs about Qualitative Research Questions
What is a qualitative research question.
Qualitative research questions focus on ways to gather deep insights into people’s experiences, beliefs, and perceptions. Such questions invite detailed narrative responses.
Can qualitative research questions change during the study?
It’s not uncommon for qualitative research questions to evolve during the course of a study. As preliminary data is collected and analyzed, new insights may emerge that prompt a qualitative researcher to refine their questions.
How are qualitative questions used in business?
Businesses use qualitative questions to uncover valuable insights. They can explore customer behavior, employee satisfaction, or market trends. One example could be: “What factors drive consumer loyalty to our brand?”
Are there specific words to use in qualitative research questions?
Yes, use words like “describe,” “explain,” and “how” to frame qualitative questions. These terms promote more detailed and comprehensive answers. They are key to qualitative analysis.

Improve Performance and Grow your Website
Ready to transform your digital presence? Let's create magic together! book our services now!

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 22 April 2024
The design and evaluation of gamified online role-play as a telehealth training strategy in dental education: an explanatory sequential mixed-methods study
- Chayanid Teerawongpairoj 1 ,
- Chanita Tantipoj 1 &
- Kawin Sipiyaruk 2
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 9216 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Health care
- Health services
- Public health
To evaluate user perceptions and educational impact of gamified online role-play in teledentistry as well as to construct a conceptual framework highlighting how to design this interactive learning strategy, this research employed an explanatory sequential mixed-methods design. Participants were requested to complete self-perceived assessments toward confidence and awareness in teledentistry before and after participating in a gamified online role-play. They were also asked to complete a satisfaction questionnaire and participate in an in-depth interview to investigate their learning experience. The data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, paired sample t-test, one-way analysis of variance, and framework analysis. There were 18 participants who completed self-perceived assessments and satisfaction questionnaire, in which 12 of them participated in a semi-structured interview. There were statistically significant increases in self-perceived confidence and awareness after participating in the gamified online role-play ( P < 0.001). In addition, the participants were likely to be satisfied with this learning strategy, where usefulness was perceived as the most positive aspect with a score of 4.44 out of 5, followed by ease of use (4.40) and enjoyment (4.03). The conceptual framework constructed from the qualitative findings has revealed five key elements in designing a gamified online role-play, including learner profile, learning settings, pedagogical components, interactive functions, and educational impact. The gamified online role-play has demonstrated its potential in improving self-perceived confidence and awareness in teledentistry. The conceptual framework developed in this research could be considered to design and implement a gamified online role-play in dental education. This research provides valuable evidence on the educational impact of gamified online role-play in teledentistry and how it could be designed and implemented in dental education. This information would be supportive for dental instructors or educators who are considering to implement teledentistry training in their practice.
Similar content being viewed by others

Games in dental education: playing to learn or learning to play?
Andresa Costa Pereira & Anthony Damien Walmsley

A bibliometric analysis of the use of the Gamification Octalysis Framework in training: evidence from Web of Science
Sattwik Mohanty & Prabu Christopher B
Helping general dental practitioners use the Index of Orthodontic Treatment Need: an assessment of available educational apps
David G. Murray, Gautham Sivamurthy & Peter Mossey
Introduction
Telehealth has gained significant attention from various organization due to its potential to improve healthcare quality and accessibility 1 . It can be supportive in several aspects in healthcare, including medical and nursing services, to enhance continuous monitoring and follow-up 2 . Its adoption has increased substantially during the COVID-19 pandemic, aiming to provide convenient healthcare services 3 . Even though the COVID-19 outbreak has passed, many patients still perceive telehealth as an effective tool in reducing a number of visits and enhancing access to health care services 4 , 5 . This supports the use of telehealth in the post-COVID-19 era.
Teledentistry, a form of telehealth specific to dentistry, has been employed to improve access to dental services 6 . This system offers benefits ranging from online history taking, oral diagnosis, treatment monitoring, and interdisciplinary communication among dental professionals, enabling comprehensive and holistic treatment planning for patients 7 . Teledentistry can also reduce travel time and costs associated with dental appointments 8 , 9 , 10 . There is evidence that teledentistry serves as a valuable tool to enhance access to dental care for patients 11 . Additionally, in the context of long-term management in patients, telehealth has contributed to patient-centered care, by enhancing their surrounding environments 12 . Therefore, teledentistry should be emphasized as one of digital dentistry to enhance treatment quality.
Albeit the benefits of teledentistry, available evidence demonstrates challenges and concerns in the implementation of telehealth. Lack of awareness and knowledge in the use of telehealth can hinder the adoption of telehealth 13 . Legal issues and privacy concerns also emerge as significant challenges in telehealth use 14 . Moreover, online communication skills and technology literacy, including competency in using technological tools and applications, have been frequently reported as challenges in teledentistry 15 , 16 . Concerns regarding limitations stemming from the lack of physical examination are also significant 17 . These challenges and complexities may impact the accuracy of diagnosis and the security and confidentiality of patient information. Therefore, telehealth training for dental professionals emerges as essential prerequisites to effectively navigate the use of teledentistry, fostering confidence and competence in remote oral healthcare delivery.
The feasibility and practicality of telehealth in dental education present ongoing challenges and concerns. Given the limitations of teledentistry compared to face-to-face appointments, areas of training should encompass the telehealth system, online communication, technical issues, confidentiality concerns, and legal compliance 18 . However, there is currently no educational strategy that effectively demonstrates the importance and application of teledentistry 19 . A role-play can be considered as a teaching strategy where learners play a role that closely resembles real-life scenarios. A well-organized storytelling allows learner to manage problematic situations, leading to the development of problem-solving skill 20 , 21 . When compared to traditional lecture-based learning, learners can also enhance their communication skills through conversations with simulated patients 22 , 23 . In addition, they could express their thoughts and emotions during a role-play through experiential learning 20 , 24 , 25 . Role-play through video teleconference would be considered as a distance learning tool for training dental professionals to effectively use teledentistry.
While there have been studies supporting online role-play as an effective learning tool due to its impact of flexibility, engagement, and anonymity 26 , 27 , no evidence has been yet reported whether or not this learning strategy could have potential for training teledentistry. Given the complicated issues in telehealth, role-play for training teledentistry should incorporate different learning aspects compared to face-to-face communication with patients. In addition, game components have proved to be supportive in dental education 28 , 29 . Consequently, this research aimed to evaluate user perceptions and educational impact of gamified online role-play to enhance learner competence and awareness in using teledentistry as well as to construct a conceptual framework highlighting how to design and implement this interactive learning strategy. This research would introduce and promote the design and implementation of gamified online role-play as a learning tool for training teledentistry. To achieve the aim, specific objectives were established as follows:
1. To design a gamified online role-play for teledentistry training.
2. To investigate learner perceptions regarding their confidence and awareness in the use of teledentistry after completing the gamified online role-play.
3. To explore user satisfactions toward the use of gamified online role-play.
4. To develop a conceptual framework for designing and implementing a gamified online role-play for teledentistry training.
Materials and methods
Research design.
This research employed an explanatory sequential mixed-methods design, where a quantitative phase was firstly performed followed by a qualitative phase 30 , 31 . The quantitative phase was conducted based on pre-experimental research using one-group pretest–posttest design. Participants were requested to complete self-perceived assessments toward confidence and awareness in the use of teledentistry before and after participating in a gamified online role-play. They were also asked to complete a satisfaction questionnaire in using a gamified online role-play for training teledentistry. The qualitative phase was afterwards conducted to explore in-depth information through semi-structured interviews, in order to enhance an understanding of the quantitative phase, and to develop a conceptual framework for designing and implementing an online role-play for training teledentistry.
A gamified online role-play for training teledentistry
A gamified online role-play was designed and developed by the author team. To ensure its educational impact was significant, the expected learning outcomes were formulated based on insights gathered from a survey with experienced instructors from the Department of Advanced General Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University. These learning outcomes covered areas of online communication skill, technical issues, technology literacy of patients, limitations of physical examination, and privacy concerns of personal information. Learning scenario and instructional content were subsequently designed to support learners in achieving the expected learning outcomes, with their alignments validated by three experts in dental education. A professional actress underwent training to role-play a patient with a dental problem, requesting a virtual consultation or teledentistry. Before conducting data collection, the simulated patient was required to undergo a training and adjusting process with a pilot group under supervision of two experts in advanced general dentistry and dental education who had experience with teledentistry to ensure realism and completeness of learning content.
According to the role-play scenario, an actress was assigned to portray a 34-year-old female with chief complaints of pain around both ears, accompanied by difficulties in chewing food due to tooth loss. She was instructed to express her anxiety and nervousness about addressing these issues. Additionally, it was specified that she could not take a day off from work during this period. Despite this constraint, she required a dental consultation to receive advice for initial self-care, as her symptoms significantly impacted her daily life. Furthermore, she was designated to encounter difficulties with the technological use of the teledentistry platform.
The game components were implemented into the online role-play to enhance motivation and engagement. As challenge and randomness appear to be game elements 32 , 33 , five challenge cards were designed and embedded into the online role-play, where a participant was asked to randomly select one of them before interacting with the simulated patient. The challenging situations were potential technical concerns which could occur frequently during video conferencing, including network problems (e.g., internet disconnection and poor connection) and audiovisual quality issues. The participants were blinded to the selected card, while it was revealed to only the simulated patient. The challenging conditions were mimicked by the organizers and simulated patient, allowing learners to deal with difficulties. Therefore, both challenges and randomness were implemented into this learning intervention not only to create learning situations but also to enhance engagement.
A feedback system was carefully considered and implemented into the gamified online role-play. Immediate feedback appears to be a key feature of interactive learning environments 29 . Formative feedback was instantly delivered to learners through verbal and non-verbal communication, including words (content), tone of voice, facial expressions, and gestures of the simulated patient. This type of feedback allowed participants to reflect on whether or not their inputs were appropriate, enabling them to learn from their mistakes, or so-called the role of failure 34 . Summative feedback was also provided at the end of the role-play through a reflection from a simulated patient and suggestions from an instructor.
Learners were able to interact with the simulated patient using an online meeting room by Cisco WebEx. According to the research setting (Fig. 1 ), a learner was asked to participate in the role-play activity using a computer laptop in a soundproof room, while a simulated patient was arranged in a prepared location showing her residential environment. The researcher and instructor also joined the online meeting room and observed the interaction between the simulated patient and learners during the role-play activity whether or not all necessary information was accurately obtained. The role-play activity took around 30 minutes.
A diagram demonstrating the setting of gamified online role-play.
Research participants
Quantitative phase.
The participants in this research were postgraduate students from the Residency Training Program in Advanced General Dentistry at Mahidol University Faculty of Dentistry in academic year 2022, using a volunteer sampling. This program was selected because its objective was to develop graduates capable of integrating competencies from various dental disciplines to provide comprehensive dental care for both normal patients and those with special needs. Therefore, teledentistry should be a supportive component of their service. The recruitment procedure involved posting a recruiting text in the group chat of the residents. Those interested in participating in the research were informed to directly contact us to request more information, and they were subsequently allowed to decide whether they would like to participate. This approach ensured that participation was voluntary. Although there could be a non-response bias within this non-probability sampling technique 35 , it was considered as appropriate for this study, as participants were willing to have contribution in the learning activity, and therefore accurate and reliable research findings with no dropout could be achieved 36 .
The inclusion and exclusion criteria were established to determine the eligibility of prospective participants for this research. This study included postgraduate students from Years 1 to 3 in the Residency Training Program in Advanced General Dentistry at Mahidol University Faculty of Dentistry, enrolled during the academic year 2022. They were also required to at least complete the first semester to be eligible for this research to ensure familiarity with comprehensive dental care. However, they were excluded if they had previous involvement in the pilot testing of the gamified online role-play or if they were not fluent in the Thai language. The sample size was determined using a formula for two dependent samples (comparing means) 37 . To detect a difference in self-perceived confidence and awareness between pre- and post-assessments at a power of 90% and a level of statistical significance of 1%, five participants were required. With an assumed dropout rate of 20%, the number of residents per year (Year 1–3) was set to be 6. Therefore, 18 residents were required for this research.
Qualitative phase
The participants from the quantitative phase were selected for semi-structured interviews using a purposive sampling. This sampling method involved the selection of information-rich participants based on specific criteria deemed relevant to the research objective and to ensure a diverse representation of perspectives and experiences within the sample group 38 . In this research, the information considered for the purposive sampling included demographic data (e.g., sex and year of study), along with self-perceived assessment scores. By incorporating perceptions from a variety of participants, a broad spectrum of insights from different experiences in comprehensive dental practice and diverse improvement levels in self-perceived confidence and awareness could inform the design and implementation of the training program effectively. The sample size for this phase was determined based on data saturation, wherein interviews continued until no new information or emerging themes were retrieved. This method ensured thorough exploration of the research topic and maximized the richness of the qualitative data obtained.
Outcome assessments
To evaluate the gamified online role-play, a triangular design approach was employed, enabling the researchers to compare the research outcomes from different assessment methods. In this research, self-perceived assessments (confidence and awareness) in teledentistry, satisfactions toward gamified online role-play, and learner experience were assessed to assure the quality and feasibility of the gamified online role-play.
Self-perceived confidence and awareness toward teledentistry
All participants were requested to rate their perceptions of teledentistry before and after participating in the gamified online role-play (Supplementary material 1 ). The self-perceived assessment was developed based on previous literature 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 . The assessment scores would inform whether or not the participants could improve their self-perceived confidence and awareness through a learning activity. The assessment consisted of two parts, which were (1) self-perceived confidence and (2) self-perceived awareness. Each part contained six items, which were similar between the pre- and post-assessments. All items were designed using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 being ‘strongly disagree’ and 5 being ‘strongly agree’.
Satisfactions toward the gamified online role-play
All participants were asked to complete the satisfaction questionnaire after participating in the gamified online role-play, to investigate whether or not they felt satisfied with their learning (Supplementary material 2 ). The questionnaire was developed based on previous literature regarding gamification and role-play 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 . Most of the items were designed using a 5-point Likert scale, where 1 being ‘very dissatisfied’ and 5 being ‘very satisfied’. They were grouped into three aspects, which were (1) Perceived usefulness, (2) Perceived ease of use, and (3) Perceived enjoyment.
Learner experiences within the gamified online role-play
Semi-structured interviews were conducted with the purposively selected participants to gather in-depth information regarding their learning experiences within the gamified online role-play. This technique allowed researchers to ask additional interesting topics raised from the responses of participants. A topic guide for interviews were constructed based on the findings of previous literature 45 , 46 , 47 . The interview was conducted in a private room by a researcher who was trained in conducting qualitative research including interviews. The interview sessions took approximately 45–60 minutes, where all responses from participants were recorded using a digital audio recorder with their permission. The recorded audios were transcribed using a verbatim technique by a transcription service under a confidential agreement.
Validity and reliability of data collection tools
To enhance the quality of self-perceived assessment and satisfaction questionnaire, they were piloted and revised to assure their validity and reliability. According to the content validity, three experts in advanced general dentistry were asked to evaluate the questionnaire, where problematic items were iteratively revised until they achieved the index of item-objective congruence (IOC) higher than 0.5. To perform a test–retest reliability, the validated versions of both self-perceived assessment and satisfaction questionnaire were afterwards piloted in residents from other programs, and the data were analyzed using an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), where the values of all items were 0.7 or greater. The data from the first pilot completion of both data collection tools were analyzed using Cronbach’s alpha to ensure the internal consistency of all constructs. The problematic items were deleted to achieve the coefficient alpha of 0.7 or greater for all constructs, which was considered as acceptable internal consistency.
Data analysis
The quantitative data retrieved from self-perceived assessment and satisfaction questionnaire were analyzed with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences software (SPSS, version 29, IBM Corp.). Descriptive statistics were performed to present an overview of the data. The scores from pre- and post-assessments were analyzed using a paired sample t-test to evaluate whether or not the participants would better self-perceive their confidence and awareness in teledentistry after participating in the gamified online role-play. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to compare whether or not there were statistically significant differences in self-perceived assessment and satisfaction scores among the three academic years.
The qualitative data retrieved from semi-structured interviews were analyzed using a framework analysis, where its procedure involved transcription, familiarization with the interview data, coding, developing an analytical framework, indexing, charting, and data interpreting qualitative findings 48 . In this research, the initial codes had been pre-defined from previous literature and subsequently adjusted following the analysis of each transcript to develop an analytical framework (themes and subthemes), requiring several iterations until no additional codes emerged. Subsequently, the established categories and codes were applied consistently across all transcripts (indexing). The data from each transcript were then charted to develop a matrix, facilitating the management and summarization of qualitative findings. This method enabled the researchers to compare and contrast differences within the data and to identify connections between categories, thereby exploring their relationships and informing data interpretation.
The procedure of framework analysis necessitated a transparent process for data management and interpretation of emerging themes to ensure the robustness of research 49 . The transparency of this analytic approach enabled two researchers (C.Te. and K.S.) to independently analyze the qualitative data, and the emerging themes afterwards were discussed to obtain consensus among the researchers. This technique can be considered as a triangular approach to assure the intercoder reliability and internal validity of this research. The transparent process also allowed an external expert in dental education to verify the accuracy of the analysis. All emerging themes and the decision on data saturation were based on a discussion of all researchers until an agreement was made. NVivo (version 14, QSR International) was used to performed the qualitative data analysis. Subsequently, a conceptual framework was constructed to demonstrate emerging themes and subthemes together with their relationships.
Ethical consideration
The ethical approval for the study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Faculty of Dentistry and Faculty of Pharmacy, Mahidol University on 29 th September 2022, the ethical approval number: MU-DT/PY-IRB 2022/049.2909. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Although the data were not anonymous in nature as they contained identifiable data, they were coded prior to the analysis to assure confidentiality of participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
There were 18 residents from Year 1 to 3 of the Residency Training Program in Advanced General Dentistry who participated in this research (six from each year). Of these, there were 14 females and 4 males. There was no participant dropout, as all of them completed all required tasks, including the pre- and post-perceived assessments, gamified online role-play, and satisfaction questionnaire. According to the purposive sampling, the participants from the quantitative phase were selected for semi-structured interviews by considering sex, year of study, and self-perceived assessment scores. Twelve students (ten females and two males) participated in semi-structured interviews, where their characteristics are presented in Table 1 .
Internal consistency of all constructs
The data collected from the research participants, in addition to the pilot samples, were analyzed with Cronbach’s alpha to confirm the internal consistency. The coefficient alpha of all constructs demonstrated high internal consistency, as demonstrated in Table 2 .
Self-perceived assessments toward confidence and awareness of teledentistry
There were statistically significant increases in the assessment scores of self-perceived confidence and awareness after participating in the gamified online role-play ( P < 0.001). According to Table 3 , there was an increase in self-perceived confidence from 3.38 (SD = 0.68) for the pre-assessment to 4.22 (SD = 0.59) for the post-assessment ( P < 0.001). The findings of self-perceived awareness also showed score improvement from 4.16 (SD = 0.48) to 4.55 (SD = 0.38) after interacting with the simulated patient ( P < 0.001).
According to Fig. 2 , participants demonstrated a higher level of self-perceived assessments for both self-confidence and awareness in all aspects after participating in the gamified online role-play for teledentistry training.
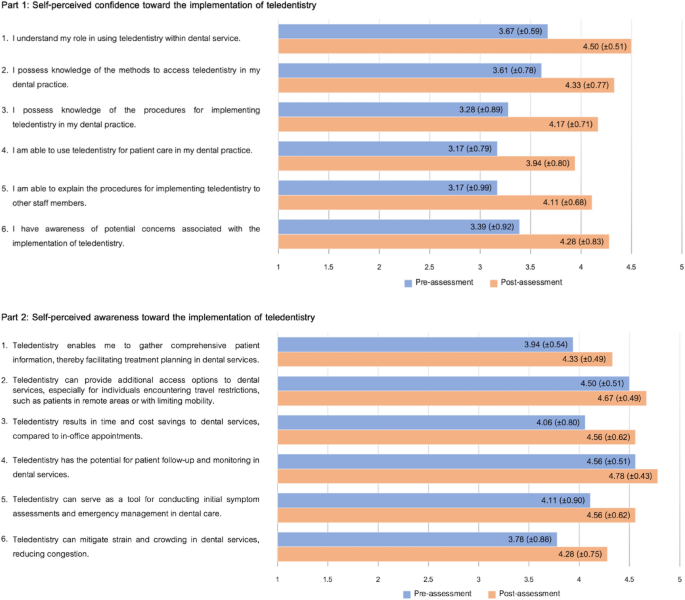
Self-perceived assessments toward confidence and awareness of teledentistry.
When comparing the self-perceived assessment scores toward confidence and awareness in the use of teledentistry among the three years of study (Year 1–3), there were no statistically significant differences in the pre-assessment, post-assessment score, and score difference (Table 4 ).
Satisfactions toward the use of gamified online role-play
According to Fig. 3 , participants exhibited high levels of satisfaction with the use of gamified online role-play across all three aspects. The aspect of usefulness received the highest satisfaction rating with a score of 4.44 (SD = 0.23) out of 5, followed by ease of use and enjoyment, scoring 4.40 (SD = 0.23) and 4.03 (SD = 0.21), respectively. Particularly, participants expressed the highest satisfaction levels regarding the usefulness of gamified online role-play for identifying their role (Mean = 4.72, SD = 0.46) and developing problem-solving skills associated with teledentistry (Mean = 4.61, SD = 0.50). Additionally, they reported satisfaction with the learning sequence presented in the gamified online role-play (Mean = 4.61, SD = 0.50). However, participants did not strongly perceive that the format of the gamified online role-play could engage them with the learning task for an extended period (Mean = 3.72, SD = 0.83).
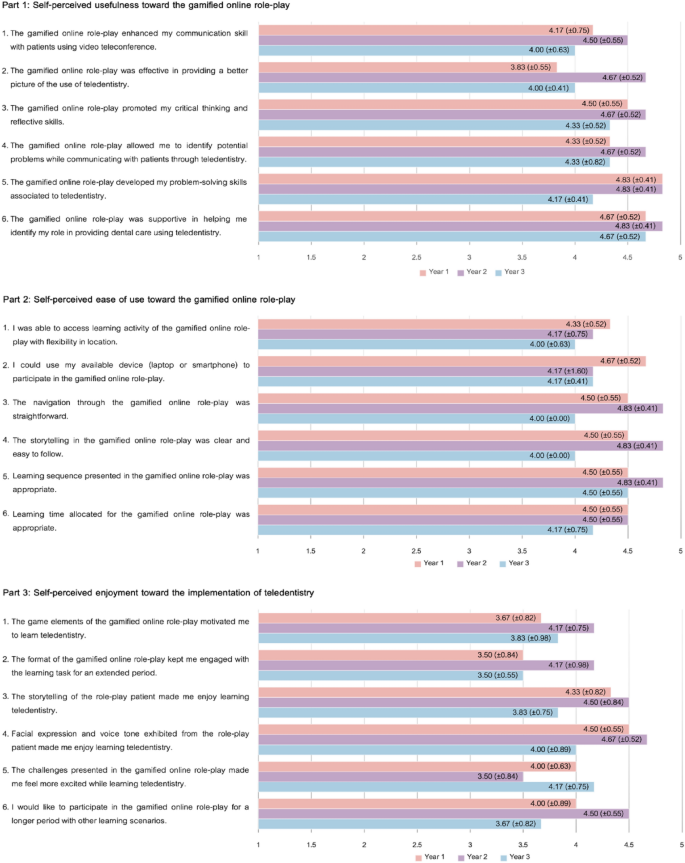
Satisfactions toward the use of gamified online role-play.
When comparing the satisfaction levels perceived by participants from different academic years (Table 5 ), no statistically significant differences were observed among the three groups for all three aspects ( P > 0.05).
Following the framework analysis of qualitative data, there were five emerging themes, including: (1) learner profile, (2) learning settings of the gamified online role-play, (3) pedagogical components, (4) interactive functions, and (5) educational impact.
Theme 1: Learner profile
Learner experience and preferences appeared to have impact on how the participants perceived the use of gamified online role-play for teledentistry training. When learners preferred role-play or realized benefits of teledentistry, they were likely to support this learning intervention. In addition, they could have seen an overall picture of the assigned tasks before participating in this research.
“I had experience with a role-play activity when I was dental undergraduates, and I like this kind of learning where someone role-plays a patient with specific personalities in various contexts. This could be a reason why I felt interested to participate in this task (the gamified online role-play). I also believed that it would be supportive for my clinical practice.” Participant 12, Year 1, Female “Actually, I' have seen in several videos (about teledentistry), where dentists were teaching patients to perform self-examinations, such as checking their own mouth and taking pictures for consultations. Therefore, I could have thought about what I would experience during the activity (within the gamified online role-play).” Participant 8, Year 2, Female
Theme 2: Learning settings of the gamified online role-play
Subtheme 2.1: location.
Participants had agreed that the location for conducting a gamified online role-play should be in a private room without any disturbances, enabling learners to focus on the simulated patient. This could allow them to effectively communicate and understand of the needs of patient, leading to a better grasp of lesson content. In addition, the environments of both learners and simulated patient should be authentic to the learning quality.
“The room should be a private space without any disturbances. This will make us feel confident and engage in conversations with the simulated patient.” Participant 10, Year 1, Female “… simulating a realistic environment can engage me to interact with the simulated patient more effectively ...” Participant 8, Year 2, Female
Subtheme 2.2: Time allocated for the gamified online role-play
The time allocated for the gamified online role-play in this research was considered as appropriate, as participants believed that a 30-minutes period should be suitable to take information and afterwards give some advice to their patient. In addition, a 10-minutes discussion on how they interact with the patient could be supportive for participants to enhance their competencies in the use of teledentistry.
“… it would probably take about 20 minutes because we would need to gather a lot of information … it might need some time to request and gather various information … maybe another 10-15 minutes to provide some advice.” Participant 7, Year 1, Female “I think during the class … we could allocate around 30 minutes for role-play, … we may have discussion of learner performance for 10-15 minutes ... I think it should not be longer than 45 minutes in total.” Participant 6, Year 2, Female
Subtheme 2.3: Learning consequence within a postgraduate curriculum
Most participants suggested that the gamified online role-play in teledentistry should be arranged in the first year of their postgraduate program. This could maximize the effectiveness of online role-play, as they would be able to implement teledentistry for their clinical practice since the beginning of their training. However, some participants suggested that this learning approach could be rearranged in either second or third year of the program. As they already had experience in clinical practice, the gamified online role-play would reinforce their competence in teledentistry.
"Actually, it would be great if this session could be scheduled in the first year … I would feel more comfortable when dealing with my patients through an online platform." Participant 11, Year 2, Male "I believe this approach should be implemented in the first year because it allows students to be trained in teledentistry before being exposed to real patients. However, if this approach is implemented in either the second or third year when they have already had experience in patient care, they would be able to better learn from conversations with simulated patients." Participant 4, Year 3, Male
Theme 3: Pedagogical components
Subtheme 3.1: learning content.
Learning content appeared to be an important component of pedagogical aspect, as it would inform what participants should learn from the gamified online role-play. Based on the interview data, participants reported they could learn how to use a video teleconference platform for teledentistry. The conditions of simulated patient embedded in an online role-play also allowed them to realize the advantages of teledentistry. In addition, dental problems assigned to the simulated patient could reveal the limitations of teledentistry for participants.
“The learning tasks (within the gamified online role-play) let me know how to manage patients through the teleconference.” Participant 5, Year 2, Female “… there seemed to be limitations (of teledentistry) … there could be a risk of misdiagnosis … the poor quality of video may lead to diagnostic errors … it is difficult for patients to capture their oral lesions.” Participant 3, Year 2, Female
Subtheme 3.2: Feedback
During the use of online role-play, the simulated patient can provide formative feedback to participants through facial expressions and tones of voice, enabling participants to observe and learn to adjust their inquiries more accurately. In addition, at the completion of the gamified online role-play, summative feedback provided by instructors could summarize the performance of participants leading to further improvements in the implementation of teledentistry.
“I knew (whether or not I interacted correctly) from the gestures and emotions of the simulated patient between the conversation. I could have learnt from feedback provided during the role-play, especially from the facial expressions of the patient.” Participant 11, Year 2, Male “The feedback provided at the end let me know how well I performed within the learning tasks.” Participant 2, Year 1, Female
Theme 4: Interactive functions
Subtheme 4.1: the authenticity of the simulated patient.
Most participants believed that a simulated patient with high acting performance could enhance the flow of role-play, allowing learners to experience real consequences. The appropriate level of authenticity could engage learners with the learning activity, as they would have less awareness of time passing in the state of flow. Therefore, they could learn better from the gamified online role-play.
"It was so realistic. ... This allowed me to talk with the simulated patient naturally ... At first, when we were talking, I was not sure how I should perform … but afterwards I no longer had any doubts and felt like I wanted to explain things to her even more." Participant 3, Year 2, Female "At first, I believed that if there was a factor that could influence learning, it would probably be a simulated patient. I was impressed by how this simulated patient could perform very well. It made the conversation flow smoothly and gradually." Participant 9, Year 3, Female
Subtheme 4.2: Entertaining features
Participants were likely to be satisfied with the entertaining features embedded in the gamified online role-play. They felt excited when they were being exposed to the unrevealed challenge which they had randomly selected. In addition, participants suggested to have more learning scenarios or simulated patients where they could randomly select to enhance randomness and excitement.
“It was a playful experience while communicating with the simulated patient. There are elements of surprise from the challenge cards that make the conversation more engaging, and I did not feel bored during the role-play.” Participant 4, Year 3, Male “I like the challenge card we randomly selected, as we had no idea what we would encounter … more scenarios like eight choices and we can randomly choose to be more excited. I think we do not need additional challenge cards, as some of them have already been embedded in patient conditions.” Participant 5, Year 2, Female
Subtheme 4.3: Level of difficulty
Participants suggested the gamified online role-play to have various levels of difficulty, so learners could have a chance to select a suitable level for their competence. The difficulties could be represented through patient conditions (e.g., systemic diseases or socioeconomic status), personal health literacy, and emotional tendencies. They also recommended to design the gamified online role-play to have different levels where learners could select an option that is suitable for them.
“The patient had hidden their information, and I needed to bring them out from the conversation.” Participant 12, Year 1, Female “Patients' emotions could be more sensitive to increase level of challenges. This can provide us with more opportunities to enhance our management skills in handling patient emotions.” Participant 11, Year 2, Male “… we can gradually increase the difficult level, similar to playing a game. These challenges could be related to the simulated patient, such as limited knowledge or difficulties in communication, which is likely to occur in our profession.” Participant 6, Year 2, Female
Theme 5: Educational impact
Subtheme 5.1: self-perceived confidence in teledentistry, communication skills.
Participants were likely to perceive that they could learn from the gamified online role-play and felt more confident in the use of teledentistry. This educational impact was mostly achieved from the online conversation within the role-play activity, where the participants could improve their communication skills through a video teleconference platform.
“I feel like the online role-play was a unique form of learning. I believe that I gained confidence from the online communication the simulated patient. I could develop skills to communicate effectively with real patients.” Participant 11, Year 2, Male “I believe it support us to train communication skills ... It allowed us to practice both listening and speaking skills more comprehensively.” Participant 4, Year 3, Male
Critical thinking and problem-solving skills
In addition to communication skills, participants reported that challenges embedded in the role-play allowed them to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which were a set of skills required to deal with potential problems in the use of teledentistry.
"It was a way of training before experiencing real situations … It allowed us to think critically whether or not what we performed with the simulated patients was appropriate." Participant 7, Year 1, Female “It allowed us to learn how to effectively solve the arranged problems in simulated situation. We needed to solve problems in order to gather required information from the patient and think about how to deliver dental advice through teledentistry.” Participant 11, Year 2, Male
Subtheme 5.2: Self perceived awareness in teledentistry
Participants believed that they could realize the necessity of teledentistry from the gamified online role-play. The storytelling or patient conditions allowed learners to understand how teledentistry could have both physical and psychological support for dental patients.
“From the activity, I would consider teledentistry as a convenient tool for communicating with patients, especially if a patient cannot go to a dental office”. Participant 5, Year 2, Female “I learned about the benefits of teledentistry, particularly in terms of follow-up. The video conference platform could support information sharing, such as drawing images or presenting treatment plans, to patients.” Participant 8, Year 2, Female
A conceptual framework of learning experience within a gamified online role-play
Based on the qualitative findings, a conceptual framework was developed in which a gamified online role-play was conceptualized as a learning strategy in supporting learners to be able to implement teledentistry in their clinical practice (Fig. 4 ).
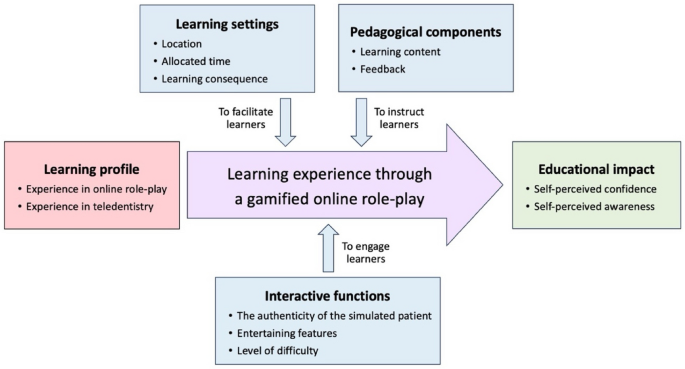
The conceptual framework of key elements in designing a gamified online role-play.
The conceptual framework has revealed key elements to be considered in designing a gamified online role-play. Learner profile, learning settings, pedagogical components, and interactive functions are considered as influential factors toward user experience within the gamified online role-play. The well-designed learning activity will support learners to achieve expected learning outcomes, considered as educational impact of the gamified online role-play. The contributions of these five key elements to the design of gamified online role-play were interpreted, as follows:
Learner profile: This element tailors the design of gamified online role-plays for teledentistry training involves considering the background knowledge, skills, and experiences of target learners to ensure relevance and engagement.
Learning settings: The element focuses the planning for gamified online role-plays in teledentistry training involves selecting appropriate contexts, such as location and timing, to enhance accessibility and achieve learning outcomes effectively.
Pedagogical components: This element emphasizes the alignment between learning components and learning outcomes within gamified online role-plays, to ensure that the content together with effective feedback design can support learners in improving their competencies from their mistakes.
Interactive functions: This element highlights interactivity features integrated into gamified online role-plays, such as the authenticity and entertaining components to enhance immersion and engagement, together with game difficulty for optimal flow. All these features should engage learners with the learning activities until the achievement of learner outcomes.
Educational impact: This element represents the expected learning outcomes, which will inform the design of learning content and activities within gamified online role-plays. In addition, this element could be considered to evaluate the efficacy of gamified online role-plays, reflecting how well learning designs align with the learning outcomes.
A gamified online role-play can be considered as a learning strategy for teledentistry according to its educational impact. This pedagogical approach could mimic real-life practice, where dental learners could gain experience in the use of teledentistry in simulated situations before interacting with actual patients. Role-play could provide learners opportunities to develop their required competencies, especially communication and real-time decision-making skills, in a predictable and safe learning environment 20 , 23 , 46 . Potential obstacles could also be arranged for learners to deal with, leading to the enhancement of problem-solving skill 50 . In addition, the recognition of teledentistry benefits can enhance awareness and encourage its adoption and implementation, which could be explained by the technology acceptance model 51 . Therefore, a gamified online role-play with a robust design and implementation appeared to have potential in enhancing self-perceived confidence and awareness in the use of teledentistry.
The pedagogical components comprised learning content, which was complemented by assessment and feedback. Learners could develop their competence with engagement through the learning content, gamified by storytelling of the online role-play 52 , 53 . Immediate feedback provided through facial expression and voice tone of simulated patients allowed participants to learn from their failure, considered as a key feature of game-based learning 29 , 45 . The discussion of summative feedback provided from an instructor at the end of role-play activity could support a debriefing process enabling participants to reflect their learning experience, considered as important of simulation-based game 54 . These key considerations should be initially considered in the design of gamified online role-play.
The interactive functions can be considered as another key component for designing and evaluating the gamified online role-play 45 . Several participants enjoyed with a learning process within the gamified online role-play and suggested it to have more learning scenarios. In other words, this tool could engage learners with an instructional process, leading to the achievement of learning outcomes 29 , 45 . As challenge and randomness appear to be game elements 32 , 33 , this learning intervention assigned a set of cards with obstacle tasks for learners to randomly pick up before interacting with simulated patients, which was perceived by participants as a feature to make the role-play more challenging and engaging. This is consistent with previous research, where challenging content for simulated patients could make learners more engaged with a learning process 55 . However, the balance between task challenges and learner competencies is certainly required for the design of learning activities 56 , 57 . The authenticity of simulated patient and immediate feedback could also affect the game flow, leading to the enhancement of learner engagement 45 . These elements could engage participants with a learning process, leading to the enhancement of educational impact.
The educational settings for implementing gamified online role-play into dental curriculum should be another concern. This aspect has been recognized as significant in existing evidence 45 . As this research found no significant differences in all aspects among the three groups of learners, this learning intervention demonstrated the potential for its implementation at any time of postgraduate dental curriculum. This argument can be supported by previous evidence where a role-play could be adaptable for learning at any time, as it requires a short learning period but provides learners with valuable experience prior to being exposed in real-life scenarios 58 . This strategy also provides opportunities for learners who have any question or concern to seek advice or guidance from their instructors 59 . Although the gamified online role-play can be arranged in the program at any time, the first academic year should be considered, as dental learners would be confidence in implementing teledentistry for their clinical practice.
While a gamified online role-play demonstrated its strengths as an interactive learning strategy specifically for teledentistry, there are a couple of potential drawbacks that need to be addressed. The requirement for synchronous participation could limit the flexibility of access time for learners (synchronous interactivity limitation). With only one learner able to engage with a simulated patient at a time (limited participants), more simulated patients would be required if there are a number of learners, otherwise they would need to wait for their turn. Time and resources are significantly required for preparing simulated patients 60 . Despite the use of trained and calibrated professional actors/actresses, inauthenticity may be perceived during role-plays, requiring a significant amount of effort to achieve both interactional and clinical authenticities 46 . Future research could investigate asynchronous learning approaches utilizing non-player character (NPC) controlled by an artificial intelligence system as a simulated patient. This setup would enable multiple learners to have the flexibility to engage with the material at their own pace and at times convenient to them 29 . While there are potential concerns about using gamified online role-plays, this interactive learning intervention offers opportunities for dental professionals to enhance their teledentistry competency in a safe and engaging environment.
Albeit the robust design and data collection tools to assure reliability and validity as well as transparency of this study, a few limitations were raised leading to a potential of further research. While this research recruited only postgraduate students to evaluate the feasibility of gamified online role-play in teledentistry training, further research should include not only experienced dental practitioners but also undergraduate students to confirm its potential use in participants with different learner profiles. More learning scenarios in other dental specialties should also be included to validate its effectiveness, as different specialties could have different limitations and variations. Additional learning scenarios from various dental disciplines should be considered to validate the effectiveness of gamified online role-plays, as different specialties may present unique limitations and variations. A randomized controlled trial with robust design should be required to compare the effectiveness of gamified online role-play with different approaches in training the use of teledentistry.
Conclusions
This research supports the design and implementation of a gamified online role-play in dental education, as dental learners could develop self-perceived confidence and awareness with satisfaction. A well-designed gamified online role-play is necessary to support learners to achieve expected learning outcomes, and the conceptual framework developed in this research can serve as a guidance to design and implement this interactive learning strategy in dental education. However, further research with robust design should be required to validate and ensure the educational impact of gamified online role-play in dental education. Additionally, efforts should be made to develop gamified online role-play in asynchronous learning approaches to enhance the flexibility of learning activities.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, up-on reasonable request. The data are not publicly available due to information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
Van Dyk, L. A review of telehealth service implementation frameworks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 11 (2), 1279–1298 (2014).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bartz, C. C. Nursing care in telemedicine and telehealth across the world. Soins. 61 (810), 57–59 (2016).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lin, G.S.S., Koh, S.H., Ter, K.Z., Lim, C.W., Sultana, S., Tan, W.W. Awareness, knowledge, attitude, and practice of teledentistry among dental practitioners during COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicina (Kaunas). 58 (1), 130 (2022).
Wolf, T.G., Schulze, R.K.W., Ramos-Gomez, F., Campus, G. Effectiveness of telemedicine and teledentistry after the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 19 (21), 13857 (2022).
Gajarawala, S. N. & Pelkowski, J. N. Telehealth benefits and barriers. J. Nurse Pract. 17 (2), 218–221 (2021).
Jampani, N. D., Nutalapati, R., Dontula, B. S. & Boyapati, R. Applications of teledentistry: A literature review and update. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 1 (2), 37–44 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Khan, S. A. & Omar, H. Teledentistry in practice: literature review. Telemed. J. E. Health. 19 (7), 565–567 (2013).
Baheti, M. J. B. S., Toshniwal, N. G. & Misal, A. Teledentistry: A need of the era. Int. J. Dent. Med. Res. 1 (2), 80–91 (2014).
Google Scholar
Datta, N., Derenne, J., Sanders, M. & Lock, J. D. Telehealth transition in a comprehensive care unit for eating disorders: Challenges and long-term benefits. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 53 (11), 1774–1779 (2020).
Bursell, S. E., Brazionis, L. & Jenkins, A. Telemedicine and ocular health in diabetes mellitus. Clin. Exp. Optom. 95 (3), 311–327 (2012).
da Costa, C. B., Peralta, F. D. S. & Ferreira de Mello, A. L. S. How has teledentistry been applied in public dental health services? An integrative review. Telemed. J. E. Health. 26 (7), 945–954 (2020).
Heckemann, B., Wolf, A., Ali, L., Sonntag, S. M. & Ekman, I. Discovering untapped relationship potential with patients in telehealth: A qualitative interview study. BMJ Open. 6 (3), e009750 (2016).
Pérez-Noboa, B., Soledispa-Carrasco, A., Padilla, V. S. & Velasquez, W. Teleconsultation apps in the COVID-19 pandemic: The case of Guayaquil City, Ecuador. IEEE Eng. Manag. Rev. 49 (1), 27–37 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Wamsley, C. E., Kramer, A., Kenkel, J. M. & Amirlak, B. Trends and challenges of telehealth in an academic institution: The unforeseen benefits of the COVID-19 global pandemic. Aesthetic Surg. J. 41 (1), 109–118 (2020).
Jonasdottir, S. K., Thordardottir, I. & Jonsdottir, T. Health professionals’ perspective towards challenges and opportunities of telehealth service provision: A scoping review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 167 , 104862 (2022).
Tan, S. H. X., Lee, C. K. J., Yong, C. W. & Ding, Y. Y. Scoping review: Facilitators and barriers in the adoption of teledentistry among older adults. Gerodontology. 38 (4), 351–365 (2021).
Minervini, G. et al. Teledentistry in the management of patients with dental and temporomandibular disorders. BioMed. Res. Int. 2022 , 7091153 (2022).
Edirippulige, S. & Armfield, N. Education and training to support the use of clinical telehealth: A review of the literature. J. Telemed. Telecare. 23 (2), 273–282 (2017).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mariño, R. & Ghanim, A. Teledentistry: A systematic review of the literature. J. Telemed. Telecare. 19 (4), 179–183 (2013).
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Armitage-Chan, E. & Whiting, M. Teaching professionalism: Using role-play simulations to generate professionalism learning outcomes. J. Vet. Med. Educ. 43 (4), 359–363 (2016).
Spyropoulos, F., Trichakis, I. & Vozinaki, A.-E. A narrative-driven role-playing game for raising flood awareness. Sustainability. 14 (1), 554 (2022).
Jiang, W. K. et al. Role-play in endodontic teaching: A case study. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 23 (4), 281–288 (2020).
PubMed Google Scholar
Vizeshfar, F., Zare, M. & Keshtkaran, Z. Role-play versus lecture methods in community health volunteers. Nurse Educ. Today. 79 , 175–179 (2019).
Nestel, D. & Tierney, T. Role-play for medical students learning about communication: Guidelines for maximising benefits. BMC Med. Educ. 7 , 3 (2007).
Gelis, A. et al. Peer role-play for training communication skills in medical students: A systematic review. Simulat. Health. 15 (2), 106–111 (2020).
Cornelius, S., Gordon, C. & Harris, M. Role engagement and anonymity in synchronous online role play. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 12 (5), 57–73 (2011).
Bell, M. Online role-play: Anonymity, engagement and risk. Educ. Med. Int. 38 (4), 251–260 (2001).
Sipiyaruk, K., Gallagher, J. E., Hatzipanagos, S. & Reynolds, P. A. A rapid review of serious games: From healthcare education to dental education. Eur. J. Dent. Educ. 22 (4), 243–257 (2018).
Sipiyaruk, K., Hatzipanagos, S., Reynolds, P. A. & Gallagher, J. E. Serious games and the COVID-19 pandemic in dental education: An integrative review of the literature. Computers. 10 (4), 42 (2021).
Morse, J.M., Niehaus, L. Mixed Method Design: Principles and Procedures. (2016).
Creswell, J. W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches 3rd edn. (SAGE Publications, 2009).
Cheng, V. W. S., Davenport, T., Johnson, D., Vella, K. & Hickie, I. B. Gamification in apps and technologies for improving mental health and well-being: Systematic review. JMIR Ment. Health. 6 (6), e13717 (2019).
Gallego-Durán, F. J. et al. A guide for game-design-based gamification. Informatics. 6 (4), 49 (2019).
Gee, J. P. Learning and games. In The Ecology of Games: Connecting Youth, Games, and Learning (ed. Salen, K.) 21–40 (MIT Press, 2008).
Cheung, K. L., ten Klooster, P. M., Smit, C., de Vries, H. & Pieterse, M. E. The impact of non-response bias due to sampling in public health studies: A comparison of voluntary versus mandatory recruitment in a Dutch national survey on adolescent health. BMC Public Health. 17 (1), 276 (2017).
Murairwa, S. Voluntary sampling design. Int. J. Adv. Res. Manag. Social Sci. 4 (2), 185–200 (2015).
Chow, S.-C., Shao, J., Wang, H. & Lokhnygina, Y. Sample Size Calculations in Clinical Research (CRC Press, 2017).
Book Google Scholar
Palinkas, L. A. et al. Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Administration Policy Mental Health Mental Health Services Res. 42 (5), 533–544 (2015).
McIlvried, D. E., Prucka, S. K., Herbst, M., Barger, C. & Robin, N. H. The use of role-play to enhance medical student understanding of genetic counseling. Genet. Med. 10 (10), 739–744 (2008).
Schlegel, C., Woermann, U., Shaha, M., Rethans, J.-J. & van der Vleuten, C. Effects of communication training on real practice performance: A role-play module versus a standardized patient module. J. Nursing Educ. 51 (1), 16–22 (2012).
Manzoor, I. M. F. & Hashmi, N. R. Medical students’ perspective about role-plays as a teaching strategy in community medicine. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 22 (4), 222–225 (2012).
Cornes, S., Gelfand, J. M. & Calton, B. Foundational telemedicine workshop for first-year medical students developed during a pandemic. MedEdPORTAL. 17 , 11171 (2021).
King, J., Hill, K. & Gleason, A. All the world’sa stage: Evaluating psychiatry role-play based learning for medical students. Austral. Psychiatry. 23 (1), 76–79 (2015).
Arayapisit, T. et al. An educational board game for learning orofacial spaces: An experimental study comparing collaborative and competitive approaches. Anatomical Sci. Educ. 16 (4), 666–676 (2023).
Sipiyaruk, K., Hatzipanagos, S., Vichayanrat, T., Reynolds, P.A., Gallagher, J.E. Evaluating a dental public health game across two learning contexts. Educ. Sci. 12 (8), 517 (2022).
Pilnick, A. et al. Using conversation analysis to inform role play and simulated interaction in communications skills training for healthcare professionals: Identifying avenues for further development through a scoping review. BMC Med. Educ. 18 (1), 267 (2018).
Lane, C. & Rollnick, S. The use of simulated patients and role-play in communication skills training: A review of the literature to August 2005. Patient Educ. Counseling. 67 (1), 13–20 (2007).
Gale, N. K., Heath, G., Cameron, E., Rashid, S. & Redwood, S. Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 13 (1), 117 (2013).
Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., Nicholls, C. M. & Ormston, R. Qualitative Research Practice: A Guide for Social Science Students and Researchers (Sage, 2014).
Chen, J. C. & Martin, A. R. Role-play simulations as a transformative methodology in environmental education. J. Transform. Educ. 13 (1), 85–102 (2015).
Davis, F. D. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. Manag. Inform. Syst. Quart. 13 (3), 319–340 (1989).
Novak, E., Johnson, T. E., Tenenbaum, G. & Shute, V. J. Effects of an instructional gaming characteristic on learning effectiveness, efficiency, and engagement: Using a storyline for teaching basic statistical skills. Interact. Learn. Environ. 24 (3), 523–538 (2016).
Marchiori, E. J. et al. A narrative metaphor to facilitate educational game authoring. Comput. Educ. 58 (1), 590–599 (2012).
Luctkar-Flude, M. et al. Effectiveness of debriefing methods for virtual simulation: A systematic review. Clin. Simulat. Nursing. 57 , 18–30 (2021).
Joyner, B. & Young, L. Teaching medical students using role play: Twelve tips for successful role plays. Med. Teach. 28 (3), 225–229 (2006).
Csikszentmihalyi, M. Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Performance (HarperCollins Publishers, 1990).
Buajeeb, W., Chokpipatkun, J., Achalanan, N., Kriwattanawong, N. & Sipiyaruk, K. The development of an online serious game for oral diagnosis and treatment planning: Evaluation of knowledge acquisition and retention. BMC Med. Educ. 23 (1), 830 (2023).
Littlefield, J. H., Hahn, H. B. & Meyer, A. S. Evaluation of a role-play learning exercise in an ambulatory clinic setting. Adv. Health. Sci. Educ. Theory Pract. 4 (2), 167–173 (1999).
Alkin, M. C. & Christie, C. A. The use of role-play in teaching evaluation. Am. J. Evaluat. 23 (2), 209–218 (2002).
Lovell, K. L., Mavis, B. E., Turner, J. L., Ogle, K. S. & Griffith, M. Medical students as standardized patients in a second-year performance-based assessment experience. Med. Educ. Online. 3 (1), 4301 (1998).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express our sincere gratitude to participants for their contributions in this research. We would also like to thank the experts who provided their helpful suggestions in the validation process of the data collection tools.
This research project was funded by the Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University. The APC was funded by Mahidol University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Advanced General Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Chayanid Teerawongpairoj & Chanita Tantipoj
Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Kawin Sipiyaruk
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; methodology, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; validation, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; investigation, C.Te. and K.S.; formal analysis, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; resources, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; data curation, C.Ta. and K.S.; writing-original draft preparation, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S.; writing-review and editing, C.Te., C.Ta., and K.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kawin Sipiyaruk .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information 1., supplementary information 2., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Teerawongpairoj, C., Tantipoj, C. & Sipiyaruk, K. The design and evaluation of gamified online role-play as a telehealth training strategy in dental education: an explanatory sequential mixed-methods study. Sci Rep 14 , 9216 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58425-9
Download citation
Received : 30 September 2023
Accepted : 28 March 2024
Published : 22 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58425-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Dental education
- Distance learning
- Game-based learning
- Gamification
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
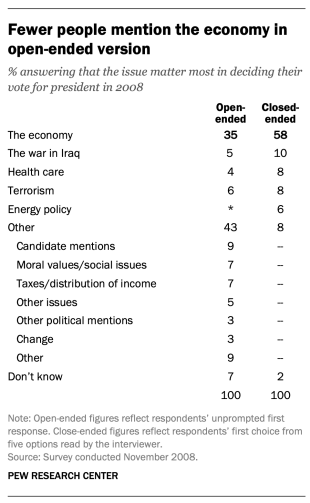
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
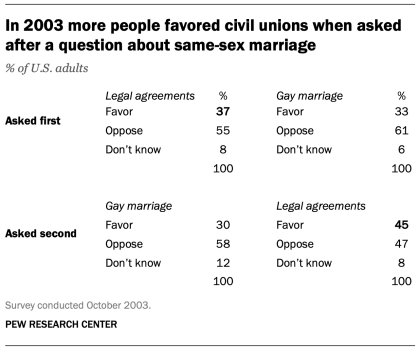
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
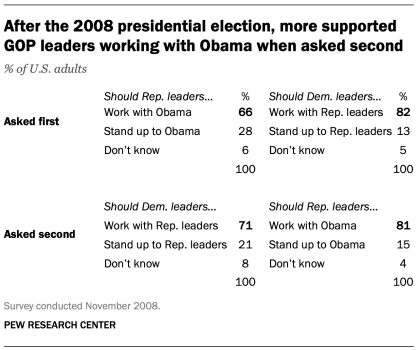
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Chapter 2. Research Design Getting Started. When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a "research proposal" that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research. Types of quantitative research designs. Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
The qualitative researcher today faces a baffling array of options for con-ducting qualitative research. Numerous inquiry strategies (Denzin & Lincoln, 2005), inquiry traditions (Creswell, 1998), qualitative approaches (Miller & Crabtree, 1992), and design types (Creswell, 2007) are available for selec-tion. What criteria should govern whether ...
In other words, qualitative research uncovers social processes and mechanisms undergirding human behavior. In this chapter, we will discuss how to design a qualitative research project using two of the most common qualitative research methods: in-depth interviewing and ethnographic observations (also known as ethnography or participant ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
that the research design of a qualitative study differs from that of a study that starts with an understanding to be tested, where often the hypothesis literally dictates the form, quantity, and scope of required data. This sort of design preempts other ways of looking at the research question. Qualitative research is usually not preemptive ...
A research design is based on an integration of the theories, concepts, goals, contexts, beliefs, and sets of relationships that shape a specific topic. In addition, it is shaped by responding to the realities and perspectives of participants and contexts of a study. In a solid qualitative research design, framing theory and key constructs are ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
Qualitative research designs are research methods that collect and analyze non-numerical data. The research uncovers why or how a particular behavior or occurrence takes place. The information is usually subjective and in a written format instead of numerical. Researchers may use interviews, focus groups, case studies, journaling, and open ...
Research design refers to the overall plan, structure or strategy that guides a research project, from its conception to the final analysis of data. Research designs for quantitative studies include descriptive, correlational, experimental and quasi-experimenta l designs. Research designs for qualitative studies include phenomenological ...
When conducting qualitative research, it is important to follow best practices to ensure the rigor, validity, and trustworthiness of your study. Here are some top best practices for qualitative research design: 1. Clearly Define Research Questions: Begin by clearly defining your research questions or objectives.
Moreover, qualitative designing processes essentially accommodate the features of constructivist knowledge and understandings of the quality of qualitative research (see Chap. 9).Like almost all other aspects of naturalist qualitative inquiry, this view of design is close to the everyday-life meaning of designing and planning any endeavor.
Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced. Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002.
The burden of offering adequate sample sizes in research has been one of. the major criticisms against qualitative s tudies. One of the most acceptable standards in qualitative research is to ...
Revised on 30 January 2023. Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which ...
Abstract. This chapter provides an outline of key concepts in qualitative research design for healthcare simulation. It explores three landmarks that provide orientation to researchers: (1) a defined purpose for the research; (2) an articulation of the researcher's worldview; and (3) an overarching approach to research design.
This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods. Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
To perform qualitative research, you must choose at least one research design approach that fits your topic. It is not uncommon for a researcher to employ more than one approach throughout their study. Here are five common design approaches: 1. Historical Study. A historical study is the ideal choice for studies that involve extensive ...
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PAPER 45 research problem. For example, the purpose of this study is to examine the prevalence of the use of synthetic marijuana use among preteens which will lead to a prevention and intervention model to be used in community centers citywide. Significance of the Study.
Qualitative research uncovers the details of human behavior, beliefs, and feelings. It gives us insights that numbers can't always tell. These research questions help us understand the "how" and "why" of things. In this article, we'll look at six examples of good qualitative questions. We aim to highlight how picking the right ...
Research design. This research employed an explanatory sequential mixed-methods design, where a quantitative phase was firstly performed followed by a qualitative phase 30,31.The quantitative ...
We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups, cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on ...