
- On-Campus Graduate Programs
- Online Master’s Progams
- Curricular Practical Training
- Engineering Alumni Program
- Engineering Library
- Academic Options
- Billing and Tuition
- Dissertation Information
- Graduation Procedures
- Master’s Thesis Information
- Student Code of Conduct
- Graduate Advising
- Graduate Program Contacts
- RAS Information + Hours
- Graduate Student Wellness + Resources
- Student Wellness Information
- Student Clubs + Organizations
- Graduate Student Awards
- Make a Gift
- Current Students
- Student Handbook
- Master’s Thesis

Master's Thesis
Writing a thesis is optional for some master’s programs and not required. There are abundant opportunities for personalized interaction with faculty through research courses, independent studies, and seminars. If a student chooses to write a thesis, it requires eight courses and either two research credits (5970), or in some cases with program specific approval, one research credit (5970) and one independent study (5990). Two credits must be completed for a letter grade for successful completion of the master’s thesis.
A thesis or research paper based on joint work with other researchers is allowed, provided that a unique and separate document is presented by each degree candidate. The candidate must include a concise account of his or her contribution to the whole work. Authorship of a master’s thesis or research paper by more than one degree candidate is not allowed.
University Style Guide for Master’s Thesis
Please submit your thesis electronically at this time to Graduate Engineering. Directions will be sent via email after the graduation application closes for that period.
Font, Spacing, and Margin Requirements Any non-italic font 10-12 points in size should be used. Headings may be larger. For enhanced screen readability, use Arial (10pt), Courier New (10pt), Georgia (11pt), Times New Roman (12 pt), or Verdana (10pt) font. For footnotes, figures, citations, charts and graphs, a font of 8 point or larger should be used. Italic type may be used for quotations, words in a foreign language, occasional emphasis, or book titles. For the sake of readability, it is recommended that the text of the dissertation be double-spaced (except for footnotes, long quoted passages, and lists of tables and figures, which are single-spaced). If desired, authors may chose to single-space the abstract and/or thesis manuscript.
Allow one and one-half inches for the left margin and one inch for all other margins. All text, including page numbers, must fit within these margins. Please remember to include the title page in the margin allowance. Organization of the Manuscript Pages must appear in the following order:
Title Page Dedication (optional) Acknowledgment (optional) Abstract (optional) Table of Contents (mandatory for theses 50 pages or longer) List of Tables (optional) List of Figures/Illustrations (optional) Main Text Appendices (optional) Bibliography/Works Cited
Title Page The Title Page must follow the sample format . The author’s full legal name must appear on the Title Page and the completed thesis must have electronic signatures when deposited electronically to Graduate Engineering. The sample shows how to list a co-supervisor if you have one. If not, please omit from your Title Page and list only the supervisor and director/chair’s names and signatures. Some Master’s Program’s have a Program Director, while others only have their Graduate Group Chair. If you are unsure if you have a director or chair, please talk with your program coordinator/administrator so you have that person’s title listed properly on the Title Page. Although the Title Page counts as page “i” of the preliminary pages, no page number appears on the Title Page. A Table of Contents m ust be included if the thesis is 50 pages or longer.
Pagination All pages (except the Title Page: page i) must have a page number. For the preliminary pages (dedication, acknowledgements, table of contents, lists of graphs, tables, and illustrations), use small Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, …). For the text and appendices (if any), use Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, …). Remember that page numbers must also appear within the margins specified above.
Other Requirements For citations, footnotes, references, and grammar, you may follow the guidelines in the Chicago Manual of Style, the MLA Handbook, or the appropriate manual in your field of study.
Student Handbook sections:
- Graduate Programs
- Academic Standing Requirements
- Registration Procedures
- Forms and Requests
- Penn Policies
- Graduate Student Resources
- Research Support Plan for Ph.D. students
Return to Table of Contents
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).


Creating an Outline for Your Master’s Thesis
1. introduction.
Your master’s thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master’s thesis is the longest document that they’ve ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
2. Criteria for Success
The most important criterion for success is that you’ve shown an outline with your chapter breakdown to your advisor. Your advisor is the one that formally signs off on your thesis as completed, so their feedback is the most important.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements.
- Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field.
- Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique. Master’s thesis literature reviews typically have at least 60 citations throughout the entire document
- Methods – Explain how you produced your results
- Results – Show your results and comment on their significance and implications.
- Conclusion – Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work.
Having an outline for your master’s thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master’s thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks.
4. Analyze Your Audience
The most important audience member for your master’s thesis is your advisor, as they are ultimately the person that signs off on whether or not your thesis is sufficient enough to graduate. The needs of any other audience members are secondary.
Ideally, a good master’s thesis is accessible to people that work in your field. In some cases, master’s theses are passed on to newer students so that that research can continue. In these cases, the thesis is used as a guide to introduce newer students to the research area. If you intend for your thesis to be used as a guide for new students, you may spend more time explaining the state of the field in your introduction and literature review. Additionally, your thesis will be posted publicly on DSpace , MIT’s digital repository for all theses.
5. Best Practices
5.1. identify your claims.
A key element to figuring out the unique structure to your master’s thesis is identifying the claims of your work. A claim is an answer to a research question or gap. Your thesis can have both a higher level claim and also lower level claims that motivate the research projects that you worked on. Identifying your claims will help you spot the key objectives which you want to highlight in the thesis. This will keep your writing on topic.
Some examples are shown below:
Gap/Question : There are no field-portable microplastic sensing technologies to measure their distribution in the environment.
→ Claim : Impedance spectroscopy can be used in a microfluidic device to rapidly distinguish organic matter from polymers.
Gap/Question: How effective are convolutional neural networks for pose estimation during in-space assembly?
→ Claim : Convolutional neural networks can be used to estimate the pose of satellites, but struggle with oversaturated images and images with multiple satellites.
5.2. Support Your Claims
Once you have identified your claim, the next step is to identify evidence that will support it. The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that you make. Figure 1 and 2 demonstrate two different structures to support a claim. In one outline, the claim is best supported by a linear structure that describes the building, testing, and validation of a model. In another outline, the claim is best supported by a trifold structure, where three independent methods are discussed. Depending on the extent of the evidence, you could break this trifold structure into 3 separate chapters, or they could all be discussed in a singular chapter. The value of identifying claims and evidence is that it helps you organize your paper coherently at a high level. The number of chapters that are output as a result of your claim identification is up to you and what you think would be sufficient discussion for a chapter within your thesis.
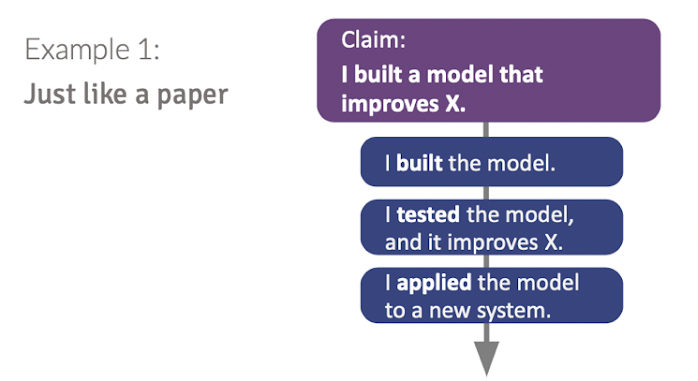
5.3. Connect the Evidence to Your Claims with Reasoning
One common mistake that students make when writing their thesis is treating each chapter as an isolated piece of writing. While it is helpful to break down the actual task of thesis writing into chapter-size pieces, these chapters should have some connection to one another. For your outline, it is ideal to identify what these connections were. Perhaps what made you start on one project was that you realized the weaknesses in your prior work and you wanted to make improvements. For readers who were not doing the research with you, describing the connections between your work in different chapters can help them understand the motivation and value of why you pursued each component.
5.4. Combine Your Claims, Evidence, and Reasoning to Produce Your Outline
Once you have identified your claims, the evidence you have surrounding each claim, and the reasoning that connects each piece of your work, you can now create your full outline, putting the pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle. An example outline is provided as an annotated example.
There are no requirements for minimum or maximum number of chapters that your master’s thesis can have. Therefore, when translating your outline to a literal chapter breakdown, you should feel free to use as many chapters as needed. If your methods section for a claim is extremely long, it may make more sense to have it be a standalone chapter, as shown in the attached annotated pdf.
6. Additional Resources
Every IAP, the Comm Lab hosts a workshop on how to write your master’s thesis. This workshop provides tips for writing each of these sections, and steps you through the process of creating an outline.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Example 1. structure diagram and table of contents, example 2. table of contents.
- Technical Support
- Find My Rep
You are here
How to Write a Master's Thesis
- Yvonne N. Bui - San Francisco State University, USA
- Description
See what’s new to this edition by selecting the Features tab on this page. Should you need additional information or have questions regarding the HEOA information provided for this title, including what is new to this edition, please email [email protected] . Please include your name, contact information, and the name of the title for which you would like more information. For information on the HEOA, please go to http://ed.gov/policy/highered/leg/hea08/index.html .
For assistance with your order: Please email us at [email protected] or connect with your SAGE representative.
SAGE 2455 Teller Road Thousand Oaks, CA 91320 www.sagepub.com
“Yvonne Bui’s How to Write a Master’s Thesis should be mandatory for all thesis track master’s students. It steers students away from the shortcuts students may be tempted to use that would be costly in the long run. The step by step intentional approach is what I like best about this book.”
“This is the best textbook about writing an M.A. thesis available in the market.”
“This is the type of textbook that students keep and refer to after the class.”
Excellent book. Thorough, yet concise, information for students writing their Master's Thesis who may not have had a strong background in research.
Clear, Concise, easy for students to access and understand. Contains all the elements for a successful thesis.
I loved the ease of this book. It was clear without extra nonsense that would just confuse the students.
Clear, concise, easily accessible. Students find it of great value.
NEW TO THIS EDITION:
- Concrete instruction and guides for conceptualizing the literature review help students navigate through the most challenging topics.
- Step-by-step instructions and more screenshots give students the guidance they need to write the foundational chapter, along with the latest online resources and general library information.
- Additional coverage of single case designs and mixed methods help students gain a more comprehensive understanding of research methods.
- Expanded explanation of unintentional plagiarism within the ethics chapter shows students the path to successful and professional writing.
- Detailed information on conference presentation as a way to disseminate research , in addition to getting published, help students understand all of the tools needed to write a master’s thesis.
KEY FEATURES:
- An advanced chapter organizer provides an up-front checklist of what to expect in the chapter and serves as a project planner, so that students can immediately prepare and work alongside the chapter as they begin to develop their thesis.
- Full guidance on conducting successful literature reviews includes up-to-date information on electronic databases and Internet tools complete with numerous figures and captured screen shots from relevant web sites, electronic databases, and SPSS software, all integrated with the text.
- Excerpts from research articles and samples from exemplary students' master's theses relate specifically to the content of each chapter and provide the reader with a real-world context.
- Detailed explanations of the various components of the master's thesis and concrete strategies on how to conduct a literature review help students write each chapter of the master's thesis, and apply the American Psychological Association (APA) editorial style.
- A comprehensive Resources section features "Try It!" boxes which lead students through a sample problem or writing exercise based on a piece of the thesis to reinforce prior course learning and the writing objectives at hand. Reflection/discussion questions in the same section are designed to help students work through the thesis process.
Sample Materials & Chapters
1: Overview of the Master's Degree and Thesis
3: Using the Literature to Research Your Problem
For instructors
Select a purchasing option, related products.

Graduate School
Master’s thesis guidelines.
- Academics & Research
- Rules & Regulations
A master’s student with a thesis requirement will submit the file through Brown's electronic theses and dissertation (ETD) system . The system is designed to collect and archive the thesis or dissertation as a text-based PDF file. An electronic file submitted through the ETD will appear in the Library's discovery service and in the Brown digital repository .
Web Searches and Unrestricted Downloads
In the spirit of the dissemination of new knowledge that is a hallmark of higher education, a thesis or dissertation will be subject to web searches and unrestricted downloads unless the student requests to opt out of the system and have the thesis or dissertation unavailable for download outside of the Brown community. A request to restrict download access to a thesis or dissertation has an initial two-year window from the time of degree conferral. Guidelines associated with restricted dissertation access are:
- The full text version will be available for download only to members of the Brown community.
- Web searches including the citation and abstract of restricted theses or dissertations will continue to be available to the general public.
- After two years the restriction will elapse.
- Restrictions on full text download may be renewed for two-year periods up to a total of ten years from the date of degree conferral. Requests for additional two-year restrictions should be made to the Graduate School.
- Any requests to extend the restriction beyond ten years must go to the Graduate Council for approval.
- In cases where the thesis or dissertation is a co-worked piece and there is disagreement between the student and the advisor over whether the material will or will not be available for download outside of the Brown community, the dispute will be brought before the Graduate Council for resolution.
To use the ETD system, the student must possess a valid username and password for accessing Brown’s computer network. If you are unable to create an account in the system, please contact [email protected] for assistance.
Graduate students are eligible to have degrees conferred, and to receive their diploma, at three different times over the course of the academic year.
For students who complete their degree requirements the preceding summer term. The Application to Graduate opens on July 1, 2024 and closes on September 6, 2024. Degrees are conferred on October 20, 2024.
For students who complete their requirements the preceding fall term. The Application to Graduate opens on October 1, 2024 and closes on January 10, 2025. Degrees are conferred on February 9, 2025.
For students who complete their requirements over the preceding spring term. The dissertation deadline is May 1, 2024. Please note, the Application to Graduate deadline is April 19, 2024.
The master's thesis and all of the associated forms and documents related to the completion of the degree must be submitted to the Graduate School by the deadlines listed above.
Registration
If a student registers for Semester I and completes all of the requirements for the degree during that semester, a fee for Semester II will not be charged.
View Sample Title Page
The Signature Page
As part of the overall completion process, the student must separately submit one signature page, which may be sent electronically to [email protected] . The signature page should bear the signature of the director (not the graduate representative or chairperson). The typed name of the director should appear under the signature line. Electronic signatures are acceptable. An unsigned copy of the signature page should be uploaded to the ETD system .
View Sample Signature Page
Every effort should be made to have the manuscript as perfect as possible in form and appearance. Pages containing handwritten corrections, typewritten strikeovers and unsightly erasures and the like will not be accepted. Good references for editorial details are the MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Modern Language Association), Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses and Dissertations (University of Chicago Press), and The Chicago Manual of Style (University of Chicago Press). The department should also be consulted regarding its policies or preferences in matters of format and style.
If publication of the thesis is anticipated, the medium of publication likely to be used should be considered when preparing the manuscript. If it is known in advance that the thesis will be published by a particular publisher or journal, the editorial practices of that publisher or journal should be followed. The form of footnotes and bibliography, in particular, may vary with different publishers and journals.
Type and Spacing Standard
Typefaces set to print at 10-, 11-, or 12-point font are acceptable. Typing or printing should be double-spaced, except for footnotes (single-space footnotes, with double spacing to separate one note from the next).
Page Numbers
Be consistent. Either put all page numbers (both Roman and Arabic) at the top of the page, or put all page numbers (both Roman and Arabic) at the bottom of the page.
Most theses consist of preliminary pages which are numbered using Roman numerals, and the thesis proper, which is numbered using Arabic numerals.
The preliminary pages must appear in the following order:
- Title page (do not number)
- Signature page (ii)
- Vita* (iii)
- Preface and acknowledgments (iv)
- Table of contents (v)
- List of tables vi List of illustrations (vii)
Should any element of the preliminary pages be longer than one page, number the pages consecutively. The preliminary pages should appear in this order but not necessarily with the page numbers shown above.
The thesis proper (including introduction, main body of the text, illustrations, appendices, and bibliography) is numbered using Arabic numerals. The numbering begins with 1 and runs consecutively to the end.
* The vita is an optional statement giving a short biography of the candidate, including institutions attended, degrees and honors, titles of publications, teaching or professional experience, and other pertinent information. Do not include date or location of birth or phone numbers.
Dating the Thesis
Because degrees are conferred three times a year, the title page should include the date that the degree is conferred.
The Abstract
If it is appropriate for the thesis to be accompanied by an abstract, it should, in a concise manner, present the problem of the dissertation, discuss the materials and procedure or methods used, and state the results or conclusions. Mathematical formulas, diagrams, and other illustrative materials should be avoided. The abstract should not be part of the thesis itself nor should it be included in the table of contents. It should be headed as follows:
Abstract of (TITLE OF THESIS), by (AUTHOR'S NAME), Degree [A.M., or ScM.], Brown University, May (YEAR IN WHICH DEGREE IS TO BE AWARDED).
The abstract should be prepared carefully since it will be published without editing or revision. The abstract should be double-spaced and may not exceed 350 words (maximum 2,450 characters — including spaces and punctuation — about 70 characters per line with a maximum of 35 lines).
Submission of Final Thesis
When the thesis is submitted electronically to the Graduate School, it must be in final form. It may not be revised in any way after it is presented. See the list of required items below and note that some, where noted, may be sent electronically to the Graduate School’s Academic Affairs Manager, Barbara Bennett. The thesis will not be accepted and the student’s degree will not be conferred if any item from this list is missing or incomplete. The online submission system will send notifications when each document has been received and approved by the Graduate School.
- One copy of the title page, which may be sent electronically.
- One signed signature page, which may be sent electronically to to [email protected] .
Digital Supplementary Material
Students interested in depositing digital supplementary materials along with their thesis are welcome to contact the Library for assistance. Please contact: Andrew Creamer in the Library at [email protected] .
Publishing the Master's Thesis
It is University policy that all research done at the University under its sponsorship must be freely published without restriction. Since 1954, the Graduate School has required that dissertations be published. In 1985, the Graduate Council reaffirmed that decision and approved the following policy:
"All Ph.D. dissertations and Master's theses will be open documents. The Graduate Council will not recommend the awarding of the Ph.D. or Master's degree until the dissertation or thesis is submitted to the Graduate School and accorded unlimited distribution status."
Exceptions to this requirement will be made only if there is a letter from a publisher stating that the dissertation will be published within one year after the degree is awarded and that requests that circulation of the dissertation be withheld for twelve months after the degree is conferred. Six months will be allowed for the clearing of a patent.
If you have a question about temporarily removing your dissertation from the Library's digital repository , please contact [email protected] .
The Diploma
The Office of the Registrar's Application to Graduate provides the degree candidate with an opportunity to indicate how the diploma name should appear. Otherwise, the name that will appear on the diploma and in the Commencement program, and under which the Library will catalog the dissertation, is the name under which the candidate is officially registered. Any request for a change of registered name should be addressed to the Office of the Registrar and accompanied by supporting legal documentation, such as a court order, marriage license, passport, driver’s license, or social security card.
Certificate of Completion
If all academic requirements for the degree and all financial obligations have been met before May 1, the Office of the Registrar will issue a certificate of completion within three weeks of the candidate's request.
If you have any questions regarding the submission of your thesis, please contact Barbara Bennett in the Graduate School at (401) 863-2843.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Master’s Thesis: A Guide for Students

A master’s thesis is an academic research output that is expected to showcase a student’s competence in a higher level of research as compared to an undergraduate one. The primary objective of a master’s thesis is to assess a student on the depth of their understanding, knowledge, and competence on the subject of their choice. It provides a scholarly and research foundation for students to build on if they are interested in pursuing higher academic degrees and professional work.
Benefits of Writing a Master’s Thesis
Undertaking a master’s thesis program enhances your career and academic prospects. In the academic sphere, those who have completed a master’s thesis program are in a more advantageous position when they seek admission to a PhD program. Research-focused disciplines, in particular, usually favour students who have completed their master’s thesis. Opting for a master’s thesis program also gives researchers the opportunity to pursue their interest area through study and research. Further, through the process of thesis writing, students also develop their skills in writing, putting forth an informed argument and developing research questions. A well-developed thesis can also be published as a research paper in peer-reviewed journals, thereby enhancing future academic and career prospects.
Thesis Masters and Non-thesis Masters Program: Differences
It is critical to note that all master’s programs do not have a thesis requirement. At the same time, some programs allow students to choose between a thesis and a non-thesis master’s program. In a thesis Master’s program, you are required to prepare a comprehensive scholarly paper under the advice of a faculty member that demonstrates the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking that you have developed during the program. Hence, it is a mandatory requirement for the completion of your degree. However, in a non-thesis master’s program, you are not expected to write a thesis. You are nevertheless required to take additional classes and, by the end of the program, complete a Capstone project, a comprehensive exam, or a summary project.
Master’s thesis and PhD Dissertation: Differences
A Master’s thesis is very different from a PhD dissertation, though often, the words thesis and dissertation are used interchangeably not only by students but also by the wider academic community and publishers.
- A PhD dissertation is an original research by the doctoral candidate that contributes something new to the existing body of knowledge in the field, such as new theories and information. This should not have been published previously. In contrast, a master’s thesis is a scholarly paper that involves original testing of ideas and demonstrates the knowledge and skills the student has acquired and built during the master’s program.
- A master’s thesis deals or engages more with existing research or secondary knowledge, though depending on the subject, there can be research of primary sources as well. Here, the student certainly has to bring in their critical and analytical skills. The sources of data will generally be research papers, scholarly books, journal articles, government reports, statistics, and so on. However, in a PhD dissertation, the focus is on generating new and novel data, resulting in an original piece of work that external subject experts will evaluate. Hence, apart from the sources of data mentioned for the Master’s thesis, the significant component of sources of data for PhD dissertation will be generated from interviews, focus groups, surveys, laboratory experiments and so on.
- A master’s thesis is presented at the end of the master’s program, which is about one or two years. The thesis is a critical part of completing the degree. A PhD dissertation takes a considerable amount of time, ranging from 4 to 7 years. By this time, the candidate should have completed, apart from their dissertation, other requirements such as fulfilling a set of coursework, attending seminars/ conferences, presenting papers at seminars and publishing papers in peer-reviewed journals.
- The master’s thesis is completed and submitted at the end of the master’s program. The PhD dissertation is presented to earn the PhD degree.
- Another major difference between the two is the length. While a master’s thesis may be between 50 and 100 pages, the Ph.D. dissertation is more detailed, in-depth, and comprehensive, with a length of up to 400 pages.
While all Master’s programs do not have a thesis requirement, completing a thesis provides a scholarly and research foundation for students to pursue higher academic degrees and professional work. A master’s thesis program can be a valuable experience for students interested in pursuing higher academic degrees and professional work in research-focused disciplines.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed. Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Make Your Thesis Supervision Work for You
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)
Authorship in Academia: Ghost, Guest, and Gift Authorship
Quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, you may also like, 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content.
Master's Thesis Guide
A master’s thesis must show that the student truly applies a scientific approach to research and understands the main questions and doctrine related to the chosen topic.
The thesis must also put forth an original contribution, which, as an article, could be published without major corrections. The final text should range in length between 20,000 and 25,000 words but may not exceed 35,000 words (between 100 and 130 pages). The thesis is comprised of the following steps:
- Preparation of a research proposal
- Theoretical framework
- Methodology
- Data collection
- Data analysis
- Thesis preparation
- Thesis defence before a committee of professors
The thesis supervisor, or co-supervisor, will form a thesis committee to help guide the thesis, and may discuss the selection of thesis committee members with the student. The committee will comprise the following members:
- the thesis supervisor or co-supervisor;
- two other professors who have expertise in fields related to the thesis project. One member may be from another faculty.
The student is responsible for submitting through service request the Master's Thesis Committee Member List . This form will state the research topic along with the names of the thesis committee members.
The thesis proposal
The student drafts a thesis proposal, whose length should not exceed 20 pages (excluding tables and list of references) using the following conventions: 1.5 line spacing; Times New Roman, 12-point font; 2.5cm margins, numbered pages and single-side printing.
This document will include the following elements:
- statement of problem;
- theoretical or conceptual framework;
- literature review;
- one or more research questions;
- a methodological framework (e.g. a research plan, participants, tools, procedure);
- the contribution of the research to the field of education;
- a relevant and exhaustive list of references.
The order in which these elements are presented may vary.
Although there is no evaluation grid for the thesis proposal, the committee members will submit written comments to the thesis supervisor before the approval meeting between the thesis supervisor, the committee members and the student.
Thesis approval meeting
The thesis supervisor and the committee members will meet to discuss their evaluation of the thesis proposal with the student, who will be advised on how to improve the quality of his/her research.
In light of this discussion, the thesis committee will take one of the following decisions:
- Option 1: Satisfactory – The student may continue to conduct the research as proposed.
- Option 2: Unsatisfactory – The student may not continue to conduct the research as proposed. In such cases, the reasons for this decision are stated and the student must submit a revised version of the research proposal to the committee and another meeting of the committee must take place. A grade of NS will be entered in the students file.
The supervisor submits a duly completed Approval of the Master of Arts in Education (MA) Thesis Proposal form to the academic secretariat at [email protected] , and a copy of the form is added to the student’s file.
Ethics approval
Once the research proposal has been approved, the student will submit a request for ethics approval for any research involving human subjects to the Office of Research Ethics and Integrity . Students who fail to comply with this requirement may be subject to academic sanctions.
When requesting ethics approval, the student will need to submit a duly signed copy of the Approval of the Master of Arts in Education (MA) Thesis Proposal as proof that the thesis proposal has been approved.
Thesis format
1. monograph thesis.
The monograph thesis is the most usual form in the humanities and social sciences and it resembles a non-fiction book in that it deals in depth with a particular topic.
In a monograph thesis, a student presents a proposition or a “thesis” and the research findings to support it. The student reads existing research on the topics and may accept or reject it partially or totally.
The thesis usually follows a simple overall format: it begins with an introduction, which is followed by a main section or several sections, and ends with a conclusion. The students should keep these in mind but also remember that not all of these components will be required or even recommended for the particular field of study, so it is always best if they check with their own academic unit and supervisor.
For more information please consult the following link: Monograph components .
2. Article-format thesis
Students who wish to write a thesis in an article format must first notify the thesis supervisor, co-supervisor and thesis committee members, and obtain their approval. The student must submit a request at [email protected] for approval from the Faculty’s graduate studies director by checking of the appropriate box on the Approval of the Master of Arts in Education (MA) Thesis Proposal form.
A thesis submitted in article format must meet the following requirements:
- The article must be substantial and equivalent to a monograph. The student must be the sole, or first and principle, author. If the student is not the sole author, the student must have contributed at least two-thirds of the original content and writing of the article. The student must formally specify his/her contribution. The article must be considered equivalent to a master’s thesis.
- The article may have been published during the student’s time as an active student. Alternatively, it may have been submitted for publication, or may be in the form of a manuscript ready for submission for publication, in a peer-reviewed academic journal. If the article has already been published, a copy of the article as published must be included in the thesis, with the permission of the journal. If the committee members require changes or additions, these must be added as an appendix, since a published article cannot be modified.
- The manuscript must be typed, with 1.5 line spacing in 12-point, Times New Roman font with 2.5cm margins. The manuscript must be page numbered, single-paged (printed on one side only) and unbound.
For more information please consult the following link: Components of a thesis in a series of articles.
Submission of the thesis for evaluation
Master’s students must submit a service request through uoZone four weeks before submitting their thesis for evaluation, failing to do so will delay the evaluation process. This request must include the following document:
- The List of examiners for the evaluation of the thesis form that includes at least two eligible internal examiners.
The service request will be sent to the program director for approval.
Review how to submit a service request.
The Approval of the Master's Thesis Deposit form must be signed by all committee members and thesis supervisor and must be submitted with the thesis in uoZone .
Check the Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies website for information on thesis submission, evaluation and defence.
The Thesis Process
The thesis is an opportunity to work independently on a research project of your own design and contribute to the scholarly literature in your field. You emerge from the thesis process with a solid understanding of how original research is executed and how to best communicate research results. Many students have gone on to publish their research in academic or professional journals.
To ensure affordability, the per-credit tuition rate for the 8-credit thesis is the same as our regular course tuition. There are no additional fees (regular per-credit graduate tuition x 8 credits).
Below are the steps that you need to follow to fulfill the thesis requirement. Please know that through each step, you will receive guidance and mentorship.
1. Determine Your Thesis Topic and Tentative Question
When you have completed between 24 and 32 credits, you work with your assigned research advisor to narrow down your academic interests to a relevant and manageable thesis topic. Log in to MyDCE , then ALB/ALM Community to schedule an appointment with your assigned research advisor via the Degree Candidate Portal.
Thesis Topic Selection
We’ve put together this guide to help frame your thinking about thesis topic selection.
Every effort is made to support your research interests that are grounded in your ALM course work, but faculty guidance is not available for all possible projects. Therefore, revision or a change of thesis topic may be necessary.
- The point about topic selection is particularly pertinent to scientific research that is dependent upon laboratory space, project funding, and access to private databases. It is also critical for our candidates in ALM, liberal arts fields (English, government, history, international relations, psychology, etc.) who are required to have Harvard faculty direct their thesis projects. Review Harvard’s course catalog online ( my.harvard.edu ) to be sure that there are faculty teaching courses related to your thesis topic. If not, you’ll need to choose an alternative topic.
- Your topic choice must be a new area of research for you. Thesis work represents thoughtful engagement in new academic scholarship. You cannot re-purpose prior research. If you want to draw or expand upon your own previous scholarship for a small portion of your thesis, you need to obtain the explicit permission of your research advisor and cite the work in both the proposal and thesis. Violations of this policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
2. Prepare Prework for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) Course or Tutorial
The next step in the process is to prepare and submit Prework in order to gain registration approval for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) tutorial or course. The Prework process ensures that you have done enough prior reading and thinking about your thesis topic to benefit from the CTP.
The CTP provides an essential onramp to the thesis, mapping critical issues of research design, such as scope, relevance to the field, prior scholarly debate, methodology, and perhaps, metrics for evaluating impact as well as bench-marking. The CTP identifies and works through potential hurdles to successful thesis completion, allowing the thesis project to get off to a good start.
In addition to preparing, submitting, and having your Prework approved, to be eligible for the CTP, you need to be in good standing, have completed a minimum of 32 degree-applicable credits, including the statistics/research methods requirement (if pertinent to your field). You also need to have completed Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (if pertinent to your field). If you were admitted after 9/1/2023 Engaging in Scholarly Conversation (A and B) is required, if admitted before 9/1/2023 this series is encouraged.
Advising Note for Biology, Biotechnology, and Bioengineering and Nanotechnology Candidates : Thesis projects in these fields are designed to support ongoing scientific research happening in Harvard University, other academic institutions, or life science industry labs and usually these are done under the direction of a principal investigator (PI). Hence, you need to have a thesis director approved by your research advisor prior to submitting CTP prework. Your CTP prework is then framed by the lab’s research. Schedule an appointment with your research advisor a few months in advance of the CTP prework deadlines in order to discuss potential research projects and thesis director assignment.
CTP Prework is sent to our central email box: [email protected] between the following firm deadlines:
- April 1 and June 1 for fall CTP
- September 1 and November 1 for spring CTP.
- August 1 and October 1 for the three-week January session (ALM sustainability candidates only)
- International students who need a student visa to attend Harvard Summer School should submit their prework on January 1, so they can register for the CTP on March 1 and submit timely I-20 paperwork. See international students guidelines for more information.
Your research advisor will provide feedback on your prework submission to gain CTP registration approval. If your prework is not approved after 3 submissions, your research advisor cannot approve your CTP registration. If not approved, you’ll need to take additional time for further revisions, and submit new prework during the next CTP prework submission time period for the following term (if your five-year degree completion deadline allows).
3. Register and Successfully Complete the Crafting the Thesis Proposal Tutorial or Course
Once CTP prework is approved, you register for the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP) course or tutorial as you would any other course. The goal of the CTP is to produce a complete, well-written draft of a proposal containing all of the sections required by your research advisor. Creating an academically strong thesis proposal sets the foundation for a high-quality thesis and helps garner the attention of a well-respected thesis director. The proposal is normally between 15 to 25 pages in length.
The CTP tutorial is not a course in the traditional sense. You work independently on your proposal with your research advisor by submitting multiple proposal drafts and scheduling individual appointments. You need to make self-directed progress on the proposal without special prompting from the research advisor. You receive a final grade of SAT or UNSAT (failing grade).
The CTP for sustainability is a three-week course in the traditional sense and you receive a letter grade, and it must be B- or higher to receive degree credit for the course.
You are expected to incorporate all of your research advisor’s feedback and be fully committed to producing an academically strong proposal leading to a thesis worthy of a Harvard degree. If you are unable to take advice from your research advisor, follow directions, or produce an acceptable proposal, you will not pass the CTP.
Successful CTP completion also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred to the Administrative Board.
Maximum of two attempts . If you don’t pass that CTP, you’ll have — if your five-year, degree-completion date allows — just one more attempt to complete the CTP before being required to withdraw from the program. If you fail the CTP just once and have no more time to complete the degree, your candidacy will automatically expire. Please note that a WD grade counts as an attempt.
If by not passing the CTP you fall into poor academic standing, you will need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before enrolling in the CTP for your second and final time, only if your five-year, degree-completion date allows. If you have no more time on your five-year clock, you will be required to withdraw.
Human Subjects
If your thesis, regardless of field, will involve the use of human subjects (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations), you will need to have your research vetted by the Committee on the Use of Human Subjects (CUHS) of Harvard University. Please review the IRB LIFECYCLE GUIDE located on the CUHS website. Your research advisor will help you prepare a draft copy of the project protocol form that you will need to send to CUHS. The vetting process needs to be started during the CTP tutorial, before a thesis director has been assigned.
4. Thesis Director Assignment and Thesis Registration
We expect you to be registered in thesis soon after CTP completion or within 3 months — no later. You cannot delay. It is critical that once a research project has been approved through the CTP process, the project must commence in a timely fashion to ensure the academic integrity of the thesis process.
Once you (1) successfully complete the CTP and (2) have your proposal officially approved by your research advisor (RA), you move to the thesis director assignment phase. Successful completion of the CTP is not the same as having an officially approved proposal. These are two distinct steps.
If you are a life science student (e.g., biology), your thesis director was identified prior to the CTP, and now you need the thesis director to approve the proposal.
The research advisor places you with a thesis director. Do not approach faculty to ask about directing your thesis. You may suggest names of any potential thesis directors to your research advisor, who will contact them, if they are eligible/available to direct your thesis, after you have an approved thesis proposal.
When a thesis director has been identified or the thesis proposal has been fully vetted by the preassigned life science thesis director, you will receive a letter of authorization from the Assistant Dean of Academic Programs officially approving your thesis work and providing you with instructions on how to register for the eight-credit Master’s Thesis. The letter will also have a tentative graduation date as well as four mandatory thesis submission dates (see Thesis Timetable below).
Continuous Registration Tip: If you want to maintain continued registration from CTP to thesis, you should meet with your RA prior to prework to settle on a workable topic, submit well-documented prework, work diligently throughout the CTP to produce a high-quality proposal that is ready to be matched with a thesis director as soon as the CTP is complete.
Good academic standing. You must be good academic standing to register for the thesis. If not, you’ll need to complete additional courses to bring your GPA up to the 3.0 minimum prior to registration.
Thesis Timetable
The thesis is a 9 to 12 month project that begins after the Crafting the Thesis Proposal (CTP); when your research advisor has approved your proposal and identified a Thesis Director.
The date for the appointment of your Thesis Director determines the graduation cycle that will be automatically assigned to you:
Once registered in the thesis, we will do a 3-month check-in with you and your thesis director to ensure progress is being made. If your thesis director reports little to no progress, the Dean of Academic Programs reserves the right to issue a thesis not complete (TNC) grade (see Thesis Grading below).
As you can see above, you do not submit your thesis all at once at the end, but in four phases: (1) complete draft to TA, (2) final draft to RA for format review and academic integrity check, (3) format approved draft submitted to TA for grading, and (4) upload your 100% complete graded thesis to ETDs.
Due dates for all phases for your assigned graduation cycle cannot be missed. You must submit materials by the date indicated by 5 PM EST (even if the date falls on a weekend). If you are late, you will not be able to graduate during your assigned cycle.
If you need additional time to complete your thesis after the date it is due to the Thesis Director (phase 1), you need to formally request an extension (which needs to be approved by your Director) by emailing that petition to: [email protected] . The maximum allotted time to write your thesis, including any granted extensions of time is 12 months.
Timing Tip: If you want to graduate in May, you should complete the CTP in the fall term two years prior or, if a sustainability student, in the January session one year prior. For example, to graduate in May 2025:
- Complete the CTP in fall 2023 (or in January 2024, if a sustainability student)
- Be assigned a thesis director (TD) in March/April 2024
- Begin the 9-12 month thesis project with TD
- Submit a complete draft of your thesis to your TD by February 1, 2025
- Follow through with all other submission deadlines (April 1, April 15 and May 1 — see table above)
- Graduate in May 2025
5. Conduct Thesis Research
When registered in the thesis, you work diligently and independently, following the advice of your thesis director, in a consistent, regular manner equivalent to full-time academic work to complete the research by your required timeline.
You are required to produce at least 50 pages of text (not including front matter and appendices). Chapter topics (e.g., introduction, background, methods, findings, conclusion) vary by field.
6. Format Review — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
All ALM thesis projects must written in Microsoft Word and follow a specific Harvard University format. A properly formatted thesis is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without it.
Your research advisor will complete the format review prior to submitting your thesis to your director for final grading according to the Thesis Timetable (see above).
You must use our Microsoft Word ALM Thesis Template or Microsoft ALM Thesis Template Creative Writing (just for creative writing degree candidates). It has all the mandatory thesis formatting built in. Besides saving you a considerable amount of time as you write your thesis, the preprogrammed form ensures that your submitted thesis meets the mandatory style guidelines for margins, font, title page, table of contents, and chapter headings. If you use the template, format review should go smoothly, if not, a delayed graduation is highly likely.
Format review also includes a check on the proper use of sources according to our academic integrity guidelines. Violations of our academic integrity policy will be referred directly to the Administrative Board.
7. Mandatory Thesis Archiving — Required of all Harvard Graduate Students and Part of Your Graduation Requirements
Once your thesis is finalized, meaning that the required grade has been earned and all edits have been completed, you must upload your thesis to Harvard University’s electronic thesis and dissertation submission system (ETDs). Uploading your thesis ETDs is an explicit degree requirement; you cannot graduate without completing this step.
The thesis project will be sent to several downstream systems:
- Your work will be preserved using Harvard’s digital repository DASH (Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard).
- Metadata about your work will be sent to HOLLIS (the Harvard Library catalog).
- Your work will be preserved in Harvard Library’s DRS2 (digital preservation repository).
By submitting work through ETDs @ Harvard you will be signing the Harvard Author Agreement. This license does not constrain your rights to publish your work subsequently. You retain all intellectual property rights.
For more information on Harvard’s open access initiatives, we recommend you view the Director of the Office of Scholarly Communication (OSC), Peter Suber’s brief introduction .
Thesis Grading
You need to earn a grade of B- or higher in the thesis. All standard course letter grades are available to your thesis director. If you fail to complete substantial work on the thesis, you will earn a grade of TNC (thesis not complete). If you have already earned two withdrawal grades, the TNC grade will count as a zero in your cumulative GPA.
If you earn a grade below B-, you will need to petition the Administrative Board for permission to attempt the thesis for a second and final time. The petition process is only available if you are in good academic standing and your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time. Your candidacy will automatically expire if you do not successfully complete the thesis by your required deadline.
If approved for a second attempt, you may be required to develop a new proposal on a different topic by re-enrolling in the CTP and being assigned a different thesis director. Tuition for the second attempt is calculated at the current year’s rate.
If by not passing the thesis you fall into poor academic standing, you’ll need to take additional degree-applicable courses to return to good standing before re-engaging with the thesis process for the second and final time. This is only an option if your five-year, degree-completion deadline allows for more time.
The Board only reviews cases in which extenuating circumstances prevented the successful completion of the thesis.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Graduate School
How to Write a Master's Thesis Proposal
How to write a master’s thesis proposal is one of the most-asked questions by graduate students. A master's thesis proposal involves a copious amount of data collection, particular presentation ethics, and most importantly, it will become the roadmap to your full thesis. Remember, you must convince your committee that your idea is strong and unique, and that you have done enough legwork to begin with the first few drafts of your final thesis. Your proposal should serve as a foundational blueprint on which you will later build your entire project. To have the perfect thesis proposal, you need to have original ideas, solid information, and proper presentation. While it is a good idea to take assistance from thesis writing services , you still need to personally understand the elements that contribute to a master’s thesis proposal worthy of approval. In this blog, we will discuss the process of writing your master’s thesis proposal and give you tips for making your proposal strong. Stay tuned!
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 8 min read
How to decide the goals for your master's thesis.
If you are pursuing a master’s or a PhD , you will be undertaking a major research paper or a thesis. Thus, writing a thesis proposal becomes inevitable. Your major objective for pursuing a master’s degree is to improve your knowledge in your field of study. When you start your degree, you delve deeper into different concepts in your discipline and try to search for answers to all kinds of questions. If you come across a question that no one can answer, you can select that question as your research thesis topic.
A master's thesis proposal will have multiple sections depending on your decided layout. These sections will continuously support your argument and try to convince the reader of your core argument. The structure will also help you arrange the various parts of the paper to have a greater impact on the readers. A paper should always begin with you giving a brief summary of the topic and how you have come across it. The introduction is particularly important because it will give the readers a brief idea about the topic of discussion and win their interest in the matter.
After the summary has been given, slowly you need to progress into the body of the thesis proposal which would explain your argument, research methodology, literary texts that have a relation to the topic, and the conclusion of your study. It would be similar to an essay or a literary review consisting of 3 or 4 parts. The bibliography will be placed at the end of the paper so that people can cross-check your sources.
Let's take a look at the sections most master's thesis proposals should cover. Please note that each university has its own guidelines for how to structure and what to include in a master’s thesis proposal. The outline we provide below is general, so please make sure to follow the exact guidelines provided by your school:
Restate your primary argument and give us a glimpse of what you will include in the main master\u2019s thesis. Leave the reader wanting more. Your research proposal should talk about what research chapters you are trying to undertake in your final thesis. You can also mention the proposed time in which you will complete these chapters. ","label":"Conclusion and proposed chapters","title":"Conclusion and proposed chapters"}]" code="tab1" template="BlogArticle">
A thesis proposal needs to be convincing enough to get approval. If the information is not enough to satisfy the evaluation committee, it would require revision. Hence, you need to select and follow the right methodology to make your argument convincing. When a research proposal is presented, the reader will determine the validity of your argument by judging the strength of your evidence and conclusions. Therefore, even writige:ng a proposal will require extensive research on your part. You should start writing your thesis proposal by working through the following steps.
Interested in a summary of the points covered below? Check out this infographic:
Exploring your topic in detail
You need to delve deeper into your chosen topic to see if your idea is original. In the process of this exploration, you will find tons of materials that will be supportive of your argument. When choosing your research topic and the problem you want to explore, you should always consider your primary research interest (yes, the one which you had mentioned in your research interest statement during grad school applications) for a better master’s thesis. You have a high probability of performing better in an area that you have always liked as compared to any other research area or topic.
Reviewing the literature
You have to include all the sources from where you have formed your argument and mention them in the thesis proposal. If you neglect to mention important source texts, the reader may consider it to be plagiarism. Furthermore, you want to keep track of all your research because it will be easier to provide references if you know the exact source of each piece of information.
Finding opposing arguments for your study
You should also mention any texts that would counter your argument and try to disprove their claims in the thesis. Make sure to use evidence if you try to disprove the counterarguments you face.

Emphasizing the importance of your research
At the end of the thesis proposal, you need to convince the reader why your proposal is important to your chosen field of study, which would ultimately help you in getting your topic approved. Thus, it is essential to outline the importance of your research thoroughly.
Drafting your proposal
After doing proper research, you should go ahead and draft your proposal. Remember you will not get it right in just one draft, it will take at least 50 attempts to come up with a satisfactory proposal. You should proofread your draft several times and even have a fellow student review it for you before sending it further to your research supervisor.
Getting your proposal evaluated by your supervisor
After you have written sufficient drafts, you need to get your proposal evaluated by your research supervisor. This is necessary to meet the graduate research requirements. It will ensure the clarity and correctness of your proposal. For your supervisor to evaluate your proposal, you should complete the research methodology part along with sufficient proposed work.
Since your supervisor will play a crucial role in your master's research thesis, you must choose a supervisor who can be your ultimate guide in writing your master's thesis. They will be your partner and support system during your study and will help you in eliminating obstacles to achieving your goal.
Choosing the ideal supervisor is a pretty daunting task. Here’s how you can go about the process:
You should approach your professor with an open mind and discuss the potential goals of your research. You should hear what they think and then if you both mutually agree, you can choose them as your supervisor for your master\u2019s thesis. "}]">
Length of a Master’s Thesis Proposal
The length of a master’s thesis proposal differs from university to university and depends on the discipline of research as well. Usually, you have to include all the above-mentioned sections, and the length is around 8 pages and can go up to 12-15 pages for subjects such as the liberal arts. Universities might also define the number of words in the guidelines for your master’s thesis proposal and you have to adhere to that word limit.
Are you debating between pursuing a Masters or a PhD? This video has details that can help you decide which is best for you:
How to Format a Research Thesis Proposal Correctly?
Now that you know how to write a thesis proposal, you must make it presentable. Although your school might give your specific instructions, you can keep in mind some of the general advice:
- You can use some basic font like Times New Roman and keep the font size to 10 or 12 points.
- The left margin should be 1.5 inches and all other margins should be 1 inch each.
- You should follow double-spacing for your content.
- The first line of paragraphs should be indented 0.5 inches and the paragraphs should be left or center aligned.
Tips to Write a Strong Master's Thesis Proposal
When you are writing your master’s thesis proposal, you should keep these tips in mind to write an excellent master’s thesis proposal with all the correct elements to get approval from the evaluating committee:
Select your research objectives wisely
You should be clear on what you wish to learn from your research. Your learning objectives should stem from your research interests. If you are unsure, refer to your grad school career goals statement to review what you wanted out of grad school in the first place. Then, choose your objectives around it.
Write a clear title
The title of your research proposal should be concise and written in a language that can be understood easily by others. The title should be able to give the reader an idea of your intended research and should be interesting.
Jot down your thoughts, arguments, and evidence
You should always start with a rough outline of your arguments because you will not miss any point in this way. Brainstorm what you want to include in the proposal and then expand those points to complete your proposal. You can decide the major headings with the help of the guidelines provided to you.
Focus on the feasibility and importance
You should consider whether your research is feasible with the available resources. Additionally, your proposal should clearly convey the significance of your research in your field.
Use simple language
Since the evaluation committee can have researchers from different subject areas, it is best to write your proposal in a simple language that is understandable by all.
Stick to the guidelines
Your university will be providing the guidelines for writing your research proposal. You should adhere to those guidelines strictly since your proposal will be primarily evaluated on the basis of those.
Have an impactful opening section
It is a no-brainer that the opening statement of your proposal should be powerful enough to grasp the attention of the readers and get them interested in your research topic. You should be able to convey your interest and enthusiasm in the introductory section.
Peer review prior to submission
Apart from working with your research supervisor, it is essential that you ask some classmates and friends to review your proposal. The comments and suggestions that they give will be valuable in helping you to make the language of your proposal clearer.
You have worked hard to get into grad school and even harder on searching your research topic. Thus, you must be careful while building your thesis proposal so that you have maximum chances of acceptance.
If you're curious how your graduate school education will differ from your undergraduate education, take a look at this video so you know what to expect:
Writing the perfect research proposal might be challenging, but keeping to the basics might make your task easier. In a nutshell, you need to be thorough in your study question. You should conduct sufficient research to gather all relevant materials required to support your argument. After collecting all data, make sure to present it systematically to give a clearer understanding and convince the evaluators to approve your proposal. Lastly, remember to submit your proposal well within the deadline set by your university. Your performance at grad school is essential, especially if you need a graduate degree to gain admission to med school and your thesis contributes to that performance. Thus, start with a suitable research problem, draft a strong proposal, and then begin with your thesis after your proposal is approved.
In your master’s thesis proposal, you should include your research topic and the problem statement being addressed in your research, along with a proposed solution. The proposal should explain the importance and limitations of your research.
The length of a master’s thesis proposal is outlined by the university in the instructions for preparing your master’s thesis proposal.
The time taken to write a master’s thesis proposal depends upon the study which you are undertaking and your discipline of research. It will take a minimum time of three months. The ideal time can be around six months.
You should begin your master’s thesis proposal by writing an introduction to your research topic. You should state your topic clearly and provide some background. Keep notes and rough drafts of your proposal so you can always refer to them when you write the first real draft.
The basic sections that your master’s thesis proposal should cover are the problem statement, research methodology, proposed activities, importance, and the limitations of your research.
A master’s thesis proposal which clearly defines the problem in a straightforward and explains the research methodology in simple words is considered a good thesis proposal.
You can use any classic font for your master’s thesis proposal such as Times New Roman. If you are recommended a specific font in the proposal guidelines by your institution, it would be advisable to stick to that.
The ideal font size for your master’s thesis proposal will be 10 or 12 points.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webinar:
How to make your grad school application stand out, (and avoid the top 5 mistakes that get most rejected).
Time Sensitive. Limited Spots Available:
We guarantee you'll get into grad school or you don't pay.
Swipe up to see a great offer!
Types of Theses
Three types of gallatin ma theses.
Each graduate student in the Gallatin School completes a final thesis as the culmination of their work toward a Master of Arts degree. The thesis may take one of three forms: a research thesis, an artistic thesis, or a project thesis. In each case, the thesis represents a synthesis of the student’s accumulated knowledge and skill and an opportunity to display the ideas, practices and skills learned through the program. While the master’s thesis, unlike a doctoral dissertation, does not have to create new knowledge or break new ground, it does display the student’s ability to go beyond the mere collection of information into synthesis, analysis, judgment and interpretation. Moreover, it should demonstrate the student’s familiarity with a substantial body of thought and literature and illustrate mastery of some self-chosen field of study.
Below you will find descriptions of the three types of theses:
Research Thesis
Artistic thesis, project thesis.
Current MA students who are interested in seeing sample theses should consult the Gallatin Master's Thesis Archive , which is accessible with an NYU Net ID.
Students pursuing the research option produce and defend a substantial research essay, the thesis of which is demonstrably related to the student’s course of study and ongoing conversations with the primary adviser. The adviser and defense panelists are the ultimate arbiters of whether the thesis satisfies a reasonable understanding of a project worthy of the master’s degree. However, in general and at minimum, a successful Gallatin MA research thesis demonstrates sufficient mastery of relevant academic fields as well as a critical grasp of the scholarship and methods that currently define those fields. The thesis essay is a logically-constructed argument that presents its central points on the basis of research and critical interpretation. The sources and objects of study may cover the spectrum from archival materials to critical theory to statistical surveys and personal interviews, but the student should carefully choose sources in consultation with the primary adviser, and with reference to questions about what constitutes legitimate source within the student’s field(s). The research thesis essay must be more than a "review of the literature" but the demand for original findings is lower than that faced by doctoral candidates. Significantly original contributions are of course highly commendable, but the excellence of an MA research thesis essay may lie in its critical and creative synthesis, articulation of a fresh perspective on the work of others, or identification of new, research-based questions that themselves shed light on existing problems within fields. Generally speaking, the final research thesis essay should be at least 50 pages and not exceed 80 pages (not including appendices and bibliographic material). Students and advisers are encouraged to talk with the program's academic directors about these expectations whenever necessary.
back to top
The artistic thesis is appropriate for those students who wish to display the creative process in the performing, visual or literary arts. A student might make a film or video; choreograph an evening of dance; act in a play; mount an exhibit of paintings; write a screenplay, novel, play or collection of short stories; or choose another artistic endeavor. The artistic thesis represents the culmination of a Gallatin arts concentration in which the student has studied the genre under consideration.
The artistic thesis comprises both the artistic project and three accompanying essays. Therefore, you should conceive of the artistic thesis as a unified piece composed of the creative work and the essays which enhance it. Members of the faculty committee will assess both the artistic work and the essays. The essays include:
- an academic research paper related to the field of artistic work;
- an essay on artistic aims and process;
- a technical essay.
Please note: The technical essay does not apply to those students who are submitting a literary work.
Some General Advice
Be careful to keep records and a log of the artistic project as it evolves. This information can be used in the Technical Essay.
If a student is writing a work of fiction, poems, a play, etc., for the thesis, the student will submit this work to their adviser and other readers along with the essays. However, if the student is presenting a performance, they will need to arrange to have their adviser and other members of their committee see the performance. The student is responsible for coordinating schedules and for notifying committee members so that everyone can view the piece. The student should notify the thesis reviewer of the date of the performance at least one month in advance. In the event that one or more of the committee cannot attend the scheduled event, the student should arrange to have the performance videotaped so people can see it later. Except in unusual circumstances, the student must submit the first draft of the thesis to their adviser no more than three months after the performance.
Essays for the Artistic Thesis
Background Research Essay
As stated above, this essay follows the description for the standard research essay. It is a scholarly endeavor and differs from the standard essay in terms of length and focus. The length is approximately 25 to 40 pages. The focus of the essay is related to the artistic work and explores some aspect of that work that the student wishes to study and develop through outside research. The essay might take the form of an analysis of a performance or literary genre; a history of an art form or phenomenon; a philosophical study of an aesthetic concept; or a critical/biographical analysis of the work of an influential artistic figure.
Artistic Aims Essay
In this essay, the student is required to articulate their goals in mounting their particular artistic project. For example, what was the student trying to accomplish in writing short stories, a screenplay, a novel, presenting an evening of dances or songs, making a film or mounting an art exhibit? What were the aesthetic choices made and why? The student should also explain their approach to the artistic work (their style, genre, or school), any relevant influences on the work, how the student's training influenced their artistic choices, and the student's intentions for particular elements of the creative work. After the student has carefully and clearly articulated these goals, they need to explain how their actual artistic work meets the stated goals. The student should use examples from their artistic project to illustrate these ideas. This essay should be approximately 10-15 pages in length.
Technical Essay
This essay is a description of the steps the student actually took to physically mount their production. The student will need to include such technical details as arranging for rehearsal and performance space; choosing the performers; finding/creating, costumes, materials, lights; raising funds and getting institutional support. This essay should be approximately 10 pages in length.
Students may submit a portfolio, if appropriate. This would consist of any material, such as photos, slides, fliers, programs, videotapes, audiotapes etc. which might constitute an appendix and which might be helpful to a fuller understanding of the thesis.
The project thesis consists of two elements: (1) the project, a professional activity designed and executed primarily by the student as a way of solving a problem, and (2) an accompanying essay about the project. This thesis is especially appropriate for students in such fields as business, education, social work or public administration. The project thesis may appeal to those students who are active in their profession and who take responsibility for the creation of some kind of program or practice.
Students should understand that the project cannot simply propose a professional activity; the design for such an activity must actually be carried out (at least in a pilot version) and evaluated. Some examples of projects: a student in education may develop and apply a new strategy for teaching reading to recent immigrants; a person working in a corporation may construct new methods for managing financial information; or a community worker in a settlement house may organize a group of local residents to combat drug abuse.
At each step, the student should be careful to keep in touch with their adviser and with any other expert who can help them in their process. The student should keep careful records of the process by taking detailed notes of conversations, meetings, interviews, etc. If at all possible, the student should arrange to have the members of their committee, especially their adviser, witness the project first-hand: Visit the site, talk with key actors, watch the program in operation. (This direct contact is highly recommended, but not required.)
Essays for the Project Thesis
The project thesis essay may take a number of forms and include a range of information. It ought to discuss at least the following elements:
Consider the institutional or social context within which the project takes place. Describe the organization, the potential clientele or participants, and the larger environment (social, economic and political conditions surrounding the problem and the project).
Describe the particular problem or need that you address in the project. What causes that problem? How extensive is it? Have other attempts to solve the problem been made; if so, what were their shortcomings, and why are you trying another approach? Place the problem in its professional and academic context by referring to the appropriate literature. Program
Describe the goals and objectives of the project and what the student hoped to accomplish. Describe how the program was designed and structured; for example, what kinds of activities did participants engage in, and in what sequence? What kinds of resources and techniques were used? Justify the strategies and tactics used by citing appropriate professional and academic literatures.
Implementation
Describe how the plan was carried out. Use as much detail as needed to give the reader a sense of what actually happened, and to indicate the extent to which the reality matched the plan.
Describe the criteria for assessing the project and evaluation methods used. Justify the criteria and methods by referring to appropriate literatures. To what extent did the project accomplish the goals and objectives identified earlier?
Citing relevant literature and the practical contingencies of the project, explain why the project did or did not achieve its stated purposes. Describe the factors (political, social, organizational, financial, psychological, etc.) that contributed to the process and to the outcomes. What changes--either conceptual or practical--would the student make if they were to repeat or extend the project? What would the student leave in place? Describe what was learned from the project about the original problem and about the student's strategy and tactics. Also consider the professional and theoretical implications of the project.
If necessary, put relevant documentary materials (flyers, important correspondence, budgets, etc.) in appendices.
Master’s Program Research, Thesis, and Capstone Information
General research and thesis information.
All Boston University theses and dissertations are submitted to the library electronically. Submitting your thesis or dissertation to Boston University Libraries is the last step to fulfill at the University before you graduate and are awarded your degree. A diploma application must be submitted prior to this step. Use only the Thesis template GMS provides, do not use any other templates.
- Guide for Writers of Dissertation and Thesis
- GMS Thesis Guideline Landscape Page Numbering
- GMS Faculty List
- IRB 101 for BUMC Graduate Students IRB Submission with Mary-Tara Roth, Director, Clinical Research Resources Office (CRRO). View Video Recording or Slides.
- Research Support
- Video Tutorials for Thesis & Dissertation Electronic Submission
- The Mugar Library requires that a copyright page be added to all theses/dissertations. Please add a copyright page after the title page and include it on the Table of Contents. Make sure you re-number all the preliminary pages appropriately. Adding the copyright page does not mean you must register for copyright. You can find a sample of the copyright page in the Masters Thesis Prepage Template (updated Jan/2014).
- Dissertation-and-Thesis-Formatting-Tips-2023
- Spellcheck Tutorial
- Do not use google documents to write your thesis.
- When graduate students submit a dissertation to the Library via the online ETD Administrator, they are now able to complete the process with an online payment. If you have any questions about this service you can contact Brendan McDermott, Thesis/Dissertation Coordinator at [email protected] or (617) 353-9387.
- Sample Embargo Letter Requesting Circulation Restriction for Thesis Most students do not request delayed circulation however if desired (due to special circumstances such as a pending patent), you will need to submit an Embargo letter requesting Circulation Restriction – embargo options are one year or two years. Embargo letter must be signed by student and primary reader and submitted to the GMS Registrar with the final thesis/dissertation paperwork by the deadline. Signature from the GMS Provost will be obtained by the GMS Registrar.
Master's GMS Thesis Template & Capstone Information
- NOTE: The Research Guide For Writers Of Theses (#1 above) There is no longer a word limit to the length of the abstract, but please be concise.
- NOTE: Minimum length for MAMS theses is 40 pages (research thesis) or 45 pages (literature thesis), excluding the Prepages, Appendices, References and Vita.
- Biomedical Research Technologies Capstone Information
- Clinical Research Capstone Project, Practicum and Directed Study Information
- Genetic Counseling Capstone Project Information
- Health Professions Education Practicum and Capstone Guidelines
- Oral Health Sciences Capstone & Thesis Information
Required Plagiarism Check Prior to Thesis Submission
All capstone, and thesis documents must be scanned using Turnitin plagiarism detection software prior to final submission to your Program/ Department and the Registrar.
- Turnitin similarity report must be approved by your mentor, advisor, first reader (BU faculty) or external committee member(s) depending on the GMS program.
- Turnitin similarity report must be submitted to your program director prior to thesis submission to the registrar
- This is the student’s responsibility.
Turnitin Directions : Turnitin compares your work with existing online publications and allows you to confidentially check your written work for potential plagiarism. With a close inspection of the Turnitin results, you may also identify incorrect quotations and missing citations. All students have access to the online tool throughout their time in GMS. Directions and tips for usage can be found here .
If you have problems with Turnitin please reach out to Dr. Theresa Davies for assistance ( [email protected] )
Google Doc Turnitin Draft Coach : If you use Google Doc for writing your paper, you also have the option to use Google Doc Turnitin Draft Coach for checking the initial drafts of your work. However, note that as a requirement for submitting your thesis, you should generate and download the Turnitin similarity report through this GMS Plagiarism Check Blackboard course.
Thesis Electronic Signatures
Electronic Signatures For MA & MS Students: Provisional acceptanc e by Boston University Libraries of electronic signatures in lieu of original signatures on the separately submitted and signed Readers’ Approval pages through electronic signatures or signature images have been extended for theses and dissertations for the January 2024 graduation deadline. There are several options for signature, such as electronic via Adobe Acrobat or inserting a signature image. The students should work with their first and second readers to find the best solution and follow guidelines sent by the GMS Registrar’s Office [email protected].
BU Open Access Information and ProQuest
- Open Access Information
- Open Access FAQ’s
- FAQ: Embargoes & Electronic Theses & Dissertations (ETD)
ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
- Theses electronically submitted in 2014 or later are now searchable via Proquest
Master's Thesis Research
Prereq: All course work toward the degree must be completed. Note: Registration for this course is not available via telephone (UK-VIP) or webUK. For enrollment information contact the Graduate School at 257-4905.
Half-time to full-time work on thesis. May be repeated to a maximum of six semesters.
- Communications
- Computer Science
- Criminal Justice
- Environmental Management
- Forensic Psychology
- Healthcare Admin
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Social work
- Special Education
- Sports Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Adult Education
- Business Intelligence
- Early Childhood Education
- Educational Technology
- Homeland Security
- Information Systems Security
- Information Technology
- International Business
- Management Information Systems
- Nonprofit Management
- School Counseling
- Academic Publishing Guide
- Building a Graduate School Resume or CV
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
- Expert Guide to Studying Abroad
- FAQ: Online Master's Degrees
- Grad School Guide Book
- Graduate School for Students with Disabilities
- Green Graduate Degrees
- How to Be a Successful Grad Student
- How to Choose the Right Graduate Program
- How to Get a Master's Degree in an Unrelated Field
- How to Transfer College Credits in Grad School
- How to Write a Winning Personal Statement
- Inside Graduate Admissions
- Ivy League Grad Schools
- Master's Degrees for Veterans
- Master's Degree for Women
- Mental Health in Grad School
- Progressive LGBTQ Graduate Degrees
- Should You Apply for a Graduate School Assistantship?
- Surviving Grad School with a Family
- Taking a Gap Year Before Grad School
- Women in STEM Graduate Resources
- Writing a Successful Statement of Purpose
- Alternative Ways to Pay for School
- The Best Part-Time Jobs During Grad School
- Company Funded Graduate School
- FAFSA For Grad Students
- Financial Aid Resources
- Graduate Student Loans
- Paying for Your Master's Degree
- Paying Off Student Loans
- Paying for Your PhD
- Fellowship Opportunities
- LGBTQ Scholarships
- MBA Scholarships
- Scholarship Resources
- Scholarships for Veterans
- Scholarships for Women
- Crushing the GRE Guidebook
- GMAT Guidebook
- Guide to the LSAT
- MCAT Prep for Medical School
- Study Guide: Exam Resources
- TOEFL Prep for Non-Native English Speakers
- Resources Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree
As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees , with more citizens joining these ranks each year. As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations. When considering their options, many question whether to enroll in a master's requiring a thesis or not. The following guide examines some of the reasons degree seekers may want to write a thesis while also highlighting why they might not. Students on the fence about this important decision can find expert advice, actionable tips, and relevant guidance to help them make an informed choice in the guide that follows.
Understanding the Master's Thesis
What is the difference between a thesis & non-thesis master's program, the decision not to do a thesis.
As students research various master's programs in their chosen discipline, it's common to find that many degrees require a thesis – especially if they want to enter a research-heavy field. While this word gets thrown around a lot in academia, some learners may want more information regarding what it entails in order to make an informed decision.
What is a Master's Thesis?
The master's thesis is an original piece of scholarship allowing the student to dig into a topic and produce an expanded document that demonstrates how their knowledge has grown throughout the degree program. These documents require significant independent research of primary and secondary sources and, depending on the subject, may require interviews and/or surveys to support the overarching argument.
Individual schools and departments dictate the length of these documents, but they typically range between 60 and 100 pages – or approximately 20,000 to 40,000 words. While tackling a document of such heft may seem overwhelming at first, learners need not fret. Each master's candidate receives a faculty advisor early in their tenure to provide support, feedback, and guidance throughout the process. Because the final thesis is expected to be of a publishable quality, learners seeking the highest marks typically send their supervisor excerpts of the document as they write to ensure they are on the right track.
When picking a thesis topic, no magical formula exists. Students should consider their interests and read extensively on that topic to get a better sense of existing scholarship. They should also speak to other academics working in that sphere to familiarize themselves with ongoing projects. Only after they feel reasonably well-read should they begin looking for uncovered angles or interesting ways of using emerging methodologies to bring new light to the topic.
When considering formatting, degree seekers should check with their specific schools and departments, as they may have unique requirements. To get a general understanding of what to expect, learners can review Simon Fraser University's guidelines on thesis formatting. After completing the thesis, some programs require an oral defense before a committee while others read the document and provide a grade. Check with your prospective schools to get a better sense of procedure.
Format & Components of a Master's Thesis
While this guide attempts to provide helpful and actionable information about the process of deciding whether to follow a thesis or non-thesis track in a master's program, readers should remember that specific components and requirements of a thesis vary according to discipline, university, and department. That being said, some commonalities exist across all these – especially when it comes to what students must include in their final drafts.
As the first section a reader encounters after moving through the table of contents and other anterior text, the introductory allows the writer to firmly establish what they want to accomplish. Sometimes also called the "research question" section, the introductory must clearly state the goals of the paper and the overarching hypothesis guiding the argument. This should be written in a professional yet accessible tone that allows individuals without specializations in the field to understand the text.
This section allows learners to demonstrate their deep knowledge of the field by providing context to existing texts within their chosen discipline Learners review the main bodies of work, highlighting any issues they find within each. Constructive criticism often centers around shortcomings, blind spots, or outdated hypotheses.
Students use this section to explain how they went about their work. While scientists may point to a specific method used to reach conclusions, historians may reference the use of an emerging framework for understanding history to bring new light to a topic. The point of this section is to demonstrate the thought processes that led to your findings.
This section allows for learners to show what they learned during the research process in a non-biased way. Students should simply state what information they gathered by utilizing a specific framework or methodology and arrange those findings, without interpretation, in an easy-to-read fashion.
After providing readers with all the necessary information, the discussion section exists for candidates to interpret the raw data and demonstrate how their research led to a new understanding or contributed a unique perspective to the field. This section should directly connect to the introduction by reinforcing the hypothesis and showing how you answered the questions posed.
Even though the previous sections give prospective degree seekers a better sense of what to expect if they decide to write a thesis during their master's program, they don't necessarily help learners decide whether to pursue a thesis or non-thesis track. The following section highlights some of the reasons students frequently choose to complete a thesis or bypass the process altogether by providing a pros and cons list.
Why a Thesis Program
- Especially when entering a research-heavy discipline, completing a thesis shows prospective schools and employers that you possess the skills needed for researching and writing long-form reports.
- Students hoping to pursue a Ph.D. stand in better stead with admissions panels if they wrote a thesis during a master's program.
- Individuals hoping to enter a field that values syntax and grammar often better their writing skills by completing a thesis.
- Students who write a thesis can submit the final product to various academic journals, increasing their chances of getting published.
- Theses expand students' understanding of what they're capable of, deepen their ability to carry out an argument, and develop their skills in making connections between ideas.
Why a Non-thesis Program
- Because they don't require a significant written product, non-thesis master's tend to take less time to complete.
- Often mirrors a bachelor's program in terms of structure, allowing learners to complete classes and take exams without a great deal of research or writing.
- Students who excel in project-based assignments can continue building skills in this arena rather than focusing on skills they don't plan to use (e.g. research)
- Provides learners the opportunity to work more closely and more frequently with faculty on real-world projects since they don't spend hundreds of hours researching/writing.
- Allows learners to take more classes and gain hands-on skills to fill the time they would have spent researching and writing a thesis.
How to Choose a Master's Program: FAQs
Within some academic disciplines and professional fields, research and writing plays a key role in work done on a daily basis. Because of this, master's programs in these fields require learners to complete theses to compete against peers and be seen as competent in their work. Other disciplines, conversely, rely on other tools to accomplish work and progress ideas – making theses less important.
Yes. Master's programs focused more on application than research typically don't require a thesis – although they may still give students the option. Examples of common non-thesis master's programs include nursing, business, and education.
Even though non-thesis students won't be writing a 100-page paper, that doesn't mean they avoid completing a significant project. In place of a thesis, most applied master's programs require students to take part in at least one internship or complete a culminating project. These projects typically ask learners to take what they learned throughout coursework and create an expansive final project – examples include case studies, creative works, or portfolios.
While students who followed a non-thesis path routinely receive acceptance to Ph.D. programs, those with theses often find the process easier. Even if a learner pursues a Ph.D. in a discipline that isn't research-heavy, admissions panels still want to get a sense of your academic interests and ability to engage in independent, nuanced thought. Students with theses can provide solid proof of these skills, while those without may struggle to demonstrate preparedness as thoroughly.
The answer to this question depends on many factors, but typically it is okay not to do a thesis if you plan to enter a field that doesn't depend heavily on research or writing, or if you don't plan to complete a Ph.D.
Students wanting to work in academic, research, or writing should always opt for the thesis track. They should also follow this path if they have any doctoral degree aspirations.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to complete a thesis rests with the individual student. Figuring out how to proceed on this front requires lots of careful consideration, and learners should ensure they consider various aspects before coming to a final decision. The following section helps students consider how they should and should not come to a conclusion.
Dos and Don'ts of Choosing a Thesis or Non-thesis Program
- Consider the longevity of your decision: will you feel the same in 5-10 years or are you making a decision based on current desires?
- Talk to others who with experience in this area. Ask them questions about their decision-making process and if they regret their choice.
- Research potential thesis topics before starting a program. Going in with a game plan can help you feel more confident and settled about the process than if you're scrambling for a topic while in school.
- Reach out to prospective schools to speak with faculty and/or current students following both tracks. This will provide knowledge specific to the school while also expanding your network if you choose to attend there.
- Research Ph.D. entrance requirements to ascertain if the majority expect learners to possess a thesis when applying. This will give you a sense of whether you may experience issues later on if you do not complete one.
- Decide not to complete a thesis simply because you have never taken on such a task and feel overwhelmed or fearful that you will fail.
- Complete a thesis simply because you think it will look good on your resume. Theses require intense devotion over an extended amount of time; learners who complete them without conviction often find the process miserable.
- Forget to research alternatives to writing a thesis. Just because you don't complete a research paper doesn't mean a non-thesis track lacks rigor or challenging coursework.
- Forget to read examples of theses by previous students. If you feel overwhelmed by the task, reading work other people have done can often make the task at hand feel less scary.
- Let yourself off easy by taking the non-thesis path. If you find you have extra time in the program, talk to your advisor about taking more classes, develop meaningful projects for yourself, or see about presenting at an academic conference.
From the Expert

Sudiksha Joshi, Ph.D. is a learning advocate. Her mission is to empower our youth to think bigger, bolder thoughts and forge a career path that will change the world. She taps into her natural curiosity and ability to identify strengths to help students and those in transition find their path from feeling lost in the traditional ways of achieving success to charting their own path. Her work has been featured in Forbes, Huffington Post, Thrive Global, Medium and LinkedIn.
Why might a student decide to follow a thesis track? Why might they follow a non-thesis track?
A student might decide to take a thesis track if she/he wants to pursue a Ph.D. Also, if the students want to focus on careers where research and writing have a strong focus, the students opt for the thesis option. Research assistantships at the graduate level are also more often available to students who opt for the thesis option.
A student who might feel that writing is not one of their strengths might choose to go the non-thesis track. Likewise, a student who has other work commitments may find a non-thesis option more convenient.
Do you have any tips for deciding on a program?
I chose a thesis option because being able to conduct independent research was a big reason to go to graduate school. Also, showing the ability that I could do research was what afforded me research assistantships which meant that my tuition was paid for and I got a stipend that paid for expenses while I was in graduate school. This also allowed me the opportunity to work closely with the faculty mentor that provided me with the support and the accountability I wanted.
I would not recommend taking a non-thesis option if all the degree requires is for you to take courses. You have little to show in terms of your learning other than your grades unless you are already working on something on the side that does that for you and all you need is a certificate.
Opt for a non-thesis option if you can still work closely with a professor or on a project and if you'd rather be involved in multiple projects rather than focus on a single project. If you already have a good (informed) reason for choosing one over the other, go for it.
What's the most important thing to consider when choosing a program?
The most important thing to consider when choosing a program is getting excited about the projects that at least one of the faculty members are involved in. Do some research and see why you are excited about a particular work that at least one of the faculty members have been involved in.
Who should students talk to when considering options?
Students should talk to other students and also reach out directly to the graduate coordinator and even individual faculty members. This means that students should have done prior homework and have some good questions ready. Asking good questions will get you at least halfway through to make the right decision.
Like what you're reading?
How to create a great thesis defense presentation: everything you need to know
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera April 13, 2024
Ready to take on your thesis defense presentation? It’s not just about wrapping up years of study; it’s your moment to share your insights and the impact of your work. A standout presentation can make all the difference. It’s your chance to highlight the essentials and really connect with your audience.
This is where Prezi comes into play. Forget about flipping through slide after slide. With Prezi, you craft a narrative that pulls your audience in. It simplifies the complex, ensuring your key points hit home. Let’s explore how Prezi can help transform your thesis defense into a successful presentation.

What is a thesis defense presentation and why are they needed?
Whether you’re preparing for a master’s thesis defense or a Ph.D. thesis defense, this final step in your academic journey is the one with the most significance, as it dramatically influences your final grade. It’s also your chance to display the dedication and effort you’ve put into your research, a way to demonstrate how significant your work is.
So, why is this such a big deal? A good presentation helps convince your teachers that your research is solid and makes a difference in your field. It’s your time to answer questions, show that your research methods were sound, and point out what’s new and interesting about your work. In the end, a great thesis defense presentation helps you finish strong and makes sure you leave a lasting impression as you wrap up this chapter of your academic life.
Best practices for making a successful thesis defense presentation
In order to craft a standout thesis defense presentation, you need to do more than just deliver research findings. Here are some key strategies to ensure success, and how Prezi can play a crucial role in elevating your presentation.
Start with a strong introduction
Kick-off with an engaging introduction that lays out your research question, its significance, and your objectives. This initial segment grabs attention and sets the tone. Using Prezi’s zoom feature can make your introduction pop by visually underscoring key points, helping your audience grasp the importance of your work right from the start.
Organize your presentation clearly
A coherent structure is essential for guiding your audience through your thesis defense presentation. Prezi can help by offering a map view of your content’s layout upfront, providing a clear path through your introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. This clarity keeps your audience engaged and makes your arguments easier to follow.
Incorporate multimedia elements
Adding multimedia elements like videos, audio clips, and animations can greatly improve the appeal of your thesis defense presentation. Prezi supports the seamless integration of these elements, allowing you to bring your research to life in a more vibrant and engaging way. Videos can serve as powerful testimonials or demonstrations, while animations can help illustrate complex processes or changes over time. This variety keeps your audience engaged and helps convey your message in a more exciting way.
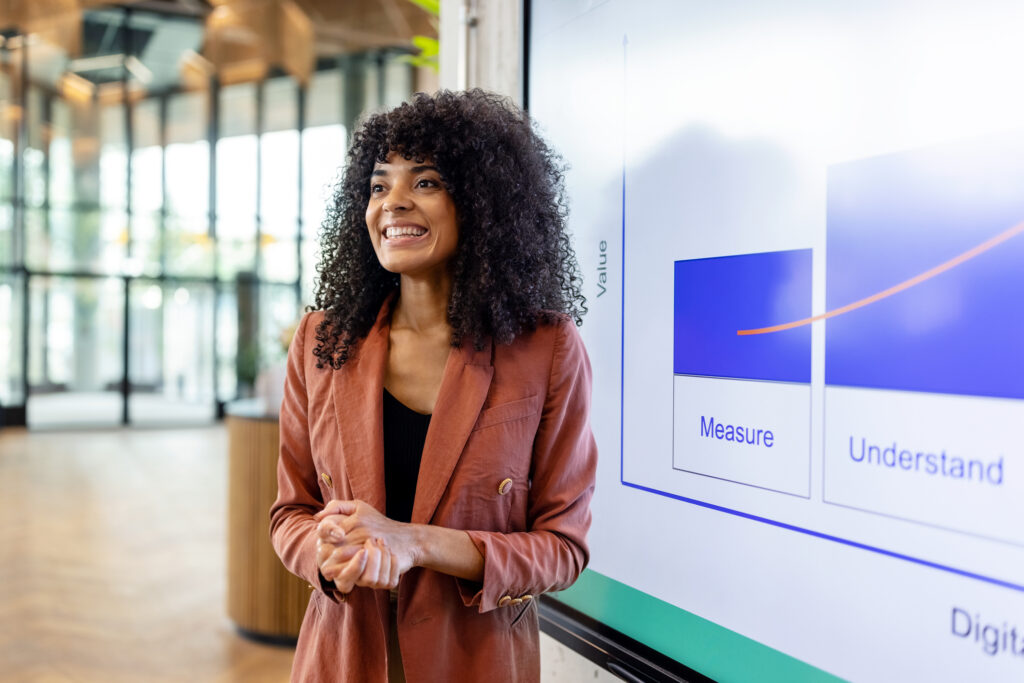

Simplify complex data
Your findings need to be presented in a way that’s easy for your audience to understand. Prezi shines here, with tools that transform intricate data into clear, engaging visuals. By implementing charts and graphs into your presentation, you can make your data stand out and support your narrative effectively.
Engage your audience
Make your thesis defense a two-way conversation by interacting with your audience. Whether it’s through questions, feedback, or direct participation, engagement is key. Prezi allows for a flexible presentation style, letting you navigate sections in response to audience input, creating a dynamic and engaging experience.
Highlight key takeaways
Emphasize the key takeaways of your research throughout your presentation to ensure your audience grasps the most critical aspects of your work. With Prezi, you can use spotlighting and strategic zooming to draw attention to these takeaways, making them stand out. This method helps reinforce your main points, ensuring they stick with your audience long after your presentation concludes. By clearly defining what your audience should remember, you guide their understanding and appreciation of your research’s value and implications.
Practice makes perfect
Confidence in delivery comes from thorough practice. Familiarize yourself with every aspect of your thesis defense presentation, including timing, voice control, and gestures. Prezi Video is a great tool for rehearsing, as it allows you to blend your presentation materials with your on-camera performance, mirroring the live defense setting and helping you polish your delivery.

End with a lasting impression
Conclude your presentation powerfully by summarizing your main findings, their implications, and future research directions. Prezi’s ability to zoom out and show the big picture at your conclusion helps reinforce how each section of your presentation contributes to your overall thesis, ensuring your research leaves a memorable impact on your audience.
By using these tips and taking advantage of what Prezi offers, you can make your thesis defense presentation really stand out. It’ll not only hit the mark with your audience but also clearly show why your research matters.
Meeting tight deadlines with Prezi
Facing a looming deadline for your thesis defense presentation? Prezi offers smart solutions to help you create a polished and engaging presentation quickly, even if it feels like you’re down to the wire.
A closer look at Prezi AI features
Prezi AI is a standout feature for those pressed for time. It assists in structuring your presentation efficiently, suggesting design elements and layouts that elevate your content. This AI-driven approach means you can develop a presentation that looks meticulously planned and executed in a fraction of the time it would normally take. The result? A presentation that communicates the depth and value of your research clearly and effectively, without the last-minute rush being evident. Here’s what Prezi AI can do:
- Streamlined creation process: At the core of Prezi’s efficiency is the AI presentation creator . Perfect for those last-minute crunch times, it’s designed to tackle tight deadlines with ease.
- Easy start: Kick off your presentation creation with just a click on the “Create with AI” button. Prezi AI guides you through a smooth process, transforming your initial ideas or keywords into a structured and visually appealing narrative.
- Visual impact: There’s no need to dive deep into design details. Simply provide some basic input, and Prezi AI will craft it into a presentation that grabs and holds your audience’s attention, making your thesis defense visually compelling.
- AI text editing: Spending too much time fine-tuning your message? Prezi AI text editing features can help. Whether you need to expand on a concept, clarify complex terms, or condense your content without losing impact, Prezi AI streamlines these tasks.
- Content refinement: Adjust text length for deeper explanation, simplify language for better understanding, and ensure your presentation’s content is precise and to the point. Prezi AI editing tools help you refine your message quickly, so you can focus on the essence of your research.
Using Prezi Video for remote thesis defense presentations
For remote thesis defenses, Prezi Video steps up to ensure your presentation stands out. It integrates your on-screen presence alongside your presentation content, creating a more personal and engaging experience for your audience. This is crucial in maintaining attention and interest, particularly in a virtual format where keeping your audience engaged presents additional challenges. Prezi Video makes it seem as though you’re presenting live alongside your slides, helping to simulate the in-person defense experience and keep your audience focused on what you’re saying.
Using these advanced Prezi features, you can overcome tight deadlines with confidence, ensuring your thesis defense presentation is both impactful and memorable, no matter the time constraints.
The Prezi experience: what users have to say
Prezi users have shared compelling insights on how the platform’s unique features have revolutionized their presentations. Here’s how their experiences can inspire your thesis defense presentation:
Storytelling with Prezi
Javier Schwersensky highlights the narrative power of Prezi: “This is a tool that is going to put you ahead of other people and make you look professional and make your ideas stand out,” he remarks. For your thesis defense, this means Prezi can help you craft a narrative that not only presents your research but tells a story that captures and retains the committee’s interest.
Flexibility and creativity
Tamara Montag-Smit appreciates Prezi for its “functionality of the presentation that allows you to present in a nonlinear manner.” This flexibility is key in a thesis defense, allowing you to adapt your presentation flow in real time based on your audience’s engagement or questions, ensuring a more dynamic and interactive defense.
The open canvas
Vitek Dočekal values Prezi’s open canvas , which offers “creative freedom” and the ability to “create a mind map and determine how to best present my ideas.” For your thesis defense, this means Prezi lets you lay out and show off your work in a way that makes sense and grabs your audience’s attention, turning complicated details into something easy and interesting to follow.
Engagement and retention
Adam Rose points out the engagement benefits of Prezi: “Being able to integrate videos is extremely effective in capturing their attention.” When you need to defend a thesis, using Prezi to include videos or interactive content can help keep your committee engaged, making your presentation much more memorable.
These real insights show just how effective Prezi is for crafting truly influential presentations. By incorporating Prezi into your thesis defense presentation, you can create a defense that not only shows how strong your research is but also leaves a lasting impression on your audience.
Thesis defense presentations for inspiration
Prezi is much more than a platform for making presentations; it’s a place where you can find inspiration by browsing presentations that other Prezi users have made. Not only that, but Prezi offers numerous templates that would be useful for thesis defense presentations, making the design process much easier. Here are a few examples that you may find helpful:
Research project template by Prezi
This Prezi research project template stands out as an ideal choice for thesis defense presentations due to its well-structured format that facilitates storytelling from start to finish. It begins with a clear introduction and problem statement, setting a solid foundation for the narrative. The inclusion of sections for user research, interviews, demographics, and statistics allows for a detailed presentation of the research process and findings, which are crucial when defending a thesis.
Visual elements like user mapping and journey maps help make complex information understandable and engaging, which is crucial for maintaining the committee’s attention. Additionally, addressing pain points and presenting prototypes showcases problem-solving efforts and practical applications of the research. The template culminates in a conclusion that ties everything together, emphasizing the research’s impact and future possibilities. Its comprehensive yet concise structure makes it an excellent tool for communicating the depth and significance of your work in a thesis defense.
Civil rights movement Prezi
This Prezi on the Civil Rights Movement exemplifies an effective thesis defense presentation by seamlessly blending structured content, multimedia enhancements, and dynamic navigation. It organizes information into coherent sections like “About,” “Key Events,” and “Key People,” offering a comprehensive view ideal for a thesis presentation. The strategic use of videos adds depth, providing historical context in a dynamic way that text alone cannot, enhancing the audience’s engagement and understanding.
Furthermore, Prezi’s open canvas feature brings the narrative to life, allowing for a fluid journey through the Civil Rights Movement. This method of presentation, with its zooming and panning across a virtual canvas, not only captivates but also helps to clarify the connections between various elements of the research, showcasing how to effectively communicate complex ideas in a thesis defense.
AI-assisted history template
This AI-assisted presentation template stands out as a great choice for thesis defense presentations, especially for those rooted in historical research. By merging striking visuals with rich, informative content, you can use this template to craft a narrative that breathes life into past events, guiding the audience on an engaging journey through time. Its sequential storytelling approach, empowered by Prezi AI , ensures a smooth transition from one historical point to the next, demonstrating the depth and continuity of your research. This template showcases Prezi AI’s capability to enhance narrative flow. By integrating advanced visuals and text, it captivates audiences and makes it an invaluable tool for presenting complex historical theses in a clear, compelling way.
Master your final grade with a Prezi thesis defense presentation
Preparing for a thesis defense, whether for a master’s or Ph.D., is a pivotal moment that significantly influences your final grade. It’s your platform to demonstrate the dedication behind your research and its importance in your field. A well-executed presentation convinces your educators of your research’s validity and your ability to bring fresh perspectives to light.
To craft a successful thesis defense presentation, Prezi’s innovative features can be a game-changer. Prezi can empower you to transform presentations into captivating stories and provide you with the flexibility and creative freedom needed to make your presentation an outstanding success. Incorporating videos or utilizing Prezi’s non-linear presentation style can keep your committee engaged and emphasize your research’s significance.
Prezi also serves as a hub of inspiration, offering templates perfect for thesis defenses. From structured research project templates to dynamic historical narratives, Prezi provides tools that communicate your thesis’s depth and significance effectively, ensuring you leave a memorable impact on your audience. So, it’s time to revamp your thesis defense presentation and change it from dull to inspirational with Prezi.

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations
Should I Get a Master's Before a Doctoral Degree?
Do you need a master's degree to get a Ph.D.? No, but experts suggest considering these key factors before deciding.
Should I Get a Master's Before a Ph.D?

Getty Images
A master’s eases the transition to graduate work and may make you more competitive when applying to doctoral programs.
Although it's not usually a requirement, earning a master’s degree before applying to a Ph.D. or other doctoral program can be a good way to get accustomed to graduate-level coursework while gaining valuable research experience and connections in your field.
But it can also be an expensive and time-consuming detour on the route to a doctorate, so it’s important to consider whether the benefits of earning a master’s before a Ph.D. outweigh the cost.
Here are some factors experts say you should weigh.
Reasons to Get a Master’s Degree First
Karin Ash, a graduate consultant at Accepted, a college admissions consulting firm, says the research experience students can gain through a master’s tends to give them an edge in doctoral admissions.
Master's studies can also expand opportunities for students who already have significant research work behind them. Ash notes that some students she works with have research experience but choose to explore other research areas through a master's before deciding on a focus for their doctoral studies.
If your undergraduate major was fairly different from what you plan to study at a graduate level, getting a master’s degree first can help bridge the gap, says Julie Posselt, a professor of education and associate dean of the University of Southern California Graduate School. Posselt, who earned her master's before pursuing doctoral studies, says master’s studies can also help you decide whether what you’re studying is right for your academic interests and career goals .
“I learned through my master's program that the field that I had started to pursue was much more narrow than what I wanted for the long term,” Posselt says. “So instead of investing five years in a field, I was able to invest a shorter amount of time – two years – and then make the decision that if someday I wanted a Ph.D., it was going to need to be in a broader field than the one that I had during my master's.”
Ash and Posselt say a master’s can be a good way to network with experts in your field of interest and make connections that will be valuable in a future career.
“A lot of STEM students tell me they don’t have professors who know them as their classes are large,” Ash wrote in an email. “Obtaining a master’s degree will allow them to develop relationships with professors who can then write substantive recommendation letters .”
Reasons to Go Straight to a Doctoral Program
Master's degrees can be expensive , and students often don't receive significant funding to complete their studies.
“My concern is the increasing debt that American students have from their undergraduate education," Posselt says, "and the fact that most master's programs don't fund them, and as a result, students have to take out significant loans" to complete a master’s.
"I always encourage students, if they're going to get a master's degree, to try to find a place where they can get funding along the way,” she says.
On the other hand, Ash says it’s common for Ph.D. programs to be fully funded , so it may be unnecessarily costly to earn a master’s degree first – especially if it means taking out student loans .
In addition to considering the tuition cost, Posselt says it’s important to consider the earnings you could lose by delaying the start of your career by a year or two to pursue a master’s degree.
It's also worth investigating whether the doctoral program you're considering will accept some of the credits you earn in a master's program, as that could shorten your doctoral studies. But Posselt says the transferability of master's-level coursework is relatively weak and varies by institution.
Even if you do apply master's coursework to your Ph.D., it may not be worthwhile.
"Many Ph.D. programs will accept credits from courses taken at the master's level if the coursework is relevant to the program," Ash says. "However, often the applicant is veering to a more specialized education and will need to take the appropriate coursework to become proficient in that subject area. This could mean they end up with many more credits than needed to graduate."
If you’re still unsure whether you should pursue a master’s first, Posselt says it’s important to consider the leverage the degree could have when it comes to doctoral admissions. A master’s is more valuable in some fields than others, she notes, so consulting with advisers and mentors from your undergraduate studies is a good way to determine how useful it will be when pursuing doctoral work.
Grad Degree Jobs With $100K+ Salaries

Tags: graduate schools , education , students
You May Also Like
An mba and management consulting.
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

Med School Access for Minority Students
Cole Claybourn May 2, 2024

Different jobs with med degree
Jarek Rutz April 30, 2024

Completing Medical School in Five Years
Kate Rix April 30, 2024

Dealing With Medical School Rejection
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. April 30, 2024

Should You Take the LSAT More Than Once?
Gabriel Kuris April 29, 2024

How to Win a Fulbright Scholarship
Cole Claybourn and Ilana Kowarski April 26, 2024

What to Ask Law Students and Alumni
Gabriel Kuris April 22, 2024

Find a Strong Human Rights Law Program
Anayat Durrani April 18, 2024

Environmental Health in Medical School
Zach Grimmett April 16, 2024

Centre for Research on Bilingualism
Can algorithms translate the world luana fleury awarded aslas 2024 prize for best master's thesis.
Luana Candido Fleury, master's student in spring 2023 at the Centre for Research on Bilingualism, has been awarded the ASLA 2024 Prize for best master's thesis: "Can algorithms translate the world? A digital discourse analysis of Google Translate’s algorithmic agency in the translation of news reports."

The thesis makes a substantial and pioneering contribution to the field of Critical Discourse Analysis that focuses on digitalized content.
"The study investigates the mediation of meanings by Google Translate's algorithmic agency, focusing on the translation of news reports from English to Portuguese, the official language of Brazil. The findings of the thesis illuminate how Google Translate's algorithmic decisions reshape language and representation, constructing and enacting power by renaming reality and reshaping evaluations." (from the Jury's reasoning)

2024 ASLA thesis prize winners (in Swedish: 2024 års uppsatspristagare utsedda (ASLA))
What does it mean to you to receive an award for your thesis?
– The motivation behind the ASLA 2024 prize, reflects the dedication and effort I put into investigating the mediation of meanings by Google Translate's, says Luana.
– My work demonstrates that algorithmic decisions reshape language and representation, constructing and enacting power by renaming reality and reshaping evaluations. Since my defense in 2022, this topic has become even more pertinent, and discussions regarding the impact of generative artificial intelligence and its ethical boundaries have become even more urgent.
– I look forward to continuing my contribution to this field and would be happy to engage in a conversation on the many topics that stem from it.
Read more on LinkedIn: Luana Fleury
Luana received the the award for best master's thesis (Swedish masteruppsats) together with Helena Textorius, who received the award for best master's thesis (Swedish magisteruppsats) in 2024. See our Swedish site:
Att göra musik. Helena Textorius har fått ASLA:s pris 2024 för bästa magisteruppsats 2023
The thesis can be downloaded as full text from the Publication database DiVA:
Can algorithms translate the world? A digital discourse analysis of Google Translate’s algorithmic agency in the translation of news reports
About ASLA:s Prize for best thesis (in Swedish: ASLA:s uppsatspris)
The Master's programme
Master’s Programme in Language Science with a Specialisation in Bilingualism
ASLA, The Swedish Association for Applied Linguistics (Association suédoise de linguistique appliquée) is the Swedish branch of the international association of applied linguistics, AILA (Association internationale de linguistique appliquée). ASLA’s aim is to promote research concerning practical problems to do with language, facilitate contacts between language researchers in Sweden and other countries and encourage participation in AILA’s research networks.
Last updated: April 29, 2024
Source: Centre for Research on Bilingualism
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Families
- People Search
- Mission & Vision
- Accreditation
- History & Traditions
- Institutional Disclosures
- Application Process
- Costs to Attend
- Financial Aid
- Visiting Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Meet Your Counselors
- For Admitted Students
- Admissions Forms
- Dual Enrollment
- Graduate Admissions
- Find Your Program
- Colleges and Schools
- 100% Online Degrees
- Student Success
- Office of the Registrar
- Academic Bulletins
- Academic Leadership
- Felix G. Woodward Library
- Student Life & Engagement
- Campus Safety
- Student Wellness
- Current Student
- Faculty/Staff
- Parent/Family
Alumna Kaytah Mejia wins best thesis award for military mindset research at graduate conference
By: Victoria Godinez May 1, 2024
Austin Peay State University graduate Kaytah Mejia, who finished her master’s degree in industrial-organizational psychology in December 2023, recently earned the Best Thesis of 2023 award from the Tennessee Conference of Graduate Schools.

Her thesis, “The Impact of Organizational Justice Perception on Organizational Commitment: “Exploration on the Military Mindset,” showcased her commitment to understanding complex organizational dynamics and involved countless hours of work .
“My research was the hardest thing I have ever done, even more so than childbirth and military service, simply because of the mental challenge that it takes to overcome,” she said, reflecting on her journey through APSU’s Master of Science in Industrial-Organizational Psychology that began in August 2021.
Throughout her academic tenure, Mejia demonstrated a passion for her field. She served as a graduate teaching assistant and collaborated closely with mentors such as Dr. Kevin Harris, Dr. Nicole Knickmeyer, Dr. Jessica Haatz and Dr. David Earnest.
Before pursuing her master’s degree, Mejia obtained a Bachelor of Science in psychology from APSU, where she discovered her desire to pursue a master’s. She said Dr. Adriane Sanders’ Intro to Applied Psychology course sparked her interest in the intersection of psychology and the workplace.
Mejia's involvement in research projects enriched her academic pursuits , which included collaborations with faculty on a COVID survey and socioemotional mindfulness research for Moshi Kids. Her unique perspective and drive to excel academically and professionally were shaped by her background as an adopted Latina/Hispanic/Native American woman and her experience as a former Army medic in Germany.
“We spend roughly one-third of our lives working,” Mejia said. “After my military service, I realized how I could fit into the puzzle of bringing positive changes into the workspace.”
After completing her master’s degree, Mejia applied her knowledge and skills to her career and became the HR screening specialist at Project 2231 in Clarksville. Leveraging her expertise in workplace ethics, human resources and organizational development, she plays a vital role in the HR department and contributes to the company’s growth and success.
Mejia said her accomplishments, including her award-winning thesis, were made possible with the support of her mentors, committee members and family. She credited Earnest, Harris, and Dr. Chanda Murphy for guiding her through the challenging research process and pushing her to surpass her expectations.
“I was sitting in my car and cried happy tears,” she said. “I never thought I would have won, and having done so, I was extremely proud of myself. This is a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity, and I am so grateful for experiencing it.”
Interested in following Mejia’s footsteps in industrial-organizational psychology? APSU offers an MSIO program that prepares students for diverse roles. Learn more at https://www.apsu.edu/ioprogram .

Office of Neuroscience Research
Thesis Defense: Vivian Kitainda (Plant and Microbial Biosciences Program) – “Molecular Mechanisms Behind Methionine – Derived Glucosinolate Diversity in Brassica Plants”
Thesis lab: Joseph Jez (WashU Biology)
For inquiries contact Vivian at [email protected] .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Tip #2: Begin Work on the Thesis Statement and Break Up the Thesis into Manageable Sections. After selecting an appropriate topic and developing a central research question for the thesis statement, it is then necessary to apply the research and writing skills you have learned throughout your degree program.
A master's thesis is a written document highlighting knowledge gathered throughout the graduate degree, a unique perspective into the domain of study, an understanding of scientific and research methodology, and one's ability to analyze and interpret research outcomes.
Master's Thesis. Writing a thesis is optional for some master's programs and not required. There are abundant opportunities for personalized interaction with faculty through research courses, independent studies, and seminars. If a student chooses to write a thesis, it requires eight courses and either two research credits (5970), or in some ...
As stated above, a thesis is the final project required in the completion of many master's degrees. The thesis is a research paper, but it only involves using research from others and crafting your own analytical points. On the other hand, the dissertation is a more in-depth scholarly research paper completed mostly by doctoral students.
The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names.
minimum of ten days for all members of the thesis committee to review the thesis. Step 1: Prepare the content of your presentation. The content of your presentation is the mirror of your thesis ...
A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent - usually it'll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries. To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you'll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic.
Your master's thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master's thesis is the longest document that they've ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
The Third Edition of How to Write a Master's Thesis is a comprehensive manual on how to plan and write a five-chapter master's thesis, and a great resource for graduate students looking for concrete, applied guidance on how to successfully complete their master's degrees. While research methods and statistics courses may teach students the ...
Rules & Regulations. A master's student with a thesis requirement will submit the file through Brown's electronic theses and dissertation (ETD) system. The system is designed to collect and archive the thesis or dissertation as a text-based PDF file. An electronic file submitted through the ETD will appear in the Library's discovery service ...
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
A master's thesis is an academic research output that is expected to showcase a student's competence in a higher level of research as compared to an undergraduate one. The primary objective of a master's thesis is to assess a student on the depth of their understanding, knowledge, and competence on the subject of their choice. ...
A master's thesis must show that the student truly applies a scientific approach to research and understands the main questions and doctrine related to the chosen topic. The thesis must also put forth an original contribution, which, as an article, could be published without major corrections.
The Thesis Process. The thesis is an opportunity to work independently on a research project of your own design and contribute to the scholarly literature in your field. You emerge from the thesis process with a solid understanding of how original research is executed and how to best communicate research results.
Research output should be publishable in an academic journal. Master's thesis is meant for academic masters programmes. Master's thesis should be done within six months - one year. Equivalent to 6 course units (18 credits) Minimum should be 25,000 words (Approx. 100 pages) to 50,000 words (Approx. 200 pages).
A master's thesis proposal which clearly defines the problem in a straightforward and explains the research methodology in simple words is considered a good thesis proposal. 7. What font is best for a master's thesis proposal? You can use any classic font for your master's thesis proposal such as Times New Roman.
The thesis may take one of three forms: a research thesis, an artistic thesis, or a project thesis. In each case, the thesis represents a synthesis of the student's accumulated knowledge and skill and an opportunity to display the ideas, practices and skills learned through the program. While the master's thesis, unlike a doctoral ...
GMS Thesis Template 2022. NOTE: The Research Guide For Writers Of Theses (#1 above) There is no longer a word limit to the length of the abstract, but please be concise. NOTE: Minimum length for MAMS theses is 40 pages (research thesis) or 45 pages (literature thesis), excluding the Prepages, Appendices, References and Vita.
A master's is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers. All master's involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master's thesis. Others focus on professional training for a ...
A Thesis Proposal is a document that sets forth what is to be studied as a thesis project, why and in what way. It contains a number of important sections. The purpose of the proposal is to communicate the plan for the work to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies via the First Reader (principal thesis advisor) and a Second Reader.
OATD.org aims to be the best possible resource for finding open access graduate theses and dissertations published around the world. Metadata (information about the theses) comes from over 1100 colleges, universities, and research institutions. OATD currently indexes 7,230,360 theses and dissertations. About OATD (our FAQ). Visual OATD.org
Master's Thesis Research. Prereq: All course work toward the degree must be completed. Note: Registration for this course is not available via telephone (UK-VIP) or webUK. For enrollment information contact the Graduate School at 257-4905. Half-time to full-time work on thesis. May be repeated to a maximum of six semesters.
Choosing Between a Thesis or Non-thesis Master's Degree. As of 2015, approximately 25.4 million Americans held advanced degrees, with more citizens joining these ranks each year. As studies continue to show the career advancement and salary benefits of completing a master's degree, more and more students elect to pursue advanced educations ...
A coherent structure is essential for guiding your audience through your thesis defense presentation. Prezi can help by offering a map view of your content's layout upfront, providing a clear path through your introduction, methodology, results, and conclusion. This clarity keeps your audience engaged and makes your arguments easier to follow.
Getty Images. A master's eases the transition to graduate work and may make you more competitive when applying to doctoral programs. Although it's not usually a requirement, earning a master's ...
Luana Candido Fleury, master's student in spring 2023 at the Centre for Research on Bilingualism, has been awarded the ASLA 2024 Prize for best master's thesis: "Can algorithms translate the world? A digital discourse analysis of Google Translate's algorithmic agency in the translation of news reports."
Alumna Kaytah Mejia wins best thesis award for military mindset research at graduate conference. By: Victoria Godinez May 1, 2024 Austin Peay State University graduate Kaytah Mejia, who finished her master's degree in industrial-organizational psychology in December 2023, recently earned the Best Thesis of 2023 award from the Tennessee Conference of Graduate Schools.
Office of Neuroscience Research. MSC 8111-96-07-7122. 4370 Duncan Ave. St. Louis, Missouri 63110. [email protected]
Erica Nadolski wins two presentation awards for her thesis research! Tuesday, April 23, 2024. Student Oral Presentation award. Congrats to Erica for these outstanding accomplishments! Fourth-year GCDB student Erica Nadolski recently attend the Society for Comparative and Integrative Biology Annual meeting in Seattle, Washington. During the ...