
Statistics Made Easy

How to Identify a Left Tailed Test vs. a Right Tailed Test
In statistics, we use hypothesis tests to determine whether some claim about a population parameter is true or not.
Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis , which take the following forms:
H 0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter = ≤, ≥ some value
H A (Alternative Hypothesis): Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value
There are three different types of hypothesis tests:
- Two-tailed test: The alternative hypothesis contains the “≠” sign
- Left-tailed test: The alternative hypothesis contains the “<” sign
- Right-tailed test: The alternative hypothesis contains the “>” sign
Notice that we only have to look at the sign in the alternative hypothesis to determine the type of hypothesis test.
Left-tailed test: The alternative hypothesis contains the “<” sign Right-tailed test: The alternative hypothesis contains the “>” sign
The following examples show how to identify left-tailed and right-tailed tests in practice.
Example: Left-Tailed Test
Suppose it’s assumed that the average weight of a certain widget produced at a factory is 20 grams. However, one inspector believes the true average weight is less than 20 grams.
To test this, he weighs a simple random sample of 20 widgets and obtains the following information:
- n = 20 widgets
- x = 19.8 grams
- s = 3.1 grams
He then performs a hypothesis test using the following null and alternative hypotheses:
H 0 (Null Hypothesis): μ ≥ 20 grams
H A (Alternative Hypothesis): μ < 20 grams
The test statistic is calculated as:
- t = ( x – µ) / (s/√ n )
- t = (19.8-20) / (3.1/√ 20 )
According to the t-Distribution table , the t critical value at α = .05 and n-1 = 19 degrees of freedom is – 1.729 .
Since the test statistic is not less than this value, the inspector fails to reject the null hypothesis. He does not have sufficient evidence to say that the true mean weight of widgets produced at this factory is less than 20 grams.
Example: Right-Tailed Test
Suppose it’s assumed that the average height of a certain species of plant is 10 inches tall. However, one botanist claims the true average height is greater than 10 inches.
To test this claim, she goes out and measures the height of a simple random sample of 15 plants and obtains the following information:
- n = 15 plants
- x = 11.4 inches
- s = 2.5 inches
She then performs a hypothesis test using the following null and alternative hypotheses:
H 0 (Null Hypothesis): μ ≤ 10 inches
H A (Alternative Hypothesis): μ > 10 inches
- t = (11.4-10) / (2.5/√ 15 )
According to the t-Distribution table , the t critical value at α = .05 and n-1 = 14 degrees of freedom is 1.761 .
Since the test statistic is greater than this value, the botanist can reject the null hypothesis. She has sufficient evidence to say that the true mean height for this species of plant is greater than 10 inches.
Additional Resources
How to Read the t-Distribution Table One Sample t-test Calculator Two Sample t-test Calculator
Featured Posts

Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for professional businesses in both healthcare and retail. I’m passionate about statistics, machine learning, and data visualization and I created Statology to be a resource for both students and teachers alike. My goal with this site is to help you learn statistics through using simple terms, plenty of real-world examples, and helpful illustrations.
2 Replies to “How to Identify a Left Tailed Test vs. a Right Tailed Test”
This was so helpful you are a life saver. Thank you so much
Left-tailed test example, -2.885 is less than -1.729, why you mention -2.885 is “not lesss” …
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

8.1: The Elements of Hypothesis Testing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 130263

Learning Objectives
- To understand the logical framework of tests of hypotheses.
- To learn basic terminology connected with hypothesis testing.
- To learn fundamental facts about hypothesis testing.
Types of Hypotheses
A hypothesis about the value of a population parameter is an assertion about its value. As in the introductory example we will be concerned with testing the truth of two competing hypotheses, only one of which can be true.
Definition: null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis
- The null hypothesis , denoted \(H_0\), is the statement about the population parameter that is assumed to be true unless there is convincing evidence to the contrary.
- The alternative hypothesis , denoted \(H_a\), is a statement about the population parameter that is contradictory to the null hypothesis, and is accepted as true only if there is convincing evidence in favor of it.
Definition: statistical procedure
Hypothesis testing is a statistical procedure in which a choice is made between a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis based on information in a sample.
The end result of a hypotheses testing procedure is a choice of one of the following two possible conclusions:
- Reject \(H_0\) (and therefore accept \(H_a\)), or
- Fail to reject \(H_0\) (and therefore fail to accept \(H_a\)).
The null hypothesis typically represents the status quo, or what has historically been true. In the example of the respirators, we would believe the claim of the manufacturer unless there is reason not to do so, so the null hypotheses is \(H_0:\mu =75\). The alternative hypothesis in the example is the contradictory statement \(H_a:\mu <75\). The null hypothesis will always be an assertion containing an equals sign, but depending on the situation the alternative hypothesis can have any one of three forms: with the symbol \(<\), as in the example just discussed, with the symbol \(>\), or with the symbol \(\neq\). The following two examples illustrate the latter two cases.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
A publisher of college textbooks claims that the average price of all hardbound college textbooks is \(\$127.50\). A student group believes that the actual mean is higher and wishes to test their belief. State the relevant null and alternative hypotheses.
The default option is to accept the publisher’s claim unless there is compelling evidence to the contrary. Thus the null hypothesis is \(H_0:\mu =127.50\). Since the student group thinks that the average textbook price is greater than the publisher’s figure, the alternative hypothesis in this situation is \(H_a:\mu >127.50\).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
The recipe for a bakery item is designed to result in a product that contains \(8\) grams of fat per serving. The quality control department samples the product periodically to insure that the production process is working as designed. State the relevant null and alternative hypotheses.
The default option is to assume that the product contains the amount of fat it was formulated to contain unless there is compelling evidence to the contrary. Thus the null hypothesis is \(H_0:\mu =8.0\). Since to contain either more fat than desired or to contain less fat than desired are both an indication of a faulty production process, the alternative hypothesis in this situation is that the mean is different from \(8.0\), so \(H_a:\mu \neq 8.0\).
In Example \(\PageIndex{1}\), the textbook example, it might seem more natural that the publisher’s claim be that the average price is at most \(\$127.50\), not exactly \(\$127.50\). If the claim were made this way, then the null hypothesis would be \(H_0:\mu \leq 127.50\), and the value \(\$127.50\) given in the example would be the one that is least favorable to the publisher’s claim, the null hypothesis. It is always true that if the null hypothesis is retained for its least favorable value, then it is retained for every other value.
Thus in order to make the null and alternative hypotheses easy for the student to distinguish, in every example and problem in this text we will always present one of the two competing claims about the value of a parameter with an equality. The claim expressed with an equality is the null hypothesis. This is the same as always stating the null hypothesis in the least favorable light. So in the introductory example about the respirators, we stated the manufacturer’s claim as “the average is \(75\) minutes” instead of the perhaps more natural “the average is at least \(75\) minutes,” essentially reducing the presentation of the null hypothesis to its worst case.
The first step in hypothesis testing is to identify the null and alternative hypotheses.
The Logic of Hypothesis Testing
Although we will study hypothesis testing in situations other than for a single population mean (for example, for a population proportion instead of a mean or in comparing the means of two different populations), in this section the discussion will always be given in terms of a single population mean \(\mu\).
The null hypothesis always has the form \(H_0:\mu =\mu _0\) for a specific number \(\mu _0\) (in the respirator example \(\mu _0=75\), in the textbook example \(\mu _0=127.50\), and in the baked goods example \(\mu _0=8.0\)). Since the null hypothesis is accepted unless there is strong evidence to the contrary, the test procedure is based on the initial assumption that \(H_0\) is true. This point is so important that we will repeat it in a display:
The test procedure is based on the initial assumption that \(H_0\) is true.
The criterion for judging between \(H_0\) and \(H_a\) based on the sample data is: if the value of \(\overline{X}\) would be highly unlikely to occur if \(H_0\) were true, but favors the truth of \(H_a\), then we reject \(H_0\) in favor of \(H_a\). Otherwise we do not reject \(H_0\).
Supposing for now that \(\overline{X}\) follows a normal distribution, when the null hypothesis is true the density function for the sample mean \(\overline{X}\) must be as in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): a bell curve centered at \(\mu _0\). Thus if \(H_0\) is true then \(\overline{X}\) is likely to take a value near \(\mu _0\) and is unlikely to take values far away. Our decision procedure therefore reduces simply to:
- if \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu <\mu _0\) then reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far to the left of \(\mu _0\);
- if \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu >\mu _0\) then reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far to the right of \(\mu _0\);
- if \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu \neq \mu _0\) then reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far away from \(\mu _0\) in either direction.
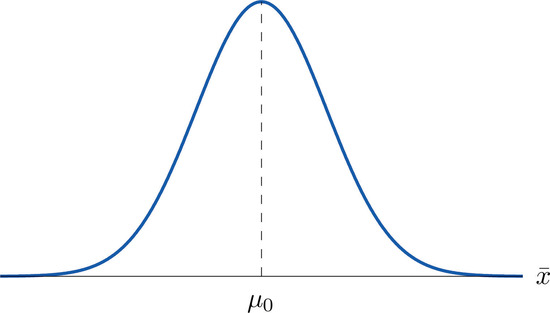
Think of the respirator example, for which the null hypothesis is \(H_0:\mu =75\), the claim that the average time air is delivered for all respirators is \(75\) minutes. If the sample mean is \(75\) or greater then we certainly would not reject \(H_0\) (since there is no issue with an emergency respirator delivering air even longer than claimed).
If the sample mean is slightly less than \(75\) then we would logically attribute the difference to sampling error and also not reject \(H_0\) either.
Values of the sample mean that are smaller and smaller are less and less likely to come from a population for which the population mean is \(75\). Thus if the sample mean is far less than \(75\), say around \(60\) minutes or less, then we would certainly reject \(H_0\), because we know that it is highly unlikely that the average of a sample would be so low if the population mean were \(75\). This is the rare event criterion for rejection: what we actually observed \((\overline{X}<60)\) would be so rare an event if \(\mu =75\) were true that we regard it as much more likely that the alternative hypothesis \(\mu <75\) holds.
In summary, to decide between \(H_0\) and \(H_a\) in this example we would select a “rejection region” of values sufficiently far to the left of \(75\), based on the rare event criterion, and reject \(H_0\) if the sample mean \(\overline{X}\) lies in the rejection region, but not reject \(H_0\) if it does not.
The Rejection Region
Each different form of the alternative hypothesis Ha has its own kind of rejection region:
- if (as in the respirator example) \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu <\mu _0\), we reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far to the left of \(\mu _0\), that is, to the left of some number \(C\), so the rejection region has the form of an interval \((-\infty ,C]\);
- if (as in the textbook example) \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu >\mu _0\), we reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far to the right of \(\mu _0\), that is, to the right of some number \(C\), so the rejection region has the form of an interval \([C,\infty )\);
- if (as in the baked good example) \(H_a\) has the form \(H_a:\mu \neq \mu _0\), we reject \(H_0\) if \(\bar{x}\) is far away from \(\mu _0\) in either direction, that is, either to the left of some number \(C\) or to the right of some other number \(C′\), so the rejection region has the form of the union of two intervals \((-\infty ,C]\cup [C',\infty )\).
The key issue in our line of reasoning is the question of how to determine the number \(C\) or numbers \(C\) and \(C′\), called the critical value or critical values of the statistic, that determine the rejection region.
Definition: critical values
The critical value or critical values of a test of hypotheses are the number or numbers that determine the rejection region.
Suppose the rejection region is a single interval, so we need to select a single number \(C\). Here is the procedure for doing so. We select a small probability, denoted \(\alpha\), say \(1\%\), which we take as our definition of “rare event:” an event is “rare” if its probability of occurrence is less than \(\alpha\). (In all the examples and problems in this text the value of \(\alpha\) will be given already.) The probability that \(\overline{X}\) takes a value in an interval is the area under its density curve and above that interval, so as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) (drawn under the assumption that \(H_0\) is true, so that the curve centers at \(\mu _0\)) the critical value \(C\) is the value of \(\overline{X}\) that cuts off a tail area \(\alpha\) in the probability density curve of \(\overline{X}\). When the rejection region is in two pieces, that is, composed of two intervals, the total area above both of them must be \(\alpha\), so the area above each one is \(\alpha /2\), as also shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\).
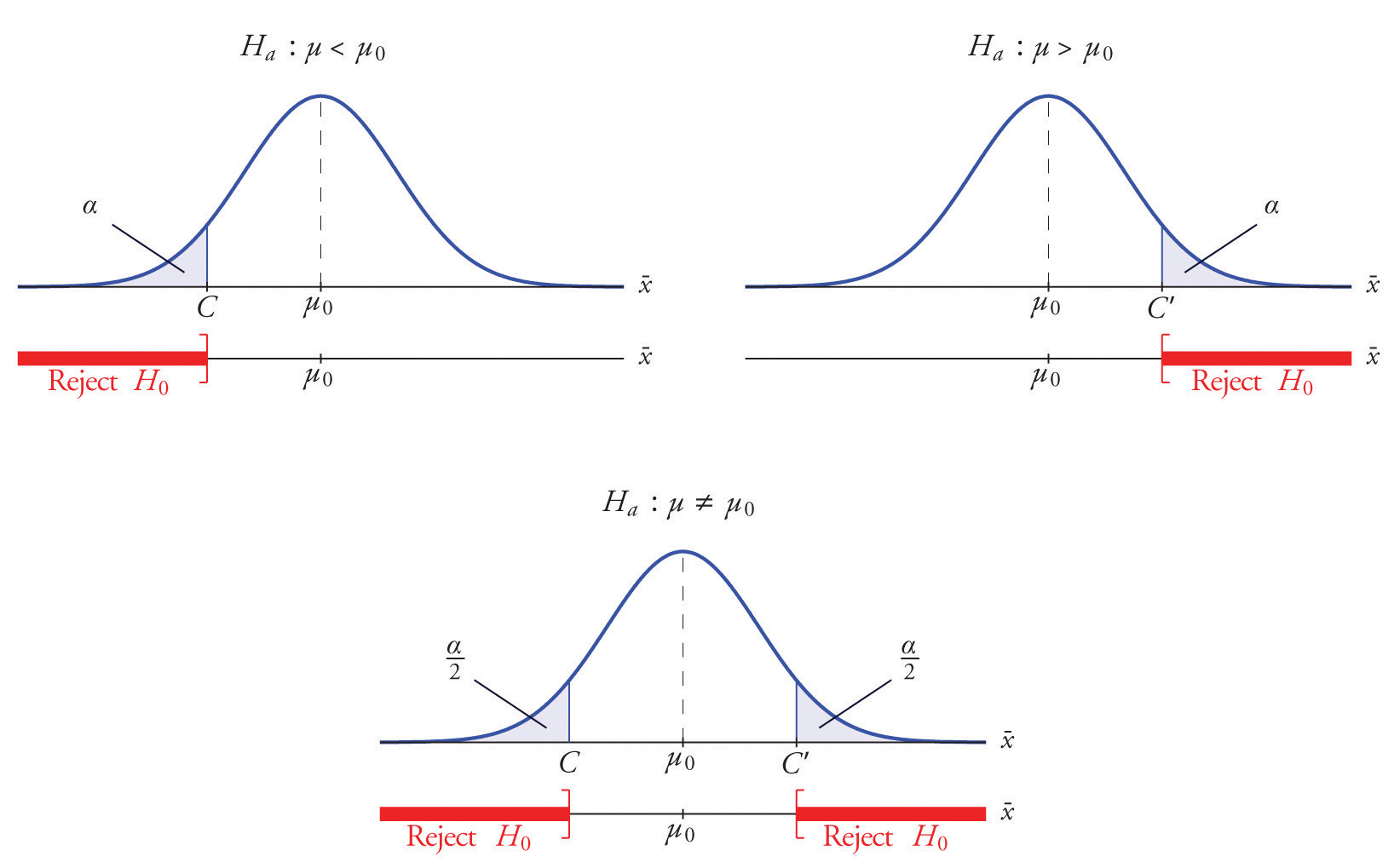
The number \(\alpha\) is the total area of a tail or a pair of tails.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
In the context of Example \(\PageIndex{2}\), suppose that it is known that the population is normally distributed with standard deviation \(\alpha =0.15\) gram, and suppose that the test of hypotheses \(H_0:\mu =8.0\) versus \(H_a:\mu \neq 8.0\) will be performed with a sample of size \(5\). Construct the rejection region for the test for the choice \(\alpha =0.10\). Explain the decision procedure and interpret it.
If \(H_0\) is true then the sample mean \(\overline{X}\) is normally distributed with mean and standard deviation
\[\begin{align} \mu _{\overline{X}} &=\mu \nonumber \\[5pt] &=8.0 \nonumber \end{align} \nonumber \]
\[\begin{align} \sigma _{\overline{X}}&=\dfrac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}} \nonumber \\[5pt] &= \dfrac{0.15}{\sqrt{5}} \nonumber\\[5pt] &=0.067 \nonumber \end{align} \nonumber \]
Since \(H_a\) contains the \(\neq\) symbol the rejection region will be in two pieces, each one corresponding to a tail of area \(\alpha /2=0.10/2=0.05\). From Figure 7.1.6, \(z_{0.05}=1.645\), so \(C\) and \(C′\) are \(1.645\) standard deviations of \(\overline{X}\) to the right and left of its mean \(8.0\):
\[C=8.0-(1.645)(0.067) = 7.89 \; \; \text{and}\; \; C'=8.0 + (1.645)(0.067) = 8.11 \nonumber \]
The result is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\). α = 0.1
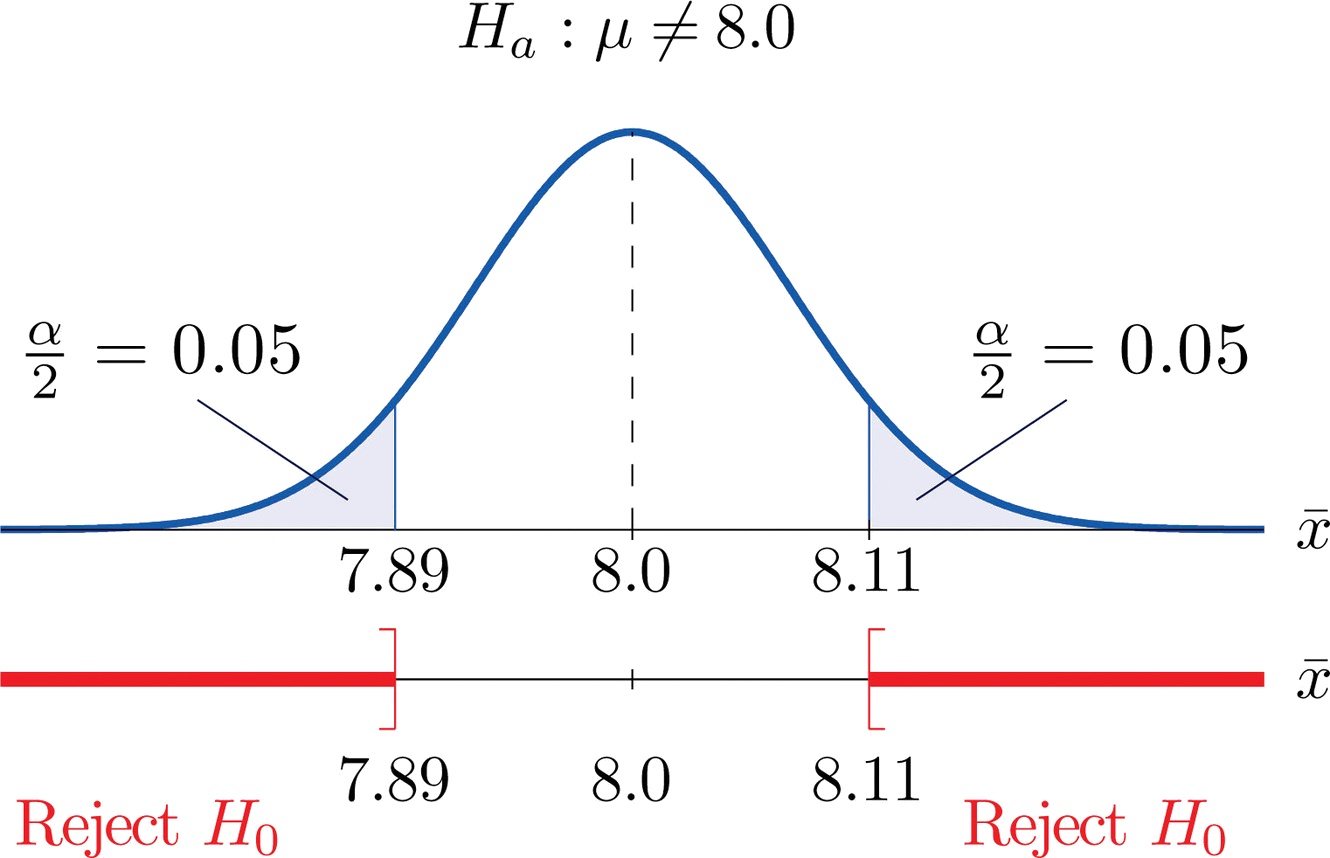
The decision procedure is: take a sample of size \(5\) and compute the sample mean \(\bar{x}\). If \(\bar{x}\) is either \(7.89\) grams or less or \(8.11\) grams or more then reject the hypothesis that the average amount of fat in all servings of the product is \(8.0\) grams in favor of the alternative that it is different from \(8.0\) grams. Otherwise do not reject the hypothesis that the average amount is \(8.0\) grams.
The reasoning is that if the true average amount of fat per serving were \(8.0\) grams then there would be less than a \(10\%\) chance that a sample of size \(5\) would produce a mean of either \(7.89\) grams or less or \(8.11\) grams or more. Hence if that happened it would be more likely that the value \(8.0\) is incorrect (always assuming that the population standard deviation is \(0.15\) gram).
Because the rejection regions are computed based on areas in tails of distributions, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\), hypothesis tests are classified according to the form of the alternative hypothesis in the following way.
Definitions: Test classifications
- If \(H_a\) has the form \(\mu \neq \mu _0\) the test is called a two-tailed test .
- If \(H_a\) has the form \(\mu < \mu _0\) the test is called a left-tailed test .
- If \(H_a\) has the form \(\mu > \mu _0\)the test is called a right-tailed test .
Each of the last two forms is also called a one-tailed test .
Two Types of Errors
The format of the testing procedure in general terms is to take a sample and use the information it contains to come to a decision about the two hypotheses. As stated before our decision will always be either
- reject the null hypothesis \(H_0\) in favor of the alternative \(H_a\) presented, or
- do not reject the null hypothesis \(H_0\) in favor of the alternative \(H_0\) presented.
There are four possible outcomes of hypothesis testing procedure, as shown in the following table:
As the table shows, there are two ways to be right and two ways to be wrong. Typically to reject \(H_0\) when it is actually true is a more serious error than to fail to reject it when it is false, so the former error is labeled “ Type I ” and the latter error “ Type II ”.
Definition: Type I and Type II errors
In a test of hypotheses:
- A Type I error is the decision to reject \(H_0\) when it is in fact true.
- A Type II error is the decision not to reject \(H_0\) when it is in fact not true.
Unless we perform a census we do not have certain knowledge, so we do not know whether our decision matches the true state of nature or if we have made an error. We reject \(H_0\) if what we observe would be a “rare” event if \(H_0\) were true. But rare events are not impossible: they occur with probability \(\alpha\). Thus when \(H_0\) is true, a rare event will be observed in the proportion \(\alpha\) of repeated similar tests, and \(H_0\) will be erroneously rejected in those tests. Thus \(\alpha\) is the probability that in following the testing procedure to decide between \(H_0\) and \(H_a\) we will make a Type I error.
Definition: level of significance
The number \(\alpha\) that is used to determine the rejection region is called the level of significance of the test. It is the probability that the test procedure will result in a Type I error .
The probability of making a Type II error is too complicated to discuss in a beginning text, so we will say no more about it than this: for a fixed sample size, choosing \(alpha\) smaller in order to reduce the chance of making a Type I error has the effect of increasing the chance of making a Type II error . The only way to simultaneously reduce the chances of making either kind of error is to increase the sample size.
Standardizing the Test Statistic
Hypotheses testing will be considered in a number of contexts, and great unification as well as simplification results when the relevant sample statistic is standardized by subtracting its mean from it and then dividing by its standard deviation. The resulting statistic is called a standardized test statistic . In every situation treated in this and the following two chapters the standardized test statistic will have either the standard normal distribution or Student’s \(t\)-distribution.
Definition: hypothesis test
A standardized test statistic for a hypothesis test is the statistic that is formed by subtracting from the statistic of interest its mean and dividing by its standard deviation.
For example, reviewing Example \(\PageIndex{3}\), if instead of working with the sample mean \(\overline{X}\) we instead work with the test statistic
\[\frac{\overline{X}-8.0}{0.067} \nonumber \]
then the distribution involved is standard normal and the critical values are just \(\pm z_{0.05}\). The extra work that was done to find that \(C=7.89\) and \(C′=8.11\) is eliminated. In every hypothesis test in this book the standardized test statistic will be governed by either the standard normal distribution or Student’s \(t\)-distribution. Information about rejection regions is summarized in the following tables:
Every instance of hypothesis testing discussed in this and the following two chapters will have a rejection region like one of the six forms tabulated in the tables above.
No matter what the context a test of hypotheses can always be performed by applying the following systematic procedure, which will be illustrated in the examples in the succeeding sections.
Systematic Hypothesis Testing Procedure: Critical Value Approach
- Identify the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Identify the relevant test statistic and its distribution.
- Compute from the data the value of the test statistic.
- Construct the rejection region.
- Compare the value computed in Step 3 to the rejection region constructed in Step 4 and make a decision. Formulate the decision in the context of the problem, if applicable.
The procedure that we have outlined in this section is called the “Critical Value Approach” to hypothesis testing to distinguish it from an alternative but equivalent approach that will be introduced at the end of Section 8.3.
Key Takeaway
- A test of hypotheses is a statistical process for deciding between two competing assertions about a population parameter.
- The testing procedure is formalized in a five-step procedure.
- Comprehensive Learning Paths
- 150+ Hours of Videos
- Complete Access to Jupyter notebooks, Datasets, References.

Hypothesis Testing – A Deep Dive into Hypothesis Testing, The Backbone of Statistical Inference
- September 21, 2023
Explore the intricacies of hypothesis testing, a cornerstone of statistical analysis. Dive into methods, interpretations, and applications for making data-driven decisions.

In this Blog post we will learn:
- What is Hypothesis Testing?
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing 2.1. Set up Hypotheses: Null and Alternative 2.2. Choose a Significance Level (α) 2.3. Calculate a test statistic and P-Value 2.4. Make a Decision
- Example : Testing a new drug.
- Example in python
1. What is Hypothesis Testing?
In simple terms, hypothesis testing is a method used to make decisions or inferences about population parameters based on sample data. Imagine being handed a dice and asked if it’s biased. By rolling it a few times and analyzing the outcomes, you’d be engaging in the essence of hypothesis testing.
Think of hypothesis testing as the scientific method of the statistics world. Suppose you hear claims like “This new drug works wonders!” or “Our new website design boosts sales.” How do you know if these statements hold water? Enter hypothesis testing.
2. Steps in Hypothesis Testing
- Set up Hypotheses : Begin with a null hypothesis (H0) and an alternative hypothesis (Ha).
- Choose a Significance Level (α) : Typically 0.05, this is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true. Think of it as the chance of accusing an innocent person.
- Calculate Test statistic and P-Value : Gather evidence (data) and calculate a test statistic.
- p-value : This is the probability of observing the data, given that the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value (typically ≤ 0.05) suggests the data is inconsistent with the null hypothesis.
- Decision Rule : If the p-value is less than or equal to α, you reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative.
2.1. Set up Hypotheses: Null and Alternative
Before diving into testing, we must formulate hypotheses. The null hypothesis (H0) represents the default assumption, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) challenges it.
For instance, in drug testing, H0 : “The new drug is no better than the existing one,” H1 : “The new drug is superior .”
2.2. Choose a Significance Level (α)
When You collect and analyze data to test H0 and H1 hypotheses. Based on your analysis, you decide whether to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or fail to reject / Accept the null hypothesis.
The significance level, often denoted by $α$, represents the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
In other words, it’s the risk you’re willing to take of making a Type I error (false positive).
Type I Error (False Positive) :
- Symbolized by the Greek letter alpha (α).
- Occurs when you incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis . In other words, you conclude that there is an effect or difference when, in reality, there isn’t.
- The probability of making a Type I error is denoted by the significance level of a test. Commonly, tests are conducted at the 0.05 significance level , which means there’s a 5% chance of making a Type I error .
- Commonly used significance levels are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10, but the choice depends on the context of the study and the level of risk one is willing to accept.
Example : If a drug is not effective (truth), but a clinical trial incorrectly concludes that it is effective (based on the sample data), then a Type I error has occurred.
Type II Error (False Negative) :
- Symbolized by the Greek letter beta (β).
- Occurs when you accept a false null hypothesis . This means you conclude there is no effect or difference when, in reality, there is.
- The probability of making a Type II error is denoted by β. The power of a test (1 – β) represents the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis.
Example : If a drug is effective (truth), but a clinical trial incorrectly concludes that it is not effective (based on the sample data), then a Type II error has occurred.
Balancing the Errors :

In practice, there’s a trade-off between Type I and Type II errors. Reducing the risk of one typically increases the risk of the other. For example, if you want to decrease the probability of a Type I error (by setting a lower significance level), you might increase the probability of a Type II error unless you compensate by collecting more data or making other adjustments.
It’s essential to understand the consequences of both types of errors in any given context. In some situations, a Type I error might be more severe, while in others, a Type II error might be of greater concern. This understanding guides researchers in designing their experiments and choosing appropriate significance levels.
2.3. Calculate a test statistic and P-Value
Test statistic : A test statistic is a single number that helps us understand how far our sample data is from what we’d expect under a null hypothesis (a basic assumption we’re trying to test against). Generally, the larger the test statistic, the more evidence we have against our null hypothesis. It helps us decide whether the differences we observe in our data are due to random chance or if there’s an actual effect.
P-value : The P-value tells us how likely we would get our observed results (or something more extreme) if the null hypothesis were true. It’s a value between 0 and 1. – A smaller P-value (typically below 0.05) means that the observation is rare under the null hypothesis, so we might reject the null hypothesis. – A larger P-value suggests that what we observed could easily happen by random chance, so we might not reject the null hypothesis.
2.4. Make a Decision
Relationship between $α$ and P-Value
When conducting a hypothesis test:
We then calculate the p-value from our sample data and the test statistic.
Finally, we compare the p-value to our chosen $α$:
- If $p−value≤α$: We reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis. The result is said to be statistically significant.
- If $p−value>α$: We fail to reject the null hypothesis. There isn’t enough statistical evidence to support the alternative hypothesis.
3. Example : Testing a new drug.
Imagine we are investigating whether a new drug is effective at treating headaches faster than drug B.
Setting Up the Experiment : You gather 100 people who suffer from headaches. Half of them (50 people) are given the new drug (let’s call this the ‘Drug Group’), and the other half are given a sugar pill, which doesn’t contain any medication.
- Set up Hypotheses : Before starting, you make a prediction:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): The new drug has no effect. Any difference in healing time between the two groups is just due to random chance.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The new drug does have an effect. The difference in healing time between the two groups is significant and not just by chance.
Calculate Test statistic and P-Value : After the experiment, you analyze the data. The “test statistic” is a number that helps you understand the difference between the two groups in terms of standard units.
For instance, let’s say:
- The average healing time in the Drug Group is 2 hours.
- The average healing time in the Placebo Group is 3 hours.
The test statistic helps you understand how significant this 1-hour difference is. If the groups are large and the spread of healing times in each group is small, then this difference might be significant. But if there’s a huge variation in healing times, the 1-hour difference might not be so special.
Imagine the P-value as answering this question: “If the new drug had NO real effect, what’s the probability that I’d see a difference as extreme (or more extreme) as the one I found, just by random chance?”
For instance:
- P-value of 0.01 means there’s a 1% chance that the observed difference (or a more extreme difference) would occur if the drug had no effect. That’s pretty rare, so we might consider the drug effective.
- P-value of 0.5 means there’s a 50% chance you’d see this difference just by chance. That’s pretty high, so we might not be convinced the drug is doing much.
- If the P-value is less than ($α$) 0.05: the results are “statistically significant,” and they might reject the null hypothesis , believing the new drug has an effect.
- If the P-value is greater than ($α$) 0.05: the results are not statistically significant, and they don’t reject the null hypothesis , remaining unsure if the drug has a genuine effect.
4. Example in python
For simplicity, let’s say we’re using a t-test (common for comparing means). Let’s dive into Python:
Making a Decision : “The results are statistically significant! p-value < 0.05 , The drug seems to have an effect!” If not, we’d say, “Looks like the drug isn’t as miraculous as we thought.”
5. Conclusion
Hypothesis testing is an indispensable tool in data science, allowing us to make data-driven decisions with confidence. By understanding its principles, conducting tests properly, and considering real-world applications, you can harness the power of hypothesis testing to unlock valuable insights from your data.
More Articles
Correlation – connecting the dots, the role of correlation in data analysis, sampling and sampling distributions – a comprehensive guide on sampling and sampling distributions, law of large numbers – a deep dive into the world of statistics, central limit theorem – a deep dive into central limit theorem and its significance in statistics, skewness and kurtosis – peaks and tails, understanding data through skewness and kurtosis”, similar articles, complete introduction to linear regression in r, how to implement common statistical significance tests and find the p value, logistic regression – a complete tutorial with examples in r.
Subscribe to Machine Learning Plus for high value data science content
© Machinelearningplus. All rights reserved.

Machine Learning A-Z™: Hands-On Python & R In Data Science
Free sample videos:.


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.1: Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 10211

- Kyle Siegrist
- University of Alabama in Huntsville via Random Services
Basic Theory
Preliminaries.
As usual, our starting point is a random experiment with an underlying sample space and a probability measure \(\P\). In the basic statistical model, we have an observable random variable \(\bs{X}\) taking values in a set \(S\). In general, \(\bs{X}\) can have quite a complicated structure. For example, if the experiment is to sample \(n\) objects from a population and record various measurements of interest, then \[ \bs{X} = (X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n) \] where \(X_i\) is the vector of measurements for the \(i\)th object. The most important special case occurs when \((X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n)\) are independent and identically distributed. In this case, we have a random sample of size \(n\) from the common distribution.
The purpose of this section is to define and discuss the basic concepts of statistical hypothesis testing . Collectively, these concepts are sometimes referred to as the Neyman-Pearson framework, in honor of Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson, who first formalized them.
A statistical hypothesis is a statement about the distribution of \(\bs{X}\). Equivalently, a statistical hypothesis specifies a set of possible distributions of \(\bs{X}\): the set of distributions for which the statement is true. A hypothesis that specifies a single distribution for \(\bs{X}\) is called simple ; a hypothesis that specifies more than one distribution for \(\bs{X}\) is called composite .
In hypothesis testing , the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis . The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\).
An hypothesis test is a statistical decision ; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative, or to fail to reject the null hypothesis. The decision that we make must, of course, be based on the observed value \(\bs{x}\) of the data vector \(\bs{X}\). Thus, we will find an appropriate subset \(R\) of the sample space \(S\) and reject \(H_0\) if and only if \(\bs{x} \in R\). The set \(R\) is known as the rejection region or the critical region . Note the asymmetry between the null and alternative hypotheses. This asymmetry is due to the fact that we assume the null hypothesis, in a sense, and then see if there is sufficient evidence in \(\bs{x}\) to overturn this assumption in favor of the alternative.
An hypothesis test is a statistical analogy to proof by contradiction, in a sense. Suppose for a moment that \(H_1\) is a statement in a mathematical theory and that \(H_0\) is its negation. One way that we can prove \(H_1\) is to assume \(H_0\) and work our way logically to a contradiction. In an hypothesis test, we don't prove anything of course, but there are similarities. We assume \(H_0\) and then see if the data \(\bs{x}\) are sufficiently at odds with that assumption that we feel justified in rejecting \(H_0\) in favor of \(H_1\).
Often, the critical region is defined in terms of a statistic \(w(\bs{X})\), known as a test statistic , where \(w\) is a function from \(S\) into another set \(T\). We find an appropriate rejection region \(R_T \subseteq T\) and reject \(H_0\) when the observed value \(w(\bs{x}) \in R_T\). Thus, the rejection region in \(S\) is then \(R = w^{-1}(R_T) = \left\{\bs{x} \in S: w(\bs{x}) \in R_T\right\}\). As usual, the use of a statistic often allows significant data reduction when the dimension of the test statistic is much smaller than the dimension of the data vector.
The ultimate decision may be correct or may be in error. There are two types of errors, depending on which of the hypotheses is actually true.
Types of errors:
- A type 1 error is rejecting the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when \(H_0\) is true.
- A type 2 error is failing to reject the null hypothesis \(H_0\) when the alternative hypothesis \(H_1\) is true.
Similarly, there are two ways to make a correct decision: we could reject \(H_0\) when \(H_1\) is true or we could fail to reject \(H_0\) when \(H_0\) is true. The possibilities are summarized in the following table:
Of course, when we observe \(\bs{X} = \bs{x}\) and make our decision, either we will have made the correct decision or we will have committed an error, and usually we will never know which of these events has occurred. Prior to gathering the data, however, we can consider the probabilities of the various errors.
If \(H_0\) is true (that is, the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_0\)), then \(\P(\bs{X} \in R)\) is the probability of a type 1 error for this distribution. If \(H_0\) is composite, then \(H_0\) specifies a variety of different distributions for \(\bs{X}\) and thus there is a set of type 1 error probabilities.
The maximum probability of a type 1 error, over the set of distributions specified by \( H_0 \), is the significance level of the test or the size of the critical region.
The significance level is often denoted by \(\alpha\). Usually, the rejection region is constructed so that the significance level is a prescribed, small value (typically 0.1, 0.05, 0.01).
If \(H_1\) is true (that is, the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_1\)), then \(\P(\bs{X} \notin R)\) is the probability of a type 2 error for this distribution. Again, if \(H_1\) is composite then \(H_1\) specifies a variety of different distributions for \(\bs{X}\), and thus there will be a set of type 2 error probabilities. Generally, there is a tradeoff between the type 1 and type 2 error probabilities. If we reduce the probability of a type 1 error, by making the rejection region \(R\) smaller, we necessarily increase the probability of a type 2 error because the complementary region \(S \setminus R\) is larger.
The extreme cases can give us some insight. First consider the decision rule in which we never reject \(H_0\), regardless of the evidence \(\bs{x}\). This corresponds to the rejection region \(R = \emptyset\). A type 1 error is impossible, so the significance level is 0. On the other hand, the probability of a type 2 error is 1 for any distribution defined by \(H_1\). At the other extreme, consider the decision rule in which we always rejects \(H_0\) regardless of the evidence \(\bs{x}\). This corresponds to the rejection region \(R = S\). A type 2 error is impossible, but now the probability of a type 1 error is 1 for any distribution defined by \(H_0\). In between these two worthless tests are meaningful tests that take the evidence \(\bs{x}\) into account.
If \(H_1\) is true, so that the distribution of \(\bs{X}\) is specified by \(H_1\), then \(\P(\bs{X} \in R)\), the probability of rejecting \(H_0\) is the power of the test for that distribution.
Thus the power of the test for a distribution specified by \( H_1 \) is the probability of making the correct decision.
Suppose that we have two tests, corresponding to rejection regions \(R_1\) and \(R_2\), respectively, each having significance level \(\alpha\). The test with region \(R_1\) is uniformly more powerful than the test with region \(R_2\) if \[ \P(\bs{X} \in R_1) \ge \P(\bs{X} \in R_2) \text{ for every distribution of } \bs{X} \text{ specified by } H_1 \]
Naturally, in this case, we would prefer the first test. Often, however, two tests will not be uniformly ordered; one test will be more powerful for some distributions specified by \(H_1\) while the other test will be more powerful for other distributions specified by \(H_1\).
If a test has significance level \(\alpha\) and is uniformly more powerful than any other test with significance level \(\alpha\), then the test is said to be a uniformly most powerful test at level \(\alpha\).
Clearly a uniformly most powerful test is the best we can do.
\(P\)-value
In most cases, we have a general procedure that allows us to construct a test (that is, a rejection region \(R_\alpha\)) for any given significance level \(\alpha \in (0, 1)\). Typically, \(R_\alpha\) decreases (in the subset sense) as \(\alpha\) decreases.
The \(P\)-value of the observed value \(\bs{x}\) of \(\bs{X}\), denoted \(P(\bs{x})\), is defined to be the smallest \(\alpha\) for which \(\bs{x} \in R_\alpha\); that is, the smallest significance level for which \(H_0\) is rejected, given \(\bs{X} = \bs{x}\).
Knowing \(P(\bs{x})\) allows us to test \(H_0\) at any significance level for the given data \(\bs{x}\): If \(P(\bs{x}) \le \alpha\) then we would reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\); if \(P(\bs{x}) \gt \alpha\) then we fail to reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\). Note that \(P(\bs{X})\) is a statistic . Informally, \(P(\bs{x})\) can often be thought of as the probability of an outcome as or more extreme than the observed value \(\bs{x}\), where extreme is interpreted relative to the null hypothesis \(H_0\).
Analogy with Justice Systems
There is a helpful analogy between statistical hypothesis testing and the criminal justice system in the US and various other countries. Consider a person charged with a crime. The presumed null hypothesis is that the person is innocent of the crime; the conjectured alternative hypothesis is that the person is guilty of the crime. The test of the hypotheses is a trial with evidence presented by both sides playing the role of the data. After considering the evidence, the jury delivers the decision as either not guilty or guilty . Note that innocent is not a possible verdict of the jury, because it is not the point of the trial to prove the person innocent. Rather, the point of the trial is to see whether there is sufficient evidence to overturn the null hypothesis that the person is innocent in favor of the alternative hypothesis of that the person is guilty. A type 1 error is convicting a person who is innocent; a type 2 error is acquitting a person who is guilty. Generally, a type 1 error is considered the more serious of the two possible errors, so in an attempt to hold the chance of a type 1 error to a very low level, the standard for conviction in serious criminal cases is beyond a reasonable doubt .
Tests of an Unknown Parameter
Hypothesis testing is a very general concept, but an important special class occurs when the distribution of the data variable \(\bs{X}\) depends on a parameter \(\theta\) taking values in a parameter space \(\Theta\). The parameter may be vector-valued, so that \(\bs{\theta} = (\theta_1, \theta_2, \ldots, \theta_n)\) and \(\Theta \subseteq \R^k\) for some \(k \in \N_+\). The hypotheses generally take the form \[ H_0: \theta \in \Theta_0 \text{ versus } H_1: \theta \notin \Theta_0 \] where \(\Theta_0\) is a prescribed subset of the parameter space \(\Theta\). In this setting, the probabilities of making an error or a correct decision depend on the true value of \(\theta\). If \(R\) is the rejection region, then the power function \( Q \) is given by \[ Q(\theta) = \P_\theta(\bs{X} \in R), \quad \theta \in \Theta \] The power function gives a lot of information about the test.
The power function satisfies the following properties:
- \(Q(\theta)\) is the probability of a type 1 error when \(\theta \in \Theta_0\).
- \(\max\left\{Q(\theta): \theta \in \Theta_0\right\}\) is the significance level of the test.
- \(1 - Q(\theta)\) is the probability of a type 2 error when \(\theta \notin \Theta_0\).
- \(Q(\theta)\) is the power of the test when \(\theta \notin \Theta_0\).
If we have two tests, we can compare them by means of their power functions.
Suppose that we have two tests, corresponding to rejection regions \(R_1\) and \(R_2\), respectively, each having significance level \(\alpha\). The test with rejection region \(R_1\) is uniformly more powerful than the test with rejection region \(R_2\) if \( Q_1(\theta) \ge Q_2(\theta)\) for all \( \theta \notin \Theta_0 \).
Most hypothesis tests of an unknown real parameter \(\theta\) fall into three special cases:
Suppose that \( \theta \) is a real parameter and \( \theta_0 \in \Theta \) a specified value. The tests below are respectively the two-sided test , the left-tailed test , and the right-tailed test .
- \(H_0: \theta = \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0\)
- \(H_0: \theta \ge \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \lt \theta_0\)
- \(H_0: \theta \le \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \gt \theta_0\)
Thus the tests are named after the conjectured alternative. Of course, there may be other unknown parameters besides \(\theta\) (known as nuisance parameters ).
Equivalence Between Hypothesis Test and Confidence Sets
There is an equivalence between hypothesis tests and confidence sets for a parameter \(\theta\).
Suppose that \(C(\bs{x})\) is a \(1 - \alpha\) level confidence set for \(\theta\). The following test has significance level \(\alpha\) for the hypothesis \( H_0: \theta = \theta_0 \) versus \( H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0 \): Reject \(H_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \notin C(\bs{x})\)
By definition, \(\P[\theta \in C(\bs{X})] = 1 - \alpha\). Hence if \(H_0\) is true so that \(\theta = \theta_0\), then the probability of a type 1 error is \(P[\theta \notin C(\bs{X})] = \alpha\).
Equivalently, we fail to reject \(H_0\) at significance level \(\alpha\) if and only if \(\theta_0\) is in the corresponding \(1 - \alpha\) level confidence set. In particular, this equivalence applies to interval estimates of a real parameter \(\theta\) and the common tests for \(\theta\) given above .
In each case below, the confidence interval has confidence level \(1 - \alpha\) and the test has significance level \(\alpha\).
- Suppose that \(\left[L(\bs{X}, U(\bs{X})\right]\) is a two-sided confidence interval for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta = \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \ne \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \lt L(\bs{X})\) or \(\theta_0 \gt U(\bs{X})\).
- Suppose that \(L(\bs{X})\) is a confidence lower bound for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta \le \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \gt \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \lt L(\bs{X})\).
- Suppose that \(U(\bs{X})\) is a confidence upper bound for \(\theta\). Reject \(H_0: \theta \ge \theta_0\) versus \(H_1: \theta \lt \theta_0\) if and only if \(\theta_0 \gt U(\bs{X})\).
Pivot Variables and Test Statistics
Recall that confidence sets of an unknown parameter \(\theta\) are often constructed through a pivot variable , that is, a random variable \(W(\bs{X}, \theta)\) that depends on the data vector \(\bs{X}\) and the parameter \(\theta\), but whose distribution does not depend on \(\theta\) and is known. In this case, a natural test statistic for the basic tests given above is \(W(\bs{X}, \theta_0)\).
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
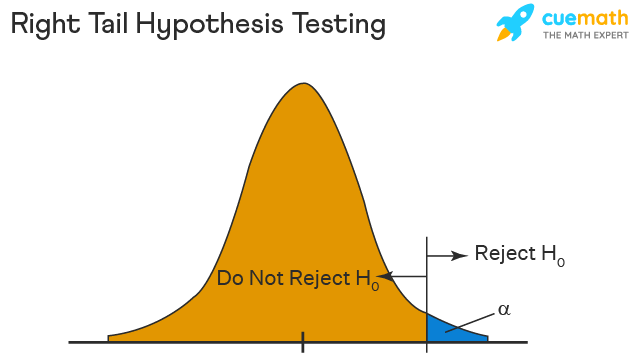
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
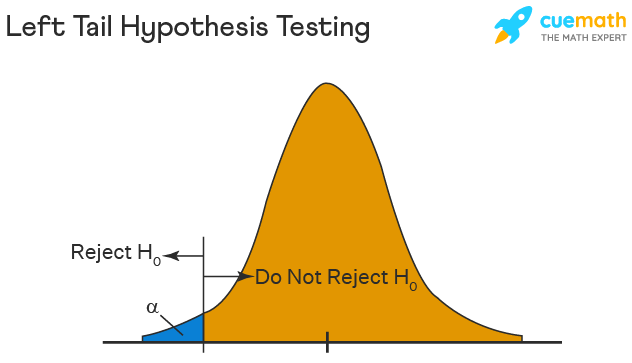
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
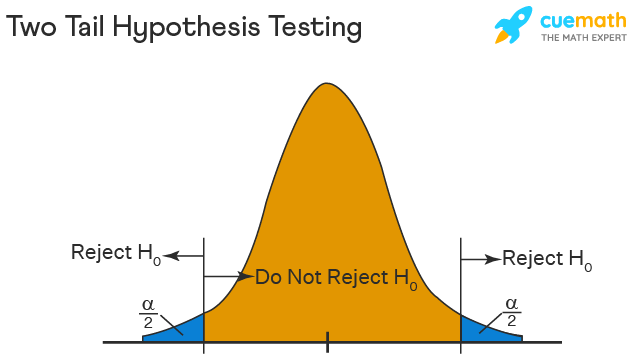
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.

What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.
Hypothesis Testing for Means & Proportions
Lisa Sullivan, PhD
Professor of Biostatistics
Boston University School of Public Health

Introduction
This is the first of three modules that will addresses the second area of statistical inference, which is hypothesis testing, in which a specific statement or hypothesis is generated about a population parameter, and sample statistics are used to assess the likelihood that the hypothesis is true. The hypothesis is based on available information and the investigator's belief about the population parameters. The process of hypothesis testing involves setting up two competing hypotheses, the null hypothesis and the alternate hypothesis. One selects a random sample (or multiple samples when there are more comparison groups), computes summary statistics and then assesses the likelihood that the sample data support the research or alternative hypothesis. Similar to estimation, the process of hypothesis testing is based on probability theory and the Central Limit Theorem.
This module will focus on hypothesis testing for means and proportions. The next two modules in this series will address analysis of variance and chi-squared tests.
Learning Objectives
After completing this module, the student will be able to:
- Define null and research hypothesis, test statistic, level of significance and decision rule
- Distinguish between Type I and Type II errors and discuss the implications of each
- Explain the difference between one and two sided tests of hypothesis
- Estimate and interpret p-values
- Explain the relationship between confidence interval estimates and p-values in drawing inferences
- Differentiate hypothesis testing procedures based on type of outcome variable and number of sample
Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
Techniques for hypothesis testing .
The techniques for hypothesis testing depend on
- the type of outcome variable being analyzed (continuous, dichotomous, discrete)
- the number of comparison groups in the investigation
- whether the comparison groups are independent (i.e., physically separate such as men versus women) or dependent (i.e., matched or paired such as pre- and post-assessments on the same participants).
In estimation we focused explicitly on techniques for one and two samples and discussed estimation for a specific parameter (e.g., the mean or proportion of a population), for differences (e.g., difference in means, the risk difference) and ratios (e.g., the relative risk and odds ratio). Here we will focus on procedures for one and two samples when the outcome is either continuous (and we focus on means) or dichotomous (and we focus on proportions).
General Approach: A Simple Example
The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reported on trends in weight, height and body mass index from the 1960's through 2002. 1 The general trend was that Americans were much heavier and slightly taller in 2002 as compared to 1960; both men and women gained approximately 24 pounds, on average, between 1960 and 2002. In 2002, the mean weight for men was reported at 191 pounds. Suppose that an investigator hypothesizes that weights are even higher in 2006 (i.e., that the trend continued over the subsequent 4 years). The research hypothesis is that the mean weight in men in 2006 is more than 191 pounds. The null hypothesis is that there is no change in weight, and therefore the mean weight is still 191 pounds in 2006.
In order to test the hypotheses, we select a random sample of American males in 2006 and measure their weights. Suppose we have resources available to recruit n=100 men into our sample. We weigh each participant and compute summary statistics on the sample data. Suppose in the sample we determine the following:
Do the sample data support the null or research hypothesis? The sample mean of 197.1 is numerically higher than 191. However, is this difference more than would be expected by chance? In hypothesis testing, we assume that the null hypothesis holds until proven otherwise. We therefore need to determine the likelihood of observing a sample mean of 197.1 or higher when the true population mean is 191 (i.e., if the null hypothesis is true or under the null hypothesis). We can compute this probability using the Central Limit Theorem. Specifically,
(Notice that we use the sample standard deviation in computing the Z score. This is generally an appropriate substitution as long as the sample size is large, n > 30. Thus, there is less than a 1% probability of observing a sample mean as large as 197.1 when the true population mean is 191. Do you think that the null hypothesis is likely true? Based on how unlikely it is to observe a sample mean of 197.1 under the null hypothesis (i.e., <1% probability), we might infer, from our data, that the null hypothesis is probably not true.
Suppose that the sample data had turned out differently. Suppose that we instead observed the following in 2006:
How likely it is to observe a sample mean of 192.1 or higher when the true population mean is 191 (i.e., if the null hypothesis is true)? We can again compute this probability using the Central Limit Theorem. Specifically,
There is a 33.4% probability of observing a sample mean as large as 192.1 when the true population mean is 191. Do you think that the null hypothesis is likely true?
Neither of the sample means that we obtained allows us to know with certainty whether the null hypothesis is true or not. However, our computations suggest that, if the null hypothesis were true, the probability of observing a sample mean >197.1 is less than 1%. In contrast, if the null hypothesis were true, the probability of observing a sample mean >192.1 is about 33%. We can't know whether the null hypothesis is true, but the sample that provided a mean value of 197.1 provides much stronger evidence in favor of rejecting the null hypothesis, than the sample that provided a mean value of 192.1. Note that this does not mean that a sample mean of 192.1 indicates that the null hypothesis is true; it just doesn't provide compelling evidence to reject it.
In essence, hypothesis testing is a procedure to compute a probability that reflects the strength of the evidence (based on a given sample) for rejecting the null hypothesis. In hypothesis testing, we determine a threshold or cut-off point (called the critical value) to decide when to believe the null hypothesis and when to believe the research hypothesis. It is important to note that it is possible to observe any sample mean when the true population mean is true (in this example equal to 191), but some sample means are very unlikely. Based on the two samples above it would seem reasonable to believe the research hypothesis when x̄ = 197.1, but to believe the null hypothesis when x̄ =192.1. What we need is a threshold value such that if x̄ is above that threshold then we believe that H 1 is true and if x̄ is below that threshold then we believe that H 0 is true. The difficulty in determining a threshold for x̄ is that it depends on the scale of measurement. In this example, the threshold, sometimes called the critical value, might be 195 (i.e., if the sample mean is 195 or more then we believe that H 1 is true and if the sample mean is less than 195 then we believe that H 0 is true). Suppose we are interested in assessing an increase in blood pressure over time, the critical value will be different because blood pressures are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) as opposed to in pounds. In the following we will explain how the critical value is determined and how we handle the issue of scale.
First, to address the issue of scale in determining the critical value, we convert our sample data (in particular the sample mean) into a Z score. We know from the module on probability that the center of the Z distribution is zero and extreme values are those that exceed 2 or fall below -2. Z scores above 2 and below -2 represent approximately 5% of all Z values. If the observed sample mean is close to the mean specified in H 0 (here m =191), then Z will be close to zero. If the observed sample mean is much larger than the mean specified in H 0 , then Z will be large.
In hypothesis testing, we select a critical value from the Z distribution. This is done by first determining what is called the level of significance, denoted α ("alpha"). What we are doing here is drawing a line at extreme values. The level of significance is the probability that we reject the null hypothesis (in favor of the alternative) when it is actually true and is also called the Type I error rate.
α = Level of significance = P(Type I error) = P(Reject H 0 | H 0 is true).
Because α is a probability, it ranges between 0 and 1. The most commonly used value in the medical literature for α is 0.05, or 5%. Thus, if an investigator selects α=0.05, then they are allowing a 5% probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative when the null is in fact true. Depending on the circumstances, one might choose to use a level of significance of 1% or 10%. For example, if an investigator wanted to reject the null only if there were even stronger evidence than that ensured with α=0.05, they could choose a =0.01as their level of significance. The typical values for α are 0.01, 0.05 and 0.10, with α=0.05 the most commonly used value.
Suppose in our weight study we select α=0.05. We need to determine the value of Z that holds 5% of the values above it (see below).

The critical value of Z for α =0.05 is Z = 1.645 (i.e., 5% of the distribution is above Z=1.645). With this value we can set up what is called our decision rule for the test. The rule is to reject H 0 if the Z score is 1.645 or more.
With the first sample we have
Because 2.38 > 1.645, we reject the null hypothesis. (The same conclusion can be drawn by comparing the 0.0087 probability of observing a sample mean as extreme as 197.1 to the level of significance of 0.05. If the observed probability is smaller than the level of significance we reject H 0 ). Because the Z score exceeds the critical value, we conclude that the mean weight for men in 2006 is more than 191 pounds, the value reported in 2002. If we observed the second sample (i.e., sample mean =192.1), we would not be able to reject the null hypothesis because the Z score is 0.43 which is not in the rejection region (i.e., the region in the tail end of the curve above 1.645). With the second sample we do not have sufficient evidence (because we set our level of significance at 5%) to conclude that weights have increased. Again, the same conclusion can be reached by comparing probabilities. The probability of observing a sample mean as extreme as 192.1 is 33.4% which is not below our 5% level of significance.
Hypothesis Testing: Upper-, Lower, and Two Tailed Tests
The procedure for hypothesis testing is based on the ideas described above. Specifically, we set up competing hypotheses, select a random sample from the population of interest and compute summary statistics. We then determine whether the sample data supports the null or alternative hypotheses. The procedure can be broken down into the following five steps.
- Step 1. Set up hypotheses and select the level of significance α.
H 0 : Null hypothesis (no change, no difference);
H 1 : Research hypothesis (investigator's belief); α =0.05
- Step 2. Select the appropriate test statistic.
The test statistic is a single number that summarizes the sample information. An example of a test statistic is the Z statistic computed as follows:
When the sample size is small, we will use t statistics (just as we did when constructing confidence intervals for small samples). As we present each scenario, alternative test statistics are provided along with conditions for their appropriate use.
- Step 3. Set up decision rule.
The decision rule is a statement that tells under what circumstances to reject the null hypothesis. The decision rule is based on specific values of the test statistic (e.g., reject H 0 if Z > 1.645). The decision rule for a specific test depends on 3 factors: the research or alternative hypothesis, the test statistic and the level of significance. Each is discussed below.
- The decision rule depends on whether an upper-tailed, lower-tailed, or two-tailed test is proposed. In an upper-tailed test the decision rule has investigators reject H 0 if the test statistic is larger than the critical value. In a lower-tailed test the decision rule has investigators reject H 0 if the test statistic is smaller than the critical value. In a two-tailed test the decision rule has investigators reject H 0 if the test statistic is extreme, either larger than an upper critical value or smaller than a lower critical value.
- The exact form of the test statistic is also important in determining the decision rule. If the test statistic follows the standard normal distribution (Z), then the decision rule will be based on the standard normal distribution. If the test statistic follows the t distribution, then the decision rule will be based on the t distribution. The appropriate critical value will be selected from the t distribution again depending on the specific alternative hypothesis and the level of significance.
- The third factor is the level of significance. The level of significance which is selected in Step 1 (e.g., α =0.05) dictates the critical value. For example, in an upper tailed Z test, if α =0.05 then the critical value is Z=1.645.
The following figures illustrate the rejection regions defined by the decision rule for upper-, lower- and two-tailed Z tests with α=0.05. Notice that the rejection regions are in the upper, lower and both tails of the curves, respectively. The decision rules are written below each figure.

Rejection Region for Lower-Tailed Z Test (H 1 : μ < μ 0 ) with α =0.05
The decision rule is: Reject H 0 if Z < 1.645.

Rejection Region for Two-Tailed Z Test (H 1 : μ ≠ μ 0 ) with α =0.05
The decision rule is: Reject H 0 if Z < -1.960 or if Z > 1.960.
The complete table of critical values of Z for upper, lower and two-tailed tests can be found in the table of Z values to the right in "Other Resources."
Critical values of t for upper, lower and two-tailed tests can be found in the table of t values in "Other Resources."
- Step 4. Compute the test statistic.
Here we compute the test statistic by substituting the observed sample data into the test statistic identified in Step 2.
- Step 5. Conclusion.
The final conclusion is made by comparing the test statistic (which is a summary of the information observed in the sample) to the decision rule. The final conclusion will be either to reject the null hypothesis (because the sample data are very unlikely if the null hypothesis is true) or not to reject the null hypothesis (because the sample data are not very unlikely).
If the null hypothesis is rejected, then an exact significance level is computed to describe the likelihood of observing the sample data assuming that the null hypothesis is true. The exact level of significance is called the p-value and it will be less than the chosen level of significance if we reject H 0 .
Statistical computing packages provide exact p-values as part of their standard output for hypothesis tests. In fact, when using a statistical computing package, the steps outlined about can be abbreviated. The hypotheses (step 1) should always be set up in advance of any analysis and the significance criterion should also be determined (e.g., α =0.05). Statistical computing packages will produce the test statistic (usually reporting the test statistic as t) and a p-value. The investigator can then determine statistical significance using the following: If p < α then reject H 0 .
- Step 1. Set up hypotheses and determine level of significance
H 0 : μ = 191 H 1 : μ > 191 α =0.05
The research hypothesis is that weights have increased, and therefore an upper tailed test is used.
- Step 2. Select the appropriate test statistic.
Because the sample size is large (n > 30) the appropriate test statistic is
- Step 3. Set up decision rule.
In this example, we are performing an upper tailed test (H 1 : μ> 191), with a Z test statistic and selected α =0.05. Reject H 0 if Z > 1.645.
We now substitute the sample data into the formula for the test statistic identified in Step 2.
We reject H 0 because 2.38 > 1.645. We have statistically significant evidence at a =0.05, to show that the mean weight in men in 2006 is more than 191 pounds. Because we rejected the null hypothesis, we now approximate the p-value which is the likelihood of observing the sample data if the null hypothesis is true. An alternative definition of the p-value is the smallest level of significance where we can still reject H 0 . In this example, we observed Z=2.38 and for α=0.05, the critical value was 1.645. Because 2.38 exceeded 1.645 we rejected H 0 . In our conclusion we reported a statistically significant increase in mean weight at a 5% level of significance. Using the table of critical values for upper tailed tests, we can approximate the p-value. If we select α=0.025, the critical value is 1.96, and we still reject H 0 because 2.38 > 1.960. If we select α=0.010 the critical value is 2.326, and we still reject H 0 because 2.38 > 2.326. However, if we select α=0.005, the critical value is 2.576, and we cannot reject H 0 because 2.38 < 2.576. Therefore, the smallest α where we still reject H 0 is 0.010. This is the p-value. A statistical computing package would produce a more precise p-value which would be in between 0.005 and 0.010. Here we are approximating the p-value and would report p < 0.010.
Type I and Type II Errors
In all tests of hypothesis, there are two types of errors that can be committed. The first is called a Type I error and refers to the situation where we incorrectly reject H 0 when in fact it is true. This is also called a false positive result (as we incorrectly conclude that the research hypothesis is true when in fact it is not). When we run a test of hypothesis and decide to reject H 0 (e.g., because the test statistic exceeds the critical value in an upper tailed test) then either we make a correct decision because the research hypothesis is true or we commit a Type I error. The different conclusions are summarized in the table below. Note that we will never know whether the null hypothesis is really true or false (i.e., we will never know which row of the following table reflects reality).
Table - Conclusions in Test of Hypothesis
In the first step of the hypothesis test, we select a level of significance, α, and α= P(Type I error). Because we purposely select a small value for α, we control the probability of committing a Type I error. For example, if we select α=0.05, and our test tells us to reject H 0 , then there is a 5% probability that we commit a Type I error. Most investigators are very comfortable with this and are confident when rejecting H 0 that the research hypothesis is true (as it is the more likely scenario when we reject H 0 ).
When we run a test of hypothesis and decide not to reject H 0 (e.g., because the test statistic is below the critical value in an upper tailed test) then either we make a correct decision because the null hypothesis is true or we commit a Type II error. Beta (β) represents the probability of a Type II error and is defined as follows: β=P(Type II error) = P(Do not Reject H 0 | H 0 is false). Unfortunately, we cannot choose β to be small (e.g., 0.05) to control the probability of committing a Type II error because β depends on several factors including the sample size, α, and the research hypothesis. When we do not reject H 0 , it may be very likely that we are committing a Type II error (i.e., failing to reject H 0 when in fact it is false). Therefore, when tests are run and the null hypothesis is not rejected we often make a weak concluding statement allowing for the possibility that we might be committing a Type II error. If we do not reject H 0 , we conclude that we do not have significant evidence to show that H 1 is true. We do not conclude that H 0 is true.

The most common reason for a Type II error is a small sample size.
Tests with One Sample, Continuous Outcome
Hypothesis testing applications with a continuous outcome variable in a single population are performed according to the five-step procedure outlined above. A key component is setting up the null and research hypotheses. The objective is to compare the mean in a single population to known mean (μ 0 ). The known value is generally derived from another study or report, for example a study in a similar, but not identical, population or a study performed some years ago. The latter is called a historical control. It is important in setting up the hypotheses in a one sample test that the mean specified in the null hypothesis is a fair and reasonable comparator. This will be discussed in the examples that follow.
Test Statistics for Testing H 0 : μ= μ 0
- if n > 30
- if n < 30
Note that statistical computing packages will use the t statistic exclusively and make the necessary adjustments for comparing the test statistic to appropriate values from probability tables to produce a p-value.
The National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) published a report in 2005 entitled Health, United States, containing extensive information on major trends in the health of Americans. Data are provided for the US population as a whole and for specific ages, sexes and races. The NCHS report indicated that in 2002 Americans paid an average of $3,302 per year on health care and prescription drugs. An investigator hypothesizes that in 2005 expenditures have decreased primarily due to the availability of generic drugs. To test the hypothesis, a sample of 100 Americans are selected and their expenditures on health care and prescription drugs in 2005 are measured. The sample data are summarized as follows: n=100, x̄
=$3,190 and s=$890. Is there statistical evidence of a reduction in expenditures on health care and prescription drugs in 2005? Is the sample mean of $3,190 evidence of a true reduction in the mean or is it within chance fluctuation? We will run the test using the five-step approach.
- Step 1. Set up hypotheses and determine level of significance
H 0 : μ = 3,302 H 1 : μ < 3,302 α =0.05
The research hypothesis is that expenditures have decreased, and therefore a lower-tailed test is used.
This is a lower tailed test, using a Z statistic and a 5% level of significance. Reject H 0 if Z < -1.645.
- Step 4. Compute the test statistic.
We do not reject H 0 because -1.26 > -1.645. We do not have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that the mean expenditures on health care and prescription drugs are lower in 2005 than the mean of $3,302 reported in 2002.
Recall that when we fail to reject H 0 in a test of hypothesis that either the null hypothesis is true (here the mean expenditures in 2005 are the same as those in 2002 and equal to $3,302) or we committed a Type II error (i.e., we failed to reject H 0 when in fact it is false). In summarizing this test, we conclude that we do not have sufficient evidence to reject H 0 . We do not conclude that H 0 is true, because there may be a moderate to high probability that we committed a Type II error. It is possible that the sample size is not large enough to detect a difference in mean expenditures.
The NCHS reported that the mean total cholesterol level in 2002 for all adults was 203. Total cholesterol levels in participants who attended the seventh examination of the Offspring in the Framingham Heart Study are summarized as follows: n=3,310, x̄ =200.3, and s=36.8. Is there statistical evidence of a difference in mean cholesterol levels in the Framingham Offspring?
Here we want to assess whether the sample mean of 200.3 in the Framingham sample is statistically significantly different from 203 (i.e., beyond what we would expect by chance). We will run the test using the five-step approach.
H 0 : μ= 203 H 1 : μ≠ 203 α=0.05
The research hypothesis is that cholesterol levels are different in the Framingham Offspring, and therefore a two-tailed test is used.
- Step 3. Set up decision rule.
This is a two-tailed test, using a Z statistic and a 5% level of significance. Reject H 0 if Z < -1.960 or is Z > 1.960.
We reject H 0 because -4.22 ≤ -1. .960. We have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that the mean total cholesterol level in the Framingham Offspring is different from the national average of 203 reported in 2002. Because we reject H 0 , we also approximate a p-value. Using the two-sided significance levels, p < 0.0001.
Statistical Significance versus Clinical (Practical) Significance
This example raises an important concept of statistical versus clinical or practical significance. From a statistical standpoint, the total cholesterol levels in the Framingham sample are highly statistically significantly different from the national average with p < 0.0001 (i.e., there is less than a 0.01% chance that we are incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis). However, the sample mean in the Framingham Offspring study is 200.3, less than 3 units different from the national mean of 203. The reason that the data are so highly statistically significant is due to the very large sample size. It is always important to assess both statistical and clinical significance of data. This is particularly relevant when the sample size is large. Is a 3 unit difference in total cholesterol a meaningful difference?
Consider again the NCHS-reported mean total cholesterol level in 2002 for all adults of 203. Suppose a new drug is proposed to lower total cholesterol. A study is designed to evaluate the efficacy of the drug in lowering cholesterol. Fifteen patients are enrolled in the study and asked to take the new drug for 6 weeks. At the end of 6 weeks, each patient's total cholesterol level is measured and the sample statistics are as follows: n=15, x̄ =195.9 and s=28.7. Is there statistical evidence of a reduction in mean total cholesterol in patients after using the new drug for 6 weeks? We will run the test using the five-step approach.
H 0 : μ= 203 H 1 : μ< 203 α=0.05
- Step 2. Select the appropriate test statistic.
Because the sample size is small (n<30) the appropriate test statistic is
This is a lower tailed test, using a t statistic and a 5% level of significance. In order to determine the critical value of t, we need degrees of freedom, df, defined as df=n-1. In this example df=15-1=14. The critical value for a lower tailed test with df=14 and a =0.05 is -2.145 and the decision rule is as follows: Reject H 0 if t < -2.145.
We do not reject H 0 because -0.96 > -2.145. We do not have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that the mean total cholesterol level is lower than the national mean in patients taking the new drug for 6 weeks. Again, because we failed to reject the null hypothesis we make a weaker concluding statement allowing for the possibility that we may have committed a Type II error (i.e., failed to reject H 0 when in fact the drug is efficacious).

This example raises an important issue in terms of study design. In this example we assume in the null hypothesis that the mean cholesterol level is 203. This is taken to be the mean cholesterol level in patients without treatment. Is this an appropriate comparator? Alternative and potentially more efficient study designs to evaluate the effect of the new drug could involve two treatment groups, where one group receives the new drug and the other does not, or we could measure each patient's baseline or pre-treatment cholesterol level and then assess changes from baseline to 6 weeks post-treatment. These designs are also discussed here.
Video - Comparing a Sample Mean to Known Population Mean (8:20)
Link to transcript of the video
Tests with One Sample, Dichotomous Outcome
Hypothesis testing applications with a dichotomous outcome variable in a single population are also performed according to the five-step procedure. Similar to tests for means, a key component is setting up the null and research hypotheses. The objective is to compare the proportion of successes in a single population to a known proportion (p 0 ). That known proportion is generally derived from another study or report and is sometimes called a historical control. It is important in setting up the hypotheses in a one sample test that the proportion specified in the null hypothesis is a fair and reasonable comparator.
In one sample tests for a dichotomous outcome, we set up our hypotheses against an appropriate comparator. We select a sample and compute descriptive statistics on the sample data. Specifically, we compute the sample size (n) and the sample proportion which is computed by taking the ratio of the number of successes to the sample size,
We then determine the appropriate test statistic (Step 2) for the hypothesis test. The formula for the test statistic is given below.
Test Statistic for Testing H 0 : p = p 0
if min(np 0 , n(1-p 0 )) > 5
The formula above is appropriate for large samples, defined when the smaller of np 0 and n(1-p 0 ) is at least 5. This is similar, but not identical, to the condition required for appropriate use of the confidence interval formula for a population proportion, i.e.,
Here we use the proportion specified in the null hypothesis as the true proportion of successes rather than the sample proportion. If we fail to satisfy the condition, then alternative procedures, called exact methods must be used to test the hypothesis about the population proportion.
Example:
The NCHS report indicated that in 2002 the prevalence of cigarette smoking among American adults was 21.1%. Data on prevalent smoking in n=3,536 participants who attended the seventh examination of the Offspring in the Framingham Heart Study indicated that 482/3,536 = 13.6% of the respondents were currently smoking at the time of the exam. Suppose we want to assess whether the prevalence of smoking is lower in the Framingham Offspring sample given the focus on cardiovascular health in that community. Is there evidence of a statistically lower prevalence of smoking in the Framingham Offspring study as compared to the prevalence among all Americans?
H 0 : p = 0.211 H 1 : p < 0.211 α=0.05
We must first check that the sample size is adequate. Specifically, we need to check min(np 0 , n(1-p 0 )) = min( 3,536(0.211), 3,536(1-0.211))=min(746, 2790)=746. The sample size is more than adequate so the following formula can be used:
This is a lower tailed test, using a Z statistic and a 5% level of significance. Reject H 0 if Z < -1.645.
We reject H 0 because -10.93 < -1.645. We have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that the prevalence of smoking in the Framingham Offspring is lower than the prevalence nationally (21.1%). Here, p < 0.0001.
The NCHS report indicated that in 2002, 75% of children aged 2 to 17 saw a dentist in the past year. An investigator wants to assess whether use of dental services is similar in children living in the city of Boston. A sample of 125 children aged 2 to 17 living in Boston are surveyed and 64 reported seeing a dentist over the past 12 months. Is there a significant difference in use of dental services between children living in Boston and the national data?
Calculate this on your own before checking the answer.
Video - Hypothesis Test for One Sample and a Dichotomous Outcome (3:55)
Tests with Two Independent Samples, Continuous Outcome
There are many applications where it is of interest to compare two independent groups with respect to their mean scores on a continuous outcome. Here we compare means between groups, but rather than generating an estimate of the difference, we will test whether the observed difference (increase, decrease or difference) is statistically significant or not. Remember, that hypothesis testing gives an assessment of statistical significance, whereas estimation gives an estimate of effect and both are important.
Here we discuss the comparison of means when the two comparison groups are independent or physically separate. The two groups might be determined by a particular attribute (e.g., sex, diagnosis of cardiovascular disease) or might be set up by the investigator (e.g., participants assigned to receive an experimental treatment or placebo). The first step in the analysis involves computing descriptive statistics on each of the two samples. Specifically, we compute the sample size, mean and standard deviation in each sample and we denote these summary statistics as follows:
for sample 1:
for sample 2:
The designation of sample 1 and sample 2 is arbitrary. In a clinical trial setting the convention is to call the treatment group 1 and the control group 2. However, when comparing men and women, for example, either group can be 1 or 2.
In the two independent samples application with a continuous outcome, the parameter of interest in the test of hypothesis is the difference in population means, μ 1 -μ 2 . The null hypothesis is always that there is no difference between groups with respect to means, i.e.,
The null hypothesis can also be written as follows: H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2 . In the research hypothesis, an investigator can hypothesize that the first mean is larger than the second (H 1 : μ 1 > μ 2 ), that the first mean is smaller than the second (H 1 : μ 1 < μ 2 ), or that the means are different (H 1 : μ 1 ≠ μ 2 ). The three different alternatives represent upper-, lower-, and two-tailed tests, respectively. The following test statistics are used to test these hypotheses.
Test Statistics for Testing H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2
- if n 1 > 30 and n 2 > 30
- if n 1 < 30 or n 2 < 30
NOTE: The formulas above assume equal variability in the two populations (i.e., the population variances are equal, or s 1 2 = s 2 2 ). This means that the outcome is equally variable in each of the comparison populations. For analysis, we have samples from each of the comparison populations. If the sample variances are similar, then the assumption about variability in the populations is probably reasonable. As a guideline, if the ratio of the sample variances, s 1 2 /s 2 2 is between 0.5 and 2 (i.e., if one variance is no more than double the other), then the formulas above are appropriate. If the ratio of the sample variances is greater than 2 or less than 0.5 then alternative formulas must be used to account for the heterogeneity in variances.
The test statistics include Sp, which is the pooled estimate of the common standard deviation (again assuming that the variances in the populations are similar) computed as the weighted average of the standard deviations in the samples as follows:
Because we are assuming equal variances between groups, we pool the information on variability (sample variances) to generate an estimate of the variability in the population. Note: Because Sp is a weighted average of the standard deviations in the sample, Sp will always be in between s 1 and s 2 .)
Data measured on n=3,539 participants who attended the seventh examination of the Offspring in the Framingham Heart Study are shown below.
Suppose we now wish to assess whether there is a statistically significant difference in mean systolic blood pressures between men and women using a 5% level of significance.
H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2
H 1 : μ 1 ≠ μ 2 α=0.05
Because both samples are large ( > 30), we can use the Z test statistic as opposed to t. Note that statistical computing packages use t throughout. Before implementing the formula, we first check whether the assumption of equality of population variances is reasonable. The guideline suggests investigating the ratio of the sample variances, s 1 2 /s 2 2 . Suppose we call the men group 1 and the women group 2. Again, this is arbitrary; it only needs to be noted when interpreting the results. The ratio of the sample variances is 17.5 2 /20.1 2 = 0.76, which falls between 0.5 and 2 suggesting that the assumption of equality of population variances is reasonable. The appropriate test statistic is
We now substitute the sample data into the formula for the test statistic identified in Step 2. Before substituting, we will first compute Sp, the pooled estimate of the common standard deviation.
Notice that the pooled estimate of the common standard deviation, Sp, falls in between the standard deviations in the comparison groups (i.e., 17.5 and 20.1). Sp is slightly closer in value to the standard deviation in the women (20.1) as there were slightly more women in the sample. Recall, Sp is a weight average of the standard deviations in the comparison groups, weighted by the respective sample sizes.
Now the test statistic:
We reject H 0 because 2.66 > 1.960. We have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that there is a difference in mean systolic blood pressures between men and women. The p-value is p < 0.010.
Here again we find that there is a statistically significant difference in mean systolic blood pressures between men and women at p < 0.010. Notice that there is a very small difference in the sample means (128.2-126.5 = 1.7 units), but this difference is beyond what would be expected by chance. Is this a clinically meaningful difference? The large sample size in this example is driving the statistical significance. A 95% confidence interval for the difference in mean systolic blood pressures is: 1.7 + 1.26 or (0.44, 2.96). The confidence interval provides an assessment of the magnitude of the difference between means whereas the test of hypothesis and p-value provide an assessment of the statistical significance of the difference.
Above we performed a study to evaluate a new drug designed to lower total cholesterol. The study involved one sample of patients, each patient took the new drug for 6 weeks and had their cholesterol measured. As a means of evaluating the efficacy of the new drug, the mean total cholesterol following 6 weeks of treatment was compared to the NCHS-reported mean total cholesterol level in 2002 for all adults of 203. At the end of the example, we discussed the appropriateness of the fixed comparator as well as an alternative study design to evaluate the effect of the new drug involving two treatment groups, where one group receives the new drug and the other does not. Here, we revisit the example with a concurrent or parallel control group, which is very typical in randomized controlled trials or clinical trials (refer to the EP713 module on Clinical Trials).
A new drug is proposed to lower total cholesterol. A randomized controlled trial is designed to evaluate the efficacy of the medication in lowering cholesterol. Thirty participants are enrolled in the trial and are randomly assigned to receive either the new drug or a placebo. The participants do not know which treatment they are assigned. Each participant is asked to take the assigned treatment for 6 weeks. At the end of 6 weeks, each patient's total cholesterol level is measured and the sample statistics are as follows.
Is there statistical evidence of a reduction in mean total cholesterol in patients taking the new drug for 6 weeks as compared to participants taking placebo? We will run the test using the five-step approach.
H 0 : μ 1 = μ 2 H 1 : μ 1 < μ 2 α=0.05
Because both samples are small (< 30), we use the t test statistic. Before implementing the formula, we first check whether the assumption of equality of population variances is reasonable. The ratio of the sample variances, s 1 2 /s 2 2 =28.7 2 /30.3 2 = 0.90, which falls between 0.5 and 2, suggesting that the assumption of equality of population variances is reasonable. The appropriate test statistic is:
This is a lower-tailed test, using a t statistic and a 5% level of significance. The appropriate critical value can be found in the t Table (in More Resources to the right). In order to determine the critical value of t we need degrees of freedom, df, defined as df=n 1 +n 2 -2 = 15+15-2=28. The critical value for a lower tailed test with df=28 and α=0.05 is -1.701 and the decision rule is: Reject H 0 if t < -1.701.
Now the test statistic,
We reject H 0 because -2.92 < -1.701. We have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that the mean total cholesterol level is lower in patients taking the new drug for 6 weeks as compared to patients taking placebo, p < 0.005.
The clinical trial in this example finds a statistically significant reduction in total cholesterol, whereas in the previous example where we had a historical control (as opposed to a parallel control group) we did not demonstrate efficacy of the new drug. Notice that the mean total cholesterol level in patients taking placebo is 217.4 which is very different from the mean cholesterol reported among all Americans in 2002 of 203 and used as the comparator in the prior example. The historical control value may not have been the most appropriate comparator as cholesterol levels have been increasing over time. In the next section, we present another design that can be used to assess the efficacy of the new drug.
Video - Comparison of Two Independent Samples With a Continuous Outcome (8:02)
Tests with Matched Samples, Continuous Outcome
In the previous section we compared two groups with respect to their mean scores on a continuous outcome. An alternative study design is to compare matched or paired samples. The two comparison groups are said to be dependent, and the data can arise from a single sample of participants where each participant is measured twice (possibly before and after an intervention) or from two samples that are matched on specific characteristics (e.g., siblings). When the samples are dependent, we focus on difference scores in each participant or between members of a pair and the test of hypothesis is based on the mean difference, μ d . The null hypothesis again reflects "no difference" and is stated as H 0 : μ d =0 . Note that there are some instances where it is of interest to test whether there is a difference of a particular magnitude (e.g., μ d =5) but in most instances the null hypothesis reflects no difference (i.e., μ d =0).
The appropriate formula for the test of hypothesis depends on the sample size. The formulas are shown below and are identical to those we presented for estimating the mean of a single sample presented (e.g., when comparing against an external or historical control), except here we focus on difference scores.
Test Statistics for Testing H 0 : μ d =0
A new drug is proposed to lower total cholesterol and a study is designed to evaluate the efficacy of the drug in lowering cholesterol. Fifteen patients agree to participate in the study and each is asked to take the new drug for 6 weeks. However, before starting the treatment, each patient's total cholesterol level is measured. The initial measurement is a pre-treatment or baseline value. After taking the drug for 6 weeks, each patient's total cholesterol level is measured again and the data are shown below. The rightmost column contains difference scores for each patient, computed by subtracting the 6 week cholesterol level from the baseline level. The differences represent the reduction in total cholesterol over 4 weeks. (The differences could have been computed by subtracting the baseline total cholesterol level from the level measured at 6 weeks. The way in which the differences are computed does not affect the outcome of the analysis only the interpretation.)
Because the differences are computed by subtracting the cholesterols measured at 6 weeks from the baseline values, positive differences indicate reductions and negative differences indicate increases (e.g., participant 12 increases by 2 units over 6 weeks). The goal here is to test whether there is a statistically significant reduction in cholesterol. Because of the way in which we computed the differences, we want to look for an increase in the mean difference (i.e., a positive reduction). In order to conduct the test, we need to summarize the differences. In this sample, we have
The calculations are shown below.
Is there statistical evidence of a reduction in mean total cholesterol in patients after using the new medication for 6 weeks? We will run the test using the five-step approach.
H 0 : μ d = 0 H 1 : μ d > 0 α=0.05
NOTE: If we had computed differences by subtracting the baseline level from the level measured at 6 weeks then negative differences would have reflected reductions and the research hypothesis would have been H 1 : μ d < 0.
- Step 2 . Select the appropriate test statistic.
This is an upper-tailed test, using a t statistic and a 5% level of significance. The appropriate critical value can be found in the t Table at the right, with df=15-1=14. The critical value for an upper-tailed test with df=14 and α=0.05 is 2.145 and the decision rule is Reject H 0 if t > 2.145.
We now substitute the sample data into the formula for the test statistic identified in Step 2.
We reject H 0 because 4.61 > 2.145. We have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that there is a reduction in cholesterol levels over 6 weeks.
Here we illustrate the use of a matched design to test the efficacy of a new drug to lower total cholesterol. We also considered a parallel design (randomized clinical trial) and a study using a historical comparator. It is extremely important to design studies that are best suited to detect a meaningful difference when one exists. There are often several alternatives and investigators work with biostatisticians to determine the best design for each application. It is worth noting that the matched design used here can be problematic in that observed differences may only reflect a "placebo" effect. All participants took the assigned medication, but is the observed reduction attributable to the medication or a result of these participation in a study.
Video - Hypothesis Testing With a Matched Sample and a Continuous Outcome (3:11)
Tests with Two Independent Samples, Dichotomous Outcome
There are several approaches that can be used to test hypotheses concerning two independent proportions. Here we present one approach - the chi-square test of independence is an alternative, equivalent, and perhaps more popular approach to the same analysis. Hypothesis testing with the chi-square test is addressed in the third module in this series: BS704_HypothesisTesting-ChiSquare.
In tests of hypothesis comparing proportions between two independent groups, one test is performed and results can be interpreted to apply to a risk difference, relative risk or odds ratio. As a reminder, the risk difference is computed by taking the difference in proportions between comparison groups, the risk ratio is computed by taking the ratio of proportions, and the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of the odds of success in the comparison groups. Because the null values for the risk difference, the risk ratio and the odds ratio are different, the hypotheses in tests of hypothesis look slightly different depending on which measure is used. When performing tests of hypothesis for the risk difference, relative risk or odds ratio, the convention is to label the exposed or treated group 1 and the unexposed or control group 2.
For example, suppose a study is designed to assess whether there is a significant difference in proportions in two independent comparison groups. The test of interest is as follows:
H 0 : p 1 = p 2 versus H 1 : p 1 ≠ p 2 .
The following are the hypothesis for testing for a difference in proportions using the risk difference, the risk ratio and the odds ratio. First, the hypotheses above are equivalent to the following:
- For the risk difference, H 0 : p 1 - p 2 = 0 versus H 1 : p 1 - p 2 ≠ 0 which are, by definition, equal to H 0 : RD = 0 versus H 1 : RD ≠ 0.
- If an investigator wants to focus on the risk ratio, the equivalent hypotheses are H 0 : RR = 1 versus H 1 : RR ≠ 1.
- If the investigator wants to focus on the odds ratio, the equivalent hypotheses are H 0 : OR = 1 versus H 1 : OR ≠ 1.
Suppose a test is performed to test H 0 : RD = 0 versus H 1 : RD ≠ 0 and the test rejects H 0 at α=0.05. Based on this test we can conclude that there is significant evidence, α=0.05, of a difference in proportions, significant evidence that the risk difference is not zero, significant evidence that the risk ratio and odds ratio are not one. The risk difference is analogous to the difference in means when the outcome is continuous. Here the parameter of interest is the difference in proportions in the population, RD = p 1 -p 2 and the null value for the risk difference is zero. In a test of hypothesis for the risk difference, the null hypothesis is always H 0 : RD = 0. This is equivalent to H 0 : RR = 1 and H 0 : OR = 1. In the research hypothesis, an investigator can hypothesize that the first proportion is larger than the second (H 1 : p 1 > p 2 , which is equivalent to H 1 : RD > 0, H 1 : RR > 1 and H 1 : OR > 1), that the first proportion is smaller than the second (H 1 : p 1 < p 2 , which is equivalent to H 1 : RD < 0, H 1 : RR < 1 and H 1 : OR < 1), or that the proportions are different (H 1 : p 1 ≠ p 2 , which is equivalent to H 1 : RD ≠ 0, H 1 : RR ≠ 1 and H 1 : OR ≠
1). The three different alternatives represent upper-, lower- and two-tailed tests, respectively.
The formula for the test of hypothesis for the difference in proportions is given below.
Test Statistics for Testing H 0 : p 1 = p
The formula above is appropriate for large samples, defined as at least 5 successes (np > 5) and at least 5 failures (n(1-p > 5)) in each of the two samples. If there are fewer than 5 successes or failures in either comparison group, then alternative procedures, called exact methods must be used to estimate the difference in population proportions.
The following table summarizes data from n=3,799 participants who attended the fifth examination of the Offspring in the Framingham Heart Study. The outcome of interest is prevalent CVD and we want to test whether the prevalence of CVD is significantly higher in smokers as compared to non-smokers.
The prevalence of CVD (or proportion of participants with prevalent CVD) among non-smokers is 298/3,055 = 0.0975 and the prevalence of CVD among current smokers is 81/744 = 0.1089. Here smoking status defines the comparison groups and we will call the current smokers group 1 (exposed) and the non-smokers (unexposed) group 2. The test of hypothesis is conducted below using the five step approach.
H 0 : p 1 = p 2 H 1 : p 1 ≠ p 2 α=0.05
- Step 2. Select the appropriate test statistic.
We must first check that the sample size is adequate. Specifically, we need to ensure that we have at least 5 successes and 5 failures in each comparison group. In this example, we have more than enough successes (cases of prevalent CVD) and failures (persons free of CVD) in each comparison group. The sample size is more than adequate so the following formula can be used:
Reject H 0 if Z < -1.960 or if Z > 1.960.
We now substitute the sample data into the formula for the test statistic identified in Step 2. We first compute the overall proportion of successes:
We now substitute to compute the test statistic.
- Step 5. Conclusion.
We do not reject H 0 because -1.960 < 0.927 < 1.960. We do not have statistically significant evidence at α=0.05 to show that there is a difference in prevalent CVD between smokers and non-smokers.
A 95% confidence interval for the difference in prevalent CVD (or risk difference) between smokers and non-smokers as 0.0114 + 0.0247, or between -0.0133 and 0.0361. Because the 95% confidence interval for the risk difference includes zero we again conclude that there is no statistically significant difference in prevalent CVD between smokers and non-smokers.
Smoking has been shown over and over to be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. What might explain the fact that we did not observe a statistically significant difference using data from the Framingham Heart Study? HINT: Here we consider prevalent CVD, would the results have been different if we considered incident CVD?
A randomized trial is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of a newly developed pain reliever designed to reduce pain in patients following joint replacement surgery. The trial compares the new pain reliever to the pain reliever currently in use (called the standard of care). A total of 100 patients undergoing joint replacement surgery agreed to participate in the trial. Patients were randomly assigned to receive either the new pain reliever or the standard pain reliever following surgery and were blind to the treatment assignment. Before receiving the assigned treatment, patients were asked to rate their pain on a scale of 0-10 with higher scores indicative of more pain. Each patient was then given the assigned treatment and after 30 minutes was again asked to rate their pain on the same scale. The primary outcome was a reduction in pain of 3 or more scale points (defined by clinicians as a clinically meaningful reduction). The following data were observed in the trial.
We now test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the proportions of patients reporting a meaningful reduction (i.e., a reduction of 3 or more scale points) using the five step approach.
H 0 : p 1 = p 2 H 1 : p 1 ≠ p 2 α=0.05
Here the new or experimental pain reliever is group 1 and the standard pain reliever is group 2.
We must first check that the sample size is adequate. Specifically, we need to ensure that we have at least 5 successes and 5 failures in each comparison group, i.e.,
In this example, we have min(50(0.46), 50(1-0.46), 50(0.22), 50(1-0.22)) = min(23, 27, 11, 39) = 11. The sample size is adequate so the following formula can be used
We reject H 0 because 2.526 > 1960. We have statistically significant evidence at a =0.05 to show that there is a difference in the proportions of patients on the new pain reliever reporting a meaningful reduction (i.e., a reduction of 3 or more scale points) as compared to patients on the standard pain reliever.
A 95% confidence interval for the difference in proportions of patients on the new pain reliever reporting a meaningful reduction (i.e., a reduction of 3 or more scale points) as compared to patients on the standard pain reliever is 0.24 + 0.18 or between 0.06 and 0.42. Because the 95% confidence interval does not include zero we concluded that there was a statistically significant difference in proportions which is consistent with the test of hypothesis result.
Again, the procedures discussed here apply to applications where there are two independent comparison groups and a dichotomous outcome. There are other applications in which it is of interest to compare a dichotomous outcome in matched or paired samples. For example, in a clinical trial we might wish to test the effectiveness of a new antibiotic eye drop for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis. Participants use the new antibiotic eye drop in one eye and a comparator (placebo or active control treatment) in the other. The success of the treatment (yes/no) is recorded for each participant for each eye. Because the two assessments (success or failure) are paired, we cannot use the procedures discussed here. The appropriate test is called McNemar's test (sometimes called McNemar's test for dependent proportions).
Vide0 - Hypothesis Testing With Two Independent Samples and a Dichotomous Outcome (2:55)
Here we presented hypothesis testing techniques for means and proportions in one and two sample situations. Tests of hypothesis involve several steps, including specifying the null and alternative or research hypothesis, selecting and computing an appropriate test statistic, setting up a decision rule and drawing a conclusion. There are many details to consider in hypothesis testing. The first is to determine the appropriate test. We discussed Z and t tests here for different applications. The appropriate test depends on the distribution of the outcome variable (continuous or dichotomous), the number of comparison groups (one, two) and whether the comparison groups are independent or dependent. The following table summarizes the different tests of hypothesis discussed here.
- Continuous Outcome, One Sample: H0: μ = μ0
- Continuous Outcome, Two Independent Samples: H0: μ1 = μ2
- Continuous Outcome, Two Matched Samples: H0: μd = 0
- Dichotomous Outcome, One Sample: H0: p = p 0
- Dichotomous Outcome, Two Independent Samples: H0: p1 = p2, RD=0, RR=1, OR=1
Once the type of test is determined, the details of the test must be specified. Specifically, the null and alternative hypotheses must be clearly stated. The null hypothesis always reflects the "no change" or "no difference" situation. The alternative or research hypothesis reflects the investigator's belief. The investigator might hypothesize that a parameter (e.g., a mean, proportion, difference in means or proportions) will increase, will decrease or will be different under specific conditions (sometimes the conditions are different experimental conditions and other times the conditions are simply different groups of participants). Once the hypotheses are specified, data are collected and summarized. The appropriate test is then conducted according to the five step approach. If the test leads to rejection of the null hypothesis, an approximate p-value is computed to summarize the significance of the findings. When tests of hypothesis are conducted using statistical computing packages, exact p-values are computed. Because the statistical tables in this textbook are limited, we can only approximate p-values. If the test fails to reject the null hypothesis, then a weaker concluding statement is made for the following reason.
In hypothesis testing, there are two types of errors that can be committed. A Type I error occurs when a test incorrectly rejects the null hypothesis. This is referred to as a false positive result, and the probability that this occurs is equal to the level of significance, α. The investigator chooses the level of significance in Step 1, and purposely chooses a small value such as α=0.05 to control the probability of committing a Type I error. A Type II error occurs when a test fails to reject the null hypothesis when in fact it is false. The probability that this occurs is equal to β. Unfortunately, the investigator cannot specify β at the outset because it depends on several factors including the sample size (smaller samples have higher b), the level of significance (β decreases as a increases), and the difference in the parameter under the null and alternative hypothesis.
We noted in several examples in this chapter, the relationship between confidence intervals and tests of hypothesis. The approaches are different, yet related. It is possible to draw a conclusion about statistical significance by examining a confidence interval. For example, if a 95% confidence interval does not contain the null value (e.g., zero when analyzing a mean difference or risk difference, one when analyzing relative risks or odds ratios), then one can conclude that a two-sided test of hypothesis would reject the null at α=0.05. It is important to note that the correspondence between a confidence interval and test of hypothesis relates to a two-sided test and that the confidence level corresponds to a specific level of significance (e.g., 95% to α=0.05, 90% to α=0.10 and so on). The exact significance of the test, the p-value, can only be determined using the hypothesis testing approach and the p-value provides an assessment of the strength of the evidence and not an estimate of the effect.
Answers to Selected Problems
Dental services problem - bottom of page 5.
- Step 1: Set up hypotheses and determine the level of significance.
α=0.05
- Step 2: Select the appropriate test statistic.
First, determine whether the sample size is adequate.
Therefore the sample size is adequate, and we can use the following formula:
- Step 3: Set up the decision rule.
Reject H0 if Z is less than or equal to -1.96 or if Z is greater than or equal to 1.96.
- Step 4: Compute the test statistic
- Step 5: Conclusion.
We reject the null hypothesis because -6.15<-1.96. Therefore there is a statistically significant difference in the proportion of children in Boston using dental services compated to the national proportion.
Hypothesis Testing Calculator
Related: confidence interval calculator, type ii error.
The first step in hypothesis testing is to calculate the test statistic. The formula for the test statistic depends on whether the population standard deviation (σ) is known or unknown. If σ is known, our hypothesis test is known as a z test and we use the z distribution. If σ is unknown, our hypothesis test is known as a t test and we use the t distribution. Use of the t distribution relies on the degrees of freedom, which is equal to the sample size minus one. Furthermore, if the population standard deviation σ is unknown, the sample standard deviation s is used instead. To switch from σ known to σ unknown, click on $\boxed{\sigma}$ and select $\boxed{s}$ in the Hypothesis Testing Calculator.
Next, the test statistic is used to conduct the test using either the p-value approach or critical value approach. The particular steps taken in each approach largely depend on the form of the hypothesis test: lower tail, upper tail or two-tailed. The form can easily be identified by looking at the alternative hypothesis (H a ). If there is a less than sign in the alternative hypothesis then it is a lower tail test, greater than sign is an upper tail test and inequality is a two-tailed test. To switch from a lower tail test to an upper tail or two-tailed test, click on $\boxed{\geq}$ and select $\boxed{\leq}$ or $\boxed{=}$, respectively.
In the p-value approach, the test statistic is used to calculate a p-value. If the test is a lower tail test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as small as the value from the sample. If the test is an upper tail test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as large as the value from the sample. In a two-tailed test, the p-value is the probability of getting a value for the test statistic at least as unlikely as the value from the sample.
To test the hypothesis in the p-value approach, compare the p-value to the level of significance. If the p-value is less than or equal to the level of signifance, reject the null hypothesis. If the p-value is greater than the level of significance, do not reject the null hypothesis. This method remains unchanged regardless of whether it's a lower tail, upper tail or two-tailed test. To change the level of significance, click on $\boxed{.05}$. Note that if the test statistic is given, you can calculate the p-value from the test statistic by clicking on the switch symbol twice.
In the critical value approach, the level of significance ($\alpha$) is used to calculate the critical value. In a lower tail test, the critical value is the value of the test statistic providing an area of $\alpha$ in the lower tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic. In an upper tail test, the critical value is the value of the test statistic providing an area of $\alpha$ in the upper tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic. In a two-tailed test, the critical values are the values of the test statistic providing areas of $\alpha / 2$ in the lower and upper tail of the sampling distribution of the test statistic.
To test the hypothesis in the critical value approach, compare the critical value to the test statistic. Unlike the p-value approach, the method we use to decide whether to reject the null hypothesis depends on the form of the hypothesis test. In a lower tail test, if the test statistic is less than or equal to the critical value, reject the null hypothesis. In an upper tail test, if the test statistic is greater than or equal to the critical value, reject the null hypothesis. In a two-tailed test, if the test statistic is less than or equal the lower critical value or greater than or equal to the upper critical value, reject the null hypothesis.
When conducting a hypothesis test, there is always a chance that you come to the wrong conclusion. There are two types of errors you can make: Type I Error and Type II Error. A Type I Error is committed if you reject the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. Ideally, we'd like to accept the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. A Type II Error is committed if you accept the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true. Ideally, we'd like to reject the null hypothesis when the alternative hypothesis is true.
Hypothesis testing is closely related to the statistical area of confidence intervals. If the hypothesized value of the population mean is outside of the confidence interval, we can reject the null hypothesis. Confidence intervals can be found using the Confidence Interval Calculator . The calculator on this page does hypothesis tests for one population mean. Sometimes we're interest in hypothesis tests about two population means. These can be solved using the Two Population Calculator . The probability of a Type II Error can be calculated by clicking on the link at the bottom of the page.
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Data Analysis Tutorial
- Python - Data visualization tutorial
- Machine Learning Projects
- Machine Learning Interview Questions
- Machine Learning Mathematics
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Project
- Deep Learning Interview Questions
- Computer Vision Tutorial
- Computer Vision Projects
- NLP Project
- NLP Interview Questions
- Statistics with Python
- 100 Days of Machine Learning
- Data Analysis with Python
Introduction to Data Analysis
- What is Data Analysis?
- Data Analytics and its type
- How to Install Numpy on Windows?
- How to Install Pandas in Python?
- How to Install Matplotlib on python?
- How to Install Python Tensorflow in Windows?
Data Analysis Libraries
- Pandas Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial - Python Library
- Data Analysis with SciPy
- Introduction to TensorFlow
Data Visulization Libraries
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Python Seaborn Tutorial
- Plotly tutorial
- Introduction to Bokeh in Python
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Univariate, Bivariate and Multivariate data and its analysis
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Measures of spread - Range, Variance, and Standard Deviation
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation using NumPy and SciPy
- Anova Formula
- Skewness of Statistical Data
- How to Calculate Skewness and Kurtosis in Python?
- Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Interpretations of Histogram
- Quantile Quantile plots
- What is Univariate, Bivariate & Multivariate Analysis in Data Visualisation?
- Using pandas crosstab to create a bar plot
- Exploring Correlation in Python
- Mathematics | Covariance and Correlation
- Factor Analysis | Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Cluster Analysis
- MANOVA Test in R Programming
- Python - Central Limit Theorem
- Probability Distribution Function
- Probability Density Estimation & Maximum Likelihood Estimation
- Exponential Distribution in R Programming - dexp(), pexp(), qexp(), and rexp() Functions
- Mathematics | Probability Distributions Set 4 (Binomial Distribution)
- Poisson Distribution - Definition, Formula, Table and Examples
- P-Value: Comprehensive Guide to Understand, Apply, and Interpret
- Z-Score in Statistics
- How to Calculate Point Estimates in R?
- Confidence Interval
- Chi-square test in Machine Learning
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Data preprocessing.
- ML | Data Preprocessing in Python
- ML | Overview of Data Cleaning
- ML | Handling Missing Values
- Detect and Remove the Outliers using Python
Data Transformation
- Data Normalization Machine Learning
- Sampling distribution Using Python
Time Series Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Time-Series, Symbolic and Biological Sequences Data
- Basic DateTime Operations in Python
- Time Series Analysis & Visualization in Python
- How to deal with missing values in a Timeseries in Python?
- How to calculate MOVING AVERAGE in a Pandas DataFrame?
- What is a trend in time series?
- How to Perform an Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test in R
- AutoCorrelation
Case Studies and Projects
- Top 8 Free Dataset Sources to Use for Data Science Projects
- Step by Step Predictive Analysis - Machine Learning
- 6 Tips for Creating Effective Data Visualizations
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.
Defining Hypotheses
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
Real life Hypothesis Testing example
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- Data Science
- Machine Learning

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
Hypothesis testing.
Key Topics:
- Basic approach
- Null and alternative hypothesis
- Decision making and the p -value
- Z-test & Nonparametric alternative
Basic approach to hypothesis testing
- State a model describing the relationship between the explanatory variables and the outcome variable(s) in the population and the nature of the variability. State all of your assumptions .
- Specify the null and alternative hypotheses in terms of the parameters of the model.
- Invent a test statistic that will tend to be different under the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Using the assumptions of step 1, find the theoretical sampling distribution of the statistic under the null hypothesis of step 2. Ideally the form of the sampling distribution should be one of the “standard distributions”(e.g. normal, t , binomial..)
- Calculate a p -value , as the area under the sampling distribution more extreme than your statistic. Depends on the form of the alternative hypothesis.
- Choose your acceptable type 1 error rate (alpha) and apply the decision rule : reject the null hypothesis if the p-value is less than alpha, otherwise do not reject.
- \(\frac{\bar{X}-\mu_0}{\sigma / \sqrt{n}}\)
- general form is: (estimate - value we are testing)/(st.dev of the estimate)
- z-statistic follows N(0,1) distribution
- 2 × the area above |z|, area above z,or area below z, or
- compare the statistic to a critical value, |z| ≥ z α/2 , z ≥ z α , or z ≤ - z α
- Choose the acceptable level of Alpha = 0.05, we conclude …. ?
Making the Decision
It is either likely or unlikely that we would collect the evidence we did given the initial assumption. (Note: “likely” or “unlikely” is measured by calculating a probability!)
If it is likely , then we “ do not reject ” our initial assumption. There is not enough evidence to do otherwise.
If it is unlikely , then:
- either our initial assumption is correct and we experienced an unusual event or,
- our initial assumption is incorrect
In statistics, if it is unlikely, we decide to “ reject ” our initial assumption.
Example: Criminal Trial Analogy
First, state 2 hypotheses, the null hypothesis (“H 0 ”) and the alternative hypothesis (“H A ”)
- H 0 : Defendant is not guilty.
- H A : Defendant is guilty.
Usually the H 0 is a statement of “no effect”, or “no change”, or “chance only” about a population parameter.
While the H A , depending on the situation, is that there is a difference, trend, effect, or a relationship with respect to a population parameter.
- It can one-sided and two-sided.
- In two-sided we only care there is a difference, but not the direction of it. In one-sided we care about a particular direction of the relationship. We want to know if the value is strictly larger or smaller.
Then, collect evidence, such as finger prints, blood spots, hair samples, carpet fibers, shoe prints, ransom notes, handwriting samples, etc. (In statistics, the data are the evidence.)
Next, you make your initial assumption.
- Defendant is innocent until proven guilty.
In statistics, we always assume the null hypothesis is true .
Then, make a decision based on the available evidence.
- If there is sufficient evidence (“beyond a reasonable doubt”), reject the null hypothesis . (Behave as if defendant is guilty.)
- If there is not enough evidence, do not reject the null hypothesis . (Behave as if defendant is not guilty.)
If the observed outcome, e.g., a sample statistic, is surprising under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true, but more probable if the alternative is true, then this outcome is evidence against H 0 and in favor of H A .
An observed effect so large that it would rarely occur by chance is called statistically significant (i.e., not likely to happen by chance).
Using the p -value to make the decision
The p -value represents how likely we would be to observe such an extreme sample if the null hypothesis were true. The p -value is a probability computed assuming the null hypothesis is true, that the test statistic would take a value as extreme or more extreme than that actually observed. Since it's a probability, it is a number between 0 and 1. The closer the number is to 0 means the event is “unlikely.” So if p -value is “small,” (typically, less than 0.05), we can then reject the null hypothesis.
Significance level and p -value
Significance level, α, is a decisive value for p -value. In this context, significant does not mean “important”, but it means “not likely to happened just by chance”.
α is the maximum probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true. If α = 1 we always reject the null, if α = 0 we never reject the null hypothesis. In articles, journals, etc… you may read: “The results were significant ( p <0.05).” So if p =0.03, it's significant at the level of α = 0.05 but not at the level of α = 0.01. If we reject the H 0 at the level of α = 0.05 (which corresponds to 95% CI), we are saying that if H 0 is true, the observed phenomenon would happen no more than 5% of the time (that is 1 in 20). If we choose to compare the p -value to α = 0.01, we are insisting on a stronger evidence!
So, what kind of error could we make? No matter what decision we make, there is always a chance we made an error.
Errors in Criminal Trial:
Errors in Hypothesis Testing
Type I error (False positive): The null hypothesis is rejected when it is true.
- α is the maximum probability of making a Type I error.
Type II error (False negative): The null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false.
- β is the probability of making a Type II error
There is always a chance of making one of these errors. But, a good scientific study will minimize the chance of doing so!
The power of a statistical test is its probability of rejecting the null hypothesis if the null hypothesis is false. That is, power is the ability to correctly reject H 0 and detect a significant effect. In other words, power is one minus the type II error risk.
\(\text{Power }=1-\beta = P\left(\text{reject} H_0 | H_0 \text{is false } \right)\)
Which error is worse?
Type I = you are innocent, yet accused of cheating on the test. Type II = you cheated on the test, but you are found innocent.
This depends on the context of the problem too. But in most cases scientists are trying to be “conservative”; it's worse to make a spurious discovery than to fail to make a good one. Our goal it to increase the power of the test that is to minimize the length of the CI.
We need to keep in mind:
- the effect of the sample size,
- the correctness of the underlying assumptions about the population,
- statistical vs. practical significance, etc…
(see the handout). To study the tradeoffs between the sample size, α, and Type II error we can use power and operating characteristic curves.
What type of error might we have made?
Type I error is claiming that average student height is not 65 inches, when it really is. Type II error is failing to claim that the average student height is not 65in when it is.
We rejected the null hypothesis, i.e., claimed that the height is not 65, thus making potentially a Type I error. But sometimes the p -value is too low because of the large sample size, and we may have statistical significance but not really practical significance! That's why most statisticians are much more comfortable with using CI than tests.
There is a need for a further generalization. What if we can't assume that σ is known? In this case we would use s (the sample standard deviation) to estimate σ.
If the sample is very large, we can treat σ as known by assuming that σ = s . According to the law of large numbers, this is not too bad a thing to do. But if the sample is small, the fact that we have to estimate both the standard deviation and the mean adds extra uncertainty to our inference. In practice this means that we need a larger multiplier for the standard error.
We need one-sample t -test.
One sample t -test
- Assume data are independently sampled from a normal distribution with unknown mean μ and variance σ 2 . Make an initial assumption, μ 0 .
- t-statistic: \(\frac{\bar{X}-\mu_0}{s / \sqrt{n}}\) where s is a sample st.dev.
- t-statistic follows t -distribution with df = n - 1
- Alpha = 0.05, we conclude ….
Testing for the population proportion
Let's go back to our CNN poll. Assume we have a SRS of 1,017 adults.
We are interested in testing the following hypothesis: H 0 : p = 0.50 vs. p > 0.50
What is the test statistic?
If alpha = 0.05, what do we conclude?
We will see more details in the next lesson on proportions, then distributions, and possible tests.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In statistics, we use hypothesis tests to determine whether some claim about a population parameter is true or not.. Whenever we perform a hypothesis test, we always write a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis, which take the following forms:. H 0 (Null Hypothesis): Population parameter = ≤, ≥ some value. H A (Alternative Hypothesis): Population parameter <, >, ≠ some value
Hypothesis testing example. You want to test whether there is a relationship between gender and height. Based on your knowledge of human physiology, you formulate a hypothesis that men are, on average, taller than women. To test this hypothesis, you restate it as: H 0: Men are, on average, not taller than women. H a: Men are, on average, taller ...
Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples. Published on January 28, 2020 by Rebecca Bevans. Revised on June 22, 2023. Statistical tests are used in ... Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world. It allows you to statistically test your predictions. 2204.
In a hypothesis test, you have to decide if a claim is true or not. Before you can figure out if you have a left tailed test or right tailed test, you have to make sure you have a single tail to begin with. A tail in hypothesis testing refers to the tail at either end of a distribution curve. Area under a normal distribution curve.
The critical value for conducting the left-tailed test H0 : μ = 3 versus HA : μ < 3 is the t -value, denoted -t( α, n - 1), such that the probability to the left of it is α. It can be shown using either statistical software or a t -table that the critical value -t0.05,14 is -1.7613. That is, we would reject the null hypothesis H0 : μ = 3 ...
A Right-sided Test. This tests whether the population parameter is equal to, versus greater than, some specific value. Ho: μ = 12 vs. H 1: μ > 12. The critical region is in the right tail and the critical value is a positive value that defines the rejection zone. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The rejection zone for a right-sided hypothesis test.
Hypothesis testing is a method of statistical inference that considers the null hypothesis H₀ vs. the alternative hypothesis Ha, where we are typically looking to assess evidence against H₀. ... Choosing the Right Test. The most common hypothesis test is a t-test. However, a t-test (similarly to other tests) comes with assumptions, and if ...
S.3 Hypothesis Testing. In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail. The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data).
A standardized test statistic for a hypothesis test is the statistic that is formed by subtracting from the statistic of interest its mean and dividing by its standard deviation. For example, reviewing Example 8.1.3 8.1. 3, if instead of working with the sample mean X¯¯¯¯ X ¯ we instead work with the test statistic.
Test Statistic: z = ¯ x − μo σ / √n since it is calculated as part of the testing of the hypothesis. Definition 7.1.4. p - value: probability that the test statistic will take on more extreme values than the observed test statistic, given that the null hypothesis is true.
Hypothesis testing is a crucial procedure to perform when you want to make inferences about a population using a random sample. These inferences include estimating population properties such as the mean, differences between means, proportions, and the relationships between variables. This post provides an overview of statistical hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing is an indispensable tool in data science, allowing us to make data-driven decisions with confidence. By understanding its principles, conducting tests properly, and considering real-world applications, you can harness the power of hypothesis testing to unlock valuable insights from your data.
One-tailed hypothesis tests are also known as directional and one-sided tests because you can test for effects in only one direction. When you perform a one-tailed test, the entire significance level percentage goes into the extreme end of one tail of the distribution. In the examples below, I use an alpha of 5%.
Step 2: State the Alternate Hypothesis. The claim is that the students have above average IQ scores, so: H 1: μ > 100. The fact that we are looking for scores "greater than" a certain point means that this is a one-tailed test. Step 3: Draw a picture to help you visualize the problem. Step 4: State the alpha level.
In hypothesis testing, the goal is to see if there is sufficient statistical evidence to reject a presumed null hypothesis in favor of a conjectured alternative hypothesis.The null hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_0\) while the alternative hypothesis is usually denoted \(H_1\). An hypothesis test is a statistical decision; the conclusion will either be to reject the null hypothesis in favor ...
The P -value is, therefore, the area under a tn - 1 = t14 curve to the left of -2.5 and to the right of 2.5. It can be shown using statistical software that the P -value is 0.0127 + 0.0127, or 0.0254. The graph depicts this visually. Note that the P -value for a two-tailed test is always two times the P -value for either of the one-tailed tests.
Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant. It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis. There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
We then determine the appropriate test statistic (Step 2) for the hypothesis test. The formula for the test statistic is given below. Test Statistic for Testing H0: p = p 0. if min (np 0 , n (1-p 0 )) > 5. The formula above is appropriate for large samples, defined when the smaller of np 0 and n (1-p 0) is at least 5.
Below these are summarized into six such steps to conducting a test of a hypothesis. Set up the hypotheses and check conditions: Each hypothesis test includes two hypotheses about the population. One is the null hypothesis, notated as H 0, which is a statement of a particular parameter value. This hypothesis is assumed to be true until there is ...
Hypothesis Testing Calculator. The first step in hypothesis testing is to calculate the test statistic. The formula for the test statistic depends on whether the population standard deviation (σ) is known or unknown. If σ is known, our hypothesis test is known as a z test and we use the z distribution. If σ is unknown, our hypothesis test is ...
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Specify the null and alternative hypotheses in terms of the parameters of the model. Invent a test statistic that will tend to be different under the null and alternative hypotheses. Using the assumptions of step 1, find the theoretical sampling distribution of the statistic under the null hypothesis of step 2.
The test must be completed in one continuous session. You must begin your test within the available Virtual Test Center hours of 8:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m., Monday through Friday, except state holidays. If you do not complete your test before the end of the day's available testing time, it will register as a "Fail."