
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
The Research Proposal

83 Components of the Literature Review
Krathwohl (2005) suggests and describes a variety of components to include in a research proposal. The following sections present these components in a suggested template for you to follow in the preparation of your research proposal.
Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for what follows in your research proposal – treat it as the initial pitch of your idea. After reading the introduction your reader should:
- Understand what it is you want to do;
- Have a sense of your passion for the topic;
- Be excited about the study´s possible outcomes.
As you begin writing your research proposal it is helpful to think of the introduction as a narrative of what it is you want to do, written in one to three paragraphs. Within those one to three paragraphs, it is important to briefly answer the following questions:
- What is the central research problem?
- How is the topic of your research proposal related to the problem?
- What methods will you utilize to analyze the research problem?
- Why is it important to undertake this research? What is the significance of your proposed research? Why are the outcomes of your proposed research important, and to whom or to what are they important?
Note : You may be asked by your instructor to include an abstract with your research proposal. In such cases, an abstract should provide an overview of what it is you plan to study, your main research question, a brief explanation of your methods to answer the research question, and your expected findings. All of this information must be carefully crafted in 150 to 250 words. A word of advice is to save the writing of your abstract until the very end of your research proposal preparation. If you are asked to provide an abstract, you should include 5-7 key words that are of most relevance to your study. List these in order of relevance.
Background and significance
The purpose of this section is to explain the context of your proposal and to describe, in detail, why it is important to undertake this research. Assume that the person or people who will read your research proposal know nothing or very little about the research problem. While you do not need to include all knowledge you have learned about your topic in this section, it is important to ensure that you include the most relevant material that will help to explain the goals of your research.
While there are no hard and fast rules, you should attempt to address some or all of the following key points:
- State the research problem and provide a more thorough explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction.
- Present the rationale for the proposed research study. Clearly indicate why this research is worth doing. Answer the “so what?” question.
- Describe the major issues or problems to be addressed by your research. Do not forget to explain how and in what ways your proposed research builds upon previous related research.
- Explain how you plan to go about conducting your research.
- Clearly identify the key or most relevant sources of research you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Set the boundaries of your proposed research, in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you will study, but what will be excluded from your study.
- Provide clear definitions of key concepts and terms. As key concepts and terms often have numerous definitions, make sure you state which definition you will be utilizing in your research.
Literature Review
This is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal and it is a key component of the research proposal. As described in Chapter 5 , the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis of prior research that is related to the problem you are setting forth to investigate. Essentially, your goal in the literature review is to place your research study within the larger whole of what has been studied in the past, while demonstrating to your reader that your work is original, innovative, and adds to the larger whole.
As the literature review is information dense, it is essential that this section be intelligently structured to enable your reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your study. However, this can be easier to state and harder to do, simply due to the fact there is usually a plethora of related research to sift through. Consequently, a good strategy for writing the literature review is to break the literature into conceptual categories or themes, rather than attempting to describe various groups of literature you reviewed. Chapter V, “ The Literature Review ,” describes a variety of methods to help you organize the themes.
Here are some suggestions on how to approach the writing of your literature review:
- Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methods they used, what they found, and what they recommended based upon their findings.
- Do not be afraid to challenge previous related research findings and/or conclusions.
- Assess what you believe to be missing from previous research and explain how your research fills in this gap and/or extends previous research
It is important to note that a significant challenge related to undertaking a literature review is knowing when to stop. As such, it is important to know how to know when you have uncovered the key conceptual categories underlying your research topic. Generally, when you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations, you can have confidence that you have covered all of the significant conceptual categories in your literature review. However, it is also important to acknowledge that researchers often find themselves returning to the literature as they collect and analyze their data. For example, an unexpected finding may develop as one collects and/or analyzes the data and it is important to take the time to step back and review the literature again, to ensure that no other researchers have found a similar finding. This may include looking to research outside your field.
This situation occurred with one of the authors of this textbook´s research related to community resilience. During the interviews, the researchers heard many participants discuss individual resilience factors and how they believed these individual factors helped make the community more resilient, overall. Sheppard and Williams (2016) had not discovered these individual factors in their original literature review on community and environmental resilience. However, when they returned to the literature to search for individual resilience factors, they discovered a small body of literature in the child and youth psychology field. Consequently, Sheppard and Williams had to go back and add a new section to their literature review on individual resilience factors. Interestingly, their research appeared to be the first research to link individual resilience factors with community resilience factors.
Research design and methods
The objective of this section of the research proposal is to convince the reader that your overall research design and methods of analysis will enable you to solve the research problem you have identified and also enable you to accurately and effectively interpret the results of your research. Consequently, it is critical that the research design and methods section is well-written, clear, and logically organized. This demonstrates to your reader that you know what you are going to do and how you are going to do it. Overall, you want to leave your reader feeling confident that you have what it takes to get this research study completed in a timely fashion.
Essentially, this section of the research proposal should be clearly tied to the specific objectives of your study; however, it is also important to draw upon and include examples from the literature review that relate to your design and intended methods. In other words, you must clearly demonstrate how your study utilizes and builds upon past studies, as it relates to the research design and intended methods. For example, what methods have been used by other researchers in similar studies?
While it is important to consider the methods that other researchers have employed, it is equally important, if not more so, to consider what methods have not been employed but could be. Remember, the methods section is not simply a list of tasks to be undertaken. It is also an argument as to why and how the tasks you have outlined will help you investigate the research problem and answer your research question(s).
Tips for writing the research design and methods section:
- Specify the methodological approaches you intend to employ to obtain information and the techniques you will use to analyze the data.
- Specify the research operations you will undertake and he way you will interpret the results of those operations in relation to the research problem.
- Go beyond stating what you hope to achieve through the methods you have chosen. State how you will actually do the methods (i.e. coding interview text, running regression analysis, etc.).
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers you may encounter when undertaking your research and describe how you will address these barriers.
- Explain where you believe you will find challenges related to data collection, including access to participants and information.
Preliminary suppositions and implications
The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you anticipate that your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the area of your study. Depending upon the aims and objectives of your study, you should also discuss how your anticipated findings may impact future research. For example, is it possible that your research may lead to a new policy, new theoretical understanding, or a new method for analyzing data? How might your study influence future studies? What might your study mean for future practitioners working in the field? Who or what may benefit from your study? How might your study contribute to social, economic, environmental issues? While it is important to think about and discuss possibilities such as these, it is equally important to be realistic in stating your anticipated findings. In other words, you do not want to delve into idle speculation. Rather, the purpose here is to reflect upon gaps in the current body of literature and to describe how and in what ways you anticipate your research will begin to fill in some or all of those gaps.
The conclusion reiterates the importance and significance of your research proposal and it provides a brief summary of the entire proposed study. Essentially, this section should only be one or two paragraphs in length. Here is a potential outline for your conclusion:
- Discuss why the study should be done. Specifically discuss how you expect your study will advance existing knowledge and how your study is unique.
- Explain the specific purpose of the study and the research questions that the study will answer.
- Explain why the research design and methods chosen for this study are appropriate, and why other design and methods were not chosen.
- State the potential implications you expect to emerge from your proposed study,
- Provide a sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship currently in existence related to the research problem.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your research proposal. In a research proposal, this can take two forms: a reference list or a bibliography. A reference list does what the name suggests, it lists the literature you referenced in the body of your research proposal. All references in the reference list, must appear in the body of the research proposal. Remember, it is not acceptable to say “as cited in …” As a researcher you must always go to the original source and check it for yourself. Many errors are made in referencing, even by top researchers, and so it is important not to perpetuate an error made by someone else. While this can be time consuming, it is the proper way to undertake a literature review.
In contrast, a bibliography , is a list of everything you used or cited in your research proposal, with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem. In other words, sources cited in your bibliography may not necessarily appear in the body of your research proposal. Make sure you check with your instructor to see which of the two you are expected to produce.
Overall, your list of citations should be a testament to the fact that you have done a sufficient level of preliminary research to ensure that your project will complement, but not duplicate, previous research efforts. For social sciences, the reference list or bibliography should be prepared in American Psychological Association (APA) referencing format. Usually, the reference list (or bibliography) is not included in the word count of the research proposal. Again, make sure you check with your instructor to confirm.
An Introduction to Research Methods in Sociology Copyright © 2019 by Valerie A. Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students.
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
University Library
Write a literature review.
- Examples and Further Information
1. Introduction
Not to be confused with a book review, a literature review surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources (e.g. dissertations, conference proceedings) relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of each work. The purpose is to offer an overview of significant literature published on a topic.
2. Components
Similar to primary research, development of the literature review requires four stages:
- Problem formulation—which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues?
- Literature search—finding materials relevant to the subject being explored
- Data evaluation—determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic
- Analysis and interpretation—discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature
Literature reviews should comprise the following elements:
- An overview of the subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review
- Division of works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative theses entirely)
- Explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research
In assessing each piece, consideration should be given to:
- Provenance—What are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence (e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings)?
- Objectivity—Is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness—Which of the author's theses are most/least convincing?
- Value—Are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
3. Definition and Use/Purpose
A literature review may constitute an essential chapter of a thesis or dissertation, or may be a self-contained review of writings on a subject. In either case, its purpose is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to the understanding of the subject under review
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration
- Identify new ways to interpret, and shed light on any gaps in, previous research
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort
- Point the way forward for further research
- Place one's original work (in the case of theses or dissertations) in the context of existing literature
The literature review itself, however, does not present new primary scholarship.
- Next: Examples and Further Information >>

Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License except where otherwise noted.

Land Acknowledgement
The land on which we gather is the unceded territory of the Awaswas-speaking Uypi Tribe. The Amah Mutsun Tribal Band, comprised of the descendants of indigenous people taken to missions Santa Cruz and San Juan Bautista during Spanish colonization of the Central Coast, is today working hard to restore traditional stewardship practices on these lands and heal from historical trauma.
The land acknowledgement used at UC Santa Cruz was developed in partnership with the Amah Mutsun Tribal Band Chairman and the Amah Mutsun Relearning Program at the UCSC Arboretum .
Literature Review: 3 Essential Ingredients
The theoretical framework, empirical research and research gap
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | July 2023
Writing a comprehensive but concise literature review is no simple task. There’s a lot of ground to cover and it can be challenging to figure out what’s important and what’s not. In this post, we’ll unpack three essential ingredients that need to be woven into your literature review to lay a rock-solid foundation for your study.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Essential Ingredients
- Ingredients vs structure
- The theoretical framework (foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- Summary & key takeaways
Ingredients vs Structure
As a starting point, it’s important to clarify that the three ingredients we’ll cover in this video are things that need to feature within your literature review, as opposed to a set structure for your chapter . In other words, there are different ways you can weave these three ingredients into your literature review. Regardless of which structure you opt for, each of the three components will make an appearance in some shape or form. If you’re keen to learn more about structural options, we’ve got a dedicated post about that here .

1. The Theoretical Framework
Let’s kick off with the first essential ingredient – that is the theoretical framework , also called the foundation of theory .
The foundation of theory, as the name suggests, is where you’ll lay down the foundational building blocks for your literature review so that your reader can get a clear idea of the core concepts, theories and assumptions (in relation to your research aims and questions) that will guide your study. Note that this is not the same as a conceptual framework .
Typically you’ll cover a few things within the theoretical framework:
Firstly, you’ll need to clearly define the key constructs and variables that will feature within your study. In many cases, any given term can have multiple different definitions or interpretations – for example, different people will define the concept of “integrity” in different ways. This variation in interpretation can, of course, wreak havoc on how your study is understood. So, this section is where you’ll pin down what exactly you mean when you refer to X, Y or Z in your study, as well as why you chose that specific definition. It’s also a good idea to state any assumptions that are inherent in these definitions and why these are acceptable, given the purpose of your study.
Related to this, the second thing you’ll need to cover in your theoretical framework is the relationships between these variables and/or constructs . For example, how does one variable potentially affect another variable – does A have an impact on B, B on A, and so on? In other words, you want to connect the dots between the different “things” of interest that you’ll be exploring in your study. Note that you only need to focus on the key items of interest here (i.e. those most central to your research aims and questions) – not every possible construct or variable.
Lastly, and very importantly, you need to discuss the existing theories that are relevant to your research aims and research questions . For example, if you’re investigating the uptake/adoption of a certain application or software, you might discuss Davis’ Technology Acceptance Model and unpack what it has to say about the factors that influence technology adoption. More importantly, though, you need to explain how this impacts your expectations about what you will find in your own study . In other words, your theoretical framework should reveal some insights about what answers you might expect to find to your research questions .
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of the limited-time offer (60% off the standard price).
Need a helping hand?
2. The Empirical Research
Onto the second essential ingredient, which is empirical research . This section is where you’ll present a critical discussion of the existing empirical research that is relevant to your research aims and questions.
But what exactly is empirical research?
Simply put, empirical research includes any study that involves actual data collection and analysis , whether that’s qualitative data, quantitative data, or a mix of both . This contrasts against purely theoretical literature (the previous ingredient), which draws its conclusions based exclusively on logic and reason , as opposed to an analysis of real-world data.
In other words, theoretical literature provides a prediction or expectation of what one might find based on reason and logic, whereas empirical research tests the accuracy of those predictions using actual real-world data . This reflects the broader process of knowledge creation – in other words, first developing a theory and then testing it out in the field.
Long story short, the second essential ingredient of a high-quality literature review is a critical discussion of the existing empirical research . Here, it’s important to go beyond description . You’ll need to present a critical analysis that addresses some (if not all) of the following questions:
- What have different studies found in relation to your research questions ?
- What contexts have (and haven’t been covered)? For example, certain countries, cities, cultures, etc.
- Are the findings across the studies similar or is there a lot of variation ? If so, why might this be the case?
- What sorts of research methodologies have been used and how could these help me develop my own methodology?
- What were the noteworthy limitations of these studies?
Simply put, your task here is to present a synthesis of what’s been done (and found) within the empirical research, so that you can clearly assess the current state of knowledge and identify potential research gaps , which leads us to our third essential ingredient.

The Research Gap
The third essential ingredient of a high-quality literature review is a discussion of the research gap (or gaps).
But what exactly is a research gap?
Simply put, a research gap is any unaddressed or inadequately explored area within the existing body of academic knowledge. In other words, a research gap emerges whenever there’s still some uncertainty regarding a certain topic or question.
For example, it might be the case that there are mixed findings regarding the relationship between two variables (e.g., job performance and work-from-home policies). Similarly, there might be a lack of research regarding the impact of a specific new technology on people’s mental health. On the other end of the spectrum, there might be a wealth of research regarding a certain topic within one country (say the US), but very little research on that same topic in a different social context (say, China).
These are just random examples, but as you can see, research gaps can emerge from many different places. What’s important to understand is that the research gap (or gaps) needs to emerge from your previous discussion of the theoretical and empirical literature . In other words, your discussion in those sections needs to start laying the foundation for the research gap.
For example, when discussing empirical research, you might mention that most studies have focused on a certain context , yet very few (or none) have focused on another context, and there’s reason to believe that findings may differ. Or you might highlight how there’s a fair deal of mixed findings and disagreement regarding a certain matter. In other words, you want to start laying a little breadcrumb trail in those sections so that your discussion of the research gap is firmly rooted in the rest of the literature review.
But why does all of this matter?
Well, the research gap should serve as the core justification for your study . Through your literature review, you’ll show what gaps exist in the current body of knowledge, and then your study will then attempt to fill (or contribute towards filling) one of those gaps. In other words, you’re first explaining what the problem is (some sort of gap) and then proposing how you’ll solve it.

Key Takeaways
To recap, the three ingredients that need to be mixed into your literature review are:
- The foundation of theory or theoretical framework
- The empirical or evidence-based research
As we mentioned earlier, these are components of a literature review and not (necessarily) a structure for your literature review chapter. Of course, you can structure your chapter in a way that reflects these three components (in fact, in some cases that works very well), but it’s certainly not the only option. The right structure will vary from study to study , depending on various factors.
If you’d like to get hands-on help developing your literature review, be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the entire research journey, step by step.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

very good , as the first writer of the thesis i will need ur advise . please give me a piece of idea on topic -impact of national standardized exam on students learning engagement . Thank you .
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Study resources
- Calendar - Graduate
- Calendar - Undergraduate
- Class schedules
- Class cancellations
- Course registration
- Important academic dates
- More academic resources
- Campus services
- IT services
- Job opportunities
- Mental health support
- Student Service Centre (Birks)
- Calendar of events
- Latest news
- Media Relations
- Faculties, Schools & Colleges
- Arts and Science
- Gina Cody School of Engineering and Computer Science
- John Molson School of Business
- School of Graduate Studies
- All Schools, Colleges & Departments
- Directories

- My Library Account (Sofia) View checkouts, fees, place requests and more
- Interlibrary Loans Request books from external libraries
- Zotero Manage your citations and create bibliographies
- E-journals via BrowZine Browse & read journals through a friendly interface
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver Request a PDF of an article/chapter we have in our physical collection
- Course Reserves Online course readings
- Spectrum Deposit a thesis or article
- WebPrint Upload documents to print with DPrint
- Sofia Discovery tool
- Databases by subject
- Course Reserves
- E-journals via BrowZine
- E-journals via Sofia
- Article/Chapter Scan & Deliver
- Intercampus Delivery of Bound Periodicals/Microforms
- Interlibrary Loans
- Spectrum Research Repository
- Special Collections
- Additional resources & services
- Loans & Returns (Circulation)
- Subject & course guides
- Open Educational Resources Guide
- General guides for users
- Evaluating...
- Ask a librarian
- Research Skills Tutorial
- Quick Things for Digital Knowledge
- Bibliometrics & research impact guide
- Concordia University Press
- Copyright Guide
- Copyright Guide for Thesis Preparation
- Digital Scholarship
- Digital Preservation
- Open Access
- ORCID at Concordia
- Research data management guide
- Scholarship of Teaching & Learning
- Systematic Reviews
- How to get published speaker series
- Borrow (laptops, tablets, equipment)
- Connect (netname, Wi-Fi, guest accounts)
- Desktop computers, software & availability maps
- Group study, presentation practice & classrooms
- Printers, copiers & scanners
- Technology Sandbox
- Visualization Studio
- Webster Library
- Vanier Library
- Grey Nuns Reading Room
- Book a group study room/scanner
- Study spaces
- Floor plans
- Room booking for academic events
- Exhibitions
- Librarians & staff
- University Librarian
- Memberships & collaborations
- Indigenous Student Librarian program
- Wikipedian in residence
- Researcher-in-Residence
- Feedback & improvement
- Annual reports & fast facts
- Annual Plan
- Library Services Fund
- Giving to the Library
- Webster Transformation blog
- Policies & Code of Conduct
The Campaign for Concordia
Library Research Skills Tutorial
Log into...
- My Library account (Sofia)
- Interlibrary loans
- Article/chapter scan
- Course reserves
Quick links
How to write a literature review
What is a literature review.
The literature review is a written overview of major writings and other sources on a selected topic. Sources covered in the review may include scholarly journal articles, books, government reports, Web sites, etc. The literature review provides a description, summary and evaluation of each source. It is usually presented as a distinct section of a graduate thesis or dissertation.

Purpose of the literature review
The purpose of the literature review is to provide a critical written account of the current state of research on a selected topic:
- Identifies areas of prior scholarship
- Places each source in the context of its contribution to the understanding of the specific issue, area of research, or theory under review.
- Describes the relationship of each source to the others that you have selected
- Identifies new ways to interpret, and shed light on any gaps in, previous research
- Points the way forward for further research.
Components of the literature review
The literature review should include the following:
- Objective of the literature review
- Overview of the subject under consideration.
- particular position, those opposed, and those offering completely different arguments.
- Discussion of both the distinctiveness of each source and its similarities with the others.
Steps in the literature review process
Preparation of a literature review may be divided into four steps:
- Define your subject and the scope of the review.
- Search the library catalogue, subject specific databases and other search tools to find sources that are relevant to your topic.
- Read and evaluate the sources and to determine their suitability to the understanding of topic at hand (see the Evaluating sources section).
- Analyse, interpret and discuss the findings and conclusions of the sources you selected.
Evaluating sources
In assessing each source, consideration should be given to:
- What is the author's expertise in this particular field of study (credentials)?
- Are the author's arguments supported by empirical evidence (e.g. quantitative/qualitative studies)?
- Is the author's perspective too biased in one direction or are opposing studies and viewpoints also considered?
- Does the selected source contribute to a more profound understanding of the subject?
Examples of a published literature review
Literature reviews are often published as scholarly articles, books, and reports. Here is an example of a recent literature review published as a scholarly journal article:
Ledesma, M. C., & Calderón, D. (2015). Critical race theory in education: A review of past literature and a look to the future. Qualitative Inquiry, 21(3), 206-222. Link to the article
Additional sources on writing literature reviews
Further information on the literature review process may be found below:
- Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review
- Fink, A. (2010). Conducting research literature reviews: From the Internet to paper
- Galvin, J. (2006). Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences
- Machi, L. A., & McEvoy, B. T. (2012). The literature review: Six steps to success
Adapted with permission and thanks from How to Write a Literature Review originally created by Kenneth Lyons, McHenry Library, University of California, Santa Cruz.
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Research Process :: Step by Step
- Introduction
- Select Topic
- Identify Keywords
- Background Information
- Develop Research Questions
- Refine Topic
- Search Strategy
- Popular Databases
- Evaluate Sources
- Types of Periodicals
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Organize / Take Notes
- Writing & Grammar Resources
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Citation Styles
- Paraphrasing
- Privacy / Confidentiality
- Research Process
- Selecting Your Topic
- Identifying Keywords
- Gathering Background Info
- Evaluating Sources

Organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment, but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries
A literature review must do these things:
- be organized around and related directly to the thesis or research question you are developing
- synthesize results into a summary of what is and is not known
- identify areas of controversy in the literature
- formulate questions that need further research
Ask yourself questions like these:
- What is the specific thesis, problem, or research question that my literature review helps to define?
- What type of literature review am I conducting? Am I looking at issues of theory? methodology? policy? quantitative research (e.g. on the effectiveness of a new procedure)? qualitative research (e.g., studies of loneliness among migrant workers)?
- What is the scope of my literature review? What types of publications am I using (e.g., journals, books, government documents, popular media)? What discipline am I working in (e.g., nursing psychology, sociology, medicine)?
- How good was my information seeking? Has my search been wide enough to ensure I've found all the relevant material? Has it been narrow enough to exclude irrelevant material? Is the number of sources I've used appropriate for the length of my paper?
- Have I critically analyzed the literature I use? Do I follow through a set of concepts and questions, comparing items to each other in the ways they deal with them? Instead of just listing and summarizing items, do I assess them, discussing strengths and weaknesses?
- Have I cited and discussed studies contrary to my perspective?
- Will the reader find my literature review relevant, appropriate, and useful?
Ask yourself questions like these about each book or article you include:
- Has the author formulated a problem/issue?
- Is it clearly defined? Is its significance (scope, severity, relevance) clearly established?
- Could the problem have been approached more effectively from another perspective?
- What is the author's research orientation (e.g., interpretive, critical science, combination)?
- What is the author's theoretical framework (e.g., psychological, developmental, feminist)?
- What is the relationship between the theoretical and research perspectives?
- Has the author evaluated the literature relevant to the problem/issue? Does the author include literature taking positions she or he does not agree with?
- In a research study, how good are the basic components of the study design (e.g., population, intervention, outcome)? How accurate and valid are the measurements? Is the analysis of the data accurate and relevant to the research question? Are the conclusions validly based upon the data and analysis?
- In material written for a popular readership, does the author use appeals to emotion, one-sided examples, or rhetorically-charged language and tone? Is there an objective basis to the reasoning, or is the author merely "proving" what he or she already believes?
- How does the author structure the argument? Can you "deconstruct" the flow of the argument to see whether or where it breaks down logically (e.g., in establishing cause-effect relationships)?
- In what ways does this book or article contribute to our understanding of the problem under study, and in what ways is it useful for practice? What are the strengths and limitations?
- How does this book or article relate to the specific thesis or question I am developing?
Text written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography
- Next: Step 5: Cite Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/researchprocess
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.

Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is a good literature review?
- Types of Literature Reviews
- What are the parts of a Literature Review?
- What is the difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review?
Parts of a Literature Review
Introduction .
- To explain the focus and establish the importance of the subject
- provide the framework, selection criteria, or parameters of your literature review
- provide background or history
- outline what kind of work has been done on the topic
- briefly identify any controversies within the field or any recent research that has raised questions about earlier assumptions
- In a stand-alone literature review, this statement will sum up and evaluate the current state of this field of research
- In a review that is an introduction or preparatory to a thesis or research report, it will suggest how the review findings will lead to the research the writer proposes to undertake.
- To summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in the field
- To note major themes or topics, the most important trends, and any findings about which researchers agree or disagree
- Often divided by headings/subheadings
- If the review is preliminary to your own thesis or research project, its purpose is to make an argument that will justify your proposed research. Therefore, the literature review will discuss only that research which leads directly to your own project.
- To summarize the evidence presented and show its significance
- Rather than restating your thesis or purpose statement, explain what your review tells you about the current state of the field
- If the review is an introduction to your own research, the conclusion highlights gaps and indicates how previous research leads to your own research project and chosen methodology.
- If the review is a stand-alone assignment for a course, the conclusion should suggest any practical applications of the research as well as the implications and possibilities for future research.
- Find out what style guide you are required to follow (e.g., APA, MLA, ASA)
- Follow the guidelines to format citations and create a reference list or bibliography
- Cite Your Sources
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. adapted from UofG,McLaughlin Library
- << Previous: Types of Literature Reviews
- Next: What is the difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review? >>
- Last Updated: Nov 21, 2023 12:49 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lamission.edu/c.php?g=1190903
Los Angeles Mission College. All rights reserved. - 13356 Eldridge Avenue, Sylmar, CA 91342. 818-364-7600 | LACCD.edu | ADA Compliance Questions or comments about this web site? Please leave Feedback

- Holy Spirit Library
- Library Guides
- EDG 501 Literature Review
Components of a Literature Review
Edg 501 literature review: components of a literature review.
- Structure of a Literature Review
- Writing the Literature Review
- Databases and Searching Tips
- Examples/Writing Helps
Talk to a Librarian
Library links.
- Library Home
- Research Databases
Reference Desk 610.902.8537
The works that make up the literature review fall into three categories:
General theoretical literature
- This literature establishes the importance of your topic/research. define abstract concepts, discuss the relationships between abstract concepts, and include statistics about the problem being investigated. Landmark and classic articles are also included.
- Encyclopedia of Education
- Encyclopedia of Curriculum Studies
- Encyclopedia of Educational Psychology
- 21st Century Education
Literature on related topic areas
- These sources identify general themes that run throughout the literature. For example, a search on the topic of high stakes testing will find articles on high stakes testing and gender, socioeconomic status, inclusive education, cheating, and academic achievement.
Resources for this literature (see below) :
- Academic Search Complete This link opens in a new window
- PsycARTICLES This link opens in a new window
- PsycINFO This link opens in a new window
Literature specific to your research focus
- This literature is highly relevant. The sources isolate the issues and highlight the findings you expected when you articulated your research question or formulated your hypothesis.
Next Step: See Writing the Literature Review
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
Qualitative research methods are tools for gathering information that does not take a numerical form that can be counted and otherwise manipulated mathematically. If I live with a group of women and men and observe that males tend to dominate conversations, for example, my results consist of an interpretation based on a set of observations that I summarize in an overall impression. As such, it is a qualitative assessment of what is going on. By contrast, if I systematically count how often men and women interact and then compare the totals, my method is quantitative, because it produces numerical results.
Qualitative methods are most closely associated with participant observation , historical sociology , ethnomethodology , ethnography and ethnology . Quantitative methods are most closely associated with surveys , experiments , and other forms of numerical data gathering. Although quantitative methods are often considered superior to socalled "soft" qualitative methods, most sociologists appreciate that each provides unique and valuable insights into the workings of social life that are beyond the reach of the other.
Qualitative and quantitative research methods. (2000). In A. G. Johnson,
The Blackwell dictionary of sociology (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Blackwell
Publishers. Retrieved from Credo Reference.
Welcome to Holy Spirit Library

- << Previous: Structure of a Literature Review
- Next: Writing the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 2:33 PM
- URL: https://cabrini.libguides.com/c.php?g=268013
Holy Spirit Library 610-902-8538 [email protected] cabrini.edu/library
Organizing Research for Arts and Humanities Papers and Theses
- General Guide Information
- Developing a Topic
- What are Primary and Secondary Sources
- What are Scholarly and Non-Scholarly Sources
- Writing an Abstract
- Writing Academic Book Reviews
- Writing A Literature Review
- Using Images and other Media
What is a Literture Review
Note: This description of the elements of a literature review is geared toward researchers in the arts and humanities. Additional information on conducting literature reviews is available in Dr. Robert Labaree's libguide on organizing research in the social sciences .
A literature review is a discursive essay that critically surveys existing scholarship on a particular topic in the field. A literature review essay is a required part of a dissertation. Undergraduate students are sometimes asked to write a literature review essay as part of an assignment to help them delve into topical research. Literature reviews are also included in grant proposals.
Components of a Literature Review Essay
When organizing a literature review essay, remember to weave in the following components as needed:
- Criteria for selecting and excluding sources for your literature review;
- Citations to the works under review;
- Summary of the main ideas, arguments, theories, or methodologies of each work under review;
- Critical evaluation of how each work fits into the development of scholarship on the topic at hand, whether it breaks new evidentiary or theoretical grounds, or provides notable nuaned reading. In academic papers and dissertations, critical evaluation constitutes the bulk of the literature review essay.
Organizing a Literature Review Essay
There are several common ways to organize a literature review essay. Often literature review essays are a hybrid:
Historic : If the history of publishing sheds important light on the trajectory of scholarship on your topic, it may be useful to organize your essay chronologically by date of publication. Are earlier authors cited in subsequent publications, and if so, which ones?
Thematic : Has your topic undergone thematic reinterpretation, and how have the themes been treated by the works under review? Is there a methodological context, such as iconographic, sociological, political, religious? Do any of the works offer a methodological reevaluation or re-contextualization of evidence? It may be worthwhile to check the bibliographies of the sources you are reviewing to see who else is cited, and whether there are previous authors and works that are commonly cited by the literature you are reviewing.
Theoretical : Has the topic been influenced by theoretical developments, such as structuralism, feminism, historicism? How do the works under review contribute to, amplify on, or reorient the theoretical discourse? It may be worthwhile to check the bibliographies of the sources you are reviewing to see who else is cited, and whether there are previous authors and works that are commonly cited by the literature you are reviewing.
A literature review essay written as a chapter of a dissertation ought to be as exhaustive as possible, given the parameters of the dissertation topic. You should be clear in stating the criteria for including and excluding sources.
Remember that you are writing an essay. It should have a theme that is reflected in the opening paragraph/section, a body that provides a well constructed critical summary and synthesis of works under review, and a conclusion that may reflect on the current state of scholarship, and, if appropriate, note developing scholarly trends.
Remember to keep track of your sources, regardless of the stage of your research. The USC Libraries have an excellent guide to citation styles and to citation management software .
- << Previous: Writing Academic Book Reviews
- Next: Using Images and other Media >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/ah_writing
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.

Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet].
Chapter 9 methods for literature reviews.
Guy Paré and Spyros Kitsiou .
9.1. Introduction
Literature reviews play a critical role in scholarship because science remains, first and foremost, a cumulative endeavour ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). As in any academic discipline, rigorous knowledge syntheses are becoming indispensable in keeping up with an exponentially growing eHealth literature, assisting practitioners, academics, and graduate students in finding, evaluating, and synthesizing the contents of many empirical and conceptual papers. Among other methods, literature reviews are essential for: (a) identifying what has been written on a subject or topic; (b) determining the extent to which a specific research area reveals any interpretable trends or patterns; (c) aggregating empirical findings related to a narrow research question to support evidence-based practice; (d) generating new frameworks and theories; and (e) identifying topics or questions requiring more investigation ( Paré, Trudel, Jaana, & Kitsiou, 2015 ).
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the “literature review” or “background” section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses ( Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013 ). It may also provide a theoretical foundation for the proposed study, substantiate the presence of the research problem, justify the research as one that contributes something new to the cumulated knowledge, or validate the methods and approaches for the proposed study ( Hart, 1998 ; Levy & Ellis, 2006 ).
The second form of literature review, which is the focus of this chapter, constitutes an original and valuable work of research in and of itself ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Rather than providing a base for a researcher’s own work, it creates a solid starting point for all members of the community interested in a particular area or topic ( Mulrow, 1987 ). The so-called “review article” is a journal-length paper which has an overarching purpose to synthesize the literature in a field, without collecting or analyzing any primary data ( Green, Johnson, & Adams, 2006 ).
When appropriately conducted, review articles represent powerful information sources for practitioners looking for state-of-the art evidence to guide their decision-making and work practices ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, high-quality reviews become frequently cited pieces of work which researchers seek out as a first clear outline of the literature when undertaking empirical studies ( Cooper, 1988 ; Rowe, 2014 ). Scholars who track and gauge the impact of articles have found that review papers are cited and downloaded more often than any other type of published article ( Cronin, Ryan, & Coughlan, 2008 ; Montori, Wilczynski, Morgan, Haynes, & Hedges, 2003 ; Patsopoulos, Analatos, & Ioannidis, 2005 ). The reason for their popularity may be the fact that reading the review enables one to have an overview, if not a detailed knowledge of the area in question, as well as references to the most useful primary sources ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Although they are not easy to conduct, the commitment to complete a review article provides a tremendous service to one’s academic community ( Paré et al., 2015 ; Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Most, if not all, peer-reviewed journals in the fields of medical informatics publish review articles of some type.
The main objectives of this chapter are fourfold: (a) to provide an overview of the major steps and activities involved in conducting a stand-alone literature review; (b) to describe and contrast the different types of review articles that can contribute to the eHealth knowledge base; (c) to illustrate each review type with one or two examples from the eHealth literature; and (d) to provide a series of recommendations for prospective authors of review articles in this domain.
9.2. Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
As explained in Templier and Paré (2015) , there are six generic steps involved in conducting a review article:
- formulating the research question(s) and objective(s),
- searching the extant literature,
- screening for inclusion,
- assessing the quality of primary studies,
- extracting data, and
- analyzing data.
Although these steps are presented here in sequential order, one must keep in mind that the review process can be iterative and that many activities can be initiated during the planning stage and later refined during subsequent phases ( Finfgeld-Connett & Johnson, 2013 ; Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ).
Formulating the research question(s) and objective(s): As a first step, members of the review team must appropriately justify the need for the review itself ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ), identify the review’s main objective(s) ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ), and define the concepts or variables at the heart of their synthesis ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ; Webster & Watson, 2002 ). Importantly, they also need to articulate the research question(s) they propose to investigate ( Kitchenham & Charters, 2007 ). In this regard, we concur with Jesson, Matheson, and Lacey (2011) that clearly articulated research questions are key ingredients that guide the entire review methodology; they underscore the type of information that is needed, inform the search for and selection of relevant literature, and guide or orient the subsequent analysis. Searching the extant literature: The next step consists of searching the literature and making decisions about the suitability of material to be considered in the review ( Cooper, 1988 ). There exist three main coverage strategies. First, exhaustive coverage means an effort is made to be as comprehensive as possible in order to ensure that all relevant studies, published and unpublished, are included in the review and, thus, conclusions are based on this all-inclusive knowledge base. The second type of coverage consists of presenting materials that are representative of most other works in a given field or area. Often authors who adopt this strategy will search for relevant articles in a small number of top-tier journals in a field ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In the third strategy, the review team concentrates on prior works that have been central or pivotal to a particular topic. This may include empirical studies or conceptual papers that initiated a line of investigation, changed how problems or questions were framed, introduced new methods or concepts, or engendered important debate ( Cooper, 1988 ). Screening for inclusion: The following step consists of evaluating the applicability of the material identified in the preceding step ( Levy & Ellis, 2006 ; vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). Once a group of potential studies has been identified, members of the review team must screen them to determine their relevance ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). A set of predetermined rules provides a basis for including or excluding certain studies. This exercise requires a significant investment on the part of researchers, who must ensure enhanced objectivity and avoid biases or mistakes. As discussed later in this chapter, for certain types of reviews there must be at least two independent reviewers involved in the screening process and a procedure to resolve disagreements must also be in place ( Liberati et al., 2009 ; Shea et al., 2009 ). Assessing the quality of primary studies: In addition to screening material for inclusion, members of the review team may need to assess the scientific quality of the selected studies, that is, appraise the rigour of the research design and methods. Such formal assessment, which is usually conducted independently by at least two coders, helps members of the review team refine which studies to include in the final sample, determine whether or not the differences in quality may affect their conclusions, or guide how they analyze the data and interpret the findings ( Petticrew & Roberts, 2006 ). Ascribing quality scores to each primary study or considering through domain-based evaluations which study components have or have not been designed and executed appropriately makes it possible to reflect on the extent to which the selected study addresses possible biases and maximizes validity ( Shea et al., 2009 ). Extracting data: The following step involves gathering or extracting applicable information from each primary study included in the sample and deciding what is relevant to the problem of interest ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Indeed, the type of data that should be recorded mainly depends on the initial research questions ( Okoli & Schabram, 2010 ). However, important information may also be gathered about how, when, where and by whom the primary study was conducted, the research design and methods, or qualitative/quantitative results ( Cooper & Hedges, 2009 ). Analyzing and synthesizing data : As a final step, members of the review team must collate, summarize, aggregate, organize, and compare the evidence extracted from the included studies. The extracted data must be presented in a meaningful way that suggests a new contribution to the extant literature ( Jesson et al., 2011 ). Webster and Watson (2002) warn researchers that literature reviews should be much more than lists of papers and should provide a coherent lens to make sense of extant knowledge on a given topic. There exist several methods and techniques for synthesizing quantitative (e.g., frequency analysis, meta-analysis) and qualitative (e.g., grounded theory, narrative analysis, meta-ethnography) evidence ( Dixon-Woods, Agarwal, Jones, Young, & Sutton, 2005 ; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic. Our classification scheme is largely inspired from Paré and colleagues’ (2015) typology. Below we present and illustrate those review types that we feel are central to the growth and development of the eHealth domain.
9.3.1. Narrative Reviews
The narrative review is the “traditional” way of reviewing the extant literature and is skewed towards a qualitative interpretation of prior knowledge ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). Put simply, a narrative review attempts to summarize or synthesize what has been written on a particular topic but does not seek generalization or cumulative knowledge from what is reviewed ( Davies, 2000 ; Green et al., 2006 ). Instead, the review team often undertakes the task of accumulating and synthesizing the literature to demonstrate the value of a particular point of view ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ). As such, reviewers may selectively ignore or limit the attention paid to certain studies in order to make a point. In this rather unsystematic approach, the selection of information from primary articles is subjective, lacks explicit criteria for inclusion and can lead to biased interpretations or inferences ( Green et al., 2006 ). There are several narrative reviews in the particular eHealth domain, as in all fields, which follow such an unstructured approach ( Silva et al., 2015 ; Paul et al., 2015 ).
Despite these criticisms, this type of review can be very useful in gathering together a volume of literature in a specific subject area and synthesizing it. As mentioned above, its primary purpose is to provide the reader with a comprehensive background for understanding current knowledge and highlighting the significance of new research ( Cronin et al., 2008 ). Faculty like to use narrative reviews in the classroom because they are often more up to date than textbooks, provide a single source for students to reference, and expose students to peer-reviewed literature ( Green et al., 2006 ). For researchers, narrative reviews can inspire research ideas by identifying gaps or inconsistencies in a body of knowledge, thus helping researchers to determine research questions or formulate hypotheses. Importantly, narrative reviews can also be used as educational articles to bring practitioners up to date with certain topics of issues ( Green et al., 2006 ).
Recently, there have been several efforts to introduce more rigour in narrative reviews that will elucidate common pitfalls and bring changes into their publication standards. Information systems researchers, among others, have contributed to advancing knowledge on how to structure a “traditional” review. For instance, Levy and Ellis (2006) proposed a generic framework for conducting such reviews. Their model follows the systematic data processing approach comprised of three steps, namely: (a) literature search and screening; (b) data extraction and analysis; and (c) writing the literature review. They provide detailed and very helpful instructions on how to conduct each step of the review process. As another methodological contribution, vom Brocke et al. (2009) offered a series of guidelines for conducting literature reviews, with a particular focus on how to search and extract the relevant body of knowledge. Last, Bandara, Miskon, and Fielt (2011) proposed a structured, predefined and tool-supported method to identify primary studies within a feasible scope, extract relevant content from identified articles, synthesize and analyze the findings, and effectively write and present the results of the literature review. We highly recommend that prospective authors of narrative reviews consult these useful sources before embarking on their work.
Darlow and Wen (2015) provide a good example of a highly structured narrative review in the eHealth field. These authors synthesized published articles that describe the development process of mobile health ( m-health ) interventions for patients’ cancer care self-management. As in most narrative reviews, the scope of the research questions being investigated is broad: (a) how development of these systems are carried out; (b) which methods are used to investigate these systems; and (c) what conclusions can be drawn as a result of the development of these systems. To provide clear answers to these questions, a literature search was conducted on six electronic databases and Google Scholar . The search was performed using several terms and free text words, combining them in an appropriate manner. Four inclusion and three exclusion criteria were utilized during the screening process. Both authors independently reviewed each of the identified articles to determine eligibility and extract study information. A flow diagram shows the number of studies identified, screened, and included or excluded at each stage of study selection. In terms of contributions, this review provides a series of practical recommendations for m-health intervention development.
9.3.2. Descriptive or Mapping Reviews
The primary goal of a descriptive review is to determine the extent to which a body of knowledge in a particular research topic reveals any interpretable pattern or trend with respect to pre-existing propositions, theories, methodologies or findings ( King & He, 2005 ; Paré et al., 2015 ). In contrast with narrative reviews, descriptive reviews follow a systematic and transparent procedure, including searching, screening and classifying studies ( Petersen, Vakkalanka, & Kuzniarz, 2015 ). Indeed, structured search methods are used to form a representative sample of a larger group of published works ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Further, authors of descriptive reviews extract from each study certain characteristics of interest, such as publication year, research methods, data collection techniques, and direction or strength of research outcomes (e.g., positive, negative, or non-significant) in the form of frequency analysis to produce quantitative results ( Sylvester et al., 2013 ). In essence, each study included in a descriptive review is treated as the unit of analysis and the published literature as a whole provides a database from which the authors attempt to identify any interpretable trends or draw overall conclusions about the merits of existing conceptualizations, propositions, methods or findings ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In doing so, a descriptive review may claim that its findings represent the state of the art in a particular domain ( King & He, 2005 ).
In the fields of health sciences and medical informatics, reviews that focus on examining the range, nature and evolution of a topic area are described by Anderson, Allen, Peckham, and Goodwin (2008) as mapping reviews . Like descriptive reviews, the research questions are generic and usually relate to publication patterns and trends. There is no preconceived plan to systematically review all of the literature although this can be done. Instead, researchers often present studies that are representative of most works published in a particular area and they consider a specific time frame to be mapped.
An example of this approach in the eHealth domain is offered by DeShazo, Lavallie, and Wolf (2009). The purpose of this descriptive or mapping review was to characterize publication trends in the medical informatics literature over a 20-year period (1987 to 2006). To achieve this ambitious objective, the authors performed a bibliometric analysis of medical informatics citations indexed in medline using publication trends, journal frequencies, impact factors, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) term frequencies, and characteristics of citations. Findings revealed that there were over 77,000 medical informatics articles published during the covered period in numerous journals and that the average annual growth rate was 12%. The MeSH term analysis also suggested a strong interdisciplinary trend. Finally, average impact scores increased over time with two notable growth periods. Overall, patterns in research outputs that seem to characterize the historic trends and current components of the field of medical informatics suggest it may be a maturing discipline (DeShazo et al., 2009).
9.3.3. Scoping Reviews
Scoping reviews attempt to provide an initial indication of the potential size and nature of the extant literature on an emergent topic (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Daudt, van Mossel, & Scott, 2013 ; Levac, Colquhoun, & O’Brien, 2010). A scoping review may be conducted to examine the extent, range and nature of research activities in a particular area, determine the value of undertaking a full systematic review (discussed next), or identify research gaps in the extant literature ( Paré et al., 2015 ). In line with their main objective, scoping reviews usually conclude with the presentation of a detailed research agenda for future works along with potential implications for both practice and research.
Unlike narrative and descriptive reviews, the whole point of scoping the field is to be as comprehensive as possible, including grey literature (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005). Inclusion and exclusion criteria must be established to help researchers eliminate studies that are not aligned with the research questions. It is also recommended that at least two independent coders review abstracts yielded from the search strategy and then the full articles for study selection ( Daudt et al., 2013 ). The synthesized evidence from content or thematic analysis is relatively easy to present in tabular form (Arksey & O’Malley, 2005; Thomas & Harden, 2008 ).
One of the most highly cited scoping reviews in the eHealth domain was published by Archer, Fevrier-Thomas, Lokker, McKibbon, and Straus (2011) . These authors reviewed the existing literature on personal health record ( phr ) systems including design, functionality, implementation, applications, outcomes, and benefits. Seven databases were searched from 1985 to March 2010. Several search terms relating to phr s were used during this process. Two authors independently screened titles and abstracts to determine inclusion status. A second screen of full-text articles, again by two independent members of the research team, ensured that the studies described phr s. All in all, 130 articles met the criteria and their data were extracted manually into a database. The authors concluded that although there is a large amount of survey, observational, cohort/panel, and anecdotal evidence of phr benefits and satisfaction for patients, more research is needed to evaluate the results of phr implementations. Their in-depth analysis of the literature signalled that there is little solid evidence from randomized controlled trials or other studies through the use of phr s. Hence, they suggested that more research is needed that addresses the current lack of understanding of optimal functionality and usability of these systems, and how they can play a beneficial role in supporting patient self-management ( Archer et al., 2011 ).
9.3.4. Forms of Aggregative Reviews
Healthcare providers, practitioners, and policy-makers are nowadays overwhelmed with large volumes of information, including research-based evidence from numerous clinical trials and evaluation studies, assessing the effectiveness of health information technologies and interventions ( Ammenwerth & de Keizer, 2004 ; Deshazo et al., 2009 ). It is unrealistic to expect that all these disparate actors will have the time, skills, and necessary resources to identify the available evidence in the area of their expertise and consider it when making decisions. Systematic reviews that involve the rigorous application of scientific strategies aimed at limiting subjectivity and bias (i.e., systematic and random errors) can respond to this challenge.
Systematic reviews attempt to aggregate, appraise, and synthesize in a single source all empirical evidence that meet a set of previously specified eligibility criteria in order to answer a clearly formulated and often narrow research question on a particular topic of interest to support evidence-based practice ( Liberati et al., 2009 ). They adhere closely to explicit scientific principles ( Liberati et al., 2009 ) and rigorous methodological guidelines (Higgins & Green, 2008) aimed at reducing random and systematic errors that can lead to deviations from the truth in results or inferences. The use of explicit methods allows systematic reviews to aggregate a large body of research evidence, assess whether effects or relationships are in the same direction and of the same general magnitude, explain possible inconsistencies between study results, and determine the strength of the overall evidence for every outcome of interest based on the quality of included studies and the general consistency among them ( Cook, Mulrow, & Haynes, 1997 ). The main procedures of a systematic review involve:
- Formulating a review question and developing a search strategy based on explicit inclusion criteria for the identification of eligible studies (usually described in the context of a detailed review protocol).
- Searching for eligible studies using multiple databases and information sources, including grey literature sources, without any language restrictions.
- Selecting studies, extracting data, and assessing risk of bias in a duplicate manner using two independent reviewers to avoid random or systematic errors in the process.
- Analyzing data using quantitative or qualitative methods.
- Presenting results in summary of findings tables.
- Interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Many systematic reviews, but not all, use statistical methods to combine the results of independent studies into a single quantitative estimate or summary effect size. Known as meta-analyses , these reviews use specific data extraction and statistical techniques (e.g., network, frequentist, or Bayesian meta-analyses) to calculate from each study by outcome of interest an effect size along with a confidence interval that reflects the degree of uncertainty behind the point estimate of effect ( Borenstein, Hedges, Higgins, & Rothstein, 2009 ; Deeks, Higgins, & Altman, 2008 ). Subsequently, they use fixed or random-effects analysis models to combine the results of the included studies, assess statistical heterogeneity, and calculate a weighted average of the effect estimates from the different studies, taking into account their sample sizes. The summary effect size is a value that reflects the average magnitude of the intervention effect for a particular outcome of interest or, more generally, the strength of a relationship between two variables across all studies included in the systematic review. By statistically combining data from multiple studies, meta-analyses can create more precise and reliable estimates of intervention effects than those derived from individual studies alone, when these are examined independently as discrete sources of information.
The review by Gurol-Urganci, de Jongh, Vodopivec-Jamsek, Atun, and Car (2013) on the effects of mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments is an illustrative example of a high-quality systematic review with meta-analysis. Missed appointments are a major cause of inefficiency in healthcare delivery with substantial monetary costs to health systems. These authors sought to assess whether mobile phone-based appointment reminders delivered through Short Message Service ( sms ) or Multimedia Messaging Service ( mms ) are effective in improving rates of patient attendance and reducing overall costs. To this end, they conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases using highly sensitive search strategies without language or publication-type restrictions to identify all rct s that are eligible for inclusion. In order to minimize the risk of omitting eligible studies not captured by the original search, they supplemented all electronic searches with manual screening of trial registers and references contained in the included studies. Study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments were performed independently by two coders using standardized methods to ensure consistency and to eliminate potential errors. Findings from eight rct s involving 6,615 participants were pooled into meta-analyses to calculate the magnitude of effects that mobile text message reminders have on the rate of attendance at healthcare appointments compared to no reminders and phone call reminders.
Meta-analyses are regarded as powerful tools for deriving meaningful conclusions. However, there are situations in which it is neither reasonable nor appropriate to pool studies together using meta-analytic methods simply because there is extensive clinical heterogeneity between the included studies or variation in measurement tools, comparisons, or outcomes of interest. In these cases, systematic reviews can use qualitative synthesis methods such as vote counting, content analysis, classification schemes and tabulations, as an alternative approach to narratively synthesize the results of the independent studies included in the review. This form of review is known as qualitative systematic review.
A rigorous example of one such review in the eHealth domain is presented by Mickan, Atherton, Roberts, Heneghan, and Tilson (2014) on the use of handheld computers by healthcare professionals and their impact on access to information and clinical decision-making. In line with the methodological guidelines for systematic reviews, these authors: (a) developed and registered with prospero ( www.crd.york.ac.uk/ prospero / ) an a priori review protocol; (b) conducted comprehensive searches for eligible studies using multiple databases and other supplementary strategies (e.g., forward searches); and (c) subsequently carried out study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments in a duplicate manner to eliminate potential errors in the review process. Heterogeneity between the included studies in terms of reported outcomes and measures precluded the use of meta-analytic methods. To this end, the authors resorted to using narrative analysis and synthesis to describe the effectiveness of handheld computers on accessing information for clinical knowledge, adherence to safety and clinical quality guidelines, and diagnostic decision-making.
In recent years, the number of systematic reviews in the field of health informatics has increased considerably. Systematic reviews with discordant findings can cause great confusion and make it difficult for decision-makers to interpret the review-level evidence ( Moher, 2013 ). Therefore, there is a growing need for appraisal and synthesis of prior systematic reviews to ensure that decision-making is constantly informed by the best available accumulated evidence. Umbrella reviews , also known as overviews of systematic reviews, are tertiary types of evidence synthesis that aim to accomplish this; that is, they aim to compare and contrast findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Umbrella reviews generally adhere to the same principles and rigorous methodological guidelines used in systematic reviews. However, the unit of analysis in umbrella reviews is the systematic review rather than the primary study ( Becker & Oxman, 2008 ). Unlike systematic reviews that have a narrow focus of inquiry, umbrella reviews focus on broader research topics for which there are several potential interventions ( Smith, Devane, Begley, & Clarke, 2011 ). A recent umbrella review on the effects of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with heart failure critically appraised, compared, and synthesized evidence from 15 systematic reviews to investigate which types of home telemonitoring technologies and forms of interventions are more effective in reducing mortality and hospital admissions ( Kitsiou, Paré, & Jaana, 2015 ).
9.3.5. Realist Reviews
Realist reviews are theory-driven interpretative reviews developed to inform, enhance, or supplement conventional systematic reviews by making sense of heterogeneous evidence about complex interventions applied in diverse contexts in a way that informs policy decision-making ( Greenhalgh, Wong, Westhorp, & Pawson, 2011 ). They originated from criticisms of positivist systematic reviews which centre on their “simplistic” underlying assumptions ( Oates, 2011 ). As explained above, systematic reviews seek to identify causation. Such logic is appropriate for fields like medicine and education where findings of randomized controlled trials can be aggregated to see whether a new treatment or intervention does improve outcomes. However, many argue that it is not possible to establish such direct causal links between interventions and outcomes in fields such as social policy, management, and information systems where for any intervention there is unlikely to be a regular or consistent outcome ( Oates, 2011 ; Pawson, 2006 ; Rousseau, Manning, & Denyer, 2008 ).
To circumvent these limitations, Pawson, Greenhalgh, Harvey, and Walshe (2005) have proposed a new approach for synthesizing knowledge that seeks to unpack the mechanism of how “complex interventions” work in particular contexts. The basic research question — what works? — which is usually associated with systematic reviews changes to: what is it about this intervention that works, for whom, in what circumstances, in what respects and why? Realist reviews have no particular preference for either quantitative or qualitative evidence. As a theory-building approach, a realist review usually starts by articulating likely underlying mechanisms and then scrutinizes available evidence to find out whether and where these mechanisms are applicable ( Shepperd et al., 2009 ). Primary studies found in the extant literature are viewed as case studies which can test and modify the initial theories ( Rousseau et al., 2008 ).
The main objective pursued in the realist review conducted by Otte-Trojel, de Bont, Rundall, and van de Klundert (2014) was to examine how patient portals contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The specific goals were to investigate how outcomes are produced and, most importantly, how variations in outcomes can be explained. The research team started with an exploratory review of background documents and research studies to identify ways in which patient portals may contribute to health service delivery and patient outcomes. The authors identified six main ways which represent “educated guesses” to be tested against the data in the evaluation studies. These studies were identified through a formal and systematic search in four databases between 2003 and 2013. Two members of the research team selected the articles using a pre-established list of inclusion and exclusion criteria and following a two-step procedure. The authors then extracted data from the selected articles and created several tables, one for each outcome category. They organized information to bring forward those mechanisms where patient portals contribute to outcomes and the variation in outcomes across different contexts.
9.3.6. Critical Reviews
Lastly, critical reviews aim to provide a critical evaluation and interpretive analysis of existing literature on a particular topic of interest to reveal strengths, weaknesses, contradictions, controversies, inconsistencies, and/or other important issues with respect to theories, hypotheses, research methods or results ( Baumeister & Leary, 1997 ; Kirkevold, 1997 ). Unlike other review types, critical reviews attempt to take a reflective account of the research that has been done in a particular area of interest, and assess its credibility by using appraisal instruments or critical interpretive methods. In this way, critical reviews attempt to constructively inform other scholars about the weaknesses of prior research and strengthen knowledge development by giving focus and direction to studies for further improvement ( Kirkevold, 1997 ).
Kitsiou, Paré, and Jaana (2013) provide an example of a critical review that assessed the methodological quality of prior systematic reviews of home telemonitoring studies for chronic patients. The authors conducted a comprehensive search on multiple databases to identify eligible reviews and subsequently used a validated instrument to conduct an in-depth quality appraisal. Results indicate that the majority of systematic reviews in this particular area suffer from important methodological flaws and biases that impair their internal validity and limit their usefulness for clinical and decision-making purposes. To this end, they provide a number of recommendations to strengthen knowledge development towards improving the design and execution of future reviews on home telemonitoring.
9.4. Summary
Table 9.1 outlines the main types of literature reviews that were described in the previous sub-sections and summarizes the main characteristics that distinguish one review type from another. It also includes key references to methodological guidelines and useful sources that can be used by eHealth scholars and researchers for planning and developing reviews.
Typology of Literature Reviews (adapted from Paré et al., 2015).
As shown in Table 9.1 , each review type addresses different kinds of research questions or objectives, which subsequently define and dictate the methods and approaches that need to be used to achieve the overarching goal(s) of the review. For example, in the case of narrative reviews, there is greater flexibility in searching and synthesizing articles ( Green et al., 2006 ). Researchers are often relatively free to use a diversity of approaches to search, identify, and select relevant scientific articles, describe their operational characteristics, present how the individual studies fit together, and formulate conclusions. On the other hand, systematic reviews are characterized by their high level of systematicity, rigour, and use of explicit methods, based on an “a priori” review plan that aims to minimize bias in the analysis and synthesis process (Higgins & Green, 2008). Some reviews are exploratory in nature (e.g., scoping/mapping reviews), whereas others may be conducted to discover patterns (e.g., descriptive reviews) or involve a synthesis approach that may include the critical analysis of prior research ( Paré et al., 2015 ). Hence, in order to select the most appropriate type of review, it is critical to know before embarking on a review project, why the research synthesis is conducted and what type of methods are best aligned with the pursued goals.
9.5. Concluding Remarks
In light of the increased use of evidence-based practice and research generating stronger evidence ( Grady et al., 2011 ; Lyden et al., 2013 ), review articles have become essential tools for summarizing, synthesizing, integrating or critically appraising prior knowledge in the eHealth field. As mentioned earlier, when rigorously conducted review articles represent powerful information sources for eHealth scholars and practitioners looking for state-of-the-art evidence. The typology of literature reviews we used herein will allow eHealth researchers, graduate students and practitioners to gain a better understanding of the similarities and differences between review types.
We must stress that this classification scheme does not privilege any specific type of review as being of higher quality than another ( Paré et al., 2015 ). As explained above, each type of review has its own strengths and limitations. Having said that, we realize that the methodological rigour of any review — be it qualitative, quantitative or mixed — is a critical aspect that should be considered seriously by prospective authors. In the present context, the notion of rigour refers to the reliability and validity of the review process described in section 9.2. For one thing, reliability is related to the reproducibility of the review process and steps, which is facilitated by a comprehensive documentation of the literature search process, extraction, coding and analysis performed in the review. Whether the search is comprehensive or not, whether it involves a methodical approach for data extraction and synthesis or not, it is important that the review documents in an explicit and transparent manner the steps and approach that were used in the process of its development. Next, validity characterizes the degree to which the review process was conducted appropriately. It goes beyond documentation and reflects decisions related to the selection of the sources, the search terms used, the period of time covered, the articles selected in the search, and the application of backward and forward searches ( vom Brocke et al., 2009 ). In short, the rigour of any review article is reflected by the explicitness of its methods (i.e., transparency) and the soundness of the approach used. We refer those interested in the concepts of rigour and quality to the work of Templier and Paré (2015) which offers a detailed set of methodological guidelines for conducting and evaluating various types of review articles.
To conclude, our main objective in this chapter was to demystify the various types of literature reviews that are central to the continuous development of the eHealth field. It is our hope that our descriptive account will serve as a valuable source for those conducting, evaluating or using reviews in this important and growing domain.
- Ammenwerth E., de Keizer N. An inventory of evaluation studies of information technology in health care. Trends in evaluation research, 1982-2002. International Journal of Medical Informatics. 2004; 44 (1):44–56. [ PubMed : 15778794 ]
- Anderson S., Allen P., Peckham S., Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Research Policy and Systems. 2008; 6 (7):1–12. [ PMC free article : PMC2500008 ] [ PubMed : 18613961 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Archer N., Fevrier-Thomas U., Lokker C., McKibbon K. A., Straus S.E. Personal health records: a scoping review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2011; 18 (4):515–522. [ PMC free article : PMC3128401 ] [ PubMed : 21672914 ]
- Arksey H., O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2005; 8 (1):19–32.
- A systematic, tool-supported method for conducting literature reviews in information systems. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2011); June 9 to 11; Helsinki, Finland. 2011.
- Baumeister R. F., Leary M.R. Writing narrative literature reviews. Review of General Psychology. 1997; 1 (3):311–320.
- Becker L. A., Oxman A.D. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Overviews of reviews; pp. 607–631.
- Borenstein M., Hedges L., Higgins J., Rothstein H. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons Inc; 2009.
- Cook D. J., Mulrow C. D., Haynes B. Systematic reviews: Synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1997; 126 (5):376–380. [ PubMed : 9054282 ]
- Cooper H., Hedges L.V. In: The handbook of research synthesis and meta-analysis. 2nd ed. Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C., editors. New York: Russell Sage Foundation; 2009. Research synthesis as a scientific process; pp. 3–17.
- Cooper H. M. Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowledge in Society. 1988; 1 (1):104–126.
- Cronin P., Ryan F., Coughlan M. Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing. 2008; 17 (1):38–43. [ PubMed : 18399395 ]
- Darlow S., Wen K.Y. Development testing of mobile health interventions for cancer patient self-management: A review. Health Informatics Journal. 2015 (online before print). [ PubMed : 25916831 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Daudt H. M., van Mossel C., Scott S.J. Enhancing the scoping study methodology: a large, inter-professional team’s experience with Arksey and O’Malley’s framework. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2013; 13 :48. [ PMC free article : PMC3614526 ] [ PubMed : 23522333 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Davies P. The relevance of systematic reviews to educational policy and practice. Oxford Review of Education. 2000; 26 (3-4):365–378.
- Deeks J. J., Higgins J. P. T., Altman D.G. In: Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Hoboken, nj : John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2008. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 243–296.
- Deshazo J. P., Lavallie D. L., Wolf F.M. Publication trends in the medical informatics literature: 20 years of “Medical Informatics” in mesh . bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2009; 9 :7. [ PMC free article : PMC2652453 ] [ PubMed : 19159472 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dixon-Woods M., Agarwal S., Jones D., Young B., Sutton A. Synthesising qualitative and quantitative evidence: a review of possible methods. Journal of Health Services Research and Policy. 2005; 10 (1):45–53. [ PubMed : 15667704 ]
- Finfgeld-Connett D., Johnson E.D. Literature search strategies for conducting knowledge-building and theory-generating qualitative systematic reviews. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 2013; 69 (1):194–204. [ PMC free article : PMC3424349 ] [ PubMed : 22591030 ]
- Grady B., Myers K. M., Nelson E. L., Belz N., Bennett L., Carnahan L. … Guidelines Working Group. Evidence-based practice for telemental health. Telemedicine Journal and E Health. 2011; 17 (2):131–148. [ PubMed : 21385026 ]
- Green B. N., Johnson C. D., Adams A. Writing narrative literature reviews for peer-reviewed journals: secrets of the trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine. 2006; 5 (3):101–117. [ PMC free article : PMC2647067 ] [ PubMed : 19674681 ]
- Greenhalgh T., Wong G., Westhorp G., Pawson R. Protocol–realist and meta-narrative evidence synthesis: evolving standards ( rameses ). bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 :115. [ PMC free article : PMC3173389 ] [ PubMed : 21843376 ]
- Gurol-Urganci I., de Jongh T., Vodopivec-Jamsek V., Atun R., Car J. Mobile phone messaging reminders for attendance at healthcare appointments. Cochrane Database System Review. 2013; 12 cd 007458. [ PMC free article : PMC6485985 ] [ PubMed : 24310741 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hart C. Doing a literature review: Releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE Publications; 1998.
- Higgins J. P. T., Green S., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions: Cochrane book series. Hoboken, nj : Wiley-Blackwell; 2008.
- Jesson J., Matheson L., Lacey F.M. Doing your literature review: traditional and systematic techniques. Los Angeles & London: SAGE Publications; 2011.
- King W. R., He J. Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2005; 16 :1.
- Kirkevold M. Integrative nursing research — an important strategy to further the development of nursing science and nursing practice. Journal of Advanced Nursing. 1997; 25 (5):977–984. [ PubMed : 9147203 ]
- Kitchenham B., Charters S. ebse Technical Report Version 2.3. Keele & Durham. uk : Keele University & University of Durham; 2007. Guidelines for performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering.
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of home telemonitoring interventions for patients with chronic diseases: a critical assessment of their methodological quality. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2013; 15 (7):e150. [ PMC free article : PMC3785977 ] [ PubMed : 23880072 ]
- Kitsiou S., Paré G., Jaana M. Effects of home telemonitoring interventions on patients with chronic heart failure: an overview of systematic reviews. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2015; 17 (3):e63. [ PMC free article : PMC4376138 ] [ PubMed : 25768664 ]
- Levac D., Colquhoun H., O’Brien K. K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Science. 2010; 5 (1):69. [ PMC free article : PMC2954944 ] [ PubMed : 20854677 ]
- Levy Y., Ellis T.J. A systems approach to conduct an effective literature review in support of information systems research. Informing Science. 2006; 9 :181–211.
- Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gøtzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P. A. et al. Moher D. The prisma statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2009; 151 (4):W-65. [ PubMed : 19622512 ]
- Lyden J. R., Zickmund S. L., Bhargava T. D., Bryce C. L., Conroy M. B., Fischer G. S. et al. McTigue K. M. Implementing health information technology in a patient-centered manner: Patient experiences with an online evidence-based lifestyle intervention. Journal for Healthcare Quality. 2013; 35 (5):47–57. [ PubMed : 24004039 ]
- Mickan S., Atherton H., Roberts N. W., Heneghan C., Tilson J.K. Use of handheld computers in clinical practice: a systematic review. bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2014; 14 :56. [ PMC free article : PMC4099138 ] [ PubMed : 24998515 ]
- Moher D. The problem of duplicate systematic reviews. British Medical Journal. 2013; 347 (5040) [ PubMed : 23945367 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Montori V. M., Wilczynski N. L., Morgan D., Haynes R. B., Hedges T. Systematic reviews: a cross-sectional study of location and citation counts. bmc Medicine. 2003; 1 :2. [ PMC free article : PMC281591 ] [ PubMed : 14633274 ]
- Mulrow C. D. The medical review article: state of the science. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1987; 106 (3):485–488. [ PubMed : 3813259 ] [ CrossRef ]
- Evidence-based information systems: A decade later. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems ; 2011. Retrieved from http://aisel .aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent .cgi?article =1221&context =ecis2011 .
- Okoli C., Schabram K. A guide to conducting a systematic literature review of information systems research. ssrn Electronic Journal. 2010
- Otte-Trojel T., de Bont A., Rundall T. G., van de Klundert J. How outcomes are achieved through patient portals: a realist review. Journal of American Medical Informatics Association. 2014; 21 (4):751–757. [ PMC free article : PMC4078283 ] [ PubMed : 24503882 ]
- Paré G., Trudel M.-C., Jaana M., Kitsiou S. Synthesizing information systems knowledge: A typology of literature reviews. Information & Management. 2015; 52 (2):183–199.
- Patsopoulos N. A., Analatos A. A., Ioannidis J.P. A. Relative citation impact of various study designs in the health sciences. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2005; 293 (19):2362–2366. [ PubMed : 15900006 ]
- Paul M. M., Greene C. M., Newton-Dame R., Thorpe L. E., Perlman S. E., McVeigh K. H., Gourevitch M.N. The state of population health surveillance using electronic health records: A narrative review. Population Health Management. 2015; 18 (3):209–216. [ PubMed : 25608033 ]
- Pawson R. Evidence-based policy: a realist perspective. London: SAGE Publications; 2006.
- Pawson R., Greenhalgh T., Harvey G., Walshe K. Realist review—a new method of systematic review designed for complex policy interventions. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy. 2005; 10 (Suppl 1):21–34. [ PubMed : 16053581 ]
- Petersen K., Vakkalanka S., Kuzniarz L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Information and Software Technology. 2015; 64 :1–18.
- Petticrew M., Roberts H. Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide. Malden, ma : Blackwell Publishing Co; 2006.
- Rousseau D. M., Manning J., Denyer D. Evidence in management and organizational science: Assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. The Academy of Management Annals. 2008; 2 (1):475–515.
- Rowe F. What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. European Journal of Information Systems. 2014; 23 (3):241–255.
- Shea B. J., Hamel C., Wells G. A., Bouter L. M., Kristjansson E., Grimshaw J. et al. Boers M. amstar is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 2009; 62 (10):1013–1020. [ PubMed : 19230606 ]
- Shepperd S., Lewin S., Straus S., Clarke M., Eccles M. P., Fitzpatrick R. et al. Sheikh A. Can we systematically review studies that evaluate complex interventions? PLoS Medicine. 2009; 6 (8):e1000086. [ PMC free article : PMC2717209 ] [ PubMed : 19668360 ]
- Silva B. M., Rodrigues J. J., de la Torre Díez I., López-Coronado M., Saleem K. Mobile-health: A review of current state in 2015. Journal of Biomedical Informatics. 2015; 56 :265–272. [ PubMed : 26071682 ]
- Smith V., Devane D., Begley C., Clarke M. Methodology in conducting a systematic review of systematic reviews of healthcare interventions. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2011; 11 (1):15. [ PMC free article : PMC3039637 ] [ PubMed : 21291558 ]
- Sylvester A., Tate M., Johnstone D. Beyond synthesis: re-presenting heterogeneous research literature. Behaviour & Information Technology. 2013; 32 (12):1199–1215.
- Templier M., Paré G. A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Communications of the Association for Information Systems. 2015; 37 (6):112–137.
- Thomas J., Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. bmc Medical Research Methodology. 2008; 8 (1):45. [ PMC free article : PMC2478656 ] [ PubMed : 18616818 ]
- Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Information Systems ( ecis 2009); Verona, Italy. 2009.
- Webster J., Watson R.T. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: Writing a literature review. Management Information Systems Quarterly. 2002; 26 (2):11.
- Whitlock E. P., Lin J. S., Chou R., Shekelle P., Robinson K.A. Using existing systematic reviews in complex systematic reviews. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2008; 148 (10):776–782. [ PubMed : 18490690 ]
This publication is licensed under a Creative Commons License, Attribution-Noncommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0): see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
- Cite this Page Paré G, Kitsiou S. Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews. In: Lau F, Kuziemsky C, editors. Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach [Internet]. Victoria (BC): University of Victoria; 2017 Feb 27.
- PDF version of this title (4.5M)
- Disable Glossary Links
In this Page
- Introduction
- Overview of the Literature Review Process and Steps
- Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations
- Concluding Remarks
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed

Recent Activity
- Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Ev... Chapter 9 Methods for Literature Reviews - Handbook of eHealth Evaluation: An Evidence-based Approach
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
Learning together for better health using an evidence-based Learning Health System framework: a case study in stroke
- Helena Teede 1 , 2 na1 ,
- Dominique A. Cadilhac 3 , 4 na1 ,
- Tara Purvis 3 ,
- Monique F. Kilkenny 3 , 4 ,
- Bruce C.V. Campbell 4 , 5 , 6 ,
- Coralie English 7 ,
- Alison Johnson 2 ,
- Emily Callander 1 ,
- Rohan S. Grimley 8 , 9 ,
- Christopher Levi 10 ,
- Sandy Middleton 11 , 12 ,
- Kelvin Hill 13 &
- Joanne Enticott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4480-5690 1
BMC Medicine volume 22 , Article number: 198 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
In the context of expanding digital health tools, the health system is ready for Learning Health System (LHS) models. These models, with proper governance and stakeholder engagement, enable the integration of digital infrastructure to provide feedback to all relevant parties including clinicians and consumers on performance against best practice standards, as well as fostering innovation and aligning healthcare with patient needs. The LHS literature primarily includes opinion or consensus-based frameworks and lacks validation or evidence of benefit. Our aim was to outline a rigorously codesigned, evidence-based LHS framework and present a national case study of an LHS-aligned national stroke program that has delivered clinical benefit.
Current core components of a LHS involve capturing evidence from communities and stakeholders (quadrant 1), integrating evidence from research findings (quadrant 2), leveraging evidence from data and practice (quadrant 3), and generating evidence from implementation (quadrant 4) for iterative system-level improvement. The Australian Stroke program was selected as the case study as it provides an exemplar of how an iterative LHS works in practice at a national level encompassing and integrating evidence from all four LHS quadrants. Using this case study, we demonstrate how to apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement and embed real-world research for optimising healthcare improvement. We emphasize the transition from research as an endpoint, to research as an enabler and a solution for impact in healthcare improvement.
Conclusions
The Australian Stroke program has nationally improved stroke care since 2007, showcasing the value of integrated LHS-aligned approaches for tangible impact on outcomes. This LHS case study is a practical example for other health conditions and settings to follow suit.
Peer Review reports
Internationally, health systems are facing a crisis, driven by an ageing population, increasing complexity, multi-morbidity, rapidly advancing health technology and rising costs that threaten sustainability and mandate transformation and improvement [ 1 , 2 ]. Although research has generated solutions to healthcare challenges, and the advent of big data and digital health holds great promise, entrenched siloes and poor integration of knowledge generation, knowledge implementation and healthcare delivery between stakeholders, curtails momentum towards, and consistent attainment of, evidence-and value-based care [ 3 ]. This is compounded by the short supply of research and innovation leadership within the healthcare sector, and poorly integrated and often inaccessible health data systems, which have crippled the potential to deliver on digital-driven innovation [ 4 ]. Current approaches to healthcare improvement are also often isolated with limited sustainability, scale-up and impact [ 5 ].
Evidence suggests that integration and partnership across academic and healthcare delivery stakeholders are key to progress, including those with lived experience and their families (referred to here as consumers and community), diverse disciplines (both research and clinical), policy makers and funders. Utilization of evidence from research and evidence from practice including data from routine care, supported by implementation research, are key to sustainably embedding improvement and optimising health care and outcomes. A strategy to achieve this integration is through the Learning Health System (LHS) (Fig. 1 ) [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Although there are numerous publications on LHS approaches [ 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ], many focus on research perspectives and data, most do not demonstrate tangible healthcare improvement or better health outcomes. [ 6 ]
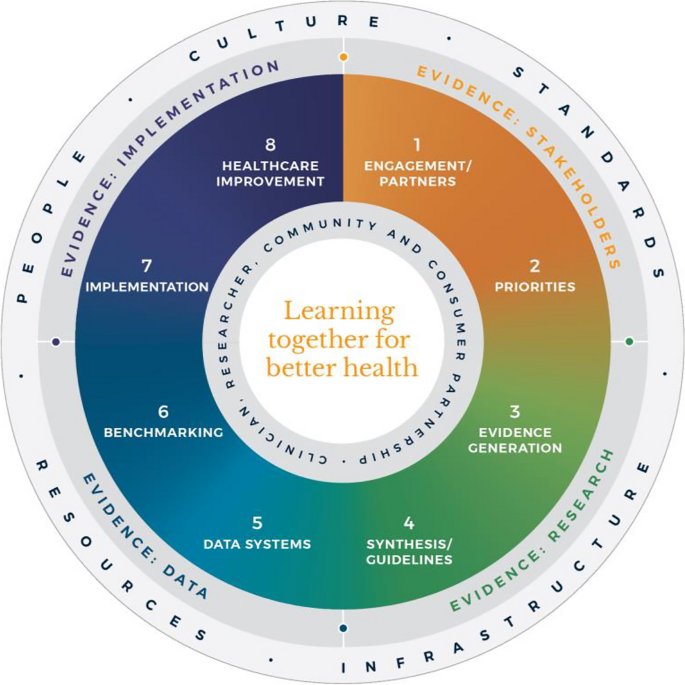
Monash Learning Health System: The Learn Together for Better Health Framework developed by Monash Partners and Monash University (from Enticott et al. 2021 [ 7 ]). Four evidence quadrants: Q1 (orange) is evidence from stakeholders; Q2 (green) is evidence from research; Q3 (light blue) is evidence from data; and, Q4 (dark blue) is evidence from implementation and healthcare improvement
In developed nations, it has been estimated that 60% of care provided aligns with the evidence base, 30% is low value and 10% is potentially harmful [ 13 ]. In some areas, clinical advances have been rapid and research and evidence have paved the way for dramatic improvement in outcomes, mandating rapid implementation of evidence into healthcare (e.g. polio and COVID-19 vaccines). However, healthcare improvement is challenging and slow [ 5 ]. Health systems are highly complex in their design, networks and interacting components, and change is difficult to enact, sustain and scale up. [ 3 ] New effective strategies are needed to meet community needs and deliver evidence-based and value-based care, which reorients care from serving the provider, services and system, towards serving community needs, based on evidence and quality. It goes beyond cost to encompass patient and provider experience, quality care and outcomes, efficiency and sustainability [ 2 , 6 ].
The costs of stroke care are expected to rise rapidly in the next decades, unless improvements in stroke care to reduce the disabling effects of strokes can be successfully developed and implemented [ 14 ]. Here, we briefly describe the Monash LHS framework (Fig. 1 ) [ 2 , 6 , 7 ] and outline an exemplar case in order to demonstrate how to apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement and embed real-world research for optimising healthcare. The Australian LHS exemplar in stroke care has driven nationwide improvement in stroke care since 2007.
An evidence-based Learning Health System framework
In Australia, members of this author group (HT, AJ, JE) have rigorously co-developed an evidence-based LHS framework, known simply as the Monash LHS [ 7 ]. The Monash LHS was designed to support sustainable, iterative and continuous robust benefit of improved clinical outcomes. It was created with national engagement in order to be applicable to Australian settings. Through this rigorous approach, core LHS principles and components have been established (Fig. 1 ). Evidence shows that people/workforce, culture, standards, governance and resources were all key to an effective LHS [ 2 , 6 ]. Culture is vital including trust, transparency, partnership and co-design. Key processes include legally compliant data sharing, linkage and governance, resources, and infrastructure [ 4 ]. The Monash LHS integrates disparate and often siloed stakeholders, infrastructure and expertise to ‘Learn Together for Better Health’ [ 7 ] (Fig. 1 ). This integrates (i) evidence from community and stakeholders including priority areas and outcomes; (ii) evidence from research and guidelines; (iii) evidence from practice (from data) with advanced analytics and benchmarking; and (iv) evidence from implementation science and health economics. Importantly, it starts with the problem and priorities of key stakeholders including the community, health professionals and services and creates an iterative learning system to address these. The following case study was chosen as it is an exemplar of how a Monash LHS-aligned national stroke program has delivered clinical benefit.
Australian Stroke Learning Health System
Internationally, the application of LHS approaches in stroke has resulted in improved stroke care and outcomes [ 12 ]. For example, in Canada a sustained decrease in 30-day in-hospital mortality has been found commensurate with an increase in resources to establish the multifactorial stroke system intervention for stroke treatment and prevention [ 15 ]. Arguably, with rapid advances in evidence and in the context of an ageing population with high cost and care burden and substantive impacts on quality of life, stroke is an area with a need for rapid research translation into evidence-based and value-based healthcare improvement. However, a recent systematic review found that the existing literature had few comprehensive examples of LHS adoption [ 12 ]. Although healthcare improvement systems and approaches were described, less is known about patient-clinician and stakeholder engagement, governance and culture, or embedding of data informatics into everyday practice to inform and drive improvement [ 12 ]. For example, in a recent review of quality improvement collaborations, it was found that although clinical processes in stroke care are improved, their short-term nature means there is uncertainty about sustainability and impacts on patient outcomes [ 16 ]. Table 1 provides the main features of the Australian Stroke LHS based on the four core domains and eight elements of the Learning Together for Better Health Framework described in Fig. 1 . The features are further expanded on in the following sections.
Evidence from stakeholders (LHS quadrant 1, Fig. 1 )
Engagement, partners and priorities.
Within the stroke field, there have been various support mechanisms to facilitate an LHS approach including partnership and broad stakeholder engagement that includes clinical networks and policy makers from different jurisdictions. Since 2008, the Australian Stroke Coalition has been co-led by the Stroke Foundation, a charitable consumer advocacy organisation, and Stroke Society of Australasia a professional society with membership covering academics and multidisciplinary clinician networks, that are collectively working to improve stroke care ( https://australianstrokecoalition.org.au/ ). Surveys, focus groups and workshops have been used for identifying priorities from stakeholders. Recent agreed priorities have been to improve stroke care and strengthen the voice for stroke care at a national ( https://strokefoundation.org.au/ ) and international level ( https://www.world-stroke.org/news-and-blog/news/world-stroke-organization-tackle-gaps-in-access-to-quality-stroke-care ), as well as reduce duplication amongst stakeholders. This activity is built on a foundation and culture of research and innovation embedded within the stroke ‘community of practice’. Consumers, as people with lived experience of stroke are important members of the Australian Stroke Coalition, as well as representatives from different clinical colleges. Consumers also provide critical input to a range of LHS activities via the Stroke Foundation Consumer Council, Stroke Living Guidelines committees, and the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry (AuSCR) Steering Committee (described below).
Evidence from research (LHS quadrant 2, Fig. 1 )
Advancement of the evidence for stroke interventions and synthesis into clinical guidelines.
To implement best practice, it is crucial to distil the large volume of scientific and trial literature into actionable recommendations for clinicians to use in practice [ 24 ]. The first Australian clinical guidelines for acute stroke were produced in 2003 following the increasing evidence emerging for prevention interventions (e.g. carotid endarterectomy, blood pressure lowering), acute medical treatments (intravenous thrombolysis, aspirin within 48 h of ischemic stroke), and optimised hospital management (care in dedicated stroke units by a specialised and coordinated multidisciplinary team) [ 25 ]. Importantly, a number of the innovations were developed, researched and proven effective by key opinion leaders embedded in the Australian stroke care community. In 2005, the clinical guidelines for Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery [ 26 ] were produced, with subsequent merged guidelines periodically updated. However, the traditional process of periodic guideline updates is challenging for end users when new research can render recommendations redundant and this lack of currency erodes stakeholder trust [ 27 ]. In response to this challenge the Stroke Foundation and Cochrane Australia entered a pioneering project to produce the first electronic ‘living’ guidelines globally [ 20 ]. Major shifts in the evidence for reperfusion therapies (e.g. extended time-window intravenous thrombolysis and endovascular clot retrieval), among other advances, were able to be converted into new recommendations, approved by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council within a few months of publication. Feedback on this process confirmed the increased use and trust in the guidelines by clinicians. The process informed other living guidelines programs, including the successful COVID-19 clinical guidelines [ 28 ].
However, best practice clinical guideline recommendations are necessary but insufficient for healthcare improvement and nesting these within an LHS with stakeholder partnership, enables implementation via a range of proven methods, including audit and feedback strategies [ 29 ].
Evidence from data and practice (LHS quadrant 3, Fig. 1 )
Data systems and benchmarking : revealing the disparities in care between health services. A national system for standardized stroke data collection was established as the National Stroke Audit program in 2007 by the Stroke Foundation [ 30 ] following various state-level programs (e.g. New South Wales Audit) [ 31 ] to identify evidence-practice gaps and prioritise improvement efforts to increase access to stroke units and other acute treatments [ 32 ]. The Audit program alternates each year between acute (commencing in 2007) and rehabilitation in-patient services (commencing in 2008). The Audit program provides a ‘deep dive’ on the majority of recommendations in the clinical guidelines whereby participating hospitals provide audits of up to 40 consecutive patient medical records and respond to a survey about organizational resources to manage stroke. In 2009, the AuSCR was established to provide information on patients managed in acute hospitals based on a small subset of quality processes of care linked to benchmarked reports of performance (Fig. 2 ) [ 33 ]. In this way, the continuous collection of high-priority processes of stroke care could be regularly collected and reviewed to guide improvement to care [ 34 ]. Plus clinical quality registry programs within Australia have shown a meaningful return on investment attributed to enhanced survival, improvements in quality of life and avoided costs of treatment or hospital stay [ 35 ].
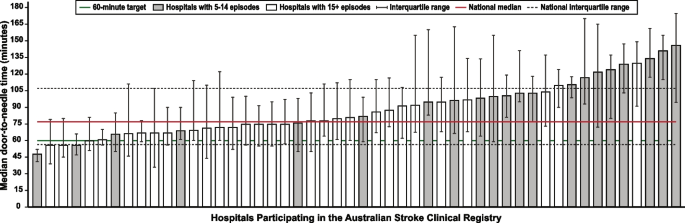
Example performance report from the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry: average door-to-needle time in providing intravenous thrombolysis by different hospitals in 2021 [ 36 ]. Each bar in the figure represents a single hospital
The Australian Stroke Coalition endorsed the creation of an integrated technological solution for collecting data through a single portal for multiple programs in 2013. In 2015, the Stroke Foundation, AuSCR consortium, and other relevant groups cooperated to design an integrated data management platform (the Australian Stroke Data Tool) to reduce duplication of effort for hospital staff in the collection of overlapping variables in the same patients [ 19 ]. Importantly, a national data dictionary then provided the common data definitions to facilitate standardized data capture. Another important feature of AuSCR is the collection of patient-reported outcome surveys between 90 and 180 days after stroke, and annual linkage with national death records to ascertain survival status [ 33 ]. To support a LHS approach, hospitals that participate in AuSCR have access to a range of real-time performance reports. In efforts to minimize the burden of data collection in the AuSCR, interoperability approaches to import data directly from hospital or state-level managed stroke databases have been established (Fig. 3 ); however, the application has been variable and 41% of hospitals still manually enter all their data.
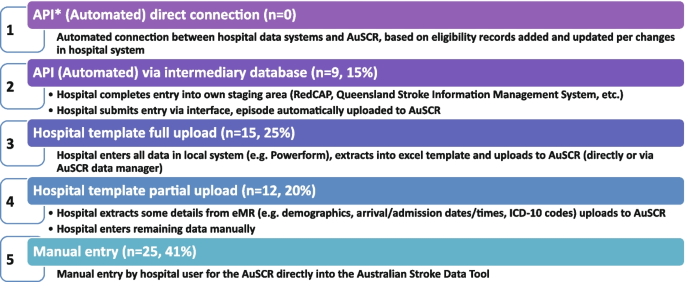
Current status of automated data importing solutions in the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry, 2022, with ‘ n ’ representing the number of hospitals. AuSCR, Australian Stroke Clinical Registry; AuSDaT, Australian Stroke Data Tool; API, Application Programming Interface; ICD, International Classification of Diseases; RedCAP, Research Electronic Data Capture; eMR, electronic medical records
For acute stroke care, the Australian Commission on Quality and Safety in Health Care facilitated the co-design (clinicians, academics, consumers) and publication of the national Acute Stroke Clinical Care Standard in 2015 [ 17 ], and subsequent review [ 18 ]. The indicator set for the Acute Stroke Standard then informed the expansion of the minimum dataset for AuSCR so that hospitals could routinely track their performance. The national Audit program enabled hospitals not involved in the AuSCR to assess their performance every two years against the Acute Stroke Standard. Complementing these efforts, the Stroke Foundation, working with the sector, developed the Acute and Rehabilitation Stroke Services Frameworks to outline the principles, essential elements, models of care and staffing recommendations for stroke services ( https://informme.org.au/guidelines/national-stroke-services-frameworks ). The Frameworks are intended to guide where stroke services should be developed, and monitor their uptake with the organizational survey component of the Audit program.
Evidence from implementation and healthcare improvement (LHS quadrant 4, Fig. 1 )
Research to better utilize and augment data from registries through linkage [ 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 ] and to ensure presentation of hospital or service level data are understood by clinicians has ensured advancement in the field for the Australian Stroke LHS [ 41 ]. Importantly, greater insights into whole patient journeys, before and after a stroke, can now enable exploration of value-based care. The LHS and stroke data platform have enabled focused and time-limited projects to create a better understanding of the quality of care in acute or rehabilitation settings [ 22 , 42 , 43 ]. Within stroke, all the elements of an LHS culminate into the ready availability of benchmarked performance data and support for implementation of strategies to address gaps in care.
Implementation research to grow the evidence base for effective improvement interventions has also been a key pillar in the Australian context. These include multi-component implementation interventions to achieve behaviour change for particular aspects of stroke care, [ 22 , 23 , 44 , 45 ] and real-world approaches to augmenting access to hyperacute interventions in stroke through the use of technology and telehealth [ 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 ]. The evidence from these studies feeds into the living guidelines program and the data collection systems, such as the Audit program or AuSCR, which are then amended to ensure data aligns to recommended care. For example, the use of ‘hyperacute aspirin within the first 48 h of ischemic stroke’ was modified to be ‘hyperacute antiplatelet…’ to incorporate new evidence that other medications or combinations are appropriate to use. Additionally, new datasets have been developed to align with evidence such as the Fever, Sugar, and Swallow variables [ 42 ]. Evidence on improvements in access to best practice care from the acute Audit program [ 50 ] and AuSCR is emerging [ 36 ]. For example, between 2007 and 2017, the odds of receiving intravenous thrombolysis after ischemic stroke increased by 16% 9OR 1.06 95% CI 1.13–1.18) and being managed in a stroke unit by 18% (OR 1.18 95% CI 1.17–1.20). Over this period, the median length of hospital stay for all patients decreased from 6.3 days in 2007 to 5.0 days in 2017 [ 51 ]. When considering the number of additional patients who would receive treatment in 2017 in comparison to 2007 it was estimated that without this additional treatment, over 17,000 healthy years of life would be lost in 2017 (17,786 disability-adjusted life years) [ 51 ]. There is evidence on the cost-effectiveness of different system-focussed strategies to augment treatment access for acute ischemic stroke (e.g. Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program [ 52 ] and Melbourne Mobile Stroke Unit ambulance [ 53 ]). Reciprocally, evidence from the national Rehabilitation Audit, where the LHS approach has been less complete or embedded, has shown fewer areas of healthcare improvement over time [ 51 , 54 ].
Within the field of stroke in Australia, there is indirect evidence that the collective efforts that align to establishing the components of a LHS have had an impact. Overall, the age-standardised rate of stroke events has reduced by 27% between 2001 and 2020, from 169 to 124 events per 100,000 population. Substantial declines in mortality rates have been reported since 1980. Commensurate with national clinical guidelines being updated in 2007 and the first National Stroke Audit being undertaken in 2007, the mortality rates for men (37.4 deaths per 100,000) and women (36.1 deaths per 100,0000 has declined to 23.8 and 23.9 per 100,000, respectively in 2021 [ 55 ].
Underpinning the LHS with the integration of the four quadrants of evidence from stakeholders, research and guidelines, practice and implementation, and core LHS principles have been addressed. Leadership and governance have been important, and programs have been established to augment workforce training and capacity building in best practice professional development. Medical practitioners are able to undertake courses and mentoring through the Australasian Stroke Academy ( http://www.strokeacademy.com.au/ ) while nurses (and other health professionals) can access teaching modules in stroke care from the Acute Stroke Nurses Education Network ( https://asnen.org/ ). The Association of Neurovascular Clinicians offers distance-accessible education and certification to develop stroke expertise for interdisciplinary professionals, including advanced stroke co-ordinator certification ( www.anvc.org ). Consumer initiative interventions are also used in the design of the AuSCR Public Summary Annual reports (available at https://auscr.com.au/about/annual-reports/ ) and consumer-related resources related to the Living Guidelines ( https://enableme.org.au/resources ).
The important success factors and lessons from stroke as a national exemplar LHS in Australia include leadership, culture, workforce and resources integrated with (1) established and broad partnerships across the academic-clinical sector divide and stakeholder engagement; (2) the living guidelines program; (3) national data infrastructure, including a national data dictionary that provides the common data framework to support standardized data capture; (4) various implementation strategies including benchmarking and feedback as well as engagement strategies targeting different levels of the health system; and (5) implementation and improvement research to advance stroke systems of care and reduce unwarranted variation in practice (Fig. 1 ). Priority opportunities now include the advancement of interoperability with electronic medical records as an area all clinical quality registry’s programs needs to be addressed, as well as providing more dynamic and interactive data dashboards tailored to the need of clinicians and health service executives.
There is a clear mandate to optimise healthcare improvement with big data offering major opportunities for change. However, we have lacked the approaches to capture evidence from the community and stakeholders, to integrate evidence from research, to capture and leverage data or evidence from practice and to generate and build on evidence from implementation using iterative system-level improvement. The LHS provides this opportunity and is shown to deliver impact. Here, we have outlined the process applied to generate an evidence-based LHS and provide a leading exemplar in stroke care. This highlights the value of moving from single-focus isolated approaches/initiatives to healthcare improvement and the benefit of integration to deliver demonstrable outcomes for our funders and key stakeholders — our community. This work provides insight into strategies that can both apply evidence-based processes to healthcare improvement as well as implementing evidence-based practices into care, moving beyond research as an endpoint, to research as an enabler, underpinning delivery of better healthcare.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
Australian Stroke Clinical Registry
Confidence interval
- Learning Health System
World Health Organization. Delivering quality health services . OECD Publishing; 2018.
Enticott J, Braaf S, Johnson A, Jones A, Teede HJ. Leaders’ perspectives on learning health systems: A qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:1087.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Melder A, Robinson T, McLoughlin I, Iedema R, Teede H. An overview of healthcare improvement: Unpacking the complexity for clinicians and managers in a learning health system. Intern Med J. 2020;50:1174–84.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Alberto IRI, Alberto NRI, Ghosh AK, Jain B, Jayakumar S, Martinez-Martin N, et al. The impact of commercial health datasets on medical research and health-care algorithms. Lancet Digit Health. 2023;5:e288–94.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dixon-Woods M. How to improve healthcare improvement—an essay by Mary Dixon-Woods. BMJ. 2019;367: l5514.
Enticott J, Johnson A, Teede H. Learning health systems using data to drive healthcare improvement and impact: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2021;21:200.
Enticott JC, Melder A, Johnson A, Jones A, Shaw T, Keech W, et al. A learning health system framework to operationalize health data to improve quality care: An Australian perspective. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:730021.
Dammery G, Ellis LA, Churruca K, Mahadeva J, Lopez F, Carrigan A, et al. The journey to a learning health system in primary care: A qualitative case study utilising an embedded research approach. BMC Prim Care. 2023;24:22.
Foley T, Horwitz L, Zahran R. The learning healthcare project: Realising the potential of learning health systems. 2021. Available from https://learninghealthcareproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/LHS2021report.pdf . Accessed Jan 2024.
Institute of Medicine. Best care at lower cost: The path to continuously learning health care in America. Washington: The National Academies Press; 2013.
Google Scholar
Zurynski Y, Smith CL, Vedovi A, Ellis LA, Knaggs G, Meulenbroeks I, et al. Mapping the learning health system: A scoping review of current evidence - a white paper. 2020:63
Cadilhac DA, Bravata DM, Bettger J, Mikulik R, Norrving B, Uvere E, et al. Stroke learning health systems: A topical narrative review with case examples. Stroke. 2023;54:1148–59.
Braithwaite J, Glasziou P, Westbrook J. The three numbers you need to know about healthcare: The 60–30-10 challenge. BMC Med. 2020;18:1–8.
Article Google Scholar
King D, Wittenberg R, Patel A, Quayyum Z, Berdunov V, Knapp M. The future incidence, prevalence and costs of stroke in the UK. Age Ageing. 2020;49:277–82.
Ganesh A, Lindsay P, Fang J, Kapral MK, Cote R, Joiner I, et al. Integrated systems of stroke care and reduction in 30-day mortality: A retrospective analysis. Neurology. 2016;86:898–904.
Lowther HJ, Harrison J, Hill JE, Gaskins NJ, Lazo KC, Clegg AJ, et al. The effectiveness of quality improvement collaboratives in improving stroke care and the facilitators and barriers to their implementation: A systematic review. Implement Sci. 2021;16:16.
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Acute stroke clinical care standard. 2015. Available from https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/our-work/clinical-care-standards/acute-stroke-clinical-care-standard . Accessed Jan 2024.
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Acute stroke clinical care standard. Sydney: ACSQHC; 2019. Available from https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/publications-and-resources/resource-library/acute-stroke-clinical-care-standard-evidence-sources . Accessed Jan 2024.
Ryan O, Ghuliani J, Grabsch B, Hill K, G CC, Breen S, et al. Development, implementation, and evaluation of the Australian Stroke Data Tool (AuSDaT): Comprehensive data capturing for multiple uses. Health Inf Manag. 2022:18333583221117184.
English C, Bayley M, Hill K, Langhorne P, Molag M, Ranta A, et al. Bringing stroke clinical guidelines to life. Int J Stroke. 2019;14:337–9.
English C, Hill K, Cadilhac DA, Hackett ML, Lannin NA, Middleton S, et al. Living clinical guidelines for stroke: Updates, challenges and opportunities. Med J Aust. 2022;216:510–4.
Cadilhac DA, Grimley R, Kilkenny MF, Andrew NE, Lannin NA, Hill K, et al. Multicenter, prospective, controlled, before-and-after, quality improvement study (Stroke123) of acute stroke care. Stroke. 2019;50:1525–30.
Cadilhac DA, Marion V, Andrew NE, Breen SJ, Grabsch B, Purvis T, et al. A stepped-wedge cluster-randomized trial to improve adherence to evidence-based practices for acute stroke management. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2022.
Elliott J, Lawrence R, Minx JC, Oladapo OT, Ravaud P, Jeppesen BT, et al. Decision makers need constantly updated evidence synthesis. Nature. 2021;600:383–5.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
National Stroke Foundation. National guidelines for acute stroke management. Melbourne: National Stroke Foundation; 2003.
National Stroke Foundation. Clinical guidelines for stroke rehabilitation and recovery. Melbourne: National Stroke Foundation; 2005.
Phan TG, Thrift A, Cadilhac D, Srikanth V. A plea for the use of systematic review methodology when writing guidelines and timely publication of guidelines. Intern Med J . 2012;42:1369–1371; author reply 1371–1362
Tendal B, Vogel JP, McDonald S, Norris S, Cumpston M, White H, et al. Weekly updates of national living evidence-based guidelines: Methods for the Australian living guidelines for care of people with COVID-19. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;131:11–21.
Grimshaw JM, Eccles MP, Lavis JN, Hill SJ, Squires JE. Knowledge translation of research findings. Implement Sci. 2012;7:50.
Harris D, Cadilhac D, Hankey GJ, Hillier S, Kilkenny M, Lalor E. National stroke audit: The Australian experience. Clin Audit. 2010;2:25–31.
Cadilhac DA, Purvis T, Kilkenny MF, Longworth M, Mohr K, Pollack M, et al. Evaluation of rural stroke services: Does implementation of coordinators and pathways improve care in rural hospitals? Stroke. 2013;44:2848–53.
Cadilhac DA, Moss KM, Price CJ, Lannin NA, Lim JY, Anderson CS. Pathways to enhancing the quality of stroke care through national data monitoring systems for hospitals. Med J Aust. 2013;199:650–1.
Cadilhac DA, Lannin NA, Anderson CS, Levi CR, Faux S, Price C, et al. Protocol and pilot data for establishing the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry. Int J Stroke. 2010;5:217–26.
Ivers N, Jamtvedt G, Flottorp S, Young J, Odgaard-Jensen J, French S, et al. Audit and feedback: Effects on professional practice and healthcare outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev . 2012
Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Economic evaluation of clinical quality registries. Final report. . 2016:79
Cadilhac DA, Dalli LL, Morrison J, Lester M, Paice K, Moss K, et al. The Australian Stroke Clinical Registry annual report 2021. Melbourne; 2022. Available from https://auscr.com.au/about/annual-reports/ . Accessed 6 May 2024.
Kilkenny MF, Kim J, Andrew NE, Sundararajan V, Thrift AG, Katzenellenbogen JM, et al. Maximising data value and avoiding data waste: A validation study in stroke research. Med J Aust. 2019;210:27–31.
Eliakundu AL, Smith K, Kilkenny MF, Kim J, Bagot KL, Andrew E, et al. Linking data from the Australian Stroke Clinical Registry with ambulance and emergency administrative data in Victoria. Inquiry. 2022;59:469580221102200.
PubMed Google Scholar
Andrew NE, Kim J, Cadilhac DA, Sundararajan V, Thrift AG, Churilov L, et al. Protocol for evaluation of enhanced models of primary care in the management of stroke and other chronic disease (PRECISE): A data linkage healthcare evaluation study. Int J Popul Data Sci. 2019;4:1097.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mosalski S, Shiner CT, Lannin NA, Cadilhac DA, Faux SG, Kim J, et al. Increased relative functional gain and improved stroke outcomes: A linked registry study of the impact of rehabilitation. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30: 106015.
Ryan OF, Hancock SL, Marion V, Kelly P, Kilkenny MF, Clissold B, et al. Feedback of aggregate patient-reported outcomes (PROs) data to clinicians and hospital end users: Findings from an Australian codesign workshop process. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e055999.
Grimley RS, Rosbergen IC, Gustafsson L, Horton E, Green T, Cadigan G, et al. Dose and setting of rehabilitation received after stroke in Queensland, Australia: A prospective cohort study. Clin Rehabil. 2020;34:812–23.
Purvis T, Middleton S, Craig LE, Kilkenny MF, Dale S, Hill K, et al. Inclusion of a care bundle for fever, hyperglycaemia and swallow management in a national audit for acute stroke: Evidence of upscale and spread. Implement Sci. 2019;14:87.
Middleton S, McElduff P, Ward J, Grimshaw JM, Dale S, D’Este C, et al. Implementation of evidence-based treatment protocols to manage fever, hyperglycaemia, and swallowing dysfunction in acute stroke (QASC): A cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2011;378:1699–706.
Middleton S, Dale S, Cheung NW, Cadilhac DA, Grimshaw JM, Levi C, et al. Nurse-initiated acute stroke care in emergency departments. Stroke. 2019:STROKEAHA118020701.
Hood RJ, Maltby S, Keynes A, Kluge MG, Nalivaiko E, Ryan A, et al. Development and pilot implementation of TACTICS VR: A virtual reality-based stroke management workflow training application and training framework. Front Neurol. 2021;12:665808.
Bladin CF, Kim J, Bagot KL, Vu M, Moloczij N, Denisenko S, et al. Improving acute stroke care in regional hospitals: Clinical evaluation of the Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program. Med J Aust. 2020;212:371–7.
Bladin CF, Bagot KL, Vu M, Kim J, Bernard S, Smith K, et al. Real-world, feasibility study to investigate the use of a multidisciplinary app (Pulsara) to improve prehospital communication and timelines for acute stroke/STEMI care. BMJ Open. 2022;12:e052332.
Zhao H, Coote S, Easton D, Langenberg F, Stephenson M, Smith K, et al. Melbourne mobile stroke unit and reperfusion therapy: Greater clinical impact of thrombectomy than thrombolysis. Stroke. 2020;51:922–30.
Purvis T, Cadilhac DA, Hill K, Reyneke M, Olaiya MT, Dalli LL, et al. Twenty years of monitoring acute stroke care in Australia from the national stroke audit program (1999–2019): Achievements and areas of future focus. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2023.
Cadilhac DA, Purvis T, Reyneke M, Dalli LL, Kim J, Kilkenny MF. Evaluation of the national stroke audit program: 20-year report. Melbourne; 2019.
Kim J, Tan E, Gao L, Moodie M, Dewey HM, Bagot KL, et al. Cost-effectiveness of the Victorian Stroke Telemedicine program. Aust Health Rev. 2022;46:294–301.
Kim J, Easton D, Zhao H, Coote S, Sookram G, Smith K, et al. Economic evaluation of the Melbourne mobile stroke unit. Int J Stroke. 2021;16:466–75.
Stroke Foundation. National stroke audit – rehabilitation services report 2020. Melbourne; 2020.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Heart, stroke and vascular disease: Australian facts. 2023. Webpage https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/heart-stroke-vascular-diseases/hsvd-facts/contents/about (accessed Jan 2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The following authors hold National Health and Medical Research Council Research Fellowships: HT (#2009326), DAC (#1154273), SM (#1196352), MFK Future Leader Research Fellowship (National Heart Foundation #105737). The Funders of this work did not have any direct role in the design of the study, its execution, analyses, interpretation of the data, or decision to submit results for publication.
Author information
Helena Teede and Dominique A. Cadilhac contributed equally.
Authors and Affiliations
Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation, 43-51 Kanooka Grove, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Helena Teede, Emily Callander & Joanne Enticott
Monash Partners Academic Health Science Centre, 43-51 Kanooka Grove, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Helena Teede & Alison Johnson
Stroke and Ageing Research, Department of Medicine, School of Clinical Sciences at Monash Health, Monash University, Level 2 Monash University Research, Victorian Heart Hospital, 631 Blackburn Rd, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Dominique A. Cadilhac, Tara Purvis & Monique F. Kilkenny
Stroke Theme, The Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health, University of Melbourne, Heidelberg, VIC, Australia
Dominique A. Cadilhac, Monique F. Kilkenny & Bruce C.V. Campbell
Department of Neurology, Melbourne Brain Centre, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Bruce C.V. Campbell
Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Dentistry and Health Sciences, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
School of Health Sciences, Heart and Stroke Program, University of Newcastle, Hunter Medical Research Institute, University Drive, Callaghan, NSW, Australia
Coralie English
School of Medicine and Dentistry, Griffith University, Birtinya, QLD, Australia
Rohan S. Grimley
Clinical Excellence Division, Queensland Health, Brisbane, Australia
John Hunter Hospital, Hunter New England Local Health District and University of Newcastle, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Christopher Levi
School of Nursing, Midwifery and Paramedicine, Australian Catholic University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Sandy Middleton
Nursing Research Institute, St Vincent’s Health Network Sydney and and Australian Catholic University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Stroke Foundation, Level 7, 461 Bourke St, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Kelvin Hill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
HT: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. DAC: conception, design and initial draft, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. TP: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, approved the submitted version. MFK: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. BC: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. CE: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. AJ: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. EC: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, approved the submitted version. RSG: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. CL: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. SM: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. KH: revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content, provided essential literature and case study examples, approved the submitted version. JE: conception, design and initial draft, developed the theoretical formalism for learning health system framework, approved the submitted version. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ Twitter handles
@HelenaTeede
@DominiqueCad
@Coralie_English
@EmilyCallander
@EnticottJo
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Helena Teede or Dominique A. Cadilhac .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests, additional information, publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Teede, H., Cadilhac, D.A., Purvis, T. et al. Learning together for better health using an evidence-based Learning Health System framework: a case study in stroke. BMC Med 22 , 198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03416-w
Download citation
Received : 23 July 2023
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-024-03416-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence-based medicine
- Person-centred care
- Models of care
- Healthcare improvement
BMC Medicine
ISSN: 1741-7015
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Open access
- Published: 10 May 2024
Community-based participatory-research through co-design: supporting collaboration from all sides of disability
- Cloe Benz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6950-8855 1 ,
- Will Scott-Jeffs 2 ,
- K. A. McKercher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4417-585X 3 ,
- Mai Welsh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7818-0115 2 , 4 ,
- Richard Norman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3112-3893 1 ,
- Delia Hendrie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5022-5281 1 ,
- Matthew Locantro 2 &
- Suzanne Robinson ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5703-6475 1 , 5
Research Involvement and Engagement volume 10 , Article number: 47 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
820 Accesses
Metrics details
As co-design and community-based participatory research gain traction in health and disability, the challenges and benefits of collaboratively conducting research need to be considered. Current literature supports using co-design to improve service quality and create more satisfactory services. However, while the ‘why’ of using co-design is well understood, there is limited literature on ‘ how ’ to co-design. We aimed to describe the application of co-design from start to finish within a specific case study and to reflect on the challenges and benefits created by specific process design choices.
A telepractice re-design project has been a case study example of co-design. The co-design was co-facilitated by an embedded researcher and a peer researcher with lived experience of disability. Embedded in a Western Australian disability organisation, the co-design process included five workshops and a reflection session with a team of 10 lived experience and staff participants (referred to as co-designers) to produce a prototype telepractice model for testing.
The findings are divided into two components. The first describes the process design choices made throughout the co-design implementation case study. This is followed by a reflection on the benefits and challenges resulting from specific process design choices. The reflective process describes the co-designers’ perspective and the researcher’s and organisational experiences. Reflections of the co-designers include balancing idealism and realism, the value of small groups, ensuring accessibility and choice, and learning new skills and gaining new insights. The organisational and research-focused reflections included challenges between time for building relationships and the schedules of academic and organisational decision-making, the messiness of co-design juxtaposed with the processes of ethics applications, and the need for inclusive dissemination of findings.
Conclusions
The authors advocate that co-design is a useful and outcome-generating methodology that proactively enables the inclusion of people with disability and service providers through community-based participatory research and action. Through our experiences, we recommend community-based participatory research, specifically co-design, to generate creative thinking and service design.
Plain language summary
Making better services with communities (called co-design) and doing research with communities (e.g. community-based participatory research) are ways to include people with lived experience in developing and improving the services they use. Academic evidence shows why co-design is valuable, and co-design is increasing in popularity. However, there needs to be more information on how to do co-design. This article describes the process of doing co-design to make telepractice better with a group of lived experience experts and staff at a disability organisation. The co-design process was co-facilitated by two researchers – one with a health background and one with lived experience of disability. Telepractice provides clinical services (such as physiotherapy or nursing) using video calls and other digital technology. The co-design team did five workshops and then reflected on the success of those workshops. Based on the groups’ feedback, the article describes what worked and what was hard according to the co-designers and from the perspective of the researchers and the disability organisation. Topics discussed include the challenge of balancing ideas with realistic expectations, the value of small groups, accessibility and choice opportunities and learning new skills and insights. The research and organisational topics include the need to take time and how that doesn’t fit neatly with academic and business schedules, how the messiness of co-design can clash with approval processes, and different ways of telling people about the project that are more inclusive than traditional research. The authors conclude that co-design and community-based participatory research go well together in including people with lived experience in re-designing services they use.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Co-design has the potential to positively impact co-designers and their community, researchers, and organisations. Co-design is defined as designing with, not for, people [ 1 ] and can reinvigorate business-as-usual processes, leading to new ideas in industry, community and academia. As co-design and community-based participatory research gain traction, the challenges and benefits of collaborative research between people with lived experience and organisations must be considered [ 2 ].
Disability and healthcare providers previously made decisions for individuals as passive targets of an intervention [ 3 ]. By contrast, the involvement of consumers in their care [ 4 ] has been included as part of accreditation processes [ 4 ] and shown to improve outcomes and satisfaction. For research to sufficiently translate into practice, consumers and providers should be involved actively, not passively [ 4 , 5 ].
Approaches such as community-based participatory research promote “a collaborative approach that equitably involves community members, organisational representatives and researchers in all aspects of the research process” [ 6 ] (page 1). This approach originated in public health research and claims to empower all participants to have a stake in project success, facilitating a more active integration of research into practice and decreasing the knowledge to practice gap 6 . Patient and public involvement (PPI) increases the probability that research focus, community priorities and clinical problems align, which is increasingly demanded by research funders and health systems [ 7 ].
As community-based participatory research is an overarching approach to conducting research, it requires a complementary method, such as co-production, to achieve its aims. Co-production has been attributed to the work of Ostrom et al. [ 8 ], with the term co-design falling under the co-production umbrella. However, co-design can be traced back to the participatory design movement [ 9 ]. The term co-production in the context of this article includes co-planning, co-discovery, co-design, co-delivery, and co-evaluation [ 10 ]. Within this framework, the concept of co-design delineates the collaborative process of discovery, creating, ideating and prototyping to design or redesign an output [ 11 ]. The four principles of co-design, as per McKercher [ 1 ], are sharing power, prioritising relationships, using participatory means and building capacity [ 1 ]. This specific method of co-design [ 1 ] has been used across multiple social and healthcare publications [ 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 ].
A systematic review by Ramos et al. [ 15 ] describes the benefits of co-design in a community-based participatory-research approach, including improved quality and more satisfactory services. However, as identified by Rahman et al. [ 16 ], the ‘ why ’ is well known, but there is limited knowledge of ‘ how ’ to co-design. Multiple articles provide high-level descriptions of workshops or briefly mention the co-design process [ 13 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Pearce et al. [ 5 ] include an in-depth table of activities across an entire co-creation process, however within each part i.e., co-design, limited descriptions were included. A recent publication by Marwaa et al. [ 20 ] provides an in-depth description of two workshops focused on product development, and Tariq et al. [ 21 ] provides details of the process of co-designing a research agenda. Davis et al. [ 11 ] discuss co-design workshop delivery strategies summarised across multiple studies without articulating the process from start to finish. Finally, Abimbola et al. [ 22 ] provided the most comprehensive description of a co-design process, including a timeline of events and activities; however, this project only involved clinical staff and did not include community-based participation.
As “We know the why, but we need to know the how-to” [ 16 ] (page 2), of co-design, our primary aim was to describe the application of co-design from start to finish within a specific case study. Our secondary aim was to reflect on the challenges and benefits created by specific process design choices and to provide recommendations for future applications of co-design.
Overview of telepractice project
The case study, a telepractice redesign project, was based at Rocky Bay, a disability support service provider in Perth, Australia [ 23 ]. The project aimed to understand the strengths and pain points of telepractice within Rocky Bay. We expanded this to include telepractice in the wider Australian disability sector. The project also aimed to establish potential improvements to increase the uptake and sustainability of Rocky Bay’s telepractice service into the future. Rocky Bay predominantly serves people under the Australian National Disability Insurance Scheme (NDIS) [ 24 ] by providing a variety of services, including allied health (e.g. physiotherapy, dietetics, speech pathology, etc.), nursing care (including continence and wound care), behaviour support and support coordination [ 23 ]—Rocky Bay services metropolitan Perth and regional Western Australia [ 23 ].
The first author, CB, predominantly conducted this research through an embedded researcher model [ 25 ] between Curtin University and Rocky Bay. An embedded researcher has been defined as “those who work inside host organisations as members of staff while also maintaining an affiliation with an academic institution” [ 25 ] (page 1). They had some prior contextual understanding which stemmed from being a physiotherapist who had previously delivered telehealth in an acute health setting. A peer researcher, WSJ, with lived experience of disability, worked alongside CB. They had no previous experience in research or co-design, this was their first paid employment and they had an interest in digital technology. Peer Researcher is a broad term describing the inclusion of a priority group or social network member as part of the research team to enhance the depth of understanding of the communities to which they belong [ 26 ]. Including a peer researcher in the team promoted equity, collective ownership, and better framing of the research findings to assist with connecting with people with lived experience. These outcomes align with key components of community-based participatory research and co-design [ 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 ].
Person-first language was used as the preference of experts with lived experience who contributed to this research to respect and affirm their identity. However, we respect the right to choose and the potential for others to prefer identity-first language [ 31 ].
A summary of the structure of the phases completed before co-design workshops are represented in Fig. 1 below. Ethical approval for the project was received iteratively before each phase on the timeline (Fig. 1 ) from the Curtin Human Research Ethics Committee (HRE2021-0731). The reporting of this article has been completed in line with the Guidance for Reporting Involvement of Patients and the Public (GRIPP2) checklist [ 7 ].
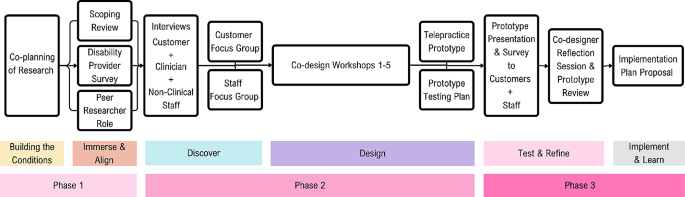
Summary of telepractice co-design project structure [ 1 ]
Here, we present an outline of the chosen research methods with descriptions of each process design choice and supporting reasons and examples specific to the study. The format is in chronological order, with further details of each step provided in Appendix 1 (Supplementary Material 1).
Methods and results
Process of co-production and preparation for co-design.
Co-production was chosen as the planning method for the study, as the inclusion of community members (Rocky Bay Lived experience experts and Staff) in each step of the research process would increase buy-in and make the research more likely to meet their needs [ 5 ]. An example of co-planning (part of co-production) includes the study steering committee, with a lived experience expert, clinician and project sponsor representatives collaborating on the selection of study aim, methods and recruitment processes. Another example of co-planning, co-design, and co-delivery was recruiting a peer researcher with disability, who worked with the embedded researcher throughout the study design and delivery.
The second process design choice was to attempt to build safe enough conditions for community participation, as people who feel unsafe or unwelcome are less likely to be able to participate fully in the research [ 1 ]. Building conditions for safety was applied by repeatedly acknowledging power imbalances, holding space for community input, and anticipating and offering accessibility adjustments without judgment.
Getting started
Understanding and synthesising what is already known about telepractice experiences and learning from lived experience was prioritised as the first step in the process. We paired a scoping review of the literature with scoping the lived experiences of the community [ 32 ]. Our reasoning was to understand whether the findings aligned and, secondly, to learn what had already been done and to ask what was next, rather than starting from the beginning [ 1 ]. Examples of strategies used in this step included interviewing clinicians and service provider Managers across Australia to establish how they implemented telepractice during the pandemic and understand their views of what worked and what did not. The second learning process occurred onsite at Rocky Bay, with people with lived experience, clinicians and other support staff, whom the embedded researcher and peer researcher interviewed to understand experiences of telepractice at Rocky Bay.
The authors presented the interview findings during focus groups with Rocky Bay participants to share the learnings and confirm we had understood them correctly. The groups were divided into staff and lived experience cohorts, allowing for peer discussions and sharing of common experiences. This helped build relationships and a sense of familiarity moving into the workshop series.
Co-design workshops
This section outlines specific components of the co-design workshop preparation before describing each of the five workshops and the final reflection session.
Staff and community co-designers
Two process design choices were implemented to form the co-design group. The first was to prioritise lived experience input as there are generally fewer opportunities for lived experience leadership in service design [ 16 ], and because the disability community have demanded they be included where the focus impacts them [ 33 ]. To acknowledge the asymmetry of power between community members, people with lived experience of disability and professionals, we ensured the co-design group had at least the same number of lived experience experts as staff.
The second priority for the co-design group was to include people for whom involvement can be difficult to access (e.g. people who are isolated for health reasons and cannot attend in-person sessions, people who live in supported accommodation, part-time staff, and people navigating the dual-role of staff member while disclosing lived experience). It was important to learn from perspectives not commonly heard from and support equity of access for participants [ 4 ].
Workshop series structure
When structuring the workshop series, lived experience co-designers nominated meeting times outside standard work hours to reduce the impact of co-design on work commitments and loss of income while participating. The workshops were designed to be delivered as a hybrid of in-person and online to give co-designers a choice on how they wanted to interact. The workshops were designed as a series of five sequential 90-minute workshops, where co-designers voted for the first workshop to be predominantly in-person and the remainder of the workshops online. Some co-designers chose to attend the initial session in person to build rapport. However, the virtual option remained available. The subsequent online sessions reduced the travel burden on co-designers, which the co-designers prioritised over further face-to-face meetings.
Workshop facilitators
To maintain familiarity and ensure predictability for co-designers, the workshops were co-facilitated by the embedded researcher and peer researcher. The co-facilitators built on relationships formed through previous interactions (interviews and focus groups), and each facilitator represented part of the co-designer group as a clinician or a person with disability. An extra support person was tasked with supporting the co-designers with disability to break down tasks and increase the accessibility of activities. The reason for selecting the support person was that they could contribute their skills as a school teacher to support the communication and completion of activities, and they had no previous experience with disability services to influence the co-designers opinions. This role was adapted from the provocateur role described by McKercher [ 1 ].
Pre-workshop preparations
To prepare for the workshops, each co-designer was asked to complete a brief survey to ensure the co-facilitators understood co-designers collect preferences and needs ahead of the session to enable preparation and make accommodations. The survey included pronouns, accessibility needs and refreshment preferences. Following the survey, the co-facilitators distributed a welcome video; the peer researcher, a familiar person, was videoed explaining what to expect, what not to expect and expected behaviours for the group to support a safe environment [ 1 ]. This process design choice was made to allow co-designers to alleviate any potential anxieties due to not having enough information and to increase predictability.
Workshop resources and supports
As the first workshop was in-person, specific process choices were made to ensure co-designers felt welcome and to uphold the dignity of co-designers with lived experience [ 34 ]. Examples of process design choices include facilitating transport and parking requests, providing easy access to the building and room, making a sensory breakout room available and having the peer researcher waiting at the entrance to welcome and guide people to the workshop room.
After reaching the workshop room, all co-designers received an individualised resource pack to equalise access to workshop materials, aiming again to balance power in a non-discriminatory way [ 11 ]. The resource pack included name tags with pronouns, individualised refreshments, a fidget toy [ 35 ] whiteboard markers and a human bingo activity described in a later section. An easy-to-apply name tag design was selected after consulting a co-designer with an upper limb difference. Further details on the resource packs are included in Appendix 1 (Supplementary Material 1).
Enabling different kinds of participation
We provided non-verbal response cards to each co-designer as communication preferences vary significantly within the disability community. The cards were intended to benefit any co-designer who struggled to use the response buttons on MS teams. The co-facilitators co-created the Yes, No, and In-the-middle response cards (Fig. 2 ) and were guided by recommendations by Schwartz and Kramer [ 29 ]. They found that people with intellectual disability were more likely to respond “yes” if the negative option included a frowning face or red-coloured images, as choosing these types of alternatives was perceived as being negative or would cause offence [ 29 ].
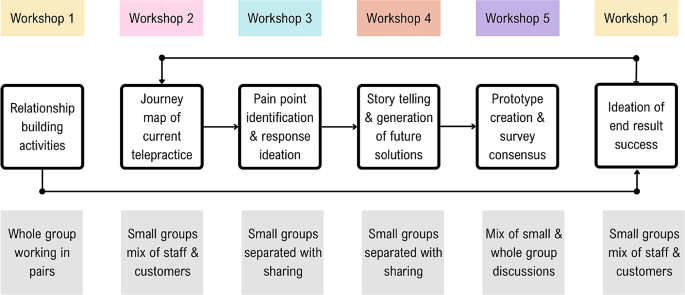
Non-verbal response cards
A summary of the structure and purpose of each of the five workshops is shown in Fig. 3 , followed by a more in-depth discussion of the strategies employed in each workshop.

Outline of workshop and group structures
Workshop 1: the beginning
Human Bingo was the first workshop activity, as it aimed to support relationship building in an inclusive way for both in-person and online attendees. The activity asked each co-designer to place a name in each worksheet box of someone who fit the described characteristic of that square(for example, someone who likes cooking). To include the two online attendees, laptops were set up with individual videocall streams and noise cancelling headphones enabling the online co-designers to interact one-on-one with others during the activities.
The second activity used The Real Deal cards by Peak Learning [ 36 ] to ask the co-designers to sort cards to prioritise the top five experiences and feelings they would want in a future version of telepractice. This activity aimed to set initial priorities for the redesign of telepractice [ 1 ]. Small groups with a mix of lived experience experts and staff were tasked with negotiating and collaborating to produce their top five desired experiences and feelings for future service success.
A follow-up email was sent after the session to thank co-designers, provide closure, invite feedback and let co-designers know what to expect from the next session.
Workshop 2: mapping the journey
In the second workshop, held online, the co-facilitators explained the journey mapping process and showed a draft of how the visual representation would likely look (Fig. 4 ). As the first step, co-designers were tasked with completing a series of activities to analyse lived experience interview data on the current experience of telepractice for lived experience experts. Small mixed groups were created, prioritising the needs of the lived experience experts to have staff who would be the best fit in supporting them to work through the task [ 1 ]. The small groups were allocated interview quotes corresponding to the steps of a customer journey through telepractice and asked to identify strengths, challenges and emotions associated with the current Telepractice service journey at Rocky Bay [ 1 ]. Further details on the journey map analysis are described in Appendix 1 (Supplementary Material 1) and in a published article co-authored by the co-designers (Benz et al. [ 37 ]).
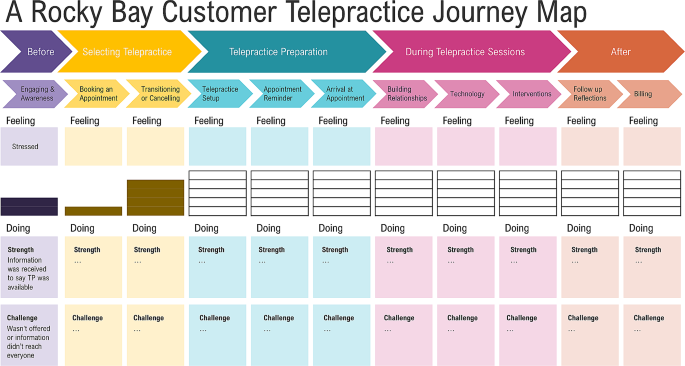
Draft journey map visualisation
After workshop two, the embedded researcher drafted a journey map by compiling the co-designer group responses to the analysis activity, which was then circulated for feedback and confirmation. The completed journey map is published with further details on the process in an article co-authored with the co-designers, Benz et al. [ 37 ].
Workshop 3: ideas for addressing pain points
For the third workshop, the co-facilitators selected activities to be completed separately by lived experience and staff co-designers. The lived experience expert activity involved exploring preferences for improving pain points identified through the journey map. The lived experience expert activity was facilitated by the peer researcher and support person and included questions such as, how would it be best to learn how to use telepractice? Visual prompt cards were shared to support idea creation, where lived experience expert co-designers could choose any option or suggest an alternative (Fig. 5 ).
Option cards for Lived experience expert co-designer workshop activity
Simultaneously, the staff co-designers completed a parallel activity to address pain points from a service delivery point of view. These pain points were identified in the clinical and non-clinical staff interviews and from the journey map summary of lived experience expert interviews (analysed in Workshop 2). Staff co-designers completed a mind map based on service blueprinting guidelines by Flowers and Miller [ 38 ]. The activity used service blueprinting to identify a list of opportunities for improvement, with four prompts for co-designers to commence planning the actions required to implement these improvements. The foci of the four prompts were roles, policies, technology and value proposition [ 38 ] (described further in Appendix 1 (Supplementary Material 1)). Each of the four prompts were completed for the ten proposed opportunities for improvement to draft plans for future telepractice service delivery.
Workshop 4: story telling and generation of future state solutions
In the fourth workshop, we introduced the concept of prototyping [ 39 ] as a designerly way to test co-designers’ ideas for improving telepractice according to desirability, feasibility and viability with a wider audience of lived experience experts and staff. The co-designers helped to plan the prototyping, and accessibility was a key consideration in selecting a prototype, as the group were conscious of the target audience.
Creating the prototype was collaborative, allowing co-designers to produce an output representing their ideas. They selected a video storyboard prototype with a staff and customer version formatted similarly to a children’s book. It included cartoon animations completed on PowerPoint, voiceover narration, closed captioning and an introductory explanation from two co-designers.
After workshop four, the co-designers collaborated on the customer and staff prototypes during the two weeks between workshops four and five, with support and input from the facilitators. The prototype files were co-produced, with different co-designers working on the visual aspects, the script for the main audio narration and the introductory explanation.
Workshop 5: finishing the story
The co-design group reviewed the draft prototypes in the final workshop, with specific attention paid to the story’s cohesiveness.
The feedback questionnaire was then created to be completed by viewers outside of the co-design group after engaging with either the staff or the customer prototype. The survey allowed Rocky Bay customers and staff to contribute ideas. Following thoughtful discussions, consensus was reached by all co-designers on the final survey questions (Appendix 2 (Supplementary Material 1)).
A reflection activity concluded the final workshop, allowing co-designers to provide feedback on the co-design process, elements for improvement and aspects they valued in participating in the project. Their reflections on the benefits and challenges of co-design in this study are included in the section Co-designer’s perspectives of the workshop series , with the reflection questions included in Appendix 3 (Supplementary Material 1).
Post prototype reflection session
The prototype feedback responses were reviewed with co-designers in a final reflection session. The group then discussed adaptations to the implementation plan for proposal to Rocky Bay. Following the survey discussion, co-designers reviewed proposed service principles for the new telepractice implementation recommendations. These principles aim to align any future decisions in the implementation and service provision stages of the telepractice project with the intentions of the co-designers. An additional reflection activity was completed, specific to the telepractice proposal they had produced and the prototyping process. Feedback relevant to subsequent discussions of the challenges and benefits of co-design is included in the following section: Co-designer’s perspectives of the workshop series , with the reflection prompts in Appendix 3 (Supplementary Material 1).
Benefits and challenges
Learnings derived from completing a study of this kind are complex. However, it is necessary to reflect on which strategies used in the project were beneficial and which strategies created challenges - anticipated and unexpected. These reflections are discussed in two sections, the first being the challenges and benefits reflected upon by co-designers. The second set of reflections relates to organisational and research project-level benefits and challenges from the perspective of clinical department managers and researchers involved in the project.
Co-designer’s perspectives of the workshop series
Co-designers were positive overall about the workshop series. Responses to a prompt for one-word descriptors of their experience included “captivating, innovative, fulfilling, exciting, insightful, helpful, eye-opening and informative ” .
Co-designing as a team
A foundational strategy implemented in this project was the intentional collaboration of lived experience experts with staff; this linked to the co-design principle of prioritising relationships and sharing power. Multiple reflections commented on feeling like a team and that having diverse perspectives across the group was beneficial.
It was especially interesting to hear the perspective of clinicians (for us, the other side of Telepractice). [Lived experience expert Co-designer]
Additionally, the combination of facilitators, including an embedded researcher with an allied health clinical background, a peer researcher with lived experience and a support person with strengths in breaking down tasks, provided different facets of support and task modelling to the co-designers throughout the process.
Balancing idealism and realism
There is an inherent challenge in collaboration between lived experience experts and service providers, whereby co-designers formulate ideas for service improvement and then, in good faith, propose required changes to be implemented. Strategies to support imagination and idealism while being honest about the constraints of what can be delivered were implemented in the context of this project. This was essential to reinforce to co-designers that their contributions and ideas are valid while tempering their hopes with the truth that organisational change is challenging and funding for change is limited. Co-designers were encouraged to be cognisant of ideas that would require high investment (cost and time) and which ideas faced fewer barriers to implementation. This strategy did not prevent the ideation of changes and prioritising what mattered most to them, and co-designers felt it was beneficial in adding a level of consideration regarding what investments they deemed necessary versus those that would be nice to have. For example, having a person to call for help was viewed as necessary, while a nice to have was more advanced technological features.
I feel that the prototype is useful; however, I worry that nothing will be carried over to the Rocky Bay Service. I feel like more customers will want to access telepractice, and Rocky Bay now needs to start the implementation process to ensure that telepractice is utilised, including processes, education and training. [Clinician Co-designer]
The value of small groups
Working in small groups was another beneficial strategy, aiming to create a more hospitable environment for co-designers to voice their thoughts. The small groups varied across activities and workshops, with facilitators intentionally pairing groups that would best support the lived experience of expert co-designers completing activities. As described in the workshop sections, some activities suited mixed groups, whereas others suited lived experience expert and staff-specific groups. Two reflective comments demonstrated the benefit of the small groups, one from a clinician who reflected on supporting a fellow co-designer:
I found that in our group, all of us had a say; however, [Lived Experience Co-designer name] was a bit overwhelmed at times, so I tried to support her with that. [Clinician Co-designer]
And a lived experience expert co-designer additionally reflected:
The breakout rooms were a very good idea. It can be quite intimidating speaking in front of the main group. I found it much easier to participate in the smaller groups . [Lived experience expert Co-designer]
The second session included an unplanned whole group activity, which challenged co-designers. Co-designers reflections of this experience demonstrate the benefits of smaller groups:
I did feel that at the end when the whole group did the task, there wasn’t as much collaboration as there were quite a few more assertive participants, so the quieter ones just sat back. [Clinician Co-designer]
Accessibility and choice
A challenge navigated throughout the workshop series with a diverse group of co-designers was meeting their varying individual health and other needs. This required responding in sensitive, non-judgemental, and supportive ways to encourage co-designers to engage fully. Examples of support include the presence of a support person and adaption of resource packs for co-designers who have difficulty swallowing (re: refreshments), as well as the previously mentioned non-verbal response cards and accessible name tags.
Accessibility supports were also provided for the peer researcher during facilitation activities, including pre-written scripts to provide clarity when explaining tasks to the co-design group, written reminders and regular check-ins. A lived experience expert co-designer reflected that it was beneficial that they could tell the peer researcher was nervous but appreciated that he was brave and made them feel like they did not need to be perfect if the peer researcher was willing to give it a go.
When facilitating the sessions, the embedded researcher and peer researcher identified that the workshops were long and, at times, mentally strenuous. One co-designer requested “more breaks during each session” . Breaks were offered frequently; however, upon reflection, we would schedule regular breaks to remove the need for co-designers to accept the need for a break in front of the group. The instructions for each activity were visual, verbal and written and given at the start of a task. However, once the co-designers were allocated to breakout rooms, they could no longer review the instructions. Many co-designers suggested that having the instructions in each breakout room’s chat window would have been a valuable visual reminder.
One thing I think might of helped a little is having the instructions in the chat as I know I that I listened but couldn’t recall some of the instructions for the group task. [Lived experience expert Co-designer]
Learning new skills and gaining new insight
The co-designers considered that the benefits of working together included learning new skills and widening their understanding of research, the services they provide or use, and the differences between the priorities of lived experience experts and staff. Two lived experience experts commented that the opportunity to learn collaboration skills and create cartoons using PowerPoint were valuable skills for them to utilise in the future. One clinician reflected that the process of co-design had improved their clinical practice and increased their use of telepractice:
My practice is 100% better. I am more confident in using telepractice and more confident that, as a process, it doesn’t reduce the impact of the service- in some ways, it has enhanced it when customers are more relaxed in their own environments. I have not seen my stats, but my use of telepractice has increased significantly, too. [Clinician Co-designer]
The management co-designer acknowledged that although ideas across the group may be similar, prioritisation of their importance can vary dramatically:
Whilst all the feedback and potential improvements were very similar, some things that I viewed as not an issue, was very different to a customer’s perspective. [Management Co-designer]
Overall, the workshop series challenged co-designers. However, the provision of a supportive and accessible environment resulted in mutual benefits for the research, organisation, and co-designers themselves. The strategy for facilitating the workshops was to pose challenges, support the co-designers in rising to meet them, and take into account their capabilities if provided with the right opportunity. A lived experience expert co-designer summarised the effectiveness of this strategy:
I found the activities to be challenging without being too difficult. Each activity provided enough guidance and structure to encourage interesting group discussions and make collaboration easy. [Lived experience expert Co-designer]
Research and organisational reflections of benefits and challenges of co-design
A significant challenge in completing this project was that building foundational relationships and trust takes time. While the authors view this trust as the foundation on which community-based participatory research and co-design are built, they note the direct tension of the time needed to develop these foundational relationships with the timeline expectations of academic and organisational decision-making. The flexibility required to deliver a person-centred research experience for the co-designers resulted in regular instances when timeline extensions were required to prioritise co-designer needs over efficiency. The result of prioritising co-designer needs over research timeline efficiency was an extended timeline that was significantly longer than expected, which sometimes created a disconnect between the flexibility of co-design and the rigidity in traditional academic and organisational processes.
The impacts of a longer-than-expected timeline for completion of the co-design process included financial, project scope, and sponsorship challenges. The project’s initial scope included a co-implementation and co-evaluation phase; however, due to the three-year time constraint, this was modified to conclude following the prototyping process. Whilst the three-year period set expectations for project sponsors and other collaborators from Rocky Bay, the wider context for the project varied significantly and rapidly over this period. This included two changes in Rocky Bay supervisor and one change in Rocky Bay project sponsor. Additionally, one of the academic supervisors left Curtin. This challenge indicates that the project would benefit from key role succession planning.
The peer researcher role was beneficial in providing an opportunity for a person with lived experience to join the study in a strength-based role and experience academic and business processes. However, challenges arose with the timeline extensions, which required this part-time, casual role to be extended by seven months. While the contract extension posed budgetary challenges, the role was viewed as vital to the completion of the project.
While an essential component of research, particularly involving vulnerable populations, ethical approvals proved challenging due to the non-traditional research methods involved in co-design. It was evident to the authors that while the ethics committee staff adhered to their processes, they were bound by a system that did not have adequate flexibility to work with newer research methods, such as co-design. Multiple methods in this study were heavily integrated into the community, including embedded research, peer research and co-design.
The present ethics process provided a comprehensive review focusing on planned interactions within research sessions (e.g. interviews and workshops). Unfortunately, this failed to account for a wider view, including the initial co-production prior to ethical application and anecdotal interactions that occurred regularly in the organic co-design process. In addition to the repeated submissions required to approve the sequential study format, these interactions created a significant workload for the research team and ethics office. These challenges were compounded by the need to navigate Rocky Bay’s organisational processes and changing business needs within ethical approval commitments.
In the authors’ opinion, prioritising the inclusion of lived experience experts in co-creating outputs to disseminate findings was beneficial. The co-creation enabled an authentic representation of the study to audiences regarding community-based participatory research and co-design method implementation. For example, the presentation of a panel discussion at a conference in which the peer researcher could prerecord his responses to questions as his preferred method of participation. All posters presented by the project were formatted to be accessible to lay consumers and were collaboratively produced, with the additional benefit of the posters being displayed across Rocky Bay hubs for customers and staff to gain study insights.
Due to the co-design method’s dynamic nature, some budgetary uncertainty was challenging to navigate. However, financial and non-financial remuneration for all non-staff participants in the project was prioritised. As previously discussed, the position of peer researcher was a paid role; additionally, all lived experience expert participants were remunerated at a rate of AUD 30/hour in the form of gift cards. The carer representative on the steering committee recommended using gift cards to avoid income declaration requirements from government benefits people may receive. Non-financial remuneration for the valuable time and contribution of the co-designer group included co-authorship on an article written regarding the Journey Map they produced (Benz et al. [ 37 ]) and acknowledgement in any other appropriate outputs. The implementation proposal provided to Rocky Bay included recommendations for continued inclusion and remuneration of co-designers.
Setting a new bar for inclusion
Another benefit to reflect upon, which may be the most significant legacy of the project, was setting the precedence for the inclusion of people with disability in decision-making roles in future projects and research conducted by the University and Rocky Bay. After this project commenced, other Rocky Bay clinical projects have similarly elevated the voices of lived experience in planning and conducting subsequent quality improvement initiatives.
I’m lucky enough to have been part of a lot of projects. But I guess I probably haven’t been a part of continuous workshops, pulling in all perspectives of the organisation perfectly… So, collaboration and getting insight from others I haven’t usually was a very unique experience, and I definitely found value if this were to continue in other projects. [Manager Co-designer]
In summary, the findings from using a co-design method for the telepractice research study produced a series of benefits and presented the researchers with multiple challenges. The findings also addressed a literature gap, presenting in-depth descriptive methods to demonstrate how co-design can be applied to a specific case.
Drawn from these findings, the authors identified six main points which form the basis of this discussion. These include (1) the fact that the necessary time and resources required to commit to co-design process completion adequately were underestimated at the outset, (2) there is a need to support the health, well-being and dignity of lived experience expert participants, (3) academic ethical processes have yet to adapt to address more participatory and integrated research methods, (4) strategies used to foster strong collaborative relationships across a diverse group were valued by all participants, (5) better delineation between terminologies such as co-design and community-based participatory research or patient and public involvement would improve the clarity of research methods and author intent and, (6) broader non-traditional impacts that participatory research can create should be better quantified and valued in the context of research impact. Each point will now be discussed in further detail.
In underestimating the time and resources required to complete the telepractice study, a scope reduction was required. This scope reduction removed the study’s originally planned co-implementation and co-evaluation phases. While Harrison et al. [ 40 ] and Bodden and Elliott [ 41 ] advocate for more frequent and comprehensive evaluation of co-designed initiatives, the authors acknowledge that this became no longer feasible within the study constraints. A growing body of literature indicates expected timelines for completed co-production projects from co-planning to co-evaluation. An example by Pearce et al. [ 5 ] indicated that a timeline of five years was reasonable. In contrast, a more limited co-design process was completed with a shorter timeline by Tindall et al. [ 13 ]. Although neither of these articles were published when this study commenced, they are complementary in building an evidence base for future research to anticipate an adequate timeline.
While co-design and other co-production processes are resource and time-intensive, the investment is essential to prioritise the health and other needs of potentially vulnerable population groups in the context of an imbalance of power [ 42 ]. In exploring the concept of dignity for people with disability, Chapman et al. [ 34 ] indicated that recognising the right to make decisions and proactively eliminating or minimising barriers to inclusion are key to protecting dignity. Community participation in decision-making processes such as this study can result in messy and unpredictable outcomes. However, the onus must be placed on policymakers, organisations, and academia to acknowledge this sufficiently rather than demand conformity [ 15 ].
The authors posit that the study would have benefited from an alternative ethics pathway, which may provide additional required flexibility while upholding the rigour of the ethical review process. The increasing frequency of participatory research studies indicates that challenges experienced by the authors of this study are unlikely to be isolated. Lloyd [ 43 ] described challenges regarding information gathered in-between, before and after structured research sessions, reflecting that they relied on personal judgement of the intent to consent for research use. Similarly, Rowley [ 44 ] reflected on the ethical complexities of interacting with families and respecting their confidentiality within the context of being integrated within an organisation. While these studies were co-production in child protection and education, the ethical challenges of their reflections parallel those experienced in the telepractice study. The risks posed by inadequate ethical support in these contexts are that increased poor ethical outcomes will occur, especially in the in-between times of co-design. Therefore, an ethics pathway that involves more frequent brief liaisons with a designated ethics representative to update project progress and troubleshoot ethical considerations may better support researchers to safeguard study participants.
We believe the decision to complete a sequential workshop series with a consistent group of diverse co-designers, led by co-facilitators, was a strength of the co-design process implemented in the telepractice re-design project. The group worked together across a series of workshops, which enabled them to build solid working relationships. Pearce et al. [ 5 ], Rahman et al. [ 16 ] and Tindall et al. [ 13 ] also demonstrated a collaborative whole-team approach to co-design. By contrast, studies that involved separate workshops with different cohorts or multiple of the same workshop did not demonstrate strong collaboration between co-designers [ 18 , 19 , 20 ]. Nesbitt et al. [ 19 ] explicitly highlighted that they would improve their method by completing sequential workshops with a continuous cohort. Stephens et al. [ 45 ] found that small mixed groups were not sufficient to support the participation of people with disability, indicating that the choice to intentionally balance groups to meet the lived experience expert co-designer’s needs may have been an impacting factor on our success.
A lack of clarity in the terminology used in co-design and community-based participatory practice was identified during the completion of this study. We found that co-design frequently meant either a collaborative design process or good participatory practices [ 46 ]. When viewing the structure of the telepractice re-design project, the overarching research approach was community-based participatory-research, and the method was co-design [ 9 ]. The delineation between the overarching approach and methods clarifies the misappropriation of the term co-design with the intent of meaning public participation [ 46 ] rather than the joint process of creative thinking and doing to design an output [ 11 ]. The use of the two-level structure appears more prominent in the United Kingdom, whereas Fox et al. [ 47 ] systematic review assessing public or patient participants identified that 60% of studies originated from the United Kingdom, compared to the next highest 16% for Canada or 4% from Australia and the United States. To improve clarity and reduce confusion about the terminology used, the authors advocate for greater awareness and implementation of the delineation between the concepts of a community-based-participatory-research/patient or public involvement approach versus the co-design method.
An example of co-design being used where alternate terms such as community-based participatory processes (or research) may be more relevant was the most recent amendment to the act governing the NDIS under which this project resided [ 48 ]. The term co-design could be interpreted as an intent to collaborate with people with disability for equitable involvement in all aspects of the NDIS [ 48 ]. It is proposed that the differentiation of these terms would assist in clarifying the intent of the study and dissuade inaccurate expectations of community involvement or design processes.
Implementing community-based participatory research has demonstrated the potential to create an impact that expands further than the original aim of the study. The skills learned by co-designers, the learning of the research team in collaboration with people with disability, the engagement and skill-building of a peer researcher with lived experience, the organisations who engaged in the co-design process and the academic and lay people who engaged with research outputs, all carry a piece of the impact of the co-design process. Rahman et al. [ 16 ] contend that co-design processes positively impact communities. In the context of this study, the peer researcher was included in the National Disability Insurance Agency’s quarterly report as an example of strength-based employment opportunities, which significantly positively impacted his career prospects [ 49 ]. This project provided skills for people with disability that they value and improved the clinical practice of clinician co-designers, which echoes the conclusions of Ramos et al. [ 15 ], who described that participants felt valued and experienced improved self-esteem. There is additional intent from the authors to positively impact disability providers and academia, to advocate for greater collaboration, and to provide open-access publications to provide a stronger evidence base for co-design in clinical practice and service delivery.
Strengths and limitations
The study provides reflective evidence to support the challenges and benefits experienced during the implementation of the study. However, a limitation in the project’s design was the exclusion of outcome measures to assess the impact of process design choices directly. Stephens et al. [ 45 ] completed targeted outcome measures correlating to accessibility adaptations in co-design and conceded that the variability of findings and individual needs reduced the usefulness of these measures.
The reduction of project scope enabled the completion of the study within the limitations of budgeting and timeline restrictions. Although the scope of the project had some flexibility, there were limitations to how far this could be extended as resources were not infinite, and staffing changes meant that organisational priorities changed. Including implementation and evaluation would have improved the study’s rigour. However, Rocky Bay now has the opportunity to implement internally without potential research delays and restrictions.
The blended and flexible approach to the co-design process was a strength of the study as it met the co-designers needs and maximised the project’s potential inclusivity. This strength has the potential to positively impact other studies that can modify some of the process design choices to suit their context and increase inclusivity [ 11 ]. It is believed that the messiness of co-design is important in meeting the needs and context of each individual study; therefore, no two co-design processes should look the same.
The authors concede that the inclusion of a cohort of people with disability and clinical staff does not represent the entirety of their communities, and their proposed changes may cause some parts of the disability community to experience increased barriers [ 50 ]. It is important to note that while the co-designers who participated in this project provided initial design developments, future opportunities remain to iterate the proposed telepractice service and continue to advocate for equitable access for all.
Recommendations for future studies
Recommendations from this study fall into two categories: recommendations for those intending to utilise the described methods and recommendations for future avenues of research inquiry. For those intending to implement the methods, the primary recommendations are to build ample time buffers into the project schedule, implement key role succession planning and set remuneration agreements at the outset, and work together as partners with the mindset that all contributors are creative [ 51 ] with important expertise and invaluable insights if supported appropriately.
Regarding avenues for future inquiry, we recommend investigating a more dynamic and flexible ethics process that may utilise more frequent short consultations to respond to ethical considerations during the emergent co-design and participatory research.
In the authors’ opinion, supported by co-designers experiences, co-design is a useful and outcome-generating methodology that can proactively enable the inclusion of people with disability and service providers in a community-based participatory research approach. The process is both time and resource-intensive; however, in our opinion, the investment is justified through the delivery of direct research benefits and indirect wider community benefits. We advocate for using community-based participatory-research/processes paired with co-design to generate creative thinking within service design processes. Through co-design processes, we recommend collaborating with a single diverse group of co-designers who have the time and space to build trusting working relationships that enable outputs representative of the group consensus.
Data availability
The dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is predominantly included within the article (and its additional files). However, due to the small number of co-designers reflecting upon the research, despite deidentification, there is a reasonable assumption of identification; therefore, the reflection activity response supporting data is not available.
Abbreviations
Australian Dollar
Guidance for Reporting Involvement of Patients and the Public 2 Checklist
Human Research Ethics Committee
Doctor of Philosophy
Patient and Public Involvement
Microsoft Teams
National Disability Insurance Scheme
McKercher KA. Beyond Sticky Notes doing co-design for Real: mindsets, methods, and movements. 1 ed. Sydney, NSW: Beyond Sticky Notes; 2020. p. 225.
Google Scholar
Mullins RM, Kelly BE, Chiappalone PS, Lewis VJ. No-one has listened to anything I’ve got to say before’: co-design with people who are sleeping rough. Health Expect. 2021;24(3):930–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.13235 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ekman I, Swedberg K, Taft C, Lindseth A, Norberg A, Brink E, et al. Person-centered Care — Ready for Prime Time. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2011;4248–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcnurse.2011.06.008 . [cited 3/9/2022];10.
National Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare. Partnering with Consumers Standard. Australia: National Commission on Safety and Quality in Healthcare. 2021. https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/standards/nsqhs-standards/partnering-consumers-standard .
Pearce T, Maple M, McKay K, Shakeshaft A, Wayland S. Co-creation of new knowledge: good fortune or good management? Res Involv Engagem. 2022;8(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-022-00394-2 .
Article Google Scholar
Bordeaux BC, Wiley C, Tandon SD, Horowitz CR, Brown PB, Bass EB. Guidelines for writing manuscripts about community-based participatory research for peer-reviewed journals. Prog Community Health Partnersh. 2007;1(3):281–8. https://doi.org/10.1353/cpr.2007.0018 .
Staniszewska S, Brett J, Simera I, Seers K, Mockford C, Goodlad S, et al. GRIPP2 reporting checklists: tools to improve reporting of patient and public involvement in research. Res Involv Engagem. 2017;3(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-017-0062-2 .
Ostrom E, Baugh W, Guarasci R, Parks R, Whitaker G. Community Organization and the Provision of Police Services. Sage; 1973.
Masterson D, Areskoug Josefsson K, Robert G, Nylander E, Kjellström S. Mapping definitions of co-production and co-design in health and social care: a systematic scoping review providing lessons for the future. Health Expect. 2022;25(3):902–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.13470 .
Bibb J. Embedding lived experience in music therapy practice: Towards a future of co-designed, co-produced and co-delivered music therapy programs in Australia. Australian Journal of Music Therapy [Journal Article]. 2022 [cited 2023/08/21];33(2):25–36. https://doi.org/10.3316/informit.829441047529429 .
Davis A, Gwilt I, Wallace N, Langley J. Low-contact Co-design: considering more flexible spatiotemporal models for the co-design workshop. Strategic Des Res J. 2021;14(1):124–37. https://doi.org/10.4013/sdrj.2021.141.11 .
Claborn KR, Creech S, Whittfield Q, Parra-Cardona R, Daugherty A, Benzer J. Ethical by design: engaging the community to co-design a Digital Health Ecosystem to Improve Overdose Prevention efforts among highly vulnerable people who use drugs. Front Digit Health [Original Research]. 2022;4:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fdgth.2022.880849 .
Tindall RM, Ferris M, Townsend M, Boschert G, Moylan S. A first-hand experience of co‐design in mental health service design: opportunities, challenges, and lessons. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2021;30(6):1693–702. https://doi.org/10.1111/inm.12925 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Wahlin DW, Blomkamp DE. Making global local: global methods, local planning, and the importance of genuine community engagement in Australia. Policy Des Pract. 2022;5(4):483–503. https://doi.org/10.1080/25741292.2022.2141489 .
Ramos M, Forcellini FA, Ferreira MGG. Patient-centered healthcare service development: a literature review. Strategic Des Res J. 2021;14(2):423–37. https://doi.org/10.4013/sdrj.2021.142.04 .
Rahman A, Nawaz S, Khan E, Islam S. Nothing about us, without us: is for us. Res Involv Engagem. 2022;8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-022-00372-8 .
Harrison R, Manias E, Ellis L, Mimmo L, Walpola R, Roxas-Harris B, et al. Evaluating clinician experience in value-based health care: the development and validation of the Clinician experience measure (CEM). BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-08900-8 .
Kerr JAS, Whelan M, Zelenko O, Harper-Hill K, Villalba C. Integrated Co-design: a model for co-designing with multiple stakeholder groups from the ‘Fuzzy’ front-end to Beyond Project Delivery. Int J Des. 2022;16(2):1–17. https://doi.org/10.57698/v16i2.06 .
Nesbitt K, Beleigoli A, Du H, Tirimacco R, Clark RA. User experience (UX) design as a co-design methodology: lessons learned during the development of a web-based portal for cardiac rehabilitation. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2022;21(2):178–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurjcn/zvab127 .
Marwaa MN, Guidetti S, Ytterberg C, Kristensen HK. Using experience-based co-design to develop mobile/tablet applications to support a person-centred and empowering stroke rehabilitation. Res Involv Engagem. 2023;9(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-023-00472-z .
Tariq S, Grewal EK, Booth R, Nat B, Ka-Caleni T, Larsen M, et al. Lessons learned from a virtual community-based Participatory Research project: prioritizing needs of people who have diabetes and experiences of homelessness to co-design a participatory action project. Res Involv Engagem. 2023;9(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-023-00456-z .
Abimbola S, Li C, Mitchell M, Everett M, Casburn K, Crooks P, et al. On the same page: co-designing the logic model of a telehealth service for children in rural and remote Australia. Digit Health. 2019;5:2055207619826468–2055207619826468. https://doi.org/10.1177/2055207619826468 .
Rocky Bay. Rocky Bay Annual Report FY 2021–2022. Perth. 2022. https://www.rockybay.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Rocky-Bay-Annual-Report-21-22.pdf .
National Disability Insurance Agency. What is the NDIS? [Internet]. 2021 [updated 14.08.2021. https://www.ndis.gov.au/understanding/what-ndis .
Reen G, Page B, Oikonomou E. Working as an embedded researcher in a healthcare setting: a practical guide for current or prospective embedded researchers. J Eval Clin Pract. 2022;28(1):93–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.13593 .
Bell S, Aggleton P, Gibson A. Peer Research in Health and Social Development 1st Edition ed. London: Routledge; 2021. p. 286.
Book Google Scholar
Curran T, Jones M, Ferguson S, Reed M, Lawrence A, Cull N, et al. Disabled young people’s hopes and dreams in a rapidly changing society: a co-production peer research study. Disabil Soc. 2021;36(4):561–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/09687599.2020.1755234 .
Kelly B, Friel S, McShane T, Pinkerton J, Gilligan E. I haven’t read it, I’ve lived it! The benefits and challenges of peer research with young people leaving care. Qualitative Social work: QSW: Res Pract. 2020;19(1):108–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/1473325018800370 .
Schwartz AE, Kramer JM. Inclusive approaches to developing content valid patient-reported outcome measure response scales for youth with intellectual/developmental disabilities. Br J Learn Disabil. 2021;49(1):100–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/bld.12346 .
Webb P, Falls D, Keenan F, Norris B, Owens A, Davidson G, et al. Peer researchers’ experiences of a co-produced research project on supported decision-making. Res Involv Engagem. 2022;8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-022-00406-1 .
People with Disability Australia. PWDA Language Guide: A guide to language about disability. Sydney, Australia. 2021. https://pwd.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/PWDA-Language-Guide-v2-2021.pdf .
Peters MDJGC, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil H. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews (2020 version). In: Aromataris E MZ, editor. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis, JBI, 2020: JBI; 2020.
Australian Broadcasting Commission. ‘My purpose is changing perceptions’: Australian of the Year Dylan Alcott’s speech in full [Internet]. 2022 [cited 17.08.2023]. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2022-01-26/dylan-alcott-australian-of-the-year-speech-in-full/100783308 .
Chapman K, Dixon A, Ehrlich C, Kendall E. Dignity and the importance of acknowledgement of Personhood for people with disability. Qual Health Res. 2024;34(1–2):141–53. https://doi.org/10.1177/10497323231204562 .
Flattery S. Stim Joy: Using Multi-Sensory Design to Foster Better Understanding of the Autistic Experience: ProQuest Dissertations Publishing; 2023.
Peak Learning. The Real Deal [Internet]. 2023 [cited 6.10.2023]. https://www.peaklearning.com/trd/ .
Benz C, Scott-Jeffs W, Revitt J, Brabon C, Fermanis C, Hawkes M, et al. Co-designing a telepractice journey map with disability customers and clinicians: partnering with users to understand challenges from their perspective. Health Expect. 2023;1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/hex.13919 .
Flowers E, Miller ME. Your Guide to Blueprinting The Practical Way. 1 ed. USA: Practical By Design 2022. 134 p. pp. 1-134.
Blomkvist J. Benefits of Service Level Prototyping. Des J. 2016;19(4):545–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/14606925.2016.1177292 .
Harrison R, Ní Shé É, Debono D, Chauhan A, Newman B. Creating space for theory when codesigning healthcare interventions. J Eval Clin Pract. 2023;29(4):572–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.13720 .
Bodden S, Elliott J. Finding space for Shared futures. Edinb Archit Res. 2022;37:90–104.
Page K. Ethics and the co-production of knowledge. Public Health Research & Practice. 2022:1–5. https://www.phrp.com.au/issues/june-2022-volume-32-issue-2/ethics-and-co-production/ .
Lloyd J. Life in a lanyard: developing an ethics of embedded research methods in children’s social care. J Children’s Serv. 2021;16(4):318–31. https://doi.org/10.1108/JCS-12-2019-0047 . [cited 2023/12/05];.
Rowley H. Going beyond procedure:engaging with the ethical complexities of being an embedded researcher. Manage Educ. 2014;28(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892020613510119 .
Stephens L, Smith H, Epstein I, Baljko M, McIntosh I, Dadashi N, et al. Accessibility and participatory design: time, power, and facilitation. CoDesign. 2023;1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/15710882.2023.2214145 .
Gardner G, McKercher KA. But is it co-design? And if it is, so what? 2021. https://healthvoices.org.au/issues/nov-2021/but-is-it-co-design-and-if-it-is-so-what .
Fox G, Lalu MM, Sabloff T, Nicholls SG, Smith M, Stacey D, et al. Recognizing patient partner contributions to health research: a systematic review of reported practices. Res Involv Engagem. 2023;9(1):1–30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-023-00488-5 .
National Disability Insurance Agency. 2022 NDIS legislation amendments Australia; 2022. https://www.ndis.gov.au/news/7975-2022-ndis-legislation-amendments-july-update .
National Disability Insurance Agency. Report to disability ministers for Q4 of Y10 Summary Part A Australia. 2023. https://www.ndis.gov.au/about-us/publications/quarterly-reports .
Lid IM. Universal Design and disability: an interdisciplinary perspective. Disabil Rehabil. 2014;36(16):1344–9. https://doi.org/10.3109/09638288.2014.931472 .
Sanders E, Stappers PJ. Co-creation and the New landscapes of Design. CoDesign. 2008;4:5–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/15710880701875068 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the contribution of Rocky Bay as the industry partner of this project and would like to thank the Co-designers of this project, without whom none of this was possible. The research team would also like to thank Katie Harris for her time and support throughout the workshop series, which were invaluable to the completion of the project and the formation of the published study.
The article forms part of a PhD project funded by the first author, CB’s Australian Government Research Training Program (RTP) scholarship.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Population Health, Curtin University, Bentley, Australia
Cloe Benz, Richard Norman, Delia Hendrie & Suzanne Robinson
Rocky Bay, Mosman Park, WA, Australia
Will Scott-Jeffs, Mai Welsh & Matthew Locantro
Beyond Sticky Notes, Sydney, Australia
K. A. McKercher
Therapy Focus, Bentley, Australia
Deakin Health Economics, Institute for Health Transformation, Deakin University, Melbourne, Australia
Suzanne Robinson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CB and MW liaised with the steering committee and conceived the study and structure. SR, DH and RN guided the protocol development and ethics approval. KAM provided methodological support to the project and subject matter expertise. CB and WJS completed participant recruitment, facilitation of workshops and data collection. KAM and CB ideated the format and content of the article. CB completed data analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and approved of the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cloe Benz .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent.
The study was approved by the Curtin University Human Research Ethics Committee (ID# HRE2021-0731), and all participants provided written informed consent before engaging in any research activity.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Cloe Benz, Richard Norman, Delia Hendrie & Suzanne Robinson do not have any competing interests to declare. Will Scott-Jeffs, Matthew Locantro and Mai Welsh, for all or part of the study period were employed by Rocky Bay a Not-For-Profit Disability Service provider who function as the industry partner for the project. K.A. McKercher is the author of a co-design method book referenced in the article. McKercher also runs a business that helps people co-design.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1:
Appendix 1–3
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Benz, C., Scott-Jeffs, W., McKercher, K.A. et al. Community-based participatory-research through co-design: supporting collaboration from all sides of disability. Res Involv Engagem 10 , 47 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-024-00573-3
Download citation
Received : 13 November 2023
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-024-00573-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Community-based participatory-research
- Telepractice
- Lived experience
- Embedded researcher
- Digital health
- Patient and public involvement
Research Involvement and Engagement
ISSN: 2056-7529
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Environmental impacts of artificial turf: a scoping review
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- S. M. Bø ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0007-2358-8053 1 ,
- R. A. Bohne 1 &
- J. Lohne 1
111 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Artificial turfs represent a large environmental issue in terms of waste, microplastic pollution and leaching of chemicals. Artificial turfs are made of several components, the shock absorbing pad, backing, stabilizing infill, performance infill and artificial grass fibers. Common for these, except the stabilizing infill, is being made of plastic and chemicals being released to the environment. The purpose of this article is to investigate current research on the environmental impact of artificial turfs for football fields. This is done by presenting the state-of-the-art through a review of 40 articles and grey reports. Studies concerning the chemical content of rubber granules and microplastics lost to the environment represent most of the findings. The methods applied vary to a great extent, and more research is needed to further understand the environmental impact of artificial turfs. This study provides an overview of the previous work performed and highlights knowledge gaps and will be of help during further research on the environmental impacts of artificial turfs.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
With more than 265 million registered players, football (soccer) is one of the most popular sports worldwide (Federation Internationale de Football Association 2007 ). Football is often played on artificial turfs, especially in areas with harsh winters (i.e. Scandinavian countries), as they are all-weather play (Larsen et al. 2015 ). Artificial turfs are typically made of an underlying shock absorbing pad, synthetic green grass fibers, a stabilizing infill (quartz sand) to keep the turf in place, and a performance infill (e.g. styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) granules from end-of-life tires) to ensure playability of the field (Larsen et al. 2015 ). SBR is currently the preferred infill type (KG2021 2020 ; Larsen et al. 2015 ). Artificial turfs represent a significant environmental issue in terms of waste, microplastic pollution and leaching of chemicals (Norwegian Environment Agency, n.d; Norwegian Environmental Agency 2021 ).
First, artificial turf generate waste in terms of plastics, microplastics, sand and performance infill (Bø et al. 2020 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). A typical 11-a-side football field is 6400 m 2 and weighs approximately 225 tons, holding a lifetime of 10–12 years (Larsen et al. 2015 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ; NFF 2021 ). In Norway, expected amounts of waste are 26,900 tons/year, were 52% is plastic waste (Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). Ongoing recycling initiatives, such as Re-Match or TeBe Sport, provide the opportunity of recycling and reusing materials, which reduces waste.
Second, artificial turfs are assumed to be the second largest land-based source of microplastics (plastics < 5 mm in size) released to the environment (Norwegian Environment Agency, n.d). It is estimated an annual loss of 16,000 tons/year to the environment by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA 2023 ). Microplastics are released to the environment by the user of the field, use of maintenance equipment, run off to surrounding soil and waters and by snow removal (Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Gustavsen 2019 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ). Restrictions and regulations of intentionally added microplastics in artificial turfs are pursued on both a domestic level of individual nations and within the European Union (ECHA 2021 , n.d; Forurensningsforskriften). This is done to prevent further loss to the environment (ECHA 2021 , n.d; Forurensningsforskriften).
Third, the manufacturing process to produce artificial turfs requires large amounts of water, energy, and non-renewable petroleum-based materials (e.g., polyethylene) to make the turf. CO 2 -emissions from artificial turfs occur during manufacturing, production, transportation, installation, maintenance and at end of life (e.g., incineration of fields) (FIFA 2017 ).
Last, installing artificial turf will have an impact on the local environment. Research show that the use of specific types of performance infill lead to leaching of heavy metals (e.g., Zinc) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) (Berger 2021 ; Celeiro et al. 2021b ; Cheng et al. 2014 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Rabben 2020 ).
Research questions and structure of study
To investigate current research on the environmental impact of artificial turfs, a scoping review methodology is carried out, following Arksey and O'Malley ( 2005 ). This study addresses the following two research questions:
What research has been performed on the impact of artificial turf on the environment?
What are the existing research gaps?
In the following, the methodology of the scoping review is presented in “ Materials and methods ” section. Results from the analysis of studies are presented in “ Results and discussions ” section. The discussion in “ Conclusions ” section follows the same structure as the presented results. Finally, in Sect. 5, the two research questions are addressed and suggestions for further research is provided. The scoping review was carried out in Norway in 2023.
Materials and methods
A scoping review methodology is utilized, following the five guidelines provided by Arksey and O'Malley ( 2005 ) These five stages are visualized in the flow-chart in Fig. 1 .
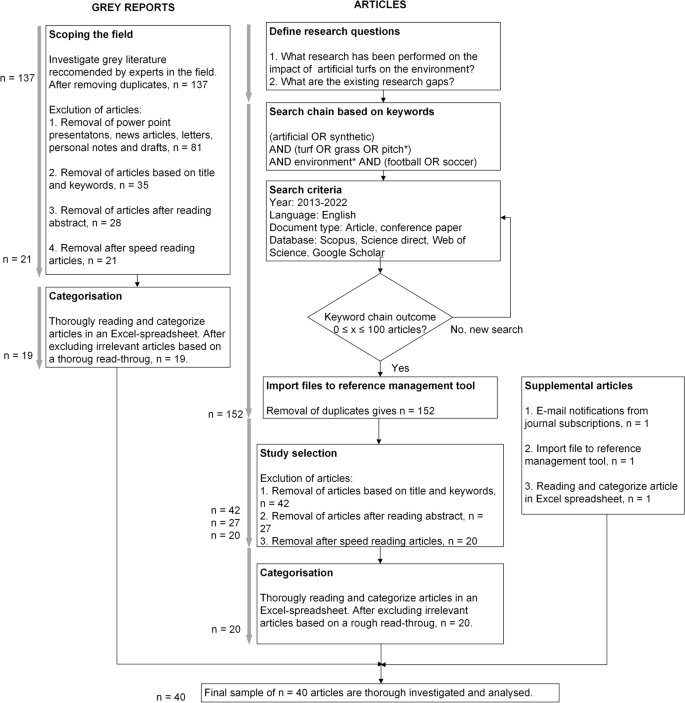
This scoping review described as a flow chart-model. Left hand side indicates the process of grey reports, and right-hand side indicates the process of articles. Resulting in a final sample of 40 grey reports and articles being included in this scoping review
Scoping the field: grey literature
Before beginning the scoping review, a total of 137 grey literature publications recommended by experts in the field were investigated. One expert has collected grey literature for the last ten years while working with sports facilities, and the second expert is an industry contact. Both are from Norway. No separate search for grey literature has been carried out. First, power point presentations, news articles, letters and personal notes and drafts were removed, reducing to 81 grey reports. Further exclusion of grey publications was made by first reading the title and keywords, resulting in a reduction to a sample of 35. Then, by reading abstracts the sample was further reduced to 28. After speed-reading the publications entirely, the sample was decreased to 21. Last, after a thorough readthrough, a final sample of 19 was kept for further investigations. Articles were excluded if they did not align with research question 1: What research has been performed on the impact of artificial turfs on the environment? An overview of the exclusion criteria is found in Table 1 .
Identifying studies: research publications
Based on the research question, search terms and synonyms for each term were identified. A search string based on keywords was found to be: (artificial OR synthetic) AND (turf OR grass OR pitch*) AND environment* AND (football OR soccer). Search criteria were set to be English scientific articles or conference papers, published between 2013 and 2022. The reason for this was the building of artificial turfs started in full force in the beginning of the 2010s and environmental concerns of artificial turfs was raised in the end of 2010s (Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). The following scientific databases/search portals were used: Scopus, Science direct, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. The software Publish or Perish was utilized to aid the search in Google Scholar (Harzing 2007 ). The search was limited to a maximum of 100 most top cited. The software retrieves both articles and non-articles, where the non-articles were removed manually. To include research being published while the scoping review was performed, an e-mail notification was put up in all databases (except Google Scholar) to get notified if articles were published on the same search chain of keywords. The e-mail push-notification resulted in 1 article (Kole et al. 2023 ).
When a search generated less than one hundred and more than zero, they were imported to the reference management tool End Note (Clarivate 2023 ). After retrieving articles from all databases, removal of duplicates was performed. A total of 152 articles were retrieved.
Selection of studies
The exclusion of articles was done in three steps. First, exclusion was done by eliminating articles based on reading their title and keywords. This resulted in a reduction to 42 articles. If title and keywords were relevant, the abstract was read. This further diminished the selection of articles to 27. Last, if the abstract seemed relevant, the article was roughly read through. Articles were excluded if they were found to be out of the scope or if they were irrelevant based on the first research question. This last step resulted in 20 articles. Final exclusion criteria are presented in Table 2 .
Charting the data
A total of 40 articles, grey reports (19) and articles (21) were categorized. This process was done simultaneously for the grey reports and the articles. Categorization of the was done in an Excel-spread sheet. The title and publication year of the article was retrieved. In addition, the name of journal where the article was published, name of first and last author, geographical affiliation of first and last author was noted. Notes on the aim, method, results, area of focus, and implication of study were collected from the articles abstract.
Results and discussions
The following section outlines findings from the scoping review process. No articles from earlier than 2013 were collected from the database search, and no grey reports published before 2015 were recommended. Therefore, the trend line of publications per year is not presented.
Geographical affiliation
In Fig. 2 , the geographical affiliation of the first author is represented. Twelve countries are represented. 54% of studies geographical affiliation from Scandinavia and 90% from Europe. Only three articles are affiliated outside Europe: two in USA (Massey et al. 2020 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ) and one in China (Cheng et al. 2014 ).
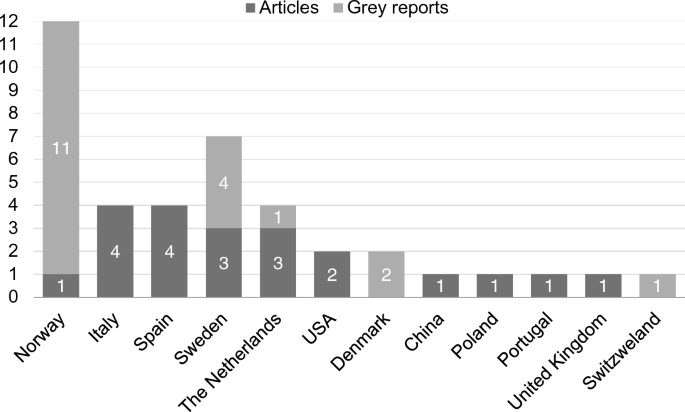
Overview of geographical affiliation of first author for articles and grey reports
Scientific journals
In Fig. 3 , the scientific journals are visualized. Investigation of what scientific journals the reviewed articles are published in, reveals a wide range of journals utilized. Fifteen different journals have accepted twenty articles. Seven out of twenty are published in three journals, where Chemosphere (Celeiro et al. 2021b , 2018 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ) and Science of the Total environment (Armada et al. 2022 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a ; Kole et al. 2023 ) are most frequently used .
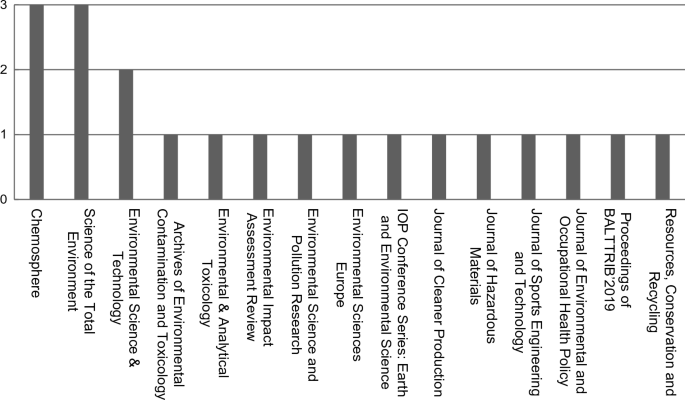
The figure indicates the journals that articles reviewed in this scoping review study are published in
Methods utilized in articles and grey reports
The methods utilized are divided into quantitative, qualitative, mixed method (where both a quantitative and qualitative approach has been performed), and literature review. Specific methods are noted and elaborated in the following subsections. In studies were more than one method is utilized, their main method is visualized in Figs. 4 and 5 .
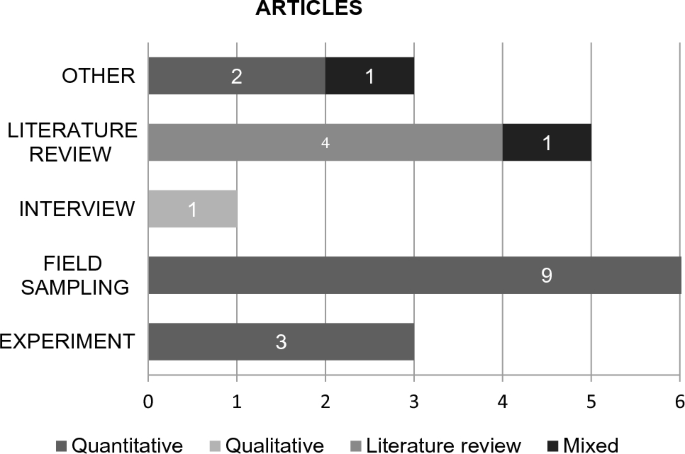
Presentation of methods found in the sample of articles, and gives an indication on the method being quantitative, qualitative, a literature review or mixed method
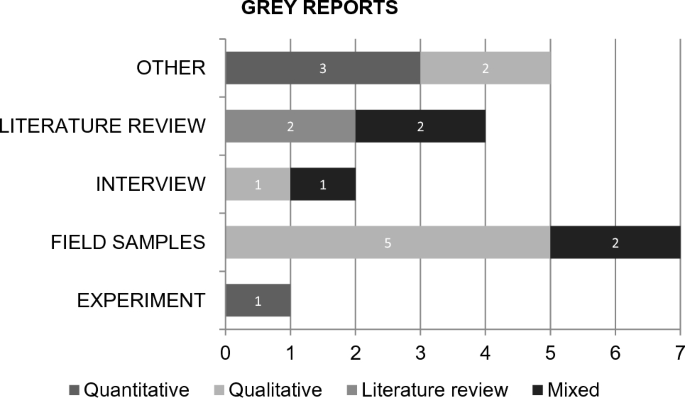
The most utilized method for both articles and grey reports was field sampling (Armada et al. 2022 ; Berger 2021 ; Brandsma et al. 2019 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a , b ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Rabben 2020 ; Regnell 2017 ; Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ). There were nine articles using field sampling as main method, all of them quantitative, then complimented with a chemical analysis to determine the presence or release of PAHs, heavy metals, volatile organic compounds (VOC), and/or chlorinated paraffins in samples, or air pollution (Armada et al. 2022 ; Brandsma et al. 2019 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a , b ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ). Seven grey reports utilized field sampling as their main method (Berger 2021 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Rabben 2020 ; Regnell 2017 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ). Five focused on investigating the release of microplastics to the environment, either to water or soil (Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Regnell 2017 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ). Two studies took field samples from water and soil to identify the presence of heavy metals (Berger 2021 ; Rabben 2020 ).
Experiments
Three articles use an experimental set up to investigate respectively the soil contamination of heavy metals, air pollution by rubber granules, and how the pitch degrades and microplastic lost to the environment (Fleming et al. 2020 ; Olofsson and Lyu 2019 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ). One study ran a 34-day experiment on 100 earthworms in soil contaminated with crumb-rubber (Pochron et al. 2017 ). The second used a pendulum rig to investigate the transmission of a migration of particles from artificial turfs (Olofsson and Lyu 2019 ). And the last experimented with maintenance interventions, to get a deeper understanding of the mechanisms how the turf degrades and quantifying the effects of intervention, in addition a database of 750 turfs was investigated (Fleming et al. 2020 ).
One grey report used a large-scale experiment, where 12,000 participants played 2 × 15 min games, then collecting all rubber granules stuck to their clothes. This was to investigate microplastic loss to the environment by users of the field (Forskningskampanjen 2017 ).
One article use semi-structured interview as method, in addition to document analysis and an open-ended questionnaire, to investigate barriers for sustainable practices within the artificial turf industry (de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ). Two grey reports use interviews with experts in the field and industry leaders, or municipalities, as their main method (Krång et al. 2019 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). The interviews are categorized as both structured (Krång et al. 2019 ) and unstructured (Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ), both aiming to increase the knowledge of microplastics lost from artificial turfs to the environment.
- Literature review
Literature review is used by five articles as the main method, to understand the environmental impact of PAHs, VOCs, and heavy metals (Cheng et al. 2014 ; Gomes et al. 2021 ; Massey et al. 2020 ), microplastics (Kole et al. 2023 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ). One reviewed published articles, books, and grey literature (Cheng et al. 2014 ). The second article reviews grey reports on microplastics from artificial turfs lost to the environment (Verschoor et al. 2021 ). Neither states the method of how the literature review was performed. The third investigates 72 articles on potentially harmful chemicals in SBR rubber granules (Gomes et al. 2021 ). The third literature review investigates government agency reports and peer-reviewed studies to complement their chemical analysis of different performance infill types (Massey et al. 2020 ). The last estimates mitigation of microplastics from the fields by a systematic review. (Kole et al. 2023 ).
Four grey reports investigate microplastic loss to the environment by literature review as main method (Lassen et al. 2015 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). None describe their methodology. Three reports include their data sources (Lassen et al. 2015 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ).
Three articles have been categorized as “other” in their methods. Research on the life cycle of an artificial turf with SBR as performance infill and compare it to a natural turf has been done (Russo et al. 2022 ). This was done by a product environmental footprint approach, based on a life cycle assessment (LCA)-method (Russo et al. 2022 ). LCA-methodology is also used to investigate greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption from artificial turfs (Magnusson and Mácsik 2017 ). One study utilizes a material flow analysis (MFA) of Norwegian artificial turfs roughly estimate SBR lost to the environment annually (Bø et al. 2020 ).
Five grey reports fall under the “other” category and consist of both quantitative and qualitative studies. One larger survey (n = 253) maps maintenance, operation, design, and location of artificial turfs in Norway (Rambøll 2017 ). A mapping of microplastics released to the environment has been performed by observation of 42 artificial turfs (Gustavsen 2019 ). In 2019, a case study of an artificial turf in Kalmar in Sweden was published, investigating how minimal the release of microplastics can be if right measurements are implemented (Regnell 2019 ). A document/database-study was done by Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) to investigate the environmental impact of artificial turfs in their database (FIFA 2017 ) Last, an MFA was done to quantify release of microplastics from artificial turfs to the aquatic environment (Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ).
Chemicals in artificial turfs
SBR is the most utilized performance infill in artificial turf. As they are made from end-of-life tires, they could potentially contain PAHs and VOCs, semi-volatile organic hydrocarbons (SVOCs), heavy metals, or phthalates (ECHA 2017 ). Research found that these chemicals can be released to the environment and could represent a risk to the environment, and risk assessment should be performed for all performance infill types (Magnusson and Mácsik 2017 ).
By performing a hazard-based analysis of a wide range of performance infill used for artificial turfs, a conclusion was reached that none of the performance infill types used for artificial turfs are completely free from concerns relating to the environment (Massey et al. 2020 ).
The presence of PAHs and VOCs from rubber granules has been identified and assessed in several studies by different chemical analysis (Armada et al. 2022 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a , b ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ). From investigating 91 infill samples from 17 countries and 4 continents, a worldwide confirmation was done of the presence of PAHs in rubber granules from artificial turfs (Armada et al. 2022 ). PAHs and VOCs are present in almost every tested infill type, except shoe materials, acrylic-coated sand and mineral- or plant-based types (Massey et al. 2020 ). Alternative infill types, such as cork, do not contain PAHs and are suggested as a safer and more sustainable alternative to rubber granules for artificial turfs (Armada et al. 2022 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a ).
PAHs leaching to the environment can occur and represents a potential risk for the aquatic environment (Celeiro et al. 2021b , 2018 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ). It is argued that SBR does not represent an environmental risk based on the quantities of PAHs leaching to the environment being scarce (Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ). It is still important to consider the size and classification of SBR, as they are microplastics, in relation to environmental aspects. New applications of the material should be considered (Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ). Non-plastic infill is recommended as microplastics are an environmental concern (Armada et al. 2022 ).
SBR samples exhibit a significant presence of high concentrations of heavy metals (Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Gomes et al. 2021 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ). Leaching of these heavy metals occurs and ends up in the surrounding environment (Gomes et al. 2021 ; Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ). As the particle size of SBR decreases, the leaching of heavy metals increases (Cheng et al. 2014 ). This leaching, except Zinc, is found to be low and not to cause concern (Marsili et al. 2015 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ). Though, some studies put attention to the number of heavy metals leaching into the environment, especially Zinc, Ni and Cr, as an increased amount will enhance the ecotoxicity, and could affect the life of plants and animals close to the turf (Cheng et al. 2014 ; Gomes et al. 2021 ). A high leaching potential of Zinc from artificial turfs with SBR is found, but it is argued that due to the dilution that will occur it does not represent an environmental risk (Berger 2021 ). Larger amounts of ground contaminated with Zinc accumulating in the soil have been found where snow contaminated with rubber granules has been stored during winter (Rabben 2020 ).
Chlorinated paraffins have been identified in rubber granules. Further investigation of the leaching from rubber granules should be done, to better understand mitigation and leaching mechanisms of rubber granules and their impact on the environment (Brandsma et al. 2019 ).
Sustainability of artificial turfs
Research implies that fine dust of rubber granules, PAHs, VOCs, and other organic substances can pollute the air, but are found to comply with regulations (Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Cheng et al. 2014 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ). Performance infill of ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber (EPDM), compared to SBR and thermo plastic elastomers (TPE), generates more airborne particles (Olofsson and Lyu 2019 ). When comparing the exposure risks of PAHs through air, artificial turfs do not represent any larger environmental risks than comparing to the surrounding city in urban areas (Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ). Outdoor facilities have a lower concentration of PAHs, compared to indoor facilities (Celeiro et al. 2021a ; Gomes et al. 2021 ).
The carbon footprint of a 9000 m 2 artificial turf with a 10-year lifetime (including manufacturing, transportation, installation, maintaining and disposing) is estimated to be 55.6 t/CO 2 , around 3 times more than a natural turf of the same size (Cheng et al. 2014 ). If it is impossible to recover the artificial turf at end-of-life, CO 2 -emissions could double (Cheng et al. 2014 ). A key to improve the sustainability of artificial turfs is to enhance the recovery technology (FIFA 2017 ; Russo et al. 2022 ).
According to Magnusson and Mácsik ( 2017 ), when performing an LCA-analysis of artificial turfs, it is seen that the greenhouse gas-emissions significantly correlates with materials, maintenance and removal of turf. GHG-emissions are larger with TPE as performance infill, than EPDM, and reuse of materials can potentially decrease emissions and energy use (Magnusson and Mácsik 2017 ).
There are barriers actors have to overcome to enhance the environmental sustainability of their artificial turfs (de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ). A good dialogue, good information flow and education regarding environmental sustainability of artificial turfs is one of the obstacles. To improve the sustainability of turfs, a standardization of the procurement process have been suggested, in addition to enhancing the maintenance practice to ensure longer viability of artificial turfs and reduce waste (de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ).
Release of microplastics to the environment
Microplastics will be lost from artificial turfs to the environment (Bø et al. 2020 ; Gustavsen 2019 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ). This occurs due to the current design, operation, and maintenance of the artificial turfs (Bø et al. 2020 ). Investigations of loss/year has been carried out (Fleming et al. 2020 ). Loss of performance infill has been found to be equal to a change in performance infill depth of 0.8 mm/year, after year 3–4 (Fleming et al. 2020 ). One should carefully implement compaction as a cause for the need for refilling fields as refilling compaction can occur, not solely because they are lost to the surrounding environment (Verschoor et al. 2021 ). A significant amount of research identifying microplastic loss has been carried out. The amount of microplastics lost to the environment varies from turf to turf and from country to country, varying from 0.0001 to 5 tons/year/field (Bø et al. 2020 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Kole et al. 2023 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ).
There are numerous routes where microplastics can enter the environment surrounding the artificial turf: By the players using the field, use of maintenance equipment, run off to the surrounding soil and waters and by snow removal (Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ). The loss found outside fields decreases with distance to the turf (Haave 2018 ).
Best practices
FIFA states that the choice of infill material used should be considered as a means to mitigate the environmental impact of artificial turfs (FIFA 2017 ). Organic infills have the lowest impact on the environment, compared to infills of polymers (FIFA 2017 ). By using a shock pad the environmental impact will be reduced (FIFA 2017 ).
In addition to improving the turf design, microplastic loss can be reduced to as little as 0.1 kg/field/year by implementing “best practices” for how the artificial turf should be used and maintained (Regnell 2019 ). This could for example be to implement a fence around the field or implement a surface for snow storage during winter (Regnell 2019 ). Implementing measures will effectively reduce microplastic loss to the environment (Haave et al. 2022 ). Some municipalities are already actively working on reducing microplastic loss by implementing best practices, already have experienced a reduction in loss to the environment (Krång et al. 2019 ). Lack of knowledge, resources, and regulations about best practice, in addition to the turf design, are stated as barriers to actively reduce microplastic loss (Rambøll 2017 ).
In Norway, according to Mørk-Kontny and Mekki ( 2022 ), the expected amounts of waste generated in the period 2020–2045 is expected to be 26,900 tons/year (33,100 tons every 12 year). The recycling facilities separate sand and rubber granules from the turf. If the components are of good quality, they will be used (FIFA 2017 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). If the turf is too worn and cannot be further utilized in other areas, it is material or energy recovered, or landfilled (Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ). A full closed loop-process of handling artificial turfs at their end-of-life is still being developed (FIFA 2017 ).
This paper has addressed what research has been performed on the impact of artificial turf on the environment and what are the existing research gaps. In the following, we assess these questions separately, before providing an outline of how the limitations of the study have influenced the analysis.
Research performed on the impact of artificial turfs on the environment
The studies found in this scoping review are investigating artificial turf fields made of synthetic grass fibers with SBR used as performance infill, utilized for recreational football. In addition, a few studies investigate turfs using newer alternatives to performance infill, such as cork/coconut, crushed olive pits or sand (Armada et al. 2022 ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; FIFA 2017 ). Alternative types of performance infill are a fairly new field of study, as SBR has been the preferred infill type since the 1990s (KG2021 2020 ).
An interesting observation, that cannot be generalized due to the small sample size, is that the most prominent countries in research on environmental impact of artificial turfs are from Scandinavia (21). In sum, 35 studies are conducted in Europe. First, this could be due to the regulations introduced on a national level in the individual countries or ECHAs regulation on PAHs in artificial turfs, or the European Green Deal with an initiative of addressing microplastics in the environment (ECHA 2021 , n.d; Forurensningsforskriften). Second, artificial turfs in an environmental setting might be a “new” field of study and is less researched in other countries outside Europe. Last, the recommended grey report could be biased by the expert’s background being Scandinavian.
When investigating the studies performed, there is no methodological approach standing out. As many studies have the same main topic, i.e., microplastic lost to the environment, their method utilized vary greatly (e.g., field sampling (16), experiments (4), literature reviews (9), interviews (3), survey (1), case study (1), observation (1) and document study (1)). Differences in methodology, contextual differences, and lack of standardization renders comparison of results challenging. A variation on utilized methods has the advantage of data quantity, but consequently inaccuracy in data quality.
Most articles in the sample utilize one main method (e.g. Bø et al. 2020 ; Cheng et al. 2014 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ; Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 )), while grey reports often combine methods (e.g. Gustavsen 2019 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ; Rabben 2020 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 )).
Field sampling and analysis of these to identify chemical composition or content of microplastics is the most used method (Armada et al. 2022 ; Berger 2021 ; Brandsma et al. 2019 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a , b ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Rabben 2020 ; Regnell 2017 ; Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ). Field sampling gives the opportunity to obtain samples from many different locations and areas on the turf, though challenging to generalize.
Literature reviews are frequently utilized to summarize existing knowledge of impact on the environment (Cheng et al. 2014 ; Gomes et al. 2021 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Massey et al. 2020 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). The literature reviews in the sample are lacking transparency in their methodology, as the majority fail to elucidate data retrieval and analysis (e.g. Lassen et al. 2015 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 )). Three studies use unstructured, semi-structured and structured interviews to get a better understanding, identify key-issues and feedback from individuals possessing expertise and knowledge of the environmental impact of artificial turf in addition to compliment quantitative data (de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ).
Some studies provide a “flow chart” to support field sampling or literature review (Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Regnell 2017 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). These “flow charts” are called MFA. No proper MFA-methodology, however, is identified (e.g. lack of system boundary and unbalanced flows).
The biggest difference between the published articles and the recommended grey reports is their area of focus. The majority of existing articles concentrates on the content and leaching of PAH, VOCs, and heavy metals from SBR into the surrounding environment, as well as air pollution and GHG-emissions (Armada et al. 2022 ; Brandsma et al. 2019 ; Celeiro et al. 2021a , b ; Celeiro et al. 2018 ; Cheng et al. 2014 ; de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ; Gomes et al. 2021 ; Grynkiewicz-Bylina et al. 2022 ; Magnusson and Mácsik 2017 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Massey et al. 2020 ; Olofsson and Lyu 2019 ; Pochron et al. 2017 ; Ruffino et al. 2013 ; Russo et al. 2022 ; Schilirò et al. 2013 ). Conversely, grey reports primarily explore the loss of microplastics to the environment (Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Gustavsen 2019 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Larsen et al. 2015 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). Grey reports (17) and articles (4) state that loss of microplastics in the form of rubber granules occur (Bø et al. 2020 ; Fleming et al. 2020 ; Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Gustavsen 2019 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ; Rabben 2020 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). The amount lost varying from 0.0001 to 5 tons/year/field (Bø et al. 2020 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). Loss can happen through several paths, by the user of the field, maintenance of the field, snow removal and run off to surrounding soil and waters (e.g. Bø et al. 2020 ; Fleming et al. 2020 ; Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Regnell 2019 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 )). As microplastics represents an incredible environmental issue some best practices are suggested (de Bernardi and Waller 2022 ; FIFA 2017 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Regnell 2019 ).
Research gaps
While scoping the field, 40 relevant studies were retrieved from a sample of 290 studies (153 articles and 137 grey reports). On the basis of the exclusion criteria (Tables 1 , 2 ), a subset of 78 studies (72 articles, 6 grey reports) were deemed irrelevant due their focus on artificial turfs impact on human health, injuries and biomechanics. Research gaps found in this study are influenced by the nature of its scope, as it is limited to literature on the environmental impacts of artificial turfs. By addressing the following areas of research, a more comprehensive understanding of the environmental impact of artificial turfs can be found. In particular, themes related to end-of-life options, regulatory changes, flow analysis, carbon footprint, and lifetime concerns, including termination.
First, artificial turfs have a lifetime of 10–12 years (Larsen et al. 2015 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ; NFF 2021 ). Research has been performed on the amounts of annual waste amounts from artificial turfs, but limited research is found on efficient recycling methods or sustainable end-of-life options (Bø et al. 2020 ; FIFA 2017 ; Mørk-Kontny and Mekki 2022 ).
Second, the loss of microplastics is researched from different perspectives, from loss by the users of the fields to case study of the optimal design of an artificial turf to reduce loss (Bø et al. 2020 ; Fleming et al. 2020 ; Forskningskampanjen 2017 ; Haave 2018 ; Haave et al. 2022 ; Korbøl 2018 ; Krång et al. 2019 ; Lassen et al. 2015 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Rambøll 2017 ; Regnell 2017 , 2019 ; Sundt et al. 2016 ; Tandeberg and Raabe 2017 ; Verschoor et al. 2021 ; Verschoor and Werner 2017 ; Wallberg et al. 2016 ). Loss off microplastic is stated to occur, but no standardized method for quantifying loss has been utilized or developed. There are few studies on the design (e.g., alternative performance infill materials), maintenance, and operation of artificial turfs to minimize microplastics lost to the environment in the sample (Bø et al. 2020 ; FIFA 2017 ; Regnell 2019 ). Existing knowledge on the efficiency of regulations or methods for preventing microplastic loss is limited.
Surprisingly, only a single study is found in the sample discussing the current EU policy to ban rubber granules (Verschoor et al. 2021 ). The study stated as a worst-case scenario, the policy is deemed ineffective and potentially without value (Verschoor et al. 2021 ). Research addressing regulations and policies implemented on a national and international level is lacking coverage, and could be of value for decision-makers, municipalities and owners of sports facilities.
Third, incorporation of LCAs and MFAs to enhance the understanding of circularity, flows, stocks, resource consumption, GHG-emissions, energy- or water consumption remains limited in the sample (Bø et al. 2020 ; Løkkegaard et al. 2019 ; Magnusson and Mácsik 2017 ; Russo et al. 2022 ). The MFAs in the sample investigate artificial turfs with performance infill containing polymer, but studies including alternative performance infill materials (e.g., coconut or granulated olive cores) are scarce.
Last, the environmental impact of chemicals from SBR as performance infill has been investigated and reveals leaching of heavy metals (e.g., Zinc) and PAHs to the surrounding soil and air (Berger 2021 ; Celeiro et al. 2021b ; Cheng et al. 2014 ; Marsili et al. 2015 ; Rabben 2020 ). Comprehensive chemical analysis of the artificial turf, leaching behavior and mechanisms, risk assessments, and the effect of aging and weathering, especially for alternative performance infill, are still lacking.
Limitations
First, grey article publications recommended by experts in the field could be influenced by the current discussion on the release of microplastics from artificial turf fields. The recommended grey report could be biased by the expert’s background being Scandinavia. Articles could be left out from their recommendation, though they thematically are within the scope of this study. Second, when comparing a classic systematic review with a scoping review, the latter is a less rigid approach. This gives the scoping review-method flexibility for a rapid search. Third, all articles are English and most of the grey reports are in Scandinavian (15). One would believe that great football nations such as Italy, Spain, France, Germany, or Brazil are publishing research on the topic, but in their language. Thus, knowledge in other languages could be omitted. Fourth, this scoping review study is limited in time. This means that new articles and grey reports may be published at any time and could be missed or overlooked. If reproducing this work, because of time being a limiting factor, one could have a larger selection of studies in the future. Last, this scoping review aims to provide an overview of the current knowledge and gaps, it does not evaluate the quality or the causes of the presented results.
This study has highlighted substantial environmental consequences of using artificial turfs; at the same time little research that focuses specifically on these consequences has been found.
In the last decade, 40 studies have been identified on the environmental impact of artificial turfs, and this scoping review reveals a wide range of methods utilized and multiplicity of topics connected to the environmental impact. Research has been found on artificial turfs used for recreational sports. Most of the studies investigate SBR from car tires, and their content of different chemicals and heavy metals that could affect the surrounding environment. A few studies investigate airborne particles polluting the air, where outdoor turfs are less polluted than indoor facilities. Materials utilized in artificial turf and how it is handled at end of life will greatly impact emissions and energy use. Most grey reports investigate loss of microplastics. They are lost to the environment surrounding the artificial turfs. It is hard to estimate how much is lost annually from each turf, as this varies with the turf’s location, facility design, use, maintenance, snow removal and run off.
First, there is no standardized method in assessing the artificial turf’s environmental impact. Methods used in the sample vary giving the advantage of data quantity and inaccuracy in data quality. Second, it is worth noticing that 90% of the studies included were conducted within Europe. Third, LCAs and MFAs would increase the understanding of the circularity, materials, flows, and stocks of artificial turfs. In addition, studies on waste-management and sustainable end-of-life options, or recovery technologies, for artificial turfs would contribute to the field. Research on regulations and policies implemented on a national and international level would possibly be beneficial for decision-makers, municipalities, and owners of sports facilities. Last, research should include comprehensive chemical analysis including, but not limited to, leaching mechanisms, risk assessments and the effect of aging and weathering.
Implications
In practical terms, the findings suggest that urban planners and managers of sports facilities should consider emissions of airborne particles, leaching of heavy metals and loss of microplastics, when renovating or building new artificial turfs. Materials utilized should be carefully chosen (e.g. follow current regulations reduce microplastic emissions (ECHA, n.d)).
Measures have been done in Europe to reduce microplastics added to products (ECHA, n.d). The regulation prohibits sales of microplastics, and products with intentionally added microplastics. It has a transition period of eight years, with an intention on reducing emission of microplastics to the environment (ECHA, n.d). Hence, artificial turfs with SBR and other synthetic polymer particles (< 5 mm in size) is prohibited to be sold after eight years. As artificial turf fields with SBR can be used continuously during and after the transition period, the regulation should be improved to further prevent microplastic emissions. First, facility owners should educate users of the fields about microplastics emissions. Second, facility owners should dispose microplastics that is lost from the field (e.g.due to players, heavy rainfall, or snow removal) in a responsible manner (e.g.return to field or recycling). Last, countries experiencing heavy snow during winter could benefit from having snow deposits, aimed at preventing loss of microplastics during maintenance.
Research on current regulations and policies related to loss of microplastics are lacking coverage and should be prioritized.
Arksey H, O’Malley L (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 8(1):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Article Google Scholar
Armada D, Llompart M, Celeiro M, Garcia-Castro P, Ratola N, Dagnac T, de Boer J (2022) Global evaluation of the chemical hazard of recycled tire crumb rubber employed on worldwide synthetic turf football pitches. Sci Total Environ 812:152542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152542
Article CAS Google Scholar
Berger S (2021) Kartlegging av sinkavrenning fra kunstgressbaner. https://www.godeidrettsanlegg.no/publikasjon/kartlegging-av-sinkavrenning-fra-kunstgressbaner . Accessed 12 June 2023
Brandsma SH, Brits M, Groenewoud QR, van Velzen MJM, Leonards PEG, de Boert J (2019) Chlorinated paraffins in car tires recycled to rubber granulates and playground tiles. Environ Sci Technol 53(13):7595–7603. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01835
Bø SM, Bohne RA, Aas B, Hansen LM (2020) Material flow analysis for Norway’s artificial turfs. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/588/4/042068
Celeiro M, Armada D, Dagnac T, de Boer J, Llompart M (2021a) Hazardous compounds in recreational and urban recycled surfaces made from crumb rubber: Compliance with current regulation and future perspectives. Sci Total Environ 755:142566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142566
Celeiro M, Armada D, Ratola N, Dagnac T, de Boer J, Llompart M (2021b) Evaluation of chemicals of environmental concern in crumb rubber and water leachates from several types of synthetic turf football pitches. Chemosphere 270:128610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128610
Celeiro M, Dagnac T, Llompart M (2018) Determination of priority and other hazardous substances in football fields of synthetic turf by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: a health and environmental concern. Chemosphere 195:201–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.063
Cheng H, Hu Y, Reinhard M (2014) Environmental and health impacts of artificial turf: a review. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4044193
Clarivate (2023). EndNote. https://endnote.com
de Bernardi C, Waller JH (2022) A quest for greener grass: value-action gap in the management of artificial turf pitches in Sweden. J Clean Prod 380:134861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134861
ECHA (2017) An evaluation of the possible health risks of recycled rubber granules usedas infill in synthetic turf sports fields. https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/13563/annexxv_report_rubber_granules_en.pdf/dbcb4ee6-1c65-af35-7a18-f6ac1ac29fe4 Accessed 8 July 2023
ECHA (2021) Opinion related to the request by the Executive Director of ECHA under Art. 77(3)(c) of REACH to prepare a supplementary opinion on: CEN technical report 17519 on risk management measures for artificial pitches and the ESTC study on their effectiveness and the proposed derogation for polymers without carbon atoms in their structure. ECHA/RAC/ A77-O-0000006949–54–01/F. https://echa.europa.eu/documents/10162/17229/art77_3c_mpinfillandnewderogationforpolymers_opi_rac_en.pdf/b85be7e7-c0a8-649a-a0db-56e89e39b3d5?t=1619618145726 Accessed 8 July 2023
ECHA (2023) Granules and mulches on sports pitches and playgrounds. https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/granules-mulches-on-pitches-playgrounds Accessed 13 August 2023
ECHA (n.d) Microplastics . from https://echa.europa.eu/hot-topics/microplastics Accessed 3 April 2023
Federation Internationale de Football Association (2007) Big Count: FIFA survey. https://digitalhub.fifa.com/m/77057f201f8021e3/original/bvuzw21jwf0vvlim8ac7-pdf.pdf Accessed 8 August 2023
FIFA (2017) Environmental Impact Study on Artificial Football Turf
Fleming PR, Watts C, Forrester S (2020) A new model of third generation artificial turf degradation, maintenance interventions and benefits. J Sports Eng Technol 234(1):19–33. https://doi.org/10.1177/1754337120961602
Forskningskampanjen (2017) Sjekk kunstgressbanen. https://www.miljolare.no/aktiviteter/kunstgress/rapport . Accessed 18 July 2022
Forskrift om begrensning av forurensning. https://lovdata.no/dokument/SF/forskrift/2004-06-01-931/KAPITTEL_7-6#KAPITTEL_7-6 . Accessed 1 July 2022
Gomes FO, Rocha MR, Alves A, Ratola N (2021) A review of potentially harmful chemicals in crumb rubber used in synthetic football pitches. J Hazard Mater 409:124998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124998
Grynkiewicz-Bylina B, Rakwic B, Słomka-Słupik B (2022) Tests of rubber granules used as artificial turf for football fields in terms of toxicity to human health and the environment. Sci Rep 12(1):6683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10691-1
Gustavsen, L. (2019). Kunstgressbaner i vannområdet Leira-Nitelva. En undersøkelse av gummigranulat på avveie . https://www.godeidrettsanlegg.no/publikasjon/kunstgressbaner-i-vannomrade-leira-nitelva-en-undersokelse-av-gummigranulat-pa-avveie Accessed 8 July 2023
Harzing AW (2007) Publish or Perish. https://harzing.com/resources/publish-or-perish
Haave M (2018) Preliminær undersøkelse av mikroplast og gummigranulat ved kunstgressbaner. https://www.godeidrettsanlegg.no/sites/default/files/bilder/Preliminaer-undersokelse-mikroplast-gummigranulat-kunstgressbaner-2018.pdf Accessed 18 February 2023
Haave M, Henriksen T, Gomiero A, Bye-Ingebrigsen E (2022) Kartlegging av mikroplastkilder i urbant miljø fra land til sjø - kilder, mengder og spredning
KG2021 (2020) Kunstgressets historie. Gode idrettsanlegg. https://www.godeidrettsanlegg.no/publikasjon/kunstgressets-historie Accessed 18 January 2023
Kole PJ, Van Belleghem FGAJ, Stoorvogel JJ, Ragas AMJ, Löhr AJ (2023) Tyre granulate on the loose; How much escapes the turf? A systematic literature review. Sci Total Environ 903:166221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166221
Korbøl O (2018) Microplastics in freshwater sediments: An investigation of stream sediments downstream of artificial football turfs, Norwegian University of Life Sciences
Krång A-S, Olshammar M, Edlund D, Hållén J, Stenfors E, Winberg von Friesen L (2019) Sammanställning av kunskap och åtgärdsförslag för att minska spridning av mikroplast från konstgräsplaner och andra utomhusanläggningar för idrott och lek
Larsen G, Kvalheim G, Halvorsen O, Roa M, Myhrvold O (2015) Veileder: Kunstgressboka https://www.regjeringen.no/no/dokumenter/veileder-kunstgressboka-v-0975-b/id2425810/
Lassen C, Hansen SF, Magnusson K, Hartmann NB, Rehne Jensen P, Nielsen TG, Brinch A (2015) Microplastics: occurrence, effects and sources of releases to the environment in Denmark
Løkkegaard H, Malmgren-Hansen B, Nilsson NH (2019) Massebalancer af gummigranulat, som forsvinder fra kunstgræsbaner: med fokus på utledning til vandmiljøet
Magnusson S, Mácsik J (2017) Analysis of energy use and emissions of greenhouse gases, metals and organic substances from construction materials used for artificial turf. Resour Conserv Recycl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.03.007
Marsili L, Coppola D, Bianchi N, Maltese D, Bianchi M, Fossi MC (2015) Release of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals from rubber crumb in synthetic turf fields: preliminary hazard assessment for athletes. J Environ Anal Toxicol 5:265. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.100026
Massey R, Pollard L, Jacobs M, Onasch J, Harari H (2020) Artificial turf infill: a comparative assessment of chemical contents. New Solut J Environ Occup Health Policy 30(1):10–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/1048291120906206
Mørk-Kontny CF, Mekki M (2022) Kassert kunstgress og plastholdig, løst fyllmateriale M-2414|2022. https://www.miljodirektoratet.no/publikasjoner/2022/desember/kassert-kunstgress-og-plastholdig-lost-fyllmateriale/
NFF (2021) Oversikt anlegg i Norge - Kretsvis oversikt over anlegg i Norge. https://www.fotball.no/klubb-og-leder/anleggsutvikling/oversikt-anlegg-i-norge/ . Accessed 01 May 2021
Norwegian Environment Agency (n.d) Mikroplast finnes overalt i naturen. https://miljostatus.miljodirektoratet.no/mikroplast . Accessed 24 May 2023
Norwegian Environmental Agency (2021) Gummigranulat fra kunstgressbaner. https://www.miljodirektoratet.no/ansvarsomrader/avfall/avfallstyper/gummigranulat-fra-kunstgressbaner/ . Accessed 02 March 2023
Olofsson U, Lyu Y (2019) A pendulum RIG study on airborne transmission and migration of particles from artificial football turf. In: Proceedings of 10th international scientific conference BALTTRIB 2019
Pochron ST, Fiorenza A, Sperl C, Ledda B, Lawrence Patterson C, Tucker CC, Tucker W, Ho YL, Panico N (2017) The response of earthworms (Eisenia fetida) and soil microbes to the crumb rubber material used in artificial turf fields. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.091
Rabben EL (2020) Tiltaksplan for håndtering av forurenset grunn - Øya kunstgressbane, Malvik
Rambøll (2017) Kartlegging av håndtering av granulat på kunstgressbaner M-954. https://www.miljodirektoratet.no/publikasjoner/2018/januar-2018/kartlegging-av-handtering-av-granulat-pa-kunstgressbaner-2017/
Regnell F (2017) Mikroplaster från Kontgräsplaner. Orsaker till spridning av mikroplaster samt en kvalitativ analyse av spridningen til dränarings- och dagvattenbrunnar Royal Institute of Technology.
Regnell F (2019) Mikroplastspridning från en modernt utformad konstgräsplan med skyddsåtgärder. https://www.ragnsellstyrerecycling.com/globalassets/tyre-company/dokument/rapport---mikroplastspridning-fran-en-modernt-utformad-konstgrasplan-med-skyddsatgarder.pdf
Ruffino B, Fiore S, Zanetti MC (2013) Environmental-sanitary risk analysis procedure applied to artificial turf sports fields. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(7):4980–4992. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1390-2
Russo C, Cappelletti GM, Nicoletti GM (2022) The product environmental footprint approach to compare the environmental performances of artificial and natural turf. Environ Impact Assess Rev 95:106800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.10680
Schilirò T, Traversi D, Degan R, Pignata C, Alessandria L, Scozia D, Bono R, Gilli G (2013) Artificial turf football fields: Environmental and mutagenicity assessment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 64(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9792-1
Sundt P, Skogesal O, Schulze P-E (2016) Primary microplastic: pollution: Measures and reduction potentials in Norway
Tandeberg I, Raabe EB (2017) Kartlegging av gummigranulat-/mikroplastavrenning fra idrettsbaner. https://www.godeidrettsanlegg.no/sites/default/files/bilder/Hovedrapport%20Gummigranulat.pdf
Verschoor AJ, van Gelderen A, Hofstra U (2021) Fate of recycled tyre granulate used on artificial turf. Environ Sci Eur 33:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00459-1
Verschoor AJ, Werner S (2017) Assessment document of land-based inputs of microplastics in the marine environment
Wallberg P, Keiter S, Andersen TJ, Nordenadler M (2016) Däckmaterial i konstgräsplaner. https://www.sdab.se/media/1120/daeckmaterial_i_konstgraesplaner.pdf
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous experts in the field for valuable suggestions on grey reports.
Open access funding provided by NTNU Norwegian University of Science and Technology (incl St. Olavs Hospital - Trondheim University Hospital). This work is funded by Centre for Sports Facilities and Technology at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and the Ministry of Culture and Equality in Norway (22/5700-8).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Høgskoleringen 7a, 7491, Trondheim, Norway
S. M. Bø, R. A. Bohne & J. Lohne
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to S. M. Bø .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (XLSX 71 KB)
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bø, S.M., Bohne, R.A. & Lohne, J. Environmental impacts of artificial turf: a scoping review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05689-3
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2023
Revised : 04 December 2023
Accepted : 25 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05689-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial turf
- Synthetic turf
- Microplastics
- Environment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Literature Review. This is the most time-consuming aspect in the preparation of your research proposal and it is a key component of the research proposal. As described in Chapter 5, the literature review provides the background to your study and demonstrates the significance of the proposed research. Specifically, it is a review and synthesis ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Compiling and synthesizing literature as a justification for one's own research is a key element of most academic work. Nonetheless, both the strategies and components of literature reviews vary based on the genre, length, and prospective audience of a text. This resource gives advice on how to effectively
Literature Review A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources that provides an overview of a particular topic. Literature reviews are a collection of the most relevant and significant publications regarding that topic in order to provide a comprehensive look at what has been said on the topic and by whom.
A literature review is a collection of selected articles, books and other sources about a specific subject. The purpose is to summarize the existing research that has been done on the subject in order to put your research in context and to highlight what your research will add to the existing body of knowledge.
A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the ...
1. Introduction. Not to be confused with a book review, a literature review surveys scholarly articles, books and other sources (e.g. dissertations, conference proceedings) relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, providing a description, summary, and critical evaluation of each work. The purpose is to offer an overview of significant literature published on a topic.
The Research Gap. The third essential ingredient of a high-quality literature review is a discussion of the research gap (or gaps).. But what exactly is a research gap? Simply put, a research gap is any unaddressed or inadequately explored area within the existing body of academic knowledge. In other words, a research gap emerges whenever there's still some uncertainty regarding a certain ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Examples of a published literature review Literature reviews are often published as scholarly articles, books, and reports. Here is an example of a recent literature review published as a scholarly journal article: Ledesma, M. C., & Calderón, D. (2015). Critical race theory in education: A review of past literature and a look to the future.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis.
The basic components of a literature review include: a description of the publication; a summary of the publication's main points; ... Do Your Research Review a number of texts that most closely pertain to your topic and position, and are written by relevant scholars. Understand who the top voices are in your topic's academic field, and be ...
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
Literature Review Literature reviews are a collection of the most relevant and significant publications regarding that topic in order to provide a comprehensive look at what has been said on the topic and by whom. The basic components of a literature review include: a description of the publication a summary of the publication's main points
In a stand-alone literature review, this statement will sum up and evaluate the current state of this field of research; In a review that is an introduction or preparatory to a thesis or research report, it will suggest how the review findings will lead to the research the writer proposes to undertake. Body Purpose:
Components of a Literature Review. The works that make up the literature review fall into three categories: General theoretical literature. This literature establishes the importance of your topic/research. define abstract concepts, discuss the relationships between abstract concepts, and include statistics about the problem being investigated.
Note: This description of the elements of a literature review is geared toward researchers in the arts and humanities. Additional information on conducting literature reviews is available in Dr. Robert Labaree's libguide on organizing research in the social sciences.. A literature review is a discursive essay that critically surveys existing scholarship on a particular topic in the field.
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
In general, literature reviews are structured in a similar way to a standard essay, with an introduction, a body and a conclusion. These are key structural elements. Additionally, a stand-alone extended literature review has an abstract. Throughout, headings and subheadings are used to divide up the literature review into meaningful sections.
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
This short report guides the reader through the types of narrative reviews and describes the narrative review process from conception to completion. This report is an overview on the topic of literature reviews and serves to provide guidance regarding how and when to use a narrative review approach. Authors have many purposes for selecting the narrative review of the literature including ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
In developed nations, it has been estimated that 60% of care provided aligns with the evidence base, 30% is low value and 10% is potentially harmful [].In some areas, clinical advances have been rapid and research and evidence have paved the way for dramatic improvement in outcomes, mandating rapid implementation of evidence into healthcare (e.g. polio and COVID-19 vaccines).
Background As co-design and community-based participatory research gain traction in health and disability, the challenges and benefits of collaboratively conducting research need to be considered. Current literature supports using co-design to improve service quality and create more satisfactory services. However, while the 'why' of using co-design is well understood, there is limited ...
CSR decoupling refers to the misalignment between a company's stated CSR policies and its actual practices, resulting in issues like diminished financial performance and heightened risk. While initially explored in developed economies such as the US, recent research has shifted focus towards developing nations like China. However, a comprehensive review of CSR decoupling literature in the ...
Artificial turfs represent a large environmental issue in terms of waste, microplastic pollution and leaching of chemicals. Artificial turfs are made of several components, the shock absorbing pad, backing, stabilizing infill, performance infill and artificial grass fibers. Common for these, except the stabilizing infill, is being made of plastic and chemicals being released to the environment ...