Multiple Case Research Design
- First Online: 10 November 2021

Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
4766 Accesses
5 Citations
This chapter addresses the peculiarities, characteristics, and major fallacies of multiple case research designs. The major advantage of multiple case research lies in cross-case analysis. A multiple case research design shifts the focus from understanding a single case to the differences and similarities between cases. Thus, it is not just conducting more (second, third, etc.) case studies. Rather, it is the next step in developing a theory about factors driving differences and similarities. Also, researchers find relevant information on how to write a multiple case research design paper and learn about typical methodologies used for this research design. The chapter closes with referring to overlapping and adjacent research designs.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bruns, W. J., & McKinnon, S. M. (1993). Information and managers: A field study. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 5 , 84–108.
Google Scholar
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (2007). Theory building from cases: Opportunities and challenges. Academy of Management Journal, 50 (1), 25–32.
Article Google Scholar
Ferreira, L. D. & Merchant, K. A. (1992). Field research in management accounting and control: A review and evaluation . Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Keating, P. J. (1995). A framework for classifying and evaluating the theoretical contributions of case research in management accounting. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 7 , 66–86.
Lillis, A. M., & Mundy, J. (2005). Cross-sectional field studies in management accounting research—closing the gaps between surveys and case studies. Journal of Management Accounting Research, 17 (1), 119–141.
Ragin, C. C. (2009). Reflections on casing and case-oriented research (pp. 522–534). The Sage handbook of case-based method.
Ridder, H.-G. (2017). The theory contribution of case study research designs. Business Research, 10 (2), 281–305.
Stake, R. E. (2005). Qualitative case studies. In N.K. Denzin & Y.S. Lincoln (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (3rd ed., pp. 443–466).
Vaughan, D. (1992). Theory elaboration: The heuristics of case analysis. What is a case?. In C.C. Ragin & H.S. Becker (Eds.), Exploring the foundations of social inquiry (pp. 173–202). Cambridge University Press.
Walsham, G. (2006). Doing interpretive research. European Journal of Information Systems, 15 (3), 320–330.
Yin, R. K. (2014). Case study research. Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ – Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug , Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2021). Multiple Case Research Design. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_9
Published : 10 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-34356-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-34357-6
eBook Packages : Business and Economics (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Research Guides
Multiple Case Studies
Nadia Alqahtani and Pengtong Qu
Description
The case study approach is popular across disciplines in education, anthropology, sociology, psychology, medicine, law, and political science (Creswell, 2013). It is both a research method and a strategy (Creswell, 2013; Yin, 2017). In this type of research design, a case can be an individual, an event, or an entity, as determined by the research questions. There are two variants of the case study: the single-case study and the multiple-case study. The former design can be used to study and understand an unusual case, a critical case, a longitudinal case, or a revelatory case. On the other hand, a multiple-case study includes two or more cases or replications across the cases to investigate the same phenomena (Lewis-Beck, Bryman & Liao, 2003; Yin, 2017). …a multiple-case study includes two or more cases or replications across the cases to investigate the same phenomena
The difference between the single- and multiple-case study is the research design; however, they are within the same methodological framework (Yin, 2017). Multiple cases are selected so that “individual case studies either (a) predict similar results (a literal replication) or (b) predict contrasting results but for anticipatable reasons (a theoretical replication)” (p. 55). When the purpose of the study is to compare and replicate the findings, the multiple-case study produces more compelling evidence so that the study is considered more robust than the single-case study (Yin, 2017).
To write a multiple-case study, a summary of individual cases should be reported, and researchers need to draw cross-case conclusions and form a cross-case report (Yin, 2017). With evidence from multiple cases, researchers may have generalizable findings and develop theories (Lewis-Beck, Bryman & Liao, 2003).
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches (3rd ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Lewis-Beck, M., Bryman, A. E., & Liao, T. F. (2003). The Sage encyclopedia of social science research methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2017). Case study research and applications: Design and methods . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Key Research Books and Articles on Multiple Case Study Methodology
Yin discusses how to decide if a case study should be used in research. Novice researchers can learn about research design, data collection, and data analysis of different types of case studies, as well as writing a case study report.
Chapter 2 introduces four major types of research design in case studies: holistic single-case design, embedded single-case design, holistic multiple-case design, and embedded multiple-case design. Novice researchers will learn about the definitions and characteristics of different designs. This chapter also teaches researchers how to examine and discuss the reliability and validity of the designs.
Creswell, J. W., & Poth, C. N. (2017). Qualitative inquiry and research design: Choosing among five approaches . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
This book compares five different qualitative research designs: narrative research, phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, and case study. It compares the characteristics, data collection, data analysis and representation, validity, and writing-up procedures among five inquiry approaches using texts with tables. For each approach, the author introduced the definition, features, types, and procedures and contextualized these components in a study, which was conducted through the same method. Each chapter ends with a list of relevant readings of each inquiry approach.
This book invites readers to compare these five qualitative methods and see the value of each approach. Readers can consider which approach would serve for their research contexts and questions, as well as how to design their research and conduct the data analysis based on their choice of research method.
Günes, E., & Bahçivan, E. (2016). A multiple case study of preservice science teachers’ TPACK: Embedded in a comprehensive belief system. International Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 11 (15), 8040-8054.
In this article, the researchers showed the importance of using technological opportunities in improving the education process and how they enhanced the students’ learning in science education. The study examined the connection between “Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge” (TPACK) and belief system in a science teaching context. The researchers used the multiple-case study to explore the effect of TPACK on the preservice science teachers’ (PST) beliefs on their TPACK level. The participants were three teachers with the low, medium, and high level of TPACK confidence. Content analysis was utilized to analyze the data, which were collected by individual semi-structured interviews with the participants about their lesson plans. The study first discussed each case, then compared features and relations across cases. The researchers found that there was a positive relationship between PST’s TPACK confidence and TPACK level; when PST had higher TPACK confidence, the participant had a higher competent TPACK level and vice versa.
Recent Dissertations Using Multiple Case Study Methodology
Milholland, E. S. (2015). A multiple case study of instructors utilizing Classroom Response Systems (CRS) to achieve pedagogical goals . Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (Order Number 3706380)
The researcher of this study critiques the use of Classroom Responses Systems by five instructors who employed this program five years ago in their classrooms. The researcher conducted the multiple-case study methodology and categorized themes. He interviewed each instructor with questions about their initial pedagogical goals, the changes in pedagogy during teaching, and the teaching techniques individuals used while practicing the CRS. The researcher used the multiple-case study with five instructors. He found that all instructors changed their goals during employing CRS; they decided to reduce the time of lecturing and to spend more time engaging students in interactive activities. This study also demonstrated that CRS was useful for the instructors to achieve multiple learning goals; all the instructors provided examples of the positive aspect of implementing CRS in their classrooms.
Li, C. L. (2010). The emergence of fairy tale literacy: A multiple case study on promoting critical literacy of children through a juxtaposed reading of classic fairy tales and their contemporary disruptive variants . Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (Order Number 3572104)
To explore how children’s development of critical literacy can be impacted by their reactions to fairy tales, the author conducted a multiple-case study with 4 cases, in which each child was a unit of analysis. Two Chinese immigrant children (a boy and a girl) and two American children (a boy and a girl) at the second or third grade were recruited in the study. The data were collected through interviews, discussions on fairy tales, and drawing pictures. The analysis was conducted within both individual cases and cross cases. Across four cases, the researcher found that the young children’s’ knowledge of traditional fairy tales was built upon mass-media based adaptations. The children believed that the representations on mass-media were the original stories, even though fairy tales are included in the elementary school curriculum. The author also found that introducing classic versions of fairy tales increased children’s knowledge in the genre’s origin, which would benefit their understanding of the genre. She argued that introducing fairy tales can be the first step to promote children’s development of critical literacy.
Asher, K. C. (2014). Mediating occupational socialization and occupational individuation in teacher education: A multiple case study of five elementary pre-service student teachers . Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (Order Number 3671989)
This study portrayed five pre-service teachers’ teaching experience in their student teaching phase and explored how pre-service teachers mediate their occupational socialization with occupational individuation. The study used the multiple-case study design and recruited five pre-service teachers from a Midwestern university as five cases. Qualitative data were collected through interviews, classroom observations, and field notes. The author implemented the case study analysis and found five strategies that the participants used to mediate occupational socialization with occupational individuation. These strategies were: 1) hindering from practicing their beliefs, 2) mimicking the styles of supervising teachers, 3) teaching in the ways in alignment with school’s existing practice, 4) enacting their own ideas, and 5) integrating and balancing occupational socialization and occupational individuation. The study also provided recommendations and implications to policymakers and educators in teacher education so that pre-service teachers can be better supported.
Multiple Case Studies Copyright © 2019 by Nadia Alqahtani and Pengtong Qu is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification
More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Multiple Case Research Design
In: research design in business and management.
- Author & abstract
- Related works & more
Corrections
(Hochschule Luzern)
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

The case study approach
Sarah crowe.
1 Division of Primary Care, The University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
Kathrin Cresswell
2 Centre for Population Health Sciences, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Ann Robertson
3 School of Health in Social Science, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
Anthony Avery
Aziz sheikh.
The case study approach allows in-depth, multi-faceted explorations of complex issues in their real-life settings. The value of the case study approach is well recognised in the fields of business, law and policy, but somewhat less so in health services research. Based on our experiences of conducting several health-related case studies, we reflect on the different types of case study design, the specific research questions this approach can help answer, the data sources that tend to be used, and the particular advantages and disadvantages of employing this methodological approach. The paper concludes with key pointers to aid those designing and appraising proposals for conducting case study research, and a checklist to help readers assess the quality of case study reports.
Introduction
The case study approach is particularly useful to employ when there is a need to obtain an in-depth appreciation of an issue, event or phenomenon of interest, in its natural real-life context. Our aim in writing this piece is to provide insights into when to consider employing this approach and an overview of key methodological considerations in relation to the design, planning, analysis, interpretation and reporting of case studies.
The illustrative 'grand round', 'case report' and 'case series' have a long tradition in clinical practice and research. Presenting detailed critiques, typically of one or more patients, aims to provide insights into aspects of the clinical case and, in doing so, illustrate broader lessons that may be learnt. In research, the conceptually-related case study approach can be used, for example, to describe in detail a patient's episode of care, explore professional attitudes to and experiences of a new policy initiative or service development or more generally to 'investigate contemporary phenomena within its real-life context' [ 1 ]. Based on our experiences of conducting a range of case studies, we reflect on when to consider using this approach, discuss the key steps involved and illustrate, with examples, some of the practical challenges of attaining an in-depth understanding of a 'case' as an integrated whole. In keeping with previously published work, we acknowledge the importance of theory to underpin the design, selection, conduct and interpretation of case studies[ 2 ]. In so doing, we make passing reference to the different epistemological approaches used in case study research by key theoreticians and methodologists in this field of enquiry.
This paper is structured around the following main questions: What is a case study? What are case studies used for? How are case studies conducted? What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided? We draw in particular on four of our own recently published examples of case studies (see Tables Tables1, 1 , ,2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) and those of others to illustrate our discussion[ 3 - 7 ].
Example of a case study investigating the reasons for differences in recruitment rates of minority ethnic people in asthma research[ 3 ]
Example of a case study investigating the process of planning and implementing a service in Primary Care Organisations[ 4 ]
Example of a case study investigating the introduction of the electronic health records[ 5 ]
Example of a case study investigating the formal and informal ways students learn about patient safety[ 6 ]
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table (Table5), 5 ), the central tenet being the need to explore an event or phenomenon in depth and in its natural context. It is for this reason sometimes referred to as a "naturalistic" design; this is in contrast to an "experimental" design (such as a randomised controlled trial) in which the investigator seeks to exert control over and manipulate the variable(s) of interest.
Definitions of a case study
Stake's work has been particularly influential in defining the case study approach to scientific enquiry. He has helpfully characterised three main types of case study: intrinsic , instrumental and collective [ 8 ]. An intrinsic case study is typically undertaken to learn about a unique phenomenon. The researcher should define the uniqueness of the phenomenon, which distinguishes it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study uses a particular case (some of which may be better than others) to gain a broader appreciation of an issue or phenomenon. The collective case study involves studying multiple cases simultaneously or sequentially in an attempt to generate a still broader appreciation of a particular issue.
These are however not necessarily mutually exclusive categories. In the first of our examples (Table (Table1), 1 ), we undertook an intrinsic case study to investigate the issue of recruitment of minority ethnic people into the specific context of asthma research studies, but it developed into a instrumental case study through seeking to understand the issue of recruitment of these marginalised populations more generally, generating a number of the findings that are potentially transferable to other disease contexts[ 3 ]. In contrast, the other three examples (see Tables Tables2, 2 , ,3 3 and and4) 4 ) employed collective case study designs to study the introduction of workforce reconfiguration in primary care, the implementation of electronic health records into hospitals, and to understand the ways in which healthcare students learn about patient safety considerations[ 4 - 6 ]. Although our study focusing on the introduction of General Practitioners with Specialist Interests (Table (Table2) 2 ) was explicitly collective in design (four contrasting primary care organisations were studied), is was also instrumental in that this particular professional group was studied as an exemplar of the more general phenomenon of workforce redesign[ 4 ].
What are case studies used for?
According to Yin, case studies can be used to explain, describe or explore events or phenomena in the everyday contexts in which they occur[ 1 ]. These can, for example, help to understand and explain causal links and pathways resulting from a new policy initiative or service development (see Tables Tables2 2 and and3, 3 , for example)[ 1 ]. In contrast to experimental designs, which seek to test a specific hypothesis through deliberately manipulating the environment (like, for example, in a randomised controlled trial giving a new drug to randomly selected individuals and then comparing outcomes with controls),[ 9 ] the case study approach lends itself well to capturing information on more explanatory ' how ', 'what' and ' why ' questions, such as ' how is the intervention being implemented and received on the ground?'. The case study approach can offer additional insights into what gaps exist in its delivery or why one implementation strategy might be chosen over another. This in turn can help develop or refine theory, as shown in our study of the teaching of patient safety in undergraduate curricula (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 , 10 ]. Key questions to consider when selecting the most appropriate study design are whether it is desirable or indeed possible to undertake a formal experimental investigation in which individuals and/or organisations are allocated to an intervention or control arm? Or whether the wish is to obtain a more naturalistic understanding of an issue? The former is ideally studied using a controlled experimental design, whereas the latter is more appropriately studied using a case study design.
Case studies may be approached in different ways depending on the epistemological standpoint of the researcher, that is, whether they take a critical (questioning one's own and others' assumptions), interpretivist (trying to understand individual and shared social meanings) or positivist approach (orientating towards the criteria of natural sciences, such as focusing on generalisability considerations) (Table (Table6). 6 ). Whilst such a schema can be conceptually helpful, it may be appropriate to draw on more than one approach in any case study, particularly in the context of conducting health services research. Doolin has, for example, noted that in the context of undertaking interpretative case studies, researchers can usefully draw on a critical, reflective perspective which seeks to take into account the wider social and political environment that has shaped the case[ 11 ].
Example of epistemological approaches that may be used in case study research
How are case studies conducted?
Here, we focus on the main stages of research activity when planning and undertaking a case study; the crucial stages are: defining the case; selecting the case(s); collecting and analysing the data; interpreting data; and reporting the findings.
Defining the case
Carefully formulated research question(s), informed by the existing literature and a prior appreciation of the theoretical issues and setting(s), are all important in appropriately and succinctly defining the case[ 8 , 12 ]. Crucially, each case should have a pre-defined boundary which clarifies the nature and time period covered by the case study (i.e. its scope, beginning and end), the relevant social group, organisation or geographical area of interest to the investigator, the types of evidence to be collected, and the priorities for data collection and analysis (see Table Table7 7 )[ 1 ]. A theory driven approach to defining the case may help generate knowledge that is potentially transferable to a range of clinical contexts and behaviours; using theory is also likely to result in a more informed appreciation of, for example, how and why interventions have succeeded or failed[ 13 ].
Example of a checklist for rating a case study proposal[ 8 ]
For example, in our evaluation of the introduction of electronic health records in English hospitals (Table (Table3), 3 ), we defined our cases as the NHS Trusts that were receiving the new technology[ 5 ]. Our focus was on how the technology was being implemented. However, if the primary research interest had been on the social and organisational dimensions of implementation, we might have defined our case differently as a grouping of healthcare professionals (e.g. doctors and/or nurses). The precise beginning and end of the case may however prove difficult to define. Pursuing this same example, when does the process of implementation and adoption of an electronic health record system really begin or end? Such judgements will inevitably be influenced by a range of factors, including the research question, theory of interest, the scope and richness of the gathered data and the resources available to the research team.
Selecting the case(s)
The decision on how to select the case(s) to study is a very important one that merits some reflection. In an intrinsic case study, the case is selected on its own merits[ 8 ]. The case is selected not because it is representative of other cases, but because of its uniqueness, which is of genuine interest to the researchers. This was, for example, the case in our study of the recruitment of minority ethnic participants into asthma research (Table (Table1) 1 ) as our earlier work had demonstrated the marginalisation of minority ethnic people with asthma, despite evidence of disproportionate asthma morbidity[ 14 , 15 ]. In another example of an intrinsic case study, Hellstrom et al.[ 16 ] studied an elderly married couple living with dementia to explore how dementia had impacted on their understanding of home, their everyday life and their relationships.
For an instrumental case study, selecting a "typical" case can work well[ 8 ]. In contrast to the intrinsic case study, the particular case which is chosen is of less importance than selecting a case that allows the researcher to investigate an issue or phenomenon. For example, in order to gain an understanding of doctors' responses to health policy initiatives, Som undertook an instrumental case study interviewing clinicians who had a range of responsibilities for clinical governance in one NHS acute hospital trust[ 17 ]. Sampling a "deviant" or "atypical" case may however prove even more informative, potentially enabling the researcher to identify causal processes, generate hypotheses and develop theory.
In collective or multiple case studies, a number of cases are carefully selected. This offers the advantage of allowing comparisons to be made across several cases and/or replication. Choosing a "typical" case may enable the findings to be generalised to theory (i.e. analytical generalisation) or to test theory by replicating the findings in a second or even a third case (i.e. replication logic)[ 1 ]. Yin suggests two or three literal replications (i.e. predicting similar results) if the theory is straightforward and five or more if the theory is more subtle. However, critics might argue that selecting 'cases' in this way is insufficiently reflexive and ill-suited to the complexities of contemporary healthcare organisations.
The selected case study site(s) should allow the research team access to the group of individuals, the organisation, the processes or whatever else constitutes the chosen unit of analysis for the study. Access is therefore a central consideration; the researcher needs to come to know the case study site(s) well and to work cooperatively with them. Selected cases need to be not only interesting but also hospitable to the inquiry [ 8 ] if they are to be informative and answer the research question(s). Case study sites may also be pre-selected for the researcher, with decisions being influenced by key stakeholders. For example, our selection of case study sites in the evaluation of the implementation and adoption of electronic health record systems (see Table Table3) 3 ) was heavily influenced by NHS Connecting for Health, the government agency that was responsible for overseeing the National Programme for Information Technology (NPfIT)[ 5 ]. This prominent stakeholder had already selected the NHS sites (through a competitive bidding process) to be early adopters of the electronic health record systems and had negotiated contracts that detailed the deployment timelines.
It is also important to consider in advance the likely burden and risks associated with participation for those who (or the site(s) which) comprise the case study. Of particular importance is the obligation for the researcher to think through the ethical implications of the study (e.g. the risk of inadvertently breaching anonymity or confidentiality) and to ensure that potential participants/participating sites are provided with sufficient information to make an informed choice about joining the study. The outcome of providing this information might be that the emotive burden associated with participation, or the organisational disruption associated with supporting the fieldwork, is considered so high that the individuals or sites decide against participation.
In our example of evaluating implementations of electronic health record systems, given the restricted number of early adopter sites available to us, we sought purposively to select a diverse range of implementation cases among those that were available[ 5 ]. We chose a mixture of teaching, non-teaching and Foundation Trust hospitals, and examples of each of the three electronic health record systems procured centrally by the NPfIT. At one recruited site, it quickly became apparent that access was problematic because of competing demands on that organisation. Recognising the importance of full access and co-operative working for generating rich data, the research team decided not to pursue work at that site and instead to focus on other recruited sites.
Collecting the data
In order to develop a thorough understanding of the case, the case study approach usually involves the collection of multiple sources of evidence, using a range of quantitative (e.g. questionnaires, audits and analysis of routinely collected healthcare data) and more commonly qualitative techniques (e.g. interviews, focus groups and observations). The use of multiple sources of data (data triangulation) has been advocated as a way of increasing the internal validity of a study (i.e. the extent to which the method is appropriate to answer the research question)[ 8 , 18 - 21 ]. An underlying assumption is that data collected in different ways should lead to similar conclusions, and approaching the same issue from different angles can help develop a holistic picture of the phenomenon (Table (Table2 2 )[ 4 ].
Brazier and colleagues used a mixed-methods case study approach to investigate the impact of a cancer care programme[ 22 ]. Here, quantitative measures were collected with questionnaires before, and five months after, the start of the intervention which did not yield any statistically significant results. Qualitative interviews with patients however helped provide an insight into potentially beneficial process-related aspects of the programme, such as greater, perceived patient involvement in care. The authors reported how this case study approach provided a number of contextual factors likely to influence the effectiveness of the intervention and which were not likely to have been obtained from quantitative methods alone.
In collective or multiple case studies, data collection needs to be flexible enough to allow a detailed description of each individual case to be developed (e.g. the nature of different cancer care programmes), before considering the emerging similarities and differences in cross-case comparisons (e.g. to explore why one programme is more effective than another). It is important that data sources from different cases are, where possible, broadly comparable for this purpose even though they may vary in nature and depth.
Analysing, interpreting and reporting case studies
Making sense and offering a coherent interpretation of the typically disparate sources of data (whether qualitative alone or together with quantitative) is far from straightforward. Repeated reviewing and sorting of the voluminous and detail-rich data are integral to the process of analysis. In collective case studies, it is helpful to analyse data relating to the individual component cases first, before making comparisons across cases. Attention needs to be paid to variations within each case and, where relevant, the relationship between different causes, effects and outcomes[ 23 ]. Data will need to be organised and coded to allow the key issues, both derived from the literature and emerging from the dataset, to be easily retrieved at a later stage. An initial coding frame can help capture these issues and can be applied systematically to the whole dataset with the aid of a qualitative data analysis software package.
The Framework approach is a practical approach, comprising of five stages (familiarisation; identifying a thematic framework; indexing; charting; mapping and interpretation) , to managing and analysing large datasets particularly if time is limited, as was the case in our study of recruitment of South Asians into asthma research (Table (Table1 1 )[ 3 , 24 ]. Theoretical frameworks may also play an important role in integrating different sources of data and examining emerging themes. For example, we drew on a socio-technical framework to help explain the connections between different elements - technology; people; and the organisational settings within which they worked - in our study of the introduction of electronic health record systems (Table (Table3 3 )[ 5 ]. Our study of patient safety in undergraduate curricula drew on an evaluation-based approach to design and analysis, which emphasised the importance of the academic, organisational and practice contexts through which students learn (Table (Table4 4 )[ 6 ].
Case study findings can have implications both for theory development and theory testing. They may establish, strengthen or weaken historical explanations of a case and, in certain circumstances, allow theoretical (as opposed to statistical) generalisation beyond the particular cases studied[ 12 ]. These theoretical lenses should not, however, constitute a strait-jacket and the cases should not be "forced to fit" the particular theoretical framework that is being employed.
When reporting findings, it is important to provide the reader with enough contextual information to understand the processes that were followed and how the conclusions were reached. In a collective case study, researchers may choose to present the findings from individual cases separately before amalgamating across cases. Care must be taken to ensure the anonymity of both case sites and individual participants (if agreed in advance) by allocating appropriate codes or withholding descriptors. In the example given in Table Table3, 3 , we decided against providing detailed information on the NHS sites and individual participants in order to avoid the risk of inadvertent disclosure of identities[ 5 , 25 ].
What are the potential pitfalls and how can these be avoided?
The case study approach is, as with all research, not without its limitations. When investigating the formal and informal ways undergraduate students learn about patient safety (Table (Table4), 4 ), for example, we rapidly accumulated a large quantity of data. The volume of data, together with the time restrictions in place, impacted on the depth of analysis that was possible within the available resources. This highlights a more general point of the importance of avoiding the temptation to collect as much data as possible; adequate time also needs to be set aside for data analysis and interpretation of what are often highly complex datasets.
Case study research has sometimes been criticised for lacking scientific rigour and providing little basis for generalisation (i.e. producing findings that may be transferable to other settings)[ 1 ]. There are several ways to address these concerns, including: the use of theoretical sampling (i.e. drawing on a particular conceptual framework); respondent validation (i.e. participants checking emerging findings and the researcher's interpretation, and providing an opinion as to whether they feel these are accurate); and transparency throughout the research process (see Table Table8 8 )[ 8 , 18 - 21 , 23 , 26 ]. Transparency can be achieved by describing in detail the steps involved in case selection, data collection, the reasons for the particular methods chosen, and the researcher's background and level of involvement (i.e. being explicit about how the researcher has influenced data collection and interpretation). Seeking potential, alternative explanations, and being explicit about how interpretations and conclusions were reached, help readers to judge the trustworthiness of the case study report. Stake provides a critique checklist for a case study report (Table (Table9 9 )[ 8 ].
Potential pitfalls and mitigating actions when undertaking case study research
Stake's checklist for assessing the quality of a case study report[ 8 ]
Conclusions
The case study approach allows, amongst other things, critical events, interventions, policy developments and programme-based service reforms to be studied in detail in a real-life context. It should therefore be considered when an experimental design is either inappropriate to answer the research questions posed or impossible to undertake. Considering the frequency with which implementations of innovations are now taking place in healthcare settings and how well the case study approach lends itself to in-depth, complex health service research, we believe this approach should be more widely considered by researchers. Though inherently challenging, the research case study can, if carefully conceptualised and thoughtfully undertaken and reported, yield powerful insights into many important aspects of health and healthcare delivery.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AS conceived this article. SC, KC and AR wrote this paper with GH, AA and AS all commenting on various drafts. SC and AS are guarantors.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/11/100/prepub
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the participants and colleagues who contributed to the individual case studies that we have drawn on. This work received no direct funding, but it has been informed by projects funded by Asthma UK, the NHS Service Delivery Organisation, NHS Connecting for Health Evaluation Programme, and Patient Safety Research Portfolio. We would also like to thank the expert reviewers for their insightful and constructive feedback. Our thanks are also due to Dr. Allison Worth who commented on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
- Yin RK. Case study research, design and method. 4. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Keen J, Packwood T. Qualitative research; case study evaluation. BMJ. 1995; 311 :444–446. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Halani L, Bhopal R, Netuveli G, Partridge M, Car J. et al. Facilitating the Recruitment of Minority Ethnic People into Research: Qualitative Case Study of South Asians and Asthma. PLoS Med. 2009; 6 (10):1–11. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinnock H, Huby G, Powell A, Kielmann T, Price D, Williams S, The process of planning, development and implementation of a General Practitioner with a Special Interest service in Primary Care Organisations in England and Wales: a comparative prospective case study. Report for the National Co-ordinating Centre for NHS Service Delivery and Organisation R&D (NCCSDO) 2008. http://www.sdo.nihr.ac.uk/files/project/99-final-report.pdf
- Robertson A, Cresswell K, Takian A, Petrakaki D, Crowe S, Cornford T. et al. Prospective evaluation of the implementation and adoption of NHS Connecting for Health's national electronic health record in secondary care in England: interim findings. BMJ. 2010; 41 :c4564. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pearson P, Steven A, Howe A, Sheikh A, Ashcroft D, Smith P. the Patient Safety Education Study Group. Learning about patient safety: organisational context and culture in the education of healthcare professionals. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2010; 15 :4–10. doi: 10.1258/jhsrp.2009.009052. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Harten WH, Casparie TF, Fisscher OA. The evaluation of the introduction of a quality management system: a process-oriented case study in a large rehabilitation hospital. Health Policy. 2002; 60 (1):17–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8510(01)00187-7. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stake RE. The art of case study research. London: Sage Publications Ltd.; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Smeeth L, Ashcroft R. Randomised controlled trials in primary care: scope and application. Br J Gen Pract. 2002; 52 (482):746–51. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane R, Verba S. Designing Social Inquiry. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Information technology as disciplinary technology: being critical in interpretative research on information systems. Journal of Information Technology. 1998; 13 :301–311. doi: 10.1057/jit.1998.8. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- George AL, Bennett A. Case studies and theory development in the social sciences. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Eccles M. the Improved Clinical Effectiveness through Behavioural Research Group (ICEBeRG) Designing theoretically-informed implementation interventions. Implementation Science. 2006; 1 :1–8. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-1-1. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Netuveli G, Hurwitz B, Levy M, Fletcher M, Barnes G, Durham SR, Sheikh A. Ethnic variations in UK asthma frequency, morbidity, and health-service use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2005; 365 (9456):312–7. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sheikh A, Panesar SS, Lasserson T, Netuveli G. Recruitment of ethnic minorities to asthma studies. Thorax. 2004; 59 (7):634. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hellström I, Nolan M, Lundh U. 'We do things together': A case study of 'couplehood' in dementia. Dementia. 2005; 4 :7–22. doi: 10.1177/1471301205049188. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Som CV. Nothing seems to have changed, nothing seems to be changing and perhaps nothing will change in the NHS: doctors' response to clinical governance. International Journal of Public Sector Management. 2005; 18 :463–477. doi: 10.1108/09513550510608903. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln Y, Guba E. Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barbour RS. Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog? BMJ. 2001; 322 :1115–1117. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7294.1115. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mays N, Pope C. Qualitative research in health care: Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ. 2000; 320 :50–52. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7226.50. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mason J. Qualitative researching. London: Sage; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brazier A, Cooke K, Moravan V. Using Mixed Methods for Evaluating an Integrative Approach to Cancer Care: A Case Study. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008; 7 :5–17. doi: 10.1177/1534735407313395. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, Huberman M. Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook. 2. CA: Sage Publications Inc.; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pope C, Ziebland S, Mays N. Analysing qualitative data. Qualitative research in health care. BMJ. 2000; 320 :114–116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.114. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cresswell KM, Worth A, Sheikh A. Actor-Network Theory and its role in understanding the implementation of information technology developments in healthcare. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2010; 10 (1):67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-10-67. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Malterud K. Qualitative research: standards, challenges, and guidelines. Lancet. 2001; 358 :483–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05627-6. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Case study research: design and methods. 2. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Yin R. Enhancing the quality of case studies in health services research. Health Serv Res. 1999; 34 :1209–1224. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green J, Thorogood N. Qualitative methods for health research. 2. Los Angeles: Sage; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Howcroft D, Trauth E. Handbook of Critical Information Systems Research, Theory and Application. Cheltenham, UK: Northampton, MA, USA: Edward Elgar; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blakie N. Approaches to Social Enquiry. Cambridge: Polity Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doolin B. Power and resistance in the implementation of a medical management information system. Info Systems J. 2004; 14 :343–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2575.2004.00176.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bloomfield BP, Best A. Management consultants: systems development, power and the translation of problems. Sociological Review. 1992; 40 :533–560. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shanks G, Parr A. Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Systems. Naples; 2003. Positivist, single case study research in information systems: A critical analysis. [ Google Scholar ]
From David E. Gray \(2014\). Doing Research in the Real World \(3rd ed.\) London, UK: Sage.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.

Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Home > JCPS > Vol. 15 (2022) > No. 2
Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision
A systematic approach to multiple case study design in professional counseling and counselor education.
Charmayne R. Adams , University of Nebraska at Omaha Follow Casey A. Barrio Minton , University of Tennessee Follow Jennifer Hightower , Idaho State University Follow Ashley J. Blount , University of Nebraska at Omaha Follow
Document Type
Case study, multiple case study, qualitative research, research design, counseling
Subject Area
Counseling, Counselor Education, Higher Education Counseling, Mental Health Counseling, Rehabilitation Counseling, School Counseling
Case study research is a qualitative methodology that allows researchers to explore complex phenomena in a structured way, that is rigorous and provides an enormous amount of depth. Three scholars are credited with major contributions to the case study literature: Merriam (1998), Stake (1995/2006), and Yin (1994). The purpose of this paper is to explore case study design for use in the counseling profession. The authors provide instruction on the case study scholars, data collection, analysis, and reporting for both single and multiple case study research designs. Finally, implications for student counselors, counselor educators, and counseling professionals are provided.
Recommended Citation
Adams, C. R., Barrio Minton, C. A., Hightower, J., & Blount, A. J. (2022). A Systematic Approach to Multiple Case Study Design in Professional Counseling and Counselor Education. Journal of Counselor Preparation and Supervision, 15 (2). Retrieved from https://digitalcommons.sacredheart.edu/jcps/vol15/iss2/24
Since June 01, 2022
To view the content in your browser, please download Adobe Reader or, alternately, you may Download the file to your hard drive.
NOTE: The latest versions of Adobe Reader do not support viewing PDF files within Firefox on Mac OS and if you are using a modern (Intel) Mac, there is no official plugin for viewing PDF files within the browser window.
- Journal Home
- About this Journal
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Submit Article
- Most Popular Papers
Advanced Search
ISSN: 2164-3288
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
- Open access
- Published: 02 April 2024
Adopting, implementing and assimilating coproduced health and social care innovations involving structurally vulnerable populations: findings from a longitudinal, multiple case study design in Canada, Scotland and Sweden
- Gillian Mulvale ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0546-6910 1 ,
- Jenn Green 1 ,
- Glenn Robert 2 , 5 ,
- Michael Larkin 3 ,
- Nicoline Vackerberg 4 , 5 ,
- Sofia Kjellström 5 ,
- Puspita Hossain 6 ,
- Sandra Moll 7 ,
- Esther Lim 8 , 9 &
- Shioma-Lei Craythorne 3
Health Research Policy and Systems volume 22 , Article number: 42 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Innovations in coproduction are shaping public service reform in diverse contexts around the world. Although many innovations are local, others have expanded and evolved over time. We know very little, however, about the process of implementation and evolution of coproduction. The purpose of this study was to explore the adoption, implementation and assimilation of three approaches to the coproduction of public services with structurally vulnerable groups.
We conducted a 4 year longitudinal multiple case study (2019–2023) of three coproduced public service innovations involving vulnerable populations: ESTHER in Jönköping Region, Sweden involving people with multiple complex needs (Case 1); Making Recovery Real in Dundee, Scotland with people who have serious mental illness (Case 2); and Learning Centres in Manitoba, Canada (Case 3), also involving people with serious mental illness. Data sources included 14 interviews with strategic decision-makers and a document analysis to understand the history and contextual factors relating to each case. Three frameworks informed the case study protocol, semi-structured interview guides, data extraction, deductive coding and analysis: the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research, the Diffusion of Innovation model and Lozeau’s Compatibility Gaps to understand assimilation.
The adoption of coproduction involving structurally vulnerable populations was a notable evolution of existing improvement efforts in Cases 1 and 3, while impetus by an external change agency, existing collaborative efforts among community organizations, and the opportunity to inform a new municipal mental health policy sparked adoption in Case 2. In all cases, coproduced innovation centred around a central philosophy that valued lived experience on an equal basis with professional knowledge in coproduction processes. This philosophical orientation offered flexibility and adaptability to local contexts, thereby facilitating implementation when compared with more defined programming. According to the informants, efforts to avoid co-optation risks were successful, resulting in the assimilation of new mindsets and coproduction processes, with examples of how this had led to transformative change.
Conclusions
In exploring innovations in coproduction with structurally vulnerable groups, our findings suggest several additional considerations when applying existing theoretical frameworks. These include the philosophical nature of the innovation, the need to study the evolution of the innovation itself as it emerges over time, greater attention to partnered processes as disruptors to existing power structures and an emphasis on driving transformational change in organizational cultures.
Peer Review reports
Growing recognition by governments internationally of the need to involve the perspectives of people using public services when designing, delivering and improving those services has been described as a Participatory Zeitgeist reflecting the “spirit of our time” [ 1 , 2 (p247)]. Researchers and designers have developed various approaches drawn from different disciplines and using different labels (for example, codesign, cocreation, coproduction) that align with principles in the citizen engagement literature [ 3 ]. These approaches recognize that service users have experiences and assets and can contribute to service design and delivery along with professional expertise, rather than simply being passive recipients of services designed and delivered by others [ 3 , 4 ]. While these approaches can be used with anyone, they have been increasingly applied to promote the inclusion of structurally vulnerable populations in the design and delivery of innovative health and social care services that seek to support them.
While coproduction has the potential to reform inequitable structures and social processes, excluding vulnerable groups or involving them in a tokenistic manner may unintentionally reinforce existing power imbalances [ 4 , 5 ]. For example, gaps have been noted between the rhetoric of service user involvement in international mental health policy and the readiness to adopt such policies in practice [ 6 ]. Challenges have also been noted in incorporating the voices of individuals with complex needs in improving care coordination across health and social services [ 7 ].
Despite increasing attention to coproduction in the literature and practice, knowledge gaps exist with respect to the implementation of coproduction involving vulnerable populations in different contexts [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. An international symposium of coproduction researchers and people with lived experience held in Birmingham, England in 2017 identified the need for research to understand how exemplary coproduction innovations involving structurally vulnerable groups originated and their assimilation into routine practice [ 11 ]. To our knowledge, established implementation science models have yet to be applied to coproduction, where service users and service providers are cocreating innovations during the process of implementation [ 12 ].
In this paper, we present findings from a longitudinal case study exploring the factors and processes that influence the adoption, implementation and assimilation of three diverse coproduced public service innovations involving structurally vulnerable groups. We explored the perspectives of strategic leaders involved in advancing coproduction processes involving vulnerable groups. Our analysis proceeds through the lens of existing frameworks from the literature to discuss the outer context (economic, social, political, geographical), inner context (organizational and community considerations), individual factors, innovation features and process considerations [ 13 ].
Conceptual foundations: coproduction, structural vulnerability and implementation processes
Coproduction: Coproduction has been defined as “… involvement of public service users in the design, management, delivery and/or evaluation of public services” [ 4 ]. A core feature of coproduction approaches is that they are applied in a flexible manner, dynamically and innovatively responding to local needs and context [ 14 ].
Structural vulnerability: We adopt the term structurally vulnerable populations to recognize that vulnerability is not inherent in these populations but rather in the social, economic and political systems in which they are embedded [ 15 , 16 ]. Examples include individuals who may require multiple health and/or other public services, including people with complex and intersecting health needs (for example, heart failure and dementia) along with poverty, homelessness and/or being members of newcomer or racialized groups. Structural barriers (for example, lack of trust, language, cultural, scheduling, financial) and power relations may prevent them from engaging in coproduction.
Adoption, implementation and assimilation: We draw on and combine elements from three theoretical frameworks to guide this research. The first is the Diffusion Of Innovation (DOI) model [ 17 ], which identifies how political, social, economic, cultural, and organizational factors and processes affect fidelity and adoption during the diffusion of service innovation. The second is the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (CFIR) [ 18 , 19 ], which demonstrates the importance of contextual factors at multiple levels (external context, internal context, innovation features, processes and individual characteristics) in shaping the implementation of service improvements. The third is Lozeau et al.’s (2002) compatibility gaps [ 20 ], which characterize different forms of assimilation of innovations into routine practice [ 20 , 21 ]. Based on these frameworks, we define innovation as a novel set of behaviours, routines and ways of working that are directed at improving health outcomes, administrative efficiency, cost effectiveness or users’ experiences, and that are implemented by planned and coordinated action [ 20 ]. We define adoption as the incremental considerations and progressive individual and collective decision-making from pre-contemplation through exploration by which organizations ultimately decide to adopt the innovation (programme/model/process). Implementation describes the formal strategies to promote the integration of innovations into existing practices. Assimilation is the informal process by which, over time, innovations become part of routine ways of doing things. Assimilation can be characterized as (a) transformation when there is high fidelity to the model and the organization adjusts its functioning to fit the assumptions of the model; (b) customization when the model is adapted to the context and the organization adjusts its practices; (c) loose coupling whereby the innovation is adopted only superficially, while the functioning of the organization remains largely unaffected; or (d) co-optation whereby the innovation becomes captured and distorted to reinforce existing organizational roles and power structures [ 21 ].
Study aim and design
We adopt a longitudinal multiple case study approach to understand the dynamic nature by which three coproduced innovations intended to address the needs of vulnerable populations were adopted, implemented and assimilated [ 22 ]. Case study research is well suited to studying contemporary phenomena in their real-life contexts, and theory is often adopted to focus the analysis, allowing the theory to be augmented or revised based on emerging findings [ 22 ]. To meet the criteria of being a ‘case’, an innovation had to be underpinned by a coproduction model involving structurally vulnerable populations in the design, management, delivery and/or evaluation of a public service that has advanced through these phases. Concepts from the CFIR, DOI and assimilation frameworks described above informed the case study protocol, semi-structured interview questions, data extraction and coding.
Case selection
The three cases were selected through the networks of the investigators to illustrate how coproduction involving vulnerable populations can be advanced in different contexts: the region of Jönköping, Sweden striving for better patient outcomes and experiences by tailoring care to the needs of people with multiple complex needs (Case 1 – ESTHER); the city of Dundee, Scotland aiming to advance the recovery of people with mental illness through greater collaboration with those with lived experience and among service organizations (Case 2 – Making Recovery Real [MRR]); and a rural and an urban branch of a national community mental health organization in a Canadian province that adapted the English Recovery College model of coproduced educational programming to support the recovery of people with serious mental illness (Case 3 – Canadian Mental Health Association [CMHA] Manitoba and Winnipeg and CMHA Central branches’ Learning Centres in Manitoba, Canada) (see Tables 1 , 2 and 3 ).
The study team were familiar with each of these cases and were confident in having good access to them over time. Additionally, their different national contexts offered the opportunity to consider macro-level factors. While each of these countries’ health and social care systems are largely publicly funded, funding is the responsibility of different levels of government (municipal, provincial and/or national) and services are administered and delivered primarily by local governments and/or designated authorities (see Table 4 ).
Data sources and collection
Data sources include relevant academic and grey literature identified through electronic searches and/or recommended or shared by local gatekeepers and key informants to inform the background case context for the individual case analyses, and the interview guides (see Table 5 , and Table S1 in Additional file 1 for more details). Research team members (GM, JG, GR, NV, PH, SC, SS) conducted 45–60 minute long semi-structured interviews in person or online between November 2019 and August 2021. To help understand the history and context of each case, key informants were strategic decision-makers and programme managers affiliated at the time with the organizations leading, participating in or supporting the local initiatives, and who were familiar with the history of how the coproduced innovations emerged, their developmental timeline and coproduction’s role in the overall system. Footnote 1
The interview guide questions probed about this history with a focus on the contextual factors that influenced adoption and implementation and the extent to which coproduction has been assimilated into routine practice. Data were gathered through investigator field notes, the audio-recording and transcription of interviews, timelines, hand-written notes and/or audio-recordings of team meetings to capture member checking with local collaborators, and case team memos of decision points.
To maintain participant anonymity, participant codes are used in the text, identified by a location code (for Case 1, JKG = Jönköping, Sweden; for Case 2, DND = Dundee, Scotland; for Case 3, OTH = Other [for example, national, international informants], PLP = Portage la Prairie, Manitoba, Canada; WPG = Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada), and a participant number (that is, 01, 02, 03 and so on). For example, an informant from Dundee could be DND-03. Note that the perspectives of service providers and people with lived experience of structural vulnerability were not the focus here but are considered in subsequent waves of our data collection to understand their experiences of coproduction in practice.
Data analysis
A common coding framework was developed iteratively to capture factors and processes influencing adoption, implementation and assimilation by combining elements of the theoretical frameworks to remove overlap and promote consistency of understanding when coding and interpreting the data. Table S2 presents this in more detail (see Additional file 2 ).
The initial data extraction was performed by the research team affiliated with each case, and the project research coordinator worked with the local research coordinator for each case to ensure consistency across cases. Documentary evidence analysis primarily informed our understanding of the historical context and overview of each case. All data were coded and analysed using a deductive approach; a common coding scheme and thematic analysis were employed, respectively, based on the theoretical propositions and concepts in the CFIR and DOI models, and allowing for emergent themes, particularly in relation to the coproduction context [ 22 ]. A visual timeline was created to understand the initiation and growth of coproduction in each case. Interview data was triangulated with documentary evidence and field notes. Analysis proceeded on a case-by-case basis, followed by a cross-case analysis.
Qualitative validity and reliability
The research team comprised four members who were familiar with one of the three cases prior to the study (the ESTHER case), as well as eight members who were not familiar with any of the cases. One member of the team had been closely involved with the development of the ESTHER case over a long period of time. The use of a common and detailed case study protocol and data management system, central and local research coordination by case, monthly investigator meetings and tri-annual full team meetings including collaborating organization representatives were strategies used to enhance qualitative validity. The common coding framework and frequent team discussions helped to ensure consistency and enhanced reliability. Data were triangulated across sources, the analysis was triangulated across investigators and theories, and member checked at various stages with the full team of investigators and collaborators [ 23 ].
Ethical considerations
Research ethics clearance was obtained from the relevant academic research ethics boards (McMaster University Research Ethics Board [MREB Project ID 2066], Aston University Ethics Committee [Rec Ref #1611]; King’s College London Research Ethics Office [Reference Number MOD-19/20-17350]; SingHealth Centralized Institutional Review Board [CIRB Ref# 2020/2341]; and Swedish Ethical Review Authority [Etikprövningsmyndigheten, Dnr 2019-06373]), and in light of this, ethics review was waived by the boards of the collaborating organizations (Canadian Mental Health Association, Manitoba & Winnipeg branch, the East of Scotland Research Ethics Service). Participants received letters of information outlining the study objectives, protocol and risks prior to consenting in writing. Data were collected and stored locally and shared across sites as anonymized, encrypted and password-protected files.
We outline the historical context and analysis of contextual factors influencing adoption and implementation, discuss assimilation by case and then present a cross-case analysis. Tables 1 , 2 and 3 above capture the key features of each case, Figs. 1 , 2 and 3 summarize the adoption, implementation and assimilation timelines, and Tables 6 , 7 and 8 summarize the cross-case analysis.
Historical context: ESTHER is a complex system of public health and social care services run by 13 municipal councils in Region Jönköping County, Sweden that has brought intersectoral health and social care providers together since the 1990s to increase coordination and to redefine service experiences around the needs of the person receiving the services. In a context of restricted public sector funding, ESTHER began in 1997, initially for 2 years, with the aim of finding ways to meet population health needs using approaches other than increased hospital bed capacity. Hospital leaders in Region Jönköping County aimed to transform ways of working and to prevent hospital admissions through what informants called “radical customization”, which considered the needs of individual patients using a bottom-up change process referred to as health process re-engineering. This approach 'shadowed' a patient with complex needs through their health service experience journey and included interviews and surveys with patients, staff and government officials and observations of care encounters and processes to gain new insights into what was needed to improve the system from the patient perspectives. Storytelling of the experience of 'Esther', a persona of an elderly person with complex health needs, actualized this process, pointing out what needed to be done differently by demonstrating the importance of focusing on the experience of the person receiving care. The lessons learned from ESTHER fuelled health and social service-wide change, including coproduction with patients beginning in 2006 through patient roles on advisory committees and councils, and has expanded to include initiatives such as ESTHER cafes, ESTHER coach training and ESTHER family meetings, among others.
Adoption: In the ESTHER case 'adoption' of coproduction was an emergent phenomenon that took place over a 10 year period as ongoing improvement efforts, aimed from the outset at better capturing the lived experience of people with complex needs, evolved in terms of how their perspectives were incorporated in design and decision-making. This initially began with interviews and shadowing patients and bringing staff on board with this approach, until by 2006, Esthers became more directly involved in coproducing system improvements. In the internal context , healthcare process re-engineering efforts since the 1990s centred on the question of “What is best for Esther?” and demonstrated the importance of person-centred care and emphasizing the experiences of the person in need of complex care, laying the foundation for a coproduction approach to emerge. In the external context , system-wide efforts by health and social leaders to create a system map led to ESTHER becoming more than a health quality improvement project but rather a health and social systems-wide movement. From a process perspective, the initial project’s evaluation results indicated a 20% reduction in hospital beds, an achievement that earned recognition in the external context through two national awards. As project funding ended, the benefits of the ESTHER philosophy were recognized, and ESTHER transitioned from a project to a 'network' without funding. Over the next few years, the ESTHER Network further developed as 'cousins' emerged across Sweden, and the approach was adopted in other countries, including Italy, England, Scotland and France.
By 2006, ESTHER in Sweden transitioned toward adopting coproduction approaches that actively invited participation of people with lived experience expertise (Esthers) in coproducing ongoing innovations; however, this process was emergent and not uniform. The flexibility of a guiding philosophy was a key feature that enabled this emergence of innovation in the coproduction approach. By this time, some individual system leaders had come to recognize that keeping the focus on value and what is best for the person being treated in their daily lives would lead to better results than a preoccupation with resources and cost cutting. ESTHER had transformed relationships internally in hospitals to team-based (doctor‒nurse) coleadership and externally across the region via interorganizational collaboration between hospitals, primary care, community care and social care to improve Esthers’ care journeys. These collaborative ways of working were preparation for collaboration with Esthers, helping to create receptivity among senior leaders to coproduction. Nonetheless, at this stage of adoption there was still some internal resistance, particularly at middle management and staff levels, as Esthers began attending and sharing stories about their experiences at leadership meetings.
“I think one of the most important decisions was to take patient in the room. In addition, there was a lot of resistance”. [JKG-01]
Implementation: Once the decision to work directly with Esthers was taken, the implementation of coproduction has continued to unfold, albeit unevenly and opportunistically. Around this time, factors in the outer context shaped ESTHER’s continued development, as Esthers became increasingly present in local patient committees and began to participate in and influence the ESTHER steering committee. While ongoing primary care reform was a distraction for many health service managers, an external network of Esthers developed from different programmes across municipalities, and annual ESTHER 'family' meetings were held, where Esthers could convene to share experiences and ideas, strengthening the grassroots support. ESTHER was again gaining international recognition, becoming the subject of a BBC documentary film and being declared “one of the coolest innovations in the world” by CNN.
In the internal context , further developments included the creation of internal structures that were funded to support greater involvement of patients with multiple vulnerabilities in coproduction activities: The ESTHER Competence Center, training healthcare teams to follow the ESTHER philosophy, and ESTHER Coach quality improvement training programmes for approximately 30 health and social service providers to become new ESTHER Coaches each year, and with growing numbers of Esthers as faculty. Key features of the approach were supportive of grassroots growth. Coaches developed innovations on an ongoing basis with input from Esthers, and health and social service providers remarked that the ESTHER philosophy takes them back to the reasons they entered their professions. At the same time, the bottom-up nature driving innovation continued to be threatening to some individuals in senior leadership positions who were more distanced from observing the benefits.
“ESTHER is very much bottom-up. So, you are very close to ESTHER … you see what’s going on and what you can do better. The steering is from the bottom, and then the managers got a bit threatened. I think there was suddenly too much; the movement was suddenly too big. So, people were reacting to that. …That still is a challenge”. [JKG-01]
Creative approaches have been used to foster growth despite this resistance. Small changes such as renaming committees have enabled participation by Esthers.
“We had our ESTHER Strategy Days. It was once a year that we had a really big gathering about what we are going to focus on. And we invited managers, we invited the coaches, we invited Esthers. So, one-third of the group [of 30] were Esthers and the other were working in health and social care. And, for me, that was a very big success, but it also became a threat. So, they took it away because they said you can’t have strategy day because you are not a manager. So, we changed the name. Now we have the ESTHER Inspiration Day”. [JKG-01]
The implementation process has been incremental and iterative to balance the grassroots pressure for innovation with the internal resistance to patients as equal partners, while ensuring real change results. As an example, in 2007, ESTHER cafes were introduced to connect Esthers and to identify the improvement possibilities most important to Esther. These cafes continue to be held four times per year and have attracted a wide audience, including clinicians and politicians. Esthers share their stories to help leaders and practitioners understand individual experiences, but the process also builds credibility: it requires a check-in with leaders and service providers about what they heard and whether that is consistent with what the storyteller feels is most important, and agreements are reached before the meeting ends about specific action(s) that will be taken to address what is important to Esthers.
“When we listen to a story, we ask the group, ‘What did you hear?’ And we are trying to confirm whether we are hearing different things than [what] Esthers really mean. So, the staff sometimes think, ‘This is very important’. But when we give that back to Esther, she says, ‘Well, that’s not so important for me. For me, this is important’. So, the ESTHER cafe is an activity to identify improvement possibilities. That’s one of the activities”. [JKG-02]
Assimilation: By 2016, ESTHER had evolved from being a network to becoming assimilated as a mindset – the central concept driving innovation in the system in the Jönköping Region. By this time, the decision was made to withdraw funding specific to ESTHER other than to support coach education and to have no single person responsible as leader, as it is intended to be fully assimilated as part of the normal way of working. At the same time, without dedicated funding and leadership, questions remain about sustainability.
“As I said, it is a mindset. Now it is implemented in these programs – the question: ‘What’s best for Esther?’– you will find you can’t find one person who is responsible for ESTHER in Sweden, but there is a programme group and the programme group is trying to find out ways how to spread it in the whole region, because we have some difficulties there. It’s a mindset and it should be part of the daily work. And we are getting there. I think it’s very much dependent who is leading all these kind of leadership programmes, and do they really take the ESTHER philosophy to heart?” [JKG-02]
At this point, all steering groups were removed, being seen as no longer necessary. This removal of infrastructure (formal structures, funding) initially concerned committed leaders, with a risk of co-optation of the ESTHER concept without true adherence in practice. However, there was a widespread sense among interviewees that the ESTHER philosophy has been assimilated as a core value that continues to influence all activities, permeating the culture to become the routine practice in Jönköping.
“It’s a very normal mindset in one of our hospitals to ask the question, ‘What’s best for Esther?’ That’s just a normal way of working and people are just using that word and that question”. [JKG-FL-01]
See Fig. 1 for a summary of the Case 1 adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline.
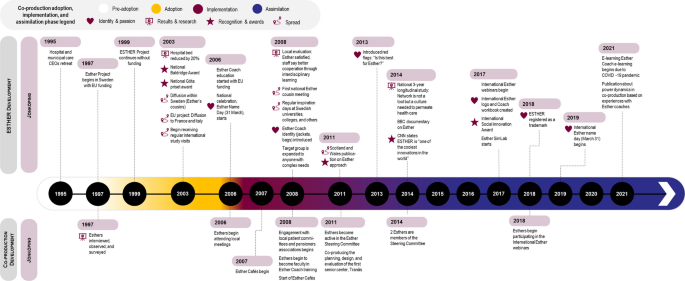
Case 1 ESTHER coproduction adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline
Historical context: Making Recovery Real gives people with lived experience of mental health difficulties the opportunity to be at the centre of decision-making, service design and practice development in the community of Dundee, Scotland by changing the terms of the dialogue about recovery, mental health and well-being. It began in 2015 as a collaboration of 10 local public, voluntary and community organizations who responded to a call from the Scottish Recovery Network (SRN) to work together to take a new approach to improve the experience and outcomes for people living with mental illness. Initially, the partner organizations endeavoured to develop and deliver more recovery-focused policies and practice by centring lived experience in answering the question: “How can we make recovery real in Dundee?” They brought together interested people, including those with lived experience, at collaborative cafes; a series of events where priorities and accompanying actions were identified, and where participants were equal contributors to the process and its outcomes. To foster the integration of lived experience into system design and practice, the priorities identified were to (i) collect and share recovery stories so that lived experience is at the core of service design, delivery and practice; (ii) develop peer support roles and training; and (iii) celebrate recovery [ 24 ].
Adoption: In the external context , the mental health system remained dominated by the medical model, a lack of system innovation and acute services prioritized over community services. Yet, recent Scottish health and social care system integration has supported partnership working. Simultaneously, SRN, a national voluntary organization established in 2004 to promote recovery principles within the mental health system, was shifting from working with the National Health Service towards building coalitions of change within communities and a whole-systems approach to promoting recovery. SRN solicited proposals from local groups and organizations, offering their support for community-based collaborations that would involve people with lived experience in developing local initiatives to support mental health.
Factors in Dundee’s internal context also converged to support a proposal put forward to SRN for an innovative approach. First, the Dundee Third Sector Interface (TSI), which supports the representation of third sector organizations in local authority planning, had been working to better involve people with lived experience in mental health system planning, and meetings with their network members were becoming more recovery focused. A recent inquiry into mental health services and a fairness commission on poverty (a longstanding local issue) also motivated the local council and Health and Social Care Partnership (HSCP) to take innovative action focused on prevention versus mitigation.
“And I think the Health and Social Care Partnership realized that they needed to do more than mitigation … they have been really, really clear on the need for new ways of doing things for about the last 10, 15 years”. [DND-02]
Furthermore, Dundee City was preparing to develop a new mental health strategic plan and, in the hope of influencing the strategic priorities and the future approach to engagement locally, the TSI brought partners from across community services, the local authority and representative groups who had been attempting to make change in the system to submit a proposal for SRN’s support. Individual leaders from within the partner organizations, motivated by their own lived or professional experience, were drawn by the innovation’s features : to support any concerned citizen to contribute their inherent resources through meaningful involvement and an asset-based approach:
“… So lived experience is essential, bringing people together, involving everybody who wants to be involved in each aspect of the process; so, firstly in agreeing what it is they want to achieve, then in making sure that it is carried out, also in having an actual role in actively carrying it out, so not just identifying things other people should do but having a vested interest and an active contribution to the activities that are going to be – whatever it is that’s going to be done differently, basically”. [DND-04]
SRN acted as a change agency, helping to alleviate tensions among the coalition and supporting their process of exploring the opportunity and submitting a successful proposal.
Implementation: First, SRN helped to bring the individuals involved together to establish a shared vision for the process among the local integration bodies (TSI and HSCP) and a TSI-supported service user network, reducing competition among the service provider partners. Within the inner context of the partnership, there was a commitment to coproduction processes and peer support as a critical opportunity to incorporate more lived experience into the mental health system. Despite these efforts, some of the original partners could not align themselves with the experience-led approach and discontinued their involvement knowing they could return at any time. Undaunted, the remaining partners proceeded by working with the “willing”, beginning with increasing local knowledge of recovery approaches and exploring what recovery meant to local citizens.
“… at the very start, it was a case of, ‘Right. We don’t really know where we want this to go. And actually, are we the ones to be dictating where this should go? No, we’re not. What’s most important is that we’re listening to people with lived experience, people on the ground, and they should be the ones that are telling us what needs to be changing’. So from the beginning, the sort of first step was looking at how we can engage with local people. And we were really keen to make sure that it was meaningful … And we thought this involvement can’t be tokenistic. People need to be on board, and it needs to be collaborative from the start”. [DND-05]
To build connection and trust between participants while shifting to a peer-led approach, the implementation process involved facilitating a series of coproduced, discussion-based events where people with lived experience were invited to be involved in all stages from planning and executing the events, to identifying and achieving priorities. The role of professionals shifted to “being on tap, not on top” [DND-02]. SRN provided developmental support to the Dundee partners to deliver the events, the features of which were welcoming and inclusive, avoiding formal presentations in favour of fun, health-promoting activities that allowed community members to feel heard, and demonstrated alignment with their own ideas and values.
“… what we did—and I would say I think that really set the tone – was rather than have lots of presentations, what we did was, at the event, we welcomed everybody, but we invited lots of the groups to run taster sessions of the things they did. So, that actually brought a lot of people with lived experience because they were coming along to demonstrate their finger painting. There was hula-hooping. There was wellness action planning. There was how to sleep well [sessions]. And in every corner of this venue, there was little groups of people who were painting pebbles, things like that. And then in the afternoon, we had a big conversation happen, world café style. And the sort of comments we got from people were, ‘I felt this was my event. This was for me. It wasn’t for them, the professionals’”. [DND-02]
From these discussions, it emerged that understanding local experiences of personal recovery was the most preferred and effective conveyor of local knowledge and motivator for change for the range of stakeholders. Storytelling became the primary vehicle for relationship building. Peoples’ stories were compiled into a film that premiered at a well-attended, prestigious 'red-carpet' event at a local cinema house, and subsequently became a tool to foster collaborative conversations at engagement events.
“And the film galvanised things and I think because we’d moved beyond that individual telling their story to having a 20 minute film of people reflecting on recovery, which is quite different from telling a story, say, of illness”. [DND-02]
The film drew strategic attention to MRR. This culminated into a consensus to embed recovery, backing for continued peer support and recovery work into the new Dundee Mental Health Strategy and accompanying action plan.
Assimilation: The MRR partner organizations have adopted a peer-led approach to their efforts to promote mental health recovery going forwards. Partners are also now far more involved in collectively determining the distribution of funding through the HSCP and in designing new mental health services.
Locally, the MRR approach has also been included in the Dundee Mental Health Strategy, granting the third sector more influence and collective power in local health and social care planning. The adoption of the MRR approach by the Dundee HSCP has strengthened the importance of mental health locally, dovetailing with the recommendations of the independent inquiry on poverty. At the national level, a Scottish government funding programme to increase the number of mental health workers in community-based services provided an opportunity for the HSCP to fund additional peer support roles, a key initiative within MRR.
Overall, the MRR partnership can be said to have had a transformative effect locally. It has led to better working relationships between providers and continues to drive progress. Furthermore, lived experience is being built into the system infrastructure through actions prioritized in experience-centred collaborative conversations: expansion of the local peer recovery network, development of peer support roles, implementation of peer-led services, peer support training provision and building recovery awareness. A key feature of ongoing progress has been that lived experience partners have been able to move in and out of active participation roles throughout the process, as their recovery journeys and contexts have allowed.
“There was that sense of collaboration that continued ... We kind of all came together to discuss how we felt our organizations could contribute to that bigger picture and the strategic objectives moving forward, and not just the strategic objectives in relation to Making Recovery Real but the wider kind of city and what they were looking for in relation to the local mental health strategy and the city plan”. [DND-05]
Participants describe the process as a difficult yet joyful and rewarding journey. For some organizations, the introduction of the MRR approach has motivated significant recovery-oriented change in their values and structure, further cementing system-level impact.
“Making Recovery Real has really been – I suppose we’ve adopted the principles and approaches … We try to adopt those as far as possible in all of our work. And we don’t badge it all Making Recovery Real, but we use the learning from it, I would say, in everything we do now, everything in the programme”. [DND-04]
See Fig. 2 for a summary of the Case 2 adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline.
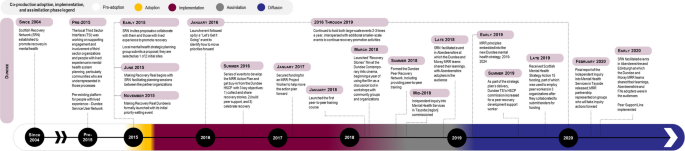
Case 2 Making Recovery Real coproduction adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline
Historical context: CMHA Learning Centres began development in Manitoba in 2015 as a coproduced adaptation and renaming of Recovery Colleges, which originated in England in 2009 with a focus on people with lived/living experience of serious mental illness. The aim of Recovery Colleges is to bring the lived experience of people with mental illness and other community members together with professional expertise to locally plan, develop and deliver educational courses about mental health and recovery, with the aim of empowering people to support their mental health and well-being. The concept of recovery education originated in the USA [ 25 , 26 ], and before adopting the Recovery College model, CMHA Winnipeg had offered psychosocial rehabilitation (PSR)-based recovery education since the early 1990s. In 2015, the CMHA Winnipeg branch leader conducted an internal evaluation of this programming, which suggested that improvement was needed to meet the psychosocial health and well-being needs of the community. Around the same time, the new leader of the CMHA Central branch in Portage la Prairie, Manitoba sought a fresh approach to its clubhouse programme, a mutual support drop-in centre, in response to member feedback. Leaders and service users of both branches embraced the Recovery College and coproduction approach to better meet client needs. CMHA Learning Centres build on the Recovery College principles, with the programming and the target audience expanded to promote living well among the broader population, as well as recovery education for people with lived experience of mental illness. The CMHA Central branch’s Thrive Learning Centre and the CMHA Winnipeg and Manitoba branch’s Well-being Learning Centre opened in September 2017 and January 2018, respectively.
Adoption: In the external context , the national policy context was supportive of a recovery and well-being approach; it was the focus of consultations over the 2008–2012 period prior to the release of Canada’s mental health strategy [ 27 ]. This enabled Manitoba bureaucrats to pressure provincial government leaders to cosponsor a 'Recovery Days in Mental Health' conference held in Winnipeg in June 2015. An English Recovery College champion was a keynote speaker and sparked interest in the model among CMHA branches in Manitoba. The Winnipeg Regional Health Authority (RHA), the major funder of the Winnipeg CMHA branch, also supported recovery and mental health promotion approaches. Informants reported that Manitoba’s culture of innovation and solidarity, with its many small rural communities, also aligned with the coproduction philosophy of inclusive innovation.
In the internal context , the Recovery College model resonated with existing branch cultures of deep commitment to recovery-oriented work and strong peer support foundations. CMHA’s federated structure allowed each branch autonomy to develop its own programming, with support from a national office. Attractive innovation features were the existing evidence base, emphasis on lived experience through coproduction in course development and facilitation, opportunity for student skill building, and flexibility to accommodate local needs and strengths. The instructional climate was also appealing, as it could offer people with lived experience a sense of community and could promote their self-efficacy and confidence while reducing the power imbalance and fostering relationships between staff and students. The Recovery College model could also offer a more immediate response in terms of educational support to people needing care and facing long wait times for traditional services.
“I would say there’s probably many other things besides instruction. I think there’s relationship-building that happens so there are connections between students and between the facilitators and the learners. It’s the development of a space that allows for people to develop skills that are unrelated to the content. So, people also learn skills like sharing in a group context, so confidence-building, self-efficacy. When you can cultivate a skill in one area, you build confidence, and you start to believe that you have the ability to learn and to develop new skills. So that sense of self-efficacy is very integral to the recovery and well-being journey”. [WPG-02]
The importance of individual characteristics was demonstrated as passionate leaders in the Winnipeg and Central branches who were committed to advancing upstream mental health promotion and PSR were impressed by the model and together, they researched it further to inform adoption decisions. The coproduction process aligned with CMHA’s “nothing about us without us” approach and could foster a sense of ownership. In both branches, the name Recovery College was changed to Learning Centre during the adoption process, which better resonated with community and agency participants.
Implementation: In the external context , in early 2017, CMHA Winnipeg and Central branches met with CMHA National to implement Learning Centres. Although no new funding was made available by the RHAs, philosophical support enabled the repurposing of existing funding for recovery education and peer support. In 2018, CMHA National and CMHA Winnipeg leadership visited England to meet recovery-focused mental health services experts and to see the model in action. This visit was crucial in fostering strong relationships between the model initiators and CMHA leaders who discovered common visions to widen the target audience to anyone in the community interested in mental health issues, thereby making mental health a universal concern and promoting a living well approach. Collaboration with an Ontario-based psychiatric hospital, with similar values and interest in Recovery Colleges, supported programme evaluation to produce evidence of effectiveness.
Internally , the Winnipeg and Central branches collaborated on initial model and course development, and took a staged approach to opening their Learning Centres. In the Central branch, where resources were tighter and there was a large geographic area to serve, creative approaches to leverage local support and assets were used. Health professional placement students supported the small branch to prepare for launch and in doing so, encouraged staff buy-in. Another peer service organization provided funding support and this, along with community grants, covered staffing, technology, social marketing and other costs that are traditionally not eligible for provincial funding.
“[A] critical moment would be the establishment of a partnership. I think that was a critical moment. I walked away and I know my staff did, too, with an immense sense of relief after I could tell them that [a peer Manitoban mental health community organization] was on board to help make this a reality”. [PLP-22]
The Winnipeg branch also leveraged internal resources, including an existing peer support group whose members assisted in developing the first five courses.
“And so we actually relied on some communities that existed within our CMHA. So we had a group of individuals who are peer supporters to one another. They had taken our workshops in the past. And then they created, on their own, their own support group, and designed that support group based on their needs and on an educational focus. So we actually asked them if they would be our initial coproduction group”. [WPG-04]
The passion of individual CMHA staff and leaders, many with their own lived experience, made them champions who demonstrated their commitment to valuing expertise derived from lived experience. These individuals also helped build the external linkages with organizations and key people both nationally and internationally. Innovation features allowed for initial small-scale implementation, leveraging local assets and community strengths before expanding further. The flexibility to offer “something for everyone” and promote “living well in your community” garnered broad interest and unanimous buy-in from community members. The flexibility of the model also allowed the Winnipeg branch to retain PSR influences from their colleagues at Boston College.
The collaborative coproduction process fostered a sense of ownership, friendship building, balance across perspectives and acceptance within the classroom. This affirming process allowed room for creative input and for trial and error, with the process itself evolving to become more effective over time. It also facilitated the expansion of course offerings, as students were encouraged to lead future course development. Accompanying changes to the physical space and staff roles helped in welcoming the whole community, meeting the needs of vulnerable groups in society and addressing access barriers.
Assimilation: The Central branch has been unable to coproduce new Learning Centre material during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet it continues to offer its existing content. The Winnipeg Learning Centre was able to shift to virtual and then hybrid online and in-person coproduction activities, while ensuring fidelity to the core Recovery College principles.
“And some of the other things that are in the fidelity assessment are: Are you recovery-focused? Are you community-focused? Are you collaborating with the people who are consuming your services? So, it’s a really easy fidelity to conform to but also have room to be kind of creative because they’re not dictating what courses you should have. The fidelity is that you provide courses”. [WPG-04]
In Winnipeg, the Learning Centre continues to expand and evolve, and is reported to have had a gradual but transformative impact on organizational context and values within the branch, by providing a universally accessible platform that demonstrates the value of engaging people with lived experience at every step. The coproduction approach to course development has ensured that content remains current and relevant through creativity, diversity and responsiveness to people’s needs. Leaders’ commitment to the model and ongoing evaluation to ensure it is meeting local needs have supported wider assimilation of coproduction approaches in other branch programming as well. New leadership in the Central branch has expressed the desire to revive the Learning Centre’s coproduction activities.
See Fig. 3 for a summary of the Case 3 adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline.
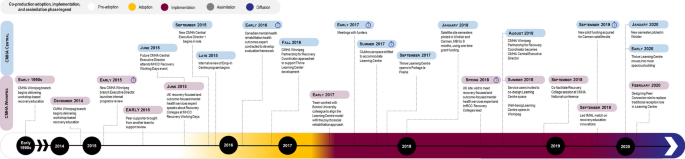
Case 3 CMHA Learning Centres coproduction adoption, implementation and assimilation timeline
Cross-case comparison
Adoption: Shifting ideas in the public policy realm and supportive external change agents created a conducive external context . In Cases 1 and 2, shifting ideas pertained to interprofessional and intersectoral collaboration and in Case 3, national and provincial discussions about a recovery and well-being orientation were important precursors to coproduction with people with lived experience. Internally , tension for change was evident in all cases; however, the process by which this unfolded differed, as a natural progression of ongoing improvement efforts in Cases 1 and 3 and as a deliberate response to an opportunity created by an external change agent for local system-wide transformative change in Case 2. In all cases, passionate individuals , many with their own lived experience, and a philosophical approach that resonated deeply and widely was a core feature leading to adoption (see Table 6 ).
Implementation: In all three cases, building local partnerships and/or networks in the external context was integral to implementation. These partnerships and networks helped to overcome internal resistance within existing power structures (Case 1), created a community coalition that could move forwards in the face of resistance within traditional mental health services (Case 2), and offered material support and expertise to support implementation (Case 3). In Cases 1 and 2, there was no 'programme' per se, rather a philosophy steered by guiding questions, and in Case 3, the Recovery College model itself was designed to realize its embedded philosophy through coproduced educational programming. These features drove a micro-level movement for change (all cases) that was locally adapted, for example, to become “something for everyone” (in Case 3). Philosophical alignment also helped in building trust across collaborating organizations to support implementation and as a shared foundation for overcoming differences during implementation. Implementation proceeded incrementally at the grassroots level in all cases and by working with the willing (see Table 7 ).
Assimilation: There have been different forms of assimilation across all three cases, with transformative impacts not only on the organizations involved but with impacts extending to the broader organizational and political context. A widely embraced mindset in the region, new structures and a growing international network (Case 1); impact on the local mental health strategy and continuing transformative effects on partnerships among community agencies (Case 2); and assimilation to other programmes and branches (Case 3) are some of the ongoing transformative impacts.
In Case 3, assimilation was characterized by customization, as both branches have changed the name and broadened the reach of Recovery Colleges, while maintaining fidelity to core principles. At the same time, challenges to sustaining such transformative change going forward were a concern without targeted leadership and funding (see Table 8 ).
The analysis of these cases of adoption, implementation and assimilation of innovation demonstrates a range of factors from existing frameworks that shaped the stories of these coproduced innovations. The analysis also suggests additional considerations beyond established frameworks when aiming to engage structurally vulnerable people in coproduction activities that can help to overcome structural barriers and address power differentials in legacy systems.
Existing frameworks and models were very helpful in pointing to the interplay between the many factors operating at different levels in each context. These comprehensive frameworks provided a wide lens that was useful for thoroughly investigating different contextual elements. However, at times, this comprehensiveness made it difficult to tease out the essential causal story from our data to understand how each set of coproduced innovations emerged [ 28 ]. In our analysis, existing frameworks were most helpful when comparing across cases to identify overarching patterns, such as the influence of shifting policy ideas and external change agents in the external context during adoption and the role of community partners and network building in the implementation phase.
At the same time, particularly compelling considerations involving structurally vulnerable groups identified here were less evident in existing frameworks. Notably, there were two important differences in the nature of the ‘programme’ in this context. First, existing frameworks suggest a predefined 'programme' to adopt; however, there was no predefined programme per se in two of our cases. Instead, change was more ideological/philosophical in nature, captured simply by a set of guiding questions (two cases) or embedded as a central feature of an existing program with lots of room for customization (one case). The central philosophy in these cases corresponded to efforts to raise the profile of traditionally marginalized voices by shifting normative paradigms about what types of knowledge (for example, lived experience) and whose voices (for example, structurally vulnerable service users) should be heard in traditional systems. Second, the process (coproduction) could not be disentangled from this essential philosophy and, in some cases, it was met with considerable resistance. Including vulnerable people as genuine partners in coproducing innovations was perceived as a 'threat' to some managers (Case 1) or to the prevailing orthodoxy of 'Quality Improvement' (Case 2).
These 'programme' features suggest a second consideration in terms of implementation processes . The clear intention to shift the existing power balance in systems and within organizations needed a set of resources that went beyond the capacity of any one organization. While high-level leaders with their own lived experience were instrumental in providing vision and support, the implementation process relied heavily on relationship building across partner organizations and networking at the grassroots levels rather than on top-down directives. Meaningful service user involvement was considered critical in making transformative service and system culture change, often disrupting traditional structures, networks and communication. Shared values, the development of a group-based belief system, core activities and a different relational environment and leadership [ 29 , 30 ] are central to social movement theories. Furthermore, the definitive objective of stepping outside organizations within the formal healthcare system to instead derive a new way of working across many community organizations led by people with lived experiences is not clearly captured in existing frameworks, which typically speak to innovation within existing structures of power in organizations and systems.
Finally, the cases analysed here suggest important differences in temporal dynamics at play that were not elaborated in existing models. Consistent with concepts of change in complex adaptive systems and theories of policy path dependence and agenda setting, adoption could occur through a slow internal tension for change that built over time and culminated in coproduction as a natural evolution of ongoing improvement efforts or through seemingly sudden 'transformative' reform where a confluence of interested groups came together in the face of an opportunity to do something differently. Ideas about change in complex adaptive systems such as emergence, self-organization, adaptation, change over time, distributed control and tipping points [ 31 ], and from policy literature such as path dependence [ 32 ], multiple streams theory [ 33 ] and distributed control could be informative in this respect [ 34 ]. Our participants suggested that because each case relates to a set of concepts and principles that were collectively generated over time, there was a need to better understand this process as it unfolded.
While existing models were helpful in considering a wide range of factors to consider and recent updates suggest a movement away from concepts such as 'programme' to 'innovation' [ 19 ], the temporal, relational and power dimensions discussed here were validated by our collaborators as equally important considerations. Exploring these dimensions will be the focus of future work.
Limitations and future work
This work is subject to several limitations. First, it is based on a case study of three examples of coproduction of health and social care innovations in different national contexts in the northern hemisphere. The findings may not be transferable elsewhere. Furthermore, when considering our findings in relation to the CFIR, DOI and assimilation frameworks, it is important to note that these frameworks were not specifically developed for an innovation process involving service users at all stages of innovation adoption, implementation and assimilation. However, the limitations in adopting and applying these frameworks here have led to a careful examination of what is unique to coproduction processes involving vulnerable populations. A forthcoming contribution will try to capture these unique elements and position them within the innovation, power, and social movement literatures. Finally, the analysis here is primarily based on our 'wave 1' home site findings from this longitudinal case study, and new insights may be gained from a deeper evaluation of our wave 2 and wave 3 findings. The latter pertain to processes of ongoing coproduction in practice and diffusion to other contexts, respectively, and will be analysed in forthcoming work.
While our case study was extremely helpful in identifying core considerations for factors influencing the adoption, implementation and assimilation of three cases of coproduced health and social care innovations, several nuanced considerations when applying existing theoretical frameworks in the coproduction context emerged: the nature of the 'intervention' being a philosophy rather than a concrete set of steps, the intertwining of intervention and process and the need to study evolution of the intervention itself as it emerges over time, greater attention to partnered processes as disruptors to existing power structures and an emphasis on driving transformational change in organizational cultures. Future work will explore these considerations further.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to the study’s small sample size and the key informants’ roles as leaders within small organizations, making it difficult to deidentify their data. However, the datasets are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
In some cases, these individuals also had lived experience of vulnerability that also motivated their work, but this was not a specific requirement for study participation.
Abbreviations
Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research
(SingHealth) Centralized Institutional Review Board
Canadian Mental Health Association
Diffusion of innovation
Health and Social Care Partnership
McMaster University Research Ethics Board
Making Recovery Real
Portage la Prairie
Psychosocial rehabilitation
Regional health authority
Scottish Recovery Network
Third sector interface
United States
Robert G, Locock L, Williams O, Cornwell J, Donetto S, Goodrich J. Co-producing and co-designing. In: Dixon-Woods M, Martin G, editors. Elements of improving quality and safety in healthcare. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2022.
Google Scholar
Palmer V, Weavell W, Callander R, Piper D, Richard L, Maher L, et al. The Participatory Zeitgeist: an explanatory theoretical model of change in an era of coproduction and codesign in healthcare improvement. Med Humanit. 2018;45:247-57.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
McGeachie M, Power G. Co-production in Scotland—a policy overview. 2017.
Osborne S, Radnor Z, Stokosch K. Co-production and the co-creation of value in public services. Public Manag Rev. 2016;18(5):645–59.
Article Google Scholar
Iedema R, Merrick E, Piper D, Britton K, Gray J, Verma R, et al. Codesigning as a discursive practice in emergency health services: the architecture of deliberation. J Appl Behav Sci. 2010;46(1):73–91.
Sandhu S, Priebe S, Leavey G, Harrison I, Krotofil J, McPherson P, et al. Intentions and experiences of effective practice in mental health specific supported accommodation services: a qualitative interview study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2017;17(1):1–13.
Vackerberg N, Andersson A-C, Peterson A, Karltun A. What is best for Esther? A simple question that moves mindsets and improves care. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):873.
Brown PR, Head BW. Navigating tensions in co-production: a missing link in leadership for public value. Public Adm. 2019;97(2):250–63.
First Nations Information Governance Centre. The First Nations principles of OCAP® [Internet]. Akwesasne (ON): First Nations Information Governance Centre (FNIGC); [cited 2023 Nov 12]. Available from: https://fnigc.ca/ocap-training/
Fotaki M. Co-production under the financial crisis and austerity: a means of democratizing public services or a race to the bottom? J Manag Inq. 2015;24(4):433–8.
Mulvale G, Robert G. Special issue- engaging vulnerable populations in the co-production of public services. Int J Public Adm. 2021;44(9):711–4.
Williamson V, Larkin M, Reardon T, Pearcey S, Button R, Green I, et al. School-based screening for childhood anxiety problems and intervention delivery: a codesign approach. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):e058089.
Nelson EC, Batalden PB, Godfrey MM. Quality by design: a clinical microsystems approach. 1st ed. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 2007.
Batalden M, Batalden P, Margolis P, Seid M, Armstrong G, Opipari-Arrigan L, et al. Coproduction of healthcare service. BMJ Qual Saf. 2016;25(7):509–17.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Grabovschi C, Loignon C, Fortin M. Mapping the concept of vulnerability related to health care disparities: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13(94):1–11.
Katz A, Hardy B-J, Firestone M, Lofters A, Morton-Ninomiya ME. Vagueness, power and public health: use of ‘vulnerable’ in public health literature. Crit Public Health. 2020;30(5):601-11.
Greenhalgh T, Robert G, MacFarlane F, Bate P, Kyriakidou O. Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: systematic review and recommendations. Milbank Q. 2004;82(4):581–629.
Damschroder LJ, Aron DC, Keith RE, Kirsh SR, Alexander JA, Lowery JC. Fostering implementation of health services research findings into practice: a consolidated framework for advancing implementation science. Implement Sci. 2009;4(50).
Damschroder LJ, Reardon CM, Opra Widerquist MA, Lowery J. The updated Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research based on user feedback. Implement Sci. 2022;17(1):1–16.
Lozeau D, Langley A, Denis J-L. The corruption of managerial techniques by organizations. Human Relat. 2002;55(5):537–64.
Robert G, Sarre S, Maben J, Griffiths P, Chable R. Exploring the sustainability of quality improvement interventions in healthcare organisations: a multiple methods study of the 10-year impact of the ‘Productive Ward: Releasing Time to Care’ programme in English acute hospitals. BMJ Qual Saf. 2020;29:31–40.
Yin RK. Case study research and applications: design and methods. 6th ed. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2018.
Maxwell JA. Designing a qualitative study. In: Bickman L, Rog DJ, editors. The SAGE handbook of applied social research methods. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications, Inc.; 2009. p. 214–53.
Sharp C. Making Recovery Real in Dundee: A review with the Scottish Recovery Network. Scottish Recovery Network. Glasgow: Scottish Recovery Network; 2018.
Crowther A, Taylor A, Toney R, Meddings S, Whale T, Jennings H, et al. The impact of Recovery Colleges on mental health staff, services and society. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. 2019;28(5):481–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Anfossi A. The current state of Recovery Colleges in the UK: final report. Nottingham, UK: Implementing Recovery through Organisational Change (ImROC) and Nottinghamshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust; 2017.
Mental Health Commission of Canada. Changing Directions Changing Lives: The Mental Health Strategy for Canada. Calgary, Canada: Mental Health Commission of Canada; 2012.
Giacomini M, Bourgeault I, Dingwall R, De Vries, R. Theory matters in qualitative health research. In: The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Methods in Health Research. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.; 2010. p. 125–56.
Chapter Google Scholar
Tremblay M-C, Martin DH, Macaulay AC, Pluye P. Can we build on social movement theories to develop and improve community-based participatory research? A framework synthesis review. Am J Community Psychol. 2017;59(3-4):333–62.
Maton K. Empowering community settings: agents of individual development, community betterment, and positive social change. Am J Community Psychol. 2008;41:4–21.
Boehnert J. The visual representation of complexity: sixteen key characteristics of complex systems. In: Proceedings of RSD7, Relating Systems Thinking and Design 7; 2018 Oct 23-26; Turin, Italy. Available at http://openresearch.ocadu.ca/id/eprint/2737/
Pierson P. When effect becomes cause: policy feedback and political change. World Politics. 1993;45(4):595–628.
Kingdon JW. Agendas, alternatives and public policies. 2nd ed. New York: Longman; 1995.
Greenhalgh T, Jackson C, Shaw S, Janamian T. Achieving research impact through co-creation in community-based health services; literature review and case study. Milbank Q. 2016;94(2):392–429.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all participants in this study for giving their time and for sharing their experiences. We also thank the study’s collaborators who provided important background to the cases contributing to the research design/direction, acted as local gatekeepers to the cases and/or who helped to interpret the data. Over the life of the research project, the collaborators have been: Louise Christie (Scottish Recovery Network), Marion Cooper (CMHA Manitoba & Winnipeg), Olivia Hanley (formerly of the Scottish Community Development Centre), Greg Kyllo (formerly of CMHA National), Erica McDiarmid (formerly of CMHA National), Susan Paxton (Scottish Community Development Centre), Denise Silverstone (CMHA National), Stephanie Skakun (CMHA Manitoba & Winnipeg) and Nicoline Vackerberg (Region Jönköping County). Without their involvement, this study would not have been possible. Finally, we thank Sophie Sarre for her contributions to wave 1 interviewing and early coding framework development and data coding.
This manuscript draws on research supported by the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council Partnership Development grant no. 890-2018-0116. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
DeGroote School of Business, McMaster University, 4350 South Service Road, Suite 421, Burlington, ON, L7L 5R8, Canada
Gillian Mulvale & Jenn Green
Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, Midwifery and Palliative Care, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom
Glenn Robert
Institute of Health and Neurodevelopment, Aston University, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Michael Larkin & Shioma-Lei Craythorne
Region Jönköping County, Jönköping, Sweden
Nicoline Vackerberg
The Jönköping Academy for Improvement of Health and Welfare, School of Health and Welfare, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden
Glenn Robert, Nicoline Vackerberg & Sofia Kjellström
Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact (HEI), Faculty of Health Sciences, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Puspita Hossain
School of Rehabilitation Science, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Sandra Moll
School of Health and Welfare, Jönköping University, Jönköping, Sweden
SingHealth Office of Regional Health, Singapore Health Services, Singapore, Singapore
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GM, GR, ML, SK and SM conceived of and designed the study. GM, JG, NV, EL and SC collected and analysed the data under the guidance of GM, GR, ML and SK. GM, JG and PH interpreted the data. GM, GR, JG and PH drafted the manuscript. ML, NV, SK, SM, EL and SC reviewed and commented on different versions of the paper. GR, GM and JG revised the manuscript following peer review, in consultation with the other authors. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gillian Mulvale .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Research ethics clearance was obtained from the relevant academic research ethics boards (McMaster University Research Ethics Board [MREB Project ID 2066], Aston University Ethics Committee [Rec Ref #1611]; King’s College London Research Ethics Office [Reference Number MOD-19/20-17350]; SingHealth Centralised Institutional Review Board [CIRB Ref# 2020/2341]; and Swedish Ethical Review Authority [Etikprövningsmyndigheten, Dnr 2019-06373]), and in light of this, ethics review was waived by the boards of the collaborating organizations (Canadian Mental Health Association, Manitoba & Winnipeg branch, the East of Scotland Research Ethics Service). Participants received letters of information outlining the study objectives, protocol and risks prior to consenting in writing.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was received from all key informants.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. All authors approved the final version of the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Provides additional details about the sampling frame (that is, the organizations the interviewees are associated with, the document titles and types).
Additional file 2.
Demonstrates how concepts from the CFIR, DOI, and compatibility gaps frameworks were incorporated into the coding framework.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Mulvale, G., Green, J., Robert, G. et al. Adopting, implementing and assimilating coproduced health and social care innovations involving structurally vulnerable populations: findings from a longitudinal, multiple case study design in Canada, Scotland and Sweden. Health Res Policy Sys 22 , 42 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01130-w
Download citation
Received : 12 November 2023
Accepted : 05 March 2024
Published : 02 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-024-01130-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coproduction
- Structurally vulnerable populations
- Implementation
- Assimilation
- Transformation
Health Research Policy and Systems
ISSN: 1478-4505
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A multiple case research design shifts the focus from understanding a single case to the differences and similarities between cases. Thus, it is not just conducting another (second, third, etc.) case study. Rather, it is the next step in developing a theory about factors driving differences and similarities. Often case studies result from ...
Multiple-case study design however has a distinct advantage over a single case study design. Multiple-case studies are generally considered more compelling and robust, and worthy of undertaking. This is because a multiple case study design has a greater chance of weeding out data collection errors and prejudices, and produces a more acceptable ...
The multiple case study design is a valuable qualitative research tool in studying the links between the personal, social, behavioral, psychological, organizational, cultural, and environmental factors that guide organizational and leadership development. Case study research is essential for the in-depth study of participants' perspectives on ...
A multiple case studies approach was adopted that spanned over 2 years, as it is difficult to investigate all the aspects of a phenomenon in a single case study (Cruzes, Dybå, Runeson, & Höst, 2015). The purpose here is to suggest, help, and guide future research students based on what authors have learned while conducting an in-depth case ...
The study used the multiple-case study design and recruited five pre-service teachers from a Midwestern university as five cases. Qualitative data were collected through interviews, classroom observations, and field notes. The author implemented the case study analysis and found five strategies that the participants used to mediate occupational ...
Case study research is typically extensive; it draws on multiple methods of data collection and involves multiple data sources. The researcher begins by identifying a specific case or set of cases to be studied. Each case is an entity that is described within certain parameters, such as a specific time frame, place, event, and process.
Besides discussing case study design, data collection, and analysis, the refresher ... or multiple cases—what then might be labeled as a single-or a multiple-case study. 1 Whether single or multiple, you also can choose to keep your case holistic or to have embedded subcases within an overall holistic case. The resulting two-by-two
A multiple case research design shifts the focus from understanding a single case to the differences and similarities between cases. Thus, it is not just conducting more (second, third, etc.) case studies. Rather, it is the next step in developing a theory about factors driving differences and similarities.
When choosing a single case over a multiple-case design, five rationales might apply; the single case may be (i) critical, (ii) unusual, (iii) common, (iv ... . Multiple cases are typically used for replication of an intervention and to present different context. In a multiple case study, there is a commonality among the cases, enabling ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
The multiple case study design is a valuable qualitative research tool in studying the links between the personal, social, behavioral, psychological, organizational, cultural, and environmental factors that guide organizational and leadership development. Case study research is essential for the in-depth study of participants' perspectives on ...
Chapter objectives. After reading this chapter you will be able to: Describe the purpose of case studies. Plan a systematic approach to case study design. Recognize the strengths and limitations of case studies as a research method. Compose a case study report that is appropriately structured and presented.
The case study method, and in particular the multiple-case studies design, offers LIS researchers a proven tool for achieving a deep understanding of a specific phenomenon—-for example, the ...
3.1.1 Format of a case study. Except to identify the case and the specific type of a case study that shall be implemented, the researchers have to consider if it's wisely to make a single case study, or if it's better to do a multiple case study, for the understanding of the phenomenon.
Another design characteristic of a case study is whether the design is single case or multiple case. There may be different reasons for choosing a[p. 11 ↓ ] single-case design. A case may be considered unique, prototypical, salient, or revelatory to the understanding of a phenomenon or problem. Analogous to Newton's experimentum
This essay sharpens and refreshes the multi-case theory-building approach, sometimes termed The "Eisenhardt Method.". The Method's singular aim is theory building, especially with multiple cases and theoretical logic. Its defining features (e.g. research questions without obvious answers, careful case selection, well-identified constructs ...
The multiple-case design was the best research design for this study, as it allowed the researcher to use best practices from the two international universities in order to develop a conceptual framework for the University of Johannesburg. The major benefit of using a multiple-case design was that multiple perspectives of the individuals
This study attempts to answer when to write a single case study and when to write a multiple case study. It will further answer the benefits and disadvantages with the different types. The literature review, which is based on secondary sources, is about case studies. Then the literature review is discussed and analysed to reach a conclusion ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Case study research is a qualitative methodology that allows researchers to explore complex phenomena in a structured way, that is rigorous and provides an enormous amount of depth. Three scholars are credited with major contributions to the case study literature: Merriam (1998), Stake (1995/2006), and Yin (1994). The purpose of this paper is to explore case study design for use in the ...
Study aim and design. We adopt a longitudinal multiple case study approach to understand the dynamic nature by which three coproduced innovations intended to address the needs of vulnerable populations were adopted, implemented and assimilated [].Case study research is well suited to studying contemporary phenomena in their real-life contexts, and theory is often adopted to focus the analysis ...
An interconnected research question is how regulation modifies the organisational design of firms, i.e. how firms optimally react and transform their internal organisation, decision-making and operations. Occasionally, new regulations or standards oblige firms to disclose more information on corporate governance and on their business operations.