- Get started Get started for free
Figma design
Design and prototype in one place
Collaborate with a digital whiteboard
Translate designs into code
Get the desktop, mobile, and font installer apps
See the latest features and releases
- Prototyping
- Design systems
- Wireframing
- Online whiteboard
- Team meetings
- Strategic planning
- Brainstorming
- Diagramming
- Product development
- Web development
- Design handoff
- Product managers
Organizations
Config 2024
Register to attend in person or online — June 26–27

Creator fund
Build and sell what you love
User groups
Join a local Friends of Figma group
Learn best practices at virtual events
Customer stories
Read about leading product teams
Stories about bringing new ideas to life
Get started
- Developer docs
- Best practices
- Reports & insights
- Resource library
- Help center

What is a use case? How to write one, examples, + template
Designing a product takes more than listing features and goals. Before the first smartphone came out, how would you describe the ways users interact with it? Calling it a cellphone you can browse the web on is a good start, but that doesn’t explain the complexity of its systems. To map out the ways users interact with a system, tool, or product, you need a use case.
Use cases are descriptions of the ways users interact with systems to accomplish tasks or reach goals. Mapping these interactions can improve early planning and ensure a smooth development cycle. To help you work them into project planning, we’ll define a use case, explain how to write one, and share examples.
What is a use case
A use case explains how users interact with a product or system. It outlines the flow of user inputs, establishing successful and failed paths to meeting goals. This allows product teams to better understand what a system does, how it performs, and why errors occur. You can write one out or diagram a use case model for visual thinkers.
Use cases vary in complexity depending on your audience or system. But across the board, your use case should identify a few key components. The most important ones include:
- Actor: anything exhibiting behavior that interacts with a system, such as a single user, a team, or another piece of software
- System: the product or service with defined functionality
- Goal: the purpose or objective users reach with a system’s features
Actors, systems, and goals build the foundation for a use case. When you begin tracking system interactions, a few new elements come into play:
- Stakeholder(s): someone with a stake or interest in a system’s performance
- Primary actor: the actor who initiates a system’s function to reach a goal
- Preconditions: underlying factors required for the use case to happen
- Triggers: events that begin a use case
- Basic flows: use cases where systems work as intended to reach a goal
- Alternate flows: different outcomes based on when and how a system veers off course
Types of use cases
Use cases come in two forms: business and system. A system use case is a detailed look at how users interact with each part of a system. It highlights how unique inputs and contexts cause the system to reach different outcomes. This level of detail highlights how a system’s individual functions work in any scenario.
Business use cases paint a more general picture of how a user might interact with your business to reach their goals. Instead of focusing on technical detail, it’s a cause-and-effect description of different inputs. For example, if you run a code debugging platform, your business use case explains how users enter their code and receive error notices.
Some teams like to write a business use case to outline a system’s processes before development. As developers begin their work, a manager will outline more technical system use cases to follow.
Use scenario vs. use case
Use cases show all the ways a system functions when trying to reach goals, but a scenario only depicts one example. In a scenario, the system can succeed or fail at reaching the user’s goals. Put simply, multiple use scenarios build a use case.
Use case vs. user story
Use cases depict how users interact with a system, and user stories describe features from the user’s perspective. As a result, user stories are much shorter than use cases, typically consisting of brief descriptions teams use as a jumping-off point in development. Additionally, use cases can assist multiple teams in an organization, while user stories help product teams build their tool.
Use case vs. test case
While a use case covers how users and system features work to reach goals, test cases verify if a single feature works correctly. Unlike use cases, test cases look at functionality in isolation.
For example, a test case might involve validating login functionality on an email platform, ensuring users can log in on any browser at any time after creating their account.
How to write a use case
Writing a use case sounds complex, but only requires understanding your system and its users. You can write a use case by following these six steps:
1. Describe your system
Start by describing your system, or the product or service you and your team will build. Focus your description on what your system does for users. In a business use case, you can keep this background general and explain what it accomplishes. For a system use case, give an under-the-hood description of how your product functions.
Define your system by asking:
- What form does it take: product, service, or software?
- What features does it offer?
- What goals can you accomplish with it?
- How does it meet those goals?
- What can you learn about the system from other documents like project charters ?
2. Identify the actors
Actors generally refer to users and customers but can apply to any outside force that engages with your system. Your actor needs well-defined behaviors explaining how and why actors use your system.
Identify actors by asking:
- Are they individuals, teams, hardware, or another system?
- Will primary and secondary actors share the same behavior?
- Will stakeholders take on the role of actors in your use case?
3. Define your actors’ goals
Use cases highlight the outcome actors want from a system. Remember to focus on your actors’ wants over the system’s capabilities to understand why users come to your system. In some cases, customers want to use systems for more than one objective. Listing each of these objectives creates a more robust use case.
4. Create a scenario
In a use case, scenarios are the sequence of actions customers take when using a system and the flow of effects from that interaction. Your basic flows cover scenarios where a system works as intended. A user approaches the system, enters the right inputs, and your system helps them reach their goals.
Start with these successful, basic flows to create a baseline. You can use process mapping techniques to identify potential issues in the next flows.
5. Consider alternate flows
After writing a successful scenario, write alternate flows that lead to different outcomes. Typically, alternate flows involve the misuse of a system that keeps actors from reaching their goals. However, you can also note internal errors that cause a system to break down or unintended ways systems can reach goals.
Alternate flows show how different actors use a system and succeed or fail. They give a more nuanced view of everything your system can do to help you troubleshoot.
6. Repeat steps 2–5 to compile your use case
With enough variation of actors, goals, and scenarios, you can show how your system functions. Compiling these flows together gives you a use case, which can improve development and inform other documents like project status reports .
With simple systems, you can change a few elements to see every potential outcome. However complex systems may have too many elements to see each outcome. In cases like this, you can focus on testing the most common interactions. You can also design systems to prevent untested com
Try Figma’s use case template
Ready to start brainstorming use cases? Try the Figma use case template to break down your systems and find new solutions.
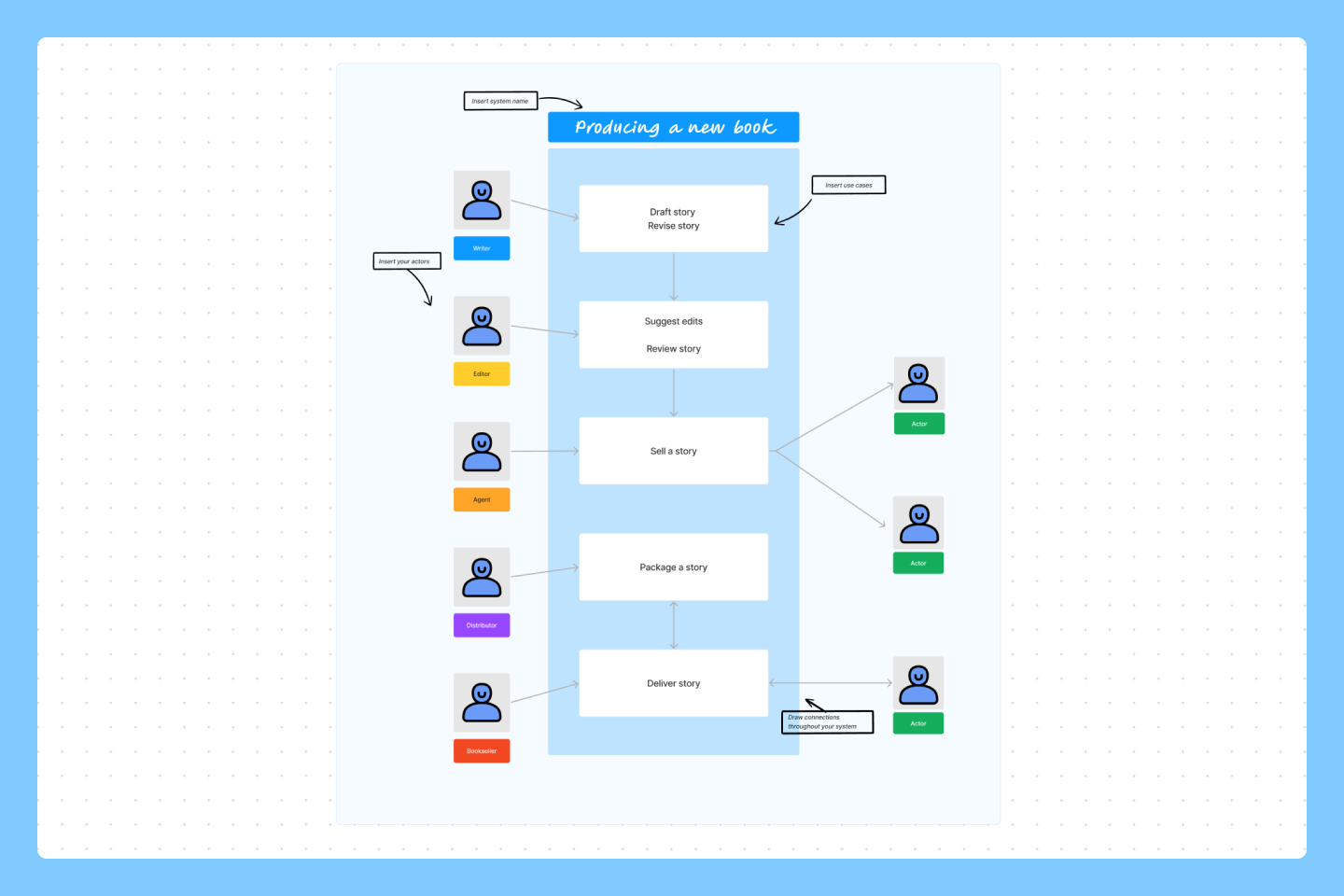
Use case example
Assume you’re a product manager developing a mobile banking app for your company. Your platform needs to streamline user registration and account setup. Here’s a sample use case format based on this app:
Background information:
- System: a mobile banking app
- Primary actor: customers who want to open an account
- Secondary actor: underwriters and automated tools calculating interest rates and maximum principal balances
- Goals: save time on account registration and onboarding
- Stakeholders: the CEO and product VP of your company
- Preconditions: users download the app and meet account requirements
- Triggers: the user chooses to create a new account from the app
- Basic flow: Users download your app and choose to create a new account. The application collects information about the user’s other accounts and credit scores. From there, it automatically shares the accounts they qualify for and their interest rates. The user finds an account that suits their needs and registers.
- Alternate flow 1: Users enter their financial information and the app quickly generates account options. However, each account defaults to the highest interest rate their financial background allows. So, users abandon the app to find a lower rate.
- Alternate flow 2: The onboarding process works as intended, but the app faces compliance issues such as Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. While the app can provide account options, extra compliance steps slow the process.
- Alternate flow 3: Because the app only looks at other accounts and credit scores, it can’t offer a full range of account options. For example, it can only offer credit cards and lines of credit. So, customers looking for mortgages have to go elsewhere.
Benefits of use cases
In the planning stage, use cases define your project scope, requirements, and roadmap. Teams can also discuss the best user outcomes and design a path to them. With alternate flows, you can also anticipate risks before they hurt a user’s experience. If that isn’t enough reason to pen one, here are a few other benefits of use cases:
- Explains value: Use cases explain a system’s features in plain terms. So, when pitching your plans to stakeholders, a use case makes your system easier to understand.
- Predicts costs: A use case outlines the complexity of a system. More complexity may come with additional features or safeguards. By learning how complex your system is, you can estimate development costs.
- Improves planning: Without a use case, designers and developers focus on what a system does, not how it does it. However, use cases help teams consider all the ways to implement features and safeguards.
- Shares alternative uses: Not all alternative flows in a system lead to failed outcomes. Mapping out different scenarios finds new solutions to old problems or expands your understanding of what a system can accomplish.
Perfect your use cases with FigJam
Use cases go beyond describing what your product can do. They give stakeholders and teams a clear picture of user interactions and successful outcomes. Whether adding a new feature, rapid prototyping , or redesigning a system, your planning should start with writing a use case.
The more insights into actors, interactions, and outcomes, the better—which is why it's important to collaborate on use cases with your team and stakeholders. A shared online whiteboard like FigJam streamlines collaboration between remote teams to help you build out comprehensive use cases. Our gallery of 300+ templates can bring teams together at any stage of development.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a use case? Definition, template, and how to write one

For requirements collection and high-level stakeholder communication, product managers need to be able to describe how a consumer will interact with a system or product. This can include a description of the product’s users, how they interact with the product, and what it does.

A great way to visually represent this information is by creating a use case.
In this guide, we’ll define what a use case is, describe the elements therein and what they are designed to do, and walk through how to build a use case step by step.
We’ll also look at some use case examples to show what they look like in practice.
If you’d like to write your own use case while following along with this article, here is a free use case template . To use the template, select File > Make a copy from the top menu bar.
What is a use case?
A use case is a description of how a user interacts with a system or product. Companies build use cases to establish success scenarios, failure scenarios, and any important variants or exceptions.
Many organizations leverage use case modeling tools — such as Miro, LucidChart, and SmartDraw, for some examples — to write or visually represent a use case.
Use cases are frequently employed in software development environments to simplify complicated concepts, but they can be just as important in project management for gathering requirements and defining a project’s scope.
Who creates use cases?
Product management , product development , and product testing domains all use the use case methodology. Product managers and developers employ use cases in a similar manner: as a design tool to specify how the system will react to user activities. However, there are some key differences.
Product managers typically document user-focused use cases whereas developers document product-focused use cases. The user-focused use cases are primarily concerned with the user and their objectives. These are then passed to developers to guide decision-making during the product development process.
Product developers frequently add technical and design elements to provide crucial context. This set of improved use cases gives the development team the insight it needs to start designing, creating, and testing the product and its features.
What is a use case designed to do?
A use case is designed to reveal system demands early on in the process.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Use cases concentrate on the system’s users rather than the system itself. A user case should be understandable to all stakeholders , not only developers and testers, because they are mostly narrative prose. This includes customers, users, and executives.
During the early planning stages, you should involve whichever roles are best suited to solve the problem at hand. This encourages end users to buy into the solution and reduces surprises once the system is put into place.
Each use case is designed specifically to cover only one application of the system. That said, a key advantage of use case modeling is that it also covers all potential problems. Finding minor requirements early on in the project saves a ton of time by identifying exceptions to a successful scenario.
Finally, after you create a use case, you can use it to guide the creation of many other software development components, such as object models, test case definitions, user documentation, and project planning (cost, complexity, and scheduling estimations).
As a product manager, one of the best justifications for creating use cases is that they serve as genuine connecting points. They should be truly understandable to both business and technical users so that everybody can comment on them.
Business analysts leverage use cases as a communication tool to align people to take a common approach and share a common understanding of what the software aims to accomplish.
A technical product manager, on the other hand, might employ use cases to reach business stakeholders without using tech jargon — talking more about what the system does than how it does it. When you get down to the dirty work of coding, this will really help you accelerate and clarify communication to ensure that you’re building what the business genuinely needs and desires.
Elements of a use case
Let’s break down the components of a typical use case and explain the purpose and objective of each.
Actors are the people or things that interact with your system. An actor could be an individual, a company, a team, or something else entirely. Anything that exists outside of a system and engages in some sort of interaction with it qualifies as an actor.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
The stakeholder who gets the ball rolling with an interaction to achieve a goal using your system is known as the primary actor.
Your system, which some people refer to as a scene, is composed of a number of decisions and interactions made by your actors.
The results of an actor’s interactions with the system are your goals.
Your system may produce several outputs in some circumstances while only producing one in others. Before continuing, consider modifying your method if you encounter any barriers to achieving your goal.
Preconditions
Preconditions are assertions or realities regarding what must occur prior to and following the use case.
Often, software developers are aware of the actions that must come before the next one.
For example, let’s say an online shopper clicks on a product to get a detailed description and customer feedback. The Add to cart button won’t show up until the item is in stock and accessible at the warehouse.
A use case that operates flawlessly and exactly as intended with no exceptions or mistakes in the run is known as the fundamental flow or main success scenario. This frequently serves as a starting point when developing various features.
Knowing how a typical scenario operates can help you write accurate code and come up with alternative flows.
Alternative flows
A deviation from the primary success scenario is known as an alternative path or alternative flow. This typically manifests when a system-level error occurs.
In this section of the use case, you frequently list the most probable or noteworthy exceptions an actor might make. Alternative flows in the e-commerce example might include:
- Adding items to favorites instead of a shopping cart
- Sharing items with friends or family members
- Looking at reviews and comments about a product or service
What does a use case diagram look like?
In a use case diagram, stick figures are the most typical way to depict actors .
The use cases/goals you create will be horizontal ovals with a few words of text inside detailing each activity; you can use various colors to indicate different goals.
Associations that depict the connections between components use solid and dotted lines.
Each set of use cases within a system are grouped together by system boundary boxes , which are rectangles.
An example of a use case diagram for a medical clinic application might look something like this:
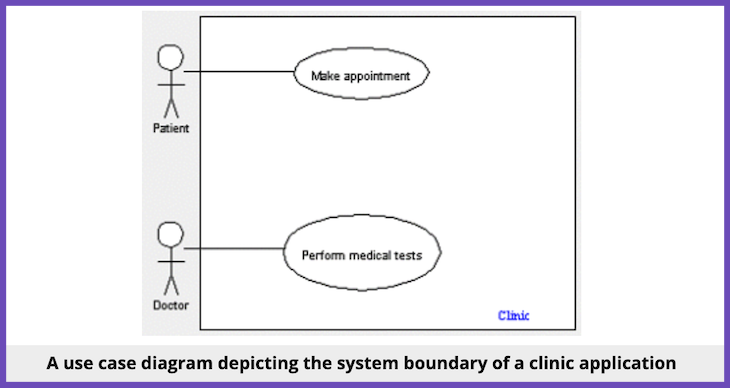
How to write a use case
To write a use case, complete the following steps:
- Determine the target audience for the product
- Select a user from that list
- Determine what, exactly, the user wants to do with the product and create a separate use case for each action
- Determine the typical flow of events for each use case when the user uses the product
- In the use case description, describe the fundamental course. Give examples of what the user performs and what the system responds with so that the user is aware of both
- Consider alternative courses of action and include them to “expand” the use case once the fundamental process has been presented
- Search for connections between the use cases. Extract these and mark them as typical use cases for courses
- Repeat steps 2–7 for all other users
Use case template
You can use the template below to assist you in writing your own use case:
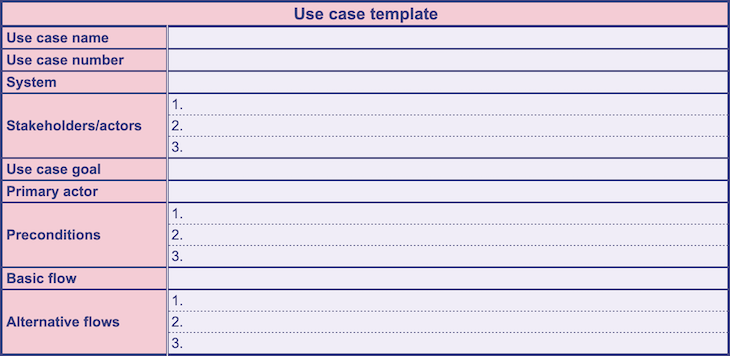
To use this use case template , click here and make a copy by selecting File > Make a copy from the top menu bar.
Use case example
To show how the steps outlined above work in practice, let’s look at an example use case of a housekeeper doing laundry:
- Actors — Residents, housekeeper, etc.
- Primary actor — Housekeeper
- Goals — To do laundry, fold all items, iron clothes if necessary
- Preconditions — It is a Friday and there is laundry in the laundry room
The basic flow for this use case example is as follows:
The housekeeper comes to the laundry room on Friday. They organize the available laundry. After that, they clean and then dry each load. They folds the articles that need folding, then iron and hang the wrinkled items
Alternative flows :
- The housekeeper irons any wrinkled items before putting them on a hanger
- The housekeeper rewashes anything she finds to be still dirty
Use cases help product teams understand a system’s functions from the viewpoint of distinct users. They help stakeholders across the organization visually understand the various flows and how user groups interact with the system.
Use cases also support the development team when generating concepts and assessing the viability of the use cases. Use case definition is a crucial phase in the software development process and is a critical skill for any product manager.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Leader Spotlight: Linking customer satisfaction metrics to business outcomes, with Darlene Miranda
Darlene Miranda discusses the importance of creating an obvious link between customer experience metrics and the business outcome.

A guide to optimizing the digital customer experience
The digital customer experience (DCX) refers to the journey your customers embark on when they interact with your product.
Leader Spotlight: Improving product development through documentation, with Mark Francis
Mark Francis discusses the importance of stakeholders across all business groups embracing the need for documentation and transparency.

A guide to crafting your brand strategy
Brand strategy is one of the most underestimated forces that shapes the trajectory of your products and services.

One Reply to "What is a use case? Definition, template, and how to write one"
ok. This was useful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Filter by Keywords
Product Management
How to create user-focused use cases for ideal success scenarios [with examples].
Robert Hales
ClickUp Contributor
December 30, 2023
Are you steering a project, deciphering intricate business processes, or engineering complex software solutions? If so, you’re well aware that success hinges on clarity and precision. Good news! Use cases may spare you and your clients a great deal of trouble.
Imagine you’re constructing a building. Blueprints guide you, outlining each room’s purpose and layout. This is exactly what a use case is: a blueprint to guide system requirements and resulting project operations. It helps map out processes across user interactions, helping you build a system tailored to user goals and needs. 🏗️
A stitch in time saves nine, and similarly, mastering use cases now can save you countless hours later. In this practical guide, we’ll explain:
- The significance of a use case-driven approach in software development
- Steps to write a use case for multiple scenarios
Benefits of use cases in business processes
Step 1: come up with the title and description, step 2: identify the actors, step 3: identify the actors’ goal, step 4: capture stakeholders and their interests, step 5: specify pre-conditions or assumptions, step 6: outline basic flow, step 7: determine exceptions or error conditions, step 8: include extensions or variations to how the system functions, step 9: consider alternative flows, create and manage your use cases in clickup docs, try writing use cases with ai, use case #1: online shopping wishlist, use case #2: travel itinerary management.
What Is a Use Case, and What Purpose Does It Serve?
Use cases are indispensable for understanding user-specific interactions and narratives (or user stories) to create the intended design for a system.
In technical terms, a use case is a detailed description that outlines how a user will interact with an IT solution to achieve a specific goal. It maps out the steps they take , with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
If you’re new to use cases, you’re probably wondering why you should care about it. The truth is that every software development process carries the burden of user-focused project planning. It’s critical to understand the service or system requirements beforehand so that your end product works perfectly and is profitable.
This is where a use case comes in, helping you visualize user interactions from start to finish and pinpoint any hiccups along the way . Think of it as a walkthrough in a strategic game where every move is crucial. Your input, the system’s response, specific processes, and the final outcome are all explicitly stated, leaving no room for ambiguity in decisions.
The idea here is to help project managers, business analysts, and software developers align themselves on what the end user desires in a software application or a system , taking the guesswork out of the picture. The result? Smarter decisions on:
- Features to prioritize
- Design scope
- Bugs to fix
Tip: Need a quick start? Use the ClickUp User Story Mapping Template to initiate use case mapping right away! Its built-in infinite Whiteboard helps you track and prioritize user stories within minutes.
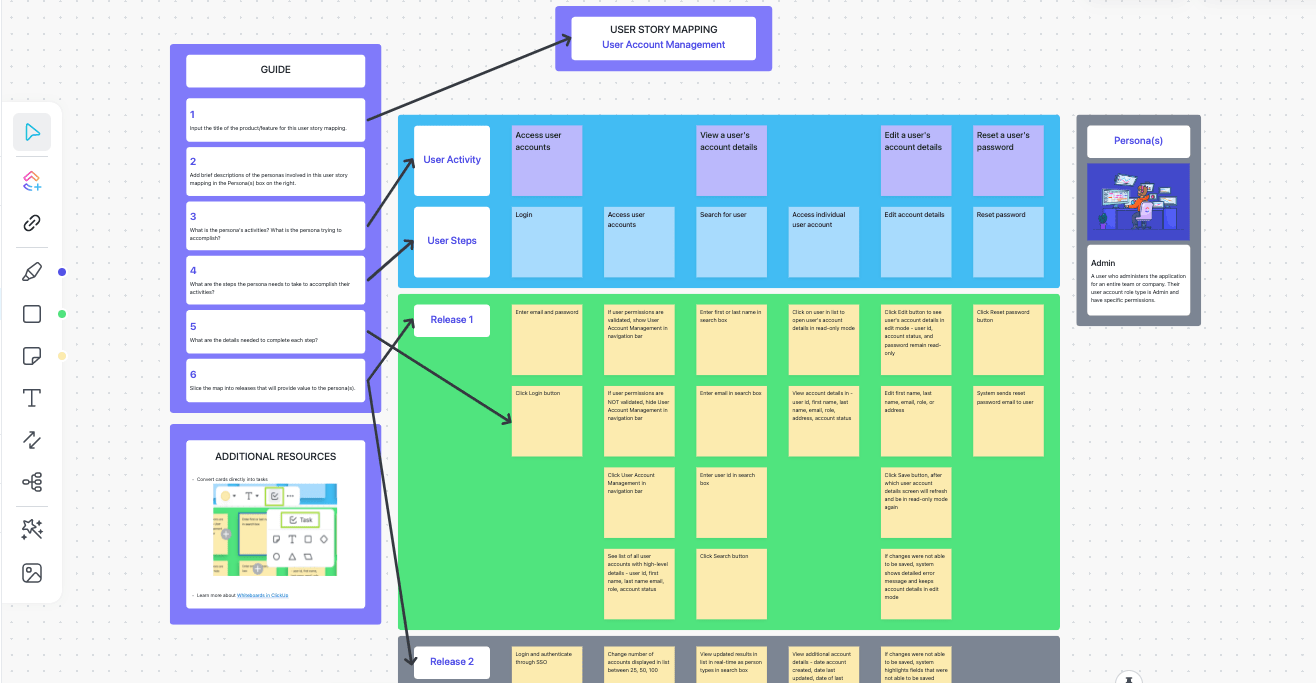
Use cases offer several benefits in developing and managing software systems and projects . Here are seven key advantages for various business stakeholders:
- Clarity into specific interactions : Use cases provide a clear understanding of how users interact with a system, helping define and document functional requirements
- Focused communication : Use cases serve as a bridge between business stakeholders , aligning developers, designers, project managers, and clients
- Identification of how a system behaves : They help identify and document various ways users interact with the system. This includes both normal and exceptional scenarios, providing a comprehensive view of the system’s expected behavior
- Project planning : Use cases help in planning by breaking down the desired functionalities into manageable units addressing specific system goals
- Flexibility : They provide a flexible framework that can accommodate modifications (alternative flows) or additions without disrupting the overall system flow
- Documentation and training : Use cases serve as valuable workflow documentation for future reference. They provide insights that can be useful for training new development team members
- Risk identification : By exploring various success and failure scenarios, use cases assist in identifying potential risks and challenges early in the development process
What to Include in a Project’s Use Case: With Practical Steps
Use cases can include a number of elements depending on the scale and complexity of the system you’re building. Here are some of the most significant options:
- Title and description
- Actors (users)
- Stakeholders
- Pre-conditions
- Exception to the basic flow
- Variations or what-if scenarios
- Alternative flows
These points can be better explained when we explore the practical side of things. Refer to the sections below to understand how to include these elements and distill complex use case scenarios into actionable steps .
Any use case study must have an engaging title. Keep it concise, specific, and indicative of the use case’s purpose. For instance, the title Optimizing Online Checkout: A Use Case for E-Commerce Conversion Enhancement immediately conveys the focus and scope.
Next, your case description should set the context concisely, pinpointing the use case actor or user, the system in question, and the ultimate goal. Here’s an example: This use case outlines the steps taken by an online shopper to complete a purchase, highlighting the system’s response at each interaction to ensure a smooth transaction and reduce cart abandonment.
Keep your language sharp, directly addressing the innovative outcomes you seek.
These are not Hollywood stars but rather the key entities— individuals, groups, or even other systems —interacting with the system under scrutiny. Identifying these actors is akin to casting characters in a play; each has a role, a purpose, and a set of actions that contribute to the unfolding narrative. 🎭
Actors within a use case diagram can be categorized as either primary or secondary . A primary actor seeks the system’s assistance by themselves to achieve a specific goal. On the other hand, a secondary actor provides a service to the system as a direct result of the primary use case. The system initiates interaction with the secondary actor for information or completion of a goal.
Let’s say a user applies for a loan online, which makes them the primary actor. In response to the loan application, the system triggers another resource to calculate interest rates—that resource is the secondary actor.
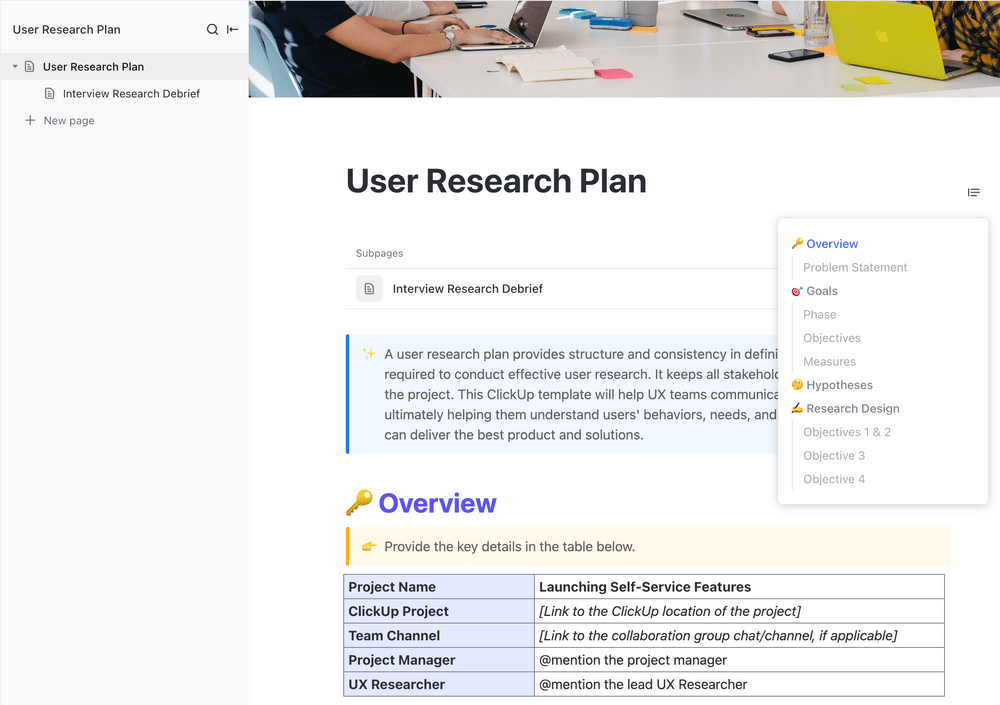
If you’re still in the research phase and need help identifying the primary actor, you may want to document your findings through the ClickUp User Research Plan Template . Its built-in features help software and UX teams map out user behavior and resolve problems within apps, websites, or projects in an orderly manner.
Whether an actor is buying a product, signing up for a newsletter, or using a website, their goal is the driving force behind their interaction with your services . It’s your job to understand these goals so you can design a system that helps them achieve them in the most efficient way possible.
Let’s consider a real-world example: if you’re running a retail website, a customer’s goal might be to purchase a product in minimal steps. This use case would require you to outline the steps customers need to take to complete that purchase, from selecting the item to finalizing the payment.
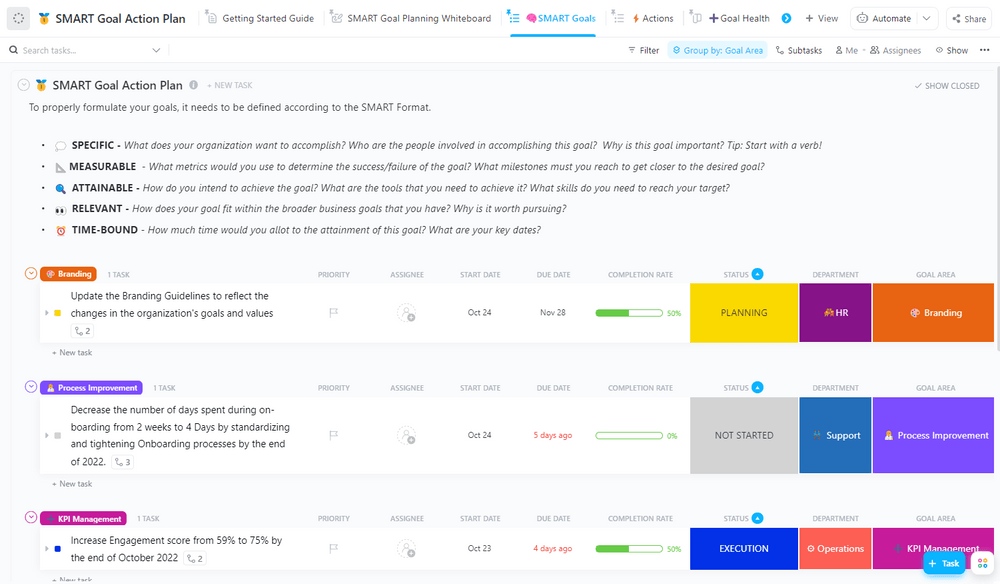
Use this ClickUp SMART Goal Action Plan Template to list out the goals of all identified actors and monitor how they’re addressed by your team.
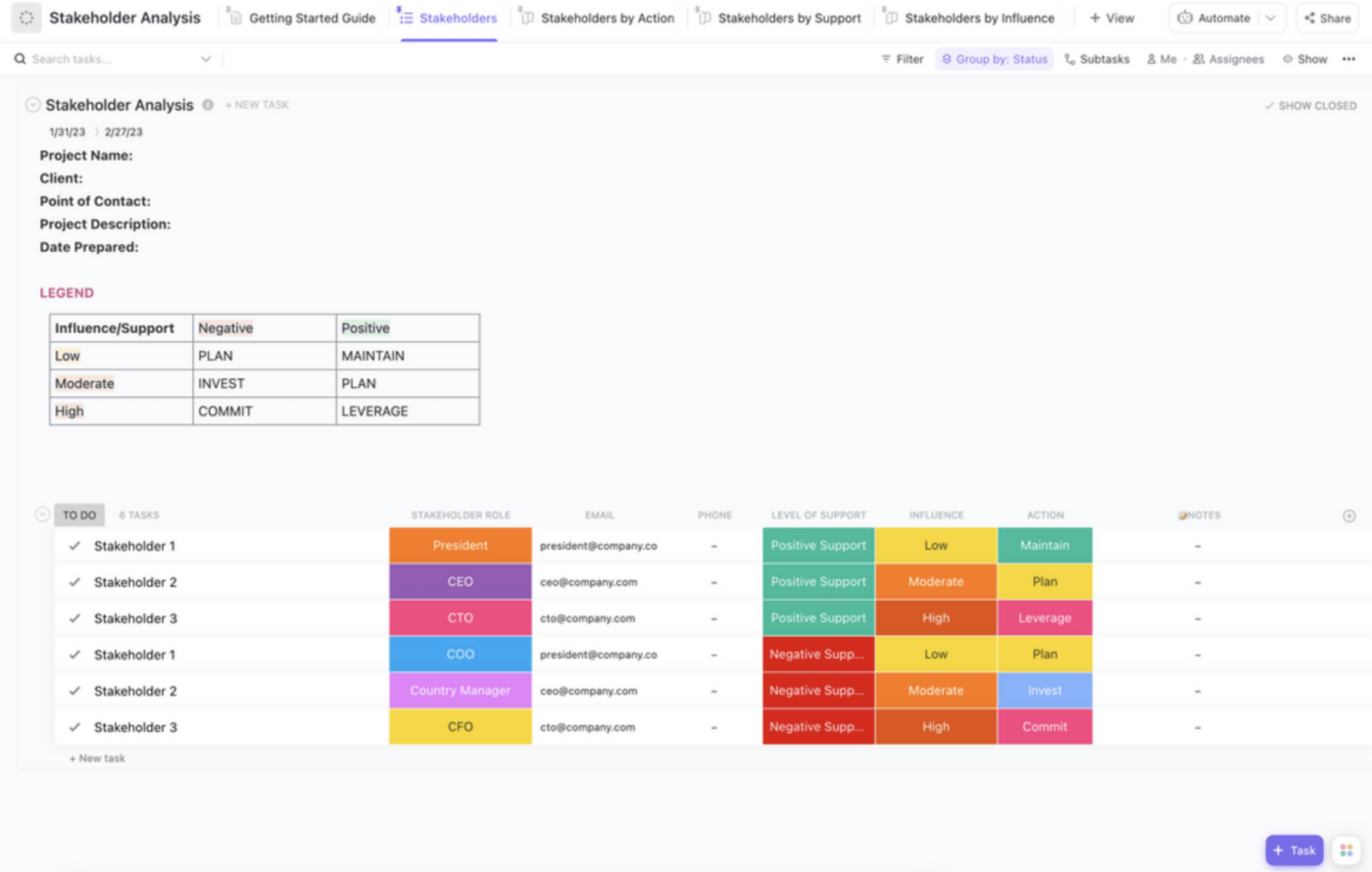
It’s super vital to identify all the stakeholders and understand their interests to ensure your use case is effective. A stakeholder could be an end-user, a system administrator, or even external actors or systems interacting with your service. They all have unique needs and expectations. Here’s what you should do:
- List all possible stakeholders involved in the use case
- For each stakeholder, identify their interests or what they aim to gain from the use case. For instance, a potential Interest for an online shopper would be an Intuitive and efficient user experience
- Consider how the use case can be fulfilled without compromising the overall goals
- Regularly revisit this list as your project or product develops , ensuring new needs are accounted for
Stakeholder analysis can be a stressful job, especially when there are multiple use cases to monitor. We recommend using quality stakeholder mapping templates to structure the process.
Pre-conditions set the stage for action, ensuring that all necessary conditions are in place before the use case is initiated. Think must-haves for your scenario to work—like having an internet connection for an online transaction or a user account for access to a members-only area. Imagine the scenario from the user’s perspective and identify and list these prerequisites clearly.
Here’s an illustration showing how pre-conditions are used to outline use cases and automate the workflow for a banking website:

This is the minimum viable product (MVP) scenario, the one where everything clicks, and your use case unfolds just as envisioned. No errors, no hiccups, just a straightforward path to a happy user.
Imagine a scenario where a customer purchases a book from an online store. The basic flow would be:
- The customer logs in to their account
- They search for a book by title, author, or genre
- The customer reviews the book and adds it to their cart
- They proceed to checkout, confirm shipping details, and select a payment method
- They review the order summary and place the order
- A confirmation email is sent to the customer
Each step here is supposed to be clear and necessary, guiding the user towards a satisfying transaction. Fall back on the ClickUp User Flow Template to design efficient use case pathways and share them with your team.
These exceptions represent scenarios where the standard process flow doesn’t apply. Think about what could go wrong and how your system should respond. You can:
- Consider realistic scenarios : Think about all the ways an operation might deviate or lead to failure scenarios. This could be due to technical issues, user errors, or unexpected circumstances
- Document each exception : Clearly describe each exception, including its cause, effect, and how your system should respond
- Prioritize exceptions : Rank exceptions based on their likelihood and impact on user experience
Think of these as what-if scenarios that keep your processes agile . Say if a customer abandons their shopping cart, what’s the next step? This perhaps calls for creating an extension that activates a follow-up email sequence or a special discount offer to re-engage them.
Use cases should adapt to real-world complexities, offering innovative solutions that maintain user engagement. It’s about anticipating the unexpected and scripting a response that turns challenges into opportunities.
Consider alternative courses if challenges or process deviations occur. Imagine you’re designing a use case for an online shopping cart system.
Main Success Scenario (MSS):
- The user adds items to the cart
- The user proceeds to checkout and confirms payment
What if an item is out of stock?
- The system notifies the user immediately
- The system recommends similar products
What if the payment is declined?
- Prompt the user to try a different payment method
- Offer to save the cart for later completion
What if network issues occur?
- Save the user’s progress automatically
- Inform the user and attempt to reconnect
For each what-if , develop an alternative path that guides your system to a successful outcome.
How to Write Effective Use Cases with ClickUp
Now that we have a thorough knowledge of the process of developing use cases, let’s explore how to write one professionally with ClickUp . This all-in-one project management tool comes with abundant user documentation and use case writing features. Let’s break down the process to showcase just how effortless it can be.🌹
To kick off your business use case model in ClickUp, head to ClickUp Docs , the platform’s integrated solution for creating and storing all types of documents—from user manuals and test case definitions to technical requirements.
Starting fresh? Great, create a new doc. You can use one of ClickUp’s free flowcharting templates to create use case diagrams or case study templates to document user research. Everything will be accessible from a centralized location, making it easier to keep track of the best possible outcome scenario or develop alternative paths.
Invite members from product and marketing teams to work on your use case document in real time. You may want to create Folders to store multiple use cases for your project. The best part is that you can connect your Docs with other project tasks to ensure a smooth work experience.
Let’s dive into the fun stuff! In the Doc editor, just type /ai. Boom! The ClickUp AI modal appears, ready for action. Click on Write with AI to get the party started. Type in your use case topic and add relevant technical requirements to generate a professional-grade, well-structured use case presentation within seconds.
Even with the AI-generated use cases, you’re in control. You can:
- Insert the content elsewhere : Seamlessly insert the AI-generated content into your Doc. Or, just copy-paste and merge it with manually written use cases
- Edit inputs : If the narrative needs a personal touch, edit your prompt or topic to guide the AI in the direction you want
- Regenerate : Fancy a different twist? Explore varied responses from the AI with the same prompt
- Give AI more direction : Extend the conversation by providing additional prompts or directions and get more contextual responses 🤖
Besides generating text, ClickUp AI can also fix the grammar and tone of your existing documents and even summarize lengthy case studies to save you time.
Examples of Use Cases for Software Development Projects
Let’s dive into some business use case examples to better illustrate what they look like and how they can streamline your projects.
An e-commerce platform aims to introduce a wishlist feature that enhances the online shopping experience for users.
Actors : Online shoppers
Goals : Add items to a wishlist; view wishlist contents
Stakeholders : E-commerce platform, online shoppers, product vendors, marketing team, developers
Pre-conditions : User must be logged in and browsing available products
Basic flow :
- User logs into the e-commerce platform
- User browses available products
- User selects the option to add a product to their wishlist
- System adds the selected product to the user’s wishlist
- User can view and manage their wishlist at any time
- System provides personalized product recommendations based on wishlist items
Extensions/Variations:
- Implement a notification system to alert users when wishlist items are on sale
- Allow users to share their wishlist with friends or family for gift suggestions
Exceptions/Error conditions:
- If a selected product is no longer available, notify the user and provide alternate courses
- In case of technical issues, ensure users can still browse and add items to their wishlist without disruptions
Alternative flow :
- User selects the option to view their existing wishlist
- System displays a list of items in the user’s wishlist
- User can remove items from the wishlist or proceed to purchase
- System updates the wishlist and provides relevant suggestions for additional items
A travel planning app wants to implement a feature for users to create and manage their travel itineraries.
Actors : Travelers, travel app
Goals : Create and edit travel itineraries; receive recommendations
Stakeholders : Travel app companies, travelers, local businesses, tourism boards, developers
Pre-conditions : User must be logged in and have a trip planned
- User logs in
- User selects the option to create a new travel itinerary
- User inputs trip details, including destinations and dates
- System generates an initial itinerary and suggests local attractions
- User can modify the itinerary and add custom activities
- System provides real-time updates and recommendations based on user preferences
Extensions/Variations :
- Integrate a weather forecast feature for each destination
- Allow users to share their itineraries with fellow travelers.
Exceptions/Error conditions :
- If a selected attraction is closed or unavailable during the planned date, notify the user and suggest alternatives
- In case of a connectivity issue, ensure users can still access and modify their itineraries offline
- User logs into the travel app
- The user chooses an existing route
- System displays the current itinerary, including booked accommodations and activities
- User can modify the itinerary, add new activities, or remove existing ones
- System updates the itinerary and adjusts recommendations accordingly
Closing the Case on Success
Whether you’re looking to fine-tune your business process or enhance customer experience, use case modeling is a great tool for visual problem-solvers. If you need an observable result quickly, rely on the strategic use case development tools within ClickUp to accelerate your project timelines and bring your business objectives to fruition. 🍉
Sign up to explore the free-to-use solution .
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
What is a use case?
Last updated
10 February 2024
Reviewed by
Mary Mikhail
When projects involve multiple stakeholders, it's important to communicate information efficiently and effectively.
Whether it’s describing how a product works or how customers interact with it, clearly representing information can make all the difference.
A use case is one way to share information. They simplify complex ideas and offer a way to share information visually.
While software development often works with use cases, businesses across industries can benefit from them. Let’s learn more about the topic, including use case examples.
- Use case meaning
A use case is a methodology to organize system requirements.
It comprises a set of possible sequences of interactions between systems and users in a defined environment with a particular goal.
The use case document includes the environment, goal, and other details to provide a clear picture of the system and overall project.
Use cases are invaluable for software developers, helping them identify potential errors in the system and fix them early on.
They’re also incredibly beneficial for project management, offering context to anyone involved, from stakeholders to customer service representatives.
Use cases vs. user stories
Use cases and user stories can benefit project management and development teams. However, distinct differences exist between the two.
User stories are short-form descriptions from a customer’s perspective. They are the story's beginning, setting the stage for a specific feature or workflow.
Use cases offer greater context, including:
The goal of the use case
The series of paths the system could take
Post-conditions, defining the actions the system takes after the use case
Use case vs. test case
People commonly interchange use and test cases, but they have distinct objectives.
A test case is a group of test inputs and anticipated results that lead to the further development of a particular test objective. You can reuse test cases. They keep teams aligned, validate software features, and can lead to improved software quality.
On the other hand, use cases focus on end-user interaction with the system, seeing how well specific users interact with a system rather than testing out software features. They are based on system requirements and support different paths, while test cases support a single outcome.
- What's the purpose of a use case?
A use case has multiple purposes. Use cases can establish requirements, outlining how users interact with the system.
They can also manage scope, reducing dreaded scope creep and providing context for all development team members.
One of the most obvious benefits of a use case is that it can reveal potential problems early in the process. Establishing use cases in your development project ensures you'll create a product that is better equipped to serve everyone who interacts with it.
Who creates use cases?
Product managers can keep the team aligned as they address and complete objectives, all while keeping the concerns of the system's users in mind.
While managers typically control the document, team members can add context or additional details to the use case.
Product developers often add technical and design elements to the use case, which gives the development team necessary insights into the design and creation of the product.
- Types of use cases
There are two primary types of use cases:
Business use cases
Business use cases are also referred to as "abstract-level use cases." They tend to be high-level, with a more abstract description that refers only to the business process and actors involved. Business use cases define the actions the business must perform to provide observable results.
System use cases
System use cases have more detail than business use cases. They include the specific system processes that must happen to fulfill the project's goal. System use cases are also known as "implementation use cases."
Companies can use both cases. Many project managers start with business use cases to provide high-level overviews before moving on to system use cases for a more granular level of detail.
- Six elements of a use case
A typical use case contains the following six elements, whether high-level or micro-detailed:
In the context of a use case, an actor is anyone who performs a behavior or interacts with your system. An actor doesn't have to be an individual. It can also be a company or a team.
The system is the product that provides the backdrop for your actors’ interactions. It is also called the scene or the subject.
Goals are the results of the participating actor's interactions with the system. You can discuss these goals at the project’s outset with all stakeholders and members of the development team.
4. Preconditions
In any use case, it’s crucial to meet certain conditions before and after the use case. These are called preconditions. They’re invaluable for software developers, allowing them to visualize the steps users experience as they interact with the system.
5. Basic flow
The basic flow is when a use case operates as outlined and intended, with no deviations or errors. Deviations are normal, so a basic flow is often the starting point for development.
6. Alternative flows
Alternative flows are when any deviations occur from the basic flow. This can manifest when a system-level error occurs or when users interact with the system in unexpected ways.
- What to know about use case diagrams
- How to write a use case
To write a use case, clearly define the target audience you want to focus on. From your target audience, isolate a single user. They can serve as the actor for your use case.
Work with your development team to create an outline that includes the typical flow of events when the actor uses the product or service. This is the basic flow you and your team operate from.
Include alternative flows in the use case. Provide examples of how to proceed in the event of all flows so your development team has more to work with.
Once the use case is complete, share it with those involved in the project. Consider the feedback you receive and incorporate it into the use case as necessary.
- Use case templates
There's no single format for use cases. Depending on the nature of your project and your company's needs, you could include or eliminate various sections.
You can use this basic section outline as a starting point for your use case:
Use case name
System details
Actors/primary actor
Preconditions
Alternative flows
Stakeholders
You might also include a priority in your use case to define the project's urgency.
Including a use case diagram with your outline can also be helpful to provide visual cues to any non-technical people reviewing the use case.
How do you identify an actor in a use case?
An actor in a use case is someone who interacts with the system. To identify an actor for your use case, consider what the system handles and what is handled outside the system.
Additionally, consider what the actor needs from the system and the expected outcome.
Who is a secondary actor in a use case?
A secondary actor in a use case provides a service to the system you’re refining. Secondary actors do not trigger interactions with the use case and are often termed "supporting actors" by those involved in the project.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 23 March 2023
Last updated: 29 June 2023
Last updated: 25 June 2023
Last updated: 23 May 2023
Last updated: 27 June 2023
Last updated: 27 March 2023
Last updated: 21 March 2024
Last updated: 30 March 2024
Last updated: 26 May 2023
Last updated: 12 April 2023
Last updated: 22 July 2023
Last updated: 10 August 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
What Is a Use Case?
April 25, 2022 - 7 min read
A use case is a concept used in software development, product design, and other fields to describe how a system can be used to achieve specific goals or tasks. It outlines the interactions between users or actors and the system to achieve a specific outcome.
In this article, we’ll dive into the details of what use cases are, how they are used in software development, and their benefits. We’ll also explore common types of use cases and provide some tips on how to create effective use cases.
Moreover, to help you effectively manage your project's use cases, we’ll offer a pre-built requirements management template that can help you gather all the necessary information and ensure all stakeholders are aligned on the project’s goals.
What is a use case? Use cases explained
A use case is a description of the ways in which a user interacts with a system or product. A use case may establish the success scenarios, the failure scenarios, and any critical variations or exceptions. A use case can be written or made visual with the help of a use case model tool.
The history of the use case
Swedish computer scientist Ivar Jacobson presented the first article on use cases in 1987, describing how the technique was used at telecommunications company Ericsson to capture system requirements. In 1992, Jacobson co-authored the book "Object-Oriented Software Engineering — A Use Case Driven Approach," which helped popularize use cases for specifying functional requirements in software development.

Jacobson later joined American software engineers Grady Booch and James Rumbaugh to create the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which introduced a standard way to visualize the design of a system. Since then, the technique has been adapted into use case writing "templates" to streamline the capture of high-level requirements.
What is the purpose of a use case?
The purpose of a use case is to:
- Manage scope
- Establish requirements
- Outline the ways a user will interact with the system
- Visualize system architecture
- Communicate technical requirements to business stakeholders
- Risk management
Why do project managers need to know about use cases?
Project managers need to know about use cases because they help communicate strategy to stakeholders and bridge the gap between business justification and technical requirements.
PMI also notes that “use cases provide a structure for gathering customer requirements and setting the project scope.” But what does that mean in practical terms?
Let’s say that you are a project manager for an education tech firm. Your company’s latest product idea is an app for students where they can receive live tuition for a monthly subscription fee. Creating a use case for this application can tell stakeholders and the project team who the customer is, how the customer will interact with the product, and what the scope gap meaning and requirements of the project will be.
How to write a use case for a project
When presented in written form, a use case can be a helpful piece of project documentation. Use cases are a common requirements artifact , and they can smoothen communication across technical and business stakeholders.
Depending on the intended audience and system under discussion, the use case can be as detailed or basic as needed. A use case document should establish and identify a few key components — these are:
- System : A system is the product, service, or software under discussion.
- Actors : An actor is a user or anything else that exhibits behavior when interacting with the system. The actor could be another system, a piece of hardware, or an entire organization. There are four types of actors: a system under discussion, an internal actor, a primary actor, and a secondary actor. The most commonly referred to are the latter two systems. A primary actor initiates the interaction with the system, while a secondary actor may provide a service to the system.
- Scenario : In “Applying UML and Patterns,” Larman notes that “a scenario is a specific sequence of actions and interactions between actors and the system under discussion; it is also called a use case instance.”
- Use case : A use case outlines the success and failure scenarios that can occur when the actor(s) interact with the system. In this section, you’d establish the main success scenario, i.e., the most desirable outcome between the actor and the system. You would also establish the alternative paths, which explain what happens in the event of failure or error.
Let’s take a look at a simple use case example:
- Use case for meal delivery application : Individuals can use an app to place food orders directly to restaurants. When the user places an order, they are prompted to pay through the app or pay when the food arrives. Once that is confirmed, the restaurant will receive a request through their system. The food will then be prepared, packaged, and delivered to the individual. In this case, the app must be able to receive orders, process payments, and communicate with the restaurant electronically.
- System : Food delivery application
- Primary actor : Customer ordering a meal
- Scenario : The user browses restaurant options. Once the preferred restaurant is selected, they place an order through the application. The user pays online or verifies they will pay in person. The order is sent from the app to the restaurant’s internal system. The restaurant worker receives and processes the electronic order. This use case illustrates how both the customer and restaurant employee (the actors) interact with the food delivery application (the system) and the expected outcome of each interaction. This helps sketch a framework for what is expected in the development stage. The app must be able to process payments, for example.
What is a use case model?
A use case model is a visual representation of the interactions between an actor and a system. As PMI also notes, use case models depict processes, which helps to further express preconditions and triggers.
A use case model is commonly expressed using UML (Universal Modeling Language). In these visualizations, there are three main components: the system, the actors, and the use case.
The system is represented by a rectangle or “boundary box." Actors are shown as stick people outside of the boundary box, while the use cases are presented as text in ovals within the box. Solid and dashed lines represent the association between the actors and the system’s use cases.
Use case model example:

(Source: Visual Paradigm Online )
What is the difference between a use case model and a use case diagram?
A use case diagram is simply a type of use case model. A use case model diagram uses text and shapes to represent the relationship between a user and a system.
Primarily, use case model diagrams are used to:
- Visualize the flow and behavior of the system
- Illustrate the functionality of the system
- Represent key system-user interactions
Depending on the system, a use case model diagram can vary in complexity, showing basic associations or expanding to show multiple exceptions.
Utilizing use cases with Wrike
Utilizing use cases with Wrike can streamline your product development process and help ensure your software meets the needs of its users.
With Wrike’s requirements management template , you can track all of your use case requirements in one place. When it’s time to plan and execute your project, Wrike’s project scheduling template can help you create a clear, actionable plan that keeps your team on track. Try Wrike today and see how easy it is to incorporate use cases into your product development process.

Nicky is a former Content Marketing Manager of Wrike.
Related articles

Wrike Recognized by TrustRadius for Industry-Leading Usability and Customer Service
Wrike earns two awards from TrustRadius for its best-in-class usability and customer service. Find out how to get started with the world’s leading digital work hub.

A Quick Guide to Client Communication Skills
Client communication skills are crucial for delivering impressive work and retaining your best clients. Here’s what you need to know to communicate effectively.

Why Emotional Intelligence Matters in the Workplace (Infographic)
Strong emotional intelligence in the workplace is essential for project and team success. Learn more about improving emotional intelligence as a leader.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
- System Design Tutorial
- What is System Design
- System Design Life Cycle
- High Level Design HLD
- Low Level Design LLD
- Design Patterns
- UML Diagrams
- System Design Interview Guide
- Crack System Design Round
- System Design Bootcamp
- System Design Interview Questions
- Microservices
- Scalability
- System Design Life Cycle | SDLC (Design)
- System Design Tutorial for Front-End Developers
- Pipelining vs Scripting
- Message Queues | System Design
- Design a webpage that can show the status of 10M+ users including: name, photo, badge and points | System Design
- Which Scalability approach is right for our Application? | System Design
- Bare Metal Servers | Networks in System Design
- Object Oriented Principles in OOAD
- Designing Parking Lot (Garage) System | System Design
- Design Reddit | System Design
- Redundancy | System Design
- 3 Essentials for E-commerce Architecture
- Design Restaurant Management System | System Design
- Package Diagram | Introduction, Elements, Use Cases and Benefits
- MACH architecture | System Design for Ecommerce Website
- What is a Memory Pool?
- Different Types of API Gateways?
- Designing Content Delivery Network (CDN) | System Design
- Fault Tolerance in System Design
Use Case Diagrams | Unified Modeling Language (UML)
A Use Case Diagram is a vital tool in system design, it provides a visual representation of how users interact with a system. It serves as a blueprint for understanding the functional requirements of a system from a user’s perspective, aiding in the communication between stakeholders and guiding the development process.

Important Topics for the Use Case Diagrams
- What is a Use Case Diagram in UML?
- Use Case Diagram Notations
- Use Case Diagram Relationships
- How to draw a Use Case diagram in UML?
- What are common Use Case Diagram Tools and Platforms?
- What are Common Mistakes and Pitfalls while making Use Case Diagram?
- What can be Use Case Diagram Best Practices?
- What are the Purpose and Benefits of Use Case Diagrams?
1. What is a Use Case Diagram in UML?
A Use Case Diagram is a type of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram that represents the interaction between actors (users or external systems) and a system under consideration to accomplish specific goals. It provides a high-level view of the system’s functionality by illustrating the various ways users can interact with it.

2. Use Case Diagram Notations
UML notations provide a visual language that enables software developers, designers, and other stakeholders to communicate and document system designs, architectures, and behaviors in a consistent and understandable manner.
1.1. Actors
Actors are external entities that interact with the system. These can include users, other systems, or hardware devices. In the context of a Use Case Diagram, actors initiate use cases and receive the outcomes. Proper identification and understanding of actors are crucial for accurately modeling system behavior.
.webp)
1.2. Use Cases
Use cases are like scenes in the play. They represent specific things your system can do. In the online shopping system, examples of use cases could be “Place Order,” “Track Delivery,” or “Update Product Information”. Use cases are represented by ovals.

1.3. System Boundary
The system boundary is a visual representation of the scope or limits of the system you are modeling. It defines what is inside the system and what is outside. The boundary helps to establish a clear distinction between the elements that are part of the system and those that are external to it. The system boundary is typically represented by a rectangular box that surrounds all the use cases of the system.
Purpose of System Boundary:
- Scope Definition: It clearly outlines the boundaries of the system, indicating which components are internal to the system and which are external actors or entities interacting with the system.
- Focus on Relevance: By delineating the system’s scope, the diagram can focus on illustrating the essential functionalities provided by the system without unnecessary details about external entities.

3. Use Case Diagram Relationships
In a Use Case Diagram, relationships play a crucial role in depicting the interactions between actors and use cases. These relationships provide a comprehensive view of the system’s functionality and its various scenarios. Let’s delve into the key types of relationships and explore examples to illustrate their usage.
3.1. Association Relationship
The Association Relationship represents a communication or interaction between an actor and a use case. It is depicted by a line connecting the actor to the use case. This relationship signifies that the actor is involved in the functionality described by the use case.
Example: Online Banking System
- Actor: Customer
- Use Case: Transfer Funds
- Association: A line connecting the “Customer” actor to the “Transfer Funds” use case, indicating the customer’s involvement in the funds transfer process.
.webp)
3.2. Include Relationship
The Include Relationship indicates that a use case includes the functionality of another use case. It is denoted by a dashed arrow pointing from the including use case to the included use case. This relationship promotes modular and reusable design.
Example: Social Media Posting
- Use Cases: Compose Post, Add Image
- Include Relationship: The “Compose Post” use case includes the functionality of “Add Image.” Therefore, composing a post includes the action of adding an image.

3.3. Extend Relationship
The Extend Relationship illustrates that a use case can be extended by another use case under specific conditions. It is represented by a dashed arrow with the keyword “extend.” This relationship is useful for handling optional or exceptional behavior.
Example: Flight Booking System
- Use Cases: Book Flight, Select Seat
- Extend Relationship: The “Select Seat” use case may extend the “Book Flight” use case when the user wants to choose a specific seat, but it is an optional step.

3.4. Generalization Relationship
The Generalization Relationship establishes an “is-a” connection between two use cases, indicating that one use case is a specialized version of another. It is represented by an arrow pointing from the specialized use case to the general use case.
Example: Vehicle Rental System
- Use Cases: Rent Car, Rent Bike
- Generalization Relationship: Both “Rent Car” and “Rent Bike” are specialized versions of the general use case “Rent Vehicle.”

4. How to draw a Use Case diagram in UML?
Step 1: identify actors.
Determine who or what interacts with the system. These are your actors. They can be users, other systems, or external entities.
Step 2: Identify Use Cases
Identify the main functionalities or actions the system must perform. These are your use cases. Each use case should represent a specific piece of functionality.
Step 3: Connect Actors and Use Cases
Draw lines (associations) between actors and the use cases they are involved in. This represents the interactions between actors and the system.
Step 4: Add System Boundary
Draw a box around the actors and use cases to represent the system boundary. This defines the scope of your system.
Step 5: Define Relationships
If certain use cases are related or if one use case is an extension of another, you can indicate these relationships with appropriate notations.
Step 6: Review and Refine
Step back and review your diagram. Ensure that it accurately represents the interactions and relationships in your system. Refine as needed.
Step 7: Validate
Share your use case diagram with stakeholders and gather feedback. Ensure that it aligns with their understanding of the system’s functionality.
Let’s understand how to draw a Use Case diagram with the help of an Online Shopping System:
2. use cases:.
- Browse Products
- Add to Cart
- Manage Inventory (Admin)
3. Relations:
- The Customer can browse products, add to the cart, and complete the checkout.
- The Admin can manage the inventory.
Below is the usecase diagram of an Online Shopping System:

5. What are common Use Case Diagram Tools and Platforms?
Several tools and platforms are available to create and design Use Case Diagrams. These tools offer features that simplify the diagram creation process, facilitate collaboration among team members, and enhance overall efficiency. Here are some popular Use Case Diagram tools and platforms:
6.1. Lucidchart
- Cloud-based collaborative platform.
- Intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
- Real-time collaboration and commenting.
- Templates for various diagram types.
- Integration with other tools like Jira and Confluence.
6.2. draw.io
- Free, open-source diagramming tool.
- Works offline and can be integrated with Google Drive, Dropbox, and others.
- Offers a wide range of diagram types, including Use Case Diagrams.
- Customizable shapes and themes.
6.3. Microsoft Visio
- Part of the Microsoft Office suite.
- Supports various diagram types, including Use Case Diagrams.
- Integration with Microsoft 365 for collaborative editing.
- Extensive shape libraries and templates.
6.4. SmartDraw
- User-friendly diagramming tool.
- Templates for different types of diagrams, including Use Case Diagrams.
- Integration with Microsoft Office and Google Workspace.
- Auto-formatting and alignment features.
6.5. PlantUML
- Open-source tool for creating UML diagrams.
- Text-based syntax for diagram specification.
- Integrates with various text editors and IDEs.
- Supports collaborative work using version control systems.
6. What are Common Mistakes and Pitfalls while making Use Case Diagram?
Avoiding common mistakes ensures the accuracy and effectiveness of the Use Case Diagram. Here are key points for each mistake:
6.1. Overcomplication:
- Mistake: Including excessive detail in the diagram.
- Impact: Confuses stakeholders and complicates understanding.
- Prevention: Focus on essential use cases and maintain an appropriate level of abstraction.
6.3. Ambiguous Relationships:
- Mistake: Unclear relationships between actors and use cases.
- Impact: Causes misinterpretation of system interactions.
- Prevention: Clearly define and label relationships with proper notation.
6.3. Inconsistent Naming Conventions:
- Mistake: Inconsistent naming of actors and use cases.
- Impact: Causes confusion and hinders communication.
- Prevention: Establish and adhere to a consistent naming convention.
6.4. Misuse of Generalization:
- Mistake: Incorrect use of generalization relationships.
- Impact: Misrepresentation of the “is-a” relationship between use cases or actors.
- Prevention: Ensure accurate usage to represent specialization relationships.
6.5. Overlooking System Boundaries:
- Mistake: Not clearly defining the system boundary.
- Impact: Challenges understanding of the system’s scope.
- Prevention: Clearly enclose relevant actors and use cases within a system boundary.
6.6. Lack of Iteration:
- Mistake: Treating the diagram as a static artifact.
- Impact: May become outdated and not reflect the current state of the system.
- Prevention: Use an iterative approach, updating the diagram as the system evolves.
7. What can be Use Case Diagram Best Practices?
Creating effective and clear Use Case Diagrams is crucial for communicating system functionality and interactions. Here are some best practices to follow:
7.1 Keep it Simple:
- Focus on High-Level Functionality: Avoid unnecessary details and concentrate on representing the system’s primary functionalities.
- Use Concise Language: Use clear and concise language for use case and actor names to enhance readability.
7.2 Consistency:
- Naming Conventions: Maintain a consistent naming convention for use cases and actors throughout the diagram. This promotes clarity and avoids confusion.
- Formatting Consistency: Keep a consistent format for elements like ovals (use cases), stick figures (actors), and lines to maintain a professional look.
7.3. Organize and Align:
- Logical Grouping: Organize use cases into logical groups to represent different modules or subsystems within the system.
- Alignment: Maintain proper alignment of elements to make the diagram visually appealing and easy to follow.
7.4. Use Proper Notation:
- Consistent Symbols: Adhere to standard symbols for actors (stick figures), use cases (ovals), and relationships to ensure understanding.
- Proper Line Types: Clearly distinguish between association, include, extend, and generalization relationships using appropriate line types.
7.5. Review and Iterate:
- Feedback Loop: Regularly review the diagram with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Iterative Process: Use an iterative process, updating the diagram as the system evolves or more information becomes available.
By following these best practices, you can create Use Case Diagrams that effectively communicate the essential aspects of a system, fostering a shared understanding among stakeholders and facilitating the development process.
8. What are the Purpose and Benefits of Use Case Diagrams?
The Use Case Diagram offers numerous benefits throughout the system development process. Here are some key advantages of using Use Case Diagrams:
- Use Case Diagrams provide a visual representation of the system’s functionalities and interactions with external entities.
- This visualization helps stakeholders, including non-technical ones, to understand the system’s high-level behavior.
- Use Case Diagrams serve as a powerful communication tool, facilitating discussions between stakeholders, developers, and designers.
- They provide a common language for discussing system requirements, ensuring a shared understanding among diverse team members.
- During the requirements analysis phase, Use Case Diagrams help in identifying, clarifying, and documenting user requirements.
- They capture the various ways users interact with the system, aiding in a comprehensive understanding of system functionality.
- Use Case Diagrams center around user goals and scenarios, emphasizing the perspective of external entities (actors).
- This focus on user interactions ensures that the system is designed to meet user needs and expectations.
- In the system design phase, Use Case Diagrams aid in designing how users (actors) will interact with the system.
- They contribute to the planning of the user interface and help in organizing system functionalities.
- Use Case Diagrams are valuable for deriving test cases and validating system behavior.
- Testers can use the diagrams to ensure that all possible scenarios, including alternative and exceptional paths, are considered during testing.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, a Use Case Diagram in UML serves as a powerful tool for capturing and visualizing the functional requirements and interactions within a system. By representing actors, use cases, and their relationships in a clear and concise manner, this diagram provides a high-level overview of the system’s behavior.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Geeks Premier League 2023
- Geeks Premier League
- System Design
- 10 Best Slack Integrations to Enhance Your Team's Productivity
- 10 Best Zendesk Alternatives and Competitors
- 10 Best Trello Power-Ups for Maximizing Project Management
- Google Rolls Out Gemini In Android Studio For Coding Assistance
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Home » Use Case Analysis » Exploring Use Cases and Scenarios in Software Development
Exploring Use Cases and Scenarios in Software Development
- Posted on October 13, 2023
- / Under UML , Use Case Analysis
Introduction
In the intricate landscape of software development, where precision and clarity are paramount, the utilization of use cases and scenarios stands as a beacon guiding developers through the maze of requirements and functionalities. Let’s embark on a journey through the definitions, frameworks, and methodologies that make use cases and scenarios indispensable in the development process.
Understanding the Use Case
At its essence, a use case is a comprehensive collection of interactions between external actors and a system. It serves as a structured means of capturing and documenting the functional requirements of a system. In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), a standardized modeling language in software engineering, a use case is defined as “the specification of a sequence of actions, including variants, that a system (or entity) can perform, interacting with actors of the system.”
The Anatomy of a Use Case
Typically, each use case is a nuanced entity comprising a primary scenario, often referred to as the main course of events. This primary scenario outlines the typical and essential interactions between the system and its external actors under normal conditions. Additionally, a use case may encompass zero or more secondary scenarios, offering alternative courses of events that deviate from the primary path. These secondary scenarios enrich the overall understanding of the system’s behavior, accounting for variations, exceptions, or alternative user interactions.
Bridging the Gap Between Requirements and Development
In the realm of software development methodologies, the use case modeling emphasizes capturing user requirements through use cases, which are subsequently refined into scenarios. This iterative process ensures that the evolving needs and expectations of users are seamlessly integrated into the development lifecycle.
- A scenario, in the context of use cases, represents one specific path or flow through a use case. It narrates a sequence of events that unfold during a particular execution of the system. Scenarios provide a granular view of how the system behaves under different conditions, offering insights into the nuanced facets of its functionality.
The Sequence Diagram: Transforming Scenarios into Visual Blueprints
The journey from use cases to scenarios is completed with the modeling of scenarios using sequence diagrams . A sequence diagram is a visual representation that illustrates the interactions between various components of the system during the execution of a use case. It serves as a blueprint for system design, providing developers with a clear guide on how different elements of the system should interact to fulfill user requirements.
Use Case Modeling Case Study – From Use case to Scenarios and Sequence diagrams
Let’s delve into the essence of use cases and scenarios and explore their significance in the realm of software engineering.
1. Use Case Definition:
- Scenario: The team begins by identifying a fundamental use case: “User Places an Order.” This use case encapsulates the primary interaction between the user and the system, representing the core functionality of the online shopping platform.
2. Refining Use Case into Scenarios:
- The user adds items to the cart, proceeds to checkout, provides shipping details, and confirms the order.
- A variant where the user applies a discount code during checkout, impacting the final order total.
- Addressing the scenario where an item in the cart is out of stock, requiring user notification and decision-making.
3. Modeling Scenarios with Sequence Diagrams:
Each scenario is then translated into a sequence diagram, providing a visual representation of the interactions between different components of the system during the execution of the use case.
- Actors: User, Shopping Cart, Inventory System, Payment Gateway, Order Processing System.
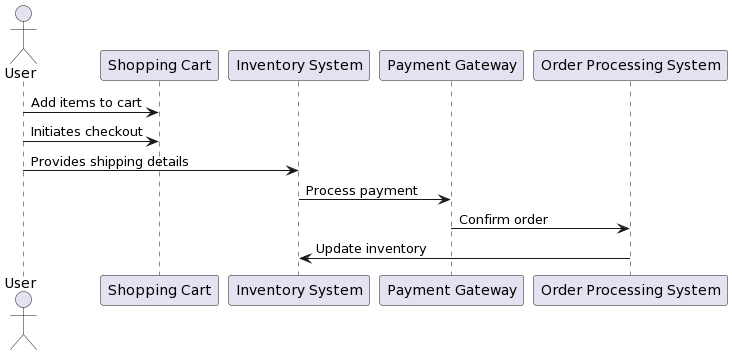
- Additional interactions with the Discount Service are depicted, showing how the discount code affects the order total.
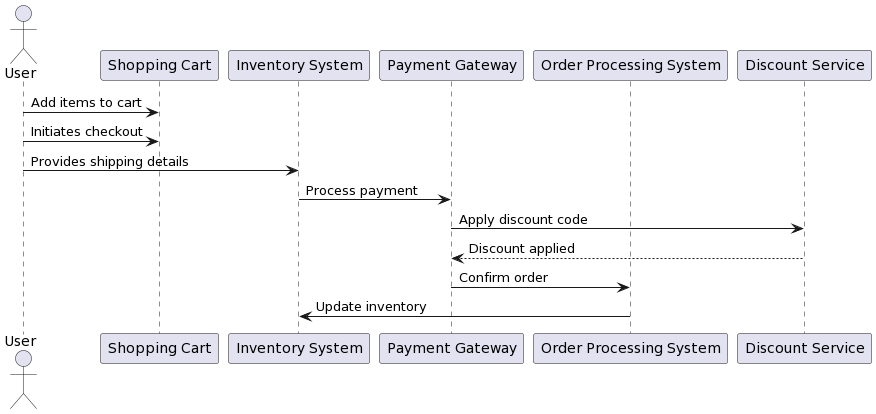
Purpose of the Process
- The use case provides a high-level overview, scenarios offer detailed paths, and sequence diagrams bring a visual clarity to the system interactions. This progression ensures that everyone involved, from developers to stakeholders, has a shared understanding of the system’s behavior.
- Breaking down the use case into scenarios allows for a more granular analysis of user requirements. This, in turn, aids in identifying potential challenges, edge cases, and dependencies.
- Sequence diagrams serve as a blueprint for system design. They guide developers in understanding how different components of the system need to interact to fulfill user requirements.
Benefits of the Process
- By refining a use case into scenarios and modeling them with sequence diagrams, the team ensures a more accurate and precise understanding of user interactions and system responses.
- The sequence diagrams become a valuable resource for test case generation. Test scenarios can be derived directly from the interactions depicted in the diagrams, ensuring comprehensive testing coverage.
- The process of refining use cases and modeling scenarios aligns well with iterative development methodologies. It allows the team to adapt to evolving requirements and continuously refine the system design.
In the realm of software development, the use of Use Cases, Scenarios, and Sequence Diagrams emerges as a structured and indispensable approach to capturing, analyzing, and visualizing system functionalities. The journey begins with the definition of a Use Case, a comprehensive collection of interactions between external actors and a system. In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), a Use Case is specified as “the sequence of actions, including variants, that a system can perform, interacting with its actors.”
A Use Case typically comprises a primary scenario, representing the main course of events, and may include zero or more secondary scenarios, offering alternative paths to the primary scenario. The Rational Unified Process (RUP), a robust software development framework, emphasizes capturing user requirements as Use Cases, which are subsequently refined into Scenarios.
Scenarios, in turn, delve into one specific path or flow through a Use Case, providing a detailed sequence of events during a particular system execution. This refinement process aids in clear communication, meticulous requirement analysis, and serves as a foundation for iterative development methodologies.
The transition from Use Cases to Scenarios culminates in the modeling of these scenarios using Sequence Diagrams. These visual blueprints illustrate the interactions between different system components during the execution of a Use Case. The purpose of this process is multi-faceted:
- The structured progression ensures effective communication between technical teams and stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding of the system’s behavior.
- Breaking down Use Cases into Scenarios facilitates a granular analysis of user requirements, identifying potential challenges, edge cases, and dependencies.
- Sequence Diagrams serve as blueprints for system design, offering visual guidance for developers on how different components should interact to fulfill user requirements.
- Integrated with methodologies like RUP, this process aligns seamlessly with iterative development practices, accommodating evolving requirements and allowing for continuous refinement.
In a nutshell, this meticulous journey from Use Cases to Scenarios and Sequence Diagrams provides a systematic and structured approach in software development. It ensures accuracy, precision, and adaptability, ultimately contributing to the successful development and deployment of robust, user-centric systems.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Visual Paradigm Online
- Request Help
- Customer Service
- Community Circle
- Demo Videos
- Visual Paradigm
- YouTube Channel
- Academic Partnership
16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing
Updated: September 08, 2020
Published: July 30, 2020
When you're thinking about investing in a product or service, what's the first thing you do?

Usually, it’s one or both of the following: You'll likely ask your friends whether they've tried the product or service, and if they have, whether they would recommend it. You'll also probably do some online research to see what others are saying about said product or service. Nowadays, 90% of consumers used the internet to find a local business in the last year , and 82% of consumers read online reviews. This shows that the majority of people are looking to peers to make a purchasing decision. Most customers know that a little online research could spare them from a bad experience and poor investment of your budget.

What Is a Marketing Case Study?
A case study is the analysis of a particular instance (or "case") of something to demonstrate quantifiable results as a result of the application of something. In marketing, case studies are used as social proof — to provide buyers with the context to determine whether they're making a good choice.
A marketing case study aims to persuade that a process, product, or service can solve a problem. Why? Because it has done so in the past. By including the quantitative and qualitative outcomes of the study, it appeals to logic while painting a picture of what success looks like for the buyer. Both of which can be powerful motivators and objection removers.
Why Use Case Studies?
In essence, case studies are an invaluable asset when it comes to establishing proof that what you're offering is valuable and of good quality.
According to HubSpot's State of Marketing Report 2020 , 13% of marketers name case studies as one of the primary forms of media used within their content strategy. This makes them the fifth most popular type of content, outshined only by visual content, blogs, and ebooks.
Okay, so you know case studies work. The question is, how do they work? And how can you squeeze the most value out of them?
When to Use a Case Study
Here are the ways you can market your case studies to get the most out of them.
As a Marketing or Sales Asset
1. use a case study template to create pdfs for email or downloads . .
Do not underestimate the value of providing social proof at just the right time in order to add value and earn their business. Case studies are extremely effective in the consideration stage of the buyer's journey when they are actively comparing solutions and providers to solve a problem they're experiencing.
For this reason, case studies in an independent PDF format can be helpful in both marketing and sales. Marketers can use these PDFs as downloads in web content or email campaigns. Sales reps can utilize these assets in demonstrations, in a follow-up, or to overcome objections.
The easiest way to create PDF case studies is by using a case study template . Doing so can decrease the amount of time you spend creating and designing your case study without sacrificing aesthetics. In addition, you can ensure that all your case studies follow a similar branded format.
We've created a great case study template (and kit!) that's already locked and loaded for you to use. All you have to do is input your own text and change the fonts and colors to fit your brand. You can download it here .
On Your Website
2. have a dedicated case studies page..
You should have a webpage exclusively for housing your case studies. Whether you call this page "Case Studies, "Success Studies," or "Examples of Our Work," be sure it's easy for visitors to find.
Structure on that page is key: Initial challenges are clear for each case, as well as the goals, process, and results.
Get Inspired: Google’s Think With Google is an example of a really well structured case study page. The copy is engaging, as are the goals, approach, and results.
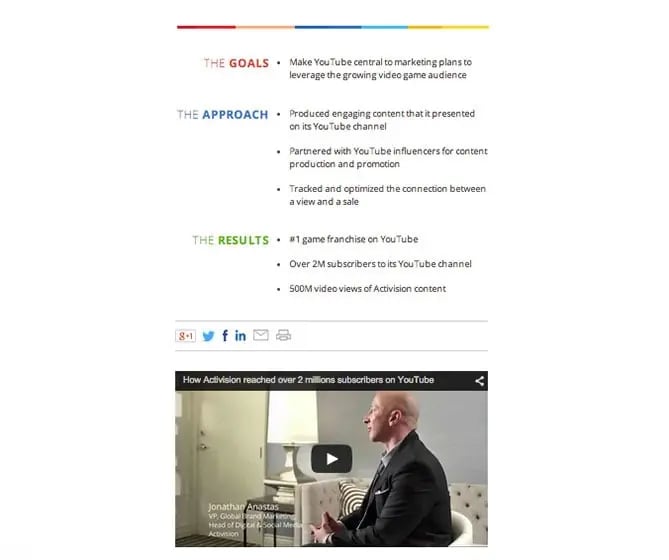
3. Put case studies on your home page.
Give website visitors every chance you can to stumble upon evidence of happy customers. Your home page is the perfect place to do this.
There are a number of ways you can include case studies on your homepage. Here are a few examples:
- Customer quotes/testimonials
- A call-to-action (CTA) to view specific case studies
- A slide-in CTA that links to a case study
- A CTA leading to your case studies page
Get Inspired: Theresumator.com incorporates testimonials onto their homepage to strengthen their value proposition.

Bonus Tip: Get personal.
Marketing gurus across the world agree that personalised marketing is the future . You can make your case studies more powerful if you find ways to make them “match” the website visitors that are important to you.
People react to familiarity -- for instance, presenting someone from London with a case study from New York may not resonate as well as if you displayed a case study from the U.K. Or you could choose to tailor case studies by industry or company size to the visitor. At HubSpot, we call this "smart content."
Get Inspired: To help explain smart content, have a look at the example below. Here, we wanted to test whether including testimonials on landing pages influenced conversion rates in the U.K. The landing page on the left is the default landing page shown to visitors from non-U.K. IP addresses. For the landing page on the right, we used smart content to show testimonials to visitors coming from U.K. IP addresses.
4. Implement slide-in CTAs.
Pop-ups have a reputation for being annoying, but there are ways to implement that that won't irk your website visitors. These CTAs don't have to be huge, glaring pop-ups -- instead, relevant but discreet slide-in CTAs can work really well.
For example, why not test out a slide-in CTA on one of your product pages, with a link to a case study that profiles a customer who's seen great results using that product?
Get Inspired: If you need some help on creating sliders for your website, check out this tutorial on creating slide-in CTAs .
5. Write blog posts about your case studies.
Once you publish a case study, the next logical step would be to write a blog post about it to expose your audience to it. The trick is to write about the case study in a way that identifies with your audience’s needs. So rather than titling your post “Company X: A Case Study," you might write about a specific hurdle, issue, or challenge the company overcame, and then use that company's case study to illustrate how the issues were addressed. It's important not to center the blog post around your company, product, or service -- instead, the customer’s challenges and how they were overcome should take centre stage.
For example, if we had a case study that showed how one customer generated twice as many leads as a result of our marketing automation tool, our blog post might be something along the lines of: "How to Double Lead Flow With Marketing Automation [Case Study]." The blog post would then comprise of a mix of stats, practical tips, as well as some illustrative examples from our case study.
Get Inspired: Check out this great example of a blog post from Moz , titled "How to Build Links to Your Blog – A Case Study."
6. Create videos from case studies.
Internet services are improving all the time, and as a result, people are consuming more and more video content. Prospects could be more likely to watch a video than they are to read a lengthy case study. If you have the budget, creating videos of your case studies is a really powerful way to communicate your value proposition.
Get Inspired: Check out one of our many video testimonials for some ideas on how to approach your own videos.
7. Use case studies on relevant landing pages.
Once you complete a case study, you'll have a bank of quotes and results you can pull from. Including quotes on product pages is especially interesting. If website visitors are reading your product pages, they are in a "consideration" mindset, meaning they are actively researching your products, perhaps with an intent to buy. Having customer quotes placed strategically on these pages is a great way to push them over the line and further down the funnel.
These quotes should be measured, results-based snippets, such as, “XX resulted in a 70% increase in blog subscribers in less an 6 months” rather than, “We are proud to be customers of XX, they really look after us."
Get Inspired: I really like the way HR Software company Workday incorporates video and testimonials into its solutions pages.
Off Your Website
8. post about case studies on social media..
Case studies make for perfect social sharing material. Here are a few examples of how you can leverage them on social:
- Share a link to a case study and tag the customer in the post. The trick here is to post your case studies in a way that attracts the right people to click through, rather than just a generic message like, “New Case Study ->> LINK." Make sure your status communicates clearly the challenge that was overcome or the goal that was achieved. It's also wise to include the main stats associated with the case study; for example, "2x lead flow," "125% increase in X," and so on.
- Update your cover image on Twitter/Facebook showing a happy customer. Our social media cover photo templates should help you with this!
- Add your case study to your list of publications on LinkedIn.
- Share your case studies in relevant LinkedIn Groups.
- Target your new case studies to relevant people on Facebook using dark posts. ( Learn about dark posts here. )
Get Inspired: MaRS Discovery District posts case studies on Twitter to push people towards a desired action.
9. Use case studies in your email marketing.
Case studies are particularly suited to email marketing when you have an industry-segmentable list. For example, if you have a case study from a client in the insurance industry, emailing your case study to your base of insurance-related contacts can be a really relevant addition to a lead nurturing campaign.
Case studies can also be very effective when used in product-specific lead nurture workflows in reactivating opportunities that have gone cold. They can be useful for re-engaging leads that have gone quiet and who were looking at specific areas of your product that the case study relates to.
Get Inspired: It's important that your lead nurture workflow content includes the appropriate content for where prospects are in the sales cycle. If you need help on how to do this, check out our post on how to map lead nurturing content to each stage in sales cycle .
Pro tip: When sending emails, don't forget about the impact a good email signature can make. Create your own using our free Email Signature Generator .
10. Incorporate case studies into your newsletters.
This idea is as good for your client relations as it is for gaining the attention of your prospects. Customers and clients love feeling as though they're part of a community. It’s human nature. Prospects warm to companies that look after their customers; companies whose customers are happy and proud to be part of something. Also, whether we are willing to admit it or not, people love to show off!
Get Inspired: Newsletters become stale over time. Give your newsletters a new lease of life with our guide on how to create newsletters that don't suck .
11. Equip your sales team with case studies.
Tailored content has become increasingly important to sales reps as they look to provide value on the sales call. It's estimated that consumers go through 70-90% of the buyer's journey before contacting a vendor. This means that the consumer is more knowledgeable than ever before. Sales reps no longer need to spend an entire call talking about the features and benefits. Sales has become more complex, and reps now need to be armed with content that addresses each stage of the buyer’s process. Case studies can be really useful when it comes to showing prospects how successful other people within a similar industry has benefited from your product or service.
Get Inspired: Case studies are just one type of content that helps your sales team sell. They don't always work by themselves, though. Check out our list of content types that help sales close more deals .
12. Sneak a case study into your email signature.
Include a link to a recent case study in your email signature. This is particularly useful for salespeople. Here's what my email signature looks like:

Get Inspired: Did you know that there are lots more ways you can use your email signature to support your marketing? Here are 10 clever suggestions for how you can do this.
13. Use case studies in training.
Having customer case studies is an invaluable asset to have when onboarding new employees. It aids developing their buy-in, belief in, and understanding of your offering.
Get Inspired: Have you completed our Inbound Certification course yet? During our classes, we use case studies to show how inbound marketing is applied in real life.
In Lead-Gen Content
14. include case studies in your lead gen efforts..
There are a number of offers you can create based off of your case studies, in the form of ebooks, templates, and more. For example you could put together an ebook titled “A step-by-step guide to reaching 10,000 blog subscribers in 3 months…just like XX did.” You could create a more in-depth version of the case study with access to detailed statistics as an offer. (And don’t forget, you can also u se quotes and statistics from case studies on the landing page promoting the ebook, which adds credibility and could increase your conversion rates.) Or, you could create a template based on your customer's approach to success.
Get Inspired: If you think you need to be an awesome designer put together beautiful ebooks, think again. Create ebooks easily using these customisable ebook templates .
You can also use case studies to frame webinars that document how to be successful with X. Using case studies in webinars is great middle-of-the-funnel content and can really help move your leads further down the funnel towards becoming sales qualified leads.
Get Inspired: Webinars are really effective as part of a lead nurturing workflow. Make sure your next webinar is spot on by following these simple webinar tips.
15. Create a bank of evergreen presentations.
It’s important to build up a bank of evergreen content that employees across your organisation can use during presentations or demos. Case studies are perfect for this.
Put together a few slides on the highlights of the case study to stir people’s interest, and then make them available to your sales and customer-facing teams. It's helpful if the marketer who created the presentation is the one who presents it to anyone who might use them in the future. This ensures they can explain the presentation clearly and answer any questions that might arise.
Get Inspired: What to create presentations people want to use? Here's a list of tools to make your presentations great.
16. Create SlideShares based on case studies.
Following on from a few short slides, you could also put together a more detailed presentation of the case study and upload it to SlideShare. After all, not only is SlideShare SEO-friendly (because Google indexes each presentation), but there is a huge pre-existing audience on SlideShare of over 60 million users you can tap into. SlideShare presentations are also easy to embed and share, and allow you to capture leads directly from the slides via a lead capture form.
Get Inspired: Want to generate more leads with SlideShare, but not sure how to get started? Check out this blog post .
Now that you understand the value of a marketing case study and the different ways that they can be used in your content marketing (and even sales) strategy, your next step is to think about what would convince your target audience to do business with you.
Have you recently accomplished something big for a client? Do you have a process or product with demonstrable results? What do your potential clients hope that you'll do for them?
The answers to those questions will help you craft compelling content for your case study. Then, all that's left is putting it into your audience's hands in formats they want to consume.

Editor's note: This post was originally published in January 2015 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![use case study meaning 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![use case study meaning How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![use case study meaning What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Use Case or Case Study? When to Use Each in Your Content Strategy

Use cases and case studies focus on the real-world application of a product or solution, and both are important tools in the B2B content strategist’s toolkit. But don’t confuse them! They are distinctly different content types, and deploying each of them at the right point in the buyer’s journey is crucial to making sure they resonate with your audience.
But how do you choose between them? And what separates a good use case or case study from a really great one? We’ve got you covered. In this blog post, we’ll explain:
- The difference between use cases and case studies
- Where they fit into the buyer’s journey
- How to make these content assets compelling—and use them to build a connected content journey
What Is a Use Case? Definition and Examples
A use case illustrates how a product or solution solves for a particular pain point, customer type, or scenario. It frames the product in terms of the customer’s goals and careabouts, which is a powerful way to highlight its value even when customers aren’t familiar with your company or what it does.
Because of this, use cases are best used at the awareness stage, early in the buyer’s journey. They’re especially useful for search, since customers at this stage are looking for a way to solve their problem (and searching for keywords and phrases related to that problem).
Here’s an example: An IT manager is looking for solutions to enable her company’s employees to use their own devices for work. She may or may not know exactly what kind of product she’s looking for; either way, she doesn’t have a specific provider in mind. Searching for “bring your own device” brings up a product page where that’s listed as a use case, leading her to learn more about that product.

What Is a Case Study? Definition and Examples
A case study (sometimes called a customer story) is a real-world story about how a customer successfully used a product or solution to achieve a goal. According to the Content Marketing Institute’s 2022 B2B Content Marketing report , 73 percent of the most successful content marketers used case studies in their content strategy.
A case study is typically much more detailed than a use case, and includes information such as background on the customer, pain points, objectives, how they deployed the product or solution, and the results. Unlike a use case, which is a straightforward explanation of how a product addresses a problem, a case study is driven by storytelling.
Because case studies are so detailed, they belong later in the buyer’s journey, typically at the consideration or decision stage. At this point, customers are looking at how other companies have solved the problem they’re having. They’re looking for evidence—quantifiable data; tangible results—and they’re willing to spend more time on an asset that provides it.
Let’s look at an example. A case study about Salesforce customer ENGIE, a group committed to accelerating the transition to a carbon-neutral world, explores how ENGIE used Salesforce products to unify data and build customer relationships—and does so in great detail. In fact, the entire case study clocks in at nearly 1,700 words, plus a video, pull quotes, and statistic highlights.

How to Make a Use Case or Case Study Great
Despite the obvious differences between them, the key to making your use case or case study great is the same: Focus on the customer’s point of view.
For use cases, this means using search data and other customer research to ensure that your content is targeting problems and pain points that your customers actually have, rather than your internal marketing terms or what you think they should be searching for.
For case studies, this means making the customer the hero of the story. Too many marketers focus on the company or product when writing a case study. It’s true that a customer at the consideration stage is more invested in learning about your product, but what they really want to know is how it can make them successful. Instead of focusing on product features, focus on customer results.
The ENGIE case study above is an excellent example. Salesforce and its products aren’t mentioned until paragraph 6, and throughout the narrative, the focus is squarely on the customer and its achievements.
Use Cases vs. Case Studies in the Content Journey
We’ve highlighted some of the differences between a use case and a case study. But they also have commonalities, which you can use to build a connected content journey. One way to do this is to bring the use cases you’ve identified with search data into your case studies. Although your customer’s product knowledge and attitude toward your company evolves throughout the buyer’s journey, their careabouts and pain points remain the same, and this is a great way to call back to content they may have seen earlier in the buying process and create a cohesive experience.
This can also go in the other direction. A common mistake marketers make is to try to position case studies as an awareness asset. We’ve already discussed why case studies should live at the consideration stage, but what if you’ve got a really compelling case study and want to use it for awareness content? The answer: Take a bite-sized chunk, like a quotation or testimonial, and use it in landing pages, social media banners, and other awareness content. A true case study needs lots of background to be effective (and users don’t want to invest that much time at the awareness stage), but a strong testimonial can grab attention all on its own.
And there you have it: all the information you need to create great use cases and case studies—and to place them where they’ll be most effective in the buyer’s journey. In addition to boosting your content marketing efforts, making the most of your use cases and case studies will help you build the connective tissue that leads to a progressive and holistic content experience.
Talk to Tendo
Tendo’s team of experienced content strategists can provide actionable insights on your content journey and help you create use cases, case studies, and other content assets that stand out from the crowd. Explore our content strategy services or get in touch with our team .
« Back to Thought Leadership Index
Subscribe for Content Strategy Trends and Guidance
Get our monthly e-newsletter with Tendo’s latest thought leadership and content resources for B2B leaders.

You may also like…

Tendo Communications Acquires PointOne Digital

Bridge Your Marketing and Sales Teams with Content

Drive the Buyer’s Journey with Content

Creating Engaging Experiences Through Online Communities | Episode 4 | The B2B Content Experience Podcast
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Hey there! Free trials are available for Standard and Essentials plans. Start for free today.
What Is a Case Study and Why You Should Use Them
Case studies can provide more insights into your business while helping you conduct further research with robust qualitative data analysis to learn more.
If you're in charge of running a company, then you're likely always looking for new ways to run your business more efficiently and increase your customer base while streamlining as many processes as possible.
Unfortunately, it can sometimes be difficult to determine how to go about implementing the proper program in order to be successful. This is why many business owners opt to conduct a case study, which can help significantly. Whether you've been struggling with brand consistency or some other problem, the right case study can identify why your problem exists as well as provide a way to rectify it.
A case study is a great tool that many businesses aren't even aware exists, and there are marketing experts like Mailchimp who can provide you with step-by-step assistance with implementing a plan with a case study. Many companies discover that not only do they need to start a blog in order to improve business, but they also need to create specific and relevant blog titles.
If your company already has a blog, then optimizing your blog posts may be helpful. Regardless of the obstacles that are preventing you from achieving all your professional goals, a case study can work wonders in helping you reverse this issue.

What is a case study?
A case study is a comprehensive report of the results of theory testing or examining emerging themes of a business in real life context. Case studies are also often used in the healthcare industry, conducting health services research with primary research interest around routinely collected healthcare data.
However, for businesses, the purpose of a case study is to help small business owners or company leaders identify the issues and conduct further research into what may be preventing success through information collection, client or customer interviews, and in-depth data analysis.
Knowing the case study definition is crucial for any business owner. By identifying the issues that are hindering a company from achieving all its goals, it's easier to make the necessary corrections to promote success through influenced data collection.
Why are case studies important?
Now that we've answered the questions, "what is a case study?" Why are case studies important? Some of the top reasons why case studies are important include:

- Understand complex issues: Even after you conduct a significant amount of market research , you might have a difficult time understanding exactly what it means. While you might have the basics down, conducting a case study can help you see how that information is applied. Then, when you see how the information can make a difference in business decisions, it could make it easier to understand complex issues.
- Collect data: A case study can also help with data tracking . A case study is a data collection method that can help you describe the information that you have available to you. Then, you can present that information in a way the reader can understand.
- Conduct evaluations: As you learn more about how to write a case study, remember that you can also use a case study to conduct evaluations of a specific situation. A case study is a great way to learn more about complex situations, and you can evaluate how various people responded in that situation. By conducting a case study evaluation, you can learn more about what has worked well, what has not, and what you might want to change in the future.
- Identify potential solutions: A case study can also help you identify solutions to potential problems. If you have an issue in your business that you are trying to solve, you may be able to take a look at a case study where someone has dealt with a similar situation in the past. For example, you may uncover data bias in a specific solution that you would like to address when you tackle the issue on your own. If you need help solving a difficult problem, a case study may be able to help you.
Remember that you can also use case studies to target your audience . If you want to show your audience that you have a significant level of expertise in a field, you may want to publish some case studies that you have handled in the past. Then, when your audience sees that you have had success in a specific area, they may be more likely to provide you with their business. In essence, case studies can be looked at as the original method of social proof, showcasing exactly how you can help someone solve their problems.
What are the benefits of writing a business case study?
Although writing a case study can seem like a tedious task, there are many benefits to conducting one through an in depth qualitative research process.

- Industry understanding: First of all, a case study can give you an in-depth understanding of your industry through a particular conceptual framework and help you identify hidden problems that are preventing you from transcending into the business world.
- Develop theories: If you decide to write a business case study, it provides you with an opportunity to develop new theories. You might have a theory about how to solve a specific problem, but you need to write a business case study to see exactly how that theory has unfolded in the past. Then, you can figure out if you want to apply your theory to a similar issue in the future.
- Evaluate interventions: When you write a business case study that focuses on a specific situation you have been through in the past, you can uncover whether that intervention was truly helpful. This can make it easier to figure out whether you want to use the same intervention in a similar situation in the future.
- Identify best practices: If you want to stay on top of the best practices in your field, conducting case studies can help by allowing you to identify patterns and trends and develop a new list of best practices that you can follow in the future.
- Versatility: Writing a case study also provides you with more versatility. If you want to expand your business applications, you need to figure out how you respond to various problems. When you run a business case study, you open the door to new opportunities, new applications, and new techniques that could help you make a difference in your business down the road.
- Solve problems: Writing a great case study can dramatically improve your chances of reversing your problem and improving your business.
- These are just a few of the biggest benefits you might experience if you decide to publish your case studies. They can be an effective tool for learning, showcasing your talents, and teaching some of your other employees. If you want to grow your audience , you may want to consider publishing some case studies.
What are the limitations of case studies?
Case studies can be a wonderful tool for any business of any size to use to gain an in-depth understanding of their clients, products, customers, or services, but there are limitations.
One limitation of case studies is the fact that, unless there are other recently published examples, there is nothing to compare them to since, most of the time, you are conducting a single, not multiple, case studies.
Another limitation is the fact that most case studies can lack scientific evidence.

Types of case studies
There are specific types of case studies to choose from, and each specific type will yield different results. Some case study types even overlap, which is sometimes more favorable, as they provide even more pertinent data.
Here are overviews of the different types of case studies, each with its own theoretical framework, so you can determine which type would be most effective for helping you meet your goals.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are pretty straightforward, as they're not difficult to interpret. This type of case study is best if there aren't many variables involved because explanatory case studies can easily answer questions like "how" and "why" through theory development.
Exploratory case studies
An exploratory case study does exactly what its name implies: it goes into specific detail about the topic at hand in a natural, real-life context with qualitative research.
The benefits of exploratory case studies are limitless, with the main one being that it offers a great deal of flexibility. Having flexibility when writing a case study is important because you can't always predict what obstacles might arise during the qualitative research process.
Collective case studies
Collective case studies require you to study many different individuals in order to obtain usable data.
Case studies that involve an investigation of people will involve many different variables, all of which can't be predicted. Despite this fact, there are many benefits of collective case studies, including the fact that it allows an ongoing analysis of the data collected.
Intrinsic case studies
This type of study differs from the others as it focuses on the inquiry of one specific instance among many possibilities.
Many people prefer these types of case studies because it allows them to learn about the particular instance that they wish to investigate further.
Instrumental case studies
An instrumental case study is similar to an intrinsic one, as it focuses on a particular instance, whether it's a person, organization, or something different.
One thing that differentiates instrumental case studies from intrinsic ones is the fact that instrumental case studies aren't chosen merely because a person is interested in learning about a specific instance.

Tips for writing a case study
If you have decided to write case studies for your company, then you may be unsure of where to start or which type to conduct.
However, it doesn't have to be difficult or confusing to begin conducting a case study that will help you identify ways to improve your business.
Here are some helpful tips for writing your case studies:
1. Your case study must be written in the proper format
When writing a case study, the format that you should be similar to this:

Administrative summary
The executive summary is an overview of what your report will contain, written in a concise manner while providing real-life context.
Despite the fact that the executive summary should appear at the beginning of your case studies, it shouldn't be written until you've completed the entire report because if you write it before you finish the report, this summary may not be completely accurate.
Key problem statement
In this section of your case study, you will briefly describe the problem that you hope to solve by conducting the study. You will have the opportunity to elaborate on the problem that you're focusing on as you get into the breadth of the report.
Problem exploration
This part of the case study isn't as brief as the other two, and it goes into more detail about the problem at hand. Your problem exploration must include why the identified problem needs to be solved as well as the urgency of solving it.
Additionally, it must include justification for conducting the problem-solving, as the benefits must outweigh the efforts and costs.
Proposed resolution
This case study section will also be lengthier than the first two. It must include how you propose going about rectifying the problem. The "recommended solution" section must also include potential obstacles that you might experience, as well as how these will be managed.
Furthermore, you will need to list alternative solutions and explain the reason the chosen solution is best. Charts can enhance your report and make it easier to read, and provide as much proof to substantiate your claim as possible.
Overview of monetary consideration
An overview of monetary consideration is essential for all case studies, as it will be used to convince all involved parties why your project should be funded. You must successfully convince them that the cost is worth the investment it will require. It's important that you stress the necessity for this particular case study and explain the expected outcome.
Execution timeline
In the execution times of case studies, you explain how long you predict it will take to implement your study. The shorter the time it will take to implement your plan, the more apt it is to be approved. However, be sure to provide a reasonable timeline, taking into consideration any additional time that might be needed due to obstacles.
Always include a conclusion in your case study. This is where you will briefly wrap up your entire proposal, stressing the benefits of completing the data collection and data analysis in order to rectify your problem.
2. Make it clear and comprehensive
You want to write your case studies with as much clarity as possible so that every aspect of the report is understood. Be sure to double-check your grammar, spelling, punctuation, and more, as you don't want to submit a poorly-written document.
Not only would a poorly-written case study fail to prove that what you are trying to achieve is important, but it would also increase the chances that your report will be tossed aside and not taken seriously.
3. Don't rush through the process
Writing the perfect case study takes time and patience. Rushing could result in your forgetting to include information that is crucial to your entire study. Don't waste your time creating a study that simply isn't ready. Take the necessary time to perform all the research necessary to write the best case study possible.
Depending on the case study, conducting case study research could mean using qualitative methods, quantitative methods, or both. Qualitative research questions focus on non-numerical data, such as how people feel, their beliefs, their experiences, and so on.
Meanwhile, quantitative research questions focus on numerical or statistical data collection to explain causal links or get an in-depth picture.
It is also important to collect insightful and constructive feedback. This will help you better understand the outcome as well as any changes you need to make to future case studies. Consider using formal and informal ways to collect feedback to ensure that you get a range of opinions and perspectives.
4. Be confident in your theory development
While writing your case study or conducting your formal experimental investigation, you should have confidence in yourself and what you're proposing in your report. If you took the time to gather all the pertinent data collected to complete the report, don't second-guess yourself or doubt your abilities. If you believe your report will be amazing, then it likely will be.
5. Case studies and all qualitative research are long
It's expected that multiple case studies are going to be incredibly boring, and there is no way around this. However, it doesn't mean you can choose your language carefully in order to keep your audience as engaged as possible.
If your audience loses interest in your case study at the beginning, for whatever reason, then this increases the likelihood that your case study will not be funded.
Case study examples
If you want to learn more about how to write a case study, it might be beneficial to take a look at a few case study examples. Below are a few interesting case study examples you may want to take a closer look at.
- Phineas Gage by John Martin Marlow : One of the most famous case studies comes from the medical field, and it is about the story of Phineas Gage, a man who had a railroad spike driven through his head in 1848. As he was working on a railroad, an explosive charge went off prematurely, sending a railroad rod through his head. Even though he survived this incident, he lost his left eye. However, Phineas Gage was studied extensively over the years because his experiences had a significant, lasting impact on his personality. This served as a case study because his injury showed different parts of the brain have different functions.
- Kitty Genovese and the bystander effect : This is a tragic case study that discusses the murder of Kitty Genovese, a woman attacked and murdered in Queens, New York City. Shockingly, while numerous neighbors watched the scene, nobody called for help because they assumed someone else would. This case study helped to define the bystander effect, which is when a person fails to intervene during an emergency because other people are around.
- Henry Molaison and the study of memory : Henry Molaison lost his memory and suffered from debilitating amnesia. He suffered from childhood epilepsy, and medical professionals attempted to remove the part of his brain that was causing his seizures. He had a portion of his brain removed, but it completely took away his ability to hold memories. Even though he went on to live until the age of 82, he was always forced to live in the present moment, as he was completely unable to form new memories.
Case study FAQs
When should you do a case study.
There are several scenarios when conducting a case study can be beneficial. Case studies are often used when there's a "why" or "how" question that needs to be answered. Case studies are also beneficial when trying to understand a complex phenomenon, there's limited research on a topic, or when you're looking for practical solutions to a problem.
How can case study results be used to make business decisions?
You can use the results from a case study to make future business decisions if you find yourself in a similar situation. As you assess the results of a case study, you can identify best practices, evaluate the effectiveness of an intervention, generate new and creative ideas, or get a better understanding of customer needs.
How are case studies different from other research methodologies?
When compared to other research methodologies, such as experimental or qualitative research methodology, a case study does not require a representative sample. For example, if you are performing quantitative research, you have a lot of subjects that expand your sample size. If you are performing experimental research, you may have a random sample in front of you. A case study is usually designed to deliberately focus on unusual situations, which allows it to shed new light on a specific business research problem.
Writing multiple case studies for your business
If you're feeling overwhelmed by the idea of writing a case study and it seems completely foreign, then you aren't alone. Writing a case study for a business is a very big deal, but fortunately, there is help available because an example of a case study doesn't always help.
Mailchimp, a well-known marketing company that provides comprehensive marketing support for all sorts of businesses, can assist you with your case study, or you can review one of their own recently published examples.
Mailchimp can assist you with developing the most effective content strategy to increase your chances of being as successful as possible. Mailchimp's content studio is a great tool that can help your business immensely.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Human-generated content, empowered by AI.
FREE eBook: Establish Authorship & Build Authority Online
When and How to Use a Case Study for Research
May 17, 2021 (Updated: May 4, 2023)

Quick Navigation
What Is Case Study Research?
Types of case studies, when should you use a case study, case study benefits, case study limitations, how to write a case study.
Imagine your company receives a string of negative reviews online. You notice a few common themes among the complaints, but you still aren’t quite sure what went wrong. Or suppose an old blog post suddenly went viral, and you’d like to know why and how to do it again. In both of these situations, a case study could be the best way to find answers.
A case study is a process whereby researchers examine a specific subject in a thorough, detailed way. The subject of a case study could be an individual, a group, a community, a business, an organization, an event, or a phenomenon. Regardless of the type of subject, case studies are in-depth investigations designed to identify patterns and cause-and-effect relationships. Case studies are often used by researchers in the field of psychology , medicine, business, social work, anthropology, education, or political science.
Because they are singular in their focus and often rely on qualitative data, case studies tend to be highly subjective. The results of a single case study cannot always be generalized and applied to the larger population. However, case studies can be valuable tools for developing a thesis or illustrating a principle. They can help researchers understand, describe, compare, and evaluate different aspects of an issue or question.

Image via Flickr by plings
Case studies can be classified according to their purpose or their subject. For instance, a case study can focus on any of the following:
- A person: Some case studies focus on one particular person. Often, the subject will be an individual with some rare characteristic or experience.
- A group: Group case studies could look at a family, a group of coworkers, or a friend group. It could be people thrown together by circumstance or who share some bond or relationship. A group case study could even focus on an entire community of people.
- An organization: An organizational case study could focus on a business, a nonprofit, an institution, or any other formal entity. The study could look at the people in the organization, the processes they use, or an incident at the organization.
- A location: An event case study focuses on a specific area. It could be used to study environmental and population changes or to examine how people use the location.
- An event: Event case studies can be used to cover anything from a natural disaster to a political scandal. Often, these case studies are conducted retrospectively, as an investigation into a past event.
In addition to different types of subjects, case studies often have different designs or purposes. Here are a few of the most common types of case studies:
- Explanatory: An explanatory case study tries to explain the why or how behind something. This type of case study works well when studying an event or phenomenon, like an airplane crash or unexpected power outage.
- Descriptive: A descriptive, or illustrative, case study is designed to shed light on an unfamiliar subject. Case studies like this provide in-depth, real-world examples of whatever the researcher wants to help the audience understand. For instance, a descriptive case study could focus on the experience of a mother with postpartum depression or on a young adult who has aged out of the foster care system.
- Exploratory: An exploratory case study, or pilot case study, often serves as the first step in a larger research project. Researchers may use a case study to help them narrow their focus, draft a specific research question, and guide the parameters of a formal, large-scale study.
- Intrinsic: An intrinsic case study has no goal beyond a deeper understanding of its subject. In this type of study, researchers are not trying to make generalized conclusions, challenge existing assumptions, or make any compare-and-contrast connections. The most interesting thing about the study is the subject itself.
- Critical Instance: A critical instance case study is similar to an explanatory or intrinsic study. Like an intrinsic study, it may have no predetermined purpose beyond investigating the subject. Like an explanatory study, it may be used to explain a cause-and-effect relationship. A critical instance case study may also be used to call into question a commonly held assumption or popular theory.
- Instrumental: An instrumental case study is the opposite of an intrinsic study because it serves a purpose beyond understanding the immediate subject. In this type of study, researchers explore a larger question through an individual case or cases. For instance, researchers could use a handful of case studies to investigate the relationship between social media use and happiness.
- Cumulative: A cumulative, or collective, case study uses information from several past studies as the basis for a new study. Because it takes into account multiple case studies, a cumulative study allows for greater generalization than a single case study. It can also be a more time- and cost-effective option since it makes use of existing research.
Case studies are often used in the exploratory phase of research to gather qualitative data. They can also be used to create, support, or refute a hypothesis and guide future research. For instance, a marketing professional might conduct a case study to discover why a viral ad campaign was so successful . They can then take any lessons they glean from the case study and apply them to future marketing efforts. A psychologist could use a case study to form a theory about the best way to treat a specific disorder. That theory could then be tested later through a large-scale controlled study.
Case studies are a good way to explore a real-world topic in-depth, illustrate a point, discuss the implications or meaning of an event, or compare the experiences of different individuals. A trainer may use a case study to bring to life what would otherwise be an abstract series of recommended action steps or to spark a conversation about how to respond in a specific scenario. Similarly, professors can use case studies to highlight key concepts from a lecture and pose questions to test students’ understanding of the material.
In some situations, case studies are the only way to compile quantitative data in an ethical manner. For instance, many of the recommendations that doctors make regarding what is or is not safe during pregnancy are based on case studies. It wouldn’t be ethical to conduct a controlled study that exposes pregnant women to potentially harmful substances, so doctors rely on the anecdotal evidence provided by case studies to find correlations and draw their conclusions.
Case studies can also be used to gather data that would be otherwise impossible or impractical to obtain. Students often use case studies for their thesis or dissertation when they lack the time or resources to conduct large-scale research. Zoologists might use existing case studies to determine the success rate of reintroducing rehabilitated animals into the wild. A historian could use case studies to explore the strategies used by dictators to gain and maintain power.

Image via Flickr by calebmmartin
Case studies can be used on their own or as a complement to other research methods, depending on the situation. The examples above are just a few instances where case studies can be useful. Case studies also work well for the following:
Providing Insight Through Qualitative Data
Case studies generally provide more qualitative data as opposed to quantitative data , and that makes them an invaluable tool for gathering insight into complex topics. Psychologists, for instance, use case studies to better understand human behavior. Crafting theories on the motives behind human actions would be difficult with quantitative data alone. The information gleaned through case studies may be subjective, but so is much of what makes us human. As individuals, we each have a unique blend of emotions, attitudes, opinions, motivations, and behaviors. Objective quantitative data is rarely the best way to identify and explain these nuances.
By their very nature, case studies allow more more intensive, in-depth study than other research methods. Rather than aiming for a large sample size, case studies follow a single subject. Often case studies are conducted over a longer period of time, and the narrow focus allows researchers to gather more detail than would be possible in a study of thousands of people. The information gleaned may not be representative of the broader population, but it does provide richer insight into the subject than other research methods.
Identifying Avenues for Future Research
Case studies are often used as the first step in a larger research project. The results of a case study cannot necessarily be generalized, but they can help researchers narrow their focus. For instance, researchers in the medical field might conduct a case study on a patient who survived an injury that typically proves fatal.
Over the course of the study, researchers may identify two or three ways in which this patient’s situation differed from others they have seen. Perhaps they identify something unique in the patient’s DNA or lifestyle choices or in the steps doctors took to treat the injury. Letting that information guide them, researchers could use other methods to deepen their understanding of those factors and perhaps develop new treatments or preventative recommendations.
Case studies can also be used in the fields of social work, politics, and anthropology to draw attention to a widespread problem and spur more research. A detailed narrative about one person’s experience will inspire more compassion than an academic paper filled with quantitative data. Stories often have a greater impact than statistics.
Challenging, Testing, or Developing Theories
Case studies can be particularly useful in the process of forming and testing theories. A case study may lead researchers to form a new theory or call into a question an existing one. They are an invaluable tool for identifying exceptions to a rule or disproving conventional wisdom.
For instance, a medical professional may write a case study about a patient who exhibited atypical symptoms to assert that the list of symptoms for a condition should be expanded. A psychologist could use a case study to determine whether the new treatment they devised for depression is effective, or to demonstrate that existing treatment methods are flawed. As the result of a case study, a marketing professional could suggest that consumers values have changed and that marketing best practices should be updated accordingly.
Enabling the Study of Unique Subjects
Some subjects would be impossible, impractical, or unethical to study through other research methods. This is true in the case of extremely rare phenomenon, many aspects of human behavior, and even some medical conditions.
Suppose a medical professional would like to gather more information about multiple-birth pregnancies with four or more fetuses. More information would be helpful because we have less information about them, but the reason we have less information is because they are so rare. Conducting case studies of a few women who are currently pregnant with multiples or have given birth to multiples in the past may be the only practical way to research them.
Case studies can also be used to gain insight into historical events and natural phenomenon — things we are not able to repeat at will. Case studies have also been used to study subjects such as a feral child , child prodigies, rare psychological conditions, crisis response, and more.
Helping People Better Understand Nuanced Concepts
Educators incorporate case studies into their lectures for a reason. Walking students through a detailed case study can make the abstract seem more real and draw out the nuances of a concept. Case studies can facilitate engaging discussions, spark thoughtful questions, and give students a chance to apply what they have learned to real-world situations.
Outside the classroom, case studies can be used to illustrate complex ideas. For instance, a well-constructed case study can highlight the unintended consequences of a new piece of legislation or demonstrate that depression does not always manifest in an obvious way. Case studies can help readers and listeners understand and care about an issue that does not directly affect them.
Despite their benefits, case studies do come with a few limitations. Compared to other research methods, case studies are often at a disadvantage in terms of the following:
Replicability
In most cases, scientists strive to create experiments that can be repeated by others. That way, other scientists can perform their own research and compare their results to those of the initial study. Assuming these other scientists achieve similar results, the replicability of the experiment lends credibility to the findings and theories of the original researchers.
One limitation of case studies is that they are often difficult, if not impossible, to replicate. Although this fact does not diminish the value of case studies, it does demonstrate that case studies are not a good fit for every research problem — at least, not on their own. Additional research would have to be performed to corroborate the results and prove or disprove any generalized theories generated by a case study.
Generalization
Generalization is another area in which case studies cannot match other research methods. A case study can help us challenge existing theories and form new ones, but its results cannot necessarily be generalized. The data we gather from a case study is only valid for that specific subject, and we cannot assume that our conclusions apply to the broader population.
Researchers or readers can attempt to apply the principles from a particular case to similar situations or incorporate the results into a more comprehensive theory. However, a case study by itself can only prove the existence of certain possibilities and exceptions, not a general rule.
Reliability
The reliability of case studies may be called into question for two reasons. The first objection centers on the fallibility of human memory and the question of whether subjects are being honest. Many case studies rely on subjects to self-report biographical details, their state of mind, their thoughts and feelings, or their behaviors.
The second issue is the Hawthorne effect, which refers to the tendency of individuals to modify their behavior when they know they are being observed. This effect makes it nearly impossible for researchers to ensure that the observations and conclusions of their case study are reliable.
Researcher Bias
Researcher bias is another potential issue with case studies. The results of a case study are by nature subjective and qualitative rather than objective and qualitative, and any findings rely heavily on the observations and narrative provided by the researcher. Even the best researchers are still human, and no matter how hard they try to remain objective, they will not be able to keep their findings completely free of bias.
Researchers may have biases they are not even aware of. A researcher may over-identify with the subject and lose the benefit of a dispassionate outside perspective. If the researcher already has an opinion on the subject, they may subconsciously overlook or discount facts that contradict their pre-existing assumptions. Researcher bias can affect what the researcher observes and records, as well as how they interpret and apply their observations.
Case studies can be time-consuming and expensive to conduct. Crafting a thorough case study can be a lengthy project due to the intensive, detailed nature of this type of research. Plus, once the information has been gathered, it must be interpreted. Between the observation and analysis, a case study could take months or even years to complete. Researchers will need to be heavily involved in every step of the process, putting in a lot of time, energy, focus, and effort to ensure that the case study is as informative as possible.
Now that you understand the benefits, limitations, and types of case studies, you can follow these steps to write your own:
- Determine your objective. Write out your research problem, question, or goal. If you aren’t sure, ask yourself questions like, “What am I trying to accomplish? What do I need to know? What will success look like?” Be clear and specific. Your answers will help you choose the right type of case study for your needs.
- Review the research. Before delving into your case study, take some time to review the research that is already available. The information you gather during this preliminary research can help guide your efforts.
- Choose a subject. Decide what or who the subject of your case study will be. For instance, if you are conducting a case study to find out how businesses have been affected by new CDC guidelines, you will need to choose a specific restaurant or retailer. In some cases, you may need to draft a release form for the subject to sign so that you will be able to publish your study.
- Gather information. Case studies about a person, organization, or group may rely on questionnaires or interviews to gather information. If you are studying an event, you might use a combination of academic research and witness interviews. In some cases, you will record your own observations as part of the study.
- Write a report. Most case studies culminate in a written report, similar to a research paper. Most case studies include five sections : an introduction, a literature review, an explanation of your methods, a discussion of your findings and the implications, followed by a conclusion.
- Publish your findings. Once you’ve written your case study, consider the most engaging way to present your findings. A well-written research article is a good place to start, but going a step further will maximize the impact of your research. For instance, you could design an infographic to highlight key findings or commission an animated video to turn your case study into a visual narrative.
Whether research is your primary occupation or only an incidental part of your job, you can benefit from a solid understanding of what case studies are, how they work, and when to use them. Use the information and steps above to design and write a case study that will provide the answers you’re looking for.
CopyPress writer
More from the author:
Quick Navigation What Does a Content Manager Do? Who Does a Content Manager Report To? Are Content Managers Paid...
In our digital age, it’s important to know the best ways to reach your target audience and boost your...
The best content marketing conferences offer the chance to learn more about the industry and provide networking opportunities with...
RECENT ARTICLES
Read More About Measurement

27 Nov 2023

31 Oct 2023

23 May 2023
- Discounts and promotions
- Delivery and payment
Cart is empty!
Case study definition

Case study, a term which some of you may know from the "Case Study of Vanitas" anime and manga, is a thorough examination of a particular subject, such as a person, group, location, occasion, establishment, phenomena, etc. They are most frequently utilized in research of business, medicine, education and social behaviour. There are a different types of case studies that researchers might use:
• Collective case studies
• Descriptive case studies
• Explanatory case studies
• Exploratory case studies
• Instrumental case studies
• Intrinsic case studies
Case studies are usually much more sophisticated and professional than regular essays and courseworks, as they require a lot of verified data, are research-oriented and not necessarily designed to be read by the general public.
How to write a case study?
It very much depends on the topic of your case study, as a medical case study and a coffee business case study have completely different sources, outlines, target demographics, etc. But just for this example, let's outline a coffee roaster case study. Firstly, it's likely going to be a problem-solving case study, like most in the business and economics field are. Here are some tips for these types of case studies:
• Your case scenario should be precisely defined in terms of your unique assessment criteria.
• Determine the primary issues by analyzing the scenario. Think about how they connect to the main ideas and theories in your piece.
• Find and investigate any theories or methods that might be relevant to your case.
• Keep your audience in mind. Exactly who are your stakeholder(s)? If writing a case study on coffee roasters, it's probably gonna be suppliers, landlords, investors, customers, etc.
• Indicate the best solution(s) and how they should be implemented. Make sure your suggestions are grounded in pertinent theories and useful resources, as well as being realistic, practical, and attainable.
• Carefully proofread your case study. Keep in mind these four principles when editing: clarity, honesty, reality and relevance.
Are there any online services that could write a case study for me?
Luckily, there are!
We completely understand and have been ourselves in a position, where we couldn't wrap our head around how to write an effective and useful case study, but don't fear - our service is here.
We are a group that specializes in writing all kinds of case studies and other projects for academic customers and business clients who require assistance with its creation. We require our writers to have a degree in your topic and carefully interview them before they can join our team, as we try to ensure quality above all. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
• Select the topic and the deadline of your case study.
• Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with.
• Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
• Select your payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed writers, online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
- Open access
- Published: 09 April 2024
Creating culturally-informed protocols for a stunting intervention using a situated values-based approach ( WeValue InSitu ): a double case study in Indonesia and Senegal
- Annabel J. Chapman 1 ,
- Chike C. Ebido 2 , 3 ,
- Rahel Neh Tening 2 ,
- Yanyan Huang 2 ,
- Ndèye Marème Sougou 4 ,
- Risatianti Kolopaking 5 , 6 ,
- Amadou H. Diallo 7 ,
- Rita Anggorowati 6 , 8 ,
- Fatou B. Dial 9 ,
- Jessica Massonnié 10 , 11 ,
- Mahsa Firoozmand 1 ,
- Cheikh El Hadji Abdoulaye Niang 9 &
- Marie K. Harder 1 , 2
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 987 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
77 Accesses
Metrics details
International development work involves external partners bringing expertise, resources, and management for local interventions in LMICs, but there is often a gap in understandings of relevant local shared values. There is a widespread need to better design interventions which accommodate relevant elements of local culture, as emphasised by recent discussions in global health research regarding neo-colonialism. One recent innovation is the concept of producing ‘cultural protocols’ to precede and guide community engagement or intervention design, but without suggestions for generating them. This study explores and demonstrates the potential of an approach taken from another field, named WeValue InSitu , to generate local culturally-informed protocols. WeValue InSitu engages stakeholder groups in meaning-making processes which ‘crystallize’ their envelope of local shared values, making them communicable to outsiders.
Our research context is understanding and reducing child stunting, including developing interventions, carried out at the Senegal and Indonesia sites of the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub. Each national research team involves eight health disciplines from micro-nutrition to epigenetics, and extensive collection of samples and questionnaires. Local culturally-informed protocols would be generally valuable to pre-inform engagement and intervention designs. Here we explore generating them by immediately following the group WeValue InSitu crystallization process with specialised focus group discussions exploring: what local life practices potentially have significant influence on the environments affecting child stunting, and which cultural elements do they highlight as relevant. The discussions will be framed by the shared values, and reveal linkages to them. In this study, stakeholder groups like fathers, mothers, teachers, market traders, administrators, farmers and health workers were recruited, totalling 83 participants across 20 groups. Themes found relevant for a culturally-informed protocol for locally-acceptable food interventions included: specific gender roles; social hierarchies; health service access challenges; traditional beliefs around malnutrition; and attitudes to accepting outside help. The concept of a grounded culturally-informed protocol, and the use of WeValue InSitu to generate it, has thus been demonstrated here. Future work to scope out the advantages and limitations compared to deductive culture studies, and to using other formative research methods would now be useful.
Peer Review reports
Although progress has been made towards the SDG of ‘Zero Hunger by 2025’, the global rates of malnutrition and stunting are still high [ 1 ]. Over the past 20 years, researchers have implemented interventions to reduce undernutrition, specifically focussing on the first 1000 days of life, from conception to 24 months [ 2 ]. However, due to both differing determinants between countries [ 3 , 4 ] as well as varying contextual factors, it is clear that no single fixed approach or combination of approaches can be relied on when implementing stunting interventions [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Furthermore, when external researchers design interventions for local areas in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) they can often overlook relevant local cultural factors that consequently act as barriers to intervention uptake and reduce their effectiveness, such as geographical factors and the levels of migration in certain populations [ 8 , 9 ], or social norms or perceptions relating to accepting outside help, and power dynamics related to gender [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. The inclusion of cultural level factors in behaviour change interventions has been proposed as a requirement for effective interventions [ 13 ]. However, despite the breadth of literature highlighting the negative impacts from failing to do this, the lack of integration or even regard of local culture remains a persistent problem in Global Health Research [ 14 ], possibly hindering progress towards the SDGs. Thus, there is a need for approaches to integrate local cultural elements into intervention design.
This lack of understanding of relevant local culture, social norms and shared values also has ethical implications. The field of Global Health Ethics was predominantly developed in the Global North, in High Income Countries (HICs), embedding values common in those countries such as the prominence of individual autonomy [ 15 , 16 ]. Researchers from HICs carrying out research in LMICs may wrongly assume that values held in the Global North are universal [ 14 ] and disregard some local values, such as those related to family and collective decision making, which are core to many communities in LMICs. It is therefore important for outside researchers to have an understanding of relevant local values, culture and social norms before conducting research in LMICs so as not to impose values that do not align with local culture and inadvertently cause harm or offence [ 16 , 17 ]. The importance of this is compounded by the colonial history that is often present in relationships between research communities in HICs and LMICs, and the fact that the majority of the funding and leading institutions are still located in the Global North [ 18 , 19 ]. Thus, conscious steps must be taken to avoid neo-colonialism in Global Health Research [ 20 ]. From a health-equity perspective, it is essential to ensure that those in vulnerable communities are not hindered from involvement in interventions to improve nutrition. Encouraging uptake by such communities could be provided if salient local shared values, norms and culture were taken into account [ 21 ].
In a recent paper, Memon et al., (2021) highlight the usefulness of first creating a cultural protocol that can precede and guide subsequent stages of community engagement or intervention design to ensure that salient local values are known to external researchers coming into the community [ 16 ]. We adopt the use of the concept of a cultural protocol, referring to locally-generated guidance about key values, norms, behaviours and customs relevant to working with the local community. However, we prefer the term, ‘culturally-informed protocol’ since this relates to only cultural elements deemed salient by the researchers, and locally, rather than any comprehensive notion of culture, nor extending beyond the research context.
Memon et al. (2021), point out links between the creation of such a protocol and existing codes of practice that have already been created for some cultures such as the Te Ara Tika, a Guideline for Māori Research Ethics [ 22 ]. Currently, research and interventions in Global Health can be informed by a stage of formative research involving one-to-one interviews, focus groups or direct observations, which can sometimes be ethnographic in nature such as within Focussed Ethnographic Studies or Rapid Assessment Procedures [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. Although these methods can be effective to inform intervention designs, they have disadvantages like: can take long periods to complete [ 26 ], can be resource intensive [ 26 ] and can lack cultural acceptability [ 27 ]. These limitations may account for the frequent neglect of their use generally, highlighted by Aubel and Chibanda (2022) [ 14 ]. Additionally, none of these methods work towards making explicit local values, or towards the creation of a culturally-informed protocol. In brief, the literature suggests a need to develop alternative methods of Formative Research for understanding locally relevant cultural elements, that are less time-consuming and can generate data that is more easily translatable to intervention design. In addition, these approaches must be applicable in different cultures. Additionally, the protocols produced must be actionable and practical not only for guiding interactions between research teams but also for guiding the initial stages of intervention design.
The work presented here aims to address several of these needs. It includes an exploration of the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) approach because that has previously been shown, in environmental management domains, to offer a way to gather in-depth values-based perspectives from a target population [ 28 , 29 ] It was first created through action research, and co-designed to enable civil society organisations to better understand and measure the values-based aspects of their work [ 30 ]. The core WeValue InSitu process (detailed in Table 1 ) involves the crystallization of shared values, with a facilitator guiding a group of participants with shared experiences, through cycles of tacit meaning-making (using a stage of photo-elicitation and triggering) [ 31 ], until they can articulate more explicitly their shared values, in concise and precise statements. These statements are then linked together in a framework by the participants. In an example case in Nigeria, the results of the WVIS approach hinted at the creation of a culturally-informed protocol through an analysis of the shared values frameworks to find cultural themes for the creation of an indicator tool that was used to evaluate several development scenarios based on their social acceptability [ 29 ].
Furthermore, it has been found that if a group of WVIS participants take part in a specialised focus group discussion (FGD), named Perspectives EXploration (PEX:FGD) immediately afterward the main workshop, then they easily and articulately express their perspectives on the topics raised for discussion - and with allusions to the shared values they had crystallised just prior. In an example from Shanghai, the PEX:FGDs focussed on eliciting perspectives on climate change, which were shown to be closely linked with the cultural themes existing within the shared values frameworks produced immediately prior [ 32 ]. In that case, the PEX:FGDs allowed the cultural themes generated during the main WVIS workshop to be linked more closely to the research question. Those results suggested that the WVIS plus PEX:FGD approach could be used to create a specialised culturally-informed protocol for improved intervention design.
In the study presented here, the WVIS approach was explored for the purpose of creating culturally-informed protocols to inform the planning of interventions within two localities of the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub [ 33 ]. The work was carried out in two parts. Firstly, the WVIS main workshop was used to elicit cultural themes within the target communities, indicating key elements to consider to ensure ethical engagement. Secondly, the PEX focus group discussions focussed on life practices related to stunting which we explored for the purpose of tailoring the culturally-informed protocols to the specific purpose of improving the design of an example intervention. The Action Against Stunting Hub works across three sites where stunting is highly prevalent but via different determinants: East Lombok in Indonesia (estimated 36% of under-fives stunted), Kaffrine in Senegal (estimated 16% of under-fives stunted) and Hyderabad in India (estimated 48% of under-fives stunted) [ 34 ]. We propose that, the information about local shared values in a given site could be used to inform the design of several interventions, but for our specific exploration the focus here is a proposed ‘egg intervention’, in which pregnant women would be provided with an egg three times per week as supplement to their diet. This study proposes that identifying shared values within a community, alongside information about local life practices, provides critical cultural information on the potential acceptability and uptake of this intervention which can be used to generate culturally-informed protocols consisting of recommendations for improved intervention design.
In this paper we aim to explore the use of the WVIS approach to create culturally-informed protocols to guide engagement and inform the design of localised egg interventions to alleviate stunting in East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. We do this by analysing data about local shared values that are crystallized using the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) process to provide clear articulation of local values, followed by an analysis of life practices discussed during PEX:FGD to tailor the culturally-informed protocols for the specific intervention design.
Study setting
This research was exploratory rather than explanatory in nature. The emphasis was on demonstrating the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) approach to develop culturally-informed protocols of practical use in intervention design, in different cultural sites. This study was set within a broader shared-values workstream within the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub project [ 33 ]. The Hub project, which was co-designed and co-researched by researchers from UK, Indonesia, Senegal and India, involves cohorts of 500 women and their babies in each site through pregnancy to 24 months old, using cross-disciplinary studies across gut health, nutrition, food systems, micro-nutrition, home environment, WASH, epigenetics and child development to develop a typology of stunting. Alongside these health studies are studies of the shared values of the communities, obtained via the WVIS approach described here, to understand the cultural contexts of that diverse health data. In this study the data from East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal were used: India’s data were not yet ready, and these two countries were deemed sufficient for this exploratory investigation.
The WVIS approach
The WVIS approach is a grounded scaffolding process which facilitates groups of people to make explicit their shared values in their own vocabulary and within their own frames (details in Fig. 1 and activities in Table 1 ). The first stage of the WVIS is Contextualisation, whereby the group identifies themselves and set the context of their shared experiences, for example, as ‘mothers in East Lombok, Indonesia’. Subsequently, there is a stage of Photo Elicitation, in which the group are first asked to consider what is important, meaningful or worthwhile to them about their context (e.g., ‘being mothers in East Lombok, Indonesia’) and then asked to choose photos from a localised set that they can use as props to help describe their answer to the group [ 29 ]. After this, a localised Trigger List is used. This Trigger List consists of 109 values statements that act as prompts for the group. Examples of these values statements are included below but all the statements begin with “it is important to me/us that…”. The group are asked to choose which statements within the trigger list resonate with them, and those are taken forward for group intersubjective discussion. After a topic of their shared values has been explored, the group begin to articulate and write down their own unique statements of them. These also all begin with “It is important to me/us that…”. After discussing all pressing topics, the group links the written statements on the table into a unique Framework, and one member provides a narrative to communicate it to ‘outsiders’. The WVIS provides a lens of each group’s local shared values, and it is through this lens that they view the topics in the focus group discussions which immediately follow, termed Perspectives EXplorations (PEX:FGDs).
Schematic of the macro-level activities carried out during the WeValue InSitu ( WVIS ) main workshop session
This results in very grounded perspectives being offered, of a different nature to those obtained in questionnaires or using external frameworks [ 31 ]. The specific PEX:FGD topics are chosen as pertinent to stunting contextual issues, including eating habits, food systems and environments, early educational environments, and perceptions of stunting. The local researchers ensured that all topics were handled sensitively, with none that could cause distress to the participants. The data for this study were collected over 2 weeks within December 2019–January 2020 in workshops in East Lombok, Indonesia, and 2 weeks within December 2020 in Kaffrine, Senegal.
The PEX:FGDs were kept open-ended so that participants could dictate the direction of the discussion, which allowed for topics that may not have been pre-considered by the facilitators to arise. Sessions were facilitated by local indigenous researchers, guided in process by researchers more experienced in the approach, and were carried out in the local languages, Bahasa in East Lombok, Indonesia and French or Wolof in Kaffrine, Senegal.
Development of localised WVIS materials
Important to the WVIS approach is the development of localised materials (Table 1 ). The main trigger list has been found applicable in globalised places where English is the first language, but otherwise the trigger lists are locally generated in the local language, incorporating local vocabulary and ways of thinking. To generate these, 5–8 specific interviews are taken with local community members, by indigenous university researchers, eliciting local phrases and ways of thinking. This is a necessary step because shared tacit values cannot be easily accessed without using local language. Examples of localised Trigger Statements produced this way are given below: (they all start with: “It is important to me/us that…”):
…there is solidarity and mutual aid between the people
…I can still be in communication with my children, even if far away
…husbands are responsible for the care of their wives and family
…the town council fulfils its responsibility to meet our needs
…people are not afraid of hard, and even manual work
Study participants
The group participants targeted for recruitment, were selected by local country Hub co-researchers to meet two sets of requirements. For suitability for the WVIS approach they should be between 3 and 12 in number; belong to naturally existing groups that have some history of shared experiences; are over 18 years old; do not include members holding significantly more power than others; and speak the same native language. For suitability in the PEX:FGD to offer life practices with relevance to the research topic of stunting, the groups were chosen to represent stakeholders with connections to the food or learning environment of children (which the Action Against Stunting Hub refer to as the Whole Child approach) [ 33 ]. The university researchers specialising in shared values from the UK, and Senegal and Indonesia respectively, discussed together which stakeholder groups might be appropriate to recruit. The local researchers made the final decisions. Each group was taken through both a WVIS workshop and the immediately-subsequent PEX:FGD.
Data collection and analysis
Standard data output from the WeValue session includes i) the jointly-negotiated bespoke Statements of shared values, linked together in their unique Framework, and ii) an oral recording of a descriptive Narrative of it, given by the group. These were digitized to produce a single presentation for each group as in Fig. 2 . It represents the synthesised culmination of the crystallisation process: a portrait of what was ‘important’ to each stakeholder group. Separately, statements from the group about the authenticity/ownership of the statements are collected.

An illustrative example of one digitized Shared Values Framework and accompanying Narrative from a teacher’s group in East Lombok, Indonesia. The “…” refers to each statement being preceded by “It is important to us that…”
When these Frameworks of ‘Statements of Shared Values’ are viewed across all the groups from one locality (Locality Shared Values Statements), they provide portraits of ‘what is important’ to people living there, often in intimate detail and language. They can be used to communicate to ‘outsiders’ what the general cultural shared values are. In this work the researchers thematically coded them using Charmaz constructionist grounded theory coding [ 35 ] to find broad Major Cultural Themes within each separate locality.
The second area of data collection was in the post- WVIS event: the PEX:FGD for each group. A translator/interpreter provided a running commentary during these discussions, which was audio recorded and then transcribed. The specific topics raised for each group to discuss varied depending on their local expertise. This required completely separate workstreams of coding of the dataset with respect to each topic. This was carried out independently by two researchers: one from UK (using NVivo software (Release 1.3.1)) and one from the local country, who resolved any small differences. All the transcripts were then collated and inductively, interpretively analysed to draw out insights that should be relayed back to the Action Against Stunting Hub teams as contextual material.
The extracts of discussion which were identified as relevant within a particular Hub theme (e.g. hygiene) were then meta-ethnographically synthesised [ 36 ] into ‘Hub Theme Statements’ on each topic, which became the core data for later communication and interrogation by other researchers within the Action Against Stunting Hub. These statements are interpretations of participants’ intended meanings, and links from each of them to data quotes were maintained, enabling future interpretations to refer to them for consistency checks between received and intended meaning.
In this investigation, those Hub Theme Statements (derived from PEX:FGD transcripts) were then deductively coded with respect to any topics with potential implications of the egg intervention. Literature regarding barriers and facilitators to nutrition interventions indicated the following topics could be relevant: attitudes to accepting help; community interactions; cooking and eating habits; traditional beliefs about malnutrition; sharing; social hierarchies [ 12 , 37 , 38 ] to which we added anything related to pregnancy or eggs. This analysis produced our Egg Intervention Themes from the data.
The Major Cultural Themes and Egg Intervention Themes were then used to create a set of culture-based recommendations and intervention specific recommendations respectively for each locality. These recommendations were then combined to form specialized culturally-informed protocols for the egg intervention in each locality: East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. The process is displayed schematically in Fig. 3 .
Schematic representation of the method of production of the culturally-informed protocol for each locality
The preparation of the localised WVIS materials at each site took 6 hours of interview field work, and 40 person hours for analysis. The 10 workshops and data summaries were concluded within 10 workdays by two people (80 person hours). The analysis of the PEX:FGD data took a further 80 person hours. Thus, the total research time was approximately 200 person hours.
The stakeholder group types are summarised in Table 2 . The data is presented in three parts. Firstly, the Major Cultural Themes found in East Lombok, Indonesia and in Kaffrine, Senegal are described – the ones most heavily emphasised by participants. Then, the Egg Intervention Themes and finally, the combined set of Recommendations to comprise a culturally-informed protocol for intervention design for each location. Quotations are labelled INDO or SEN for East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal, respectively.
Major cultural themes from frameworks and narratives
These were derived from the Locality Shared Values Statements produced in the WVIS .
East Lombok, Indonesia
Religious values.
Islamic values were crucially important for participants from East Lombok, Indonesia and to their way of life. Through living by the Quran, participating in Islamic community practices, and teaching Islamic values to their children, participants felt they develop their spirituality and guarantee a better afterlife for themselves and their children. Participants stated the Quran tells them to breastfeed their children for 2 years, so they do. Despite no explicit religious official curriculum in Kindergarten, the teachers stated that it was important to incorporate religious teaching.
“East Lombok people always uphold the religious values of all aspects of social life.”
“It is important for me to still teach religious values even though they are not clearly stated in the curriculum.” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
“In Quran for instance, we are told to breastfeed our kids for 2 years. We can even learn about that ” – Workshop 3 INDO (mothers).
Related to this was the importance of teaching manners to children and preventing them from saying harsh words. Teachers stated that it was important to create a happy environment for the children and to ensure that they are polite and well-behaved. Similarly, mothers emphasised the need to teach their children good religious values to ensure they will be polite and helpful to their elders.
“Children don’t speak harsh words.”
“My children can help me like what I did to my parents”.
– Workshop 8 INDO (mothers).
Togetherness within families and the community
The Locality Shared Values Frameworks stressed the importance of togetherness, both within family and community. Comments mentioned it being important that people rely heavily on their family and come together in times of need to support each other and provide motivation. This was also important more broadly, in that people in society should support each other, and that children grow up to contribute to society. This was also reflected in comments around roles within the family. Despite women being primary care givers, and men working to finance the family, participants stated that they follow a process of consultation to make decisions, and when facing hardships.
“that we have the sense of kinship throughout our society”.
“We have togetherness as mothers”.
“For the family side, whatever happens we need to be able to be united as a whole family. We need to have the [sense of] forgiveness for the sake of the children” – Workshop 2 INDO (mothers).
Attitudes about extra-marital pregnancy
In East Lombok, Indonesia, it was essential to both mothers and fathers that pregnancy happened within a marriage, this was to ensure that the honour of the family was upheld and that the lineage of the child was clear. The potential danger to health that early pregnancies can cause was also acknowledged.
“If they don’t listen to parents’ advice, there will be the possibility of pre-marital pregnancy happening, which will affect the family [so much].
The affect is going to be ruining the good name, honour and family dignity. When the children [are] born outside [of] marriage, she or he will have many difficulties like getting a birth certificate [and] having a hard time when registering to school or family” - Workshop 4 INDO (mothers).
“ To make sure that our children avoid getting married at a very young age and moreover [avoid] having free sex so that they will not get pregnant before the marriage” - Workshop 9 INDO (fathers).
Kaffrine, Senegal
The Major Cultural Themes which emerged from the Kaffrine data are described below. As these are grounded themes, they are different than those seen in East Lombok, Indonesia.
Access to healthcare
A recurring theme amongst the groups in Kaffrine were aspirations of affordable and easy-to-access healthcare. Community health workers stated the importance of encouraging women to give birth in hospitals and spoke of the importance of preventing early pregnancy which result from early marriages. Giving birth in hospitals was also a concern for Public Office Administrators who highlighted that this leads to subsequent issues with registering children for school. Mothers and fathers stated the importance of being able to afford health insurance and access healthcare so that they could take care of themselves.
“That the women give birth in the hospital” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWS).
“To have affordable health insurance ” – Workshop 10 SEN (mothers).
“To have access to health care ” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
“It is important that women give birth in the hospital in order to be able to have a certificate that allows us to establish the civil status” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
Additionally, Community health workers spoke of their aspiration to have enough supplements to provide to their community so as to avoid frustration at the lack of supply, and mothers spoke of their desire to be provided with supplements.
“To have dietary supplements in large quantities to give them to all those who need them, so as not to create frustration” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWS).
Another aspect of access to healthcare, was mistrust between fathers and community health workers. Community health workers explained that sometimes men can blame them when things go wrong in a pregnancy or consider their ideas to be too progressive. Thus, to these community health workers the quality of endurance was very important.
“Endurance (Sometimes men can accuse us of influencing their wives when they have difficulties in conceiving)” – Workshop 5 SEN (CHWs).
Another recurring theme was the importance of having secure employment and a means to support themselves; that there were also jobs available for young people, and that women had opportunities to make money to help support the family. This included preventing early marriages so girls could stay in school. Having jobs was stated as essential for survival and important to enable being useful to the community and society.
“To have more means of survival (subsistence) to be able to feed our families”.
“To have a regular and permanent job”.
“We assure a good training and education for our children so that they will become useful to us and the community”.
“ Our women should have access to activities that will support us and lessen our burden” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
It was considered very important to have a religious education and respect for religious elders. Moreover, living by, and teaching, religious values such as being hard working, humble and offering mutual aid to others, was significant for people in Kaffrine.
“Have an education in the Islamic Culture (Education that aligns with the culture of Islam)”.
“Respect toward religious leaders” – Workshop 3 SEN (fathers).
“ To organize religious discussions to develop our knowledge about Islam ” - Workshop 10 SEN (mothers).
“ Have belief and be prayerful and give good counselling to people ” - Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Egg intervention themes from each country from perspectives EXplorations focus group discussion data
Below are results of analyses of comments made during the PEX:FGDs in East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. The following codes were used deductively: attitudes to accepting outside help, traditional gender roles, food sharing, traditional beliefs, social hierarchies and understanding of stunting and Other. These topics were spoken about during open discussion and were not the subject of direct questions. For example, topics relating to traditional gender roles came up in East Lombok, during conversations around the daily routine. Thus, in order to more accurately reflect the intended meaning of the participants, these were labelled food practices, under the “Other” theme. If any of the themes were not present in the discussion, they are not shown below.
Attitudes to accepting outside help
Few mentions were made that focussed on participants attitudes to accepting outside help, but participants were sure that they would not make changes to their menus based on the advice of outside experts. Additionally, teachers mentioned that they are used to accepting help from local organisations that could to help them to identify under-developed children.
“ We don’t believe that [the outsiders are] going to change our eating habits or our various menus ” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
Traditional gender roles
In East Lombok, mothers spoke about how their husbands go to work and then provide them with daily money to buy the food for the day. However, this was discussed in relation to why food is bought daily and is thus discussed below in the topics Other – Food practices.
Food sharing
In East Lombok, Indonesia, in times when they have extra food, they share it with neighbours, in the hope that when they face times of hardship, their neighbours will share with them. Within the household, they mentioned sharing food from their plate with infants and encouraging children to share. Some mothers mentioned the importance of weekly meetings with other mothers to share food and sharing food during celebrations.
“ Sometimes we share our food with our family. So, when we cook extra food, we will probably send over the food to our neighbour, to our families. So, sometimes, with the hope that when we don’t have anything to eat, our neighbour will pay for it and will [share with] us.” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
“Even they serve food for the kids who come along to the house. So, they teach the kids to share with their friends. They provide some food. So, whenever they play [at their] house, they will [eat] the same.” – Workshop 2 INDO (Mothers).
Understanding of stunting
The teachers in East Lombok were aware of child stunting through Children’s Development Cards provided by local healthcare organizations. They stated that they recognise children with nutrition problems as having no patience period, no expression, no energy for activities and less desire to socialise and play with other children. The teachers said that stunted children do not develop the same as other children and are not as independent as children who are the proper height and weight for their development. They also stated that they recognise stunted children by their posture, pale faces and bloated stomachs. They explained how they usually use the same teaching methods for stunting children, but will sometimes allow them to do some activities, like singing, later, once the other children are leaving.
“ They have no patience period, don’t have any energy to do any of the activities. No expression, only sitting down and not mingling around with the kids. They are different way to learn. They are much slower than the other kids .” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
“ When they are passive in singing, they will do it later when everyone else is leaving, they just do it [by] themselves ” – Workshop 1 INDO (teachers).
Specific views on eggs
In East Lombok, Indonesia, there were no superstitions or traditional beliefs around the consumption of eggs. When asked specifically on their views of eggs, and if they would like to be provided with eggs, women in East Lombok said that they would be happy to accept eggs. They also mentioned that eggs were a food they commonly eat, feed to children and use for convenience. Eggs were considered healthy and were common in their house.
“ We choose eggs instead. If we don’t have time, we just probably do some omelettes or sunny side up. So, it happens, actually when we get up late, we don’t have much time to be able to escort our kids to the school, then we fry the eggs or cook the instant noodles. And it happens to all mothers. So, if my kids are being cranky, that’s what happens, I’m not going to cook proper meals so, probably just eggs and instant noodles.” – Workshop 3 INDO (Mothers).
Other important topics – food practices
Some detailed themes about food practices were heard in East Lombok, Indonesia. The women were responsible for buying and preparing the food, which they purchased daily mainly due to the cost (their husbands were paid daily and so provided them with a daily allowance) and lack of storage facilities. They also bought from mobile vendors who came to the street, because they could buy very small amounts and get occasional credit. The mother decided the menu for the family and cooked once per day in the morning: the family then took from this dish throughout the day. Mothers always washed their fruits and vegetables and tried to include protein in their meals when funds allowed: either meat, eggs, tofu or tempeh.
“ One meal a day. They [the mothers] cook one time and they [the children] can eat it all day long. Yes, they can take it all day long. They find that they like [to take the food], because they tend to feel hungry.” – Workshop 6 INDO (Mothers).
“ They shop every day because they don’t have any storage in their house and the other factor is because the husband has a daily wage. They don’t have monthly wage. In the morning, the husband gives the ladies the money and the ladies go to the shop for the food. ” – Workshop 4 INDO (Mothers).
In Kaffrine, the following themes emerged relating to an egg intervention: they were different in content and emphasis to Lombok and contained uniquely local cultural emphases.
Mothers were welcoming of eggs as a supplement to improve their health during pregnancy and acknowledged the importance of good nutrition during pregnancy. However, they also mentioned that their husbands can sometimes be resistant to accepting outside help and provided an example of a vaccination programme in which fathers were hesitant to participate. However, participants stated that the Government should be the source of assistance to them (but currently was not perceived to be so).
“But if these eggs are brought by external bodies, we will hesitate to take it. For example, concerning vaccination some fathers hesitate to vaccinate their children even if they are locals who are doing it. So, educating the fathers to accept this is really a challenge” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Some traditional gender roles were found to be strong. The participants emphasised that men are considered the head of the household, as expected in Islam, with the mother as primary caregiver for children. This is reflected in the comments from participants regarding the importance of Islam and living their religious values. The men thus made the family decisions and would need to be informed and agree to any family participation in any intervention – regardless of the education level of the mother. The paternal grandmother also played a very important role in the family and may also make decisions for the family in the place of the father. Community Health Workers emphasised that educating paternal grandmothers was essential to improve access to healthcare for women.
“There are people who are not flexible with their wives and need to be informed. Sometimes the mother-in-law can decide the place of the husband. But still, the husband’s [permission] is still necessary.” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
“[We recommend] communication with mothers-in-law and the community. Raise awareness through information, emphasizing the well-being of women and children.” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
“The [grand]mothers take care of the children so that the daughters in-law will take care of them in return So it’s very bad for a daughter in law not to take care of her mother in-law. Society does not like people who distance themselves from children.” – Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Social hierarchies
In addition to hierarchies relating to gender/position in the family such as grandmothers have decision making power, there was some mention of social hierarchies in Kaffrine, Senegal. For example, during times of food stress it was said that political groups distribute food and elected officials who choose the neighbourhoods in which the food will be distributed. Neighbourhood leaders then decide to whom the food is distributed, meaning there is a feeling that some people are being left out.
“ It’s political groups that come to distribute food or for political purposes…organizations that often come to distribute food aid, but in general it is always subject to a selection on the part of elected officials, in particular the neighbourhood leaders, who select the people they like and who leave the others ” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Participants explained that during mealtimes, the family will share food from one large plate from which the father will eat first as a sign of respect and courtesy. Sometimes, children would also eat in their neighbour’s house to encourage them to eat.
“ Yes, it happens that we use that strategy so that children can eat. Note that children like to imitate so that’s why we [send them to the neighbour’s house]” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs)”.
Traditional beliefs about malnutrition
In Kaffrine, Senegal, some participants spoke of traditional beliefs relating to malnutrition, which are believed by fewer people these days. For example, uncovered food might attract bad spirits, and any person who eats it will become ill. There were a number of food taboos spoken of which were thought to have negative consequences for the baby, for example watermelon and grilled meat which were though to lead to birth complications and bleeding. Furthermore, cold water was thought to negatively impact the baby. Groups spoke of a tradition known as “bathie” in which traditional healers wash stunted children with smoke.
“ There are traditional practices called (Bathie) which are practiced by traditional healers. Parents are flexible about the practice of Bathie ” – Workshop 1 SEN (CHWs).
Causes of malnutrition and stunting were thought to be a lack of a balanced diet, lack of vitamin A, disease, intestinal worms, poor hygiene, socio-cultural issues such as non-compliance with food taboos, non-compliance with exclusive breastfeeding and close pregnancies. Malnutrition was also thought by some to be hereditary. Numerous signs of malnutrition were well known amongst the groups in Kaffrine. For example, signs of malnutrition were thought to be a big bloated belly, diarrhoea, oedema of the feet, anaemia, small limbs and hair loss as well as other symptoms such as red hair and a pale complexion. Despite this, malnutrition was thought to be hard to identify in Kaffrine as not all children will visit health centres, but mothers do try to take their babies heights and weights monthly. The groups were aware of the effect of poverty on the likelihood of stunting as impoverished parents cannot afford food. Furthermore, the groups mentioned that there is some stigma towards stunted children, and they can face mockery from other children although most local people feel pity and compassion towards them. Malnourished children are referred to as Khiibon or Lonpogne in the local language of Wolof.
“ It is poverty that is at the root of malnutrition, because parents do not have enough money [and] will have difficulty feeding their families well, so it is the situation of poverty that is the first explanatory factor of malnutrition here in Kaffrine” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
“It can happen that some children are the victim of jokes for example of mockery from children of their same age, but not from adults and older ” – Workshop 9 SEN (administrators).
Pregnancy beliefs
In Kaffrine, Senegal, there were concerns around close pregnancies, and pregnancies in women who were too young, and for home births. Within the communities there was a stigma around close pregnancies, which prevented them from attending antenatal appointments. Similarly, there were superstitions around revealing early pregnancies, which again delayed attendance at health centres.
Groups acknowledged the role of good nutrition, and mentioned some forbidden foods such as salty foods, watermelon and grilled meat (which sometimes related back to a traditional belief that negative impacts would be felt in the pregnancy such as birth complications and bleeding). Similarly, drinking cold water was thought to negatively affect the baby. Beneficial foods mentioned included vegetables and meat, during pregnancy.
“ Often when a woman has close pregnancies, she can be ashamed, and this particularly delays the time of consultation” – Workshop 5 SEN (CHWs).
“Yes, there are things that are prohibited for pregnant women like salty foods” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
In Kaffrine, Senegal, some participants spoke of a traditional belief that if a pregnant woman consumes eggs then her baby might be overweight, or have problems learning how to talk. Despite this, mothers in Kaffrine said that they would be happy to accept eggs as a supplement, although if supplements are provided that require preparation (such as powdered supplements), they would be less likely to accept them.
“These restrictions are traditional, and more women no longer believe that eggs will cause a problem to the child. But if these eggs are brought by external bodies, we will hesitate to take it.” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
“They don’t eat eggs before the child starts speaking (the child only eats eggs when he starts talking). This is because it’s very heavy and can cause bloating and may also lead to intestinal problems.” – Workshop 4 SEN (grandmothers).
Other important topics – access to health services
For the participants in Kaffrine, Senegal, accessing health services was problematic, particularly for pre- and post-natal appointments, which faced frequent delays. Some women had access due to poor roads and chose to give birth at home. Access issues were further compounded by poverty and social factors, as procedures in hospitals can be costly, and women with close pregnancies (soon after an earlier one) can feel shame from society and hide their pregnancy.
“Women really have problems of lack of finances. There are social services in the hospital; but those services rarely attend to women without finances. Even when a child dies at birth they will require money to do the necessary procedure ” – Workshop 11 SEN (CHWs).
Creation of the culturally-informed protocols
Recommendations that comprise a culturally-informed protocol for intervention design in each locality are given in Table 3 .
The Major Cultural Themes, and specific Egg Intervention Themes drawn out from only 9–11 carefully planned group sessions in each country provided a rich set of recommendations towards a culturally-informed protocol for the localised design of a proposed Egg Intervention for both East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal. A culturally-informed protocol designed in this way comprises cultural insights which are worthy of consideration in local intervention design and should guide future stages of engagement and provide a platform from which good rapport and trust can be built between researchers and the community [ 16 ]. For example, in Kaffrine, Senegal, the early involvement of husbands and grandmothers is crucial, which reflects values around shared decision making within families that are noted to be more prevalent in LMICs, in contrast to individualistic values in HICs [ 16 , 39 ]. Similarly, due to strong religious values in both East Lombok, Indonesia and Kaffrine, Senegal, partnerships with Islamic leaders is likely to improve engagement. Past studies show the crucial role that religious leaders can play in determining social acceptability of interventions, particularly around taboo topics such as birth spacing [ 40 ].
The WVIS plus PEX:FGD method demonstrated here produced both broad cultural themes from shared values, which were in a concise and easy-to-understand format which could be readily communicated with the wider Action Against Stunting Hub, as well as life practices relevant to stunting in Kaffrine, Senegal and in East Lombok, Indonesia. Discussions of shared values during the WVIS main workshop provided useful cultural background within each community. PEX:FGD discussion uncovered numerous cultural factors within local life practices that could influence on the Egg Intervention engagement and acceptability. Combining themes from the WVIS workshop and PEX:FGDs allowed for specific recommendations to be made towards a culturally-informed protocol for the design of an Egg Intervention that included both broad cultural themes and specific Intervention insights (Table 3 ). For example, in Kaffrine, Senegal, to know that the husband’s authoritative family decision-making for health care (specific) is rooted in Islamic foundations (wider cultural) points to an Intervention Recommendation within the protocol, involving consultations with Islamic Leaders to lead community awareness targeting fathers. Similarly, in East Lombok, Indonesia the (specific) behaviour of breastfeeding for 2 years was underpinned by (wider cultural) shared values of living in Islam. This understanding of local values could prevent the imposition of culturally misaligned values, which Bernal and Adames (2017) caution against [ 17 ].
There are a number of interesting overlaps between values seen in the WVIS Frameworks and Narratives and the categories of Schwartz (1992) and The World Values Survey (2023) [ 41 , 42 ]. For example, in both Kaffrine, Senegal and East Lombok, Indonesia, strong religious values were found, and the groups spoke of the importance of practicing their religion with daily habits. This would align with traditional and conservation values [ 41 , 43 ]. Furthermore, in Kaffrine, Senegal participants often mentioned the importance of mutual aid within the community, and similar values of togetherness and respect in the community were found in East Lombok, Indonesia. These would seem to align with traditional, survival and conservation values [ 41 , 43 ]. However, the values mentioned by the groups in the WVIS workshops are far more specific, and it is possible that through asking what is most worthwhile, valuable and meaningful about their context, the participants are able to prioritise which aspects of their values are most salient to their daily lives. Grounded shared values such as these are generally neglected in Global Health Research, and values predominant in the Global North are often assumed to be universal [ 14 ]. Thus, by excluding the use of a predefined external framework, we minimized the risk of imposing our own ideas of values in the community, and increased the relevance, significance and local validity of the elicited information [ 28 ].
Participatory methods of engagement are an essential step in conducting Global Health Research but there is currently a paucity of specific guidance for implementing participatory methods in vulnerable communities [ 16 , 44 ]. In addition, there is acknowledgement in the literature that it is necessary to come into communities in LMICs without assumptions about their held values, and to use bottom-up participatory approaches to better understand local values [ 14 , 16 ]. The WVIS plus PEX:FGD methodology highlighted here exemplifies a method that is replicable in multiple country contexts [ 28 , 32 ] and can be used to crystallize local In Situ Shared Values which can be easily communicated to external researchers. Coupled with the specialised FGD (PEX:FGD), values-based perceptions of specific topics (in this case stunting) can be elicited leading to the creation of specific Culture-based recommendations. This therefore takes steps to answer the call by Memon and colleagues (2021) for the creation of cultural protocols ahead of conducting research in order to foster ethical research relationships [ 16 ]. We believe that the potential usefulness of the WVIS approach to guide engagement and inform intervention design is effectively demonstrated in this study and WVIS offers a method of making explicit local values in a novel and valuable way.
However, we acknowledge that our approach has several limitations. It has relied heavily on the local university researchers to debate and decide which participant stakeholder groups should be chosen, and although they did this in the context of the Whole Child approach, it would have been advantageous to have involved cultural researchers with a deeper understanding of cultural structures, to ensure sufficient opportunities for key cultural elements to emerge. This would have in particular strengthened the intervention design derived from the PEX:FGD data. For example, we retrospectively realised that our study could have been improved if grandmothers had been engaged in East Lombok. Understanding this limitation leads to suggestion for further work: to specifically investigate the overlap of this approach with disciplinary studies of culture, where social interactions and structures are taken into account via formal frameworks.
There are more minor limitations to note. For example, the WVIS approach can only be led by a trained and experienced facilitator: not all researchers can do this. A training programme is currently under development that could be made more widely available through online videos and a Handbook. Secondly, although the groups recruited do not need to be representative of the local population, the number recruited should be increased until theoretical saturation is achieved of the themes which emerge, which was not carried out in this study as we focussed on demonstrating the feasibility of the tool. Thirdly, there is a limit to the number of topics that can be explored in the PEX:FGDs within the timeframe of one focus group (depending on the stamina of the participants), and so if a wider range of topics need formative research, then more workshops are needed. Lastly, this work took place in a large, highly collaborative project involving expert researchers from local countries as well as international experts in WVIS : other teams may not have these resources. However, local researchers who train in WVIS could lead on their own (and in this Hub project such training was available).
The need for better understanding, acknowledgement and integration of local culture and shared values is increasing as the field of Global Health Research develops. This study demonstrates that the WVIS plus PEX:FGD shared values approach provides an efficient approach to contextualise and localise interventions, through eliciting and making communicable shared values and local life practices which can be used towards the formation of a culturally-informed protocols. Were this method to be used for intervention design in future, it is possible that more focus should be given to existing social structures and support systems and a greater variety of stakeholders should be engaged. This study thus contributes to the literature on methods to culturally adapt interventions. This could have significant implications for improving the uptake of nutrition interventions to reduce malnutrition through improved social acceptability, which could help progression towards the goal of Zero Hunger set within the SDGs. The transferability and generalisability of the WVIS plus PEX:FGD approach should now be investigated further in more diverse cultures and for providing formative research information for a wider range of research themes. Future studies could also focus on establishing its scaling and pragmatic usefulness as a route to conceptualising mechanisms of social acceptability, for example a mechanism may be that in communities with strong traditional religious values, social hierarchies involving religious leaders and fathers exist and their buy-in to the intervention is crucial to its social acceptability. Studies could also focus on the comparison or combination of WVIS plus PEX:FGD with other qualitative methods used for intervention design and implementation.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request [email protected], Orcid number 0000–0002–1811-4597. These include deidentified Frameworks of Shared Values and Accompanying Narrative from each Group; deidentified Hub Insight Statements of relevant themes.
World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Driving commitment for nutrition within the UN Decade of Action on Nutrition: policy brief. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
Google Scholar
Victora CG, Christian P, Vidaletti LP, Gatica-Domínguez G, Menon P, Black RE. Revisiting maternal and child undernutrition in low-income and middle-income countries: variable progress towards an unfinished agenda. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1388–99.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Aguayo VM, Nair R, Badgaiyan N, Krishna V. Determinants of stunting and poor linear growth in children under 2 years of age in India: an in-depth analysis of Maharashtra's comprehensive nutrition survey. Matern Child Nutr. 2016;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):121–40.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Beal T, Tumilowicz A, Sutrisna A, Izwardy D, Neufeld LM. A review of child stunting determinants in Indonesia. Matern Child Nutr. 2018;14(4):e12617.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hossain M, Choudhury N, Adib Binte Abdullah K, Mondal P, Jackson AA, Walson J, et al. Evidence-based approaches to childhood stunting in low and middle income countries: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 2017;102(10):903–9.
Brar S, Akseer N, Sall M, Conway K, Diouf I, Everett K, et al. Drivers of stunting reduction in Senegal: a country case study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(Suppl 2):860s–74s.
Heidkamp RA, Piwoz E, Gillespie S, Keats EC, D'Alimonte MR, Menon P, et al. Mobilising evidence, data, and resources to achieve global maternal and child undernutrition targets and the sustainable development goals: an agenda for action. Lancet. 2021;397(10282):1400–18.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Goudet SM, Bogin BA, Madise NJ, Griffiths PL. Nutritional interventions for preventing stunting in children (birth to 59 months) living in urban slums in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;6(6):Cd011695.
PubMed Google Scholar
Desai S, Misra M, Das A, Singh RJ, Sehgal M, Gram L, et al. Community interventions with women's groups to improve women's and children's health in India: a mixed-methods systematic review of effects, enablers and barriers. BMJ Glob Health. 2020;5(12)
Muraya KW, Jones C, Berkley JA, Molyneux S. Perceptions of childhood undernutrition among rural households on the Kenyan coast – a qualitative study. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):693.
Isler J, Sawadogo NH, Harling G, Bärnighausen T, Adam M, Sié A, et al. 'If he sees it with his own eyes, he will understand': how gender informed the content and delivery of a maternal nutrition intervention in Burkina Faso. Health Policy Plan. 2020;35(5):536–45.
Zaidi S, Das JK, Khan GN, Najmi R, Shah MM, Soofi SB. Food supplements to reduce stunting in Pakistan: a process evaluation of community dynamics shaping uptake. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1046.
Wight D, Plummer M, Ross D. The need to promote behaviour change at the cultural level: one factor explaining the limited impact of the MEMA kwa Vijana adolescent sexual health intervention in rural Tanzania. A process evaluation. BMC Public Health. 2012;12(1):788.
Aubel J, Chibanda D. The neglect of culture in global health research and practice. BMJ Glob Health. 2022;7(9):e009914.
Article PubMed Central Google Scholar
Myser C. Defining "global health ethics": offering a research agenda for more bioethics and multidisciplinary contributions-from the global south and beyond the health sciences-to enrich global health and global health ethics initiatives. J Bioeth Inq. 2015;12(1):5–10.
Memon R, Asif M, Khoso AB, Tofique S, Kiran T, Chaudhry N, et al. Recognising values and engaging communities across cultures: towards developing a cultural protocol for researchers. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):47.
Bernal G, Adames C. Cultural adaptations: conceptual, ethical, contextual, and methodological issues for working with Ethnocultural and majority-world populations. Prev Sci. 2017;18(6):681–8.
Glickman SW, McHutchison JG, Peterson ED, Cairns CB, Harrington RA, Califf RM, et al. Ethical and scientific implications of the globalization of clinical research. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(8):816–23.
King KF, Kolopack P, Merritt MW, Lavery JV. Community engagement and the human infrastructure of global health research. BMC Med Ethics. 2014;15(1):84.
Horton R. Offline: is global health neocolonialist? Lancet. 2013;382(9906):1690.
Article Google Scholar
Woodward EN, Matthieu MM, Uchendu US, Rogal S, Kirchner JE. The health equity implementation framework: proposal and preliminary study of hepatitis C virus treatment. Implement Sci. 2019;14(1):26.
The Pūtaiora Writing Group. Te Ara Tika Guidelines for Māori research ethics: A framework for researchers and ethics committee members. Health Research Council of New Zealand. (no date). Online, Accessed 5 th May 2023. Available from: http://www.hrc.govt.nz/sites/default/files/2019-06/Resource%20Library%20PDF%20-%20Te%20Ara%20Tika%20Guidelines%20for%20Maori%20Research%20Ethics.pdf
Pelto GH, Armar-Klemesu M, Siekmann J, Schofield D. The focused ethnographic study 'assessing the behavioral and local market environment for improving the diets of infants and young children 6 to 23 months old' and its use in three countries. Matern Child Nutr. 2013;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):35–46.
Bentley ME, Johnson SL, Wasser H, Creed-Kanashiro H, Shroff M, Fernandez Rao S, et al. Formative research methods for designing culturally appropriate, integrated child nutrition and development interventions: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014;1308:54–67.
Kodish S, Aburto N, Dibari F, Brieger W, Agostinho SP, Gittelsohn J. Informing a behavior change communication strategy: formative research findings from the scaling up nutrition movement in Mozambique. Food Nutr Bull. 2015;36(3):354–70.
Mattes RD, Rowe SB, Ohlhorst SD, Brown AW, Hoffman DJ, Liska DJ, et al. Valuing the diversity of research methods to advance nutrition science. Adv Nutr. 2022;13(4):1324–93.
Robert RC, Bartolini RM, Creed-Kanashiro HM, Verney SA. Using formative research to design context-specific animal source food and multiple micronutrient powder interventions to improve the consumption of micronutrients by infants and young children in Tanzania, Kenya, Bangladesh and Pakistan. Matern Child Nutr. 2021;17(2):e13084.
Sethamo OA, Masika RJ, Harder MK. Understanding the role of crystallizing local shared values in fostering effective community engagement in adaptation planning in Botswana. Clim Dev. 2020;12(5):448–56.
Odii EC, Ebido CC, Harder MK. A values-based approach for generating localized social indicators for use in sustainability assessment and decision-making: test case of brownfield soft reuse in Nigeria. Sci Total Environ. 2020;711:135045.
Podger D, Piggot G, Zahradnik M, Janoušková S, Velasco I, Hak T, et al. The earth charter and the ESDinds initiative: developing indicators and assessment tools for civil society organisations to examine the values dimensions of sustainability projects. J Educ Sustain Dev. 2010;4(2):297–305.
Odii BC, Huang Y, Bouvrie N, Harder MK. Cycles of meaning-making crystallization in the WeValue InSitu process as clear contributions towards transformative learning. J Clean Prod. 2021;304:127024.
Huang Y, Wu W, Xue Y, Harder MK. Perceptions of climate change impacts on city life in Shanghai: through the lens of shared values. Cleaner Prod Lett. 2022;3:100018.
Action Against Stunting Hub. UKRI GCRF action against stunting: alleviating child undernutrition, globally. 2020. URL: https://actionagainststunting.org/ [Accessed 15/08/2022].
UNICEF. Nutrition country profiles . 2010. URL: https://data.unicef.org/resources/nutrition-country-profiles/ [Accessed 10/05/2023].
Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. 2nd ed. London: SAGE; 2014.
Noblit GW, Hare RD, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: synthesizing qualitative studies: sage; 1988.
Stelle I, McDonagh LK, Hossain I, Kalea AZ, Pereira DIA. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1140.
Muraya KW, Jones C, Berkley JA, Molyneux S. "If it's issues to do with nutrition…I can decide…": gendered decision-making in joining community-based child nutrition interventions within rural coastal Kenya. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(suppl_5):v31–v9.
Aubel J. Grandmothers — a neglected family resource for saving newborn lives. BMJ Glob Health. 2021;6(2):e003808.
Egeh AA, Dugsieh O, Erlandsson K, Osman F. The views of Somali religious leaders on birth spacing - a qualitative study. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019;20:27–31.
Schwartz SH. Universals in the content and structure of values: Theoretical advances and empirical tests in 20 countries. Advances in experimental social psychology. 25: Elsevier; 1992. p. 1–65.
World Values Survey Association. Findings and insights, 2020 [Available from: https://www.worldvaluessurvey.org/WVSContents.jsp .]
Inglehart R, Welzel C. Value change and the persistence of cultural traditions. Modernization, cultural change, and democracy: the human development sequence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2005. p. 48–76.
Glandon D, Paina L, Alonge O, Peters DH, Bennett S. 10 best resources for community engagement in implementation research. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(10):1457–65.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the Hub PI, Claire Heffernan, for feedback on a late draft of the manuscript.
The Action Against Stunting Hub is funded by the Medical Research Council through the UK Research and Innovation (UKRI) Global Challenges Research Fund (GCRF), Grant No.: MR/S01313X/1.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Values & Sustainability Research Group, School of Architecture, Technology and Engineering, University of Brighton, Brighton, UK
Annabel J. Chapman, Mahsa Firoozmand & Marie K. Harder
Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
Chike C. Ebido, Rahel Neh Tening, Yanyan Huang & Marie K. Harder
Department of Zoology and Environmental Biology, University of Nigeria, Nsukka, Nigeria
Chike C. Ebido
Preventive Medicine and Public Health, Université Cheikh Anta Diop (UCAD), Dakar, Senegal
Ndèye Marème Sougou
Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah, Jakarta, Indonesia
Risatianti Kolopaking
Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization Regional Centre for Food and Nutrition (SEAMEO RECFON) Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Risatianti Kolopaking & Rita Anggorowati
International Research Laboratory (IRL 3189) Environnement santé et sociétés/CNRS/UCAD, Dakar, Senegal
Amadou H. Diallo
Department of Medical Records and Health Information, Faculty of Health and Technology, Universitas Bandung, Bandung, Indonesia
Rita Anggorowati
Laboratory of Cultural Anthropology, IFAN, Université Cheikh Anta Diop (UCAD), Dakar, Senegal
Fatou B. Dial & Cheikh El Hadji Abdoulaye Niang
School of Education, Languages and Linguistics, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, UK
Jessica Massonnié
Department of Learning and Leadership, IOE, UCL’s Faculty of Education and Society, University College London, London, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MKH formulated the initial research question and study design. AJC developed the specific research question. Data collection in Senegal involved CCE, NMS, AHD, FBD, RNT, CEHAN and JM. Data collection in Indonesia involved RA, RK, YH and MKH. Cultural interpretation in Senegal Involved AHD, FBD, NMS, RNT and JM. Analysis involved AJC and MF. AJC and MKH wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marie K. Harder .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The research was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and has been approved by the Ethics Review Board of the University of Brighton, and national ethics committees for research in Indonesia and Senegal. Informed consent was obtained in the local vernacular language, Bahasa, French or Wolof. Participants retained a copy of the informed consent document for reference.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Chapman, A.J., Ebido, C.C., Tening, R.N. et al. Creating culturally-informed protocols for a stunting intervention using a situated values-based approach ( WeValue InSitu ): a double case study in Indonesia and Senegal. BMC Public Health 24 , 987 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18485-y
Download citation
Received : 27 September 2023
Accepted : 29 March 2024
Published : 09 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-18485-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health intervention
- Shared values
- Culturally-informed protocol
- Cultural factors
- WeValue InSitu
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is a use case. A use case explains how users interact with a product or system. It outlines the flow of user inputs, establishing successful and failed paths to meeting goals. This allows product teams to better understand what a system does, how it performs, and why errors occur. You can write one out or diagram a use case model for ...
A use case is a description of how a user interacts with a system or product. Companies build use cases to establish success scenarios, failure scenarios, and any important variants or exceptions. Many organizations leverage use case modeling tools — such as Miro, LucidChart, and SmartDraw, for some examples — to write or visually represent ...
A use case is a methodology used in system analysis to identify, clarify and organize system requirements. The use case is made up of a set of possible sequences of interactions between systems and users in a particular environment and related to a particular goal. The method creates a document that describes all the steps taken by a user to ...
Step 1: Come up with the title and description. Any use case study must have an engaging title. Keep it concise, specific, and indicative of the use case's purpose. For instance, the title Optimizing Online Checkout: A Use Case for E-Commerce Conversion Enhancement immediately conveys the focus and scope.
Use case meaning. A use case is a methodology to organize system requirements. It comprises a set of possible sequences of interactions between systems and users in a defined environment with a particular goal. The use case document includes the environment, goal, and other details to provide a clear picture of the system and overall project.
A use case is a concept used in software development, product design, and other fields to describe how a system can be used to achieve specific goals or tasks. It outlines the interactions between users or actors and the system to achieve a specific outcome. In this article, we'll dive into the details of what use cases are, how they are used ...
A Use Case Diagram is a type of Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagram that represents the interaction between actors (users or external systems) and a system under consideration to accomplish specific goals. It provides a high-level view of the system's functionality by illustrating the various ways users can interact with it. Unmute. 2.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A use case diagram is a graphical representation used in use case modeling to visualize and communicate these interactions and relationships. In a use case diagram, you'll typically see actors represented as stick figures, and the use cases (specific functionalities or features) as ovals or rectangles. Lines and arrows connect the actors to ...
Use Case Modeling Case Study - From Use case to Scenarios and Sequence diagrams. Let's delve into the essence of use cases and scenarios and explore their significance in the realm of software engineering. 1. Use Case Definition: Scenario: The team begins by identifying a fundamental use case: "User Places an Order." This use case ...
Simply put, a use case is a description of all the ways an end-user wants to "use" a system. These "uses" are like requests of the system, and use cases describe what that system does in response to such requests. In other words, use cases describe the conversation between a system and its user (s), known as actors.
14. Include case studies in your lead gen efforts. There are a number of offers you can create based off of your case studies, in the form of ebooks, templates, and more. For example you could put together an ebook titled "A step-by-step guide to reaching 10,000 blog subscribers in 3 months…just like XX did.".
A case study is typically much more detailed than a use case, and includes information such as background on the customer, pain points, objectives, how they deployed the product or solution, and the results. Unlike a use case, which is a straightforward explanation of how a product addresses a problem, a case study is driven by storytelling.
Here are a few: 1. Illustrative case study: Researchers use observations on every angle of a specific case, generally resulting in a thorough and deep data analysis. 2. Exploratory case study: Primarily used to identify research questions and qualitative methods to explore in subsequent studies, this type of case study is frequently in use in ...
A use case is a methodology, created by Ivar Jacobson in 1986, designed to understand how a customer interacts with a product. There are two types of use cases: business and system. In business ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
A case study is a comprehensive report of the results of theory testing or examining emerging themes of a business in real life context. Case studies are also often used in the healthcare industry, conducting health services research with primary research interest around routinely collected healthcare data.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Case studies are a good way to explore a real-world topic in-depth, illustrate a point, discuss the implications or meaning of an event, or compare the experiences of different individuals. ... Similarly, professors can use case studies to highlight key concepts from a lecture and pose questions to test students' understanding of the material.
1. "A Case In Point". Meaning: This phrase is used to highlight a specific example that supports or illustrates a larger point or argument. Example sentence: "The success of Company X, which implemented a comprehensive marketing strategy, is a case in point for the effectiveness of well-executed case studies.".
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows: • Select the topic and the deadline of your case study. • Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the writing process you struggle with. • Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
Study setting. This research was exploratory rather than explanatory in nature. The emphasis was on demonstrating the usefulness of the WeValue InSitu (WVIS) approach to develop culturally-informed protocols of practical use in intervention design, in different cultural sites.This study was set within a broader shared-values workstream within the UKRI GCRF Action Against Stunting Hub project [].