
- Global Relocation Services
- Global Consulting
- Partnerships
- Atlas World Group
- Social Responsibility

Relocation Insights

International Short-Term Assignments
International short-term assignments are a useful global mobility tool, that provide companies with a resource to support critical strategic needs while mitigating mobility program costs. Short-term assignments may also be used in a developmental capacity providing high potential employees an opportunity to grow in their career. Short-term assignments commonly range from 3 to 12 months in duration.
One of the biggest challenges of global mobility is compliance with applicable immigration, tax, employment, and permanent establishment laws. Laws that change quickly and vary from country to country can take companies by surprise. A carefully crafted short-term assignment program and comprehensive policy can help avoid potential hazards. Having a consistent program with clearly defined parameters will allow the focus to remain on compliance.
Program Development
As with all mobility programs, short-term assignments can be structured as a single policy applicable to all, tiered based on factors such as business need or job level, or as a structured core/flex program. When developing a short-term assignment program, whether for the first time or revising an existing policy, these initial steps are recommended:
- Consider the overall company culture, mobility philosophy, business objectives of the international short-term assignment program, and common assignment objectives.
- Identify employee job levels and demographics.
- Reflect on the importance of the employee experience as well as how the assignment policy can support DEI initiatives.
- Determine the most common assignment durations and locations, if possible, to estimate the anticipated cost of the benefits under consideration.
These initial steps will, in turn, help the company determine the desired parameters of the program. A common example of how a company’s overall company culture influences mobility policy can be seen in eligibility of family members under a short-term assignment. Some companies may decide that short-term assignees may not be accompanied by families and reflect that in policy eligibility language. Some companies will not support families going on the assignment, but do not expressly reject families from accompanying at their own expense. While others with a more family focused culture will allow accompaniment and provide some supporting benefits.
Assignment duration is also a key factor in short-term assignment program design. These assignments can have varying ranges from as short as 30 days or up to 18 months. They are most commonly defined as longer than 90 days or up to one year. However, knowing company intentions regarding durations helps in determining parameters and components. For example, if assignments are typically shorter in duration, the policy may not include parameters for home leave. If the assignments are typically the full year, the company may decide to include a home leave. If there is a possibility that the assignment may extend beyond 1 year, the company should be prepared to address whether benefits change or the employee transitions to another type of mobility policy. If short-term assignments are a new phenomenon and assignment durations are unknown at the time of program development, it will be important to revisit the policy as the assignment program matures.
A brief description of the components commonly found in international short-term assignment programs follows. It is important to note that note every component has to be included in order to have a successful program, and regional variances/culture may also dictate which components are included. There may also be variations on the inclusions and descriptions below as these descriptions are based on an unaccompanied employee.
International Short Term Assignment Program Components
Enable cookie tracking
You must enable cookie tracking to continue. For more details please consult our Privacy Policy.
The Mercer Mobility Exchange website and its divisional websites may be translated for your convenience using translation software powered by Google Translate, a free online language translation service that can translate text and web pages into different languages. Reasonable efforts have been made to verify the reliability of the translation service, however, no automated translation is perfect nor is it intended to replace human translators. Mercer does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Some pages may not be accurately translated due to the limitations of the translation software. Text in images, PDF files, Word documents or other document types cannot be translated. The official text is the English version of the website. Any discrepancies or differences created in the translation are not binding and have no legal effect for compliance or enforcement purposes. If any questions arise related to the accuracy of the information contained in the translated website, please refer to the English version of the website which is the official version
Short-term assignments
Short-term international assignments usually last between 3 and 12 months, and allow companies to transfer skills, knowledge and resources quickly and cost effectively, providing a quick response to business needs.
However, living costs for short-term assignees are different from other categories of mobile workers. Mercer’s technology and data solutions can help you handle the related issues with efficiency and ease.

Short Term Travel Cost Report
Forecast the cost of short-term assignments, commuter assignments or extended business travels with ease and accuracy. The report accounts for the costs of airfares, accommodation, car rental as well as per diem allowances, providing data in up to 3 currencies.
Per Diem Allowance Calculator 2.0
Determine fair and cost-efficient per diem rates suitable for short-term assignees and business travelers.
Alternative International Assignments (AIA) Survey
Benchmark your policies with our latest data gathered from 200+ multinational organizations worldwide. The survey explores the use of international assignments other than long-term expatriate assignments: short-term assignments , permanent moves / one-way transfers , and commuter assignments .
Contact your consultant or use our form to discuss available options and order data.
Assignment segmentation As managing a globally mobile workforce grows more complicated, assignment policy segmentation offers more flexibility and a broader range of solutions.
Business travel allowances Looking for daily allowances for business travellers?
More tech solutions See what other tools Mercer offers that streamline the work of building assignment compensation packages.
Get the latest global mobility news, event invitations, and articles from Mercer. sign up now
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
Managing International Assignments
International assignment management is one of the hardest areas for HR professionals to master—and one of the most costly. The expense of a three-year international assignment can cost millions, yet many organizations fail to get it right. Despite their significant investments in international assignments, companies still report a 42 percent failure rate in these assignments. 1
With so much at risk, global organizations must invest in upfront and ongoing programs that will make international assignments successful. Selecting the right person, preparing the expatriate (expat) and the family, measuring the employee's performance from afar, and repatriating the individual at the end of an assignment require a well-planned, well-managed program. Knowing what to expect from start to finish as well as having some tools to work with can help minimize the risk.
Business Case
As more companies expand globally, they are also increasing international assignments and relying on expatriates to manage their global operations. According to KPMG's 2021 Global Assignment Policies and Practices Survey, all responding multinational organizations offered long-term assignments (typically one to five years), 88 percent offered short-term assignments (typically defined as less than 12 months), and 69 percent offered permanent transfer/indefinite length.
Managing tax and tax compliance, cost containment and managing exceptions remain the three principal challenges in long-term assignment management according to a 2020 Mercer report. 2
Identifying the Need for International Assignment
Typical reasons for an international assignment include the following:
- Filling a need in an existing operation.
- Transferring technology or knowledge to a worksite (or to a client's worksite).
- Developing an individual's career through challenging tasks in an international setting.
- Analyzing the market to see whether the company's products or services will attract clients and users.
- Launching a new product or service.
The goal of the international assignment will determine the assignment's length and help identify potential candidates. See Structuring Expatriate Assignments and the Value of Secondment and Develop Future Leaders with Rotational Programs .
Selection Process
Determining the purpose and goals for an international assignment will help guide the selection process. A technical person may be best suited for transferring technology, whereas a sales executive may be most effective launching a new product or service.
Traditionally, organizations have relied on technical, job-related skills as the main criteria for selecting candidates for overseas assignments, but assessing global mindset is equally, if not more, important for successful assignments. This is especially true given that international assignments are increasingly key components of leadership and employee development.
To a great extent, the success of every expatriate in achieving the company's goals in the host country hinges on that person's ability to influence individuals, groups and organizations that have a different cultural perspective.
Interviews with senior executives from various industries, sponsored by the Worldwide ERC Foundation, reveal that in the compressed time frame of an international assignment, expatriates have little opportunity to learn as they go, so they must be prepared before they arrive. Therefore, employers must ensure that the screening process for potential expatriates includes an assessment of their global mindset.
The research points to three major attributes of successful expatriates:
- Intellectual capital. Knowledge, skills, understanding and cognitive complexity.
- Psychological capital. The ability to function successfully in the host country through internal acceptance of different cultures and a strong desire to learn from new experiences.
- Social capital. The ability to build trusting relationships with local stakeholders, whether they are employees, supply chain partners or customers.
According to Global HR Consultant Caroline Kersten, it is generally understood that global leadership differs significantly from domestic leadership and that, as a result, expatriates need to be equipped with competencies that will help them succeed in an international environment. Commonly accepted global leadership competencies, for both male and female global leaders, include cultural awareness, open-mindedness and flexibility.
In particular, expatriates need to possess a number of vital characteristics to perform successfully on assignment. Among the necessary traits are the following:
- Confidence and self-reliance: independence; perseverance; work ethic.
- Flexibility and problem-solving skills: resilience; adaptability; ability to deal with ambiguity.
- Tolerance and interpersonal skills: social sensitivity; observational capability; listening skills; communication skills.
- Skill at handling and initiating change: personal drivers and anchors; willingness to take risks.
Trends in international assignment show an increase in the younger generation's interest and placement in global assignments. Experts also call for a need to increase female expatriates due to the expected leadership shortage and the value employers find in mixed gender leadership teams. See Viewpoint: How to Break Through the 'Mobility Ceiling' .
Employers can elicit relevant information on assignment successes and challenges by means of targeted interview questions with career expatriates, such as the following:
- How many expatriate assignments have you completed?
- What are the main reasons why you chose to accept your previous expatriate assignments?
- What difficulties did you experience adjusting to previous international assignments? How did you overcome them?
- On your last assignment, what factors made your adjustment to the new environment easier?
- What experiences made interacting with the locals easier?
- Please describe what success or failure means to you when referring to an expatriate assignment.
- Was the success or failure of your assignments measured by your employers? If so, how did they measure it?
- During your last international assignment, do you recall when you realized your situation was a success or a failure? How did you come to that determination?
- Why do you wish to be assigned an international position?
Securing Visas
Once an individual is chosen for an assignment, the organization needs to move quickly to secure the necessary visas. Requirements and processing times vary by country. Employers should start by contacting the host country's consulate or embassy for information on visa requirements. See Websites of U.S. Embassies, Consulates, and Diplomatic Missions .
Following is a list of generic visa types that may be required depending on the nature of business to be conducted in a particular country:
- A work permit authorizes paid employment in a country.
- A work visa authorizes entry into a country to take up paid employment.
- A dependent visa permits family members to accompany or join employees in the country of assignment.
- A multiple-entry visa permits multiple entries into a country.
Preparing for the Assignment
An international assignment agreement that outlines the specifics of the assignment and documents agreement by the employer and the expatriate is necessary. Topics typically covered include:
- Location of the assignment.
- Length of the assignment, including renewal and trial periods, if offered.
- Costs paid by the company (e.g., assignment preparation costs, moving costs for household goods, airfare, housing, school costs, transportation costs while in country, home country visits and security).
- Base salary and any incentives or allowances offered.
- Employee's responsibilities and goals.
- Employment taxes.
- Steps to take in the event the assignment is not working for either the employee or the employer.
- Repatriation.
- Safety and security measures (e.g., emergency evacuation procedures, hazards).
Expatriates may find the reality of foreign housing very different from expectations, particularly in host locations considered to be hardship assignments. Expats will find—depending on the degree of difficulty, hardship or danger—that housing options can range from spacious accommodations in a luxury apartment building to company compounds with dogs and armed guards. See Workers Deal with Affordable Housing Shortages in Dubai and Cairo .
Expats may also have to contend with more mundane housing challenges, such as shortages of suitable housing, faulty structures and unreliable utility services. Analyses of local conditions are available from a variety of sources. For example, Mercer produces Location Evaluation Reports, available for a fee, that evaluate levels of hardship for 14 factors, including housing, in more than 135 locations.
Although many employers acknowledge the necessity for thorough preparation, they often associate this element solely with the assignee, forgetting the other key parties involved in an assignment such as the employee's family, work team and manager.
The expatriate
Consider these points in relation to the assignee:
- Does the employee have a solid grasp of the job to be done and the goals established for that position?
- Does the employee understand the compensation and benefits package?
- Has the employee had access to cultural training and language instruction, no matter how similar the host culture may be?
- Is the employee receiving relocation assistance in connection with the physical move?
- Is there a contact person to whom the employee can go not only in an emergency but also to avoid becoming "out of sight, out of mind"?
- If necessary to accomplish the assigned job duties, has the employee undergone training to get up to speed?
- Has the assignee undergone an assessment of readiness?
To help the expatriate succeed, organizations are advised to invest in cross-cultural training before the relocation. The benefits of receiving such training are that it: 3
- Prepares the individual/family mentally for the move.
- Removes some of the unknown.
- Increases self-awareness and cross-cultural understanding.
- Provides the opportunity to address questions and anxieties in a supportive environment.
- Motivates and excites.
- Reduces stress and provides coping strategies.
- Eases the settling-in process.
- Reduces the chances of relocation failure.
See Helping Expatriate Employees Deal with Culture Shock .
As society has shifted from single- to dual-income households, the priorities of potential expatriates have evolved, as have the policies organizations use to entice employees to assignment locations. In the past, from the candidate's point of view, compensation was the most significant component of the expatriate package. Today more emphasis is on enabling an expatriate's spouse to work. Partner dissatisfaction is a significant contributor to assignment failure. See UAE: Expat Husbands Get New Work Opportunities .
When it comes to international relocation, most organizations deal with children as an afterthought. Factoring employees' children into the relocation equation is key to a successful assignment. Studies show that transferee children who have a difficult time adjusting to the assignment contribute to early returns and unsuccessful completion of international assignments, just as maladjusted spouses do. From school selection to training to repatriation, HR can do a number of things to smooth the transition for children.
Both partners and children must be prepared for relocation abroad. Employers should consider the following:
- Have they been included in discussions about the host location and what they can expect? Foreign context and culture may be more difficult for accompanying family because they will not be participating in the "more secure" environment of the worksite. Does the family have suitable personal characteristics to successfully address the rigors of an international life?
- In addition to dual-career issues, other common concerns include aging parents left behind in the home country and special needs for a child's education. Has the company allowed a forum for the family to discuss these concerns?
The work team
Whether the new expatriate will supervise the existing work team, be a peer, replace a local national or fill a newly created position, has the existing work team been briefed? Plans for a formal introduction of the new expatriate should reflect local culture and may require more research and planning as well as input from the local work team.
The manager/team leader
Questions organization need to consider include the following: Does the manager have the employee's file on hand (e.g., regarding increases, performance evaluations, promotions and problems)? Have the manager and employee engaged in in-depth conversations about the job, the manager's expectations and the employee's expectations?
Mentors play an important role in enhancing a high-performing employee's productivity and in guiding his or her career. In a traditional mentoring relationship, a junior executive has ongoing face-to-face meetings with a senior executive at the corporation to learn the ropes, set goals and gain advice on how to better perform his or her job.
Before technological advances, mentoring programs were limited to those leaders who had the time and experience within the organization's walls to impart advice to a few select people worth that investment. Technology has eliminated those constraints. Today, maintaining a long-distance mentoring relationship through e-mail, telephone and videoconferencing is much easier. And that technology means an employer is not confined to its corporate halls when considering mentor-mentee matches.
The organization
If the company is starting to send more employees abroad, it has to reassess its administrative capabilities. Can existing systems handle complicated tasks, such as currency exchanges and split payrolls, not to mention the additional financial burden of paying allowances, incentives and so on? Often, international assignment leads to outsourcing for global expertise. Payroll, tax, employment law, contractual obligations, among others, warrant an investment in sound professional advice.
Employment Laws
Four major U.S. employment laws have some application abroad for U.S. citizens working in U.S.-based multinationals:
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act.
- The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA).
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
- The Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (USERRA).
Title VII, the ADEA and the ADA are the more far-reaching among these, covering all U.S. citizens who are either:
- Employed outside the United States by a U.S. firm.
- Employed outside the United States by a company under the control of a U.S. firm.
USERRA's extraterritoriality applies to veterans and reservists working overseas for the federal government or a firm under U.S. control. See Do laws like the Fair Labor Standards Act and the Family and Medical Leave Act apply to U.S. citizens working in several other countries?
Employers must also be certain to comply with both local employment law in the countries in which they manage assignments and requirements for corporate presence in those countries. See Where can I find international employment law and culture information?
Compensation
Companies take one of the following approaches to establish base salaries for expatriates:
- The home-country-based approach. The objective of a home-based compensation program is to equalize the employee to a standard of living enjoyed in his or her home country. Under this commonly used approach, the employee's base salary is broken down into four general categories: taxes, housing, goods and services, and discretionary income.
- The host-country-based approach. With this approach, the expatriate employee's compensation is based on local national rates. Many companies continue to cover the employee in its defined contribution or defined benefit pension schemes and provide housing allowances.
- The headquarters-based approach. This approach assumes that all assignees, regardless of location, are in one country (i.e., a U.S. company pays all assignees a U.S.-based salary, regardless of geography).
- Balance sheet approach. In this scenario, the compensation is calculated using the home-country-based approach with all allowances, deductions and reimbursements. After the net salary has been determined, it is then converted to the host country's currency. Since one of the primary goals of an international compensation management program is to maintain the expatriate's current standard of living, developing an equitable and functional compensation plan that combines balance and flexibility is extremely challenging for multinational companies. To this end, many companies adopt a balance sheet approach. This approach guarantees that employees in international assignments maintain the same standard of living they enjoyed in their home country. A worksheet lists the costs of major expenses in the home and host countries, and any differences are used to increase or decrease the compensation to keep it in balance.
Some companies also allow expatriates to split payment of their salaries between the host country's and the home country's currencies. The expatriate receives money in the host country's currency for expenses but keeps a percentage of it in the home country currency to safeguard against wild currency fluctuations in either country.
As for handling expatriates taxes, organizations usually take one of four approaches:
- The employee is responsible for his or her own taxes.
- The employer determines tax reimbursement on a case-by-case basis.
- The employer pays the difference between taxes paid in the United States and the host country.
- The employer withholds U.S. taxes and pays foreign taxes.
To prevent an expatriate employee from suffering excess taxation of income by both the U.S. and host countries, many multinational companies implement either a tax equalization or a tax reduction policy for employees on international assignments. Additionally, the United States has entered into bilateral international social security agreements with numerous countries, referred to as "totalization agreements," which allow for an exemption of the social security tax in either the home or host country for defined periods of time.
A more thorough discussion of compensation and tax practices for employees on international assignment can be found in SHRM's Designing Global Compensation Systems toolkit.
How do we handle taxes for expatriates?
Can employers pay employees in other countries on the corporate home-country payroll?
Measuring Expatriates' Performance
Failed international assignments can be extremely costly to an organization. There is no universal approach to measuring an expatriate's performance given that specifics related to the job, country, culture and other variables will need to be considered. Employers must identify and communicate clear job expectations and performance indicators very early on in the assignment. A consistent and detailed assessment of an expatriate employee's performance, as well as appraisal of the operation as a whole, is critical to the success of an international assignment. Issues such as the criteria for and timing of performance reviews, raises and bonuses should be discussed and agreed on before the employees are selected and placed on international assignments.
Employees on foreign assignments face a number of issues that domestic employees do not. According to a 2020 Mercer report 4 , difficulty adjusting to the host country, poor candidate selection and spouse or partner's unhappiness are the top three reasons international assignments fail. Obviously, retention of international assignees poses a significant challenge to employers.
Upon completion of an international assignment, retaining the employee in the home country workplace is also challenging. Unfortunately, many employers fail to track retention data of repatriated employees and could benefit from collecting this information and making adjustments to reduce the turnover of employees returning to their home country.
Safety and Security
When faced with accident, injury, sudden illness, a disease outbreak or politically unstable conditions in which personal safety is at risk, expatriate employees and their dependents may require evacuation to the home country or to a third location. To be prepared, HR should have an evacuation plan in place that the expatriate can share with friends, extended family and colleagues both at home and abroad. See Viewpoint: Optimizing Global Mobility's Emergency Response Plans .
Many companies ban travel outside the country in the following circumstances:
- When a travel advisory is issued by the World Health Organization, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, International SOS or a government agency.
- When a widespread outbreak of a specific disease occurs or if the risk is deemed too high for employees and their well-being is in jeopardy.
- If the country is undergoing civil unrest or war or if an act of terrorism has occurred.
- If local management makes the decision.
- If the employee makes the decision.
Once employees are in place, the decision to evacuate assignees and dependents from a host location is contingent on local conditions and input from either internal sources (local managers, headquarters staff, HR and the assignee) or external sources (an external security or medical firm) or both. In some cases, each host country has its own set of evacuation procedures.
Decision-makers should consider all available and credible advice and initially transport dependents and nonessential personnel out of the host country by the most expeditious form of travel.
Navigating International Crises
How can an organization ensure the safety and security of expatriates and other employees in high-risk areas?
The Disaster Assistance Improvement Program (DAIP)
Repatriation
Ideally, the repatriation process begins before the expatriate leaves his or her home country and continues throughout the international assignment by addressing the following issues.
Career planning. Many managers are responsible for resolving difficult problems abroad and expect that a well-done job will result in promotion on return, regardless of whether the employer had made such a promise. This possibly unfounded assumption can be avoided by straightforward career planning that should occur in advance of the employee's accepting the international assignment. Employees need to know what impact the expatriate assignment will have on their overall advancement in the home office and that the international assignment fits in their career path.
Mentoring. The expatriate should be assigned a home-office mentor. Mentors are responsible for keeping expatriates informed on developments within the company, for keeping the expatriates' names in circulation in the office (to help avoid the out-of-sight, out-of-mind phenomenon) and for seeing to it that expatriates are included in important meetings. Mentors can also assist the expatriate in identifying how the overseas experience can best be used on return. Optimum results are achieved when the mentor role is part of the mentor's formal job duties.
Communication. An effective global communication plan will help expatriates feel connected to the home office and will alert them to changes that occur while they are away. The Internet, e-mail and intranets are inexpensive and easy ways to bring expatriates into the loop and virtual meeting software is readily available for all employers to engage with global employees. In addition, organizations should encourage home-office employees to keep in touch with peers on overseas assignments. Employee newsletters that feature global news and expatriate assignments are also encouraged.
Home visits. Most companies provide expatriates with trips home. Although such trips are intended primarily for personal visits, scheduling time for the expatriate to visit the home office is an effective method of increasing the expatriate's visibility. Having expatriates attend a few important meetings or make a presentation on their international assignment is also a good way to keep them informed and connected.
Preparation to return home. The expatriate should receive plenty of advance notice (some experts recommend up to one year) of when the international assignment will end. This notice will allow the employee time to prepare the family and to prepare for a new position in the home office. Once the employee is notified of the assignment's end, the HR department should begin working with the expatriate to identify suitable positions in the home office. The expatriate should provide the HR department with an updated resume that reflects the duties of the overseas assignment. The employee's overall career plan should be included in discussions with the HR professional.
Interviews. In addition to home leave, organizations may need to provide trips for the employee to interview with prospective managers. The face-to-face interview will allow the expatriate to elaborate on skills and responsibilities obtained while overseas and will help the prospective manager determine if the employee is a good fit. Finding the right position for the expatriate is crucial to retaining the employee. Repatriates who feel that their new skills and knowledge are underutilized may grow frustrated and leave the employer.
Ongoing recognition of contributions. An employer can recognize and appreciate the repatriates' efforts in several ways, including the following:
- Hosting a reception for repatriates to help them reconnect and meet new personnel.
- Soliciting repatriates' help in preparing other employees for expatriation.
- Asking repatriates to deliver a presentation or prepare a report on their overseas assignment.
- Including repatriates on a global task force and asking them for a global perspective on business issues.
Measuring ROI on expatriate assignments can be cumbersome and imprecise. The investment costs of international assignments can vary dramatically and can be difficult to determine. The largest expatriate costs include overall remuneration, housing, cost-of-living allowances (which sometimes include private schooling costs for children) and physical relocation (the movement to the host country of the employee, the employee's possessions and, often, the employee's family).
But wide variations exist in housing expenses. For example, housing costs are sky-high in Tokyo and London, whereas Australia's housing costs are moderate. Another significant cost of expatriate assignments involves smoothing out differences in pay and benefits between one country and another. Such cost differences can be steep and can vary based on factors such as exchange rates (which can be quite volatile) and international tax concerns (which can be extremely complex).
Once an organization has determined the costs of a particular assignment, the second part of the ROI challenge is calculating the return. Although it is relatively straightforward to quantify the value of fixing a production line in Puerto Rico or of implementing an enterprise software application in Asia, the challenge of quantifying the value of providing future executives with cross-cultural perspectives and international leadership experience can be intimidating.
Once an organization determines the key drivers of its expatriate program, HR can begin to define objectives and assess return that can be useful in guiding employees and in making decisions about the costs they incur as expatriates. Different objectives require different levels and lengths of tracking. Leadership development involves a much longer-term value proposition and should include a thorough repatriation plan. By contrast, the ROI of an international assignment that plugs a skills gap is not negatively affected if the expatriate bolts after successfully completing the engagement.
Additional Resources
International Assignment Management: Expatriate Policy and Procedure
Introduction to the Global Human Resources Discipline
1Mulkeen, D. (2017, February 20). How to reduce the risk of international assignment failure. Communicaid. Retrieved from https://www.communicaid.com/cross-cultural-training/blog/reducing-risk-international-assignment-failure/
2Mercer. (2020). Worldwide Survey of International Assignment Policies and Practices. Retrieved from https://mobilityexchange.mercer.com/international-assignments-survey .
3Dickmann, M., & Baruch, Y. (2011). Global careers. New York: Routledge.
4Mercer. (2020). Worldwide Survey of International Assignment Policies and Practices. Retrieved from https://mobilityexchange.mercer.com/international-assignments-survey
Related Articles

Rising Demand for Workforce AI Skills Leads to Calls for Upskilling
As artificial intelligence technology continues to develop, the demand for workers with the ability to work alongside and manage AI systems will increase. This means that workers who are not able to adapt and learn these new skills will be left behind in the job market.

Employers Want New Grads with AI Experience, Knowledge
A vast majority of U.S. professionals say students entering the workforce should have experience using AI and be prepared to use it in the workplace, and they expect higher education to play a critical role in that preparation.

The Pros and Cons of ‘Dry’ Promotions
Hr daily newsletter.
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption
Short-Term Assignments: Key Considerations and Essential Information
By Tracy Langlois, CRP, GMS
Short-term work assignments have been steadily increasing over the years and certain factors like the pandemic have shined a light on vulnerabilities within numerous industries. For instance, the demand for travel nurses has never been higher, as certain staffing agencies need to fill voids and provide additional support at hospitals all over the US. Other companies are asking employees to train new hires at different locations or attend workshop programs and conferences out of state. Those working in media may need to spend days, weeks, or months in different locations covering news stories. HR representatives are focusing on talent mobility, which may require employees to take on short-term work assignments for specialized training and upward growth within a company.
No matter the industry or reason, employers are recognizing the value of short-term assignments, as well as the logistical steps required to smoothly transition their employees from point A to B. With that in mind, CapRelo put together an overview of short-term assignments, so your company knows what is needed to assist your employee during the hectic transition of a short-term assignment.
What is a Short-Term Assignment?
A temporary assignment is defined as a work stint lasting for one year or less. A short-term assignment can be a series of shorter rotational assignments or an assignment that requires an employee to stay in one place for the entire duration. Similar to temporary duty assignments in the military, short-term assignments are not permanent and are meant to carry out a specific purpose. Companies may send one employee or a whole team out on temporary assignments, depending on the industry and work goal.
What is the Purpose of a Short-Term Assignment?
There are plenty of different reasons why companies would send their staff out on short-term assignments. For instance, an employee may need to assist a branch that’s struggling to perform and help them to increase their sales numbers. It’s also not uncommon for staff to oversee different departments during a company merger, requiring temporary assignments to ensure company policies are being carried out consistently across the board. Perhaps limited resources have prevented staff at different locations from being properly cross-trained, necessitating the need for temporary work trips.
Whether three weeks or three months long, short-term assignments typically require companies to cover lodging, food, transportation, and other travel-related expenses with stipends.
Benefits and Challenges of Short-Term Assignments
While short-term assignments sound like a breeze, they can pose some serious challenges for both the employee and the company itself. International short-term assignments can pose tax and immigration issues if companies don’t comply with the laws and regulations in each country. Secondly, some countries have turbulent landscapes, which could potentially put staff at risk. Employees may also get stranded in the assignment country due to canceled flights or COVID-related concerns, further implicating the company when temporary assignments do not go according to plan.
On the flip side, a company can create a robust talent mobility strategy with initiatives that reward current and new hires willing to take on short-term assignments. For instance, paying employees during travel time can lead to higher retention rates. Companies can also train staff across locations to improve their skills, eliminating any consistency errors. A change of scenery might help employees to improve productivity as well, especially in locations that offer plenty of sunshine and warm weather for post-work relaxation.
Short-Term Assignment FAQs
- Are Short-Term Assignments International? Short-term assignments can be either domestic (within a country) or international (across country borders). Certain companies like Amazon, FedEx, and Apple are known for leading the way with the most corporate travel, requiring employees to rack up airline miles to fulfill their job duties.
- How Does the IRS Define Short-Term Assignments? The IRS defines short-term assignments as work in one location that can be reasonably completed in one year or less (and is). Employees typically file taxes with their home state. If a work assignment lasts for longer than a year then it is considered an indefinite assignment, prompting an employee’s tax home to change.
- What is Relocation Tax Assistance? Before 2018, any moving-related payments or reimbursements to employees were not included in their annual reportable wages. These expenses did not require withholding taxes and would have been paid by the employee and later deducted. The Tax Cuts and Job Act of 2017 changed the way payroll handled relocation expenses. Nowadays, employers can offer relocation tax assistance or tax gross-ups. A tax gross-up simply means that a company provides a larger payment sum to the employee to compensate for the taxes that will be withheld from their payment if that employee is relocating somewhere new.
- Do Family Members Join Employees on Short-Term Assignments? When it comes to temporary assignments, most companies do not assist families to join the employee in the new location if the assignment is expected to have a duration of six months or less. Assignments greater than six months may include company support for family accompaniment. Some companies will offer to pay for visits home after a certain amount of time has passed for employees who are not accompanied. This could be anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks after the start of the assignment but depends on the company’s unique policies.
How Can Companies Assist Employees?
Companies should have well-defined relocation policies in place before sending employees out on temporary assignments. The policy should include details on the relocation services and benefits which will be provided to employees and who will be assisting them with these services. It is important to note for international cases that proper immigration documentation is required before the start of the assignment. Letters of assignment (LOA)s should also be created for employee and company signature and should include specifics on the location and duration of the assignment and specific benefits. Companies should have a dedicated budget in place to assist with short-term assignment relocation expenditures; a comprehensive cost estimate including tax costs can be prepared in advance to ensure appropriate approvals can be obtained. A survey of HR professionals conducted in partnership with CapRelo found that 33% of participants stated their relocation policies have been updated to accommodate employees’ mental health and well-being, which is another factor that should be taken into consideration to help employees cope better with their new surroundings.
Do You Need a Relocation Program?
So, you’re ready to send your employees out on short-term assignments, but don’t know where to start? Whether you need help transferring one employee intra-country, or flying a whole team across the globe for specialized training, we can help.
At CapRelo , we provide relocation solutions for companies that need them, covering a host of services including cost estimate preparation, corporate housing, auto shipment, property management, travel services, immigration coordination, and much more.
Our team specializes in seamless transfer operations and sorts out all of the logistical steps before your employee’s short-term assignment so you can have peace of mind knowing that they are in the best of hands. Allow us to take one more thing off your plate and contact our highly qualified team at CapRelo today to get started.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share with Email
Insights + Resources
Finding cost savings in your workforce mobility program, caprelo insider march 2024, caprelo insider february 2024, navigating troubled waters: the ripple effect of recent incidents on global shipping through suez and panama canals.
- Employer Tech
- Employee Tech
- Client Login
- Transferee Login
Taking Another Look at Short Term Assignments and Talent Mobility
Corporate Relocation , Domestic Relocation , Employee Relocation , Talent Mobility

The Covid pandemic has spurred companies and employees to reassess work models and locations, and to consider more flexible, cost-effective ways to achieve business objectives. While not new, short-term assignments can be an effective workaround to current obstacles to employee relocation —from reluctance to relocate to a frenzied real estate market and global restrictions.
Short-term assignments are a “lite” form of talent mobility, enabling businesses to achieve specific, finite project objectives with less expense and disruption. International short term assignments have a longer history, arising as a relatively inexpensive alternative to global relocation . Domestic short-term assignments became more popular over the past 15 years, as the U.S. recovered from the Great Recession.
Objective of Short-Term Assignments
Companies originally devised short-term assignments as a developmental opportunity for high potential, junior-level employees. The employee had the opportunity to meet and work with employees in a different company location, master new skills and hone leadership abilities. This opportunity can increase the employee’s job satisfaction and loyalty and help the company to retain a promising employee. Employees who shine in STAs can be candidates for promotion and future STAs or possibly a traditional global assignment.
Short-term assignments also can be an effective way for more experienced employees to share their expertise with other parts of the organization. A company might deploy a manager to oversee the opening of a new company location, lead a merger or acquisition or bring specific IT or other technical expertise to another company location. In these examples, permanent relocation might not be necessary, but a brief business trip wouldn’t be enough.
Tax Implications of Short Term Assignment Jobs
The IRS treats short-term assignments more like business travel than relocation expenses . Relocation expenses are employee benefits and must be reported on the relocating employee’s W-2 for the year. Most companies gross many of these expenses up to cover the tax obligation, creating another expense for the company.
The IRS definition of a short-term assignment is very precise: the company must expect it to last for less than one year and it must actually last for less than one year. In this case, the IRS considers travel, lodging and certain other expenses to be business expenses that are deductible for the employer and not W-2 benefits to the employee.
Assignments can change in scope or length once underway, and this can influence the tax treatment. The minute an employer determines the assignment is going to extend longer than a year, the reimbursed expenses from that point forward become a taxable benefit to the employee. This applies whether the company reimburses the employee directly or pays expenses on his/her behalf.
So short-term assignments can last longer than a year (this is particularly common with rotational assignments), but the company will sacrifice some of the cost-savings of shorter-length assignments. The scope of work will be one consideration in deciding whether a short-term assignment or relocation makes better business sense.
Learn More About Short Term Assignments
Within the mobility arena, short-term developmental assignments are gaining traction with companies looking to support business growth and employee development while controlling costs. This creative strategy allows businesses to deploy talent where needed without making the financial commitment inherent in a permanent domestic relocation or a long-term international assignment, but not without careful consideration. Download the Short Term Assignments White Paper
Keep Exploring This Topic.
Get more expert insight on what matters most for your business -- keep checking out the TRC blog.

Navigating the New Norm: Understanding Why Companies are Requiring Return to Office
Talent Mobility , telecommuting , U.S. Relocation
Many companies are implementing a Return to Office (RTO) policy for their employees, and as employees wonder why companies are requiring return to office, they’re learning that they have to balance their requirements with employee pushback. A survey of 1,000 corporate...

Helping Relocating Employees Make an Informed Choice Between New Construction and Existing Homes
Corporate Relocation , Domestic Relocation , Real Estate trends , U.S. Relocation , Uncategorized
For relocating employees embarking on their relocation journey, finding the right home helps ensure a smooth transition to the new locale. New and existing homes have pros and cons, and deciding whether to invest in new construction or opt for an existing property is...

Domestic Relocation Services: The Final Move and Other Relocation Benefits
Corporate Relocation , Domestic Relocation , Employee Relocation , Relocation Policy , Relocation Tax Assistance , Talent Mobility , Uncategorized
As part of a company's domestic relocation services, the final move benefit has remained consistent, apart from the repeal of the moving expense deduction as part of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Most companies reimburse final move expenses after the trip has taken...

Employee Relocation Benefits: Destination Home Finding
Corporate Relocation , Domestic Relocation , Employee Relocation , Relocation Policy , Talent Mobility
Relocation benefits that include a destination home-finding trip is a domestic relocation best practice across industries. The home-finding trip allows employees and their families to familiarize themselves with the area, explore potential homes for purchase or rent,...
Ready to make your relocation program even better? Let’s move.
You’ve got a destination. We’ve got the plan to get you there. Let’s get started.
Talk to a relocation specialist today

- Combined Shape Created with Sketch. Search
- Person icon Created with Sketch. Sign in
Short-term assignments 2022 report: 10 takeaways
Short-term assignments (STAs) continue to be a popular option for global mobility and are quickly evolving into an ED&I Mobility vehicle. These opportunities have the potential to allow more diverse employee populations to gain experiences that will enhance career paths and diversify an organization’s leadership pipeline. This makes it more important than ever to ensure STA policy lines up with typical practices.
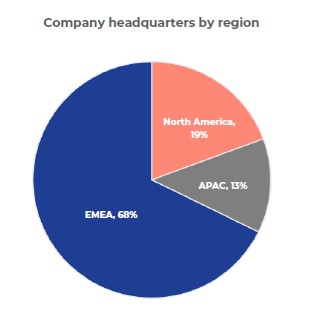
- 68% of policies are from EMEA-based companies. This predominance reflects the use of STAs globally. Given the geography of the EMEA region (vs North America), STAs are a realistic option for many reasons that companies transfer employees (e.g., skill development, filling a position gap, etc.).
- Half of the policies specify that STAs are unaccompanied, typically attributed to the limited assignment duration, which most commonly ranges from three (62%) – twelve (83%) months.
- Immigration assistance (addressed in 89% of STA and LTA policies).
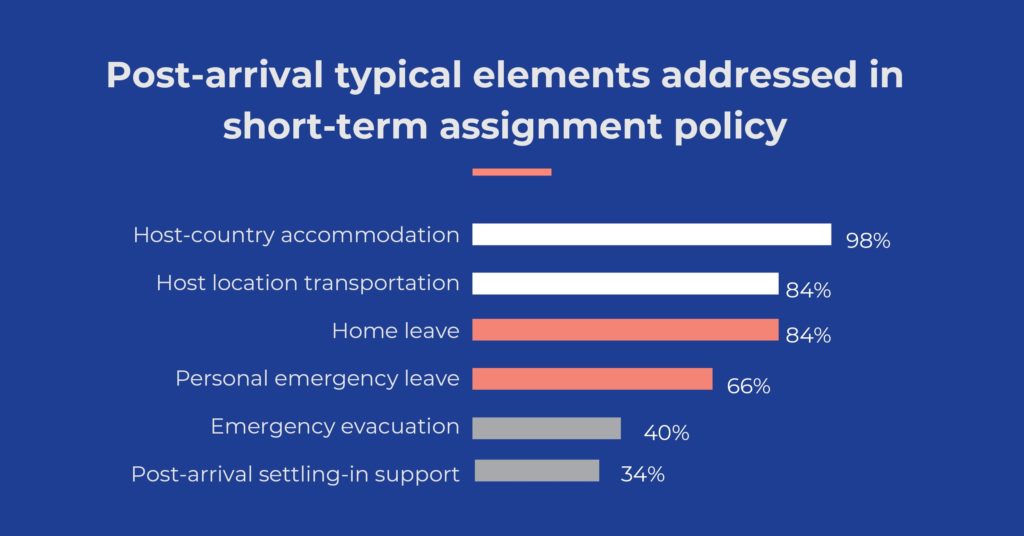
- Travel to the host location (87% of STA policies vs 92% of LTA policies).
- Cultural training (61% STA vs 67% LTA).
- Language training (61% STA vs 78% LTA). Just as in LTA policy, the use of cultural and language training typically requires approval.
- 90% of policies address health insurance for short-term assignees. It is becoming common to provide an international program for short-term assignees, as stated in 41% of policies (55% use this approach for LTAs).
- 34% of STA policies address settling-in assistance, compared to 46% of LTA policies. Assistance typically focuses on single assignees who are in country for a limited duration that might require: assistance with establishing a bank account, locating shopping facilities, public transportation, local services, religious institutions, and social opportunities.
- Home leave is addressed in 84% of STA policies (vs 90% of LTA policies). The major difference is the timing of the trips. For STAs, the most common frequency is one trip every three months (33%). Though many policies vary frequency based on assignment circumstances such as duration, accompaniment status, or distance between the home and host country.
- STA policy rarely includes the shipment of household goods; rather, most (52%) assist with an air shipment of personal effects or excess baggage charges only (30%).
- Few (23%) provide a pre-move trip. Primarily because most (72%) provide furnished accommodations rather than have the employee find their own housing.
- Fewer (47%) provide temporary living for STAs than the 98% that address it in LTA policies.
- It is not as common to provide a hardship allowance for STAs (32%) as it is for LTAs (53%).
- Use of a relocation allowance is not as common for STAs as it is for LTAs: 47% vs. 84%, respectively.
- Most companies (63%) retain employees on their home country compensation and provide a per diem or reimbursement for daily living expenses while on an STA.
The lower cost profile of short-term assignments – due to single status, shorter duration, simpler support – continues to contribute to the popularity of this move type. For companies reviewing their STA policies, it can be very beneficial to see what the typical practices are and how they differ from their LTA counterparts.
Five common myths about short-term assignments
Myth #1: an sta is pretty much the same as an lta – just shorter..
Fact: The differences between these two assignment types are notable and significant. Long-term assignments are typically investments in the future. Their considerable use of resources (people and money) makes them worthwhile for business-building initiatives such as leadership training, market expansion, management roles where local candidates are not available and new product development. These are all goals that require a long term to complete. Short-term assignments are better suited to initiatives that can be completed in under a year. Global exposure, filling a job gap, short-term projects and skill building are examples of realistic STA assignment objectives.
Myth #2: Employees on short-term assignments need less support than those on long-term assignments.
Fact: Replace “less” with “some of the same but also different” and you would be correct! For example, short-term assignees need assistance with some of the same things as long-term assignees (immigration and tax compliance, travel, arranging housing, becoming familiar with the assignment location, etc.). But they also need different things, given that most short-term assignees remain on home-country compensation and retain many home-country expenses. For example, they need a per diem to cover daily living costs in the host location. Since many STAs are single-status, employees may have left immediate family in the home location. Therefore, trips home are a greater need for STAs than they are for LTAs.
Myth #3: It sounds like an STA is really just a glorified business trip.
Fact: Aside from the primary distinction that a business trip is typically no more than a month and an STA is typically 3-12 months, the business objectives are different, too. This is a key issue.

Myth #4: Short-term assignees don’t need the same cultural or language training as long-term assignees.
Fact: The fact that short-term assignees need to quickly get up and running, live in the local area and succeed in the business environment often dictates that they require the same or similar training as long-term assignees. Of course, there are times when a short-term assignee is needed for work that is primarily solitary and does not require local language skills. In this case, more condensed training may be sufficient.
Myth #5: We should be more concerned about the challenges of long-term vs. short-term assignments, given their bigger goals, longer time in the host country and greater cost to the company.
Fact: STAs may impact a more diverse pool of employees than LTAs do. Companies may not recognize the challenges different demographics may encounter on STAs as they do for LTAs. For example, an employee may turn down an LTA because a same-sex partner cannot accompany but that employee may undertake an STA single-status. However, that employee still needs to be successful in the local environment. Similar ED&I considerations may be necessary for many populations (women, younger employees, older employees, etc.). It is important to address the same factors for these employees on STAs as one would if they were embarking on an LTA.
To benchmark your STA policy and discover more emerging trends, download our 2022 expert report here .
If you have any questions regarding this article or would like to find out more about other services, please contact Lisa Johnson (Global Practice Leader, Consulting Services) at [email protected] .
Related Topics
Share this post, get the latest from crown world mobility.
Receive our monthly newsletter and stay up to date on a wide range of issues impacting mobility and employee relocations.

PPC Landing Page
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- I'm interested in Please select Getting a Quote Managing a Mobility Program Domestic Moving International Moving Visa and Immigration Managing my Assignees Using a Lump Sum Payment
- My location is * Start typing country name Andorra Antigua And Barbuda Argentina Aruba Australia Austria Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belgium Belize Bermuda Botswana Brazil Bulgaria Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Chile China Christmas Islands Colombia Cook Islands Costa Rica Cote D'ivoire Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Germany Greece Guam Guernsey Hong Kong Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Ireland Isle Of Man Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jersey Jordan Kenya Kosovo Kuwait Latvia Luxembourg Macau Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Malta Martinique Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nigeria Norway Oman Pakistan Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Pitcairn Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Russian Federation Saint Barthélemy Saint Kitts And Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin (French Part) Saipan Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Serbia Seychelles Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands South Korea Spain Sri Lanka St. Vincent & The Grenadines Sudan Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Taiwan Tanzania Thailand Trinidad And Tobago Tristan Da Cunha Tunisia Turkey Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Vanuatu Vatican City State Venezuela Vietnam Virgin Islands (British) Virgin Islands (US) Zimbabwe
- Hidden Would you like to receive relevant updates from Crown? Yes No
- I am happy for Crown to use these details to contact me for marketing purposes.
- Hidden My region is Select a location North America South America Middle East Asia Central & Eastern Europe UK & Northern Europe Oceania Africa Southern & Western Europe
- Hidden Lead Source (LeadSourceCode)
- Hidden Lead Type (smsmt_LeadType)
- Hidden Rating (LeadQualityCode)
- Hidden CWM (smsmt_WorldMobility)
- Hidden CRM (smsmt_Records)
- Hidden CFA (smsmt_FineArt)
- Hidden CWS (smsmt_IsWorkPlaceRelocations)
- Hidden CL (smsmt_IsCrownLogistics)
- Hidden CR (smsmt_Relocations)
- Hidden From Web Lead (smsmt_fromweblead)
- Hidden Blank Field
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
By submitting this form you consent to the terms of our Privacy Policy and agree to receive relevant updates from Crown World Mobility.
- International
- Self-Service Moves
- Program Management
- Supply chain management
- Process and Technology
Client login
Use the log in below to access a generic version of our customer portal. For client specific versions of the portal see communications from your Crown consultant.
Relocating employee
Use the log in below to access our customer portal.
Employee login
You May Also Be Interested In

2024 Mobility Trends: Is relocation still a tool for improving employee engagement?
Download our expert report today and explore the evolving relationship between employee engagement and corporate relocation

Providing dynamic support in a volatile world
Given the unprecedented pace and scale of change since 2019, here we explore the ways we have been forging a new path to deliver the best experiences for assignees and their employers.

Global Mobility Forum Melbourne 2024
Join Crown in Melbourne on 9 May 2024. Network, benchmark, collaborate and connect with industry peers.

- Mobile Equity Services
- Mobile Workforce Management
- Mobility Tax Compliance and Consulting
- Private Client Services
- In the News
- Resource Center
- My GTN Portal

Pros and Cons of Different Assignment Structures for Mobility Programs
As companies adjust to the new reality of work and reassess their mobility programs, there is an opportunity for them to examine the costs associated with running their mobility programs and explore innovative solutions. We are witnessing a renewed interest in mobility as companies seek to adopt the best structure for their business and employees. While non-traditional forms such as remote and hybrid work are becoming more prevalent, there is also renewed interest in both short and long-term assignments.
This innovation has already been reflected in the evolution of new mobility policies supporting employees working from outside of their usual office locations, including “ Work from Anywhere ” or “Virtual Assignment” policies. Many companies have also increased their use of non-traditional assignment types such as business travelers or short-term rotations.
Download part one of our "Future of Mobility Survey: Remote Work" to discover how HR and mobility managers are creating policies that tackle the unique challenges posed by a remote workforce.
Based on these evolving trends, it may be easy for organizations to overlook the use of more traditional mobility arrangements to support their business growth and talent management goals. However, long-term assignments, short-term assignments, and permanent transfers each have attributes that warrant consideration when determining the most appropriate way to meet the objectives for your company and employees.
As mobility programs continue to evolve, it is important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of traditional assignment types and permanent transfers. Let's take a closer look at the benefits and drawbacks of these options.
Traditional assignment types – long-term and short-term assignments
One of the most commonly used relocation types is an “assignment.” An assignment is the relocation of an employee from one country to another for a specific period of time. A long-term assignment will generally exceed one year, where a short-term assignment will generally be shorter than one year. Below we have outlined some of the benefits and drawbacks for these assignment types.
Benefits and drawbacks of long-term assignments
Long-term or expatriate assignments have long been a popular option for companies who need to transfer or obtain expertise, set up new entities/markets, or provide career development opportunities, especially for future global leaders within the organization. Here, the longer-term nature of the assignment lends itself to building better long-term relationships and in-depth knowledge that can be invaluable to your organization.
From an employee perspective, another benefit of a long-term assignment is the possibility of remaining on their Home country payroll. In this way, employees can often:
- Receive compensation in their Home country currency, avoiding the need to convert Host country currency in order to pay Home country expenses such as student loans or mortgages.
- Participate in the Home country benefit plans. For example, a US citizen/resident employee on a 3-year assignment to the UK can continue contributing to the Home country 401(k), flexible spending plans, and will remain covered by Home country incentive compensation plans.
- Continue participation in Home country social security. In this way, there will be no break in the required time period to meet the coverage requirement for receiving the social security payments upon retirement. For employees at a later stage in their career, continued participation in Home country social security may be a deal-breaker.
Despite these benefits, a major drawback of the long-term assignment is often cost. Assignments can be more expensive to the company due to several factors, including:
- Providing additional allowances and benefits for the assignee. Common examples of these additional compensation elements include cost-of-living adjustments, hardship allowances, Host country housing, and moving expenses.
- Meeting additional compliance requirements. Employees may now have Home and Host country tax filings. And your organization may have Home and Host country reporting and withholding obligations, including related administration expenses such as the cost of establishing and running a shadow payroll.
- Implementing a tax reimbursement policy for your assignee. Tax equalization remains the most common policy for long-term assignments.
- Handling on-going costs incurred for immigration, tax planning, budgeting, internal administration, etc.
- Failing to benefit from the expertise gained by your assignees by not retaining them as employees or finding a suitable position to use their new skills upon repatriation.
It is important to note that proper planning and policies can help to reduce or eliminate many of these drawbacks.
As many factors, including employment, tax, and immigration law, and the availability of bilateral tax and social security agreements can impact the tax and payroll requirements for an assignment, it is important to consult with your mobility tax and legal advisors to make sure the long-term assignment is structured in an appropriate way.
Benefits and drawbacks of short-term assignments
Short-term assignments may allow companies to achieve several of the same benefits as longer-term scenarios, while also addressing several of the challenges. Benefits to the company of using short-term international assignments include:
- Like long-term assignments, an employee on a short-term assignment will often continue to receive compensation in the Home country payroll, seeing the same benefits as described above.
- The company may be able to offer a more modest compensation and allowance package to the employee, helping to reduce the overall tax and assignment costs to the company.
- For US tax purposes, certain reimbursements such as temporary lodging and per diems may be paid tax-free for certain temporary assignments of one year or less. Other countries may have similar rules for temporary assignments.
- Depending on the availability of income tax treaties and social security agreements, Host country taxes may be avoided or limited. For example, an employee on a 5-month assignment from the US to the UK may be able to avoid UK income tax if they will spend less than 183 days in the UK during a 12-month period, remain on the US payroll, and have their compensation expenses continue to be borne by the US entity. The availability of a social security totalization agreement would also provide for the ability to continue on US rather than UK social security through obtainment of a certificate of coverage from the US Social Security Administration.
- Short-term international assignments could result in a larger pool of potential employees for the international assignment program.
Despite these additional benefits, the shorter duration of the assignment may ultimately not provide enough time to allow the organization and assignee to accomplish all the objectives of the assignment. Additionally, the employee may not have enough time to fully “settle in” and develop relationships with the Host country office and clients.
Short-term assignments, as compared to a long-term or expatriate assignment, typically (but not always) result in a lower tax and assignment cost to the company. However, it is important to consider factors that may lead to additional cost, such as:
- Depending on location and the scenario, paying an employee under the expatriate policy may be less costly than providing a per diem and reimbursement of expenses.
- Administering a short-term international assignment may take more time than a long-term assignment. This could happen due to the length of the short-term assignment changing and requiring more constant support by the program administrator and/or tax services provider (e.g., monitoring the assignment).
- There are certain exclusions (e.g., Foreign Earned Income, Housing) and foreign tax credits available on a qualifying employee’s US federal individual income tax return that help alleviate double taxation that might occur as a result of an international assignment. These exclusions and credits may result in a lower tax cost to the company if the assignment is just over one year, rather than short-term.
- An employee on an expatriate assignment will often break state residency during the assignment period; an employee on a short-term international assignment generally will not break state residency. Thus, the state tax cost for the company will often be higher for the short-term international assignment.
Benefits and drawbacks of permanent transfers
Another commonly used relocation type is a permanent transfer or “transfer.” A transfer is a one-way relocation of an employee to a Host country for an indefinite period. In a typical transfer scenario, the individual will become an employee of the Host country entity, with Host country payroll and benefits.
Transferees will typically receive less company support than assignees. For example, instead of receiving allowances designed to keep an individual in a neutral purchasing position in comparison to their Home location (i.e., through provision of housing, cost-of-living, and other allowances), a transferee may receive a local pay package with limited or no allowances. Instead of tax equalization, they may only receive limited tax compliance assistance such as tax return preparation in the Home and Host countries for the year of transfer. Due to reduced support, transfer cases may initially have lower overall costs for the company than assignments.
Permanent transfers are often considered in scenarios where specific skills are needed/not available in the Host location, where the cost of an assignment is considered too high, or for employee-initiated moves . Because of the transfer to local payroll, administrative costs and complexities may also be reduced as the Host country entity would handle any reporting or withholding obligations. In addition, the risk of creating a taxable presence for the Home country entity (e.g., permanent establishment) is also reduced as the individual has severed employment ties in the Home country. However, despite these potential benefits, a transferred employee will likely receive compensation in Host country currency, and Host country benefits may differ from Home country benefits. Transferees are generally not eligible to contribute to Home country retirement/benefit plans such as the 401(k) plan for US employees, or contribute to Home country social security, which may be a significant drawback for those that are at senior or executive level or those approaching retirement. Additionally, employees take on exchange rate risk, potential cost-of-living issues, and potentially higher taxes.
From a talent management perspective, it may also be more difficult or costly to later relocate an employee who has been transferred rather than assigned to a location. A transferee will now be tied to a pay package and cost-of-living in the Host location, which will create a new point of reference for future moves.
What is the best relocation type for your company?
As has been shown, the type of relocation best suited for a given employee and your organization will be based on many factors. Key questions to consider include:
- Why is the employee moving? Is the move initiated by the individual or needed by the organization?
- What are the organizational goals relating to the move? Is the timeline for the proposed relocation reasonable to achieve these objectives?
- Does the employee’s career and personal goals align with the proposed scenario?
- Does the scenario support the longer-term career development objectives for the employee—e.g., will there be ongoing support to make sure the investment in the employee is not lost due to not having an appropriate repatriation plan?
Effective management of cross-border assignments can help firms that are trying to grow their business in key global markets while simultaneously reducing costs. There is no one-size-fits-all approach, hence, every assignment type and policy should be closely reviewed by the company based on the specific assignment objectives.
If you have questions about different assignment structures or how they could impact your global mobility program, schedule a free consultation with our team. We are happy to discuss your specific situation.


Author Mark Tirpak

6900 Wedgwood Rd N, Ste 400
Maple Grove, MN 55311
+1.888.486.2695 | [email protected]
- Our Services
- Mobile Equity
- Mobile Workforce
- Mobility Tax
- Private Clients
- Your Resources
- Global Coverage
- Transition Process
- Philanthropy
© 2024 Global Tax Network TERMS OF USE AGREEMENT PRIVACY POLICIES PRIVACY AND SECURITY
Support for you during the COVID-19 pandemic

- News Mobility News Mobility Minute Mobility Magazine
- Events Conferences Webinars Corporate HR Networking
- Learning Certified Relocation Professional Certification Global Mobility Specialist Certification Learning Portal
- Research ResearchPage Infographics
- Public Policy
- My Tools My Account Career Portal Forms Portal Learning Portal Mobility Magazine
Key Considerations When Structuring Short-Term Packages
Short-term international assignments have many tricky nuances related to immigration, employment law, payroll, tax, and other related perspectives..
Managing short term assignments has become a major challenge for many companies, as different departments and business units frequently initiate them. Assumptions that sometimes are made with respect to the nature and duration of a short-term assignment, as well as the taxation, immigration, and other issues surrounding the assignment, can get an employer and the employee into difficulties.
Many employees consider international assignments important to improving their career prospects. ECA research shows that use of short-term assignments, which typically last from three to 12 months, has risen considerably over the past decade, with short-term assignees making up more than 20% of companies’ internationally mobile workforces. Factors contributing to the rise in popularity of short-term assignments include changing workforce demographics, the need to plug skills gaps and accelerate the development of employees with leadership potential, increased focus on costs, and their use as a means to overcome mobility barriers.
For both employer and employee, short-term assignments fulfill many of the criteria demanded by our 21st-century lifestyles: flexibility, variety, immediacy, and minimal family disruption.
How Do Companies Structure Packages?
There is a wide range of practices among companies in the level of living allowances, the types of incentives, and even the number of times they will pay for trips home for employees to visit their families.
Daily Living Expenses
Nearly 20% of companies report that they reimburse actual day-to-day living expenses for their assignees. What is the most effective approach? That depends on the number and type of short-term assignees that a company is trying to manage. Several research participants apply more than one approach to cover costs, taking into account variables such as the type of accommodation, length of assignment, etc.
According to ECA’s research, fewer than 50% of companies say they provide mobility incentives for short-term assignments (which typically run from 10% to 15% of the monthly base salary), whereas this mobility allowance is commonly paid for long-term assignments (62% of companies using the home-based approach). The other 50% of companies will usually argue that, as short-term assignees normally leave their families at home, they are far less exposed to “hardship factors” than assignees who have their families living with them at the host location. Conversely, the payment of a location allowance is more prevalent with companies in the construction, civil engineering, mineral and mining, nonprofit, oil and gas, and telecommunications sectors, with the number of companies providing this allowance increasing to over two-thirds.
Employees undertaking short-term assignments are rarely accompanied by their partner and/or family, who often opt to stay at home because of the shorter nature of the assignment. This leads to a wide variation in practice relating to trips home. It is surprising, given that this is a critical policy issue, that many companies do not appear to have clear guidelines in place. Typically, companies permit one company-funded trip home every 12 weeks for employees whose families have remained at home. However, some companies allow the partner to visit the assignee in the host country in lieu of the assignee returning home.
Increasing the Pool
With proper planning and administration, short-term assignments can be an effective and efficient means of increasing the pool of potential employees for the international assignment program. M
David Remedios is head of consultancy with ECA International LLC. He can be reached at +44 (0)20 7351 5000 or [email protected].
The above information is excerpted from an article that appears in the September 2019 issue of Mobility magazine.

Short term mobility and relocation packages
REQUEST A REMOVAL QUOTE
Where are you moving from * Please select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua & Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia & Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Central African Republic Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Congo Democratic Republic Costa Rica Cote d'Ivoire Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador East Timor Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea North Korea South Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar (Burma) Namibia Nauru Nepal The Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestinian State* Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru The Philippines Poland Portugal Qatar Romania Russia Rwanda St. Kitts & Nevis St. Lucia St. Vincent & The Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome & Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Togo Tonga Trinidad & Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States of America Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican City (Holy See) Venezuela Vietnam Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Where are you moving to * Please select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua & Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bhutan Bolivia Bosnia & Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Central African Republic Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Congo Democratic Republic Costa Rica Cote d'Ivoire Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador East Timor Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea North Korea South Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Macedonia Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar (Burma) Namibia Nauru Nepal The Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Palestinian State* Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru The Philippines Poland Portugal Qatar Romania Russia Rwanda St. Kitts & Nevis St. Lucia St. Vincent & The Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome & Principe Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Syria Taiwan Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Togo Tonga Trinidad & Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States of America Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Vatican City (Holy See) Venezuela Vietnam Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe
Relocation packages designed to support your short-term international assignment policies
What is the definition of a short-term assignment.
A short-term assignment (STA) is typically defined as an employee international assignment of more than 30 days and up to 12 months.
A short-term assignment does not normally include a change of residence and does not always include the relocating employee being accompanied by their partners or family. It may also be part of a group move project. They are popular because they enable employers to complete smaller specific projects, fill temporary skills gaps and are commonly used as developmental opportunities for staff as part of a company’s broader talent programme.
We have developed a short-term relocation package to support this requirement.

Expert relocation coordination and cost management
We provide management of your short-term assignments through coordinating a range of services which provide a high level of support for your relocating employees, as well as managing costs.

Relocation package core services to support an assignment of 1-12 months
• Immigration coordination • Temporary accommodation booking with negotiation of lower rates • Mini international move service • Settling-in support • Expense processing

Recommended flexible options
• On-assignment support

Rotational and group move projects
If your relocating employee is working on a rotational assignment basis, then we can manage their experience so that they have the same Relocation Manager supporting them throughout.
If your short-term assignments are part of a group project, we can provide a project management team and group move programme to support your relocating employees. This can include creating cost efficiencies by group booking accommodation together.

Developmental assignments and graduate move options
If your short-term assignments are part of a developmental programme or a graduate move scheme, we can consult with you to optimise the programmes and the packages to provide the most economical and highest level of support available.

Global Mobility Consulting Services
• Policy benchmarking and development • Data sourcing for CoLA and Relocation Costs • Assignment cost estimates calculations • Letters of assignment

Ensure your shot-term assignments are effective and compliant with Gerson Relocation
Great customer experiences start here.
Very pleasent and helpful. Nothing too much trouble.
Mr M H moved from London, UK to Toronto, Canada
Very helpful and patient even when things got packed that we had to get out again!
Mr M E moved from Enfield, UK to Dorset, UK
Thanks to Graham, Nick and the entire crew!
Mr C D M moved from UK to Singapore
Friendly and helpful crew.
Ms T W moved from USA to Cambridgeshire, UK

Privacy Overview

Managing Short-term Assignments
Like all areas of the working world, global mobility is evolving. Businesses are providing employees with increased flexibility by offering different forms of international assignment. Where once expat assignments lasted three to five years, now assignments vary in range.
A short-term assignment can be a more cost effective way of achieving specific goals in another market without disrupting an employee’s life too much.
What is a short-term assignment?
- A short-term assignment (STA) is an international project that usually lasts between 3 and 12 months. They allow organisations to transfer resources, knowledge and skills cost effectively and quickly providing fast response to business needs. For some companies short-term assignments are becoming more popular than their long-term equivalent due to changing workforce demographics, skills shortages and the need to provide more flexibility to employees.
- Just because employees are away for less time does not make STA’s easier. In fact, short-term assignments may be more difficult as there is a need to hit the ground running and accomplish a lot quickly.
- When it comes to short-term assignments, thorough preparation is more important. Potential pitfalls that can cause problems for professionals in an overseas office for a short period include:
- Failure to build key relationships
- Culture shock
- Alienating local colleagues
- When planning an STA pre-departure training is important but pre-departure preparation is essential.
Preparing short-term assignees before assignment
Preparing for a short-term assignment is challenging. It may need to go further than providing the soon to be expat with clear understanding of their role or overview of the local culture. Short-term assignees with aggressive deadlines may fall into a common expat error of trying to introduce initiatives without sufficient knowledge of local circumstances or alienating colleagues.
For these kinds of assignments pre-departure preparation must go much further than training on what to expect, it should allow the soon to be expat to begin their assignment before they leave.
Developing personal network in advance
Help employees prepare in advance for life in their temporary home by doing everything possible to acquire relevant information about life there:
- Arrange meetings with employees from the host country that are working in your current location
- Encourage the employee to join groups from that country in your city
- Make the most of web-based platforms like LinkedIn or Meetup to enable future expats to become more aware of life and work etiquette before they leave
Virtual introductions to colleagues
Gauge local support and understand perspective, supporting short term assignees on assignment, are the team willing to participate, is their role clear.
At the outset of the assignment it is important for the expat to share:
- The assignment goals
- The expat’s role
- Expectations for employees
This does not have to be completed on day one but may be useful within a few weeks of the assignment starting. This way, any gaps in expectation or issues that arise can be ironed out quickly to provide the assignment with the best chance of success.
Maintaining their personal support system
Even though short-term assignees are not going to be overseas for long, having a support network outside of work still matters. This is where the groundwork put in before the assignee arrived should pay dividends. Help expats find work life balance by continuing a hobby they have at home, locally, from yoga to rock climbing, hopefully there’ll be a group or venue where they can let off some steam after a busy day in the office.
It is also important STA’s remain connected to colleagues in head office particularly if the medium term plan is they return to a role there. Arranging intermittent virtual check ins is a great way to ensure there are no surprises when they return to head office.
Achieving Short term assignment goals
Sufficient time for knowledge transfer, local owners of the initiative .
The last thing your business wants is to spend all that time and money on an STA only for everything to revert to how it was previously as soon as that person leaves. Key to long-term implementation is ensuring there are local owners of the initiative who will continue to grow the programme once the assignment is over.
Ultimately any global mobility practice should aim to create solutions that are employee centric while also being relevant and cost effective ways to achieve company goals. Although there is likely to always be place for longer term assignments, their short-term counterparts may be the right solution in certain scenarios.
Managing short-term assignees may be challenging but looking after their health while they are away does not have to be. We have group international health insurance schemes tailored to the needs of your business.
Related articles

The Case for Home Office Programmes
With the rise of remote work and distributed teams, companies are increasingly recognising the importance of robust home office programmes.
While most people who get COVID-19 recover quickly, for some it can cause symptoms that last for weeks or even months.
The dangers of vaping
Health experts are warning about the serious health risks associated with vaping.
Discover the health risks of vaping, from heart and lung damage to addiction. Learn about global efforts to regulate e-cigarettes and protect your health.
Mental Health and Long COVID
Long COVID can result in a number of mental health issues for patients, and it’s important to know the signs, symptoms and how to manage them.
Navigating Long COVID: Benefits and Support
In this post, we’ll explore 10 key employee benefits and supports that employers can provide staff working with long COVID.
COVID Leave Policy: Managing the Return to Work
Employers are facing the challenges of managing employee absences and facilitating a safe return to work for team members with their COVID leave policies.
How to deal with gaslighting
Gaslighting is a form of manipulative behaviour that attempts to make you question your memories or perception of reality and can even make you think you’re going crazy.
How to Manage Long COVID as an Expat
Getting sick while living abroad as an expat can be challenging. Here is some crucial information to know if you’re an expat wondering how to manage long COVID.
Developing a Long COVID Policy for Employees
In this blog post, we'll explore the different types of acne and give some actionable tips to address each type.
Living with Rosacea: Tips and Tricks
While we all may experience a flushed complexion every now and then, living with rosacea can be much more difficult.
Managing Psoriasis Flare-Ups
If you or someone you love is managing psoriasis and struggling to find relief, you can find some effective strategies in our guide.
How to Soothe Eczema-Prone Skin
In this blog post, we'll delve into practical tips and skincare strategies designed to provide relief on how to soothe eczema-prone skin.
Exploring the Different Types of Acne
The link between highly processed foods and brain health.
Eating highly processed foods is linked to age-related cognitive decline and mental health issues, according to research.
Short-term Assignments

This online course provides a deep dive into all aspects of compensation and benefits, tax governance, immigration compliance and payroll considerations for short-term international assignments.
Short-term assignments (STAs) are evolving to become an essential means of moving talent for a wide range of purposes. For both employer and employee, they can also help to overcome mobility barriers typically associated with long-term assignments. However, short-term assignments have many tricky nuances and management of these can pose a major challenge for mobility teams.
Taught across five interactive modules, our online course will guide you through the basic principles of short-term assignments, and how to structure remuneration packages and navigate the various compliance challenges. By the end of course, you will have acquired the practical knowledge needed to deliver successful, compliant and cost-effective STAs.
Providing an engaging learning experience, this self-paced training incorporates case studies, quizzes and exercises to help cement your learning, which can be completed in your own time, from anywhere.
Who this course is for and fees
Our online course is available to in-house mobility/HR teams or colleagues involved in managing their company's short-term assignments. Perfect for anyone new to mobility as well as those wanting to refresh their knowledge of all aspects of remuneration and compliance for STAs.
Course access and duration
The course is accessed via MyECA. Please sign in* to view your regional currency and to purchase the course (fees subject to tax, where applicable):
GBP 190 EUR 260 USD 310 AUD 390
*Don't have a MyECA account? Please sign up and select "I'd like to purchase online training".
Offering excellent value for money, we provide access to the course for 90 days. Learners are given the opportunity to complete the modules at their own pace, with time to revisit topics and browse the additional resources listed to further aid their understanding. Experienced HR professionals looking to refresh and fill any gaps in their knowledge could run through the core learning content in around two hours.
Course content
Five bite-size modules to guide you through the key principles of delivering successful short-term assignments:
Topic 1: Background & context
Get to grips with the different types of short-term international work and their nuances
Topic 2: Compensation
Master the different types of allowances typically paid (incl. COLAs, per diems, and short-term allowances)
Topic 3: Support & benefits
Gain awareness of the typical relocation support and assignment benefits offered
Topic 4: Payroll considerations
Become familiar with payroll considerations and how to deliver short-term assignment pay
Topic 5: Compliance considerations
Grasp how to navigate compliance challenges such as immigration and taxation for STAs
Buy training
Please sign in to register online for this course.
Terms and conditions
Access to ECA’s online training is subject to ECA’s Terms and Conditions for Consulting Services which can be found here .
One user per licence only. Refunds for yet to be started courses, or substitution of users is at the discretion of ECA. The course will remain open for a duration of 90 days from the first access.
The registration data you submit is for ECA’s use only as detailed according to our Privacy Policy .
Short-term International Assignments
A Means of Developing Cultural Sensitivity and Building Networks in a Global Company?
Cite this chapter

- Anne-Marie Søderberg &
- Mette Zølner
922 Accesses
1 Citations
Multinational companies (MNCs) face an increasing need for leaders with international job experience, openness towards people with other cultural backgrounds and receptiveness to other ways of doing business within the organization. Traditionally, such cross-cultural skills and abilities are acquired during long-term expatriation and nurtured through training and mentoring. However, long-term assignments are expensive for companies (Stahl & Björkman, 2006, pp. 167–168) and strenuous for many employees. The HR manager’s remarks above raise a relevant question as to whether cultural sensitivity can be nurtured through a number of shorter stays in several regions, in particular because many international assignees have had internships abroad or studied at foreign universities and thus are expected to have quite a different take on working in multicultural business contexts than their parents’ generation.
We have huge difficulties in recruiting people for long-term expatriation due to dual careers. […] Short-term assignments are much cheaper for the company and more feasible, and they might build a cornerstone in a future development towards achieving a global mindset. The young generation grew up in a global world! (HR manager in MNC)
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Boyacigiller, N., Beechler, S., Taylor, S., & Levy, O. (2004). The crucial yet elusive global mindset. In Lane, H. W., Maznevski, M. L., Mendenhall, M. E., & McNett, J. (Eds.), Handbook of global management: A guide to managing complexity (pp. 81–93). Malden, MA: Blackwell.
Google Scholar
Brown, P., & Levinson, S. C. (1987). Politeness: Some universals in language usage. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Caligiuri, P., Tarique, I., & Jacobs, R. (2009). Selection for international assignments. Human Resource Management Review , 19 (3), 251–262.
Article Google Scholar
Collings, D. G., Scullion, H., & Morley, M. J. (2007). Changing patterns of global staffing in the multinational enterprise: Challenges to the conventional expatriate assignment and emerging alternatives. Journal of World Business, 42 , 198–213.
Dowling, P. J., Festing, M., & Engle, A. D. (Eds.). (2008). International human resource management. Managing people in a multinational context. London: Thomson.
Evans, P., Pucik, V., & Barsoux, J. L. (2002). The global challenge: frameworks for international human resource management. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hall, E. (1976). Beyond culture. New York: Anchor Press Doubleday.
Johnson, J. P., Lenartowicz, T., & Apud, S. (2006). Cross-cultural competence in international business. Toward a definition and a model. Journal of International Business Studies, 37 , 525–543.
Mayerhofer, H., Hartmann, L. C., Michelitsch-Riedl, G., & Kollinger, I. (2004). Flex-patriate assignments: A neglected issue in global staffing. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 15 , 1371–1389.
Mäkelä, K., & Suutari, V.(2009). Global careers: A social capital paradox. International Journal of Human Resource Management , 20 (5), 992–1008.
Maznevski, M. L., & Lane, H. W. (2003). Shaping the global mindset: Designing educational experiences for effective global thinking and action.
Book Google Scholar
In Boyacigiller, N., Goodman, R. M., & Phillips, M. (Eds.), Crossing cultures: Insights from master teachers (pp. 171–184) New York: Routledge.
McKenna, S., Ducharme, M. J., & Budworth, M. H. (2009). What happens on tour stays on tour: Failure of teams on short term international assignment. Research and Practice in Human Resource Management , 17 (1), 112–127.
Osland, J. S., Bird, A., Mendenhall, M. E., & Osland, A. (2006). Developing of global leadership capabilities and global mindset: A review. In Stahl, G. K., & Björkman, I. (Eds.), Handbook of international human resource management (pp. 197–222). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Roberts, K., Kossek, E. E., & Ozeki, C. (1998). Managing the global workforce: Challenges and strategies. Academy of Management Executive , 12 (4), 93–106.
Selmer, J. (2002). To train or not to train. European expatriate managers in China. International Journal of Cross Cultural Management, 2 (1), 37–51.
Scullion, H., Collings, D.G., & Gunnigle, P. (2007). International human resource management in the 21st century: Emerging themes and contemporary debates, Human Resource Management Journal , 17 (4), 309–318.
Shapiro, J. M., Ozanne, J. L., & Saatcioglu, B. (2008). An interpretive examination of the development of cultural sensitivity in international business. Journal of International Business Studies, 39 , 71–87.
Stahl, G. K., & Björkman, I. (2006). Handbook of international human resource management. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Starr, T. L. (2009). Repatriation and short-term assignments: An exploration into expectations, change and dilemmas. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 20 (2), 286–300.
Starr, T. L., & Currie, G. (2009). ‘Out of sight but still in the picture’: short-term international assignments and the influential role of family. International Journal of Human Resource Management , 20 (6), 1421–1438.
Tahvanainen, M., Welch, D., & Worm, V. (2005). Implications of short-term international assignments. European Management Journal, 23 , 663–673.
Thomas, D. C., & Fitzsimmons, S. (2008). Cross cultural skills and abilities. From communication competence to cultural intelligence. In Smith, P. B., Peterson, M. F., & Thomas, D. C. (Eds.), Handbook of cross-cultural management research (pp. 201–215). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Thomas, D. C., & Lazarova, M. B. (2006). Expatriate adjustment and performance: A critical review. In Stahl, G.K., & Björkman, I. (Eds.), Handbook of international human resource management (pp. 247–264). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Thomas, D. C., Lazarova, M. B., & Inkson, K. (2005). Global careers: New phenomenon or new perspectives? Journal of World Business, 40 , 340–347.
Tung, R. (1998). A contingency framework of selection and training of expatriates revisited. Human Resource Management Review, 8(1 ), 23–37.
Download references
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Copenhagen Business School, Copenhagen, Denmark
Martine Cardel Gertsen ( Independent Researcher and Writer ), Anne-Marie Søderberg ( Professor ) & Mette Zølner ( Associate Professor ) ( Independent Researcher and Writer ), ( Professor ) & ( Associate Professor )
Copyright information
© 2012 Anne-Marie Søderberg and Mette Zølner
About this chapter
Søderberg, AM., Zølner, M. (2012). Short-term International Assignments. In: Gertsen, M.C., Søderberg, AM., Zølner, M. (eds) Global Collaboration: Intercultural Experiences and Learning. Palgrave Macmillan, London. https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137026064_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/9781137026064_7
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, London
Print ISBN : 978-1-349-33096-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-137-02606-4
eBook Packages : Palgrave Business & Management Collection Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
International short-term assignments are a useful global mobility tool, that provide companies with a resource to support critical strategic needs while mitigating mobility program costs. Short-term assignments may also be used in a developmental capacity providing high potential employees an opportunity to grow in their career. Short-term assignments commonly range from 3 to 12 months in ...
The three broad categories of international assignments consist of short term, extended and traditional long term assignments. ... Short term assignments are up to 6 months duration. The purpose of these assignments is often for management development or problem solving and can include roles such as project supervision until a more longterm ...
Short-term assignments. Short-term international assignments usually last between 3 and 12 months, and allow companies to transfer skills, knowledge and resources quickly and cost effectively, providing a quick response to business needs. However, living costs for short-term assignees are different from other categories of mobile workers.
The role of an assignment letter (agreement) Short-term assignments are highly complex. Hence, it is crucial to have proper documentation in place to clarify and provide guidance. An effective assignment letter not only benefits the employee, but also the employer (HR, legal, tax and payroll, for instance). The assignment letter should clearly ...
International assignment management is one of the hardest areas for HR professionals to master—and one of the most costly. ... 88 percent offered short-term assignments (typically defined as ...
International short-term assignments can pose tax and immigration issues if companies don't comply with the laws and regulations in each country. Secondly, some countries have turbulent landscapes, which could potentially put staff at risk. Employees may also get stranded in the assignment country due to canceled flights or COVID-related ...
A short-term international assignment is the deployment of an employee overseas to complete a task usually within a period of three months to a year. Short-term international assignments became popular early in the millennium as a means of addressing recruitment gaps, talent shortages and focusing on strategic global projects.
International assignments are usually subdivided in "short-term assignments," lasting seven to twelve months, and "long-term assignments" lasting one to three years in some companies up to five years. Assignments up to six months are most often handled as business trips.
Short-term assignments are a "lite" form of talent mobility, enabling businesses to achieve specific, finite project objectives with less expense and disruption. International short term assignments have a longer history, arising as a relatively inexpensive alternative to global relocation. Domestic short-term assignments became more ...
For both employer and employee, short-term assignments fulfil many of the criteria demanded by our 21st century lifestyles: flexibility, variety, immediacy and minimal family disruption. Research shows that use of short-term assignments, which typically last from three to 12 months, has risen considerably over the past decade with short-term ...
An international assignment is a temporary work position located in another country and requires our employee to temporarily relocate to fulfil this role. The international assignment is deemed to be short-term if it is for a period of between 3 months up to one year. Most international short-term assignments in [Global Company Name] are a ...
January 12 2022. Short-term assignments (STAs) continue to be a popular option for global mobility and are quickly evolving into an ED&I Mobility vehicle. These opportunities have the potential to allow more diverse employee populations to gain experiences that will enhance career paths and diversify an organization's leadership pipeline.
A short-term international assignment as an expat offers a wealth of opportunities for personal and professional growth. By thoroughly preparing and planning for your assignment, embracing the local culture, and maintaining your routine, you can make the most of this transformative experience. While the expat lifestyle offers freedom and ...
Short-term international assignments could result in a larger pool of potential employees for the international assignment program. Despite these additional benefits, the shorter duration of the assignment may ultimately not provide enough time to allow the organization and assignee to accomplish all the objectives of the assignment ...
A short-term international assignment usually lasts for a year or less. Employers generally have a specific goal for the employees they send on short-term assignments, such as facilitating training, completing a particular project, or temporarily filling a vacancy. Many short-term assignments are single-status, whereby only the employee travels ...
assignments to short-term international assignments (Starr et al . , 2009) [28] and in most cases assignees may not accompany the family (Petrovic, 2000) [1] .
Short-term assignments (STAs) are typically international assignments that last less than one year. STAs were increasing in popularity prior to the pandemic as a way of achieving international objectives without the sometimes prohibitive cost of a long term expat assignment.Research from 2018 showed that short term assignees are often younger than their long term counterparts and many leave ...
With proper planning and administration, short-term assignments can be an effective and efficient means of increasing the pool of potential employees for the international assignment program. David Remedios is head of consultancy with ECA International LLC. He can be reached at +44 (0)20 7351 5000 or [email protected].
A short-term assignment (STA) is typically defined as an employee international assignment of more than 30 days and up to 12 months. A short-term assignment does not normally include a change of residence and does not always include the relocating employee being accompanied by their partners or family. It may also be part of a group move ...
Introduction. Short-term international assignments have received limited attention in international human resource management. As a category of international staffing alternatives (Collings, Scullion, & Morley, 2007), the mention is typically a paragraph differentiating short-term international assignments from other international staffing options (e.g., Dickmann and Baruch, 2011, Doherty and ...
A short-term assignment (STA) is an international project that usually lasts between 3 and 12 months. They allow organisations to transfer resources, knowledge and skills cost effectively and quickly providing fast response to business needs. For some companies short-term assignments are becoming more popular than their long-term equivalent due ...
Short-term Assignments. This online course provides a deep dive into all aspects of compensation and benefits, tax governance, immigration compliance and payroll considerations for short-term international assignments. Short-term assignments (STAs) are evolving to become an essential means of moving talent for a wide range of purposes.
Repatriation and short-term assignments: An exploration into expectations, change and dilemmas. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 20 (2), 286-300. Article Google Scholar. Starr, T. L., & Currie, G. (2009). 'Out of sight but still in the picture': short-term international assignments and the influential role of family.