- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources

Writing Research Papers
- Writing a Literature Review
When writing a research paper on a specific topic, you will often need to include an overview of any prior research that has been conducted on that topic. For example, if your research paper is describing an experiment on fear conditioning, then you will probably need to provide an overview of prior research on fear conditioning. That overview is typically known as a literature review.
Please note that a full-length literature review article may be suitable for fulfilling the requirements for the Psychology B.S. Degree Research Paper . For further details, please check with your faculty advisor.
Different Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews come in many forms. They can be part of a research paper, for example as part of the Introduction section. They can be one chapter of a doctoral dissertation. Literature reviews can also “stand alone” as separate articles by themselves. For instance, some journals such as Annual Review of Psychology , Psychological Bulletin , and others typically publish full-length review articles. Similarly, in courses at UCSD, you may be asked to write a research paper that is itself a literature review (such as, with an instructor’s permission, in fulfillment of the B.S. Degree Research Paper requirement). Alternatively, you may be expected to include a literature review as part of a larger research paper (such as part of an Honors Thesis).
Literature reviews can be written using a variety of different styles. These may differ in the way prior research is reviewed as well as the way in which the literature review is organized. Examples of stylistic variations in literature reviews include:
- Summarization of prior work vs. critical evaluation. In some cases, prior research is simply described and summarized; in other cases, the writer compares, contrasts, and may even critique prior research (for example, discusses their strengths and weaknesses).
- Chronological vs. categorical and other types of organization. In some cases, the literature review begins with the oldest research and advances until it concludes with the latest research. In other cases, research is discussed by category (such as in groupings of closely related studies) without regard for chronological order. In yet other cases, research is discussed in terms of opposing views (such as when different research studies or researchers disagree with one another).
Overall, all literature reviews, whether they are written as a part of a larger work or as separate articles unto themselves, have a common feature: they do not present new research; rather, they provide an overview of prior research on a specific topic .
How to Write a Literature Review
When writing a literature review, it can be helpful to rely on the following steps. Please note that these procedures are not necessarily only for writing a literature review that becomes part of a larger article; they can also be used for writing a full-length article that is itself a literature review (although such reviews are typically more detailed and exhaustive; for more information please refer to the Further Resources section of this page).
Steps for Writing a Literature Review
1. Identify and define the topic that you will be reviewing.
The topic, which is commonly a research question (or problem) of some kind, needs to be identified and defined as clearly as possible. You need to have an idea of what you will be reviewing in order to effectively search for references and to write a coherent summary of the research on it. At this stage it can be helpful to write down a description of the research question, area, or topic that you will be reviewing, as well as to identify any keywords that you will be using to search for relevant research.
2. Conduct a literature search.
Use a range of keywords to search databases such as PsycINFO and any others that may contain relevant articles. You should focus on peer-reviewed, scholarly articles. Published books may also be helpful, but keep in mind that peer-reviewed articles are widely considered to be the “gold standard” of scientific research. Read through titles and abstracts, select and obtain articles (that is, download, copy, or print them out), and save your searches as needed. For more information about this step, please see the Using Databases and Finding Scholarly References section of this website.
3. Read through the research that you have found and take notes.
Absorb as much information as you can. Read through the articles and books that you have found, and as you do, take notes. The notes should include anything that will be helpful in advancing your own thinking about the topic and in helping you write the literature review (such as key points, ideas, or even page numbers that index key information). Some references may turn out to be more helpful than others; you may notice patterns or striking contrasts between different sources ; and some sources may refer to yet other sources of potential interest. This is often the most time-consuming part of the review process. However, it is also where you get to learn about the topic in great detail. For more details about taking notes, please see the “Reading Sources and Taking Notes” section of the Finding Scholarly References page of this website.
4. Organize your notes and thoughts; create an outline.
At this stage, you are close to writing the review itself. However, it is often helpful to first reflect on all the reading that you have done. What patterns stand out? Do the different sources converge on a consensus? Or not? What unresolved questions still remain? You should look over your notes (it may also be helpful to reorganize them), and as you do, to think about how you will present this research in your literature review. Are you going to summarize or critically evaluate? Are you going to use a chronological or other type of organizational structure? It can also be helpful to create an outline of how your literature review will be structured.
5. Write the literature review itself and edit and revise as needed.
The final stage involves writing. When writing, keep in mind that literature reviews are generally characterized by a summary style in which prior research is described sufficiently to explain critical findings but does not include a high level of detail (if readers want to learn about all the specific details of a study, then they can look up the references that you cite and read the original articles themselves). However, the degree of emphasis that is given to individual studies may vary (more or less detail may be warranted depending on how critical or unique a given study was). After you have written a first draft, you should read it carefully and then edit and revise as needed. You may need to repeat this process more than once. It may be helpful to have another person read through your draft(s) and provide feedback.
6. Incorporate the literature review into your research paper draft.
After the literature review is complete, you should incorporate it into your research paper (if you are writing the review as one component of a larger paper). Depending on the stage at which your paper is at, this may involve merging your literature review into a partially complete Introduction section, writing the rest of the paper around the literature review, or other processes.
Further Tips for Writing a Literature Review
Full-length literature reviews
- Many full-length literature review articles use a three-part structure: Introduction (where the topic is identified and any trends or major problems in the literature are introduced), Body (where the studies that comprise the literature on that topic are discussed), and Discussion or Conclusion (where major patterns and points are discussed and the general state of what is known about the topic is summarized)
Literature reviews as part of a larger paper
- An “express method” of writing a literature review for a research paper is as follows: first, write a one paragraph description of each article that you read. Second, choose how you will order all the paragraphs and combine them in one document. Third, add transitions between the paragraphs, as well as an introductory and concluding paragraph. 1
- A literature review that is part of a larger research paper typically does not have to be exhaustive. Rather, it should contain most or all of the significant studies about a research topic but not tangential or loosely related ones. 2 Generally, literature reviews should be sufficient for the reader to understand the major issues and key findings about a research topic. You may however need to confer with your instructor or editor to determine how comprehensive you need to be.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
By summarizing prior research on a topic, literature reviews have multiple benefits. These include:
- Literature reviews help readers understand what is known about a topic without having to find and read through multiple sources.
- Literature reviews help “set the stage” for later reading about new research on a given topic (such as if they are placed in the Introduction of a larger research paper). In other words, they provide helpful background and context.
- Literature reviews can also help the writer learn about a given topic while in the process of preparing the review itself. In the act of research and writing the literature review, the writer gains expertise on the topic .
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
- UCSD Library Psychology Research Guide: Literature Reviews
External Resources
- Developing and Writing a Literature Review from N Carolina A&T State University
- Example of a Short Literature Review from York College CUNY
- How to Write a Review of Literature from UW-Madison
- Writing a Literature Review from UC Santa Cruz
- Pautasso, M. (2013). Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Computational Biology, 9 (7), e1003149. doi : 1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
1 Ashton, W. Writing a short literature review . [PDF]
2 carver, l. (2014). writing the research paper [workshop]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Research Paper Structure
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Before you write your essay, it’s important to analyse the task and understand exactly what the essay question is asking. Your lecturer may give you some advice – pay attention to this as it will help you plan your answer.
Next conduct preliminary reading based on your lecture notes. At this stage, it’s not crucial to have a robust understanding of key theories or studies, but you should at least have a general “gist” of the literature.
After reading, plan a response to the task. This plan could be in the form of a mind map, a summary table, or by writing a core statement (which encompasses the entire argument of your essay in just a few sentences).
After writing your plan, conduct supplementary reading, refine your plan, and make it more detailed.
It is tempting to skip these preliminary steps and write the first draft while reading at the same time. However, reading and planning will make the essay writing process easier, quicker, and ensure a higher quality essay is produced.
Components of a Good Essay
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features.
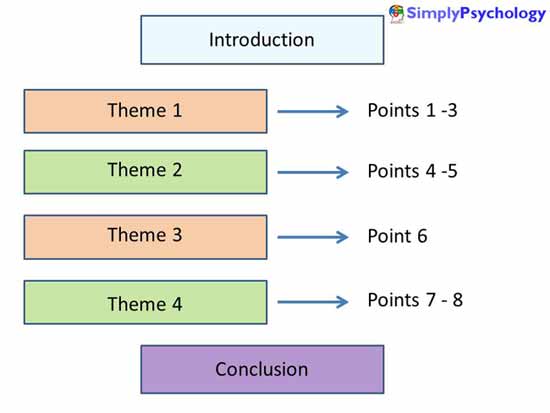
- Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”. The introduction, main body and conclusion should all be linked.
- Each paragraph should comprise a main theme, which is illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
- Knowledge and Understanding – recognize, recall, and show understanding of a range of scientific material that accurately reflects the main theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Evaluation – arguments should be supported by appropriate evidence and/or theory from the literature. Evidence of independent thinking, insight, and evaluation of the evidence.
- Quality of Written Communication – writing clearly and succinctly with appropriate use of paragraphs, spelling, and grammar. All sources are referenced accurately and in line with APA guidelines.
In the main body of the essay, every paragraph should demonstrate both knowledge and critical evaluation.
There should also be an appropriate balance between these two essay components. Try to aim for about a 60/40 split if possible.
Most students make the mistake of writing too much knowledge and not enough evaluation (which is the difficult bit).
It is best to structure your essay according to key themes. Themes are illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
Choose relevant points only, ones that most reveal the theme or help to make a convincing and interesting argument.
Knowledge and Understanding
Remember that an essay is simply a discussion / argument on paper. Don’t make the mistake of writing all the information you know regarding a particular topic.
You need to be concise, and clearly articulate your argument. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.
Each paragraph should have a purpose / theme, and make a number of points – which need to be support by high quality evidence. Be clear why each point is is relevant to the argument. It would be useful at the beginning of each paragraph if you explicitly outlined the theme being discussed (.e.g. cognitive development, social development etc.).
Try not to overuse quotations in your essays. It is more appropriate to use original content to demonstrate your understanding.
Psychology is a science so you must support your ideas with evidence (not your own personal opinion). If you are discussing a theory or research study make sure you cite the source of the information.
Note this is not the author of a textbook you have read – but the original source / author(s) of the theory or research study.
For example:
Bowlby (1951) claimed that mothering is almost useless if delayed until after two and a half to three years and, for most children, if delayed till after 12 months, i.e. there is a critical period.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need is fulfilled a person seeks to fullfil the next one, and so on.
As a general rule, make sure there is at least one citation (i.e. name of psychologist and date of publication) in each paragraph.
Remember to answer the essay question. Underline the keywords in the essay title. Don’t make the mistake of simply writing everything you know of a particular topic, be selective. Each paragraph in your essay should contribute to answering the essay question.
Critical Evaluation
In simple terms, this means outlining the strengths and limitations of a theory or research study.
There are many ways you can critically evaluate:
Methodological evaluation of research
Is the study valid / reliable ? Is the sample biased, or can we generalize the findings to other populations? What are the strengths and limitations of the method used and data obtained?
Be careful to ensure that any methodological criticisms are justified and not trite.
Rather than hunting for weaknesses in every study; only highlight limitations that make you doubt the conclusions that the authors have drawn – e.g., where an alternative explanation might be equally likely because something hasn’t been adequately controlled.
Compare or contrast different theories
Outline how the theories are similar and how they differ. This could be two (or more) theories of personality / memory / child development etc. Also try to communicate the value of the theory / study.
Debates or perspectives
Refer to debates such as nature or nurture, reductionism vs. holism, or the perspectives in psychology . For example, would they agree or disagree with a theory or the findings of the study?
What are the ethical issues of the research?
Does a study involve ethical issues such as deception, privacy, psychological or physical harm?
Gender bias
If research is biased towards men or women it does not provide a clear view of the behavior that has been studied. A dominantly male perspective is known as an androcentric bias.
Cultural bias
Is the theory / study ethnocentric? Psychology is predominantly a white, Euro-American enterprise. In some texts, over 90% of studies have US participants, who are predominantly white and middle class.
Does the theory or study being discussed judge other cultures by Western standards?
Animal Research
This raises the issue of whether it’s morally and/or scientifically right to use animals. The main criterion is that benefits must outweigh costs. But benefits are almost always to humans and costs to animals.
Animal research also raises the issue of extrapolation. Can we generalize from studies on animals to humans as their anatomy & physiology is different from humans?
The PEC System
It is very important to elaborate on your evaluation. Don’t just write a shopping list of brief (one or two sentence) evaluation points.
Instead, make sure you expand on your points, remember, quality of evaluation is most important than quantity.
When you are writing an evaluation paragraph, use the PEC system.
- Make your P oint.
- E xplain how and why the point is relevant.
- Discuss the C onsequences / implications of the theory or study. Are they positive or negative?
For Example
- Point: It is argued that psychoanalytic therapy is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority.
- Explain: Because psychoanalytic therapy involves talking and gaining insight, and is costly and time-consuming, it is argued that it is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority. Evidence suggests psychoanalytic therapy works best if the client is motivated and has a positive attitude.
- Consequences: A depressed client’s apathy, flat emotional state, and lack of motivation limit the appropriateness of psychoanalytic therapy for depression.
Furthermore, the levels of dependency of depressed clients mean that transference is more likely to develop.
Using Research Studies in your Essays
Research studies can either be knowledge or evaluation.
- If you refer to the procedures and findings of a study, this shows knowledge and understanding.
- If you comment on what the studies shows, and what it supports and challenges about the theory in question, this shows evaluation.
Writing an Introduction
It is often best to write your introduction when you have finished the main body of the essay, so that you have a good understanding of the topic area.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your introduction.
Ideally, the introduction should;
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which “lie behind” the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. “Signpost” the essay’s key argument, (and, if possible, how this argument is structured).
Introductions are very important as first impressions count and they can create a h alo effect in the mind of the lecturer grading your essay. If you start off well then you are more likely to be forgiven for the odd mistake later one.
Writing a Conclusion
So many students either forget to write a conclusion or fail to give it the attention it deserves.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your conclusion.
Ideally the conclusion should summarize the key themes / arguments of your essay. State the take home message – don’t sit on the fence, instead weigh up the evidence presented in the essay and make a decision which side of the argument has more support.
Also, you might like to suggest what future research may need to be conducted and why (read the discussion section of journal articles for this).
Don”t include new information / arguments (only information discussed in the main body of the essay).
If you are unsure of what to write read the essay question and answer it in one paragraph.
Points that unite or embrace several themes can be used to great effect as part of your conclusion.
The Importance of Flow
Obviously, what you write is important, but how you communicate your ideas / arguments has a significant influence on your overall grade. Most students may have similar information / content in their essays, but the better students communicate this information concisely and articulately.
When you have finished the first draft of your essay you must check if it “flows”. This is an important feature of quality of communication (along with spelling and grammar).
This means that the paragraphs follow a logical order (like the chapters in a novel). Have a global structure with themes arranged in a way that allows for a logical sequence of ideas. You might want to rearrange (cut and paste) paragraphs to a different position in your essay if they don”t appear to fit in with the essay structure.
To improve the flow of your essay make sure the last sentence of one paragraph links to first sentence of the next paragraph. This will help the essay flow and make it easier to read.
Finally, only repeat citations when it is unclear which study / theory you are discussing. Repeating citations unnecessarily disrupts the flow of an essay.
Referencing
The reference section is the list of all the sources cited in the essay (in alphabetical order). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms every time you cite/refer to a name (and date) of a psychologist you need to reference the original source of the information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites, then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
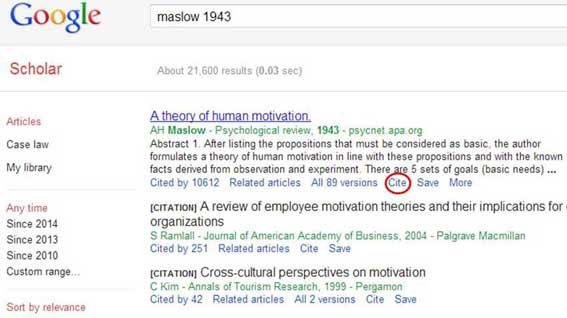
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
36 What Is Psychological Criticism?
One of the key principles of psychological criticism is the idea that literature can be used to explore and understand the human psyche, including unconscious and repressed desires and fears. For example, psychoanalytic criticism might explore how the characters in a work of literature are shaped by their early childhood experiences or their relationships with their parents.
Psychological criticism can be applied to any genre of literature, from poetry to novels to plays, and can be used to analyze a wide range of literary works, from classic literature to contemporary bestsellers. It is often used in conjunction with other critical approaches, such as feminist or postcolonial criticism, to explore the ways in which psychological factors intersect with social and cultural factors in the creation and interpretation of literary works.
Learning Objectives
- Deliberate on what approach best suits particular texts and purposes (CLO 1.4)
- Using a literary theory, choose appropriate elements of literature (formal, content, or context) to focus on in support of an interpretation (CLO 2.3)
- Be exposed to a variety of critical strategies through literary theory lenses, such as formalism/New Criticism, reader-response, structuralism, deconstruction, historical and cultural approaches (New Historicism, postcolonial, Marxism), psychological approaches, feminism, and queer theory. (CLO 4.2)
- Learn to make effective choices about applying critical strategies to texts that demonstrate awareness of the strategy’s assumptions and expectations, the text’s literary maneuvers, and the stance one takes in literary interpretation (CLO 4.4)
- Be exposed to the diversity of human experience, thought, politics, and conditions through the application of critical theory (CLO 6.4)

Excerpts from Psychological Criticism Scholarship
I have a confession to make that is likely rooted in my unconscious (or perhaps I am repressing something): I don’t much care for Sigmund Freud. But his psychoanalytic approach underpins psychological criticism in literary studies, so it’s important to be aware of psychoanalytic concepts and how they can be used in literary analysis. We will read a few examples of psychological criticism below, starting with a primary text, a theoretical explanation of psychoanalytic theory, Freud’s “First Lecture” (1920). In this reading, Freud gives a broad outline of the two main tenets of his theories: 1) that our behaviors are often indicators of psychic processes that are unconscious; and 2) that sexual impulses are at the root of mental disorders as well as cultural achievements. In the second and third readings, I share two example of literary criticism, one written by a medical doctor in 1910 that use Freud’s Oedipus complex theories to explicate William Shakespeare’s play Hamlet, and the second, a modern example of psychological theory applied to the same play. To appreciate how influential Freud’s theories have been on the study of Hamlet , try a simple JSTOR search with “Freud” and “Hamlet” as your key terms. When I tried this in October 2023, the search yielded 7,420 results.
From “First Lecture” in A General Introduction to Psychoanalysis by Sigmund Freud (1920)
With two of its assertions, psychoanalysis offends the whole world and draws aversion upon itself. One of these assertions offends an intellectual prejudice, the other an aesthetic-moral one. Let us not think too lightly of these prejudices; they are powerful things, remnants of useful, even necessary, developments of mankind. They are retained through powerful affects, and the battle against them is a hard one. The first of these displeasing assertions of psychoanalysis is this, that the psychic processes are in themselves unconscious, and that those which are conscious are merely isolated acts and parts of the total psychic life. Recollect that we are, on the contrary, accustomed to identify the psychic with the conscious. Consciousness actually means for us the distinguishing characteristic of the psychic life, and psychology is the science of the content of consciousness. Indeed, so obvious does this identification seem to us that we consider its slightest contradiction obvious nonsense, and yet psychoanalysis cannot avoid raising this contradiction; it cannot accept the identity of the conscious with the psychic. Its definition of the psychic affirms that they are processes of the nature of feeling, thinking, willing; and it must assert that there is such a thing as unconscious thinking and unconscious willing. But with this assertion psychoanalysis has alienated, to start with, the sympathy of all friends of sober science, and has laid itself open to the suspicion of being a fantastic mystery study which would build in darkness and fish in murky waters. You, however, ladies and gentlemen, naturally cannot as yet understand what justification I have for stigmatizing as a prejudice so abstract a phrase as this one, that “the psychic is consciousness.” You cannot know what evaluation can have led to the denial of the unconscious, if such a thing really exists, and what advantage may have resulted from this denial. It sounds like a mere argument over words whether one shall say that the psychic coincides with the conscious or whether one shall extend it beyond that, and yet I can assure you that by the acceptance of unconscious processes you have paved the way for a decisively new orientation in the world and in science. Just as little can you guess how intimate a connection this initial boldness of psychoanalysis has with the one which follows. The next assertion which psychoanalysis proclaims as one of its discoveries, affirms that those instinctive impulses which one can only call sexual in the narrower as well as in the wider sense, play an uncommonly large role in the causation of nervous and mental diseases, and that those impulses are a causation which has never been adequately appreciated. Nay, indeed, psychoanalysis claims that these same sexual impulses have made contributions whose value cannot be overestimated to the highest cultural, artistic and social achievements of the human mind. According to my experience, the aversion to this conclusion of psychoanalysis is the most significant source of the opposition which it encounters. Would you like to know how we explain this fact? We believe that civilization was forged by the driving force of vital necessity, at the cost of instinct-satisfaction, and that the process is to a large extent constantly repeated anew, since each individual who newly enters the human community repeats the sacrifices of his instinct-satisfaction for the sake of the common good. Among the instinctive forces thus utilized, the sexual impulses play a significant role. They are thereby sublimated, i.e., they are diverted from their sexual goals and directed to ends socially higher and no longer sexual. But this result is unstable. The sexual instincts are poorly tamed. Each individual who wishes to ally himself with the achievements of civilization is exposed to the danger of having his sexual instincts rebel against this sublimation. Society can conceive of no more serious menace to its civilization than would arise through the satisfying of the sexual instincts by their redirection toward their original goals. Society, therefore, does not relish being reminded of this ticklish spot in its origin; it has no interest in having the strength of the sexual instincts recognized and the meaning of the sexual life to the individual clearly delineated. On the contrary, society has taken the course of diverting attention from this whole field. This is the reason why society will not tolerate the above-mentioned results of psychoanalytic research, and would prefer to brand it as aesthetically offensive and morally objectionable or dangerous. Since, however, one cannot attack an ostensibly objective result of scientific inquiry with such objections, the criticism must be translated to an intellectual level if it is to be voiced. But it is a predisposition of human nature to consider an unpleasant idea untrue, and then it is easy to find arguments against it. Society thus brands what is unpleasant as untrue, denying the conclusions of psychoanalysis with logical and pertinent arguments. These arguments originate from affective sources, however, and society holds to these prejudices against all attempts at refutation.
Excerpts from “The Œdipus-Complex as an Explanation of Hamlet’s Mystery: A Study in Motive” by Ernest Jones (1910)
The particular problem of Hamlet, with which this paper is concerned, is intimately related to some of the most frequently recurring problems that are presented in the course of psycho-analysis [sic], and it has thus seemed possible to secure a new point of view from which an answer might be offered to questions that have baffled attempts made along less technical routes. Some of the most competent literary authorities have freely acknowledged the inadequacy of all the solutions of the problem that have up to the present been offered, and from a psychological point of view this inadequacy is still more evident. The aim of the present paper is to expound an hypothesis which Freud some nine years ago suggested in one of the footnotes to his Traumdeutung ,·so far as I am aware it has not been critically discussed since its publication. Before attempting this it will be necessary to make a few general remarks about the nature of the problem and the previous solutions that have been offered. The problem presented by the tragedy of Hamlet is one of peculiar interest in at least two respects. In the first place the play is almost universally considered to be the chief masterpiece of one of the greatest minds the world has known. It probably expresses the core of Shakspere’s [sic] philosophy and outlook on life as no other work of his does, and so far excels all his other writings that many competent critics would place it on an entirely separate level from them. It may be expected, therefore, that anything which will give us the key to the inner meaning of the play will necessarily give us the clue to much of the deeper workings of Shakspere’s mind. In the second place the intrinsic interest of the play is exceedingly great. The central mystery in it, namely the cause of Hamlet’s hesitancy in seeking to obtain revenge for the murder of his father, has well been called the Sphinx of modern Literature. It has given rise to a regiment of hypotheses, and to a large library of critical and controversial literature; this is mainly German and for the most part has grown up in the past fifty years. No review of the literature will here be attempted…. The most important hypotheses that have been put forward are sub-varieties of three main points of view. The first of these sees the difficulty in the performance of the task in Hamlet’s temperament, which is not suited to effective action of any kind; the second sees it in the nature of the task, which is such as to be almost impossible of performance by any one; and the third in some special feature in the nature of the task which renders it peculiarly difficult or repugnant to Hamlet…. No disconnected and meaningless drama could have produced the effects on its audiences that Hamlet has continuously done for the past three centuries. The underlying meaning of the drama may be totally obscure, but that there is one, and one which touches on problems of vital interest to the human heart, is empirically demonstrated by the uniform success with which the drama appeals to the most diverse audiences. To hold the contrary is to deny all the canons of dramatic art accepted since the time of Aristotle. Hamlet as a masterpiece stands or falls by these canons. We are compelled then to take the position that there is some cause for Hamlet’s vacillation which has not yet been fathomed. If this lies neither in his incapacity for action in general, nor in the inordinate difficulty of the task in question, then it must of necessity lie in the third possibility, namely in some special feature of the task that renders it repugnant to him. This conclusion, that Hamlet at heart does not want to carry out the task, seems so obvious that it is hard to see how any critical reader of the play could avoid making it…. It may be asked: why has the poet not put in a clearer light the mental trend we are trying to discover? Strange as it may appear, the answer is the same as in the case of Hamlet himself, namely, he could not, because he was unaware of its nature. We shall later deal with this matter in connection with the relation of the poet to the play. But, if the motive of the play is so obscure, to what can we attribute its powerful effect on the audience? This can only be because the hero’s conflict finds its echo in a similar inner conflict in the mind of the hearer, and the more intense is this already present conflict the greater is the effect of the drama. Again, the hearer himself does not know the inner cause of the conflict in his mind, but experiences only the outer manifestations of it. We thus reach the apparent paradox that the hero, the poet, and the audience are all profoundly moved by feelings due to a conflict of the source of which they are unaware [emphasis added]. The extensive experience of the psycho-analytic researches carried out by Freud and his school during the past twenty years has amply demonstrated that certain kinds of mental processes shew a greater tendency to be “repressed” ( verdrangt ) than others. In other words, it is harder for a person to own to himself the existence in his mind of some mental trends than it is of others. In order to gain a correct perspective it is therefore desirable briefly to enquire into the relative frequency with which various sets of mental processes are “repressed.” One might in this connection venture the generalisation that those processes are most likely to be “repressed” by the individual which are most disapproved of by the particular circle of society to whose influence he bas chiefly been subjected. Biologically stated, this law would run: ”That which is inacceptable to the herd becomes inacceptable to the individual unit,” it being understood that the term herd is intended in the sense of the particular circle above defined, which is by no means necessarily the community at large. It is for this reason that moral, social, ethical or religious influences are hardly ever ”repressed,” for as the individual originally received them from his herd, they can never come into conflict with the dicta of the latter. This merely says that a man cannot be ashamed of that which he respects; the apparent exceptions to this need not here be explained. The contrary is equally true, namely that mental trends “repressed” by the individual are those least acceptable to his herd; they are, therefore, those which are, curiously enough, distinguished as “natural” instincts, as contrasted with secondarily acquired mental trends. It only remains to add the obvious corollary that, as the herd unquestionably selects from the “natural” instincts the sexual ones on which to lay its heaviest ban, so is it the various psycho-sexual trends that most often are “repressed” by the individual. We have here an explanation of the clinical experience that the more intense and the more obscure is a given case of deep mental conflict the more certainly will it be found, on adequate analysis, to centre about a sexual problem. On the surface, of course, this does not appear so, for, by means of various psychological defensive mechanisms, the depression, doubt, and other manifestations of the conflict are transferred on to more acceptable subjects, such as the problems of immortality, future of the world, salvation of the soul, and so on. Bearing these considerations in mind, let us return to Hamlet. It should now be evident that the conflict hypotheses above mentioned, which see Hamlet’s “natural” instinct for revenge inhibited by an unconscious misgiving of a highly ethical kind, are based on ignorance of what actually happens in real life, for misgivings of this kind are in fact readily accessible to introspection. Hamlet’s self-study would speedily have made him conscious of any such ethical misgivings, and although he might subsequently have ignored them, it would almost certainly have been by the aid of a process of rationalization which would have enabled him to deceive himself into believing that such misgivings were really ill founded; he would in any case have remained conscious of the nature of them. We must therefore invert these hypotheses, and realise that the positive striving for revenge was to him the moral and social one, and that the suppressed negative striving against revenge arose in some hidden source connected with his more personal, “natural” instincts. The former striving has already been considered, and indeed is manifest in every speech in which Hamlet debates the matter; the second is, from its nature, more obscure and has next to be investigated. This is perhaps most easily done by inquiring more intently into Hamlet’s precise attitude towards the object of his vengeance, Claudius, and towards the crimes that have to be avenged. These are two, Claudius’ incest with the Queen, and his murder of his brother. It is of great importance to note the fundamental difference in Hamlet’s attitude towards these two crimes. Intellectually of course he abhors both, but there can be no question as to which arouses in him the deeper loathing. Whereas the murder of his father evokes in him indignation, and a plain recognition of his obvious duty to avenge it, his mother’s guilty conduct awakes in him the intensest horror. Now, in trying to define Hamlet’s attitude towards his uncle we have to guard against assuming offhand that this is a simple one of mere execration, for there is a possibility of complexity arising in the following way: The uncle has not merely committed each crime, he has committed both crimes, a distinction of considerable importance, for the combination of crimes allows the admittance of a new factor, produced by the possible inter-relation of the two, which prevents the result from being simply one of summation. In addition it has to be borne in mind that the perpetrator of the crimes is a relative, and an exceedingly near relative. The possible inter-relation of the crimes, and the fact that the author of them is an actual member of the family on which they were perpetrated, gives scope for a confusion in their influence on Hamlet’s mind that may be the cause of the very obscurity we are seeking to clarify.
Introduction to “Ophelia’s Desire” by James Marino (2017)
Every great theory is founded on a problem it cannot solve. For psychoanalytic criticism, that problem is Ophelia. Sigmund Freud’s Oedipal reading of Hamlet , mutually constitutive with his reading of Oedipus Rex , initiates the project of Freudian literary interpretation. But that reading must, by its most basic logic, displace Ophelia and render her an anomaly. If the Queen is Hamlet’s primary erotic object, why does he have another love interest? Why such a specific and unusual love interest? The answer that Freud and his disciples offer is that Hamlet’s expressions of love or rage toward Ophelia are displace-ments of his cathexis on the queen. That argument is tautological—one might as easily say that Hamlet displaces his cathected frustration with Ophelia onto the Queen—and requires that some evidence from the text be ignored—“No, good mother,” Hamlet tells the Queen, “here’s metal more attractive”—but the idea of the Queen as Hamlet’s primary affective object remains a standard orthodoxy, common even in feminist Freudians’ readings of Hamlet . Janet Adelman’s Suffocating Mothers , for example, takes the mother-son dyad as central, while Julia Reinhard Lupton and Kenneth Reinhard highlight the symbolic condensation of Ophelia with the Queen. The argument for Ophelia as substitute object may reach its apotheosis in Jacques Lacan’s famous essay on Hamlet, which begins with “that piece of bait named Ophelia” only to use her as an example of Hamlet’s estrangement from his own desire. Margreta de Grazia’s “Hamlet” without Hamlet has illuminated how the romantic tradition of Hamlet criticism, from which Freud’s own Hamlet criticism derives, focuses on Hamlet’s psychology at the expense of the play’s other characters, who are reduced to figures in the Prince’s individual psychomachia. While psychoanalytic reading objectifies all of Hamlet ’s supporting characters, Ophelia is not even allowed to be an object in her own right. Insistently demoted to a secondary or surrogate object, Ophelia becomes mysteriously super-fluous, like a symptom unconnected from its cause. Ophelia is the foundational problem, the nagging flaw in psychoanalytic criticism’s cornerstone. The play becomes very different if Ophelia is decoupled from the Queen and read as an independent and structurally central character, as a primary object of desire, and even as a desiring subject in her own right. I do not mean to describe the character as a real person, with a fully human psychology; Ophelia is a fiction, constructed from intersecting and contradicting generic expectations. But in those generic terms Ophelia is startlingly unusual, indeed unique, in ways that psychoanalytic criticism has been reluctant to recognize. If stage characters become individuated to the extent that they deviate from established convention, acting against type, then Ophelia is one of William Shakespeare’s most richly individual heroines. And if Shakespeare creates the illusion of interiority, or invites his audience to collaborate in that illusion, by withholding easy explanations of motive, Ophelia’s inner life is rich with mystery. Attention to the elements of Ophelia’s character that psychoanalytic readings resist or repress illuminates the deeper fantasies shaping psychoanalytic discourse. The literary dreams underpinning psychoanalysis are neither simply to be debunked nor to be reconstituted, but to be analyzed. If, as the debates over psychoanalysis over the last three decades have shown, much of Freudian thinking is not science, then it is fantasy; and fantasy, as Freud himself teaches, rewards strict attention. Ophelia, rightly attended, may tell us something about Hamlet, and about Hamlet, that critics have not always wished to know. To see Ophelia clearly would also make it clear how closely Hamlet resembles her and how faithfully his tragic arc follows hers.
Beyond Freud: Applying Psychological Theories to Literary Texts
Fortunately, we are not limited to Freud when we engage in psychological criticism. We can choose any psychological theory. Here are just a few you might consider:
- Carl Jung’s archetypes: humans have a collective unconscious that includes universal archetypes such as the shadow, the persona, and the anima/us.
- B.F. Skinner’s behaviorism: all behaviors are learned through conditioning.
- Jacques Lacan’s conception of the real, the imaginary, and the symbolic.
- Erik Erikson’s eight stages of psychosocial development: describes the effects of social development across a person’s lifespan.
- Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory of moral development: explains how people develop moral reasoning.
- Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs: people’s basic needs need to be met before they can pursue more advanced emotional and intellectual needs.
- Elisabeth Kübler-Ross’ s five stages of grief: a framework for understanding loss.
- Mamie Phipps Clark and Kenneth Bancroft Clark’s work on internalized racism.
- Derald Wing Sue and David Sue’s work with Indigenous spiritual frameworks and mental health.
It’s important to differentiate this type of criticism from looking at “mental health” or considering how the poem affects our emotions. When we are exploring how a poem makes us feel, this is subjective reader response, not psychological criticism. Psychological criticism involves analyzing a literary work through the lens of a psychological theory, exploring characters’ motivations, behaviors, and the author’s psychological influences. Here are a few approaches you might take to apply psychological criticism to a text:
- Psychological Theories: Familiarize yourself with the basics of key psychological theories, such as Freudian psychoanalysis, Jungian archetypes, or cognitive psychology. This knowledge provides a foundation for interpreting characters and their actions. It’s best to choose one particular theory to use in your analysis.
- Author’s Background: Research the author’s life and background. Explore how their personal experiences, relationships, and psychological state might have influenced the creation of characters or the overall themes of the text. Also consider what unconscious desires or fears might be present in the text. How can the text serve as a window to the author’s mind? The fictional novel Hamnet by Maggie O’Farrell uses the text of Hamlet along with the few facts that are known about Shakespeare’s life to consider how the play could be read as an expression of the author’s grief at losing his 11-year-old son.
- Character Analysis: Examine characters’ personalities, motivations, and conflicts. Consider how their experiences, desires, and fears influence their actions within the narrative. Look for signs of psychological trauma, defense mechanisms, or unconscious desires. You can see an example of this in the two literary articles above, where the authors consider Hamlet’s and Ophelia’s motivations and conflicts.
- Symbolism and Imagery: Analyze symbols and imagery in the text. Understand how these elements may represent psychological concepts or emotions. For example, a recurring symbol might represent a character’s repressed desires or fears.
- Themes and Motifs: Identify recurring themes and motifs. Explore how these elements reflect psychological concepts or theories. For instance, a theme of isolation might be analyzed in terms of its impact on characters’ mental states. An example of a motif in Hamlet would be the recurring ghost.
- Archetypal Analysis: Jungian analysis is one of my personal favorite approaches to take to texts. You can apply archetypal psychology to identify universal symbols or patterns in characters. Carl Jung’s archetypes , such as the persona, shadow, or anima/animus, can provide insights into the deeper layers of character development.
- Psychological Trajectories: Trace the psychological development of characters throughout the narrative. Identify key moments or events that shape their personalities and behaviors. Consider how these trajectories contribute to the overall psychological impact of the text.
- Psychoanalytic Concepts: If relevant, apply psychoanalytic concepts such as id, ego, and superego . Explore how characters navigate internal conflicts or succumb to unconscious desires. Freudian analysis can uncover hidden motivations and tensions.
Because psychological criticism involves interpretation, there may be multiple valid perspectives on a single text. When using this critical method, I recommend focusing on a single psychological approach (e.g. choose Freud or Jung; don’t try to do both).
Let’s practice with Emily Dickinson’s poem “A Narrow Fellow in the Grass,” using Freud’s psychoanalytic theories as our psychological approach. Read the poem first, then use the questions below to guide your interpretation of the poem.
A Narrow Fellow in the Grass* (1865)
BY EMILY DICKINSON

A narrow fellow in the grass Occasionally rides: You may have met him, —did you not, His notice sudden is.
The grass divides as with a comb, A spotted shaft is seen; And then it closes at your feet And opens further on.
He likes a boggy acre. A floor too cool for corn. Yet when a child, and barefoot, I more than once, at morn,
Have passed, I thought, a whip-lash Unbraiding in the Sun.— When, stooping to secure it, It wrinkled, and was gone.
Several of nature’s people I know, and they know me; I feel for them a transport Of cordiality;
But never met this fellow, Attended or alone, Without a tighter breathing, And zero at the bone.
*I’ve used the “corrected” version published in 1865. Here is a link to the transcribed version from the original manuscript.
Here are a few questions to consider as you apply Freudian psychoanalysis to the poem.
- Imagery and Motifs: This poem is one of just 10 Emily Dickinson poems published during her lifetime. The editor chose a different title for the poem: “The Snake” . How does adding this title change the reader’s experience with the poem? Which words in the poem seem odd in the context of this title? In a Freudian reading of the poem, what would the snake (if it is a snake) represent?
- Repression and Symbolism: How might the “narrow Fellow in the Grass” symbolize repressed desires or memories in the speaker’s subconscious? What elements in the poem suggest a hidden, perhaps uncomfortable, aspect of the speaker’s psyche?
- Penis Envy: In Freudian theory, penis envy refers to a girl’s desire for male genitalia. How does this concept apply to the poem? Dickinson’s handwritten version of the poem says “boy” instead of “child” in line 11. How does this change impact how we read the poem?
- Unconscious Fears and Anxiety (Zero at the Bone): The closing lines mention a “tighter Breathing” and feeling “Zero at the Bone.” How can Freud’s ideas about the unconscious and anxiety be applied here? What might the encounter with the Fellow reveal about the speaker’s hidden fears or anxieties, and how does it impact the speaker on a deep, unconscious level?
- Punctuation: The manuscript versions of this poem do not use normal punctuation conventions. Instead, the author uses a dash. How does this change our reading of the poem? What does her use of dashes imply about her psychological state?
As with New Historicism, you’ll need to do some research and cite a source for the psychological theory you apply. Introduce the psychological theory, then use it to analyze the poem. Make sure to support your analysis with specific textual evidence from the poem. Use line numbers to refer to specific parts of the text.
You’ll want to come up with a thesis statement that you can support with the evidence you’ve found.
Freudian Analysis Thesis Statement: In Emily Dickinson’s poem “A Narrow Fellow in the Grass,” the encounter with a snake serves as a symbolic manifestation of repressed desires, unconscious fears, and penis envy, offering a Freudian exploration of the complex interplay between the conscious and unconscious mind.
How would this thesis statement be different if you had chosen a different approach–for example, Erik Erikson’s theory of child development? How does this analysis differ from a New Criticism approach? Do you think that a Freudian approach is useful in helping readers to appreciate this poem?
The Limitations of Psychological Criticism
While psychological criticism provides valuable insights into the human psyche and enriches our understanding of literary works, it also has its limitations. Here are a few:
- Subjectivity: Psychological interpretations often rely on subjective analysis, as different readers may perceive and interpret psychological elements in a text differently. The lack of objective criteria can make it challenging to establish a universally accepted interpretation. However, using an established psychological theory can help to address this concern.
- Authorial Intent: Inferring an author’s psychological state or intentions based on their work can be speculative. Without direct evidence from the author about their psychological motivations, interpretations may be subjective and open to debate.
- Overemphasis on Individual Psychology: Psychological criticism may focus heavily on individual psychology and neglect broader social, cultural, or historical contexts that also influence literature. This narrow focus may oversimplify the complexity of human experience.
- Stereotyping Characters: Applying psychological theories to characters may lead to oversimplified or stereotypical portrayals. Characters might be reduced to representing specific psychological concepts, overlooking their multifaceted nature. Consider the scholarly readings above and how Ophelia has traditionally been read as an accessory to Hamlet rather than as a fully developed character in her own right.
- Neglect of Formal Elements: Psychological criticism may sometimes neglect formal elements of a text, such as structure, style, and language, in favor of exploring psychological aspects. This oversight can limit a comprehensive understanding of the literary work.
- Inconsistency in Psychoanalytic Theories: Different psychoanalytic theories exist, and scholars may apply competing frameworks, leading to inconsistent interpretations. For example, a Freudian interpretation may differ significantly from a Jungian analysis.
- Exclusion of Reader Response: While psychological criticism often explores the author’s psyche, it may not give sufficient attention to the diverse psychological responses of readers. The reader’s own psychology and experiences contribute to the meaning derived from a text. In formal literary criticism, as we noted above, this type of approach is considered to be subjective reader response, but it might be an interesting area of inquiry that is traditionally excluded from psychological criticism approaches.
- Neglect of Positive Aspects: Psychological criticism may sometimes focus too much on negative or pathological aspects of characters, overlooking positive psychological dimensions and the potential for growth and redemption within the narrative (we care a lot more about what’s wrong with Hamlet than what’s right with him).
Acknowledging these limitations helps balance the use of psychological criticism with other literary approaches, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of a literary work.
Psychological Criticism Scholars
There is considerable overlap in psychological criticism scholarship. With this type of approach, some psychologists/psychiatrists use literary texts to demonstrate or explicate psychological theories, while some literary scholars use psychological theories to interpret works. Here are a few better-known literary scholars who practice this type of criticism:
- Sigmund Freud, who used Greek literature to develop his theories about the psyche
- Carl Jung, whose ideas of the archetypes are fascinating
- Alfred Adler, a student of Freud’s who particularly focused on literature and psychoanalysis
- Jacques Lacan, a French psychoanalyst whose ideas of the real, the imaginary, and the symbolic provide interesting insights into literary texts.
Further Reading
- Adler, Alfred. The Individual Psychology of Alfred Adler . Ed. Heinz and Rowena R. Ansbacher. New York: Anchor Books, 1978. Print.
- Çakırtaş, Önder, ed. Literature and Psychology: Writing, Trauma and the Self . Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2018.
- Eagleton, Terry. “Psychoanalysis.” Literary Theory: An Introduction . Minneapolis: U of Minnesota P, 1983. 151-193. Print
- Freud. Sigmund. The Ego and the Id. https://www.sas.upenn.edu/~cavitch/pdf-library/Freud_SE_Ego_Id_complete.pdf Accessed 31 Oct. 2023. – A General Introduction to Psychoanalysis. Project Gutenberg eBook #38219. https://www.gutenberg.org/cache/epub/38219/pg38219.txt – The Interpretation of Dreams . 1900. Oxford: Oxford UP, 1999. https://psychclassics.yorku.ca/Freud/Dreams/dreams.pdf
- Hart, F. Elizabeth (Faith Elizabeth). “The Epistemology of Cognitive Literary Studies.” Philosophy and Literature , vol. 25 no. 2, 2001, p. 314-334. Project MUSE , https://doi.org/10.1353/phl.2001.0031 .
- Ingarden, Roman, and John Fizer. “Psychologism and Psychology in Literary Scholarship.” New Literary History , vol. 5, no. 2, 1974, pp. 213–23. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.2307/468392. Accessed 26 Oct. 2023.
- Jones, Ernest. “The Œdipus-Complex as an Explanation of Hamlet’s Mystery: A Study in Motive.” The American Journal of Psychology , vol. 21, no. 1, 1910, pp. 72–113. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.2307/1412950 . Accessed 26 Oct. 2023.
- Knapp, John V. “New Psychologies in Literary Criticism.” Interdisciplinary Literary Studies , vol. 7, no. 2, 2006, pp. 102–21. JSTOR , http://www.jstor.org/stable/41209945 . Accessed 31 Oct. 2023.
- Marino, James J. “Ophelia’s Desire.” ELH , vol. 84, no. 4, 2017, pp. 817–39. JSTOR , https://www.jstor.org/stable/26797511 . Accessed 26 Oct. 2023.
- Willburn, David. “Reading After Freud.” Contemporary Literary Theory. Ed. G. Douglas Atkins and Laura Morrow. Amherst: U of Massachusetts P, 1989. 158-179.
- Shupe, Donald R. “Representation versus Detection as a Model for Psychological Criticism.” The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism , vol. 34, no. 4, 1976, pp. 431–40. JSTOR , https://doi.org/10.2307/430577 . Accessed 31 Oct. 2023.
- Zizek, Slavoj. How to Read Lacan. New York: Norton, 2007.
Critical Worlds Copyright © 2024 by Liza Long is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
50+ Research Topics for Psychology Papers
How to Find Psychology Research Topics for Your Student Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
- Specific Branches of Psychology
- Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
- Human Cognition
- Human Development
- Critique of Publications
- Famous Experiments
- Historical Figures
- Specific Careers
- Case Studies
- Literature Reviews
- Your Own Study/Experiment
Are you searching for a great topic for your psychology paper ? Sometimes it seems like coming up with topics of psychology research is more challenging than the actual research and writing. Fortunately, there are plenty of great places to find inspiration and the following list contains just a few ideas to help get you started.
Finding a solid topic is one of the most important steps when writing any type of paper. It can be particularly important when you are writing a psychology research paper or essay. Psychology is such a broad topic, so you want to find a topic that allows you to adequately cover the subject without becoming overwhelmed with information.
I can always tell when a student really cares about the topic they chose; it comes through in the writing. My advice is to choose a topic that genuinely interests you, so you’ll be more motivated to do thorough research.
In some cases, such as in a general psychology class, you might have the option to select any topic from within psychology's broad reach. Other instances, such as in an abnormal psychology course, might require you to write your paper on a specific subject such as a psychological disorder.
As you begin your search for a topic for your psychology paper, it is first important to consider the guidelines established by your instructor.
Research Topics Within Specific Branches of Psychology
The key to selecting a good topic for your psychology paper is to select something that is narrow enough to allow you to really focus on the subject, but not so narrow that it is difficult to find sources or information to write about.
One approach is to narrow your focus down to a subject within a specific branch of psychology. For example, you might start by deciding that you want to write a paper on some sort of social psychology topic. Next, you might narrow your focus down to how persuasion can be used to influence behavior .
Other social psychology topics you might consider include:
- Prejudice and discrimination (i.e., homophobia, sexism, racism)
- Social cognition
- Person perception
- Social control and cults
- Persuasion, propaganda, and marketing
- Attraction, romance, and love
- Nonverbal communication
- Prosocial behavior
Psychology Research Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
Exploring a psychological disorder or a specific treatment modality can also be a good topic for a psychology paper. Some potential abnormal psychology topics include specific psychological disorders or particular treatment modalities, including:
- Eating disorders
- Borderline personality disorder
- Seasonal affective disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Antisocial personality disorder
- Profile a type of therapy (i.e., cognitive-behavioral therapy, group therapy, psychoanalytic therapy)
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition
Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include:
- False memories
- Speech disorders
- Problem-solving
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Development
In this area, you might opt to focus on issues pertinent to early childhood such as language development, social learning, or childhood attachment or you might instead opt to concentrate on issues that affect older adults such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease.
Some other topics you might consider include:
- Language acquisition
- Media violence and children
- Learning disabilities
- Gender roles
- Child abuse
- Prenatal development
- Parenting styles
- Aspects of the aging process
Do a Critique of Publications Involving Psychology Research Topics
One option is to consider writing a critique paper of a published psychology book or academic journal article. For example, you might write a critical analysis of Sigmund Freud's Interpretation of Dreams or you might evaluate a more recent book such as Philip Zimbardo's The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil .
Professional and academic journals are also great places to find materials for a critique paper. Browse through the collection at your university library to find titles devoted to the subject that you are most interested in, then look through recent articles until you find one that grabs your attention.
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Famous Experiments
There have been many fascinating and groundbreaking experiments throughout the history of psychology, providing ample material for students looking for an interesting term paper topic. In your paper, you might choose to summarize the experiment, analyze the ethics of the research, or evaluate the implications of the study. Possible experiments that you might consider include:
- The Milgram Obedience Experiment
- The Stanford Prison Experiment
- The Little Albert Experiment
- Pavlov's Conditioning Experiments
- The Asch Conformity Experiment
- Harlow's Rhesus Monkey Experiments
Topics of Psychology Research About Historical Figures
One of the simplest ways to find a great topic is to choose an interesting person in the history of psychology and write a paper about them. Your paper might focus on many different elements of the individual's life, such as their biography, professional history, theories, or influence on psychology.
While this type of paper may be historical in nature, there is no need for this assignment to be dry or boring. Psychology is full of fascinating figures rife with intriguing stories and anecdotes. Consider such famous individuals as Sigmund Freud, B.F. Skinner, Harry Harlow, or one of the many other eminent psychologists .
Psychology Research Topics About a Specific Career
Another possible topic, depending on the course in which you are enrolled, is to write about specific career paths within the field of psychology . This type of paper is especially appropriate if you are exploring different subtopics or considering which area interests you the most.
In your paper, you might opt to explore the typical duties of a psychologist, how much people working in these fields typically earn, and the different employment options that are available.
Topics of Psychology Research Involving Case Studies
One potentially interesting idea is to write a psychology case study of a particular individual or group of people. In this type of paper, you will provide an in-depth analysis of your subject, including a thorough biography.
Generally, you will also assess the person, often using a major psychological theory such as Piaget's stages of cognitive development or Erikson's eight-stage theory of human development . It is also important to note that your paper doesn't necessarily have to be about someone you know personally.
In fact, many professors encourage students to write case studies on historical figures or fictional characters from books, television programs, or films.
Psychology Research Topics Involving Literature Reviews
Another possibility that would work well for a number of psychology courses is to do a literature review of a specific topic within psychology. A literature review involves finding a variety of sources on a particular subject, then summarizing and reporting on what these sources have to say about the topic.
Literature reviews are generally found in the introduction of journal articles and other psychology papers , but this type of analysis also works well for a full-scale psychology term paper.
Topics of Psychology Research Based on Your Own Study or Experiment
Many psychology courses require students to design an actual psychological study or perform some type of experiment. In some cases, students simply devise the study and then imagine the possible results that might occur. In other situations, you may actually have the opportunity to collect data, analyze your findings, and write up your results.
Finding a topic for your study can be difficult, but there are plenty of great ways to come up with intriguing ideas. Start by considering your own interests as well as subjects you have studied in the past.
Online sources, newspaper articles, books , journal articles, and even your own class textbook are all great places to start searching for topics for your experiments and psychology term papers. Before you begin, learn more about how to conduct a psychology experiment .
What This Means For You
After looking at this brief list of possible topics for psychology papers, it is easy to see that psychology is a very broad and diverse subject. While this variety makes it possible to find a topic that really catches your interest, it can sometimes make it very difficult for some students to select a good topic.
If you are still stumped by your assignment, ask your instructor for suggestions and consider a few from this list for inspiration.
- Hockenbury, SE & Nolan, SA. Psychology. New York: Worth Publishers; 2014.
- Santrock, JW. A Topical Approach to Lifespan Development. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Literary Theory and Criticism
Home › Psycholinguistics: An Essay
Psycholinguistics: An Essay
By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on October 30, 2017 • ( 1 )
A BRIEF HISTORY
Interest in the mind and language both date back for millennia, with a documented history of language study going back 2,500 years and spread across many cultures (including India, China, Mesopotamia, and Greece). Documented interest in the mind and knowledge—the foundations of what we consider to be psychology—also dates back, in one form or another, at least as early as language study, and perhaps earlier. However, modern versions of both linguistics and psychology are much more recent, with modern psychology tracing back to Wilhelm Wundt’s lab in Leipzig in the late 1800s and modern linguistics tracing back to roughly the same time. Both fields have undergone some revolutions in even that relatively short time, with both fields experiencing some major shifts in the mid1900s that are still felt today.
From the beginning of psychology, there has been an interest in language. Wilhelm Wundt, for example, published a book on language ( die Sprache ) in 1900. This book, with 1,367 pages by its 1913 edition, covered a number of topics that are still very much relevant in current psycholinguistics, including child language acquisition, sign language, language perception, and grammatical structure. The interest between the domains of language and psychology was mutual and, as Blumenthal (1987) discussed, many linguists of the day were also interested in Wundt’s work and attended his lectures at the University of Leipzig, including several influential language researchers such as Leonard Bloomfield, Ferdinand de Saussure, and Edward Boas. For example, Bloomfield’s approach to analyzing the structure of language is important to almost all modern theories of grammar. De Saussure made a critical distinction that is still part of how language researchers think about language: langue , which is the knowledge of a language system that exists collectively among speakers of a language, and parole, which is the use of that system.
While Wundt was an experimentalist, he also acknowledged the importance of internal mental states and viewed language as importantly reflecting mental representations. He viewed the sentence as a key unit of language, and sought to show how universal characteristics of human information processing, like attention and memory, would influence its production and comprehension. This is really not so different from what modern psycholinguistic researchers are doing, though the route from Wundt’s experiments to the present day is not entirely direct.
Wundt was not the only researcher at that time interested in language, of course, and in fact there was some conflict between Wundt’s approach and others, including approaches that disagreed with the idea of a unified mental representation and other types of “introspective” approaches. In fact, at the turn of the century there were quite a number of competing perspectives on psychology, which led one linguist of the day, Bernard Delburck, to suggest that linguists might do better to part ways with psychology. This is largely what happened, and for the next 30 to 40 years linguistics focused instead on the formal aspects of language—sound systems, grammatical structures, word formation rules—without much reference to the mental processing needed for their actual use. This approach still forms a core aspect of linguistic study today.
Although Wundt’s work clearly foreshadows modern views and topics on psycholinguistics, his influence declined following the First World War. Bloomfield, once a proponent of Wundt’s approach, had turned to behaviourism instead by 1933 when he published one of his major contributions to linguistics, a book simply called Language . In psychology, behaviourism was a movement in which the study of mental states was more or less rejected, and the idea that one could account for human behaviour in terms of mental states or representation was discounted. In linguistic terms, this meant a stronger focus on descriptive accounts of language rather than studying language as a window onto human mind. Perhaps the most famous attempt to account for language processing in a behaviourist tradition comes from B.F. Skinner’s 1957 Verbal Behaviour in which language is not a complex mental construct with rules and representations, but instead is reduced to, well, verbal behaviour. As such, it can be explained, according to Skinner, in terms of the same conditioning theory that applied to other behaviours, such as classical and operant conditioning, in which links between stimuli and outcomes are formed and shaped by experience. For example, a child saying “I want milk” may result in the child receiving a glass of milk, and this reinforces (or conditions) the use of this verbal behaviour.
The trouble was that there are a number of aspects of language that cannot be explained by classical and operant conditioning. In a famous critique of Skinner’s book, Noam Chomsky (1957) successfully argued against verbal behaviourism with several key points. Crucially, as we shall see in chapter 2, language is recursive and can produce an infinite number of sentences from a finite set of systematic rules and representations. The complexities of language that these rules create are difficult (if not impossible) to account for in simple stimulus–response terms. As part of his arguments, Chomsky reintroduced the idea of mental representations back to the study of language. He also drew an important distinction between the knowledge that one has about a language, called “competence” and the use of the language, “performance” (similar to the distinction of langue and parole drawn by Ferdinand de Saussure roughly 60 years earlier). Chomsky’s influence on modern linguistics and psycholinguistics is profound, and his focus on competence (as opposed to performance) drew linguistics heavily in this direction. On the other hand, psychology continued to be quite interested in the concept of language performance. Nonetheless, several of Chomsky’s proposals about the nature of syntactic structure, and in particular his work on transformation grammar, prompted experimentation by psychologists in the 1960s to see whether the linguistic processes proposed were psychological processes. For example, one could reasonably ask whether structures that were proposed to be more complex linguistically would cause longer processing times. The results were mixed—research showed that there was an important relationship between linguistic structure and psychological processing, but didn’t support the particular relationship proposed by transformational grammar, despite initial successes. Also, it became increasingly clear that this distinction between competence and performance was not trivial, and that the competence theories proposed by linguists could not simply be transferred to performance. Another difficulty was that linguistic theories were changing rapidly and that made it more difficult for psychologists to test them.
As a result, there was relatively little interaction between the study of psychology and linguistics for the next couple of decades. Psychologists were still interested in language—very much so—but focused more on issues of performance, such as the processes by which syntactic structures are constructed in real time, how ambiguities in language are resolved, and how word knowledge is accessed upon encountering a word. Linguists were still interested in language as a mental phenomenon, but focused on issues of competence—what knowledge of a language entails, and formulating theories that could apply to all languages, regardless of the apparent differences among them.
The separation between these two fields was not to last. Starting in the late 1980s and early 1990s, there was a renewed interest in psycholinguistics as a joint venture between linguists and psychologists, and these days many researchers have been trained in both disciplines (as well as other fields). Substantial advances in related disciplines, including neuroscience, computer science, and cognitive science have given researchers interested in language processing a huge new set of resources, both in terms of knowledge and tools. We now have researchers working on computational models of language processing, informed by current knowledge about how the brain works. We have researchers working at the intersection of language and other cognitive abilities, including not just working memory, but things like scene perception and reasoning.
Psycholinguistics
Psycholinguistics is concerned with the relationship between language and the mind. This distinguishes it from sociolinguistics, on the one hand, where the focus is on the social dimension of language, and stylistics, on the other, where it is on the expressive functions of language. Psycholinguistics explores the psychological processes involved in using language. It asks how we store words and syntactic structures in the brain, what processes of memory are involved, and how we understand and produce speech. These are all of considerable practical importance when it comes to understanding language disorders. But above all, psycholinguists are interested in the acquisition of language: with how children learn.
Many linguists feel that if we can understand the internal mechanism which enables children to learn language so quickly we shall have penetrated one of the deepest secrets of the mind. To what extent are humans programmed from birth to acquire language? Is there such a thing as a language gene? Or is it simply that we have a general cognitive, or mental, ability that enables us to pick up language quickly? All of these issues are part of an ongoing debate within linguistics. Currently, the genetic view of language ability holds the field. Book by the psycholinguist Steven Pinker , entitled The Language Instinct (1995), makes a strong case for considering the elements of linguistic knowledge to be innate. This fits in very neatly with the Chomskyan concept of universal grammar: the idea that there is a common underlying structure to every language, the knowledge of which we are born with.
Psycholinguistics, then, is at the theoretical cutting edge of linguistics and, as such, is pretty heady stuff. So the question is, how can we begin studying it? First of all, we can be encouraged by the fact that much of the recent literature on the subject is very accessible. There is a strong tradition within linguistics of popularising the results of research in ways that demand little previous knowledge. The work of Pinker , mentioned above, and, in particular, Jean Aitchison , provide excellent ways into the subject. In these works one can find discussions of the various methods by which psycholinguists gather their evidence and how they set about analysing it. Secondly, as with sociolinguistics, one can carry out simple observational tasks oneself.
The most effective way to do this is to observe and monitor the speech of one or two young children over a period of time. You need to have in mind, of course, what you are looking for and the purpose of the activity. Your initial concern is to identify distinctive usages, either in sounds, syntax, or word meanings. You will be surprised in doing so how much of children’s speech you have hitherto taken for granted. The next stage is to establish what kind of rule your informants are following in producing these usages. Psycholinguistics proceeds on the principle that children’s use of language is rule-governed. You could start with observing how children form the plural and the past tense. These probably comprise the most conspicuous ‘errors’ in childhood speech. Young children will frequently say tooths and mouses , instead of teeth and mice , and holded and finded , instead of held and found . These are examples of over-generalisation the extension of a rule beyond its proper limits. In these cases the child knows the regular rule for forming the plural and the past tense but doesn’t know that these particular words are irregular. Having established the presence of this phenomenon, you can then test to see whether all irregular forms are regularised or only some, and how long it takes a child when corrected to acquire the correct form. It’s on the basis of experiments like these that psycholinguists form hypotheses about how children memorise forms and self-correct.

Over-generalisation is a frequent phenomenon in language development. It can be found not only in syntactic usage but also in word meanings. Many young children will sometimes refer to all animals as dogs or call all vehicles cars , and perhaps more disconcertingly, all men, dad . Discovering the limits of these words, what they do, and do not, apply to, is a useful way of penetrating the child’s semantic system. It can take time, for example, for children to learn that words can refer to separate things. When a child refers to milk , for instance, does s/he mean the whole process of pouring it into a mug and placing it down, or does it have the restricted meaning we are used to? Children also under-generalise; indeed, undergeneralisation is probably a more frequent phenomenon than its counterpart. A child may often only be able to use words in a particular context. It’s not uncommon for children to call their own shoes shoes but not know what someone else’s are called.
An initial way into psycholinguistics is to carry out some field research of your own into the acquisition of language, using a couple of basic concepts as your guides. On the basis of this, you can speculate about the kinds of lexical, syntactic, and semantic knowledge which your informants possess. If you do this it will enrich your understanding of the linguistic literature which you read. You will also find that it adds to your knowledge of how language changes; because all of us under- and over-generalise. Over-generalisation is one of the processes behind the loss of inflections from Anglo-Saxon times; we used to have many more irregular forms then than we do now. The morphology of modern English has developed as a consequence of generalising particular ways of forming the plural and past tense into regular paradigms. And it is also a key process in dialectal change. People who say I loves him are generalising the rule for the third person singular to cover all forms of the present tense. And in using a word like deer with its modern meaning we are under-generalising it: its Anglo-Saxon original, deor , meant an animal.
Having begun in a fairly simple way you can extend the process and consider more complex aspects of language acquisition: the formation of the negative, for instance. It takes some time for children to acquire the specific rule about attaching the negative to the auxiliary verb. Initially they will tend to put it at the beginning of the word string: no Jenny have it . Later the child decides to put the negative after the first noun phrase: cat no drink ; he no throw it . The interesting thing about these rules is that the child cannot have acquired them from listening to adult discourse. They have been generated from scratch. And yet they are commonly followed by most children. Are they then a representation of some internal grammar in the child’s brain? Does the child start out with a set of possibilities for the formation of the negative and narrow them down as s/he encounters confirmation or disconfirmation from the speech of others? Questions like these form the basis of much psycholinguistic enquiry. It’s impossible to see directly into the brain so all we have is the second-hand evidence of language to work on. Over the years psycholinguists have amassed a good deal of observational data and case history analysis, all of which you can work through in time, but it is no substitute at the outset for making your own observations, and for using your linguistic knowledge to speculate about how we manage what is, arguably, the most amazing learning feat of our lives.
Share this:
Categories: Uncategorized
Tags: Jean Aitchison , Linguistics , Literary Criticism , Literary Theory , Noam Chomsky , Psychoanalysis , Psycholinguistics , Psycholinguistics background , Psycholinguistics history , Psycholinguistics: An Essay , Steven Pinker , The Language Instinct
Related Articles

Please look at the paper https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10936-020-09701-y , it may answer many of the questions raised by you. Pramod Kumar Agrawal
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Psychology and Literature
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Save to Library
- Last »
- The Strange Case of Billy Biswas Follow Following
- Arun Joshi Follow Following
- Existentialism and Literature Follow Following
- Cognitive Literary Theory, Literature and Cognition, Evolutionary Psychology and Literature Follow Following
- Empirical Aesthetics Follow Following
- Neuroaesthetics Follow Following
- Biocultural theory Follow Following
- Netnography Follow Following
- English Literature Follow Following
- Terence McKenna Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Dr. Sreekumar's English Literature & Career Advancement
- Shakespeare
- Criticism & Theory
- Grammar & Linguistics
Monday 3 April 2017
Psychology and literature--carl gustav jung, bharathiar university , mphil (english) study materials , paper ii – approaches to literature, c.g.jung (lodge, pp 175-227), psychology and literature, carl gustav jung, 13 comments:.

Thanks for the nice blog. It was very useful for me. I'm happy I found this blog. Thank you for sharing with us,I too always learn something new from your post. England
For those who have to teach these "hi-fi abstract ideas" to the present generation of students, including the university research scholars, your block is an useful one. you have made it as simple as possible. In fact, even in this simple narration there are many abstract derivations. Still, yours is one of the easiest narrations from the point of view of students. Thanks. N. Balasubramanian English Dept, Sri Ram Nallamani College, Tenkasi.
Sir,I'm happy to find this blog, particularly this page. thank you so much for creating this notes and it is really awesome to help me...
Sir, i'm really happy to find this nice blog. it was very useful for me. I learned a lot about to post useful things on my page via your blog. this post is really easy to understand for students like me. Thanks a lot for this page.
sir, can you please send me the source of this notes? it will be helpful for my research...
I want to know how i study archetypal of novel with young theory
It's really helpful sir. Thank u so much. Can I have Freud,Erich Auerbach and Northp frye
Dear Sreekumar : First of all I thank you for a detailed information about CGJung, unconsciousness, psycho analysis which is a main factor in evolution of human brain n mind. Sir, I have one question that is haunting me is that; whether there is Reincaration (rebirth in ordinary terms) and whether Jung has revealed something about it. Kindly mail me to : [email protected]
Dear Dr Sreekumar, I would like to thank you for detailed article on Carl Jung 's theory. It is quite helpful for those who want to know the basics and how Jung differs from Freud. In Indian classical literature one of the nine rasas is "bibhasta "...is visionary mode associated with the portrayal of bobhasta?
Respected Sir, It was very helpful. Thank you for sharing your insight with all of us.
Unhealthy relationships can become a source of chronic stress. Stress can spill over into the rest of your life, including your career. Chronic stress stemming from negative behaviours such as criticism and hostility in relationships has also been linked to poor mental health.2227546669 VIEW MORE:- psychologist near me with fees
Thanks for providing this information sf
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Psychology and Literature
From the book collected works of c. g. jung, volume 15.
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.
Chapters in this book (14)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature and Psychology: Writing, Trauma and the Self 3 aporia, the unclaimed psychic injury that cannot be put or cohesively narrated by language, has been one of the most intriguing concepts in the field of trauma studies. A new possibility emerged, the possibility that the unclaimed experience finds representation in other ways - hidden in
guide focuses on three of the main psychological papers: the psychological literature review, the article critique, and the classic research paper. This guide was created with the assistance of Dr. Barry and Dr. Kotchick, all from the Psychology Department at Loyola University of Maryland. While specifically geared
Identify and define the topic that you will be reviewing. 2. Conduct a literature search. 3. Read through the research that you have found and take notes. 4. Organize your notes and thoughts; create an outline. 5. Write the literature review itself and edit and revise as needed.
Literature as directed towards 'an addressable thou, an addressable reality' ... In her essay on Camus' The Plague ... (p. 272). Kittang (Citation 1985) argues that such a method based solely on the reader's psychology ultimately becomes nothing more than an autobiography and a variant of the biographical analysis of authorship. As I ...
Common Types of Psychology Papers Research psychologists engage in a variety of kinds of writing, including grant proposals, research applications and renewals, review articles, research articles, and textbooks. As a student, you are most likely to be asked to write one of two types of papers, either a report of your own actual
Literature, which intertwines within such fields as history, philosophy, sociology, psychology and so on, is a discipline wherein language is used as a medium of expression so as to interpret man ...
through, step by step, the process of writing an essay or term paper in psychology. The section on Academic Honesty in Writing reinforces information you have previously received about using sources responsibly (and avoiding plagiarism). The Do's and Don'ts for Effective Writing in Psychology include examples of common mistakes made by
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which "lie behind" the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. "Signpost" the essay's key argument, (and, if possible, how. this argument is structured).
Search the research literature Read the articles Write the literature review Structure How to proceed: describe, compare, evaluate Tips Conclusion WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW? Literature reviews survey research on a particular area or topic in psychology. Their main purpose is to knit together theories and results from multiple studies to give ...
Freud and Lacan are generally the major figures of interest in psychological approaches to literature. Other perspectives-such as cognitive and Darwinian psychology-have, admittedly, begun to ...
This research paper analyzes the relationship between Literature and Psychology and how they are connected with each other in order to portray the characters more beautifully. Psychology plays a very important role in the literature whether we talk about the one who writes the story or the one who reads it. It makes a strong connection between ...
Psychological criticism is a critical approach to literature that employs psychological theories to examine aspects of a literary work as a way to better understand both the author's mind and the characters, themes, and other elements of the text. Thus, the mind is at the center of our target as we learn more about psychological criticism.
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition. Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include: Dreams. False memories. Attention. Perception.
Psycholinguistics: An Essay By NASRULLAH MAMBROL on October 30, 2017 • ( 1). A BRIEF HISTORY. Interest in the mind and language both date back for millennia, with a documented history of language study going back 2,500 years and spread across many cultures (including India, China, Mesopotamia, and Greece).
The interplay of literature and psychology, the cross-section of these areas opens up vast possibilities for literary studies, but, at the same time, they cause just as many dilemmas: the reader enters an uncertain terrain when s/he endeavours to lay down the foundations for his/her reading at the cross-sections of the two disciplines.
Recent papers in Psychology and Literature. Top Papers; Most Cited Papers; Most Downloaded Papers; ... The interplay of literature and psychology, the cross-section of these areas opens up vast possibilities for literary studies, but, at the same time, they cause just as many dilemmas: the reader enters an uncertain terrain when s/he endeavours ...
Semantic Scholar extracted view of "Psychology and Literature" by C. Jung et al. ... Search 217,434,540 papers from all fields of science. Search. Sign In Create Free Account. DOI: 10.4324/9780203426784_PSYCHOLOGY_AND_LITERATURE; Corpus ID: 151970191; Psychology and Literature
Psychology focuses on human behavior and its causes while literature represents human behavior through fiction. Both branches of social sciences are interrelated and study human
Psychology in Literature. By. Aparna Joshi. Abstract. The basic plot points in English Literature are often rooted in the author' s. understanding of the human mind, when later scholars ...
Psychology and Literature by Carl Jung Jung‟s concept of psychology is closer with Literature than Freudian psychology. In his studies we find a fusion of Psychology, Anthropology and Literature. According to Jung, „Psychology is ... The present essay is notable for its attempt to discuss the social role of a creative
Recently published articles from subdisciplines of psychology covered by more than 90 APA Journals™ publications. For additional free resources (such as article summaries, podcasts, and more), please visit the Highlights in Psychological Research page. Browse and read free articles from APA Journals across the field of psychology, selected by ...
C.G.Jung (Lodge, pp 175-227) Carl Gustav Jung (1875 -1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential not only in psychiatry but also in anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy and religious studies. Freud wanted him to be his potential heir to carry on his "new ...
Psychology and Literature. V. "Ulysses": A Monologue. Picasso. Bibliography. Index. Psychology and Literature was published in Collected Works of C. G. Jung, Volume 15 on page 84.
3 likes, 0 comments - edu.assignment.expert.writerJanuary 6, 2024 on : "#ukstudy #studyinuk #ukvisa #studyabroad #uk #canada #usvisa #canadastudy #study #ukeducation #ukstudyvisa #india #ukadmissions #europe #immigration #ukadmission #ielts #canadavisa #cyprus #europevisa #odctravels #studyatus #education #us #admission #dse #studentvisa #dsefighter #canadaadmission #odcbirthservice We are ...