- A Step-by-Step Guide to A3 Problem Solving Methodology
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Problem-solving is an important component of any business or organization. It entails identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems in order to improve processes, drive results, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. A3 Problem solving is one of the most effective problem-solving methodologies.
A3 Problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that originated with the lean manufacturing methodology. It visualizes the problem-solving process using a one-page document known as an A3 report. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and concise manner.
A3 Problem Solving has numerous advantages, including improved communication, better decision-making, increased efficiency, and reduced waste. It is a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes and industries, and it is especially useful for solving complex and multi-faceted problems.
In this blog post, we will walk you through the A3 Problem Solving methodology step by step. Whether you are new to A3 Problem Solving or simply want to improve your skills, this guide will help you understand and apply the process in your workplace.

Table of Contents
What is a3 problem solving.
A3 Problem Solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that makes use of a one-page document called an A3 report to visually represent the process. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and concise manner. The method was created within the framework of the Lean manufacturing methodology and is based on the principles of continuous improvement and visual management.
Looking for a A3 Problem solving template? Click here
Origin and History of A3 Problem Solving
A3 Problem Solving was developed by Toyota Motor Corporation and was first used in the manufacture of automobiles. The term “A3” refers to the size of the paper used to create the report, which is an ISO standard known as “A3”. The goal of the A3 report is to provide a visual representation of the problem-solving process that all members of the organisation can easily understand and share. A3 Problem Solving has been adopted by organisations in a variety of industries over the years, and it has become a widely used and recognised method for problem-solving.
Key Principles of A3 Problem Solving
The following are the key principles of A3 Problem Solving:
- Define the problem clearly and concisely
- Gather and analyze data to gain a deep understanding of the problem
- Identify the root causes of the problem
- Develop and implement effective solutions
- Evaluate results and continuously improve
These principles serve as the foundation of the A3 Problem Solving methodology and are intended to assist organisations in continuously improving and achieving their objectives. Organizations can effectively solve problems, identify areas for improvement, and drive results by adhering to these principles.
Step 1: Define the Problem
Importance of clearly defining the problem.
The first step in the A3 Problem Solving process is critical because it lays the groundwork for the remaining steps. To define the problem clearly and accurately, you must first understand the problem and identify the underlying root cause. This step is critical because if the problem is not correctly defined, the rest of the process will be based on incorrect information, and the solution developed may not address the issue effectively.
The significance of defining the problem clearly cannot be overstated. It aids in the collection and analysis of relevant data, which is critical for developing effective solutions. When the problem is clearly defined, the data gathered is more relevant and targeted, resulting in a more comprehensive understanding of the issue. This will enable the development of solutions that are more likely to be effective because they are founded on a thorough and accurate understanding of the problem.
However, if the problem is not clearly defined, the data gathered may be irrelevant or incorrect, resulting in incorrect conclusions and ineffective solutions. Furthermore, the process of collecting and analysing data can become time-consuming and inefficient, resulting in resource waste. Furthermore, if the problem is not accurately defined, the solutions developed may fail to address the root cause of the problem, resulting in ongoing issues and a lack of improvement.
Techniques for Defining the Problem
The first step in the A3 Problem Solving process is to clearly and accurately define the problem. This is an important step because a clearly defined problem will help to ensure that the appropriate data is collected and solutions are developed. If the problem is not clearly defined, incorrect data may be collected, solutions that do not address the root cause of the problem, and time and resources may be wasted.
A problem can be defined using a variety of techniques, including brainstorming , root cause analysis , process mapping , and Ishikawa diagrams . Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages and can be used in a variety of situations depending on the nature of the problem.
Best Practice for Defining the Problem
In addition to brainstorming, root cause analysis, process mapping, and Ishikawa diagram s, best practices should be followed when defining a problem in A3 Problem Solving. Among these best practices are:
- Define the issue in a specific and quantifiable way: It is critical to be specific and concise when defining the problem, as well as to quantify the problem in terms of its impact. This will help to ensure that all stakeholders understand the problem and that data collection is focused on the right areas.
- Focus on the problem’s root cause: The A3 Problem Solving methodology is intended to assist organisations in identifying and addressing the root cause of a problem, rather than just the symptoms. Organizations can ensure that their solutions are effective and long-lasting by focusing on the root cause of the problem.
- Ascertain that all stakeholders agree on the problem’s definition: All stakeholders must agree on the definition of the problem for the A3 Problem Solving process to be effective. This ensures that everyone is working towards the same goal and that the solutions developed are relevant and appropriate.
- Consider the problem’s impact on the organisation and its stakeholders: It is critical to consider the impact of the problem on the organisation and its stakeholders when defining it. This will assist in ensuring that the appropriate data is gathered and that the solutions developed are relevant and appropriate.
Organizations can ensure that their problem is defined in a way that allows for effective data collection, analysis, and solution development by following these best practices. This will aid in the development of appropriate solutions and the effective resolution of the problem, resulting in improvements in the organization’s processes and outcomes.
Step 2: Gather Data
Gathering data in a3 problem solving.
Data collection is an important step in the A3 Problem Solving process because it allows organisations to gain a thorough understanding of the problem they are attempting to solve. This step entails gathering pertinent information about the problem, such as data on its origin, impact, and any related factors. This information is then used to help identify root causes and develop effective solutions.
One of the most important advantages of data collection in A3 Problem Solving is that it allows organisations to identify patterns and trends in data, which can be useful in determining the root cause of the problem. This information can then be used to create effective solutions that address the problem’s root cause rather than just its symptoms.
In A3 Problem Solving, data collection is a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders, including those directly impacted by the problem and those with relevant expertise or experience. Stakeholders can ensure that all relevant information is collected and that the data is accurate and complete by working together.
Overall, data collection is an important step in the A3 Problem Solving process because it serves as the foundation for effective problem-solving. Organizations can gain a deep understanding of the problem they are attempting to solve and develop effective solutions that address its root cause by collecting and analysing relevant data.
Data Collection Methods
In A3 Problem Solving, several data collection methods are available, including:
- Observations
- Process diagrams
The best data collection method will be determined by the problem being solved and the type of data required. To gain a complete understanding of the problem, it is critical to use multiple data collection methods.
Tools for Data Analysis and Visualization
Once the data has been collected, it must be analysed and visualised in order to gain insights into the problem. This process can be aided by the following tools:
- Excel Spreadsheets
- Flow diagrams
- Pareto diagrams
- Scatter Plots
- Control diagrams
These tools can assist in organising data and making it easier to understand. They can also be used to generate visual representations of data, such as graphs and charts, to communicate the findings to others.
Finally, the data collection and analysis step is an important part of the A3 Problem Solving process. Organizations can gain a better understanding of the problem and develop effective solutions by collecting and analysing relevant data.
Step 3: Identify Root Causes
Identifying the root causes of the problem is the third step in the A3 Problem Solving process. This step is critical because it assists organisations in understanding the root causes of a problem rather than just its symptoms. Once the underlying cause of the problem is identified, it can be addressed more effectively, leading to more long-term solutions.
Overview of the Root Cause Analysis Process
The process of determining the underlying causes of a problem is known as root cause analysis. This process can assist organisations in determining why a problem is occurring and what can be done to prevent it from recurring in the future. The goal of root cause analysis is to identify the underlying cause of a problem rather than just its symptoms, allowing it to be addressed more effectively.
To understand Root cause analysis in more detail check out RCA in our Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course Root Cause Analysis section
Techniques for Identifying Root Causes
There are several techniques for determining the root causes of a problem, including:
- Brainstorming
- Ishikawa diagrams (also known as fishbone diagrams)
- Root Cause Tree Analysis
These methods can be used to investigate the issue in-depth and identify potential root causes. Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the problem and identify the underlying causes that must be addressed by using these techniques.
Best Practices for Conducting Root Cause Analysis
It is critical to follow these best practices when conducting root cause analysis in A3 Problem Solving:
- Make certain that all stakeholders participate in the root cause analysis process.
- Concentrate on determining the root cause of the problem rather than just its symptoms.
- Take into account all potential root causes, not just the most obvious ones.
- To identify root causes, use a systematic approach, such as the 5 Whys or root cause tree analysis.
Organizations can ensure that root cause analysis is carried out effectively and that the root cause of the problem is identified by adhering to these best practises. This will aid in the development of appropriate solutions and the effective resolution of the problem.
Step 4: Develop Solutions
Developing solutions is the fourth step in the A3 Problem Solving process. This entails generating ideas and options for dealing with the problem, followed by selecting the best solution. The goal is to develop a solution that addresses the root cause of the problem and prevents it from recurring.
Solution Development in A3 Problem Solving
A3 solution development Problem solving is an iterative process in which options are generated and evaluated. The data gathered in the previous steps, as well as the insights and understanding gained from the root cause analysis, guide this process. The solution should be based on a thorough understanding of the problem and address the underlying cause.
Techniques for Developing Solutions
There are several techniques that can be used to develop solutions in A3 Problem Solving, including:
- Brainwriting
- Solution matrix
- Multi voting
- Force field analysis
These techniques can help to generate a range of options and to select the best solution.
Best Practice for Developing Solutions
It is critical to follow the following best practices when developing solutions in A3 Problem Solving:
- Participate in the solution development process with all stakeholders.
- Make certain that the solution addresses the underlying cause of the problem.
- Make certain that the solution is feasible and achievable.
- Consider the solution’s impact on the organisation and its stakeholders.
Organizations can ensure that the solutions they develop are effective and sustainable by adhering to these best practises. This will help to ensure that the problem is addressed effectively and that it does not reoccur.
Step 5: Implement Solutions
The final and most important step in the A3 Problem Solving methodology is solution implementation. This is the stage at which the identified and developed solutions are put into action to address the problem. This step’s goal is to ensure that the solutions are effective, efficient, and long-lasting.
The implementation Process
The implementation process entails putting the solutions developed in the previous step into action. This could include changes to processes, procedures, and systems, as well as employee training and education. To ensure that the solutions are effective, the implementation process should be well-planned and meticulously executed.
Techniques for Implementing Solutions
A3 Problem Solving solutions can be implemented using a variety of techniques, including:
- Piloting the solution on a small scale before broadening its application
- Participating in the implementation process with all relevant stakeholders
- ensuring that the solution is in line with the goals and objectives of the organisation
- Monitoring the solution to determine its effectiveness and make any necessary changes
Best Practice for Implementing Solutions
It is critical to follow these best practices when implementing solutions in A3 Problem Solving:
Make certain that all relevant stakeholders are involved and supportive of the solution. Have a clear implementation plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources required. Continuously monitor and evaluate the solution to determine its efficacy and make any necessary changes. Encourage all stakeholders to communicate and collaborate openly. Organizations can ensure that solutions are effectively implemented and problems are effectively addressed by adhering to these best practices. The ultimate goal is to find a long-term solution to the problem and improve the organization’s overall performance.
In conclusion, A3 Problem Solving is a comprehensive and structured methodology for problem-solving that can be applied in various industries and organisations. The A3 Problem Solving process’s five steps – Define the Problem, Gather Data, Identify Root Causes, Develop Solutions, and Implement Solutions – provide a road map for effectively addressing problems and making long-term improvements.
Organizations can improve their problem-solving skills and achieve better results by following the key principles, techniques, and best practices outlined in this guide. As a result, both the organisation and its stakeholders will benefit from increased efficiency, effectiveness, and satisfaction. So, whether you’re an experienced problem solver or just getting started, consider incorporating the A3 Problem Solving methodology into your work and start reaping the benefits right away.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
Practical Problem Solving Tools for Factory and Office
February 5, 2022
Many tools exist to address deviations and defects, but only a few are simple yet effective to address daily issues in manufacturing, development, administration.
When starting systematic trouble-shooting, it is important to choose the right approach. Using a comprehensive method that requires 50 pages to solve a simple problem is a waste of time, while solving a complex problem with a simple tool will most likely not reveal the hidden causes. The optimal choice of Problem Solving Tools depends on the type of issues to be addressed. Before going into details, let’s first review the most common methods used today.
Comparing Popular Methods: 3W, PDCA, 8D, A3, DMAIC, 7STEP
At their core, all scientific approaches follow a similar logic: take quick action to prevent the problem from getting worse and then define the gap, analyze the gap, identify causes, take action, evaluate impact, and embed the solution so that the problem will not reoccur.
- 3W : When the issue is small and the solution is obvious, a formal analysis is not required. The 3W-method defines What to do, Who to do it, by When . This “quick-fix” or “just-do-it” is commonly applied at daily team meetings to contain and correct snags and minor issues.
- PDCA : The Deming or Shewhart cycle “Plan-Do-Check-Act” is the classic method, used by over 80% companies that practice systematic problem solving. PDCA is effective for medium-size problems that require a systematic analysis to uncover underlying causes.
- 8D : The eight disciplines (8D) are commonly used in automotive, and the problem-solving process (PSP) in avionics. Both methods are similar, using 8 steps to address complex problems with focus on a fast reaction to non-conformances, completing the first three steps within three days.
- A3 : The A3-report, developed by Toyota, is an 8-step improvement and problem-solving process that fits on one sheet of paper. The A3-report is most effective to address small- to medium-size problems, and to structure improvement projects.
- DMAIC : The 5-step Six Sigma process “Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control” is a data-centric solving method. DMAIC is used to structure projects and solve complex situations that require statistical analysis to develop the solution, e.g. adjust process parameters to reduce yield loss.
- 7STEP : This seven-step (7S) problem-solving process shares elements with the A3 and 8D, but does not include a formal step for containment. Because of this weakness, the 7STEP process is rarely used today, replaced by 8D to address major deviations and PDCA for smaller issues.
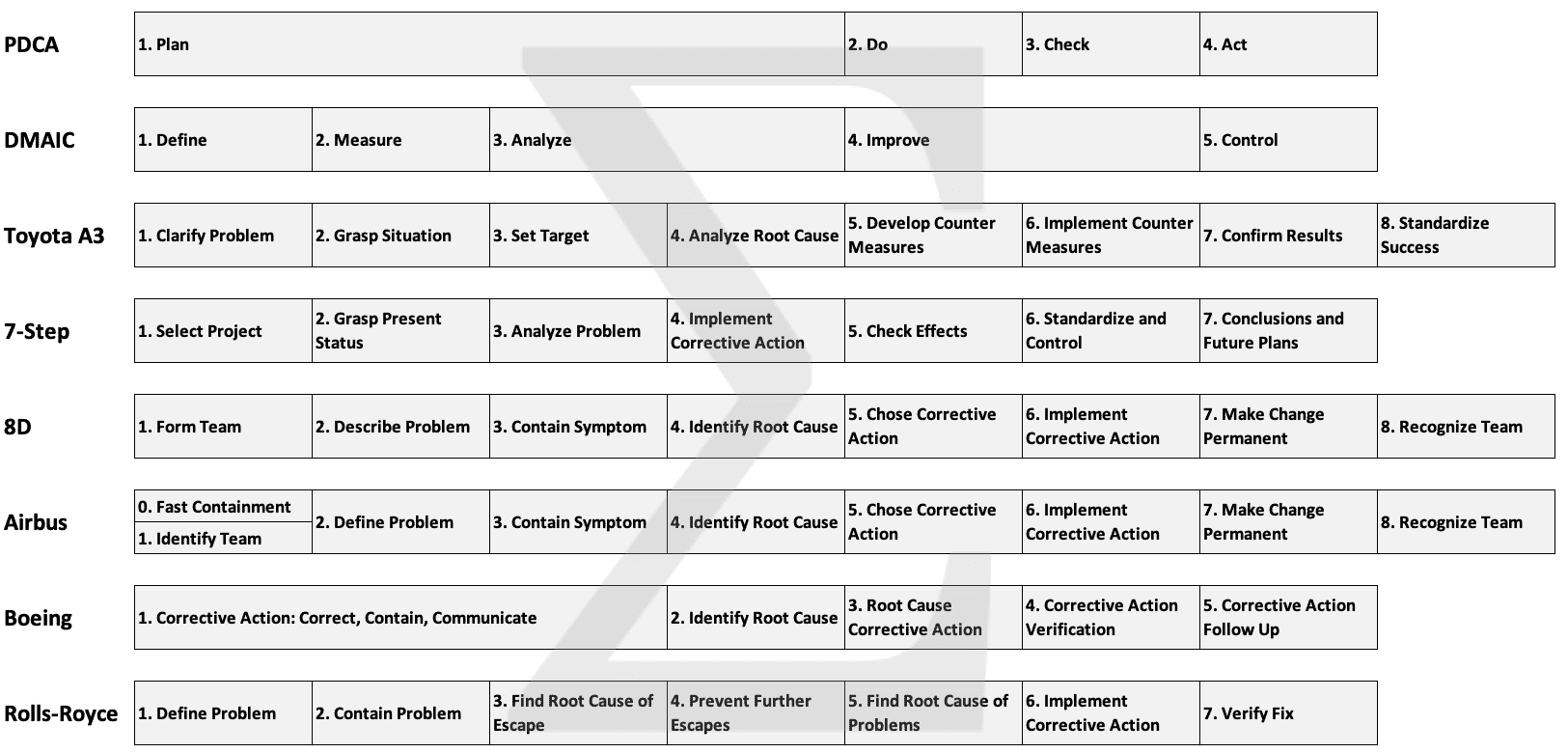
Comparing the most-popular processes for trouble-shooting and root-cause analysis shows how similar they are. For example, the PDCA planning phase covers the first three steps in DMAIC and the first five steps in A3 and 8D. Of all those processes, there are two that stick out, that all others are based on – PDCA and 8D – they are therefore considered the “mother” and “father” of practical problem solving tools used today.
Answer 5 Questions to Select the Best Method
When it comes to choosing the right process, it merely depends on the complexity of the situation to address. The more complex or severe, the more formal steps should be applied to make sure no step is missed. Here are five questions that will help you selecting the best process:
- Is the issue small, medium, or large?
- Is the solution obvious or unknown?
- Is it reoccurring or a single incident?
- Is it a single cause or multiple causes?
- Is statistical data analysis required?
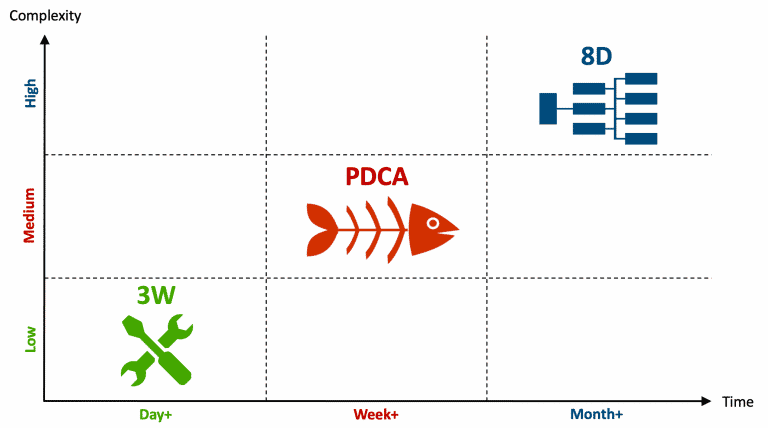
3 Practical Problem Solving Tools: Fix, Fish, Tree
There are three practical, yet effective tools to address daily issues in factory and office: The 3W or “Fix” because it is quick, simple, informal;, the PDCA or “Fish” because it is based on the Ishikawa or Fishbone diagram;, and the 8D or “Tree” because it uses logical trees to analyze complex root causes.
- Fix: use 3W (What-Who-When) for informal trouble-shooting , finding a quick action to fix a small issue within a day .
- Fish: use PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) to analyze simple and repeat issues within a week , using the fishbone diagram.
- Tree: use 8D (Eight Disciplines) to systematically eliminate multiple root-causes or complex problems within a month .
Tools and Templates to Eliminate Root Causes
To encourage people to go beyond containment and quick fixes, the method they use must be simple and practical, but also effective and efficient. Over the course of several years, we have tested dozens of different templates and found that the following two forms work best by far. Why? Because the user is given a clear structure, enhanced with pictograms, and the entire solving process can be completed on a single sheet, the key for broad adoption.
The PDCA and 8D templates have proven to be extremely effective in addressing non-conformances; they are practical problem solving tools for teams in manufacturing, quality control, product development, healthcare, back office, and corporate administration to successfully resolve daily issues and prevent them from coming back. You can download the free toolkit in 22 languages here .
Use PDCA Template to Solve Simple Problems
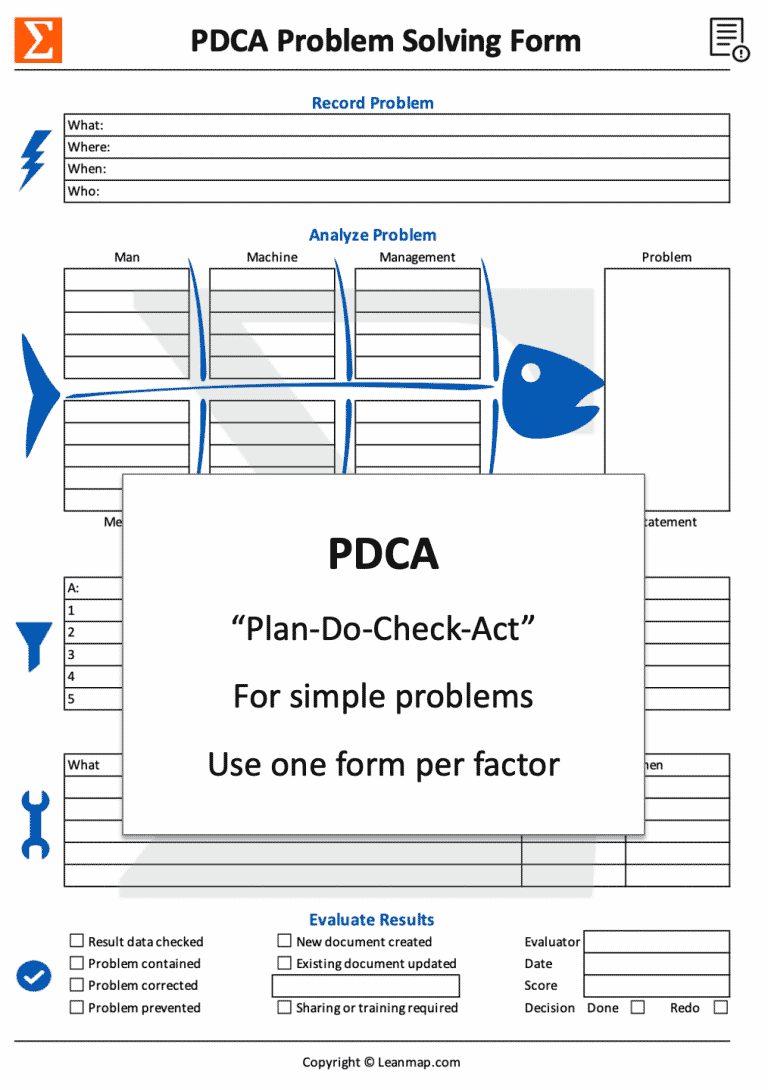
4 Steps to Eliminate Simple Causes
- Plan-1 Record Problem : Describe what happened, where and when, and who is involved solving it.
- Plan-2 Analyze Problem : Assign potential causes to categories: Man, Method, Machine, Material, Management, Milieu (Environment).
- Plan-3 Identify Causes : Ask “why” to drill down to root causes; for complex problems, use several forms, one per branch or issue.
- Do Implement Actions : Create and implement an action plan to contain, correct, and prevent the problem from reoccurring.
- Check Results and Act : Review impact, standardize solution; close the case or initiate further actions by starting a new PDCA cycle.
Use 8D Template to Solve Complex Problems
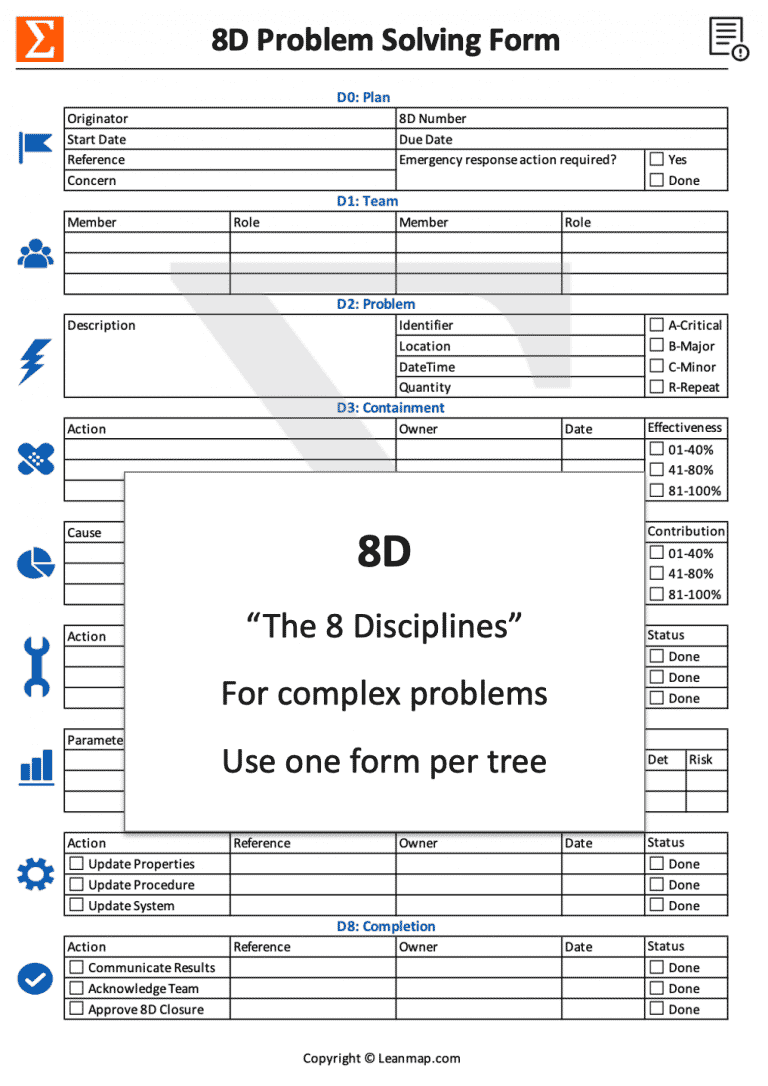
8 Steps to Eliminate Complex Causes
- D0 Plan : Register problem and define emergency response.
- D1 Team : Identify team members to address the problem.
- D2 Problem : Grasp the situation and describe the problem.
- D3 Containment : Prevent the problem from spreading.
- D4 Diagnostics : Identify direct causes and root causes.
- D5 Correction : Define and prioritize corrective actions.
- D6 Validation : Implement actions and evaluate effectiveness.
- D7 Prevention : Systemize solutions to prevent reoccurrence.
- D8 Completion : Transfer knowledge and recognize contributors.
Become an Effective Problem Solver by Applying Practical Tools and Learning Battle-Tested Methods

Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
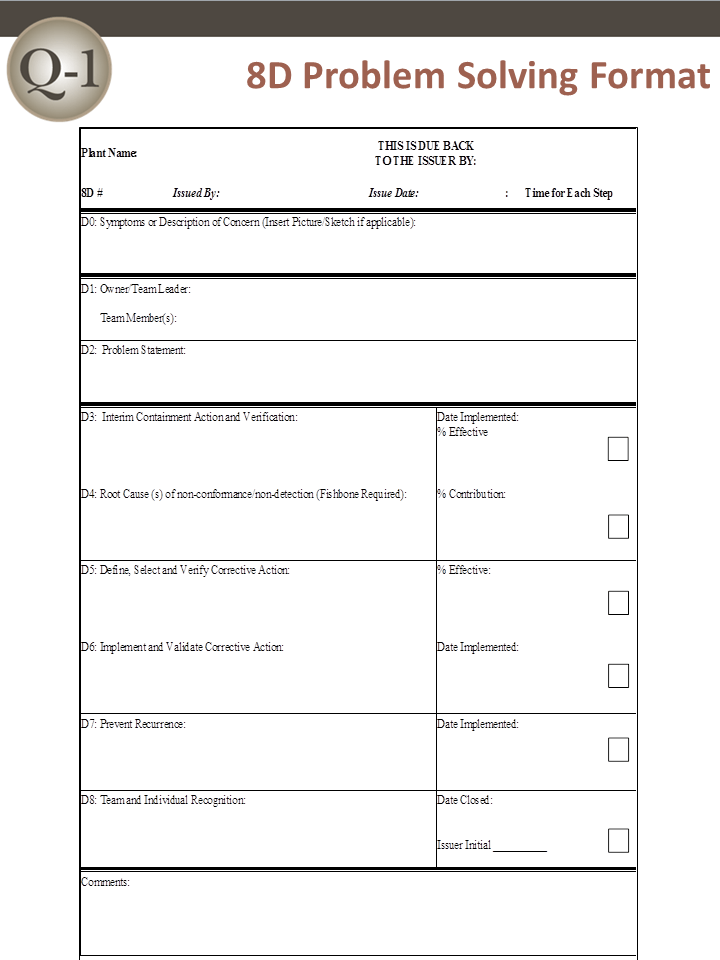
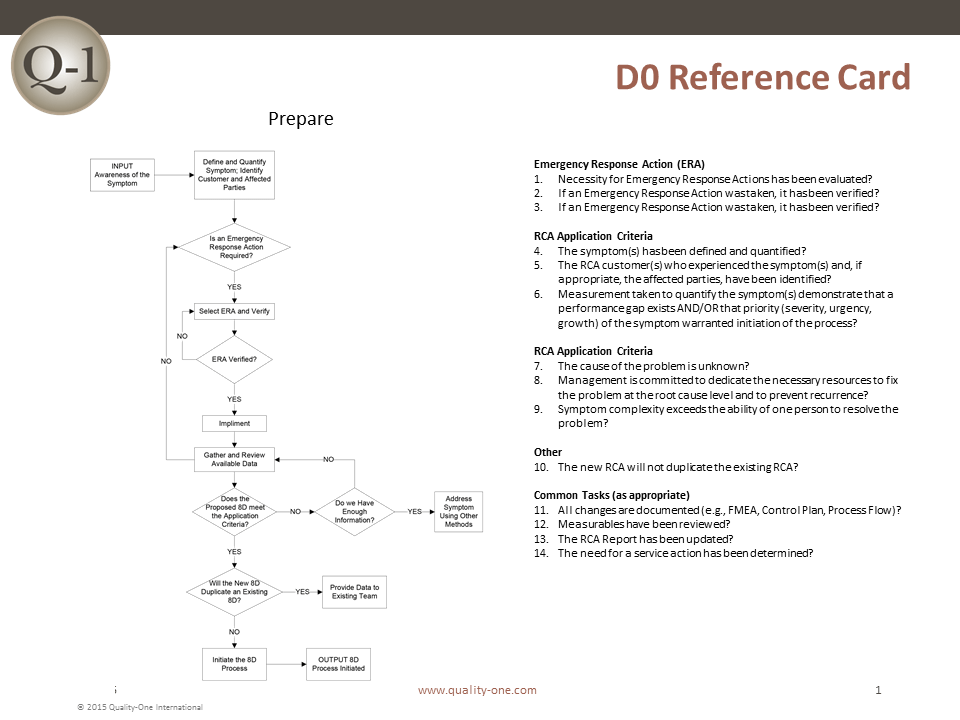
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
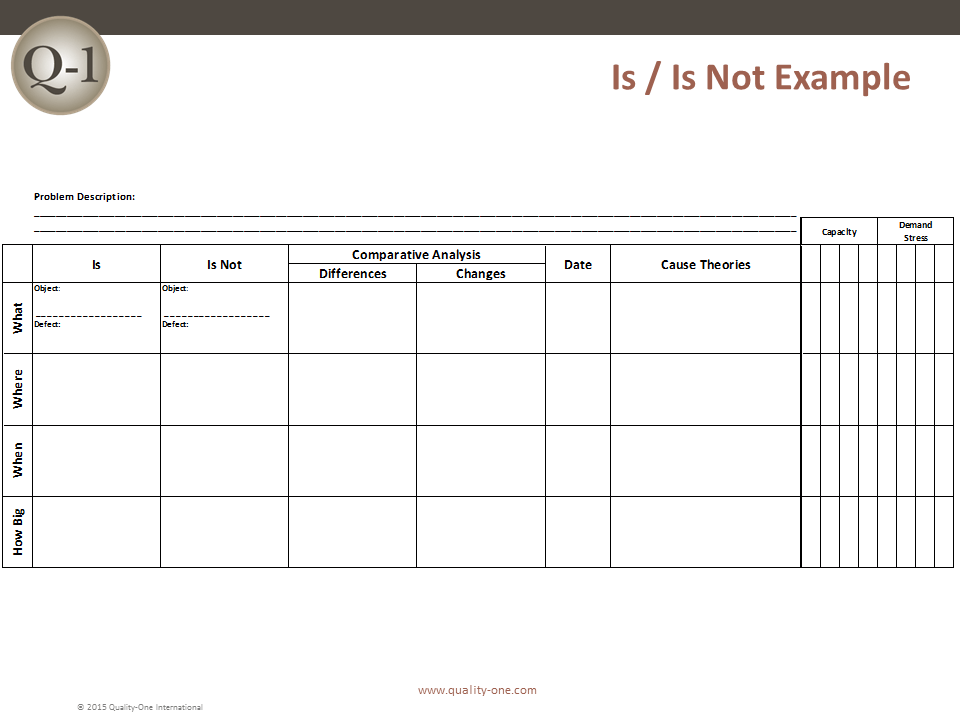
D2: Describe the Problem
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
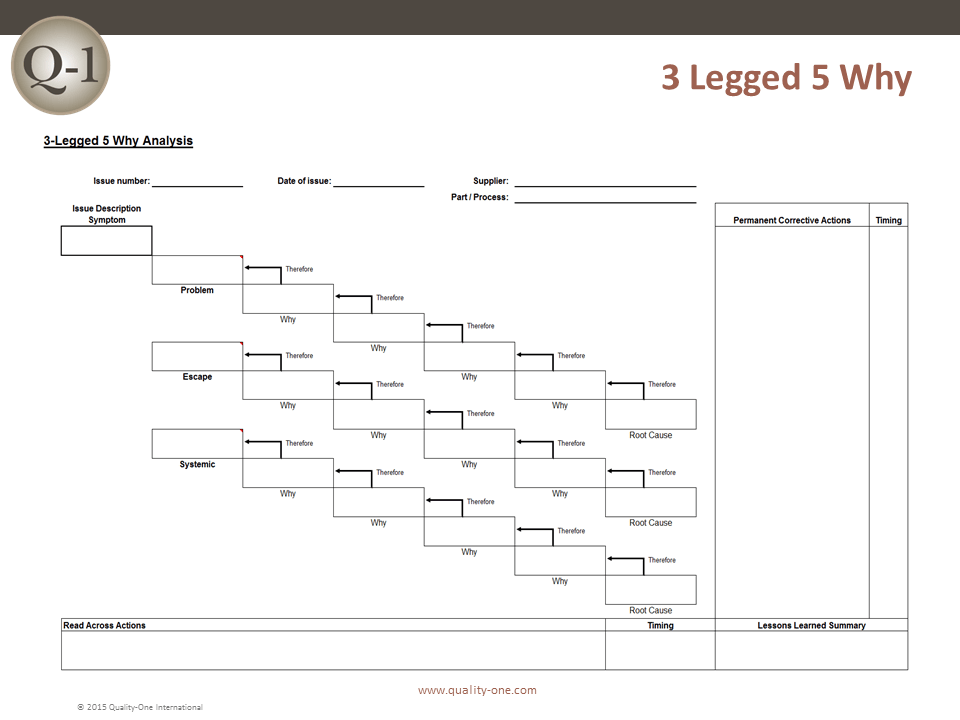
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in
- Application Profiles
- Hartford Global Consulting Services
- Case Studies
- Our History
- Global Team
- Manufacturing Capabilities
- Our Quality
- Who We Work With

- Special Bearings
- Cage Bearings
- Needle Bearings
- Drawn Cup Needle Bearings
- Cage Needle Bearings
- Thrust Bearings
- Plastic Bearings
- Ball & Roller Retainer Assemblies
- Ball Sleeves
- FAQ – Custom Bearing Assemblies
- Chrome Steel Balls
- Stainless Steel Balls
- Carbon Steel Balls
- Brass Balls
- Tungsten Carbide Balls
- Precision Glass Balls
- Plastic Balls
- Small Ball Pack Program
- Balls for Valves
- FAQ – Precision Balls
- Roller Ball Bearings
- Bearing Cages/Separators
- Bearing Races
- Bearing Sleeves / Wear Sleeves
- Needle Bearing Retainers
- Tripot / Tripod Ball – CV Joint
- FAQ – Bearing Parts
- Pins & Shafts
- Knurled Pins
- FAQ – Precision Pins
- Needle Rollers
- Precision Rollers
- Special End Rollers
- Tapered Rollers
- FAQ – Precision Rollers
- CNC Capability
- Agriculture
- Consumer Goods
- Electronics
- Recreational

- Industries & Applications
- Bearing Parts
- Custom Bearing Assemblies
- Precision Balls
- Precision Pins & Rollers
- Capabilities
Hartford Technologies Blog
35 lean manufacturing tools: the ultimate list, what is kaizen.
Kaizen is the Japanese word for “continual improvement.” The term refers to activities that improve every function of a business and is generally applied to manufacturing but can be used to make almost any business more efficient.
By definition, Kaizen includes the involvement of all employees, from upper management to assembly line workers and can be used to improve every process in a supply chain, from purchasing to logistics. The lean manufacturing tool was first used by the Japanese in World War Two and was a major influence of the book “The Toyota Way.”
What is the goal of Kaizen?
Kaizen seeks to improve standardized processes to eliminate waste, fix workflow issues, and solve business problems.
How is Kaizen implemented? The Kaizen method generally involves 5 primary steps:
- Identify the problem area that will be given focus.
- Utilize videotape to analyze the current method.
- Test and evaluate improvement tactics.
- Implement improvements.
- Analyze results and present them to upper management for feedback.
What is Kaizen most applicable to?
The Automotive Industry. The Toyota Production System made the tool famous. If problems occur within the production process, Toyota assembly line personnel and their supervisors are expected to stop the production process and begin a Kaizen.
2) One-Piece Flow

What is One-Piece Flow?
One-piece flow is the sequence of a product or service through a process that is one unit at a time. One-piece flow is the opposite of batch processing, where a large number of products are created at once and they are sent through the manufacturing process as a batch or group. In One-Piece Flow the focus is on the manufacturing of the product itself rather than the waiting, transportation, and storage of the product.
What are the advantages of One-Piece Flow?
The advantages are:
- Ability to detect defects earlier and more accurately.
- More flexibility for customization and meeting customer demands.
- Reduces costs by eliminating waste.
- Reduce the amount of work in progress to make each step more efficient.
- Easier to predict shipment times.
To increase efficiency, companies can choose to implement One-Piece Flow or simply reduce the number of products produced in a batch.
What is Jidoka?
Jidoka was invented in 1896 and was used to stop the shuttle of an automatic loom in a case where a thread broke. Not only did this reduce the number of defects when threading, it allowed operators to operate multiple looms at once instead of having to watch only one in case something went wrong. It is essentially automation with a human element.
What are the principles of Jidoka?
The principles can be broken down into four steps:
- Discover an abnormality or problem.
- Stop the operation process.
- Fix the problem at hand.
- Discover the root cause to prevent future issues.
The primary innovation Jidoka brought to lean manufacturing is the idea of examining a manufacturing issue in the middle of the process rather than at the end. Inspecting throughout the manufacturing process can play a key role in preventing defects and fixing problems before they cause significant damage.
4) Poka Yoke
Source: medium.com
What is Poka Yoke?
Poke Yoke was developed by Toyota and is very similar to Jidoka. The idea of Poka Yoke is to prevent mistakes from becoming defects. Mistakes, it argues, are inevitable, but defects that reach customers are preventable. The goal is to create a form of quality control that highlights defects automatically and eventually takes humans out of the equation.
Why use Poka Yoke?
The tool was invented because of human error. Humans who perform repetitive manufacturing tasks day in and day out can very easily miss common mistakes and defects. Automation was necessary to improve the manufacturing process.
A real-life example of Poka Yoke? An alarm that goes off automatically when you leave a car without turning off the headlights. Another example is a conveyor belt that rejects an underweight product. The goal is to prevent mistakes automatically, without human inspection.
5) Visual Management
What is visual management.
Visual Management is a communication technique that uses visual aids to convey messages quicker and more efficiently
What is the goal of Visual Management?
The objectives of Visual Management are:
- Clarify waste.
- Display problems in a simpler way.
- Indicate your efficiency goals.
- Increase effective communication.
An example of Visual Management? Stock controls, auditing boards, and shadow boards. Oftentimes, visual management can improve communication and help improve efficiency. Other times, visual aids can become confusing and too much to remember.
Where is Visual Management best applied? Work instructions can often be simplified and far easier to understand when visual aids are included. For example, if a work must build a piece of furniture from multiple parts, it will often be better understood in a visual format. It is particularly useful for tasks that are difficult to explain with words alone. Another example may be showing works a picture of a completed task.
What is Kanban?
Kanban is the Japanese word for “Signal Card.” In previous decades, manufacturing workers would fill out a signal card when a part was running low. The signal card would be sent to a team or employee whose job was to order more of that part. Today, this process is mostly computerized. The idea of Kanban is to buy more parts only when needed.
The goal of Kanban? The primary goal of Kanban is to reduce waste. If parts are only bought when needed, you are less likely to waste time, money, or space ordering unnecessary parts. However, if parts are bought automatically, without knowing if they are needed, it can cut into a company’s profits.
The strategy creates more efficient processes because the strategy is implemented based on consumer demand. If there is a lot of demand for a product only then should you order more. If there isn’t sufficient demand, companies can prevent unnecessary orders.
7) Demand Management
Source: fourquadrant.com
What is Demand Management?
Demand Management is a lean tool used to identify all demand coming from an external environment, manage it, and input it into a supply chain within a company.
The goal of Demand Management:
Demand Management has three primary goals:
- Improve forecast accuracy.
- Lessen investment in inventory.
- Create a more effective balance between supply and demand.
How is Demand Management implemented? The main element of implementing Demand Management is creating a more transparent supply chain. Companies must ensure transparency from all suppliers working with a company, from the largest to the smallest. By ensuring that every player in the supply chain is transparent, you can begin to create a more efficient supply chain.
Next, companies must determine, which inventory is unnecessary and can be reduced. Having too much inventory is expensive and difficult to maintain. Ultimately, this technique gets products out to consumers more efficiently.
8) Heijunka
What is heijunka.
Heijunka is the Japanese word for “leveling.” Heijunka is meant to level the type and quantity of production, while reducing batching. Ford Motor was once known for manufacturing cars in batches. Toyota used Heijunka to minimize batching and create a more efficient manufacturing process.
What is the goal of Heijunka? To reduce inventories, capital costs, manpower, and production time to a minimum.
When is Heijunka implemented? According to many lean experts, Heijunka is best implemented after a company has already implemented more basic lean principles?
What’s a good example of Heijunka? Say a hat manufacturer receives 500 orders for hats every week. 100 on Monday, 50 on Tuesday, 50 on Wednesday, and 300 on Thursday. Instead of manufacturing 500 hats at the beginning of the week or the exact amount needed each day, the company would produce exactly 100 hats per-day. By producing the same amount every day, the factory can optimize the manufacturing process for 100 hats and therefore create a more efficient process.
9) Just in Time
What is just in time.
As you could probably guess, Just in Time is a lean tool that calls for the production of what a customer wants, when they want it, in the quantity they want it, and where they want it. Instead of creating a large stock of a product that sits in warehouses, you only create as much of an item as a customer actually wants. This reduces unnecessary inventory and ensures that companies only spend on stock that will be paid for.
What is the history of Just in Time?
Just in Time was invented by Toyota during WWII. The tool was invented at a time when producing extra stock was simply too expensive and not possible. Companies could only afford to produce what a customer actually wanted.
The idea for Just in Time came from a visit to US supermarkets by Toyota managers. They noticed that shelves were only filled when a product ran out, not before that.
10) Takt Time
what is takt time.
What is the goal of Takt Time? The goal of Takt is to deliver the right product to the right customer at the right time, all with minimal waste. It ensures that products are manufactured in the most efficient way, while meeting consumer demand.
Another goal of Takt Time is to create a solid flow of operations within a supply chain. Measuring Takt Time will allow managers to determine capacity and synchronization issues within a supply chain and then find proper solutions.
Example of Takt Time? Here is an example:
Total Time: 8 Hrs X 60 Min = 480 Min
Breaks: 50 Min
Time Available : 430 Min
Customer Demand in 8 Hrs: 100 Pieces
Takt Time: 430 / 100 = 4.3 Min = 258 Sec
11) Bottleneck Analysis
What is a bottleneck, the goal of bottleneck analysis.
When should Bottleneck Analysis be implemented? When managers or operators suspect that the manufacturing process is taking too long. At this point, managers will try to determine exactly where the bottleneck is occurring.
What is Andon?
How is it used? In manufacturing, Andon lights are generally used in assembly lines. Different colored lights are used to signal different problems and actions required. Operators may turn on an Andon in order to signal that there is a problem in an assembly line. In an office setting, a red colored light (Andon) may signal that a fax machine or printer is broken.
In cars, warning lights on a car’s dashboard would be examples of Andons. Andons work best when they are highly visible and easy to understand. They must go hand in hand with an action. So, for example, an Andon warning light on a car that signals low gas, would indicate a clear action: fill up the tank with more gas.
Source: agileleanhouse.com
What is Gemba?
How is Gemba implemented?
Gemba is a step by step process:
- Engineers physically go to manufacturing floor to observe processes.
- Engineers collect data and understand the work being done
- Engineers ask questions.
- Engineers learn about problems and come up with solutions.
Gemba Walks refer staff taking the time to walk through the factory, examine what is going on, and determine if there are any issues. In the lean management philosophy, staff are expected to do Gemba Walks at least once a week.
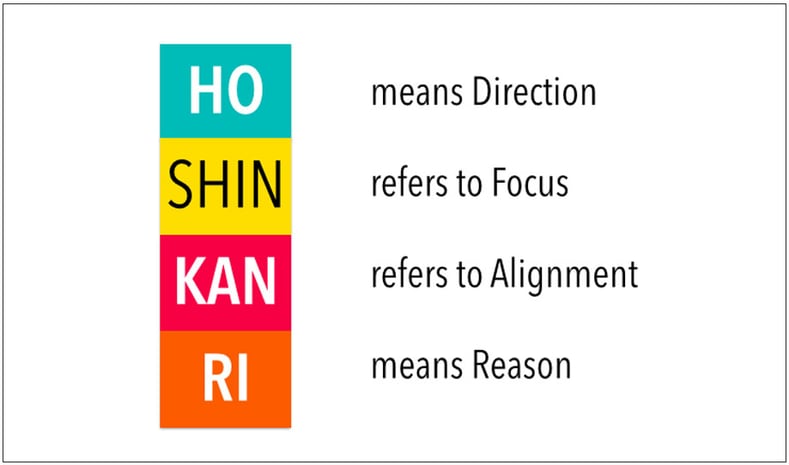
What is Hoshin Kanri?
What is the goal of Hoshin Kanri? The goal of Hoshin Kanri is to determine your strategic objectives and then align them with specific resources and action plans to meet those objectives.
What are the 7-steps of Hoshin Kanri?
The 7-steps of Hoshin Kanri:
- Determine an organizational vision. Figure out what your current mission and long-term vision is.
- Establish breakthrough objectives. Determine what significant improvements a business needs in the next three to five years.
- Come up with annual objectives to complete on a yearly basis.
- Determine metrics to measure objectives.
- Implement objectives.
- Review objectives monthly. Determine your progress each month to see where your business needs improvement.
- Review objectives yearly. Determine your progress each year to see where your business needs improvement.
15) Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Source: wikihow.com
What is OEE?
OEE is a system used to measure manufacturing productivity. It measures the percentage of time that a manufacturer is truly productive. So, a 100% would mean that a manufacturer is productive 100% of the time. OEE includes measurement of quality, performance, and availability.
What is the goal of OEE?
By measuring productivity in terms of time, manufacturers can gain insight into how to improve overall manufacturing performance. The system helps to identify waste, track progress, and improve manufacturing equipment efficiency.
What do quality, performance, and availability really mean?
- Quality measures the number of defects. A 100% score indicates that there are zero defects.
- Performance measures slow cycles and stops. A 100% score indicates everything is running as quickly as possible.
- Availability takes into account any stops. A 100% score indicates that the process is always running during set production times.
16) Cellular Manufacturing

What is Cellular Manufacturing?
Cellular Manufacturing is the process of producing similar products in one cell. The product, in Cellular Manufacturing, moves through the production process in a single unit without interruptions. In Cellular Manufacturing, similar products can be produced on the same assembly line.
What are the benefits of Cellular Manufacturing?
The benefits of Cellular Manufacturing include:
- Group similar products together to reduce the time of changeover.
- Effectively utilize space during the entire production process.
- Increase flexibility and transparency.
- Reduce lead time.
- Increase overall productivity.
- Enhance teamwork and communication between employees and departments.
Example of Cellular Manufacturing? A metallic case arrives in a factory and needs to be assembled. Assembly requires a variety of different steps. The goal of Cellular Manufacturing is for all the steps to occur in one area, in a single cell. This reduces the time it takes to transport the parts during the production process.
17) Continuous Improvement
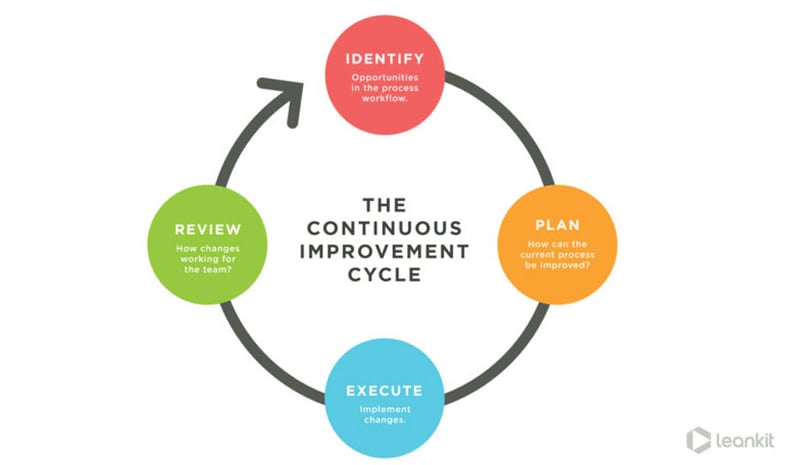
Source: mktgcdn.leankit.com
What is Continuous Improvement?
Continuous Improvement is a methodology within lean manufacturing that advocates following formal practices to improve efficiency over time.
What are the benefits of Continuous Improvement?
The benefits of Continuous Improvement include:
- Efficient workflows.
- Saves time.
- Reduces cost.
- Reduces resources needed.
How is Continuous Improvement implemented? Continuous Improvement is implemented in four steps:
- Figure out what needs improvement and create a plan.
- After the plan is complete, implement the plan.
- Collect data to figure out if the plan worked and if it needs improvement.
- Once the plan has worked on a small scale, implement it on a wider scale.
18) Total Productive Maintenance
Source: nevilleclarke.com
What is Total Productive Maintenance?
Total Productive Maintenance is a lean tool used to prevent machine downtime within the production process. The goal is to limit downtime as much as possible to increase production efficiency
How is Total Productive Maintenance implemented?
Total Productive Maintenance includes three main components:
- Preventative maintenance. These included planned maintenance activities that are regularly scheduled. The crew will perform these periodically throughout the year. It includes checking all equipment for problems and fixing any issues. The goal is to prevent problems before they occur.
- Corrective maintenance. Managers and crew check equipment and determine whether problematic equipment needs to be replaced altogether. Oftentimes, it is more cost-effective to replace equipment before they break. Replacing equipment can often increase efficiency and profits.
- Maintenance prevention. This procedure makes sure that all equipment bought is exactly what’s needed. Buying faulty or incorrect equipment can result in increased maintenance responsibilities and and production inefficiencies down the line.
19) Total Quality Management
Source: smartsheet.com
What is Total Quality Management?
Total Quality Management is an organizational effort to improve the quality of a manufactured product. The goal is to increase the quality of every single step in an organizational workflow.
What are the origins of Total Quality Management? Total Quality Management was first implemented in 1923 by Walter Shewhard while he was working at Bell Telephone Laboratories. It was later used by Japanese Manufacturers and implemented on a mass scale in the 1980s.
What are the principles of Total Quality Management?
There are a few main principles of Total Quality Management:
- Focus on the customer. The goal of Total Quality Management is to improve the product offered to customers and therefore keep customers satisfied.
- Strategy. Total Quality Management requires a strategic approach that utilizes a set methodology.
- Continuous improvement. Ensuring quality takes time and it must be analyzed and improved annually.
20) Root Cause Analysis
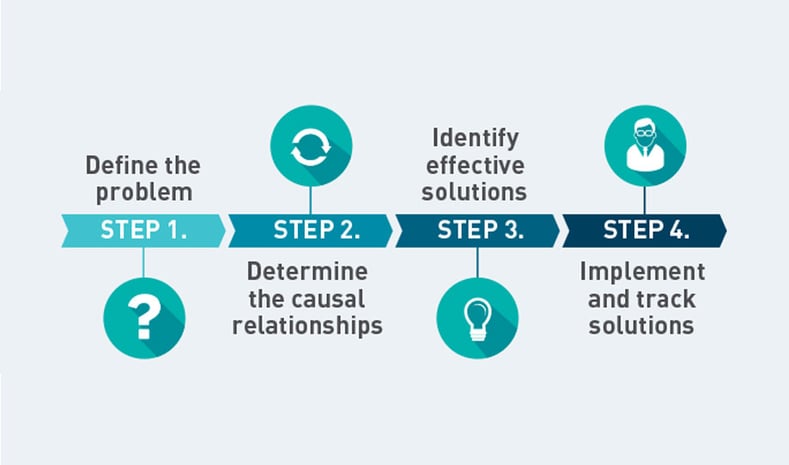
Source: apollorootcause.com
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis is a lean problem-solving method that aims to get to the root of a problem. The philosophy of RCA is predicated on the idea that it’s best to treat the root cause of a problem, not the obvious symptoms. By treating the root cause, manufacturers can eliminate larger problems down the road. Still, Root Cause Analysis will generally not fix problems in one try and is generally an iterative process.
What are the main principles of Root Cause Analysis?
The main principles of Root Cause Analysis include:
- Root Cause Analysis aims to identify the root cause of a problem to prevent it from ever occurring again. It’s a long-term solution.
- Root Cause Analysis must be an investigative and systematic process to work effectively.
- Every problem only has one root cause.
21) Value Stream Mapping
What is value stream mapping.
Value Stream Mapping is a lean tool that uses a flow diagram to depict every step of a process.
What is Value Stream Mapping used for?
Value Stream Mapping serves three main purposes:
- Identify waste.
- Reduce manufacturing time.
- Make the entire manufacturing process more efficient.
What is Value Stream Mapping applicable to? Value Stream Mapping can be applicable in almost any industry, but it is primarily used for logistics, supply chain, product development, and administrative processes.
What data should be collected to create a Value Stream Mapping? Some data points to collect for Value Stream Mapping include:
- Number of operators.
- Number of shifts worked.
- Batch size.
- The time it takes to make one product.
- The time it takes to switch from one product to the next.
- How much time factory can run.
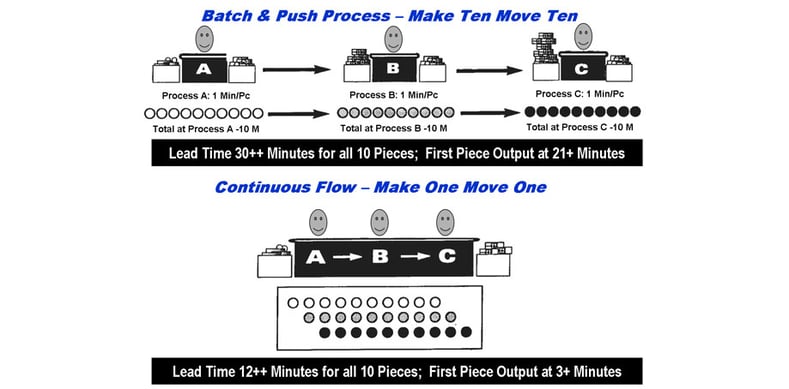
Source: agilelea.com
What is Continuous Flow?
Continuous Flow is the opposite of batch production and is closely associated with Kanban and Just-in-Time. The goal of Continuous Flow is to use ongoing examination and improvement to integrate all elements of production. By aiming for a Continuous Flow production process, waste and other problems come to the surface and can then be solved. Ultimately, many lean principles and tools center around creating a Continuous Flow production process.
The Continuous Flow process generally involves a factory running 24/7 without interruption and with little waste. Areas like oil refining, metal smelting, and natural gas processing are ideal for the Continuous Flow process.
What are the benefits of Continuous Flow?
The benefits of Continuous Flow include:
- Continuity.
- Waste-less process.
- No time wasted.
23) Lean Audit

Source: exegens.com
What is a Lean Audit?
A Lean Audit is a tool used to determine how well lean manufacturing principles are working in a factory or company.
How is a Lean Audit implemented?
A Lean Audit generally has 5 steps:
- Identify the objective of your audit. This involves determining what lean processes you are already using and coming up with metrics to decide how well they are working. The goal of a lean audit should be to improve overall efficiency, reduce waste, and lower production costs.
- Determine who will conduct the audit. Lean Audits are best performed by a third party team in order to ensure objectivity, however, senior management may choose to conduct the audit internally.
- Create a point system to measure progress.
- Use a system to perform the audit. Ideally, a Lean Audit will be performed using lean principles.
- Follow up with the audit to ensure that all problems get fixed. Ideally, Lean Audits should be performed on a small-scale monthly and on a large-scale yearly.
24) Quick Changeover
What is quick changeover.
Changeover is the amount of time it takes to change a piece of equipment between the production of one item to the next. In Lean, the goal is to ensure a Quick Changeover.
An example of Quick Changeover?
A pit crew at a car race is a great example of a Quick Changeover. The quicker a crew can a changeover, the better chance a racer has of winning. A slow changeover will often result in losing a race.
What are the benefits of Quick Changeover?
The main benefits of Quick Changeover are:
- Reduce the amount of defects.
- Reduce inventory costs.
- More production flexibility.
- Better chance of on-time delivery.
25) Right First Time
What is right first time.
Right First Time is a lean philosophy that stresses getting processes right the first time, every time. The concept involves planning and a deep understanding of manufacturing processes.
How is Right First Time implemented?
Right First Time has 3 primary steps:
- Track performance. The first step of Right First Time is figuring out how often you’re getting your manufacturing processes right the first time. Search for areas in the manufacturing process where things do not go smoothly the first time around. By identifying the problems, you can figure out where your manufacturing processes need work.
- Improve performance with a systematic process. Often, the biggest problem manufacturers have is human error. The more systematic a process becomes, the more likely you can get things right the first time.
- Identify areas of waste and use the Right First Time tool to cut them out. Main areas to focus on include inventory, overproduction, defects, and transportation.
26) 7 Wastes Source: blog.triaster.co.uk
What is 7 wastes.
In lean manufacturing, 7 Wastes refers to seven typical places manufacturers have waste. Using the 7 Wastes tool, manufacturers can determine where they have waste and can improve their processes in each area. The method was invented by Toyota and is an integral part of the Toyota production system.
What are the 7 Wastes?
The 7 Wastes are as follows:
- Overproduction. Overproduction refers to producing a product before it is needed. In the Toyota production system, products are produced only when there is customer demand.
- Waiting. Waiting refers to the time between one operation and the next.
- Transporting. Transportation adds no value to a product and only too much transporting only increases the risk of defects.
- Inappropriate processing. This refers to using overly expensive equipment to accomplish tasks that can be processed by simpler and most cost-effective equipment.
- Unnecessary inventory. The goal is to reduce inventory to what’s needed.
- Excessive motion. Human motion should be reduced in the manufacturing process.
- Defects. Reducing defects is crucial for reducing costs.
27) Six Big Losses
Source : e-qms.co.uk
What are the Six Big Losses?
Six Big Losses refers to the six most common reasons for ineffective production. TPM and OEE are generally used to eliminate the Six Big Losses.
- Breakdowns. Breakdowns refer to machine failure and the need for intensive maintenance.
- Setup/Adjustment. Setup/Adjustment refers to changeover and machine warm-up.
- Idling. Idling refers to jams, obstructions, and cleaning.
- Speed. Speed refers to operator efficiency and machine wear down.
- Defects in process and rework. Defects refer to product damages and the need for corrections.
- Start-up losses. Start-up losses refer to improper assembly and losses due to product defects.
28) SMART Goals
What are smart goals.
SMART Goal is a method to set goals productively. To effectively use lean manufacturing methods, management must set proper goals to strive for. Ideally, those goals should be clearly defined and communicated.
What does SMART stand for? For a goal to be achieved it should be:
- Specific. A goal should be concrete and based on facts and figures.
- Measurable. Results must be quantified with clear numbers.
- Attainable. Goals should be attainable and not too ambitious. Impossible goals hurt employee morale.
- Realistic. Similar to attainable, goals must be set realistically based on available resources and time.
- Time-based. Goals must be given a realistic due date based on available resources.
What are KPIs?
KPI is an acronym for Key Performance Metric and it refers to metrics used to assess and analyze manufacturing efficiency. KPIs are essentially metrics set by management to measure the success of lean manufacturing goals.
What are some common manufacturing KPIs?
Some common manufacturing KPIs include:
- Speed. Measuring speed is essential for increasing efficiency and profits.
- Count. This refers to the amount of product produced.
- Reject ratio. Manufacturing processes will sometimes produce scrap. Reducing scrap is essential for increasing productivity.
- Takt time. This can refer to the amount of time it takes to produce a product or the amount of time it takes for one specific operation. Measuring this can help identify where there are bottlenecks or constraints in the manufacturing process.
- Downtime. Breakdown or machine changeover often causes downtime. Lean seeks to reduce downtime as much as possible.
30) The 5S Method

What is The 5S Method?
The 5S Method refers to five Japanese and English terms that begin with an “S” and provide a workplace organization method.
What does each “S” stand for?
- Sort (Seiri): Decide which items in a factory are necessary and which ones are not. Get rid of the ones that are not.
- Straighten (Seiton): Make sure every item in a factory is in the right place. Items should be easy to find and access.
- Shine (Seiso): Clean the factory regularly. By getting rid of dirt, garbage, etc. you can more easily identify problems in the manufacturing process.
- Standardize (seiketsu): Create standards to ensure a clean and neat factory floor.
- Sustain (shitsuke): Create habits that ensure standards are met over the long term. Set responsibilities for managers and operators to ensure that habits are set.
What is SMED?
SMED stands for Single-Minute Exchange or Die. The goal of SMED is to get all changeovers and startups down to 10 minutes. Each step should be one minute or less. By reducing setup time, factories can greatly improve efficiency. SMED as invented by Frederick Taylor in 1911 and was later used by Ford Motors in 1915.
What are the main principles of SMED?
- Identify all changeover tasks.
- Analyze each task to determine purpose.
- Determine low cost solutions.
- Goal should be to reduce changeover time.
What are the steps to implement SMED? The steps to perform SMED are as follows:
- Separate internal from external setup operations
- Convert internal to external setup
- Standardize functions
- Use functional clamps or eliminate fasteners altogether
- Use intermediate jigs
- Adopt parallel operations
- Eliminate adjustments
- Mechanization
32) A3 Problem Solving
Source: sixsigmaconcept.com
What is A3 Problem Solving?
A3 Problem Solving is a problem solving method that uses a structured, continued growth methodology to improve manufacturing practices. The method was invented by Toyota and is based on the work of Edward Deming.
How is A3 Problem Solving implemented?
A3 Problem Solving has 7 steps:
- Determine what is the company generally trying to fix.
- Analyze the current situation. What is currently being done?
- Decide what the company’s goals are. What specifically will be accomplished?
- Determine what the gap is between current processes and where the company wants to be.
- Come up with possible solutions and determine what the barriers will be.
- Decide on a plan. What will the new process look like?
- Follow up. Track results and figure out what’s working.
What is PDCA?
PDCA stand s for Plan-Do-Check-Act and is a four-step method for creating and carrying out change. The PDCA method is a cycle and is repeated over and over again in order to drive continuous improvement.
When is PDCA used?
PDCA is primarily used when:
- Conducting an improvement project.
- Designing a repetitive work process.
- Developing a new process or product design.
- Implementing changes in the manufacturing process.
What are the PDCA steps?
PDCA steps include:
- Plan. Find an area that needs improvement and plan a change.
- Do. Test the change on a small-scale.
- Check. Check how the test went by analyzing the results and determining what you’ve learned.
- Act. Take action based on what you’ve learned. If the change you made did not work, start from the beginning and determine a different test. Use your failures to determine where you will go next.
34) Standardized Work
Source: truenorththinking.ca
What is Standardized Work?
Standardized Work is a tool used to document current best practices, improve the standard, and ensure that the new standard becomes a baseline for improvement.
What does Standardized Work improve?
Standardized Work improves 3 important aspects of the manufacturing process:
- The rate at which products are produced in order to meet customer demand.
- The operator’s work sequence to produce products at that time rate.
- The standard inventory is needed to ensure a smooth manufacturing process.
What are the benefits of Standardized Work? The main benefits of Standardized Work include:
- Better documentation of current processes.
- Easier training for operators.
- Few injuries and strains.
- Baseline to make improvements.
- Reduces variability.
- Adds discipline to a work culture.
- Promotes problem solving.
- Increases teamwork across the organization.
Source: qualityaretegroup.com
What is 5 Whys?
5 Whys is a lean method used to determine the root cause of a problem. Managers repeat the question “Why?” and each answer forms a basis for the next question. This process continues until a conclusion is reached. The 5 Whys technique was developed by Sakichi Toyoda and has been used by Toyota to improve its manufacturing processes. The 5 Whys technique generally requires persistence and determination for it to work effectively.
What are the rules surrounding 5 Whys?
In order to properly perform 5 Whys, managers should follow a variety of rules:
- Use paper or a whiteboard, not a laptop or computer.
- Clearly define the problem and make sure every team member understands it.
- Use a step-by-step process to find the root cause. Avoid jumping to conclusions.
- Identify what the causes are, not the symptoms.
- Use logic, not emotion.
- Focus on making sure answers are as precise as possible.
- Use the customer’s point of view when answering the “Why” questions.
- Facts and knowledge should be the basis for each answer.

Subscribe to Email Updates
Posts by topic.
- Precision Ball (27)
- Engineering Trends (23)
- Procurement Trends (21)
- Custom Bearings (20)
- Medical Manufacturing (20)
- Quality Control (13)
- CNC Machining (11)
- News & Updates (11)
- Bearing Parts (10)
- Lean Manufacturing (9)

Featured Resources

The 8-Step Problem-Solving Method

- November 22, 2021
Table Of Contents
What is the 8-step problem-solving method, the 8 steps and the problem-solving process, the culture of problem-solving.
- Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA)
- Gain Problem-Solving Support
As a manufacturing professional, you know how important it is to stay organized, keep your goals in mind and strive for success. But with all of the responsibilities and daily tasks piling up, it takes effort to find and stick to a process that can keep you on track.
Luckily, there’s a tried and trusted way to achieve success in the manufacturing industry.
The eight-step problem-solving process is a structured method that guides you through the various steps of solving issues. Unlike other problem-solving processes that are often broad, the eight-step method takes you through each individual step, from identifying the problem to taking actionable steps to success.
Instead of changing a few things at a middling level that will probably break down again later, you can unearth the roots of problems and build success from the ground up.
For a fundamental breakdown of how to fix problems and lead your manufacturing team to success, here are the eight steps of the problem-solving process.
1. Identify the Problem
The first step in the process is to identify the problem. Identify why this is a problem, how you discovered it and how it impacts your business. Also note when the problem started and how long it has been going on.
If the problem is small, you can try to contain it and may not need additional steps to fix it. However, if the problem is complex, move forward through the process.
2. Define the Problem
The next step involves breaking down the problem and defining what it is. It’s important to be as clear as you can with this step — a vague problem will hinder the process, whereas a clearly defined issue will allow you to take actionable steps to fix it.
Analyze factors like how high of a priority it is to solve the problem. You can also look to data and other resources to clarify or help you understand the concern.
3. Make a Goal
Create an end goal. Envision what fixing this problem would look like and feel like. What would it accomplish? How would it help you? Map out all the ways fixing this problem would benefit you and use it for motivation to achieve your goal. Set a timeline to figure how long it will take to accomplish that goal.
4. Find the Root of the Problem
Often problems are byproducts of deeper, more central problems, so make sure you dig deep enough to find out what is really causing the issue. If the problem is large and complex, break it down into individual parts.
Gather information and use it to identify the deeper issues of the problem and validate what you think the real concern may be. Take time at this step to really focus on the deep problem — executing this step effectively will save you a lot of time down the road.

5. Develop Actionable Steps
Create a list of realistic steps you can take to combat the problem. You can start with a large list and combine or subtract steps, but it’s important you come up with various ways to attack the problem. Use this action plan to draw up a strategy to get at the root of the problem. Each step should be specific and detail-focused — any steps that are vague or tedious will only take up time and cause confusion.
6. Execute Steps
Now that the plan is in place, all you have to do is follow through on your actionable steps. Illustrate the steps you’re taking to your team, explain why you’re taking them and delegate any steps that another employee has to perform to execute your plan.
Communication is key in this step. In most cases, you won’t be executing the plan all by yourself, so make sure you’re expressing the goals and motives of each step with your team so they can see how it connects to the bigger picture.
7. Observe and Evaluate
Monitor your strategy carefully and see how it relates to the original problem. Is it working? Is it only creating more problems? Gather data, talk to your team and be thorough and objective in your evaluation. You might have to readjust your plan as you gain new information, or you may meet your goals and the plan will be successful.
8. Continue the Process
If the plan worked, find ways to continue integrating these steps into your team’s daily routine. If they didn’t work, go back to the goal-setting process or identify some more aspects of the problem — there may be a deeper concern you missed the first time around. Communicate to your team about how the plan went.
In the future, continue using the eight-step process to solve issues and build momentum with your team.
It’s important to build a culture of problem-solving in your manufacturing plant. It can be easy to fall into the trap of “Band-Aid” solutions — quick fixes without digging into the deeper problems.
It’s believed that the eight-step problem-solving process was actually created by the Toyota Motor Corporation to achieve their admired production standards.
From the lore of Toyota, we get some great eight-step problem-solving examples. Taiichi Ohno , the father of the Toyota Production System, observed his workers fixing only the first level of cause when their machines stopped working. To combat this, he developed a problem-solving method to methodically break down each problem of the machine until he found the root cause. Only then could he truly fix the machine.
It’s one of many eight-step problem-solving examples, and it shows the importance of creating a process to increase productivity.
Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) and the 8-Step Problem-Solving Process Differences
The eight-step problem-solving process is an expanded version of the Plan, Do, Check, Act cycle . The first five steps of the 8-step process fall under the planning step, while steps six, seven and eight all correspond to the do, check and act steps. The eight-step process is a more detailed, methodical version of PDCA problem-solving, and converts a vague cycle into something a bit more specific and actionable.

Gain the Problem-Solving Support You Need With MANTEC
MANTEC is the best resource center for manufacturing companies in South Central Pennsylvania. We’re a non-profit that solves any problems a manufacturing facility could have, including sales and marketing , process improvement , manufacturing technology and workforce engagement .
Our expert staff has had vast experience in the manufacturing industry, and we can provide the guidance you need to get your business running at top efficiency. Our services are affordable and extremely valuable. Contact us today!
Related Posts

In the dynamic landscape of business, achieving and maintaining an International Organization for Standardization (ISO)…

Manufacturers need to build agility into their businesses and processes to respond and recover faster…

Understanding market trends and consumer behaviors become more critical as the world becomes increasingly digitized.…

- Subscribe Today!
- Current Issue
- Machinery Lubrication Level 1
- Machinery Lubrication Level 2
- Oil Analysis Level 2
- Oil Analysis Level 3
- Machinery Lubrication Engineering
- Online Training
- International Training
- Reliable Plant Conference
- Machinery Lubrication Conference
- Buyer's Guide

Problem-solving techniques for a high-performance team
While most people associate lean with tools and principles such as value stream mapping, one-piece flow, kanban, 5-S, Total Productive Maintenance and kaizen events, few people think about the more mundane aspects of lean. Problem solving is one of the keys to a successful lean implementation because it empowers all of those involved.
Lean manufacturing has a unique way of solving problems. It does not just look at the effect of the problem and try to cover it with a Band-Aid. Rather, the root cause of the problem is identified and the root cause, as well as all contributing factors, is eliminated from the system, process or infrastructure in order to permanently solve the problems. What is the difference in these two approaches? Simple, when you find and rectify the root causes, the problem will be solved forever. Even other problems occurring due to these root causes will be eliminated in this effort.
It is very clear now that we must find out the root causes of the problems before we think about rectifying them in lean manufacturing environments. So, how should we do this? What are the tools available to perform these tasks? Let’s look at what problem solving is about. We’ll begin by asking the question: “What is a problem?” A good definition of a problem is a variation from a recognized standard. In other words, you need to know how things should be before you can recognize a possible cause for them not being that way. After a problem has been recognized, a formal problem-solving process should be applied.
High performance work teams typically use four problem-solving tools: 1. Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) 2. 5-Why Analysis 3. Ishakawa (Fishbone) Diagram 4. Simplified Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (SFMEA)
Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) The Deming PDCA cycle provides effective guidelines for successful problem solving. The cycle includes:
Plan Clearly Define the Problem (P1) “A problem clearly stated is a problem half solved”. Although it seems like a trivial step, the team should not take this step lightly. It is important to begin this problem-solving journey with a clear, concise problem statement. If this is not done properly, it could lead to one of the following: excessive time in cause identification due to a broad problem statement, predisposing the team to a particular solution, or problem solving turns into solution implementation rather than root-cause identification and remedy.
Collect Evidence of Problem (P2) This activity focuses on obtaining information/data to clearly demonstrate that the problem does exist. In the case of team problem solving, this should be a quick exercise since the reliability engineering function must have been looking at data in order to create the team. The output of this activity will be a list of evidence statements (or graphs) to illustrate that the problem exists, its size and the chronic nature of it.
Identification of Impacts or Opportunities (P3) This part of the Plan segment focuses on identifying the benefits if this problem solving is successful. This activity needs to be thought of in two different perspectives because Project Team work can take the form of control work, e.g. fixing a problem that stands in the way of expected results or pure improvement (attempting to take results to a new level of performance). In each case the output of this activity will be a list of statements. The impact statements and opportunity statements should be stated in terms of loss of dollars, time, “product”, rework, processing time and/or morale.
Measurement of Problem (P4) Before problem solving proceeds, it is important for the team to do a quick check on the issue of how valid or reliable the data is on which the team is making the decision to tackle the problem. For the parameter(s) that are being used as evidence of the problem, is there any information known by the team that would question the validity, accuracy or reliability of the data? This question should be examined whether we are relying on an instrument, a recorder or people to record information or data. If the team suspects that there are significant issues that “cloud” the data, then these measurement problems need to be addressed, fixed and new measures obtained before proceeding with the other segments of PDCA.
Measure(s) of Effectiveness (P5) At this point, the team needs to identify how they intend to measure success of their problem-solving efforts. This is one of the most important steps in PDCA and one that certainly differentiates it from traditional problem solving . The strategy is to agree on what and how, to obtain the benchmark “before” reading, perform the PDCA activities and re-measure or obtain the “after” measure. At that point, the team will need to decide whether they need to recycle through PDCA in order to achieve their pre-stated objective.
Do Generate Possible Causes (D1) To avoid falling into the mode of solution implementation or trial and error problem solving, the team needs to start with a “blank slate” and from a fresh perspective lay out all possible causes of the problem. From this point, the team can use data and its collective knowledge and experience to sort through the most feasible or likely major causes. Proceeding in this manner will help ensure that the team will ultimately get at root causes of problems and won’t stop at the treatment of other symptoms. The best tool to facilitate this thinking is the Cause and Effect Diagram done by those people most knowledgeable and closest to the problem.
Broke-Need-Fixing Causes Identified, Worked On (D2) Before proceeding to carry out either an Action Plan (for Cause Remedies) or an Experimental Test Plan, there are often parts of the process that are “broke”. This could take on many different forms.
Write Experimental Test or Action Plan (D3/4) Depending upon the type of problem being worked on, the PDCA strategy will take one of two different directions at this point. The direction is based on whether it is a “data-based” problem or “data-limited” problem. Shown in the table below is the distinction between these two strategies and in particular, the difference between an Action Plan and Experimental Test Plan. Note that in some cases, it will be necessary to use a combination of Action Plans and Experimental Test Plans. That is, for some cause areas an Action Plan is appropriate and for other causes within the same problem, carrying out an Experimental Test Plan is the best route.
Write Action Plan for Cause Remedies (D3) In order to get to the point of writing the Action Plan, the team needs to brainstorm possible solutions or remedies for each of the “cause areas” and reach consensus on the prioritized solutions. This work can be carried out as a team or split into sub-teams. Either way, the entire team will have to reach agreement on proposed remedies and agree to the Action Plan. The Action Plan will be implemented in the Check segment.
Write Experimental Test Plan (D4) The Experimental Test Plan is a document which shows the experimental test(s) to be carried out. This will verify whether a root cause that has been identified really does impact the dependent variable of interest. Sometimes this can be one test that will test all causes at once or it could be a series of tests.
Note: If there is a suspicion that there is an interaction between causes, those causes should be included in the same test.
The Experimental Test Plan should reflect:
Time/length of test
How the cause factors will be altered during the trials
Dependent variable (variable interested in affecting) of interest
Any noise variables that must be tracked
Items to be kept constant
Everyone involved in the Experimental Test Plan(s) should be informed before the test is run. This should include:
Purpose of the test
Experimental Test Plan (details)
How they will be involved
Key factors to ensure good results
When solutions have been worked up, the team should coordinate trial implementation of the solutions and the “switch on/off” data analysis technique.
Resources Identified (D5) Once the Experimental Test Plan or the Action Plan is written, it will be fairly obvious to the team what resources are needed to conduct the work. For resources not on the team, the team should construct a list of who is needed, for what reason, the time frame and the approximate amount of time that will be needed. This information will be given to the Management Team.
Revised PDCA Timetable (D6) At this point, the team has a much better feel for what is to be involved in the remainder of its PDCA activities. They should adjust the rough timetables that had been projected in the Plan segment. This information should be updated on the team Plan, as well as taken to the Management Team.
Management Team Review/Approval (D7) The team has reached a critical point in the PDCA cycle. The activities they are about to carry out will have obvious impact and consequences to the department. For this reason, it is crucial to make a presentation to the Management Team before proceeding. This can be done by the team leader or the entire team. The content/purpose of this presentation is:
Present team outputs to date
Explain logic leading up to the work completed to date
- Present and get Management Team approval for
− Measure of Effectiveness with “before” measure − Priority causes − Action Plan (for Cause Remedies) or Experimental Test Plan − Revised PDCA timetable
Check Carry out Experimental Test or Action Plan (C1/C2) Depending upon the nature of the problem, the team will be carrying out either of these steps:
Conduct Experimental Test Plan(s) to test and verify root causes or
Work through the details of the appropriate solutions for each cause area. Then, through data, verify to see if those solutions were effective.
Carry out Action Plan (C1) In the case of Action Plans, where solutions have been worked up and agreed to by the team, the “switch on/switch off” techniques will need to be used to verify that the solutions are appropriate and effective. To follow this strategy, the team needs to identify the dependent variable – the variable that the team is trying to impact through changes in cause factors.
Carry out Experimental Test Plan (C2) During the Check segment, the Experimental Tests to check all of the major prioritized causes are to be conducted, data analyzed and conclusions drawn and agreed to by the team.
Analyze Data from Experimental or Action Plan (C3) Typically, one person from the team is assigned the responsibility to perform the analysis of the data from the Test Plan. When necessary, this person should use the department or plant resource available to give guidance on the proper data analysis tools and/or the interpretation of outputs. The specific tools that should be used will depend upon the nature of the Test Plan.
Decisions-Back to Do Stage or Proceed (C4) After reviewing the data analysis conclusions about the suspected causes or solutions that were tested, the team needs to make a critical decision of what action to take based on this information.
Implementation Plan to Make Change Permanent (C5) The data analysis step could have been performed in either of the following contexts:
After the Action Plan (solutions) was carried out, data analysis was performed to see if the dependent variable was impacted. If the conclusions were favorable, the team could then go on to develop the Implementation Plan.
The Experimental Test Plan was conducted; data was analyzed to verify causes. If the conclusions were favorable (significant causes identified), the team must then develop solutions to overcome those causes before proceeding to develop the Implementation Plan. (e.g., It was just discovered through the Test Plan that technician differences contribute to measurement error.)
Force Field on Implementation (C6) Once the Implementation Plan is written, the team should do a Force Field Analysis on factors pulling for and factors pulling against a successful implementation – success in the sense that the results seen in the test situation will be realized on a permanent basis once the solutions are implemented.
Management Team Review/Approval (C7) The team has reached a very critical point in the PDCA cycle and needs to meet with the Management Team before proceeding. This meeting is extremely important, because the team will be going forward with permanent changes to be made in operations. The Management Team not only needs to approve these changes but also the way in which they will be implemented.
Act Carry out Implementation Plan (A1) If the team has written a complete, clear and well thought through Implementation Plan, it will be very obvious what work needs to be done, by whom and when to carry out the Act segment of the PDCA cycle. The team should give significant attention to assure communications and training is carried out thoroughly, so department members will know what is changing, why the change is being made and what they need to do specifically to make implementation a success.
Post-Measure of Effectiveness (A2) After all changes have been made and sufficient time has passed for the results of these changes to have an effect, the team needs to go out and gather data on all of the Measures of Effectiveness. The data then needs to be analyzed to see if a significant shift has occurred .
Analyze Results vs. Team Objectives (A3) In the previous step, the team looked at whether the Measure(s) of Effectiveness had been impacted in any significant way by the permanent implementation of the changes. The team cannot stop here. If the answer to that question is favorable, then the team needs to verify if the amount of improvement was large enough to meet the team objective.
Team Feedback Gathered (A4) Once the team decision has been made that the PDCA cycle has been successfully completed (based on Measure of Effectiveness change), the team needs to present this information to the Management Team. Before this is done, the team leader needs to gather feedback from the team. This feedback will be in the form of a questionnaire that all team members (including the team leader) should fill out. The results will be tallied by the team leader and recorded on form A3.
Management Team Close-out Meeting (A5) Before disbanding, the team needs to conduct a close-out meeting with the Management Team. The major areas to be covered in this meeting are:
Wrap up any implementation loose ends
Review Measure of Effectiveness results, compare to team objective
Ensure team documentation is complete and in order
Share team member feedback on team experiences (standardized forms and informal discussion)
5-Why Problem Solving When you have a problem, go to the place where the problem occurred and ask the question “Why” five times. In this way, you will find the root causes of the problem and you can start treating them and rectifying the problem.
5-Why analysis is a technique that doesn’t involve data segmentation, hypothesis testing, regression or other advanced statistical tools, and in many cases can be completed without a data collection plan. By repeatedly asking the question “Why” at least five times, you can peel away the layers of symptoms which can lead to the root cause of a problem.
Here is a simple example of applying the 5-Why analysis to determine the root cause of a problem. Let’s suppose that you received a large number of customer returns for a particular product. Let’s attack this problem using the five whys:
1. Question: Why are the customers returning the product? Answer: 90 percent of the returns are for dents in the control panel.
2. Question: Why are there dents in the control panel? Answer: The control panels are inspected as part of the shipping process. Thus, they must be damaged during shipping.
3. Question: Why are they damaged in shipment? Answer: Because they are not packed to the packaging specification.
4. Question: Why are they not being packed per the packaging spec? Answer: Because shipping does not have the packaging spec.
5. Question: Why doesn’t shipping have the packaging spec? Answer: Because it is not part of the normal product release process to furnish shipping with any specifications.
Using the five whys in this case revealed that a flaw in the product release process resulted in customers’ returning of a product.
Ishikawa Diagram In some cases, a problem can be due to more than one root cause or may have multiple forcing functions that either singularly, or in combination, will result in the problem. The 5-Why process may not provide the ability to address these more complex problems. The pictorial representation of this root cause analysis can be achieved using an Ishikawa or Cause and Effect Diagram . Because of its shape, this process is also called a Fishbone Diagram . This helps people communicate the root cause and the potential contributing factors and/or forcing function in a simple, straightforward graphic format. This method is very clear way of representing the relationship between the root cause of the problem and all of the possible factors that may be associated with the problem.
The Cause and Effect Diagram or Fishbone Diagram is a graphical tool for identifying the relationship between a problem and its potential causes. One of the most effective ways of constructing such a diagram is to brainstorm potential causes in a team environment. For example, a cause and effect diagram might be used to determine possible causes of a recurring defect in a manufacturing process.
The Fishbone Diagram is drawn to resemble the skeleton of a fish, with the issue (problem or process condition) on the right side. The major cause categories are written in the boxes on the left side of Cause and Effect Diagram. Summarize the major causes under the categories. These categories are usually Methods, Measurements, Machines, Materials and People.
Under each category, identify potential causes for the problem relating to the category. For example, if the fact that incorrect parts are being delivered to the assembly is a potential cause for the problem being addressed, that would be listed as a branch under “Materials.”
Both Fishbone Diagrams and the Five Why analysis are simple, very useful methods for problem solving. One of the first steps to creating a Lean culture is to turn every employee into a problem solver. This should begin with teaching the use of “The Five Why’s” on a regular basis.
Simplified Failure Modes and Effects Analysis Simplified Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (SFMEA) is a top-down method of analyzing a design, and is widely used in industry. In the U.S., automotive companies such as Chrysler, Ford and General Motors require that this type of analysis be carried out. There are many different company and industry standards, but one of the most widely used is the Automotive Industry Action Group(AIAG). Using this standard you start by considering each component or functional block in the system and how it can fail, referred to as failure modes. You then determine the effect of each failure mode, and the severity on the function of the system. Then you determine the likelihood of occurrence and of detecting the failure. The procedure is to calculate the Risk Priority Number, or RPN, using the formula: RPN = Severity × Occurrence × Detection
The second stage is to consider corrective actions which can reduce the severity or occurrence, or increase detection. Typically, you start with the higher RPN values, which indicate the most severe problems, and work downwards. The RPN is then recalculated after the corrective actions have been determined. The intention is to get the RPN to the lowest value.
Conclusion These four tools can be effectively utilized by natural work teams to resolve most problems that could confront them as part of their day-to-day activities. None require special skills. Instead, they rely on native knowledge, common sense and logic. The combined knowledge, experience and skills of the team is more than adequate for success.
Daily problem-solving tips in a lean organization:
Keep what may seem like ‘little problems’ from adding up and becoming big problems in the future. The only way to work on tomorrow’s problems is to work on the problems today while they are still small.
Use visual management and standard work tools to catch problems before they start adding up.
Build the skills, tools and systems needed to deal with those problems as soon as possible.
Start using 5-Why analysis. Continue asking “Why?” at different stages in order to dig deeper into the root cause of a problem.
Use Plan-Do-Check-Act, or PDCA. Without fully understanding the cause of what is happening in a situation, an organization will not have the control in its processes in order to sustain lean.
Understand that the small problems are a valuable contribution for future results.
About the author: Keith Mobley is a consultant with Life Cycle Engineering. He has earned an international reputation as one of the premier consultants in the fields of plant performance optimization, reliability engineering, predictive maintenance and effective management. He has more than 35 years of direct experience in corporate management, process design and troubleshooting. For the past 16 years, he has helped hundreds of clients worldwide achieve and sustain world-class performance. Mobley is actively involved in numerous professional organizations. Currently, he is a member of the technical advisory boards of: American National Standards Institute (ANSI), International Standards Organization (ISO) as well as American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and others. He is also a Distinguished Lecturer for ASME International. To learn more, visit www.LCE.com .

15 Essential Lean Manufacturing Tools and Principles
Of the many lean manufacturing tools and principles in use today, these are some of the fundamental tools and principles you must understand to have a basic familiarity with lean.
Use this guide start-to-finish for a general overview of lean manufacturing tools, or skip to the topic of your choosing using the quick links below.
Quick Links
- Value and Waste
- Standard Work
- Visual Management
- Continuous Flow
- Quick Changeover
- Value Stream Mapping
- Problem Solving
- Lean Management
#1 Value and Waste

What is value?
Value is defined as “whatever the customer wants.”
A value-adding activity is therefore an activity that creates value for the customer. This is something like: snapping, bending, stitching, sawing, painting, filling, etc.
What is waste?
Waste is everything else that is not value-added. There are 7 identified forms of waste, which include the following:
- Transportation
- Over processing
- Over production
An 8th waste is sometimes added to represent wasted human potential. This is the waste of a disengaged workforce and is typically a failure of management.
Why does value and waste matter?
Eliminating waste is at the heart of lean manufacturing and central to the world class performance achieved by lean organizations.
Waste is everywhere and in everything that we do; the opportunity for improvement is found in eliminating these wastes. Then, value can flow!
#2 Stability (and the 4M)

What is stability and the 4M?
Stability is a prerequisite to any performing process. It can be evaluated via the 4M’s of man, machine, material, and method.
If there is instability in any of these four categories, the process will not support lean methods and continuous improvement. If you try to move forward, you may even find yourself like a dog chasing its tail!
Why does stability matter?
Every other activity or tool you might use with lean depends on sufficient stability of the process in question. You must learn to see instability for what it is and learn to stabilize it before moving forward.
#3 Standard Work (or Standardized Work)

What is standard work?
Standard work is a scientific approach to stabilizing the methods used in an activity. There are many ways to document standard work but make no mistake: this is not just a “standard operating procedure” (SOP)!
Standard work comes in the common forms of traditional standardized work, a simple 8-step process, TWI job instruction, video, and more.
Why does standard work matter?
In the famous words of Taichii Ohno, “Without a standard there can be no kaizen.” Standard work is the starting point for kaizen and the baseline for continuous improvement. Without it, there is nothing to compare to.
Massive performance gains can be achieved by stabilizing production methods with standard work and training effectively. It also aids in quality, problem-solving, team member engagement, and continuous improvement.

What is 5S?
5S is a productivity tool that increases efficiency and makes abnormalities visible.
It’s composed of five disciplines: sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain.
Why does 5S matter?
If you’re going to do well with lean, it’s important to master the basics. 5S is one of them!
It’s a primary tool to preserve the output of processes and make problems visible.
#5 Kaizen (aka Continuous Improvement)
What is kaizen.
Kaizen is the Japanese word for “good change” and represents the idea of continuous improvement.
Very often, people misunderstand kaizen to be an event-based practice scheduled over 5+ days of focused activity.
But the deeper and truer meaning of kaizen is the practice of creating small changes made by everyone, every day, everywhere.
Why does kaizen matter?
In many regards, kaizen is the essence of lean and the Toyota Production System. It’s a system of continuous improvement in which everyone participates every day.
If you don’t learn to practice kaizen, you’ll never eliminate waste at a world-class level.
#6 Heijunka (aka Leveled Production)

What is heijunka?
Heijunka is the lean concept of “leveled production” and is essential to establishing stability. It is a hallmark of a flexible lean production system.
Toyota uses a specific kind of production leveling called “every part every interval” (EPEI), but other methods of production leveling exist.
Why does heijunka matter?
It’s one of the ultimate forms of stabilization, which eliminates waste and makes your production system predictable.
#7 Visual Management (aka Visual Factory or Visual Controls)

What is visual management?
Visual management has to do with the scientific managing of processes following the PDCA method of comparing expected vs. actual performance.
It is more than simply making the workplace colorful and labelled! It’s also more than extensive use of charts, graphs, and data.
Why does visual management matter?
Visual management is like the nerve-system of a lean organization. It is a feedback-loop system that accelerates problem-solving and preserves the output of production processes.
It is also considered a crucial component for creating a lean culture (along with leader standard work and daily accountability).
#8 Continuous Flow

What is continuous flow?
Continuous flow is about making processes move in small batches vs. big batches, and “one-piece flow” is the ideal. Various methods are used to improve flow including cellular manufacturing, kanban (pull systems), quick changeover, and minimum lot sizes.
Why does continuous flow matter?
Massive benefits can be achieved for lead time reduction, productivity, quality, and operational flexibility using the concept of continuous flow.

#9 Takt Time

What is takt time?
Takt time is the pace of production and is calculated by dividing planned production time by customer demand. For example, this results in a rate of 46 seconds per part.
Why does takt time matter?
It is used as a design specification in continuous flow processes so that the flow of production activities is smooth and steady. This eliminates the waste of overburden (muri) and unevenness (mura).
It is also used effectively to assess actual vs. expected performance, since the expected performance is determined using takt time.
#10 Kanban (Pull Systems)

What is kanban?
Kanban is a physical or digital signal that triggers production activities in small batches, and only when needed! It comes in various forms including: a kanban card, a 2 bin system, or kanban supermarket.
Why does kanban matter?
It’s not always possible to create one-piece flow or continuous flow between all operations. In these situations a pull system is useful to “pull” material and information to where it is needed.
With these two strategies (pull systems and continuous flow) the wastes of traditional batch-and-queue manufacturing can be wonderfully reduced.
#11 Quick Changeover (aka SMED)

What is a quick changeover?
A quick changeover is a strategy of reducing setup times associated with changeover activities. In many cases, setups can be reduced to a “single digit” i.e. less than 10 minutes.
This is a synonym for the Toyota term “single minute exchange of die” (SMED).
Why do quick changeovers matter?
Reducing batch size is cost-prohibitive for equipment designed for batch processing unless the setup time can be reduced.
By applying quick changeover concepts and reducing setup times, the batch size is reduced, work in process (WIP) inventories are reduced, and flow is improved.
#12 Value Stream Mapping (VSM)

What is value stream mapping?
Value stream mapping is a tool used to draw, analyze, and improve the flow of material and information through a “value stream.” The value stream is the complete series of activities required to produce a product or service from start to finish.
Why does value stream mapping matter?
This tool allows management to strategically redesign a value stream from its current state into a desired future state.
It can be used to plan the conversion of entire product families from traditional methods into lean methods of continuous flow and pull.

What is jidoka?
Built-in quality, automation with abnormality detection, andon, and multi-process handling are all contained within the concept of jidoka.
With this practice in play, equipment, team members, and processes immediately stop whenever a problem or abnormality is detected.
Why does jidoka matter?
Jidoka is a mindset and set of practices used to create world class first time quality. Instead of endlessly firefighting, lean organizations apply jidoka methods to build quality in at the source.
#14 Problem Solving

What is problem solving?
Lean problem-solving typically draws from an common assortment of tools and a clear problem-solving process.
This problem-solving process is characterized by defining problems in the context of the big picture, thinking multi-dimensionally, going to the gemba, applying the PDCA cycle (Deming Cycle), and documenting the problem-solving effort in a standard format.
Why does problem solving matter?
Disciplined and scientific problem-solving is at the core of lean thinking. To make progress and reach your goals, you’ll have to learn how to flex these problem-solving muscles.
#15 Lean Management

What is lean management?
Lean management is a “paradigm-shift” from traditional management and can be understood through cultural artifacts of lean management and less tangible management behavior.
The cultural artifacts are often captured through the trinity of practices of leader standard work, a daily accountability process, and visual controls.
Less tangible cultural characteristics include humility, elevating the role of the team leader and team member, learn by doing, scientific experimentation, failing early and often, and more.
Why does lean management matter?
Lean tools don’t stick unless the management system is also converted towards lean management practices.
If you’re going to “become lean,” you can’t overlook the importance of transforming your management system and underlying beliefs and practices.
Get Everyone Trained in Lean Manufacturing Tools and Principles
Want to learn more or get others trained? Checkout our Fundamentals of Lean course, covering all these tools and more!
Learn more about the Fundamentals of Lean

Problem Solving in Manufacturing: How to Use A3 & DMAIC Effectively
Sales acceleration workshop, lorem ipsum dolor sub title..

Named after the “A-3” sized paper used for documentation, A3 problem solving teaches employees how to rapidly address manufacturing problems, effectively communicate solutions and monitor results. This approach is typically used by Lean manufacturing practitioners to support Kaizen events. When combined with the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) methodology, this technique enables teams to clearly define problems, uncover potential root causes and develop corrective actions to ensure real results. With each step of learning, planning and solving explicitly documented, the final A3 report provides a convenient summary of the completed project.
UNDERSTANDING THE DMAIC PROCESS Going through the entire process, each step involves the following:
Define – What is the opportunity for improvement? In this first step, the team must determine:
- What is the problem and what improvements could come from this project?
- Why is this problem/opportunity important? Identify why time and effort should be invested into this project. Ideally, this will align with larger company objectives.
Measure – What is the current performance? This section defines key metrics in performance that must be tracked and measured, such as:
- Variation, cost and lead time
- Work in Process (WIP)
- Number of people involved
- Distance traveled or space required
- Number of handoffs
- First Pass Yield
Data that is not already known must be gathered. All this information combined provides a current state of the process while making apparent any existing issues or areas for improvement.
Analyze – What is the cause of this poor performance? Evaluate the process and conduct root cause analysis to identify and verify the problem. This can be accomplished through various problem-solving methods, such as 5-Why or Fishbone Diagrams.
Improve – What improvements must be implemented to eliminate waste and reduce variation? In this step, the team works to establish and schedule countermeasures to prevent or mitigate the problems identified in the analyze phase. Several Lean Six Sigma tools, including 5S, Standard Work or Kanban, may assist in this improvement process.
Control – How can the results be sustained? The goal of this step is to determine how improvements will be sustained over time. Ensure all action items are complete and establish new metrics to monitor the changes. The process owner is responsible for making sure the new Standard Work is being followed consistently. Holding weekly meetings with those involved will assist with maintaining accountability.
APPLYING THE DMAIC PROCESS IN THE REAL WORLD Together, these five steps create a logical and structured approach to improving processes, with all ideas and actions carefully captured in the A3 report. To understand what this process looks like when applied to a business, read on to see how one of our clients recently completed these steps during their Kaizen event.
- Define – The company identified inefficiencies in their welding/assembly processes.
- Measure – The organization sought to increase production to meet increased product goals and sales forecasts. However, as evidenced by their performance metrics, something was holding the team back from achieving this.
- Analyze – Looking deeper into the process, the team realized too much time was spent making lists to coordinate tasks between departments, and the lists were quickly becoming obsolete each day. The success of the kitting department depended on the ability of the welding department to stay on schedule, which often fell behind.
- Improve – A visual scheduling process was put in place to coordinate the workflow among departments. Additionally, the concept of a Focused Factory Hot Run Shop was implemented to keep the main production process running while only one team member completed all specialized orders separately.
- Control – The schedule list now reflects all the latest information in their ERP system. These improvements are projected to generate $5 million in new sales each year and $40,000 in cost savings from a $10,000 investment.
When implemented correctly, A3 problem solving using the DMAIC methodology can resolve any operational problem while promising real results. Learn how The Center can support your next problem-solving project here or contact [email protected] to speak with our experts now. MEET OUR EXPERT

Since 1991, the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center has assisted Michigan’s small and medium-sized businesses to successfully compete and grow. Through personalized services designed to meet the needs of clients, we develop more effective business leaders, drive product and process innovation, promote company-wide operational excellence and foster creative strategies for business growth and greater profitability. Find us at www.the-center.org .
Recent Posts
Post archive.
8D Manufacturing Report: Your Guide to Effective Problem Solving
- Written by Brecht Plasschaert
- Compliance , Lean Manufacturing
- Updated on January 10, 2024
- Published on August 16, 2022
Manufacturing companies are the backbone of any economy. They produce goods for local or international markets, employ people, and keep their customers happy.
That’s why manufacturers often use 8D reports to identify and solve problems before they impact their production and business to ensure the quality of produced goods. The methodology was developed by Toyota Motors Manufacturing (TMM) in Japan in the 1960s to help the company achieve better performance.
For companies who want to compete with other manufacturers around the world, it’s essential to identify and track root causes of non-conformities or problems in a production environment. This helps them achieve a high level of product efficiency and quality, which translates into lower costs and higher profits.
In this article we cover the ins and outs of 8D reporting, how to use it, and the advantages it may offer to your workforce.
Download our 8D template as well to make your problem-solving process simpler.
The 8D method structure
The 8D problem-solving method is a systematic approach to problem solving that emphasizes team participation. This method generally covers:
- Identifying the Problem — You must first identify what is wrong with the process or operation.
- Determining Causes — After identifying a problem, you will have to determine its root cause(s). This may not be easy, but it’s imperative if you want to fix your processes and prevent future problems from arising again.
- Developing Corrective Action — Once you’ve identified the causes of your problems and analyzed all possible solutions, it’s time to develop corrective actions. Create a plan for how each possible solution would work (i.e., “if we use this part instead,” or “if we add these people,” etc.). You’ll also need metrics and checkpoints throughout this process to ensure that everything is working as intended.
The 8 disciplines
The eight disciplines (8D) follow a logical sequence of eight steps. It’s one of the most common methods used in manufacturing because it’s a structured approach, but it can also be applied to other industries.
D1: Create a team When using 8D, it is important to have a cross-functional team with individuals from different disciplines to assist you cover more territory. There should be two subgroups for the team members:
- Core members: people who are more data-driven and typical product, process, and data experts.
- Subject Matter Experts (SME): members who may contribute to brainstorming, research, and process observation. Bring in fresh SMEs without hesitation to assist with any step of the process.
These team members have to be equipped with the knowledge necessary to identify the issue and implement solutions.
D2: Describe the problem
The problem description is a narrative that describes the issue in detail and should be understood across the team members. It explains how the issue happened, what impact it had on your business, and why you need to fix it. The problem description should include:
- The underlying causes of your problem (the root cause). Why did this happen?
- What’s the impact of this issue? How much money are you losing because of this? What other problems does it cause within your company?
- How will fixing these underlying causes help solve or prevent future issues related to this one?
Here are some techniques and tools to identify and formulate the problems:
- 5 Why’s formulation
- Affinity Diagram
- Fishbone Diagram
- Is / Is Not method
D3: Develop a containment plan
Once you have identified, isolated, and controlled your manufacturing process problems, it’s time to create a plan for containment. You need clear descriptions so that everyone understands what they’re supposed to do in order to solve this issue. Be aware, an Interim Containment Action (ICA) is a temporary plan and should only be replaced with the Permanent Corrective Action (PCA) after completing 8D.
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
You might find yourself wandering down several rabbit holes before reaching this point. Be patient and methodical as you work through each step in your investigation process. This process should always be guided by facts rather than assumptions or guesses about what could be going wrong behind closed doors at your company’s factories overseas!
Review your results, then talk with your team about potential causes of the issue. Each probable root cause is mapped to the issue statement and any associated test results as part of the root cause analysis. Be cautious to rule out all probable reasons; hazy brainstorming and careless analysis might lead you to miss important details.
Some methods during this step include:
- Comparative Analysis
- Development of Root Cause Theories
- Verification of Root Cause Theories
- Review Process Flow Diagrams
- Determine Escape Points, the closest point in the process where root cause could be found
In addition to determining the underlying causes, attempt to remember when and why you first discovered the issue in the process. This is called an escape point, and there can be more than one.
D5: Formulate Permanent Corrective Actions (PCA)
Corrective actions should be based on the root cause analysis. The first step in formulating corrective actions is to determine the root cause of the failure mode. To do this, you will need to analyze all of your data and identify which potential factors contributed to the problem. Once you have determined what caused the failure, you can then come up with ways of preventing similar failures from occurring in the future.
For example, if an assembly line stops due to an electrical issue with one machine, it would not make sense to fix just one machine; rather, you should look at all machines on that line and make sure they have proper electrical connections so that they are able to function properly.
So when something goes wrong, you will have a plan for fixing it before it causes even bigger problems down the road. There are several steps involved in creating an effective corrective action plan:
- Plan out how long it will take before implementing any changes that can help fix whatever issue has arisen;
- Create an actionable plan detailing exactly what needs changing;
- Check in at regular intervals on progress made toward completing this project so that no one gets forgotten along its path until completion (this includes monitoring by both parties involved)
- If necessary take appropriate steps like adding more resources or reallocating existing ones when delays arise from unforeseen factors such as weather conditions etc .”
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
Interim measures are temporary solutions to a problem. They can be used to prevent further damage or to allow time for a permanent solution to be implemented. Interim measures can also be used to reduce the impact of the problem until it is solved.
When you have identified an issue in your business, create an action plan that includes interim measures as well as final goals and expectations. If there is some sort of delay in implementing these interim measures, report back on progress at least monthly so management stays up-to-date on what is happening within your department and company at large.
Some activities during the 6D step include:
- Creating a project plan
- Share the plan with relevant parties.
- Use metrics to verify progress
D7: Monitoring of corrective measures
Monitoring is a key part of the 8D method. Monitoring is a way to check if a corrective action is working, or if it needs to be changed or completed. It’s also a way to check if the root cause has been addressed, and if your company has learned anything new from the incident that could help prevent future errors.
Your team needs to retain and document the shared knowledge that was gained while identifying, resolving, and preventing this problem. It’s important to review existing documents or procedures and update them accordingly to improve future outcomes.
Activities you need to keep in mind during this step are:
- Reviewing comparable products and procedures to avoid other problems.
- Creating or updating work instructions and procedures.
- Capturing new industry standards and procedures.
- Confirming the most recent failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA).
- Confirming the revision of control plans.
D8: Recognize team and individual efforts
Giving feedback to ensure a good outcome is crucial for any team to flourish. Recognize the efforts and labor that each person has put into what they have brought to the process at this moment.
The tasks in this stage consist of:
- Archive 8D for later use.
- Keep track of your learnings to enhance your problem-solving techniques.
- Comparisons of the before and after
- Celebration and acknowledgement of the group
How to Write an 8D report for your company when you have a product defect or a problem to solve?
An 8D report is a tool for managing a problem. It consists of eight columns and four rows:
- The first row, called the title row, lists each column’s name.
- Define the Problem
- Determine Causes
- Develop Solutions
- Verify Solutions
- Control Risks
- Document Your Improvements and Lessons Learned (optional)
- Closeout (optional).
- 1a through 7a include action steps related to 1 through 7 above;
- 6b includes an optional section that can be used if it becomes necessary to document lessons learned from this process at some later time (e.g., after you implement Solution 3b).
8D Report Pros and Cons for manufacturers
8d report advantages:.
More awareness of the root cause (s)
It improves your quality control processes by identifying the potential causes of nonconformance at each stage of production and prioritizes corrective action steps based on their risk level, priority, impact, probability, etc., thus ensuring that you address the system issues first before they result in incurring costs due to rework/scrap or adverse customer response or regulatory intervention.
Enhanced quality control strategies and plans.
8D enables you to reduce lead times by identifying where bottlenecks are occurring within a process so that resource allocation can be adjusted accordingly in order to improve throughput while maintaining quality standards (i.e., having sufficient workers available at all stages). This can also help with preventing employee burnout by covering more shifts so there is less overtime required from employees who might otherwise be tired from working too many hours without breaks when there is high demand for their services during peak times (like Christmas shopping season).
Avoid future problems
The 8D report can help your manufacturing company avoid costly mistakes, as you can see exactly where problems may occur and take action to prevent them.
Team-based approach
An 8D report gives you an opportunity to check if everything is running smoothly and confirm that everyone understands their tasks and responsibilities. With this information at hand, it’s easier to make improvements based on what works best or needs improvement in different areas of your business. In addition, it’s easy to access historical data on procedures and products.
Better communication flows
Finally, It also allows for better communication flows between teams responsible for different processes in the manufacturing process and reduces the amount of time spent investigating issues that aren’t really problems.
8D report Cons:
Extensive training
There aren’t many cons to applying 8D problem solving techniques. The most important one is that it will require that people who take part in problem-solving activities obtain the right training and instructions on how 8D operates.
They will also need to comprehend other closely linked concepts related to 8D issue solving methodologies. Examples of these may be pareto charts , process maps, fishbone diagrams, and more.
Lack in flexibility
In addition, an 8D report is not a good tool when there are several problems at once or when an issue in the manufacturing process needs immediate attention.
Dedicated budget
An 8D report also has requirements that smaller enterprises with fewer resources can find complicated and costly. For example: you need to have a dedicated budget to provide extensive training so your team has the right knowledge to do the job right.
Technology to Assist in 8D Reporting for manufacturers
There are a number of software solutions available to help companies implement 8D programs and manage their Supplier Quality Management (SQM) efforts.
Why should you digitize your 8D processes?
Automating the 8D report process will ensure that all problems are captured and reported consistently, with no one falling through the cracks.
It facilitates collaboration across teams and departments. All stakeholders will have access to information on the status of every problem as it progresses through its lifecycle, so they can respond quickly if an issue arises or make suggestions for how best to resolve it. This saves time and allows everyone involved in a particular issue to feel more connected with one another than they otherwise would be able to do without this kind of technology at their disposal.
8D Solutions
8D reporting is a powerful tool for monitoring progress and identifying issues in manufacturing. This can help you improve your processes, reduce cost, and increase profits. With the help of technology, you can easily keep track of your 8D reports. Here are some solutions to assist manufacturers with this process:
A program like SAP or Oracle ERP allows you to integrate 8D reporting into your system. This way, all information is in one place and updated automatically.
A no-code software tool like Azumuta allows you to integrate 8D reporting into your system. This way, all information is in one place and updated automatically. Easily capture data with your phone or tablet , while offline from the field at any time! Create an 8D report right away and distribute it to your stakeholders and coworkers and track corrective actions to team members through a single app.
With real-time data, companies can improve communication among team members, improve problem solving skills for individuals on the team (including managers), and develop new solutions for existing issues based on past experience with similar problems at other locations or companies.
Microsoft Office
If you don’t want to invest in new software at this time but still want an easy way to manage your project issues and progress, consider using an online database like Excel for managing risks, defects, quality assurance methods, etc. This will allow you to access information from anywhere with a laptop or mobile device. This way is rather tedious though and important information can be lost.
Digitize your 8D Processes
As you can see, there are many benefits to using a software for 8D reporting. While it may seem like a lot of work initially, once you get the hang of it, it will be easy to maintain and manage your 8D records. The most important thing is to start now! Make sure that your company gets started on an 8D reporting software today so that your team can begin documenting problems as soon as possible!
See how our platform can help streamline data collection, increase productivity, and increase quality assurance with a demo of Azumuta.
Don't forget to share this post!
In this article.
Recent Blog Updates
What Is Heavy Industry?
Azumuta is now compatible with bartender, what is light industry, how to prepare your team for an iatf 16949 certification, how to get an iatf 16949 certification, what is iatf 16949 certification [free template], what is standard work [free templates], how to fulfill the belgian federal learning account requirements with azumuta.

Top 25 Lean Tools & Techniques

Exploring Lean
There are a lot of great ideas to explore in lean. So, where should you begin?
One way to start is to survey the most important lean tools, with a brief description and a short explanation of how each tool can improve your manufacturing operations.
If a tool captures your interest or resonates with you in some way – explore it further to decide if it is something to pursue now…or later. Many of these tools can be successfully used in isolation, which makes it much easier to get started. On the other hand, the benefits will compound as more tools are used, as they support and reinforce each other.
25 Lean Manufacturing Tools
What is 5s.
5S organizes the work area:
- Sort: eliminate that which is not needed
- Straighten: organize remaining items
- Shine: clean and inspect work area
- Standardize: write standards for above
- Sustain: regularly apply the standards
How does 5S help?
5S eliminates waste that results from a poorly organized work area (e.g., wasting time looking for a tool).
Learn more about 5S
What is Andon?
Andon is a visual feedback system for the plant floor that indicates production status, alerts when assistance is needed, and empowers operators to stop the production process.
How does Andon help?
Andon acts as a real-time communication tool for the plant floor that brings immediate attention to problems as they occur – so they can be instantly addressed.
Learn more about Andon at Vorne.com

Bottleneck Analysis
What is bottleneck analysis.
Bottleneck Analysis identifies which part of the manufacturing process limits the overall throughput and improves the performance of that part of the process.
How does Bottleneck Analysis help?
Bottleneck Analysis improves throughput by strengthening the weakest link in the manufacturing process.
Continuous Flow
What is continuous flow.
Continuous Flow is manufacturing where work-in-process smoothly flows through production with minimal (or no) buffers between steps of the manufacturing process.
How does Continuous Flow help?
Continuous Flow eliminates many forms of waste (e.g., inventory, waiting time, and transport).
Gemba (The Real Place)
What is gemba.
Gemba is a philosophy that reminds us to get out of our offices and spend time on the plant floor – the place where real action occurs.
How does Gemba help?
Gemba promotes a deep and thorough understanding of real-world manufacturing issues – by first-hand observation and by talking with plant floor employees.
Heijunka (Level Scheduling)
What is heijunka.
Heijunka is a form of production scheduling that purposely manufactures in much smaller batches by sequencing (mixing) product variants within the same process.
How does Heijunka help?
Heijunka reduces lead times (since each product or variant is manufactured more frequently) and inventory (since batches are smaller).
Hoshin Kanri (Policy Deployment)
What is hoshin kanri.
Hoshin Kanri aligns the goals of the company (Strategy), with the plans of middle management (Tactics) and the work performed on the plant floor (Action).
How does Hoshin Kanri help?
Hoshin Kanri ensures that progress towards strategic goals is consistent and thorough – eliminating the waste that comes from poor communication and inconsistent direction.
Learn more about Hoshin Kanri
Jidoka (Autonomation)
What is jidoka.
Jidoka is the idea that manufacturers should design equipment to partially automate the manufacturing process (partial automation is typically much less expensive than full automation) and to automatically stop when defects are detected.
How does Jidoka help?
After Jidoka, workers can frequently monitor multiple stations (reducing labor costs) and many quality issues can be detected immediately (improving quality).
Just-In-Time (JIT)
What is just-in-time.
Just-In-Time pulls parts through production based on customer demand instead of pushing parts through production based on projected demand. Relies on many lean tools, such as Continuous Flow, Heijunka, Kanban, Standardized Work, and Takt Time .
How does Just-In-Time help?
Just-In-Time is highly effective in reducing inventory levels. Improves cash flow and reduces space requirements.
Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
What is kaizen.
Kaizen is a strategy where employees work together proactively to achieve regular, incremental improvements in the manufacturing process.
Learn more about Kaizen
How does Kaizen help?
Kaizen combines the collective talents of a company to create an engine for continually eliminating waste from manufacturing processes.
Kanban (Pull System)
What is kanban.
Kanban is a method of regulating the flow of goods both within the factory and with outside suppliers and customers. Based on automatic replenishment through signal cards that indicate when more goods are needed.
How does Kanban help?
Kanban eliminates waste from inventory and overproduction. Can eliminate the need for physical inventories, instead relying on signal cards to indicate when more goods need to be ordered.
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)
What are kpis.
KPIs are metrics designed to track and encourage progress towards critical goals of the organization. Strongly promoted KPIs can be extremely powerful drivers of behavior – so it is important to carefully select KPIs that will drive desired behavior.
How do KPIs help?
The best manufacturing KPIs:
- Are aligned with top-level strategic goals (thus helping to achieve those goals)
- Are effective at exposing and quantifying waste (OEE is a good example)
- Are readily influenced by plant floor employees (so they can drive results)
Learn more about Manufacturing KPIs at Vorne.com
Muda (Waste)
What is muda.
Muda is anything in the manufacturing process that does not add value from the customer’s perspective.
How does Muda help?
Muda doesn’t help. Muda means ‘waste’. The elimination of muda (waste) is the primary focus of lean manufacturing.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
What is overall equipment effectiveness.
OEE is a framework for measuring productivity loss for a given manufacturing process. Three categories of loss are tracked:
- Availability (e.g., downtime)
- Performance (e.g., slow cycles)
- Quality (e.g., rejects)
How does Overall Equipment Effectiveness help?
OEE provides a benchmark/baseline and a means to track progress in eliminating waste from a manufacturing process. 100% OEE means perfect production (manufacturing only good parts, as fast as possible, with no downtime).
Learn more about OEE at OEE.com
PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act)
What is pdca.
PDCA is an iterative methodology for implementing improvements:
- Plan: establish plan and expected results
- Do: implement plan
- Check: verify expected results achieved
- Act: review and assess; do it again
How does PDCA help?
PDCA applies a scientific approach to making improvements:
- Plan: develop a hypothesis
- Do: run experiment
- Check: evaluate results
- Act: refine your experiment; try again
Poka-Yoke (Error Proofing)
What is poka-yoke.
Poka-Yoke designs error detection and prevention into production processes with the goal of achieving zero defects.
How does Poka-Yoke help?
It is difficult (and expensive) to find all defects through inspection, and correcting defects typically gets significantly more expensive at each stage of production.
Root Cause Analysis
What is root cause analysis.
Root Cause Analysis is a problem solving methodology that focuses on resolving the underlying problem instead of applying quick fixes that only treat immediate symptoms of the problem. A common approach is to ask why five times – each time moving a step closer to discovering the true underlying problem.
How does Root Cause Analysis help?
Root Cause Analysis helps to ensure that a problem is truly eliminated by applying corrective action to the “root cause” of the problem.
Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED)
What is single-minute exchange of die.
Single-Minute Exchange of Die reduces setup (changeover) time to less than 10 minutes. SMED techniques include:
- Convert setup steps to be external (performed while the process is running)
- Simplify internal setup (e.g., replace bolts with knobs and levers)
- Eliminate non-essential operations
- Create Standardized Work instructions
How does Single-Minute Exchange of Die help?
SMED enables manufacturing in smaller lots, reduces inventory, and improves customer responsiveness.
Learn more about SMED at Vorne.com
Six Big Losses
What is six big losses.
The Six Big Losses are six categories of productivity loss that are almost universally experienced in manufacturing:
- Setup/Adjustments
- Small Stops
- Reduced Speed
- Startup Rejects
- Production Rejects
How does Six Big Losses help?
The Six Big Losses provide a framework for attacking the most common causes of waste in manufacturing.
Learn more about Six Big Losses at Vorne.com
SMART Goals
What are smart goals.
SMART Goals are: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-Specific.
How do SMART Goals help?
SMART Goals help to ensure that goals are effective.
Standardized Work
What is standardized work.
Standardized Work is documented procedures for manufacturing that capture best practices (including the time to complete each task). It must be “living” documentation that is easy to change.
How does Standardized Work help?
Standardized Work eliminates waste by consistently applying best practices. Forms a baseline for future improvement activities.
What is Takt Time?
Takt Time is the pace of production (e.g., manufacturing one piece every 34 seconds) that aligns production with customer demand. Calculated as Planned Production Time / Customer Demand.
How does Takt Time help?
Takt Time provides a simple, consistent, and intuitive method of pacing production. Is easily extended to provide an efficiency goal for the plant floor (Actual Pieces / Target Pieces).
Learn more about Takt Time at Vorne.com
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
What is total productive maintenance.
TPM is a holistic approach to maintenance that focuses on proactive and preventative maintenance to maximize the operational time of equipment. TPM blurs the distinction between maintenance and production by placing a strong emphasis on empowering operators to help maintain their equipment.
How does Total Productive Maintenance help?
TPM creates a shared responsibility for equipment that encourages greater involvement by plant floor workers. In the right environment, this can be very effective in improving productivity (increasing uptime, reducing cycle times, and eliminating defects).
Learn more about TPM at Vorne.com
Value Stream Mapping
What is value stream mapping.
Value Stream Mapping is a tool used to visually map the flow of production. Shows the current and future state of processes in a way that highlights opportunities for improvement.
How does Value Stream Mapping help?
Value Stream Mapping exposes waste in the current processes and provides a roadmap for improvement through the future state.
Visual Factory
What is visual factory.
A Visual Factory uses visual indicators, displays, and controls throughout the manufacturing plant to improve the communication of information.
How does Visual Factory help?
Visual Factory makes the state and condition of manufacturing processes easily accessible and very clear – to everyone.
Learn more about the Visual Factory at Vorne.com
WHAT YOU SHOULD DO NEXT...
1. Learn more about how our product, Vorne XL, can help you eliminate waste and significantly improve OEE.
Vorne XL is the simplest and fastest way to monitor and improve production. It's a one-time cost and takes just a day to install. And you can try it completely free for 90 days.
2. Download our FREE package of tools to supercharge your manufacturing productivity
The package includes leadership lessons, training guides, meeting and report templates, summaries of key concepts, project organizers, and more. You'll also receive our monthly newsletter for free. Unsubscribe at any time.
3. Sign up for our monthly newsletter
Get free monthly updates with proven methods for improving our manufacturing productivity. Unsubscribe at any time.
Explore Lean Thinking and Practice / Problem-Solving
Problem-Solving
Explore the process that’s foundational to assuring every individual becomes engaged by arming them with methods they can use to overcome obstacles and improve their work process.
Overcoming obstacles to achieve or elevate a standard
In a lean management system, everyone is engaged in ongoing problem-solving that is guided by two characteristics:
- Everything described or claimed should be based on verifiable facts, not assumptions and interpretations.
- Problem-solving is never-ending; that is, it begins rather than ends when an improvement plan is implemented. The implementation process is a learning opportunity to discover how to make progress toward the target condition.
Lean thinkers & practitioners understand that the problem-solving process is impeded if you make the common mistake of mechanically reaching for a familiar or favorite problem-solving methodology or, worse, jump quickly to a solution.
Leaders and teams avoid this trap by recognizing that most business problems fall into four categories, each requiring different thought processes, improvement methods, and management cadences.
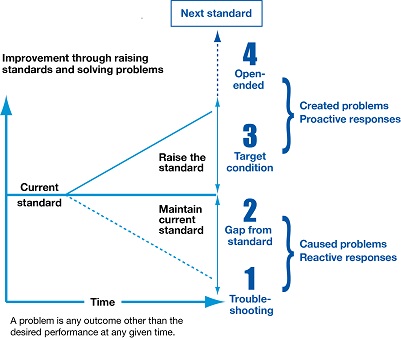
The Four Types of Problems
Type 1: Troubleshooting: reactive problem-solving that hinges upon rapidly returning abnormal conditions to known standards. It provides some immediate relief but does not address the root cause.
Type 2: Gap from Standard: structured problem-solving that focuses on defining the problem, setting goals, analyzing the root cause, and establishing countermeasures, checks, standards, and follow-up activities. The aim is to prevent the problem from recurring by eliminating its underlying causes.
Type 3: Target Condition: continuous improvement ( kaizen ) that goes beyond existing standards of performance. It may utilize existing methods in new, creative ways to deliver superior value or performance toward a new target state of improvement.
Type 4: Open-ended: innovative problem-solving based on creativity, synthesis, and recognition of opportunity. It establishes new norms that often entail unexpected products, processes, systems, or value for the customer well beyond current levels.
By helping everyone in the organization to understand the importance of taking ownership of seeing and solving all types of problems, lean thinking & practice:
- Engenders a sense of empowerment and autonomy in all workers, which in turn promotes engagement in and ownership of the work process
- Enables organizations to overcome obstacles at their source, so they do not become more significant problems upstream
Ultimately, building a problem-solving culture creates a competitive advantage that is difficult for competitors to match.
Relevant Posts

Problem Solving
Why the A3 Process Involves More than Filling in Boxes
Article by Tracey Richardson

Big Problems? Start Small
Article by Josh Howell

What’s your problem
Article, Video by John Shook
Recent Posts

Revolutionizing Logistics: DHL eCommerce’s Journey Applying Lean Thinking to Automation
Podcast by Matthew Savas

Transforming Corporate Culture: Bestbath’s Approach to Scaling Problem-Solving Capability

Teaching Lean Thinking to Kids: A Conversation with Alan Goodman
Podcast by Alan Goodman and Matthew Savas
Relevant Products

Four Types of Problems
by Art Smalley

Managing to Learn: Using the A3 management process
by John Shook

Getting Home
by Liz McCartney and Zack Rosenburg

Steady Work
by Karen Gaudet
Relevant Events
June 10, 2024 | Coach-Led Online Course
Managing to Learn
June 12, 2024 | Morgantown, PA
Building a Lean Operating and Management System
Online – On-Demand, Self-Paced
Problem Definition Practice
Be the first to learn of new learning opportunities and the latest practical, actionable information. subscribe to an lei newsletter., join us on social, privacy overview.
Problem Solving: What Skills do Manufacturers use to Get the Job Done?

Problem solving in engineering is important, but finding solutions to manufacturing processing problems is crucial to maintaining the flow of the entire supply chain. So, what skills do Manufacturers use?

In manufacturing problem solving, a key method stands out: Lean. This problem solving method focuses in on eliminating waste and finding a solution as quickly and efficiently as possible. This is by far the leading method that manufacturing engineers use to solve problems throughout the production process, so let’s take a look at some of it’s various methods at getting the job done.
Lean manufacturing is broader than just problem solving, it is a way of approaching design, manufacturing, and virtually every aspect of production. This could be said of any problem solving method, after all, as engineers we are trained to anticipate problems and design around projected issues. Looking first at a way to prevent problems from occurring, we can see the process of 5S. 5S is essentially a way of categorizing your workspace and your thought process through, you guessed it, five S categories. This process goes Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain. First you sort your workspace and processes into respective categories, then you organize them, clean and inspect the workstation, create a standard method of workflow, then regularly sustain all of the above processes. Following along with 5S problem solving, or should we say problem prevention, method will allow you to be the most efficient manufacturer you can be.

However, what happens if you actually encounter a problem? After all, even the most categorized and standardized workflow is still going to run into the occasional problem. Your problem is ultimately going to differ depending on your industry, but whatever it may be, we need to apply Root Cause Analysis to the situation. As tempting as it may be to just fix a problem by slapping on some duct tape, it becomes important as a manufacturer to get down to the initial cause. In this method, we have to tap into our inner 5-year-old and ask why as much as humanly possible. Generally, however, it’s good to stop somewhere in the range of asking 5 times as not to annoy your coworkers. When we get into the habit of asking “why?” we begin to see that a small problem on the surface may actually be evidence of a bigger problem developing deeper in your manufacturing process. So, work to solve the root problem, not just the surface issues.
Finding the root cause can take a long time if your process isn’t designed to facilitate problem solving. This means no haphazard engineering, as fun as it may be. It’s important to maintain a Standardized Work Procedure to allow for quick and easy problem solving. As you may be starting to tell, a lot of the Lean problem solving methods aren’t actually problem solving, rather they’re problem prevention.
In many senses, preventing problems from occurring can drastically increase your value as an engineer, although this tends to be a more thankless side of the industry. As a manufacturer, we have to be willing to go the extra mile in the planning and design phase to make problem solving easier down the line. If you do encounter a problem and your assembly line is a mess, try to approach it in the most methodological way possible, and ultimately find the root cause. Working fast is great to keep the assembly line moving, but it means nothing if bigger problems occur in the future as a result.
Lean Production
Reliable Plant
Image Sources:
Related Articles

Add comment
There are no comments
Privacy | Do not sell or share my personal information | Cookie preferences | Report noncompliance | Terms of use | © 2023 Autodesk Inc. All rights reserved
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Manufacturing Process Improvement: Fixing Errors and Abnormalities Quickly
August 10, 2023.
TBM Consulting

In this blog, we discuss how to address errors in manufacturing by using manufacturing process improvement problem-solving methods for effective manufacturing risk management.
Resiliency, the ability to overcome challenges, is a defining factor in whether we “make it or break it” as individuals, teams, or enterprises. This is a particularly crucial trait in manufacturing risk management, and it’s a skill that can be honed through manufacturing process improvements.
In this two-part e-guide series, Boosting Existing Systems & Resources to Maximize Production , we provide in-depth, step-by-step guides for enhancing your existing Operational Management System (OMS). Part one of the guide, Developing the Framework & Tools for Effective Operational Management, provides changes manufacturing leaders can make to set themselves up for success. Part two of the guide, Addressing Errors & Abnormalities: Proven Methods , is all about troubleshooting common challenges manufacturing operations managers often face.
In part one of this blog series, we provided approaches manufacturing leaders can implement for increased production efficiency in your OMS. In this blog, we’ll review problem-solving strategies for how to address errors in manufacturing to help address errors and abnormalities quickly and effectively.
Topics include:
Investigative Problem-Solving Strategies
How To Make More Effective Manufacturing Process Improvements
Investigative Problem-solving Strategies
When faced with errors and abnormalities, manufacturers have two choices depending on the scope and complexity of the situation: apply a quick fix, or take a calculated, investigative approach. When problems are multifaceted, difficult to resolve, or recurring, leadership needs to take care to swiftly fix the issue at its core so it solves the problem once and for all. Four problem-solving tools can help leadership get organized and set up for success when it comes to how to address errors in manufacturing:
The Five Whys
Pareto analysis
Fishbone diagrams
A3 methodology
Previous SafetyChain blogs have discussed the Toyota Production System (TPS) and how it kickstarted lean manufacturing . Another product of the TPS to aid in manufacturing process improvement is a problem-solving strategy called the 5 Whys. The general premise of the 5 Whys is to continuously ask the question “Why?” until you reach the true root cause of the error that occurred.
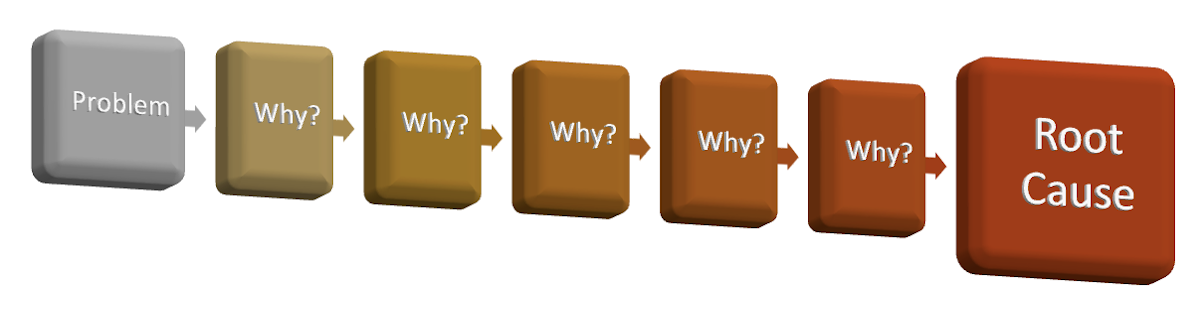
The classic example provided by the TPS concerns a malfunctioning welding robot:
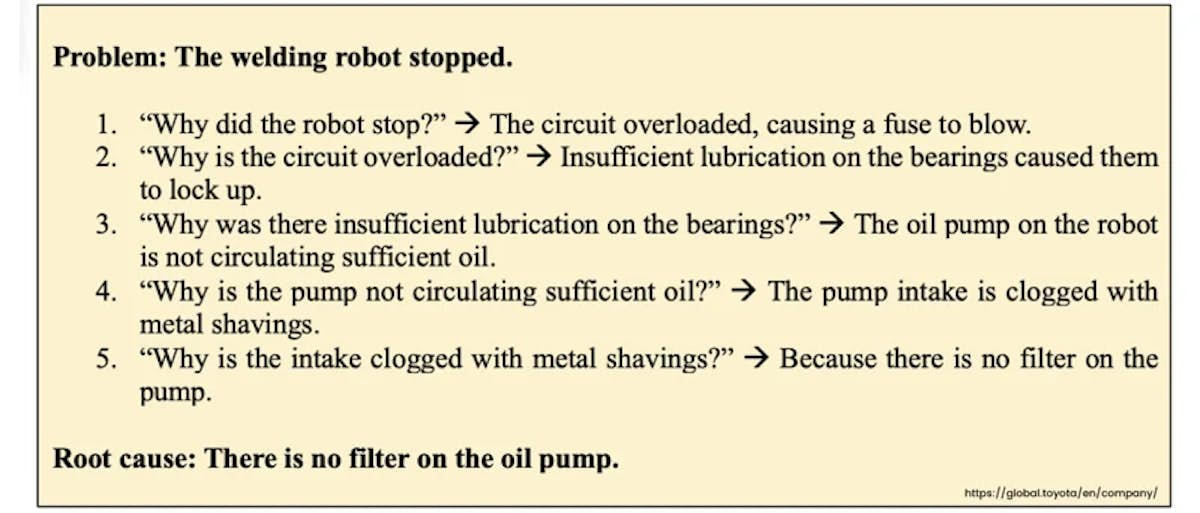
Begin with the most basic form of your issue, such as the error that occurred. Now, ask yourself, why did that error occur? Chances are, your response to this question will not be the root cause, and it’s going to take several more whys to move from symptoms of the error, to the actual root cause itself. The actual number of whys is arbitrary, as long as you get to the root cause. You will know when you’ve gotten to the root cause because it’s actionable, and you can generally trace multiple, higher levels of whys back to a particular root cause .
For example, missing a production deadline because the materials weren’t ready, because there wasn’t enough time to produce them, because workers had to prioritize other projects, because there weren’t enough workers for the total number of projects, all points to a labor shortage problem. Identifying the core problem is the first step to improving manufacturing risk management.
Pareto Analysis
You may not have heard of the Italian researcher Vilfredo Pareto, but perhaps you’re familiar with a theory based on his work: the 80/20 rule.
The 80/20 rule is a widely applicable interdisciplinary theory that postulates that roughly 20% of external factors are the causes of 80% of all outputs.
The 80/20 rule was popularized by Joseph M. Juran in 1937, based on his studies of Vilfredo Pareto’s 1906 publication. Pareto discovered that approximately 20% of Italy’s population owned 80% of the country’s land, and similar distributions held across other countries he surveyed. Juran wondered if this same rule, that only a few factors impact the larger picture, could be applied to other areas of economics as well, and in fact, it could.
The 80/20 rule has since been applied to a wide variety of fields with success, such as engineering, computer science, occupational safety, and more. Pareto Analysis is now considered to be an interdisciplinary method for optimizing decision-making processes. As applied to problem-solving in manufacturing, 80% of problems can be traced to 20% of root causes or defects.
A Pareto Chart can be used to help narrow down where your biggest problem areas are so you can implement manufacturing process improvement changes.
To make your own Pareto chart, follow these steps:
First, list the problems you’re having.
Then, for each problem, determine what the error was that caused the problem.
Finally, create your Pareto chart — typically displayed as a bar graph — to determine which errors are most affecting your business.
The ASQ provides a free, downloadable template to help you get started with creating your own Pareto chart.
Fishbone Diagrams
Fishbone diagrams, also known as Ishikawa diagrams for the engineering professor at the University of Tokyo who first created the diagrams in the 1960s, Kaoru Ishikawa, are a useful tool to pair with the 5 Whys when relationships between problems may not be straightforward.
In a fishbone diagram, the problem is the fish’s head and other bones are the causes. Major causes (which can also be thought of as categories; see discussion in the next paragraph) are identified as ribs that directly branch out from the fish’s backbone, and root causes are eventually identified as bones that branch out from the ribs. Once the root causes are identified, leadership can move to implement manufacturing risk management measures.
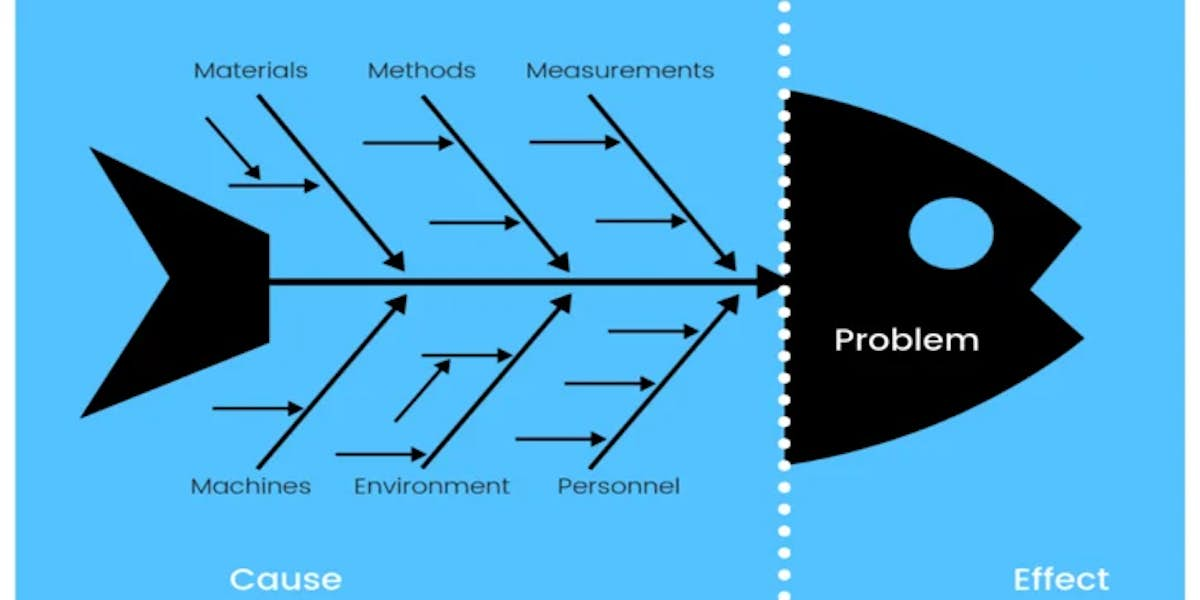
Fishbone diagrams typically follow the so-called 6Ps of manufacturing to serve as categories to identify potential causes, an update to the 6Ms of manufacturing to support important changes within the industry. The categories are helpful in narrowing down whether the root cause of a problem is stemming from a process-related issue or a product-related issue, for example:
The ASQ provides a free, downloadable template to help you get started with creating your own fishbone diagram.
A3 Methodology
It’s just a piece of paper. But, it’s one of the most effective lean tools available to manufacturing engineers. Austin Weber / AssemblyMag
Yet another brainchild of the Toyota lean manufacturing system, A3 is a tool for breaking problems and projects down to their core. The name “A3” refers to the international paper size A3 that was originally used for this strategy because it was the largest, faxable size of paper, so the information could easily be distributed and collaborated on throughout multiple departments and offices. That’s it though — that’s all you get: just one sheet of paper on which to condense your objective down to its most fundamental components.
Interesting fact:
Paper sizes are geometrically related to the zeroth size within their series (e.g., A series, B series, etc.). Within the A series, each successive paper size is almost exactly half of the area of the previous paper size. So a single A0 page — the largest within the series — can fit two A1 pages within the same area; a single A1 page can fit two A2 pages within the same area; a single A2 paper can fit two A3 pages within the same area, and so forth.
An A3 can technically contain information in any format, but it’s often paired with visual tools like the 5 Whys, Pareto Analysis, and Fishbone Diagrams to help narrow down the root of the issue when problem-solving. The rule of thumb is to use visuals and hard data in the form of tables, graphs, and charts as much as possible in place of text to give teams an at-a-glance understanding of the situation and solution.
How to Make More Effective Manufacturing Process Improvements
Manufacturing risk management starts with having a plan to respond to errors and abnormalities as they occur, so you can take them in stride and implement resolutions fast. By understanding the strategies behind how to respond to challenges effectively, leadership can choose the correct approach to make manufacturing process improvements.
Learn more about how to address errors in manufacturing in our eGuide, Addressing Errors & Abnormalities: Proven Methods .
About the author: TBM is a global operations consulting firm with an emphasis on operations, lean, and supply chain consulting for manufacturers and distributors.

- (888) 847-4632
- (904) 474-8333

In manufacturing waste is everything in the factory that doesn’t add value to the process. This waste fits into 8 categories.
- Inventory – Making more than customers’ demand leads to unnecessary stock. These products get in the way of other processes and run the risk of being obsolete and unsellable. Only produce what is ordered to reduce excess inventory.
- Transportation – Moving tools, materials, parts, etc. from one location to another. It is important to transport stuff quickly, safely, and efficiently. Not having the right equipment, or having to wait for the right equipment, will lead to delays.
- Motion – Extra walking, bending, or moving to reach commonly needed items. Frequently used items should be at point of use. Keeping tools and other equipment in convenient locations reduces unneeded movement. This speeds up the process and reduces exhaustion.
- Waiting – Delays between processes, machines, etc. Idling the next stage by a delay in your stage slows down the entire process.
- Over processing – Duplicate processing and redundant operations slow down the process. Think about what you need to do the job and how the process can be more efficient.
- Defects – Rework, scrap, customer quality complaints. This one is literal waste. If the finished product is junk it must be thrown away. Reducing defects is one of the key components of reducing waste.
- Skills – Underutilized skills and capabilities, not listening, not changing. A smart worker always looks to see how he or she can improve the job. Fostering employee growth, taking feedback, and assuming new responsibilities will reduce waste. An employee may be great at one process but even better at another with a little training. It could be hard to lose them, but it would be wasteful not to utilize them to their full potential.
Improve Efficiency
Now that we’ve isolated potential wastes the next step is to see how we can prevent them. The best way to do this is to look at the 3-S method.
- Set in Order
This is a productivity tool to help everyone eliminate clutter to focus on value added activities and improve workflow. By splitting things like tools into groups (sort), putting them in their proper places (set in order), and keeping them in proper working condition (shine) we can improve the entire process.
The goal is to organize the workspace in a way that allows work to flow without extra effort (see Motion and Waiting above). Work does not flow smoothly when you must stop and search for things. For example, don’t put a tool that you use with your right hand on the left side. It may seem like a small thing, but small inefficiencies add up.
Engineering the Process
By focusing on inefficiencies and reducing waste we established an engineered, repeatable process. Analyzing the situation makes abnormalities visible and helps streamline the process. This is done through big actions like evaluating personnel to small actions like promoting cleanliness. This is all part of problem solving in the manufacturing environment.
The main Moffitt factory, Moffitt West , implements these manufacturing problems solving practices daily. This factory has been in operation for decades by principles such as these into practice. That is what makes Moffitt the Natural Solution for ventilation.
Recent Posts
- What is the Best Warehouse Fan?
- Moffitt Ventilation Solutions – Natural & More
- Cooling a Warehouse in Summer
- Data Center Cooling System – Natural Cooling
- Centrifugal Fans made by the Ventilation Experts
- CFD Modeling (16)
- Commercial Ventilation (27)
- Cost Savings (26)
- Energy Savings (34)
- Green Ventilation (22)
- Heating (3)
- Hybrid Ventilation (4)
- Industrial Ventilation (93)
- Installation (31)
- Lunch & Learn (4)
- Maintenance (17)
- Manufacturing (12)
- Moffitt (34)
- Natural Cooling (16)
- Natural Daylighting (8)
- Natural Smoke Relief (9)
- Natural Solutions (49)
- Natural Ventilation (91)
- Natural Ventilator Maintenance (1)
- Powered Ventilation (37)
- Pressure Gravity System® (10)
- Product Comparison (8)
- Safety (21)
- Science (33)
- Testimonial (10)
- Wall Louvers (6)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A3 Problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that originated with the lean manufacturing methodology. It visualizes the problem-solving process using a one-page document known as an A3 report. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and ...
Both methods are similar, using 8 steps to address complex problems with focus on a fast reaction to non-conformances, completing the first three steps within three days. A3: The A3-report, developed by Toyota, is an 8-step improvement and problem-solving process that fits on one sheet of paper. The A3-report is most effective to address small ...
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. The strength of the 8D process lies ...
What is A3 Problem Solving? A3 Problem Solving is a problem solving method that uses a structured, continued growth methodology to improve manufacturing practices. The method was invented by Toyota and is based on the work of Edward Deming. How is A3 Problem Solving implemented? A3 Problem Solving has 7 steps:
The 8 Steps and the Problem-Solving Process. The Culture of Problem-Solving. Plan, Do, Check, Act (PDCA) Gain Problem-Solving Support. As a manufacturing professional, you know how important it is to stay organized, keep your goals in mind and strive for success. But with all of the responsibilities and daily tasks piling up, it takes effort to ...
Lean manufacturing has a unique way of solving problems. It does not just look at the effect of the problem and try to cover it with a Band-Aid. Rather, the root cause of the problem is identified and the root cause, as well as all contributing factors, is eliminated from the system, process or infrastructure in order to permanently solve the ...
This problem-solving process is characterized by defining problems in the context of the big picture, thinking multi-dimensionally, going to the gemba, applying the PDCA cycle (Deming Cycle), and documenting the problem-solving effort in a standard format. Why does problem solving matter? Disciplined and scientific problem-solving is at the ...
Named after the "A-3" sized paper used for documentation, A3 problem solving teaches employees how to rapidly address manufacturing problems, effectively communicate solutions and monitor results. This approach is typically used by Lean manufacturing practitioners to support Kaizen events. When combined with the DMAIC (Define, Measure ...
The 8D problem-solving method is a systematic approach to problem solving that emphasizes team participation. This method generally covers: ... Finally, It also allows for better communication flows between teams responsible for different processes in the manufacturing process and reduces the amount of time spent investigating issues that aren ...
Bottleneck Analysis identifies which part of the manufacturing process limits the overall throughput and improves the performance of that part of the process. ... Root Cause Analysis is a problem solving methodology that focuses on resolving the underlying problem instead of applying quick fixes that only treat immediate symptoms of the problem ...
The Four Types of Problems. Type 1: Troubleshooting: reactive problem-solving that hinges upon rapidly returning abnormal conditions to known standards. It provides some immediate relief but does not address the root cause. Type 2: Gap from Standard: structured problem-solving that focuses on defining the problem, setting goals, analyzing the ...
The eight disciplines (8D) model is a problem solving approach typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals, and is most commonly used by the automotive industry but has also been successfully applied in healthcare, retail, finance, government, and manufacturing. The purpose of the 8D methodology is to identify, correct, and ...
Practical problem solving is the processes or methods to be used for solving realistic problems in order to achieve goals. This research focus on all aspects of practical problem solving, which aims to collect successful studies regarding practical problem solving in manufacturing technologies. All of the collected papers provide novel methods ...
A core element of a lean and learning production system are processes that show deviations and employees who resolve root causes. If a problem occurs, systematic problem-solving processes enable to find and implement a sustainable solution. The concepts of problem-solving described in scientific literature are rarely successfully applied in ...
Problem solving is a vital skill in manufacturing, where issues can arise at any stage of the production process and affect quality, cost, and customer satisfaction. A structured problem solving ...
In manufacturing problem solving, a key method stands out: Lean. This problem solving method focuses in on eliminating waste and finding a solution as quickly and efficiently as possible. This is by far the leading method that manufacturing engineers use to solve problems throughout the production process, so let's take a look at some of it ...
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) is the umbrella way of thinking (Read why PDCA is the engine of lean ).Well done PDCA is a way of improving your way toward specific business needs. We have True North (a general concept of perfection), business plans, annual plans, and daily management. Then throughout the organization we want people using PDCA to find ...
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions. With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so.
In this blog, we discuss how to address errors in manufacturing by using manufacturing process improvement problem-solving methods for effective manufacturing risk management. Resiliency, the ability to overcome challenges, is a defining factor in whether we "make it or break it" as individuals, teams, or enterprises.
Steps in the Problem-Solving Process. Next, we will look at the steps in a typical problem-solving process and how those can be impacted by smart manufacturing solutions. Combined Steps in the Process
Keywords: systematic problem solving process; Manufacturing Analytics; digitalization; Industrie 4.0 1. Introduction Complexity in production is constantly growing, i.e. through high number of variants, fast changing customer demands and technically challenging products and processes. This results in an increased number of failure modes and ...
Manufacturing Problem Solving - Value Added Process Diagram. In manufacturing waste is everything in the factory that doesn't add value to the process. This waste fits into 8 categories. Inventory - Making more than customers' demand leads to unnecessary stock. These products get in the way of other processes and run the risk of being ...
To apply problem-solving skills for ensuring quality control in manufacturing engineering, particularly through root cause analysis, you can follow these steps: 1. Identify the Problem: Clearly ...