Pharmaceutics I – B. Pharma 1st Semester Notes
Table of Contents

Scope: Pharmaceutics 1st Semester Notes is designed to impart fundamental knowledge on the preparatory pharmacy with the arts and science of preparing the different conventional dosage forms.
Objectives: Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
Know the history of the profession of pharmacy
Understand the basics of different dosage forms, pharmaceutical incompatibilities , and pharmaceutical calculations
Understand the professional way of handling the prescription
Preparation of various conventional dosage forms
Course Content: Pharmaceutics Notes 1st Semester

Pharmaceutics UNIT – I
Historical background and development of the profession of pharmacy: History of the profession of Pharmacy in India in relation to pharmacy education, industry, and organization, Pharmacy as a career,
Pharmacopoeias: Introduction to IP, BP, USP and Extra Pharmacopoeia.
Dosage forms: Introduction to dosage forms, classification, and definitions
Prescription: Definition, Parts of prescription, handling of Prescription, and Errors in prescription.
Posology: Definition, Factors affecting posology. Pediatric dose calculations are based on age, body weight, and body surface area.
Pharmaceutics UNIT – II
Pharmaceutical calculations: Weights and measures – Imperial & Metric system, Calculations involving percentage solutions, allegation, proof spirit, and isotonic solutions based on freezing point and molecular weight.
Powders: Definition, classification, advantages and disadvantages, Simple & compound powders – official preparations, dusting powders, effervescent, efflorescent and hygroscopic powders, eutectic mixtures. Geometric dilutions.
Liquid dosage forms: Advantages and disadvantages of liquid dosage forms.
Excipients used in the formulation of liquid dosage forms. Solubility enhancement techniques
Pharmaceutics UNIT – III
Monophasic liquids: Definitions and preparations of Gargles, Mouthwashes, Throat Paint, Eardrops, Nasal drops, Enemas, Syrups, Elixirs, Liniments, and Lotions.
Biphasic liquids:
Suspensions: Definition, advantages and disadvantages, classifications, Preparation of suspensions; Flocculated and Deflocculated suspension & stability problems and methods to overcome.
Emulsions: Definition, classification, emulsifying agent, test for the identification of the type of emulsion, Methods of preparation & stability problems, and methods to overcome.
Pharmaceutics UNIT – IV
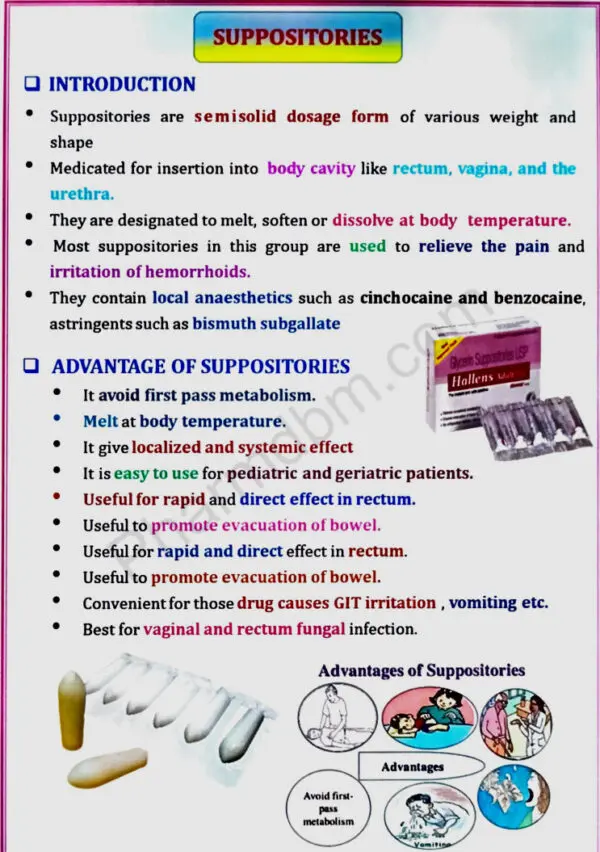
Suppositories: Definition, types, advantages and disadvantages, types of bases, methods of preparations. Displacement value & its calculations, evaluation of suppositories.
Pharmaceutical incompatibilities: Definition, classification, physical, chemical, and therapeutic incompatibilities with examples.
Pharmaceutics UNIV – V
Semisolid dosage forms: Definitions, classification, mechanisms and factors influencing dermal penetration of drugs. Preparation of ointments, pastes, creams, and gels. Excipients are used in semi-solid dosage forms. Evaluation of semi-solid dosages forms

pharmaceutics 1 notes pdf download
PHARMACEUTICS I (Practical)
a) Syrup IP’66
b) Compound syrup of Ferrous Phosphate BPC’68
2. Elixirs
a) Piperazine citrate elixir
b) Paracetamol pediatric elixir
3. Linctus
a) Terpin Hydrate Linctus IP’66
b) Iodine Throat Paint (Mandles Paint)
4. Solutions
a) Strong solution of ammonium acetate
b) Cresol with soap solution
c) Lugol’s solution
5. Suspensions
a) Calamine lotion
b) Magnesium Hydroxide mixture
c) Aluminum Hydroxide gel
6. Emulsions
a) Turpentine Liniment
b) Liquid paraffin emulsion
7. Powders and Granules
a) ORS powder (WHO)
b) Effervescent granules
c) Dusting powder
D)Divded powders
8. Suppositories
a) Glycero gelatin suppository
b) Coca-butter suppository
c) Zinc Oxide suppository
8. Semisolids
a) Sulphur ointment
b) Non-staining-iodine ointment with methyl salicylate
c) Carbopal gel
9. Gargles and Mouthwashes
a) Iodine gargle
b) Chlorhexidine mouthwash
Pharmaceutics Recommended Books: (Latest Editions)
1. H.C. Ansel et al., Pharmaceutical Dosage Form and Drug Delivery System, Lippincott Williams and Walkins, New Delhi.
2. Carter S.J., Cooper and Gunn’s-Dispensing for Pharmaceutical Students, CBS publishers, New Delhi.
3. M.E. Aulton, Pharmaceutics, the Science& Dosage Form Design, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.
4. Indian pharmacopoeia.
5. British pharmacopoeia.
6. Lachmann. Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy,Lea& Febiger Publisher, The University of Michigan.
7. Alfonso R. Gennaro Remington. The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, Lippincott Williams, New Delhi.
8. Carter S.J., Cooper and Gunn’s. Tutorial Pharmacy, CBS Publications, New Delhi.
9. E.A. Rawlins, Bentley’s Text Book of Pharmaceutics, English Language Book Society, Elsevier Health Sciences, USA.
10. Isaac Ghebre Sellassie: Pharmaceutical Pelletization Technology, Marcel Dekker, INC, New York.
11. Dilip M. Parikh: Handbook of Pharmaceutical Granulation Technology, Marcel Dekker, INC, New York.
12. Francoise Nieloud and Gilberte Marti-Mestres: Pharmaceutical Emulsions and Suspensions, Marcel Dekker, INC, New York.
Comments are closed.

Pharmaceutics 1 Notes pdf – Bpharm 1st Semester

Free Download Pharmaceutics 1 Notes in pdf – Bpharm 1st Semester . High quality, well-structured, and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Welcome to Pharmdbm.com
Pharmdbm provides standard or well-structured Notes for Bpharm students. The notes are free to download. Each semester notes of Bpharm are available on www.pharmdbm.com.
In this post you can download notes of Pharmaceutics 1 (BP103T). All units are available to download for free.
Pharmaceutics 1 Notes Unit 1 – 5
Unit – 1, historical background and development of profession of pharmacy, dosage forms, prescription, posology.

UNIT – 2
Pharmaceutical calculations, powders, liquid dosage forms.

UNIT – 3
Monophasic liquids, biphasic liquids – suspensions & emulsions.

UNIT – 4
Suppositories, pharmaceutical incompatibilities.
UNIT – 5
Semisolid dosage forms.


Scope of Pharmaceutics 1
This course is designed to impart a fundamental knowledge on the preparatory pharmacy with arts and science of preparing the different conventional dosage forms.
Objectives of Pharmaceutics 1
Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
- Know the history of profession of pharmacy.
- Understand the basics of different dosage forms, pharmaceutical incompatibilities and pharmaceutical calculations.
- Understand the professional way of handling the prescription.
- Preparation of various conventional dosage.
Syllabus of Pharmaceutics 1
Historical background and development of profession of pharmacy: History of profession of Pharmacy in India in relation to pharmacy education, industry and organization, Pharmacy as a career, Pharmacopoeias: Introduction to IP, BP, USP and Extra Pharmacopoeia.
Dosage forms: Introduction to dosage forms, classification and definitions
Prescription: Definition, Parts of prescription, handling of Prescription and Errors in prescription.
Posology: Definition, Factors affecting posology. Pediatric dose calculations based on age, body weight and body surface area.
Pharmaceutical calculations: Weights and measures – Imperial & Metric system, Calculations involving percentage solutions, alligation, proof spirit and isotonic solutions based on freezing point and molecular weight.
Powders: Definition, classification, advantages and disadvantages,Simple & compound powders – official preparations, dusting powders, effervescent, efflorescent and hygroscopic powders, eutectic mixtures. Geometric dilutions.
Liquid dosage forms: Advantages and disadvantages of liquid dosage forms. Excipients used in formulation of liquid dosage forms. Solubility enhancement techniques
Monophasic liquids: Definitions and preparations of Gargles, Mouthwashes, Throat Paint, Eardrops, Nasal drops, Enemas, Syrups, Elixirs, Liniments and Lotions.
Biphasic liquids –
Suspensions: Definition, advantages and disadvantages, classifications, Preparation of suspensions; Flocculated and Deflocculated suspension & stability problems and methods to overcome.
Emulsions: Definition, classification, emulsifying agent, test for the identification of type ofEmulsion, Methods of preparation & stability problems and methods to overcome.
Suppositories: Definition, types, advantages and disadvantages, types of bases, methods of preparations. Displacement value & its calculations, evaluation of suppositories.
Pharmaceutical incompatibilities: Definition, classification, physical, chemical and therapeutic incompatibilities with examples.
Semisolid dosage forms: Definitions, classification, mechanisms and factors influencing dermal penetration of drugs. Preparation of ointments, pastes, creams and gels. Excipients used in semi solid dosage forms. Evaluation of semi solid dosages forms
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- B PHARM NOTES
- _Semester 1
- _Semester 2
- _Semester 3
- _Semester 4
- _Semester 5
- _Semester 6
- _Semester 7
- _Semester 8
Pharmaceutics I B pharmacy Semester 1 free notes
Handwritten Notes

BP103T. PHARMACEUTICS- I (Theory)

You may like these posts
Post a comment.
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.
Popular Posts

Biostatisitcs And Research Methodology 8 Semester Notes

Social And Preventive Pharmacy 8 Semester Notes

Pharmaceutical Regulatory Science 8 Semester Notes

- Privacy Policy
@2023 Pharmacy Notes
Contact form
Pharmaceutics 1 - Unit 1
Historical background and development of profession of pharmacy: History of profession of Pharmacy in India in relation to pharmacy education, industry and organization, Pharmacy as a career, Pharmacopoeias: Introduction to IP, BP, USP and Extra Pharmacopoeia. Dosage forms: Introduction to dosage forms, classification and definitions Prescription: Definition, Parts of prescription, handling of Prescription and Errors in prescription. Posology: Definition, Factors affecting posology. Pediatric dose calculations based on age, body weight and body surface area.

COMMENTS
Suppositories: Definition, types, advantages and disadvantages, types of bases, methods of preparations. Displacement value & its calculations, evaluation of suppositories. Pharmaceutical incompatibilities: Definition, classification, physical, chemical and therapeutic incompatibilities with examples. UNIV – V.
Understand the basics of different dosage forms, pharmaceutical incompatibilities, and pharmaceutical calculations. Understand the professional way of handling the prescription. Preparation of various conventional dosage forms. Course Content: Pharmaceutics Notes 1st Semester. Pharmaceutics UNIT – I
Free Download Pharmaceutics 1 Notes in pdf - Bpharm 1st Semester. High quality, well-structured and Standard Notes that are easy to remember.
Bachelor of Pharmacy complete notes of every year (every semester). You can also get PDF.
B.Pharma 1st Sem PDF Study Materials Download. We are Providing Bachelor of Pharmacy 1st semester Study Notes, Books, Handwritten Practical Files and Previous Five-Year Question Papers of All Subjects like H.A.P, Pharmaceutical analysis, Pharmaceutics and Inorganic Chemistry Free of Cost.
1) Partition Co-efficient principle is used in the partition chromatography, where it helps in separation, purification and identification. 2) The partitioning principle is involved in the prolonged release of drugs.
Pharmaceutics 1. Unit 1. Historical background and development of profession of pharmacy: History of profession of Pharmacy in India in relation to pharmacy education, industry and organization, Pharmacy as a career, Pharmacopoeias: Introduction to IP, BP, USP and Extra Pharmacopoeia.
This document provides instructions for a pharmacy course assignment on pharmaceutics. Students are asked to write short notes on different dosage forms available, techniques for labeling dispensed preparations, and types of coloring and flavoring agents used in preparations.
Pharmaceutics 1 - Unit 3 Syllabus Monophasic liquids: Definitions and preparations of Gargles, Mouthwashes, Throat Paint, Eardrops, Nasal drops, Enemas, Syrups, Elixirs, Liniments and Lotions.
Prescription: Definition, Parts of prescription, handling of Prescription and Errors in prescription. Posology: Definition, Factors affecting posology. Pediatric dose calculations based on age, body weight and body surface area.