

35 Amazing School Project Invention Ideas

Are you a middle school student looking for some inspiration for your next invention? Look no further! In this blog post, we’ll be sharing some innovative and creative school invention ideas that are perfect for middle school students.
First up, how about inventing a smart backpack? This backpack could have features like built-in charging ports for your devices, solar panels for recharging on the go, and even a tracking system to prevent losing it. Another great idea is creating a mobile app that helps students manage their time and assignments more efficiently. It could include features like reminders, calendars, and to-do lists. For those interested in science, consider inventing a water filtration system or a solar-powered oven.
The possibilities are endless! With a little creativity and hard work, you can come up with an invention that could change the world.
Here are the top 35 invention ideas for you to ace in your project:
1. A Solar-Powered Phone Charger
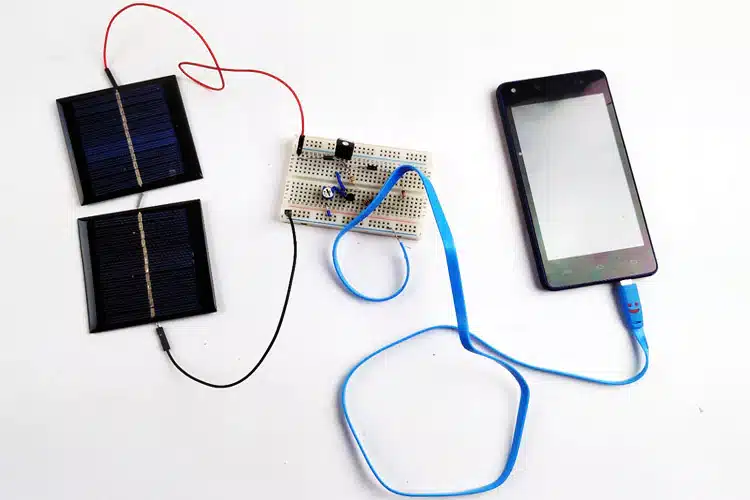
To make a solar-powered phone charger, you will need a solar panel, a voltage regulator, a rechargeable battery, and a USB port. First, connect the solar panel to the voltage regulator, making sure the positive and negative wires are correctly aligned. Then, connect the voltage regulator to the rechargeable battery, following the same procedure. Finally, connect the USB port to the battery, ensuring the positive and negative wires are aligned correctly. Once everything is connected, your solar-powered phone charger should be ready to use!
2. A Self-Watering Plant System
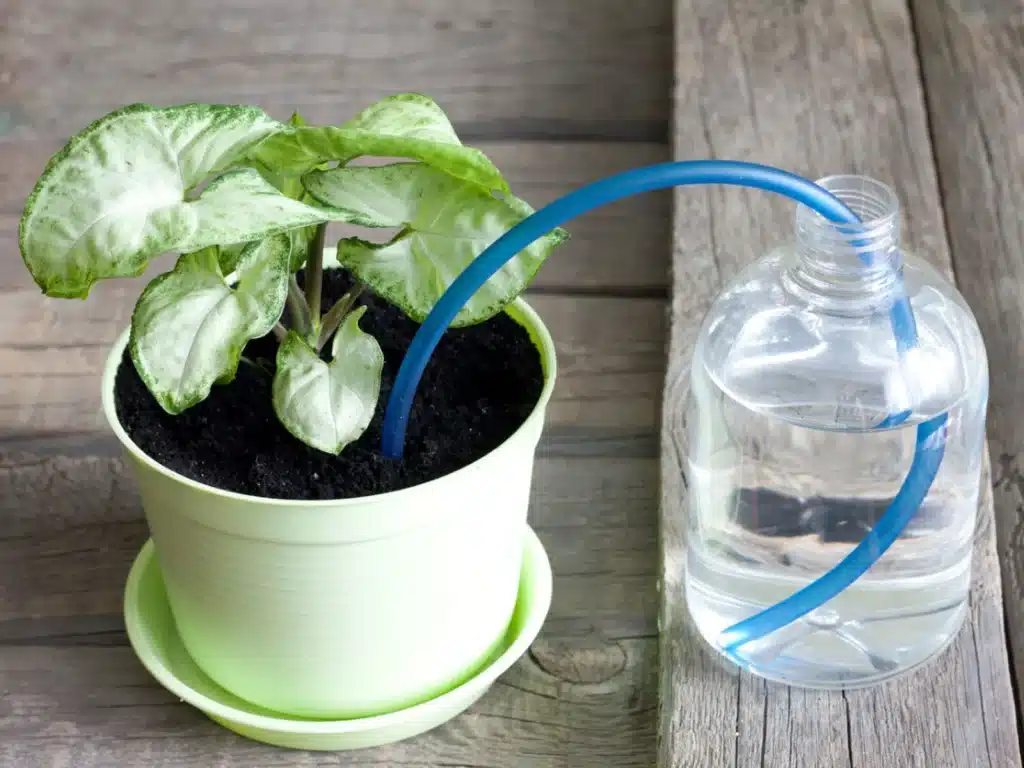

For a self-watering plant system, you will need a few supplies. First, you’ll need a container to hold your plant and water. You’ll also need a wick or rope to draw water up from the reservoir to the soil and some ground for your plant to grow in. To assemble your self-watering plant system, start by drilling a small hole in the bottom of your container for drainage. Then, cut a length of wick or rope that is long enough to reach from the bottom of your container to the top of your soil. Insert one end of the wick through the drainage hole and place the other end on top of the soil. Next, fill the bottom of your container with water, making sure the wick is submerged. Then, add soil to the top of your container and plant your desired plant. As the soil dries out, the wick will draw water up from the reservoir, keeping your plant hydrated.
3. A Bike Lock that Doubles as a Phone Holder
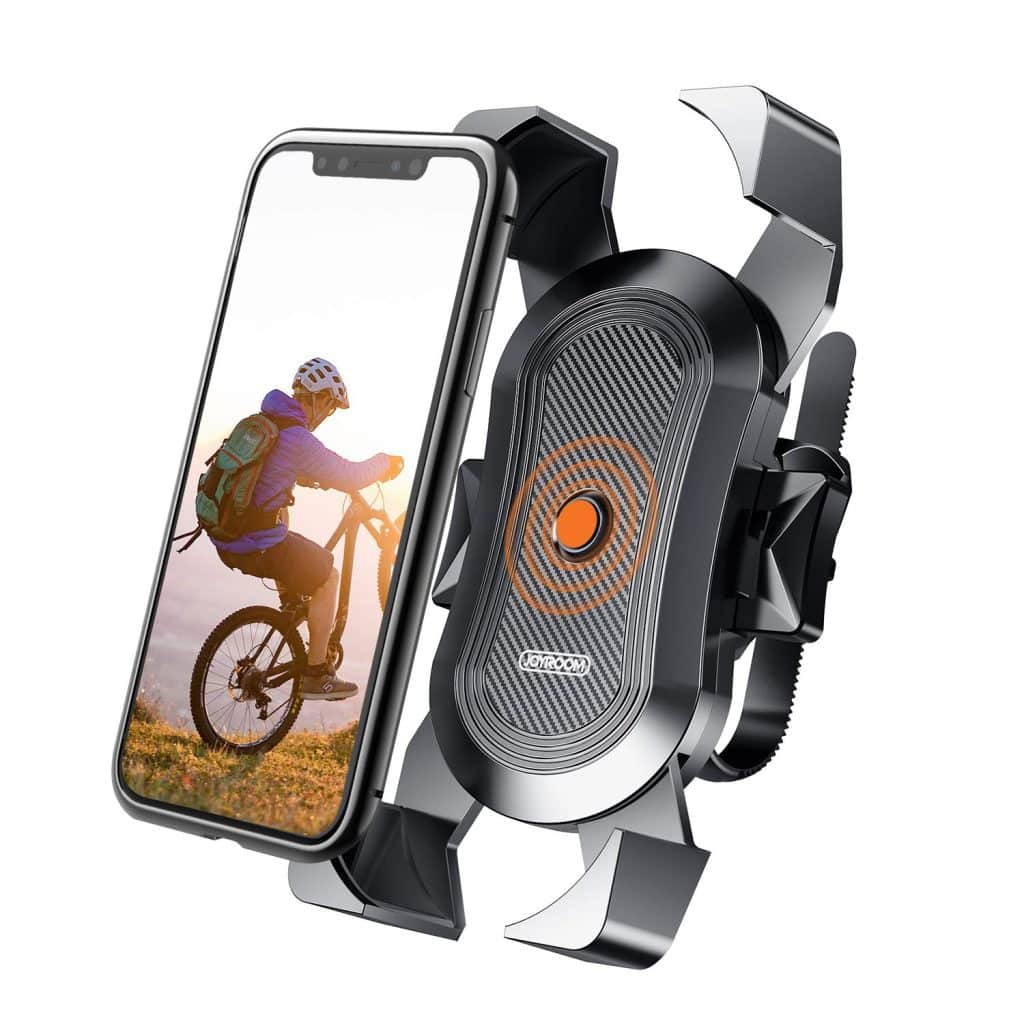

A bike lock that doubles as a phone holder is going to be interesting. For this, you will need a sturdy bike lock and a phone mount that can fit securely onto the lock. First, attach the phone mount to the lock, ensuring that it is tightly secured. Next, place your phone on the mount and adjust it to your preferred angle for viewing. Lastly, wrap the lock around your bike frame or post and secure it in place. Now, you have a convenient way to keep your phone within reach while also keeping your bike secure.
4. A Backpack with Built-In LED Lights for Safety
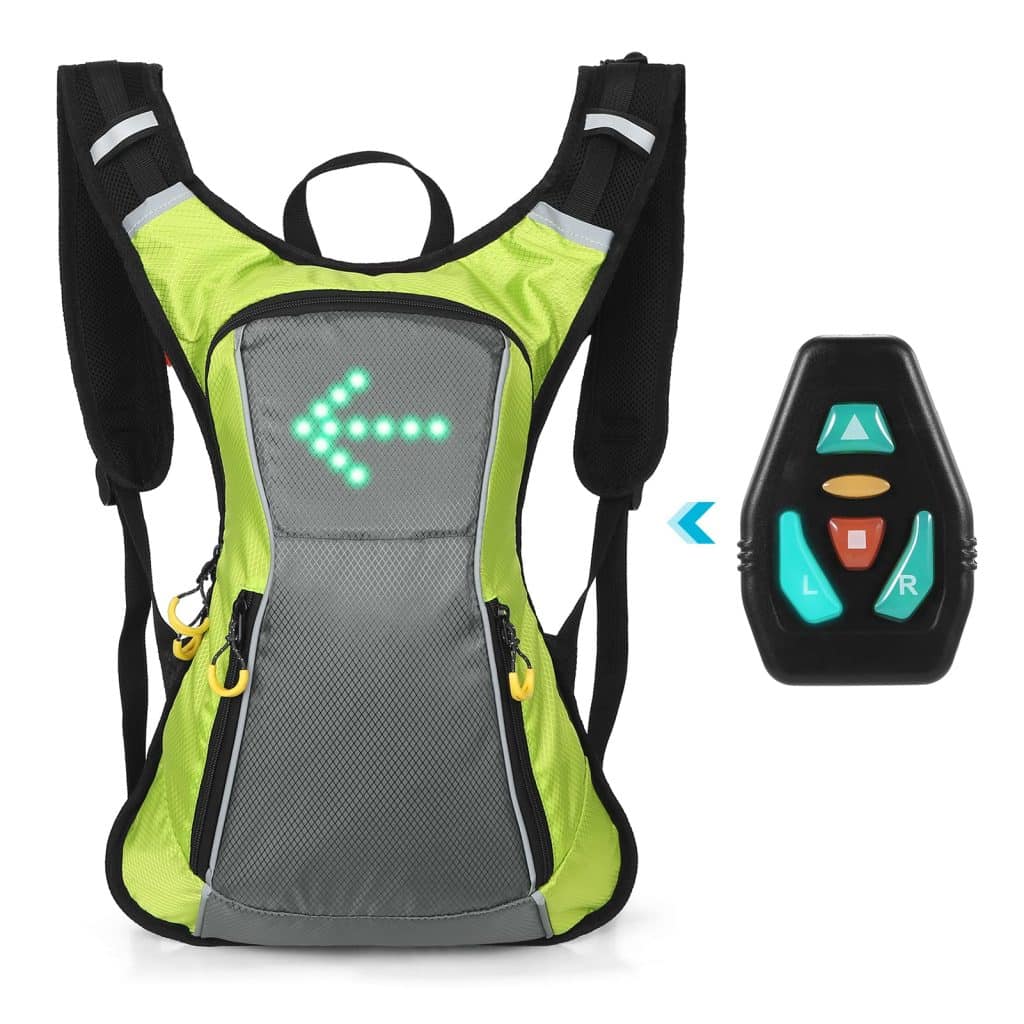

A backpack with built-in LED lights for safety can be made by using a backpack, LED strip lights, a battery pack, and a switch. First, measure the length of the backpack straps and cut the LED strip lights to fit. Then, attach the LED lights to the straps using adhesive tape. Next, attach the battery pack to the backpack with adhesive tape or a clip. Finally, attach the switch to the backpack in a convenient location. Test the lights to ensure they work properly.
5. A Portable Study Desk that Fits in a Locker
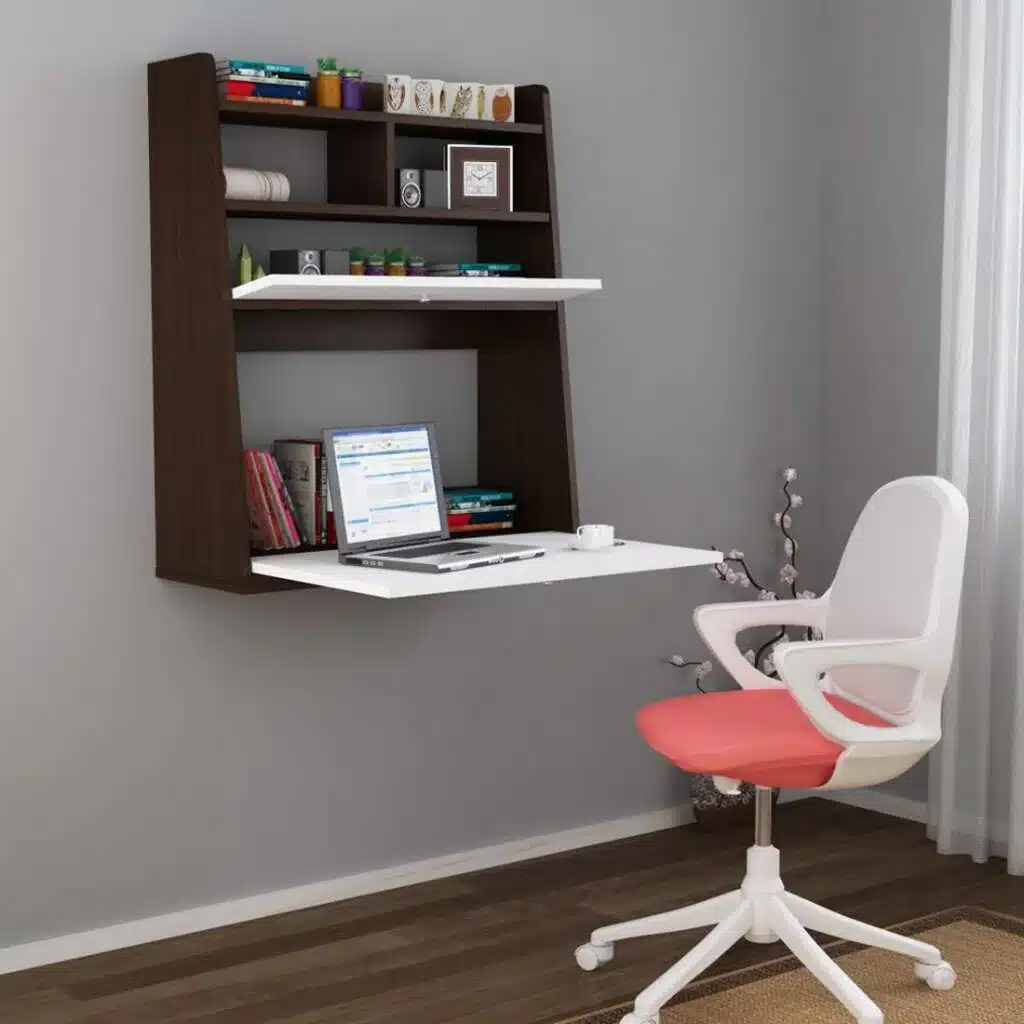

Looking to create a study desk that can easily fit inside a locker? You’ll need a few materials to get started. First, grab a piece of plywood that will serve as the desk’s surface and cut it to your desired size. Then, attach folding legs to the bottom of the plywood using screws and hinges. Be sure that the legs are sturdy enough to support the weight of the desk. Next, create a frame around the desk surface using PVC pipes or wooden dowels to ensure stability and prevent wobbling. Finally, attach a handle to the side of the desk for easy carrying. And there you have it – your very own portable study desk!
6. An Automatic Pencil Sharpener

If you’re tired of constantly having to buy new pencils or struggling to sharpen them manually, consider making your own DIY automatic pencil sharpener! With just a few simple materials, you can create a device that will sharpen your pencils quickly and efficiently. Start by gathering a small motor, battery pack, and a switch. Then, attach a sharpening blade to the motor and connect everything together using wires. Finally, mount the device onto a sturdy base and test it out on a few pencils.
7. A Device That Helps You Find Lost Items
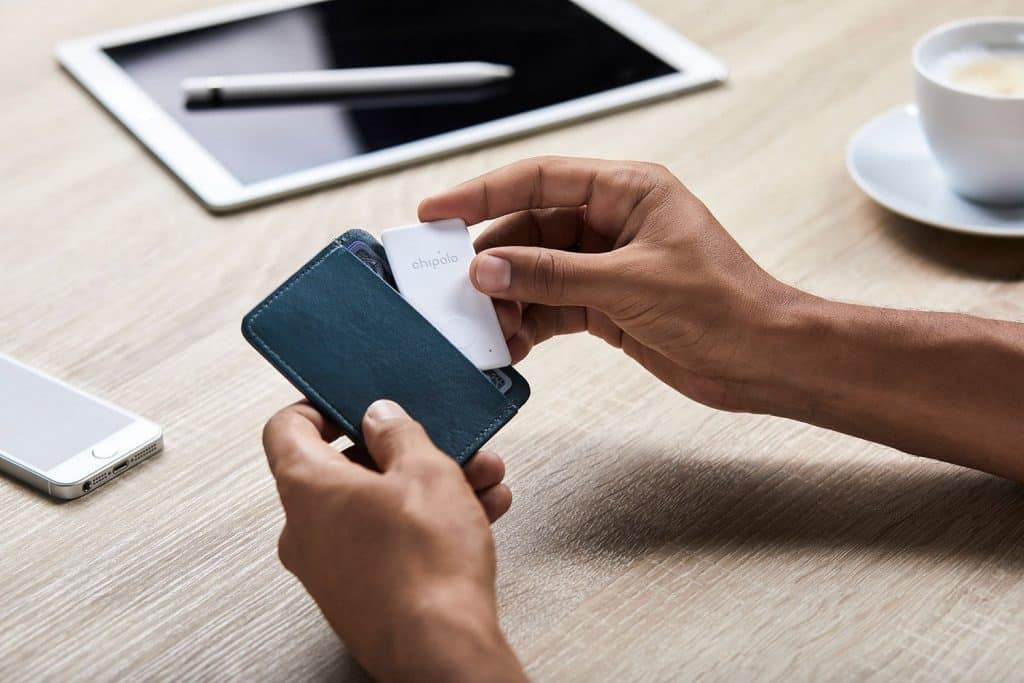

Great idea, isn’t it? One way to start would be to research Bluetooth and GPS technology, which are key technologies used in the Find-It-Yourself device. You could also consider creating an accompanying app that allows users to set up virtual boundaries and receive notifications when their lost item is detected within the boundary. It’s important to keep the device small and portable so that it can easily be attached to any item.
8. An Intelligent Mirror that Gives You Skincare Advice
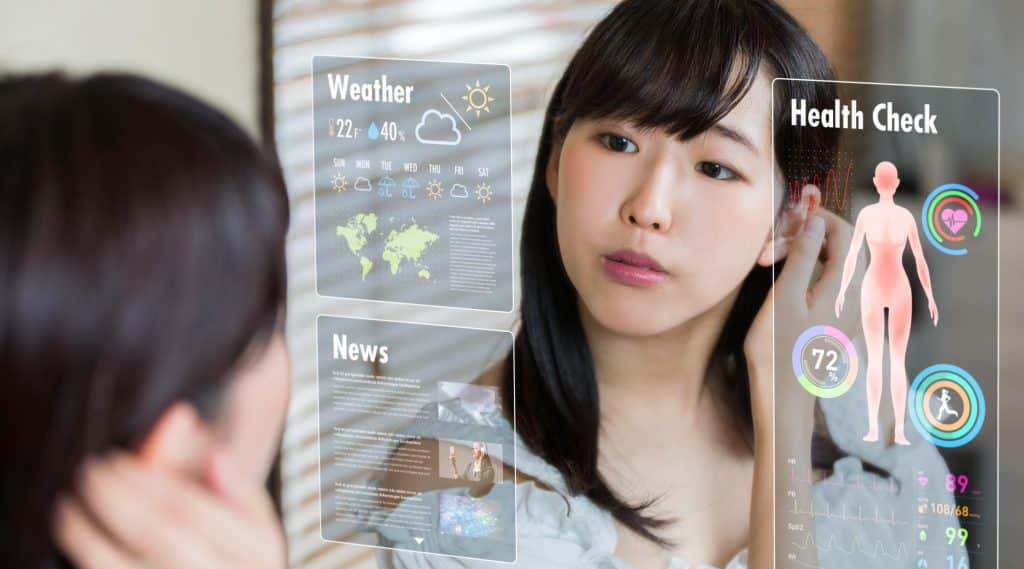

To create an intelligent mirror that gives you skincare advice, you will need to start with a regular mirror and add some technology. First, install a camera behind the mirror that can take high-quality images of your face. Next, use facial recognition software to analyze your skin and identify any areas that need attention. You can then program the mirror to provide customized skincare advice based on your individual needs. This could include recommending specific products, suggesting changes to your skincare routine, or providing tips for better self-care.
9. A Temperature-Controlled Water Bottle

To make a temperature-controlled water bottle, you will need a few materials, such as a water bottle, a thermometer, a heating element, and a cooling element. Start by inserting the thermometer into the water bottle to get an accurate reading of the temperature. Next, attach the heating and cooling elements to the water bottle. The heating element will raise the temperature of the water, while the cooling element will lower it. Connect both elements to a control system that will regulate the temperature of the water.
10. A Noise-Canceling Earplug for Studying

One way to create a noise-canceling earplug for studying is by using a combination of materials that are readily available. Start by purchasing a pair of foam earplugs and a set of noise-canceling headphones. Cut off the ear cups from the headphones and remove the speakers from them. Apply a generous amount of hot glue to the earplugs and attach the speakers to them. Once the glue has dried, cover the speakers with the ear cups and test the earplugs by playing some music. The result should be a pair of earplugs that block out ambient noise while still allowing you to listen to your study music.
11. A Device That Helps You Organize Your School Supplies

If you’re looking for a way to organize your school supplies, why not try making your own DIY device? With just a few materials and some basic crafting skills, you can create a customized organizer that fits your needs perfectly. Start by choosing the size and shape of your organizer, then gather materials like cardboard, fabric, and glue. Cut and fold the cardboard into the desired shape, cover it with fabric, and add compartments for your pencils, pens, highlighters, and other supplies. With a little creativity and effort, you can have a functional and stylish organizer that will make your school days easier.
12. A Basketball Hoop that Doubles as a Laundry Hamper

To create a basketball hoop that doubles as a laundry hamper, you must have a large cylindrical laundry basket, a basketball hoop, and sturdy adhesive. Securely attach the basketball hoop to the top of the laundry basket and ensure it is firmly fastened. Then, place the laundry basket in your desired location and start shooting your dirty clothes into the hoop! This DIY project is both practical and entertaining, making laundry duty much more enjoyable.
13. A Chair that Doubles as a Backpack

To invent a chair that doubles as a backpack, you would need to think about the design and functionality of both items. It would be important to consider the weight and balance of the backpack when the chair is being used, as well as the comfort and stability of the chair when it is being carried on one’s back. You may want to explore materials that are lightweight yet sturdy and experiment with different folding mechanisms to make the transformation from chair to backpack seamless.
14. A Smartwatch that Reminds You to Drink Water

A way to create a smartwatch that reminds you to drink water is by incorporating sensors that measure the amount of water you consume throughout the day. The watch could then remind you to drink water at regular intervals through vibrations, messages on the screen, or even a voice assistant. It’s important to make the watch user-friendly and visually appealing, taking into consideration the size, style, and interface that would be most intuitive for users.
15. A Book Stand that Holds Your Book Open for You
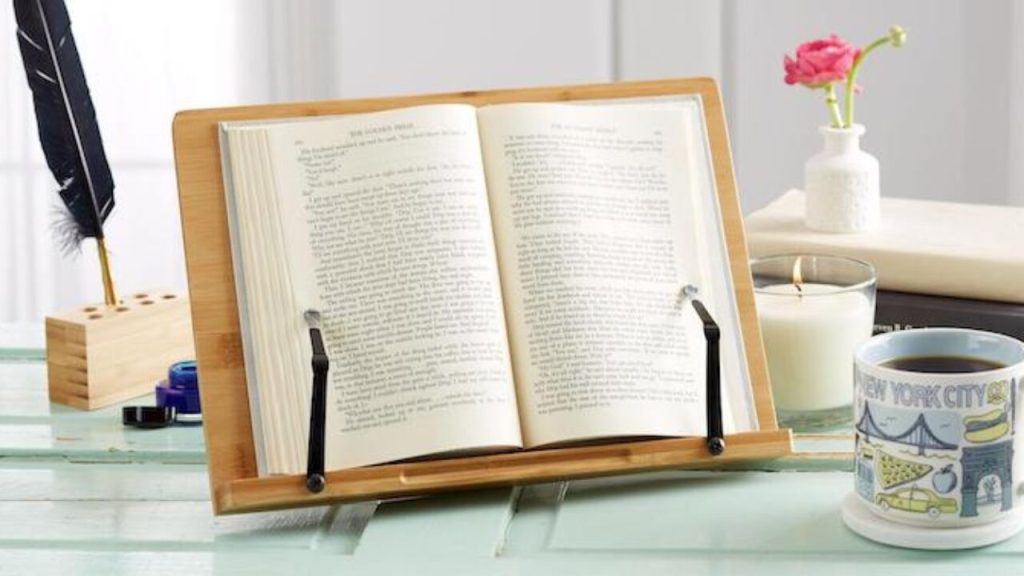

A book stand that holds your book open for you, yes, interesting! You will need a few materials. First, you will need a sturdy piece of cardboard or a thin piece of wood. You will also need a ruler, a pencil, a pair of scissors, and some tape. Start by measuring and marking out a rectangle on your cardboard or wood that is slightly larger than the size of your book. Cut out the rectangle using your scissors. Next, cut a slit in the middle of the rectangle that is just wide enough to fit the spine of your book. Make sure the slit is centered in the rectangle. Fold the two sides of the rectangle up at a slight angle to create a stand for your book. Use tape to secure the sides in place. Finally, place your book on the stand, with the spine resting in the slit.
16. A Creative Bookmark that Remembers Where You Left
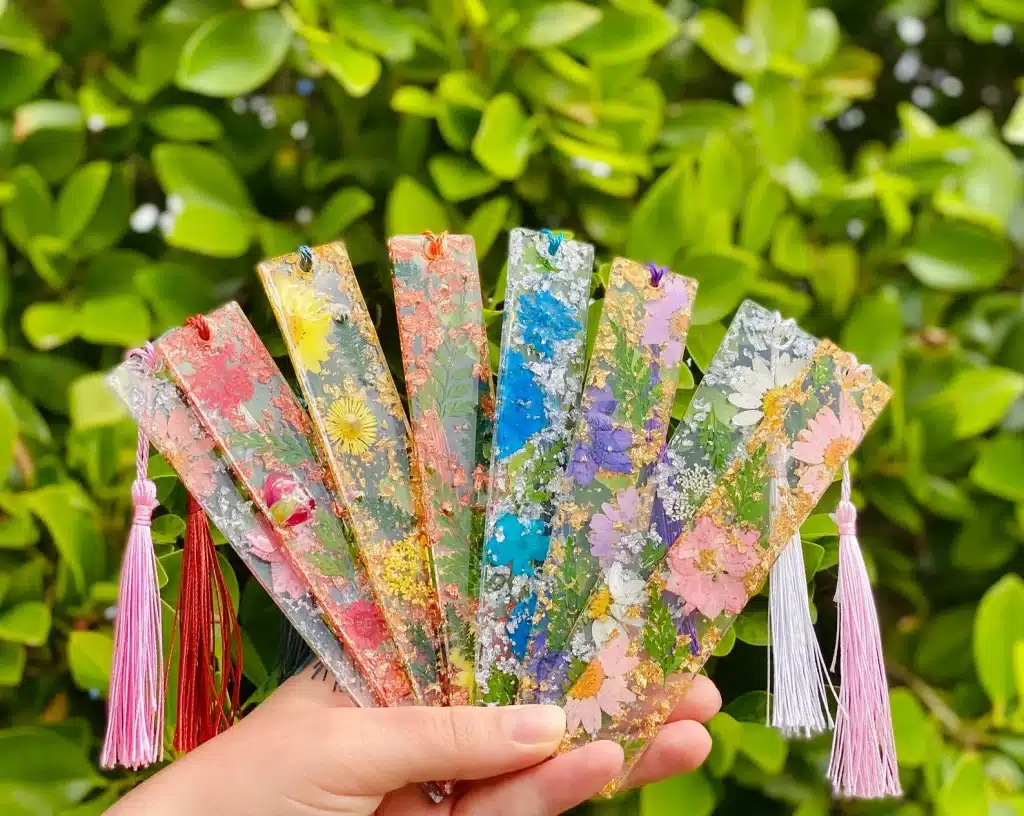

Are you tired of losing your place in your favorite book? Do you find yourself constantly flipping through pages trying to remember where you left off? Well, have no fear! With this creative bookmark, you’ll never lose your place again. It’s easy to make, and you’ll wonder how you ever lived without it. Plus, it’s a great way to add a personal touch to your reading experience.
17. A Device That Helps You Find Parking Spots at School
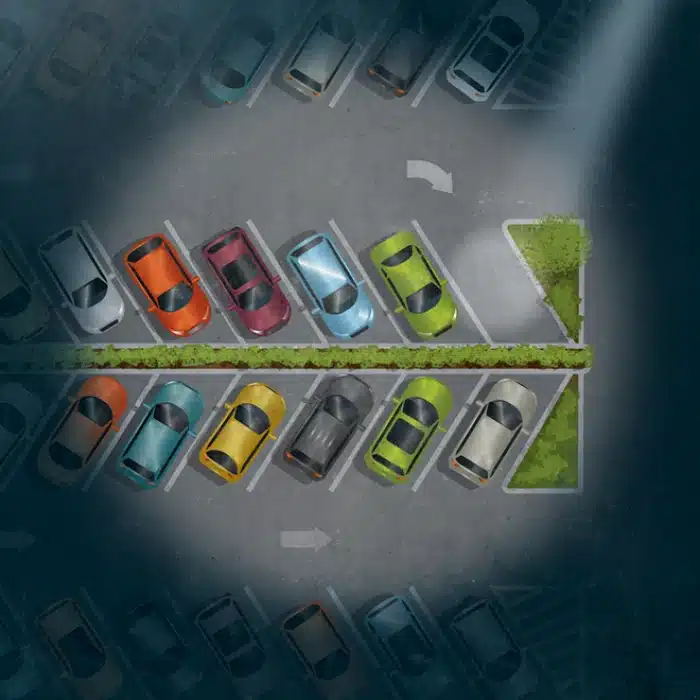

Have you ever been late for class because you couldn’t find a parking spot at school? Well, imagine having a device that helps you locate available spots with just a few taps on your phone. This innovative device uses real-time data to guide you to the nearest available parking spot, saving you time and reducing stress.
18. A Wearable GPS Tracker for Students on Field Trips
Creating a wearable GPS tracker for students on field trips is a straightforward process. You’ll need a GPS module, a microcontroller, a battery, and a wristband or clothing clip to attach to the student’s attire. Begin by connecting the GPS module to the microcontroller and programming it to transmit the location data to a website or app. Next, attach the battery to power the device. Finally, attach the GPS tracker to the student’s wristband or clothing clip so that it can be conveniently worn and tracked throughout the field trip.
19. A Device That Helps You Organize Your Locker
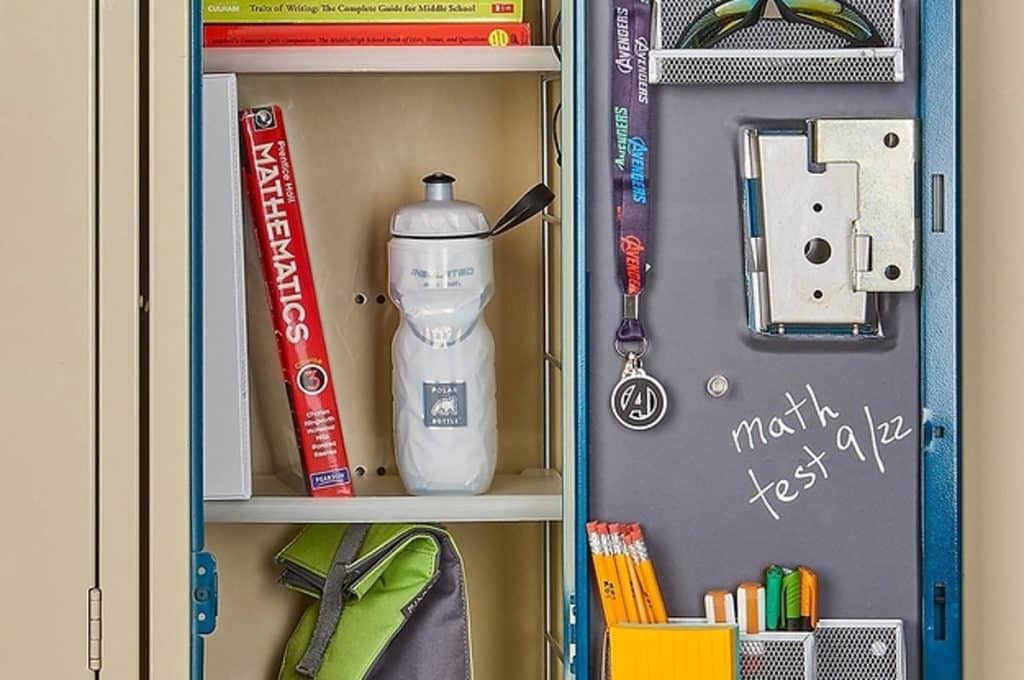

To make a device that helps you organize your locker and make it interactive, you could start by brainstorming the features you want it to have. Some ideas could include a touchscreen display, voice commands, and an inventory system that tracks the items in your locker. Once you have a clear idea of what you want, you can start building the device using a microcontroller like an Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
20. A Water-Resistant Backpack for Rainy Days
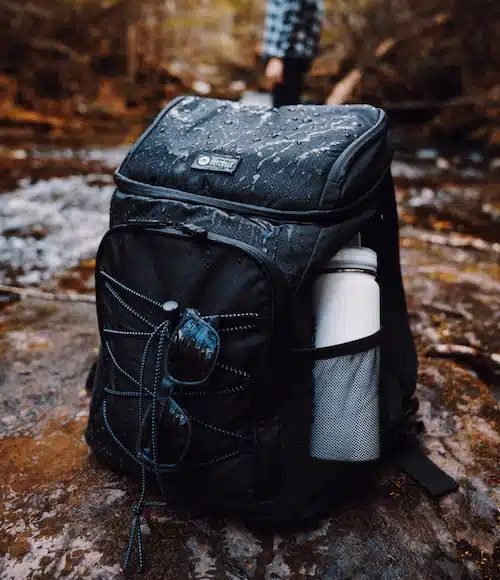

Are you tired of worrying about your belongings getting soaked on a rainy day? Well, we have a solution for you! With a few simple steps, you can create a water-resistant backpack that will keep your belongings safe and dry. Not only will this save you from the hassle of carrying around a bulky umbrella, but it will also give you peace of mind knowing that your valuables are protected.
21. A Device to Keep Track of Your Homework Assignments

Do you often find it difficult to keep track of your homework assignments? If so, don’t worry; you’re not alone. Here’s a fun and engaging solution that can help you stay organized and on top of your work. Create a colorful and personalized chart or calendar that you can hang in your study area. Use stickers or markers to mark off each assignment as you complete it, and set goals for yourself to stay motivated. You can even add motivational quotes or pictures to keep you inspired. With this device, you’ll never miss an assignment again!
22. A Water Filter Bottle

To make a water filter bottle DIY project, start by finding a plastic bottle and cutting it in half. Then, fill the bottom half with a layer of small rocks, followed by a layer of sand, and finally, a layer of activated charcoal. Place the top half of the bottle back on, and poke a few small holes in the cap. When you pour water into the top of the bottle, it will filter through the layers and come out clean and drinkable from the bottom. This is a great way to learn about water filtration and make a useful tool for outdoor adventures!
23. A Smart Recycling Bin

For a smart recycling bin, you should have a regular recycling bin, a microcontroller board such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi, a distance sensor, a servo motor, and a Wi-Fi module. First, attach the distance sensor to the front of the recycling bin so that it can detect when someone approaches it. Then, connect the distance sensor to the microcontroller board. Next, you will need to connect the servo motor to the microcontroller board. The servo motor will be responsible for opening and closing the lid of the recycling bin. You can program the microcontroller to open the lid when the distance sensor detects someone approaching the bin and then close the lid once the person has finished depositing their recyclables. Finally, connect the Wi-Fi module to the microcontroller board so that you can control the recycling bin remotely.
24. Sling Shot Pen
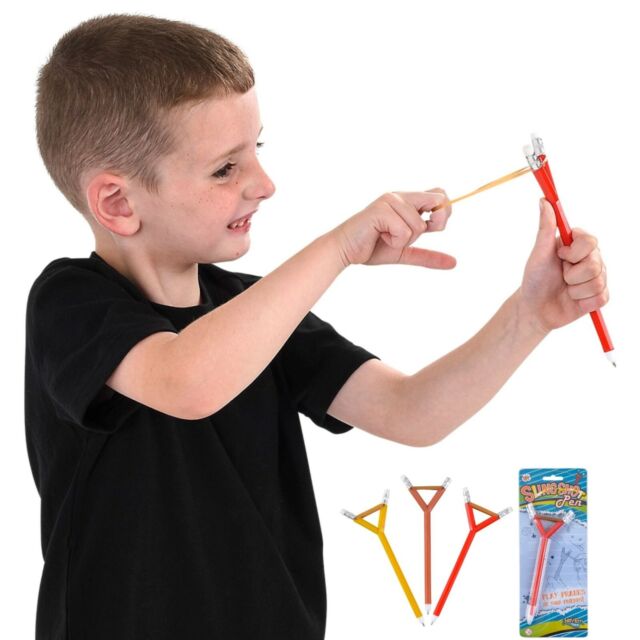

To make a simple pen sling shot invention, you will need a pen, a rubber band, and a small piece of paper. First, remove the ink cartridge from the pen and discard it. Next, stretch the rubber band around the middle of the pen and secure it in place. Finally, fold the small piece of paper in half and place it in between the rubber band and the pen. Now, your pen slingshot is ready to use!
25. An Interesting Board Game
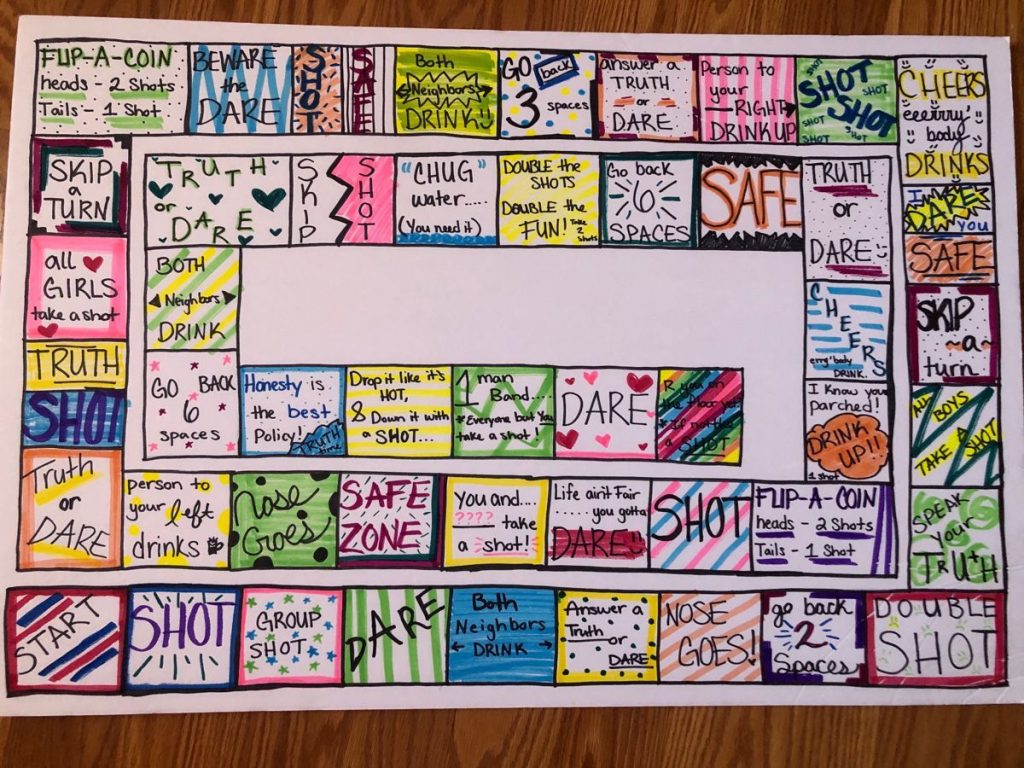
Creating an interesting board game requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. First, determine the theme and objective of the game. Next, establish the rules and mechanics that will govern gameplay. Consider adding elements of chance or strategy to keep things exciting. Additionally, we design and create visually appealing game pieces and a game board that complements the theme.
26. A Smart Bike Lock
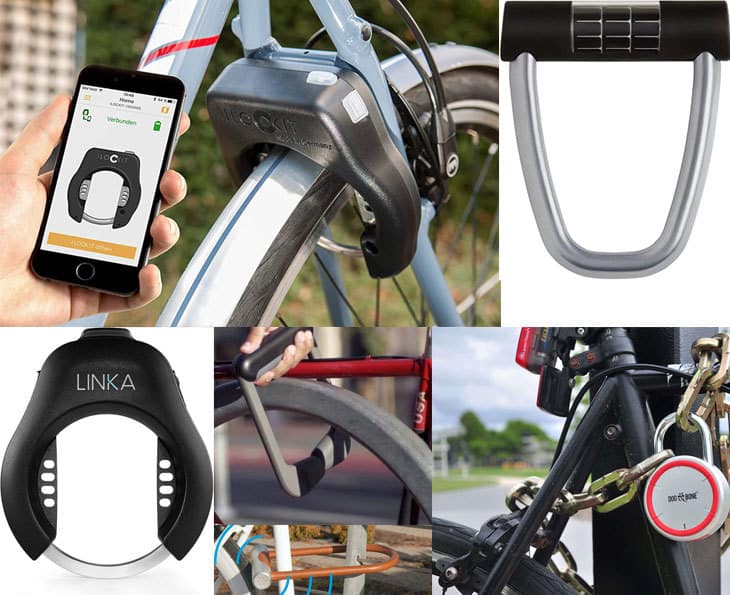

To make a smart bike lock, you will need a few components, such as a microcontroller, a Bluetooth module, a motor, a battery, and a lock mechanism. You should start by programming the microcontroller to receive, and process commands from a smartphone app through the Bluetooth module. Then, you can connect the motor to the lock mechanism to control the opening and closing of the lock. Finally, you need to power the system with a battery and test it thoroughly before attaching it to your bike.
27. A Touch Sensor Eye Glass Wiper
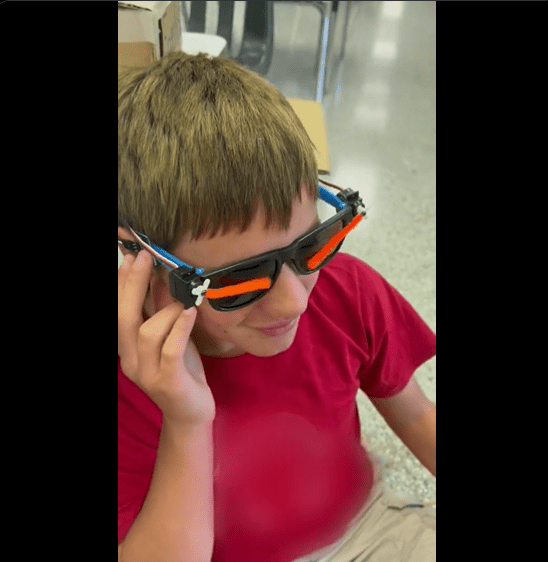

To make a touch sensor eyeglass wiper, you will need a few basic materials. First, find a small piece of conductive foam and cut it into a circular shape. Then, attach a small piece of conductive tape to the foam. Next, attach a small motor to the foam using some adhesive. Finally, attach a small piece of cloth to the motor using some adhesive. Once everything is attached, connect the motor to a battery and test the touch sensor. If everything works correctly, you should be able to touch the sensor and activate the motor to wipe your glasses.
28. A Mechanical Hand

Have you ever thought about the incredible impact a prosthetic hand could have on someone’s life? With a mechanical hand, individuals with limb differences can regain their independence and perform everyday tasks that were once difficult or impossible. Making a mechanical hand may seem like a daunting task, but with the right materials and instructions, it can be a rewarding project. By creating a prosthetic hand, you have the opportunity to change someone’s life for the better.
29. A Straw Rocket

Looking to create a fun and exciting activity for yourself or your kids? Look no further than making straw rockets! With just a few simple materials, you can create your own mini rockets and launch them into the air for hours of entertainment. Here’s how: Materials: – Drinking straws – Paper – Scissors – Tape – Markers (optional). Start by cutting a small triangle from a piece of paper. This will be the nose cone for your rocket. Next, roll up another piece of paper tightly around the drinking straw. This will be the body of your rocket. Use tape to secure the nose cone to the top of the rocket body. Decorate your rocket with markers if you’d like. Now it’s time to launch! Place the drinking straw in your mouth and blow hard, shooting the rocket into the air.
30. A Bottle Vacuum Cleaner

Do you want to keep your home clean and free of dust and debris without breaking the bank? Look no further than creating your own bottle vacuum cleaner! Not only is it a cost-effective solution, but it’s also a great way to repurpose items you already have at home. To make your own bottle vacuum cleaner, you’ll need a plastic bottle, a vacuum cleaner hose, duct tape, and a pair of scissors. First, cut off the bottom of the plastic bottle and discard it. Then, take the vacuum cleaner hose and insert it into the opening of the bottle. Use duct tape to secure the hose to the bottle, ensuring that there are no air leaks. Now, your bottle vacuum cleaner is ready to use!
31. A Wobble Bot

Looking to create a Wobble Bot? You’ve come to the right place! Here’s how you can make one of your own and gather your materials. You’ll need a motor, a battery pack, wires, a plastic cup, and some hot glue. Attach the motor to the bottom of the plastic cup using hot glue. Connect the wires from the battery pack to the motor, making sure they are securely attached. Add some weight to the top of the cup, like a small ball or a weighted bead. Turn on the motor and watch your Wobble Bot go!
32. A Smartphone Projector
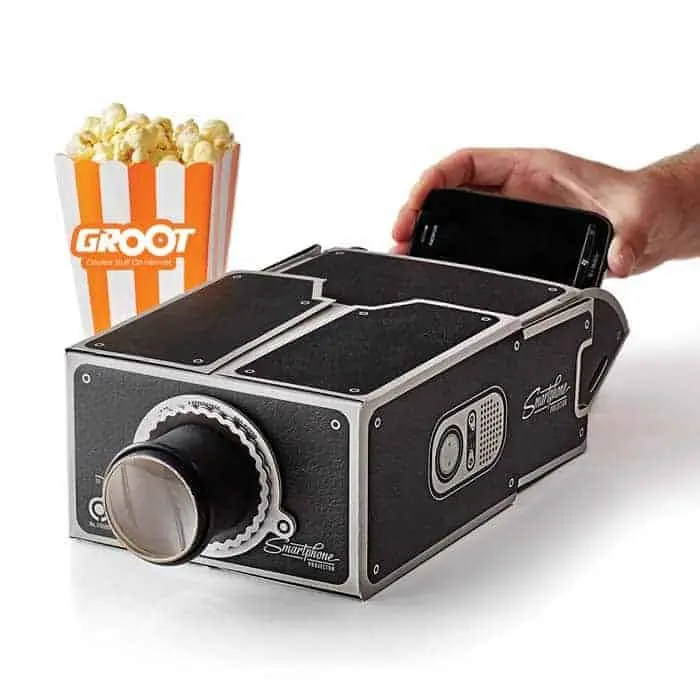

To make a smartphone projector, you will need a cardboard box, a magnifying glass, a sharp knife, a ruler, and some tape. Cut out a rectangular hole on one side of the cardboard box, leaving a border of about 2 cm on all sides. This will be the projection screen. On the opposite side of the box, cut out a smaller rectangular hole about the size of your smartphone screen. Take the magnifying glass and tape it over the smaller hole. Make sure it is centered and secured in place. Place your smartphone inside the box, with the screen facing toward the magnifying glass. Turn on a video or movie on your smartphone and adjust the focus by moving the phone back and forth until the image on the projection screen is clear. And there you have it, your very own smartphone projector!
33. A Harvest Rainwater
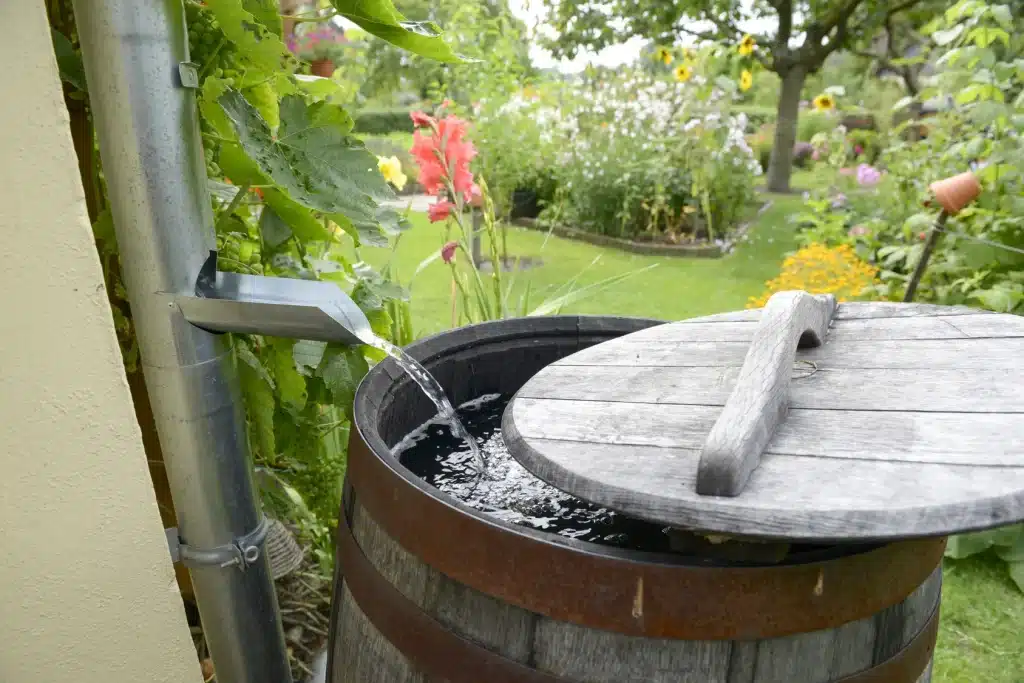

Harvesting rainwater is not only an eco-friendly practice, but it can also save you money on water bills and help conserve our planet’s precious resources. By collecting rainwater, you can use it for tasks such as watering plants, washing your car, or even flushing your toilet. Plus, it’s easy to do! All you need is a rain barrel or cistern, some basic plumbing tools, and a little bit of time.
34. A Hand Sanitizer Machine

Keeping your hands clean and free from germs is more important than ever. And what better way to ensure your safety than by making your very own hand sanitizer machine? With this machine, you’ll never have to worry about running out of hand sanitizer again. Plus, it’s incredibly easy to make. First, gather all the materials you’ll need: a small pump, a container for the hand sanitizer, tubing, and a power source. Once you have everything, attach the tubing to the pump and the container. Make sure it’s securely attached to both ends. Next, connect the pump to a power source, either a battery or plug it into an outlet. Fill the container with hand sanitizer and test your machine by pressing the pump. Making your own hand sanitizer machine is not only convenient but also cost-effective.
35. A Paper Bag Invention

To make a paper bag invention, you will need a few basic materials, including a paper bag, scissors, glue, and any decorations you want to add. First, lay the paper bag flat on a surface and cut off the bottom of the bag. Then, cut the remaining bag in half lengthwise. Next, take one of the halves and fold it in half, creating a crease in the center. Then, fold the top corners of the bag down towards the center crease, creating a triangle shape. Fold the remaining edges of the bag up and over the triangle shape, creating a pocket. Secure the edges with glue. Repeat these steps with the other half of the bag. Once complete, you can decorate the pockets with stickers, markers, or any other craft supplies you have on hand.
Summing It Up
All in all, middle school students have a wealth of creativity, and their innovative minds can be harnessed to come up with some amazing inventions. With the right guidance and support, students can identify problems, brainstorm ideas, and create solutions that can make a difference in the world.
From eco-friendly products to apps that solve everyday problems, the possibilities are endless. The key is to encourage students to think outside the box, work collaboratively, and embrace failure as a stepping stone to success. By providing access to resources, mentorship, and opportunities to showcase their ideas, we can empower our young inventors and inspire a new generation of problem-solvers.
Let’s encourage our middle school students to unleash their creativity and make a positive impact on the world!

Jonathan Green is an esteemed Education Specialist with an impressive track record. He holds a Master's degree in Education alongside bearing expertise in Child Psychology. He began his career as a special education teacher, gaining insights into diverse learning needs. His previous experience includes leading teacher training programs and authoring several papers on early childhood education. His extensive experience is reflected in his insightful articles and webinars. Outside of his professional life, Jonathan is an enthusiastic gardener and a volunteer at local community education centers.

40 Funny Monkey Jokes that Will Make Kids Jump Up Their Beds

25 Fun and Engaging Music Games and Activities for Kids
Related posts.

How Haiku Poets Find Inspiration in Nature?

How Can Verb-Based Exercises Help Children with Speech Delays?

Finding the Verb in a Sentence – Neither Easy, Nor Hard Anymore!

Outdoor Educational Activities for Children

How Do You Create a Reader-Friendly Environment at Home?

How Can I Teach Verbs to Kids in a Fun and Engaging Way?
Pingback: What Places in School Are High Risk for Contamination? - illustrated Tea Cup
Pingback: What Did Nikola Tesla Invent? - illustrated Tea Cup
Pingback: What Could Life Be without Technology? - illustrated Tea Cup
Write A Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Child Development
- DIY Crafts & Projects
- Learning Games
- Indoor & Outdoor Activities
- Party Games
- Party Ideas
- Book Recommendations
- Educational Insights
- Art & Painting
- Sensory & STEM Activities
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
35 Smart Invention Ideas and Activities To Inspire Innovative Kids
Encourage them to create something to make the world a better place!

The world around us is full of items that started in someone else’s imagination. From light bulbs and airplanes to peanut butter and shampoo, inventors have used new ideas to make the world a better place. Want to encourage students to be innovative? Introduce them to famous inventors everyone should know , and then encourage them to try one of these incredible invention ideas for kids—or come up with one of their own!
Tip: Help kids learn about the design process and try some simple invention challenges with this guide from Oregon State University: Invent It. Build It.
Real-Life Inventions by Kids
Kids might believe they’re too young to invent anything meaningful. Prove them wrong by sharing these inspiring stories of real-life kids who made something new that the world really needed. Then, use these innovations as a springboard to brainstorm more invention ideas for kids to try.
One of the world’s most popular frozen treats was originally invented by an 11-year-old! Learn more about Frank Epperson’s story from NPR.
Invention Idea: Invent a new and delicious portable food item, preferably one that’s healthy too.
Braille is a system of raised dots that allow those who are visually impaired to read with their fingers. This groundbreaking system was the brainchild of a teenager! Discover the story of Louis Braille at Forbes.
Invention Idea: Create a new way to help those with physical challenges communicate better with others.
Pediatric IV Backpack
When Kylie Simonds was receiving her cancer treatment, she found the large IV she had to lug around just one more frustration. To solve the problem, she invented an IV backpack to make the experience better for future kids. Read about Kylie’s inspiring story at ABC News.
Invention Idea: Design an innovative product to make things easier for kids undergoing any type of medical treatment.
Alzheimer Alert System
When Kenneth Shinozuka was 15, he wanted to find a way to keep his grandfather safe in case he wandered off and got lost. His invention, a pressure-activated messaging sock, won him worldwide acclaim. Find out more about Kenneth’s story at WebMD.
Invention Idea: Devise a new way to keep people safe in dangerous situations.
After reading yet another story about a child who died in a hot car after being forgotten by caregivers, 14-year-old Alissa Chavez decided to do something about it. Her invention, Hot Seat, notifies parents if they walk away from their child in a car seat. Here’s more about Alissa and her invention from Raising Smart Girls.
Invention Idea: Devise a product to make the lives of parents and kids easier or safer.
STEM Challenge Invention Ideas for Kids
STEM challenges are always classroom favorites, but many of them present real opportunities for kids to come up with a clever new invention. Start with these STEM challenge invention ideas, then take a look at our STEM topic pages for even more activities .
Rube Goldberg Machine
These silly machines use a series of extraordinary steps to accomplish a single simple task. Students use them to learn about chain reactions, but they can also inspire creativity when it comes to solving problems. Set a basic task, like ringing a bell, and challenge kids to come up with the wackiest possible ways to make it happen!
Learn more: Rube Goldberg Machine at Tinkerlab
Smartphone Projector
This is a popular classroom STEM project that utilizes a shoebox and magnifying lenses. Once kids have the basic concept down, encourage them to come up with a more advanced version with additional features like zoom, remote control, etc.
Learn more: Smartphone Projector at The STEM Laboratory
Ideal Living Space
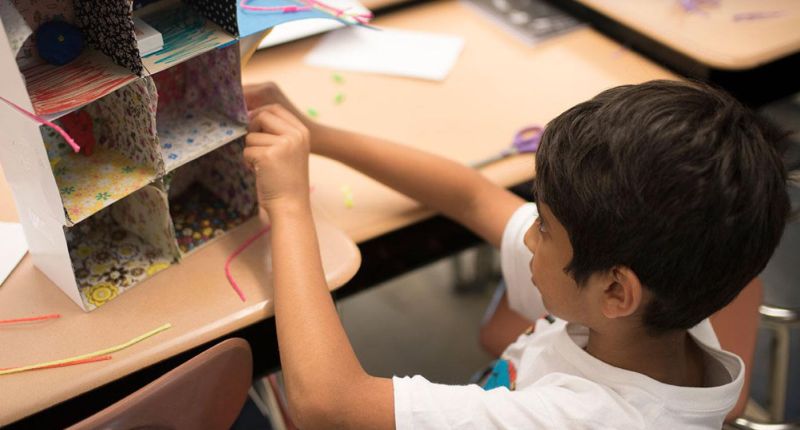

Using basic materials like cardboard, paper, tape, and glue, kids design a living space that seems perfect to them. Urge them to learn more about different kinds of living spaces around the world, and to think about what would make a room, house, or other space more comfortable or eco-friendly.
Learn more: Living Space Challenge at Invent.org
Indoor Composter
Composting keeps food out of landfills and creates better soil for growing crops. But not everyone has room in their yard for a compost heap. Ask students to design an indoor composter instead, one that every family can keep in their kitchen.
Learn more: Indoor Composter at Science Buddies
Water Filter
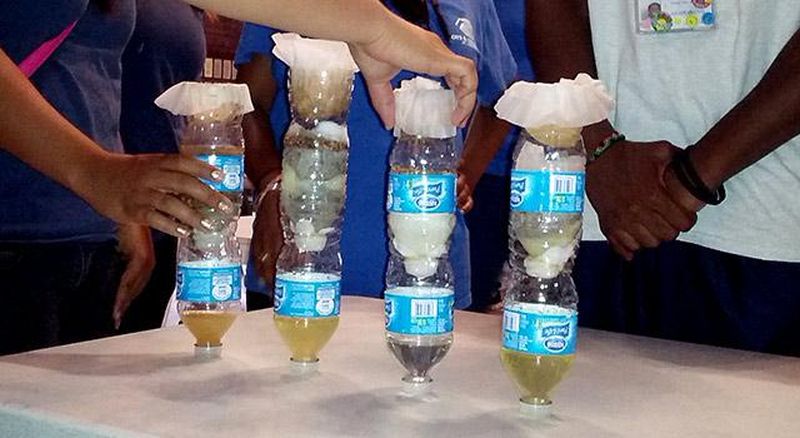

Many people in the world lack easy access to clean drinking water. Challenge students to come up with a clever water filter, one that’s inexpensive, effective, and easy to use.
Learn more: Water Filtration Challenge at NASA JPL
Microplastics Intervention
Microplastics, tiny bits of plastic less than 5 mm long, can be harmful to animal life (including humans), especially when they get into the water supply. Take the Microfiber Innovation Challenge, and devise a new way to prevent microplastics from causing harm to our planet.
Learn more: Microfiber Innovation Challenge
Oil Spill Cleanup
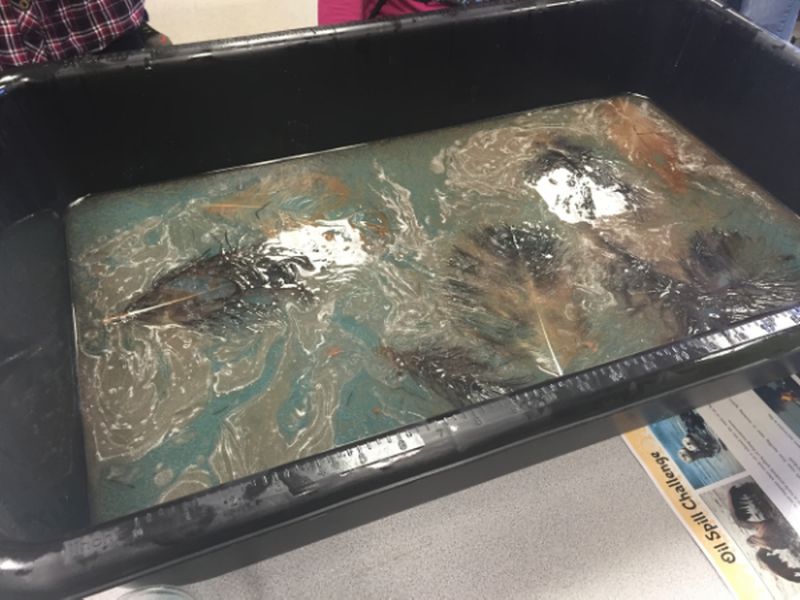

An oil spill can cause massive environmental damage, both in the ocean and on land. Innovate new, more efficient ways to clean up after an accidental spill, helping return the Earth and its creatures to good health.
Learn more: Oil Spill Challenge at Vivify STEM
Egg Drop Container
This is a classic school STEM challenge, but it really does have broader applications. In addition to designing a container to protect an egg from a fall, encourage kids to take the next step and propose a real-life purpose for their container.
Learn more: Egg Drop at STEAMsational
Mechanical Hand
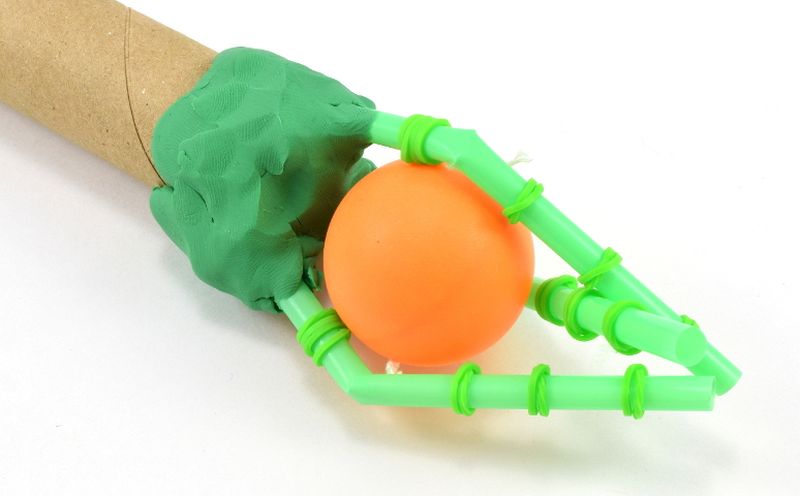

Use simple materials to create a mechanical hand in this kid-favorite STEM challenge. Or take this invention idea a step further and challenge kids to create a mechanical hand or other artificial limb that could benefit those who’ve lost their own.
Learn more: Mechanical Hand at Science Buddies
Something From Nothing
The rules for this invention are … there are no rules! It’s the ultimate freestyle challenge. Provide a variety of general supplies, but allow kids to use other items from around the classroom or house as well. If they’re having trouble getting started, ask them to complete this phrase: “I wish I had a _____ that could ______.”
Learn more: Something From Nothing at Invent.org
“Build a Better …” Invention Ideas for Kids
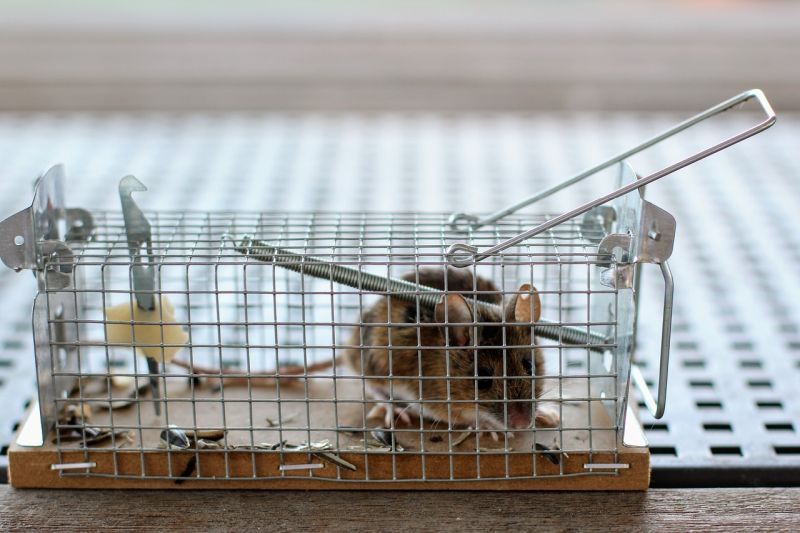

Many inventors got their start by trying to improve on something that already existed. Challenge kids to come up with better, more effective versions of some of these existing products:
- Portable shelter (e.g., a tent)
- Squirrel-proof bird feeder
- Pet product (e.g., a toy, bed, food/water dish)
- Toothpaste container
- Alarm clock
- Beverage container
- Garden tool
- Educational toy
- School desk and/or chair
- Smartphone app for kids
- Toy box/storage
Invention Contests for Kids
Think you’ve come up with something really innovative? Looking for a fun classroom activity to challenge and inspire future inventors? Enter these invention contests for a chance to see kids’ innovations produced on a wider scale, and even win cash and prizes!
Kids Invent Stuff
The brains behind this popular YouTube channel love creating the ideas of kid inventors! They accept submissions through their website, then choose their favorite innovations to build and feature in new videos on their channel.
Past winners: periscope hat, drill-powered shoes, finger forks
Thomas Edison Pitch Contest
Students in grades 4-12 create and pitch invention ideas in a variety of categories. They have the chance to win prizes ranging from T-shirts and gift cards to a 3D printer for your school. They’ll even send you a maker kit full of valuable supplies to help you get started!
Past winners: smart recycling bin, easy parking app, water-runoff turbine
Young Inventor Challenge
Connect with professionals in the toy and game industry when you develop and pitch a new invention for this contest. Winners may earn the chance to have their design built and sold by one of the sponsoring companies! The contest is open to kids ages 6-18 and requires a pitch video and prototype.
Past winners: Goo Shoe, Draw Into Crime, Ship of Treasure
Invention Convention
Teachers can use the Invention Convention curriculum in their classrooms, helping students develop projects to enter into local, regional, and national competitions. It’s open to kids in grades K-12, with winners eligible for all sorts of prizes.
Past winners: Wrap-n-Go pencil holder, smart mailbox, manure mover
ExploraVision
This STEM competition asks entrants to pick a technology they want to improve, then research and submit a project detailing their proposed ideas. The contest has different requirements and categories for various ages, so this one is great for K-12 students.
Past winners: artificial photosynthesis system, magnetic propulsion rocket launcher, mosquito trap
Love these invention ideas and challenges? Check out 50 STEM Activities To Help Kids Think Outside the Box .
Plus, get more teaching ideas and inspiration straight to your inbox when you sign up for our free newsletters , you might also like.
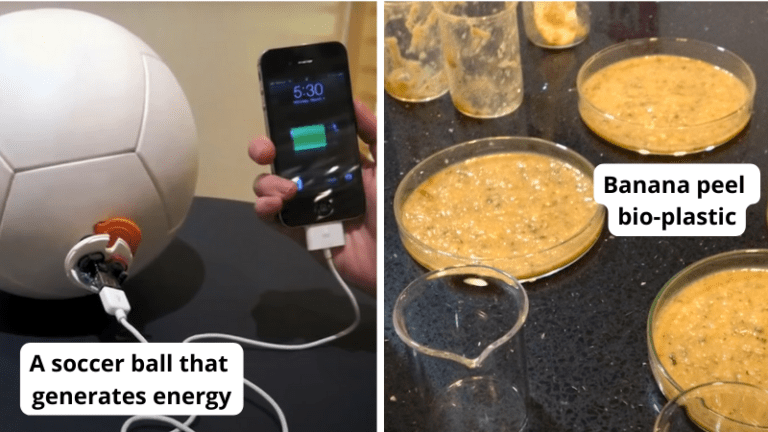

15 Awesome Invention Videos for Kids
From a soccer ball that generates energy to banana peel bio-plastic. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

45 Amazing School Invention Ideas For Middle School Students
Categories Activities & Ideas
Children love to be creative. Uninhibited by the do’s and don’ts of the world, they often have the best ideas.
Working on a school invention project is a great way to allow those creative juices to flow.

In this guide, we’ve included X school invention ideas for middle school students that will definitely generate that light bulb moment.
1. Eco-friendly Lunch Box
This invention is perfect for celebrating Earth Day.
Students can create a lunch box with separate compartments for different types of food.
It would be made of biodegradable materials and have a built-in compost bin for food scraps.
This teaches students about sustainability and waste reduction.
2. Interactive Study Notebook
Design a notebook with built-in prompts, quizzes, and challenges related to various subjects.
It could even come with a companion app for additional interactive features and to check answers.
3. Self-Watering Plant Pot
Design a pot that can water plants using stored rainwater.
This invention would have a built-in rain collection system and a slow-drip mechanism to keep the soil moist.
It’s a hands-on way to understand plant biology and environmental science.
4. Solar-powered Charging Station
Construct a portable station using small solar panels that can charge devices like phones or tablets.
This would be a great way to introduce students to renewable energy sources and electronics.
5. Adjustable Desks
A desk that can be easily adjusted for height or angle, allowing students to work while standing or sitting. This can promote better posture and healthier study habits.
6. Temperature-sensitive Clothing
Design clothing that changes color or pattern based on the temperature.
This could help students understand the principles behind thermochromic dyes and how temperature affects materials.
7. Noise-canceling Study Booths
Work with your class to create small, portable booths or tents that students can set up in noisy areas.
The booths would use noise-canceling technology or materials to provide a quiet space for studying or reading.
8. Recycling Game Board
Design a board game that educates players about recycling, waste reduction, and environmental conservation.
Players would learn which items can be recycled, how recycling processes work, and the importance of reducing waste.
9. Edible Science Kits
Kits that allow students to conduct edible experiments.
For example, they could learn about chemical reactions by making candy or understand plant biology by growing edible sprouts.
10. Digital Flashcard Keychain
A small, portable digital device that allows students to input and review flashcards for study purposes.
It can be attached to backpacks or pencil cases for easy access.
11. Homework Organizer App
An application that integrates with the school’s assignment system, allowing students to prioritize tasks, set reminders, and track progress on long-term projects.
12. Solar-Powered Desk Lamp
A desk lamp using a small solar panel. It can be charged during the day and used at night, teaching students about the utility of renewable energy.
13. Reusable Whiteboard Notebook
A notebook made of whiteboard material that allows students to jot down notes, solve math problems, or sketch diagrams.
It can then be erased for reuse, promoting sustainability.
14. Ergonomic Backpack Design
Invent a backpack that distributes weight evenly across the shoulders and back, reducing strain. This could involve adjustable straps, lumbar support, and compartment organization.
15. Smart Pencil
A pencil equipped with sensors to detect and correct grip, helping students develop proper writing habits.

16. Hydration Reminder Water Bottle
A water bottle with built-in sensors to remind students to drink water throughout the day.0
It might light up or make a sound at regular intervals or when the bottle senses it hasn’t been opened for a while.
17. Interactive History Timeline
A digital or physical timeline that allows students to dive deeper into specific historical events. When they select an event, it provides more details, images, and even quizzes.
18. 3D Geography Puzzle
A puzzle that helps students learn about world geography.
As they piece together continents and countries, they can delve deeper into the culture, history, and significance of each region.
19. Book Swap Platform
A digital platform or physical bulletin board where students can list books they’ve finished reading and are willing to swap.
This promotes reading and sustainability, as books get a second life.
20. Safety Reflective School Uniform Add-ons
Attachable reflective materials that can be placed on school uniforms or backpacks, ensuring that students are visible when walking or cycling to and from school in the dark.
21. Bookmark Reminder
A bookmark with a built-in timer.
If a student reads for a certain amount of time, it gives a gentle alert, encouraging regular reading breaks or signifying achievement for sustained reading.
22. Magnetic Locker Organizer
Modular magnetic containers or shelves that can easily be added, removed, or rearranged inside a metal locker, helping students keep their lockers organized.
23. Color-coded Subject Binders
Binders with color-coded sections and tabs corresponding to different school subjects, allowing for easier organization of notes and assignments.
24. Homework Priority Wheel
A wheel students can spin each evening.
They place their assignments on it, and as they spin, it helps them decide which task to tackle first, adding an element of fun to homework.
25. Self-cleaning Lunchbox
A lunchbox lined with a material that can easily be wiped clean or even has a built-in mechanism to brush out crumbs and spills, making cleaning more straightforward.
26. Pencil With Built-in Eraser Detector
A pencil that gives a subtle alert when the eraser is almost worn out, reminding students to replace or get a new pencil.
27. Backpack Weight Indicator
A small device attached to a backpack strap that indicates when the bag’s weight might be harmful to the student’s back, promoting better health.
28. Reusable Sticky Notes
Made from a material that can be written on and erased multiple times, these notes are both eco-friendly and cost-efficient.
29. Automatic Pencil Sharpener Trash Detector
A sharpener that alerts the user when its waste compartment is almost full, preventing messy overflows.
30. Homework Completion Chart
A chart where students can place stickers or marks when they complete homework, giving them a visual representation of their consistency and achievements.
31. Adjustable Book Holder
A portable device that can hold a book open at various angles, making hands-free reading more comfortable, especially for heavy textbooks.
32. Silent Fidget Tools
Tools designed for students who need to keep their hands busy during class but don’t want to cause distractions. These could be silent spinners, moldable materials, or texture pads.
33. Lunch Money Keeper
A small, attachable pouch on lunch bags where students can securely keep their lunch money, preventing loss.
34. Desk Divider for Focused Work
A lightweight, foldable board that students can set up around their desks when they need to concentrate, minimizing visual distractions.
35. Paper Plate Sundial
Using a paper plate and a pencil, students can create a basic sundial. The student writes the hours around the plate’s edge, places the pencil in the center (standing upright), and aligns it with true north.
Throughout the day, the pencil’s shadow will indicate the time. This project offers insights into ancient timekeeping and the Earth’s rotation.

36. Fidget Pencil
A regular pencil can be modified with various fidget elements. For instance, attach small, quiet beads or rings around the top or incorporate a silent spinner at its end.
This invention aids students who concentrate better when their hands are occupied without distracting others.
37. Bionic Hand
A basic mechanical hand can be constructed using popsicle sticks, string, and straws. By attaching strings to each finger and pulling them, the “bionic” fingers can mimic basic hand movements. This project is fantastic for understanding basic anatomy and mechanics.
38. Scented Study Cards
Flashcards infused with calming scents like lavender or mint.
These can help students relax while studying, potentially enhancing memory retention.
39. Temperature-sensitive Clothing Patch
Attachable cloth patches that change color according to body temperature, helping students be aware if they’re overheating during physical activities.
40. Magnetic Shoe Clips
Magnetic clips that can keep shoelaces tied. This invention prevents tripping hazards, especially during sports or recess.
41. Locker Moisture Absorber
A simple sachet filled with rice or silica gel beads to keep lockers free from moisture and potential mold, ensuring books and clothes stay dry.
42. Ergonomic Grip Enhancer
Using moldable materials like soft rubber or clay, students can customize their pencil or pen grips to make writing more comfortable.
43. Solar Powered Mini Fan
A small fan powered by a solar cell, which can be attached to the inside of a window or a sunny spot on a desk. It can provide a little breeze, especially during warmer days.
44. Eco-friendly Seedling Pots From Newspaper
Instead of buying plastic pots for seedlings, students can craft pots using old newspapers. By folding and molding the newspaper into small pots, they can plant seeds directly into them.
45. Homemade Acoustic Amplifier
Using a cardboard roll (from paper towels or toilet paper) and two paper cups, students can create a simple amplifier for their smartphones.
The phone is placed at the end of the cardboard roll, and the roll is then fitted between two paper cups with slits cut out to hold it. When music or sound is played from the phone, the cardboard roll and paper cups amplify the sound.
Some of the above inventions are good for getting your class to think outside of the box.
While others can easily be created so your students can see their ideas come to life.
Whether you’re planning on making these with your class or just discussing ideas, your students will love all of the above.
- Recent Posts
- Homeschooling In High School: Pros And Cons - February 24, 2024
- How Do I Withdraw My Child From School To Homeschool? - February 23, 2024
- How To Not Go Crazy Homeschooling Kids: A Guide For Frazzled Parents - February 22, 2024
Related Posts:

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- CORE CURRICULUM
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Literature, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Literature, 6-12" aria-label="Into Literature, 6-12"> Into Literature, 6-12
- LITERACY > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Reading, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Reading, K-6" aria-label="Into Reading, K-6"> Into Reading, K-6
- INTERVENTION
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > English 3D, 4-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English 3D, 4-12" aria-label="English 3D, 4-12"> English 3D, 4-12
- LITERACY > INTERVENTION > Read 180, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Read 180, 3-12" aria-label="Read 180, 3-12"> Read 180, 3-12
- LITERACY > READERS > Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4" aria-label="Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4"> Hero Academy Leveled Libraries, PreK-4
- LITERACY > READERS > HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5" aria-label="HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5"> HMH Reads Digital Library, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5" aria-label="inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5"> inFact Leveled Libraries, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > Rigby PM, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Rigby PM, K-5" aria-label="Rigby PM, K-5"> Rigby PM, K-5
- LITERACY > READERS > Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5"> Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5
- SUPPLEMENTAL
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12" aria-label="A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12"> A Chance in the World SEL, 8-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Amira Learning, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Amira Learning, K-6" aria-label="Amira Learning, K-6"> Amira Learning, K-6
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > JillE Literacy, K-3" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="JillE Literacy, K-3" aria-label="JillE Literacy, K-3"> JillE Literacy, K-3
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable, 3-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable, 3-12" aria-label="Writable, 3-12"> Writable, 3-12
- LITERACY > SUPPLEMENTAL > ASSESSMENT" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ASSESSMENT" aria-label="ASSESSMENT"> ASSESSMENT
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8" aria-label="Arriba las Matematicas, K-8"> Arriba las Matematicas, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Go Math!, K-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Go Math!, K-6" aria-label="Go Math!, K-6"> Go Math!, K-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12" aria-label="Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12"> Into Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, 8-12
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Math, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Math, K-8" aria-label="Into Math, K-8"> Into Math, K-8
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math Expressions, PreK-6" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math Expressions, PreK-6" aria-label="Math Expressions, PreK-6"> Math Expressions, PreK-6
- MATH > CORE CURRICULUM > Math in Focus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math in Focus, K-8" aria-label="Math in Focus, K-8"> Math in Focus, K-8
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Classcraft, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classcraft, K-8" aria-label="Classcraft, K-8"> Classcraft, K-8
- MATH > SUPPLEMENTAL > Waggle, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Waggle, K-8" aria-label="Waggle, K-8"> Waggle, K-8
- MATH > INTERVENTION > Math 180, 5-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Math 180, 5-12" aria-label="Math 180, 5-12"> Math 180, 5-12
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, K-5" aria-label="Into Science, K-5"> Into Science, K-5
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Into Science, 6-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Into Science, 6-8" aria-label="Into Science, 6-8"> Into Science, 6-8
- SCIENCE > CORE CURRICULUM > Science Dimensions, K-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science Dimensions, K-12" aria-label="Science Dimensions, K-12"> Science Dimensions, K-12
- SCIENCE > READERS > inFact Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="inFact Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="inFact Leveled Readers, K-5"> inFact Leveled Readers, K-5
- SCIENCE > READERS > Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5" aria-label="Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5"> Science & Engineering Leveled Readers, K-5
- SCIENCE > READERS > ScienceSaurus, K-8" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="ScienceSaurus, K-8" aria-label="ScienceSaurus, K-8"> ScienceSaurus, K-8
- SOCIAL STUDIES > CORE CURRICULUM > HMH Social Studies, 6-12" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="HMH Social Studies, 6-12" aria-label="HMH Social Studies, 6-12"> HMH Social Studies, 6-12
- SOCIAL STUDIES > SUPPLEMENTAL > Writable" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Writable" aria-label="Writable"> Writable
- For Teachers
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Coachly" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Coachly" aria-label="Coachly"> Coachly
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Teacher's Corner" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Teacher's Corner" aria-label="Teacher's Corner"> Teacher's Corner
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Teachers > Live Online Courses" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Live Online Courses" aria-label="Live Online Courses"> Live Online Courses
- For Leaders
- PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT > For Leaders > The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> The Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- MORE > undefined > Assessment" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Assessment" aria-label="Assessment"> Assessment
- MORE > undefined > Early Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Early Learning" aria-label="Early Learning"> Early Learning
- MORE > undefined > English Language Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="English Language Development" aria-label="English Language Development"> English Language Development
- MORE > undefined > Homeschool" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Homeschool" aria-label="Homeschool"> Homeschool
- MORE > undefined > Intervention" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Intervention" aria-label="Intervention"> Intervention
- MORE > undefined > Literacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Literacy" aria-label="Literacy"> Literacy
- MORE > undefined > Mathematics" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Mathematics" aria-label="Mathematics"> Mathematics
- MORE > undefined > Professional Development" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Professional Development" aria-label="Professional Development"> Professional Development
- MORE > undefined > Science" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Science" aria-label="Science"> Science
- MORE > undefined > undefined" data-element-type="header nav submenu">
- MORE > undefined > Social and Emotional Learning" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social and Emotional Learning" aria-label="Social and Emotional Learning"> Social and Emotional Learning
- MORE > undefined > Social Studies" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Studies" aria-label="Social Studies"> Social Studies
- MORE > undefined > Special Education" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Special Education" aria-label="Special Education"> Special Education
- MORE > undefined > Summer School" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Summer School" aria-label="Summer School"> Summer School
- BROWSE RESOURCES
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Classroom Activities" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Classroom Activities" aria-label="Classroom Activities"> Classroom Activities
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Customer Success Stories" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Success Stories" aria-label="Customer Success Stories"> Customer Success Stories
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Digital Samples" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Digital Samples" aria-label="Digital Samples"> Digital Samples
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Events" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Events" aria-label="Events"> Events
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Grants & Funding" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Grants & Funding" aria-label="Grants & Funding"> Grants & Funding
- BROWSE RESOURCES > International" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="International" aria-label="International"> International
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Research Library" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Research Library" aria-label="Research Library"> Research Library
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Shaped - HMH Blog" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Shaped - HMH Blog" aria-label="Shaped - HMH Blog"> Shaped - HMH Blog
- BROWSE RESOURCES > Webinars" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Webinars" aria-label="Webinars"> Webinars
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Contact Sales" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Contact Sales" aria-label="Contact Sales"> Contact Sales
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal" aria-label="Customer Service & Technical Support Portal"> Customer Service & Technical Support Portal
- CUSTOMER SUPPORT > Platform Login" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Platform Login" aria-label="Platform Login"> Platform Login
- Learn about us
- Learn about us > About" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="About" aria-label="About"> About
- Learn about us > Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion" aria-label="Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion"> Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Learn about us > Environmental, Social, and Governance" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Environmental, Social, and Governance" aria-label="Environmental, Social, and Governance"> Environmental, Social, and Governance
- Learn about us > News Announcements" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="News Announcements" aria-label="News Announcements"> News Announcements
- Learn about us > Our Legacy" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Our Legacy" aria-label="Our Legacy"> Our Legacy
- Learn about us > Social Responsibility" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Social Responsibility" aria-label="Social Responsibility"> Social Responsibility
- Learn about us > Supplier Diversity" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Supplier Diversity" aria-label="Supplier Diversity"> Supplier Diversity
- Join Us > Careers" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Careers" aria-label="Careers"> Careers
- Join Us > Educator Input Panel" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Educator Input Panel" aria-label="Educator Input Panel"> Educator Input Panel
- Join Us > Suppliers and Vendors" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Suppliers and Vendors" aria-label="Suppliers and Vendors"> Suppliers and Vendors
- Divisions > Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)" aria-label="Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)"> Center for Model Schools (formerly ICLE)
- Divisions > Heinemann" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="Heinemann" aria-label="Heinemann"> Heinemann
- Divisions > NWEA" data-element-type="header nav submenu" title="NWEA" aria-label="NWEA"> NWEA
- Platform Login
SOCIAL STUDIES
PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT
Invention Convention Ideas for School Projects

As your students start brainstorming invention convention ideas, you may hear them say they can't think of anything to invent. In invention conventions, students generally develop creative innovations to solve real-world problems.
Annually, more than 100,000 students also participate in Invention Convention Worldwide . Students are ultimately invited to present their inventions at Nationals by way of local contests. Teams of up to four students may participate, and this year's competition will be held virtually. Find your local Invention Convention program here .
Invention Projects for Middle and High School Students
We've come up with the inventions listed below that students can use as sources of inspiration when brainstorming their own ideas.
Helping-Hand Inventions
- Device that cleans gutters
- Plastic product that holds a book while you eat
- Rake that allows you to pick up leaves without bending over
- Robot that distributes and collects student papers
- Device to hold objects for disabled people who use a walker
- Alert that signals when mail has been delivered to a roadside mailbox
- Wrapping paper that doesn't require tape
- Bird feeder that protects feed from wind and rain
- Drying rack for gloves
- Liquid that covers fade marks on blue jeans
Fun Inventions
- New board game
- New candy bar
- Comfortable swing set
- Computer program that includes graphics and music for entertaining children aged 3 months to 4 years
Inventions for Staying Organized and Mess-Free
- Billfold that organizes money by denomination for blind people
- Clothing tags to help match and coordinate clothes
- Computer program that catalogs videotapes
- Toothpaste cap that minimizes waste and mess
- Ice cream container that minimizes mess
- Chocolate-candy device that prevents ice cream cones from dripping

Health and Safety Inventions
- Dog collar that lights up at night
- Support that prevents an infant from falling over
- Glove with a light for signaling turns when riding a bike at night
- Outdoor flashing light that helps police, firemen, or other emergency workers find the house that made a call for assistance
- Bus-stop night light
- Hearing-aid guard
- Lunch-box alarm that goes off when an unauthorized person opens the box
- Child's seat that fits a shopping cart
- Light switch for young children
Inventions for Comfort
- Leg cast sock to keep toes warm
- Device that prevents blisters from forming on hands when raking, shoveling, or sweeping
- Comforter for cats
- Device that makes it easier to swallow pills
- Rain poncho designed for use when riding a bicycle
- Eyeglass defogging device
Have More Invention Project Ideas?
If you have more good invention ideas for school to share, email us at [email protected] or reach out on Twitter ( @HMHCo ) or Facebook .
Looking for hands-on science lessons and activities for Grades K–5 ? Explore Into Science , our new phenomena-based science solution.
Find middle school science project ideas with teacher and podcast guest Autumn Rivera.
- Activities & Lessons
Related Reading

2024 Happy Teacher Appreciation Week Ideas
Brenda Iasevoli Shaped Executive Editor
March 20, 2024

15 Fun Summer School Activities for Elementary and Middle School Students
March 18, 2024

13 Mother’s Day Celebration Ideas in School
Marcela Grillo Writer, Girls Write Now
March 12, 2024
The Innovative Spirit
Changing Our World For the Better
17 Inventions That Could Make Going Back to School a Little Bit Easier
From an aromatic alarm clock to a school bus locator system, these patented products could help students and parents with the transition
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino
Senior Editor
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/86/b4/86b4fa37-6273-480a-a7a6-c5cb740ddc4d/patentcollage.jpg)
There are the staples of school supply lists: Elmer's glue, crayons, loose-leaf paper, pocket folders, three-ring binders and pencils. And then there are those less essential but highly desirable things—gel pens and scented markers, pencil cases and locker decorations—that spark store-aisle debates between parents and kids embarking on a new school year.
A search through the United States Patent and Trademark Office archives turns up loads of inventions that parents and children can appreciate this time of year. A walkie-talkie pen? How about a gumball-dispensing t-shirt for the first day? These 17 quirky products could ease the sometimes rocky transtion back to school.
The Robot Lunch Box
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/18/cd/18cdaf58-8e7a-4c81-951c-85e58bb37dff/4666042.jpg)
Open a special compartment in this lunch box, and it turns into a robot! The inventors of the product, patented in 1987, wanted to make their very own "Transformer," given the popularity of the cartoon series.
The Smelly Alarm Clock
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/23/e4/23e4b9cd-107c-414e-9655-2c79c1d57295/5321669.jpg)
Why wake up to a piercing buzzer or nagging parents when you could set an aromatic alarm clock to coax you out of bed with a pleasant-smelling mist?
The Gumball-Dispensing T-Shirt
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/cb/24/cb24e40a-9b9e-45d7-9653-5d9f2351fd5c/4120053.jpg)
Guaranteed to make you some friends, just make sure that you have enough inventory for the entire class.
The Walkie-Talkie Pen
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/ed/96/ed96f97a-2eb6-45d2-b14c-b47a920195e1/20050130594.jpg)
No need to pass notes with this "walkie-talkie pen." Just be prepared for teacher to confiscate it, especially if you try swapping test answers.
The Creepy Pet Vest
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/b2/5f/b25f20a4-0559-4f8f-a4ef-be7b9deae335/5901666.jpg)
This vest with transparent passageways and pockets for pets, like gerbils and hamsters, is a show (and tell) stopper!
A Ring That Mutes the TV
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/df/bb/dfbbf671-89e6-40b9-b0d9-12f618831778/6778380.jpg)
Nothing says "It's homework time!" like this TV mute finger ring, patented in 2004.
The Talking Lunch Box
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/1f/db/1fdb63b3-6827-4188-a45a-86806cfcb462/6347706.jpg)
Mom or Dad can record a voice message in this lunch box patented in 2002, so your kids will never forget to leave dessert for last.
Socks With Secret Pockets
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/25/2c/252cc693-e40e-4202-aab6-85a39878b9e4/5836019-1.jpg)
Stash your lunch money in these socks, with hidden pockets.
The Backpack Jacket
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/c9/75/c97557c1-8fa3-4b29-adc7-ebf8db7bbcdd/5123117.jpg)
This clever backpack has a built-in jacket.
The School Bus Locator
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/7f/1c/7f1c60d3-d843-4e30-a3af-2a59cfdd9fc0/5144301.jpg)
Before GPS tracking apps , this "school bus locator system," patented in 1992, could save you from missing the bus. It consists of a radio transmitter on the bus and a receiver in your home that lights up, as a first warning, and then emits a sound when the bus is about one quarter mile away.
The Ultimate Locker Organizer
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/60/d8/60d8b19e-ecfc-4c4a-9eda-9fdc79d85951/20080185946.jpg)
Pens, books, a cell phone and snacks all have their place in this locker organizer.
Disposable Gym Clothes
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/3f/e6/3fe6740b-6dd3-4b69-b488-dc67a1ab5603/20050059945.jpg)
Perfect for gym class, this "disposable clothing" is made to withstand physical activity and lined with perspiration-absorbent material.
A Shopping Cart That Keeps Track of Your Spending
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/cb/c0/cbc006e1-1f73-4d13-9d96-877ba6b6cd21/07648068-201.jpg)
This shopping cart, with a scanning device mounted to it, gives back-to-school shoppers a running total of their spending.
Be One With Your Bike
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/5f/ab/5fab0812-66f4-48aa-ac32-33638f29b079/06805657-20041019-d00000.jpg)
If you have a downhill commute, consider biking to school on this "body-connected bike." Or pull it out at recess. Squeeze your knees together to brake.
A Cuddly Sleeping Bag
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/f1/fc/f1fc1985-27c9-437e-bf38-e2cb3e8c8613/5515559.jpg)
Moms and Dads, when you are not there to hug your napping kindergartner, this "child's security enhancing sleeping bag," patented in 1996, will.
The Lip Balm Pen
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/e2/d7/e2d73bd7-cc3c-4967-b97e-0609854add1f/20130170888.jpg)
Pen on one end, lip balm on the other. Simple as that.
The Game of School
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer/ba/e2/bae23627-e6db-404a-a149-64dd72d73494/4368889.jpg)
To be first-day ready, it wouldn't hurt to play this board game that simulates the school experience. According to the 1983 patent, the game "gives insight into the roles, values, desires and goals of both teacher, student and others within the school environment and perhaps a better understanding of the underlying institution."
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/megan.png)
Megan Gambino | | READ MORE
Megan Gambino is a senior web editor for Smithsonian magazine.
History Cooperative
The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?
The inventor of homework may be unknown, but its evolution reflects contributions from educators, philosophers, and students. Homework reinforces learning, fosters discipline, and prepares students for the future, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern education. Ongoing debates probe its balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility, prompting innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning. As education evolves, the enigma of homework endures.
Table of Contents
Who Invented Homework?
While historical records don’t provide a definitive answer regarding the inventor of homework in the modern sense, two prominent figures, Roberto Nevelis of Venice and Horace Mann, are often linked to the concept’s early development.
Roberto Nevelis of Venice: A Mythical Innovator?
Roberto Nevelis, a Venetian educator from the 16th century, is frequently credited with the invention of homework. The story goes that Nevelis assigned tasks to his students outside regular classroom hours to reinforce their learning—a practice that aligns with the essence of homework. However, the historical evidence supporting Nevelis as the inventor of homework is rather elusive, leaving room for skepticism.
While Nevelis’s role remains somewhat mythical, his association with homework highlights the early recognition of the concept’s educational value.
Horace Mann: Shaping the American Educational Landscape
Horace Mann, often regarded as the “Father of American Education,” made significant contributions to the American public school system in the 19th century. Though he may not have single-handedly invented homework, his educational reforms played a crucial role in its widespread adoption.
Mann’s vision for education emphasized discipline and rigor, which included assigning tasks to be completed outside of the classroom. While he did not create homework in the traditional sense, his influence on the American education system paved the way for its integration.
The invention of homework was driven by several educational objectives. It aimed to reinforce classroom learning, ensuring knowledge retention and skill development. Homework also served as a means to promote self-discipline and responsibility among students, fostering valuable study habits and time management skills.
Why Was Homework Invented?
The invention of homework was not a random educational practice but rather a deliberate strategy with several essential objectives in mind.
Reinforcing Classroom Learning
Foremost among these objectives was the need to reinforce classroom learning. When students leave the classroom, the goal is for them to retain and apply the knowledge they have acquired during their lessons. Homework emerged as a powerful tool for achieving this goal. It provided students with a structured platform to revisit the day’s lessons, practice what they had learned, and solidify their understanding.
Homework assignments often mirrored classroom activities, allowing students to extend their learning beyond the confines of school hours. Through the repetition of exercises and tasks related to the curriculum, students could deepen their comprehension and mastery of various subjects.
Fostering Self-Discipline and Responsibility
Another significant objective behind the creation of homework was the promotion of self-discipline and responsibility among students. Education has always been about more than just the acquisition of knowledge; it also involves the development of life skills and habits that prepare individuals for future challenges.
By assigning tasks to be completed independently at home, educators aimed to instill valuable study habits and time management skills. Students were expected to take ownership of their learning, manage their time effectively, and meet deadlines—a set of skills that have enduring relevance in contemporary education and beyond.
Homework encouraged students to become proactive in their educational journey. It taught them the importance of accountability and the satisfaction of completing tasks on their own. These life skills would prove invaluable in their future endeavors, both academically and in the broader context of their lives.
When Was Homework Invented?
The roots of homework stretch deep into the annals of history, tracing its origins to ancient civilizations and early educational practices. While it has undergone significant evolution over the centuries, the concept of extending learning beyond the classroom has always been an integral part of education.
Earliest Origins of Homework and Early Educational Practices
The idea of homework, in its most rudimentary form, can be traced back to the earliest human civilizations. In ancient Egypt , for instance, students were tasked with hieroglyphic writing exercises. These exercises served as a precursor to modern homework, as they required students to practice and reinforce their understanding of written language—an essential skill for communication and record-keeping in that era.
In ancient Greece , luminaries like Plato and Aristotle advocated for the use of written exercises as a tool for intellectual development. They recognized the value of practice in enhancing one’s knowledge and skills, laying the foundation for a more systematic approach to homework.
The ancient Romans also played a pivotal role in the early development of homework. Young Roman students were expected to complete assignments at home, with a particular focus on subjects like mathematics and literature. These assignments were designed to consolidate their classroom learning, emphasizing the importance of practice in mastering various disciplines.
READ MORE: Who Invented Math? The History of Mathematics
The practice of assigning work to be done outside of regular school hours continued to evolve through various historical periods. As societies advanced, so did the complexity and diversity of homework tasks, reflecting the changing needs and priorities of education.
The Influence of Educational Philosophers
While the roots of homework extend to ancient times, the ideas of renowned educational philosophers in later centuries further contributed to its development. John Locke, an influential thinker of the Enlightenment era, believed in a gradual and cumulative approach to learning. He emphasized the importance of students revisiting topics through repetition and practice, a concept that aligns with the principles of homework.
Jean-Jacques Rousseau, another prominent philosopher, stressed the significance of self-directed learning. Rousseau’s ideas encouraged the development of independent study habits and a personalized approach to education—a philosophy that resonates with modern concepts of homework.

Homework in the American Public School System
The American public school system has played a pivotal role in the widespread adoption and popularization of homework. To understand the significance of homework in modern education, it’s essential to delve into its history and evolution within the United States.
History and Evolution of Homework in the United States
The late 19th century marked a significant turning point for homework in the United States. During this period, influenced by educational reforms and the growing need for standardized curricula, homework assignments began to gain prominence in American schools.
Educational reformers and policymakers recognized the value of homework as a tool for reinforcing classroom learning. They believed that assigning tasks for students to complete outside of regular school hours would help ensure that knowledge was retained and skills were honed. This approach aligned with the broader trends in education at the time, which aimed to provide a more structured and systematic approach to learning.
As the American public school system continued to evolve, homework assignments became a common practice in classrooms across the nation. The standardization of curricula and the formalization of education contributed to the integration of homework into the learning process. This marked a significant departure from earlier educational practices, reflecting a shift toward more structured and comprehensive learning experiences.
The incorporation of homework into the American education system not only reinforced classroom learning but also fostered self-discipline and responsibility among students. It encouraged them to take ownership of their educational journey and develop valuable study habits and time management skills—a legacy that continues to influence modern pedagogy.
Controversies Around Homework
Despite its longstanding presence in education, homework has not been immune to controversy and debate. While many view it as a valuable educational tool, others question its effectiveness and impact on students’ well-being.
The Homework Debate
One of the central controversies revolves around the amount of homework assigned to students. Critics argue that excessive homework loads can lead to stress, sleep deprivation, and a lack of free time for students. The debate often centers on striking the right balance between homework and other aspects of a student’s life, including extracurricular activities, family time, and rest.
Homework’s Efficacy
Another contentious issue pertains to the efficacy of homework in enhancing learning outcomes. Some studies suggest that moderate amounts of homework can reinforce classroom learning and improve academic performance. However, others question whether all homework assignments contribute equally to learning or whether some may be more beneficial than others. The effectiveness of homework can vary depending on factors such as the student’s grade level, the subject matter, and the quality of the assignment.
Equity and Accessibility
Homework can also raise concerns related to equity and accessibility. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may have limited access to resources and support at home, potentially putting them at a disadvantage when it comes to completing homework assignments. This disparity has prompted discussions about the role of homework in perpetuating educational inequalities and how schools can address these disparities.
Alternative Approaches to Learning
In response to the controversies surrounding homework, educators and researchers have explored alternative approaches to learning. These approaches aim to strike a balance between reinforcing classroom learning and promoting holistic student well-being. Some alternatives include:
Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning emphasizes hands-on, collaborative projects that allow students to apply their knowledge to real-world problems. This approach shifts the focus from traditional homework assignments to engaging, practical learning experiences.
Flipped Classrooms
Flipped classrooms reverse the traditional teaching model. Students learn new material at home through video lectures or readings and then use class time for interactive discussions and activities. This approach reduces the need for traditional homework while promoting active learning.
Personalized Learning
Personalized learning tailors instruction to individual students’ needs, allowing them to progress at their own pace. This approach minimizes the need for one-size-fits-all homework assignments and instead focuses on targeted learning experiences.
The Ongoing Conversation
The controversies surrounding homework highlight the need for an ongoing conversation about its role in education. Striking the right balance between reinforcing learning and addressing students’ well-being remains a complex challenge. As educators, parents, and researchers continue to explore innovative approaches to learning, the role of homework in the modern educational landscape continues to evolve. Ultimately, the goal is to provide students with the most effective and equitable learning experiences possible.
Unpacking the Homework Enigma
Homework, without a single inventor, has evolved through educators, philosophers, and students. It reinforces learning, fosters discipline and prepares students. From ancient times to modern education, it upholds timeless values. Yet, controversies arise—debates on balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility persist. Innovative alternatives like project-based and personalized learning emerge. Homework’s role evolves with education.
How to Cite this Article
There are three different ways you can cite this article.
1. To cite this article in an academic-style article or paper , use:
<a href=" https://historycooperative.org/who-invented-homework/ ">The Homework Dilemma: Who Invented Homework?</a>
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Run your own Little Inventors activities!
If you are a teacher wanting something fun and rewarding to inspire your students, or a parent looking for a creative activity for a rainy day – Little Inventors has everything you need to embrace the spirit of imagination and support your students in coming up with marvellous, ingenious and bonkers invention ideas!
Little Inventors provides free curriculum-linked resource packs, personal inventors’ logs, mini-challenges to help you bring creativity in your classroom or at home!
Download our resources and get inventing!
If you are an Artsmark school , we are official partners and you can use any of our resources to deliver great creativity projects in your school!

- Challenges & collections
- Mini challenges
Climate Champions Resource Pack
Download this pack for free to take on the challenge and discover all whole host of activities and resources bursting with life!

Open Challenge video
![homework invention ideas [rs:300]](https://www.littleinventors.org/theme/inventors/img/spotlight/small-screen.png?cts=1711131123)
Download the video to watch offline.
Open challenge resource pack.
Always engaging and ready for any situation, our Little Inventors resource pack explains what inventing is and gives you all you need to deliver a workshop about all kinds of ingenious inventions.

Grab the entire pack full of activities!
Download the little inventors drawing sheet.
Do you have an invention idea? We welcome them all. Download this drawing sheet, draw out your idea then upload it to our website. We look forward to seeing your invention ideas!

Download for free
Get making with cardboard artist lottie smith.
Calling all Little Inventors! You have thought of an invention idea, drawn it, and now you want to take it to the next step - take inspiration from Little Inventors Magnificent Maker and cardboard artist Lottie Smith and make your own prototype!

Run a Little Inventors after-school club!
Our resources are perfect to run a full meaningful project exploring topics through the lens of invention from developing ideas to creating a wonderful display for your school, something to take pride in! This is a great way to encourage and stretch children’s creativity and problem-solving skills and an insight in the whole process of bringing an idea to life from concept to exhibition.
![homework invention ideas [rs:300]](https://www.littleinventors.org/theme/inventors/img/resources/resource-pack.png?cts=1711131123)
Guidelines for Magnificent Makers
Download to find out how to become a Magnificent Maker!
If you would like to exhibit all of your school’s uploaded invention ideas in your very own Little Inventors gallery online, please contact [email protected] for more details.
It is a great way to share what all your students’ ideas and show them off to the rest of the Little Inventors World!
View an example gallery
- View all teaching vacancies
- View all locations
- Barking & Dagenham
- View all subjects
- Business studies & Economics
- Sociology & Psychology
- View all job types
- Primary school
- Secondary school
- View our variety of SEND roles
Online Portal
If you are registered to work with us already, you can log in here
Register to work with us

Your Career• 3 Min read
6th September 2020
Creative Homework Ideas
How can you create homework assignments that build on the day’s lessons and encourage creative, student-led learning? It’s a challenge for most teachers, especially as motivating pupils to complete homework can add a whole extra layer to your lesson plans. But it’s essential to bridge the gap between teacher and student learning – the skills gained through independent study reinforces knowledge from your class, as well as a host of other benefits:
- Extended learning time – outside of the constraints of the school day, students are free to learn at their own pace and in their own environment.
- Independent learning – vital skills for exam preparation and higher education
- Teaches students to be resourceful and to overcome challenges independently.
- Gives students the freedom to be creative in their learning, gain valuable problem-solving skills and confidence in their own abilities.
Tips For Setting Creative Homework
- Plan independent learning both in and out of the classroom – you can monitor students effectiveness and address issues that may arise in the classroom before they become problematic for pupils at home.
- Don’t leave homework assignment to the end of the lesson, rushing through the task might leave some students confused which inevitably leads to a lower homework completion rate. Write plenty of time for explaining homework assignments into your lesson planning – read our Beginner’s Guide To Lesson Planning here
- Homework should to not too easy nor not too hard, offering pupils a challenge that reinforced the topics learnt during the day
- Give room for creative expression – allowing students to add their own diagrams, decorations or chose their own project topics from a selection.
- Try using peer or self-assessment to mark homework – a double whammy of reducing your workload and allowing pupils to take control of their own learning.
- Include timings and explicit steps for completing more complicated assignments, especially for pupils that you anticipate might struggle. Comprehension of the task is the biggest hurdle in getting pupils to work on an independent basis.
- Self-driven projects, posters, creative tasks and research are more exciting than standard comprehension tasks and might encourage pupils that find sitting and writing dull or hard to complete the homework set – give students the freedom to learn and be creative in their home study.
- Provide specific instructions and internet safety reminders for research-led assignments. It’s very easy for children to find research overwhelming with a vast amount of information available online. Provide suggested websites and links in your homework to keep things on track!
- Don’t introduce a new topic for homework – keep it to topics that you’ve already covered in class
- Taking note of the subjects that excite and engage your class and set homework accordingly – try keeping dryer topics and for the classroom so that you can monitor engagement
- Mark work promptly – essential to keep students motivated to complete work in their own time!
- Offering students the opportunity to select the homework that they would like to do from a selection guarantees a higher rate of completion. We’ve seen some teachers create grids or sheets of homework assignments for the pupils to select, or offer baskets of activities for younger children to take home and complete with an adult.
Creative Homework Ideas For All Ages
Coming up with innovative ways for students to reinforce their knowledge at home can be difficult – many of these ideas would be suitable for lots of subjects with a little tweaking!
Book a CCS Consultation
Our East Anglia team are on hand to support your school or MAT with bespoke recruitment solutions, arrange a consultation with the team today.
Recommended for you
Celebrating st. patrick’s day in the classroom.
Dia Duit! The 17th of March is St. Patrick's Day in the...
- Your Career
Ways to support your students during Ramadan
What is Ramadan? Ramadan, the ninth month of the Islamic calendar has...
International Women’s Day in the Classroom
International Women's Day is a global day that celebrates women and their...
You're now visiting Engage Education, United Kingdom
Take a look at some of the fantastic opportunities we’re currently recruiting for in the UK.
Privacy Overview
- Our Mission
Collaboration: Key to Innovation
Creating curriculum, and in particular, project-based learning units, is like telling a story through lesson design. The story I have been telling these past two weeks centers on blossoming young inventors looking to solve the minor but irritating problems of our day-to-day life. As a language arts teacher who loves science, this kind of unit excites me -- and that excitement trickles down to my middle school students.
There are many components to the unit: brainstorming, research, development, design, cost analysis, collaboration, and pitching. They are using art, writing, math, science, and probably countless other elements that focus on real-world content and communication.
One of the resources that I have the kids use to prime their pumps for innovative thinking is Quirky.com . Quirky basically has three tabs in its menu bar that say it all: Invent, Influence, and Shop. You can submit an invention, shop for inventions, and the coolest part of all, give input to influence the decisions an inventor makes as they move along their timeline toward final production. Finding Quirky was like finding a Mecca of meaningfulness. It's a real-world example of collaboration between people looking to solve a problem.
Students love to talk and give their opinions. Therefore, it's vital to leverage their nature in every subject area. For this reason, I reached out to Quirky, not just as a model for my students to explore, but to learn more closely how collaboration feeds their innovation.
Real-World Collaboration
We use collaboration in classrooms for students to grow in their ability to communicate. We also use it because what results is greater than having worked in isolation. Quirky agrees.
Edutopia: Why is discussion so important in science/STEM classrooms?
Quirky: We believe that collaboration and learning from one's peers are essential to innovation and learning. We collaborate with community members online, and community members collaborate with each other on their ideas. All of this incorporates discussion in writing, in person, and over the phone or through video conferencing. As individuals, we learn the most from our peers and counterparts. Being able to ask questions, bounce ideas off one another, and receive feedback are fundamental to the learning process. They ultimately help us grasp complex concepts much faster than we could if we were simply being lectured to, taking tests, and doing homework.
(In my own classroom, my middle school students form learning groups that create Team Charters or Collaboration Contracts that give guidance in how often they will meet and in what methods. The students meet via Google Hangout or Skype. Some agree to answer emails within 24 hours. Others agree to meet face-to-face after school. The key with student feedback groups is to have them set expectations of each other ahead of time. -- Heather)
How does Quirky leverage collaboration among its stakeholders?
Inventors submit their ideas to Quirky; Quirky community members influence their ideas through researching, voting, and commenting. These influencers help Quirky staff develop the idea into a real product through contributing in market, design, pricing, and branding.
(My own twist on this process was to have my students send each other Google Forms that asked for peer feedback regarding the name of the product, the price point , the slogan , and the level of need. -- Heather)
What social media outlets are most often used by the invention community?
Twitter and Facebook are heavily used by our community to form sub-communities and share their ideas. Pinterest is also used for sharing products and ideas.
(In fact, a number of my students also asked if they could start Facebook pages or Tumblr accounts to help get feedback from other students. In the end, we all created webpages that were used to promote our mythical products. -- Heather)
Getting Students Started
They assure me that a student doesn't have to know engineering to be inventive, but the Quirky folks did have advice on getting started in what I'm calling their atmosphere of collaborative innovation .
1. Start with a Problem
Make sure that problem is something you experience every day but is not limited to you or your immediate family (the best problems are widely felt).
I had my students tour their homes and classrooms looking for inspiration. I had them create a bulleted list of irksome problems for each room. This list ended up reflecting a whole day's worth of puzzles that a student can tackle.
2. Brainstorm as Many Solutions as You Can
Don't worry about how silly or out-there they are. Use research to come up with the solution that best solves the problem and that you are most capable of making.
Have students doodle, flip through books, look at Rube Goldberg pictures . Give them exposure to the innovative thinking around them. From there, my students wrote a problem statement that helped them frame their ideas in more formal writing.
3. Design That Solution
Sketch out your solution so that you have an idea of what it will look like. Prototype your solution so that you can test it in action. TinkerCAD and 123D Design are simple 3D modeling programs that inventors of all ages can use to convey their invention. Digital sketching programs such as Paper and Sketchbook are great if you aren't quite ready to build your own 3D models.
4. Collaborate and Get Feedback from Others
Create and share your elevator pitch to gather feedback. Use feedback to refine your solution.
My eighth grade students wrote elevator speeches like this one:
5. Present and Promote Your Creation
Inventors can create their own blogs to promote their inventions, work with assistance programs such as Dragon Innovation in Boston, or share them with online communities such as Thingiverse, Instructables, and Behance.
My students created websites using Weebly, Wix, eMaze, and Google Sites. Their pages informed and argued using text, data, description, and original 3D designs. We even wrote reviews of our products mimicking those we saw for household items on Amazon.
Making Classroom Invention Authentic
I often wonder how to involve authentic audiences in the end of my project-based learning units. What happens at the end of their learning story? Have they convinced their board of education to allow for this? Have they raised the money to buy that?
When tackling an invention unit, there are great opportunities to showcase student work to an audience greater than yourself. To begin with, your school can host an Invention Convention . Invite local STEM professionals to help evaluate the products. Submit to Quirky or to the Scholastic Klutz contest.
The goal, says Quirky, is to "make invention accessible, both by providing a means to turn invention ideas into real products and by educating aspiring inventors on the fundamentals of product development." Product development uses all the core subjects, but it begins with teachers willing to create their own atmosphere of collaborative innovation.
Editor's Note : If you want to learn more day-to-day details about Heather's Invention Unit, check out her book, DIY Project Based Learning for Math and Science , due out in fall. In the meantime, check out Quirky for their soon-to-be-released curriculum guides.

The History of Homework: Why Was it Invented and Who Was Behind It?
- By Emily Summers
- February 14, 2020
Homework is long-standing education staple, one that many students hate with a fiery passion. We can’t really blame them, especially if it’s a primary source of stress that can result in headaches, exhaustion, and lack of sleep.
It’s not uncommon for students, parents, and even some teachers to complain about bringing assignments home. Yet, for millions of children around the world, homework is still a huge part of their daily lives as students — even if it continues to be one of their biggest causes of stress and unrest.
It makes one wonder, who in their right mind would invent such a thing as homework?
Who Invented Homework?
Pliny the younger: when in ancient rome, horace mann: the father of modern homework, the history of homework in america, 1900s: anti-homework sentiment & homework bans, 1930: homework as child labor, early-to-mid 20th century: homework and the progressive era, the cold war: homework starts heating up, 1980s: homework in a nation at risk, early 21 st century, state of homework today: why is it being questioned, should students get homework pros of cons of bringing school work home.

Online, there are many articles that point to Roberto Nevilis as the first educator to give his students homework. He created it as a way to punish his lazy students and ensure that they fully learned their lessons. However, these pieces of information mostly come from obscure educational blogs or forum websites with questionable claims. No credible news source or website has ever mentioned the name Roberto Nevilis as the person who invented homework . In fact, it’s possible that Nevilis never even existed.
As we’re not entirely sure who to credit for creating the bane of students’ existence and the reasons why homework was invented, we can use a few historical trivia to help narrow down our search.
Mentions of the term “homework” date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger , an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches. But some would argue that the assignment wasn’t exactly the type of written work that students have to do at home nowadays. Only introverted individuals with a fear of public speaking would find it difficult and stressful.
It’s also safe to argue that since homework is an integral part of education, it’s probable that it has existed since the dawn of learning, like a beacon of light to all those helpless and lost (or to cast darkness on those who despise it). This means that Romans, Enlightenment philosophers, and Middle Age monks all read, memorized, and sang pieces well before homework was given any definition. It’s harder to play the blame game this way unless you want to point your finger at Horace Mann.
In the 19 th century, Horace Mann , a politician and educational reformer had a strong interest in the compulsory public education system of Germany as a newly unified nation-state. Pupils attending the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given mandatory assignments that they needed to complete at home during their own time. This requirement emphasized the state’s power over individuals at a time when nationalists such as Johann Gottlieb Fichte were rallying support for a unified German state. Basically, the state used homework as an element of power play.
Despite its political origins, the system of bringing school assignments home spread across Europe and eventually found their way to Horace Mann, who was in Prussia at that time. He brought the system home with him to America where homework became a daily activity in the lives of students.
Despite homework being a near-universal part of the American educational experience today, it hasn’t always been universally accepted. Take a look at its turbulent history in America.
In 1901, just a few decades after Horace Mann introduced the concept to Americans, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California . The ban affected students younger than 15 years old and stayed in effect until 1917.
Around the same time, prominent publications such as The New York Times and Ladies’ Home Journal published statements from medical professionals and parents who stated that homework was detrimental to children’s health.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework as a type of child labor . Since laws against child labor had been passed recently during that time, the proclamation painted homework as unacceptable educational practice, making everyone wonder why homework was invented in the first place.
However, it’s keen to note that one of the reasons why homework was so frowned upon was because children were needed to help out with household chores (a.k.a. a less intensive and more socially acceptable form of child labor).
During the progressive education reforms of the late 19 th and early 20 th centuries, educators started looking for ways to make homework assignments more personal and relevant to the interests of individual students. Maybe this was how immortal essay topics such as “What I Want to Be When I Grow Up” and “What I Did During My Summer Vacation” were born.
After World War II, the Cold War heated up rivalries between the U.S. and Russia. Sputnik 1’s launch in 1957 intensified the competition between Americans and Russians – including their youth.
Education authorities in the U.S. decided that implementing rigorous homework to American students of all ages was the best way to ensure that they were always one step ahead of their Russian counterparts, especially in the competitive fields of Math and Science.
In 1986, the U.S. Department of Education’s pamphlet, “What Works,” included homework as one of the effective strategies to boost the quality of education. This came three years after the National Commission on Excellence in Education published “ Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform .” The landmark report lambasted the state of America’s schools, calling for reforms to right the alarming direction that public education was headed.
Today, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens have once again started questioning why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
Homework now is facing major backlash around the world. With more than 60% of high school and college students seeking counselling for conditions such as clinical depression and anxiety, all of which are brought about by school, it’s safe to say that American students are more stressed out than they should be.
After sitting through hours at school, they leave only to start on a mountain pile of homework. Not only does it take up a large chunk of time that they can otherwise spend on their hobbies and interests, it also stops them from getting enough sleep. This can lead to students experiencing physical health problems, a lack of balance in their lives, and alienation from their peers and society in general.
Is homework important and necessary ? Or is it doing more harm than good? Here some key advantages and disadvantages to consider.
- It encourages the discipline of practice
Using the same formula or memorizing the same information over and over can be difficult and boring, but it reinforces the practice of discipline. To master a skill, repetition is often needed. By completing homework every night, specifically with difficult subjects, the concepts become easier to understand, helping students polish their skills and achieve their life goals.
- It teaches students to manage their time
Homework goes beyond just completing tasks. It encourages children to develop their skills in time management as schedules need to be organized to ensure that all tasks can be completed within the day.
- It provides more time for students to complete their learning process
The time allotted for each subject in school is often limited to 1 hour or less per day. That’s not enough time for students to grasp the material and core concepts of each subject. By creating specific homework assignments, it becomes possible for students to make up for the deficiencies in time.
- It discourages creative endeavors
If a student spends 3-5 hours a day on homework, those are 3-5 hours that they can’t use to pursue creative passions. Students might like to read leisurely or take up new hobbies but homework takes away their time from painting, learning an instrument, or developing new skills.
- Homework is typically geared toward benchmarks
Teachers often assign homework to improve students’ test scores. Although this can result in positive outcomes such as better study habits, the fact is that when students feel tired, they won’t likely absorb as much information. Their stress levels will go up and they’ll feel the curriculum burnout.
- No evidence that homework creates improvements
Research shows that homework doesn’t improve academic performance ; it can even make it worse. Homework creates a negative attitude towards schooling and education, making students dread going to their classes. If they don’t like attending their lessons, they will be unmotivated to listen to the discussions.
With all of the struggles that students face each day due to homework, it’s puzzling to understand why it was even invented. However, whether you think it’s helpful or not, just because the concept has survived for centuries doesn’t mean that it has to stay within the educational system.
Not all students care about the history of homework, but they all do care about the future of their educational pursuits. Maybe one day, homework will be fully removed from the curriculum of schools all over the world but until that day comes, students will have to burn the midnight oil to pass their requirements on time and hopefully achieve their own versions of success.
About the Author
Emily summers.

Take a Tour of an Adolescent Eating Disorder Treatment Center

9 Subjects You Could Study in College

Here Are 10 Subjects You Can Study in College

Choosing the Right Montessori Nursery A Guide for Parents

Debunking the Myth of Roberto Nevilis: Who Really Invented Homework?

Is the D Important in Pharmacy? Why Pharm.D or RPh Degrees Shouldn’t Matter

How to Email a Professor: Guide on How to Start and End an Email Conversation

Everything You Need to Know About Getting a Post-Secondary Education

Grammar Corner: What’s The Difference Between Analysis vs Analyses?


Who Invented Homework? A Big Question Answered with Facts

Crystal Bourque

Delving into the intriguing history of education, one of the most pondered questions arises: Who invented homework?
Love it or hate it, homework is part of student life.
But what’s the purpose of completing these tasks and assignments? And who would create an education system that makes students complete work outside the classroom?
This post contains everything you’ve ever wanted to know about homework. So keep reading! You’ll discover the answer to the big question: who invented homework?
Who Invented Homework?
The myth of roberto nevilis: who is he, the origins of homework, a history of homework in the united states, 5 facts about homework, types of homework.
- What’s the Purpose of Homework?
- Homework Pros
- Homework Cons
When, How, and Why was Homework Invented?

Daniel Jedzura/Shutterstock.com
To ensure we cover the basics (and more), let’s explore when, how, and why was homework invented.
As a bonus, we’ll also cover who invented homework. So get ready because the answer might surprise you!
It’s challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework.
For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. Ancient philosophers would read and develop their teachings outside the classroom. While this might not sound like homework in the traditional form we know today, one could argue that these methods helped to form the basic structure and format.
So let’s turn to recorded history to try and identify who invented homework and when homework was invented.
Pliny the Younger

Credit: laphamsquarterly.org
We can trace the term ‘homework’ back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger (61—112 CE), an oratory teacher, often told his students to practice their public speaking outside class.
Pliny believed that the repetition and practice of speech would help students gain confidence in their speaking abilities.
Johann Gottlieb Fichte

Credit: inlibris.com
Before the idea of homework came to the United States, Germany’s newly formed nation-state had been giving students homework for years.
It wasn’t until German Philosopher Johann Gottlieb Fichte (1762—1814) helped to develop the Volksschulen (People’s Schools) that homework became mandatory.
Fichte believed that the state needed to hold power over individuals to create a unified Germany. A way to assert control over people meant that students attending the Volksshulen were required to complete assignments at home on their own time.
As a result, some people credit Fichte for being the inventor of homework.
Horace Mann

Credit: commons.wikimedia.org
The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century.
So who created homework in the United States?
Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational reformer, spent some time in Prussia. There, he learned more about Germany’s Volksshulen and homework practices.
Mann liked what he saw and brought this system back to America. As a result, homework rapidly became a common factor in students’ lives across the country.

Credit: medium.com
If you’ve ever felt curious about who invented homework, a quick online search might direct you to a man named Roberto Nevilis, a teacher in Venice, Italy.
As the story goes, Nevilis invented homework in 1905 (or 1095) to punish students who didn’t demonstrate a good understanding of the lessons taught during class.
This teaching technique supposedly spread to the rest of Europe before reaching North America.
Unfortunately, there’s little truth to this story. If you dig a little deeper, you’ll find that these online sources lack credible sources to back up this myth as fact.
In 1905, the Roman Empire turned its attention to the First Crusade. No one had time to spare on formalizing education, and classrooms didn’t even exist. So how could Nevilis spread the idea of homework when education remained so informal?
And when you jump to 1901, you’ll discover that the government of California passed a law banning homework for children under fifteen. Nevilis couldn’t have invented homework in 1905 if this law had already reached the United States in 1901.

Inside Creative House/Shutterstock.com
When it comes to the origins of homework, looking at the past shows us that there isn’t one person who created homework. Instead, examining the facts shows us that several people helped to bring the idea of homework into Europe and then the United States.
In addition, the idea of homework extends beyond what historians have discovered. After all, the concept of learning the necessary skills human beings need to survive has existed since the dawn of man.
More than 100 years have come and gone since Horace Mann introduced homework to the school system in the United States.
Therefore, it’s not strange to think that the concept of homework has changed, along with our people and culture.
In short, homework hasn’t always been considered acceptable. Let’s dive into the history or background of homework to learn why.
Homework is Banned! (The 1900s)
Important publications of the time, including the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times, published articles on the negative impacts homework had on American children’s health and well-being.
As a result, California banned homework for children under fifteen in 1901. This law, however, changed again about a decade later (1917).
Children Needed at Home (The 1930s)
Formed in 1923, The American Child Health Association (ACHA) aimed to decrease the infant mortality rate and better support the health and development of the American child.
By the 1930s, ACHA deemed homework a form of child labor. Since the government recently passed laws against child labor , it became difficult to justify homework assignments.

Studio Romantic/Shutterstock.com
A Shift in Ideas (The 1940s—1950s)
During the early to mid-1900s, the United States entered the Progressive Era. As a result, the country reformed its education system to help improve students’ learning.
Homework became a part of everyday life again. However, this time, the reformed curriculum required teachers to make the assignments more personal.
As a result, students would write essays on summer vacations and winter breaks, participate in ‘show and tell,’ and more.
These types of assignments still exist today!
Homework Today (The 2000s)
In 2022, the controversial nature of homework is once again a hot topic of discussion in many classrooms.
According to one study , more than 60% of college and high school students deal with mental health issues like depression and anxiety due to homework. In addition, the large number of assignments given to students takes away the time students spend on other interests and hobbies. Homework also negatively impacts sleep.
As a result, some schools have implemented a ban or limit on the amount of homework assigned to students.
Test your knowledge and check out these other facts about homework:
- Horace Mann is also known as the ‘father’ of the modern school system (read more about Who Invented School ).
- With a bit of practice, homework can improve oratory and writing skills. Both are important in a student’s life at all stages.
- Homework can replace studying. Completing regular assignments reduces the time needed to prepare for tests.
- Homework is here to stay. It doesn’t look like teachers will stop assigning homework any time soon. However, the type and quantity of homework given seems to be shifting to accommodate the modern student’s needs.
- The optimal length of time students should spend on homework is one to two hours. Students who spent one to two hours on homework per day scored higher test results.

Ground Picture/Shutterstock.com
The U.S. Department of Education provides teachers with plenty of information and resources to help students with homework.
In general, teachers give students homework that requires them to employ four strategies. The four types of homework types include:
- Practice: To help students master a specific skill, teachers will assign homework that requires them to repeat the particular skill. For example, students must solve a series of math problems.
- Preparation: This type of homework introduces students to the material they will learn in the future. An example of preparatory homework is assigning students a chapter to read before discussing the contents in class the next day.
- Extension: When a teacher wants to get students to apply what they’ve learned but create a challenge, this type of homework is assigned. It helps to boost problem-solving skills. For example, using a textbook to find the answer to a question gets students to problem-solve differently.
- Integration: To solidify the learning experience for students, teachers will create a task that requires the use of many different skills. An example of integration is a book report. Completing integration homework assignments help students learn how to be organized, plan, strategize, and solve problems on their own.
Ultimately, the type of homework students receive should have a purpose, be focused and clear, and challenge students to problem solve while integrating lessons learned.
What’s the Purpose of Homework?

LightField Studios/Shutterstock.com
Homework aims to ensure students understand the information they learn in class. It also helps teachers to assess a student’s progress and identify strengths and weaknesses.
For example, teachers use different types of homework like book reports, essays, math problems, and more to help students demonstrate their understanding of the lessons learned.
Does Homework Improve the Quality of Education?
Homework is a controversial topic today. Educators, parents, and even students often question whether homework is beneficial in improving the quality of education.
Let’s explore the pros and cons of homework to try and determine whether homework improves the quality of education in schools.
Homework Pros:
- Time Management Skills : Assigning homework with a due date helps students to develop a schedule to ensure they complete tasks on time.
- More Time to Learn : Students encounter plenty of distractions at school. It’s also challenging for students to grasp the material in an hour or less. Assigning homework provides the student the opportunity to understand the material.
- Improves Research Skills : Some homework assignments require students to seek out information. Through homework, students learn where to seek out good, reliable sources.
Homework Cons:
- Reduced Physical Activity : Homework requires students to sit at a desk for long periods. Lack of movement decreases the amount of physical activity, often because teachers assign students so much homework that they don’t have time for anything else.
- Stuck on an Assignment: A student often gets stuck on an assignment. Whether they can’t find information or the correct solution, students often don’t have help from parents and require further support from a teacher.
- Increases Stress : One of the results of getting stuck on an assignment is that it increases stress and anxiety. Too much homework hurts a child’s mental health, preventing them from learning and understanding the material.
Some research shows that homework doesn’t provide educational benefits or improve performance.
However, research also shows that homework benefits students—provided teachers don’t give them too much. Here’s a video from Duke Today that highlights a study on the very topic.
Homework Today
Maybe one day, students won’t need to submit assignments or complete tasks at home. But until then, many students understand the benefits of completing homework as it helps them further their education and achieves future career goals.
Before you go, here’s one more question: how do you feel about homework? Do you think teachers assign too little or too much? Get involved and start a discussion in the comments!
The picture on the front page: Evgeny Atamanenko/Shutterstock.com

The topic of tutoring has recently been gaining popularity among parents. Some are dissatisfied with…

Even in today’s world, child trafficking is still a huge problem. Incidents of human trafficking…

Have you ever stopped to consider: who invented school? In many places around the world,…
Subscribe now!
Glad you've joined us🎉🎉.
The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2022 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2021 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2020 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2019 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2018 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2017 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
How to Set Up and Start Using a Cash App Account
Jazz research questions, interesting essay topics to write about japanese culture, good research topics about japanese art, jane eyre essay topics, most interesting invisible man essay topics to write about, most interesting jaguar essay topics to write about, most interesting jackson pollock essay topics to write about, good essay topics on italian renaissance, good research topics about islamophobia, who invented homework.

Homework is a part of life for children, parents, and educators. But who came up with the concept of homework? What happened to make it a standard in education? Here’s a quick rundown of homework’s history in the United States .
Homework’s Origins: Myth vs. History
Who was the first person to invent homework? We may never know for sure. Its history has been shaped by a variety of persons and events. Let’s start with two of its key influencers.
The Dubious Roberto Nevelis of Venice
Homework is typically credited to Roberto Nevelis of Venice, Italy, who invented it in 1095—or 1905, depending on your sources. However, upon closer examination, he appears to be more of an internet legend than a genuine figure.
Horace Mann
Horace Mann, a 19th-century politician and educational reformer, was a pivotal figure in the development of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, was passionate about the newly unified nation-state of Germany’s obligatory public education system.
Mandatory tasks were assigned to Volksschulen (“People’s Schools”) students to complete at home on their own time. When liberals like Johann Gottlieb Fichte were striving to organize support for a unified German state, this demand highlighted the state’s authority over the individual. While homework had been established before Fichte’s participation with the Volksschulen, his political goals can be considered a catalyst for its adoption as an educational requirement.
Horace Mann was a driving force behind creating government-run, tax-funded public education in America. During a journey to Germany in 1843, he witnessed the Volkschule system at work and brought back several of its ideals, including homework.
The American Public School System’s Homework
Homework has not always been generally embraced, despite being a near-universal element of the American educational experience. Parents and educators continue to dispute its benefits and drawbacks, as they have for more than a century.
The 1900s: Anti-homework sentiment and homework bans
A homework prohibition was enacted in the Pacific state of California in 1901, barely a few decades after the idea of homework crossed the Atlantic. The restriction, which applied to all students under the age of 15, lasted until 1917.
Around the same period, renowned magazines such as the Ladies’ Home Journal and The New York Times published remarks from parents and medical professionals portraying homework as harmful to children’s health.1930: Homework as Child Labor
A group called the American Child Health Association deemed homework a form of child labor in 1930. This statement represented a less-than-favorable view of homework as an appropriate educational method, given that laws barring child labor had recently been implemented.
Early-to-Mid 20th Century: Homework and the Progressive Era
Teachers began looking for ways to make homework more personal and meaningful to individual students throughout the second half of the 19th and 20th-century modern educational changes. Could this be the origin of the enduring essay topic, “What I Did on My Summer Vacation?”
The Cold War: Homework Heats Up
Following WWII, the Cold War heightened tensions between the United States and Russia in the 1950s. The flight of Sputnik 1 in 1957 increased Russian-American enmity, particularly among their youngsters.
The best way to ensure that American students did not fall behind their Russian counterparts, especially in the extremely competitive fields of science and mathematics, was for education officials in the United States to assign demanding homework.
The 1980s: A Nation at Risk’s Homework
What Works, a 1986 publication from the US Department of Education, listed homework as one of the most effective instructional tactics. This followed three years after the groundbreaking study
Early 21st Century: Homework Bans Return
Many educators and other concerned individuals are questioning the value of homework once again. On the subject, several publications have been published.
These include:
- The Case Against Homework: How Homework Is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It by Sarah Bennett and Nancy Kalish (2006)
- The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents (Third Edition) by Duke University psychologist Dr. Harris Cooper (2007)
- The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning by education professor Dr. Etta Kralovec and journalist John Buell (2000)
Homework is still a contentious topic nowadays. Some schools are enacting homework bans similar to those enacted at the start of the century. Teachers have varying opinions on the bans, while parents attempt to cope with the disruption to their daily routine that such bans cause.
Flipped Classroom: Everything You Need to Know
25 black history month activities.
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.
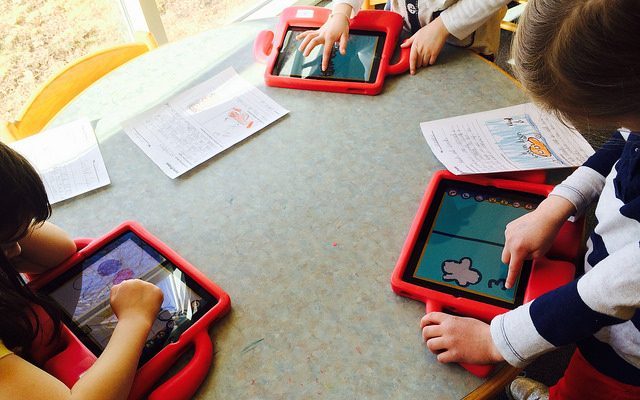

Using EdTech To Get Your Learners Motivated and Active!

What Are the Benefits of Digital Textbooks?

Why EdTech Alone Can’t Change America’s Schools
What are the benefits of using virtual reality in k-12 schools.

Pass or Fail: Teacher Professionalism and How to Boost It
5 best social media practices for higher education.
Encyclopedia of Innovators and Innovations
- Social Innovations
Who Invented Homework? Tracing the Origins and Innovators

Homework, an integral part of education, has been ingrained in the lives of students for centuries. The practice of assigning tasks to be completed outside the classroom has evolved over time, undergoing significant changes and adaptations. Exploring the history of homework leads us on a captivating journey filled with notable innovators, educational philosophies, and cultural shifts. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the origins of homework, uncovering the minds behind its inception, and highlighting key milestones along the way.
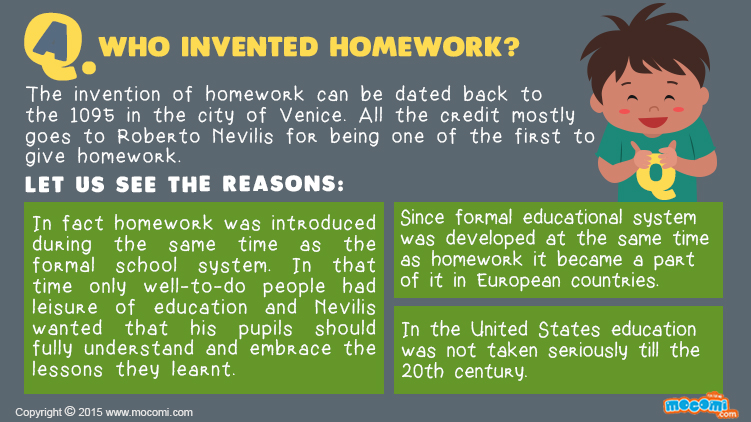
- Ancient Roots and Early Influences:
a. Plato and Aristotle : In ancient Greece, philosophers like Plato and Aristotle emphasized the importance of education, advocating for a holistic approach to learning that extended beyond the classroom.
b. Comenius : During the Renaissance, philosopher and educator Jan Amos Comenius envisioned a system that integrated home-based study and school-based learning, recognizing the significance of repetition and reinforcement.
c. Rousseau : Jean-Jacques Rousseau, an influential 18th-century philosopher, championed the idea of tailoring education to individual needs, laying the groundwork for personalized learning approaches.
- The Advent of Modern Homework:
a. Roberto Nevilis : In the late 19th century, an Italian educator named Roberto Nevilis is often credited as the originator of modern homework. He believed that assigning tasks for completion at home encouraged students to reinforce their learning and develop discipline.
b. Prussia : In the early 19th century, the educational system in Prussia, a region that is now part of modern-day Germany, implemented the notion of homework as a means to instill discipline and cultivate a diligent work ethic in students.
c. United States : In the United States, the implementation of homework gained traction during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, as the nation sought to strengthen its education system. Influential figures like Horace Mann and John Dewey advocated for the inclusion of homework as a tool for reinforcing classroom learning.
- Educational Philosophies and Homework:
a. Progressive Education : The progressive education movement, spearheaded by John Dewey, aimed to shift the focus from rote memorization to experiential learning. Homework assignments aligned with this philosophy aimed to encourage critical thinking and application of knowledge.
b. Behaviorism : Behaviorism, championed by psychologists like B.F. Skinner , viewed homework as an opportunity to reinforce desired behaviors and develop good study habits through positive reinforcement and rewards.
c. Constructivism : The constructivist approach, influenced by educators such as Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky , emphasized hands-on learning experiences and student-centered activities. Homework assignments aligned with constructivism focused on fostering independent thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Technological Advancements and Homework:
a. Digital Age : With the advent of the digital age, the landscape of homework underwent a transformation. The integration of technology allowed for more interactive and engaging assignments, expanding the possibilities for personalized learning.
b. Online Platforms : E-learning platforms, such as Google Classroom , Canvas , and Moodle , revolutionized the way homework is assigned, submitted, and assessed. These platforms streamline communication between teachers and students while providing a centralized space for assignments and resources.
c. Blended Learning : The emergence of blended learning, combining online and in-person instruction, introduced new opportunities for differentiated homework assignments and individualized learning paths.
Origins of Homework: Myth vs. History

Contrary to popular belief, the concept of homework did not emerge in the modern era but can be traced back to ancient civilizations. Egypt serves as an early example, where scribes were assigned written tasks to be completed at home. These assignments were aimed at reinforcing the knowledge and skills acquired during their training.
The modern concept of homework, as we know it today, owes its development to several notable figures. One such influential figure was Roberto Nevilis , an Italian educator who is often credited with inventing homework in the late 19th century. Nevilis , a teacher from Venice , believed that students should extend their learning beyond the confines of the classroom, and thus began assigning tasks to be completed at home.
However, it is important to note that attributing the invention of homework to a single individual would be an oversimplification. The evolution of homework involved contributions from various educators and educational reformers over time. Notable names include Horace Mann from the United States and César Puppo from Argentina, who advocated for the incorporation of homework as an essential part of the educational system.
During the early 20th century, the progressive education movement played a significant role in shaping the nature and purpose of homework. Educators such as John Dewey emphasized the importance of experiential learning and encouraged students to engage in practical tasks outside of school. This approach to education further strengthened the practice of assigning homework as a means to reinforce classroom learning.
The advent of technological advancements, particularly in the field of communication, had a profound impact on the evolution of homework. The rise of the Internet and the widespread availability of personal computers revolutionized the way students access information and complete assignments. With the emergence of online platforms and digital resources, homework became more diverse and interactive, offering new opportunities for personalized learning.
Homework practices vary across different countries and cultures. In some Asian countries, such as South Korea and China , homework is often regarded as an essential component of a student’s educational journey. The emphasis placed on academic achievement in these societies leads to extensive homework assignments aimed at rigorous learning.
Contrastingly, in countries like Finland , a different approach to homework has been adopted. Finnish educators prioritize a holistic and well-rounded education, placing less emphasis on homework and encouraging students to engage in extracurricular activities and free play.
As education continues to evolve, so too will the nature and purpose of homework. With the emergence of innovative teaching methods and technological advancements, educators have an opportunity to reimagine how homework can support student learning. Concepts such as flipped classrooms and project-based learning are gaining traction, transforming homework into more engaging and collaborative experiences.
Pliny the Younger and Homework:

Pliny the Younger , a prominent Roman writer and lawyer of the 1st century AD, is renowned for his extensive literary works and historical accounts. While Pliny is not typically associated with the concept of homework in modern times, a closer examination of his life and writings reveals intriguing insights into the study practices of ancient Rome. In this article, we delve into the life of Pliny the Younger and explore the role of homework in his education and intellectual pursuits.
Born as Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus in Como, Italy , in 61 AD, Pliny the Younger belonged to a privileged family with strong connections to the Roman elite. Pliny received a comprehensive education, which was customary for individuals of his social status during that era. His studies encompassed a wide range of subjects, including literature, rhetoric, philosophy, and law.
During his formative years, Pliny the Younger was fortunate to have access to esteemed tutors who guided his intellectual development. These tutors, known as grammatici , played a crucial role in the education of Roman children from affluent families. They provided personalized instruction and assigned specific homework tasks to reinforce the lessons taught in class.
Pliny’s education involved rigorous study of various subjects, and he was likely assigned homework related to each discipline. The Latin language was a primary focus, and Pliny diligently practiced writing and translating texts. Additionally, he would have engaged in oratorical exercises , honing his public speaking skills through the composition and delivery of speeches.
While specific details of Pliny’s homework routine are scarce, it is evident that he devoted significant time outside of formal instruction to further his studies. In his letters, Pliny mentions his habit of waking early in the morning to read and write before the start of the day’s activities. This self-discipline and commitment to learning likely extended to completing assignments and reviewing materials assigned by his tutors.
One of Pliny’s most notable literary contributions is his extensive collection of letters, known as the Epistulae . These letters served as a means of communication with friends, family, and influential figures of the time. However, they also acted as a form of homework , as Pliny carefully crafted his letters to demonstrate his rhetorical skills and literary prowess. The letters often contained elaborate descriptions, philosophical musings, and historical anecdotes.
Pliny’s educational experiences were not unique to him alone. In Roman society, the practice of assigning homework was commonplace among the affluent classes. Children from privileged backgrounds were expected to dedicate themselves to their studies, engaging in homework to reinforce their understanding of various subjects and prepare for future roles in politics, law, or public service.
Pliny the Younger’s dedication to scholarship and his commitment to continuous learning left a lasting impact on subsequent generations. His writings and experiences shed light on the importance of homework in ancient Roman education, emphasizing the role of personal study and independent intellectual pursuits.
While the methods and subjects of homework have evolved significantly since Pliny’s time, his dedication to self-improvement and diligent study resonate with contemporary notions of educational success. Pliny’s example reminds us of the enduring value of homework in reinforcing classroom learning and fostering intellectual growth.
Homework As a Punishment? Debunking the Myth

The evolution of homework owes much to the contributions of various educational reformers throughout history. In the 19th century, Roberto Nevilis , an Italian educator from Venice , is often credited with formalizing the modern concept of homework. Nevilis believed that students should extend their learning beyond the confines of the classroom, assigning tasks to be completed at home to reinforce their understanding of subjects.
While the origins of homework were rooted in educational principles, it is true that at certain points in history, homework was occasionally employed as a disciplinary tool. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, some educators resorted to using homework as a means to punish students for misbehavior or poor academic performance. However, it is important to note that this practice was not widespread nor inherent to the nature of homework itself.
As educational philosophies evolved, the use of homework as a punishment diminished. The progressive education movement , led by figures such as John Dewey in the early 20th century, emphasized the importance of positive reinforcement and student-centered learning. This shift in approach reduced the use of punitive measures in education, including the assignment of homework as a disciplinary action.
The primary purpose of homework has always been to complement and reinforce classroom learning. Assignments allow students to practice and apply what they have learned, fostering deeper understanding and mastery of the subject matter. Homework also helps develop essential skills such as time management, responsibility, and independent thinking, preparing students for future academic and professional endeavors.
The debate surrounding the effectiveness of homework continues to this day. Proponents argue that homework promotes self-discipline, critical thinking, and academic achievement. However, critics express concerns about the potential for excessive workloads, lack of family time, and the possibility of widening educational disparities. Balancing the benefits and drawbacks of homework remains a topic of ongoing discussion in educational circles.
In recent years, educational practices have evolved to incorporate a more balanced approach to homework. Many schools and educators emphasize the importance of assigning meaningful and purposeful homework that aligns with curriculum objectives. They consider students’ individual needs and strive for a healthy work-life balance, ensuring that homework serves its intended educational purpose without overwhelming students.
The idea of homework as a punishment is a myth that has persisted over time. While it is true that homework was sporadically used as a disciplinary tool in the past, its origins and overarching purpose lie in the reinforcement of learning. Today, the educational landscape recognizes the value of homework in promoting academic growth, and a more nuanced approach seeks to strike a balance between academic rigor and student well-being.
Confucius – First Teacher:

Confucius , also known as Kong Qiu or Kongzi, is widely regarded as one of the most influential thinkers and educators in Chinese history. Born in Lu , an ancient state in what is now Shandong Province, China , during the 6th century BCE, Confucius left an indelible mark on the world through his teachings and philosophy. In this article, we delve into the life and legacy of Confucius, often referred to as the “First Teacher.”
Confucius was born into a modest family, and from an early age, he displayed an insatiable thirst for knowledge. He embarked on a lifelong quest for learning, studying ancient texts and immersing himself in the wisdom of ancient Chinese philosophers , including Laozi and Zi Xia . Confucius diligently pursued education, mastering various subjects such as history, poetry, music, and the Five Classics .
Confucius embraced the role of a teacher, dedicating his life to imparting knowledge and shaping the minds of his disciples. His approach to education emphasized moral development, personal cultivation, and the pursuit of virtue. Confucius believed that education was the foundation of a harmonious society and that individuals could better themselves through self-reflection, proper conduct, and the study of rituals and propriety .
Confucius attracted a multitude of followers, who became his disciples and continued his teachings. Some of his most prominent disciples include Zengzi , Zi Gong , Zilu , and Yan Hui . Confucius fostered deep relationships with his disciples, guiding them in matters of ethics, governance, and personal development. Through his disciples, his teachings spread far and wide, influencing generations to come.
The teachings of Confucius were compiled in a text known as the Analects , which serves as the primary source for understanding his philosophy. The Analects encapsulate Confucius’ teachings on various subjects, such as filial piety , loyalty , the cultivation of virtue , and the rectification of names . Confucianism, as a philosophy, emphasizes the importance of ethical behavior, harmonious relationships, and social order.
Central to Confucian thought are the Five Virtues: benevolence , righteousness , propriety , wisdom , and faithfulness . Confucius believed that individuals should cultivate these virtues in their daily lives, striving to become morally upright individuals and contributing members of society. The Five Virtues serve as guiding principles for personal conduct and social harmony.
Confucius ‘ influence extended far beyond his own lifetime. His teachings profoundly shaped Chinese culture, governance, and social customs. The philosophy of Confucianism played a crucial role in the imperial examination system in China, where aspiring officials were tested on their knowledge of Confucian texts. Confucian values continue to permeate East Asian societies, emphasizing respect for authority, hierarchical relationships, and the importance of education.
Roberto Nevelis – Father of Homework:

Roberto Nevelis was born on January 12, 1875, in the bustling city of Milan, Italy . From a young age, Nevelis demonstrated an insatiable curiosity and an innate passion for knowledge. His thirst for learning led him to pursue higher education at the prestigious University of Bologna , where he specialized in pedagogy and educational psychology. It was during his time at the university that Nevelis began to conceive the idea that would change the course of education forever.
Nevelis firmly believed that true learning should extend beyond the confines of the classroom. Inspired by the works of influential philosophers and educators like Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi and John Dewey, he recognized the need for students to engage in independent study to reinforce and deepen their understanding of the subjects they were taught. This realization gave birth to what we now know as homework .
Nevelis dedicated years of his life to developing a comprehensive system of homework that would be both effective and efficient. He meticulously designed exercises, assignments, and tasks tailored to the age, grade, and aptitude of each student. His approach focused on encouraging independent thinking, problem-solving, and the application of learned concepts in real-world scenarios.
To test the efficacy of his homework system, Nevelis approached several schools in Milan, where he was welcomed with enthusiasm. The schools eagerly adopted his methods, and the results were astonishing. Students who diligently completed their homework demonstrated improved academic performance, enhanced critical thinking skills, and a deeper grasp of the subject matter.
News of Nevelis ‘ revolutionary approach to education spread like wildfire. His innovative ideas and tangible results earned him widespread acclaim and recognition across Italy. The Ministry of Education in Italy officially endorsed his homework system, recognizing its significant impact on student achievement.
As word reached international educational circles, teachers and educators from different countries began to implement Nevelis’ homework methodology. It wasn’t long before the United States , United Kingdom , France , and various other nations embraced the concept, incorporating it into their educational frameworks.
Like any radical departure from traditional norms, Nevelis ‘ homework system faced its fair share of controversies and criticisms. Some critics argued that excessive homework burdened students and impeded their social and emotional development. Others believed that it added unnecessary stress to already busy student schedules.
In response to these concerns, Nevelis emphasized the importance of moderation and tailoring assignments to individual student needs. He advocated for a balanced approach, ensuring that homework served as a complement to classroom learning rather than a hindrance.
Horace Mann – The First School:

Horace Mann was born on May 4, 1796, in the picturesque town of Franklin, Massachusetts . Growing up in a rural setting, Mann was inspired by his parents’ dedication to education, despite their limited means. Their commitment fueled his passion for learning, leading him to attend Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island. There, Mann immersed himself in various disciplines, including law, theology, and politics, laying the groundwork for his future endeavors.
Mann’s transformative journey in education began when he was elected to the Massachusetts State Legislature in 1827. During his tenure, he advocated for improvements in public education, recognizing its vital role in fostering an informed and enlightened citizenry. Inspired by the educational philosophies of Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi and Henry Barnard , Mann resolved to reshape the educational landscape.
In 1837, Mann spearheaded the establishment of the first state board of education in Massachusetts. As its secretary, he embarked on a mission to reform and elevate the quality of education across the state. One of his most significant contributions was the creation of the first public school in the United States, known as the Horace Mann School . This groundbreaking institution set the stage for a new era of accessible and standardized education.
Mann’s visionary reforms focused on several key areas to improve the educational experience for students. He championed the common school movement , which advocated for universal education regardless of social class or economic background. Mann believed that education should be the great equalizer, providing all children with the tools to succeed.
Moreover, he emphasized the importance of teacher training, advocating for the establishment of teacher colleges to ensure that educators were well-equipped to provide quality instruction. Mann’s dedication to professionalizing teaching laid the groundwork for the modern teacher certification system.
Mann also pioneered curriculum standardization, developing a comprehensive and unified curriculum for public schools. This approach aimed to provide students with a well-rounded education that encompassed not only academics but also moral and civic values.
Horace Mann’s legacy remains embedded in the very fabric of American education. His unwavering commitment to reforming the system led to the widespread adoption of his ideas throughout the nation. Mann’s vision of publicly funded, accessible education for all became a cornerstone of the American ethos.
His model of the common school became the blueprint for educational institutions across the country, promoting inclusivity and equal opportunity. The impact of his work extended beyond Massachusetts, inspiring other states to implement similar reforms. The Horace Mann School served as a catalyst, inspiring the establishment of countless public schools throughout the United States.
Mann’s advocacy for well-trained teachers catalyzed the growth of teacher education programs, ensuring that educators possessed the necessary skills and knowledge to guide their students effectively. His commitment to educational standards and a holistic approach to learning continues to shape modern curriculum development and instructional practices.
Mr. Henry Fischel – Pioneering Exams:

Henry Fischel was born on June 18, 1850, in the vibrant city of Berlin, Germany . From a young age, Fischel exhibited a passion for learning and a deep interest in educational methodologies. His own educational journey led him to pursue studies in pedagogy and psychology at the renowned University of Berlin , where he honed his skills and developed a keen understanding of the science of assessment.
Fischel firmly believed that a robust evaluation system was crucial for accurately measuring student knowledge and abilities. Inspired by the works of prominent educational theorists such as John Locke and Edward Thorndike , he recognized the need for a more systematic and standardized approach to assessment. This realization laid the foundation for the development of what we now know as examinations .
Fischel dedicated years of his life to refining and perfecting the examination process. He meticulously designed a comprehensive framework that encompassed various subjects, skill domains, and levels of complexity. Fischel’s approach aimed to measure not only rote memorization but also critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical abilities.
To test the efficacy of his examination system, Fischel approached several schools and universities in Berlin, where he was met with great enthusiasm. Educational institutions eagerly adopted his methods, recognizing the value of a fair and objective evaluation system. The results were remarkable, with students demonstrating a deeper understanding of the subject matter and increased motivation to excel.
Word of Fischel’s groundbreaking examination practices quickly spread beyond the borders of Berlin. Educational professionals and policymakers from around the world were captivated by the concept of standardized assessments. The University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom was among the first to adopt Fischel’s examination system, recognizing its potential to provide a rigorous and unbiased evaluation of students’ knowledge.
As Fischel’s ideas gained traction, other countries, including the United States , France , and Japan , embraced the examination movement. Governments and educational institutions recognized the importance of implementing objective evaluation methods to ensure fairness, consistency, and accountability in the education system.
Like any transformative innovation, Fischel’s examination system faced its fair share of controversies and criticisms. Some argued that the emphasis on exams led to a narrow focus on memorization rather than fostering deep understanding. Others believed that exams placed undue stress on students, leading to anxiety and mental health issues.
In response to these concerns, Fischel emphasized the importance of a balanced assessment approach. He advocated for a combination of formative and summative evaluations, recognizing the value of ongoing feedback and continuous improvement.
Demerits of Homework :
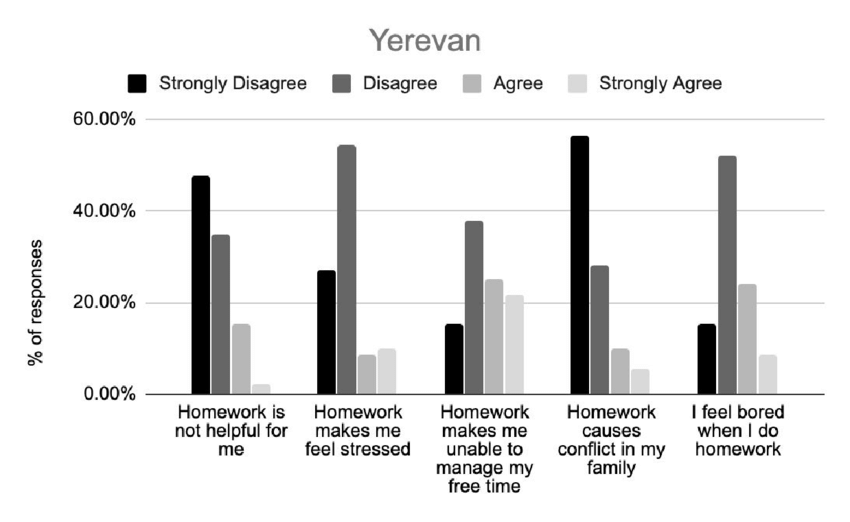
Homework as we know it today has a long history, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece . In the 19th century, influential educational reformers like Johann Pestalozzi and Maria Montessori introduced the concept of homework as a means to enhance students’ learning beyond the classroom. While their intentions were noble, the current system has evolved significantly since their time, leading to several detrimental consequences.
The Overwhelming Workload
One of the primary demerits of homework lies in the overwhelming workload imposed on students. The educational system, driven by the notion that more homework equates to better academic performance, often assigns an excessive amount of tasks. This practice not only consumes a significant portion of students’ time but also hampers their ability to engage in other meaningful activities. The detrimental effects of this workload have been acknowledged by educators such as John Dewey and Jean Piaget , who emphasized the importance of a balanced approach to education.
Limited Creativity and Exploration
Homework often focuses on repetitive exercises and rote memorization, leaving little room for creativity and exploration. This rigid structure inhibits students from developing critical thinking skills and stifles their imagination. Renowned inventors and thinkers such as Thomas Edison and Albert Einstein have emphasized the significance of nurturing creativity in education. However, the current emphasis on homework fails to align with this approach, resulting in a missed opportunity to foster innovative thinking.
Detrimental Impacts on Mental Health
The excessive pressure and stress associated with homework can have detrimental effects on students’ mental health. Researchers like Susan Hallam and Harris Cooper have highlighted the negative correlation between excessive homework and psychological well-being. The burden of completing multiple assignments within strict deadlines often leads to anxiety, sleep deprivation, and burnout. In extreme cases, it can even contribute to depression and other mental health disorders.
Inequity in Access and Support
Another significant demerit of homework lies in the inequity it perpetuates. Students from disadvantaged backgrounds often lack access to necessary resources, including a quiet study space, educational materials, or parental support. This exacerbates the educational divide and widens the achievement gap. Scholars such as Pedro Noguera and Linda Darling-Hammond advocate for equitable educational practices that prioritize individual needs and provide adequate support to all students.
Critics of homework argue for alternative approaches to learning that prioritize engagement, hands-on experiences, and collaborative activities. Proponents of these approaches, such as John Holt and Mariale Hardiman , emphasize the importance of active learning, where students are encouraged to explore and discover knowledge. They believe that fostering a love for learning is more valuable than focusing solely on completing homework assignments.
Key Dates of Homework Invention :
- Ancient Civilizations and the Birth of Homework
The roots of homework can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia . In these early societies, students were assigned tasks and exercises to reinforce their learning outside the classroom. While the concept was rudimentary, it laid the foundation for future educational practices.
- The Influence of Greek Philosophers
During the Classical period in Greece, influential philosophers like Socrates , Plato , and Aristotle recognized the importance of practice and repetition in learning. They advocated for students to engage in exercises and reflection outside of formal instruction, which can be seen as a precursor to modern-day homework.
- The Renaissance and the Rise of Private Tutoring
With the advent of the Renaissance in the 14th century, education saw significant changes. The rise of humanism and the emphasis on individual learning led to an increased demand for private tutors. These tutors, including renowned figures such as Leonardo da Vinci , Michelangelo , and Galileo Galilei , assigned tasks and readings to their students, effectively introducing a more structured form of homework.
- Johann Pestalozzi and the Modernization of Homework
In the late 18th and early 19th centuries, Johann Pestalozzi , a Swiss educator, made significant contributions to the evolution of homework. Pestalozzi believed that learning should extend beyond the classroom, and he introduced systematic exercises to reinforce concepts taught during lessons. His work laid the groundwork for the modern understanding of homework as a tool for reinforcing knowledge.
- The Industrial Revolution and the Expansion of Education
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought about sweeping changes in society, including the expansion of education. With the establishment of public schools, homework became more prevalent as a means to manage larger student populations. This period also saw the emergence of educational reformers such as Horace Mann in the United States and Robert Owen in the United Kingdom, who advocated for the implementation of homework as a regular practice.
- Maria Montessori and Progressive Education
In the early 20th century, Maria Montessori , an Italian physician and educator, developed the Montessori Method, an alternative approach to education. Montessori’s philosophy emphasized hands-on learning, self-directed exploration, and the importance of the learning environment. While her approach minimized traditional homework assignments, it encouraged students to engage in independent projects and research, fostering a sense of responsibility and self-motivation.
- Digital Age and the Transformation of Homework
The advent of the digital age in the late 20th century brought about a new era in homework practices. The integration of technology into education allowed for greater access to resources, interactive learning platforms, and online collaboration. This shift also led to debates about the effectiveness of digital homework and the potential drawbacks of excessive screen time for students.
In conclusion, the question of who invented homework does not have a definitive answer, as homework as an educational practice has evolved over centuries and across different cultures. Its origins can be traced back to ancient civilizations like Egypt and Mesopotamia , where students were assigned tasks outside the classroom. Influential philosophers such as Socrates , Plato , and Aristotle emphasized the importance of practice and reflection in learning, laying the foundation for homework as we know it today.
Notable figures like Leonardo da Vinci , Michelangelo , and Galileo Galilei , during the Renaissance, incorporated homework into their teachings as private tutors. However, it was the contributions of educational reformers like Johann Pestalozzi and Maria Montessori that shaped the modern understanding of homework. Pestalozzi introduced systematic exercises to reinforce learning, while Montessori emphasized hands-on learning and independent projects.
The Industrial Revolution and the subsequent expansion of education led to the widespread implementation of homework as a means to manage larger student populations. Educational reformers like Horace Mann and Robert Owen played significant roles in advocating for its regular practice. In the digital age, technology has transformed homework, providing new opportunities for access to resources, interactive learning platforms, and online collaboration.
While homework has been a longstanding educational tradition, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations and challenges. Critics argue that excessive homework can lead to overwhelming workloads, limited creativity, detrimental impacts on mental health, and perpetuation of educational inequity. Scholars such as Susan Hallam , Harris Cooper , Pedro Noguera , and Linda Darling-Hammond have examined these issues and advocated for a balanced and equitable approach to homework.
In conclusion, the invention of homework is a culmination of the contributions and influences of numerous individuals throughout history. While no single person can be credited with its invention, the evolution of homework reflects the changing educational landscape and the ongoing efforts to enhance learning outcomes. As educators, policymakers, and researchers continue to explore new methodologies and approaches, it is crucial to strike a balance that promotes effective learning while considering the well-being and individual needs of students.
References:
Cooper, H. (2001). Homework for all—In moderation. Educational Leadership, 58(7), 34-38. Darling-Hammond, L., & Ifill-Lynch, O. (2006). If they’d only do their work! Educational Leadership, 63(1), 8-13. Hallam, S. (2006). Homework: The evidence. London Review of Education, 4(3), 277-291. Mann, H. (1841). Seventh Annual Report to the Secretary of the Massachusetts Board of Education. Montessori, M. (1912). The Montessori method: Scientific pedagogy as applied to child education in “the children’s houses” with additions and revisions by the author. Noguera, P. A. (2003). City schools and the American dream: Reclaiming the promise of public education. Teachers College Press. Pestalozzi, J. H. (1831). How Gertrude Teaches Her Children: An Attempt to Help Mothers to Teach Their Own Children and an Account of the Method. Plato. (2010). The Republic. Oxford University Press. Socrates. (2010). The Last Days of Socrates: Euthyphro, The Apology, Crito, Phaedo.
Related Posts

Who Invented Google? The Evolution of Google
The Evolution of the Piano: Tracing the Inventors and Innovators
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Who Invented Homework and Why

Who Invented Homework
Italian pedagog, Roberto Nevilis, was believed to have invented homework back in 1905 to help his students foster productive studying habits outside of school. However, we'll sound find out that the concept of homework has been around for much longer.
Homework, which most likely didn't have a specific term back then, already existed even in ancient civilizations. Think Greece, Rome, and even ancient Egypt. Over time, homework became standardized in our educational systems. This happened naturally over time, as the development of the formal education system continued.
In this article, we're going to attempt to find out who invented homework, and when was homework invented, and we're going to uncover if the creator of homework is a single person or a group of them. Read this article through to the end to find out.
Who Created Homework and When?
The concept of homework predates modern educational systems, with roots in ancient Rome. However, Roberto Nevilis is often, yet inaccurately, credited with inventing homework in 1905.Depending on various sources, this invention is dated either in the year 1095 or 1905.
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history.
The practice of assigning students work to be done outside of class time can be traced back to ancient civilizations, such as Rome, where Pliny the Younger (AD 61–113) encouraged his students to practice public speaking at home to improve their oratory skills.
It's important to note that the idea of formalized homework has evolved significantly over centuries, influenced by educational theories and pedagogical developments. The purpose and nature of homework have been subjects of debate among educators, with opinions varying on its effectiveness and impact on student learning and well-being.
It might be impossible to answer when was homework invented. A simpler question to ask is ‘what exactly is homework?’.
If you define it as work assigned to do outside of a formal educational setup, then homework might be as old as humanity itself. When most of what people studied were crafts and skills, practicing them outside of dedicated learning times may as well have been considered homework.
Let’s look at a few people who have been credited with formalizing homework over the past few thousand years.
Roberto Nevilis
Stories and speculations on the internet claim Roberto Nevilis is the one who invented school homework, or at least was the first person to assign homework back in 1905.
Who was he? He was an Italian educator who lived in Venice. He wanted to discipline and motivate his class of lackluster students. Unfortunately, claims online lack factual basis and strong proof that Roberto did invent homework.
Homework, as a concept, predates Roberto, and can't truly be assigned to a sole inventor. Moreover, it's hard to quantify where an idea truly emerges, because many ideas emerge from different parts of the world simultaneously or at similar times, therefore it's hard to truly pinpoint who invented this idea.
Pliny the Younger
Another culprit according to the internet lived a thousand years before Roberto Nevilis. Pliny the Younger was an oratory teacher in the first century AD in the Roman Empire.
He apparently asked his students to practice their oratory skills at home, which some people consider one of the first official versions of homework.
It is difficult to say with any certainty if this is the first time homework was assigned though because the idea of asking students to practice something outside classes probably existed in every human civilization for millennia.
Horace Mann
To answer the question of who invented homework and why, at least in the modern sense, we have to talk about Horace Mann. Horace Mann was an American educator and politician in the 19th century who was heavily influenced by movements in the newly-formed German state.
He is credited for bringing massive educational reform to America, and can definitely be considered the father of modern homework in the United States. However, his ideas were heavily influenced by the founding father of German nationalism Johann Gottlieb Fichte.
After the defeat of Napoleon and the liberation of Prussia in 1814, citizens went back to their own lives, there was no sense of national pride or German identity. Johann Gottlieb Fichte came up with the idea of Volkschule, a mandatory 9-year educational system provided by the government to combat this.
Homework already existed in Germany at this point in time but it became a requirement in Volkschule. Fichte wasn't motivated purely by educational reform, he wanted to demonstrate the positive impact and power of a centralized government, and assigning homework was a way of showing the state's power to influence personal and public life.
This effort to make citizens more patriotic worked and the system of education and homework slowly spread through Europe.
Horace Mann saw the system at work during a trip to Prussia in the 1840s and brought many of the concepts to America, including homework.
Who Invented Homework and Why?
Homework's history and objectives have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changing educational goals. Now, that we've gone through its history a bit, let's try to understand the "why". The people or people who made homework understood the advantages of it. Let's consider the following:
- Repetition, a key factor in long-term memory retention, is a primary goal of homework. It helps students solidify class-learned information. This is especially true in complex subjects like physics, where physics homework help can prove invaluable to learning effectively.
- Homework bridges classroom learning with real-world applications, enhancing memory and understanding.
- It identifies individual student weaknesses, allowing focused efforts to address them.
- Working independently at their own pace, students can overcome the distractions and constraints of a classroom setting through homework.
- By creating a continuous learning flow, homework shifts the perspective from viewing each school day as isolated to seeing education as an ongoing process.
- Homework is crucial for subjects like mathematics and sciences, where repetition is necessary to internalize complex processes.
- It's a tool for teachers to maximize classroom time, focusing on expanding understanding rather than just drilling fundamentals.
- Responsibility is a key lesson from homework. Students learn to manage time and prioritize tasks to meet deadlines.
- Research skills get honed through homework as students gather information from various sources.
- Students' creative potential is unleashed in homework, free from classroom constraints.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Who Invented Homework: Development in the 1900s
Thanks to Horace Mann, homework had become widespread in the American schooling system by 1900, but it wasn't universally popular amongst either students or parents.
The early 1900s homework bans
In 1901, California became the first state to ban homework. Since homework had made its way into the American educational system there had always been people who were against it for some surprising reasons.
Back then, children were expected to help on farms and family businesses, so homework was unpopular amongst parents who expected their children to help out at home. Many students also dropped out of school early because they found homework tedious and difficult.
Publications like Ladies' Home Journal and The New York Times printed statements and articles about the detrimental effects of homework on children's health.
The 1930 child labor laws
Homework became more common in the U.S. around the early 1900s. As to who made homework mandatory, the question remains open, but its emergence in the mainstream sure proved beneficial. Why is this?
Well, in 1930, child labor laws were created. It aimed to protect children from being exploited for labor and it made sure to enable children to have access to education and schooling. The timing was just right.
Speaking of homework, if you’re reading this article and have homework you need to attend to, send a “ do my homework ” request on Studyfy and instantly get the help of a professional right now.
Progressive reforms of the 1940s and 50s
With more research into education, psychology and memory, the importance of education became clear. Homework was understood as an important part of education and it evolved to become more useful and interesting to students.
Homework during the Cold War
Competition with the Soviet Union fueled many aspects of American life and politics. In a post-nuclear world, the importance of Science and Technology was evident.
The government believed that students had to be well-educated to compete with Soviet education systems. This is the time when homework became formalized, accepted, and a fundamental part of the American educational system.
1980s Nation at Risk
In 1983 the National Commission on Excellence in Education published Nation at Risk:
The Imperative for Educational Reform, a report about the poor condition of education in America. Still in the Cold War, this motivated the government in 1986 to talk about the benefits of homework in a pamphlet called “What Works” which highlighted the importance of homework.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
Who Invented Homework: The Modern Homework Debate
Like it or not, homework has stuck through the times, remaining a central aspect in education since the end of the Cold War in 1991. So, who invented homework 😡 and when was homework invented?
We’ve tried to pinpoint different sources, and we’ve understood that many historical figures have contributed to its conception.
Horace Mann, in particular, was the man who apparently introduced homework in the U.S. But let’s reframe our perspective a bit. Instead of focusing on who invented homework, let’s ask ourselves why homework is beneficial in the first place. Let’s consider the pros and cons:
- Homework potentially enhances memory.
- Homework helps cultivate time management, self-learning, discipline, and cognitive skills.
- An excessive amount of work can cause mental health issues and burnout.
- Rigid homework tasks can take away time for productive and leisurely activities like arts and sports.
Meaningful homework tasks can challenge us and enrich our knowledge on certain topics, but too much homework can actually be detrimental. This is where Studyfy can be invaluable. Studyfy offers homework help.
All you need to do is click the “ do my assignment ” button and send us a request. Need instant professional help? You know where to go now.
Frequently asked questions
Who made homework.
As stated throughout the article, there was no sole "inventor of homework." We've established that homework has already existed in ancient civilizations, where people were assigned educational tasks to be done at home.
Let's look at ancient Greece; for example, students at the Academy of Athens were expected to recite and remember epic poems outside of their institutions. Similar practices were going on in ancient Egypt, China and Rome.
This is why we can't ascertain the sole inventor of homework. While history can give us hints that homework was practiced in different civilizations, it's not far-fetched to believe that there have been many undocumented events all across the globe that happened simultaneously where homework emerged.
Why was homework invented?
We've answered the question of "who invented homework 😡" and we've recognized that we cannot pinpoint it to one sole inventor. So, let's get back to the question of why homework was invented.
Homework arose from educational institutions, remained, and probably was invented because teachers and educators wanted to help students reinforce what they learned during class. They also believed that homework could improve memory and cognitive skills over time, as well as instill a sense of discipline.
In other words, homework's origins can be linked to academic performance and regular students practice. Academic life has replaced the anti-homework sentiment as homework bans proved to cause partial learning and a struggle to achieve conceptual clarity.
Speaking of, don't forget that Studyfy can help you with your homework, whether it's Python homework help or another topic. Don't wait too long to take advantage of expert help when you can do it now.
Is homework important for my learning journey?
Now that we've answered questions on who created homework and why it was invented, we can ask ourselves if homework is crucial in our learning journey.
At the end of the day, homework can be a crucial step to becoming more knowledgeable and disciplined over time.
Exercising our memory skills, learning independently without a teacher obliging us, and processing new information are all beneficial to our growth and evolution. However, whether a homework task is enriching or simply a filler depends on the quality of education you're getting.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 15 November 2021
How to turn your ideas into patents
Andy Tay is a science writer in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Spinning off companies to exploit products and ideas developed at universities and research institutions can help to address societal challenges and make a real-world impact. Such moves can also be lucrative for scientists who are prepared to take their concepts into industry.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03438-x
Related Articles

- Intellectual-property rights

‘Woah, this is affecting me’: why I’m fighting racial inequality in prostate-cancer research
Career Q&A 20 MAR 24
So … you’ve been hacked
Technology Feature 19 MAR 24

Four years on: the career costs for scientists battling long COVID
Career Feature 18 MAR 24

Can non-profits beat antibiotic resistance and soaring drug costs?
News Feature 28 FEB 24
Optimally generate policy-based evidence before scaling
Perspective 14 FEB 24

Scientists question cancer tests that use microscopic nematode worms
News 20 DEC 23

Research funders must join the fight for equal access to medicines
Editorial 30 JAN 24
Avoid patenting AI-generated inventions
Correspondence 03 OCT 23

‘Benevolent’ patent extensions could raise billions for R&D in poorer countries
Comment 25 SEP 23
Recruitment of Talent Positions at Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
Call for top experts and scholars in the field of science and technology.
Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University
Assistant Professor in Plant Biology
The Plant Science Program in the Biological and Environmental Science and Engineering (BESE) Division at King Abdullah University of Science and Te...
Saudi Arabia (SA)
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Warmly Welcomes Talents Abroad
“Qiushi” Distinguished Scholar, Zhejiang University, including Professor and Physician
No. 3, Qingchun East Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang (CN)
Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital Affiliated with Zhejiang University School of Medicine
Postdoctoral Associate
Our laboratory at the Washington University in St. Louis is seeking a postdoctoral experimental biologist to study urogenital diseases and cancer.
Saint Louis, Missouri
Washington University School of Medicine Department of Medicine
Recruitment of Global Talent at the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
The Institute of Zoology (IOZ), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is seeking global talents around the world.
Beijing, China
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Who Invented School Homework? [When, Where & How]
You can remember just sitting down and doing homework—no worries, no stress, and getting an A on your paper. School was the best time of your life. Ok, maybe that’s not true, but the point is you would always wonder who invented school homework.
The very first homework assignment can be traced all the way back to 1905 when an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis first invented the idea. He wanted his students to get used to thinking for themselves, so he gave them assignments that would require them to look up information and use it in their work.
Whether you’re a student trying to get ahead, or a parent wondering about homework for your own children, this article will help you to get a better understanding of the whole story about homework.
Interested in who invented school tests? Let’s find out here.
What Was the Original Purpose of Homework?
Who invented math homework, who invented holiday homework, who invented summer homework, who invented homework meme, the invention of homework, why homework is bad for high school students, who was roberto novelis, why does homework exist, when was school homework first invented, was homework invented as a punishment, · performance of creative works (essay writing, etc.), · performance of written exercises, · mastering material under study according to the textbook, · performance of oral exercises, · the 1900s (anti-homework), · the 1930s (homework as child labor), · the 1980s, · early 21st century, school homework today, why does homework exist, is homework illegal in california, why do students dislike homework, why should homework be banned from schools, who invented school homework and why.

The person who invented school homework in 1905 is a man named Roberto Nevilis. He created this new way of learning to help students who were struggling with their lessons.
Nevills was passionate about education and had a special interest in how children learn best. He believed that children should be treated as individuals with unique abilities and needs.
He also believed that children should be encouraged to take responsibility for their own learning.
Nevilis realized that some of his students were not getting enough practice at home, so he decided to make a plan that would give them extra practice without them even knowing it.
He made up a booklet of questions for the students to answer about their lessons and gave it to them at the end of each day.
The next morning, he collected the booklets from his students and returned them with corrections and new questions for them to answer during recess.
This system became very popular with teachers all over Europe because it made learning more interesting for both students and teachers alike!
Homework is meant to reinforce what we have already learned during the day.
This can be seen through taking notes in class and then reviewing them after class by doing homework assignments.
This is the reason why many parents are against the idea of giving their children homework.
They believe that if their children did not do their homework, then they should not be punished for it.
The invention of math homework is credited to a man named Roberto Nevilis.
He was born in 1881, and he studied at the University of Rome.
While there, he became interested in mathematics and decided to pursue a career in teaching.
Math homework is a type of assignment that students are required to complete at home.
The purpose of this assignment is to help students learn the material they learn in class, and also to reinforce it.
Math homework can be completed on a variety of subjects, but one of the most common types is algebra and geometry.
The tradition of giving children holiday homework goes back to the 1920s.
It was thought to be a good way to keep children occupied over Christmas and New Year.
The practice became popular amongst schools in America and spread to Britain during World War II when many schools were evacuated to the countryside.
The practice continued after the war ended, but has since declined in popularity.
However, some schools still use it as a way of helping pupils keep up their grades during long periods away from school.
Read about the inventor of school uniforms .
In the 20th century, summer homework was invented to ensure that students did not forget what they learned during the school year.
Homework was a way for parents and teachers to ensure that students retained their knowledge.
Summer homework has been around for decades, but some parents don’t think it’s necessary. In fact, some argue that it’s harmful.
The debate over whether or not summer homework for school is good for children continues today.
Students may have different opinions about whether or not summer homework is necessary.
Some students enjoy being able to relax during the summer months and have time to do other activities.
Homework memes have become an internet sensation and the inventor is nowhere to be found.
The fact that the inventor of the homework meme is unknown adds to the mystery, making it more popular than ever.
The original source of the meme is unknown. It could be a high school student or even a college student.
Whoever it was, they definitely did not expect homework memes to become so popular.
The invention of homework is a bit complicated. Some say that Roberto Nevilis invented homework in the 20th century.
Others claim that it existed in Ancient Greece. However, most people agree that the Russians did make homework assignments first.
Homework was used as a way to teach children moral values and ethics .
Nevilis’ homework is said to be one of the most important inventions of all time.
It was an invention that revolutionized education and changed the way people think about learning.
It is said that he came up with this idea while working as a teacher in a local school in Greece.
One day after class, he found himself sitting alone in his room wondering if there was anything else he could do to help his students learn more effectively.
Who Invented Homework for Students?

The first person who invented school homework for students was Roberto Nevilis, an Italian teacher.
The idea behind homework was to improve students’ knowledge and, at the same time, to punish lazy students
He believed that if students were allowed to practice skills and concepts at home, their understanding of those things would be greater.
He also felt that homework could help teach responsibility and independence by giving students an opportunity to apply what they had learned in new situations outside of school.
Nevilis’ idea spread quickly throughout Europe and later to North America.
Today, homework is still used as a tool for teaching students important skills related to math, a science tutoring business, language arts, and more!
High school students are under a lot of pressure. Between preparing for college and dealing with the stress of being in high school, homework can be a huge burden for many students. Here are some reasons why homework is bad for high school students:
- It takes time away from other activities that are more important to them, like spending time with friends or practicing sports.
- Homework can cause stress, which can lead to mental health issues like depression or anxiety.
- Homework can lead to poor grades because it takes away from the time students have to study for tests and quizzes in class, which leads to lower grades on those tests and quizzes (and possibly even failure).
Many people wonder did Roberto Novelis invent homework. The answer is: YES.
Roberto Novelis was an Italian teacher who invented school homework. He was born in 1877 and died in 1957 at the age of 80.
Roberto was a teacher at the University of Padua in Italy, where he worked for 52 years.
One day, while he was teaching his students about algebraic equations, he realized that they did not understand what he was saying.
So instead of repeating himself and giving them more examples, he decided to give them homework instead.
Roberto wanted to see if it would help his students understand better if they practiced on their own time instead of during class time.
It worked! His students were able to practice at home until they understood what the lesson was about and could answer questions correctly when he gave them back their assignments later in class.
Why Was Homework Invented?
If you’re curious about why homework was invented you should know that initially homework was invented because of the need to strengthen students’ understanding of the lessons they were taught in class.
While some teachers used it as a punishment, others used it as a way to ensure that their students understood and embraced the lessons fully.
Homework was invented because of the need to strengthen students’ understanding of the lessons they were taught in class.
It was used to punish students who were not paying attention in class, or who could not pay attention due to other responsibilities.
Homework was also used as an extension of classroom learning, where the students are given an assignment that requires them to apply what they have learned by creating something new based on their knowledge base.
Homework exists because it’s a good way to practice what you’ve learned in class.
It also helps you learn how to study and manage your time, so when you go into the real world, you’ll be able to keep up with all the things you need to do.
It can help you identify gaps in your understanding of concepts, which can then be filled by another activity or lesson at home or in class.
Homework is a great way for teachers to see how well students are grasping their lessons, and it allows them to adjust their teaching methods as needed.
When Was School Homework Invented?
You might wonder when was homework invented. Well, the answer is that it wasn’t until the beginning of the 20th century.
In fact, it’s hard to imagine a world without schoolwork at all!
But before then, children were expected to spend their time doing things that were more useful for their families or communities.
But in the early 1900s, more and more people started going to school for longer periods.
And as more children went to school for longer periods, they needed additional assignments that would help them learn new concepts—and this was when homework became popularized!
In many schools homework was a part of the punishment for lazy and naughty students.
Nowadays, we don’t think twice about handing our kids assignments or asking them to do extra work at home. But remember: It wasn’t always like that!
To be even more precise, school homework was first invented in 1905 by an Italian teacher named Roberto Nevilis.
This practice spread to other countries and gained popularity.
Years after it was first invented, giving students homework every day became standard in most schools around the world.
The reason why this practice became so popular around the world was that it helped students learn more about the subjects they were studying and improve their grades, which in turn made them more likely to succeed in life.
Did you know that homework was originally invented as a form of punishment?
It’s true! The practice of assigning students homework began in the late 19th century when educators believed that children needed to be taught how to spend their free time productively.
It wasn’t until the late 20th century that researchers discovered the benefits of homework, and it became an essential part of classroom learning.
However, some experts believe that homework is counterproductive and harmful to students’ health.
According to them, take-home assignments are stressful and overburden students.
Types Of Homework
There are many types of homework you can do, and they all serve different purposes. Here are just a few of them:
Writing essays is one of the most effective ways for students to learn how to express themselves in writing style
Students should use their imagination and creativity when doing this type of homework. This type of homework helps students develop their imagination and creativity skills.
Students are given specific tasks, which they have to solve as part of their homework. Their task is to master the material under study according to the textbook and perform it in an exam or a test.
A student has an opportunity to perform oral exercises during his/her free time outside school.
If a student wants to participate in any kind of competition, he/she must practice his/her presentation skills as much as possible before participating in competitions.
History of Homework in Schools in America
Although homework is a mainstay of American education today, it hasn’t always been.
Take a look at the history of school homework in America.
Horace Mann introduced homework to the American education system in 1848.
In 1901, just a few decades after his introduction, homework was banned in the Pacific state of California.
In 1930, the American Child Health Association declared homework a form of child labor and said that it should be abolished because recent laws prohibiting such activities were passed at around the same time.
In its pamphlet, “What Works,” the Department of Education recommended homework as an effective strategy to boost the quality of education.
The report lambasted the state of American public education and called for reforms to right the alarming direction it was headed.
In America, education has changed dramatically since the 1800s.
Nowadays, many educators, students, parents, and other concerned citizens are asking why homework was invented and if it’s still valuable.
These days, looking at school homework is all about making sure that students can do the work they need to do to be college-ready.
Teachers want their students to think critically, resolve problems, and work collaboratively to prepare them for life after high school.
To accomplish this, teachers are shifting away from traditional methods of learning and grading and towards more modern methods of showing students what they need to improve upon.
This means that teachers are often looking at things like group projects, group discussions, and mini-lessons instead of individual tests or essays as ways for students to demonstrate their understanding of concepts.
If you have any questions you can first check this section. Here you can find some of the most common questions when it comes to this topic.
Homework exists to help you take control of your workload, increase your time management skills, and learn how to problem solve independently.
There are no laws against homework in California. In fact, many teachers and schools require students to do homework as part of their learning process.
Students dislike homework because they feel it takes too much time, is boring and pointless, and/or interferes with their social lives.
Research suggests a link between homework and mental health issues in young people, as well as poor academic performance. In middle schoolers, more than 90 minutes of homework per night is associated with lower test scores in math tutoring science.
In conclusion, Roberto Novelis, a man who invented school homework, improved the education system.
He created homework and it made teachers more accountable for what they teach their students.
What are your thoughts on homework? Do you believe that it is helping students or hurting them? Leave your thoughts in the comments below.
Who Invented Sign Language? [When, Where & How]
Who Invented High School? [When, Where & Why]

Uncovering the Past, Shaping the Future.
- [email protected]
- Privacy policy
- Terms of use
Copyright © 2024 Nevada investors
Origin and Death of Homework Inventor: Roberto Nevilis

Roberto Nevilis is known for creating homework to help students learn on their own. He was a teacher who introduced the idea of giving assignments to be done outside of class. Even though there’s some debate about his exact role, Nevilis has left a lasting impact on education, shaping the way students around the world approach their studies.
Homework is a staple of the modern education system, but few people know the story of its origin.
The inventor of homework is widely considered to be Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the early 20th century.
We will briefly explore Nevilis’ life, how he came up with the concept of homework, and the circumstances surrounding his death.
Roberto Nevilis: The Man Behind Homework Roberto Nevilis was born in Venice, Italy, in 1879. He was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education.
He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education. After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
Table of Contents
How Homework Was Born
The Birth of Homework According to historical records, Nevilis was frustrated with the lack of discipline in his classroom. He found that students were often too focused on playing and not enough on learning.
To solve this problem , he came up with the concept of homework. Nevilis assigned his students homework to reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encourage them to take their education more seriously.
How did homework become popular?
The Spread of Homework , The idea of homework quickly caught on, and soon other teachers in Italy followed Nevilis’ lead. From Italy, the practice of assigning homework spread to other European countries and, eventually, the rest of the world.
Today, homework is a standard part of the education system in almost every country, and millions of students worldwide spend countless hours each week working on homework assignments.
How did Roberto Nevilis Die?
Death of Roberto Nevilis The exact circumstances surrounding Nevilis’ death are unknown. Some reports suggest that he died in an accident, while others claim he was murdered.
However, the lack of concrete evidence has led to numerous theories and speculation about what happened to the inventor of homework.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy lives on through his impact on education.

Facts about Roberto Nevilis
- He is credited with inventing homework to punish his students who misbehaved in class.
- Some accounts suggest he was a strict teacher who believed in disciplining his students with homework.
- There is little concrete evidence to support the claim that Nevilis was the true inventor of homework.
- Some historians believe that the concept of homework has been around for much longer than in the 1900s.
- Despite the lack of evidence, Roberto Nevilis remains a popular figure in the history of education and is often cited as the inventor of homework.
The Legacy of Homework
The legacy of homework is deeply embedded in the educational landscape, reflecting a historical evolution that spans centuries. From its ambiguous origins to the diverse purposes it serves today, homework has played a pivotal role in shaping learning experiences.
While its effectiveness and necessity have been subjects of ongoing debate, homework endures as a tool for reinforcing concepts, fostering independent study habits, and preparing students for future academic and professional challenges.
In the contemporary educational context, the legacy of homework is a complex interplay of tradition, pedagogy, and evolving perspectives on the balance between academic demands and student well-being.
The Complex History of Homework
Throughout history, the evolution of homework can be traced through a series of significant developments. In ancient civilizations, such as Greece and Rome, scholars and philosophers encouraged independent study outside formal learning settings.
The Renaissance era witnessed a surge in written assignments, marking an early precursor to modern homework. The Industrial Revolution further transformed educational practices, as the need for a skilled workforce emphasized the importance of individual learning and practice.

The purposes and perceptions of homework have undergone substantial transformations over time. In the 19th century, homework was often viewed as a means of reinforcing discipline and moral values, with assignments focused on character development.
As educational philosophies evolved, particularly in the 20th century, homework assumed various roles—from a tool for drill and practice to a method for fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Perceptions of homework have fluctuated, with debates arising around issues of workload, equity, and its impact on student well-being. The complex history of homework reveals a dynamic interplay between societal expectations, educational philosophies, and changing perspectives on the purposes of academic assignments.

Conclusion – Who invented homework, and how did he die
Roberto Nevilis was a visionary educator who profoundly impacted the education system. His invention of homework has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Although the circumstances surrounding his death are unclear, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What is Roberto Nevilis’ legacy?
Roberto Nevilis’ legacy is his invention of homework, which has changed how students learn and has helped countless students worldwide improve their education.
Despite the mystery surrounding his death, Nevilis’ legacy as the inventor of homework will never be forgotten.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ background?
Roberto Nevilis was the son of a wealthy merchant and received a private education. He later studied at the University of Venice, where he received a degree in education.
After graduation, Nevilis worked as a teacher in various schools in Venice.
What was Roberto Nevilis’ impact on education?
Roberto Nevilis’ invention of homework has had a profound impact on education. By assigning homework, he helped students reinforce the lessons they learned in class and encouraged them to take their education more seriously.
This concept has spread worldwide and is now a staple of the modern education system.
Is there any evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death?
There is no concrete evidence to support the theories about Roberto Nevilis’ death, and the exact circumstances surrounding his death remain a mystery.
What was Roberto nevilis age?
It is believed that he died of old age. Not much information is available on his exact age at the time of death. Born: 1879 Died: 1954 (aged 75 years)
Where is Roberto Nevilis’s grave
While many have tried to find out about his Grave, little is known about where he is buried. Many people are querying the internet about his Grave. But frankly, I find it weird why people want to know this.
Share this:

When Was Homework Invented: Everything You Need to Know
Homework has been a controversial issue for both teachers and students. Teachers believe it is an essential aspect of academic life, despite students’ being completely opposed. As a result, a tug-of-war is necessary. A different debate is whether homework is beneficial or harmful, and when was homework invented. In this article, we shall investigate who originated homework. But first, let’s take a look at some of the misconceptions students and teachers have about homework.
Homework is now an important element of the educational process; it facilitates and improves learning. We’ve been completing tasks since we were in elementary school. And few of us were considering.
- Who developed homework?
- When was homework invented?
- When was the invention made?
- What was the aim of homework in the first place?
This article will look into when was homework invented and why and the practical worth of the at-home job that a teacher assigns. First We will consider a few things about homework. Let’s start
The Origins of Homework (History)
When Was Homework Invented? The origins of homework can be traced back to the Roman Empire. According to some, Pliny the Younger is credited with inventing the homework simulation. Pliny the Younger was a teacher who assigned homework to his Quintilian students. Pliny hoped to help his students improve their oratory talents in a less stressful setting.
Other oncoming educators were inspired to follow suit when the new method achieved significant outcomes. However, Italy’s Roberto Nevilis is officially recognized as the inventor of homework. In 1905, he invented homework. However, Nevilis created homework to penalize his students.
Homework: A Teacher’s View
Homework is particularly crucial for a student’s academic advancement, according to the majority of teachers and educators. Teachers propose a range of reasons for supporting homework in general. There are a few:-

- Homework lets you learn better
- Homework improves your academic score
- Practice makes a man perfect
- More in-depth understanding
- Conceptual clarity
- Doubt generation
- Daily revision
- Homework motivates learning
Teachers feel that homework is an important learning component because of these key benefits.
Homework: A Student’s View
In most cases, students, on the other hand, hate homework. They see it as an extra burden that takes up their relaxation time. Students frequently argue that homework is provided in excess and is a part of what the teacher cannot complete in class. There are always a few key points that students utilize to support their position. Students criticized homework for the following reasons:

- It was a waste of time
- There is an additional burden
- There is a lack of uniformity
- Insufficient motivation
- Inability to increase the value of grades
- The level of difficulty is high
- There is no holistic development
- Time commitment is excessive
- Problems with your health
- Anxiety and stress are common occurrences
The above list demonstrates that homework is not without its drawbacks. It has drawbacks, which students openly acknowledge. However, dismissing the need for homework entirely because of a few drawbacks is not the best strategy.
When Was Homework Invented: What Went Wrong?
Home learning is a crucial prerequisite for efficient educational activities, according to educators who hold traditional ideas on the learning process. It is a means to enhance pupils’ initiative, independence, uniqueness, and creative imagination, according to the person who established homework.
The following factors influence the necessity of Homework
- Concentrated assimilation of the studied material occurs during in-school learning. After that, the knowledge gained is forgotten. Homework is required to prevent this forgetting.
- Consistent comprehension and assimilation of scientific concepts are required for mastery.
- Only by dispersing the memorizing of the content being studied can the depth and strength of the material assimilation be accomplished.
- Home learning is critical for pupils’ creative capabilities and capacities to grow.
The success of homework preparation determines the success of instruction. This topic has been thought about since the invention of homework; homework organizing is the most challenging aspect of the teaching and educational process. Many parts of this subject necessitate the tutor’s undivided attention.
Role of Homework in Improving the Students’ Education?
Improving the content and arrangement of at-home chores on the subject is one method to make the learning process easier. There are many different types of assignments. Each one aims to improve the quality of students’ knowledge, improve their studying process, and systematize what they’ve learned.
Psychologists have discovered that assimilation of knowledge and activity strategies is crucial. With any arbitrary effective structure of the study process, the main perception and consolidation of knowledge during the lesson must be reinforced by subsequent thinking and application of new knowledge. And, if frontal perception and knowledge accumulation are possible, the ensuing task must be autonomous and independent.

Homework is no longer used to penalize or control students, as it was during Roberto Neville’s time. Homework allows you to devote personal time to a more in-depth study of a subject. These factors are more important than the intentions of the person when homework was invented, who created homework. You can, however, hire writing specialists to take complete any assignment you delegate to them and relieve yourself of the stress. You can hire experts for python assignment help , java assignment help , and many more.
What is the point of doing homework?
The most common reason for assigning homework is to have students practice information covered in class in order to reinforce learning and facilitate mastery of specific abilities. The material that will be covered in future lessons is introduced through preparation assignments.
Why should teachers avoid assigning homework?
Too much homework, according to studies, can be harmful to kids’ health, causing them to become frustrated and burnt out. Most teachers assign 1-2 pages of homework, which may not seem like much at first, but it may easily overwhelm a child when added together.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Advertisement
Supported by
Review: ‘3 Body Problem’ Is a Galaxy-Brained Spectacle
The Netflix sci-fi adaptation has done its physics homework, even if it sometimes falls short on the humanities.
- Share full article

By James Poniewozik
The aliens who menace humankind in Netflix’s “3 Body Problem” believe in doing a lot with a little. Specifically, they can unfold a single proton into multiple higher dimensions, enabling them to print computer circuits with the surface area of a planet onto a particle smaller than a pinprick.
“3 Body Problem,” the audacious adaptation of a hard-sci-fi trilogy by Liu Cixin, is a comparable feat of engineering and compression. Its first season, arriving Thursday, wrestles Liu’s inventions and physics explainers onto the screen with visual grandeur, thrills and wow moments. If one thing holds it back from greatness, it’s the characters, who could have used some alien technology to lend them an extra dimension or two. But the series’s scale and mind-bending turns may leave you too starry-eyed to notice.
David Benioff and D.B. Weiss, partnering here with Alexander Woo ( “The Terror: Infamy” ), are best known for translating George R.R. Martin’s incomplete “A Song of Ice and Fire” fantasy saga into “Game of Thrones.” Whatever your opinions of that series — and there are plenty — it laid out the duo’s strengths as adapters and their weaknesses as creators of original material.
Beginning with Martin’s finished novels, Benioff and Weiss converted the sprawling tomes into heady popcorn TV with epic battles and intimate conversations. Toward the end, working from outlines or less, they rushed to a finish and let visual spectacle overshadow the once-vivid characters.
In “3 Body,” however, they and Woo have a complete story to work with, and it’s a doozy. It announces its sweep up front, opening with a Chinese scientist’s public execution during Mao’s Cultural Revolution, then jumping to the present day, when a wave of notable physicists are inexplicably dying by suicide.
The deaths may be related to several strange phenomena. Experiments in particle accelerators around the world suddenly find that the last several decades’ worth of research is wrong. Brilliant scientific minds are being sent futuristic headsets of unknown provenance that invite them to join an uncannily realistic virtual-reality game. Oh, also, one night all the stars in the sky start blinking on and off.
It all suggests the working of an advanced power, not of the cuddly E.T. variety. What starts as a detective mystery, pursued by the rumpled intelligence investigator Clarence Da Shi (Benedict Wong), escalates to a looming war of the worlds. What the aliens want and what they might do to get it is unclear at first, but as Clarence intuits, “Usually when people with more advanced technology encounter people with more primitive technology, doesn’t work out well for the primitives.”
Most of the first season’s plot comes straight from Liu’s work. The biggest changes are in story structure and location. Liu’s trilogy, while wide-ranging, focused largely on Chinese characters and had specifically Chinese historical and political overtones. Benioff, Weiss and Woo have globalized the story, shifting much of the action to London, with a multiethnic cast. (Viewers interested in a more literal rendition of Liu’s story can watch last year’s stiff but thorough Chinese adaptation on Peacock.)
They’ve also given Liu’s heavy science a dose of the humanities. Liu is a brilliant novelist of speculative ideas, but his characters can read like figures from story problems. In the series, a little playful dialogue goes a long way toward leavening all the Physics 101.
So does casting. Wong puffs life into his generically hard-boiled gumshoe. Liam Cunningham (Davos Seaworth in “Thrones”) stands out as Thomas Wade, a sharp-tongued spymaster, as does Rosalind Chao as Ye Wenjie, an astrophysicist whose brutal experience in the Cultural Revolution makes her question her allegiance to humanity. Zine Tseng is also excellent as the young Ye.
More curious, if understandable, is the decision to shuffle and reconfigure characters from throughout Liu’s trilogy into a clique of five attractive Oxford-grad prodigies who carry much of the narrative: Jin Cheng (Jess Hong), a dogged physicist with personal ties to the dead-scientists case; Auggie Salazar (Eiza González), an idealistic nanofibers researcher; Saul Durand (Jovan Adepo), a gifted but jaded research assistant; Will Downing (Alex Sharp), a sweet-natured teacher with a crush on Jin; and Jack Rooney (John Bradley of “Thrones”), a scientist turned snack-food entrepreneur and the principal source of comic relief.
The writers manage to bump up Liu’s one-dimensional characterizations to two-ish, but the “Oxford Five,” with the exception of Jin, don’t feel entirely rounded. This is no small thing; in a fantastical series like “Thrones” or “Lost,” it is the memorable individuals — your Arya Starks and your Ben Linuses — who hold you through the ups and downs of the story.
The plot, however, is dizzying and the world-building immersive, and the reportedly galactic budget looks well and creatively spent on the screen. Take the virtual-reality scenes, through which “3 Body” gradually reveals its stakes and the aliens’ motives. Each character who dons the headset finds themselves in an otherworldly version of an ancient kingdom — China for Jin, England for Jack — which they are challenged to save from repeating cataclysms caused by the presence of three suns (hence the series’s title).
“3 Body” has a streak of techno-optimism even at its bleakest moments, the belief that the physical universe is explicable even when cruel. The universe’s inhabitants are another matter. Alongside the race to save humanity is the question of whether humanity is worth saving — a group of alien sympathizers, led by a billionaire environmentalist (Jonathan Pryce), decides that Earth would benefit from a good cosmic intervention.
All this attaches the show’s brainiac spectacle to big humanistic ideas. The threat in “3 Body” is looming rather than imminent — these are not the kind of aliens who pull up quick and vaporize the White House — which makes for a parallel to the existential but gradual threat of climate change. Like “Thrones,” with its White Walkers lurking beyond the Wall, “3 Body” is in part a collective-action problem.
It is also morally provocative. Liu’s novels make an argument that in a cold, indifferent universe, survival can require a hard heart; basing decisions on personal conscience can be a kind of selfishness and folly. The series is a bit more sentimental, emphasizing relationships and individual agency over game theory and determinism. But it’s willing to go dark: In a striking midseason episode, the heroes make a morally gray decision in the name of planetary security, and the consequences are depicted in horrifying detail.
Viewers new to the story should find it exciting on its own. (You do not need to have read the books first; you should never need to read the books to watch a TV series.) But the book trilogy does go to some weird, grim — and presumably challenging to film — places, and it will be interesting to see if and how future seasons follow.
For now, there’s flair, ambition and galaxy-brain twists aplenty. Sure, this kind of story is tough to pull off beginning to end (see, again, “Game of Thrones”). But what’s the thrill in creating a headily expanding universe if there’s no risk of it collapsing?
James Poniewozik is the chief TV critic for The Times. He writes reviews and essays with an emphasis on television as it reflects a changing culture and politics. More about James Poniewozik
Explore More in TV and Movies
Not sure what to watch next we can help..
“3 Body Problem,” a science fiction epic from the creators of “Game of Thrones,” has arrived on Netflix. We spoke with them about their latest project .
For the past two decades, female presidential candidates on TV have been made in Hillary Clinton’s image. With “The Girls on the Bus,” that’s beginning to change .
“Freaknik,” a new Hulu documentary, delves into the rowdy ’80s and ’90s-era spring festival that drew hundreds of thousands of Black college students to Atlanta.
Currently in two series, “The Regime” and “Alice & Jack,” the versatile actress Andrea Riseborough has played dozens of characters. What connects them? Not even she knows .
If you are overwhelmed by the endless options, don’t despair — we put together the best offerings on Netflix , Max , Disney+ , Amazon Prime and Hulu to make choosing your next binge a little easier.
Sign up for our Watching newsletter to get recommendations on the best films and TV shows to stream and watch, delivered to your inbox.

Susan Devlin
Gustavo Almeida Correia

COMMENTS
Easy inventions to make for a school project. Creative invention ideas for school projects. Invention ideas for students. Easy science inventions for students. The potato battery. Hot air balloons. Paper planes. Invention projects for high school students. Invention ideas for middle school students.
Here are the top 35 invention ideas for you to ace in your project: 1. A Solar-Powered Phone Charger. To make a solar-powered phone charger, you will need a solar panel, a voltage regulator, a rechargeable battery, and a USB port. First, connect the solar panel to the voltage regulator, making sure the positive and negative wires are correctly ...
Invention Ideas for Kids. Peggy_Marco via Pixabay. Many inventors got their start by trying to improve on something that already existed. Challenge kids to come up with better, more effective versions of some of these existing products: Mousetrap. Portable shelter (e.g., a tent) Squirrel-proof bird feeder.
Self-Watering Plant Pot. Design a pot that can water plants using stored rainwater. This invention would have a built-in rain collection system and a slow-drip mechanism to keep the soil moist. It's a hands-on way to understand plant biology and environmental science. 4. Solar-powered Charging Station.
In invention conventions, students generally develop creative innovations to solve real-world problems. Annually, more than 100,000 students also participate in Invention Convention Worldwide. Students are ultimately invited to present their inventions at Nationals by way of local contests. Teams of up to four students may participate, and this ...
Open a special compartment in this lunch box, and it turns into a robot! The inventors of the product, patented in 1987, wanted to make their very own "Transformer," given the popularity of the ...
The inventor of homework may be unknown, but its evolution reflects contributions from educators, philosophers, and students. Homework reinforces learning, fosters discipline, and prepares students for the future, spanning from ancient civilizations to modern education. Ongoing debates probe its balance, efficacy, equity, and accessibility, prompting innovative alternatives like project-based ...
Run a Little Inventors after-school club! Our resources are perfect to run a full meaningful project exploring topics through the lens of invention from developing ideas to creating a wonderful display for your school, something to take pride in! This is a great way to encourage and stretch children's creativity and problem-solving skills and ...
Idea #3 Recycled Invention. Have families, businesses, and the community donate recycled machine parts from cell phones, computers, appliances, and so forth. Spread out these parts on a table, and supply students with glue guns, duct tape, and other supplies to help them create robots or inventions with the recycled materials.
Create a board game. Complete a quiz - you could also ask students to write the quiz in groups and then swap and complete for homework. Write a lesson plan for teaching the topic to a younger class. Teach the teacher - create a poster, Complete a series of exercises. Complete a family tree, real or imaginary.
The goal, says Quirky, is to "make invention accessible, both by providing a means to turn invention ideas into real products and by educating aspiring inventors on the fundamentals of product development." Product development uses all the core subjects, but it begins with teachers willing to create their own atmosphere of collaborative innovation.
The 19th-century politician and educational reformer Horace Mann played a large role in the history of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, had a strong ...
Mentions of the term "homework" date back to as early as ancient Rome. In I century AD, Pliny the Younger, an oratory teacher, supposedly invented homework by asking his followers to practice public speaking at home. It was to help them become more confident and fluent in their speeches.
It's challenging to pinpoint the exact person responsible for the invention of homework. For example, Medieval Monks would work on memorization and practice singing. ... The idea of homework spread across Europe throughout the 19th century. So who created homework in the United States? Horace Mann (1796—1859), an American educational ...
Horace Mann. Horace Mann, a 19th-century politician and educational reformer, was a pivotal figure in the development of homework. Mann, like his contemporaries Henry Barnard and Calvin Ellis Stowe, was passionate about the newly unified nation-state of Germany's obligatory public education system. Mandatory tasks were assigned to ...
The origin of homework is often attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian educator who lived in the 20th century. Roberto Nevilis is believed to have been a school teacher in Venice, and it is ...
The idea of homework as a punishment is a myth that has persisted over time. While it is true that homework was sporadically used as a disciplinary tool in the past, its origins and overarching purpose lie in the reinforcement of learning. Today, the educational landscape recognizes the value of homework in promoting academic growth, and a more ...
The invention of homework is commonly attributed to Roberto Nevilis, an Italian pedagog who is said to have introduced it as a form of punishment for his students in 1905. However, the concept of homework predates Nevilis and has roots that go back much further in history. ... It's important to note that the idea of formalized homework has ...
That should provide leads to diversify your search and gain a more complete assessment of your idea or invention. • Consider specialist search engines. Companies such as Octimine in Munich ...
The invention of math homework is credited to a man named Roberto Nevilis. He was born in 1881, and he studied at the University of Rome. While there, he became interested in mathematics and decided to pursue a career in teaching. ... The idea behind homework was to improve students' knowledge and, at the same time, to punish lazy students.
The Spread of Homework, The idea of homework quickly caught on, and soon other teachers in Italy followed Nevilis' lead. From Italy, the practice of assigning homework spread to other European countries and, ... Roberto Nevilis' invention of homework has had a profound impact on education. By assigning homework, he helped students reinforce ...
The success of homework preparation determines the success of instruction. This topic has been thought about since the invention of homework; homework organizing is the most challenging aspect of the teaching and educational process. Many parts of this subject necessitate the tutor's undivided attention.
March 20, 2024, 5:06 a.m. ET. The aliens who menace humankind in Netflix's "3 Body Problem" believe in doing a lot with a little. Specifically, they can unfold a single proton into multiple ...
Homework Invention Ideas: 2640 Orders prepared. The various domains to be covered for my essay writing. If you are looking for reliable and dedicated writing service professionals to write for you, who will increase the value of the entire draft, then you are at the right place. The writers of PenMyPaper have got a vast knowledge about various ...