Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- Focus and Precision: How to Write Essays that Answer the Question

About the Author Stephanie Allen read Classics and English at St Hugh’s College, Oxford, and is currently researching a PhD in Early Modern Academic Drama at the University of Fribourg.
We’ve all been there. You’ve handed in an essay and you think it’s pretty great: it shows off all your best ideas, and contains points you’re sure no one else will have thought of.
You’re not totally convinced that what you’ve written is relevant to the title you were given – but it’s inventive, original and good. In fact, it might be better than anything that would have responded to the question. But your essay isn’t met with the lavish praise you expected. When it’s tossed back onto your desk, there are huge chunks scored through with red pen, crawling with annotations like little red fire ants: ‘IRRELEVANT’; ‘A bit of a tangent!’; ‘???’; and, right next to your best, most impressive killer point: ‘Right… so?’. The grade your teacher has scrawled at the end is nowhere near what your essay deserves. In fact, it’s pretty average. And the comment at the bottom reads something like, ‘Some good ideas, but you didn’t answer the question!’.

If this has ever happened to you (and it has happened to me, a lot), you’ll know how deeply frustrating it is – and how unfair it can seem. This might just be me, but the exhausting process of researching, having ideas, planning, writing and re-reading makes me steadily more attached to the ideas I have, and the things I’ve managed to put on the page. Each time I scroll back through what I’ve written, or planned, so far, I become steadily more convinced of its brilliance. What started off as a scribbled note in the margin, something extra to think about or to pop in if it could be made to fit the argument, sometimes comes to be backbone of a whole essay – so, when a tutor tells me my inspired paragraph about Ted Hughes’s interpretation of mythology isn’t relevant to my essay on Keats, I fail to see why. Or even if I can see why, the thought of taking it out is wrenching. Who cares if it’s a bit off-topic? It should make my essay stand out, if anything! And an examiner would probably be happy not to read yet another answer that makes exactly the same points. If you recognise yourself in the above, there are two crucial things to realise. The first is that something has to change: because doing well in high school exam or coursework essays is almost totally dependent on being able to pin down and organise lots of ideas so that an examiner can see that they convincingly answer a question. And it’s a real shame to work hard on something, have good ideas, and not get the marks you deserve. Writing a top essay is a very particular and actually quite simple challenge. It’s not actually that important how original you are, how compelling your writing is, how many ideas you get down, or how beautifully you can express yourself (though of course, all these things do have their rightful place). What you’re doing, essentially, is using a limited amount of time and knowledge to really answer a question. It sounds obvious, but a good essay should have the title or question as its focus the whole way through . It should answer it ten times over – in every single paragraph, with every fact or figure. Treat your reader (whether it’s your class teacher or an external examiner) like a child who can’t do any interpretive work of their own; imagine yourself leading them through your essay by the hand, pointing out that you’ve answered the question here , and here , and here. Now, this is all very well, I imagine you objecting, and much easier said than done. But never fear! Structuring an essay that knocks a question on the head is something you can learn to do in a couple of easy steps. In the next few hundred words, I’m going to share with you what I’ve learned through endless, mindless crossings-out, rewordings, rewritings and rethinkings.

Top tips and golden rules
I’ve lost count of the number of times I’ve been told to ‘write the question at the top of every new page’- but for some reason, that trick simply doesn’t work for me. If it doesn’t work for you either, use this three-part process to allow the question to structure your essay:
1) Work out exactly what you’re being asked
It sounds really obvious, but lots of students have trouble answering questions because they don’t take time to figure out exactly what they’re expected to do – instead, they skim-read and then write the essay they want to write. Sussing out a question is a two-part process, and the first part is easy. It means looking at the directions the question provides as to what sort of essay you’re going to write. I call these ‘command phrases’ and will go into more detail about what they mean below. The second part involves identifying key words and phrases.
2) Be as explicit as possible
Use forceful, persuasive language to show how the points you’ve made do answer the question. My main focus so far has been on tangential or irrelevant material – but many students lose marks even though they make great points, because they don’t quite impress how relevant those points are. Again, I’ll talk about how you can do this below.
3) Be brutally honest with yourself about whether a point is relevant before you write it.
It doesn’t matter how impressive, original or interesting it is. It doesn’t matter if you’re panicking, and you can’t think of any points that do answer the question. If a point isn’t relevant, don’t bother with it. It’s a waste of time, and might actually work against you- if you put tangential material in an essay, your reader will struggle to follow the thread of your argument, and lose focus on your really good points.
Put it into action: Step One

Let’s imagine you’re writing an English essay about the role and importance of the three witches in Macbeth . You’re thinking about the different ways in which Shakespeare imagines and presents the witches, how they influence the action of the tragedy, and perhaps the extent to which we’re supposed to believe in them (stay with me – you don’t have to know a single thing about Shakespeare or Macbeth to understand this bit!). Now, you’ll probably have a few good ideas on this topic – and whatever essay you write, you’ll most likely use much of the same material. However, the detail of the phrasing of the question will significantly affect the way you write your essay. You would draw on similar material to address the following questions: Discuss Shakespeare’s representation of the three witches in Macbeth . How does Shakespeare figure the supernatural in Macbeth ? To what extent are the three witches responsible for Macbeth’s tragic downfall? Evaluate the importance of the three witches in bringing about Macbeth’s ruin. Are we supposed to believe in the three witches in Macbeth ? “Within Macbeth ’s representation of the witches, there is profound ambiguity about the actual significance and power of their malevolent intervention” (Stephen Greenblatt). Discuss. I’ve organised the examples into three groups, exemplifying the different types of questions you might have to answer in an exam. The first group are pretty open-ended: ‘discuss’- and ‘how’-questions leave you room to set the scope of the essay. You can decide what the focus should be. Beware, though – this doesn’t mean you don’t need a sturdy structure, or a clear argument, both of which should always be present in an essay. The second group are asking you to evaluate, constructing an argument that decides whether, and how far something is true. Good examples of hypotheses (which your essay would set out to prove) for these questions are:
- The witches are the most important cause of tragic action in Macbeth.
- The witches are partially, but not entirely responsible for Macbeth’s downfall, alongside Macbeth’s unbridled ambition, and that of his wife.
- We are not supposed to believe the witches: they are a product of Macbeth’s psyche, and his downfall is his own doing.
- The witches’ role in Macbeth’s downfall is deliberately unclear. Their claim to reality is shaky – finally, their ambiguity is part of an uncertain tragic universe and the great illusion of the theatre. (N.B. It’s fine to conclude that a question can’t be answered in black and white, certain terms – as long as you have a firm structure, and keep referring back to it throughout the essay).
The final question asks you to respond to a quotation. Students tend to find these sorts of questions the most difficult to answer, but once you’ve got the hang of them I think the title does most of the work for you – often implicitly providing you with a structure for your essay. The first step is breaking down the quotation into its constituent parts- the different things it says. I use brackets: ( Within Macbeth ’s representation of the witches, ) ( there is profound ambiguity ) about the ( actual significance ) ( and power ) of ( their malevolent intervention ) Examiners have a nasty habit of picking the most bewildering and terrifying-sounding quotations: but once you break them down, they’re often asking for something very simple. This quotation, for example, is asking exactly the same thing as the other questions. The trick here is making sure you respond to all the different parts. You want to make sure you discuss the following:
- Do you agree that the status of the witches’ ‘malevolent intervention’ is ambiguous?
- What is its significance?
- How powerful is it?
Step Two: Plan

Having worked out exactly what the question is asking, write out a plan (which should be very detailed in a coursework essay, but doesn’t have to be more than a few lines long in an exam context) of the material you’ll use in each paragraph. Make sure your plan contains a sentence at the end of each point about how that point will answer the question. A point from my plan for one of the topics above might look something like this:
To what extent are we supposed to believe in the three witches in Macbeth ? Hypothesis: The witches’ role in Macbeth’s downfall is deliberately unclear. Their claim to reality is uncertain – finally, they’re part of an uncertain tragic universe and the great illusion of the theatre. Para.1: Context At the time Shakespeare wrote Macbeth , there were many examples of people being burned or drowned as witches There were also people who claimed to be able to exorcise evil demons from people who were ‘possessed’. Catholic Christianity leaves much room for the supernatural to exist This suggests that Shakespeare’s contemporary audience might, more readily than a modern one, have believed that witches were a real phenomenon and did exist.
My final sentence (highlighted in red) shows how the material discussed in the paragraph answers the question. Writing this out at the planning stage, in addition to clarifying your ideas, is a great test of whether a point is relevant: if you struggle to write the sentence, and make the connection to the question and larger argument, you might have gone off-topic.
Step Three: Paragraph beginnings and endings

The final step to making sure you pick up all the possible marks for ‘answering the question’ in an essay is ensuring that you make it explicit how your material does so. This bit relies upon getting the beginnings and endings of paragraphs just right. To reiterate what I said above, treat your reader like a child: tell them what you’re going to say; tell them how it answers the question; say it, and then tell them how you’ve answered the question. This need not feel clumsy, awkward or repetitive. The first sentence of each new paragraph or point should, without giving too much of your conclusion away, establish what you’re going to discuss, and how it answers the question. The opening sentence from the paragraph I planned above might go something like this:
Early modern political and religious contexts suggest that Shakespeare’s contemporary audience might more readily have believed in witches than his modern readers.
The sentence establishes that I’m going to discuss Jacobean religion and witch-burnings, and also what I’m going to use those contexts to show. I’d then slot in all my facts and examples in the middle of the paragraph. The final sentence (or few sentences) should be strong and decisive, making a clear connection to the question you’ve been asked:
Contemporary suspicion that witches did exist, testified to by witch-hunts and exorcisms, is crucial to our understanding of the witches in Macbeth. To the early modern consciousness, witches were a distinctly real and dangerous possibility – and the witches in the play would have seemed all-the-more potent and terrifying as a result.
Step Four: Practice makes perfect
The best way to get really good at making sure you always ‘answer the question’ is to write essay plans rather than whole pieces. Set aside a few hours, choose a couple of essay questions from past papers, and for each:
- Write a hypothesis
- Write a rough plan of what each paragraph will contain
- Write out the first and last sentence of each paragraph
You can get your teacher, or a friend, to look through your plans and give you feedback . If you follow this advice, fingers crossed, next time you hand in an essay, it’ll be free from red-inked comments about irrelevance, and instead showered with praise for the precision with which you handled the topic, and how intently you focused on answering the question. It can seem depressing when your perfect question is just a minor tangent from the question you were actually asked, but trust me – high praise and good marks are all found in answering the question in front of you, not the one you would have liked to see. Teachers do choose the questions they set you with some care, after all; chances are the question you were set is the more illuminating and rewarding one as well.
Image credits: banner ; Keats ; Macbeth ; James I ; witches .
Comments are closed.

Essay Exams
What this handout is about.
At some time in your undergraduate career, you’re going to have to write an essay exam. This thought can inspire a fair amount of fear: we struggle enough with essays when they aren’t timed events based on unknown questions. The goal of this handout is to give you some easy and effective strategies that will help you take control of the situation and do your best.
Why do instructors give essay exams?
Essay exams are a useful tool for finding out if you can sort through a large body of information, figure out what is important, and explain why it is important. Essay exams challenge you to come up with key course ideas and put them in your own words and to use the interpretive or analytical skills you’ve practiced in the course. Instructors want to see whether:
- You understand concepts that provide the basis for the course
- You can use those concepts to interpret specific materials
- You can make connections, see relationships, draw comparisons and contrasts
- You can synthesize diverse information in support of an original assertion
- You can justify your own evaluations based on appropriate criteria
- You can argue your own opinions with convincing evidence
- You can think critically and analytically about a subject
What essay questions require
Exam questions can reach pretty far into the course materials, so you cannot hope to do well on them if you do not keep up with the readings and assignments from the beginning of the course. The most successful essay exam takers are prepared for anything reasonable, and they probably have some intelligent guesses about the content of the exam before they take it. How can you be a prepared exam taker? Try some of the following suggestions during the semester:
- Do the reading as the syllabus dictates; keeping up with the reading while the related concepts are being discussed in class saves you double the effort later.
- Go to lectures (and put away your phone, the newspaper, and that crossword puzzle!).
- Take careful notes that you’ll understand months later. If this is not your strong suit or the conventions for a particular discipline are different from what you are used to, ask your TA or the Learning Center for advice.
- Participate in your discussion sections; this will help you absorb the material better so you don’t have to study as hard.
- Organize small study groups with classmates to explore and review course materials throughout the semester. Others will catch things you might miss even when paying attention. This is not cheating. As long as what you write on the essay is your own work, formulating ideas and sharing notes is okay. In fact, it is a big part of the learning process.
- As an exam approaches, find out what you can about the form it will take. This will help you forecast the questions that will be on the exam, and prepare for them.
These suggestions will save you lots of time and misery later. Remember that you can’t cram weeks of information into a single day or night of study. So why put yourself in that position?
Now let’s focus on studying for the exam. You’ll notice the following suggestions are all based on organizing your study materials into manageable chunks of related material. If you have a plan of attack, you’ll feel more confident and your answers will be more clear. Here are some tips:
- Don’t just memorize aimlessly; clarify the important issues of the course and use these issues to focus your understanding of specific facts and particular readings.
- Try to organize and prioritize the information into a thematic pattern. Look at what you’ve studied and find a way to put things into related groups. Find the fundamental ideas that have been emphasized throughout the course and organize your notes into broad categories. Think about how different categories relate to each other.
- Find out what you don’t know, but need to know, by making up test questions and trying to answer them. Studying in groups helps as well.
Taking the exam
Read the exam carefully.
- If you are given the entire exam at once and can determine your approach on your own, read the entire exam before you get started.
- Look at how many points each part earns you, and find hints for how long your answers should be.
- Figure out how much time you have and how best to use it. Write down the actual clock time that you expect to take in each section, and stick to it. This will help you avoid spending all your time on only one section. One strategy is to divide the available time according to percentage worth of the question. You don’t want to spend half of your time on something that is only worth one tenth of the total points.
- As you read, make tentative choices of the questions you will answer (if you have a choice). Don’t just answer the first essay question you encounter. Instead, read through all of the options. Jot down really brief ideas for each question before deciding.
- Remember that the easiest-looking question is not always as easy as it looks. Focus your attention on questions for which you can explain your answer most thoroughly, rather than settle on questions where you know the answer but can’t say why.
Analyze the questions
- Decide what you are being asked to do. If you skim the question to find the main “topic” and then rush to grasp any related ideas you can recall, you may become flustered, lose concentration, and even go blank. Try looking closely at what the question is directing you to do, and try to understand the sort of writing that will be required.
- Focus on what you do know about the question, not on what you don’t.
- Look at the active verbs in the assignment—they tell you what you should be doing. We’ve included some of these below, with some suggestions on what they might mean. (For help with this sort of detective work, see the Writing Center handout titled Reading Assignments.)
Information words, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject. Information words may include:
- define—give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning.
- explain why/how—give reasons why or examples of how something happened.
- illustrate—give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject.
- summarize—briefly cover the important ideas you learned about the subject.
- trace—outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form.
- research—gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you’ve found.
Relation words ask you to demonstrate how things are connected. Relation words may include:
- compare—show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different).
- contrast—show how two or more things are dissimilar.
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation.
- cause—show how one event or series of events made something else happen.
- relate—show or describe the connections between things.
Interpretation words ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Don’t see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation. Interpretation words may include:
- prove, justify—give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth.
- evaluate, respond, assess—state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons (you may want to compare your subject to something else).
- support—give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe).
- synthesize—put two or more things together that haven’t been put together before; don’t just summarize one and then the other, and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together (as opposed to compare and contrast—see above).
- analyze—look closely at the components of something to figure out how it works, what it might mean, or why it is important.
- argue—take a side and defend it (with proof) against the other side.
Plan your answers
Think about your time again. How much planning time you should take depends on how much time you have for each question and how many points each question is worth. Here are some general guidelines:
- For short-answer definitions and identifications, just take a few seconds. Skip over any you don’t recognize fairly quickly, and come back to them when another question jogs your memory.
- For answers that require a paragraph or two, jot down several important ideas or specific examples that help to focus your thoughts.
- For longer answers, you will need to develop a much more definite strategy of organization. You only have time for one draft, so allow a reasonable amount of time—as much as a quarter of the time you’ve allotted for the question—for making notes, determining a thesis, and developing an outline.
- For questions with several parts (different requests or directions, a sequence of questions), make a list of the parts so that you do not miss or minimize one part. One way to be sure you answer them all is to number them in the question and in your outline.
- You may have to try two or three outlines or clusters before you hit on a workable plan. But be realistic—you want a plan you can develop within the limited time allotted for your answer. Your outline will have to be selective—not everything you know, but what you know that you can state clearly and keep to the point in the time available.
Again, focus on what you do know about the question, not on what you don’t.
Writing your answers
As with planning, your strategy for writing depends on the length of your answer:
- For short identifications and definitions, it is usually best to start with a general identifying statement and then move on to describe specific applications or explanations. Two sentences will almost always suffice, but make sure they are complete sentences. Find out whether the instructor wants definition alone, or definition and significance. Why is the identification term or object important?
- For longer answers, begin by stating your forecasting statement or thesis clearly and explicitly. Strive for focus, simplicity, and clarity. In stating your point and developing your answers, you may want to use important course vocabulary words from the question. For example, if the question is, “How does wisteria function as a representation of memory in Faulkner’s Absalom, Absalom?” you may want to use the words wisteria, representation, memory, and Faulkner) in your thesis statement and answer. Use these important words or concepts throughout the answer.
- If you have devised a promising outline for your answer, then you will be able to forecast your overall plan and its subpoints in your opening sentence. Forecasting impresses readers and has the very practical advantage of making your answer easier to read. Also, if you don’t finish writing, it tells your reader what you would have said if you had finished (and may get you partial points).
- You might want to use briefer paragraphs than you ordinarily do and signal clear relations between paragraphs with transition phrases or sentences.
- As you move ahead with the writing, you may think of new subpoints or ideas to include in the essay. Stop briefly to make a note of these on your original outline. If they are most appropriately inserted in a section you’ve already written, write them neatly in the margin, at the top of the page, or on the last page, with arrows or marks to alert the reader to where they fit in your answer. Be as neat and clear as possible.
- Don’t pad your answer with irrelevancies and repetitions just to fill up space. Within the time available, write a comprehensive, specific answer.
- Watch the clock carefully to ensure that you do not spend too much time on one answer. You must be realistic about the time constraints of an essay exam. If you write one dazzling answer on an exam with three equally-weighted required questions, you earn only 33 points—not enough to pass at most colleges. This may seem unfair, but keep in mind that instructors plan exams to be reasonably comprehensive. They want you to write about the course materials in two or three or more ways, not just one way. Hint: if you finish a half-hour essay in 10 minutes, you may need to develop some of your ideas more fully.
- If you run out of time when you are writing an answer, jot down the remaining main ideas from your outline, just to show that you know the material and with more time could have continued your exposition.
- Double-space to leave room for additions, and strike through errors or changes with one straight line (avoid erasing or scribbling over). Keep things as clean as possible. You never know what will earn you partial credit.
- Write legibly and proofread. Remember that your instructor will likely be reading a large pile of exams. The more difficult they are to read, the more exasperated the instructor might become. Your instructor also cannot give you credit for what they cannot understand. A few minutes of careful proofreading can improve your grade.
Perhaps the most important thing to keep in mind in writing essay exams is that you have a limited amount of time and space in which to get across the knowledge you have acquired and your ability to use it. Essay exams are not the place to be subtle or vague. It’s okay to have an obvious structure, even the five-paragraph essay format you may have been taught in high school. Introduce your main idea, have several paragraphs of support—each with a single point defended by specific examples, and conclude with a restatement of your main point and its significance.
Some physiological tips
Just think—we expect athletes to practice constantly and use everything in their abilities and situations in order to achieve success. Yet, somehow many students are convinced that one day’s worth of studying, no sleep, and some well-placed compliments (“Gee, Dr. So-and-so, I really enjoyed your last lecture”) are good preparation for a test. Essay exams are like any other testing situation in life: you’ll do best if you are prepared for what is expected of you, have practiced doing it before, and have arrived in the best shape to do it. You may not want to believe this, but it’s true: a good night’s sleep and a relaxed mind and body can do as much or more for you as any last-minute cram session. Colleges abound with tales of woe about students who slept through exams because they stayed up all night, wrote an essay on the wrong topic, forgot everything they studied, or freaked out in the exam and hyperventilated. If you are rested, breathing normally, and have brought along some healthy, energy-boosting snacks that you can eat or drink quietly, you are in a much better position to do a good job on the test. You aren’t going to write a good essay on something you figured out at 4 a.m. that morning. If you prepare yourself well throughout the semester, you don’t risk your whole grade on an overloaded, undernourished brain.
If for some reason you get yourself into this situation, take a minute every once in a while during the test to breathe deeply, stretch, and clear your brain. You need to be especially aware of the likelihood of errors, so check your essays thoroughly before you hand them in to make sure they answer the right questions and don’t have big oversights or mistakes (like saying “Hitler” when you really mean “Churchill”).
If you tend to go blank during exams, try studying in the same classroom in which the test will be given. Some research suggests that people attach ideas to their surroundings, so it might jog your memory to see the same things you were looking at while you studied.
Try good luck charms. Bring in something you associate with success or the support of your loved ones, and use it as a psychological boost.
Take all of the time you’ve been allotted. Reread, rework, and rethink your answers if you have extra time at the end, rather than giving up and handing the exam in the minute you’ve written your last sentence. Use every advantage you are given.
Remember that instructors do not want to see you trip up—they want to see you do well. With this in mind, try to relax and just do the best you can. The more you panic, the more mistakes you are liable to make. Put the test in perspective: will you die from a poor performance? Will you lose all of your friends? Will your entire future be destroyed? Remember: it’s just a test.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Axelrod, Rise B., and Charles R. Cooper. 2016. The St. Martin’s Guide to Writing , 11th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Fowler, Ramsay H., and Jane E. Aaron. 2016. The Little, Brown Handbook , 13th ed. Boston: Pearson.
Gefvert, Constance J. 1988. The Confident Writer: A Norton Handbook , 2nd ed. New York: W.W. Norton and Company.
Kirszner, Laurie G. 1988. Writing: A College Rhetoric , 2nd ed. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Woodman, Leonara, and Thomas P. Adler. 1988. The Writer’s Choices , 2nd ed. Northbrook, Illinois: Scott Foresman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
To answer an essay question (EQ), students must assess the purpose of the essay question: factual recall, analysis (explanation of relationships) synthesis (application/transfer of previously learned principles) opinion
How much information to include, repeat, restate (intro needed? details needed?).
The chart below outlines 4 main types of essay questions, the verbs/cues that indicate the type of essay question and its purpose, and the strategy to be used to answer it.
Read the questions very carefully at least 2 or 3 times. Circle the main verb (= action verb/imperative) in the question and decide on the necessary rhetorical strategy for answering the question (cause-effect, comparison-contrast, definition, classification, problem-solution). Make sure you understand what type of answer the main verb calls for (a diagram a summary, details, an analysis, an evaluation). Circle all the keywords in the question. Decide if you need to write a 1-paragraph or a multi-paragraph answer. Write a brief outline of all the points you want to mention in your answer. Restate the question and answer it with a topic sentence (for a 1-paragraph answer) or a thesis statement (for a multi-paragraph answer). Answer the question according to general rules of academic writing. Use indentations; begin each paragraph with a topic sentence; support the topic sentence(s) with reasons and/or examples; use transition words to show logical organization; write a conclusion. Use correct punctuation throughout. Read over your answer again and check if all the main ideas have been included. Check your answer for grammar and punctuation.
© 2005: Christine Bauer-Ramazani ; last updated: September 02, 2019
IELTS Preparation with Liz: Free IELTS Tips and Lessons, 2024
- Test Information FAQ
- Band Scores
- IELTS Candidate Success Tips
- Computer IELTS: Pros & Cons
- How to Prepare
- Useful Links & Resources
- Recommended Books
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Speaking Part 1 Topics
- Speaking Part 2 Topics
- Speaking Part 3 Topics
- 100 Essay Questions
- On The Day Tips
- Top Results
- Advanced IELTS
100 IELTS Essay Questions
Below are practice IELTS essay questions and topics for writing task 2. The 100 essay questions have been used many times over the years. The questions are organised under common topics and essay types. IELTS often use the similar topics for their essays but change the wording of the essay question.
In order to prepare well for writing task 2, you should prepare ideas for common topics and then practise applying them to the tasks given (to the essay questions). Also see model essays and tips for writing task 2.
Below you will find:
- Essay Questions By Topic
- Essay Questions by Essay Type
Please also note that my new Grammar E-book is now available in my store along with my Ideas for Essay Topics E-book and Advanced Writing Lessons. To visit store, click here: Liz’s Store
1) Common IELTS Essay Questions
IELTS practice essay questions divided by topic. These topics have been reported by IELTS students in their tests. Essay questions have been recreated as accurately as possible.
- Art (5 essay questions)
- Business & Money (17 essay questions)
- Communication & Personality (20 essay questions)
- Crime & Punishment (12 essay questions)
- Education (17 essay questions)
- Environment (12 essay questions)
- Family & Children (8 essay questions)
- Food & Diet (13 essay questions)
- Government (6 essay questions)
- Health (9 essay questions)
- Housing, Buildings & Urban Planning (8 essay questions)
- Language (6 essay questions)
- Leisure (1 essay question)
- Media & Advertising (12 essay questions)
- Reading (5 essay questions)
- Society (10 essay questions)
- Space Exploration (3 questions)
- Sport & Exercise (6 essay questions)
- Technology (6 essay questions)
- Tourism and Travel (11 essay questions)
- Transport (7 essay questions)
- Work (17 essay questions)
2) IELTS Essay Questions by Essay Type
There are 5 main types of essay questions in IELTS writing task 2 (opinion essays, discussion essay, advantage/disadvantage essays, solution essay and direct question essays). Click on the links below to see some sample essay questions for each type.
- Opinion Essay Questions
- Discussion Essay Questions
- Solution Essay Questions
- Direct Questions Essay Titles
- Advantage / Disadvantage Essay Questions
………………………………
FREE SUBSCRIBE : Get New Lessons & Posts by Email
Type your email…
Advanced IELTS Lessons & E-books

Recent Lessons
50% discount advanced ielts lessons & e-books final day, answers to age group bar chart lesson, ielts bar chart of age groups 2024, 50% discount: advanced ielts lessons & e-books, ielts topic: urban planning, ielts listening transcripts: when and how to use them.

Click Below to Learn:
- IELTS Test Information
Copyright Notice
Copyright © Elizabeth Ferguson, 2014 – 2024
All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy & Disclaimer
- Click here: Privacy Policy
- Click here: Disclaimer
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2024 · Prose on Genesis Framework · WordPress · Log in
Essay Writing Guide
Types Of Essay
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
11 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Are you a college or high school student ready to start on a journey through the fascinating world of essay writing ? Brace yourself because you'll encounter a variety of essay types that will challenge your writing skills and creativity.
Picture this: You're handed an assignment, a blank canvas on which to express your thoughts and ideas. But here's the catch – your teacher won't always specify the type of essay you should craft. It's up to you to solve the riddle hidden within the assignment question.
But fear not!
In this blog, we'll discuss the four most common types of essays you're likely to encounter during your academic years. While these essays may share a common foundation and structure, each possesses its own unique characteristics. Let’s get started!
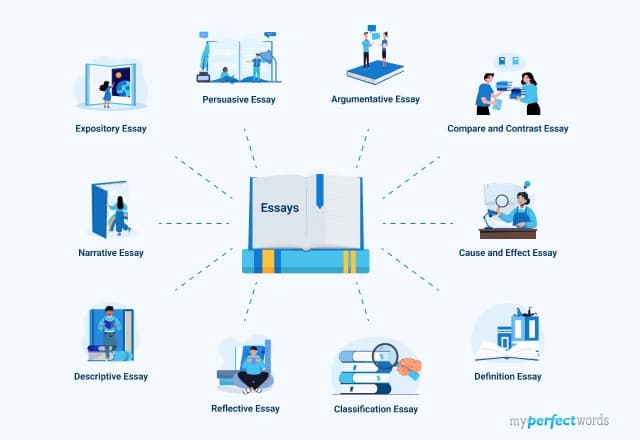
- 1. Major Types of Essays In Academic Writing
- 2. Argumentative Essay
- 3. Descriptive Essay
- 4. Expository Essay
- 5. Narrative Essay
- 6. Other Essay Types
Major Types of Essays In Academic Writing
When it comes to academic writing, understanding the different types of essays is essential. Each type serves a distinct purpose and requires a specific approach. Let's explore these essay types along with their descriptions and example prompts in the table below:
Understanding these major types of essays and the skills they assess will empower you to approach your academic writing with confidence. Depending on your assignment's requirements, you'll be better equipped to choose the appropriate essay type and showcase your writing abilities effectively.
Each type offers a unique opportunity for you to express your ideas, and arguments and perfect your specific writing skills.
Here are the key types of essay formats explained in detail, along with examples to enhance your understanding.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is an essay type that presents a well-structured argument supported by evidence and reasoning. The primary goal is to engage the reader in a discussion, provide evidence, and logically demonstrate why a particular viewpoint is more valid.
In simple words, the writer must provide evidence and remain consistent in their stance. While argumentative essays present both sides of an issue, they strongly support one perspective.
Characteristics of Argumentative Essay
- Clear Thesis: It should have a clear thesis statement to state the writer's position.
- Balanced Presentation: An argumentative essay addresses opposing views.
- Evidence: It relies on credible and relevant evidence.
- Logical Reasoning: The essay presents arguments coherently and logically.
- Persuasive Techniques: It uses persuasive techniques like ethos, pathos, and logos effectively.
- Introduction: The introduction introduces the topic and thesis, engaging the reader's interest.
- Body: The body paragraphs present arguments with supporting evidence.
- Counterargument: It addresses opposing viewpoints and refutes them.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes key points and reinforces the thesis, leaving a strong impression.
Argumentative Essay Example
Before beginning the writing process, it is better to go through some expertly crafted argumentative essay examples . This approach enables you to grasp the argumentative essay outline and writing style more effectively.
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay is a form of writing that aims to immerse readers in a sensory-rich experience. Unlike informational or persuasive essays, its primary goal is to vividly depict a person, place, object, event, or experience. The descriptive essay must evoke the senses and emotions of the reader. In simple terms, the reader should see what you saw and feel what you felt. To make it better, you can use several literary devices such as;
- Alliteration
All of them help in making the experience and your essay better.
Key Characteristics
- Sensory Detail: Descriptive essays appeal to the five senses to create a multisensory experience.
- Vivid Imagery: They use figurative language and descriptive adjectives to bring the narrative to life.
- Emotional Connection: These essays often aim to establish an emotional bond between the reader and the subject.
- Structured Approach: They typically follow an introduction-body-conclusion structure.
- Introduction: Introduces the subject and purpose, sometimes with a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Focus on specific aspects or details using sensory language and vivid descriptions.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the central theme and leaves a lasting impression.
Descriptive Essay Example
Creating a perfect descriptive essay for an assignment is not difficult if you go through some expert descriptive essay examples first.
Need more examples? Read our Descriptive Essay Examples and Writing Tips blog to get inspired!
Expository Essay
An expository essay is a type of writing that provides clear and objective explanations of a topic without expressing personal opinions. It aims to inform and educate by presenting factual information and analysis.
Therefore, it is important that you make a focused outline and stick to it throughout the process.
An expository essay incorporates a wide array of essays such as:
- Cause and effect essays
- Process essays
- Analytical essays
- Compare and contrast essays
Key Characteristics
- Objective Presentation: Expository writing maintains an impartial tone, avoiding personal biases.
- Informativeness: They focus on explaining complex ideas or processes in a straightforward manner.
- Structured: These essays follow a clear structure with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Use of Evidence: They rely on credible evidence, facts, and examples to support the topic.
- Introduction: Introduces the topic and often includes a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect and provides explanations and evidence.
- Conclusion: Restates the main idea and summarizes key points.
Expository Essay Example
Looking for more sample essays? Check out our Expository Essay Examples blog and take inspiration from a range of expository essays!
Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is a type of academic writing that tells a story or recounts a personal experience. Unlike other essays, its primary purpose is to engage and entertain the reader through storytelling.
- Narrative Structure: Follows a chronological sequence with an introduction, body, climax, and conclusion.
- First-Person Perspective: Typically written from the first-person point of view (e.g., "I" and "we") , sharing personal experiences and emotions.
- Vivid Description: Relies on descriptive language and imagery to create a clear picture of events, characters, and settings.
- Emotional Connection: Aims to establish an emotional bond with the reader by conveying the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- Introduction: Sets the stage and introduces the central theme or problem.
- Body: Presents events or experiences in chronological order with sensory details.
- Climax: Often includes a central event or turning point.
- Conclusion: Reflects on the narrative, offering insights, lessons, or resolution.
Narrative Essay Example
Wondering how to get your story into an interesting narrative? Learn the best way to write a perfect narrative essay with the help of expert narrative essay examples.
For more examples visit our blog on narrative essay examples .
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Other Essay Types
In addition to the major types of essays discussed earlier, there are several other specialized types that cater to specific audiences. These essays provide diverse avenues for writers to communicate their ideas effectively.
We will go through these essay types here.
Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is another type of academic essay. In this essay type, the writer utilizes logic and reasoning to show one’s idea is more convincing than another idea.
In writing a persuasive essay, the main aim is to persuade the reader to accept a certain point of view. The presented argument or claim must use solid evidence and sound reasoning by stating facts, examples, and quotes.
Persuasive Essay Example
Since persuasive essays are the most common type of essay, it is essential to get familiar with their writing style. For that, here is an interesting persuasive essay example that you can explore for your better understanding.
Read our persuasive essay examples blog for more samples!
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic essay in which the writer analyzes a topic bit by bit. Writing an analytical essay is not about convincing readers of your point of view. But wanting readers to agree with what you have written.
So, there is no need to use strong persuasive language in an analytical essay. Rather you should aim to provide enough analysis to make sure your argument is clear to the readers.
Analytical Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a sample analytical essay:
Read our analytical essay examples blog if you are looking for more sample essays!
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay type of essay requires you to examine your personal experiences through self-reflection. In the process of writing a reflective essay, you provide insight into what you have gained from those experiences.
What makes reflective essays different from other essay types is the fact that it examine the past experience from the present. Reflective essays take the reader through a journey of self-growth.
Reflective Essay Example
The following reflective essay example will help you get a clear idea of how to structure your analytical essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
It is a form of a textual analysis essay in which the student examines and analyzes a persuasive text. It is like an essay, speech, or visual art and analyzes the rhetorical devices used in it. Writing a rhetorical analysis essay is different from writing other essays because it will be more than adding facts only.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Here is a rhetorical analysis essay example that will help you learn better.
Check out our rhetorical analysis essay examples blog for more samples!
Literary Analysis Essay
A literary analysis essay is based on close reading and analysis of a work of literature like poetry and novel. It identifies different literary factors like themes, setting, characters, setting, and the kind of language used in it. A literary analysis essay has the same 5 paragraphs as any other essay but the main subject and topic are different.
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Need help with your literary analysis essay? Below is a sample essay to help you understand better.
Summing it Up! Now you know what are the different types of essays in academic writing that you are most likely to get assigned. However, if you still find it difficult to compose your essay, leave your piece of writing to our experts.
Whether you need an argumentative essay, narrative essay, descriptive essay, or expository essay we are here to help. Our expertise extends to all types of essays, ensuring that your academic writing needs are met with precision and excellence.
Request 'write my essay' today and let our professional writing service help you write A+ grade essays within your specified timeline!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important element in any essay.
A thesis statement is the most important part of any essay. Other than the research itself, the thesis statement is the most important part of an essay or research paper. A thesis statement summarizes the main point and essence of the argument.
What type of essay is most common at university?
Usually, university students get argumentative kinds of essays. No matter what kind of essay you write, you will need to develop an argument.
Here are some kinds of essays and the kind of arguments added to them.
- Analysis and interpretation of literary texts are discussed in literary analysis essays.
- The importance of a particular event or theory is analyzed in a history argumentative essay.
- A political theory is examined in a political argumentative essay.
Besides, there are a number of different kinds of argumentative and analysis essays.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing Essays for Exams

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
While most OWL resources recommend a longer writing process (start early, revise often, conduct thorough research, etc.), sometimes you just have to write quickly in test situations. However, these exam essays can be no less important pieces of writing than research papers because they can influence final grades for courses, and/or they can mean the difference between getting into an academic program (GED, SAT, GRE). To that end, this resource will help you prepare and write essays for exams.
What is a well written answer to an essay question?
Well Focused
Be sure to answer the question completely, that is, answer all parts of the question. Avoid "padding." A lot of rambling and ranting is a sure sign that the writer doesn't really know what the right answer is and hopes that somehow, something in that overgrown jungle of words was the correct answer.
Well Organized
Don't write in a haphazard "think-as-you-go" manner. Do some planning and be sure that what you write has a clearly marked introduction which both states the point(s) you are going to make and also, if possible, how you are going to proceed. In addition, the essay should have a clearly indicated conclusion which summarizes the material covered and emphasizes your thesis or main point.
Well Supported
Do not just assert something is true, prove it. What facts, figures, examples, tests, etc. prove your point? In many cases, the difference between an A and a B as a grade is due to the effective use of supporting evidence.
Well Packaged
People who do not use conventions of language are thought of by their readers as less competent and less educated. If you need help with these or other writing skills, come to the Writing Lab
How do you write an effective essay exam?
- Read through all the questions carefully.
- Budget your time and decide which question(s) you will answer first.
- Underline the key word(s) which tell you what to do for each question.
- Choose an organizational pattern appropriate for each key word and plan your answers on scratch paper or in the margins.
- Write your answers as quickly and as legibly as you can; do not take the time to recopy.
- Begin each answer with one or two sentence thesis which summarizes your answer. If possible, phrase the statement so that it rephrases the question's essential terms into a statement (which therefore directly answers the essay question).
- Support your thesis with specific references to the material you have studied.
- Proofread your answer and correct errors in spelling and mechanics.
Specific organizational patterns and "key words"
Most essay questions will have one or more "key words" that indicate which organizational pattern you should use in your answer. The six most common organizational patterns for essay exams are definition, analysis, cause and effect, comparison/contrast, process analysis, and thesis-support.
Typical questions
- "Define X."
- "What is an X?"
- "Choose N terms from the following list and define them."
Q: "What is a fanzine?"
A: A fanzine is a magazine written, mimeographed, and distributed by and for science fiction or comic strip enthusiasts.
Avoid constructions such as "An encounter group is where ..." and "General semantics is when ... ."
- State the term to be defined.
- State the class of objects or concepts to which the term belongs.
- Differentiate the term from other members of the class by listing the term's distinguishing characteristics.
Tools you can use
- Details which describe the term
- Examples and incidents
- Comparisons to familiar terms
- Negation to state what the term is not
- Classification (i.e., break it down into parts)
- Examination of origins or causes
- Examination of results, effects, or uses
Analysis involves breaking something down into its components and discovering the parts that make up the whole.
- "Analyze X."
- "What are the components of X?"
- "What are the five different kinds of X?"
- "Discuss the different types of X."
Q: "Discuss the different services a junior college offers a community."
A: Thesis: A junior college offers the community at least three main types of educational services: vocational education for young people, continuing education for older people, and personal development for all individuals.
Outline for supporting details and examples. For example, if you were answering the example question, an outline might include:
- Vocational education
- Continuing education
- Personal development
Write the essay, describing each part or component and making transitions between each of your descriptions. Some useful transition words include:
- first, second, third, etc.
- in addition
Conclude the essay by emphasizing how each part you have described makes up the whole you have been asked to analyze.
Cause and Effect
Cause and effect involves tracing probable or known effects of a certain cause or examining one or more effects and discussing the reasonable or known cause(s).
Typical questions:
- "What are the causes of X?"
- "What led to X?"
- "Why did X occur?"
- "Why does X happen?"
- "What would be the effects of X?"
Q: "Define recession and discuss the probable effects a recession would have on today's society."
A: Thesis: A recession, which is a nationwide lull in business activity, would be detrimental to society in the following ways: it would .......A......., it would .......B......., and it would .......C....... .
The rest of the answer would explain, in some detail, the three effects: A, B, and C.
Useful transition words:
- consequently
- for this reason
- as a result
Comparison-Contrast
- "How does X differ from Y?"
- "Compare X and Y."
- "What are the advantages and disadvantages of X and Y?"
Q: "Which would you rather own—a compact car or a full-sized car?"
A: Thesis: I would own a compact car rather than a full-sized car for the following reasons: .......A......., .......B......., .......C......., and .......D....... .
Two patterns of development:
- Full-sized car
Disadvantages
- Compact car
Useful transition words
- on the other hand
- unlike A, B ...
- in the same way
- while both A and B are ..., only B ..
- nevertheless
- on the contrary
- while A is ..., B is ...
- "Describe how X is accomplished."
- "List the steps involved in X."
- "Explain what happened in X."
- "What is the procedure involved in X?"
Process (sometimes called process analysis)
This involves giving directions or telling the reader how to do something. It may involve discussing some complex procedure as a series of discrete steps. The organization is almost always chronological.
Q: "According to Richard Bolles' What Color Is Your Parachute?, what is the best procedure for finding a job?"
A: In What Color Is Your Parachute?, Richard Bolles lists seven steps that all job-hunters should follow: .....A....., .....B....., .....C....., .....D....., .....E....., .....F....., and .....G..... .
The remainder of the answer should discuss each of these seven steps in some detail.
- following this
- after, afterwards, after this
- subsequently
- simultaneously, concurrently
Thesis and Support
- "Discuss X."
- "A noted authority has said X. Do you agree or disagree?"
- "Defend or refute X."
- "Do you think that X is valid? Defend your position."
Thesis and support involves stating a clearly worded opinion or interpretation and then defending it with all the data, examples, facts, and so on that you can draw from the material you have studied.
Q: "Despite criticism, television is useful because it aids in the socializing process of our children."
A: Television hinders rather than helps in the socializing process of our children because .......A......., .......B......., and .......C....... .
The rest of the answer is devoted to developing arguments A, B, and C.
- it follows that
A. Which of the following two answers is the better one? Why?
Question: Discuss the contribution of William Morris to book design, using as an example his edition of the works of Chaucer.
a. William Morris's Chaucer was his masterpiece. It shows his interest in the Middle Ages. The type is based on medieval manuscript writing, and the decoration around the edges of the pages is like that used in medieval books. The large initial letters are typical of medieval design. Those letters were printed from woodcuts, which was the medieval way of printing. The illustrations were by Burn-Jones, one of the best artists in England at the time. Morris was able to get the most competent people to help him because he was so famous as a poet and a designer (the Morris chair) and wallpaper and other decorative items for the home. He designed the furnishings for his own home, which was widely admired among the sort of people he associated with. In this way he started the arts and crafts movement.
b. Morris's contribution to book design was to approach the problem as an artist or fine craftsman, rather than a mere printer who reproduced texts. He wanted to raise the standards of printing, which had fallen to a low point, by showing that truly beautiful books could be produced. His Chaucer was designed as a unified work of art or high craft. Since Chaucer lived in the Middle Ages, Morris decided to design a new type based on medieval script and to imitate the format of a medieval manuscript. This involved elaborate letters and large initials at the beginnings of verses, as well as wide borders of intertwined vines with leaves, fruit, and flowers in strong colors. The effect was so unusual that the book caused great excitement and inspired other printers to design beautiful rather than purely utilitarian books.
From James M. McCrimmon, Writing with a Purpose , 7th ed. (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1980), pp. 261-263.
B. How would you plan the structure of the answers to these essay exam questions?
1. Was the X Act a continuation of earlier government policies or did it represent a departure from prior philosophies?
2. What seems to be the source of aggression in human beings? What can be done to lower the level of aggression in our society?
3. Choose one character from Novel X and, with specific references to the work, show how he or she functions as an "existential hero."
4. Define briefly the systems approach to business management. Illustrate how this differs from the traditional approach.
5. What is the cosmological argument? Does it prove that God exists?
6. Civil War historian Andy Bellum once wrote, "Blahblahblah blahed a blahblah, but of course if blahblah blahblahblahed the blah, then blahblahs are not blah but blahblah." To what extent and in what ways is the statement true? How is it false?
For more information on writing exam essays for the GED, please visit our Engagement area and go to the Community Writing and Education Station (CWEST) resources.
THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO IELTS WRITING: QUESTION TYPES
This is the second part of our guide that contains everything you need to know about the IELTS writing exam. The first section looked at how the test is graded . Sections three and four explore essay structure and frequently asked questions . This section tells you everything you need to know about IELTS writing question types. You can use the links below to explore this section.
- Opinion questions
- Both sides questions
- Problem and solution questions
Two question questions
- Describing advantages and disadvantages
Why are IELTS Writing question types important?
Many students feel overwhelmed by the different types of questions in part two of the IELTS writing exam. However, while these questions often look like too much to ever learn, it is possible to break them down into five broad types. Once you know these, you will know how to handle any IELTS writing question that you get in your exam. This article will introduce these question types and how you should go about answering each one.
Before looking at the question types, I want to look at how we’re breaking them down. The easiest way to study IELTS question types is to look at what your thesis statement and topic sentences will be. The thesis statement is a sentence in your introduction that lays out what your whole essay will be about. Topic sentences are the first sentence of each of your body paragraphs which say what those paragraphs will be about. Because these sentences essentially lay out the structure of your essay, they’re a great starting point for understanding question types.
Opinion questions
This question type asks you what you think. Usually, this will be a statement followed by ‘Do you agree or disagree?’ or ‘What is your opinion?’. For example:
Online shopping allows people to buy almost anything and have it shipped to their front door and has become increasingly popular in recent years. However, some people believe this is a negative development. What is your opinion?
For this type of question, it is easiest to have a strong opinion one way or the other. We should then give two specific reasons for our opinion. In response to this example we could write:
- Thesis statement: This essay will argue that internet shopping is, on the whole, beneficial.
- Topic sentence one: First, this type of shopping allows people to have more choice.
- Topic sentence two: Second, shopping online makes it easier for people to get more information about what they are buying through reviews.
This response ticks all the boxes for a good answer. The thesis statement gives a clear point of view while the topic sentences refer to specific points. If the topic sentences were broader, we’d struggle to cover the whole point in a few sentences.
Both sides and an opinion questions
Along with opinion-type essays, both sides and an opinion questions are one of the most common questions in the IELTS writing exam. However, unlike opinion essays, the question is more specific about what you need to cover. It’s common for students to get too nervous during the exam and only give one side of the answer. This is the easiest way to lose marks in your exam, so avoid it by keeping an eye out for this question type. You can spot it easily because it quite explicitly says ‘Compare both sides and give your opinion.’ or ‘Compare both points of view and give your opinion.’ For example:
Question: Online shopping has become increasingly popular in recent years. Some people believe that this has improved people’s lives while others believe it is damaging to both consumers and stores. Compare both sides and give your opinion.
For this question type, it’s important to compare two specific points. It’s common for students who are new to IELTS to write something like ‘First, there are some advantages.’ This is very broad and impossible to give enough detail on. A useful structure for your introduction is: ‘This essay will compare the advantage of _____ with the disadvantage of _____ and conclude that _____.’ For our sample question, this could look like:
- Thesis statement: This essay will compare the advantage of increased customer choice with the disadvantage of the environmental impact of online shopping.
- Topic sentence one: One advantage of online shopping is that it offers a greater amount of choice to customers.
- Topic sentence two: Conversely, online shopping has a negative effect on the environment.
Problem and solution Questions
A problem and solution, as you might have predicted, will ask you to give some problems and solutions. This essay type can look a few different ways. They may ask you for the causes and solutions for something or for the problems and solutions. One example is:
In recent years, online shopping has grown in popularity and overtaken shopping in-person. What are some problems caused by this and what are some solutions?
To answer this question type you should pick out two problems, one for each body paragraph. In each body paragraph, you should explain what the problem is, give examples and offer a solution. What you don’t want to do is just offer a list of problems and a list of solutions. Remember that your body paragraphs should always be focused on one specific point. One way of structuring an answer to the question above is:
- Thesis statement and outline: This essay will look at two problems this causes and their solutions. First, the environmental damage and second, the damage to local shops.
- Topic sentence one: One problem is that internet shopping involves a lot of packaging and transportation which has an impact on the environment.
- Topic sentence two: Another problem is that internet shopping is causing damage to local high street
The two-question question states something and then asks two questions. These are, in my opinion, the easiest to answer because the exam tells you exactly what you should do. Your first body paragraph should answer the first question and then your second body paragraph should answer the second question. An example of this type of question is:
In recent years, online shopping has overtaken in-person shopping in popularity. How has this affected customers? How has it affected shops?
The thesis statement should contain a brief answer to both questions. Each body paragraph should then answer one of these questions. This might look something like this:
- Thesis statement: This essay will examine how the rise of internet shopping has made shops increase their online offering and has increased customer choice.
- Topic sentence one: The heightened popularity of shopping online has forced local shops to move more of their business online.
- Topic sentence two: In addition, this change has led to consumers having more options when it comes to shopping
describing advantages and disadvantages
This essay type is a little confusing. Many IELTS guides will include questions that ask you to compare advantages and disadvantages with questions that ask you to describe them. However, these are quite different. Questions that ask you to compare the advantages and disadvantages are essentially opinion essays. You make two points and give your opinion. For an essay that asks you to describe advantages and disadvantages, you are not expected to give your own opinion. An example of this is:
The popularity of online shopping has skyrocketed over recent years. What are some advantages and disadvantages of this?
For this question, we should describe one advantage and one disadvantage in detail. We don’t need to give our opinion on it. You can use examples, explanations and reasons to do this. Our answer might be structured like this:
- Thesis statement: This essay will describe the advantage that this shopping increases choice and the disadvantage that it damages local high streets.
- Topic sentence one: One advantage is that online shopping offers shoppers more choice.
- Topic sentence two: However, a disadvantage is that online shopping has damaged community shops.
In this description of the essay types, you might have noticed that I’ve tried to use similar examples for each question type. You might have also noticed that the content of the answers to these questions can be quite similar. For example, a lot of the essays have points about increasing choice. However, the way you present that content changes depending on the question type. By studying these question types, you can learn how to present your ideas in the right way to get a high score in the IELTS exam.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Answer Essay Type Questions in Literature Examinations
Last Updated: November 14, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Tristen Bonacci . Tristen Bonacci is a Licensed English Teacher with more than 20 years of experience. Tristen has taught in both the United States and overseas. She specializes in teaching in a secondary education environment and sharing wisdom with others, no matter the environment. Tristen holds a BA in English Literature from The University of Colorado and an MEd from The University of Phoenix. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, 89% of readers who voted found the article helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 142,197 times.
Answering essay questions on literature exams can be daunting, especially with timed exams. Before the test, you should have a full understanding of how the different parts of a classical argument fit together to make a whole. The best way to quickly write an organized essay is to outline your argument before you begin your answer. With a little bit of preparation, you can ensure a good grade on your exam.
Writing Your Essay

- Create a bullet point for each point you choose to make in your paper.
- Your first point should include the introduction, statement of facts, and thesis.
- You should break up the “proof” or body paragraphs into however many points you laid out in your thesis. If you promised three points, create three bullet points. If you promised four points, create four bullet points. Remember that the body paragraphs must follow the exact order of the thesis.
- Create a point for the statement of the counterargument. You can either create a new point/paragraph for your refutation of it, or keep it all in one paragraph by making the refutation a subpoint.
- Create a point for the conclusion.

- If you're using external sources, you should include them in your outline. You don't want to accidentally leave out a great source because you got caught up in the writing and forgot about it.

- Use transition words like furthermore, similarly, or indeed to transition between agreeing ideas. [4] X Research source
- Use "conflict" transition words and phrases to transition between conflicting ideas — like the counterargument and your refutation of it. Examples include however, in contrast, on the other hand, or conversely.

- Make sure to refer back to your outline repeatedly during the writing process. This is the roadmap of your answer. Don't wander away from it and get off-course.

- If you're being graded primarily on the content of your argument, leave grammar and spelling editing for your last step.
- If you're being graded primarily on your grammar and spelling, by all means, correct your errors as you go!
- In most cases, you won't be graded on one or the other. Keep your specific teacher or standardized test in mind. Have a strategy for when you plan to correct your errors before you take the test.

- If you're in an isolated room, read the essay aloud to yourself to look for grammar errors that sound wrong. It's easier to hear mistakes than see them on the page.
- Read your sentences backwards to look for spelling errors you might skim over if you were reading the sentences normally. [5] X Research source
Structuring Your Argument

- Introduction (exordium)
- Statement of Facts (narratio)
- Thesis (partitio)
- Proof (confirmatio)
- Refutation (refutatio)
- Conclusion (peroratio)
- The introduction, statement of facts, and thesis are often grouped together in the first paragraph of the answer.

- Another way to think of the exordium is to consider where the word "introduction" comes from. The prefix "intro" means "inward," as in introspection (looking inward). "Duction" comes from the Latin root "ducere," which means "to lead." This is where we get the modern words duke (one who leads) and orchestra conductor (one who leads together). [7] X Research source [8] X Research source
- In the introduction, you want to intro + duce, or lead the reader inward, further into your argument.

- If your reader already knows the background information, you may be able to skip this section.
- In Cicero's Latin, this section was called the "narratio," which is where we get the modern word "narrator." The narrator is the voice in a book that gives readers information that can't be delivered through dialogue or action.
- The word "knowledge" itself shares a root with narration : gnoscere. [10] X Research source In this section, you give the readers the knowledge they need to follow your argument.

- Cicero's Latin word, partitio, shares a root with the modern word "partition," which means division or separation. When Beyonce sings "Driver roll up the partition, please," she's asking the driver to roll up the window that separates him from the passengers in the back.
- So the thesis is where you list out the different parts of your argument — your X, Y, and Z — in list form, separately.

- Note that it's not enough to just list a bunch of quotes and statistics from sources. That's not making an argument — it's restating someone else's information or argument.

- Don't include a counterargument without refuting it. To refute means to "beat back." [13] X Research source The only reason you include the opposing point of view is to beat it back and strengthen your own position.

- Do not transition into your conclusion with a signal phrase like "in conclusion" or "in summary." Find a less obvious, more sophisticated transition.
Expert Q&A

- Never plagiarize another author's words or ideas. You can fail the assignment or even the entire course, or get suspended or expelled from school Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Tristen Bonacci. Licensed English Teacher. Expert Interview. 21 December 2021.
- ↑ https://www.tacoma.uw.edu/sites/default/files/global/documents/library/essay_outline_worksheet.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/engagement/2/1/29/
- ↑ https://www.msu.edu/~jdowell/135/transw.html
- ↑ http://www.stlcc.edu/Student_Resources/Academic_Resources/Writing_Resources/Writing_Handouts/proofreading.pdf
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=exhort
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=duke&searchmode=none
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=conductor&searchmode=none
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=narration&allowed_in_frame=0
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/thesis-statements/
- ↑ http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=refute

About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jun 15, 2023
Did this article help you?

Masawi Clare
Mar 16, 2017
Martha Ekim
Feb 22, 2017
Thisuni Tantirige
Mar 25, 2019
Ernest Agyekum Darko
Feb 16, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks
Published on February 9, 2015 by Shane Bryson . Revised on July 23, 2023 by Shona McCombes.
This example guides you through the structure of an essay. It shows how to build an effective introduction , focused paragraphs , clear transitions between ideas, and a strong conclusion .
Each paragraph addresses a single central point, introduced by a topic sentence , and each point is directly related to the thesis statement .
As you read, hover over the highlighted parts to learn what they do and why they work.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an essay, an appeal to the senses: the development of the braille system in nineteenth-century france.
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
In France, debates about how to deal with disability led to the adoption of different strategies over time. While people with temporary difficulties were able to access public welfare, the most common response to people with long-term disabilities, such as hearing or vision loss, was to group them together in institutions (Tombs, 1996). At first, a joint institute for the blind and deaf was created, and although the partnership was motivated more by financial considerations than by the well-being of the residents, the institute aimed to help people develop skills valuable to society (Weygand, 2009). Eventually blind institutions were separated from deaf institutions, and the focus shifted towards education of the blind, as was the case for the Royal Institute for Blind Youth, which Louis Braille attended (Jimenez et al, 2009). The growing acknowledgement of the uniqueness of different disabilities led to more targeted education strategies, fostering an environment in which the benefits of a specifically blind education could be more widely recognized.
Several different systems of tactile reading can be seen as forerunners to the method Louis Braille developed, but these systems were all developed based on the sighted system. The Royal Institute for Blind Youth in Paris taught the students to read embossed roman letters, a method created by the school’s founder, Valentin Hauy (Jimenez et al., 2009). Reading this way proved to be a rather arduous task, as the letters were difficult to distinguish by touch. The embossed letter method was based on the reading system of sighted people, with minimal adaptation for those with vision loss. As a result, this method did not gain significant success among blind students.
Louis Braille was bound to be influenced by his school’s founder, but the most influential pre-Braille tactile reading system was Charles Barbier’s night writing. A soldier in Napoleon’s army, Barbier developed a system in 1819 that used 12 dots with a five line musical staff (Kersten, 1997). His intention was to develop a system that would allow the military to communicate at night without the need for light (Herron, 2009). The code developed by Barbier was phonetic (Jimenez et al., 2009); in other words, the code was designed for sighted people and was based on the sounds of words, not on an actual alphabet. Barbier discovered that variants of raised dots within a square were the easiest method of reading by touch (Jimenez et al., 2009). This system proved effective for the transmission of short messages between military personnel, but the symbols were too large for the fingertip, greatly reducing the speed at which a message could be read (Herron, 2009). For this reason, it was unsuitable for daily use and was not widely adopted in the blind community.
Nevertheless, Barbier’s military dot system was more efficient than Hauy’s embossed letters, and it provided the framework within which Louis Braille developed his method. Barbier’s system, with its dashes and dots, could form over 4000 combinations (Jimenez et al., 2009). Compared to the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet, this was an absurdly high number. Braille kept the raised dot form, but developed a more manageable system that would reflect the sighted alphabet. He replaced Barbier’s dashes and dots with just six dots in a rectangular configuration (Jimenez et al., 2009). The result was that the blind population in France had a tactile reading system using dots (like Barbier’s) that was based on the structure of the sighted alphabet (like Hauy’s); crucially, this system was the first developed specifically for the purposes of the blind.
While the Braille system gained immediate popularity with the blind students at the Institute in Paris, it had to gain acceptance among the sighted before its adoption throughout France. This support was necessary because sighted teachers and leaders had ultimate control over the propagation of Braille resources. Many of the teachers at the Royal Institute for Blind Youth resisted learning Braille’s system because they found the tactile method of reading difficult to learn (Bullock & Galst, 2009). This resistance was symptomatic of the prevalent attitude that the blind population had to adapt to the sighted world rather than develop their own tools and methods. Over time, however, with the increasing impetus to make social contribution possible for all, teachers began to appreciate the usefulness of Braille’s system (Bullock & Galst, 2009), realizing that access to reading could help improve the productivity and integration of people with vision loss. It took approximately 30 years, but the French government eventually approved the Braille system, and it was established throughout the country (Bullock & Galst, 2009).
Although Blind people remained marginalized throughout the nineteenth century, the Braille system granted them growing opportunities for social participation. Most obviously, Braille allowed people with vision loss to read the same alphabet used by sighted people (Bullock & Galst, 2009), allowing them to participate in certain cultural experiences previously unavailable to them. Written works, such as books and poetry, had previously been inaccessible to the blind population without the aid of a reader, limiting their autonomy. As books began to be distributed in Braille, this barrier was reduced, enabling people with vision loss to access information autonomously. The closing of the gap between the abilities of blind and the sighted contributed to a gradual shift in blind people’s status, lessening the cultural perception of the blind as essentially different and facilitating greater social integration.
The Braille system also had important cultural effects beyond the sphere of written culture. Its invention later led to the development of a music notation system for the blind, although Louis Braille did not develop this system himself (Jimenez, et al., 2009). This development helped remove a cultural obstacle that had been introduced by the popularization of written musical notation in the early 1500s. While music had previously been an arena in which the blind could participate on equal footing, the transition from memory-based performance to notation-based performance meant that blind musicians were no longer able to compete with sighted musicians (Kersten, 1997). As a result, a tactile musical notation system became necessary for professional equality between blind and sighted musicians (Kersten, 1997).
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Bullock, J. D., & Galst, J. M. (2009). The Story of Louis Braille. Archives of Ophthalmology , 127(11), 1532. https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2009.286.
Herron, M. (2009, May 6). Blind visionary. Retrieved from https://eandt.theiet.org/content/articles/2009/05/blind-visionary/.
Jiménez, J., Olea, J., Torres, J., Alonso, I., Harder, D., & Fischer, K. (2009). Biography of Louis Braille and Invention of the Braille Alphabet. Survey of Ophthalmology , 54(1), 142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2008.10.006.
Kersten, F.G. (1997). The history and development of Braille music methodology. The Bulletin of Historical Research in Music Education , 18(2). Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/40214926.
Mellor, C.M. (2006). Louis Braille: A touch of genius . Boston: National Braille Press.
Tombs, R. (1996). France: 1814-1914 . London: Pearson Education Ltd.
Weygand, Z. (2009). The blind in French society from the Middle Ages to the century of Louis Braille . Stanford: Stanford University Press.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bryson, S. (2023, July 23). Example of a Great Essay | Explanations, Tips & Tricks. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/example-essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Creating and Scoring Essay Tests
FatCamera / Getty Images
- Tips & Strategies
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Teaching Resources
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Curriculum and Instruction, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
Essay tests are useful for teachers when they want students to select, organize, analyze, synthesize, and/or evaluate information. In other words, they rely on the upper levels of Bloom's Taxonomy . There are two types of essay questions: restricted and extended response.
- Restricted Response - These essay questions limit what the student will discuss in the essay based on the wording of the question. For example, "State the main differences between John Adams' and Thomas Jefferson's beliefs about federalism," is a restricted response. What the student is to write about has been expressed to them within the question.
- Extended Response - These allow students to select what they wish to include in order to answer the question. For example, "In Of Mice and Men , was George's killing of Lennie justified? Explain your answer." The student is given the overall topic, but they are free to use their own judgment and integrate outside information to help support their opinion.
Student Skills Required for Essay Tests
Before expecting students to perform well on either type of essay question, we must make sure that they have the required skills to excel. Following are four skills that students should have learned and practiced before taking essay exams:
- The ability to select appropriate material from the information learned in order to best answer the question.
- The ability to organize that material in an effective manner.
- The ability to show how ideas relate and interact in a specific context.
- The ability to write effectively in both sentences and paragraphs.
Constructing an Effective Essay Question
Following are a few tips to help in the construction of effective essay questions:
- Begin with the lesson objectives in mind. Make sure to know what you wish the student to show by answering the essay question.
- Decide if your goal requires a restricted or extended response. In general, if you wish to see if the student can synthesize and organize the information that they learned, then restricted response is the way to go. However, if you wish them to judge or evaluate something using the information taught during class, then you will want to use the extended response.
- If you are including more than one essay, be cognizant of time constraints. You do not want to punish students because they ran out of time on the test.
- Write the question in a novel or interesting manner to help motivate the student.
- State the number of points that the essay is worth. You can also provide them with a time guideline to help them as they work through the exam.
- If your essay item is part of a larger objective test, make sure that it is the last item on the exam.
Scoring the Essay Item
One of the downfalls of essay tests is that they lack in reliability. Even when teachers grade essays with a well-constructed rubric, subjective decisions are made. Therefore, it is important to try and be as reliable as possible when scoring your essay items. Here are a few tips to help improve reliability in grading:
- Determine whether you will use a holistic or analytic scoring system before you write your rubric . With the holistic grading system, you evaluate the answer as a whole, rating papers against each other. With the analytic system, you list specific pieces of information and award points for their inclusion.
- Prepare the essay rubric in advance. Determine what you are looking for and how many points you will be assigning for each aspect of the question.
- Avoid looking at names. Some teachers have students put numbers on their essays to try and help with this.
- Score one item at a time. This helps ensure that you use the same thinking and standards for all students.
- Avoid interruptions when scoring a specific question. Again, consistency will be increased if you grade the same item on all the papers in one sitting.
- If an important decision like an award or scholarship is based on the score for the essay, obtain two or more independent readers.
- Beware of negative influences that can affect essay scoring. These include handwriting and writing style bias, the length of the response, and the inclusion of irrelevant material.
- Review papers that are on the borderline a second time before assigning a final grade.
- Study for an Essay Test
- How to Create a Rubric in 6 Steps
- 10 Common Test Mistakes
- Self Assessment and Writing a Graduate Admissions Essay
- UC Personal Statement Prompt #1
- Holistic Grading (Composition)
- Ideal College Application Essay Length
- How To Study for Biology Exams
- Tips to Cut Writing Assignment Grading Time
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- What You Need to Know About the Executive Assessment
- Best Practices for Subjective Test Questions
- 2019–2020 SAT Score Release Dates
- Top 10 GRE Test Tips
- What Would You Do Differently? Interview Question Tips
- A Simple Guide to Grading Elementary Students
The Lumber Room
by Saki (H.H. Munro)
The lumber room essay questions.
What role does defiance play in "The Lumber Room"?
As one of the story's dominant themes, defiance plays a major role in "The Lumber Room." From the beginning of the story, Nicholas defies his aunt's wishes for good behavior and a deferential attitude toward her authority. While the other children obey her authority and calmly eat their breakfasts of bread and milk, Nicholas brings a frog in from the garden and complains about it being in his bowl. Nicholas continues to defy his aunt when she expects him to cry as the other children make their way to the beach. Instead of crying, Nicholas chuckles at the sound of his cousin weeping in the carriage. Defiance arises next when the aunt increases his punishment by not letting him access the gooseberry garden. Nicholas knows she expects him to defy her, and he uses that expectation of defiance to his benefit, fooling her into staying outside to prevent him from getting into the garden. While she is distracted, Nicholas enjoys the delights of the lumber room, defying his aunt's restriction against children entering the room. At the end of the story, Nicholas continues to use defiance to undermine his aunt's authority, refusing to help her out of the rain-water tank. Because she told him earlier that he was not allowed into the gooseberry garden, he argues, he cannot fetch a ladder to help her escape. By pretending to adhere to the initial rule, Nicholas manages to defy her wishes yet again.
In what ways does "The Lumber Room" suggest that children can be more intelligent than adults?
"The Lumber Room" shows how adults insecure about their own authority can misunderstand a child's mentality and needs. In the story, Saki depicts Nicholas as a mischievous and shrewd boy who excels in annoying his aunt, largely through predicting her actions and feelings. When Nicholas's brother and cousins are taken to Jagborough, Nicholas does not cry, because he is perfectly aware that him being upset is the very thing that his aunt wants. Although a child in such as situation is expected to react by weeping, Nicholas refrains from such behavior because he is mature enough to understand the circumstances of the punishment. Similarly, Nicholas's entry into the lumber room is a carefully planned mission, which shows that he is organized and is capable of devising a strategic plan—qualities an adult would possess. Nicholas had even practiced turning a key in a keyhole of a door prior to entering the lumber room. When Nicholas gains access to the room, he makes sure to sprinkle some dust on the old books after going through them so they do not appear to have been disturbed. Ultimately, Nicholas's intelligence makes it possible for him to subvert his aunt's authority and have a thoroughly enjoyable day despite being grounded.
What does the lumber room symbolize?
The lumber room at the center of the story is a symbol of Nicholas's imagination. Although lumber rooms would have been common enough in Edwardian homes—little more than a storeroom of furniture and possessions not currently in use in the rest of the home—the lumber room takes on mythical proportions in Nicholas's imagination. Because children are not allowed to see what is in the lumber room, Nicholas assumes it is a repository of treasures, and, once he gains entry, he finds the room meets his expectations. He marvels at the delicate and beautiful objects that lie within, such as a fire-screen tapestry, candlesticks shaped like snakes, a teapot in the shape of a duck, and a book of illustrated birds. Ensconced in the magic of the lumber room, Nicholas uses his imagination to think about what fate will befall the huntsman on the fire screen. He also invents a life story for the colorful mandarin duck in the picture book. The imaginative potential of the lumber room stays with Nicholas until the end of the story. While everyone else sits miserably at the table, Nicholas imagines further outcomes for the huntsman, believing the man and his dogs might escape the approaching wolves.

The Lumber Room Questions and Answers
The Question and Answer section for The Lumber Room is a great resource to ask questions, find answers, and discuss the novel.
Mischief is the dominant theme in "The Lumber Room." From the beginning to the end of the story, Saki delights the reader with Nicholas's persistent playful misbehavior. In the opening scene, the narrator details how Nicholas complains of a frog...
'Nicholas is not at fault for his conduct in the short story 'The Lumber Room'.
Nicholas is just a precocious child who uses his intelligence to outsmart his domineering aunt. Ultimately, Nicholas's penchant for mischief makes the boredom of living under his aunt's rigid control bearable.
What are the similarities between aunt and Nicholas?
I don't see many similarities between Nicholas and his aunt. He is mischievious, smart, and imaginative, and disobedient. His aunt is short-sighted and without imagination. Her moments of deceit aren't good natured. The only time I really see a...
Study Guide for The Lumber Room
The Lumber Room study guide contains a biography of Saki (H.H. Munro), literature essays, quiz questions, major themes, characters, and a full summary and analysis.
- About The Lumber Room
- The Lumber Room Summary
- Character List
Documentation
Essay question type.
- Managing questions
- Question behaviours
- Question permissions
- Simple Calculated
- Drag and drop into text
- Drag and drop markers
- Drag and drop onto image
- Calculated Multichoice
- Description
- Embedded Answers (Cloze)
- Multiple Choice
- Random Short Answer Matching
- Select missing words
- Short-Answer
- Third-party question types
- Questions FAQ
Note : This page is about the essay question type in the Quiz activity. For information about the essay question type in a Lesson activity, see the documentation Building Lesson .
- 1 About the essay question type
- 2.1 Response options
- 2.2 Response template
- 2.3 Grader information
- 3 Question grading
About the essay question type
The essay question type provides the option of answering by uploading one or more files and/or entering text online. (For longer essays, text or file uploads, you may wish to consider using the Assignment activity rather than this question type.)
Essay questions are created in the same way as other quiz question types. The difference is that essay questions have to be marked manually, and the student will not get a final grade until the teacher has marked their essay.
Creating an essay question
- If you haven't yet made a quiz, access the Question bank from Course administration>Question bank and click the button 'Create a new question', choosing 'Essay'.
- If you have made a quiz, access the Edit quiz screen and from the Add drop down, choose 'Add a new question', choosing 'Essay'.
- Give the question a descriptive name - this allows you to identify it in the Question bank.
- Enter the question in the 'Question text' field. This will be the title of and information about the essay you wish them to write.
- Set the 'default mark' and any 'General Feedback' if required. This is text that appears to the student once you have graded their essay.
Response options
- 'Response format' allows you to choose what is available for the students when typing their essays, for example the regular WYSIWYG editor with or without the option to upload files, or a plain text editor (with no formatting.) No online text means they cannot type any text. You cannot select this if you don't allow attachments, as the students will have nothing to submit. If you have programming students, they may require plain text with monospaced font for their code. You should select 'HTML editor with file picker' if you wish to provide the audio and video recording buttons in the HTML editor.
- 'Require text' allows you to decide whether or not students must add text into the text editor when they do the question. If you only want them to upload a word-processed file as an essay, then you can set this to 'Text input is optional'. (Note that this setting does not force the student to type text into the text editor; they can still leave it blank and continue to another question.)
- 'Accepted file types' allows you to specify type(s) of file the students must upload.
- New in 3.11: You can set a maximum and minimum word count for the Essay question. Learners will be alerted if they write too few or too many words.
Response template
It is possible for a teacher to create a template to scaffold the student's answer in order to give them extra support. The template is then reproduced in the text editor when the student starts to answer the question. See YouTube video Essay scaffold with the Moodle quiz It is also possible to include grading information for teachers marking the essay to refer to as they assess the essays:
Grader information
Here you can store information about the evaluation for the grading persons (teachers), e.g. evaluation criteria, sample solutions, etc.
Question grading
The essay question will not be assigned a grade until it has been reviewed by a teacher and manually graded. Until that happens, the student's grade will be counted as 0 and shown as a - (dash).
To grade essays answer in quizzes using the Boost theme , click on the quiz and then, click the Results tab, in the dropdown menu choose Manual grading . For other themes, click Manual grading from the Quiz results section of your quiz administration block.
Then you can choose one question from that quiz, and grade that question for all the students.
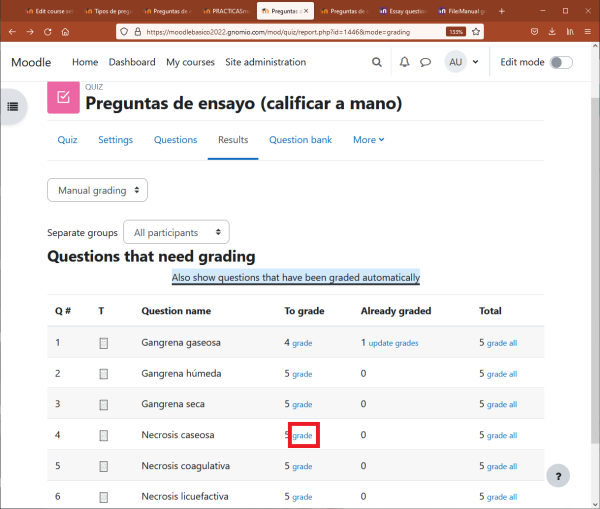
If you choose the 'Responses' tab, you can browse all the questions from all the students.. and you might discover (in the following image) that some students have nearly identical answers, which suggests cheating...

When manually grading an essay question, the grader is able to enter a custom comment in response to the essay and assign a score for the essay.
If necessary the teacher can also upload a file such as an image (or even record audio/video) in the essay grading box.
- Need help with understanding manual grading forum discussion
- Essay (auto-grade) question type - additional plugin
- The Essay module for H5P - A free HTML5-based content type that allows students to receive instant feedback to a text that they have composed. Authors can define a set of keywords that will trigger individual responses if they are found or missing in the text. Let students become creative with H5P and Essay in Moodle.
- AI text question type (essay with auto marking) by Marcus Green
Question asked by Filo student
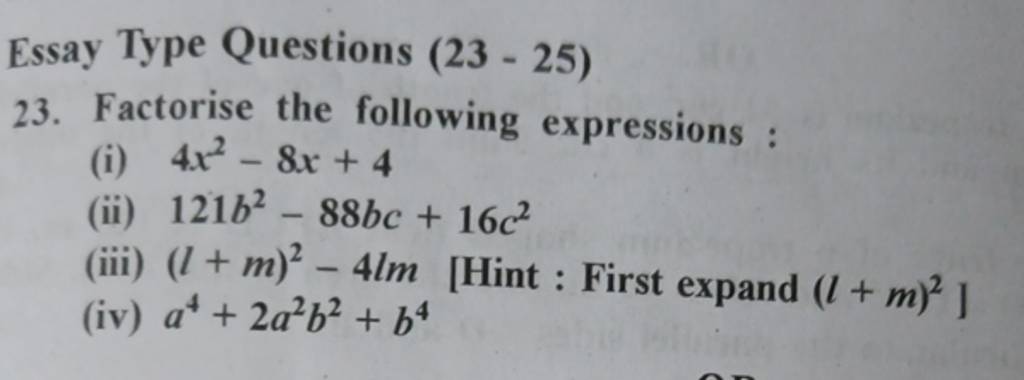
Essay Type Questions (23 - 25) 23. Factorise the following expressions :
- 4 x 2 − 8 x + 4
- 121 b 2 − 88 b c + 16 c 2
- ( l + m ) 2 − 4 l m [Hint : First expand ( l + m ) 2 ]
- a 4 + 2 a 2 b 2 + b 4
Views: 5,385 students
Updated on: Mar 24, 2024
Filo tutor solutions ( 1 )
Learn from their 1-to-1 discussion with Filo tutors.
Uploaded on: 3/24/2024
Connect instantly with this tutor
Connect now
Total classes on Filo by this tutor - 4,045
Teaches : Mathematics, SBI Examinations, IBPS
Notes from this class ( 4 pages)

Practice more questions on All topics
Views: 5,597
Exponents And Powers
Mathematics Class 8 (RD Sharma)
View 11 solutions
Views: 5,411
Algebraic Expressions And Identities
View solution
Views: 5,366
View 2 solutions
Views: 5,780
Mensuration
Students who ask this question also asked
Views: 5,064
Mathematics
Views: 5,967
View 3 solutions
Views: 5,375
Views: 5,193

Stuck on the question or explanation?
Connect with our Mathematics tutors online and get step by step solution of this question.
Are you ready to take control of your learning?
Download Filo and start learning with your favourite tutors right away!
For 30 years, it’s been the biggest question in Oswego County: ‘Where is Heidi Allen?’
- Updated: Apr. 01, 2024, 5:53 p.m. |
- Published: Mar. 31, 2024, 8:00 a.m.
A photo of the missing New Haven girl Heidi M. Allen that was provided by the family.
Heidi Allen. Submitted photo
Police cars guard the D and W Convenience store at the intersection of Rts 104 and 104b on the outskirts of New Haven Sunday afternoon. Heidi Allen disappeared from the store early Sunday morning. 4-3-94 photo by tim reese 0403 MISSING 04 PHOTO MAC ONE POST CITY DESK
PHOTO BY NICHOLAS LISI 4/4/94 ONONDAGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE SECURITY OFFICER MATTHEW MORRELL TAPES UP "MISSING" POSTERS ON ALL THE DOORS TO BUILDINS AT OCC FOR HEIDI ALLEN WHO HAS BEEN MISSING SINCE YESTARDAY. SHE WAS AN OCC STUDENT.OVER 100 POSTERS WERE PUT UP OPN CAMPUS SINCE NOON. 4/4/1994
Susan Allen, who read a lengthy statement about her daughter Heidi Allen right before sentencing is happy that Gary Thibodeau received the maximum sentence for his crime. The truck in the background is owned by her brother Jim Searles of New Haven.0807 thibodeau 5 Shared Drive Regional 8/7/95 photo by Suzanne Dunn
GARY THIBIDEAU IS LEAD INTO OSWEGO COUNTY COURT FOR ARRAINGMENT ON KIDNAPPING CHARGES OF HEIDI ALLEN. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0725
AT A FUNDRAISER TO BENIFIT THE HEIDI ALLEN SEARCH EFFORTS AT THE SCRIBA TOWN INN (A BAR), KAREEN PULLEN HANDS OVER A CASH DONATION TO THE DOOR PERSON DAN BARNEY. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0410
Assistant Federal Public Defender Randi Bianco holds a photo of Heidi Allen that was part of her confidential informant file with the Oswego County Sheriff's office along with an index card. Both were dropped in the parking lot of the convenience store where Heidi Allen was later kidnapped. Bianco was the first to testify during a hearing about the 1994 kidnapping of Heidi Allen at the Oswego County Courthouse Monday, Jan. 12, 2015. Gary Walts | [email protected]
Heidi Allen's mother Susan Allen, inside the command post at the New Haven fire department. 4-3-94 photo by tim reese 0403 MISSING 03 PHOTO MAC ONE POST CITY DESK
Gary Thibodeau of Mexico, New York being led into Oswego County Court in the kidnapping of Heidi Allen. Dick Blume | [email protected] Dick Blume
Lisa Buske stands near a sign in remembrance of her sister, Heidi Allen, in New Haven, N.Y., Thursday, April 2, 2015. Kevin Rivoli | [email protected]
Gary Thibodeau, convicted of murdering Heidi Allen in 1995, talking to girlfriend Sharon Raposa, right, before going into the Oswego, New York Court during his trial. Dick Blume | [email protected]
Lisa Buske walks near signs in remembrance of her sister, Heidi Allen, in New Haven, N.Y., Thursday, April 2, 2015. Kevin Rivoli | [email protected]
RICHARD THIBIDEAU ACCUSED OF KIDNAPPING HEIDI ALLEN LEAVES THE OSWEGO COUNTY COURTHOUSE FOR LUNCH RECESS DURING THE JURY SELECTION, WEDNESDAY. 0906 95 0906 THIB REGIONAL PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT
MEMBERS OF THE SENECA COUNTY SHERRIFFS DEPARTMENTS VOLUNTEER MOUNTED POLICE, LISTEN FOR INSTRUCTIONS FROM SHERRIFF TOM FOX AS THEY PREPARE TO HELP IN THE SEARCH FOR HEIDI ALLEN. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0411 PHOTO BY DENNNIS NETT 0411
ARMY TROOPS FROM FT.DRUM ASSISTED IN THE SEARCH FOR HEIDI ALLEN TODAY IN THE TOWN OF NEW HAVEN. THE TROOPS SEARCHED IN THE ROUGHER AREAS OF THE COUNTY INCLUDING THE SWAMPS AND HEAVILY WEEDED WOODS. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0418
Gary Thibodeau, convicted of murdering Heidi Allen in 1995, going into the Oswego, New York Court during his trial. Dick Blume | [email protected] Dick Blume
This sign is across the street of the Thibodeau home on Kenyon Rd., in Mexico. Heidi Allen
James Searles, uncle of Heidi Allen, and Heidi Allen's mom, Sue Allen, waiting for jury selection portion during Gary Thibodeau's trial at the Oswego Public Safety Building, where Thibodeau was convicted of murdering Heidi Allen in 1995. Dick Blume | [email protected] Dick Blume
PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 9/14/94 KEN AND SUE ALLEN WATCH AS A TREE IS PLANTED IN HONOR OF HEIDI ALLEN'S 19TH BIRTHDAY, AT A CEREMONY HONORING VOLUNTEERS IN THE SEARCH FOR HEIDI.
GARY THIBODEAU'S JAW DROP WHEN HEARS THE VERDICT OF GUILTY IN THE KIDNAPPING CHARGE OF HEIDI ALLEN. 0619 95
FAMILY AND FRIENDS OF HEIDI ALLEN WATCH A LIVE TELEVISION PRESS CONFERENCE OF THE ARAINGMENT OF RICHARD THIBIDEAU IN OSWEGO. SECOND FROM LEFT IN THE BACK ROW IS HEIDI ALLLEN'S BOYFREIND BRETT LAW, AND HOLDING THE TELEVISION IS ROBERT LEE A FREIND. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0525
0408 OSW SEARCH 2 NETTI'S MEGA MAC REGIONAL DETAIL SHOT OF THE ORANGE ARMBANDS THAT WERE WORN BY VOLUNTEERS WHO HELPED IN THE SEARCH OF HEIDI ALLEN. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0408
BRETT LAW , HEIDI ALLEN'S BOYFRIEND OF TWO YEARS TRIES TO THINK OF ANSWERS OF WHY HEIDI IS MISSING. BRETT SAYS HE IS THINKING KNOTHING BUT GOOD THOUGHTS. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0406
Richard Thibodeau listens to testimony on the 11th day of a hearing about the 1994 kidnapping of Heidi Allen at the Oswego County Courthouse Thursday, March 26, 2015. At left is his girlfriend Teresa Crawford. Lauren Long | [email protected]
0730 OSW BRANSHAW NETTI'S MEGA MAC REGIONAL SUZIE BRANSHAW CLOSE FRIEND TO HEIDI ALLEN, IN A PORTRAIT BY HER BEDROOM DOOR THAT HAS MANY MISSING POSTERS OF HEIDI ALLEN. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0730
BECKY STEVENSON OF MEXICO LOOKS AT HER HAPPY BIRTHDAY HEIDI BALLOON AS A CEROMONY HORNORING VOLUNTEERS IN THE SEARCH FOR HEIDI GOES ON. BECKY IS A VOLUNTEER .
17 YEAR OLD SUZIE BRANSHAW, 21 YEAR OLD MICHAEL TODD, AND 16 YEAR OLD JENNIFER SHELDON EMBRACE AND SHED TEARS IN A CANDLE LIGHT VIGIL FOR THE RETURN OF HEIDI ALLEN. THE VIGIL WAS HELD NEAR THE NEW HAVEN FIRE DEPT AND WAS ATTENDED BY ABOUT 100 PEOPLE, WHERE PRAYERS AND SONGS WERE SAID. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0408
Gary Thibodeau listens to witnesses testify during a hearing about the 1994 kidnapping of Heidi Allen at the Oswego County Courthouse Thursday, Feb. 5, 2015. David Lassman | [email protected]
5/25/94 PHOTO BY DICK BLUME RICHARD THIBODEAU, 48, OF MEXICO, GOING TO INTO OSWEGO CO. COURT ON KIDNAPPING CHARGES OF HEIDI ALLEN.
KEN ALLEN, FATHER OF HEIDI ALLEN LISTENS TO QUESTIONS FROM THE PRESS, IN THE FIRST PRESS CONFERENCE SINCE THE DISAPPEARANCE OF HIS DAUGHTER. BEHIND HIM IS HIS OTHER DAUGHTER LISA BUSKE. PHOTO BY DENNIS NETT 0413
An age progression portrait of Heidi Allen, who went missing in 1994. (Courtesy National Center for Missing and Exploited Children)
Gary Thibodeau enters at the Oswego County courtroom Friday, Feb. 6, 2015, on the eighth day of a hearing about the 1994 kidnapping of Heidi Allen. Lauren Long | [email protected]
- Rylee Kirk | [email protected]
New Haven, N.Y. — It’s the question that has been asked in Oswego County for 30 years now.
“Where is Heidi Allen?”
The question has appeared on signs posted across the county. At one point it was on balloons lining the ceiling of a church on her 19th birthday. It’s been asked in two trials, countless articles and TV specials.
Yet 30 years later it’s still unanswered.
Heidi Allen disappeared from the New Haven gas station where she was working on Easter Sunday, April 3, 1994.
Allen was an Onondaga Community College student who was working at the D&W Convenience store at state Routes 104 and 104B.
The morning started early with Allen opening the store at 5:50 a.m. Her boyfriend of two years, Brett Law, had followed her to work in his pick-up truck, he told Syracuse.com | The Post-Standard in 1994.
Allen stocked shelves and rearranged the deli counter and Law read the Sunday paper and drank coffee. He looked for interesting articles or funny cartoons and would call Allen over and the two would laugh together.
“Everything was picture perfect that morning,” Law said. “Just like us, we were, we are the perfect couple.”
Mary Duell told the paper in 1994 that she went into the store that morning and found Allen and Law “smooching.”
Duell liked the young couple, so she teased them. “Now look here - we’re not having any of this in the big town of New Haven on Easter morning!” she scolded.
Allen told her she knew Duell was coming in and did it just to bother her, Duell said.
Law told Allen he loved her and would call her in two hours, after getting more sleep. Duell and Allen chatted, talking about the girl across the street who is moving out of New Haven, about Duell’s chickens, and about Allen going to Law’s house for Easter dinner. Duell, who lives next door to the store, bought a newspaper and left around 6:45.
About an hour later the store was empty. Allen’s keys and purse on the counter and her maroon station wagon parked outside.
The last transaction recorded on the cash register came at 7:42 a.m., two packs of generic cigarettes. At 7:52 a.m., Dave Stinson flagged down a sheriff’s deputy and said the convenience store had no cashier. Police said it was likely Allen was abducted in just five minutes.
Within hours a command post was set up at the New Haven Fire Department. Law enforcement started combing the county for the teen.
Vigils were held for her. At the first candlelight vigil, less than a week after her disappearance, her four-year-old cousin addressed the crowd.
“Heidi will come home,” the boy said. “The lights will show her how to come home.”
The teen had attended Mexico High School, where she played varsity soccer, friends said. At times people wore orange and black - the colors of the school - a symbol of the search for Allen.
Two men were arrested for her abduction, Richard and Gary Thibodeau. The brothers had helped search for Allen, the newspaper reported.
Gary Thibodeau was convicted of Allen’s kidnapping and sentenced to 25 years to life in prison in 1995. He appealed several times, claiming he was innocent. He died in 2018 at age 64 from complications related to COPD.
Richard Thibodeau faced a different jury that acquitted him. For years he spoke out about his brother’s conviction, claiming Gary Thibodeau was innocent. At times Richard Thibodeau and others held signs on lawns in Oswego County about his brother’s innocence.
Richard Thibodeau died at 77 in January of this year.
Allen has been assumed dead for several years but her body has never been found. In recent years, National Center for Missing and Exploited Children released an age progression portrait of Allen.
In September 1994 Allen’s family marked her 19th birthday.
“Until you physically know something, you have to keep hoping,” her mother Susan Allen said at the time. “You know in the back of your mind that it may not be a good ending, but you must remain hopeful.”
Staff writer Rylee Kirk covers breaking news, crime and public safety. Have a tip, story idea, photo, question or comment? Reach her at 315-396-5961, on Twitter @kirk_rylee, or [email protected] .
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
Use of and/or registration on any portion of this site constitutes acceptance of our User Agreement (updated 4/4/2023), Privacy Policy and Cookie Statement , and Your Privacy Choices and Rights (updated 12/31/2023).
© 2024 Advance Local Media LLC. All rights reserved ( About Us ). The material on this site may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, cached or otherwise used, except with the prior written permission of Advance Local.
Community Rules apply to all content you upload or otherwise submit to this site.
YouTube’s privacy policy is available here and YouTube’s terms of service is available here .
Opt out of the sale or sharing of personal information
If you opt out, we won’t sell or share your personal information to inform the ads you see. You may still see interest-based ads if your information is sold or shared by other companies or was sold or shared previously.
EssayGPT Review: An In-Depth Look into the AI Essay Writing Copilot
Overview of EssayGPT
EssayGPT is an AI-powered essay writing copilot that revolutionizes the way students and researchers approach academic writing. With its clever essay AI, a range of powerful features, and a user-friendly interface, EssayGPT streamlines the essay content workflow, helping you to do easier and faster research, saving valuable time and effort.
In this review, we will delve into the various aspects of EssayGPT, its capabilities, and how its smart essay AI enhances the content writing and editing experience.
The Three Modes of EssayGPT
EssayGPT operates in three distinct modes, the Generator mode, the Writer mode, and the ScholarChat mode. Each of them serves a unique purpose and contributes to a seamless essay researching and writing experience.
Generator (AI essay generator)
EssayGPT’s Generator mode allows users to generate up to 800 words of essay content with just a simple topic sentence. As you can see from the screenshot, I can adjust the essay type and add SEO keywords according to my needs. I can also ask EssayGPT to humanize the generated results so that no AI detectors can flag my content as AI-generated.
If you want to further customize the outline as well as the titles of your essay, you can try the other “Generate Titles” button. This more advanced setting mode allows you to adjust every detailed aspect of your essays so that you will get a fully tailored output that precisely aligns with your requirements and standards.
Writer (Workspace for writing and editing essays)
EssayGPT’s Writer mode provides a comprehensive online text editor for writing and editing essays. You can start from scratch at EssayGPT’s editor, or simply upload your text document and start from there. Once your content is online, you can now utilize EssayGPT’s specially developed essay AI to effortlessly write, rewrite, summarize, or expand your essays with ease.
ScholarChat (AI research assistant chatbot)
ScholarChat is EssayGPT’s AI chatbot designed to serve as a virtual research assistant that significantly enhances the research process for users. Just let the chatbot know what you are looking for, it can quickly obtain relevant academic sources across a broad range of topics, ideal for students and researchers needing efficient and thorough research support.
EssayGPT’s Features

EssayGPT offers a range of advanced features designed to elevate your essay writing process. Here are some of its capabilities that I believe to be especially useful when writing essays of all types.
The Smart “//” Toolbar : By entering the “//” on the editor interface, you can access the smart toolbar, send your lines of command, and let EssayGPT’s intelligent essay AI rewrite, summarize, or expand your existing essays effortlessly.
Streamlined Research Process : EssayGPT is connected to a vast network of scholastic databases and academic publications, enabling quick and accurate research. Use detailed and up-to-date information to enhance the quality and credibility of your essay.
Customizable Citation System : The auto-citation system from EssayGPT makes it easy to add accurate references in academic standards, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, and more. The system can also take customized information to generate professionally formatted citations as well.
Auto Content Completion : Overcoming writer’s block is made simpler with EssayGPT’s AI auto-complete feature. The smart essay AI can analyze the context, style as well as tone of your existing writing and generate tailored suggestions to complete your essay seamlessly.
Built-in Grammar & Plagiarism Checker : EssayGPT ensures your essay is free from grammatical, syntax, and punctuation errors in order to maintain coherence, clarity, and readability. It also scans your essay content to guarantee its uniqueness and originality. Detecting any signs of plagiarism allows you to make necessary revisions, and avoid academic misconduct.
Why Use EssayGPT Instead of ChatGPT?
While ChatGPT still remains a powerful conversational chatbot, EssayGPT is specifically designed to cater to the unique needs of essay writing. Here are some notable advantages that you will not necessarily have if you are using ChatGPT:
Specialized Essay Writing Features
Unlike the general conversation style with ChatGPT, EssayGPT offers a comprehensive set of features tailored explicitly for essay and academic writing, including the dedicated essay AI, auto context-reading content completion, grammar and plagiarism checker, formatted citation assistance, and more.
Enhanced Research Capabilities
EssayGPT’s direct and instant access to academic databases and trustable publications offers a significant advantage compared to the simple conversation-based and outdated database from ChatGPT. It allows users to find and directly cite scholarly articles, helping students and academic professionals to produce more informed and authoritative essays.
Essay-Specific Assistance
EssayGPT’s AI auto-complete feature, and outline writing system, along with the comprehensive grammar and plagiarism checker specifically address common challenges faced during essay writing, ensuring high-quality, efficient, and credible output.
In conclusion, Essay GPT is a remarkable AI essay writing copilot that streamlines the essay writing process for students, researchers, and other academic professionals. Its remarkable three modes, research-focused tools and features, advanced content writing capabilities, and smartly trained essay AI make it a valuable tool for enhancing productivity and efficiency.
By the time of writing this review article, EssayGPT had just launched their specially developed EssayGPT GPTs , aimed to provide their powerful research features and writing assistance for those who have access to ChatGPT Plus, and those who are looking for an even simpler, direct chatting experience when writing essays.
Questions You Might Want to Ask
Can essaygpt generate citations in different styles.
EssayGPT offers citation formatting assistance, allowing you to cite your references accurately in various styles such as APA, MLA, Chicago, and more. You can also use the citation system to generate citations with your own referencing information.
How does EssayGPT ensure the uniqueness of my essay?
Other than the guaranteed original content creation from their expertly-trained essay AI, EssayGPT includes an accurate plagiarism checker that scans the essay content to detect any signs of plagiarism. It highlights the plagiarized text, enabling you to make necessary revisions and further maintain the originality of your work.
Can EssayGPT really handle complex research topics?
Yes, EssayGPT is directly linked to a vast network of scholastic databases and academic publications. This enables comprehensive research and fact-checking, even for complex and specialized research topics.
Can EssayGPT be used for other writing tasks besides essays?
While EssayGPT is primarily designed for essay writing, its research-oriented features and content writing capabilities can certainly be beneficial for other academic writing tasks such as informative reports, technical articles, and research papers as well.
Spotify is Trying out Video-Based Learning Courses for UK Subscribers
Xiaomi, oneplus and oppo gallery apps can now fully integrate google photos libraries, you may also like.
The Evolution of Solitaire: From Classic Card Game to Online Sensation

Is Apple’s App Store Anti-Competitive?

AIHumanize Review: Trusted AI Humanizer to Get 100% Human Score Text
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
More in Misc
Mathful Review: Your AI-Powered Math Assistant

10 Must-Have Apps for Spending Your Free Time Wisely
10 best ai homework helper for students to learn faster (free & paid), latest deals.

For ONLY $300, the Samsung Galaxy A54 is a better deal than the Galaxy A55!

Save up to $50 with this OnePlus Nord N30 Deal!

This Deal gets you Samsung’s Galaxy Tab A9 Plus with $50 Off!
- Privacy Policy
- Online Sweepstakes
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
This workbook is the first in a series of three workbooks designed to improve the. development and use of effective essay questions. It focuses on the writing and use of. essay questions. The second booklet in the series focuses on scoring student responses to. essay questions.
Essay Exams: Common Question Types When approaching any essay exam, it is important to identify what kind of response is expected—that is, what is being asked of you and what information you are required to include. This handout outlines several question types and includes key words to look for when deciding how to respond to an essay prompt.
2) Be as explicit as possible. Use forceful, persuasive language to show how the points you've made do answer the question. My main focus so far has been on tangential or irrelevant material - but many students lose marks even though they make great points, because they don't quite impress how relevant those points are.
You must be realistic about the time constraints of an essay exam. If you write one dazzling answer on an exam with three equally-weighted required questions, you earn only 33 points—not enough to pass at most colleges. This may seem unfair, but keep in mind that instructors plan exams to be reasonably comprehensive.
Make sure you understand what type of answer the main verb calls for (a diagram a summary, details, an analysis, an evaluation). Circle all the keywords in the question. Decide if you need to write a 1-paragraph or a multi-paragraph answer. Write a brief outline of all the points you want to mention in your answer. Restate the question and ...
Types of questions. Quotation + Discuss' questions. One of the most common types of essay question is a direct quotation followed by a general task word or phrase like 'Discuss' or 'To what extent do you agree?'. When answering these questions, the most important thing is to work out your argument - what you think about the ideas in the ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
8 Types of Essays. To decide which essay style best suits your needs as a writer, check out the list below: 1. Expository essay: An expository essay, also known as a definition essay, is the most basic type of essay. Expository essays aim only to explain an idea or define a concept, without making an argument.
The questions are organised under common topics and essay types. IELTS often use the similar topics for their essays but change the wording of the essay question. In order to prepare well for writing task 2, you should prepare ideas for common topics and then practise applying them to the tasks given (to the essay questions).
Essay questions typically include a list of specific keywords that teachers and professors want students to focus on when composing their responses. For instance, an essay question that asks you to "describe" an issue will be different from an essay question that asks you to "argue" a position. Both of these types of questions are part of an essay.
Expository Essay. Informative Writing, Research, Clarity. Explain the causes and effects of climate change, and discuss its impact on the environment and society. Narrative Essay. Storytelling, Narrative Structure, Engagement. Describe a memorable childhood event that had a significant impact on your life.
Most essay questions will have one or more "key words" that indicate which organizational pattern you should use in your answer. The six most common organizational patterns for essay exams are definition, analysis, cause and effect, comparison/contrast, process analysis, and thesis-support. ... The type is based on medieval manuscript writing ...
Essay questions that ask you to 'analyse' a particular topic or argument expect a thorough deconstruction of the essay subject. In other words, this word requires you to break the essay topic down into its fundamental parts. ... You must demonstrate reasoning skills with this type of question, by using evidence to make a case for or against ...
Both sides and an opinion questions. Along with opinion-type essays, both sides and an opinion questions are one of the most common questions in the IELTS writing exam. However, unlike opinion essays, the question is more specific about what you need to cover. It's common for students to get too nervous during the exam and only give one side ...
2. Fill out your outline. [2] For each point in your outline, fill in the important information that will jog your memory when writing the essay. You don't have to write in full sentences or flesh ideas out in detail — just jot down whatever you need to keep you on track when you're lost in your sentences later.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
There are two types of essay questions: restricted and extended response. Restricted Response - These essay questions limit what the student will discuss in the essay based on the wording of the question. For example, "State the main differences between John Adams' and Thomas Jefferson's beliefs about federalism," is a restricted response. What ...
The lumber room at the center of the story is a symbol of Nicholas's imagination. Although lumber rooms would have been common enough in Edwardian homes—little more than a storeroom of furniture and possessions not currently in use in the rest of the home—the lumber room takes on mythical proportions in Nicholas's imagination.
About the essay question type. The essay question type provides the option of answering by uploading one or more files and/or entering text online. (For longer essays, text or file uploads, you may wish to consider using the Assignment activity rather than this question type.) Essay questions are created in the same way as other quiz question ...
Solution For Essay Type Questions (23 - 25) 23. Factorise the following expressions : World's only instant tutoring platform. Become a tutor Partnerships About us Student login Tutor login. About us. Who we are Impact. Login. Student Tutor. Get 2 FREE Instant-Explanations on Filo ...
At one point it was on balloons lining the ceiling of a church on her 19th birthday. It's been asked in two trials, countless articles and TV specials. Yet 30 years later it's still unanswered ...
EssayGPT is an AI-powered essay writing copilot that revolutionizes the way students and researchers approach academic writing. With its clever essay AI, a range of powerful features, and a user ...