
15 Ethos Examples (Appeal to Credibility)

Ethos is one part of the so-called rhetorical triangle. In Aristotle’s Rhetoric, Ethos refers to a technical means of persuasion that has to do with the credibility of the persuader.
Aristotle claims that there are three technical means of persuasion:
“Now the proofs furnished by the speech are of three kinds. The first depends upon the moral character of the speaker, the second upon putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind, the third upon the speech itself, in so far as it proves or seems to prove” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 3).
Each of these corresponds to the three means of persuasion:
- Ethos (Appeal to credibility): Persuasion through establishing the character of the speaker.
- Pathos (Appeal to emotion) : Persuasion through putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind.
- Logos (Appeal to logic) : Persuasion through proof or seeming proof.
For Aristotle, speech consists of three things: the speaker, the hearer, and the speech. These correspond to ethos, pathos, and logos , respectively. The first of these is the subject of this article.
Definition of Ethos
In rhetoric, ethos, from the Greek word for “character,” refers to persuasion through establishing the authority of the speaker .
According to Aristotle, people follow a trustworthy speaker more readily on almost all subjects and completely so if there are no objective criteria to decide the matter.
The orator is using ethos if their speech is delivered in a manner that makes them seem worthy of confidence (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 4).
The importance of ethos in rhetoric can readily be seen through Aristotle’s example: The orator must appear to be of a certain character because this will determine how the audience is disposed towards them.
One’s dispositions toward the speaker will make all the difference,
“…for when a man is favorably disposed towards one on whom he is passing judgement, he either thinks that the accused has committed no wrong at all or that his offence is trifling; but if he hates him, the reverse is the case.” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 2, Chapter 1, Section 4).
Effective use of ethos requires three qualities: good sense, virtue, and good will (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 2, Chapter 1, Section 5). These qualities are necessary and sufficient for the orator.
15 Examples of Ethos
Example 1: the climate expert.
“As a leading climate scientist with years of experience researching this field, I can assure you that global warming is a pressing issue that requires an urgent and serious response.”
The first part of the argument above (“As a leading climate scientist with years of experience researching this field”) establishes the speaker’s credibility, which means that the primary means through which the speaker is trying to convince their audience is ethos. For a topic as complex as global warming, the average audience member is far more likely to listen to someone who establishes their credibility from the start than to someone who relies solely on pathos and logos.
Example 2: The Infectious Disease Expert
“I’ve dedicated over 40 years of my career to studying infectious diseases and their large-scale effects, so I can assert with full confidence that widespread vaccination is crucial for public health.”
It is easy to see that virtually anyone is more likely to trust the medical advice of someone who immediately establishes themselves as a seasoned professional than someone who limits their speech to logical arguments alone.
Example 3: Brand Credibility
The use of ethos is particularly frequent for brands. This is especially true when two competing brands have virtually indistinguishable products in terms of their use value. There would be no logical reason to prefer one brand to another, so each must try to appear more credible than the other.
Example 4: The Art Critic
“I’ve been an art critic for over 30 years and during that time I’ve never come across a contemporary work of art that has as many layers of meaning as this one.”
This example exploits the peculiar advantages of ethos in matters that have no objective criteria. As Aristotle said, “we feel confidence in a greater degree and more readily in persons of worth in regard to everything in general, but where there is no certainty and there is room for doubt, our confidence is absolute.” (Aristotle, Rhetoric, ca. 367-322 B.C.E./1926, Book 1, Chapter 2, Section 4).
Example 5: The Expert Witness
An expert witness is using ethos (their education, certification, experience, etc.) to establish their testimony as authoritative.
For example, an expert witness might be called up to give evidence about whether an image was doctored or if it was, indeed, the original image that is being presented. The jury is more likely to find the witness credible if they can established that they do indeed have expertise on the topic, making their statement more authoritative.
Example 6: The Seasoned Traveler
“Having visited over 60 countries around the world, my recommendations for which places to visit and which to avoid are based on my years of experience.”
In this example, the speaker is using ethos to establish trustworthiness in an area where the audience members are unlikely to have conflicting experiences. The sheer number of countries they have been to gives them some clout, although we may be having the wool pulled over our eyes if 45 of those countries were merely in transit!
Example 7: The Experienced Entrepreneur
“While I wasn’t born in a particularly well-off family, by age 22 I was already the CEO of a 100 million dollar company. I know what it’s like to go from zero to hundred when it comes to entrepreneurship, so you can rest assured that what I’m about to say is backed up by lived experience.”
The speaker’s appeal to their financial success story is an attempt to prime the audience and make the speech that will follow more persuasive and influential through the use of ethos.
Example 8: The Former Judge
“As a former judge who presided over hundreds of criminal justice cases, I’ve seen first hand what injustices our system often gives rise to.”
Not only is the speaker establishing their credibility from the start, but ethos is an especially well-suited persuasion technique in such a case because the matter at hand requires personal acquaintance with the topic. It’s not just that a judge will be more knowledgeable about criminal justice than the average person, but a judge would also have access to information that is simply unavailable for others, no matter how well-informed they may be.
Example 9: The Celebrity Endorsement
While most examples focus on how ethos can be used in speech or writing, we shouldn’t forget that ethos may also be expressed visually.
For example, using images of celebrities or doctors to advertise a product is an example of ethos, because the advertisement is trying to establish its credibility and trustworthiness.
Example 10: The Certified Personal Trainer
“As a certified personal trainer with years of experience coaching professional athletes as well as clients with diverse fitness goals, I can build a training and nutrition program that is a perfect fit for your goals.”
The speaker is using ethos in the first part of the speech to establish credibility. In the context of physical fitness, ethos often has a visual component along with the verbal: the speaker will probably be especially fit and they will make sure you see that because you’re far more likely to take advice from someone who already has the body you want.
Example 11: The Veteran Educator
“With 25 years of experience in teaching and a doctoral degree in education, I can assure you that early childhood learning lays a vital foundation for a child’s future academic and personal development.”
Here, the speaker uses their academic qualifications and extensive experience to convince the audience about the importance of early childhood education. The ethos is essential as it brings forth a certain level of expertise and credibility to the argument.
Example 12: The Renowned Chef
“Having trained in culinary schools around the world and worked in Michelin-starred restaurants, I can assure you that the art of cooking is much more than just following recipes.”
In this case, the chef uses their international experience and association with esteemed restaurants to validate their point of view about cooking. This is an excellent example of ethos, as it makes the audience value the speaker’s perspective based on their distinguished background.
Example 13: The Skilled Craftsman
“Working as a craftsman for more than 30 years, mastering techniques of pottery and sculpture, I can vouch for the therapeutic benefits of hands-on artistry.”
The speaker uses ethos to enhance the weight of their perspective, drawing upon their lifelong experience in the field of craftsmanship. The audience would likely give more credence to the speaker’s argument due to their established authority in the subject.
Example 14: The Experienced Psychologist
“As a psychologist with over two decades of clinical experience and several research papers in the field of cognitive behavior, I strongly believe that maintaining a positive mindset is crucial for mental health.”
In this instance, the psychologist uses ethos, leveraging their years of practical experience and contribution to scientific research to advocate for the importance of a positive mindset. This use of ethos enhances the credibility of their argument, making the audience more likely to accept their viewpoint.
Example 15: The Professional Environmentalist
“As a professional environmentalist, who has spent the last 20 years advocating for sustainable practices and policies, I can confidently say that adopting renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable future.”
Here, the speaker uses their long-term dedication to environmental issues and advocacy work to establish their credibility. The ethos in this argument underscores the importance of their message, making it more persuasive to the audience.
Strengths of Ethos
- Trust: In settings where the audience has little or no knowledge of the topic, the speaker’s appeals to ethos might be the most important means of persuasion. For example, if you know nothing about quantum physics, you may not be able to detect fallacies in arguments about it, and it’s not a subject that’s connected with any strong emotions, so the only thing you may rely on is the speaker’s credibility.
- Subjective topics: Ethos, as Aristotle noted, is especially useful in cases where there are no objective criteria to decide the matter. For example, the orator may make greater use of ethos when speaking about a work of art than when debating the merits of a mathematical proof.
Weaknesses of Ethos
- Insincerity: It is easy for the audience to perceive the speaker’s appeals to ethos as inauthentic. While arguments don’t generally arouse suspicion, an appeal to one’s credentials can make the audience distrust you if done unskillfully.
- Objectivity: The converse of Aristotle’s statement about the usefulness of ethos in vague matters is that its utility is limited in matters that have objective criteria. For example, ethos is of no use if the truth of the argument one makes can easily be determined by each audience member for themselves.
Ethos is one of three main technical means of persuasion. In the context of rhetoric, it refers to appeals to the persuader’s credibility and comes from the Greek word for “character.” Like other means of persuasion, it has its strengths and weaknesses.
See Also: The 5 Types of Rhetorical Situations
Aristotle. (1926). Rhetoric. In Aristotle in 23 Volumes, Vol. 22, translated by J. H. Freese. Harvard University Press. (Original work published ca. 367-322 B.C.E.)
Rapp, C. (2022). Aristotle’s Rhetoric. In E. N. Zalta (Ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2022). Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2022/entries/aristotle-rhetoric/

Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch)
Tio Gabunia is an academic writer and architect based in Tbilisi. He has studied architecture, design, and urban planning at the Georgian Technical University and the University of Lisbon. He has worked in these fields in Georgia, Portugal, and France. Most of Tio’s writings concern philosophy. Other writings include architecture, sociology, urban planning, and economics.
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 6 Types of Societies (With 21 Examples)
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Public Health Policy Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cultural Differences Examples
- Tio Gabunia (B.Arch, M.Arch) #molongui-disabled-link Social Interaction Types & Examples (Sociology)

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Chapter 6: Thinking and Analyzing Rhetorically
6.4 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel
Rhetoric, as the previous chapters have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft his or her argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that he or she is using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that he or she is trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that his or her argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like he or she is seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how is he or she doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, he or she is attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support his or her argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon that values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and his or her character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by his or her knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish his or her credibility, a n author may draw attention to who he or she is or what kinds of experience he or she has with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos, and it is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that he or she has the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept his or her argument? How can the the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we see authors
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as his or her character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When writers misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, arguments can be weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument.
In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see the next chapter, Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing by Melanie Gagich & Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Feedback/Errata
Comments are closed.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, ethos, pathos, logos, kairos: the modes of persuasion and how to use them.
General Education

Ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos all stem from rhetoric—that is, speaking and writing effectively. You might find the concepts in courses on rhetoric, psychology, English, or in just about any other field!
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising.
Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they’re used, and how to identify them!
What Are the Modes of Persuasion?
As you might have guessed from the sound of the words, ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos go all the way back to ancient Greece. The concepts were introduced in Aristotle’s Rhetoric , a treatise on persuasion that approached rhetoric as an art, in the fourth century BCE.
Rhetoric was primarily concerned with ethos, pathos, and logos, but kairos, or the idea of using your words at the right time, was also an important feature of Aristotle’s teachings.
However, kairos was particularly interesting to the Sophists, a group of intellectuals who made their living teaching a variety of subjects. The Sophists stressed the importance of structuring rhetoric around the ideal time and place.
Together, all four concepts have become the modes of persuasion, though we typically focus on ethos, pathos, and logos.

What Is Ethos?
Though you may not have heard the term before, ‘ethos’ is a common concept. You can think of it as an appeal to authority or character—persuasive techniques using ethos will attempt to persuade you based on the speaker’s social standing or knowledge. The word ethos even comes from the Greek word for character.
An ethos-based argument will include a statement that makes use of the speaker or writer’s position and knowledge. For example, hearing the phrase, “As a doctor, I believe,” before an argument about physical health is more likely to sway you than hearing, “As a second-grade teacher, I believe.”
Likewise, celebrity endorsements can be incredibly effective in persuading people to do things . Many viewers aspire to be like their favorite celebrities, so when they appear in advertisements, they're more likely to buy whatever they're selling to be more like them. The same is true of social media influencers, whose partnerships with brands can have huge financial benefits for marketers .
In addition to authority figures and celebrities, according to Aristotle, we’re more likely to trust people who we perceive as having good sense, good morals, and goodwill —in other words, we trust people who are rational, fair, and kind. You don’t have to be famous to use ethos effectively; you just need whoever you’re persuading to perceive you as rational, moral, and kind.

What Is Pathos?
Pathos, which comes from the Greek word for suffering or experience, is rhetoric that appeals to emotion. The emotion appealed to can be a positive or negative one, but whatever it is, it should make people feel strongly as a means of getting them to agree or disagree.
For example, imagine someone asks you to donate to a cause, such as saving rainforests. If they just ask you to donate, you may or may not want to, depending on your previous views. But if they take the time to tell you a story about how many animals go extinct because of deforestation, or even about how their fundraising efforts have improved conditions in the rainforests, you may be more likely to donate because you’re emotionally involved.
But pathos isn’t just about creating emotion; it can also be about counteracting it. For example, imagine a teacher speaking to a group of angry children. The children are annoyed that they have to do schoolwork when they’d rather be outside. The teacher could admonish them for misbehaving, or, with rhetoric, he could change their minds.
Suppose that, instead of punishing them, the teacher instead tries to inspire calmness in them by putting on some soothing music and speaking in a more hushed voice. He could also try reminding them that if they get to work, the time will pass quicker and they’ll be able to go outside to play.
Aristotle outlines emotional dichotomies in Rhetoric . If an audience is experiencing one emotion and it’s necessary to your argument that they feel another, you can counterbalance the unwanted emotion with the desired one . The dichotomies, expanded upon after Aristotle, are :
- Anger/Calmness
- Friendship/Enmity
- Fear/Confidence
- Shame/Shamelessness
- Kindness/Unkindness
- Pity/Indignation
- Envy/Emulation
Note that these can work in either direction; it’s not just about swaying an audience from a negative emotion to a positive one.
However, changing an audience's emotion based on false or misleading information is often seen as manipulation rather than persuasion. Getting into the hows and whys requires a dive into the ethics of rhetoric , but suffice to say that when you attempt to deceive an audience, that is manipulation.
If you really want to get an audience fired up about something, you can inspire righteous anger, which may or may not be manipulation. If somebody is offended that you’ve asked them for something, you can try making them feel sorry for you by turning indignation into pity— that’s manipulation.

What Is Logos?
Logos comes from a Greek word of multiple meanings, including “ground,” “speech,” and “reason.” In rhetoric, it specifically refers to having a sense of logic to your persuasion; logos-based rhetoric is founded in logic and reason rather than emotion, authority, or personality.
A logic-based argument appeals to a person’s sense of reason— good logos-based rhetoric will persuade people because the argument is well-reasoned and based in fact. There are two common approaches to logos: deductive and inductive arguments.
Deductive arguments build on statements to reach a conclusion —in effect, the conclusion is reached in reverse. A common method is to propose multiple true statements which are combined to reach a conclusion, such as the classic method of proving that Socrates is mortal.
All men are mortal, and Socrates is a man, therefore Socrates must be mortal.
That’s not really a case that needs to be argued, but we can apply the same framework to other arguments as well. For example, we need energy to live. Food gives the body energy. Therefore, we need food to live.
All of this is based on things we can prove, and results in a conclusion that is true , not just theorized. Deductive reasoning works on the assumption that A = B, B = C, so therefore A = C. But this also supposes that all the information is true, which is not always the case.
Sometimes the conclusions you reach with deductive reasoning can be valid, as in the reasoning makes sense, but the conclusion may not be necessarily true. If we return to the Socrates argument, we could propose that:
All men eat apples. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates must eat apples.
The problem is that we can’t prove that all men eat apples —some do, some don’t. Some might eat an apple once but never again. But based on our arguments, the conclusion that Socrates must eat apples is valid.
A strong deductive argument for logos-based reasoning will be composed of provable facts that can reach a provable conclusion. However, a valid but not entirely sound argument can also be effective—but be wary of shifting from persuasion to manipulation!
Another approach to logos-based rhetoric is inductive reasoning, which, unlike deductive reasoning, results in a probable argument rather than a definite one. That doesn’t mean that it is less effective—many scientific concepts we accept as truth are inductive theories simply because we cannot travel back in time and prove them— but rather that inductive reasoning is based on eliminating the impossible and ending in an argument that is based in sound logic and fact, but that may not necessarily be provable.
For example, all people with a cough have a cold. Kelly has a cough. Therefore, Kelly likely has a cold.
Our conclusion is likely , but not absolute. It’s possible that Kelly doesn’t have a cold—not because she doesn't have a cough, but because there are other possible causes, such as having allergies or having just breathed in some dust. The conclusion that she has a cold is likely based on data, but not absolute.
Another example would be that Kelly picks her nose. Kelly is a woman, therefore all women must pick their nose.
Inductive reasoning is based on generalizations. The first example, in which Kelly likely has a cold, makes sense because it’s based on something provable—that a sampling of people who have a cough have colds—and followed up with a likely conclusion. In the second example, this is a less sensible conclusion because it’s based on extrapolation from a single reference point.
If we reverse the claim and say that all women pick their noses, and Kelly is a woman, therefore Kelly must pick her nose, that would be more sound logic. Still not necessarily true—not all women pick their noses—but a more sound example of inductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning can still be incredibly effective in persuasion, provided that your information is well-reasoned. Inductive reasoning creates a hypothesis that can be tested; its conclusion is not necessarily true, but can be examined.
As always, be wary of venturing into manipulation, which is more likely to be based on erroneous or misleading facts.

What Is Kairos?
Kairos is the Greek word for the opportune moment, which is precisely what it means in rhetoric. According to this principle, the time in which an argument is deployed is as important as the argument itself. An argument at the wrong time or to the wrong audience will be wasted; to be effective, you must also consider when you are speaking and to whom.
In effect, kairos means choosing the correct rhetorical device to match the audience and space in which you’re attempting to persuade. If you wanted to persuade people to go vegetarian, the middle of a hot dog-eating contest is probably not the right time. Likewise, you’re probably not going to persuade a room of data-driven scientists of something by appealing to pathos or ethos; logos is probably your best bet.
In essence, kairos asks you to consider the context and atmosphere of the argument you’re making. How can you deploy your argument better considering time and space? Should you wait, or is time of the essence?
As Aristotle famously said, “Anybody can become angry—that is easy, but to be angry with the right person and to the right degree and at the right time and for the right purpose, and in the right way—that is not within everybody's power and is not easy.”
The goal of kairos is to achieve exactly that. Effective use of kairos strengthens your persuasion ability by considering how people are already feeling based on context. How can you influence or counteract that? Or maybe pathos isn’t the right approach—maybe cold hard facts, using logos, is more suited. Kairos works in conjunction with the other modes of persuasion to strengthen your argument, so as you’re putting a persuasive piece together, consider how and when it’ll be deployed!

How to Identify Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Understanding how the modes of persuasion work can make you better at identifying and picking them out. Not only is a better understanding of them useful for composing your own arguments, but it’s also beneficial when seeing other people’s arguments. When you understand how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos work, you’re less susceptible to them.
Advertising is one of the places we see the modes of persuasion most often. Looking at each of these advertisements, you can see how they use each mode of persuasion to convince audiences to convince an audience of something.
Using celebrities is a classic example of ethos, which uses authority or recognition to convince an audience of something. In this case, celebrities like Michelle Obama, Lin-Manuel Miranda, and Janelle Monáe discuss the importance of voting.
It doesn’t matter that they’re not politicians or political scientists; audiences find them appealing and genuine. When they speak of the importance of voting, audiences listen because they like what these figures have to say . If talented, famous people like this are taking the time to vote, it must be important!
Historians or those well-versed in politics might make different arguments about why audiences should vote, but in this case, the goal is to inspire people. When we see people we admire doing things, we want to do them too; hence the reason that ethos works so well.
ASPCA’s commercials are some of the most infamous examples of pathos in advertising. Sarah McLachlan’s “Angel” plays over footage of abused animals in shelters, encouraging viewers to donate money to support the organization.
It’s not hard to understand why it works; both the song and the imagery are heartbreaking! You can’t help but feel sad when you see it, and that sadness, when followed up by a prompt to donate, encourages you to take immediate action. And these ads are effective— the campaign raised millions of dollars for ASPCA .
By appealing to our emotions and making us feel sad, this advertisement encourages us to act. That’s a classic use of ethos—it influences our feelings through the one-two punch of sad music and imagery, encouraging us to perform the desired action.
In some cases, emotion and authority aren’t the right tactic. Logos often appears in tech advertisements, such as this one for the iPhone XS and XR.
Notice how the advertisement focuses on product shots and technological terms. Most audiences won’t know what an A12 bionic neural engine is, but it sounds impressive. Likewise, that “12 MPf/1.8 wide-angle lens, with larger, deeper 1.4 micron pixels” is pretty meaningless to most people, but the numbers suggest that this phone is something special because it uses scientific-sounding language.
It doesn’t matter whether audiences really understand what’s being said or not. What matters is that they feel confident that the ad is selling them something they need —in this case, impressive technological specifications that make this phone an improvement over others.
Kairos should ideally factor into all uses of the modes of persuasion, but timeliness can also be a big selling point. In this Christmas-themed M&Ms advertisement, the company uses timely humor to forge a connection between the holidays and M&Ms.
Because these commercials have been running for such a long time, there’s also a nostalgic attachment to them. Just as people look forward to new Budweiser advertisements during the Super Bowl, others look forward to seeing M&Ms or the Coca-Cola polar bear during the holidays.
Though this commercial doesn’t go out of its way to tell you the benefits of M&Ms, it does forge a connection between M&Ms and Christmas, encouraging people to purchase them around the holidays.

Examples of the Modes of Persuasion
Now that you’ve had some exposure to how ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos function and what they can do, you can test your ability to recognize them using the images below!

There are a few things to notice about this image:
- The anonymous figure
- The language
- The use of a statistic
Can you figure out which mode of persuasion this represents?
The fact that the figure is anonymous tells us it’s probably not ethos. While we might be influenced by a person who’s in shape, there’s not really an appeal here based on the person—they’re just an image to support the ad.
“DOMINATE” is a pretty loaded word, suggesting that this may have elements of pathos.
However, take a look at that statistic. Whether it’s true or not, a hard statistic like that suggests that this ad is using logos to appeal to viewers. You can draw out an argument from there—75% of users lose weight within weeks. You’re a user. Therefore, you will likely lose weight within weeks.

What do you notice about this image?
- The way the text frames the woman’s body
- The name of the perfume
- The color choice
What mode of persuasion is this?
Again, we don’t know who the model is, and perfume isn’t going to make us look like her, so we can count ethos out.
The ad seems pretty intent on making us look at certain things—the woman’s lips and chest in particular. What is it trying to make us feel?
“FORBIDDEN FRUIT” has a connotation of sensuality.
Red is a color commonly associated with passion.
When you combine the photo, the framing, the perfume name, and the color, you get a strong sense of sex appeal from the advertisement. This makes it an example of pathos—the ad is trying to make us feel a certain way . If we buy this perfume, maybe we would feel attractive, too.

How about this advertisement?
- A serious-looking photo
- Text promising “no more back pain”
- “Doctor recommended.”
Seeing a doctor might make you tempted to think the answer is logos, but there’s no appeal to logic here.
“No more back pain,” is a nice promise, but there’s no attempt to appeal to emotions, so it can’t be pathos.
What’s important in this image is the combination of the doctor in the image and the line “doctor recommended.” This doctor might not be famous, but he does have authority, making this an example of ethos.
Our confidence in this treatment grows because we trust that a doctor understands how to address back pain.

What mode of persuasion is this? Think about:
- The framing
She does look fashionable and the ad mentions stylists, so it’s possible that this is ethos.
There are no statistics or arguments being made, so the answer probably isn’t logos.
Pathos is possible, but despite having a heavily made-up model, this ad is far less about sex appeal than the previous one.
But the text mentions a specific holiday—New Year’s—suggesting that this is kairos. Kairos can, and often should, be combined with all the modes of persuasion to be even more effective. In this case, the model’s appearance could suggest either ethos or pathos in addition to kairos. The message here is that you should act now, at the beginning of the year, to take advantage of the deal and to start the year off with a new style, much like the one the model is sporting.

Key Tips for Identifying Ethos, Pathos, Logos, and Kairos
Now that you know the difference between all the modes of persuasion, you’ll have a much easier time identifying them. If you run into trouble, you can always ask questions about what you’re seeing, hearing, or reading to understand what mode of persuasion it’s using.
#1: Is It Related to a Specific Time?
If the argument is based on a specific day or context, such as Valentine’s Day or appealing only to a select group of people, such as people with dogs, it’s more likely to be kairos.
#2: Does It Involve a Celebrity or Authority Figure?
Celebrities are often a dead giveaway that an argument is using ethos. But authority figures, such as doctors, dentists, or politicians, can also be used to appeal to ethos. Even regular, everyday people can work, particularly when combined with pathos, to appeal to you based on a mutual connection you have.
#3: Does It Involve Statistics?
Statistics are a huge clue that an argument is using logos. But logos can also just be a logical argument, such as that if plants need water, and it’s hard to remember to water them, you should buy an automatic plant waterer. It makes perfect sense, making you more likely to buy it, rather than changing your habits to remember to water your plants more frequently.
#4: Does It Influence Your Emotions?
If an argument tries to change your emotions, whether by making you sad, happy, angry, or something else entirely, it’s a good indicator that it’s using pathos. Sex appeal is one of the biggest examples of pathos in advertising, appearing everywhere from makeup ads to car commercials to hamburger advertisements.
What’s Next?
Need help understanding the historical context for The Great Gatsby to perfect your kairos-based argument?
You can always combine the modes of persuasion with literary devices to make your arguments even stronger!
Learn how to say "good morning" in Japanese ! Even if it's not a mode of persuasion, it's just good manners.

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, rhetorical appeals.
Rhetorical appeals are persuasive strategies used in writing and speech to convince an audience. They consist of ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic), each serving a unique purpose in argumentation. By understanding these appeals, you can enhance your own persuasive communication and critically analyze others' arguments.

Rhetorical Appeals refer to
- Ethos : appeals to credibility
- Pathos : appeals to emotion
- Logos : appeals to logic
- Kairos : appeals to timing
Rhetors deploy a variety of rhetorical appeals depending on their rhetorical situation , thesis/research question , and mindset .
An appeal to ethos is an appeal to credibility. Writers use ethos when they use their own expertise on a topic or cite an expert on the subject. An author might refer to work credentials, degrees, etc. The writer can also “borrow” credibility by citing evidence from another author who is an expert in the topic.
Although “pathos” may sound a lot like the word “pathetic,” that isn’t what it means. Rather, pathos is an appeal to emotion. Think of the words “empathy” and “sympathy” instead of “pathetic.” When an author uses pathos, he or she is appealing to the audience’s emotions to invoke empathy and/or sympathy towards the topic as well as the author. Pathos reinforces ethos and logos. Pathos can come in a variety of forms, especially personal anecdotes and narratives. It can appeal to emotions such as anger, happiness, sadness, joy, etc. Pathos is especially used in texts that employ visuals and/or sound. Think of those super sad SPCA commercials with the haunting music and all the depressed dogs and cats who look longingly at the camera. The makers of the commercial are trying to get the audience to feel sad that these animals have not yet found a home.
The Greek word “logos” is the origin of the English word “logic.” Think of logos as an author’s use of logic to accomplish his or her purpose. An author appeals to logos by using data, statistics, relevant evidence/examples, and any other forms of proof appropriate to the topic. It also refers to the use of incomplete logic.
An appeal to kairos is an appeal to timing. When using kairos, an author attempts to convince the audience to take quick action. In this situation, an author might create a sense of urgency by setting a goal or referring to a timeline. Sometimes, the author conveys that bad things will happen if his or her suggestions are ignored.
Be careful to use these appeals correctly and with the audience in mind.
Related Articles
- Rhetorical Appeals: An Overview

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Evaluating Appeals to Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
Introduction.
As a reader and a listener, it is fundamental that you be able to recognize how writers and speakers depend upon ethos , logos , and pathos in their efforts to communicate. As a communicator yourself, you will benefit from being able to see how others rely upon ethos, logos, and pathos so that you can apply what you learn from your observations to your own speaking and writing.
Evaluate an Appeal to Ethos
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos , you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible.
A good speaker or writer leads the audience to feel comfortable with her knowledge of a topic. The audience sees her as someone worth listening to—a clear or insightful thinker, or at least someone who is well-informed and genuinely interested in the topic.
Some of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s ethos may include the following:
- Has the writer or speaker cited her sources or in some way made it possible for the audience to access further information on the issue?
- Does she demonstrate familiarity with different opinions and perspectives?
- Does she provide complete and accurate information about the issue?
- Does she use the evidence fairly? Does she avoid selective use of evidence or other types of manipulation of data?
- Does she speak respectfully about people who may have opinions and perspectives different from her own?
- Does she use unbiased language?
- Does she avoid excessive reliance on emotional appeals?
- Does she accurately convey the positions of people with whom she disagrees?
- Does she acknowledge that an issue may be complex or multifaceted?
- Does her education or experience give her credibility as someone who should be listened to on this issue?
Some of the above questions may strike you as relevant to an evaluation of logos as well as ethos—questions about the completeness and accuracy of information and whether it is used fairly. In fact, illogical thinking and the misuse of evidence may lead an audience to draw conclusions not only about the person making the argument but also about the logic of an argument.
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Ethos
In a perfect world, everyone would tell the truth and we could depend upon the credibility of speakers and authors. Unfortunately, that is not always the case. You would expect that news reporters would be objective and tell new stories based upon the facts. Janet Cooke, Stephen Glass, Jayson Blair, and Brian Williams all lost their jobs for plagiarizing or fabricated part of their news stories. Janet Cooke’s Pulitzer Prize was revoked after it was discovered that she made up “Jimmy,” an eight-year old heroin addict (Prince, 2010). Brian Williams was fired as anchor of the NBC Nightly News for exaggerating his role in the Iraq War.
Others have become infamous for claiming academic degrees that they didn’t earn as in the case of Marilee Jones. At the time of discovery, she was Dean of Admissions at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). After 28 years of employment, it was determined that she never graduated from college (Lewin, 2007). However, on her website ( http://www.marileejones.com ) she is still promoting herself as “a sought after speaker, consultant and author” (para. 1) and “one of the nation’s most experienced College Admissions Deans” (para. 2).
Beyond lying about their own credentials, authors may employ a number of tricks or fallacies to lure you to their point of view. Some of the more common techniques are described below. Others may be found in the appendix. When you recognize these fallacies being committed you should question the credibility of the speaker and the legitimacy of the argument. If you use these when making your own arguments, be aware that they may undermine or destroy your credibility.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Ethos
Ad hominem : attacking the person making an argument rather than the argument itself.
Example: “Of course that doctor advocates vaccination—he probably owns stock in a pharmaceutical company.”
False authority : relying on claims of expertise when the claimed expert (a) lacks adequate background/credentials in the relevant field, (b) departs in major ways from the consensus in the field, or (c) is biased, e.g., has a financial stake in the outcome.
Example: “Dr. X is an engineer, and he doesn’t believe in global warming.”
Guilt by association : linking the person making an argument to an unpopular person or group.
Example: “My opponent is a card-carrying member of the ACLU.”
Poisoning the well: undermining an opponent’s credibility before he or she gets a chance to speak.
Example: “The prosecution is going to bring up a series or so-called experts who are getting a lot of money to testify here today.”
Transfer fallacy : associating the argument with someone or something popular or respected; hoping that the positive associations will “rub off” onto the argument.
Examples: In politics, decorating a stage with red, white, and blue flags and bunting; in advertising, using pleasant or wholesome settings as the backdrop for print or video ads.
Name-calling : labeling an opponent with words that have negative connotations in an effort to undermine the opponent’s credibility.
Example: “These rabble-rousers are nothing but feminazis.”
Plain folk : presenting yourself as (or associating your position with) ordinary people with whom you hope your audience will identify; arguers imply that they or their supporters are trustworthy because they are ‘common people’ rather than members of the elite.
Example: “Who would you vote for—someone raised in a working-class neighborhood who has the support of Joe the Plumber or some elitist whose daddy sent him to a fancy school?”
Testimonial fallacy : inserting an endorsement of the argument by someone who is popular or respected but who lacks expertise or authority in the area under discussion.
Example: “I’m not a doctor, but I play one on TV”—a famous example of a celebrity endorsement for a cough syrup (Deis, 2011, n.p.).

The most general structure of this argument runs something like the following: Person A claims that Person A is a respected scientist or other authority; therefore, the claim they make is true.
Evaluate an Appeal to Logos
When you evaluate an appeal to logos , you consider how logical the argument is and how well-supported it is in terms of evidence. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to believe that the argument is (or is not) logical and supported by appropriate evidence.
To evaluate whether the evidence is appropriate, apply the STAR criteria: how S ufficient, T ypical, A ccurate, and R elevant is the evidence?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Logos
Diagramming the argument can help you determine if an appeal to logos is manipulative. Are the premises true? Does the conclusion follow logically from the premises? Is there sufficient, typical, accurate, and relevant evidence to support inductive reasoning? Is the speaker or author attempting to divert your attention from the real issues? These are some of the elements you might consider while evaluating an argument for the use of logos.
Pay particular attention to numbers, statistics, findings, and quotes used to support an argument. Be critical of the source and do your own investigation of the “facts.” Maybe you’ve heard or read that half of all marriages in America will end in divorce. It is so often discussed that we assume it must be true. Careful research will show that the original marriage study was flawed, and divorce rates in America have steadily declined since 1985 (Peck, 1993). If there is no scientific evidence, why do we continue to believe it? Part of the reason might be that it supports our idea of the dissolution of the American family.
Fallacies that misuse appeals to logos or attempt to manipulate the logic of an argument are discussed below. Other fallacies of logos may be found in the appendix.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Logos
Hasty generalization: jumping to conclusions based upon an unrepresentative sample or insufficient evidence.
Example: “10 of the last 14 National Spelling Bee Champions have been Indian American. Indian Americans must all be great spellers!”
Appeal to ignorance—true believer’s form: arguing along the lines that if an opponent can’t prove something isn’t the case, then it is reasonable to believe that it is the case; transfers the burden of proof away from the person making the claim (the proponent).
Example: “You can’t prove that extraterrestrials haven’t visited earth, so it is reasonable to believe that they have visited earth.”
Appeal to ignorance—skeptic’s form: confusing absence of evidence with evidence of absence; assumes that if you cannot now prove something exists, then it is shown that it doesn’t exist.
Example: “There’s no proof that starting classes later in the day will improve the performance of our high school students; therefore, this change in schedule will not work.”
Begging the question: circular argument because the premise is the same as the claim that you are trying to prove.
Example: “This legislation is sinful because it is the wrong thing to do.”
False dilemma: misuse of the either/or argument; presenting only two options when other choices exist
Example: “Either we pass this ordinance or there will be rioting in the streets.”
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: Latin phrase meaning “after this, therefore because of this”; confuses correlation with causation by concluding that an event preceding a second event must be the cause of that second event.
Example: “My child was diagnosed with autism after receiving vaccinations. That is proof that vaccines are to blame.”
Non-sequitur: Latin for “does not follow”; the conclusion cannot be inferred from the premises because there is a break in the logical connection between a claim and the premises that are meant to support it, either because a premise is untrue (or missing) or because the relationship between premises does not support the deduction stated in the claim.
Example (untrue premise): “If she is a Radford student, she is a member of a sorority. She is a Radford student. Therefore she is a member of a sorority.”
Smoke screen : avoiding the real issue or a tough question by introducing an unrelated topic as a distraction; sometimes called a red herring .
Example: “My opponent says I am weak on crime, but I have been one of the most reliable participants in city council meetings.”
Straw man: pretending to criticize an opponent’s position but actually misrepresenting his or her view as simpler and/or more extreme than it is and therefore easier to refute than the original or actual position; unfairly undermines credibility of claim if not source of claim.
Example: “Senator Smith says we should cut back the Defense budget. His position is that we should let down our defenses and just trust our enemies not to attack us!”

The red herring is as much a debate tactic as it is a logical fallacy. It is a fallacy of distraction, and is committed when a listener attempts to divert an arguer from his argument by introducing another topic. This can be one of the most frustrating, and effective, fallacies to observe.The fallacy gets its name from fox hunting, specifically from the practice of using smoked herrings, which are red, to distract hounds from the scent of their quarry. Just as a hound may be prevented from catching a fox by distracting it with a red herring, so an arguer may be prevented from proving his point by distracting him with a tangential issue.
Evaluate an Appeal to Pathos
People may be uninterested in an issue unless they can find a personal connection to it, so a communicator may try to connect to her audience by evoking emotions or by suggesting that author and audience share attitudes, beliefs, and values—in other words, by making an appeal to pathos . Even in formal writing, such as academic books or journals, an author often will try to present an issue in such a way as to connect to the feelings or attitudes of his audience.
When you evaluate pathos, you are asking whether a speech or essay arouses the audience’s interest and sympathy. You are looking for the elements of the essay or speech that might cause the audience to feel (or not feel) an emotional connection to the content.
An author may use an audience’s attitudes, beliefs, or values as a kind of foundation for his argument—a layer that the writer knows is already in place at the outset of the argument. So one of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s use of pathos is whether there are points at which the writer or speaker makes statements assuming that the audience shares his feelings or attitudes. For example, in an argument about the First Amendment, does the author write as if he takes it for granted that his audience is religious?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Pathos
Up to a certain point, an appeal to pathos can be a legitimate part of an argument. For example, a writer or speaker may begin with an anecdote showing the effect of a law on an individual. This anecdote will be a means of gaining an audience’s attention for an argument in which she uses evidence and reason to present her full case as to why the law should/should not be repealed or amended. In such a context, engaging the emotions, values, or beliefs of the audience is a legitimate tool whose effective use should lead you to give the author high marks.
An appropriate appeal to pathos is different than trying to unfairly play upon the audience’s feelings and emotions through fallacious, misleading, or excessively emotional appeals. Such a manipulative use of pathos may alienate the audience or cause them to “tune out”. An example would be the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) commercials featuring the song “ In the Arms on an Angel ” and footage of abused animals. Even Sarah McLachlan, the singer and spokesperson featured in the commercials admits that she changes the channel because they are too depressing (Brekke, 2014).
Even if an appeal to pathos is not manipulative, such an appeal should complement rather than replace reason and evidence-based argument. In addition to making use of pathos, the author must establish her credibility ( ethos ) and must supply reasons and evidence ( logos ) in support of her position. An author who essentially replaces logos and ethos with pathos alone should be given low marks.
See below for the most common fallacies that misuse appeals to pathos.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Pathos
Appeal to fear: using scare tactics; emphasizing threats or exaggerating possible dangers.
Example: “Without this additional insurance, you could find yourself broke and homeless.”
Appeal to guilt and appeal to pity : trying to evoke an emotional reaction that will cause the audience to behave sympathetically even if it means disregarding the issue at hand.
Example: “I know I missed assignments, but if you fail me, I will lose my financial aid and have to drop out.”
Appeal to popularity (bandwagon): urging audience to follow a course of action because “everyone does it.”
Example: “Nine out of ten shoppers have switched to Blindingly-Bright-Smile Toothpaste.”
Slippery Slope: making an unsupported or inadequately supported claim that “One thing inevitably leads to another.” This may be considered a fallacy of logos as well as pathos but is placed in this section because it often is used to evoke the emotion of fear.
Example: “We can’t legalize marijuana; if we do, then the next thing you know people will be strung out on heroin.”
Appeal to the people: also called stirring symbols fallacy; the communicator distracts the readers or listeners with symbols that are very meaningful to them, with strong associations or connotations.
Example: This fallacy is referred to in the sentence “That politician always wraps himself in the flag.”
Appeal to tradition: people have been done it a certain way for a long time; assumes that what has been customary in past is correct and proper.
Example: “A boy always serves as student-body president; a girl always serves as secretary.”
Loaded-Language and other emotionally charged uses of language: using slanted or biased language, including God terms, devil terms, euphemisms, and dysphemisms.
Example: In the sentence “Cutting access to food stamps would encourage personal responsibility,” the god term is “personal responsibility.” It might seem as if it would be hard to argue against “personal responsibility” or related god terms such as “independence” and “self-reliance.” However, it would require a definition of “personal responsibility,” combined with evidence from studies of people’s behavior in the face of food stamp or other benefit reductions, to argue that cutting access to food stamps would lead to the intended results.

Here is an example of a common logical fallacy known as the ad hominem argument , which is Latin for “argument against the person” or “argument toward the person.” Basically, an ad hominem argument goes like this: Person 1 makes claim X. There is something objectionable about Person 1. Therefore claim X is false.
Fallacies can crop up whenever definitions, inferences, and facts are at issue. Once we become familiar with fallacies we may start to see them everywhere. That can be good and bad. Since persuasion is ever-present, it is good to be on guard against various hidden persuaders. But whether a persuasive strategy is considered fallacious may be dependent on context. Editorials and advertisements—both political and commercial—frequently use such strategies as transfer and appeals to popularity. We need to be critically aware of the techniques of persuasion being used on us, but since we expect advertisements, political speeches, and editorials on public policy or ethical issues to try to sway us emotionally, perhaps only extreme examples deserve to be judged harshly for being fallacious.
In addition, something that looks as if it is a fallacy may turn out not to be on closer examination. For example, not everything that smacks of slippery slope is fallacious. There are indeed some genuine slippery slopes, where an initial decision or action may have both great and inevitable repercussions. So whether that fallacy has been committed depends upon what the author has done (or failed to do) to support his claim. Similarly, while personal attacks ( ad hominem ) in most cases are unfair and considered fallacious, there are special situations in which a person’s character may be directly relevant to his or her qualifications. For example, when somebody is running for political office or for a judgeship, casting doubt on his or her character may be appropriate— if one has facts to back it up—since it relates to job expectations. But wholesale character assassination remains a rhetorical ploy of the propagandist or demagogue.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of Red Herring. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/81M6vG . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of Argument from Authority. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7WGuwA . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of the Ad Hominem. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7W4WMp . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- The Logical Structure of Arguments. Provided by : Radford University. Located at : http://lcubbison.pressbooks.com/chapter/core-201-analyzing-arguments/ . Project : Core Curriculum Handbook. License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
III. Rhetorical Situation
3.5 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
Melanie Gagich; Emilie Zickel; and Terri Pantuso
Rhetoric, as the previous sections have discussed, is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints, or perhaps freedom of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text.
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals which are the three ways to classify an author’s intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to react in the manner in which the author may have intended.
Rhetorical Appeals
In composition studies, the term rhetorical appeals refers to the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms dating back to Aristotle who is traditionally viewed as the creator of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the intended outcome is achieved. Often that outcome occurs when the audience agrees with the argument or point being presented. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective.
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. Objective evidence is anything that can be proven with statistics or other facts via more than one source. Oftentimes that evidence has been validated by more than one authority in the field of study.
For example, if Dr. Smith was trying to convince her students to complete their homework, she might explain that she understands everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but that completing their homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). She could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence). This is an example of logos employed for the purposes of argument and persuasion.
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as:
- Comparison: a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic) and another, similar thing to help support your claim. It is important that the comparison is fair and valid – the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking: you argue that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim. Be careful with the latter – it can be difficult to predict that something “will” happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning: starting with a broad, general claim/example and using it to support a more specific point or claim (picture an hourglass where the sands gather in the middle)
- Inductive reasoning: using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization (consider the old question of “if your friend jumped off of a bridge, would you” to make the sweeping claim that all young people are easily persuaded to follow the crowd)
- Analogical reasoning: moves from one particular claim/example to another, seemingly sequential (sometimes this line of reasoning is used to make a guilt by association claim)
- Exemplification: use of many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration: moving beyond just including a fact, but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought: maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim. An author using pathos appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies, or sad-looking kittens, and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money. This is a classic example of the use of pathos in argument.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic, the argument, or to the author through an emotional connection. Emotions can make us vulnerable and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathos appeals might include:
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Sharing personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Using emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (what is the author trying to make the audience feel? and how are they doing that?)
- Using any information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience. This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed, or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text, try to locate where the author is trying to convince the reader by strictly using emotions because, if used to excess, pathos appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. If the only way in which an author can persuade the reader is by making him/her sad or angry, does that make for a solid, valid argument?
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Appeals using ethos are typically two faceted focusing on audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds. Examples include patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about as a way to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument ). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos, the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school thirty years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics than your cousin. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., Because I have experience with this topic – and I know my stuff! – you should trust what I am saying about this topic ). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
Character is another aspect of ethos that is different from credibility because it involves personal history and sometimes personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates – those who might be the most credible candidates – fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that they can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author get the audience to trust him or her so that they will accept their argument? How can the author make himself or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values?
In building ethical appeals, we may see authors:
- Referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker)
- Using language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker)
- Referring to their experience and/or authority with the topic (and therefore demonstrating their credibility)
- Referring to their own character, or making an effort to build their character in the text
When reading, you should always think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
When Writers Misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, Arguments can be Weakened
Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. When that happens, arguments can be weakened.
Using a social media platform, find a topic that is trending for today and create an argument using ethos, pathos, and logos for that topic.
This section contains material from:
Gagich, Melanie and Emilie Zickel. “Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined.” In A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing , by Melanie Gagich and Emilie Zickel. Cleveland: MSL Academic Endeavors. Accessed July 2019. https://pressbooks.ulib.csuohio.edu/csu-fyw-rhetoric/chapter/rhetorical-strategies-building-compelling-arguments/ Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
Logical, reasonable, or sensible; having good sense; to be sane or lucid; usually refers to a state of mind.
Sequence; the order in which things occur.
3.5 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined Copyright © 2022 by Melanie Gagich; Emilie Zickel; and Terri Pantuso is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Ethos Definition
What is ethos? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
Ethos , along with logos and pathos , is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience relevant to a particular topic, anything the speaker says or does to ensure that the audience knows about and remembers these qualifications is an example of ethos .
Some additional key details about ethos:
- Ethos shares a root with the word "ethics ." This is helpful to remember because speakers often try to establish their own strong moral character by using ethos.
- The word "ethos" is also often used to refer to a community or organization's characteristic belief or spirit, as in the sentence, "We will not give you a larger bonus than your coworkers: that is against our company's ethos of fairness." However, this guide focuses specifically on the rhetorical technique of ethos used in literature and public speaking.
- The three "modes of persuasion"— pathos , logos , and ethos —were originally defined by Aristotle.
- While ethos appeals to an audience's instinctive respect for authority, logos appeals to the audience's sense of reason, and pathos appeals to the audience's emotions.
- Ethos is used in advertising just as often as it is used in public speaking and literature. Any commercial in which a celebrity endorses a product, for example, hopes to persuade its target audience by cultivating an aura of authority or expertise through its association with the celebrity—and is therefore an example of ethos.
How to Pronounce Ethos
Here's how to pronounce ethos: ee -thos
Ethos Explained
Aristotle (the ancient Greek philosopher and scientist) first defined e thos , along with logos and pathos , in his treatise on rhetoric, Ars Rhetorica. Together, he referred to e thos , logos , and pathos as the three modes of persuasion, or sometimes simply as "the appeals." Aristotle believed that in order to have ethos a good speaker must demonstrate three things:
- Phronesis : Sound reasoning, and relevant experience or expertise.
- Arete : Moral character.
- Eunoia : Good intentions towards the audience.
Aristotle argued that a speaker in possession of these three attributes will naturally impress the audience with his or her ethos , and as a result will be better able to influence that audience. Over time, however, the definition of ethos has broadened, and the significance of the three qualities Aristotle named is now lost on anyone who hasn't studied classical Greek. So it may give more insight into the meaning of ethos to translate Aristotle's three categories into a new set of categories that make more sense in the modern era. A speaker or writer's credibility can be said to rely on each of the following:
- Within literature, it's interesting to notice when characters attempt to invoke their own authority and enhance their ethos by reminding other characters of the titles they possess. Often, this can be an indication that the character citing his or her own credentials actually feels his or her authority being threatened or challenged.
- In literature, this form of ethos is particularly relevant with respect to narrators. Authors often have their narrators profess impartiality or objectivity at the outset of a book in order to earn the reader's trust in the narrator's reliability regarding the story he or she is about to tell.
- This type of ethos translates into literature quite easily, in the sense that characters' opinions are often evaluated within the framework of their professions.
- Literary characters often use ethos to communicate similarity or likemindedness to other characters, and you can detect this by certain changes in their speech. In these situations, characters (as well as real-life speakers) often use a shibboleth— a specialized term or word used by a specific group of people—to show that they belong. For example, if you knew the name of a special chemical used to make jello, and you wanted to impress the head of a jello company, the name of that chemical would count as a shibboleth and saying it would help you show the jello executive that you're "in the know."
The Stagecraft of Ethos
In order to impress their positive personal qualities upon audiences, public speakers can use certain techniques that aren't available to writers. These include:
- Speaking in a certain manner or even with a certain accent.
- Demonstrating confident stage presence.
- Having reputable people to introduce the speaker in a positive light.
- Listing their credentials and achievements.
Put another way, the ethos of a speech can be heavily impacted by the speaker's confidence and manner of presenting him or herself.
Ethos and Ad Hominem
An ad hominem argument is a specific type of argument which involves attacking someone else's character or ethos, rather than attacking that person's position or point of view on the subject being discussed. Ad hominem attacks usually have the goal of swaying an audience away from an opponent's views and towards one's own by degrading the audience's perception of the opponent's character. For instance, if one politician attacks another as being "elite," the attacker may be seeking to make voters question whether the other politician is trustworthy or actually has the public's interest at heart. But the first politician is not in any way attacking their opponent's positions on matters of policy.
An ad hominem argument is not necessarily "wrong" or even a bad strategy, but it's generally seen as more dignified (another component of ethos ) for speakers to focus on strengthening their own ethos, and to debate their opponents based on the substance of the opposition's counterarguments. When a literary character uses an ad hominem argument, this can sometimes indicate that he or she is insecure about his or her own position regarding a certain issue.
Ethos Examples
Examples of ethos in literature.
Characters in novels often use ethos , as well as logos and pathos , to convince one another of certain arguments in the same way that a speaker in reality might use these techniques. In addition, authors often use a subtler form of ethos when establishing a narrator's reliability at the outset of a novel.
Ethos in Ayn Rand's Atlas Shrugged
In Atlas Shrugged, a group of pioneering American industrialists, financiers, and artists go on strike against a corrupt government. As the strike nears its end, its leader—John Galt—delivers a speech to the nation about his ideals. He promises that the strike will end only if Americans allow him to remake the country according to his moral code, which he explains in the following lines:
Just as I support my life, neither by robbery nor alms, but by my own effort, so I do not seek to derive my happiness from the injury or the favor of others, but earn it by my own achievement. Just as I do not consider the pleasure of others as the goal of my life, so I do not consider my pleasure as the goal of the lives of others. Just as there are no contradictions in my values and no conflicts among my desires—so there are no victims and no conflicts of interest among rational men, men who do not desire the unearned and do not view one another with a cannibal's lust, men who neither make sacrifices nor accept them.
Galt not only creates an impression of moral rectitude, but also emphasizes his own self-sufficiency. He assures his audience that he expects nothing in return from them for sharing his personal views. In this way, his ability to cultivate an aura of impartiality and objectivity enhances his ethos.
Ethos in Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter
The Scarlet Letter opens with a chapter called "The Custom-House," in which the unnamed narrator—who has a similar biography to Hawthorne—describes his job in a Custom House, a place where taxes were paid on imports in 18th century Massachusetts. The narrator's stories about his job have no relation to the actual narrative of The Scarlet Letter, except that he finds the scarlet letter of the title in the Custom House attic. This discovery inspired him to research the life of the woman who wore the embroidered letter, and to tell her story. By presenting himself as someone who merely discovered, researched, and "edited" the story the reader is about to begin, the narrator effectively creates the impression that his is a reliable historical account, thereby strengthening his ethos.
It will be seen, likewise, that this Custom-House sketch has a certain propriety, of a kind always recognised in literature, as explaining how a large portion of the following pages came into my possession, and as offering proofs of the authenticity of a narrative therein contained. This, in fact—a desire to put myself in my true position as editor, or very little more, of the most prolix among the tales that make up my volume—this, and no other, is my true reason for assuming a personal relation with the public.
Ethos in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby
In the opening lines of The Great Gatsby , the narrator, Nick Carraway, claims that he has followed one piece of his father's advice throughout his life:
In my younger and more vulnerable years my father gave me some advice that I've been turning over in my mind ever since. 'Whenever you feel like criticizing any one,' he told me, just remember that all the people in this world haven't had the advantages that you've had.'... In consequence I'm inclined to reserve all judgements, a habit that has opened up many curious natures to me and also made me the victim of not a few veteran bores. The abnormal mind is quick to detect and attach itself to this quality when it appears in a normal person, and so it came about that in college I was unjustly accused of being a politician, because I was privy to the secret griefs of wild, unknown men...
Nick's tendency to reserve judgement makes him an ideal, objective narrator, while his awareness of his own economic and social advantages makes him a perfect guide to the privileged world of The Great Gatsby. Though he describes his non-judgmental, "neutral" affect with self-deprecating humor, it's a subtle way of strengthening his ethos as a narrator, and of causing the reader to eagerly anticipate hearing the stories that "wild, unknown men" have shared with him.
Examples of Ethos in Political Speeches
Every politician recognizes that a speaker must earn an audience's respect and trust if he or she expects to be listened to. As a result, it's difficult to find a political speech that doesn't contain an example of ethos. It's particularly easy to spot ethos in action when listening to speeches by candidates for office.
Ethos in Mitt Romney's Acceptance Speech at the 2012 Republican National Convention
When he accepted the Republican presidential nomination in 2012, Romney pointed to his business success as relevant experience that would serve him well if he were to take office:
I learned the real lessons about how America works from experience. When I was 37, I helped start a small company. My partners and I had been working for a company that was in the business of helping other businesses. So some of us had this idea that if we really believed our advice was helping companies, we should invest in companies. We should bet on ourselves and on our advice. So we started a new business called Bain Capital...That business we started with 10 people has now grown into a great American success story. Some of the companies we helped start are names you know. An office supply company called Staples – where I'm pleased to see the Obama campaign has been shopping; The Sports Authority, which became a favorite of my sons. We started an early childhood learning center called Bright Horizons that First Lady Michelle Obama rightly praised.
In addition to strengthening his ethos by pointing to his past achievements, Romney also hopes to portray himself as principled, rational, and daring when he explains how his company decided to "bet on ourselves and on our advice."
Ethos in John Kasich's 2016 Ohio Primary Victory Speech
After winning his first campaign victory, 2016 presidential candidate John Kasich told his supporters about his disadvantaged yet hardworking relatives to contextualize his own rise to success:
And you know, ladies and gentlemen, my whole life has been about trying to create a climate of opportunity for people. You know, as my father carried that mail on his back and his father was a coal miner, and you know, I was just told by my cousin—I didn't realize this—that my mother, one of four [children]‚ was the only one to graduate from high school. The other three barely made it out of the eighth grade because they were poor... And you know, as I've traveled the country and I look into your eyes... You want to believe that your children are going to have ultimately a better America than what we got from our mothers and fathers. That's the great American legacy: that our kids will be better than we are.
By saying that he comes from a modest background, Kasich hopes to convey that he is "just a regular American" and that he will advocate for other hard working Americans.
Ethos in Winston Churchill's 1941 Address to Joint Session of the US Congress
In this speech to the US Congress during World War II, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill enhances the ethos of his speech by emphasizing both the qualities he shares in common with the American people and the American Democratic values instilled in him by his parents:
I am a child of the House of Commons. I was brought up in my father's house to believe in democracy. "Trust the people." That was his message. I used to see him cheered at meetings and in the streets by crowds of workingmen way back in those aristocratic Victorian days when as Disraeli said "the world was for the few, and for the very few." Therefore I have been in full harmony all my life with the tides which have flowed on both sides of the Atlantic against privilege and monopoly and I have steered confidently towards the Gettysburg ideal of government of the people, by the people, for the people.
Examples of Ethos in Advertisements
Advertisers often attempt to use ethos to influence people to buy their product. Dressing up an actor as a doctor who then extols the benefits a medication is a way that advertisers used to try to gin up a little ethos , but such obvious practices of what might be called "fake ethos" are now regularly mocked. However, any celebrity endorsement or testimonial from an expert are also attempts to build up ethos around a product's endorsement. For instance, here's a Prudential Financial commercial that ups its ethos with an appearance by Harvard social psychologist Dan Gilbert.

Why Do Writers Use Ethos?
Politicians, activists, and advertisers use ethos because they recognize that it is impossible to convince an audience of anything if its members do not believe in the speaker's credibility, morality, or authority.
The use of e thos in fiction is often different from real-world examples. Authors are not usually trying to directly influence their audience in the way politicians or advertisers are. Rather, authors often show one of their characters making use of ethos . In doing so, the author gives insight into characters' perceptions of one another, their values, and their motives.
In addition, e thos is an especially useful tool for authors looking to establish a narrator's credibility. Having a credible narrator is hugely important to the success of a literary work. Books with narrators that never establish a reasonable claim to an objective viewpoint are nearly impossible to read because everything they say is cast in doubt, so that readers come to feel like they're being lied to or "jerked around," which is fatiguing. Although often enough readers simply assume that a narrator has credibility , if you've ever read a book where you felt you simply didn't like the narrator very much—or watched a television show where you felt that none of the characters were likable or believable—that might be another sign that the writer has failed to establish a character's ethos . There are circumstances in which a writer creates an unreliable narrator —a narrator who is either purposefully or subconsciously offering a slanted narrative—but ethos is just as crucial in creating such a narrator: the author must first establish the narrator's ethos and then slowly undermine it over the course of the book.
Other Helpful Ethos Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Ethos: An in-depth explanation of ethos , and how the concept has changed over time.
- The Dictionary Definition of Ethos: A definition and etymology of the term, which comes from the Greek ethos meaning "character, custom, or habit."
- Ethos on Youtube: An excellent video from TED-Ed about the three modes of persuasion.

- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1919 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,460 quotes across 1919 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
- Common Meter
- Tragic Hero
- Rhyme Scheme
- Antanaclasis
- Formal Verse
- Climax (Figure of Speech)
- Dramatic Irony
- Blank Verse
- Pathetic Fallacy

What Are Logos, Pathos & Ethos?
A straight-forward explainer (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | June 2023
If you spend any amount of time exploring the wonderful world of philosophy, you’re bound to run into the dynamic trio of rhetorical appeals: logos , ethos and pathos . But, what exactly do they mean and how can you use them in your writing or speaking? In this post, we’ll unpack the rhetorical love triangle in simple terms, using loads of practical examples along the way.
Overview: The Rhetorical Triangle
- What are logos , pathos and ethos ?
- Logos unpacked (+ examples)
- Pathos unpacked (+ examples)
- Ethos unpacked (+ examples)
- The rhetorical triangle
What are logos, ethos and pathos?
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument . At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority.
Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but it’s important to consider a few different factors to determine the best mix for any given context. Let’s look at each rhetorical appeal in a little more detail to understand how best to use them to your advantage.

Logos appeals to the logical, reason-driven side of our minds. Using logos in an argument typically means presenting a strong body of evidence and facts to support your position. This evidence should then be accompanied by sound logic and well-articulated reasoning .
Let’s look at some examples of logos in action:
- A friend trying to persuade you to eat healthier might present scientific studies that show the benefits of a balanced diet and explain how certain nutrients contribute to overall health and longevity.
- A scientist giving a presentation on climate change might use data from reputable studies, along with well-presented graphs and statistical analyses to demonstrate the rising global temperatures and their impact on the environment.
- An advertisement for a new smartphone might highlight its technological features, such as a faster processor, longer battery life, and a high-resolution camera. This could also be accompanied by technical specifications and comparisons with competitors’ models.
In short, logos is all about using evidence , logic and reason to build a strong argument that will win over an audience on the basis of its objective merit . This contrasts quite sharply against pathos, which we’ll look at next.

Contrasted to logos, pathos appeals to the softer side of us mushy humans. Specifically, it focuses on evoking feelings and emotions in the audience. When utilising pathos in an argument, the aim is to cultivate some feeling of connection in the audience toward either yourself or the point that you’re trying to make.
In practical terms, pathos often uses storytelling , vivid language and personal anecdotes to tap into the audience’s emotions. Unlike logos, the focus here is not on facts and figures, but rather on psychological affect . Simply put, pathos utilises our shared humanness to foster agreement.
Let’s look at some examples of pathos in action:
- An advertisement for a charity might incorporate images of starving children and highlight their desperate living conditions to evoke sympathy, compassion and, ultimately, donations.
- A politician on the campaign trail might appeal to feelings of hope, unity, and patriotism to rally supporters and motivate them to vote for his or her party.
- A fundraising event may include a heartfelt personal story shared by a cancer survivor, with the aim of evoking empathy and encouraging donations to support cancer research.
As you can see, pathos is all about appealing to the human side of us – playing on our emotions to create buy-in and agreement.

Last but not least, we’ve got ethos. Ethos is all about emphasising the credibility and authority of the person making the argument, or leveraging off of someone else’s credibility to support your own argument.
The ethos card can be played by highlighting expertise, achievements, qualifications and accreditations , or even personal and professional associations and connections. Ultimately, the aim here is to foster some level of trust within the audience by demonstrating your competence, as this will make them more likely to take your word as fact.
Let’s look at some examples of ethos in action:
- A fitness equipment brand might hire a well-known athlete to endorse their product.
- A toothpaste brand might make claims highlighting that a large percentage of dentists recommend their product.
- A financial advisor might present their qualifications, certifications and professional memberships when meeting with a prospective client.
As you can see, using ethos in an argument is largely about emphasising the credibility of the person rather than the logical soundness of the argument itself (which would reflect a logos-based approach). This is particularly helpful when there isn’t a large body of evidence to support the argument.
Ethos can also overlap somewhat with pathos in that positive emotions and feelings toward a specific person can oftentimes be extended to someone else’s argument. For example, a brand that has nothing to do with sports could still benefit from the endorsement of a well-loved athlete, just because people feel positive feelings about the athlete – not because of that athlete’s expertise in the product they’re endorsing.

How to use logos, pathos and ethos
Logos, pathos and ethos combine to form the rhetorical triangle , also known as the Aristotelian triangle. As you’d expect, the three sides (or corners) of the triangle reflect the three appeals, but there’s also another layer of meaning. Specifically, the three sides symbolise the relationship between the speaker , the audience and the message .
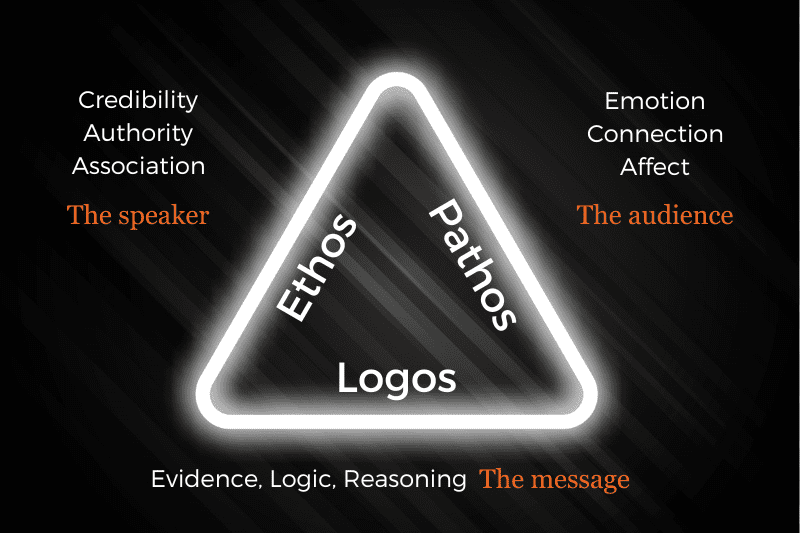
Without getting too philosophical, the key takeaway here is that logos, pathos and ethos are all tools that you can use to present a persuasive argument . However, how much you use each tool needs to be informed by careful consideration of who your audience is and what message you’re trying to convey to them.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a largely scientific audience, you’ll likely lean more heavily on the logos . Conversely, if you’re presenting a speech in which you argue for greater social justice, you may lean more heavily on the pathos to win over the hearts and minds of your audience.
Simply put, by understanding the relationship between yourself (as the person making the argument), your audience , and your message , you can strategically employ the three rhetorical appeals to persuade, engage, and connect with your audience more effectively in any context. Use these tools wisely and you’ll quickly notice what a difference they can make to your ability to communicate and more importantly, to persuade .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6 Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined
By melanie gagich and emilie zickel.
Rhetoric is the way that authors use and manipulate language in order to persuade an audience. Once we understand the rhetorical situation out of which a text is created (why it was written, for whom it was written, by whom it was written, how the medium in which it was written creates certain constraints or perhaps freedoms of expression), we can look at how all of those contextual elements shape the author’s creation of the text .
We can look first at the classical rhetorical appeals, which are the three ways to classify authors’ intellectual, moral, and emotional approaches to getting the audience to have the reaction that the author hopes for.
Rhetorical Appeals
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft their argument so that the outcome, audience agreement with the argument or point, is achieved. Aristotle defined these modes of engagement and gave them the terms that we still use today: logos, pathos, and ethos.
Logos: Appeal to Logic
Logic. Reason. Rationality. Logos is brainy and intellectual, cool, calm, collected, objective .
When an author relies on logos, it means that they are using logic, careful structure, and objective evidence to appeal to the audience. An author can appeal to an audience’s intellect by using information that can be fact checked (using multiple sources ) and thorough explanations to support key points. Additionally, providing a solid and non-biased explanation of one’s argument is a great way for an author to invoke logos.
For example, if I were trying to convince my students to complete their homework, I might explain that I understand everyone is busy and they have other classes (non-biased), but the homework will help them get a better grade on their test (explanation). I could add to this explanation by providing statistics showing the number of students who failed and didn’t complete their homework versus the number of students who passed and did complete their homework (factual evidence).
Logical appeals rest on rational modes of thinking , such as
- Comparison – including a comparison between one thing (with regard to your topic ) and another similar thing to help support your claim . It is important that the comparison is fair and valid–the things being compared must share significant traits of similarity.
- Cause/effect thinking – arguing that X has caused Y, or that X is likely to cause Y to help support your claim . Be careful with the latter–it can be difficult to predict that something will happen in the future.
- Deductive reasoning – starting with a broad, general claim /example and using it to support a more specific point or claim
- Inductive reasoning – using several specific examples or cases to make a broad generalization
- Exemplification – using many examples or a variety of evidence to support a single point
- Elaboration – moving beyond just including a fact but explaining the significance or relevance of that fact
- Coherent thought – maintaining a well-organized line of reasoning; not repeating ideas or jumping around
Pathos: Appeal to Emotions
When an author relies on pathos, it means that they are trying to tap into the audience’s emotions to get them to agree with the author’s claim . An author using pathetic appeals wants the audience to feel something: anger, pride, joy, rage, or happiness. For example, many of us have seen the ASPCA commercials that use photographs of injured puppies or sad-looking kittens and slow, depressing music to emotionally persuade their audience to donate money.
Pathos-based rhetorical strategies are any strategies that get the audience to “open up” to the topic , the argument, or the author. Emotions can make us vulnerable, and an author can use this vulnerability to get the audience to believe that their argument is a compelling one.
Pathetic appeals might include
- Expressive descriptions of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel or experience those events
- Vivid imagery of people, places, or events that help the reader to feel like they are seeing those events
- Personal stories that make the reader feel a connection to, or empathy for, the person being described
- Emotion-laden vocabulary as a way to put the reader into that specific emotional mindset (What is the author trying to make the audience feel? And how are they doing that?)
- Information that will evoke an emotional response from the audience . This could involve making the audience feel empathy or disgust for the person/group/event being discussed or perhaps connection to or rejection of the person/group/event being discussed.
When reading a text , try to locate when the author is trying to convince the reader using emotions because, if used to excess, pathetic appeals can indicate a lack of substance or emotional manipulation of the audience. See the links below about fallacious pathos for more information.
Ethos: Appeal to Values/Trust
Ethical appeals have two facets: audience values and authorial credibility/character.
On the one hand, when an author makes an ethical appeal, they are attempting to tap into the values or ideologies that the audience holds , for example, patriotism, tradition, justice, equality, dignity for all humankind, self-preservation, or other specific social, religious or philosophical values (Christian values, socialism, capitalism, feminism, etc.). These values can sometimes feel very close to emotions, but they are felt on a social level rather than only on a personal level. When an author evokes the values that the audience cares about to justify or support their argument, we classify that as ethos. The audience will feel that the author is making an argument that is “right” (in the sense of moral “right”-ness, i.e., “My argument rests upon the values that matter to you. Therefore, you should accept my argument”). This first part of the definition of ethos, then, is focused on the audience’s values.
On the other hand, this sense of referencing what is “right” in an ethical appeal connects to the other sense of ethos: the author. Ethos that is centered on the author revolves around two concepts: the credibility of the author and their character.
- Credibility of the speaker/author is determined by their knowledge and expertise in the subject at hand. For example, if you are learning about Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, would you rather learn from a professor of physics or a cousin who took two science classes in high school 30 years ago? It is fair to say that, in general, the professor of physics would have more credibility to discuss the topic of physics. To establish their credibility, an author may draw attention to who they are or what kinds of experience they have with the topic being discussed as an ethical appeal (i.e., “Because I have experience with this topic –and I know my stuff– you should trust what I am saying about this topic ”). Some authors do not have to establish their credibility because the audience already knows who they are and that they are credible.
- Character is another aspect of ethos. Character is different from credibility because it involves personal history and even personality traits. A person can be credible but lack character or vice versa. For example, in politics, sometimes the most experienced candidates–those who might be the most credible candidates–fail to win elections because voters do not accept their character. Politicians take pains to shape their character as leaders who have the interests of the voters at heart. The candidate who successfully proves to the voters (the audience) that they have the type of character that the audience can trust is more likely to win.
Thus, ethos comes down to trust. How can the author gain the audience’s trust so that the audience will accept their argument? How can the author make him or herself appear as a credible speaker who embodies the character traits that the audience values? In building ethical appeals, we see authors referring either directly or indirectly to the values that matter to the intended audience (so that the audience will trust the speaker). Authors use language, phrasing, imagery, or other writing styles common to people who hold those values, thereby “talking the talk” of people with those values (again, so that the audience is inclined to trust the speaker). Authors refer to their experience and/or authority with the topic as well (and therefore demonstrate their credibility).
When reading, you should think about the author’s credibility regarding the subject as well as their character. Here is an example of a rhetorical move that connects with ethos: when reading an article about abortion, the author mentions that she has had an abortion. That is an example of an ethical move because the author is creating credibility via anecdotal evidence and first-person narrative. In a rhetorical analysis project, it would be up to you, the analyzer, to point out this move and associate it with a rhetorical strategy.
Rhetorical Appeals Misuse
When writers misuse logos, pathos, or ethos, arguments can be weakened. Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument. It is important to understand, though, that using rhetorical appeals does not always lead to a sound, balanced argument. In fact, any of the appeals could be misused or overused. And when that happens, arguments can be weakened.
To see what a misuse of logical appeals might consist of, see Logical Fallacies.
To see how authors can overuse emotional appeals and turn-off their target audience, visit the following link from WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Pathos .
To see how ethos can be misused or used in a manner that may be misleading, visit the following link to WritingCommons.org : Fallacious Ethos
Attributions
“Rhetorical Appeals: Logos, Pathos, and Ethos Defined” by Melanie Gagich, Emilie Zickel is licensed under CC BY-NC SA 4.0
Writing Arguments in STEM Copyright © by Jason Peters; Jennifer Bates; Erin Martin-Elston; Sadie Johann; Rebekah Maples; Anne Regan; and Morgan White is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Using Rhetorical Strategies for Persuasion

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case.
Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or deductive reasoning.
Inductive reasoning takes a specific representative case or facts and then draws generalizations or conclusions from them. Inductive reasoning must be based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence. In other words, the facts you draw on must fairly represent the larger situation or population. Example:
In this example the specific case of fair trade agreements with coffee producers is being used as the starting point for the claim. Because these agreements have worked the author concludes that it could work for other farmers as well.
Deductive reasoning begins with a generalization and then applies it to a specific case. The generalization you start with must have been based on a sufficient amount of reliable evidence.Example:
In this example the author starts with a large claim, that genetically modified seeds have been problematic everywhere, and from this draws the more localized or specific conclusion that Mexico will be affected in the same way.
Avoid Logical Fallacies
These are some common errors in reasoning that will undermine the logic of your argument. Also, watch out for these slips in other people's arguments.
Slippery slope: This is a conclusion based on the premise that if A happens, then eventually through a series of small steps, through B, C,..., X, Y, Z will happen, too, basically equating A and Z. So, if we don't want Z to occur A must not be allowed to occur either. Example:
In this example the author is equating banning Hummers with banning all cars, which is not the same thing.
Hasty Generalization: This is a conclusion based on insufficient or biased evidence. In other words, you are rushing to a conclusion before you have all the relevant facts. Example:
In this example the author is basing their evaluation of the entire course on only one class, and on the first day which is notoriously boring and full of housekeeping tasks for most courses. To make a fair and reasonable evaluation the author must attend several classes, and possibly even examine the textbook, talk to the professor, or talk to others who have previously finished the course in order to have sufficient evidence to base a conclusion on.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: This is a conclusion that assumes that if 'A' occurred after 'B' then 'B' must have caused 'A.' Example:
In this example the author assumes that if one event chronologically follows another the first event must have caused the second. But the illness could have been caused by the burrito the night before, a flu bug that had been working on the body for days, or a chemical spill across campus. There is no reason, without more evidence, to assume the water caused the person to be sick.
Genetic Fallacy: A conclusion is based on an argument that the origins of a person, idea, institute, or theory determine its character, nature, or worth. Example:
In this example the author is equating the character of a car with the character of the people who built the car.
Begging the Claim: The conclusion that the writer should prove is validated within the claim. Example:
Arguing that coal pollutes the earth and thus should be banned would be logical. But the very conclusion that should be proved, that coal causes enough pollution to warrant banning its use, is already assumed in the claim by referring to it as "filthy and polluting."
Circular Argument: This restates the argument rather than actually proving it. Example:
In this example the conclusion that Bush is a "good communicator" and the evidence used to prove it "he speaks effectively" are basically the same idea. Specific evidence such as using everyday language, breaking down complex problems, or illustrating his points with humorous stories would be needed to prove either half of the sentence.
Either/or: This is a conclusion that oversimplifies the argument by reducing it to only two sides or choices. Example:
In this example where two choices are presented as the only options, yet the author ignores a range of choices in between such as developing cleaner technology, car sharing systems for necessities and emergencies, or better community planning to discourage daily driving.
Ad hominem: This is an attack on the character of a person rather than their opinions or arguments. Example:
In this example the author doesn't even name particular strategies Green Peace has suggested, much less evaluate those strategies on their merits. Instead, the author attacks the characters of the individuals in the group.
Ad populum: This is an emotional appeal that speaks to positive (such as patriotism, religion, democracy) or negative (such as terrorism or fascism) concepts rather than the real issue at hand. Example:
In this example the author equates being a "true American," a concept that people want to be associated with, particularly in a time of war, with allowing people to buy any vehicle they want even though there is no inherent connection between the two.
Red Herring: This is a diversionary tactic that avoids the key issues, often by avoiding opposing arguments rather than addressing them. Example:
In this example the author switches the discussion away from the safety of the food and talks instead about an economic issue, the livelihood of those catching fish. While one issue may affect the other, it does not mean we should ignore possible safety issues because of possible economic consequences to a few individuals.
Ethos or the ethical appeal is based on the character, credibility, or reliability of the writer. There are many ways to establish good character and credibility as an author:
- Use only credible, reliable sources to build your argument and cite those sources properly.
- Respect the reader by stating the opposing position accurately.
- Establish common ground with your audience. Most of the time, this can be done by acknowledging values and beliefs shared by those on both sides of the argument.
- If appropriate for the assignment, disclose why you are interested in this topic or what personal experiences you have had with the topic.
- Organize your argument in a logical, easy to follow manner. You can use the Toulmin method of logic or a simple pattern such as chronological order, most general to most detailed example, earliest to most recent example, etc.
- Proofread the argument. Too many careless grammar mistakes cast doubt on your character as a writer.
Pathos , or emotional appeal, appeals to an audience's needs, values, and emotional sensibilities. Pathos can also be understood as an appeal to audience's disposition to a topic, evidence, or argument (especially appropriate to academic discourse).
Argument emphasizes reason, but used properly there is often a place for emotion as well. Emotional appeals can use sources such as interviews and individual stories to paint a more legitimate and moving picture of reality or illuminate the truth. For example, telling the story of a single child who has been abused may make for a more persuasive argument than simply the number of children abused each year because it would give a human face to the numbers. Academic arguments in particular benefit from understanding pathos as appealing to an audience's academic disposition.
Only use an emotional appeal if it truly supports the claim you are making, not as a way to distract from the real issues of debate. An argument should never use emotion to misrepresent the topic or frighten people.

What is Ethos? Definition, Examples of Ethos in Literature
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is Ethos? Definition, Examples of Ethos in Literature
Ethos definition: Ethos is a rhetorical device that includes any content in an argument that is meant to appeal to ethics.
What is Ethos? Ethos as a Literary Term
What does ethos mean? Ethos is one of the three Aristotelian appeals. Ethos refers to any element of an argument that is meant to appeal to an audience’s ethics or ethical responsibilities.
A writer utilizes the three appeals in order to convince his audience of his argument. The other two appeals are pathos (emotion) and logos (logic).
Appeals to ethos are those that involve or influence the ethical reasons an audience should believe an argument.

Ethos Examples in Writing
Examples of ethos in an argument in support of education reform that appeal to ethos might include:
- I have studied this topic for the past ten years.
- This is a national problem, one every citizen and every parent should find concerning.
The first example is reference to the speaker’s credibility; the second example is an appeal to the audience’s sense of ethical responsibility.

- The idea of building a large work force of full-time employees, outside of core disciplines like engineering, is not part of the ethos of most companies in today’s tech industry, observers who have studied the industry say.
In this example, the author is contrasting the company with that of its competitors. This company has a different set of ethos, a different set of ethics and priorities. This company, unlike others in the industry, value full-time employees outside of engineers. It is an attempt to set this company on an ethical high ground above its peers.
Ethos vs. Pathos vs. Logos

Each of these is used in an argument in order to convince an audience. The argument may be heavier in one appeal over another; however, a good argument will contain some of all three appeals.
Continuing the education reform argument from above, here are additional examples for demonstration:
- How can you look at these failing students and say nothing should be done about our education system?
- No average person would ignore this problem.
- Student SAT scores are the lowest they are in 40 years.
- Given these low test scores, we should rally our efforts to reform K-12 education.
The Purpose of Ethos in Writing

First and foremost, a speaker must convince his audience that he is someone they should believe. He does this through appeals to ethos. The speaker might not directly state his credits, but he should in some way present his authority to the audience. Some speakers have innate authority (like the President) and others have to prove it.
Furthermore, most people want to do the “right” thing. That is where ethos comes into play. Through appeals to ethos, a speaker will convince the audience that agreeing with his argument is “good” and “right.”
Examples of Ethos in Literature

“When in the Course of human events it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bands which have connected them with another and to assume among the powers of the earth, the separate and equal station to which the Laws of Nature and of Nature’s God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.”
These lines appeal to ethos especially in the last clause beginning with “a decent respect”. At the time of this document’s conception, it was the “right” thing for mankind to want to separate from the British Kingdom.
This document starts with these lines because the authors intend to convince the British Crown that their separation is a just and ethical obligation.
Summary: What Does Ethos Mean in Literature?
Define ethos in literature: the definition of ethos in literature is an argument based on the ethics or credibility of the person making the argument; an appeal to ethics.
To sum up, ethos is:
- one of the three Aristotelian appeals used in argument
- an appeal to ethics
- evident in an argument in statements of the speaker’s credibility or references to why the argument is “good” or “right”

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10.6: Evaluating Appeals to Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 175820
Introduction
As a reader and a listener, it is fundamental that you be able to recognize how writers and speakers depend upon ethos , logos , and pathos in their efforts to communicate. As a communicator yourself, you will benefit from being able to see how others rely upon ethos, logos, and pathos so that you can apply what you learn from your observations to your own speaking and writing.
Evaluate an Appeal to Ethos
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos , you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible.
A good speaker or writer leads the audience to feel comfortable with her knowledge of a topic. The audience sees her as someone worth listening to—a clear or insightful thinker, or at least someone who is well-informed and genuinely interested in the topic.
Some of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s ethos may include the following:
- Has the writer or speaker cited her sources or in some way made it possible for the audience to access further information on the issue?
- Does she demonstrate familiarity with different opinions and perspectives?
- Does she provide complete and accurate information about the issue?
- Does she use the evidence fairly? Does she avoid selective use of evidence or other types of manipulation of data?
- Does she speak respectfully about people who may have opinions and perspectives different from her own?
- Does she use unbiased language?
- Does she avoid excessive reliance on emotional appeals?
- Does she accurately convey the positions of people with whom she disagrees?
- Does she acknowledge that an issue may be complex or multifaceted?
- Does her education or experience give her credibility as someone who should be listened to on this issue?
Some of the above questions may strike you as relevant to an evaluation of logos as well as ethos—questions about the completeness and accuracy of information and whether it is used fairly. In fact, illogical thinking and the misuse of evidence may lead an audience to draw conclusions not only about the person making the argument but also about the logic of an argument.
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Ethos
In a perfect world, everyone would tell the truth and we could depend upon the credibility of speakers and authors. Unfortunately, that is not always the case. You would expect that news reporters would be objective and tell new stories based upon the facts. Janet Cooke, Stephen Glass, Jayson Blair, and Brian Williams all lost their jobs for plagiarizing or fabricated part of their news stories. Janet Cooke’s Pulitzer Prize was revoked after it was discovered that she made up “Jimmy,” an eight-year old heroin addict (Prince, 2010). Brian Williams was fired as anchor of the NBC Nightly News for exaggerating his role in the Iraq War.
Others have become infamous for claiming academic degrees that they didn’t earn as in the case of Marilee Jones. At the time of discovery, she was Dean of Admissions at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). After 28 years of employment, it was determined that she never graduated from college (Lewin, 2007). However, on her website ( http://www.marileejones.com ) she is still promoting herself as “a sought after speaker, consultant and author” (para. 1) and “one of the nation’s most experienced College Admissions Deans” (para. 2).
Beyond lying about their own credentials, authors may employ a number of tricks or fallacies to lure you to their point of view. Some of the more common techniques are described below. Others may be found in the appendix. When you recognize these fallacies being committed you should question the credibility of the speaker and the legitimacy of the argument. If you use these when making your own arguments, be aware that they may undermine or destroy your credibility.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Ethos
Ad hominem : attacking the person making an argument rather than the argument itself.
Example: “Of course that doctor advocates vaccination—he probably owns stock in a pharmaceutical company.”
False authority : relying on claims of expertise when the claimed expert (a) lacks adequate background/credentials in the relevant field, (b) departs in major ways from the consensus in the field, or (c) is biased, e.g., has a financial stake in the outcome.
Example: “Dr. X is an engineer, and he doesn’t believe in global warming.”
Guilt by association : linking the person making an argument to an unpopular person or group.
Example: “My opponent is a card-carrying member of the ACLU.”
Poisoning the well: undermining an opponent’s credibility before he or she gets a chance to speak.
Example: “The prosecution is going to bring up a series or so-called experts who are getting a lot of money to testify here today.”
Transfer fallacy : associating the argument with someone or something popular or respected; hoping that the positive associations will “rub off” onto the argument.
Examples: In politics, decorating a stage with red, white, and blue flags and bunting; in advertising, using pleasant or wholesome settings as the backdrop for print or video ads.
Name-calling : labeling an opponent with words that have negative connotations in an effort to undermine the opponent’s credibility.
Example: “These rabble-rousers are nothing but feminazis.”
Plain folk : presenting yourself as (or associating your position with) ordinary people with whom you hope your audience will identify; arguers imply that they or their supporters are trustworthy because they are ‘common people’ rather than members of the elite.
Example: “Who would you vote for—someone raised in a working-class neighborhood who has the support of Joe the Plumber or some elitist whose daddy sent him to a fancy school?”
Testimonial fallacy : inserting an endorsement of the argument by someone who is popular or respected but who lacks expertise or authority in the area under discussion.
Example: “I’m not a doctor, but I play one on TV”—a famous example of a celebrity endorsement for a cough syrup (Deis, 2011, n.p.).
Evaluate an Appeal to Logos
When you evaluate an appeal to logos , you consider how logical the argument is and how well-supported it is in terms of evidence. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to believe that the argument is (or is not) logical and supported by appropriate evidence.
To evaluate whether the evidence is appropriate, apply the STAR criteria: how S ufficient, T ypical, A ccurate, and R elevant is the evidence?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Logos
Diagramming the argument can help you determine if an appeal to logos is manipulative. Are the premises true? Does the conclusion follow logically from the premises? Is there sufficient, typical, accurate, and relevant evidence to support inductive reasoning? Is the speaker or author attempting to divert your attention from the real issues? These are some of the elements you might consider while evaluating an argument for the use of logos.
Pay particular attention to numbers, statistics, findings, and quotes used to support an argument. Be critical of the source and do your own investigation of the “facts.” Maybe you’ve heard or read that half of all marriages in America will end in divorce. It is so often discussed that we assume it must be true. Careful research will show that the original marriage study was flawed, and divorce rates in America have steadily declined since 1985 (Peck, 1993). If there is no scientific evidence, why do we continue to believe it? Part of the reason might be that it supports our idea of the dissolution of the American family.
Fallacies that misuse appeals to logos or attempt to manipulate the logic of an argument are discussed below. Other fallacies of logos may be found in the appendix.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Logos
Hasty generalization: jumping to conclusions based upon an unrepresentative sample or insufficient evidence.
Example: “10 of the last 14 National Spelling Bee Champions have been Indian American. Indian Americans must all be great spellers!”
Appeal to ignorance—true believer’s form: arguing along the lines that if an opponent can’t prove something isn’t the case, then it is reasonable to believe that it is the case; transfers the burden of proof away from the person making the claim (the proponent).
Example: “You can’t prove that extraterrestrials haven’t visited earth, so it is reasonable to believe that they have visited earth.”
Appeal to ignorance—skeptic’s form: confusing absence of evidence with evidence of absence; assumes that if you cannot now prove something exists, then it is shown that it doesn’t exist.
Example: “There’s no proof that starting classes later in the day will improve the performance of our high school students; therefore, this change in schedule will not work.”
Begging the question: circular argument because the premise is the same as the claim that you are trying to prove.
Example: “This legislation is sinful because it is the wrong thing to do.”
False dilemma: misuse of the either/or argument; presenting only two options when other choices exist
Example: “Either we pass this ordinance or there will be rioting in the streets.”
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: Latin phrase meaning “after this, therefore because of this”; confuses correlation with causation by concluding that an event preceding a second event must be the cause of that second event.
Example: “My child was diagnosed with autism after receiving vaccinations. That is proof that vaccines are to blame.”
Non-sequitur: Latin for “does not follow”; the conclusion cannot be inferred from the premises because there is a break in the logical connection between a claim and the premises that are meant to support it, either because a premise is untrue (or missing) or because the relationship between premises does not support the deduction stated in the claim.
Example (untrue premise): “If she is a Radford student, she is a member of a sorority. She is a Radford student. Therefore she is a member of a sorority.”
Smoke screen : avoiding the real issue or a tough question by introducing an unrelated topic as a distraction; sometimes called a red herring .
Example: “My opponent says I am weak on crime, but I have been one of the most reliable participants in city council meetings.”
Straw man: pretending to criticize an opponent’s position but actually misrepresenting his or her view as simpler and/or more extreme than it is and therefore easier to refute than the original or actual position; unfairly undermines credibility of claim if not source of claim.
Example: “Senator Smith says we should cut back the Defense budget. His position is that we should let down our defenses and just trust our enemies not to attack us!”
Evaluate an Appeal to Pathos
People may be uninterested in an issue unless they can find a personal connection to it, so a communicator may try to connect to her audience by evoking emotions or by suggesting that author and audience share attitudes, beliefs, and values—in other words, by making an appeal to pathos . Even in formal writing, such as academic books or journals, an author often will try to present an issue in such a way as to connect to the feelings or attitudes of his audience.
When you evaluate pathos, you are asking whether a speech or essay arouses the audience’s interest and sympathy. You are looking for the elements of the essay or speech that might cause the audience to feel (or not feel) an emotional connection to the content.
An author may use an audience’s attitudes, beliefs, or values as a kind of foundation for his argument—a layer that the writer knows is already in place at the outset of the argument. So one of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s use of pathos is whether there are points at which the writer or speaker makes statements assuming that the audience shares his feelings or attitudes. For example, in an argument about the First Amendment, does the author write as if he takes it for granted that his audience is religious?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Pathos
Up to a certain point, an appeal to pathos can be a legitimate part of an argument. For example, a writer or speaker may begin with an anecdote showing the effect of a law on an individual. This anecdote will be a means of gaining an audience’s attention for an argument in which she uses evidence and reason to present her full case as to why the law should/should not be repealed or amended. In such a context, engaging the emotions, values, or beliefs of the audience is a legitimate tool whose effective use should lead you to give the author high marks.
An appropriate appeal to pathos is different than trying to unfairly play upon the audience’s feelings and emotions through fallacious, misleading, or excessively emotional appeals. Such a manipulative use of pathos may alienate the audience or cause them to “tune out”. An example would be the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) commercials featuring the song “ In the Arms on an Angel ” and footage of abused animals. Even Sarah McLachlan, the singer and spokesperson featured in the commercials admits that she changes the channel because they are too depressing (Brekke, 2014).
Even if an appeal to pathos is not manipulative, such an appeal should complement rather than replace reason and evidence-based argument. In addition to making use of pathos, the author must establish her credibility ( ethos ) and must supply reasons and evidence ( logos ) in support of her position. An author who essentially replaces logos and ethos with pathos alone should be given low marks.
See below for the most common fallacies that misuse appeals to pathos.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Pathos
Appeal to fear: using scare tactics; emphasizing threats or exaggerating possible dangers.
Example: “Without this additional insurance, you could find yourself broke and homeless.”
Appeal to guilt and appeal to pity : trying to evoke an emotional reaction that will cause the audience to behave sympathetically even if it means disregarding the issue at hand.
Example: “I know I missed assignments, but if you fail me, I will lose my financial aid and have to drop out.”
Appeal to popularity (bandwagon): urging audience to follow a course of action because “everyone does it.”
Example: “Nine out of ten shoppers have switched to Blindingly-Bright-Smile Toothpaste.”
Slippery Slope: making an unsupported or inadequately supported claim that “One thing inevitably leads to another.” This may be considered a fallacy of logos as well as pathos but is placed in this section because it often is used to evoke the emotion of fear.
Example: “We can’t legalize marijuana; if we do, then the next thing you know people will be strung out on heroin.”
Appeal to the people: also called stirring symbols fallacy; the communicator distracts the readers or listeners with symbols that are very meaningful to them, with strong associations or connotations.
Example: This fallacy is referred to in the sentence “That politician always wraps himself in the flag.”
Appeal to tradition: people have been done it a certain way for a long time; assumes that what has been customary in past is correct and proper.
Example: “A boy always serves as student-body president; a girl always serves as secretary.”
Loaded-Language and other emotionally charged uses of language: using slanted or biased language, including God terms, devil terms, euphemisms, and dysphemisms.
Example: In the sentence “Cutting access to food stamps would encourage personal responsibility,” the god term is “personal responsibility.” It might seem as if it would be hard to argue against “personal responsibility” or related god terms such as “independence” and “self-reliance.” However, it would require a definition of “personal responsibility,” combined with evidence from studies of people’s behavior in the face of food stamp or other benefit reductions, to argue that cutting access to food stamps would lead to the intended results.

Fallacies can crop up whenever definitions, inferences, and facts are at issue. Once we become familiar with fallacies we may start to see them everywhere. That can be good and bad. Since persuasion is ever-present, it is good to be on guard against various hidden persuaders. But whether a persuasive strategy is considered fallacious may be dependent on context. Editorials and advertisements—both political and commercial—frequently use such strategies as transfer and appeals to popularity. We need to be critically aware of the techniques of persuasion being used on us, but since we expect advertisements, political speeches, and editorials on public policy or ethical issues to try to sway us emotionally, perhaps only extreme examples deserve to be judged harshly for being fallacious.
In addition, something that looks as if it is a fallacy may turn out not to be on closer examination. For example, not everything that smacks of slippery slope is fallacious. There are indeed some genuine slippery slopes, where an initial decision or action may have both great and inevitable repercussions. So whether that fallacy has been committed depends upon what the author has done (or failed to do) to support his claim. Similarly, while personal attacks ( ad hominem ) in most cases are unfair and considered fallacious, there are special situations in which a person’s character may be directly relevant to his or her qualifications. For example, when somebody is running for political office or for a judgeship, casting doubt on his or her character may be appropriate— if one has facts to back it up—since it relates to job expectations. But wholesale character assassination remains a rhetorical ploy of the propagandist or demagogue.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of Red Herring. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/81M6vG . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of Argument from Authority. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7WGuwA . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of the Ad Hominem. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7W4WMp . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- The Logical Structure of Arguments. Provided by : Radford University. Located at : http://lcubbison.pressbooks.com/chapter/core-201-analyzing-arguments/ . Project : Core Curriculum Handbook. License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright

The Essential AP Guide to Ethos, Pathos, and Logos
The goal of argumentative writing is to persuade your audience that your ideas are convincing. Basically, there are three ways of doing this:
- You can convince your reader that your authority is indisputable (ethos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his emotions (pathos)
- You can convince your reader by appealing to his sense of logic and reason (logos)
Think of these different modes of persuasion, ethos, pathos, and logos, as tactics or strategies. Tactics you’ve used all your life when you use words to try to persuade someone to do something, be that agree with your opinion or buy you a new bike.
Yes, you use ethos, pathos, and logos every day.
To succeed in AP English, you need to know how to identify ethos, pathos, and logos quickly. Below is our quick guide that gives you everything you need to know to identify ethos, pathos, and logos and ace AP English.

Understand The Difference Between Ethos, Pathos, And Logos To Make Your Point
- What Is Ethos?
- What Is Pathos?
- What Is Logos?
- Examples Of Each
- What Are Mythos And Kairos?
During an argument, people will often say whatever is necessary to win. If that is the case, they would certainly need to understand the three modes of persuasion, also commonly known as the three rhetorical appeals: ethos , pathos , and logos . In short, these three words refer to three main methods that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. As you’re about to find out, the modes of persuasion are important because a speaker who knows how to effectively use them will have a significant advantage over someone who doesn’t.
The terms ethos , pathos , and logos and the theory of their use can be traced back to ancient Greece to the philosophy of Aristotle . Aristotle used these three concepts in his explanations of rhetoric , or the art of influencing the thought and conduct of an audience. For Aristotle, the three modes of persuasion specifically referred to the three major parts of an argument: the speaker ( ethos ), the argument itself ( logos ), and the audience ( pathos ). In particular, Aristotle focused on the speaker’s character, the logic and reason presented by an argument, and the emotional impact the argument had on an audience.
While they have ancient roots, these modes of persuasion are alive and well today. Put simply, ethos refers to persuasion based on the credibility or authority of the speaker, pathos refers to persuasion based on emotion, and logos refers to persuasion based on logic or reason.
By effectively using the three modes of persuasion with a large supply of rhetorical devices, a speaker or writer can become a master of rhetoric and win nearly any argument or win over any audience. Before they can do that, though, they must know exactly what ethos , pathos , and logos mean. Fortunately, we are going to look closely at each of these three ideas and see if they are really as effective as they are said to be.
⚡️ Quick summary
Ethos , pathos , and logos are the three classical modes of persuasion that a person can use to speak or write persuasively. Specifically:
- ethos (character): known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” This is the method in which a person relies on their credibility or character when making an appeal or an argument.
- pathos (emotions): known as “the appeal to emotion.” Pathos refers to the method of trying to persuade an audience by eliciting some kind of emotional reaction.
- logos (logic): known as “the appeal to reason.” This method involves using facts and logical reasoning to support an argument and persuade an audience.
What is ethos ?
The word ethos comes straight from Greek. In Greek, ethos literally translates to “habit,” “custom,” or “character.” Ethos is related to the words ethic and ethical , which are typically used to refer to behavior that is or isn’t acceptable for a particular person.
In rhetoric, the word ethos is used to refer to the character or reputation of the speaker. As a rhetorical appeal, ethos is known as “the appeal to authority” or “the appeal to credibility.” When it comes to ethos , one important consideration is how the speaker carries themself and how they present themselves to the audience: Does it seem like they know what they are talking about? Do they even believe the words they are saying? Are they an expert? Do they have some experience or skills that tell us we should listen to them?
Ethos is important in rhetoric because it often influences the opinion or mood of the audience. If a speaker seems unenthusiastic, unprepared, or inexperienced, the audience is more likely to discount the speaker’s argument regardless of what it even is. On the other hand, a knowledgeable, authoritative, confident speaker is much more likely to win an audience over.
Ethos often depends on more than just the argument itself. For example, a speaker’s word choice, grammar, and diction also contribute to ethos ; an audience may react more favorably toward a professional speaker who has a good grasp of industry jargon and enunciates clearly versus a speaker who lacks the necessary vocabulary and fails to enunciate. Ethos can also be influenced by nonverbal factors as well, such as posture, body language, eye contact, and even the speaker’s choice of clothing. For example, a military officer proudly wearing their uniform bedecked with medals will go a long way to establishing ethos without them saying a single word.
Here as a simple example of ethos :
- “As a former mayor of this city, I believe we can solve this crisis if we band together.”
The speaker uses ethos by alerting the audience of their credentials and experience. By doing so, they rely on their reputation to be more persuasive. This “as a…” method of establishing ethos is common, and you have probably seen it used in many persuasive advertisements and speeches.
What are open-ended questions and how can you use them effectively? Find out here.
What is pathos ?
In Greek, pathos literally translates to “suffering, experience, or sensation.” The word pathos is related to the words pathetic , sympathy , and empathy , which all have to do with emotions or emotional connections. Aristotle used the word pathos to refer to the emotional impact that an argument had on an audience; this usage is still mainly how pathos is used in rhetoric today.
As a rhetorical appeal, pathos is referred to as “the appeal to emotion.” Generally speaking, an author or speaker is using pathos when they are trying to persuade an audience by causing some kind of emotional reaction. When it comes to pathos , any and all emotions are on the table: sadness, fear, hope, joy, anger, lust, pity, etc.
As you probably know from your own life, emotions are a powerful motivating factor. For this reason, relying on pathos is often a smart and effective strategy for persuading an audience. Both positive and negative emotions can heavily influence an audience: for example, an audience will want to support a speaker whose position will make them happy, a speaker who wants to end their sadness, or a speaker who is opposed to something that makes them angry.
Here is a simple example of pathos :
- “Every day, the rainforests shrink and innocent animals are killed. We must do something about this calamitous trend before the planet we call our home is damaged beyond repair.”
Here, the author is trying to win over an audience by making them feel sad, concerned, or afraid. The author’s choice of words like “innocent” and “calamitous” enforce the fact that they are trying to rely on pathos .
What is logos ?
In Greek, the word logos literally translates to “word, reason, or discourse.” The word logos is related to many different words that have to do with reason, discourse, or knowledge, such as logic , logical , and any words that end in the suffixes -logy or -logue .
As a mode of persuasion and rhetorical appeal, logos is often referred to as “the appeal to reason.” If a speaker or author is relying on logos , they are typically reciting facts or providing data and statistics that support their argument. In a manner of speaking, logos does away with all of the bells and whistles of ethos and pathos and cuts to the chase by trying to present a rational argument.
Logos can be effective in arguments because, in theory, it is impossible to argue against truth and facts. An audience is more likely to agree with a speaker who can provide strong, factual evidence that shows their position is correct. On the flip side, an audience is less likely to support an argument that is flawed or entirely wrong. Going further, a speaker that presents a lot of supporting evidence and data to the audience is likely to come across as knowledgeable and someone to be listened to, which earns bonus points in ethos as well.
While Aristotle clearly valued an argument based on reason very highly, we know that logos alone doesn’t always effectively persuade an audience. In your own life, you have likely seen a rational, correct speaker lose an argument to a charismatic, authoritative speaker who may not have the facts right.
Here is a simple example of logos :
- “According to market research, sales of computer chips have increased by 300% in the last five years. Analysis of the industry tells us that the market share of computer chips is dominated by Asian manufacturers. It is clear that the Asian technology sector will continue to experience rapid growth for the foreseeable future.”
In this paragraph, the author is using data, statistics, and logical reasoning to make their argument. They clearly hope to use logos to try to convince an audience to agree with them.
Do you need persuading to take this quiz on identifying ethos, pathos, and logos? We think you’ll be a champion at it.
Examples of ethos , pathos , and logos
Ethos , pathos , and logos can all be employed to deliver compelling and persuasive arguments or to win over an audience. Let’s look at a variety of examples to see how different speakers and authors have turned to these modes of persuasion over the years.
“Come I to speak in Caesar’s funeral. He was my friend, faithful and just to me […] You all did see that on the Lupercal I thrice presented him a kingly crown, Which he did thrice refuse: was this ambition?” —Marc Antony, Julius Caesar by William Shakespeare
In this scene, Marc Antony is trying to win over the Roman people, so Shakespeare has Antony rely on ethos . Antony is establishing himself as both a person of authority in Rome (having the power to offer Caesar a crown) and an expert on Caesar’s true character (Antony was Caesar’s close friend and advisor).
“During the next five years, I started a company named NeXT, another company named Pixar, and fell in love with an amazing woman who would become my wife. Pixar went on to create the world’s first computer animated feature film, Toy Story , and is now the most successful animation studio in the world. In a remarkable turn of events, Apple bought NeXT, I returned to Apple, and the technology we developed at NeXT is at the heart of Apple’s current renaissance.” —Steve Jobs, 2005
Here, Steve Jobs is providing his background–via humblebrag – of being a major figure in several different highly successful tech companies. Jobs is using ethos to provide substance to his words and make it clear to the audience that he knows what he is talking about and they should listen to him.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
“Moreover, though you hate both him and his gifts with all your heart, yet pity the rest of the Achaeans who are being harassed in all their host; they will honour you as a god, and you will earn great glory at their hands. You might even kill Hector; he will come within your reach, for he is infatuated, and declares that not a Danaan whom the ships have brought can hold his own against him.” —Ulysses to Achilles, The Iliad by Homer
In this plea, Ulysses is doing his best to pile on the pathos . In one paragraph, Ulysses is attempting to appeal to several of Achilles’s emotions: his hatred of Hector, his infamous stubborn pride, his sympathy for civilians, and his desire for vengeance.
“I am not unmindful that some of you have come here out of great trials and tribulations. Some of you have come fresh from narrow jail cells. Some of you have come from areas where your quest—quest for freedom left you battered by the storms of persecution and staggered by the winds of police brutality.” —Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., 1963
In this excerpt from his “I Have A Dream” speech, King is using pathos to accomplish two goals at once. First, he is connecting with his audience by making it clear is aware of their plight and suffering. Second, he is citing these examples to cause sadness or outrage in the audience. Both of these effects will make an audience interested in what he has to say and more likely to support his position.
Dr. King’s “I Have A Dream” speech is recognizable and noteworthy for many reasons, including the rhetorical device he employs. Learn about it here.
“Let it be remembered how powerful the influence of a single introduced tree or mammal has been shown to be. But in the case of an island, or of a country partly surrounded by barriers, into which new and better adapted forms could not freely enter, we should then have places in the economy of nature which would assuredly be better filled up if some of the original inhabitants were in some manner modified; for, had the area been open to immigration, these same places would have been seized on by intruders. In such case, every slight modification, which in the course of ages chanced to arise, and which in any way favoured the individuals of any of the species, by better adapting them to their altered conditions, would tend to be preserved; and natural selection would have free scope for the work of improvement.” —Charles Darwin, On the Origin of the Species , 1859
In this passage, Darwin is using logos by presenting a rational argument in support of natural selection. Darwin connects natural selection to established scientific knowledge to argue that it makes logical sense that animals would adapt to better survive in their environment.
“I often echo the point made by the climate scientist James Hansen: The accumulation of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases—some of which will envelop the planet for hundreds and possibly thousands of years—is now trapping as much extra energy daily as 500,000 Hiroshima-class atomic bombs would release every 24 hours. This is the crisis we face.” —Al Gore, “The Climate Crisis Is the Battle of Our Time, and We Can Win,” 2019
In this call to action, Al Gore uses logos to attempt to convince his audience of the significance of climate change. In order to do this, Gore both cites an expert in the field and provides a scientifically accurate simile to explain the scale of the effect that greenhouse gases have on Earth’s atmosphere.
What are mythos and kairos ?
Some modern scholars may also use terms mythos and kairos when discussing modes of persuasion or rhetoric in general.
Aristotle used the term mythos to refer to the plot or story structure of Greek tragedies, i.e., how a playwright ordered the events of the story to affect the audience. Today, mythos is most often discussed as a literary or poetic term rather than a rhetorical one. However, mythos may rarely be referred to as the “appeal to culture” or the “appeal to myth” if it is treated as an additional mode of persuasion. According to this viewpoint, a speaker/writer is using mythos if they try to persuade an audience using shared cultural customs or societal values.
A commonly cited example of mythos is King’s “I Have a Dream” speech quoted earlier. King says:
“When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men—yes, black men as well as white men—would be guaranteed the ‘unalienable rights’ of ‘life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness.’ ”
Throughout the speech, King repeatedly uses American symbols and American history ( mythos ) to argue that all Americans should be outraged that Black Americans have been denied freedom and civil rights.
Some modern scholars may also consider kairos as an additional mode of persuasion. Kairos is usually defined as referring to the specific time and place that a speaker chooses to deliver their speech. For written rhetoric, the “place” instead refers to the specific medium or publication in which a piece of writing appears.
Unlike the other modes of persuasion, kairos relates to the context of a speech and how the appropriateness (or not) of a setting affects how effective a speaker is. Once again, King’s “I Have a Dream” speech is a great example of the use of kairos . This speech was delivered at the steps of the Lincoln Memorial during the 100th anniversary of the Emancipation Proclamation at the end of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Clearly, King intended to use kairos to enhance the importance and timeliness of this landmark speech.
Make your communication as smooth as can be by learning about filler words and when you should, and shouldn't, use them.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

'Vote for NOTA': Congress appeals to Indore electors

BHOPAL: Deprived of a candidate to contest the May 13 Lok Sabha polls – following the withdrawal of papers by its official nominee and rejection of papers of its “substitute” candidate – the opposition Congress has decided to appeal to people to press the None of the Above (NOTA) option in Indore parliamentary constituency.
“We’re not like the BJP that has tarnished and murdered democracy in Indore. We believe in democracy, but won’t support any of the remaining candidates in fray or ask people to boycott the election. We appeal to the people of Indore to exercise the NOTA option to teach the BJP a befitting lesson in the May 13 LS polls,” state Congress president Jitu Patwari said on Thursday.
“The BJP which once took pride in itself as the party with difference is now a party which only believes in murdering democracy, by preventing opposition party candidates from contesting the polls. Never in the past has anything like this happened here, which is the country’s cleanest city with a rich heritage. But the BJP’s recent immoral act masterminded by the MP minister Kailash Vijayvargiya has tarnished democracy in the city,” Patwari said.
“The fight to save democracy is no longer just Congress’s fight, it’s the fight of every voter in Indore. We’ll take out rallies to awaken the Indore people against BJP murdering democracy. We won’t appeal to them to boycott the May 13 election, but will only request them to exercise NOTA to strengthen the fight against murder of democracy,” Patwari said.
The former MP minister, who hails from Indore only, further alleged that the BJP guided by Vijayvargiya wanted more candidates to drop out of the fray to ensure unopposed election of sitting MP and party candidate Shankar Lalwani. “Five such candidates were with me at my house to avert pressures in Indore to withdraw from the poll race.”
He added that on coming to know about the April 29 development, former Congress president Rahul Gandhi asked him (Patwari) why did eight-times ex-MP from Indore and former LS speaker Sumitra Mahajan, who has always sworn by the politics of purity, remain silent over the development.
On April 29, in a big jolt to the Congress, its official candidate from Indore seat Akshay Kanti Bam accompanied by BJP MLA Ramesh Mendola withdrew his nomination and joined the BJP a few hours later.
Follow The New Indian Express channel on WhatsApp
Download the TNIE app to stay with us and follow the latest
Related Stories
- Evaluating Appeals to Ethos, Logos, and Pathos
Introduction
As a reader and a listener, it is fundamental that you be able to recognize how writers and speakers depend upon ethos , logos , and pathos in their efforts to communicate. As a communicator yourself, you will benefit from being able to see how others rely upon ethos, logos, and pathos so that you can apply what you learn from your observations to your own speaking and writing.
Evaluate an Appeal to Ethos
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos , you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible.
A good speaker or writer leads the audience to feel comfortable with her knowledge of a topic. The audience sees her as someone worth listening to—a clear or insightful thinker, or at least someone who is well-informed and genuinely interested in the topic.
Some of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s ethos may include the following:
- Has the writer or speaker cited her sources or in some way made it possible for the audience to access further information on the issue?
- Does she demonstrate familiarity with different opinions and perspectives?
- Does she provide complete and accurate information about the issue?
- Does she use the evidence fairly? Does she avoid selective use of evidence or other types of manipulation of data?
- Does she speak respectfully about people who may have opinions and perspectives different from her own?
- Does she use unbiased language?
- Does she avoid excessive reliance on emotional appeals?
- Does she accurately convey the positions of people with whom she disagrees?
- Does she acknowledge that an issue may be complex or multifaceted?
- Does her education or experience give her credibility as someone who should be listened to on this issue?
Some of the above questions may strike you as relevant to an evaluation of logos as well as ethos—questions about the completeness and accuracy of information and whether it is used fairly. In fact, illogical thinking and the misuse of evidence may lead an audience to draw conclusions not only about the person making the argument but also about the logic of an argument.
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Ethos
In a perfect world, everyone would tell the truth and we could depend upon the credibility of speakers and authors. Unfortunately, that is not always the case. You would expect that news reporters would be objective and tell new stories based upon the facts. Janet Cooke, Stephen Glass, Jayson Blair, and Brian Williams all lost their jobs for plagiarizing or fabricated part of their news stories. Janet Cooke’s Pulitzer Prize was revoked after it was discovered that she made up “Jimmy,” an eight-year old heroin addict (Prince, 2010). Brian Williams was fired as anchor of the NBC Nightly News for exaggerating his role in the Iraq War.
Others have become infamous for claiming academic degrees that they didn’t earn as in the case of Marilee Jones. At the time of discovery, she was Dean of Admissions at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). After 28 years of employment, it was determined that she never graduated from college (Lewin, 2007). However, on her website ( http://www.marileejones.com ) she is still promoting herself as “a sought after speaker, consultant and author” (para. 1) and “one of the nation’s most experienced College Admissions Deans” (para. 2).
Beyond lying about their own credentials, authors may employ a number of tricks or fallacies to lure you to their point of view. Some of the more common techniques are described below. Others may be found in the appendix. When you recognize these fallacies being committed you should question the credibility of the speaker and the legitimacy of the argument. If you use these when making your own arguments, be aware that they may undermine or destroy your credibility.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Ethos
Ad hominem : attacking the person making an argument rather than the argument itself.
Example: “Of course that doctor advocates vaccination—he probably owns stock in a pharmaceutical company.”
False authority : relying on claims of expertise when the claimed expert (a) lacks adequate background/credentials in the relevant field, (b) departs in major ways from the consensus in the field, or (c) is biased, e.g., has a financial stake in the outcome.
Example: “Dr. X is an engineer, and he doesn’t believe in global warming.”
Guilt by association : linking the person making an argument to an unpopular person or group.
Example: “My opponent is a card-carrying member of the ACLU.”
Poisoning the well: undermining an opponent’s credibility before he or she gets a chance to speak.
Example: “The prosecution is going to bring up a series or so-called experts who are getting a lot of money to testify here today.”
Transfer fallacy : associating the argument with someone or something popular or respected; hoping that the positive associations will “rub off” onto the argument.
Examples: In politics, decorating a stage with red, white, and blue flags and bunting; in advertising, using pleasant or wholesome settings as the backdrop for print or video ads.
Name-calling : labeling an opponent with words that have negative connotations in an effort to undermine the opponent’s credibility.
Example: “These rabble-rousers are nothing but feminazis.”
Plain folk : presenting yourself as (or associating your position with) ordinary people with whom you hope your audience will identify; arguers imply that they or their supporters are trustworthy because they are ‘common people’ rather than members of the elite.
Example: “Who would you vote for—someone raised in a working-class neighborhood who has the support of Joe the Plumber or some elitist whose daddy sent him to a fancy school?”
Testimonial fallacy : inserting an endorsement of the argument by someone who is popular or respected but who lacks expertise or authority in the area under discussion.
Example: “I’m not a doctor, but I play one on TV”—a famous example of a celebrity endorsement for a cough syrup (Deis, 2011, n.p.).

The most general structure of this argument runs something like the following: Person A claims that Person A is a respected scientist or other authority; therefore, the claim they make is true.
Evaluate an Appeal to Logos
When you evaluate an appeal to logos , you consider how logical the argument is and how well-supported it is in terms of evidence. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to believe that the argument is (or is not) logical and supported by appropriate evidence.
To evaluate whether the evidence is appropriate, apply the STAR criteria: how S ufficient, T ypical, A ccurate, and R elevant is the evidence?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Logos
Diagramming the argument can help you determine if an appeal to logos is manipulative. Are the premises true? Does the conclusion follow logically from the premises? Is there sufficient, typical, accurate, and relevant evidence to support inductive reasoning? Is the speaker or author attempting to divert your attention from the real issues? These are some of the elements you might consider while evaluating an argument for the use of logos.
Pay particular attention to numbers, statistics, findings, and quotes used to support an argument. Be critical of the source and do your own investigation of the “facts.” Maybe you’ve heard or read that half of all marriages in America will end in divorce. It is so often discussed that we assume it must be true. Careful research will show that the original marriage study was flawed, and divorce rates in America have steadily declined since 1985 (Peck, 1993). If there is no scientific evidence, why do we continue to believe it? Part of the reason might be that it supports our idea of the dissolution of the American family.
Fallacies that misuse appeals to logos or attempt to manipulate the logic of an argument are discussed below. Other fallacies of logos may be found in the appendix.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Logos
Hasty generalization: jumping to conclusions based upon an unrepresentative sample or insufficient evidence.
Example: “10 of the last 14 National Spelling Bee Champions have been Indian American. Indian Americans must all be great spellers!”
Appeal to ignorance—true believer’s form: arguing along the lines that if an opponent can’t prove something isn’t the case, then it is reasonable to believe that it is the case; transfers the burden of proof away from the person making the claim (the proponent).
Example: “You can’t prove that extraterrestrials haven’t visited earth, so it is reasonable to believe that they have visited earth.”
Appeal to ignorance—skeptic’s form: confusing absence of evidence with evidence of absence; assumes that if you cannot now prove something exists, then it is shown that it doesn’t exist.
Example: “There’s no proof that starting classes later in the day will improve the performance of our high school students; therefore, this change in schedule will not work.”
Begging the question: circular argument because the premise is the same as the claim that you are trying to prove.
Example: “This legislation is sinful because it is the wrong thing to do.”
False dilemma: misuse of the either/or argument; presenting only two options when other choices exist
Example: “Either we pass this ordinance or there will be rioting in the streets.”
Post hoc ergo propter hoc: Latin phrase meaning “after this, therefore because of this”; confuses correlation with causation by concluding that an event preceding a second event must be the cause of that second event.
Example: “My child was diagnosed with autism after receiving vaccinations. That is proof that vaccines are to blame.”
Non-sequitur: Latin for “does not follow”; the conclusion cannot be inferred from the premises because there is a break in the logical connection between a claim and the premises that are meant to support it, either because a premise is untrue (or missing) or because the relationship between premises does not support the deduction stated in the claim.
Example (untrue premise): “If she is a Radford student, she is a member of a sorority. She is a Radford student. Therefore she is a member of a sorority.”
Smoke screen : avoiding the real issue or a tough question by introducing an unrelated topic as a distraction; sometimes called a red herring .
Example: “My opponent says I am weak on crime, but I have been one of the most reliable participants in city council meetings.”
Straw man: pretending to criticize an opponent’s position but actually misrepresenting his or her view as simpler and/or more extreme than it is and therefore easier to refute than the original or actual position; unfairly undermines credibility of claim if not source of claim.
Example: “Senator Smith says we should cut back the Defense budget. His position is that we should let down our defenses and just trust our enemies not to attack us!”

The red herring is as much a debate tactic as it is a logical fallacy. It is a fallacy of distraction, and is committed when a listener attempts to divert an arguer from his argument by introducing another topic. This can be one of the most frustrating, and effective, fallacies to observe.The fallacy gets its name from fox hunting, specifically from the practice of using smoked herrings, which are red, to distract hounds from the scent of their quarry. Just as a hound may be prevented from catching a fox by distracting it with a red herring, so an arguer may be prevented from proving his point by distracting him with a tangential issue.
Evaluate an Appeal to Pathos
People may be uninterested in an issue unless they can find a personal connection to it, so a communicator may try to connect to her audience by evoking emotions or by suggesting that author and audience share attitudes, beliefs, and values—in other words, by making an appeal to pathos . Even in formal writing, such as academic books or journals, an author often will try to present an issue in such a way as to connect to the feelings or attitudes of his audience.
When you evaluate pathos, you are asking whether a speech or essay arouses the audience’s interest and sympathy. You are looking for the elements of the essay or speech that might cause the audience to feel (or not feel) an emotional connection to the content.
An author may use an audience’s attitudes, beliefs, or values as a kind of foundation for his argument—a layer that the writer knows is already in place at the outset of the argument. So one of the questions you can ask yourself as you evaluate an author’s use of pathos is whether there are points at which the writer or speaker makes statements assuming that the audience shares his feelings or attitudes. For example, in an argument about the First Amendment, does the author write as if he takes it for granted that his audience is religious?
Recognizing a Manipulative Appeal to Pathos
Up to a certain point, an appeal to pathos can be a legitimate part of an argument. For example, a writer or speaker may begin with an anecdote showing the effect of a law on an individual. This anecdote will be a means of gaining an audience’s attention for an argument in which she uses evidence and reason to present her full case as to why the law should/should not be repealed or amended. In such a context, engaging the emotions, values, or beliefs of the audience is a legitimate tool whose effective use should lead you to give the author high marks.
An appropriate appeal to pathos is different than trying to unfairly play upon the audience’s feelings and emotions through fallacious, misleading, or excessively emotional appeals. Such a manipulative use of pathos may alienate the audience or cause them to “tune out”. An example would be the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) commercials featuring the song “ In the Arms on an Angel ” and footage of abused animals. Even Sarah McLachlan, the singer and spokesperson featured in the commercials admits that she changes the channel because they are too depressing (Brekke, 2014).
Even if an appeal to pathos is not manipulative, such an appeal should complement rather than replace reason and evidence-based argument. In addition to making use of pathos, the author must establish her credibility ( ethos ) and must supply reasons and evidence ( logos ) in support of her position. An author who essentially replaces logos and ethos with pathos alone should be given low marks.
See below for the most common fallacies that misuse appeals to pathos.
Fallacies That Misuse Appeals to Pathos
Appeal to fear: using scare tactics; emphasizing threats or exaggerating possible dangers.
Example: “Without this additional insurance, you could find yourself broke and homeless.”
Appeal to guilt and appeal to pity : trying to evoke an emotional reaction that will cause the audience to behave sympathetically even if it means disregarding the issue at hand.
Example: “I know I missed assignments, but if you fail me, I will lose my financial aid and have to drop out.”
Appeal to popularity (bandwagon): urging audience to follow a course of action because “everyone does it.”
Example: “Nine out of ten shoppers have switched to Blindingly-Bright-Smile Toothpaste.”
Slippery Slope: making an unsupported or inadequately supported claim that “One thing inevitably leads to another.” This may be considered a fallacy of logos as well as pathos but is placed in this section because it often is used to evoke the emotion of fear.
Example: “We can’t legalize marijuana; if we do, then the next thing you know people will be strung out on heroin.”
Appeal to the people: also called stirring symbols fallacy; the communicator distracts the readers or listeners with symbols that are very meaningful to them, with strong associations or connotations.
Example: This fallacy is referred to in the sentence “That politician always wraps himself in the flag.”
Appeal to tradition: people have been done it a certain way for a long time; assumes that what has been customary in past is correct and proper.
Example: “A boy always serves as student-body president; a girl always serves as secretary.”
Loaded-Language and other emotionally charged uses of language: using slanted or biased language, including God terms, devil terms, euphemisms, and dysphemisms.
Example: In the sentence “Cutting access to food stamps would encourage personal responsibility,” the god term is “personal responsibility.” It might seem as if it would be hard to argue against “personal responsibility” or related god terms such as “independence” and “self-reliance.” However, it would require a definition of “personal responsibility,” combined with evidence from studies of people’s behavior in the face of food stamp or other benefit reductions, to argue that cutting access to food stamps would lead to the intended results.

Here is an example of a common logical fallacy known as the ad hominem argument , which is Latin for “argument against the person” or “argument toward the person.” Basically, an ad hominem argument goes like this: Person 1 makes claim X. There is something objectionable about Person 1. Therefore claim X is false.
Fallacies can crop up whenever definitions, inferences, and facts are at issue. Once we become familiar with fallacies we may start to see them everywhere. That can be good and bad. Since persuasion is ever-present, it is good to be on guard against various hidden persuaders. But whether a persuasive strategy is considered fallacious may be dependent on context. Editorials and advertisements—both political and commercial—frequently use such strategies as transfer and appeals to popularity. We need to be critically aware of the techniques of persuasion being used on us, but since we expect advertisements, political speeches, and editorials on public policy or ethical issues to try to sway us emotionally, perhaps only extreme examples deserve to be judged harshly for being fallacious.
In addition, something that looks as if it is a fallacy may turn out not to be on closer examination. For example, not everything that smacks of slippery slope is fallacious. There are indeed some genuine slippery slopes, where an initial decision or action may have both great and inevitable repercussions. So whether that fallacy has been committed depends upon what the author has done (or failed to do) to support his claim. Similarly, while personal attacks ( ad hominem ) in most cases are unfair and considered fallacious, there are special situations in which a person’s character may be directly relevant to his or her qualifications. For example, when somebody is running for political office or for a judgeship, casting doubt on his or her character may be appropriate— if one has facts to back it up—since it relates to job expectations. But wholesale character assassination remains a rhetorical ploy of the propagandist or demagogue.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of Red Herring. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/81M6vG . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of Argument from Authority. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7WGuwA . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Image of the Ad Hominem. Authored by : Mark Klotz. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/7W4WMp . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- The Logical Structure of Arguments. Provided by : Radford University. Located at : http://lcubbison.pressbooks.com/chapter/core-201-analyzing-arguments/ . Project : Core Curriculum Handbook. License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (available upon sign-in)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
- Quiz Survey
Reading: Types of Reading Material
- Introduction to Reading
- Outcome: Types of Reading Material
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 1
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 2
- Characteristics of Texts, Part 3
- Characteristics of Texts, Conclusion
- Self Check: Types of Writing
Reading: Reading Strategies
- Outcome: Reading Strategies
- The Rhetorical Situation
- Academic Reading Strategies
- Self Check: Reading Strategies
Reading: Specialized Reading Strategies
- Outcome: Specialized Reading Strategies
- Online Reading Comprehension
- How to Read Effectively in Math
- How to Read Effectively in the Social Sciences
- How to Read Effectively in the Sciences
- 5 Step Approach for Reading Charts and Graphs
- Self Check: Specialized Reading Strategies
Reading: Vocabulary
- Outcome: Vocabulary
- Strategies to Improve Your Vocabulary
- Using Context Clues
- The Relationship Between Reading and Vocabulary
- Self Check: Vocabulary
Reading: Thesis
- Outcome: Thesis
- Locating and Evaluating Thesis Statements
- The Organizational Statement
- Self Check: Thesis
Reading: Supporting Claims
- Outcome: Supporting Claims
- Types of Support
- Supporting Claims
- Self Check: Supporting Claims
Reading: Logic and Structure
- Outcome: Logic and Structure
- Rhetorical Modes
- Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
- Diagramming and Evaluating Arguments
- Logical Fallacies
- Self Check: Logic and Structure
Reading: Summary Skills
- Outcome: Summary Skills
- How to Annotate
- Paraphrasing
- Quote Bombs
- Summary Writing
- Self Check: Summary Skills
- Conclusion to Reading
Writing Process: Topic Selection
- Introduction to Writing Process
- Outcome: Topic Selection
- Starting a Paper
- Choosing and Developing Topics
- Back to the Future of Topics
- Developing Your Topic
- Self Check: Topic Selection
Writing Process: Prewriting
- Outcome: Prewriting
- Prewriting Strategies for Diverse Learners
- Rhetorical Context
- Working Thesis Statements
- Self Check: Prewriting
Writing Process: Finding Evidence
- Outcome: Finding Evidence
- Using Personal Examples
- Performing Background Research
- Listening to Sources, Talking to Sources
- Self Check: Finding Evidence
Writing Process: Organizing
- Outcome: Organizing
- Moving Beyond the Five-Paragraph Theme
- Introduction to Argument
- The Three-Story Thesis
- Organically Structured Arguments
- Logic and Structure
- The Perfect Paragraph
- Introductions and Conclusions
- Self Check: Organizing
Writing Process: Drafting
- Outcome: Drafting
- From Outlining to Drafting
- Flash Drafts
- Self Check: Drafting
Writing Process: Revising
- Outcome: Revising
- Seeking Input from Others
- Responding to Input from Others
- The Art of Re-Seeing
- Higher Order Concerns
- Self Check: Revising
Writing Process: Proofreading
- Outcome: Proofreading
- Lower Order Concerns
- Proofreading Advice
- "Correctness" in Writing
- The Importance of Spelling
- Punctuation Concerns
- Self Check: Proofreading
- Conclusion to Writing Process
Research Process: Finding Sources
- Introduction to Research Process
- Outcome: Finding Sources
- The Research Process
- Finding Sources
- What are Scholarly Articles?
- Finding Scholarly Articles and Using Databases
- Database Searching
- Advanced Search Strategies
- Preliminary Research Strategies
- Reading and Using Scholarly Sources
- Self Check: Finding Sources
Research Process: Source Analysis
- Outcome: Source Analysis
- Evaluating Sources
- CRAAP Analysis
- Evaluating Websites
- Synthesizing Sources
- Self Check: Source Analysis
Research Process: Writing Ethically
- Outcome: Writing Ethically
- Academic Integrity
- Defining Plagiarism
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Using Sources in Your Writing
- Self Check: Writing Ethically
Research Process: MLA Documentation
- Introduction to MLA Documentation
- Outcome: MLA Documentation
- MLA Document Formatting
- MLA Works Cited
- Creating MLA Citations
- MLA In-Text Citations
- Self Check: MLA Documentation
- Conclusion to Research Process
Grammar: Nouns and Pronouns
- Introduction to Grammar
- Outcome: Nouns and Pronouns
- Pronoun Cases and Types
- Pronoun Antecedents
- Try It: Nouns and Pronouns
- Self Check: Nouns and Pronouns
Grammar: Verbs
- Outcome: Verbs
- Verb Tenses and Agreement
- Non-Finite Verbs
- Complex Verb Tenses
- Try It: Verbs
- Self Check: Verbs
Grammar: Other Parts of Speech
- Outcome: Other Parts of Speech
- Comparing Adjectives and Adverbs
- Adjectives and Adverbs
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Try It: Other Parts of Speech
- Self Check: Other Parts of Speech
Grammar: Punctuation
- Outcome: Punctuation
- End Punctuation
- Hyphens and Dashes
- Apostrophes and Quotation Marks
- Brackets, Parentheses, and Ellipses
- Semicolons and Colons
- Try It: Punctuation
- Self Check: Punctuation
Grammar: Sentence Structure
- Outcome: Sentence Structure
- Parts of a Sentence
- Common Sentence Structures
- Run-on Sentences
- Sentence Fragments
- Parallel Structure
- Try It: Sentence Structure
- Self Check: Sentence Structure
Grammar: Voice
- Outcome: Voice
- Active and Passive Voice
- Using the Passive Voice
- Conclusion to Grammar
- Try It: Voice
- Self Check: Voice
Success Skills
- Introduction to Success Skills
- Habits for Success
- Critical Thinking
- Time Management
- Writing in College
- Computer-Based Writing
- Conclusion to Success Skills
Ethos Pathos Logos Example in Literature
This essay about the strategic use of logos in literature demonstrates how authors employ logical reasoning and factual evidence to enhance their narratives’ impact and depth. Through examples from works like George Orwell’s “Animal Farm,” Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar,” Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice,” and Rebecca Skloot’s “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks,” the essay elucidates how logos engages readers intellectually, enriching their understanding and fostering deeper engagement with the text. By recognizing and understanding the implementation of logos, readers can interrogate ideas and appreciate the literary craftsmanship on a more profound level, turning passive reading into an active dialogue with the text.
How it works
When we dive into the rich tapestry of literature, we often find ourselves ensnared not just by the eloquence of the prose or the complexity of character development, but also by the meticulous structure of the arguments presented. This is where logos comes into play—a rhetorical device that beckons us to lean into our logical faculties and be persuaded by reason. Logos, a term derived from Greek meaning “word” or “reason,” is one of the chief techniques a writer employs to engage the intellect of readers, convincing them through logical explanation and factual evidence.
By exploring various examples of logos in literature, we gain a deeper understanding of how authors craft their narratives to not only tell a story but also to argue, inform, and persuade.
Take, for instance, George Orwell’s “Animal Farm,” a narrative ripe with political undertones and ethical questions. Orwell doesn’t just spin a yarn about farm animals; he constructs a logical critique of totalitarianism. In the novella, the pig Old Major delivers a rousing speech that sets the foundation of the animals’ uprising. Old Major’s argument is methodical and clear: he presents a series of grievances regarding the exploitation of animals by humans, backed by observations and concluded with the reasoning that the removal of man will lead to a utopia for animals. His use of logos is not just in the listing of complaints but in the causal connection he draws between human behavior and animal misery— a logical pathway that convinces his animal audience of the necessity for a revolt.
Shakespeare’s “Julius Caesar” provides another profound canvas where logos is masterfully employed. The play is particularly memorable for the funeral orations by Brutus and Mark Antony, which are classic studies in persuasive speech. Brutus attempts to justify Caesar’s assassination to the Roman populace using a series of reasoned arguments, appealing to the citizens’ desire for freedom from tyranny. He logically argues that Caesar’s ambition would have hurt Rome, presenting his case with such rational calmness that the crowd is swayed. Yet, this is juxtaposed by Mark Antony’s speech, which, while famously known for its pathos, cleverly employs logos to dismantle Brutus’ arguments. Antony slyly introduces facts and rhetorical questions that expose the flaws in Brutus’ logic, showing that Caesar’s actions were often for Rome’s benefit, thus stirring doubts about the justification of the assassination.
In the realm of classic English literature, Jane Austen’s “Pride and Prejudice” subtly showcases logos through the interactions of its characters, particularly in the evolving relationship between Elizabeth Bennet and Mr. Darcy. During Darcy’s first, failed proposal, he uses logical arguments to explain his actions and feelings. He talks about overcoming his objections to her family’s lower social standing due to his overwhelming love for her. This moment is crucial, as it lays bare Darcy’s internal conflict and rationalizations, making his feelings for Elizabeth palpable and his character more nuanced. Austen’s use of logos here serves to deepen our understanding of Darcy, presenting his vulnerabilities and justifications in a way that resonates with the reader’s sense of reason.
Non-fiction also utilizes logos extensively, as seen in Rebecca Skloot’s “The Immortal Life of Henrietta Lacks.” Skloot presents a compelling narrative that also serves as an investigative critique of ethical standards in scientific research. Through meticulous documentation, interviews, and historical context, Skloot constructs a logical argument about the exploitation of Henrietta Lacks. By presenting facts and data surrounding the scientific use of Lacks’ cells, alongside the lack of consent and the impact on her family, Skloot not only informs but also builds a logical case for the need for ethical reform in medical research.
These examples illustrate how effectively logos can be woven into literature to enhance the narrative’s impact and depth. It engages readers by appealing to their intellect, challenging them to rethink assumptions and consider different perspectives through rational discourse. The use of logos enriches the reading experience, providing layers of understanding that go beyond the emotional or superficial readings of a text.
In conclusion, the strategic use of logos in literature is not merely about crafting logical arguments or presenting evidence; it’s about enhancing the persuasive power of the narrative. It invites readers into a dialogue, engaging them intellectually and sometimes morally. As we traverse through different genres and eras in literature, recognizing and understanding the implementation of logos not only enhances our appreciation of literary craftsmanship but also deepens our engagement with the text. It turns passive reading into an active interrogation of ideas, fostering a richer interaction with the works we explore.
For those looking to dive deeper into the analysis of literary techniques or any other detailed literary exploration, remember that understanding the rhetorical strategies at play can transform your reading experience, providing a more robust framework for interpretation and appreciation. For more personalized assistance and to ensure your work meets all academic standards, consider reaching out to professional resources like EduBirdie.
Cite this page
Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature. (2024, May 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature." PapersOwl.com , 1 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/ [Accessed: 3 May. 2024]
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature." PapersOwl.com, May 01, 2024. Accessed May 3, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/
"Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature," PapersOwl.com , 01-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/. [Accessed: 3-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Ethos Pathos Logos Example In Literature . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/ethos-pathos-logos-example-in-literature/ [Accessed: 3-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
A New Fitness Craze With Big Drama
Hyrox, a sporting event founded in Germany, has earned a large following for its dazzling, high-profile races.

By Calum Marsh
Calum Marsh traveled to Berlin to report on a recent Hyrox race.
The men in the starting line at Hyrox in Berlin in April practically hummed with nervous enthusiasm. A few dozen racers, part of an early morning heat, stood watching the steady tick of a five-minute countdown, displayed on a huge television overhead. Dramatic string music played on tinny loudspeakers. A booming voice intoned a rallying cry, “This is the moment you’ve been training for!” Lights twinkled. Spectators cheered.
For the founders of the fitness race Hyrox, Christian Toetzke, 55, and Moritz Furste, 39, this kind of kitschy spectacle was always part of the plan. The original brief, when they introduced the race in Hamburg, Germany in 2017, was “to create an event that is a 200,000-euro (about $214,000) production that looks like a 2,000,000-euro ($2,144,000) production,” Mr. Furste said.
Hyrox’s “modern entertainment and light effects create a very special feeling,” Mr. Toetzke said, one that he hopes will create a “new proposition for mass participation events.”
A Hyrox race combines running with several functional fitness movements, such as the farmer’s carry , the weighted lunge and the burpee broad jump . It takes about 90 minutes to complete, on average, although elite racers can finish in under an hour. The race has exploded in popularity since the end of the pandemic: More than 175,000 people are expected to participate in the more than 60 races Hyrox has organized for 2024 . Races in its most popular markets, including Britain, have sold out within minutes of going on sale.
A Level of Respect
Hyrox is not the first fitness race to emerge from nowhere and gain a cult following. What distinguishes it from fads like Tough Mudder and Spartan , according to Hyrox fans, is its athletic simplicity.
“Tough Mudder and Spartan are an experience that has a sport aspect to it,” said Hunter McIntyre, 34, a full-time fitness racer who holds the world record in Hyrox. “Hyrox is a sport that is an experience.” When Mr. McIntyre would tell people that he was doing a Tough Mudder, “it was almost embarrassing,” he said. Now, when he tells people that he does Hyrox, “there’s a level of respect to it,” he said.
“Usually when you ask someone if they did a Tough Mudder, it’s like they went with their office, and they got pictures and wore funny outfits,” Mr. McIntyre said, whereas Hyrox, he added, “is truly a sport.”
As a sport, Hyrox draws heavily from CrossFit, including the equipment it uses. Ski Erg and rowing machines, kettlebells, ropes and weighted sleds are common fixtures of CrossFit gyms. Some Hyrox movements, such as the wall ball shot, were created by CrossFit, although CrossFit workouts use these movements only occasionally, following the founder Greg Glassman’s ethos of “constantly varied high-intensity functional fitness.”
Mr. Toetzke said that he and Mr. Furste workshopped the Hyrox format at CrossFit gyms before the race was introduced. He added that while he tried CrossFit himself, he “thought it was a bit too much, a bit too hard, too injury-heavy.”
CrossFit involves many complex Olympic lifts and gymnastics skills, which can be difficult to master and, to some, dangerous to learn . Hyrox has avoided those kinds of techniques, sticking instead to simple movements that, Mr. Toetzke said, “are very hard to do wrong in a way that can hurt your body.” Despite or perhaps because of the similarities between the sports, Hyrox has deliberately positioned itself as the safer, more accessible alternative.
“Look, candidly I think they’re smart trying to leverage that,” Don Faul, CrossFit’s chief executive, said in response to these claims. “When you’re trying to enter a new space, you define yourself against the incumbent, the company that has defined the category. We’ve seen a variety of folks in the fitness space trying to take the same angle.”
Mr. Faul, 47, a former platoon commander in the United States Marines, said that the apparent difference in accessibility between CrossFit and Hyrox is really just a difference in perception.
“The vast majority of people in our gyms are everyday folks, not elite athletes,” he said, adding that people stepping into a CrossFit gym for the first time might be “incredibly surprised by how welcoming and accessible it is.”
Events Hold the Key
While many local CrossFit gyms host their own events, the only in-person competition the company organizes is its annual CrossFit Games, which is for a handful of elite athletes and is meant to crown “the fittest on earth.” That’s another reason CrossFitters often join Hyrox. It offers a chance to test their fitness live.
Though it’s difficult to say precisely how much overlap there is between CrossFit and Hyrox, Chris Hinshaw, a 60-year-old coach who trains athletes in both sports, said that “most of the people who are getting into Hyrox got their start in CrossFit.” Many of the racers on the Hyrox podiums are also elite CrossFit stars, including Mal O’Brien and Mirjam von Rohr, two of the top CrossFitters in the world.
Hyrox claims to have more than 2,500 affiliate gyms around the world, at which athletes can train for the public races. Mr. Toetzke and Mr. Furste initially told The New York Times that “about 10 percent” of these affiliates were also CrossFit gyms. In Berlin, 16 of 18 listed on the Hyrox website also offered CrossFit classes. When asked for clarification, Hyrox revised their estimate to 22 percent. Mr. Faul said that, though CrossFit does not track the number, he “would be surprised if it was that low.”
Mr. Furste seemed vexed to have to address the subject of CrossFit’s influence on Hyrox. “I absolutely don’t like this conversation,” he said. “We don’t want to take anything away from them. We love the training methodology. But in the end, apart from the functional workouts, it has nothing to do with us.”
Each sport seem to be benefiting from the other. Mr. Hinshaw, the coach, said that Hyrox and CrossFit are “really a perfect pair,” pointing out that offering both sports is are a good way for a gym owner to increase member retention. “A lot of people think they’re competitive with one another, and that is not at all true,” he said. “By the nature of who these athletes are, they’re always chasing the shiny new object.”
The question now is whether Hyrox can endure — or even continue to grow — as the blush of novelty wears off.It could also, like CrossFit, deepen in intensity while narrowing in appeal: It might inspire passion but the passion of the devoted few.
Mr. Toetzke doesn’t think so. “I don’t see the risk of becoming a sport only for committed people,” he said. “We are looking to the success and longevity and sustainability of the marathon.”
Becoming as popular as marathon running, of course, is a rather lofty ambition for an organization with events that are a fraction of a marathon’s size. (Hyrox New York, taking place on June 1, will have less than 10 percent of the New York Marathon’s participants.) But that, long term, is the goal.
“We really believe that this is the potential,” Mr. Toetzke said.
Explore Our Style Coverage
The latest in fashion, trends, love and more..
A $275 Bus Ticket to the Hamptons: After a decade of flying passengers to eastern Long Island, Blade, a helicopter charter company, is getting into the luxury coach business .
A New Fitness Craze: Hyrox, a sporting event founded in Germany, has earned a large following for its high-profile races with big drama .
Tremaine Emory’s Scars: Streetwear’s Black history raconteur survived Kanye, Supreme and a near-death experience. But can he survive the internet ?
N.F.L. Draft’s Style Winners: The next class of football stars has done some fashion homework , but the event was pretty tame compared with the N.B.A. draft.
Normcore Clothes on Sweaty Bodies: Despite having a buzzy costume designer, the clothes in “Challengers” — a new film about love, lust and tennis — are largely forgettable. Which may be the point .
Josh Kesselman's RAW Rolling Papers Win Critical Appeal
New York, New York--(Newsfile Corp. - May 1, 2024) - BBK Tobacco & Foods, the company behind RAW Rolling Papers, has achieved a notable legal victory in its trademark dispute with Central Coast Agriculture, Inc. (CCA). BBK was able to secure a win on crucial legal points brought forth in the dispute. The dispute centered around CCA's use of the name 'RAW GARDEN' for its cannabis products, which BBK claimed was an infringement on their trademark.

On April 1st 2024, the U.S. Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals issued an opinion that could be a landmark precedent within the landscape of trademark law in the cannabis industry. The appellate court's ruling sent BBK's claim against CCA back to the district court for a full trial, holding that there was sufficient evidence for a jury to find that 'RAW GARDEN' infringed BBK's RAW trademark. BBK's Founder Josh Kesselman stated, "For me, the most important thing is that smokers have the freedom to choose products based on their true merits and trust in strong established brand names rather than confusion. I'm just happy that this decision brings us one step closer to that result in this case."
In addition to this, the appeal court upheld the trial court's findings that RAW rolling papers cannot be classified as "drug paraphernalia," and also held that the trial court had jurisdiction to reject certain "intent to use" trademark applications filed by CCA with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
A spokesperson for BBK expressed the company's satisfaction with the appellate court's decisions, noting the significance of these rulings for the rolling paper industry. The court's rejection of the notion that rolling papers are "drug paraphernalia" and its affirmation of the invalidity of CCA's trademark applications mark a crucial victory for BBK.

RAW is a recognizable brand to many people in the cannabis community. The spokesperson highlighted the importance of these decisions in protecting consumers from confusion and misleading practices associated with the unauthorized use of the RAW name.
BBK says it now looks forward to presenting its case to a jury for a definitive resolution. This legal battle marks a notable chapter in the ongoing efforts to define the boundaries of trademark law in the rapidly evolving cannabis industry. The outcome of this case could influence how trademarks are viewed and enforced in related sectors moving forward.
Further information about RAW Rolling Papers and their full range of products can be found at https://rawthentic.com/ .
Email: [email protected] Website: https://www.provenmedia.com/ SOURCE: Proven Media
To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/207597

COMMENTS
Ethos (Appeal to credibility): Persuasion through establishing the character of the speaker. Pathos (Appeal to emotion): Persuasion through putting the hearer into a certain frame of mind. Logos (Appeal to logic): Persuasion through proof or seeming proof. For Aristotle, speech consists of three things: the speaker, the hearer, and the speech.
When writers misuse Logos, Pathos, or Ethos, arguments can be weakened. Above, we defined and described what logos, pathos, and ethos are and why authors may use those strategies. Sometimes, using a combination of logical, pathetic, and ethical appeals leads to a sound, balanced, and persuasive argument.
Revised on July 23, 2023. A rhetorical analysis is a type of essay that looks at a text in terms of rhetoric. This means it is less concerned with what the author is saying than with how they say it: their goals, techniques, and appeals to the audience. A rhetorical analysis is structured similarly to other essays: an introduction presenting ...
The concepts of ethos, pathos, logos, and kairos are also called the modes of persuasion, ethical strategies, or rhetorical appeals. They have a lot of different applications ranging from everyday interactions with others to big political speeches to effective advertising. Read on to learn about what the modes of persuasion are, how they're ...
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos, you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with his or her intended audience. You ask yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible.
An appeal to ethos is an appeal to credibility. Writers use ethos when they use their own expertise on a topic or cite an expert on the subject. An author might refer to work credentials, degrees, etc. The writer can also "borrow" credibility by citing evidence from another author who is an expert in the topic.
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos, you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible. A good speaker or writer leads the audience ...
In composition studies, the term rhetorical appeals refers to the use of ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms dating back to Aristotle who is traditionally viewed as the creator of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways which involves ...
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the speaker's credibility and authority. If the speaker has a high-ranking position, is an expert in his or her field, or has had life experience ...
Simply put, logos, ethos and pathos are three powerful tools that you can use to persuade an audience of your argument. At the most basic level, logos appeals to logic and reason, while pathos appeals to emotions and ethos emphasises credibility or authority. Naturally, a combination of all three rhetorical appeals packs the biggest punch, but ...
Appealing to ethos is all about using credibility, either your own as a writer or of your sources, in order to be persuasive.Essentially, ethos is about believability. Will your audience find you believable? What can you do to ensure that they do? You can establish ethos—or credibility—in two basic ways: you can use or build your own credibility on a topic, or you can use credible sources ...
Aristotle developed the concept of "ethos," "logos," and "pathos.". Ethos, logos, and pathos are elements of writing that make it more effective and persuasive. While ethos establishes the writer's credibility, logos appeals to the audience's reason, and pathos appeals to their emotions. These three concepts, also known as the ...
When writing your argumentative essay, consider implementing pathos, ethos, and logos based. approaches. All three approaches should be balanced throughout your paper in order to create a strong. point. Pathos the appeal to emotion, means to persuade an audience by purposely evoking certain emotions to make them feel the way the author wants ...
Of the many appeals used by writers, the most commonly used appeals that you'll explore with a Rhetorical Analysis essay are Ethos, Pathos, and Logos. Logos- The author uses logic and reasoning to appeal to the audience and build legitimacy. EX: More than one hundred peer-reviewed studies have been conducted over the past decade, and none ...
Rhetorical appeals refer to ethos, pathos, and logos. These are classical Greek terms, dating back to Aristotle, who is traditionally seen as the father of rhetoric. To be rhetorically effective (and thus persuasive), an author must engage the audience in a variety of compelling ways, which involves carefully choosing how to craft their ...
There are three types of rhetorical appeals, or persuasive strategies, used in arguments to support claims and respond to opposing arguments. A good argument will generally use a combination of all three appeals to make its case. Logos. Logos or the appeal to reason relies on logic or reason. Logos often depends on the use of inductive or ...
Define ethos in literature: the definition of ethos in literature is an argument based on the ethics or credibility of the person making the argument; an appeal to ethics. To sum up, ethos is: one of the three Aristotelian appeals used in argument. an appeal to ethics. evident in an argument in statements of the speaker's credibility or ...
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos, you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible. A good speaker or writer leads the audience ...
Aristotle first introduced the concept of ethos, pathos, and logos. A basic idea of these essential tools in writing is given below: Ethos: appeals to the audience by asking them to trust the ...
Once you can identify your own rhetorical appeals, you will be better able to recognize the way other writers and speakers use ethos, pathos, and logos. And then it's all downhill! Dr. Osborn works with students from all over the world to help them reach their independent, college, and graduate school goals.
Make sure your argument is persuasive by learning the three modes of persuasion—ethos, pathos, and logos—and how to effectively use them in communication.
Essay Example: Ethos, one of Aristotle's three modes of persuasion, is crucial in literature just as it is in rhetoric. In essence, ethos represents the credibility or ethical appeal of the speaker or, in literary terms, the character or narrator. When employed effectively in literature
The Use of Ethos. Ethos, deriving from the Greek word meaning "character," is one of the pillars of Aristotle's modes of persuasion, alongside logos (logic) and pathos (emotion). In the context of literature, ethos is not just about an ethical appeal or the author's credibility but also encompasses the believability of the characters ...
Essay Example: Harper Lee's "To Kill a Mockingbird" is not only a cornerstone of American literature but also a profound study in the art of persuasion, employing Aristotle's three modes of persuasion: logos, pathos, and ethos. ... **Ethos**, referring to the ethical appeal and the credibility of the characters, is embodied by Atticus Finch ...
We appeal to the people of Indore to exercise the NOTA option to teach the BJP a befitting lesson in the May 13 LS polls," state Congress president Jitu Patwari said on Thursday. "The BJP ...
When you evaluate an appeal to ethos, you examine how successfully a speaker or writer establishes authority or credibility with her intended audience. You are asking yourself what elements of the essay or speech would cause an audience to feel that the author is (or is not) trustworthy and credible. A good speaker or writer leads the audience ...
Now I Think It's a Historic Mistake. Mr. Shugerman is a law professor at Boston University. About a year ago, when Alvin Bragg, the Manhattan district attorney, indicted former President Donald ...
The use of logos enriches the reading experience, providing layers of understanding that go beyond the emotional or superficial readings of a text. In conclusion, the strategic use of logos in literature is not merely about crafting logical arguments or presenting evidence; it's about enhancing the persuasive power of the narrative. It ...
April 28, 2024. The men in the starting line at Hyrox in Berlin in April practically hummed with nervous enthusiasm. A few dozen racers, part of an early morning heat, stood watching the steady ...
May 01, 2024 at 13:29 PM EDT. New York, New York-- (Newsfile Corp. - May 1, 2024) - BBK Tobacco & Foods, the company behind RAW Rolling Papers, has achieved a notable legal victory in its trademark dispute with Central Coast Agriculture, Inc. (CCA). BBK was able to secure a win on crucial legal points brought forth in the dispute.