

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, how to help middle school students develop research skills.

As the research skills you teach middle school students can last them all their lives, it’s essential to help them develop good habits early in their school careers.
Research skills are useful in nearly every subject, whether it’s English, math, social studies or science, and they will continue to pay off for students every day of their schooling. Understanding the most important research skills that middle school students need will help reach these kids and make a long-term difference.
The research process
It is important for every student to understand that research is actually a process rather than something that happens naturally. The best researchers develop a process that allows them to fully comprehend the ideas they are researching and also turn the data into information that is usable for whatever the end purpose may be. Here is an example of a research process that you may consider using when teaching research skills in your middle school classroom:
- Form a question : Research should be targeted; develop a question you want to answer before progressing any further.
- Decide on resources : Not every resource is good for every question/problem. Identify the resources that will work best for you.
- Gather raw data : First, gather information in its rawest form; do not attempt to make sense of it at this point.
- Sort the data : After you have the information in front of you, decide what is important to you and how you will use it. Not all data will be reliable or worthwhile.
- Process information : Turn the data into usable information. This processing step may take longer than the rest combined. This is where you really see your data shape into something exciting.
- Create a final piece : This is where you would write a research paper, create a project or build a graph or other visual piece with your information. This may or may not be a formal document.
- Evaluate : Look back on the process. Where did you experience success and failure? Did you find an answer to your question?
This process can be adjusted to suit the needs of your particular classroom or the project you are working on. Just remember that the goal is not only to find the data for this particular project, but to teach your students research skills that will help them in the long run.
Research is a very important part of the learning process as well as being useful in real-life once the student graduates. Middle school is a great time to develop these skills as many high school teachers expect that students already have this knowledge.
Students who are well-prepared as researchers will be able to handle nearly any assignment that comes their way. Finding new ways to teach research skills to middle school students need will be a challenge, but the results are well worth it as you see your students succeed in your classroom and set the stage for further success throughout their schooling experience.
You may also like to read
- Web Research Skills: Teaching Your Students the Fundamentals
- Building Math Skills in High School Students
- How to Help High School Students with Career Research
- Five Free Websites for Students to Build Research Skills
- Homework in Middle School: Building a Foundation for Study Skills
- 5 Novels for Middle School Students that Celebrate Diversity
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Engaging Activities , Middle School (Grades: 6-8)
- Math Teaching Resources | Classroom Activitie...
- Online & Campus Doctorate (EdD) in Organizati...
- Master's in Reading and Literacy Education

Think Like a Researcher: Instruction Resources: #6 Developing Successful Research Questions
- Guide Organization
- Overall Summary
- #1 Think Like a Researcher!
- #2 How to Read a Scholarly Article
- #3 Reading for Keywords (CREDO)
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research (Alternate)
- #5 Integrating Sources
- Research Question Discussion
- #7 Avoiding Researcher Bias
- #8 Understanding the Information Cycle
- #9 Exploring Databases
- #10 Library Session
- #11 Post Library Session Activities
- Summary - Readings
- Summary - Research Journal Prompts
- Summary - Key Assignments
- Jigsaw Readings
- Permission Form
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence
Goal: Develop students’ ability to recognize and create successful research questions
Specifically, students will be able to
- identify the components of a successful research question.
- create a viable research question.
What Makes a Good Research Topic Handout
These handouts are intended to be used as a discussion generator that will help students develop a solid research topic or question. Many students start with topics that are poorly articulated, too broad, unarguable, or are socially insignificant. Each of these problems may result in a topic that is virtually un-researchable. Starting with a researchable topic is critical to writing an effective paper.
Research shows that students are much more invested in writing when they are able to choose their own topics. However, there is also research to support the notion that students are completely overwhelmed and frustrated when they are given complete freedom to write about whatever they choose. Providing some structure or topic themes that allow students to make bounded choices may be a way mitigate these competing realities.
These handouts can be modified or edited for your purposes. One can be used as a handout for students while the other can serve as a sample answer key. The document is best used as part of a process. For instance, perhaps starting with discussing the issues and potential research questions, moving on to problems and social significance but returning to proposals/solutions at a later date.
- Research Questions - Handout Key (2 pgs) This document is a condensed version of "What Makes a Good Research Topic". It serves as a key.
- Research Questions - Handout for Students (2 pgs) This document could be used with a class to discuss sample research questions (are they suitable?) and to have them start thinking about problems, social significance, and solutions for additional sample research questions.
- Research Question Discussion This tab includes materials for introduction students to research question criteria for a problem/solution essay.
Additional Resources
These documents have similarities to those above. They represent original documents and conversations about research questions from previous TRAIL trainings.
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? - Original Handout (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan. 2016 (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan 2016 with comments
Topic Selection (NCSU Libraries)
Howard, Rebecca Moore, Tricia Serviss, and Tanya K. Rodrigues. " Writing from sources, writing from sentences ." Writing & Pedagogy 2.2 (2010): 177-192.
Research Journal
Assign after students have participated in the Developing Successful Research Topics/Questions Lesson OR have drafted a Research Proposal.
Think about your potential research question.
- What is the problem that underlies your question?
- Is the problem of social significance? Explain.
- Is your proposed solution to the problem feasible? Explain.
- Do you think there is evidence to support your solution?
Keys for Writers - Additional Resource
Keys for Writers (Raimes and Miller-Cochran) includes a section to guide students in the formation of an arguable claim (thesis). The authors advise students to avoid the following since they are not debatable.
- "a neutral statement, which gives no hint of the writer's position"
- "an announcement of the paper's broad subject"
- "a fact, which is not arguable"
- "a truism (statement that is obviously true)"
- "a personal or religious conviction that cannot be logically debated"
- "an opinion based only on your feelings"
- "a sweeping generalization" (Section 4C, pg. 52)
The book also provides examples and key points (pg. 53) for a good working thesis.
- << Previous: #5 Integrating Sources
- Next: Research Question Discussion >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2023 2:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/think_like_a_researcher

Scaffolding Methods for Research Paper Writing

- Resources & Preparation
- Instructional Plan
- Related Resources
Students will use scaffolding to research and organize information for writing a research paper. A research paper scaffold provides students with clear support for writing expository papers that include a question (problem), literature review, analysis, methodology for original research, results, conclusion, and references. Students examine informational text, use an inquiry-based approach, and practice genre-specific strategies for expository writing. Depending on the goals of the assignment, students may work collaboratively or as individuals. A student-written paper about color psychology provides an authentic model of a scaffold and the corresponding finished paper. The research paper scaffold is designed to be completed during seven or eight sessions over the course of four to six weeks.
Featured Resources
- Research Paper Scaffold : This handout guides students in researching and organizing the information they need for writing their research paper.
- Inquiry on the Internet: Evaluating Web Pages for a Class Collection : Students use Internet search engines and Web analysis checklists to evaluate online resources then write annotations that explain how and why the resources will be valuable to the class.
From Theory to Practice
- Research paper scaffolding provides a temporary linguistic tool to assist students as they organize their expository writing. Scaffolding assists students in moving to levels of language performance they might be unable to obtain without this support.
- An instructional scaffold essentially changes the role of the teacher from that of giver of knowledge to leader in inquiry. This relationship encourages creative intelligence on the part of both teacher and student, which in turn may broaden the notion of literacy so as to include more learning styles.
- An instructional scaffold is useful for expository writing because of its basis in problem solving, ownership, appropriateness, support, collaboration, and internalization. It allows students to start where they are comfortable, and provides a genre-based structure for organizing creative ideas.
- In order for students to take ownership of knowledge, they must learn to rework raw information, use details and facts, and write.
- Teaching writing should involve direct, explicit comprehension instruction, effective instructional principles embedded in content, motivation and self-directed learning, and text-based collaborative learning to improve middle school and high school literacy.
Common Core Standards
This resource has been aligned to the Common Core State Standards for states in which they have been adopted. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, CCSS alignments are forthcoming.
State Standards
This lesson has been aligned to standards in the following states. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, standard alignments are not currently available for that state.
NCTE/IRA National Standards for the English Language Arts
- 1. Students read a wide range of print and nonprint texts to build an understanding of texts, of themselves, and of the cultures of the United States and the world; to acquire new information; to respond to the needs and demands of society and the workplace; and for personal fulfillment. Among these texts are fiction and nonfiction, classic and contemporary works.
- 2. Students read a wide range of literature from many periods in many genres to build an understanding of the many dimensions (e.g., philosophical, ethical, aesthetic) of human experience.
- 3. Students apply a wide range of strategies to comprehend, interpret, evaluate, and appreciate texts. They draw on their prior experience, their interactions with other readers and writers, their knowledge of word meaning and of other texts, their word identification strategies, and their understanding of textual features (e.g., sound-letter correspondence, sentence structure, context, graphics).
- 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes.
- 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts.
- 7. Students conduct research on issues and interests by generating ideas and questions, and by posing problems. They gather, evaluate, and synthesize data from a variety of sources (e.g., print and nonprint texts, artifacts, people) to communicate their discoveries in ways that suit their purpose and audience.
- 8. Students use a variety of technological and information resources (e.g., libraries, databases, computer networks, video) to gather and synthesize information and to create and communicate knowledge.
- 12. Students use spoken, written, and visual language to accomplish their own purposes (e.g., for learning, enjoyment, persuasion, and the exchange of information).
Materials and Technology
Computers with Internet access and printing capability
- Research Paper Scaffold
- Example Research Paper Scaffold
- Example Student Research Paper
- Internet Citation Checklist
- Research Paper Scoring Rubric
- Permission Form (optional)
Preparation
Student objectives.
Students will
- Formulate a clear thesis that conveys a perspective on the subject of their research
- Practice research skills, including evaluation of sources, paraphrasing and summarizing relevant information, and citation of sources used
- Logically group and sequence ideas in expository writing
- Organize and display information on charts, maps, and graphs
Session 1: Research Question
You should approve students’ final research questions before Session 2. You may also wish to send home the Permission Form with students, to make parents aware of their child’s research topic and the project due dates.
Session 2: Literature Review—Search
Prior to this session, you may want to introduce or review Internet search techniques using the lesson Inquiry on the Internet: Evaluating Web Pages for a Class Collection . You may also wish to consult with the school librarian regarding subscription databases designed specifically for student research, which may be available through the school or public library. Using these types of resources will help to ensure that students find relevant and appropriate information. Using Internet search engines such as Google can be overwhelming to beginning researchers.
Session 3: Literature Review—Notes
Students need to bring their articles to this session. For large classes, have students highlight relevant information (as described below) and submit the articles for assessment before beginning the session.
Checking Literature Review entries on the same day is best practice, as it gives both you and the student time to plan and address any problems before proceeding. Note that in the finished product this literature review section will be about six paragraphs, so students need to gather enough facts to fit this format.
Session 4: Analysis
Session 5: original research.
Students should design some form of original research appropriate to their topics, but they do not necessarily have to conduct the experiments or surveys they propose. Depending on the appropriateness of the original research proposals, the time involved, and the resources available, you may prefer to omit the actual research or use it as an extension activity.
Session 6: Results (optional)
Session 7: conclusion, session 8: references and writing final draft, student assessment / reflections.
- Observe students’ participation in the initial stages of the Research Paper Scaffold and promptly address any errors or misconceptions about the research process.
- Observe students and provide feedback as they complete each section of the Research Paper Scaffold.
- Provide a safe environment where students will want to take risks in exploring ideas. During collaborative work, offer feedback and guidance to those who need encouragement or require assistance in learning cooperation and tolerance.
- Involve students in using the Research Paper Scoring Rubric for final evaluation of the research paper. Go over this rubric during Session 8, before they write their final drafts.
- Strategy Guides
Add new comment
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K
- Research Skills
50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills
Please note, I am no longer blogging and this post hasn’t updated since April 2020.
For a number of years, Seth Godin has been talking about the need to “ connect the dots” rather than “collect the dots” . That is, rather than memorising information, students must be able to learn how to solve new problems, see patterns, and combine multiple perspectives.
Solid research skills underpin this. Having the fluency to find and use information successfully is an essential skill for life and work.
Today’s students have more information at their fingertips than ever before and this means the role of the teacher as a guide is more important than ever.
You might be wondering how you can fit teaching research skills into a busy curriculum? There aren’t enough hours in the day! The good news is, there are so many mini-lessons you can do to build students’ skills over time.
This post outlines 50 ideas for activities that could be done in just a few minutes (or stretched out to a longer lesson if you have the time!).
Learn More About The Research Process
I have a popular post called Teach Students How To Research Online In 5 Steps. It outlines a five-step approach to break down the research process into manageable chunks.

This post shares ideas for mini-lessons that could be carried out in the classroom throughout the year to help build students’ skills in the five areas of: clarify, search, delve, evaluate , and cite . It also includes ideas for learning about staying organised throughout the research process.
Notes about the 50 research activities:
- These ideas can be adapted for different age groups from middle primary/elementary to senior high school.
- Many of these ideas can be repeated throughout the year.
- Depending on the age of your students, you can decide whether the activity will be more teacher or student led. Some activities suggest coming up with a list of words, questions, or phrases. Teachers of younger students could generate these themselves.
- Depending on how much time you have, many of the activities can be either quickly modelled by the teacher, or extended to an hour-long lesson.
- Some of the activities could fit into more than one category.
- Looking for simple articles for younger students for some of the activities? Try DOGO News or Time for Kids . Newsela is also a great resource but you do need to sign up for free account.
- Why not try a few activities in a staff meeting? Everyone can always brush up on their own research skills!
- Choose a topic (e.g. koalas, basketball, Mount Everest) . Write as many questions as you can think of relating to that topic.
- Make a mindmap of a topic you’re currently learning about. This could be either on paper or using an online tool like Bubbl.us .
- Read a short book or article. Make a list of 5 words from the text that you don’t totally understand. Look up the meaning of the words in a dictionary (online or paper).
- Look at a printed or digital copy of a short article with the title removed. Come up with as many different titles as possible that would fit the article.
- Come up with a list of 5 different questions you could type into Google (e.g. Which country in Asia has the largest population?) Circle the keywords in each question.
- Write down 10 words to describe a person, place, or topic. Come up with synonyms for these words using a tool like Thesaurus.com .
- Write pairs of synonyms on post-it notes (this could be done by the teacher or students). Each student in the class has one post-it note and walks around the classroom to find the person with the synonym to their word.

- Explore how to search Google using your voice (i.e. click/tap on the microphone in the Google search box or on your phone/tablet keyboard) . List the pros and cons of using voice and text to search.
- Open two different search engines in your browser such as Google and Bing. Type in a query and compare the results. Do all search engines work exactly the same?
- Have students work in pairs to try out a different search engine (there are 11 listed here ). Report back to the class on the pros and cons.
- Think of something you’re curious about, (e.g. What endangered animals live in the Amazon Rainforest?). Open Google in two tabs. In one search, type in one or two keywords ( e.g. Amazon Rainforest) . In the other search type in multiple relevant keywords (e.g. endangered animals Amazon rainforest). Compare the results. Discuss the importance of being specific.
- Similar to above, try two different searches where one phrase is in quotation marks and the other is not. For example, Origin of “raining cats and dogs” and Origin of raining cats and dogs . Discuss the difference that using quotation marks makes (It tells Google to search for the precise keywords in order.)
- Try writing a question in Google with a few minor spelling mistakes. What happens? What happens if you add or leave out punctuation ?
- Try the AGoogleADay.com daily search challenges from Google. The questions help older students learn about choosing keywords, deconstructing questions, and altering keywords.
- Explore how Google uses autocomplete to suggest searches quickly. Try it out by typing in various queries (e.g. How to draw… or What is the tallest…). Discuss how these suggestions come about, how to use them, and whether they’re usually helpful.
- Watch this video from Code.org to learn more about how search works .
- Take a look at 20 Instant Google Searches your Students Need to Know by Eric Curts to learn about “ instant searches ”. Try one to try out. Perhaps each student could be assigned one to try and share with the class.
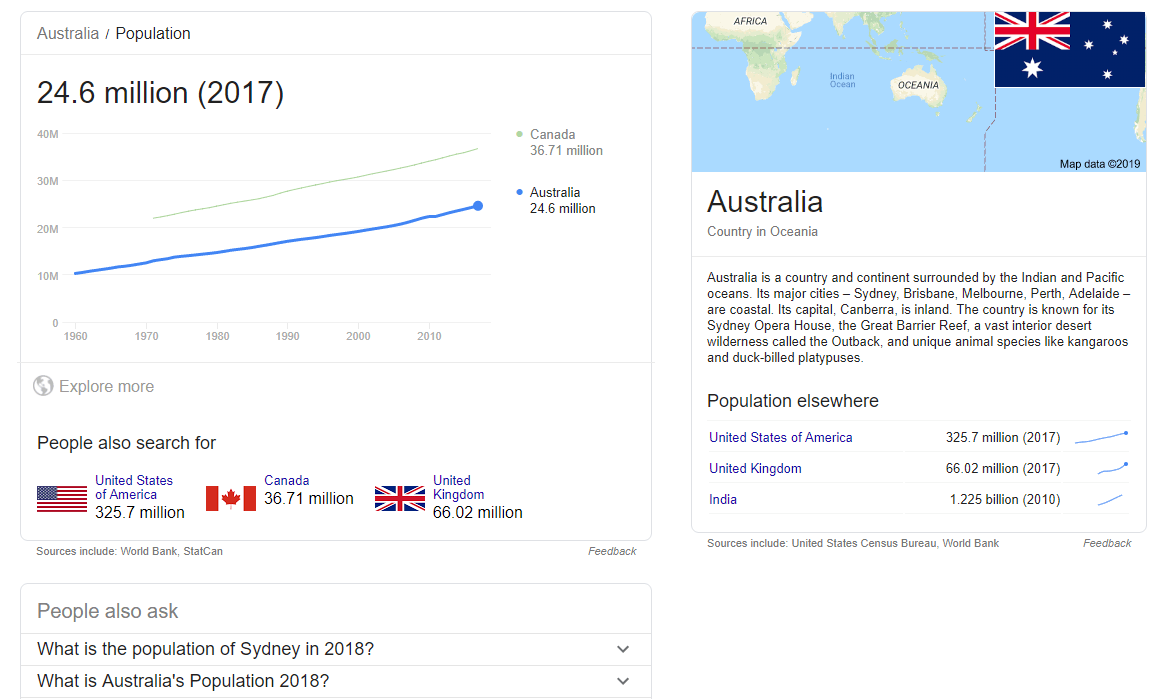
- Experiment with typing some questions into Google that have a clear answer (e.g. “What is a parallelogram?” or “What is the highest mountain in the world?” or “What is the population of Australia?”). Look at the different ways the answers are displayed instantly within the search results — dictionary definitions, image cards, graphs etc.
- Watch the video How Does Google Know Everything About Me? by Scientific American. Discuss the PageRank algorithm and how Google uses your data to customise search results.
- Brainstorm a list of popular domains (e.g. .com, .com.au, or your country’s domain) . Discuss if any domains might be more reliable than others and why (e.g. .gov or .edu) .
- Discuss (or research) ways to open Google search results in a new tab to save your original search results (i.e. right-click > open link in new tab or press control/command and click the link).
- Try out a few Google searches (perhaps start with things like “car service” “cat food” or “fresh flowers”). A re there advertisements within the results? Discuss where these appear and how to spot them.
- Look at ways to filter search results by using the tabs at the top of the page in Google (i.e. news, images, shopping, maps, videos etc.). Do the same filters appear for all Google searches? Try out a few different searches and see.
- Type a question into Google and look for the “People also ask” and “Searches related to…” sections. Discuss how these could be useful. When should you use them or ignore them so you don’t go off on an irrelevant tangent? Is the information in the drop-down section under “People also ask” always the best?
- Often, more current search results are more useful. Click on “tools” under the Google search box and then “any time” and your time frame of choice such as “Past month” or “Past year”.
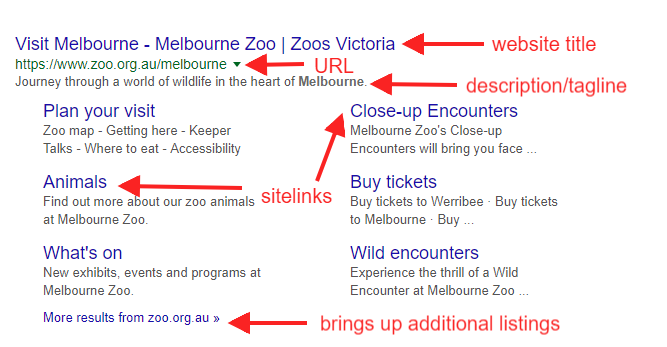
- Have students annotate their own “anatomy of a search result” example like the one I made below. Explore the different ways search results display; some have more details like sitelinks and some do not.
- Find two articles on a news topic from different publications. Or find a news article and an opinion piece on the same topic. Make a Venn diagram comparing the similarities and differences.
- Choose a graph, map, or chart from The New York Times’ What’s Going On In This Graph series . Have a whole class or small group discussion about the data.
- Look at images stripped of their captions on What’s Going On In This Picture? by The New York Times. Discuss the images in pairs or small groups. What can you tell?
- Explore a website together as a class or in pairs — perhaps a news website. Identify all the advertisements .
- Have a look at a fake website either as a whole class or in pairs/small groups. See if students can spot that these sites are not real. Discuss the fact that you can’t believe everything that’s online. Get started with these four examples of fake websites from Eric Curts.
- Give students a copy of my website evaluation flowchart to analyse and then discuss as a class. Read more about the flowchart in this post.
- As a class, look at a prompt from Mike Caulfield’s Four Moves . Either together or in small groups, have students fact check the prompts on the site. This resource explains more about the fact checking process. Note: some of these prompts are not suitable for younger students.
- Practice skim reading — give students one minute to read a short article. Ask them to discuss what stood out to them. Headings? Bold words? Quotes? Then give students ten minutes to read the same article and discuss deep reading.

All students can benefit from learning about plagiarism, copyright, how to write information in their own words, and how to acknowledge the source. However, the formality of this process will depend on your students’ age and your curriculum guidelines.
- Watch the video Citation for Beginners for an introduction to citation. Discuss the key points to remember.
- Look up the definition of plagiarism using a variety of sources (dictionary, video, Wikipedia etc.). Create a definition as a class.
- Find an interesting video on YouTube (perhaps a “life hack” video) and write a brief summary in your own words.
- Have students pair up and tell each other about their weekend. Then have the listener try to verbalise or write their friend’s recount in their own words. Discuss how accurate this was.
- Read the class a copy of a well known fairy tale. Have them write a short summary in their own words. Compare the versions that different students come up with.
- Try out MyBib — a handy free online tool without ads that helps you create citations quickly and easily.
- Give primary/elementary students a copy of Kathy Schrock’s Guide to Citation that matches their grade level (the guide covers grades 1 to 6). Choose one form of citation and create some examples as a class (e.g. a website or a book).
- Make a list of things that are okay and not okay to do when researching, e.g. copy text from a website, use any image from Google images, paraphrase in your own words and cite your source, add a short quote and cite the source.
- Have students read a short article and then come up with a summary that would be considered plagiarism and one that would not be considered plagiarism. These could be shared with the class and the students asked to decide which one shows an example of plagiarism .
- Older students could investigate the difference between paraphrasing and summarising . They could create a Venn diagram that compares the two.
- Write a list of statements on the board that might be true or false ( e.g. The 1956 Olympics were held in Melbourne, Australia. The rhinoceros is the largest land animal in the world. The current marathon world record is 2 hours, 7 minutes). Have students research these statements and decide whether they’re true or false by sharing their citations.
Staying Organised

- Make a list of different ways you can take notes while researching — Google Docs, Google Keep, pen and paper etc. Discuss the pros and cons of each method.
- Learn the keyboard shortcuts to help manage tabs (e.g. open new tab, reopen closed tab, go to next tab etc.). Perhaps students could all try out the shortcuts and share their favourite one with the class.
- Find a collection of resources on a topic and add them to a Wakelet .
- Listen to a short podcast or watch a brief video on a certain topic and sketchnote ideas. Sylvia Duckworth has some great tips about live sketchnoting
- Learn how to use split screen to have one window open with your research, and another open with your notes (e.g. a Google spreadsheet, Google Doc, Microsoft Word or OneNote etc.) .
All teachers know it’s important to teach students to research well. Investing time in this process will also pay off throughout the year and the years to come. Students will be able to focus on analysing and synthesizing information, rather than the mechanics of the research process.
By trying out as many of these mini-lessons as possible throughout the year, you’ll be really helping your students to thrive in all areas of school, work, and life.
Also remember to model your own searches explicitly during class time. Talk out loud as you look things up and ask students for input. Learning together is the way to go!
You Might Also Enjoy Reading:
How To Evaluate Websites: A Guide For Teachers And Students
Five Tips for Teaching Students How to Research and Filter Information
Typing Tips: The How and Why of Teaching Students Keyboarding Skills
8 Ways Teachers And Schools Can Communicate With Parents

10 Replies to “50 Mini-Lessons For Teaching Students Research Skills”
Loving these ideas, thank you
This list is amazing. Thank you so much!
So glad it’s helpful, Alex! 🙂
Hi I am a student who really needed some help on how to reasearch thanks for the help.
So glad it helped! 🙂
seriously seriously grateful for your post. 🙂
So glad it’s helpful! Makes my day 🙂
How do you get the 50 mini lessons. I got the free one but am interested in the full version.
Hi Tracey, The link to the PDF with the 50 mini lessons is in the post. Here it is . Check out this post if you need more advice on teaching students how to research online. Hope that helps! Kathleen
Best wishes to you as you face your health battler. Hoping you’ve come out stronger and healthier from it. Your website is so helpful.
Comments are closed.

Write a Research Question
Before you begin writing your research question, it is first important to craft a purpose statement. What can be a purpose of your study?
Examples of a purpose for a quantitative study include:
- Examining a relationship between students who take computing classes in high school and those who pursue computer science as a major in college,
- Evaluating the effectiveness of an outreach activity among underrepresented students, or
- Measuring engagement or interest in computing among middle school students.
Examples for a qualitative study include:
- Exploring parent stories about helping their students with computing homework or
- Developing a theory of effective management techniques in a computer lab.
Once you define the purpose of your study, you can then create a clear purpose statement. Purpose statements help you define your research in a straightforward manner. Here is an example of a well-defined purpose statement.
The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between the completion of an 9-week computational thinking unit among 7th and 8th grade students in a rural middle school and student achievement on mathematics exams.
This purpose statement explicitly answers these questions:
- What is the intent of the study?
- What population group is targeted in the study (i.e., age, location, etc.)?
- What was the intervention (activity or curriculum), including its duration?
After you have decided on the purpose of your study and have written your purpose statement, you can then craft your research question.
Writing a Well-crafted Research Question
Research questions provide an overarching direction for your study to follow. It guides the type of study you will choose, the type of data you will collect, and the type of analysis on the data that you will perform.
Writing good research questions, then, is an important step in framing your study. What makes a good research question? Research questions should be clear, concise, specific, neutral, and focused. They should also be complex enough that the question requires more than just a “yes” or “no” answer. An example of a thorough research question for a quantitative study follows:
Does guardian understanding of computational thinking affect student performance on computational thinking tasks among primary school students in an urban school district?
For a qualitative study, a thorough research question may look like this:
What are the major challenges teachers face when teaching computational thinking to Kindergarten, 1st grade and 2nd grade students in the United States?
Typically, research questions are not the exact question that you will actually ask the participants in your study. They, however, guide those questions.
Research questions should:
- Define what is being measured
- Define the population group
- Be neutral (not assume the intervention being studied is effective or not)
- Be able to be answered in the timeframe you have planned for the study
Depending on the study length, more than one research question can be appropriate. Your research questions will most likely be related in some way, since they will be designed to support your purpose statement.
Defining What is being Measured
Defining what is being measured is important for narrowing your research. Consider the following questions:
1A: Does participation in a one-week teacher professional development around the Exploring Computer Science curriculum result in improved teaching practices? 1B: Does participation in a one-week teacher professional development around the Exploring Computer Science curriculum result in more frequent use of inquiry-based learning pedagogical methods?
In the example above, Question 1A refers to “improved teaching practices”. “Improved teaching practices” is unclear, since there is no context for “improved” against the status quo. In Question 1B, one teaching practice, inquiry-based learning, is chosen for the study.
Defining the Population Group
Defining the population group is often missing in research questions, but it is very easy to add. Consider the following questions:
2A: Do participants in a week-long Lego Robotics summer camp have an increased likelihood of taking computer science courses at the college level?
2B: Do 11th and 12th grade students in central Illinois who participate in a week-long Lego Robotics summer camp have an increased likelihood of taking computer science courses during their first year of college?
In the Question 2A, we do not know who the participants are or where they are located. As a research question, clearly stating the population group is important for identifying the group that will be targeted in your study. Sometimes this information may be provided in context within preceding paragraphs. However, restating the population group within the research question makes the target of your study clear to your reader.
In our review of hundreds of articles for this site, we have encountered many articles that do not state whether the group is undergraduate students, primary school students, or secondary school students or in which country or setting the study takes place. It is difficult for other researchers to use or build upon research that hasn’t clearly stated the population group. Embedding this into your research question will enable others to know who the participants in your study were.
Writing Neutral Statements
A neutral statement will exclude any pre-conceived bias. Consider these questions:
3A: What elements of AP Computer Science Principles make it a more appealing course to high school-aged girls than AP Computer Science A? 3B: Is the AP Computer Science Principles course more appealing to high school-aged girls than AP Computer Science A? If so, what is seen as different and/or more appealing?
Question A assumes that the AP Computer Science Principles course is more appealing than the AP Computer Science A course for the target population (high school-aged girls). If this has been previously established in prior research and the researchers are making this a follow-up study, then Question 3A may be seen as neutral. However, if this has not been previously established, then Question 3B may be a more appropriately worded research question.
Defining a Scope/Timeframe
Research studies are projects, and just like any project, it is important to manage scope. Scope is based on your timeframe and your resources. Consider the following questions:
4A: Are middle-school girls who participate in a summer camp more likely to pursue careers in computing fields than those who do not participate in the camp? 4B: Are middle-school girls who participate in a summer camp more likely to express interest in computing-related careers than those who do not participate in the camp?
Question 4A implies that girls will be tracked from middle school through college and into their careers. This longitudinal study would take a minimum of seven years, likely more, if you count the years it would take for a 6th grader to start her career. Question 4B is finite and could be evaluated at the end of camp, three months after the camp has ended, or even the following year.
In this example, both questions could be suitable and is entirely dependent on your timeframe for your study as well as your resources.
Additional Examples
Take a look at these examples that illustrate different types of requirements for well-crafted research questions.
Example 5A: How is Scratch used to teach computational thinking? Example 5B: How are Native American high school teachers in North Dakota using Scratch to teach computational thinking?
The 5A research question is very vague. We know nothing about the population group being studied or the intervention other than one computing education tool being used (Scratch) and the concept being taught. The 5B question specifies how Scratch is being used and the population group being targeted.
Example 6A: Does a game design camp make girls interested in computing? Example 6B: What is the impact of a one-week game design camp on the interest levels in computing among 7th and 8th grade girls located in Chicago’s West Side?
Example 6A is very broad. It may be fine if you are planning on writing a book or a 200-page dissertation. For most of us, though, our studies need to be more focused so that we can complete it in 6 months or 1 or 2 years. Example 6B looks at a specific cause (impact of a one-week game design camp), a specific locale (Chicago’s West Side), and a specific group (7th and 8th grade girls). By making your research question(s) well-defined, you are more likely to be able to answer the question in the timeframe for your study.

Privacy Overview
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy
Research Activities For Middle School: Discussions, Tips, Exploration, And Learning Resources
February 6, 2024 // by Josilyn Markel
Learning to research effectively is an important skill that middle-school-aged students can learn and carry with them for their whole academic careers. The students in question will use these skills for everything from reading news articles to writing a systematic review of their sources. With increased demands on students these days, it’s never too early to introduce these sophisticated research skills.
We’ve collected thirty of the best academic lessons for middle school students to learn about sophisticated research skills that they’ll use for the rest of their lives.
1. Guiding Questions for Research
When you first give a research project to middle school students, it’s important to make sure that they really understand the research prompts. You can use this guiding questions tool with students to help them draw on existing knowledge to properly contextualize the prompt and assignment before they even pick up a pen.
Learn More: Mrs. Spangler in the Middle
2. Teaching Research Essential Skills Bundle
This bundle touches on all the writing skills, planning strategies, and so-called soft skills that students will need to get started on their first research project. These resources are especially geared towards middle school-aged students to help them with cognitive control tasks plus engaging and active lessons.
Learn More: Pinterest
3. How to Develop a Research Question
Before a middle school student can start their research time on task, they have to form a solid research question. This resource features activities for students that will help them identify a problem and then formulate a question that will guide their research project going first.
Learn More: YouTube
4. Note-Taking Skills Infographic
For a strong introduction and/or systematic review of the importance of note-taking, look no further than this infographic. It covers several excellent strategies for taking the most important info from a source, and it also gives tips for using these strategies to strengthen writing skills.
Learn More: Word Counter
5. Guide to Citing Online Sources
One of the more sophisticated research skills is learning to cite sources. These days, the internet is the most popular place to find research sources, so learning the citation styles for making detailed citations for internet sources is an excellent strategy. This is a skill that will stick with middle school students throughout their entire academic careers!
Learn More: Educator’s Technology
6. Guided Student-Led Research Projects
This is a great way to boost communication between students while also encouraging choice and autonomy throughout the research process. This really opens up possibilities for students and boosts student activity and engagement throughout the whole project. The group setup also decreases the demands on students as individuals.
Learn More: The Thinker Builder
7. Teaching Students to Fact-Check
Fact-checking is an important meta-analytic review skill that every student needs. This resource introduces probing questions that students can ask in order to ensure that the information they’re looking at is actually true. This can help them identify fake news, find more credible sources, and improve their overall sophisticated research skills.
Learn More: Just Add Students
8. Fact-Checking Like a Pro
This resource features great teaching strategies (such as visualization) to help alleviate the demands on students when it comes to fact-checking their research sources. It’s perfect for middle school-aged students who want to follow the steps to make sure that they’re using credible sources in all of their research projects, for middle school and beyond!
9. Website Evaluation Activity
With this activity, you can use any website as a backdrop. This is a great way to help start the explanation of sources that will ultimately lead to helping students locate and identify credible sources (rather than fake news). With these probing questions, students will be able to evaluate websites effectively.
10. How to Take Notes in Class
This visually pleasing resource tells students everything they need to know about taking notes in a classroom setting. It goes over how to glean the most important information from the classroom teacher, and how to organize the info in real-time, and it gives tips for cognitive control tasks and other sophisticated research skills that will help students throughout the research and writing process.
Learn More: Visualistan
11. Teaching Research Papers: Lesson Calendar
If you have no idea how you’re going to cover all the so-called soft skills, mini-lessons, and activities for students during your research unit, then don’t fret! This calendar breaks down exactly what you should be teaching, and when. It introduces planning strategies, credible sources, and all the other research topics with a logical and manageable flow.
Learn More: Discover Hub Pages
12. Google Docs Features for Teaching Research
With this resource, you can explore all of the handy research-focused features that are already built into Google Docs! You can use it to build activities for students or to make your existing activities for students more tech-integrated. You can use this tool with students from the outset to get them interested and familiar with the Google Doc setup.
13. Using Effective Keywords to Search the Internet
The internet is a huge place, and this vast amount of knowledge puts huge demands on students’ skills and cognition. That’s why they need to learn how to search online effectively, with the right keywords. This resource teaches middle school-aged students how to make the most of all the search features online.
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers
14. How to Avoid Plagiarism: “Did I Plagiarize?”
This student activity looks at the biggest faux pas in middle school research projects: plagiarism. These days, the possibilities for students to plagiarize are endless, so it’s important for them to learn about quotation marks, paraphrasing, and citations. This resource includes information on all of those and in a handy flow chart to keep them right!
Learn More: Twitter
15. 7 Tips for Recognizing Bias
This is a resource to help middle school-aged students recognize the differences between untrustworthy and credible sources. It gives a nice explanation of sources that are trustworthy and also offers a source of activities that students can use to test and practice identifying credible sources.
Learn More: We Are Teachers

16. UNESCO’s Laws for Media Literacy
This is one of those great online resources that truly focuses on the students in question, and it serves a larger, global goal. It offers probing questions that can help middle school-aged children determine whether or not they’re looking at credible online resources. It also helps to strengthen the so-called soft skills that are necessary for completing research.
Learn More: SLJ Blogs
17. Guide for Evaluating a News Article
Here are active lessons that students can use to learn more about evaluating a news article, whether it’s on a paper or online resource. It’s also a great tool to help solidify the concept of fake news and help students build an excellent strategy for identifying and utilizing credible online sources.
Learn More: Valencia College
18. Middle School Research Projects Middle School Students Will Love
Here is a list of 30 great research projects for middle schoolers, along with cool examples of each one. It also goes through planning strategies and other so-called soft skills that your middle school-aged students will need in order to complete such projects.
Learn More: Madly Learning
19. Teaching Analysis with Body Biographies
This is a student activity and teaching strategy all rolled into one! It looks at the importance of research and biographies, which brings a human element to the research process. It also helps communication between students and helps them practice those so-called soft skills that come in handy while researching.
Learn More: Study All Knight
20. Top Tips for Teaching Research in Middle School
When it comes to teaching middle school research, there are wrong answers and there are correct answers. You can learn all the correct answers and teaching strategies with this resource, which debunks several myths about teaching the writing process at the middle school level.
Learn More: Teaching ELA with Joy
21. Teaching Students to Research Online: Lesson Plan
This is a ready-made lesson plan that is ready to present. You don’t have to do tons of preparation, and you’ll be able to explain the basic and foundational topics related to research. Plus, it includes a couple of activities to keep students engaged throughout this introductory lesson.
Learn More: Kathleen Morris
22. Project-Based Learning: Acceptance and Tolerance
This is a series of research projects that look at specific problems regarding acceptance and tolerance. It offers prompts for middle school-aged students that will get them to ask big questions about themselves and others in the world around them.
Learn More: Sandy Cangelosi
23. 50 Tiny Lessons for Teaching Research Skills in Middle School
These fifty mini-lessons and activities for students will have middle school-aged students learning and applying research skills in small chunks. The mini-lessons approach allows students to get bite-sized information and focus on mastering and applying each step of the research process in turn. This way, with mini-lessons, students don’t get overwhelmed with the whole research process at once. In this way, mini-lessons are a great way to teach the whole research process!
24. Benefits of Research Projects for Middle School Students
Whenever you feel like it’s just not worth it to go to the trouble to teach your middle school-aged students about research, let this list motivate you! It’s a great reminder of all the great things that come with learning to do good research at an early age.
Learn More: Thrive in Grade Five
25. Top 5 Study and Research Skills for Middle Schoolers
This is a great resource for a quick and easy overview of the top skills that middle schoolers will need before they dive into research. It outlines the most effective tools to help your students study and research well, throughout their academic careers.
Learn More: Meagan Gets Real
26. Research with Informational Text: World Travelers
This travel-themed research project will have kids exploring the whole world with their questions and queries. It is a fun way to bring new destinations into the research-oriented classroom.
Learn More: The Superhero Teacher
27. Project-Based Learning: Plan a Road Trip
If you want your middle school-aged students to get into the researching mood, have them plan a road trip! They’ll have to examine the prompt from several angles and collect data from several sources before they can put together a plan for an epic road trip.
Learn More: Appletastic Learning
28. Methods for Motivating Writing Skills
When your students just are feeling up to the task of research-based writing, it’s time to break out these motivational methods. With these tips and tricks, you’ll be able to get your kids in the mood to research, question, and write!
29. How to Set Up a Student Research Station
This article tells you everything you need to know about a student center focused on sophisticated research skills. These student center activities are engaging and fun, and they touch on important topics in the research process, such as planning strategies, fact-checking skills, citation styles, and some so-called soft skills.
Learn More: Upper Elementary Snapshots
30. Learn to Skim and Scan to Make Research Easier
These activities for students are geared towards encouraging reading skills that will ultimately lead to better and easier research. The skills in question? Skimming and scanning. This will help students read more efficiently and effectively as they research from a variety of sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project
Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on October 19, 2023.
The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation . It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
The exact form of your question will depend on a few things, such as the length of your project, the type of research you’re conducting, the topic , and the research problem . However, all research questions should be focused, specific, and relevant to a timely social or scholarly issue.
Once you’ve read our guide on how to write a research question , you can use these examples to craft your own.
Note that the design of your research question can depend on what method you are pursuing. Here are a few options for qualitative, quantitative, and statistical research questions.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, October 19). 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-question-examples/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, evaluating sources | methods & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
MIDDLE SCHOOL MATTERS
High-quality support and resources for the middle grades
Generating Questions Toolkit

NOTE: If you participated in the MSM-PREP research study and are looking for the toolkit used during your participation, please email [email protected] so you can obtain the private link.
About the Practice
QUESTION GENERATION is a reading comprehension practice that teaches students to write questions about important information or facts from a text while they are reading. This helps students pause, think about what is being communicated, and how informatin relates across paragraphs. Studies have shown that this practice can increase comprehension of content area text.
Download our New Infographic to Share with Teachers!
Download our New Infographic!
Students use a 3-step process:
Step 1) Read a text, either in small groups, pairs, or independently.
Step 2) Pause at regular intervals to generate questions and record them in a learning log or journal.
Step 3) Answer questions and indicate where the answer was found in the text.
Students are taught to write two different types of questions: specific questions and wide questions
Professional Development Resources
PD Module–Secondary Reading Instruction: Teaching Vocabulary and Comprehension in the Content Areas (IRIS Center)
Research to Practice Article in Journal of Adolescent and Adult Literacy (Middle School Matters)
Demonstration Videos
Generating Questions Video Page (Texas Adolescent Literacy Academy)
Example Model Lessons
Modeling Specific Questions (Middle School Matters)
Modeling Wide Questions (Middle School Matters)
Instructional Materials
Student Cue Card (Middle School Matters)
Question Log (Middle School Matters)
Classroom Poster (Middle School Matters)
Sources for Other Reading Passages
Contact us at [email protected]

- Services Paper editing services Paper proofreading Business papers Philosophy papers Write my paper Term papers for sale Term paper help Academic term papers Buy research papers College writing services Paper writing help Student papers Original term papers Research paper help Nursing papers for sale Psychology papers Economics papers Medical papers Blog

206 Middle School Research Topics: Original Ideas List

As middle schoolers prepare to go to high school, they are introduced slowly to essay and research writing. They are sometimes given homework that involves picking suitable topics and writing on them. However, it should be noted that i t is not easy to write a research paper for a high grade. Middle schoolers in their preteen age are taught how to be creative, air out their opinions and conduct little research. It helps make them critical thinkers and prepares them for more writing tasks as they advance in their education. This article will help middle schoolers understand what is expected of them when asked to write an essay or research on a topic. It will also expose them to different areas where they can write and many research topics for middle school they can pick from.
What Should Be In A Middle School Research Paper?
Middle school research papers are often not required to be extended. They are in a unique position where they move from writing simple pieces to more detailed essays and research papers. This is the foundation where they learn to write excellent papers as they transcend to high school and eventually college. Writing an essay in middle school is not very different from writing in other stages. Some steps to get you started are
- Understanding the Assignment :Before you begin, you should understand your teacher’s expectations when turning in your finished work.There will be rules and procedures to follow. Know the format the essay is supposed to be written in, and keep the due dates in mind. If you do not understand any aspect of the assignment, please ask for clarification, as this will help you deliver a clear and concise essay at the end.
- Do Your Pre-Writing :Start with brainstorming on middle school research topics to determine what you would like your essay to be about. There are many options to pick from and several general subjects to break down into topics you want.
Pick up to three topics when you first brainstorm. From there, you can select the best one to write on. When you find a topic, start writing all you know about it. Create a rough paper where you jot down information from your research that will be useful in your essay. Feel free to write freely, as this will be your first draft, and you have the chance to edit it as you go.
- Edit Your Work : Editing is essential. It helps give your paper structure. From your rough work, take out parts that are not necessary and add details you think you missed. This is where you should be detailed and try to make your work as neat and correct as possible. You are almost at the end of writing the paper.When you are sure your paper is good, it is time to proofread. Check for spelling and punctuation errors. One expert way to do this is to read the report from the bottom up, and this can help you spot any spelling errors.
- Citations and References : Your teacher would have given you a format to write references for your work. Ensure that you are following the prescribed format.References will highlight the sources of the information gathered to make your essay.
What Can Middle Schoolers Write About?
There are many general subjects that middle schoolers can write about in their assignments. Streaming from what they have been taught in the classroom or their experiences outside class. Some issues that can create good middle school research paper topics include:
Science : This broad aspect covers earth science, geology, physical science, life science, and genetics. Science research paper topics for middle school will encourage the students to be interested in growth and learning how things work. Social Studies : This will involve learning about their history, other people’s cultures, human interaction, family, etc. This will create fun research topics for 6th graders, learning about life and how relationships work. Literature : This is the best time to learn about books and works of art. The literature will provide many topics to research for middle school students.
There are many more aspects that middle school students can research and write papers on. Discover more than 200 interesting research topics for middle school students below. However don’t worry if the assignment seems too difficult for you. You are only at the beginning of the path and our cheap research writing service will be happy to get you through with your paper.
Good Research Topics For Middle School
Students who have no experience writing papers and are looking for good research topics to work on are in luck. The topics below are suitable for all middle schoolers and can create detailed essays.
- Should students be compelled to wear a specific uniform?
- Textbooks or tablets: which is better to read from?
- Obesity in American youth: Causes and solutions.
- Should boys and girls be allowed to play on the same athletics team?
- Should young people be allowed to play violent video games?
- Impact of continuously playing violent video games.
- When can we say someone is spending too much time in front of the screen?
- Listening to music during class: Does it disturb concentration?
- How to recognize harmful content on the internet?
- Should all businesses be compelled to recycle?
- What is the appropriate punishment for students who engage in cyberbullying?
- Should school hours be adjusted to later in the morning?
- Should our scientists be allowed to test drugs on animals?
- Why do people’s behavior change in different settings?
- Is sex education important?
- Different types of poetry and how they came about.
- What to do if you are being bullied on the internet.
- How to have healthy self-esteem.
- Why does the human body need sleep?
- Insect repellents, are they helpful?
- Why did dinosaurs go extinct?
- What is skateboarding?
- The effects of tobacco on the body.
- Artificial tanning: Risks and benefits.
- What is spam email? Where does it come from, and how can we stop it?
- What is a desert mirage? How does it affect people?
- What are penguins? Where do they stay, and what do they eat?
- When and how was America created?
- Who are some well know and inspirational women?
- Who are some famous inventors?
- What famous inventions helped in shaping human existence?
- Steps you can take to protect yourself from scammers online.
- What is a cryptocurrency, and why is it so popular?
- What did the invention of the mobile phone do to change the world?
- How to handle stress from school.
- How can issues in the family affect a child?
- Is your school working hard enough to prevent bullying?
- Should we use mobile phones and tablets in class?
- Does technology make you smarter?
- What is an unhealthy life, and what are the effects?
- Is there any benefit of doing homework?
- What is video game addiction, and how to stop it?
- What is a museum, and what can be found in it?
- What can we do to reduce climate change?
- Is soda suitable for children?
- Does everyone have to go to college?
- Comparing homework and class assignments.
- What is physical education?
- How the internet has changed our life
- What is peer pressure?
- What effect has global warming had on the environment?
- What is racism?
- What is a healthy diet?
- Should students be able to pick what they learn?
- Do movies depict what happens in real life?
- Is arts a vital part of the school curriculum?
- What are the challenges students face?
- How do we conserve energy in our homes?
- What is pop culture?
- Should parents monitor their children’s social media?
Fun Research Topics for Middle School
Writing an essay shouldn’t always be stressful or tedious. These topics will make writing papers fun. The topics below can hold the researcher’s attention for a long time as they work on completing their project.
- How should celebrities who break the law be punished?
- What is bulletproof clothing made of?
- All there is to know about hip-hop.
- What do we know about ninjas?
- Do lie detector tests work?
- What are the ingredients contained in a hotdog?
- Sharks, how do they hunt, and what do they eat?
- How do search engines work?
- Some fascinating extinct animals, and what happened to them?
- How to manage time effectively.
- How does insufficient sleep affect the brain?
- How to let go of bad habits?
- How do parents help us grow?
- How to become a better writer.
- Are dogs and cats enemies?
- Why do parents punish children for bad behavior?
- What is the best punishment for naughty kids?
- Is magic real?
- How to save money effectively?
- What is self-development?
- How to motivate yourself to be a better student?
- When should you begin to earn money?
- What’s the secret of having a successful life?
- How not to become a game addict.
Middle School Research Project Ideas
Research shouldn’t always end as essay writing. Sometimes, you need hands-on projects to keep the middle schooler busy. The list below can serve as an ideal hub for research ideas for middle school students and work as interesting essay topics.
- Investigating what life is like inside a beehive.
- Steps in creating a movie.
- How do our brains store memories and retrieve them when we need them?
- What is a landform?
- What are some important holidays around the world, and who celebrates them?
- What are some significant symbols used in world holidays?
- Creating an ecosystem: what’s the process involved?
- Research on some exotic underwater creatures.
- What is a meteor?
- How to build a crossword puzzle.
- What is advertising: create a short advertisement campaign.
- Write the story of your life.
- Create a calendar highlighting critical events in your life.
- Create your family tree.
Science Research Topics for Middle School
Science is an exciting part of our lives. Because of science, the quality of our lives has increased, and there are many more inventions to come. These topics can engage the curious mind of the youngster and introduce them to science-related subjects to work on.
- Earthquakes: Its causes and effects.
- Computer viruses. What are they, and how do they spread?
- Evolution of human beings.
- Are human beings still evolving?
- What is alchemy?
- What is a black hole? How is it formed?
- What is a submarine? Who uses them, and how do they work?
- What is the cause of tornadoes?
- What is a sinkhole, and how do they form?
- Research on one of the planets in the solar system.
- Understanding glaciers and icebergs.
- What are volcanoes, and how do they form?
- The different types of volcanoes and what causes them.
- Who are the most famous scientists, and what are they famous for?
- What are the components of airplanes that make them fly?
- What are fossils, and what do they teach us?
- How do genetics and DNA affect how we look?
- Why does the moon change color and shape sometimes?
- What is a Lunar eclipse?
- What is pollution?
- The different types of pollution and what can be done to curb them?
- Can fruits play a part in medicine?
- What is flooding?
- What is an ecosystem?
- What measures do butterflies take to defend themselves?
- Different types of butterflies.
- What is a skeleton, and why is it an essential part of the body?
- How many bones are in a skeleton? Which are the most important?
- Who is a marine biologist?
- What is the connection between a marine biologist and the weather?
- What are the risks marine biologists face when they dive?
- Different types of fossils?
- Are whales still hunted?
- What is scientific research, and who conducts it?
- What is the job of the nervous system?
- Understanding the concept of hibernation?
- What are the necessities plants need to grow?
- Who are the people who study dinosaurs?
- Mammals and reptiles: Similarities and differences.
- Why don’t human beings float?
- What is a prism, and what does it do?
- What gives humans the ability to lift heavy things?
- What factors can cause earthquakes?
- How is wind measured?
- What differentiates a planet from a star?
- What is a galaxy? What galaxy is the earth?
- Who is an astronaut, and what is their job?
- What is a waterfall?
- Do plants drink water?
- Why do oil and water not mix?
- What is microbiology?
- How can we preserve our natural resources?
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of exploring space.
- What are bacteria, and how useful is it to humans?
- The similarities between temperature and heat.
Other Topics to Research for Middle School
We cannot run out of topics for middle schoolers, as several aspects are available to look at. Here are some other topics that can jump-start your essay writing process.
- Is it advisable for students to be with their cell phones all day?
- Should the minimum age for getting a driving license be raised?
- The differences between homeschooling and standard schooling: which is better?
- Does social media have a positive or negative impact on teenagers?
- Going vegan, is it good for your health?
- Who is a Monk, and what is his lifestyle/routine?
- How did humans domesticate cats and dogs, and why?
- How is America helping endangered animals?
- How is climate change affecting us?
- What are the effects of video games on teenagers and children?
- Do Athletes make good models?
- Who is to blame for the number of homeless people in America?
- Should we have shorter school weeks?
- Should parents monitor websites visited by their children?
- What is cybercrime?
- What can we don’t protect our environment?
- Instant messaging, do they affect literacy?
- What are the most effective ways of achieving academic excellence?
- What is a good movie that influenced us in 2023?
- Are tests a good way of judging a student’s intelligence?
- How does music help us feel better?
- How to choose the best research project ideas for middle school students.
- Why is it important to learn multiple languages?
- Do learning techniques affect behavior?
- Bullying and its effects on mental health.
- All you need to know about distant learning
- Should prayer be part of school activities?
- Do we need math formulas in real scenarios?
- When should students start undergoing leadership training?
- How to write a good essay.
- How does night vision work?
- What is the solar system?
- What is Nasa, and what do they do?
- What is a natural disaster, and what can cause one to happen?
- What is the process of becoming a president of the United States?
- How many presidents has the United States had?
- What are some of the responsibilities and privileges of the president?
- Learning about Vice Presidents and First Ladies of the United States.
- Is social media dangerous for children?
- Does the location where you grow up affect who you become?
- What is a participation trophy? Is it necessary?
- Should there be a screen time limit for children?
- What are the responsibilities of a government to its citizens?
- What is a curfew, and why do kids have them?
- Is grounding an effective punishment?
- Should physical education be necessary for everyone?
- What are some advantages of knowing how to read?
- How can cell phones be used productively while in class?
- What are the qualities of a good leader?
- What are hobbies, and what do they do for us?
- Should less homework be given to students?
- What is summer school? Does it help students?
- What age is appropriate for children to be left alone at home?
If You Need Paper Writing Help
There are many ways to brainstorm ideas for your middle school homework. The research project ideas for middle school and the topics listed above will make it easier to begin. After picking a suitable topic, the next step is writing the entire paper. This will involve a lot of research and fact-finding to get accurate information for your paper. It doesn’t end at research, as you still have to write a great essay to score high marks. This could be a daunting task for many students. Don’t be afraid to get research paper help from our professional writers. After attending class, you may not have adequate time to write your essay yourself, if this is your situation, it’s okay to search for help on the internet. A quick google search for “write my paper” will result in several websites promising to write the best essay for you. However, you need to make your research before hiring an online writer for your assignment. If you need someone to write your assignment, we can be of help. We provide fast, reliable, custom paper writing services that can be completed online. Our services are available to every student, including university, middle school, high school, and college students. Our team of writers consists of professionals and teachers who are always available to ensure that you meet your deadlines. Contact us with a message “ do my research paper for me ” and enjoy the perfect result!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Terms & Conditions Loyalty Program Privacy Policy Money-Back Policy
Copyright © 2013-2024 MyPaperDone.com
- Writing Prompts
150 Writing Prompts For Middle School (+Free Printable)
Make writing fun and easy, with these 150 writing prompts for middle school students.
The more you write, the better you become at writing. But the problem is not all middle schoolers enjoy writing. There’s always something better to do, playing video games , watching YouTube videos , hanging with friends , lazing about the house – Why bother writing, right? The trick is to understand that even the smallest piece of writing can make a huge difference in a student’s attitude towards writing.
If you unload too many lengthy assignments, such as writing 1,000 words on topic X or 3,000 about something, something – Writing can seem like a long, boring chore for some students. But if you break it down, and mix it up a bit, then your students have a real chance of actually liking writing for fun. Think of creating small writing tasks that take no longer than around 10 or 15 minutes to complete. As students complete these small tasks with ease, their confidence will grow, eventually turning them into avid young writers.
To help inspire and motivate young writers, we have created this list of 150 quick and easy writing prompts for Middle School students. Keep reading for a free printable writing pack for middle schoolers as well! Here is a quick generator that will generate a random middle school prompt for you:
For more fun writing ideas, check out this list of over 300 writing prompt for kids .
150 Writing Prompts For Middle School Students
This list of prompts is great for whenever your middle-schooler is bored and needs some quick ideas to write about:
- Make a list of at least three different opening lines for this story idea: A space knight living in outer space wants to fight a real fire-breathing dragon.
- Complete this sentence in at least three different ways: When I’m bored, I like to…
- Draw a picture of your dream house, and describe some of the coolest features it has.
- Make a top ten list of the scariest animals in the animal kingdom. You could even write down one scary fact about each animal.
- Write an acrostic poem using the letters that spell z-o-m-b-i-e.
- Describe the scariest monster that you can think of. You could even draw a picture of it.
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways: My goal for the next month is to…
- Make a top ten list of your favourite foods of all time. You could even write down one reason for why each food is your favourite.
- Create your own A-Z book or list of monsters. For A is for Abominable Snowman, B is for Bogeyman and so on.
- Research and write down five facts about an endangered species of your choice. Examples of endangered species include the blue whale, giant pandas, snow leopards and tigers.
- Create a postcard for your local town or city. What picture would you draw on the front? And what message could you include on the back?
- Write an acrostic poem using the letters that spell out your own first name. This poem could be about yourself.
- Make a top ten list of your favourite movies of all time.
- Make a top ten list of your favourite songs of all time.
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways. When I grow up I want to…
- Which is your favourite season, Winter , Spring , Summer or Autumn? Write a haiku poem about your favourite season.
- Create a party invite for a dinner party at your house. Think about the party theme, entertainment, food and dress code.
- Write down a recipe that uses eggs as one of the ingredients.
- Write a how-to guide on how to take care of a kitten or puppy.
- What do you enjoy doing on the weekends? Start by making a list of activities that you do on the weekend. Then you can pick one to write about in more detail.
- Using a photograph (or one of these picture writing prompts ), write a short caption or description to go alongside it.
- Imagine you are the owner of a new restaurant. Create a menu of the dishes you will serve at this restaurant.
- What has been the best part of your day so far? And what has been the worst part of the day?
- Imagine that you have a time machine. What year would you travel to and why?
- If you could have one superpower, what would it be and why?
- If you could keep one dinosaur as a pet, which dinosaur would you pick and why?
- Write down everything you remember from a recent nightmare that you had.
- What is your favourite country in the whole wide world? List at least five fun facts about this country.
- Make a list of at least 3 different story ideas about aliens.
- Create a character description of the world’s most evil supervillains.
- What is your greatest achievement to date? What are you most proud of and why?
- Write an action-packed scene that contains the following: A car chase, a lucky pair of socks and a talking parrot.
- What advice would you give to someone who is being bullied? You could make a list of at least three pieces of advice that you might give.
- Imagine you are stuck on a desert island. Write a diary entry of your first day on the island.
- Imagine you are a pirate sailing the seven seas. Talk about the scariest thing you faced while out at sea.
- You just discovered a new planet . Can you describe this new planet in detail? What would you call it? Does any life exist on the planet? What type of climate does it have?
- Would you rather have a magical unicorn as a pet or a fire-breathing dragon?
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways: One day I was walking through the forest and discovered…
- Write a letter to your friend about a favourite memory you have of them. You can use the following starter as inspiration: Remember that time…
- Make a list of book title ideas for a story about a girl who can go invisible whenever she wants.
- A talking cat is fast asleep, then suddenly someone wakes it up. Write down a short script between the cat, and the person arguing.
- What is the nicest thing that anyone has done for you recently?
- Make a list of 10 online safety tips to help you stay safe online.
- Can you think of at least 5 ways to prevent climate change in your daily life?
- Make a list of your top ten favourite books of all time.
- Think about a movie that you’ve seen recently. What did you enjoy most about this movie, and what did you dislike about it?
- You are just about to take a bite of an apple. And then suddenly the apple starts screaming. What do you do next?
- Describe a magical forest in great detail. What makes this forest so magical?
- Write a super scary scene, using the following starter: As I walked into the haunted house…
- What is your greatest fear? Is it possible to ever overcome this fear? If so, how would you do it?
- Make a list of at least five things you like about yourself. And then make a list of five things that you would change about yourself.
- What would the perfect day look like for you? How would it start? What activities would you do? And how does it end?
- You are standing in the playground when you hear two of your classmates making fun of your best friend. What do you do next?
- A young boy yells at his pet eagle to fly away into the wild. The eagle does not respond. Write down this scene between the two characters in great detail.
- Describe a pencil in the greatest detail possible.
- Create your own superhero character. What are their strengths and superpowers? What about their weaknesses? Also, think of a cool superhero name for them!
- What is your dream job? What skills and traits do you need to do this job well?
- Imagine that you have had the worst day ever. Write down what happened to make it so bad.
- What is your favourite colour? Now write a short rhyming poem about this colour.
- If you had three wishes, what would you wish for and why? Wishing for extra wishes is not allowed.
- Write an action-packed scene of a lion chasing a zebra in the wild from the perspective of the lion.
- Imagine you own a video gaming company. Your task is to come up with a new video game idea. Explain this new video game idea in detail.
- What would you do if you were given $1 million dollars?
- What is your favourite hobby or interest? Can you provide at least five tips for beginners who might be interested in starting this hobby?
- Make a top ten list of your favourite celebrities or YouTube stars.
- Write the opening paragraph of a fairytale about a zombie prince who has returned from the dead.
- Write an alternative ending to a fairytale that you are familiar with. For example, you could write a sad ending for Cinderella or a cliff-hanger style ending for Jack and the Beanstalk.
- Write down a conversation in a script format between two people waiting for the bus at a bus stop.
- Would you rather get abducted by aliens, or discover a magical portal to another realm in your bedroom? Explain your answer.
- Write a shape poem about your favourite food in the shape of this food.
- If you had to prepare for a zombie invasion, which three items would you pack in your bag, and why?
- Describe the most beautiful garden in the world in detail. What type of flowers would it have? Would it have any garden furniture?
- You receive a strange parcel in the middle of the night. You open the parcel to discover… Write down at least one paragraph of what you discover in the parcel.
- Use the word, ‘Stampede’ in at least three different sentences.
- Complete the following metaphor in at least three different ways: Your smile is like…
- Describe the city of the future. What would the buildings look like? How will people travel? What kind of homes will people live in?
- What is Marie Curie (the physicist) famous for? Research and write down five facts about her research and studies.
- You have just been made leader of the Kingdom of Kinloralm. As the leader, what rules would you set for the kingdom? Make a list of at least 10 rules that you will enforce.
- A witch has cast a spell on you. Every night at midnight, you turn into a werewolf. Describe this transformation in great detail. What does it feel like when you are transforming? How does your skin change? What about your teeth and fingernails?
- Using the following starter , write at least one paragraph: When I look outside the window…
- After a deep sleep, you wake up to find yourself locked inside a cage. No one else is around. What do you do next?
- You keep on having the same nightmare every night. In your nightmare, you are running as fast as you can, and then you suddenly fall. When you turn around you see… Write at least one paragraph about what you see.
- Write down at least 10 interview questions that you can ask your favourite celebrity. If you have time, you can even write down the potential answers to these questions from the perspective of the celebrity.
- Write a how-to guide on how to grow tomatoes at home.
- Make a list of at least five tips for keeping your bedroom clean.
- Would you rather drive the fastest car on Earth for one hour or own a custom-made bicycle? Explain your choice.
- Write a limerick poem about an old snail.
- Find something in your room that begins with the letter, ‘R’, and write a paragraph describing this object in detail.
- Research the history of how the first mobile phone was invented. Create a timeline of mobile phone inventions from the very first mobile to the current time.
- If you were the headteacher of your school, what changes would you make and why? Try to list and describe at least three changes.
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of having access to the internet? Try to think of at least five benefits and five drawbacks.
- Write about the best day of your life so far. Then write about the worst day of your life so far.
- Imagine that you are an agony aunt for a newspaper. A reader has written to you with the following problem: Dear Agony Aunt, I have no friends at school. And my classmates are always making fun of me… What advice would you give this reader?
- Imagine that you are a salesperson. Your task is to sell a new chocolate bar to customers. Write down a sales pitch that was selling this chocolate bar. What features would you highlight? What are the benefits of this chocolate bar?
- Can you complete the following sentence in three different ways: When I feel upset, I …
- What is the most difficult part about being in middle school? What is the best part of middle school?
- Imagine that your best friend has just revealed a huge secret. How would you react? Write down a script of the conversation between you and your best friend.
- Have you learned any new skills recently? How did you learn these?
- Imagine you are sitting at a dinner party with a group of strangers. Describe the atmosphere in great detail. Who are you sitting next to? What sort of conversations are the other guests having? What food is being served?
- Five years from now, where will you be? Will you be the same person? How would you have changed?
- Write about your plans for the weekend.
- Describe a day in the life of being a goldfish in a fishbowl at a pet shop.
- While at the seaside, a message in a bottle washes up onto the shore. You open the bottle and read the message. The message reads: Help Me! I’m stranded on an island! What do you do next?
- A mother and her son are baking some muffins in the kitchen. Write down a conversation that they might have while they bake together.
- Make a list of indoor activities you can do when it’s raining outside. Try to think of at least ten activities.
- Write down a diary entry from the perspective of an alien secretly living undercover on Earth.
- Write at least three different opening lines for the following story idea: A king needs to keep his kingdom safe from the ravenous trolls that come out at night.
- Imagine you are a secret agent cat, write about your most recent mission.
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways: If I could change the world, I would…
- If you could program a robot, what tasks would you program it to do, and why?
- Imagine you are the owner of a toy shop. Your task is to hire some toy makers. Write a job description for a toymaker. Think about the skills and traits required to become a toymaker.
- You are the owner of a zoo. Suddenly you hear people screaming as the lions are accidentally released. What do you do next?
- Your future self comes from the future to warn you about something. Write a conversation that you would have with your future self.
- If you had a choice to become a superhero or a supervillain, which one would you be and why?
- Can you think of at least three things that no one knows about you? Why have you kept these things a secret?
- During a science experiment, you mix up the wrong chemicals. The liquid turns blue and jumps out of the glass container. It then slides into your backpack. What do you do next?
- Write down at least five things that you are grateful for in your life right now.
- You notice some strange footprints in your backyard leading to your shed. You follow these footprints and discover…
- When was the last time someone upset you or hurt your feelings? How did they hurt your feelings? Do you remember what was said?
- You walk inside a magic shop. You see all sorts of weird and fun things. Describe the inside of the shop in as much detail as possible.
- Write at least three different opening lines for the following story idea: A young werewolf wants to be a human again.
- Make a list of three different story ideas about dragons.
- Write from the perspective of a kite flying high in the sky. Think about what you feel, see and hear.
- Write about your favourite subject at school. Why do you like this subject?
- Write a haiku poem about the full moon.
- Imagine you are the manager of a TV channel. Make a list of at least three new TV show ideas you can air on Saturday evening.
- You find a baby alien in your basement. What do you do next?
- Think of at least three newspaper headlines for the following article idea: The new mayor of your town/city is planning on creating more homes.
- Imagine that your pet dog has gone missing. Create a missing poster to find your dog. Remember to describe any important details relating to the dog in your power.
- Write an advertisement for the brand new mixer 3000. It mixes all the best music tracks with sounds to create the ultimate track.
- Write down three sentences. One of something interesting that happened to you today. Another of something positive that happened. And finally another sentence of something negative.
- Write down four different character descriptions. Each character must have a different background story or history when growing up.
- Imagine you had a terrible experience at a restaurant. Write a complaint letter to the restaurant manager, outlining the problems you had.
- Imagine your family is planning to go on a cruise. As you drive to the boat, a person walks up to your car window, holds up a flyer, and demands that they do what they were told. What is your family’s reply?
- As you’re making your way home, you pass by a group of people. It turns out the person who was walking next to them is a ghost. What do you do next?
- Your best friend has had a terrible year. You need to plan the best birthday party ever for them. Make a list of items that you will need for the party.
- Using the 5 W’s and 1 H technique, outline the following newspaper article idea: A new breed of wolves was discovered nearby. The 5 W’s include: What, Where, When, Who and why. The one H is How.
- Write a positive self-talk poem, using the following starter: I am…
- Take a recent picture that you have drawn at home or during art class. Using this picture, can you think of at least three ideas for stories from it?
- How can you prevent bullying in your school? Make a list of at least five different ways to prevent bullying.
- Write a list of at least 10 interview questions that you can ask your favourite teacher at school. If you want, you can actually ask these questions and write down the responses your teacher gives.
- Describe a day in the life of being a mouse that lives in your school.
- What qualities to look for in a friend? Make a list of at least 3 qualities. Also, think about what qualities you try to avoid.
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways: When I wake up in the morning, I feel…
- Do you ever wish you could do more to help people? Make a list of at least five ways you can help a friend who is going through a tough time.
- When was the last time you felt angry? How did you deal with this anger? Do you think it is okay to be angry all the time?
- Write down at least three predictions for the future. These predictions can be personal or about the world. You can use the following starter: In 10 years time…
- Do you enjoy writing? If yes, then what kind of things do you enjoy writing about. Explain your answer.
- Think about the last book you read. Which scene in the book stood out to you the most? Why did it stand out for you?
- Complete the following sentence in at least three different ways: The biggest question on my mind right now is…
What did you think of this list of quick and easy writing prompts for Middle School students? Did you find this list useful or difficult to use? Let us know in the comments below!
Printable Writing Pack for Middle Schoolers
Thank you for reading this post! You can download the free PDF writing prompts for Middle School students pack here .

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Political typology quiz.
Notice: Beginning April 18th community groups will be temporarily unavailable for extended maintenance. Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
Where do you fit in the political typology?
Are you a faith and flag conservative progressive left or somewhere in between.

Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That’s OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if it isn’t exactly right.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Watch CBS News
What is Eid al-Fitr? 6 questions about the holiday and how Muslims celebrate it, answered
By Ken Chitwood
Updated on: April 9, 2024 / 8:03 AM EDT / The Conversation
Ken Chitwood is a senior research fellow, Muslim Philanthropy Initiative at Indiana University–Purdue University Indianapolis and journalist-fellow at the Dornsife Center for Religion and Civic Culture at the University of Southern California Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences .
Eid al-Fitr, one of Islam's principal festivals, will be celebrated April 9, 2024, according to the Fiqh Council of North America . At the middle of June, Muslims will celebrate Eid al-Adha. Ken Chitwood, a scholar of global Islam, explains the two Islamic festivals.
1. What is Eid?
Eid literally means a "festival" or "feast" in Arabic. There are two major eids in the Islamic calendar per year – Eid al-Fitr earlier in the year and Eid al-Adha later.
Eid al-Fitr is a three-day-long festival and is known as the "Lesser" or "Smaller Eid" when compared to Eid al-Adha, which is four days long and is known as the "Greater Eid."

2. Why is Eid celebrated twice a year?
The two Eids recognize, celebrate and recall two distinct events that are significant to the story of Islam.
Eid al-Fitr means "the feast of breaking the fast." The fast, in this instance, is Ramadan , which recalls the revealing of the Quran to Prophet Muhammad and requires Muslims to fast from sunrise to sundown for a month.
3. How do Muslims celebrate Eid al-Fitr?
Eid al-Fitr features two to three days of celebrations that include special morning prayers. People greet each other with "Eid Mubarak," meaning "Blessed Eid" and with formal embraces. Sweet dishes are prepared at home and gifts are given to children and to those in need. In addition, Muslims are encouraged to forgive and seek forgiveness. Practices vary from country to country.
In many countries with large Muslim populations, Eid al-Fitr is a national holiday. Schools, offices and businesses are closed so family, friends and neighbors can enjoy the celebrations together. In the U.S. and the U.K., Muslims may request to have the day off from school or work to travel or celebrate with family and friends.
In countries like Egypt and Pakistan, Muslims decorate their homes with lanterns, twinkling lights or flowers. Special food is prepared and friends and family are invited over to celebrate.

In places like Jordan, with its Muslim majority population, the days before Eid al-Fitr can see a rush at local malls and special "Ramadan markets" as people prepare to exchange gifts on Eid al-Fitr.
In Turkey and in places that were once part of the Ottoman-Turkish empire such as Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, Azerbaijan and the Caucasus, it is also known as the, "Lesser Bayram" or "festival" in Turkish.
4. How do Muslims celebrate Eid al-Adha?
The other festival, Eid al-Adha, is the "feast of the sacrifice." It comes at the end of the Hajj , an annual pilgrimage by millions of Muslims to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia that is obligatory once in a lifetime, but only for those with means.
Eid al-Adha recalls the story of how God commanded Ibrahim to sacrifice his son Ismail as a test of faith. The story, as narrated in the Quran, describes Satan's attempt to tempt Ibrahim so he would disobey God's command. Ibrahim, however, remains unmoved and informs Ismail, who is willing to be sacrificed.
But, just as Ibrahim attempts to kill his son, God intervenes and a ram is sacrificed in place of Ismail. During Eid al-Adha, Muslims slaughter an animal to remember Ibrahim's sacrifice and remind themselves of the need to submit to the will of God.
5. When are they celebrated?
Eid al-Fitr is celebrated on the first day of the 10th month in the Islamic calendar.
Eid al-Adha is celebrated on the 10th day of the final month in the Islamic calendar.
The Islamic calendar is a lunar calendar, and dates are calculated based on lunar phases. Since the Islamic calendar year is shorter than the solar Gregorian calendar year by 10 to 12 days, the dates for Ramadan and Eid on the Gregorian calendar can vary year by year.
6. What is the spiritual meaning of Eid al-Fitr?
Eid al-Fitr, as it follows the fasting of Ramadan, is also seen as a spiritual celebration of Allah's provision of strength and endurance.
Amid the reflection and rejoicing, Eid al-Fitr is a time for charity, known as Zakat al-Fitr. Eid is meant to be a time of joy and blessing for the entire Muslim community and a time for distributing one's wealth.
Charity to the poor is a highly emphasized value in Islam. The Quran says ,
"Believe in Allah and his messenger, and give charity out of the (substance) that Allah has made you heirs of. For those of you who believe and give charity – for them is a great reward."
This piece incorporates materials from an article first published on Aug. 28, 2017. The dates have been updated. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license.
More from CBS News

Hamas says 3 of leader Ismail Haniyeh's sons killed in Israeli strike

Time runs out for Americans hoping to flee chaos in Haiti

Olympic triathlon might be impacted by Seine River pollution

Vietnam property tycoon sentenced to death in $27 billion fraud case

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For many middle school students (both ELLs and non-ELLs), learning the academic register of research is a new skill. This register of research found in the CCSS is of great value to all students and ELLs in particular. Step #1: Practice Writing Questions with Literature. To help transition students into generating research questions that will ...
Here is an example of a research process that you may consider using when teaching research skills in your middle school classroom: Form a question: Research should be targeted; develop a question you want to answer before progressing any further. Decide on resources: Not every resource is good for every question/problem. Identify the resources ...
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence Goal: Develop students' ability to recognize and create successful research questions Specifically, students will be able to. identify the components of a successful research question. create a viable research question.
Research paper scaffolding provides a temporary linguistic tool to assist students as they organize their expository writing. Scaffolding assists students in moving to levels of language performance they might be unable to obtain without this support. An instructional scaffold essentially changes the role of the teacher from that of giver of ...
We use the Research Essay Outline worksheet to get started, transferring our well-organized information from the Research Matrix to the outline. I often advise students to begin with the body portion of the essay, leaving the introduction and conclusion for last. This may seem awkward, but the research students have been working on naturally ...
Learn how to teach research skills to primary students, middle school students, or high school students. 50 activities that could be done in just a few minutes a day. Lots of Google search tips and research tips for kids and teachers. ... Write as many questions as you can think of relating to that topic.
Writing a Well-crafted Research Question. Research questions provide an overarching direction for your study to follow. It guides the type of study you will choose, the type of data you will collect, and the type of analysis on the data that you will perform. Writing good research questions, then, is an important step in framing your study.
practitioners across the country, the Middle School Matters Field Guide is a collection of research-based principles, practices, and strategies deemed essential for middle school success. It includes instructional practices derived from the most rigorous research conducted in the middle grades over the past 15 years. Speciically,
- Is your research question clear? - Is your research question focused? (Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.) - Is your research question complex? (Questions shouldn't have a simple yes/no answer and should require research and analysis.) • Hypothesize. After you've come up with a question ...
Learn about the online research guide for middle and high school students that will help them locate and use digitized resources, find research inspiration, definitions for primary and secondary sources, strategies for searching primary and secondary sources on the Library's website and beyond, and suggestions on citing resources appropriately.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Although students in all grades must learn to write clear research questions, we can use the Com-mon Core standards to differentiate expectations for students in grades 6, 7, and 8 (Figure 1) and ... Charles Evans Hughes Middle School. (2014). Writing research questions. [blog post]. Retrieved from Hughes News at https://lbhughes.schoolloop.com ...
Then start right here - Write an EPIC research question and it will start you off on the road to student ... Want to be successfull in your student experiments? Then start right here - Write an ...
Olivia Franklin. Engage students with interesting research topics, teach them skills to become adept independent researchers, and help them craft their end-of-unit research papers. CommonLit 360 is a comprehensive ELA curriculum for grades 6-12. Our standards-aligned units are highly engaging and develop core reading and writing skills.
The purpose of this research guide is to offer a standard format for the teaching and writing of research papers in courses at the Middle Township schools. The guide outlines the process of research, explains devices for organization of research and sources, gives examples of methods for documenting research sources within the paper, explains ...
In 8th grade, we will conduct THEMATIC RESEARCH - that is research that is based on an overarching theme. Your goal is to create a 2 - 3 "magazine-type- page" academic essay that presents information and illustrations (pictures, charts, graphs, etc.) that supports your group's theme by exploring a specific topic within the theme.
To write an effective research question, researchers should follow these steps: 1. Select a general topic of interest. 2. Ask questions about the topic. 3. Write an effective question based on the ...
22. Project-Based Learning: Acceptance and Tolerance. This is a series of research projects that look at specific problems regarding acceptance and tolerance. It offers prompts for middle school-aged students that will get them to ask big questions about themselves and others in the world around them.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Students use a 3-step process: Step 1) Read a text, either in small groups, pairs, or independently. Step 2) Pause at regular intervals to generate questions and record them in a learning log or journal. Step 3) Answer questions and indicate where the answer was found in the text. Students are taught to write two different types of questions ...
This will create fun research topics for 6th graders, learning about life and how relationships work. Literature: This is the best time to learn about books and works of art. The literature will provide many topics to research for middle school students. There are many more aspects that middle school students can research and write papers on.
Keep reading for a free printable writing pack for middle schoolers as well! Here is a quick generator that will generate a random middle school prompt for you: Click the 'Random' button to get a random middle school writing prompt. Random. For more fun writing ideas, check out this list of over 300 writing prompt for kids.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions.
Eid al-Fitr is a three-day-long festival and is known as the "Lesser" or "Smaller Eid" when compared to Eid al-Adha, which is four days long and is known as the "Greater Eid."