Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips

How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
A narrative essay tells a story. In most cases, this is a story about a personal experience you had. This type of essay , along with the descriptive essay , allows you to get personal and creative, unlike most academic writing .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a narrative essay for, choosing a topic, interactive example of a narrative essay, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about narrative essays.
When assigned a narrative essay, you might find yourself wondering: Why does my teacher want to hear this story? Topics for narrative essays can range from the important to the trivial. Usually the point is not so much the story itself, but the way you tell it.
A narrative essay is a way of testing your ability to tell a story in a clear and interesting way. You’re expected to think about where your story begins and ends, and how to convey it with eye-catching language and a satisfying pace.
These skills are quite different from those needed for formal academic writing. For instance, in a narrative essay the use of the first person (“I”) is encouraged, as is the use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Narrative essay assignments vary widely in the amount of direction you’re given about your topic. You may be assigned quite a specific topic or choice of topics to work with.
- Write a story about your first day of school.
- Write a story about your favorite holiday destination.
You may also be given prompts that leave you a much wider choice of topic.
- Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself.
- Write about an achievement you are proud of. What did you accomplish, and how?
In these cases, you might have to think harder to decide what story you want to tell. The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to talk about a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
For example, a trip where everything went according to plan makes for a less interesting story than one where something unexpected happened that you then had to respond to. Choose an experience that might surprise the reader or teach them something.
Narrative essays in college applications
When applying for college , you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities.
For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay.
In this context, choose a story that is not only interesting but also expresses the qualities the prompt is looking for—here, resilience and the ability to learn from failure—and frame the story in a way that emphasizes these qualities.
An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” is shown below.
Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
If you’re not given much guidance on what your narrative essay should be about, consider the context and scope of the assignment. What kind of story is relevant, interesting, and possible to tell within the word count?
The best kind of story for a narrative essay is one you can use to reflect on a particular theme or lesson, or that takes a surprising turn somewhere along the way.
Don’t worry too much if your topic seems unoriginal. The point of a narrative essay is how you tell the story and the point you make with it, not the subject of the story itself.
Narrative essays are usually assigned as writing exercises at high school or in university composition classes. They may also form part of a university application.
When you are prompted to tell a story about your own life or experiences, a narrative essay is usually the right response.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write a Narrative Essay | Example & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved June 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/narrative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write a descriptive essay | example & tips, how to write your personal statement | strategies & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Narrative Essay
Definition of narrative essay, difference between a narrative essay and a short story, elements of a narrative essay, how to choose a topic for narrative essay, mla and apa formats in narrative essay, reflective narrative essay, examples of narrative essays in literature, example #1: new directions (by maya angelou).
“Annie, over six feet tall, big-boned, decided that she would not go to work as a domestic and leave her “precious babes” to anyone else’s care. There was no possibility of being hired at the town’s cotton gin or lumber mill, but maybe there was a way to make the two factories work for her. In her words, “I looked up the road I was going and back the way I come, and since I wasn’t satisfied, I decided to step off the road and cut me a new path.” She told herself that she wasn’t a fancy cook but that she could “mix groceries well enough to scare hungry away and keep from starving a man.”
Example #2: Saturday Evening Post (by Russell Baker)
“When I burst in that afternoon she was in conference with an executive of the Curtis Publishing Company. She introduced me. He bent low from the waist and shook my hand. Was it true as my mother had told him, he asked, that I longed for the opportunity to conquer the world of business? My Mother replied that I was blessed with a rare determination to make something of myself. ‘That’s right,’ I whispered. ‘But have you got the grit, the character, the never-say-quit spirit it takes to succeed in business?’ My Mother said I certainly did.”
Example #3: Only Daughter (by Sandra Cisneros)
“Once several years ago, when I was just starting out my writing career, I was asked to write my own contributor’s note for an anthology I was part of, I wrote: ‘ I am the only daughter in a family of six sons. That explains everything.’ “Well, I’ve thought about that ever since, and yes, it explains a lot to me, but for the reader’s sake I should have written: ‘I am the only daughter in a Mexican family of six sons.’ Or even: ‘I am the only daughter of a Mexican father and a Mexican-American mother.’ Or: ‘I am the only daughter of a working-class family of nine.’ All of these had everything to do with who I am today.”
Function of Narrative Essay
Synonyms of narrative essay, related posts:, post navigation.
The Ultimate Narrative Essay Guide for Beginners

A narrative essay tells a story in chronological order, with an introduction that introduces the characters and sets the scene. Then a series of events leads to a climax or turning point, and finally a resolution or reflection on the experience.
Speaking of which, are you in sixes and sevens about narrative essays? Don’t worry this ultimate expert guide will wipe out all your doubts. So let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Everything You Need to Know About Narrative Essay
What is a narrative essay.
When you go through a narrative essay definition, you would know that a narrative essay purpose is to tell a story. It’s all about sharing an experience or event and is different from other types of essays because it’s more focused on how the event made you feel or what you learned from it, rather than just presenting facts or an argument. Let’s explore more details on this interesting write-up and get to know how to write a narrative essay.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of a narrative essay:
A narrative essay has a beginning, middle, and end. It builds up tension and excitement and then wraps things up in a neat package.
Real people, including the writer, often feature in personal narratives. Details of the characters and their thoughts, feelings, and actions can help readers to relate to the tale.
It’s really important to know when and where something happened so we can get a good idea of the context. Going into detail about what it looks like helps the reader to really feel like they’re part of the story.
Conflict or Challenge
A story in a narrative essay usually involves some kind of conflict or challenge that moves the plot along. It could be something inside the character, like a personal battle, or something from outside, like an issue they have to face in the world.
Theme or Message
A narrative essay isn’t just about recounting an event – it’s about showing the impact it had on you and what you took away from it. It’s an opportunity to share your thoughts and feelings about the experience, and how it changed your outlook.
Emotional Impact
The author is trying to make the story they’re telling relatable, engaging, and memorable by using language and storytelling to evoke feelings in whoever’s reading it.
Narrative essays let writers have a blast telling stories about their own lives. It’s an opportunity to share insights and impart wisdom, or just have some fun with the reader. Descriptive language, sensory details, dialogue, and a great narrative voice are all essentials for making the story come alive.
The Purpose of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is more than just a story – it’s a way to share a meaningful, engaging, and relatable experience with the reader. Includes:
Sharing Personal Experience
Narrative essays are a great way for writers to share their personal experiences, feelings, thoughts, and reflections. It’s an opportunity to connect with readers and make them feel something.
Entertainment and Engagement
The essay attempts to keep the reader interested by using descriptive language, storytelling elements, and a powerful voice. It attempts to pull them in and make them feel involved by creating suspense, mystery, or an emotional connection.
Conveying a Message or Insight
Narrative essays are more than just a story – they aim to teach you something. They usually have a moral lesson, a new understanding, or a realization about life that the author gained from the experience.
Building Empathy and Understanding
By telling their stories, people can give others insight into different perspectives, feelings, and situations. Sharing these tales can create compassion in the reader and help broaden their knowledge of different life experiences.
Inspiration and Motivation
Stories about personal struggles, successes, and transformations can be really encouraging to people who are going through similar situations. It can provide them with hope and guidance, and let them know that they’re not alone.
Reflecting on Life’s Significance
These essays usually make you think about the importance of certain moments in life or the impact of certain experiences. They make you look deep within yourself and ponder on the things you learned or how you changed because of those events.
Demonstrating Writing Skills
Coming up with a gripping narrative essay takes serious writing chops, like vivid descriptions, powerful language, timing, and organization. It’s an opportunity for writers to show off their story-telling abilities.
Preserving Personal History
Sometimes narrative essays are used to record experiences and special moments that have an emotional resonance. They can be used to preserve individual memories or for future generations to look back on.
Cultural and Societal Exploration
Personal stories can look at cultural or social aspects, giving us an insight into customs, opinions, or social interactions seen through someone’s own experience.
Format of a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays are quite flexible in terms of format, which allows the writer to tell a story in a creative and compelling way. Here’s a quick breakdown of the narrative essay format, along with some examples:
Introduction
Set the scene and introduce the story.
Engage the reader and establish the tone of the narrative.
Hook: Start with a captivating opening line to grab the reader’s attention. For instance:
Example: “The scorching sun beat down on us as we trekked through the desert, our water supply dwindling.”
Background Information: Provide necessary context or background without giving away the entire story.
Example: “It was the summer of 2015 when I embarked on a life-changing journey to…”
Thesis Statement or Narrative Purpose
Present the main idea or the central message of the essay.
Offer a glimpse of what the reader can expect from the narrative.
Thesis Statement: This isn’t as rigid as in other essays but can be a sentence summarizing the essence of the story.
Example: “Little did I know, that seemingly ordinary hike would teach me invaluable lessons about resilience and friendship.”
Body Paragraphs
Present the sequence of events in chronological order.
Develop characters, setting, conflict, and resolution.
Story Progression : Describe events in the order they occurred, focusing on details that evoke emotions and create vivid imagery.
Example : Detail the trek through the desert, the challenges faced, interactions with fellow hikers, and the pivotal moments.
Character Development : Introduce characters and their roles in the story. Show their emotions, thoughts, and actions.
Example : Describe how each character reacted to the dwindling water supply and supported each other through adversity.
Dialogue and Interactions : Use dialogue to bring the story to life and reveal character personalities.
Example : “Sarah handed me her last bottle of water, saying, ‘We’re in this together.'”
Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance.
Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative.
Example: “As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team’s helicopters.”
Provide closure to the story.
Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact.
Reflection : Summarize the key lessons learned or insights gained from the experience.
Example : “That hike taught me the true meaning of resilience and the invaluable support of friendship in challenging times.”
Closing Thought : End with a memorable line that reinforces the narrative’s message or leaves a lasting impression.
Example : “As we boarded the helicopters, I knew this adventure would forever be etched in my heart.”
Example Summary:
Imagine a narrative about surviving a challenging hike through the desert, emphasizing the bonds formed and lessons learned. The narrative essay structure might look like starting with an engaging scene, narrating the hardships faced, showcasing the characters’ resilience, and culminating in a powerful realization about friendship and endurance.
Different Types of Narrative Essays
There are a bunch of different types of narrative essays – each one focuses on different elements of storytelling and has its own purpose. Here’s a breakdown of the narrative essay types and what they mean.
Personal Narrative
Description : Tells a personal story or experience from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Reflects on personal growth, lessons learned, or significant moments.
Example of Narrative Essay Types:
Topic : “The Day I Conquered My Fear of Public Speaking”
Focus: Details the experience, emotions, and eventual triumph over a fear of public speaking during a pivotal event.
Descriptive Narrative
Description : Emphasizes vivid details and sensory imagery.
Purpose : Creates a sensory experience, painting a vivid picture for the reader.
Topic : “A Walk Through the Enchanted Forest”
Focus : Paints a detailed picture of the sights, sounds, smells, and feelings experienced during a walk through a mystical forest.
Autobiographical Narrative
Description: Chronicles significant events or moments from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Provides insights into the writer’s life, experiences, and growth.
Topic: “Lessons from My Childhood: How My Grandmother Shaped Who I Am”
Focus: Explores pivotal moments and lessons learned from interactions with a significant family member.
Experiential Narrative
Description: Relays experiences beyond the writer’s personal life.
Purpose: Shares experiences, travels, or events from a broader perspective.
Topic: “Volunteering in a Remote Village: A Journey of Empathy”
Focus: Chronicles the writer’s volunteering experience, highlighting interactions with a community and personal growth.
Literary Narrative
Description: Incorporates literary elements like symbolism, allegory, or thematic explorations.
Purpose: Uses storytelling for deeper explorations of themes or concepts.
Topic: “The Symbolism of the Red Door: A Journey Through Change”
Focus: Uses a red door as a symbol, exploring its significance in the narrator’s life and the theme of transition.
Historical Narrative
Description: Recounts historical events or periods through a personal lens.
Purpose: Presents history through personal experiences or perspectives.
Topic: “A Grandfather’s Tales: Living Through the Great Depression”
Focus: Shares personal stories from a family member who lived through a historical era, offering insights into that period.
Digital or Multimedia Narrative
Description: Incorporates multimedia elements like images, videos, or audio to tell a story.
Purpose: Explores storytelling through various digital platforms or formats.
Topic: “A Travel Diary: Exploring Europe Through Vlogs”
Focus: Combines video clips, photos, and personal narration to document a travel experience.
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Essay?
Selecting a compelling topic for your narrative essay is crucial as it sets the stage for your storytelling. Choosing a boring topic is one of the narrative essay mistakes to avoid . Here’s a detailed guide on how to choose the right topic:
Reflect on Personal Experiences
- Significant Moments:
Moments that had a profound impact on your life or shaped your perspective.
Example: A moment of triumph, overcoming a fear, a life-changing decision, or an unforgettable experience.
- Emotional Resonance:
Events that evoke strong emotions or feelings.
Example: Joy, fear, sadness, excitement, or moments of realization.
- Lessons Learned:
Experiences that taught you valuable lessons or brought about personal growth.
Example: Challenges that led to personal development, shifts in mindset, or newfound insights.
Explore Unique Perspectives
- Uncommon Experiences:
Unique or unconventional experiences that might captivate the reader’s interest.
Example: Unusual travels, interactions with different cultures, or uncommon hobbies.
- Different Points of View:
Stories from others’ perspectives that impacted you deeply.
Example: A family member’s story, a friend’s experience, or a historical event from a personal lens.
Focus on Specific Themes or Concepts
- Themes or Concepts of Interest:
Themes or ideas you want to explore through storytelling.
Example: Friendship, resilience, identity, cultural diversity, or personal transformation.
- Symbolism or Metaphor:
Using symbols or metaphors as the core of your narrative.
Example: Exploring the symbolism of an object or a place in relation to a broader theme.
Consider Your Audience and Purpose
- Relevance to Your Audience:
Topics that resonate with your audience’s interests or experiences.
Example: Choose a relatable theme or experience that your readers might connect with emotionally.
- Impact or Message:
What message or insight do you want to convey through your story?
Example: Choose a topic that aligns with the message or lesson you aim to impart to your readers.
Brainstorm and Evaluate Ideas
- Free Writing or Mind Mapping:
Process: Write down all potential ideas without filtering. Mind maps or free-writing exercises can help generate diverse ideas.
- Evaluate Feasibility:
The depth of the story, the availability of vivid details, and your personal connection to the topic.
Imagine you’re considering topics for a narrative essay. You reflect on your experiences and decide to explore the topic of “Overcoming Stage Fright: How a School Play Changed My Perspective.” This topic resonates because it involves a significant challenge you faced and the personal growth it brought about.
Narrative Essay Topics
50 easy narrative essay topics.
- Learning to Ride a Bike
- My First Day of School
- A Surprise Birthday Party
- The Day I Got Lost
- Visiting a Haunted House
- An Encounter with a Wild Animal
- My Favorite Childhood Toy
- The Best Vacation I Ever Had
- An Unforgettable Family Gathering
- Conquering a Fear of Heights
- A Special Gift I Received
- Moving to a New City
- The Most Memorable Meal
- Getting Caught in a Rainstorm
- An Act of Kindness I Witnessed
- The First Time I Cooked a Meal
- My Experience with a New Hobby
- The Day I Met My Best Friend
- A Hike in the Mountains
- Learning a New Language
- An Embarrassing Moment
- Dealing with a Bully
- My First Job Interview
- A Sporting Event I Attended
- The Scariest Dream I Had
- Helping a Stranger
- The Joy of Achieving a Goal
- A Road Trip Adventure
- Overcoming a Personal Challenge
- The Significance of a Family Tradition
- An Unusual Pet I Owned
- A Misunderstanding with a Friend
- Exploring an Abandoned Building
- My Favorite Book and Why
- The Impact of a Role Model
- A Cultural Celebration I Participated In
- A Valuable Lesson from a Teacher
- A Trip to the Zoo
- An Unplanned Adventure
- Volunteering Experience
- A Moment of Forgiveness
- A Decision I Regretted
- A Special Talent I Have
- The Importance of Family Traditions
- The Thrill of Performing on Stage
- A Moment of Sudden Inspiration
- The Meaning of Home
- Learning to Play a Musical Instrument
- A Childhood Memory at the Park
- Witnessing a Beautiful Sunset
Narrative Essay Topics for College Students
- Discovering a New Passion
- Overcoming Academic Challenges
- Navigating Cultural Differences
- Embracing Independence: Moving Away from Home
- Exploring Career Aspirations
- Coping with Stress in College
- The Impact of a Mentor in My Life
- Balancing Work and Studies
- Facing a Fear of Public Speaking
- Exploring a Semester Abroad
- The Evolution of My Study Habits
- Volunteering Experience That Changed My Perspective
- The Role of Technology in Education
- Finding Balance: Social Life vs. Academics
- Learning a New Skill Outside the Classroom
- Reflecting on Freshman Year Challenges
- The Joys and Struggles of Group Projects
- My Experience with Internship or Work Placement
- Challenges of Time Management in College
- Redefining Success Beyond Grades
- The Influence of Literature on My Thinking
- The Impact of Social Media on College Life
- Overcoming Procrastination
- Lessons from a Leadership Role
- Exploring Diversity on Campus
- Exploring Passion for Environmental Conservation
- An Eye-Opening Course That Changed My Perspective
- Living with Roommates: Challenges and Lessons
- The Significance of Extracurricular Activities
- The Influence of a Professor on My Academic Journey
- Discussing Mental Health in College
- The Evolution of My Career Goals
- Confronting Personal Biases Through Education
- The Experience of Attending a Conference or Symposium
- Challenges Faced by Non-Native English Speakers in College
- The Impact of Traveling During Breaks
- Exploring Identity: Cultural or Personal
- The Impact of Music or Art on My Life
- Addressing Diversity in the Classroom
- Exploring Entrepreneurial Ambitions
- My Experience with Research Projects
- Overcoming Impostor Syndrome in College
- The Importance of Networking in College
- Finding Resilience During Tough Times
- The Impact of Global Issues on Local Perspectives
- The Influence of Family Expectations on Education
- Lessons from a Part-Time Job
- Exploring the College Sports Culture
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education
- The Journey of Self-Discovery Through Education
Narrative Essay Comparison
Narrative essay vs. descriptive essay.
Here’s our first narrative essay comparison! While both narrative and descriptive essays focus on vividly portraying a subject or an event, they differ in their primary objectives and approaches. Now, let’s delve into the nuances of comparison on narrative essays.
Narrative Essay:
Storytelling: Focuses on narrating a personal experience or event.
Chronological Order: Follows a structured timeline of events to tell a story.
Message or Lesson: Often includes a central message, moral, or lesson learned from the experience.
Engagement: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling storyline and character development.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, using “I” and expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a plot with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Focuses on describing characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Conflict or Challenge: Usually involves a central conflict or challenge that drives the narrative forward.
Dialogue: Incorporates conversations to bring characters and their interactions to life.
Reflection: Concludes with reflection or insight gained from the experience.
Descriptive Essay:
Vivid Description: Aims to vividly depict a person, place, object, or event.
Imagery and Details: Focuses on sensory details to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
Emotion through Description: Uses descriptive language to evoke emotions and engage the reader’s senses.
Painting a Picture: Creates a sensory-rich description allowing the reader to visualize the subject.
Imagery and Sensory Details: Focuses on providing rich sensory descriptions, using vivid language and adjectives.
Point of Focus: Concentrates on describing a specific subject or scene in detail.
Spatial Organization: Often employs spatial organization to describe from one area or aspect to another.
Objective Observations: Typically avoids the use of personal opinions or emotions; instead, the focus remains on providing a detailed and objective description.
Comparison:
Focus: Narrative essays emphasize storytelling, while descriptive essays focus on vividly describing a subject or scene.
Perspective: Narrative essays are often written from a first-person perspective, while descriptive essays may use a more objective viewpoint.
Purpose: Narrative essays aim to convey a message or lesson through a story, while descriptive essays aim to paint a detailed picture for the reader without necessarily conveying a specific message.
Narrative Essay vs. Argumentative Essay
The narrative essay and the argumentative essay serve distinct purposes and employ different approaches:
Engagement and Emotion: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling story.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience or lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, sharing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a storyline with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Message or Lesson: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Argumentative Essay:
Persuasion and Argumentation: Aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s viewpoint on a specific topic.
Logical Reasoning: Presents evidence, facts, and reasoning to support a particular argument or stance.
Debate and Counterarguments: Acknowledge opposing views and counter them with evidence and reasoning.
Thesis Statement: Includes a clear thesis statement that outlines the writer’s position on the topic.
Thesis and Evidence: Starts with a strong thesis statement and supports it with factual evidence, statistics, expert opinions, or logical reasoning.
Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints and provides rebuttals with evidence.
Logical Structure: Follows a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, and a conclusion reaffirming the thesis.
Formal Language: Uses formal language and avoids personal anecdotes or emotional appeals.
Objective: Argumentative essays focus on presenting a logical argument supported by evidence, while narrative essays prioritize storytelling and personal reflection.
Purpose: Argumentative essays aim to persuade and convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, while narrative essays aim to engage, entertain, and share personal experiences.
Structure: Narrative essays follow a storytelling structure with character development and plot, while argumentative essays follow a more formal, structured approach with logical arguments and evidence.
In essence, while both essays involve writing and presenting information, the narrative essay focuses on sharing a personal experience, whereas the argumentative essay aims to persuade the audience by presenting a well-supported argument.
Narrative Essay vs. Personal Essay
While there can be an overlap between narrative and personal essays, they have distinctive characteristics:
Storytelling: Emphasizes recounting a specific experience or event in a structured narrative form.
Engagement through Story: Aims to engage the reader through a compelling story with characters, plot, and a central theme or message.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience and the lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s viewpoint, expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Focuses on developing a storyline with a clear beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Includes descriptions of characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Central Message: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Personal Essay:
Exploration of Ideas or Themes: Explores personal ideas, opinions, or reflections on a particular topic or subject.
Expression of Thoughts and Opinions: Expresses the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and perspectives on a specific subject matter.
Reflection and Introspection: Often involves self-reflection and introspection on personal experiences, beliefs, or values.
Varied Structure and Content: Can encompass various forms, including memoirs, personal anecdotes, or reflections on life experiences.
Flexibility in Structure: Allows for diverse structures and forms based on the writer’s intent, which could be narrative-like or more reflective.
Theme-Centric Writing: Focuses on exploring a central theme or idea, with personal anecdotes or experiences supporting and illustrating the theme.
Expressive Language: Utilizes descriptive and expressive language to convey personal perspectives, emotions, and opinions.
Focus: Narrative essays primarily focus on storytelling through a structured narrative, while personal essays encompass a broader range of personal expression, which can include storytelling but isn’t limited to it.
Structure: Narrative essays have a more structured plot development with characters and a clear sequence of events, while personal essays might adopt various structures, focusing more on personal reflection, ideas, or themes.
Intent: While both involve personal experiences, narrative essays emphasize telling a story with a message or lesson learned, while personal essays aim to explore personal thoughts, feelings, or opinions on a broader range of topics or themes.

A narrative essay is more than just telling a story. It’s also meant to engage the reader, get them thinking, and leave a lasting impact. Whether it’s to amuse, motivate, teach, or reflect, these essays are a great way to communicate with your audience. This interesting narrative essay guide was all about letting you understand the narrative essay, its importance, and how can you write one.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Narrative Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)

Narrative essays are a type of storytelling in which writers weave a personal experience into words to create a fascinating and engaging narrative for readers. A narrative essay explains a story from the author’s point of view to share a lesson or memory with the reader. Narrative essays, like descriptive essays , employ figurative language to depict the subject in a vivid and creative manner to leave a lasting impact on the readers’ minds. In this article, we explore the definition of narrative essays, list the key elements to be included, and provide tips on how to craft a narrative that captivates your audience.
Table of Contents
What is a narrative essay, choosing narrative essay topics, key elements in a narrative essay, creating a narrative essay outline, types of narrative essays, the pre-writing stage, the writing stage, the editing stage, narrative essay example, frequently asked questions.
Narrative essays are often based on one’s personal experience which allows the author to express himself/herself in compelling ways for the reader. They employ storytelling elements to convey the plot and captivate the reader while disclosing the story’s theme or purpose. The author must always have a purpose or theme in mind when writing a narrative essay. These essays may be assigned to high school students to assess their ability to create captivating stories based on personal experiences, or they may be required as part of a college application to assess the applicant’s personal traits. Narrative essays might be based on true events with minor tweaks for dramatic purposes, or they can be adapted from a fictional scenario. Whatever the case maybe, the goal is to tell a story, a good story!
In narrative essays, the emphasis is not so much on the narrative itself as it is on how you explain it. Narrative essay topics cover a range of experiences, from noteworthy to mundane, but when storytelling elements are used well, even a simple account can have weight. Notably, the skills required for narrative writing differ significantly from those needed for formal academic essays, and we will delve deeper into this in the next section.
You can talk about any narrative, but consider whether it is fascinating enough, has enough twists and turns, or teaches a lesson (It’s a plus if the story contains an unexpected twist at the end). The potential topics for a narrative essay are limitless—a triumphant story, a brief moment of introspection, or a voyage of self-discovery. These essays provide writers with the opportunity to share a fragment of their lives with the audience, enriching both the writer’s and the reader’s experiences. Narrative essay examples could be a write-up on “What has been your biggest achievement in life so far and what did it teach you?” or “Describe your toughest experience and how you dealt with it?”.

While narrative essays allow you to be creative with your ideas, language, and format, they must include some key components to convey the story clearly, create engaging content and build reader interest. Follow these guidelines when drafting your essay:
- Tell your story using the first person to engage users.
- Use sufficient sensory information and figurative language.
- Follow an organized framework so the story flows chronologically.
- Include interesting plot components that add to the narrative.
- Ensure clear language without grammar, spelling, or word choice errors.
Narrative essay outlines serve as the foundational structure for essay composition, acting as a framework to organize thoughts and ideas prior to the writing process. These outlines provide writers with a means to summarize the story, and help in formulating the introduction and conclusion sections and defining the narrative’s trajectory.
Unlike conventional essays that strictly adhere to the five-paragraph structure, narrative essays allow for more flexibility as the organization is dictated by the flow of the story. The outline typically encompasses general details about the events, granting writers the option to prioritize writing the body sections first while deferring the introduction until later stages of the writing process. This approach allows for a more organic and fluid writing process. If you’re wondering how to start writing a narrative essay outline, here is a sample designed to ensure a compelling and coherent narrative:
Introduction
- Hook/Opening line: The introduction should have an opening/hook sentence that is a captivating quote, question, or anecdote that grabs the reader’s attention.
- Background: Briefly introduce the setting, time, tone, and main characters.
- Thesis statement: State clearly the main theme or lesson acquired from the experience.
- Event 1 (according to occurrence): Describe the first major event in detail. Introduce the primary characters and set the story context; include sensory elements to enrich the narrative and give the characters depth and enthusiasm.
- Event 2: Ensure a smooth transition from one event to the next. Continue with the second event in the narrative. For more oomph, use suspense or excitement, or leave the plot with cliffhanger endings. Concentrate on developing your characters and their relationships, using dialog to bring the story to life.
- Event 3: If there was a twist and suspense, this episode should introduce the climax or resolve the story. Keep the narrative flowing by connecting events logically and conveying the feelings and reactions of the characters.
- Summarize the plot: Provide a concise recap of the main events within the narrative essay. Highlight the key moments that contribute to the development of the storyline. Offer personal reflections on the significance of the experiences shared, emphasizing the lasting impact they had on the narrator. End the story with a clincher; a powerful and thought-provoking sentence that encapsulates the essence of the narrative. As a bonus, aim to leave the reader with a memorable statement or quote that enhances the overall impact of the narrative. This should linger in the reader’s mind, providing a satisfying and resonant conclusion to the essay.
There are several types of narrative essays, each with their own unique traits. Some narrative essay examples are presented in the table below.
| Narrative essay type | Features | |
| 1. | Personal | Based on personal experience, insight, reflection, and emotion |
| 2. | Autobiographical | Covers life events, full length |
| 3. | Descriptive | Emphasizes detailed description for reader immersion |
| 4. | Experiential | Based on a specific experience, involving emotional responses |
| 5. | Historical | Focuses on historical events, non-fictional, facts stated using figurative language |
| 6. | Biographical | Explores an individual’s life, personality, achievements, and challenges |
| 7. | Travel | Chronicles experiences and thoughtful observations during a journey |
| 8. | Literary | Analyzes or interprets literature, includes a narrative element |
How to write a narrative essay: Step-by-step guide
A narrative essay might be inspired by personal experiences, stories, or even imaginary scenarios that resonate with readers, immersing them in the imaginative world you have created with your words. Here’s an easy step-by-step guide on how to write a narrative essay.
- Select the topic of your narrative
If no prompt is provided, the first step is to choose a topic to write about. Think about personal experiences that could be given an interesting twist. Readers are more likely to like a tale if it contains aspects of humor, surprising twists, and an out-of-the-box climax. Try to plan out such subjects and consider whether you have enough information on the topic and whether it meets the criteria of being funny/inspiring, with nice characters/plot lines, and an exciting climax. Also consider the tone as well as any stylistic features (such as metaphors or foreshadowing) to be used. While these stylistic choices can be changed later, sketching these ideas early on helps you give your essay a direction to start.
- Create a framework for your essay
Once you have decided on your topic, create an outline for your narrative essay. An outline is a framework that guides your ideas while you write your narrative essay to keep you on track. It can help with smooth transitions between sections when you are stuck and don’t know how to continue the story. It provides you with an anchor to attach and return to, reminding you of why you started in the first place and why the story matters.

- Compile your first draft
A perfect story and outline do not work until you start writing the draft and breathe life into it with your words. Use your newly constructed outline to sketch out distinct sections of your narrative essay while applying numerous linguistic methods at your disposal. Unlike academic essays, narrative essays allow artistic freedom and leeway for originality so don’t stop yourself from expressing your thoughts. However, take care not to overuse linguistic devices, it’s best to maintain a healthy balance to ensure readability and flow.
- Use a first-person point of view
One of the most appealing aspects of narrative essays is that traditional academic writing rules do not apply, and the narration is usually done in the first person. You can use first person pronouns such as I and me while narrating different scenarios. Be wary of overly using these as they can suggest lack of proper diction.
- Use storytelling or creative language
You can employ storytelling tactics and linguistic tools used in fiction or creative writing, such as metaphors, similes, and foreshadowing, to communicate various themes. The use of figurative language, dialogue, and suspense is encouraged in narrative essays.
- Follow a format to stay organized
There’s no fixed format for narrative essays, but following a loose format when writing helps in organizing one’s thoughts. For example, in the introduction part, underline the importance of creating a narrative essay, and then reaffirm it in the concluding paragraph. Organize your story chronologically so that the reader can follow along and make sense of the story.
- Reread, revise, and edit
Proofreading and editing are critical components of creating a narrative essay, but it can be easy to become weighed down by the details at this stage. Taking a break from your manuscript before diving into the editing process is a wise practice. Stepping away for a day or two, or even just a few hours, provides valuable time to enhance the plot and address any grammatical issues that may need correction. This period of distance allows for a fresh perspective, enabling you to approach the editing phase with renewed clarity and a more discerning eye.
One suggestion is to reconsider the goals you set out to cover when you started the topic. Ask yourself these questions:
- Is there a distinct beginning and end to your story?
- Does your essay have a topic, a memory, or a lesson to teach?
- Does the tone of the essay match the intended mood?
Now, while keeping these things in mind, modify and proofread your essay. You can use online grammar checkers and paraphrase tools such as Paperpal to smooth out any rough spots before submitting it for publication or submission.
It is recommended to edit your essay in the order it was written; here are some useful tips:
- Revise the introduction
After crafting your narrative essay, review the introduction to ensure it harmonizes with the developed narrative. Confirm that it adeptly introduces the story and aligns seamlessly with the conclusion.
- Revise the conclusion and polish the essay
The conclusion should be the final element edited to ensure coherence and harmony in the entire narrative. It must reinforce the central theme or lesson outlined initially.
- Revise and refine the entire article
The last step involves refining the article for consistent tone, style, and tense as well as correct language, grammar, punctuation, and clarity. Seeking feedback from a mentor or colleague can offer an invaluable external perspective at this stage.
Narrative essays are true accounts of the writer’s personal experiences, conveyed in figurative language for sensory appeal. Some narrative essay topic examples include writing about an unforgettable experience, reflecting on mistakes, or achieving a goal. An example of a personal narrative essay is as follows:
Title: A Feline Odyssey: An Experience of Fostering Stray Kittens
Introduction:
It was a fine summer evening in the year 2022 when a soft meowing disrupted the tranquility of my terrace. Little did I know that this innocent symphony would lead to a heartwarming journey of compassion and companionship. Soon, there was a mama cat at my doorstep with four little kittens tucked behind her. They were the most unexpected visitors I had ever had.
The kittens, just fluffs of fur with barely open eyes, were a monument to life’s fragility. Their mother, a street-smart feline, had entrusted me with the care of her precious offspring. The responsibility was sudden and unexpected, yet there was an undeniable sense of purpose in the air , filling me with delight and enthusiasm.
As the days unfolded, my terrace transformed into a haven for the feline family. Cardboard boxes became makeshift cat shelters and my once solitary retreat was filled with purrs and soothing meows. The mother cat, Lily, who initially observ ed me from a safe distance, gradually began to trust my presence as I offered food and gentle strokes.
Fostering the kittens was a life-changing , enriching experience that taught me the true joy of giving as I cared for the felines. My problems slowly faded into the background as evenings were spent playing with the kittens. Sleepless nights turned into a symphony of contented purring, a lullaby filled with the warmth of trust and security . Although the kittens were identical, they grew up to have very distinct personalities, with Kuttu being the most curious and Bobo being the most coy . Every dawn ushered in a soothing ritual of nourishing these feline companions, while nights welcomed their playful antics — a daily nocturnal delight.
Conclusion:
As the kittens grew, so did the realization that our paths were destined to part. Finally, the day arrived when the feline family, now confident and self-reliant, bid farewell to my terrace. It was a bittersweet moment, filled with a sense of love and accomplishment and a tinge of sadness.
Fostering Kuttu, Coco, Lulu, and Bobo became one of the most transformative experiences of my life. Their arrival had brought unexpected joy, teaching me about compassion and our species’ ability to make a difference in the world through love and understanding. The terrace, once a quiet retreat, now bore the echoes of a feline symphony that had touched my heart in ways I could have never imagined.

The length of a narrative essay may vary, but it is typically a brief to moderate length piece. Generally, the essay contains an introductory paragraph, two to three body paragraphs (this number can vary), and a conclusion. The entire narrative essay could be as short as five paragraphs or much longer, depending on the assignment’s requirements or the writer’s preference.
You can write a narrative essay when you have a personal experience to share, or a story, or a series of events that you can tell in a creative and engaging way. Narrative essays are often assigned in academic settings as a form of writing that allows students to express themselves and showcase their storytelling skills. However, you can also write a narrative essay for personal reflection, entertainment, or to communicate a message.
A narrative essay usually follows a three-part structure: – Introduction (To set the stage for the story) – Body paragraphs (To describe sequence of events with details, descriptions, and dialogue) – Conclusion (To summarize the story and reflect on the significance)
Paperpal is an AI academic writing assistant that helps authors write better and faster with real-time writing suggestions and in-depth checks for language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of published scholarly articles and 20+ years of STM experience, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to Paperpal Copilot and premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks, submission readiness and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
Webinar: how to use generative ai tools ethically in your academic writing.
- 7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Chemistry Terms: 7 Commonly Confused Words in Chemistry Manuscripts
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
What is a Descriptive Essay? How to Write It (with Examples)
You may also like, how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Narrative Essays

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a narrative essay?
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways.
Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay.
- If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a story.
This means that you must include an introduction, plot, characters, setting, climax, and conclusion.
- When would a narrative essay not be written as a story?
A good example of this is when an instructor asks a student to write a book report. Obviously, this would not necessarily follow the pattern of a story and would focus on providing an informative narrative for the reader.
- The essay should have a purpose.
Make a point! Think of this as the thesis of your story. If there is no point to what you are narrating, why narrate it at all?
- The essay should be written from a clear point of view.
It is quite common for narrative essays to be written from the standpoint of the author; however, this is not the sole perspective to be considered. Creativity in narrative essays oftentimes manifests itself in the form of authorial perspective.
- Use clear and concise language throughout the essay.
Much like the descriptive essay, narrative essays are effective when the language is carefully, particularly, and artfully chosen. Use specific language to evoke specific emotions and senses in the reader.
- The use of the first person pronoun ‘I’ is welcomed.
Do not abuse this guideline! Though it is welcomed it is not necessary—nor should it be overused for lack of clearer diction.
- As always, be organized!
Have a clear introduction that sets the tone for the remainder of the essay. Do not leave the reader guessing about the purpose of your narrative. Remember, you are in control of the essay, so guide it where you desire (just make sure your audience can follow your lead).
BibGuru Blog
Be more productive in school
- Citation Styles
How to write a narrative essay [Updated 2023]

A narrative essay is an opportunity to flex your creative muscles and craft a compelling story. In this blog post, we define what a narrative essay is and provide strategies and examples for writing one.
What is a narrative essay?
Similarly to a descriptive essay or a reflective essay, a narrative essay asks you to tell a story, rather than make an argument and present evidence. Most narrative essays describe a real, personal experience from your own life (for example, the story of your first big success).
Alternately, your narrative essay might focus on an imagined experience (for example, how your life would be if you had been born into different circumstances). While you don’t need to present a thesis statement or scholarly evidence, a narrative essay still needs to be well-structured and clearly organized so that the reader can follow your story.
When you might be asked to write a narrative essay
Although less popular than argumentative essays or expository essays, narrative essays are relatively common in high school and college writing classes.
The same techniques that you would use to write a college essay as part of a college or scholarship application are applicable to narrative essays, as well. In fact, the Common App that many students use to apply to multiple colleges asks you to submit a narrative essay.
How to choose a topic for a narrative essay
When you are asked to write a narrative essay, a topic may be assigned to you or you may be able to choose your own. With an assigned topic, the prompt will likely fall into one of two categories: specific or open-ended.
Examples of specific prompts:
- Write about the last vacation you took.
- Write about your final year of middle school.
Examples of open-ended prompts:
- Write about a time when you felt all hope was lost.
- Write about a brief, seemingly insignificant event that ended up having a big impact on your life.
A narrative essay tells a story and all good stories are centered on a conflict of some sort. Experiences with unexpected obstacles, twists, or turns make for much more compelling essays and reveal more about your character and views on life.
If you’re writing a narrative essay as part of an admissions application, remember that the people reviewing your essay will be looking at it to gain a sense of not just your writing ability, but who you are as a person.
In these cases, it’s wise to choose a topic and experience from your life that demonstrates the qualities that the prompt is looking for, such as resilience, perseverance, the ability to stay calm under pressure, etc.
It’s also important to remember that your choice of topic is just a starting point. Many students find that they arrive at new ideas and insights as they write their first draft, so the final form of your essay may have a different focus than the one you started with.
How to outline and format a narrative essay
Even though you’re not advancing an argument or proving a point of view, a narrative essay still needs to have a coherent structure. Your reader has to be able to follow you as you tell the story and to figure out the larger point that you’re making.
You’ll be evaluated on is your handling of the topic and how you structure your essay. Even though a narrative essay doesn’t use the same structure as other essay types, you should still sketch out a loose outline so you can tell your story in a clear and compelling way.
To outline a narrative essay, you’ll want to determine:
- how your story will start
- what points or specifics that you want to cover
- how your story will end
- what pace and tone you will use
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.” Also, most narrative essays will follow typical formatting guidelines, so you should choose a readable font like Times New Roman in size 11 or 12. Double-space your paragraphs and use 1” margins.
To get your creative wheels turning, consider how your story compares to archetypes and famous historical and literary figures both past and present. Weave these comparisons into your essay to improve the quality of your writing and connect your personal experience to a larger context.
How to write a narrative essay
Writing a narrative essay can sometimes be a challenge for students who typically write argumentative essays or research papers in a formal, objective style. To give you a better sense of how you can write a narrative essay, here is a short example of an essay in response to the prompt, “Write about an experience that challenged your view of yourself.”
Narrative essay example
Even as a child, I always had what people might call a reserved personality. It was sometimes framed as a positive (“Sarah is a good listener”) and at other times it was put in less-than-admiring terms (“Sarah is withdrawn and not very talkative”). It was the latter kind of comments that caused me to see my introverted nature as a drawback and as something I should work to eliminate. That is, until I joined my high school’s student council.
The first paragraph, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
The other four students making up the council were very outspoken and enthusiastic. I enjoyed being around them, and I often agreed with their ideas. However, when it came to overhauling our school’s recycling plan, we butted heads. When I spoke up and offered a different point of view, one of my fellow student council members launched into a speech, advocating for her point of view. As her voice filled the room, I couldn’t get a word in edgewise. I wondered if I should try to match her tone, volume, and assertiveness as a way to be heard. But I just couldn’t do it—it’s not my way, and it never has been. For a fleeting moment, I felt defeated. But then, something in me shifted.
In this paragraph, the writer goes into greater depth about how her existing thinking brought her to this point.
I reminded myself that my view was valid and deserved to be heard. So I waited. I let my fellow council member speak her piece and when she was finished, I deliberately waited a few moments before calmly stating my case. I chose my words well, and I spoke them succinctly. Just because I’m not a big talker doesn’t mean I’m not a big thinker. I thought of the quotation “still waters run deep” and I tried to embody that. The effect on the room was palpable. People listened. And I hadn’t had to shout my point to be heard.
This paragraph demonstrates the turn in the story, the moment when everything changed. The use of the quotation “still waters run deep” imbues the story with a dash of poetry and emotion.
We eventually reached a compromise on the matter and concluded the student council meeting. Our council supervisor came to me afterward and said: “You handled that so well, with such grace and poise. I was very impressed.” Her words in that moment changed me. I realized that a bombastic nature isn't necessarily a powerful one. There is power in quiet, too. This experience taught me to view my reserved personality not as a character flaw, but as a strength.
The final paragraph, or conclusion, closes with a statement about the significance of this event and how it ended up changing the writer in a meaningful way.
Narrative essay writing tips
1. pick a meaningful story that has a conflict and a clear “moral.”.
If you’re able to choose your own topic, pick a story that has meaning and that reveals how you became the person your are today. In other words, write a narrative with a clear “moral” that you can connect with your main points.
2. Use an outline to arrange the structure of your story and organize your main points.
Although a narrative essay is different from argumentative essays, it’s still beneficial to construct an outline so that your story is well-structured and organized. Note how you want to start and end your story, and what points you want to make to tie everything together.
3. Be clear, concise, concrete, and correct in your writing.
You should use descriptive writing in your narrative essay, but don’t overdo it. Use clear, concise, and correct language and grammar throughout. Additionally, make concrete points that reinforce the main idea of your narrative.
4. Ask a friend or family member to proofread your essay.
No matter what kind of writing you’re doing, you should always plan to proofread and revise. To ensure that your narrative essay is coherent and interesting, ask a friend or family member to read over your paper. This is especially important if your essay is responding to a prompt. It helps to have another person check to make sure that you’ve fully responded to the prompt or question.
Frequently Asked Questions about narrative essays
A narrative essay, like any essay, has three main parts: an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Structuring and outlining your essay before you start writing will help you write a clear story that your readers can follow.
The first paragraph of your essay, or introduction, sets up the context, establishing the situation and introducing the meaningful event upon which the essay will focus.
In the vast majority of cases, a narrative essay should be written in the first-person, using “I.”
The 4 main types of essays are the argumentative essay, narrative essay, exploratory essay, and expository essay. You may be asked to write different types of essays at different points in your education.
Most narrative essays will be around five paragraphs, or more, depending on the topic and requirements. Make sure to check in with your instructor about the guidelines for your essay. If you’re writing a narrative essay for a college application, pay close attention to word or page count requirements.

Make your life easier with our productivity and writing resources.
For students and teachers.

When writers set down the facts of their lives into a compelling story , they’re writing a narrative essay. Personal narrative essays explore the events of the writer’s own life, and by crafting a nonfiction piece that resonates as storytelling, the essayist can uncover deeper truths in the world.
Narrative essays weave the author’s factual lived experiences into a compelling story.
So, what is a narrative essay? Whether you’re writing for college applications or literary journals , this article separates fact from fiction. We’ll look at how to write a narrative essay through a step-by-step process, including a look at narrative essay topics and outlines. We’ll also analyze some successful narrative essay examples.
Learn how to tell your story, your way. Let’s dive into this exciting genre!
What is a Narrative Essay?
The narrative essay is a branch of creative nonfiction . Also known as a personal essay, writers of this genre are tasked with telling honest stories about their lived experiences and, as a result, arriving at certain realizations about life.
Think of personal narrative essays as nonfiction short stories . While the essay and the short story rely on different writing techniques, they arrive at similar outcomes: a powerful story with an idea, theme , or moral that the reader can interpret for themselves.
Now, if you haven’t written a narrative essay before, you might associate the word “essay” with high school English class. Remember those tedious 5-paragraph essays we had to write, on the topic of some book we barely read, about subject matter that didn’t interest us?
Don’t worry—that’s not the kind of essay we’re talking about. The word essay comes from the French essayer , which means “to try.” That’s exactly what writing a narrative essay is: an attempt at organizing the real world into language—a journey of making meaning from the chaos of life.
Narrative essays work to surface meaning from lived experience.
Narrative Essay Example
A great narrative essay example is the piece “Flow” by Mary Oliver, which you can read for free in Google Books .
The essay dwells on, as Mary Oliver puts it, the fact that “we live in paradise.” At once both an ode to nature and an urge to love it fiercely, Oliver explores our place in the endless beauty of the world.
Throughout the essay, Oliver weaves in her thoughts about the world, from nature’s noble beauty to the question “What is the life I should live?” Yet these thoughts, however profound, are not the bulk of the essay. Rather, she arrives at these thoughts via anecdotes and observations: the migration of whales, the strings of fish at high tide, the inventive rescue of a spiny fish from the waterless shore, etc.
What is most profound about this essay, and perhaps most amusing, is that it ends with Oliver’s questions about how to live life. And yet, the stories she tells show us exactly how to live life: with care for the world; with admiration; with tenderness towards all of life and its superb, mysterious, seemingly-random beauty.
Such is the power of the narrative essay. By examining the random facts of our lives, we can come to great conclusions.
What do most essays have in common? Let’s look at the fundamentals of the essay, before diving into more narrative essay examples.
Narrative Essay Definition: 5 Fundamentals
The personal narrative essay has a lot of room for experimentation. We’ll dive into those opportunities in a bit, but no matter the form, most essays share these five fundamentals.
- Personal experience
- Meaning from chaos
- The use of literary devices
Let’s explore these fundamentals in depth.
All narrative essays have a thesis statement. However, this isn’t the formulaic thesis statement you had to write in school: you don’t need to map out your argument with painstaking specificity, you need merely to tell the reader what you’re writing about.
Take the aforementioned essay by Mary Oliver. Her thesis is this: “How can we not know that, already, we live in paradise?”
It’s a simple yet provocative statement. By posing her thesis as a question, she challenges us to consider why we might not treat this earth as paradise. She then delves into her own understanding of this paradise, providing relevant stories and insights as to how the earth should be treated.
Now, be careful with abstract statements like this. Mary Oliver is a master of language, so she’s capable of creating a thesis statement out of an abstract idea and building a beautiful essay. But concrete theses are also welcome: you should compel the reader forward with the central argument of your work, without confusing them or leading them astray.
You should compel the reader forward with the central argument of your work, without confusing them or leading them astray
2. Personal Experience
The personal narrative essay is, shockingly, about personal experience. But how do writers distill their experiences into meaningful stories?
There are a few techniques writers have at their disposal. Perhaps the most common of these techniques is called braiding . Rather than focusing on one continuous story, the writer can “braid” different stories, weaving in and out of different narratives and finding common threads between them. Often, the subject matter of the essay will require more than one anecdote as evidence, and braiding helps the author uphold their thesis while showing instead of telling .
Another important consideration is how you tell your story . Essayists should consider the same techniques that fiction writers use. Give ample consideration to your essay’s setting , word choice , point of view , and dramatic structure . The narrative essay is, after all, a narrative, so tell your story how it deserves to be told.
3. Meaning from Chaos
Life, I think we can agree, is chaotic. While we can trace the events of our lives through cause and effect, A leads to B leads to C, the truth is that so much of our lives are shaped through circumstances beyond our control.
The narrative essay is a way to reclaim some of that control. By distilling the facts of our lives into meaningful narratives, we can uncover deeper truths that we didn’t realize existed.
By distilling the facts of our lives into meaningful narratives, we can uncover deeper truths that we didn’t realize existed.
Consider the essay “ Only Daughter ” by Sandra Cisneros. It’s a brief read, but it covers a lot of different events: a lonesome childhood, countless moves, university education, and the trials and tribulations of a successful writing career.
Coupled with Cisneros’ musings on culture and gender roles, there’s a lot of life to distill in these three pages. Yet Cisneros does so masterfully. By organizing these life events around her thesis statement of being an only daughter, Cisneros finds meaning in the many disparate events she describes.
As you go about writing a narrative essay, you will eventually encounter moments of insight . Insight describes those “aha!” moments in the work—places in which you come to deeper realizations about your life, the lives of others, and the world at large.
Now, insight doesn’t need to be some massive, culture-transforming realization. Many moments of insight are found in small interactions and quiet moments.
For example, In the above essay by Sandra Cisneros, her moments of insight come from connecting her upbringing to her struggle as an only daughter. While her childhood was often lonely and disappointing, she realizes in hindsight that she’s lucky for that upbringing: it helped nurture her spirit as a writer, and it helped her pursue a career in writing. These moments of gratitude work as insight, allowing her to appreciate what once seemed like a burden.
When we reach the end of the essay, and Cisneros describes how she felt when her father read one of her stories, we see what this gratitude is building towards: love and acceptance for the life she chose.
5. Literary Devices
The personal narrative essay, as well as all forms of creative writing, uses its fair share of literary devices . These devices don’t need to be complex: you don’t need a sprawling extended metaphor or an intricate set of juxtapositions to make your essay compelling.
However, the occasional symbol or metaphor will certainly aid your story. In Mary Oliver’s essay “Flow,” the author uses literary devices to describe the magnificence of the ocean, calling it a “cauldron of changing greens and blues” and “the great palace of the earth.” These descriptions reinforce the deep beauty of the earth.
In Sandra Cisneros’ essay “Only Daughter,” the author employs different symbols to represent her father’s masculinity and sense of gender roles. At one point, she lists the few things he reads—sports journals, slasher magazines, and picture paperbacks, often depicting scenes of violence against women. These symbols represent the divide between her father’s gendered thinking and her own literary instincts.
More Narrative Essay Examples
Let’s take a look at a few more narrative essay examples. We’ll dissect each essay based on the five fundamentals listed above.
Narrative Essay Example: “Letting Go” by David Sedaris
Read “Letting Go” here in The New Yorker .
Sedaris’ essay dwells on the culture of cigarette smoking—how it starts, the world it builds, and the difficulties in quitting. Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: There isn’t an explicitly defined thesis, which is common for essays that are meant to be humorous or entertaining. However, this sentence is a plausible thesis statement: “It wasn’t the smoke but the smell of it that bothered me. In later years, I didn’t care so much, but at the time I found it depressing: the scent of neglect.”
- Personal Experience: Sedaris moves between many different anecdotes about smoking, from his family’s addiction to cigarettes to his own dependence. We learn about his moving around for cheaper smokes, his family’s struggle to quit, and the last cigarette he smoked in the Charles de Gaulle airport.
- Meaning from Chaos: Sedaris ties many disparate events together. We learn about his childhood and his smoking years, but these are interwoven with anecdotes about his family and friends. What emerges is a narrative about the allure of smoking.
- Insight: Two parts of this essay are especially poignant. One, when Sedaris describes his mother’s realization that smoking isn’t sophisticated, and soon quits her habit entirely. Two, when Sedaris is given the diseased lung of a chain smoker, and instead of thinking about his own lungs, he’s simply surprised at how heavy the lung is.
- Literary Devices: Throughout the essay, Sedaris demonstrates how the cigarette symbolizes neglect: neglect of one’s body, one’s space, and one’s self-presentation.
Narrative Essay Example: “My Mother’s Tongue” by Zavi Kang Engles
Read “My Mother’s Tongue” here in The Rumpus .
Engles’ essay examines the dysphoria of growing up between two vastly different cultures and languages. By asserting the close bond between Korean language and culture, Engles explores the absurdities of growing up as a child of Korean immigrants. Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: Engles’ essay often comes back to her relationship with the Korean language, especially as it relates to other Korean speakers. This relationship is best highlighted when she writes “I glowed with [my mother’s] love, basked in the warm security of what I thought was a language between us. Perhaps this is why strangers asked for our photos, in an attempt to capture a secret world between two people.”This “secret world” forms the crux of her essay, charting not only how Korean-Americans might exist in relation to one another, but also how Engles’ language is strongly tied to her identity and homeland.
- Personal Experience: Engles writes about her childhood attachment to both English and Korean, her adolescent fallout with the Korean language, her experiences as “not American enough” in the United States and “not Korean enough” in Korea, and her experiences mourning in a Korean hospital.
- Meaning from Chaos: In addition to the above events, Engles ties in research about language and identity (also known as code switching ). Through language and identity, the essay charts the two different cultures that the author stands between, highlighting the dissonance between Western individualism and an Eastern sense of belonging.
- Insight: There are many examples of insight throughout this essay as the author explores how out of place she feels, torn between two countries. An especially poignant example comes from Engles’ experience in a Korean hospital, where she writes “I didn’t know how to mourn in this country.”
- Literary Devices: The essay frequently juxtaposes the languages and cultures of Korea and the United States. Additionally, the English language comes to symbolize Western individualism, while the Korean language comes to symbolize Eastern collectivism.
Narrative Essay Example: 3 Rules for Middle-Age Happiness by Deborah Copaken
Read “3 Rules for Middle-Age Happiness” here in The Atlantic .
Copaken’s essay explores her relationship to Nora Ephron, the screenwriter for When Harry Met Sally . Let’s analyze how this narrative essay example uses the five fundamentals of essay writing.
- Thesis: This essay hands us the thesis statement in its subtitle: “Gather friends and feed them, laugh in the face of calamity, and cut out all the things—people, jobs, body parts—that no longer serve you.”
- Personal Experience: Copaken weaves two different threads through this essay. One thread is her personal life, including a failing marriage, medical issues, and her attempts at building a happy family. The other is Copaken’s personal relationship to Ephron, whose advice coincides with many of the essay’s insights.
- Meaning from Chaos: This essay organizes its events chronologically. However, the main sense of organization is found in the title: many of the essayist’s problems can be perceived as middle-aged crises (family trouble, divorce, death of loved ones), but the solutions to those crises are simpler than one might realize.
- Insight: In writing this essay, Copaken explores her relationship to Ephron, as well as Copaken’s own relationship to her children. She ties these experiences together at the end, when she writes “The transmission of woes is a one-way street, from child to mother. A good mother doesn’t burden her children with her pain. She waits until it becomes so heavy, it either breaks her or kills her, whichever comes first.”
- Literary Devices: The literary devices in this article explore the author’s relationship to womanhood. She wonders if having a hysterectomy will make her “like less of a woman.” Also important is the fact that, when the author has her hysterectomy, her daughter has her first period. Copaken uses this to symbolize the passing of womanhood from mother to daughter, which helps bring her to the above insight.
How to Write a Narrative Essay in 5 Steps
No matter the length or subject matter, writing a narrative essay is as easy as these five steps.
1. Generating Narrative Essay Ideas
If you’re not sure what to write about, you’ll want to generate some narrative essay ideas. One way to do this is to look for writing prompts online: Reedsy adds new prompts to their site every week, and we also post writing prompts every Wednesday to our Facebook group .
Taking a step back, it helps to simply think about formative moments in your life. You might a great idea from answering one of these questions:
- When did something alter my worldview, personal philosophy, or political beliefs?
- Who has given me great advice, or helped me lead a better life?
- What moment of adversity did I overcome and grow stronger from?
- What is something that I believe to be very important, that I want other people to value as well?
- What life event of mine do I not yet fully understand?
- What is something I am constantly striving for?
- What is something I’ve taken for granted, but am now grateful for?
Finally, you might be interested in the advice at our article How to Come Up with Story Ideas . The article focuses on fiction writers, but essayists can certainly benefit from these tips as well.
2. Drafting a Narrative Essay Outline
Once you have an idea, you’ll want to flesh it out in a narrative essay outline.
Your outline can be as simple or as complex as you’d like, and it all depends on how long you intend your essay to be. A simple outline can include the following:
- Introduction—usually a relevant anecdote that excites or entices the reader.
- Event 1: What story will I use to uphold my argument?
- Analysis 1: How does this event serve as evidence for my thesis?
- Conclusion: How can I tie these events together? What do they reaffirm about my thesis? And what advice can I then impart on the reader, if any?
One thing that’s missing from this outline is insight. That’s because insight is often unplanned: you realize it as you write it, and the best insight comes naturally to the writer. However, if you already know the insight you plan on sharing, it will fit best within the analysis for your essay, and/or in the essay’s conclusion.
Insight is often unplanned: you realize it as you write it, and the best insight comes naturally to the writer.
Another thing that’s missing from this is research. If you plan on intertwining your essay with research (which many essayists should do!), consider adding that research as its own bullet point under each heading.
For a different, more fiction-oriented approach to outlining, check out our article How to Write a Story Outline .
3. Starting with a Story
Now, let’s tackle the hardest question: how to start a narrative essay?
Most narrative essays begin with a relevant story. You want to draw the reader in right away, offering something that surprises or interests them. And, since the essay is about you and your lived experiences, it makes sense to start your essay with a relevant anecdote.
Think about a story that’s relevant to your thesis, and experiment with ways to tell this story. You can start with a surprising bit of dialogue , an unusual situation you found yourself in, or a beautiful setting. You can also lead your essay with research or advice, but be sure to tie that in with an anecdote quickly, or else your reader might not know where your essay is going.
For examples of this, take a look at any of the narrative essay examples we’ve used in this article.
Theoretically, your thesis statement can go anywhere in the essay. You may have noticed in the previous examples that the thesis statement isn’t always explicit or immediate: sometimes it shows up towards the center of the essay, and sometimes it’s more implied than stated directly.
You can experiment with the placement of your thesis, but if you place your thesis later in the essay, make sure that everything before the thesis is intriguing to the reader. If the reader feels like the essay is directionless or boring, they won’t have a reason to reach your thesis, nor will they understand the argument you’re making.
4. Getting to the Core Truth
With an introduction and a thesis underway, continue writing about your experiences, arguments, and research. Be sure to follow the structure you’ve sketched in your outline, but feel free to deviate from this outline if something more natural occurs to you.
Along the way, you will end up explaining why your experiences matter to the reader. Here is where you can start generating insight. Insight can take the form of many things, but the focus is always to reach a core truth.
Insight might take the following forms:
- Realizations from connecting the different events in your life.
- Advice based on your lived mistakes and experiences.
- Moments where you change your ideas or personal philosophy.
- Richer understandings about life, love, a higher power, the universe, etc.
5. Relentless Editing
With a first draft of your narrative essay written, you can make your essay sparkle in the editing process.
Remember, a first draft doesn’t have to be perfect, it just needs to exist.
Remember, a first draft doesn’t have to be perfect, it just needs to exist. Here are some things to focus on in the editing process:
- Clarity: Does every argument make sense? Do my ideas flow logically? Are my stories clear and easy to follow?
- Structure: Does the procession of ideas make sense? Does everything uphold my thesis? Do my arguments benefit from the way they’re laid out in this essay?
- Style: Do the words flow when I read them? Do I have a good mix of long and short sentences? Have I omitted any needless words ?
- Literary Devices: Do I use devices like similes, metaphors, symbols, or juxtaposition? Do these devices help illustrate my ideas?
- Mechanics: Is every word spelled properly? Do I use the right punctuation? If I’m submitting this essay somewhere, does it follow the formatting guidelines?
Your essay can undergo any number of revisions before it’s ready. Above all, make sure that your narrative essay is easy to follow, every word you use matters, and that you come to a deeper understanding about your own life.
Above all, make sure that your narrative essay is easy to follow, every word you use matters, and that you come to a deeper understanding about your own life.
Next Steps for Narrative Essayists
When you have a completed essay, what’s next? You might be interested in submitting to some literary journals . Here’s 24 literary journals you can submit to—we hope you find a great home for your writing!
If you’re looking for additional feedback on your work, feel free to join our Facebook group . You can also take a look at our upcoming nonfiction courses , where you’ll learn the fundamentals of essay writing and make your story even more compelling.
Writing a narrative essay isn’t easy, but you’ll find that the practice can be very rewarding. You’ll learn about your lived experiences, come to deeper conclusions about your personal philosophies, and perhaps even challenge the way you approach life. So find some paper, choose a topic, and get writing—the world is waiting for your story!
Sean Glatch
Thanks for a superbly efficient and informative article…
We’re glad it was helpful, Mary!
Very helpful,, Thanks!!!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step

Essay writing comes in various styles, many of which do not demand extensive research. One such style is the narrative essay, which combines personal storytelling with academic reflection. Unlike other essay types, narrative essays are not bound by strict requirements or the need for a bibliography. They feature a more flexible structure, creative language, and a singular focus: to tell a story.
This genre provides a special opportunity for writers to connect with readers on a personal level. By sharing personal experiences and reflections, authors engage their audience emotionally while imparting meaningful messages or lessons. In the sections that follow, our custom term paper writing experts will delve into different aspects of narrative writing, from selecting a topic to structuring your essay effectively.
What Is a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay, as the name suggests, is characterized by the presence of a narrative. Unlike argumentative essays, which present and defend a position, or analytical essays, which dissect another text, narrative essays tell a coherent story. Their goal is to convey a point or impart a lesson through personal experiences. These essays are frequently assigned in high school and for college admissions.
An effective narrative essay generally follows a chronological sequence of events and exhibits three main traits:
- Centers on one main idea.
- Utilizes specific details to illustrate that idea.
- Adheres to a clear sequence of events.
Structurally, a narrative essay resembles short stories, featuring vivid descriptions, plots, characters, and discussions. However, there are key differences. These essays focus on a central theme or argument and conclude decisively, whereas short stories often leave readers with a more abstract moral or message.
A narrative essay is typically written in the first person and follows a standard format with an introduction, body, and conclusion. In contrast, short stories can adopt various formats and may not adhere to the same structured approach.
What is the Purpose of a Narrative Essay
No matter what you write — fiction, non-fiction, memoir, biography — grasping narrative writing helps you connect with your reader, giving them a glimpse of your world. Here, we outline its key purposes:
.webp)
- Academic Assignments: They fulfill requirements for school assignments, allowing students to demonstrate their understanding and creativity.
- Self-Reflection: As a key purpose of a narrative essay, this type of writing enables individuals to reflect on personal achievements or significant events, fostering introspection and self-awareness.
- Professional Endeavors: They are used when applying for jobs or scholarships, showcasing one's communication skills, experiences, and character.
- Literary Analysis: Narrative storytelling is employed in analyzing literature, providing a medium to explore themes, characters, and storytelling techniques.
- Cultural Exploration: They facilitate the exploration of different cultures, allowing individuals to share insights and experiences from diverse perspectives.
- Creative Expression: These essays offer a means of expressing oneself creatively, weaving personal narratives into compelling stories.
- Communication of Messages: Through storytelling, narrative writing conveys messages or lessons, engaging readers and imparting wisdom or insights.
- Engagement: Above all, these essays connect with the audience on a personal level, fostering empathy, understanding, and emotional resonance.
Meanwhile, if you’re willing to describe your life in greater depth, our guide on how to write an autobiography might be just what you need!
How to Write a Narrative Essay in 5 Steps
Writing a narrative essay is a unique process compared to other types of school essays. Rather than analyzing topics or defending a position, it focuses on sharing personal experiences through storytelling. By following a few straightforward steps, you can transform your ideas into an engaging narrative.
.webp)
Step 1: Start with a Topic Selection
When crafting a narrative essay, begin by selecting a topic that either relates to your personal experiences or aligns with a given prompt. If a prompt is provided, consider its requirements and brainstorm ideas that fit within its scope.
As you brainstorm, jot down key moments or points you want to include in your essay. Evaluate how each point will fit into the overall structure of your narrative and ensure it adheres to any word count limits.
Think about the tone and style you wish to adopt. Will your essay be reflective, humorous, or something else? Consider incorporating specific stylistic elements, such as repeated phrases or cliffhanger endings, to enhance your storytelling and engage your reader.
Remain flexible throughout this process. As you explore different ideas, be open to tweaking your topic, tone, and style to better suit your narrative.
For more inspiration and to skip the brainstorming phase, check out a ready-made Narrative Essay Topic list!
Step 2: Make a Clear Outline
Once you have your topic, it's time to draft your narrative essay outline. This outline serves as a blueprint, guiding you in crafting a coherent and engaging story. Start by pinpointing the main points you wish to address, such as pivotal moments or insights gained, and allocate each to a separate paragraph to maintain a clear sequence.
Your outline should help you structure the flow of your narrative, planning out the sequence of events and the level of detail to include. For example, if your essay is about a memorable trip, your outline might start with a paragraph setting the scene, followed by paragraphs describing key experiences and interactions, and concluding with reflections on how the trip impacted you.
When outlining your conclusion, think about how to effectively wrap up your story by summarizing the main events and the significance they hold. For a more systematic approach, make sure to check out how to write an essay conclusion .
| Topic: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | ||
| Challenge Description | ||
| Perseverance and Action | ||
| Reflection and Growth | ||
| Conclusion | ||
Step 3: Write Your Narrative Essay
Using your outline as a guide, now, it's time to start writing a narrative essay. Remember that narrative essays provide you with a creative outlet, so feel free to break away from the constraints of traditional academic writing styles. Captivating the reader and giving your narrative life should be your main goals.
Tip 💡 Use first-person : Infuse your essay with personal authenticity and engagement by embracing pronouns like 'I' and 'me'.
Tip 💡 Employ storytelling techniques : Draw upon the techniques employed in fiction and creative nonfiction, such as dialogue and symbolism, to enrich your narrative and captivate your audience.
Tip 💡 Demonstrate, don't merely state : Instead of blandly presenting facts, immerse your reader in your narrative by employing vivid descriptions and sensory details.
Tip 💡 Remain authentic: Preserve the integrity of your voice and experiences. Candidly share your thoughts and emotions to ensure your narrative essay resonates as genuine and relatable.
Step 4: Don't Forget to Revise
After completing your initial draft, it's essential to revise and polish your essay. Begin by taking a break to refresh your perspective before returning with a clear mind - this is one of the best tips for writing a narrative essay!
When revisiting your essay, carefully review it to ensure logical coherence and flow. Address any inconsistencies or narrative gaps, refining your essay for improved clarity. Pay attention to elements such as tense, point of view, and narrative voice throughout.
Step 5: Proofread Your Writing
Now that you understand how to end a narrative essay, don’t forget to dedicate time to meticulous proofreading to catch any lingering errors or typos. Pay close attention to formatting and citation style, if applicable.
Sharing your essay with trusted individuals such as friends, family, or educators can provide valuable feedback and fresh insights. Incorporate the feedback received, along with your own observations from the revision process, to strengthen the impact and effectiveness of your essay.
Narrative Essay Topics: The List
Let's go back to the topics and give you some handy, ready-made options. Sure, you can think of ideas on your own, but we can lend a hand with these suggestions before you commit to the writing process.
- Reflecting on earning my first degree: a pivotal milestone in my life.
- The most awful dish I’ve ever tasted: my unforgettable tale.
- How a personal experience changed my attitudes and actions.
- The worst exam experience I’ve ever had: a harrowing tale.
- Encountering something eerie: a chilling moment in my life.
- Fond memories of summer vacations during my childhood.
- The story of a heroic act that saved someone's life.
- My top tunes: songs that resonate deeply with me.
- The origins and meanings of my nicknames.
- The superpower I wish I had and why.
- A lecture that profoundly changed my perspective.
- Does my school prioritize digital skills for students?
- Great summer reads for book lovers: my top suggestions.
- The music genres and melodies that reflect my tastes and emotions.
- Passions and interests that drive my aspirations.
- My ultimate guide to spending Sundays efficiently.
- Questions and curiosities about how the world works.
- Values and principles I'd risk my life for.
- How much do I follow global current events?
- Steps I’ve taken to achieve my dream job.
Want to Be Like an Expert Writer?
Order now and let our narrative essay writer turn your experiences into a captivating and unforgettable tale
Narrative Essay Examples
For inspiration on your upcoming essay, check out these excellent samples from our essay writer . Use them as a guide to help craft your own story, ensuring that your unique voice and experiences come through in your work.
If sharing your personal stories is not your cup of tea, you can buy essays online from our expert writers, who will customize the paper to your particular writing style and tone.
Final Recap
Now that you understand what makes a narrative essay tick, you're probably itching to write your own standout piece. Let our skilled research paper writing service lend you a hand! We're here to offer personalized services tailored to your needs. By providing value with flexible pricing and quick turnaround times, we'll bring your narrative to life together!
Unlock Your Potential with Our Essays!
Order now and take the first step towards achieving your academic goals
What Is A Narrative Essay?
How to start a narrative essay, how to write a good narrative essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Added new info on narrative essay
.webp)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Narrative Essay
Last Updated: April 18, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,906,642 times.
Narrative essays are commonly assigned pieces of writing at different stages through school. Like any story, they have a plot, conflict, and characters. Typically, assignments involve telling a story from your own life that connects with class themes. It can be a fun type of assignment to write, if you approach it properly. Learn how to choose a good topic, get a solid rough draft on paper, and revise your narrative essay.
Choosing a Good Topic

- Most of the time, narrative essays will involve no outside research or references. Instead, you'll be using your personal story to provide the evidence of some point that you're trying to make. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source However, in some cases using research may enhance your story because it will allow you to provide additional detail.
- Narrative essays are a common school assignment used to test your creative story-telling skills, as well as your ability to connect some element of your personal life to a topic you might be discussing in class.

- You experienced adversity and had to overcome
- You failed and had to deal with the consequences of that failure
- Your personality or character was transformed

- Bad narrative essays are generally too broad. "My senior year of high school" or "This summer" are examples of stories that would be far too big to tell in the amount of specific detail that a good narrative essay requires. Pick a single event from the summer, or a single week of your senior year, not something that takes months to unfold.
- It's also good to limit the number of characters you introduce. Only include other characters who are absolutely essential. Every single friend from your fifth grade class will be too many names to keep track of. Pick one.

- Let your imagination fill in the gaps. When you're describing your grandmother's house and a specific weekend you remember spending there, it's not important to remember exactly what was cooked for dinner on Friday night, unless that's an important part of the story. What did your grandmother typically cook? What did it usually smell like? Those are the details we need.
- Typically, narrative essays are "non-fiction," which means that you can't just make up a story. It needs to have really happened. Force yourself to stay as true as possible to the straight story.
Writing a Draft

- It helps to limit things as much as possible. While it might seem like we need to know a bunch of specific details from your senior year, try to think of a particularly tumultuous day from that year and tell us that story. Where does that story start? Not the first day of school that year. Find a better starting point.
- If you want to tell the story of your prom night, does it start when you get dressed? Maybe. Does it start when you spill spaghetti sauce all down your dress before the dance? While that might seem like the climax of a story you want to tell, it might make a better starting place. Go straight to the drama.
- You don't need to write up a formal outline for a narrative essay unless it's part of the assignment or it really helps you write. Listing the major scenes that need to be a part of the story will help you get organized and find a good place to start.

- Don't switch perspectives throughout the story. This is a difficult and advanced technique to try to pull off, and it usually has the effect of being too complicated. There should only be one "I" in the story.
- In general, narrative essays (and short stories for that matter) should also be told in past tense. So, you would write "Johnny and I walked to the store every Thursday" not "Johnny and I are walking to the store, like we do every Thursday."
- You may be instructed to write in the 3rd person (such as he, she, it, they, them, their). If so, be consistent with your pronouns throughout the story.

- Particular details are specific and only particular to the character being described. While it may be specific to say that your friend has brown hair, green eyes, is 5 feet (1.5 m) tall with an athletic build, these things don't tell us much about the character. The fact that he only wears silk dragon shirts? Now that gives us something interesting.
- Try writing up a brief sketch of each principal character in your narrative essay, along with the specific details you remember about them. Pick a few essentials.

- Who or what is the antagonist in your story? To answer this question, you also need to find out what the protagonist wants. What is the goal? What's the best case scenario for the protagonist? What stands in the protagonist's way?
- The antagonist isn't "the bad guy" of the story, necessarily, and not every story has a clear antagonist. Also keep in mind that for some good personal narratives, you might be the antagonist yourself.

- Do a freewrite about the location that your story takes place. What do you know about the place? What can you remember? What can you find out?
- If you do any research for your narrative essay, it will probably be here. Try to find out extra details about the setting of your story, or double-check your memory to make sure it's right.

- A popular creative writing phrase tells writers to "show" not to "tell." What this means is that you should give us details whenever possible, rather than telling us facts. You might tell us something like, "My dad was always sad that year," but if you wrote "Dad never spoke when he got home from work. We heard his truck, then heard as he laid his battered hardhat on the kitchen table. Then we heard him sigh deeply and take off his work clothes, which were stained with grease."

Your words should have an impact. "Good writing does not succeed or fail on the strength of its ability to persuade. It succeeds or fails on the strength of its ability to engage you, to make you think, to give you a glimpse into someone else's head."
Revising Your Essay

- Get the theme into the very beginning of the essay. Just as a researched argument essay needs to have a thesis statement somewhere in the first few paragraphs of the essay, a narrative essay needs a topic statement or a thesis statement to explain the main idea of the story.
- This isn't "ruining the surprise" of the story, this is foreshadowing the important themes and details to notice over the course of the story as you tell it. A good writer doesn't need suspense in a narrative essay. The ending should seem inevitable.

- Scene: "On our walk to the store, Jared and I stopped at the empty grass lot to talk. 'What's your problem lately?' he asked, his eyes welling with tears. I didn't know what to tell him. I fidgeted, kicked an empty paint bucket that was rusted over at the edge of the lot. 'Remember when we used to play baseball here?' I asked him."
- Analysis: "We finished walking to the store and bought all the stuff for the big holiday dinner. We got a turkey, cornbread, cranberries. The works. The store was crazy-packed with happy holiday shoppers, but we walked through them all, not saying a word to each other. It took forever to lug it all home."

- Anything spoken by a character out loud needs to be included in quotation marks and attributed to the character speaking it: "I've never been to Paris," said James.
- Each time a new character speaks, you need to make a new paragraph . If the same character speaks, multiple instances of dialog can exist in the same paragraph.

- Revise for clarity first. Are your main points clear? If not, make them clear by including more details or narration in the writing. Hammer home your points.
- Was the decision you made about the starting place of the story correct? Or, now that you've written, might it be better to start the story later? Ask the tough questions.
- Proofreading is one part of revision, but it's a very minor part and it should be done last. Checking punctuation and spelling is the last thing you should be worried about in your narrative essay.
Sample Essay

Expert Q&A

- Be sensible while writing. It is necessary to stay on the topic rather than moving away from it. Do not lose your focus. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Divide your essay into paragraphs, according to your limit: an introduction, two body paragraph and one conclusion. Your introduction can be either a shocker one, or one just describing the setting; the conclusion can reveal a surprise, or end with just a hint of the climax, keeping the final question to be answered by the readers. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Write only when you have a perfect story to tell. When a reader finishes reading the story, he\she should feel all those emotions seep right through his\her rib cage. Only then as a narrator, have you succeeded. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/narrative-essay-examples.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/narrative_essays.html
- ↑ https://www.nytimes.com/2016/10/20/learning/lesson-plans/650-prompts-for-narrative-and-personal-writing.html
- ↑ https://miamioh.edu/hcwe/handouts/narrative-essays/index.html
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-narrative-essay
- ↑ https://crk.umn.edu/units/writing-center/how-revise-drafts
About This Article

To write a narrative essay, start by choosing an interesting personal story from your life to write about. Try to connect your story to a broader theme or topic so your essay has more substance. Then, write out your story in the past tense using the first person point of view. As you write your story, use vivid details to describe the setting and characters so readers are able to visualize what you're writing. Once you've written your essay, read it several times and make sure you've illustrated your theme or topic. To learn more from our Professor of English co-author, like how to write scenes and analyses, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Michelle Foss
Aug 10, 2018
Did this article help you?

Oct 10, 2017
Maria Belen
Dec 15, 2016
Amit Chauhan
Aug 17, 2017
Hlela Maqoqa
Oct 27, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.

- Scriptwriting
How to Write a Narrative Essay — A Step-by-Step Guide
N arrative essays are important papers most students have to write. But how does one write a narrative essay? Fear not, we’re going to show you how to write a narrative essay by breaking down a variety of narrative writing strategies. By the end, you’ll know why narrative essays are so important – and how to write your own.
How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step
Background on narrative essays.
Narrative essays are important assignments in many writing classes – but what is a narrative essay? A narrative essay is a prose-written story that’s focused on the commentary of a central theme .
Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV , and are usually about a topic that’s personal to the writer.
Everything in a narrative essay should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
In simplest terms, a narrative essay is a personal story. A narrative essay can be written in response to a prompt or as an independent exercise.
We’re going to get to tips and tricks on how to write a narrative essay in a bit, but first let’s check out a video on “story.”
How to Start a Narrative Essay • What is a Story? by Mr. Kresphus
In some regards, any story can be regarded as a personal story, but for the sake of this article, we’re going to focus on prose-written stories told in the first-person POV.

How to Start a Narrative Essay
Responding to prompts.
Many people wonder about how to start a narrative essay. Well, if you’re writing a narrative essay in response to a prompt, then chances are the person issuing the prompt is looking for a specific answer.
For example: if the prompt states “recount a time you encountered a challenge,” then chances are the person issuing the prompt wants to hear about how you overcame a challenge or learned from it.
That isn’t to say you have to respond to the prompt in one way; “overcoming” or “learning” from a challenge can be constituted in a variety of ways.
For example, you could structure your essay around overcoming a physical challenge, like an injury or disability. Or you could structure your essay around learning from failure, such as losing at a sport or performing poorly on an important exam.
Whatever it is, you must show that the challenge forced you to grow.
Maturation is an important process – and an essential aspect of narrative essays... of course, there are exceptions to the rule; lack of maturation is a prescient theme in narrative essays too; although that’s mostly reserved for experienced essay writers.
So, let’s take a look at how you might respond to a series of narrative essay prompts:
How successful are you?
This prompt begs the writer to impart humility without throwing a pity party. I would respond to this prompt by demonstrating pride in what I do while offering modesty. For example: “I have achieved success in what I set out to do – but I still have a long way to go to achieve my long-term goals.”
Who is your role model?
“My role model is [Blank] because ” is how you should start this narrative essay. The “because” is the crux of your essay. For example, I’d say “Bill Russell is my role model because he demonstrated graceful resolve in the face of bigotry and discrimination.
Do you consider yourself spiritual?
For this prompt, you should explain how you came to the conclusion of whether or not you consider yourself a spiritual person. Of course, prompt-givers will differ on how much they want you to freely express. For example: if the prompt-giver is an employee at an evangelizing organization, then they probably want to see that you’re willing to propagate the church’s agenda. Alternatively, if the prompt-giver is non-denominational, they probably want to see that you’re accepting of people from various spiritual backgrounds.
How to Write Narrative Essay
What makes a good narrative essay.
You don’t have to respond to a prompt to write a narrative essay. So, how do you write a narrative essay without a prompt? Well, that’s the thing… you can write a narrative essay about anything!
That’s a bit of a blessing and a curse though – on one hand it’s liberating to choose any topic you want; on the other, it’s difficult to narrow down a good story from an infinite breadth of possibilities.
In this next video, the team at Essay Pro explores why passion is the number one motivator for effective narrative essays.
How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step • Real Essay Examples by Essay Pro
So, before you write anything, ask yourself: “what am I passionate about?” Movies? Sports? Books? Games? Baking? Volunteering? Whatever it is, make sure that it’s something that demonstrates your individual growth . It doesn’t have to be anything major; take a video game for example: you could write a narrative essay about searching for a rare weapon with friends.
Success or failure, you’ll be able to demonstrate growth.
Here’s something to consider: writing a narrative essay around intertextuality. What is intertextuality ? Intertextuality is the relationship between texts, i.e., books, movies, plays, songs, games, etc. In other words, it’s anytime one text is referenced in another text.
For example, you could write a narrative essay about your favorite movie! Just make sure that it ultimately reflects back on yourself.
Narrative Writing Format
Structure of a narrative essay.
Narrative essays differ in length and structure – but there are some universal basics. The first paragraph of a narrative essay should always introduce the central theme. For example, if the narrative essay is about “a fond childhood memory,” then the first paragraph should briefly comment on the nature of the fond childhood memory.
In general, a narrative essay should have an introductory paragraph with a topic sentence (reiterating the prompt or basic idea), a brief commentary on the central theme, and a set-up for the body paragraphs.
The body paragraphs should make up the vast majority of the narrative essay. In the body paragraphs, the writer should essentially “build the story’s case.” What do I mean by “build the story’s case?”
Well, I mean that the writer should display the story’s merit; what it means, why it matters, and how it proves (or refutes) personal growth.
The narrative essay should always conclude with a dedicated paragraph. In the “conclusion paragraph,” the writer should reflect on the story.
Pro tip: conclusion paragraphs usually work best when the writer stays within the diegesis.
What is a Video Essay?
A video essay is a natural extension of a narrative essay; differentiated only by purpose and medium. In our next article, we’ll explain what a video essay is, and why it’s so important to media criticism. By the end, you’ll know where to look for video essay inspiration.
Up Next: The Art of Video Analysis →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- Ethos, Pathos & Logos — Definition and Examples of Persuasive Advertising Techniques
- Ultimate AV Script Template to Write Better Ads [FREE AV Script Template]
- What is Dramatic Irony? Definition and Examples
- What is Situational Irony? Definition and Examples
- How to Write a Buzzworthy Explainer Video Script [Free Template]
- 2 Pinterest
- Literary Terms
Narrative Essay
I. what is a narrative essay.
By definition, a narrative is a series of connected events – in other words, a story. An essay is a piece of writing that focuses on a specific topic. So, a narrative essay is a piece of writing that focuses on a particular story. In practice, a narrative essay is a story about a personal experience.
These essays examine how certain events affect a person’s emotions, beliefs, and outlook on life. The writer narrates an event that they lived through, and describes the experience from their personal point of view.
A narrative essay is a useful tool that invites readers into a story and shows how an event has affected a person.
II. Examples of Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can focus on any event in a person’s life. A strong narrative essay will be about an important event, one that had a significant impact on the author’s life. Some examples of the kinds of topics that a narrative essay might explore are the experiences of:
- Moving to a new place, school, or job
- Events that lead to a new understanding about life
- Overcoming challenging obstacles
- Time spent during a favorite activity
- Being involved in a large movement, such as a charity event or political protest
In fact, some narrative essays have become famous for their influence on their readers.
Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , by Frederick Douglass, is an essay that told of the author’s life in slavery. The essay tells how he overcame the challenging obstacle of escaping from slavery and starting life over as a free man. Abolitionists (anti-slavery activists) used Fredrick Douglas’s narrative essay to educate Americans about why they must end slavery.
Walden , by Henry David Thoreau, is a narrative essay about the author’s experience living in a cabin by Walden Pond for two years. He wrote about events he had while he was alone in nature, and he explained how these events led him to a new understanding about life, people, and society . The essay quickly became popular among people who were curious about reconnecting with nature.
III. Types of Narrative Essays with Topics
A memoir is an essay in which a person writes about a period in their life. The events typically cover years – even decades. A person might write a memoir in order to share an experience like the topic examples below.
- raising and training a puppy
- explaining the history of a company
- experience of learning to play a sport
b. Reflection
A reflection is a short narrative that focuses on a single event. A writer may choose to reflect on a book they just finished, their visit to a zoo, or their high school graduation. The reflection should focus on the writer’s reactions to the event, and may include a self-evaluation. Reflections can also be as informal or formal, like the topic examples below.
Sample Topics
- a journal entry of your school day
- a college entrance essay that describes an accomplishment
- a self-evaluation after playing a sport for a season
c. Personal Experience as a Participant
A narrative essay of this type is written by a person who was personally involved in an event and wants to share their experience. There is more information included in this narrative essay than in a reflection. It is also more focused on details describing the event, and less on the writer’s self-evaluation. Below are some examples for topics.
- living through a natural disaster
- participating in a school play
- new experiences on a family vacation
d. Personal Experience as an Observer
This kind of narrative essay includes journalism and reporting. It is the least personal of these types, and may not be written in first-person point-of-view (‘I’ or ‘we’). Take a look at the sample topics.
- war correspondents giving an update
- sports writers commenting on a game
- historians describing a past event
IV. Parts of Narrative Essays
A. personal point-of-view.
A strong narrative essay lets the reader know who the author is as a person. It reveals the author’s opinions, hopes, and beliefs. The reader should be able to gain insights into the author’s personality in a way that is similar to a reader getting to know a character in a work of fiction.
b. A clearly connected series of events
Without events, there is no narrative. A narrative essay is organized around a number of events. These events are linked through cause-and-effect or action- consequence.
c. Descriptive detail
A narrative essay is a personal experience, and should give the reader a feeling of being ‘there’ as the events unfold. The author will use multi-sensory descriptions (such as sights, sounds, and smells) and pay attention to details in order to ‘show’ the story to the reader.
d. Growth or change as a result of a climactic event
Readers of a narrative essay should be able to identify the most significant event in the story. This event is the climax of the narrative. The climax should lead the narrator (and the reader) to an insight or realization that causes a major change for him or her.
V. How to write a Narrative Essay
A. outline the events of the narrative.
Decide which part of the narrative is the climax, and which part contains an insight or lesson. These parts will be the focus of your essay. Organize the other events in the narrative to support this focus.
In Frederick Douglas’ essay, the climax might be the event in which he finally escapes to the north. Meanwhile, learning how to read and the new knowledge that he gains from reading would be on the outline as important events in the narrative.
b. Describe each event with precise sensory description
Focus on details that relate to your personal experiences. For instance, if the place is very important in the narrative, include details about the setting (place and time). If people play a big role in your narrative essay, take the time to describe how they look and what personality traits they have.
In his essay, Douglass uses details to describe the plantations, their locations, and several events that he witnessed as a child slave. His descriptions almost help readers imagine or picture the places and events in their minds.
c. Describe your role in each of the events
Explain how you felt and what you wanted. Describe how the events affected you emotionally.
In his essay, Douglass also describes how some of the cruel events that he witnessed scared him, as well as the happiness he felt when he was moved to live with and met the Aulds. This also helps the audience understand Douglass as a slave.
d. Identify the significance
Identify the significance of these events on your beliefs, feelings, or world view from where you stand today.
For Douglass, learning how to read was one of the most significant events in his life; it allowed him to learn and understand the injustices of slavery, which lead him to escape and become a leader in the abolitionist movement.
e. The events in the narrative should connect clearly
When you revise, be sure that the events in the narrative connect clearly and have smooth transitions between them
Your conclusion should help the reader understand the importance of your narrative essay.
Douglass concludes his essay by sharing his experience after the escape, like finding a job, and most importantly, speaking at an anti-slavery meeting. This shows the importance of how his experiences lead him to become a speaker for the abolitionist cause.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
What Is a Narrative Essay? Definition & 20+ Examples
Ever wondered how life’s vibrant, personal experiences could transform into compelling stories? Welcome to the world of narrative essays, where the art of storytelling meets the essence of self-expression.
This vibrant genre paints vivid pictures, provoking emotions and connecting readers to experiences, perhaps similar to their own or completely novel. Embark on this literary journey with us as we delve into the heart of narrative essays, unearthing the magic of narrating tales spun from threads of personal experiences, historical events, and more.
Prepare to immerse yourself in the fascinating universe where life and literature intertwine.
Table of Contents
Defining Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is a genre of writing that tells a story, often from the writer’s personal perspective. In this type of essay, the author provides a series of events, characters, and settings, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the experience. Although typically written in the first person, narrative essays can be written in the third person as well.
The purpose of a narrative essay is not only to entertain but also to convey a meaningful message or lesson. These essays can be drawn from real-life experiences or fictional scenarios, but they should be engaging and create an emotional connection with the reader. Narrative essays are often used to explore personal growth, relationships, and various worldviews and experiences.
In a narrative essay, it is essential to use vivid, descriptive language and a clear structure to help the reader follow the narrative. While engaging the reader’s emotions, the essay must maintain a consistent point of view and avoid unnecessary complexity or ambiguity.
History of Narrative Essay
The narrative essay has its roots in oral storytelling traditions dating back to ancient civilizations. The art of telling stories has been present across cultures and continents as a means to communicate, preserve history, and entertain. Early examples of narratives were usually passed down through generations of storytellers, which led narratives to transform and adapt over time.
In the Middle Ages , the invention of the printing press allowed for written narratives to become more widely accessible, leading to the rise of written narrative essays. Literature, like Chaucer’s “Canterbury Tales” and Boccaccio’s “Decameron,” showcased the importance of storytelling as a medium to understand and reflect on human experiences.
During the Romantic period in the 18th and 19th centuries , the narrative essay took on new life as authors like Samuel Taylor Coleridge and Edgar Allan Poe explored the genre’s creative and intellectual potential. They used narrative essays to express their individual perspectives and encouraged readers to think beyond conventions and social norms.
During the 20th century , the narrative essay became even more prevalent, with the rise of digital technology and the internet making it easier for writers to share their stories via blogs , social media , and online literary publications .
Today , the narrative essay has evolved into a versatile genre that continues to remain a popular form of expression in literature and the digital age.
Although the format of narrative essays has changed over the years, their central purpose — to share personal experiences , entertain readers , and reflect on the human condition — has remained consistent, contributing to the genre’s enduring appeal.
Functions of Narrative Essay
Storytelling.
Narrative essays serve as an effective platform for storytelling. Through these essays, writers impart exciting and entertaining tales to their readers as they incorporate essential elements such as plot , setting , and character .
One primary function of a narrative essay is to engage the audience by keeping them hooked. With its descriptive and vivid language style, it captures the reader’s imagination and evokes curiosity.
Narrative essays also play a role in imparting valuable knowledge and life lessons. They can portray real-life events and experiences that provide readers with a deeper understanding of the world.
These essays offer a medium for reflecting on personal experiences, growth, and emotional journeys, allowing both the writer and the reader to gain valuable insights from past events and decisions.
Though narrative essays primarily tell stories, they can also serve as a tool for persuasion. By presenting a narrative from a specific perspective, writers can subtly influence the reader’s opinions and beliefs on a particular topic.
Through sharing personal stories and experiences, narrative essays help build a connection between the writer and the reader. They create a sense of empathy and relatability, bridging the gap between different backgrounds and perspectives.
Exploration of Themes
Narrative essays allow for an in-depth exploration of themes ranging from morality to the complexities of human relationships. Writers can weave these themes into their stories to provoke thought and discussion.
Character Development
Character development is an essential aspect of narrative essays. By showcasing the growth and transformation of a character, the essay becomes more engaging and dynamic while also revealing insights into human behavior and psychology.
Characteristics of Narrative Essay
Narrative essay tells a story.
A narrative essay presents a story with a clear beginning , middle , and end . The writer’s goal is to engage the reader with vivid descriptions and captivating events, drawing them into the story and encouraging them to experience the emotions and events alongside the characters.
First-Person Perspective
Often written in first-person perspective, narrative essays allow the writer to share their experiences and thoughts with the reader. This point of view connects the reader with the protagonist, creating a more personal and intimate experience.
Characters and Dialogue
Well-developed characters and believable dialogue contribute to the overall authenticity of a narrative essay. The writer achieves this by creating dynamic characters with distinct voices and personalities, with the dialogue often propelling the story forward.
Descriptive Language
Using descriptive language helps paint a picture in the reader’s mind, immersing them in the story’s setting and atmosphere. Adjectives, sensory details, and imagery are essential tools in crafting a vivid narrative.
Plot and Structure
A narrative essay must have a clear, well-structured plot with a beginning, middle, and end. The writer unfolds the story in a way that builds tension and excitement, driving the reader to anticipate the resolution.
Chronological Order
Events in a narrative essay usually unfold in chronological order, following the natural progression of time. This allows the reader to follow the story easily and maintain their engagement.
Theme or Message
Narrative essays often explore themes or convey a message to the reader. The writer subtly weaves this message throughout the story, allowing the reader to understand and appreciate the underlying meaning gradually.
Conflict and Resolution
Conflict drives the story forward, creating excitement and tension that keeps the reader engaged. The narrative essay should present a central conflict that the characters encounter and, ultimately, resolve.
Narrative essays frequently include reflective moments, during which the writer pauses to consider the significance of the events, characters, or conflicts they are describing. These moments help the reader gain a deeper understanding of the writer’s thoughts and the message they are conveying.
Importance of Narrative Essay
Narrative essay enables individuals to articulate their emotions.
Narrative essays enable writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and experiences. They provide an opportunity for individuals to articulate their emotions and insights through storytelling. This promotes a sense of self-awareness, helping individuals better comprehend their own actions and beliefs.
Narrative Essay Engages Readers
Narrative essays engage readers by presenting stories in artistic and imaginative ways. They captivate the audience through vivid descriptions, colorful language, and emotionally resonant themes. This creates an immersive experience, allowing readers to not only learn from the writer’s experiences but also feel emotionally connected to them.
Narrative Essay Enhances One’s Communication Skills
Writing narrative essays enhances one’s communication skills. It requires clear and concise language, as well as the ability to convey ideas in an organized and coherent manner. This practice hones one’s writing ability and overall communication skills.
Narrative Essay Promotes Empathy
A well-written narrative essay promotes empathy by allowing readers to experience events from different perspectives. It encourages understanding and appreciation for the distinct viewpoints of other individuals, fostering respect and appreciation for diversity.
Narrative Essay Challenges a Writer’s Critical Thinking
Developing a narrative essay challenges a writer’s critical thinking ability to evaluate experiences and draw meaningful conclusions. This process of reflection provides an opportunity for personal growth and learning, ultimately cultivating a well-rounded individual.
Narrative Essays Convey Themes or Messages
Narrative essays often relay themes and messages that reflect the writer’s beliefs or values. By sharing these themes, writers provide insights that readers may relate to and learn from, leading to personal growth and understanding.
Narrative Essay Builds Empathy
Sharing personal stories through narrative essays can help build empathy among readers. By connecting with the experiences and emotions presented, readers have the opportunity to develop a deeper understanding of others and foster compassion in their own lives.
Narrative Essay Encourages Individuals to Explore
Narrative essays entice readers with engaging stories that are interesting and emotionally impactful. This motivation to read can foster an appreciation for literature, encouraging individuals to further explore and engage with written works.
Elements of Narrative Essay
In a narrative essay, the plot is the sequence of events that make up the story. It typically follows a chronological order and includes an exposition , rising action , climax , falling action , and resolution . Each event should contribute to the overall theme and message of the essay.
Characters are the people, animals, or other beings that participate in the story. They have individual personalities, motivations, and conflicts. The main character, or protagonist , is the central figure in a narrative essay, and readers often empathize with them as they undergo various experiences.
The setting is the time and place in which the story occurs. It can be a specific location or a more general environment. The setting contributes to the overall atmosphere and mood of the narrative essay, and it can influence how characters interact with one another.
Point of View
Point of view refers to the perspective from which the story is told. In a third-person narrative essay, the author uses “he,” “she,” “it,” or “they” to tell the story. This allows the writer to provide a more objective view, showing events and character actions without the bias of a first-person narrator.
Conflict is the struggle between opposing forces that drives the plot forward. It can be internal, within a character’s own mind or emotions, or external, between characters or against an outside force. Conflict creates tension and keeps the reader engaged in the story.
Theme refers to the underlying message or central idea that the writer wants to convey through their narrative essay. It can be a commentary on society, human nature, or other universal concepts. A strong theme helps to tie the essay together and contributes to its overall impact on the reader.
Dialogue is the conversation between characters in a narrative essay. It helps to establish character relationships, reveal information, and move the plot forward. Effective dialogue should sound natural and reflect the speaker’s personality and voice.
Narrative Structure
The narrative structure is the organization and arrangement of events in the essay. It includes elements like flashbacks , foreshadowing , and parallel plotlines to create a cohesive and engaging reading experience.
Description
The description is the use of sensory details and vivid language to help the reader visualize the story. It can include the appearance of characters, settings, and objects, as well as sounds, smells, and other sensory details. Effective description enhances the reader’s immersion in the story and supports the emotional impact.
Reflective Aspect
The reflective aspect of a narrative essay refers to the author’s insights and personal growth as a result of the events in the story. It is an opportunity for the author to analyze and reflect on the experiences and emotions they have conveyed, providing a deeper level of understanding for the reader.
Structure of Narrative Essays
Introduction.
Narrative essays generally begin with an introduction that presents the background and sets the stage for the story. This section introduces the main characters, their relationships, and the setting or context in which the story takes place.
The introduction also establishes the purpose or main idea of the essay, grabbing the reader’s attention and sparking their interest in the unfolding events.
Rising Action
The rising action includes a series of events or experiences that create tension and suspense, gradually building toward the pivotal point of the story. In this section, the writer conveys the various challenges and obstacles faced by the main characters while developing the plot and providing insights into their personalities and motivations.
The rising action helps the reader become emotionally invested in the characters and their journey.
The climax is the turning point or the most intense moment in the story, where the central conflict reaches its peak. It is at this stage that the main characters confront the challenges or adversities they have been facing, often resulting in dramatic, emotional, or transformative consequences.
The climax is a crucial moment in the narrative essay, as it determines the outcome of the story and the eventual fate of the characters.
Falling Action
Following the climax, the story enters its falling action phase . In this section, the events and repercussions of the climax begin to unfold, and tensions start to subside. The writer gradually moves towards a resolution of the main conflict while also tying up loose ends and potentially introducing ancillary outcomes that result from the central events.
Conclusion or Resolution
The conclusion or resolution offers a sense of closure or finality by addressing the outcome of the story. It may present the characters reflecting on their experiences, lessons learned, or the consequences of their actions. Ideally, the resolution leaves the reader with a feeling of satisfaction, having followed the characters on their journey and reached an appropriate conclusion.
A narrative essay may also include a reflection section, where the writer discusses the significance of the story or its broader implications. This section allows the writer to share their personal insights, thoughts, or feelings about the events in the narrative and may offer a deeper perspective on the themes or messages explored in the essay.
The reflection, when included, can help to elevate the narrative by adding depth and context to the overall story.
Popular Narrative Essay Topics
Personal experiences.
Narrative essays often focus on personal experiences as they allow the writer to share a unique story with their readers. These topics could include a memorable childhood event, a life lesson learned, or overcoming a significant obstacle.
Travel Experiences
Travel experiences are also popular in narrative essays, as they provide rich and vivid details for the reader to imagine. The writer can recount a fantastic trip, a cultural exchange experience, or even a challenging adventure, capturing the essence of the journey.
Achievements and Failures
Writing about achievements and failures enables the writer to reflect on their personal growth and share the lessons they’ve learned. Topics can range from winning a competition, conquering a fear, or overcoming failure to succeed in the end.
Relationships and Interactions
Narrative essays on relationships and interactions capture the emotions, lessons, and insights gained from interacting with others. The writer could tell a story of forming an unlikely friendship, navigating a challenging relationship, or learning from a mentor.
Historical or Current Events
Addressing historical or current events in narrative essays allows writers to share their perspectives and analyses. Stories could focus on significant moments in history, political events, or social movements, detailing how they’ve impacted the writer and their understanding of the world.
School and Work Experiences
School and work experiences can serve as compelling sources of inspiration for narrative essays. Writers can recount stories of innovative projects, first-time experiences, or memorable teachers and coworkers, sharing valuable insights and reflections.
Techniques Used in Narrative Essay Writing
When writing a narrative essay, authors should use various techniques to create an engaging and well-written piece. These techniques will help to capture the reader’s attention, establish a connection with the audience, and effectively convey the story.
Showing Rather than Telling
One critical technique used in narrative essay writing is showing rather than telling. It involves the use of vivid imagery and descriptions to draw the reader into the story. This allows the reader to create mental images of the events and experiences described in the essay.
For example, instead of merely stating that a character was sad, a writer could describe their frowning face or a tear rolling down their cheek.
Including conversations between characters helps to bring the story to life and provides insight into the thoughts and feelings of those involved. When writing dialogue, it’s essential to maintain a consistent tone and voice and pay attention to punctuation to ensure clarity for the reader.
The use of chronological order is also important when composing a narrative essay. Presenting events in the order they occurred is the most straightforward approach and helps the reader follow along effortlessly. While some writers may choose to mix up the sequence for a more dramatic effect, it is crucial to ensure that the narrative remains clear and easy to understand.
Character development plays a significant role in creating a compelling narrative essay. The thoughts, emotions, and experiences of the characters should evolve throughout the story. A well-developed character with realistic reactions and growth helps engage the reader and creates a deeper connection to the narrative.
Strong Narrative Voice
Employing a strong narrative voice is crucial to a successful narrative essay. The narrative voice can be the author’s own or a fictional character, but it should be consistent and engaging. The voice should provide a unique perspective on the events taking place and help guide the reader through the story.
Types of Narrative Essay
Personal narrative essay.
A personal narrative essay is written from the author’s perspective and shares a personal story or experience. This type of essay often involves reflection on the significance of the event, as well as how it has shaped the author’s life.
Biographical Narrative Essay
A biographical narrative essay focuses on telling the life story of an individual other than the author. It may cover key events or experiences from the person’s life and often requires research to gather accurate information about the subject.
Literacy Narrative Essay
A literacy narrative essay explores an individual’s experiences with reading , writing , or language . It can discuss how these experiences have shaped the individual’s understanding and use of language, as well as any challenges they have faced in their literacy journey.
Historical Narrative Essay
A historical narrative essay tells the story of a significant event, era, or person within a historical context. This type of essay requires the author to research and gather accurate historical information while weaving it into a well-structured narrative.
Reflective Narrative Essay
A reflective narrative essay involves the author discussing an experience or event in their life and examining its impact on their personal growth and development. The focus is on how the event has shaped the individual’s values, beliefs, or understanding of the world.
Descriptive Narrative Essay
A descriptive narrative essay aims to paint a vivid picture of a person, place, or situation through detailed observations and sensory language. It can evoke emotions and immerse the reader in the setting, creating an engaging narrative experience.
Examples of Narrative Essay in Literature
Short story, examples of narrative essay in pop culture, creative writing, how to write a narrative essay.
A narrative essay is a type of essay that tells a story or recounts an event, often through the author’s personal experiences. Writing a narrative essay can be an enlightening and engaging experience for both the writer and the reader.
Impacts of Narrative Essay on Literature
Narrative essays play a significant role in literature, as they provide authors with a platform to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a compelling manner. They enable readers to connect with the story, allowing them to empathize with the author or the characters.
Understanding of Human Experience
Narrative essays offer an opportunity for writers to share their own life experiences, making them relatable and captivating to readers. This form of writing encourages a deeper understanding of human emotions, challenges, and growth.
Exploration of Themes and Issues
Through narrative essays, authors can delve into various themes and issues, such as love, loss, friendship, conflict, and societal norms. This allows readers to see multiple perspectives, fostering critical thinking and empathy.
Development of Narrative Skills
Aspiring writers can hone their narrative skills by writing narrative essays, learning to organize their thoughts, developing interesting plotlines, and creating captivating characters. This process helps writers improve their storytelling techniques, making their work more engaging.
Reflection and Learning
Writing narrative essays encourages self-reflection and introspection, allowing authors to analyze their own experiences and learn from them. It serves as a therapeutic outlet and a learning tool for personal growth and development.
Versatility
Narrative essays are versatile forms of writing that can be adapted to various genres and styles, such as fiction , nonfiction , and even poetry . This flexibility allows writers to experiment with different forms and voices, expanding their creative horizons.
Influence on Other Literary Forms
The narrative essay format has had a profound impact on other literary forms, such as novels , short stories , and memoirs . The storytelling techniques developed through writing narrative essays contribute to the richness and depth of these other literary works.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common mistakes to avoid in a narrative essay.
Common mistakes to avoid when writing a narrative essay include a lack of focus, insufficient development of the story, and an unclear message. To avoid these pitfalls, ensure that the story has a clear central theme, develop the narrative with ample details, and convey a discernible message or lesson.
What is the difference between a narrative essay and a short story?
While both a narrative essay and a short story tell a tale, the main difference lies in their purpose. A narrative essay aims to share a personal experience and often a lesson learned from it, while a short story primarily aims to entertain. Narrative essays are usually written in the first person, while short stories can be written from any point of view.
Can a narrative essay be fictional?
Yes, while many narrative essays are based on personal experiences, they can also be entirely fictional. The key is to tell a compelling story that conveys a clear theme or message, whether it’s based on real events or is a product of the author’s imagination.
Narrative essays offer a compelling medium to share your unique stories, experiences, and perspectives. By weaving together the threads of plot, character, setting, and conflict, you can create an engaging narrative that captivates your readers, immerses them in your world, and leaves them with a lasting impression.
Remember, each narrative essay is not just about recounting a tale; it’s an opportunity to express personal growth, share lessons learned, and convey themes that resonate. So, the next time you have a story to tell, consider a narrative essay, where life’s experiences transform into a literary tapestry of meaning and connection. Happy writing!
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Aerielle Ezra
Narrative Essay
A narration is simply the telling of a story. Whenever someone recounts an event or tells a story, he or she is using narration. A narration essay recounts an event or tells a story to illustrate an idea. A narration essay may be entertaining or informative.
Five Basic Steps to Writing a Narrative Essay
- Purpose: Why are you telling the story? Every narration must have a point or purpose, usually to entertain or to inform.
- Context: You should establish the context of your narrative early in the essay. You can follow these basic guidelines: who, what, where, when.
- Point of View: A narrative essay may be written in the first-person (I) or third-person (he, she, it) point of view; do not use second person (you). If you were part of the action, the first-person provides the best perspective. If you are relating an event based upon other sources, use the third-person point of view. In some circumstances, you may be forced to choose the point of view (if, for example, you were a witness, but not a participant). Once you have decided upon a point of view, stay consistent with it.
- Details: Include enough details for clarity; however, select only the facts that are relevant.
- Organization: A narrative usually follows a chronological time line; however, you may find flashbacks a creative option as long as the narrative can be clearly followed by the reader. Most narratives are told in the past tense. You should keep tenses consistent.
Thesis Statements for Narrative Essays
To create a thesis statement, combine the claim and the supporting details in one sentence. The direction of your essay can change depending on the pattern in which you organize the supporting details.
|
| |
Once you have drafted a narrative, it’s always a good idea to ask someone else to read it. And, of course, you yourself will want to review what you have written from the standpoint of a critical reader.
Questions to Keep in Mind When Checking a Narrative
PURPOSE AND AUDIENCE. Does the narrative serve the purpose it is intended to serve? Is it appropriate for its intended audience? Does it need any additional background information or definitions?
THE STORY. Does it consist mainly of actions and events? Do they constitute a plot, with a clear beginning, middle, and end? Is every action in the narrative necessary to the plot? Have any essential actions been left out?
THE POINT. Does the narrative have a clear point to make? What is it? Is it stated explicitly in a thesis? If not, should it be?
ORGANIZATION. Is the storyline easy to follow? Are the events in chronological order? Are there any unintentional lapses in chronology or verb tense? Are intentional deviations from chronology, such as flashbacks, clearly indicated?
TRANSITIONS. Are there clear transitions to help readers follow the sequence of events? Have you checked over each transition to see that it logically connects the adjoining parts of the narrative?
DIALOGUE AND POINT OF VIEW. If there is no dialogue in the narrative, would some direct speech help bring it to life? If there is dialogue, does it sound like real people talking? Is the narrative told from a consistent, plausible point of view?
DETAILS. Does the narrative include lots of concrete details, especially sensory details (visual, olfactory, tactile, and auditory)? Does it show as well as tell? Can your reader imagine themselves there?
THE BEGINNING. Will the beginning of the narrative get the reader’s attention? How? How well does it set up what follows? How else might the narrative begin?
THE ENDING. How satisfying is it? What does it leave the reader thinking or feeling? How else might the narrative end?
Michael| 2018
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.1 Narration
Learning objectives.
- Determine the purpose and structure of narrative writing.
- Understand how to write a narrative essay.
Rhetorical modes simply mean the ways in which we can effectively communicate through language. This chapter covers nine common rhetorical modes. As you read about these nine modes, keep in mind that the rhetorical mode a writer chooses depends on his or her purpose for writing. Sometimes writers incorporate a variety of modes in any one essay. In covering the nine modes, this chapter also emphasizes the rhetorical modes as a set of tools that will allow you greater flexibility and effectiveness in communicating with your audience and expressing your ideas.
The Purpose of Narrative Writing
Narration means the art of storytelling, and the purpose of narrative writing is to tell stories. Any time you tell a story to a friend or family member about an event or incident in your day, you engage in a form of narration. In addition, a narrative can be factual or fictional. A factual story is one that is based on, and tries to be faithful to, actual events as they unfolded in real life. A fictional story is a made-up, or imagined, story; the writer of a fictional story can create characters and events as he or she sees fit.
The big distinction between factual and fictional narratives is based on a writer’s purpose. The writers of factual stories try to recount events as they actually happened, but writers of fictional stories can depart from real people and events because the writers’ intents are not to retell a real-life event. Biographies and memoirs are examples of factual stories, whereas novels and short stories are examples of fictional stories.
Because the line between fact and fiction can often blur, it is helpful to understand what your purpose is from the beginning. Is it important that you recount history, either your own or someone else’s? Or does your interest lie in reshaping the world in your own image—either how you would like to see it or how you imagine it could be? Your answers will go a long way in shaping the stories you tell.
Ultimately, whether the story is fact or fiction, narrative writing tries to relay a series of events in an emotionally engaging way. You want your audience to be moved by your story, which could mean through laughter, sympathy, fear, anger, and so on. The more clearly you tell your story, the more emotionally engaged your audience is likely to be.
On a separate sheet of paper, start brainstorming ideas for a narrative. First, decide whether you want to write a factual or fictional story. Then, freewrite for five minutes. Be sure to use all five minutes, and keep writing the entire time. Do not stop and think about what to write.
The following are some topics to consider as you get going:
The Structure of a Narrative Essay
Major narrative events are most often conveyed in chronological order , the order in which events unfold from first to last. Stories typically have a beginning, a middle, and an end, and these events are typically organized by time. Certain transitional words and phrases aid in keeping the reader oriented in the sequencing of a story. Some of these phrases are listed in Table 10.1 “Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time” . For more information about chronological order, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” and Chapter 9 “Writing Essays: From Start to Finish” .
Table 10.1 Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time
| after/afterward | as soon as | at last | before |
| currently | during | eventually | meanwhile |
| next | now | since | soon |
| finally | later | still | then |
| until | when/whenever | while | first, second, third |
The following are the other basic components of a narrative:
- Plot . The events as they unfold in sequence.
- Characters . The people who inhabit the story and move it forward. Typically, there are minor characters and main characters. The minor characters generally play supporting roles to the main character, or the protagonist .
- Conflict . The primary problem or obstacle that unfolds in the plot that the protagonist must solve or overcome by the end of the narrative. The way in which the protagonist resolves the conflict of the plot results in the theme of the narrative.
- Theme . The ultimate message the narrative is trying to express; it can be either explicit or implicit.
Writing at Work
When interviewing candidates for jobs, employers often ask about conflicts or problems a potential employee has had to overcome. They are asking for a compelling personal narrative. To prepare for this question in a job interview, write out a scenario using the narrative mode structure. This will allow you to troubleshoot rough spots, as well as better understand your own personal history. Both processes will make your story better and your self-presentation better, too.
Take your freewriting exercise from the last section and start crafting it chronologically into a rough plot summary. To read more about a summary, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” . Be sure to use the time transition words and phrases listed in Table 10.1 “Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time” to sequence the events.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your rough plot summary.
Writing a Narrative Essay
When writing a narrative essay, start by asking yourself if you want to write a factual or fictional story. Then freewrite about topics that are of general interest to you. For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Once you have a general idea of what you will be writing about, you should sketch out the major events of the story that will compose your plot. Typically, these events will be revealed chronologically and climax at a central conflict that must be resolved by the end of the story. The use of strong details is crucial as you describe the events and characters in your narrative. You want the reader to emotionally engage with the world that you create in writing.
To create strong details, keep the human senses in mind. You want your reader to be immersed in the world that you create, so focus on details related to sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch as you describe people, places, and events in your narrative.
As always, it is important to start with a strong introduction to hook your reader into wanting to read more. Try opening the essay with an event that is interesting to introduce the story and get it going. Finally, your conclusion should help resolve the central conflict of the story and impress upon your reader the ultimate theme of the piece. See Chapter 15 “Readings: Examples of Essays” to read a sample narrative essay.
On a separate sheet of paper, add two or three paragraphs to the plot summary you started in the last section. Describe in detail the main character and the setting of the first scene. Try to use all five senses in your descriptions.
Key Takeaways
- Narration is the art of storytelling.
- Narratives can be either factual or fictional. In either case, narratives should emotionally engage the reader.
- Most narratives are composed of major events sequenced in chronological order.
- Time transition words and phrases are used to orient the reader in the sequence of a narrative.
- The four basic components to all narratives are plot, character, conflict, and theme.
- The use of sensory details is crucial to emotionally engaging the reader.
- A strong introduction is important to hook the reader. A strong conclusion should add resolution to the conflict and evoke the narrative’s theme.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:
TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
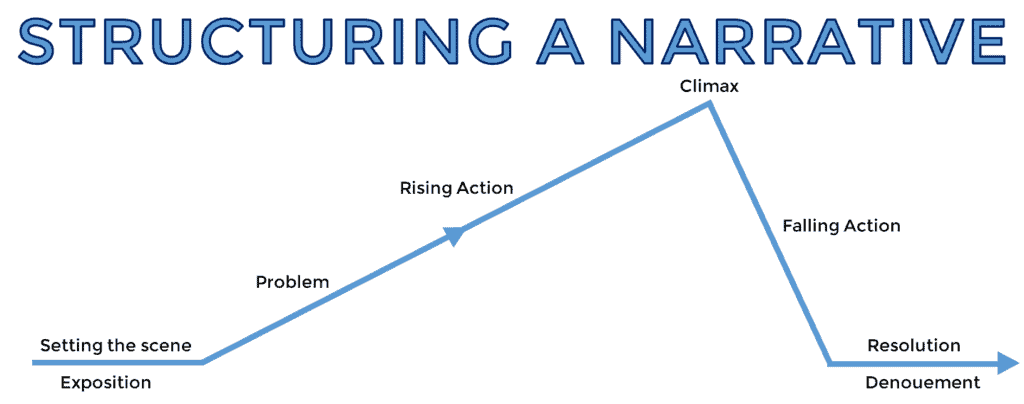
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE
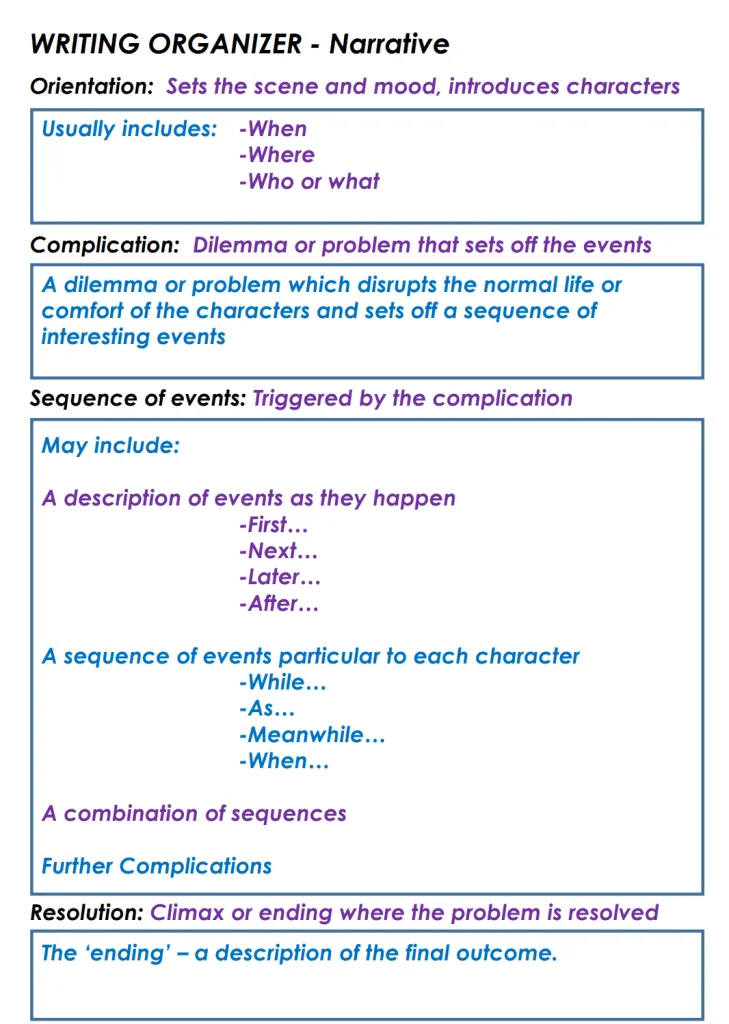
Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
A narrative essay is a type of essay that has a single motif, or a central point, around which the whole narrative revolves. All incidents, happenings, and characters revolve around a single motif presented in the narrative. A narrative essay is similar to a simple five-paragraph essay, in that it has the same format.
Here's a breakdown of the narrative essay types and what they mean. Personal Narrative. Focus: Description: Tells a personal story or experience from the writer's life. Purpose: Reflects on personal growth, lessons learned, or significant moments. Example of Narrative Essay Types: Topic: "The Day I Conquered My Fear of Public Speaking"
0 comment 2. Narrative essays are a type of storytelling in which writers weave a personal experience into words to create a fascinating and engaging narrative for readers. A narrative essay explains a story from the author's point of view to share a lesson or memory with the reader. Narrative essays, like descriptive essays, employ ...
A narrative essay is a prose-written story that's focused on the commentary of a central theme. Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that's personal to the writer. Everything in these essays should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end.
A narrative essay is written in the form of a story and clearly gives a point of view on the subject-most often that of the author. The idea of this type of essay is to engage the reader in a sensory and emotional way which will allow them to connect with that is being written about. A narrative essay will use characters, plots and themes and ...
Not every form of essay writing involves meticulous research. One form in particular—the narrative essay—combines personal storytelling with academic argument. Narrative essay authors illustrate universal lessons in their unique experiences of the world. Below, you'll find some tips to guide in this style of narrative writing. <br> ## What Is a Narrative Essay? Narrative essays make an ...
Use clear and concise language throughout the essay. Much like the descriptive essay, narrative essays are effective when the language is carefully, particularly, and artfully chosen. Use specific language to evoke specific emotions and senses in the reader. The use of the first person pronoun 'I' is welcomed. Do not abuse this guideline!
1. Pick a meaningful story that has a conflict and a clear "moral.". If you're able to choose your own topic, pick a story that has meaning and that reveals how you became the person your are today. In other words, write a narrative with a clear "moral" that you can connect with your main points. 2.
Narrative essays work to surface meaning from lived experience. Narrative Essay Example. A great narrative essay example is the piece "Flow" by Mary Oliver, which you can read for free in Google Books. The essay dwells on, as Mary Oliver puts it, the fact that "we live in paradise." At once both an ode to nature and an urge to love it ...
Step 1: Start with a Topic Selection. When crafting a narrative essay, begin by selecting a topic that either relates to your personal experiences or aligns with a given prompt. If a prompt is provided, consider its requirements and brainstorm ideas that fit within its scope.
Go straight to the drama. You don't need to write up a formal outline for a narrative essay unless it's part of the assignment or it really helps you write. Listing the major scenes that need to be a part of the story will help you get organized and find a good place to start. 2. Use a consistent point of view.
A narrative is a story that is narrated verbally or in writing. A narrative essay tells a story in essay format. It is about a personal experience and told from the author's perspective. It has a ...
Narrative essays are generally written in the first-person POV, and are usually about a topic that's personal to the writer. Everything in a narrative essay should take place in an established timeline, with a clear beginning, middle, and end. In simplest terms, a narrative essay is a personal story. A narrative essay can be written in ...
By definition, a narrative is a series of connected events - in other words, a story. An essay is a piece of writing that focuses on a specific topic. So, a narrative essay is a piece of writing that focuses on a particular story. In practice, a narrative essay is a story about a personal experience. These essays examine how certain events ...
A narrative essay is a genre of writing that tells a story, often from the writer's personal perspective. In this type of essay, the author provides a series of events, characters, and settings, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the experience. Although typically written in the first person, narrative essays can be written in the ...
You can follow these basic guidelines: who, what, where, when. Point of View: A narrative essay may be written in the first-person (I) or third-person (he, she, it) point of view; do not use second person (you). If you were part of the action, the first-person provides the best perspective. If you are relating an event based upon other sources ...
Narrative Essay Format. A narrative essay does not have the same format as other types of essay. This does not mean a narrative essay lacks structure. Remember, a good narrative essay has a strong thesis statement. It can also have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Some narrative essays will be formatted chronologically.
Narration means the art of storytelling, and the purpose of narrative writing is to tell stories. Any time you tell a story to a friend or family member about an event or incident in your day, you engage in a form of narration. In addition, a narrative can be factual or fictional. A factual story is one that is based on, and tries to be ...
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well. Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as 'creative writing' or story writing.
Literacy Narrative Examples for College Students. A literacy narrative is quite simply that: it is a story of how you became literate and how it has affected your life. To create a literacy narrative, you just need to find your story and use descriptive text to bring it to life. Learn how to write a literacy narrative through exploring original ...
WATCH | We hear from the seven political leaders gathering over the next two days to negotiate an agreement to provide voters with a clear alternative...