Soil and Agriculture
Lesson 12.1 Soil
About 38% of Earth’s land surface is used for agriculture.
- Explain 3 processes by which soil forms
- Describe the horizons that make up a soil profile
- List the four characteristics used to classify soil
Soil Composition
- Soil is made up of disintegrated rock, remains and waste of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and microorganisms.
- Renewable resource
- If depleted of nutrients, it takes a very long time (generations) to reform
Factors That Influence Soil Formation
- Forms faster in warm climates with high precipiation
- Worms and burrowing animals aerate and mix soil speeding up decomposition
- Plants add organic matter
- Affect soils exposure to sun, wind and water
- Steep slopes increase runoff and erosion
- Parent material
- The chemical and physical makeup of whatever substance the soil comes from affects its formation
- Soil takes many years (even millennia in some cases) to form
Soil Formation
- 45% mineral matter, 5% organic matter, 50% air/water
- Occurs during primary succession
- Parent material is the base geological material in a particular location
- Ex: lava, volcanic ash, rock, sand, bedrock, etc.
- Bedrock is the continuous mass of solid rock that makes up Earth’s crust.
- Weathering: Physical and chemical breaking of rocks and minerals into smaller pieces
- Physical – result of anything touching a rock such as wind and rain and changes in temperature
- Chemical – when water or other substances break down parent material transforming it into a new material
- Erosion and deposition: Pick-up, transport, and �drop-off of material from one place to another
- Decomposition: Breakdown of waste, organisms, and organic material into simple molecules
- Ex: when leaves fall off trees and are broken down by decomposers and detritivores
- Humus – dark, spongy, crumbly mass of material made up of complex organic compounds
Soil Horizons
- Soil horizons are distinct layers of soil.
- A cross-section �of soil horizons is a �soil profile.
Did You Know? In general, organic matter is concentrated in the O and A horizons, making them the most critical for agriculture.
- Has the most plant nutrients available
- Home to most of the organisms that live in soil
- Lower Horizons
- As you move downward through soil, particle size increases and organic matter decreases
- Leaching transports minerals downward
- Think of coffee grounds in a filter to understand how leaching works
- Leaching may carry substances into ground water which could pose a threat to human health
Soil Characteristics
- U.S. soil scientists define 12 major soil groups.
- Soil groups are further classified according to properties such as color, structure, pH, and texture.
- Soil texture is based on particle size.
- Color – reveals details about its composition and fertility
- dark soil = rich in nutrients, pale soil = nutrient poor
- Texture – influences soils workability, indicates how porous soil is
- Loam – soil with a relatively even mixture of sand, clay and silt
- Structure – arrangement of soil particles
- “clumpiness”
- pH – how acidic/alkaline soil is
- Affects ability to support plant growth
- Affected by acid rain and leaching
Lesson 12.2 Soil Degradation and Conservation
Some estimates predict that 50 million people could be displaced in the next 10 years due to desertification, a form of soil degradation.
A dust storm near Stratford, Texas, in 1935
- Describe some practices that can lead to soil erosion and some that can preserve it
- Describe the causes and effects of desertification
- Discuss the activities of U.S. and International agricultural organizations
- Explain how irrigation and pesticide use can cause soil pollution
- The process by which material, such as topsoil, is moved from one place to another
- Caused by natural processes and human activities
- Often occurs faster than soil is formed, depleting fertile topsoil
- Crops, trees, and other plant communities protect soil from erosion.
Did You Know? More than 19 billion hectares (47 billion acres) of the world’s croplands suffer from erosion and other forms of soil degradation resulting from human activities.
Farming Practices That �Reduce Erosion
- Intercropping: Different crops mixed together
- Helps slow erosion
- Reduces plant vulnerability to insects and disease
- Crop rotation: Crops are alternated.
- Can return nutrients to the soil
- Breaks disease and pest cycles
- Cover crops – farmers plant crops to reduce erosion after a field has been harvested and before the next season’s planting
Farming Practices that Reduce Erosion
- Shelterbelts: Tall plants block wind.
- Conservation tillage: Soil turnover is reduced.
- Require high amounts of weed-killer and fertilizer
- Improve soil quality and reduce erosion
- Terracing: Steep slopes turned into “steps”
- Only sustainable way to farm mountains
- Contour farming: Planting perpendicular to hill’s slope
- Reduces soil erosion
- Crops act as a dam that catches soil before it is washed away
Ranching Practices
- Ranching is the raising and grazing of livestock.
- Overgrazing occurs when animals eat the grasses faster than they can grow back
- Range managers encourage grazing limits and enforce them on publicly owned land.
Forestry Practices
- Forestry practices, such as clear-cutting, can increase erosion.
- Today, practices that reduce soil erosion, such as selective logging, are increasingly common.
Desertification
- Loss of more than �10% of soil productivity
- Causes: soil compaction, �erosion, overgrazing, �drought, or other factors
- Arid and semi-arid lands �are most prone.
- Affects large amounts of Earth’s land areas—up to one third, according to one estimate
- The Dust Bowl was a major desertification event in the 1930s.
Area affected by the Dust Bowl
Soil Conservation Efforts
- U.S. Soil Conservation Act (1935): Established the Soil Conservation Service, today called the Natural Resources Conservation Service
- Farmer-Centered Agricultural Resource Management Program (FARM): A United Nations effort that focuses on resource challenges in developing nations
Soil Pollution
- Irrigation – the providing of water other than precipitation to crops
- Pesticides – chemicals that kill organisms that attack or compete with plants we value
- Toxic pesticides can remain in soil for a long time, eventually filtering to groundwater and evaporate into the air
- Too much, or carelessly timed irrigation can waterlog crops and lead to salinization —a buildup of salts in upper soil horizons.
- In dry areas, evaporating water from topsoil pulls water up from lower horizons, carrying dissolved salts
- Irrigation water also contains dissolved salts
- Salinization is prevented by
- not planting crops that need a lot of water in dry areas
- Irrigating with water with low dissolved salts
- During irrigation, provide no more water than the crops need as close to the roots as possible
Did You Know? Salinization costs farmers $11 billion in crop income a year worldwide.
Lesson 12.3 Agriculture
Humans have been practicing agriculture for about 10,000 years.
- Discuss the beginnings of agriculture
- Explain the importance of industrial agriculture and the green revolution
- Identify different types of pest control
- Explain the importance of pollinators to agriculture
The Beginnings of Agriculture
- People were hunter-gatherers through most of human history, until agriculture developed about 10,000 years ago when climate became warmer
Selective Breeding and Settlement
- In early agriculture, people began planting seeds from plants they liked most, a form of selective breeding.
- Crop cultivation enabled people to settle permanently, often near water sources, and raise livestock.
- Agriculture and livestock provided a stable food supply, which allowed the development of modern civilization.
Traditional Agriculture
- Agriculture “powered” by people and animals
- Does not require fossil fuels
- Practiced widely until the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Agriculture
- Agriculture that requires the use of fossil fuels
- Involves mechanized farming technology, manufactured chemicals pesticides, synthetic fertilizers and large-scale irrigation
- To be efficient, large areas are planted with a single crop in a monoculture.
- Monocultures reduce biodiversity and risk catastrophic crop fail
Did You Know? Today, more than �25% of the world’s croplands support industrial agriculture.
The Green Revolution
- Introduced new technology, crop varieties, and farming practices to the developing world in the mid- to late 1900s
- “Green” refers to covered in plants, not environmentally friendly
- Increased crop yields and saved millions of people from starvation in India and Pakistan because developed nations shared their farming technology with developing nations such as new crop strains, pesticides, fertilizers, irrigation, etc.
- Prevented some deforestation and habitat loss by increasing yields on cultivated land
- Led to a 7000% increase in energy used by agriculture
- Worsened erosion, salinization, desertification, eutrophication, and pollution
- Use of fossil fuel powered machinery increased air pollution and contributed to global warming
Pests and Weed Control
- Pests: damages plants that are valuable to us
- Weeds: competes with our plants
- Chemical pesticides: Effective and cheap, but can lead to resistance
- Integrated pest management: Increasingly popular solution, combines chemical and biological �pest-control methods
Cactus moth larvae are used to control prickly pear cactus, but also threaten many rare, native cacti around the world.
Pest and Weed Control
- Biological pest control: purposeful introduction of organisms that eat pests/weeds to environment
- Bt – naturally occurring soil bacterium, produces protein that kills caterpillars and fly/beetle larvae
- Benefits: permanent, requires no maintenance, environmentally harmless
- Costs: introduced organisms may become invasive, may harm nontargeted organisms
Pollinators
- Pollination is the process by which plants reproduce sexually.
- Agriculture relies on pollinators, such as insects.
- Native and domesticated pollinator populations have declined due to pesticide use, parasites, and other as-of-yet unknown causes.
Did You Know? Bees and other insects pollinate 800 species of cultivated plants.
Lesson 12.4 Food Production
Each year, Earth gains 75 million people and loses 5–7 million hectares of productive cropland.
- Explain why the world needs to grow more food and to grow it sustainably
- Discuss genetically modified food
- Describe the advantages and disadvantages of industrial food production
- Discuss sustainable agriculture
Food Security
- Arable land – land suitable for farming
- Since 1960, our ability to produce food has grown faster than the human population
- but 1 billion people are hungry worldwide
- may not always be the case in the future though
- Malnutrition and undernourishment are most common in the developing world.
- Malnutrition – a shortage of nutrients that the body needs
- Agriculture scientists and policymakers are working toward food security—the guarantee of an adequate food supply for all people at all times.
Genetically Modified Organisms
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GM) - Organisms that have had their DNA modified
- Genetic Engineering – any process in which scientists directly manipulate an organism’s DNA
- Commonly engineered traits include rapid growth, pest resistance, and frost tolerance.
- In the United States, 85% of corn and 90% of soybean, cotton, and canola crops come from GM strains.
- Biotechnology – the use of genetic engineering to introduce new genes into organisms to produce more valuable products
Risks and Benefits of GM Crops
- Potential for “superpests” that are resistant to pest-resistant crops
- Contamination of non-GM plants
- Foods may be dangerous for people to eat
- Insect-resistant crops reduce the need for insecticides.
- Herbicide-resistant crops encourage tillage conservation.
Industrial Food Production: Feedlots
- Alternative to open grazing in which energy-rich food is delivered to a concentrated group of livestock or poultry
- Benefits: Reduces soil degradation and fertilizer use
- Costs: Requires antibiotic use; potential for water contamination and animal stress; steroid use in cattle; overcrowding stresses animals
Industrial Food Production: Aquaculture
- Fish farming in a controlled environment
- Benefits: Can be sustainable; reduces �by-catch; reduces fossil fuel use
- Costs: More difficult to control spread �of diseases; produces a lot of waste; �potential for farm-raised animals �to escape into wild
Did You Know? Aquaculture is the fastest-growing type of food production.
Effects of Plant Diversity
- GM plants may pollinate wild strains of plants, outcompete them and force them into extinction
- If all species of a plant are genetically the same, one pest can wipe out an entire plant species
- We have already lost genetic diversity in our crop plants
- Market forces discourage diversity
- Seed banks – organizations that preserve seeds of diverse plants as a kind of insurance policy against global crop collapse
Sustainable Agriculture
- Does not deplete soil faster than it forms
- Does not reduce the amount or quality of soil, water, and genetic diversity essential to long-term crop and livestock production
- Organic agriculture is sustainable agriculture that does not use synthetic chemicals.
- Local, small-scale agriculture reduces the use of fossil fuels and chemicals used for transportation and storage.
Did You Know? Organic food purchases increased 200% from 1999 to 2008.
What It Means to be “Organic”
- Can’t be genetically engineered, treated with radiation, produced in synthetic fertilizer
- No use of sewage sludge
- Use of pesticide is prohibited
- Must be fed 100% organic feed
- Use of hormones and antibiotics is prohibited
- Animals must have access to outdoors

- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
To view this video please enable JavaScript, and consider upgrading to a web browser that supports HTML5 video
SOIL pollution.
Published by Harriet Pierce Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "SOIL pollution."— Presentation transcript:

What are we Doing to Our Planet?

Human Impact How we affect our Earth’s surface. Agriculture Farming and raising animals. Farming can change the type of land, depending on the farming.

AH 2010 AD Amal Alghamdi 346 MIC. Identification The introduction of substances, biological organisms, or energy into the soil, resulting in.

Why is Pollution Bad for the Earth?

Environmental problems

How Human Activities affect the Environment

Learning Targets “I Can …” -Give examples of the causes of atmospheric pollution and freshwater pollution. -Explain how the Industrial Revolution impacted.

Earth Science 4.3 Water, Air, Land Resources

All organisms use resources to maintain their existence and the use of these resources has an impact on the environment Currently, the Earth is experiencing.

Our Impact on Land, Water, and Air

Solutions and Pollution Brenna Searcy. Essential Question How do foreign substances cause pollution?

Lesson Overview Lesson Overview Using Resources Wisely Chapter 6 Section 2 Using Resources Wisely Using Resources Wisely.

4.3 Water, Air, and Land Resources

Soil Pollution The way to destruction.

The main cause of climate change is the greenhouse effect. This is the warming of the surface or lower atmosphere of a planet. This is caused.

Pollution. Definition Pollution is putting harmful substances into the environment Three kinds ▫1. Air pollution ▫2. Water pollution ▫3. Land pollution.

Non-renewable & Renewable Resources.

SUPERVISION Prof. Dr. Mervat Salah

In the summer of 1969, the Cuyahoga River in Cleveland contained so much chemical waste that it caught on fire. This really got people’s attention. Water.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- My Wish List
- Compare Products
- Presentations
Soil Pollution
You must be logged in to download this file*
item details (4 Editable Slides)
(4 Editable Slides)
Related Products

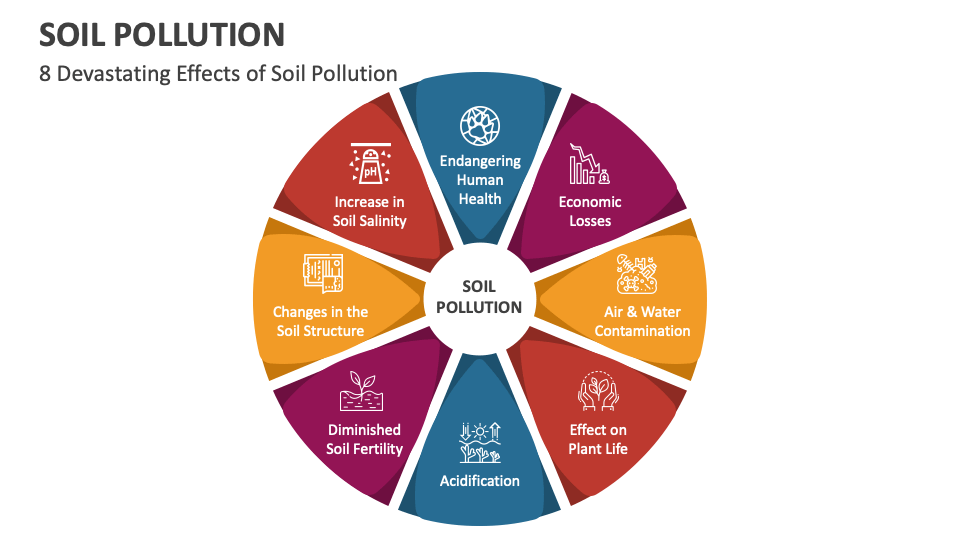
You can enhance your Microsoft PowerPoint and Google Slides presentations by using our captivating template on Soil Pollution. Grab it to describe the contamination of the soil with harmful substances such as pesticides, plastic, heavy metals, or industrial waste, which can have severe ecological and health impacts.
Environmentalists and educators can leverage this superb set to explain the devastating impacts of soil pollution, such as the increase in soil salinity, economic losses, acidification, etc. You can also depict the causes of soil pollution and different methods to control it. The beautiful hues of multiple colors enhance the modernistic and minimal look of this deck, making it perfect for your upcoming presentation.
Sizing Charts
| Size | XS | S | S | M | M | L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EU | 32 | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 |
| UK | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| US | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Bust | 79.5cm / 31" | 82cm / 32" | 84.5cm / 33" | 89.5cm / 35" | 94.5cm / 37" | 99.5cm / 39" |
| Waist | 61.5cm / 24" | 64cm / 25" | 66.5cm / 26" | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" |
| Hip | 86.5cm / 34" | 89cm / 35" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" |
| Size | XS | S | M | L | XL | XXL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK/US | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 42 | 44 |
| Neck | 37cm / 14.5" | 38cm /15" | 39.5cm / 15.5" | 41cm / 16" | 42cm / 16.5" | 43cm / 17" |
| Chest | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" | 101.5cm / 40" | 106.5cm / 42" | 111.5cm / 44" |
| Waist | 71.5cm / 28" | 76.5cm / 30" | 81.5cm / 32" | 86.5cm / 34" | 91.5cm / 36" | 96.5cm / 38" |
| Seat | 90cm / 35.4" | 95cm / 37.4" | 100cm / 39.4" | 105cm / 41.3" | 110cm / 43.3" | 115cm / 45.3" |
- All Resource
PPT Templates
Single slides.
- Pitch Deck 216 templates
- Animation 341 templates
- Vertical Report 316 templates
- Business 814 templates
- Finance 56 templates
- Construction 46 templates
- IT/Commerce 173 templates
- Medical 64 templates
- Education 45 templates
- Lifestyle 402 templates
- Pitch Decks 138 templates
- Business 547 templates
- Finance 20 templates
- Construction 75 templates
- IT/Commerce 73 templates
- Medical 27 templates
- Lifestyle 578 templates
- Pitch Decks 140 templates
- Business 469 templates
- Finance 19 templates
- Construction 64 templates
- IT/Commerce 72 templates
- Medical 29 templates
- Education 39 templates
- Lifestyle 490 templates
- Cover 266 templates
- Agenda 97 templates
- Overview 216 templates
- CEO 28 templates
- Our Team 142 templates
- Organization 48 templates
- History 38 templates
- Vision, Mission 109 templates
- Problem, Solution 193 templates
- Opportunity 154 templates
- Business Model 158 templates
- Product, Services 299 templates
- Technology 65 templates
- Market 155 templates
- Prices 56 templates
- Customers 55 templates
- Competitor 113 templates
- Business Process 151 templates
- Analysis 222 templates
- Strategy 120 templates
- Marketing, Sales 61 templates
- Profit, Loss 69 templates
- Financials 247 templates
- Timeline 122 templates
- Proposal 40 templates
- Contact Us 272 templates
- Break Slides 16 templates
- List 361 templates
- Process 351 templates
- Cycle 177 templates
- Hierarchy 98 templates
- Relationship 152 templates
- Matrix 86 templates
- Pyramid 67 templates
- Tables 145 templates
- Map 96 templates
- Puzzles 163 templates
- Graph 217 templates
- Infographics 436 templates
- SWOT 111 templates
- Icon 418 templates
- Theme Slides 138 templates
- Mockup 42 templates
- Column 315 templates
- Line 199 templates
- Pie 139 templates
- Bar 179 templates
- Area 130 templates
- X Y,Scatter 16 templates
- Stock 59 templates
- Surface 3 templates
- Doughnut 256 templates
- Bubble 65 templates
- Radar 83 templates
- Free PPT Templates 2,101 templates
- Free Keynote 2,017 templates
- Free Google Slides 2,098 templates
- Free Theme Slides 35 templates
- Free Diagram 126 templates
- Free Chart 49 templates
- New Updates
Result for ' soil pollution '
37 Templates are available.
- Sort by Accuracy
- Sort by Newest

Plastic pollution is Growing slide template
Easy editable data driven charts (pie, bar, line) Possible to change shape and color properties Professional and unique slides Ready to use presentation slides on data analytics High quality, editable pre-designed slides

Air Purifiers for Air pollution Presentation Format
Modern, simple, and clean design Completely editable presentation template Premium & modern multipurpose For professionals and educators Created with high quality slides Drag & drop image placeholders

Air pollution PPT Business
Quick and easy to customize Possible to change shape and color properties Free font used Professional look presentation Modern and clean design

Marine pollution Startup PPT Templates
Quick and easy to customize Creative slides Free images and artwork Professional look presentation Easy color change

Stop Ocean Plastic pollution PowerPoint Theme
100% vector objects & icons Professional and unique slides Beautiful presentation decks and templates Professionally designed infographic templates Creatively crafted slides All elements are editable

Air pollution - PowerPoint Presentation Download Free
Smart and innovative presentation slides Drag & drop image placeholders Free images and artwork Image placeholders

Air pollution - Free PowerPoint Templates
Drag & drop image placeholders Format: PowerPoint (.pptx) - designed with Microsoft PowerPoint 2016 Image placeholders Easy to change colors

Air pollution professional presentation
Highly editable presentation template. Easy to change colors Modern and clean design Drag & drop friendly

World Water Day PowerPoint Design
Highly editable presentation template. Scalable vectorial PowerPoint shapes and PowerPoint icons Professional and unique slides Modern and clean design 100% fully editable via Excel
Farm Flat Design Icons
Easy to edit in PowerPoint Quick and easy to customize Shapes: fully editable vector graphics

Environmental protection PowerPoint Templates for Presentation
Easy to edit and customize Built-in custom color palette Presentation photos are included; Format: PowerPoint (.pptx) - designed with Microsoft PowerPoint 2016 Data charts editable via Excel

Eco-Friendly Business PowerPoint Presentation PPT
100% vector objects & icons Completely editable presentation template Professionally designed Easy to customize without graphic design skills Creatively crafted slides

Recycling Activities PowerPoint Presentation PPT
Scalable vectorial PowerPoint shapes and PowerPoint icons Possible to change shape and color properties Professional and unique slides Rich, clean & modern slide High quality, editable pre-designed slides

Recycling ppt presentation slides
Scalable vectorial PowerPoint shapes and PowerPoint icons Shapes and text are 100% editable Easy to customize without graphic design skills Beautiful presentation decks and templates Premade color variation

Earth day best ppt template
Easy to customize without graphic design skills Fully editable vector graphics Beautiful presentation decks and templates Rich, clean & modern slide Changable into PDF, JPG, and PNG formats

Free PPT Template - Fresh Watefall
Professional business presentation Presentation photos are included; Easily editable content Easy color change

Lung Health Care PPT Presentation
Quick and easy to customize 100% vector objects & icons All images included Modern and clean design 100% fully editable via Excel Modern layouts based on master slides

Clear Valley - Free Powerpoint Sample
Modern, simple, and clean design Presentation photos are included; 4:3 aspect ratios Latest Templates support version

Free PPT Template - Valleys
No animation template 4:3 aspect ratios Landscape orientation style Creative and innovative presentation slides

Free PPT Templates - Waterfall
Modern and clean design Presentation photos are included; Clean, modern, and creative slides Easily editable content

Free Slides
Slide Members
All Rights Reserved 2024 © Copyright Slide Members
Information
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Recent Slides
- 21+ Latest weekly update Powerpoint Templates & Google slides
- 15+ New Animation Powerpoint Templates Update
- 17+ Recently Powerpoint Templates & Google slides Update

Download SOIL POLLUTION PowerPoint Presentation

Iframe embed code :
Presentation url :
Home / Social Issues / Social Issues Presentations / SOIL POLLUTION PowerPoint Presentation
SOIL POLLUTION PowerPoint Presentation

PowerPoint is the world's most popular presentation software which can let you create professional SOIL POLLUTION powerpoint presentation easily and in no time. This helps you give your presentation on SOIL POLLUTION in a conference, a school lecture, a business proposal, in a webinar and business and professional representations.
The uploader spent his/her valuable time to create this SOIL POLLUTION powerpoint presentation slides , to share his/her useful content with the world. This ppt presentation uploaded by onlinesearch in Social Issues ppt presentation category is available for free download,and can be used according to your industries like finance, marketing, education, health and many more.
About This Presentation

onlinesearch
Description : Available SOIL POLLUTION powerpoint presentation for free download which is uploaded by search an active user in belonging ppt presentation Social Issues category.
Tags : SOIL POLLUTION
Published on : Feb 10, 2014 Views : 10313 | Downloads : 87
Download Now
Share on Social Media
| - | SOIL POLLUTION Soil ecosystem – organic, inorganic constituents & microbes Soil microbes Active agents in decomposition of both plant and animal wastes – Nature’s garbage disposal system though they decompose a variety of compounds they do not act on many man made synthetic polymers Persistent molecules that fail to be metabolized or mineralized have been termed as recalcitrants |
| - | ppt slide no 2 content not found |
| - | SOIL POLLUTANTS Plastics Agro chemicals Fertilizers Heavy metals |
| - | Plastics Major part of global domestic and industrial waste Not easily biodegraded Waste plastic accumulates much thus adds to severe pollution problem Takes several years to disintegrate – 400 years to degrade mineral water bottles In USA, plastics are 7% in weight and 30% of the volume Use of biodegradable plastic solves the problem of pollution How? Photodegradable or biodegradable plastic contains an element sensitive to UV rays. In the presence of solar rays, the element is activated and breaks polymeric chain into small fragments that are easily digested |
| - | What is biodegradable plastic? During the manufacture – 6% starch and Oxidizing agent (vegetable oil) added to polymers Degraded easily In case of metallic salts Present in soil interact with oxidizing agent to form ferric oxides Attacks polymer bonds Sets degradation of plastic in motion Parallely, soil microbes break starch grains which results in an increased attack surface Finally accelerates auto oxidation process |
| - | Starch present reduces water resistance of plastic Addition of fine protective layer to the starch based plastic make it possible to obtain high degree of water resistance Future? Plastics with 50% starch in the market Biodegradable plastics offers solution to pollution due to plastics |
| - | Solid waste composition |
| - | Solid waste management hierarchy |
| - | ppt slide no 9 content not found |
| - | Agrochemical pollution Include pesticides, herbicides, fungicides Pesticides applied reach the soil ultimately Accumulation of pesticide residues in biosphere creates ecological stress causing soil, water and food contamination Persisting chemicals are hazardous to human health Total remediation is impossible Reduction of residue levels through redeeming technology (desirable) |
| - | Pesticides serve as nutrients (C,N,S) or substrate for energy - many microorganisms Certain pesticides are metabolized but does not serve as nutrient, transformation is by co-metabolism Many pesticides and their metabolites are toxic to microorganisms – Mercuric fungicides are toxic to Rhizobium, Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter |
| - | Fertilizer pollution Continuous application – Deterioration in soil properties, cultivated soils lose their characteristics Application of Amm. sulphate, Amm. chloride & Urea reduce soil pH Crops – potato, grapes, citrus, beans – sensitive to chloride toxicity Application of organic manures and biofertilizers reduce the soil from pollution |
| - | Xenobiotics Foreign and harmful substance or organism in a biological system Derived from Greek Xeno meaning stranger and Bio means life Life describes some toxic substances, parasites and Symbionts Drugs, Food and poisons when consumed in levels more than the normal dose is linked to toxicity Xenobiosis – In communities of species when two distinct species share living space At ecosystem level – toxic waste when bioaccumulation in the food chain / food web we call it Xenobiotic |
| - | Heavy metal pollution Metals with atomic number greater than 23 or more than 5 gm per ml (eg. Hg – 70gm ml-1) They are hazardous, not acceptable to biological system Toxic to man & other life forms Most are slow poison, accumulate in the body and cause serious disorders Common toxic metals- Hg, Pb, As, Cr, Cd |
| - | ppt slide no 15 content not found |
| - | Contd. |
| - | Biodegradation is not possible unlike organic pollutants Metals are not mineralized to non toxic compounds (H2O & CO2) Biomobilization is possible How? Eukaryotic organisms detoxify heavy metals by binding to polythiols and bacteria develop efficient mechanisms to tolerate them They carry the genes controlling metal resistance in chromosome and plasmids Many plasmids contain genes resistance to several metals |
| - | Biological Transformation of metals Is a detoxification mechanism by the action of microorganisms As a result metals undergo changes in valency and or conversion into organo metallic compounds Transformations Changes in valency and resulting in production of volatile or less toxic compounds Ex. Oxidation of As (III) to As (V) and Hg ion to metallic mercury Formation of organo metallic compounds by methylation Ex. Pb & Hg |
| - | Biological methods Agronomic practices Contour farming Mulching crop rotation Strip cropping Dry farming Agrostological methods Lay farming Retiring of land to grass Soil conservation |
| - | Mechanical methods Basin listing Contour terracing Other methods Gully control Afforestation Soil conservation (contd.) |
| - | Terracing – increases the amount of land used for cultivation on steep slope and mountains and reduces erosion |
| - | Contoured rows planted with alternating crops reduces soil erosion on gently sloppy land |
| - | Impact of DDT DDT – Organic chemical – Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane Is a Chlorinated Hydrocarbon Takes long time to break down in the environment Half Life – 15 years Toxic to insects but not very toxic to human Used much during the World War II to protect US troops from mosquito – borne malaria and to prevent the spread of lice and lice borne disease among civilian population in Europe Thereafter used as pesticides to protect crops and people from insect borne disease Since it was the first of its kind, it was overused and by the year 1960s, the problem related to bio magnification of DDT became apparent |
| - | Bioremediation Treatment Technologies Biostimulation Bioaugmentation Biosorption Bioaccumulation Landfarming Composting Bioventing / air sparging Phytoremediation |
| - | Air Sparging |
| - | Soil Washing Contaminated Zone Water Table Mixture Separator/Water Treatment Recovery Well Injection Well Mixture Tank water & surfactants |
| - | Bioreactor Liquid outlet Soil to drying Temperature control Agitator Vapor out Air inlet Nutrient Contaminated soil Contaminated liquid |
| - | Landfarming Tank Air Filter/Pump Gravel layer Contaminated soil |
| - | Biopiles Nutrient/moisture Gravel layer Leachate collection Impermeable layer Contaminated soil |
Frequently Asked Questions
> About SlidesFinder?
> How do I register with SlidesFinder?
Go to registration page (you can see signup link on top of website page) https://www.slidesfinder.com/signup . If you have facebook/gmail account them just click on SIGN IN WITH FACEBOOK OR SIGN IN WITH GOOGLE button, by this you will be a registered member of slidesfinder without filling any form, required detail automatically will be fatch from your account. If you do not a Facebook account, then click on "Signup". Fill all required fields and you will be a registered member of slidesfinder.
> Is slidesfinder account confirmation is mandatory?
Yes it is mandetory to active your account to login.
> Do I need to signup/login on SlidesFinder before uploading a PowerPoint presentation?
Yes, you need to login with your account before uploading presentation. Your username will be displayed on your uploaded presentation. Your registered email id is needed for sending your stats of uploaded presentation.
- Most Viewed
- Most Downloaded
- Presentation Blog
- Active Users
- READ ABOUT US
- How it works?
- SlidesFinder Blog
- LinkedIn Post Date Extractor Tool
- SLIDESFINDER
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Report an Error
- PPT Presentation Search Engine
- Request For Ppt
- PRESENTATIONS
- Featured Presentation
- Most Viewed Presentation
- Category Presentation
- Alphabetical Presentation
- Free Ppt Templates">Free Ppt Templates
- Free Premium Ppt Templates
- Premium Ppt Templates
- Premium Word Templates
Slidesfinder is a sharing website for PowerPoint presentations search and share. Find your interest in the form of powerpoint presentations on slidesfinder and save your valuable time . On Slidesfinder you get presentations from our huge library of professional ppt presentations. We believe in making your search INFORMATIVE and FUN. Find your best ppt presentation from a pool of PowerPoint presentations stacked under important industry categories like business & management, heath & Wellness,eduction & training etc. We provide unique informative PowerPoint presentation for marketers, presenters and educationists. These professional PowerPoint presentations are uploaded by professionals from across numerous industry segments.These ppt presentations are available for FREE download.
Not just finding your interest, but facilitate you broadcast your interest. We have created this platform for easy sharing of PowerPoint presentations, ensuring that these presentations get maximum exposure. Create your slidesfinder account and upload PowerPoint presentations for free, share on social media platforms and BUILD YOUR CROWD WITH PRESENTATION !!
The Great Buddha says, "Share your knowledge.It’s a way to achieve immortality"! So, start sharing knowledge and we are here to make that immortal !!
© 2013-2024 SlidesFinder. All rights reserved.
Re-productivity of content are not allowed. Without prior written permission from author, commercial use of any content is illegal.

Lecture 14 Soil Pollution:
Sep 05, 2012
430 likes | 1.72k Views
Lecture 14 Soil Pollution:. Soil Pollution: The introduction of substances, biological organisms, or energy into the soil, resulting in a change of the soil quality, which is likely to affect the normal use of the soil or endangering public health and the living environment .
Share Presentation
- environmental problems
- global soil degradation source
- bigger pollution problem
- good quarter
- immediate danger
- biochemical oxygen demand

Presentation Transcript
Lecture 14Soil Pollution: • Soil Pollution: • The introduction of substances, biological organisms, or energy into the soil, • resulting in a change of the soil quality, • which is likely to affect the normal use of the soil or endangering public health and the living environment. Ill. EPA employees wearing level "C" protective gear take soil sample in south Chicago's "cluster sites" area. Source: Ill. EPA.
wearing level “B" protective gear • Soil contaminants are spilled onto the surface through many different activities. • Most of these are the result of accidents involving the vehicles that are transporting waste material from site of origin to a disposal site. wearing level “A" protective gear Much good agricultural land is threatened by chemical pollution, particularly - as here in China - by waste products from urban centres. Chemical degradation is responsible for 12 per cent of global soil degradation Source: UNEP, Zehng Zhong Su, China, Still Pictures Drilling to determine pollution extent wearing level “D" protective gear
Others involve accidents involving vehicles (automobiles, trucks and airplanes) not transporting wastes, but carrying materials, including fuel, that when spilled contaminate the soil.
Washington state New York • Other spills are the direct action of humans pouring potentially toxic materials (solvents, paints, household cleaning agents, oil, etc.) onto the soil surface rather than disposing these materials by more appropriate means. • Illegal dumping is the disposal of waste in unauthorized areas. • It is also known as “open dumping”, “fly dumping”, and “mid-night dumping”. • Illegal dumps occur most often along isolated roadsides in remote areas of the country. • Materials often found in illegal dumps include large household appliances, tires, excess building materials, old furniture, oil, household chemicals, and common household refuse. • Video clip of dumping - http://www.dnr.mo.gov/videos.htm Iowa Missouri Virginia
Seattle, WA Pollutant on soil surface • When any liquid pollutant is on or just below the ground surface for any period of time, one of three things could happen to it, if it is not cleaned up first. • 1- pollutant might be washed away by precipitation, causing little or no harm to the ground on which it was found. • pollutants will simply accumulate somewhere else) Waco, Tx
2- the pollutant, if volatile, could evaporate, again causing little harm to the soil (however, not a solution to the bigger pollution problem, as it might become a source of air pollution). • 3- pollutant could infiltrate through the unsaturated soil, in much the same way as ground water.
Agricultural practices, including the use of agricultural chemicals, are another primary source of pollution on or near the ground surface. • Most agricultural chemicals are water-soluble nitrates and phosphates that are applied to fields, lawns and gardens to stimulate the growth of crops, grass and flowers.
Ag Chemicals • When not used by the plants the nutrients can enter streams and lakes during the run-off or leaching events. • Once in a body of water, these nutrients continue to promote the growth of plants, the resulting plant detritus is food for micro-organisms, and as the population of such organisms grows, the supply of oxygen in the water is depleted.
Algae in streams • "Biochemical Oxygen Demand", or "BOD". • Water is capable of supporting a large population of bacteria and the bacteria will have a high demand for oxygen. • Soon the oxygen supply is depleted by the bacteria and other organisms in the water now lack oxygen (fish kills)
Soil Pollution • Information needed to clean up materials added to soil include: • 1)Kind of material - organic or inorganic - is the material biodegradable, is the material dangerous to animals and humans, • 2)how much material was added to the soil, will it overload the organisms in the soil; • 3)C:N ratio of the material, are additional nutrients needed ( N & P)
Soil Pollution • 4)Kind of Soil - will the soil be able to handle the material before groundwater is contaminated, • 5)Growing conditions for the soil organisms - is it too cold, too wet etc. • 6)How long has the material been on the site - is there evidence of environmental problems, is it undergoing decomposition. • 7)Immediate danger to people and the environment - Urgency of the situation.
Bioremediation A treatment process that uses microorganisms (yeast, fungi, or bacteria) to break down, or degrade, hazardous substances into less toxic or nontoxic substances (carbon dioxide and water)
Conditions that favor Bioremediation • Temperature favorable for organisms • Water available (near field capacity) • Nutrients (N, P, K) in adequate supply • C:N ratio of material < 30:1 • Material added is similar to naturally occurring organic material • Oxygen in sufficient quantity
Biostimulation (stimulates biological activity) Bioventing(Inject air/nutrients into unsaturated zone – good for midweight petroleum, jet fuel) Biosparging(Inject air/nutrients into unsaturated and saturated zones) Bioaugmentation (inoculates soil with microbes) In-situ-Bioremediation • Less expensive • Creates less dust • Less possibility of contaminant release into environment • Good for large volumes • Slower • Doesn’t work well in clays or highly layered subsurfaces
Biostimulation cont. Biosparging
Ex-situ -Bioremediation • Easier to control • Used to treat wider range of contaminants and soil types • Costly • Faster • Slurry-phase • Soil combined with water/additives in tank, microorganisms, nutrients, oxygen added • Solid-phase • Land-farming: soil put on pad, leachate collected • Soil biopiles: soil heaped, air added • Composting: biodegradable waste mixed with bulking agent • Land Applied – waste added directly to soil which is later planted to a crop.
Slurry, Solid Phase, & Land Applied
Using Plants for pollution cleanup • Scientists are studying how plants can be used to bind up soil pollution found at national nuclear laboratories and nuclear power plants, where radioactive and other toxic wastes may reach groundwater. • Plants, soil, and microbes in the soil work together to determine which metals and nutrients plants take up from the soil. • Some plants excrete a variety of different chemicals into the soil, some of which act as signals to soil organisms. • The challenge is to find out how plants release these chemicals and how these chemicals interact with microbes and soil. • Eventually scientists may be able to induce plants to release the chemicals that immobilize wastes in the soil. • Source: UC Davis Magazine Spring 2002 • Teresa Fan at UC Davis is studying how plants can be used to remove toxic wastes from soil.
Processes affecting the dissipation of organic chemicals detoxication crop removal photo-dec. Runoff volatilization absorption & exudation chemical decomposition Biological degradation may be transformed into - harmful or harmless • leaching
Affect of soil pH on adsorption of 4 heavy metals Pb Adsorption high = Good Cu Zn Adsorption low is not good Cd 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6 6.5 7.0 Soil pH
BUTER BURN -Just how does a city go about cleaning up after a flood of melted butter? • "You hire somebody else to do it, that's how," joked Tom MacAulay, New Ulm's assistant city manager, two days after a dramatic fire destroyed much of the Associated Milk Producers Inc. (AMPI) butter-packaging plant in town, sending an estimated 1 million pounds of hot, liquid butter pouring onto nearby streets and sidewalks. • On Friday, a day after the great butter cleanup began, city and private construction crews were still going about the tricky task of removing the goo and the grease from streets, sidewalks and sewer lines. Despite steady progress, the going was slow. • "It's not everyday you get a challenge like this," MacAulay said. "It's pretty nasty." • A day earlier, crews using bobcats and tractors scooped up much of the butter that had hardened in the December cold, dumping chunk after frozen chunk into dump trucks, which hauled the grease to a nearby landfill to break down and decompose. • Boom blocks butter.
All told, an estimated $6 million worth of butter -- about half of what was stored at the plant the night of the fire -- spilled and was removed. • Yet for all the progress, much work remained Friday. • Butter that spilled into the city's storm sewer system stuck to the lining of the pipes, which will need to be jet sprayed and cleaned. And though First North Street -- where much of the butter pooled -- had been stripped clean of the worst of it, a good quarter-inch of slime remained on the pavement, even if it couldn't be seen. • "You cannot scrape all that butterfat off the street," said Tom Patterson, the city's street commissioner. "And it's even more dangerous if you can't see it." • Patterson said crews plan to cover the street with sand -- some of which was piled into a berm to stem the flow of the butter at the height of the fire -- in coming days in hopes of absorbing the remaining grease. At some point, he said, the city hopes to sweep the street clean, scoop up the sand and deposit it in a landfill, allowing the street to be reopened for traffic. • "It's something you just never would guess we'd be dealing with," Patterson said. "This is all new to everybody."
Dyad on Pollution • 1) A lot of the melted butter was soaked up with sand. • 2) What could be done with the polluted sand besides dumping it in a land fill. Do you think dumping the solid butter that was scrapped off the roads in the landfill was a good idea?
- More by User

Soil texture Soil stucture soil consistence soil density soil prorosity Soil color
????????(Soil texture). ??????? ???????????????(relative proportions) ????????????????????? sand, silt ??? clay ?????? ????????????????????????????????????????????????????????????? (inorganic paticle) ???????????????????????????????????????????????????????. 1. ????????????????? (Soil separates). ???
1.27k views • 35 slides

LECTURE 6. Soil Physical (Mechanical) Properties – Bulk density, porosity, strength, consistency. Definitions…. Atterberg limits (H. Matengu) Soil strength (L. Olver) Soil dynamics (N. Davenport) Soil micromorphology (A. Pietersen). Physical properties:
741 views • 11 slides

Lecture 1b – Soil as a Resource
Lecture 1b – Soil as a Resource. WHAT DOES SOIL DO? Soils define culture. Throughout history soil has defined human societies perhaps more strongly than any other single environmental variable. Soil fertility defines our food, our population and our economy. Soil colors define our art.
696 views • 38 slides

Soil, marine ,noise and thermal pollution
Soil, marine ,noise and thermal pollution . Soil . Formation of soil from the parent material (bedrock): mechanical weathering of rocks by temperature changes, abrasion, wind, moving water, glaciers, chemical weathering activities and lichens.
1.39k views • 31 slides

Environmental Information System for Uzbekistan
Environmental Information System for Uzbekistan. LEGISLATION. Monitoring of the environmental state. Goskomprirod i (coordinating agency). Minselvodkhoz. Goskomzem geodezcadast r. Goskomgeologiya. Uzgidrome t. Minzdrav. Monitoring System in Uzbekistan.
530 views • 29 slides

Soil Pollution and judicial trials - Search for evidence under French law
Soil Pollution and judicial trials - Search for evidence under French law . Methods, traps to avoid, success factors Jean Francois DAVID Expert près la Cour d’Appel de Versailles Président de la Compagnie Nationale des Experts Judiciaires en Environnement
187 views • 6 slides

LECTURE 6 SOIL INVERTEBRATES Reading:
LECTURE 6 SOIL INVERTEBRATES Reading: Coleman et al. (text) – Chapters 4, (6 and 7) Moldenke et al. 2000 Bohlen et al. 2004 Fender 1995. Soil organisms. Soil Invertebrate Lecture Topics. 1. Diversity of soil arthropods 2. Functional Feeding Groups:
1.05k views • 37 slides

Recall. How can we monitor air, water and soil pollution? Write down what BOD stands for and the definition. How can BOD be used to identify pollution?. Learning outcomes. You should all be able to: Describe an indirect method of measuring pollution levels. Most of you should be able to
512 views • 30 slides

Soils/ Soil & Water Relationships
Soils/ Soil & Water Relationships. The top few inches of the earth’s surface that supports plant growth. Formed from parent material (rocks and minerals) by a process known as weathering. Productivity can be lost by soil degradation, such as erosion and pollution. Soil.
497 views • 20 slides

Pollution. Types of pollution are- 1.Air Pollution. 2.Water Pollution. 3.Noise Pollution. 4.Land Pollution. Causes of Air Pollution. 1.Smoke from chimneys of factories. The Police - Synchronicity 2 - YouTube. 2.Smoke from Vehicles. Discuss L.A, TORONTO, LONDON’S MOTHS , Beijing.
1.82k views • 61 slides

Pollution of air, sea , water and soil in Poland
Pollution of air, sea , water and soil in Poland. Wojciech Olejniczak Publiczne Gimnazjum nr 2 w Staszowie kl. 2b . Poland. In the past Poland was a beautiful country. Crystal-clear water in lakes surrounded by lots of plants , being a home to countless animals ,. Poland.
369 views • 17 slides

Air, Water, and Soil Pollution
Air, Water, and Soil Pollution. A meta-study conducted in 2007 by David Pimentel at Cornell University suggests that as many as 40% of all deaths worldwide are linked to soil, water, and air pollution. Air pollution from smoke and various chemicals kills 3 million people a year worldwide.
1.15k views • 29 slides

SOIL POLLUTION
SOIL POLLUTION. SUPERVISION Prof. Dr. Mervat Salah. What causes heavy metal pollution?. What is soil pollution?. Metals have unique chemical properties. Causes Of soil pollution. Leakages from sanitary sewage. Acid rains, when fumes released from industries get mixed with rains.
4.42k views • 27 slides

Our Work on Mercury
Our Work on Mercury. Guizhou Research & Designing Institute of Environmental Science Qu Liya. Contents. Mercury Pollution in Soil Methylmercury Pollution Mercury Pollution by Coal Use Mercury Pollution Prevention & Cure. About Mercury Pollution in Soil. 1979-1981
225 views • 10 slides

Envirothon. Soil. Topics. Soil Soil Formation Soil Texture Soil Color Organic Matter pH Salinity Soil Air Compaction/Shrink-Swell Drainage Erosion Soil Surveys-How to Use Them References. Typical Loamy Soil. Typical Clayey Soil. Typical Sandy Soil. Forming Factors. Climate
774 views • 38 slides

Soil and Land Pollution RAD Guide (Ch.18-19)
Soil and Land Pollution RAD Guide (Ch.18-19). September 20, 2014. What are 2 ways that exposed rock can be weathered?. Mechanically Example: waves on a cliff Chemical Example: rusting. What is bedrock? Why is it important to soil formation?.
524 views • 26 slides

Lecture 3a Naming Soil Horizons
Lecture 3a Naming Soil Horizons. Soil horizons (layers in the soil) are named so differences between soils can be identified. Naming soil horizons takes practice. When soil scientists are describing a soil they will discuss a lot about what they are seeing and how it should be named.
451 views • 21 slides

Fundamentals of Soil Science
Fundamentals of Soil Science. Soil Organic Matter. Lecture 6 SOM’s Influence on Soil Properties and Plants. Learning Objectives. Lecture 6 – Identify factors that lead to a loss or gain of organic matter in soils Explain the conundrum of soil organic matter management
690 views • 25 slides

ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES. PEPARED BY MRS. S RATH K V III BBSR www.cbse123.co.cc. POLLUTION. Any undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, land, water or soil. 3 types of pollution- air, water and soil. POLLUTANT.
6.22k views • 27 slides

276 views • 10 slides

G.E.SOCITIES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION,SANGAMNER . PROJECT ON:- Soil pollution
G.E.SOCITIES COLLEGE OF EDUCATION,SANGAMNER . PROJECT ON:- Soil pollution. STUDENT NAME 1) Thorat Yogikant P. 2) Weljale Satish G. ACADAMIC YEAR 2010-11. POLLUTION:-.
584 views • 11 slides

Environmental Engineering Lecture 9
Environmental Engineering Lecture 9. Why do we need to treat wastewater ?. To prevent groundwater pollution To prevent sea shore pollution To prevent soil pollution To prevent marine life pollution Protection of public health To reuse the treated effluent For agriculture
561 views • 14 slides
- Preferences

SOIL pollution - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

SOIL pollution
Causes of soil pollution with the rise of concrete buildings and roads, one part of the earth that we rarely see is the soil. it has many different names, such as ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- With the rise of concrete buildings and roads, one part of the Earth that we rarely see is the soil. It has many different names, such as dirt, mud and ground. However, it is definitely very important to us. The plants that feed us grow in soil and keeping it healthy is essential to maintaining a beautiful planet. However, like all other forms of nature, soil also suffers from pollution. The pollution of soil is a common thing these days, and it happens due to the presence of man made elements.
- such as harmful gases and chemicals, agricultural pesticides, fertilizers and insecticides are the most common causes of soil pollution.
- Unhealthy waste management techniques, which are characterized by release of sewage into the large dumping grounds and nearby streams or rivers.
- Oil leaks can happen during storage and transport of chemicals. This can be seen at most of the fuel stations. The chemicals present in the fuel deteriorates the quality of soil and make them unsuitable for cultivation.
- Pollutants present in the air mixes up with the rain and fall. The polluted water could dissolve away some of the important nutrients found in soil and change the structure of the soil.
- Chemical utilization has gone up tremendously since technology provided us with modern pesticides and fertilizers. They are full of chemicals that are not produced in nature and cannot be broken down by it. As a result, they seep into the ground after they mix with water and slowly reduce the fertility of the soil.
- Soil pollution is a result of many activities and experiments done by mankind which end up contaminating the soil. Some of the main and most important effects are
- Rops and plants grown on polluted soil absorb much of the pollution and then pass these on to us. Foul smell due to industrial chemicals and gases might result in headaches, fatigue, nausea, etc., in many people.
- It is the cause of the death of many soil organisms (e.g. earthworms)
- The ecological balance of any system gets affected due to the widespread contamination of the soil. Most plants are unable to adapt when the chemistry of the soil changes so radically in a short period of time.
- The emission of toxic and foul gases from landfills pollutes the environment.
- Loss of soil and natural nutrients present in it. Plants also would not thrive in such soil, which would further result in soil erosion.
- The toxic chemicals present in the soil can decrease soil fertility and therefore decrease in the soil yield.
- The effects of pollution on soil are quite alarming and can cause huge disturbances in the ecological balance and health of living creatures on earth.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Lesson 12.2 Soil Degradation and Conservation. The process by which material, such as topsoil, is moved from one place to another. Caused by natural processes and human activities. Often occurs faster than soil is formed, depleting fertile topsoil. Crops, trees, and other plant communities protect soil from erosion.
24 THANK YOU. Download ppt "Soil pollution". Negative Due to excessive utilization or excessive removal of soil resources Soil erosion due to overgrazing Extensive deforestation Unplanned irrigation Positive Due to direct introduction of undesirable substances, radioactive wastes & deposition of air pollutants through precipitation Pollution ...
SOIL POLLUTION. An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Download presentation by click this link.
Soil Pollution Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. 1) Soil is formed over long periods of time but can be polluted by human activities like industry, agriculture, waste dumping and urbanization. 2) Soil pollution reduces soil quality and makes it unsuitable for plant growth and habitat for organisms.
134443318-soil-pollution-ppt.pptx - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. Soil pollution is caused by various human activities and can have negative effects on soil quality and human health. The main causes of soil pollution include indiscriminate use of fertilizers and pesticides, dumping of solid waste ...
Download presentation. Presentation on theme: "SOIL pollution."—. Presentation transcript: 1 SOIL pollution. 2 Causes of soil pollution. With the rise of concrete buildings and roads, one part of the Earth that we rarely see is the soil. It has many different names, such as dirt, mud and ground. However, it is definitely very important to us.
Presentation Transcript. Soil Pollution Soil is a thin covering over the land consisting of a mixture of minerals, organic material, living organisms, air and water that together support the growth of plant life. • Sources of soil pollution: • Dumping of domestic and industrial waste on soil surface results into soil pollution.
Soil characteristics and soil pollution.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. 1. The document discusses soil characteristics, sources of soil pollution, and effects and remediation of soil pollution. 2. It describes major soil characteristics like composition, formation, and properties.
You can enhance your Microsoft PowerPoint and Google Slides presentations by using our captivating template on Soil Pollution. Grab it to describe the contamination of the soil with harmful substances such as pesticides, plastic, heavy metals, or industrial waste, which can have severe ecological and health impacts.
soil pollution PPT Templates FREE for commercial and personal use! Download over 6,300+ complete free templates in high resolution. Startups & Business Executives. ... Air pollution - PowerPoint Presentation Download Free. Smart and innovative presentation slides Drag & drop image placeholders Free images and artwork Image placeholders.
Soil pollution. Soil pollution. SOIL POLLUTION Contamination of soil by human and natural activities which cause harmful effects on living beings. Sources of soil pollution. Industrial wastes Urban wastes Agricultural wastes Radioactive pollutants Biological agents. Industrial wastes. Paper mills. 17.12k views • 16 slides
PowerPoint is the world's most popular presentation software which can let you create professional SOIL POLLUTION powerpoint presentation easily and in no time. This helps you give your presentation on SOIL POLLUTION in a conference, a school lecture, a business proposal, in a webinar and business and professional representations.. The uploader spent his/her valuable time to create this SOIL ...
Title: Chapter 15 Pollution of Soil, Water, and Air 1 Chapter 15 Pollution of Soil, Water, and Air 151 Important Facts to Know. Current status and activities and conditions that threaten the environment. Environmental threats and challenges. Kinds, sources, and interactions among plant, soil, water and air pollution. Kinds and extent of damage ...
With industrial activities and historical land use practices, soil pollution can pose serious risks to both human health and the ecosystem. Fortunately, A-1 Oil Tank Removal NJ offers comprehensive soil remediation services to address these issues and restore the vitality of your land. Soil contamination is a significant environmental concern ...
Presentation Transcript. Lecture 14Soil Pollution: • Soil Pollution: • The introduction of substances, biological organisms, or energy into the soil, • resulting in a change of the soil quality, • which is likely to affect the normal use of the soil or endangering public health and the living environment. Ill.
About This Presentation. Title: SOIL pollution. Description: Causes of soil pollution With the rise of concrete buildings and roads, one part of the Earth that we rarely see is the soil. It has many different names, such as ... - PowerPoint PPT presentation. Number of Views: 14651. Avg rating:3.0/5.0.