- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center

25 Design Thinking Questions: What To Ask + Answer Examples

As Walter Isaacson, acclaimed biographer of creative genius Steve Jobs, emphasizes, “Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower.” The pursuit of innovation in business is what sets leaders apart; it’s the driving force behind the transformation of customer experiences. Every innovation, every groundbreaking product, and every revolutionary service begins with a question. That’s where the journey of design thinking questions and the power of asking comes into play.
Design Thinking isn’t just a methodology but a culture, and it’s been the driving force behind many remarkable creations. And what fuels this culture is all about asking the right questions.
Although formalized in the 21st century, design thinking has deep roots in history. In the 1950s, brilliant minds at Stanford University were already exploring new ways to enhance creative thinking. The goal was simple: breaking free from conventional problem-solving strategies. Let’s jump now to the 21st century, where design thinking has become a structured methodology at the heart of many renowned organizations’ strategies, such as Apple, Google, and Amazon.
What Are Design Thinking Questions?
The journey of design thinking is underpinned by a singular philosophy: to understand a problem truly, you must question it thoroughly and empathize with its challenges. This is where design thinking questions come into play.
Design thinking questions are open-ended, thought-provoking inquiries to understand a problem’s depths. These questions don’t just scratch the surface; they delve into the heart of the matter, searching for insights, ideas, and opportunities. The true power of these questions lies in their ability to cultivate empathy , unlock creativity , and catalyze innovative solutions.
We put together a table showcasing the elements of good design thinking questions:
These elements guide the formulation of effective design thinking questions essential for uncovering insights, sparking innovation, and solving complex problems through a human-centered approach.
What Are the Questions of Design Thinking and Their Use?
Behind design thinking, there’s a series of carefully crafted questions, each designed to guide problem-solvers through the journey of creativity and innovation. These questions serve several vital functions like:
- Empathy Building: They encourage the development of empathy for the end-users or the people affected by the problem you’re solving. These questions put you in their shoes to truly understand their needs and desires.
- Problem Definition: The right questions help you accurately define the problem you’re dealing with. You uncover hidden issues and complexities by questioning the situation from different angles.
- Ideation: Design thinking questions stimulate ideation. They fuel creativity, inspire innovative ideas, and help teams think outside the box.
- Solution Validation: Once you’ve generated ideas and developed solutions, questions become tools for validating your concepts. They help you ensure that the proposed solutions indeed address the problem.
- Continuous Improvement: Design thinking questions don’t stop with the first solution. They play a crucial role in ongoing evaluation, helping you continuously refine and enhance your offerings.
What Are the Most Important Points of Design Thinking?
To truly grasp the essence of design thinking questions, consider these vital principles that underpin the whole approach:
- User-Centric Approach: Design thinking fundamentally addresses the end-users’ needs and desires. Your questions should revolve around understanding them, their challenges, and their aspirations.
- Iterative Process: Design thinking isn’t a linear journey; it’s a continuous loop of understanding, ideating, prototyping, and testing. Questions guide you through these iterations.
- Problem Framing: Before diving into solutions, design thinking encourages an in-depth understanding of the problem itself. Your questions should focus on framing the issue from multiple perspectives.
- Collaboration: Design thinking is a collaborative effort. The questions foster teamwork, bringing together diverse skills and perspectives.
- Prototype Testing: Questions are tools for validating prototypes. The process includes creating a basic version of the solution and testing it to gather feedback, which is then incorporated into improvements.
In summary, design thinking is an innovation-driven approach that thrives on customer empathy , problem-solving, and continuous improvement, all facilitated by thought-provoking, open-ended questions.
Design Thinking Question Types
Throughout the design thinking process, specific types of questions serve as guiding stars, illuminating the path to innovation and customer-centric solutions:
- These questions go beyond the surface, delving into the heart of the matter: the people. They invite you to walk in your end-users or stakeholders’ shoes, to see the world through their eyes. When you ask empathizing questions, you’re on a quest to truly understand their needs, desires, challenges, and aspirations. It’s about peeling back the layers and getting to the core of human experiences. With empathizing questions, you unlock the profound insights needed to create solutions that genuinely resonate with people.
- In the realm of design thinking, defining the problem is an art form. These questions are like the skilled strokes of a painter’s brush, meticulously crafting the contours of the challenge at hand. They prompt you to consider the subtle details, the shades of the issue that might have gone unnoticed. With problem definition questions, you frame the challenge with precision, ensuring you’re targeting the right problem—no more, no less. They provide the scaffolding for your entire creative process.
- If empathy questions allow you to understand, ideation questions inspire you to dream to explore the uncharted territories of imagination. They’re your passport to a realm where possibilities are endless, and conventional thinking takes a back seat. These questions aren’t just about generating ideas; they’re about opening the doors to unbridled creativity. Ideation questions are open-ended, enticing you to challenge the status quo and venture into the territory of “thinking outside the box.” In this realm, groundbreaking ideas are born.
- You have ideas—bold, innovative, and possibly game-changing. But how do you know which ones have the potential to revolutionize your industry? That’s where validation questions come into play. They are the litmus test, the rigorous assessment that ensures your solutions are on target. Validation questions are the guardians of practicality, making certain that your ideas are not just impressive on paper but feasible in the real world. They help you confirm that the proposed solutions genuinely address the problem and, most importantly, the needs of your users.
- Once your solution is out in the wild, your journey doesn’t end; it transforms into an ongoing quest for refinement and enhancement. Iterative questions are the driving force behind this evolution. They encourage you to listen, learn, and adapt. With these questions, you delve into the feedback, data, and user experiences. You ask what’s working, what’s not, and most crucially, how you can make it better. Iterative questions are the engines of continuous improvement, enabling you to evolve your solutions harmoniously with the ever-changing landscape of customer needs and market dynamics.
With this arsenal of questions, design thinking becomes a powerful vehicle for innovation and transformation, propelling your organization to new heights of customer satisfaction and competitive success.
Design Thinking Success Examples
The impact of design thinking questions is most evident in the real-world examples of companies and organizations that have successfully employed this approach.
- Apple: One of the pioneers in using design thinking, Apple applies this philosophy from product design to the customer experience. They frequently ask empathizing questions like, “ How can we make the iPhone experience even more intuitive? “
- Google: Google’s work culture revolves around creative problem-solving. Their teams use ideation questions such as, “ What are new ways to simplify complex data access for users? “
- Amazon: Amazon applies design thinking to enhance its customer service and satisfaction. Questions like, “How can we make the customer’s online shopping experience more seamless and enjoyable? ” drive their innovation.
- IDEO: A global design consultancy, IDEO, is renowned for its design thinking expertise. They ask many problem definition questions to deeply understand various challenges before proposing solutions.
Free Template: 25 Design Thinking Questions (with Answer Examples)
Design thinking questions with example hypothetical answers:
Feel free to adapt these questions to your specific design thinking project and use them as a starting point for your journey into innovative problem-solving and product development.
Design Thinking Questions with QuestionPro
Integrating QuestionPro into your design thinking process can be a game-changer. Our suite of tools and solutions empowers you to formulate the right design thinking questions, collect valuable feedback, and convert insights into actionable strategies.
Whether you’re looking to enhance your product, service, or overall customer experience, our platform offers:
- Survey Design: Create custom surveys tailored to your design thinking needs with our intuitive survey builder.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback and responses effectively from diverse sources, from customers to employees.
- Data Analysis: Utilize advanced analytics to decipher the insights gained from your design thinking questions.
- Actionable Insights: Transform insights into actionable strategies for innovation and continuous improvement.
Design thinking questions are the compass guiding you through the intricate terrain of innovation. They empower you to understand, define, ideate, validate, and improve solutions.
When harnessed effectively, these questions can unlock a world of creativity and set your organization on a path to lasting success. So, embark on this journey with the right questions, and remember, innovation is just a question away.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
User Journey vs User Flow: Differences and Similarities

Best 7 Gap Analysis Tools to Empower Your Business
Apr 25, 2024

12 Best Employee Survey Tools for Organizational Excellence
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5th, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- How to solve problems using the design ...
How to solve problems using the design thinking process

The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford’s d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions to complex problems.
As humans, we’re approached with problems every single day. But how often do we come up with solutions to everyday problems that put the needs of individual humans first?
This is how the design thinking process started.
What is the design thinking process?
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you tackle complex problems by framing the issue in a human-centric way. The design thinking process works especially well for problems that are not clearly defined or have a more ambiguous goal.
One of the first individuals to write about design thinking was John E. Arnold, a mechanical engineering professor at Stanford. Arnold wrote about four major areas of design thinking in his book, “Creative Engineering” in 1959. His work was later taught at Stanford’s Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (also known as d.school), a design institute that pioneered the design thinking process.
This eventually led Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon to outline one of the first iterations of the design thinking process in his 1969 book, “The Sciences of the Artificial.” While there are many different variations of design thinking, “The Sciences of the Artificial” is often credited as the basis.
Anatomy of Work Special Report: How to spot—and overcome—the most crucial enterprise challenges
Learn how enterprises can improve processes and productivity, no matter how complex your organization is. With fewer redundancies, leaders and their teams can hit goals faster.
![problem solving design questions [Resource Card] AOW Blog Image](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/fdc408f5-063d-4ea7-8d73-cb3ec61704fc/Global-AOW23-Black-Hole?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A non-linear design thinking approach
Design thinking is not a linear process. It’s important to understand that each stage of the process can (and should) inform the other steps. For example, when you’re going through user testing, you may learn about a new problem that didn’t come up during any of the previous stages. You may learn more about your target personas during the final testing phase, or discover that your initial problem statement can actually help solve even more problems, so you need to redefine the statement to include those as well.
Why use the design thinking process
The design thinking process is not the most intuitive way to solve a problem, but the results that come from it are worth the effort. Here are a few other reasons why implementing the design thinking process for your team is worth it.
Focus on problem solving
As human beings, we often don’t go out of our way to find problems. Since there’s always an abundance of problems to solve, we’re used to solving problems as they occur. The design thinking process forces you to look at problems from many different points of view.
The design thinking process requires focusing on human needs and behaviors, and how to create a solution to match those needs. This focus on problem solving can help your design team come up with creative solutions for complex problems.
Encourages collaboration and teamwork
The design thinking process cannot happen in a silo. It requires many different viewpoints from designers, future customers, and other stakeholders . Brainstorming sessions and collaboration are the backbone of the design thinking process.
Foster innovation
The design thinking process focuses on finding creative solutions that cater to human needs. This means your team is looking to find creative solutions for hyper specific and complex problems. If they’re solving unique problems, then the solutions they’re creating must be equally unique.
The iterative process of the design thinking process means that the innovation doesn’t have to end—your team can continue to update the usability of your product to ensure that your target audience’s problems are effectively solved.
The 5 stages of design thinking
Currently, one of the more popular models of design thinking is the model proposed by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design (or d.school) at Stanford. The main reason for its popularity is because of the success this process had in successful companies like Google, Apple, Toyota, and Nike. Here are the five steps designated by the d.school model that have helped many companies succeed.
1. Empathize stage
The first stage of the design thinking process is to look at the problem you’re trying to solve in an empathetic manner. To get an accurate representation of how the problem affects people, actively look for people who encountered this problem previously. Asking them how they would have liked to have the issue resolved is a good place to start, especially because of the human-centric nature of the design thinking process.
Empathy is an incredibly important aspect of the design thinking process. The design thinking process requires the designers to put aside any assumptions and unconscious biases they may have about the situation and put themselves in someone else’s shoes.
For example, if your team is looking to fix the employee onboarding process at your company, you may interview recent new hires to see how their onboarding experience went. Another option is to have a more tenured team member go through the onboarding process so they can experience exactly what a new hire experiences.
2. Define stage
Sometimes a designer will encounter a situation when there’s a general issue, but not a specific problem that needs to be solved. One way to help designers clearly define and outline a problem is to create human-centric problem statements.
A problem statement helps frame a problem in a way that provides relevant context in an easy to comprehend way. The main goal of a problem statement is to guide designers working on possible solutions for this problem. A problem statement frames the problem in a way that easily highlights the gap between the current state of things and the end goal.
Tip: Problem statements are best framed as a need for a specific individual. The more specific you are with your problem statement, the better designers can create a human-centric solution to the problem.
Examples of good problem statements:
We need to decrease the number of clicks a potential customer takes to go through the sign-up process.
We need to decrease the new subscriber unsubscribe rate by 10%.
We need to increase the Android app adoption rate by 20%.
3. Ideate stage
This is the stage where designers create potential solutions to solve the problem outlined in the problem statement. Use brainstorming techniques with your team to identify the human-centric solution to the problem defined in step two.
Here are a few brainstorming strategies you can use with your team to come up with a solution:
Standard brainstorm session: Your team gathers together and verbally discusses different ideas out loud.
Brainwrite: Everyone writes their ideas down on a piece of paper or a sticky note and each team member puts their ideas up on the whiteboard.
Worst possible idea: The inverse of your end goal. Your team produces the most goofy idea so nobody will look silly. This takes out the rigidity of other brainstorming techniques. This technique also helps you identify areas that you can improve upon in your actual solution by looking at the worst parts of an absurd solution.
It’s important that you don’t discount any ideas during the ideation phase of brainstorming. You want to have as many potential solutions as possible, as new ideas can help trigger even better ideas. Sometimes the most creative solution to a problem is the combination of many different ideas put together.
4. Prototype stage
During the prototype phase, you and your team design a few different variations of inexpensive or scaled down versions of the potential solution to the problem. Having different versions of the prototype gives your team opportunities to test out the solution and make any refinements.
Prototypes are often tested by other designers, team members outside of the initial design department, and trusted customers or members of the target audience. Having multiple versions of the product gives your team the opportunity to tweak and refine the design before testing with real users. During this process, it’s important to document the testers using the end product. This will give you valuable information as to what parts of the solution are good, and which require more changes.
After testing different prototypes out with teasers, your team should have different solutions for how your product can be improved. The testing and prototyping phase is an iterative process—so much so that it’s possible that some design projects never end.
After designers take the time to test, reiterate, and redesign new products, they may find new problems, different solutions, and gain an overall better understanding of the end-user. The design thinking framework is flexible and non-linear, so it’s totally normal for the process itself to influence the end design.
Tips for incorporating the design thinking process into your team
If you want your team to start using the design thinking process, but you’re unsure of how to start, here are a few tips to help you out.
Start small: Similar to how you would test a prototype on a small group of people, you want to test out the design thinking process with a smaller team to see how your team functions. Give this test team some small projects to work on so you can see how this team reacts. If it works out, you can slowly start rolling this process out to other teams.
Incorporate cross-functional team members : The design thinking process works best when your team members collaborate and brainstorm together. Identify who your designer’s key stakeholders are and ensure they’re included in the small test team.
Organize work in a collaborative project management software : Keep important design project documents such as user research, wireframes, and brainstorms in a collaborative tool like Asana . This way, team members will have one central source of truth for anything relating to the project they’re working on.
Foster collaborative design thinking with Asana
The design thinking process works best when your team works collaboratively. You don’t want something as simple as miscommunication to hinder your projects. Instead, compile all of the information your team needs about a design project in one place with Asana.
Related resources
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning
Understanding dependencies in project management
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
3 ways companies can scale emissions reduction
Women’s career advice: Remember that exhaustion is not a yardstick for productivity
How, and why, to run a values-based business
Credit: Mimi Phan
Ideas Made to Matter
Design thinking, explained
Rebecca Linke
Sep 14, 2017
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled “Design Thinking” by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Since then, the design thinking process has been applied to developing new products and services, and to a whole range of problems, from creating a business model for selling solar panels in Africa to the operation of Airbnb .
At a high level, the steps involved in the design thinking process are simple: first, fully understand the problem; second, explore a wide range of possible solutions; third, iterate extensively through prototyping and testing; and finally, implement through the customary deployment mechanisms.
The skills associated with these steps help people apply creativity to effectively solve real-world problems better than they otherwise would. They can be readily learned, but take effort. For instance, when trying to understand a problem, setting aside your own preconceptions is vital, but it’s hard.
Creative brainstorming is necessary for developing possible solutions, but many people don’t do it particularly well. And throughout the process it is critical to engage in modeling, analysis, prototyping, and testing, and to really learn from these many iterations.
Once you master the skills central to the design thinking approach, they can be applied to solve problems in daily life and any industry.
Here’s what you need to know to get started.

Understand the problem
The first step in design thinking is to understand the problem you are trying to solve before searching for solutions. Sometimes, the problem you need to address is not the one you originally set out to tackle.
“Most people don’t make much of an effort to explore the problem space before exploring the solution space,” said MIT Sloan professor Steve Eppinger. The mistake they make is to try and empathize, connecting the stated problem only to their own experiences. This falsely leads to the belief that you completely understand the situation. But the actual problem is always broader, more nuanced, or different than people originally assume.
Take the example of a meal delivery service in Holstebro, Denmark. When a team first began looking at the problem of poor nutrition and malnourishment among the elderly in the city, many of whom received meals from the service, it thought that simply updating the menu options would be a sufficient solution. But after closer observation, the team realized the scope of the problem was much larger , and that they would need to redesign the entire experience, not only for those receiving the meals, but for those preparing the meals as well. While the company changed almost everything about itself, including rebranding as The Good Kitchen, the most important change the company made when rethinking its business model was shifting how employees viewed themselves and their work. That, in turn, helped them create better meals (which were also drastically changed), yielding happier, better nourished customers.
Involve users
Imagine you are designing a new walker for rehabilitation patients and the elderly, but you have never used one. Could you fully understand what customers need? Certainly not, if you haven’t extensively observed and spoken with real customers. There is a reason that design thinking is often referred to as human-centered design.
“You have to immerse yourself in the problem,” Eppinger said.
How do you start to understand how to build a better walker? When a team from MIT’s Integrated Design and Management program together with the design firm Altitude took on that task, they met with walker users to interview them, observe them, and understand their experiences.
“We center the design process on human beings by understanding their needs at the beginning, and then include them throughout the development and testing process,” Eppinger said.
Central to the design thinking process is prototyping and testing (more on that later) which allows designers to try, to fail, and to learn what works. Testing also involves customers, and that continued involvement provides essential user feedback on potential designs and use cases. If the MIT-Altitude team studying walkers had ended user involvement after its initial interviews, it would likely have ended up with a walker that didn’t work very well for customers.
It is also important to interview and understand other stakeholders, like people selling the product, or those who are supporting the users throughout the product life cycle.
The second phase of design thinking is developing solutions to the problem (which you now fully understand). This begins with what most people know as brainstorming.
Hold nothing back during brainstorming sessions — except criticism. Infeasible ideas can generate useful solutions, but you’d never get there if you shoot down every impractical idea from the start.
“One of the key principles of brainstorming is to suspend judgment,” Eppinger said. “When we're exploring the solution space, we first broaden the search and generate lots of possibilities, including the wild and crazy ideas. Of course, the only way we're going to build on the wild and crazy ideas is if we consider them in the first place.”
That doesn’t mean you never judge the ideas, Eppinger said. That part comes later, in downselection. “But if we want 100 ideas to choose from, we can’t be very critical.”
In the case of The Good Kitchen, the kitchen employees were given new uniforms. Why? Uniforms don’t directly affect the competence of the cooks or the taste of the food.
But during interviews conducted with kitchen employees, designers realized that morale was low, in part because employees were bored preparing the same dishes over and over again, in part because they felt that others had a poor perception of them. The new, chef-style uniforms gave the cooks a greater sense of pride. It was only part of the solution, but if the idea had been rejected outright, or perhaps not even suggested, the company would have missed an important aspect of the solution.
Prototype and test. Repeat.
You’ve defined the problem. You’ve spoken to customers. You’ve brainstormed, come up with all sorts of ideas, and worked with your team to boil those ideas down to the ones you think may actually solve the problem you’ve defined.
“We don’t develop a good solution just by thinking about a list of ideas, bullet points and rough sketches,” Eppinger said. “We explore potential solutions through modeling and prototyping. We design, we build, we test, and repeat — this design iteration process is absolutely critical to effective design thinking.”
Repeating this loop of prototyping, testing, and gathering user feedback is crucial for making sure the design is right — that is, it works for customers, you can build it, and you can support it.
“After several iterations, we might get something that works, we validate it with real customers, and we often find that what we thought was a great solution is actually only just OK. But then we can make it a lot better through even just a few more iterations,” Eppinger said.
Implementation
The goal of all the steps that come before this is to have the best possible solution before you move into implementing the design. Your team will spend most of its time, its money, and its energy on this stage.
“Implementation involves detailed design, training, tooling, and ramping up. It is a huge amount of effort, so get it right before you expend that effort,” said Eppinger.
Design thinking isn’t just for “things.” If you are only applying the approach to physical products, you aren’t getting the most out of it. Design thinking can be applied to any problem that needs a creative solution. When Eppinger ran into a primary school educator who told him design thinking was big in his school, Eppinger thought he meant that they were teaching students the tenets of design thinking.
“It turns out they meant they were using design thinking in running their operations and improving the school programs. It’s being applied everywhere these days,” Eppinger said.
In another example from the education field, Peruvian entrepreneur Carlos Rodriguez-Pastor hired design consulting firm IDEO to redesign every aspect of the learning experience in a network of schools in Peru. The ultimate goal? To elevate Peru’s middle class.
As you’d expect, many large corporations have also adopted design thinking. IBM has adopted it at a company-wide level, training many of its nearly 400,000 employees in design thinking principles .
What can design thinking do for your business?
The impact of all the buzz around design thinking today is that people are realizing that “anybody who has a challenge that needs creative problem solving could benefit from this approach,” Eppinger said. That means that managers can use it, not only to design a new product or service, “but anytime they’ve got a challenge, a problem to solve.”
Applying design thinking techniques to business problems can help executives across industries rethink their product offerings, grow their markets, offer greater value to customers, or innovate and stay relevant. “I don’t know industries that can’t use design thinking,” said Eppinger.
Ready to go deeper?
Read “ The Designful Company ” by Marty Neumeier, a book that focuses on how businesses can benefit from design thinking, and “ Product Design and Development ,” co-authored by Eppinger, to better understand the detailed methods.
Register for an MIT Sloan Executive Education course:
Systematic Innovation of Products, Processes, and Services , a five-day course taught by Eppinger and other MIT professors.
- Leadership by Design: Innovation Process and Culture , a two-day course taught by MIT Integrated Design and Management director Matthew Kressy.
- Managing Complex Technical Projects , a two-day course taught by Eppinger.
- Apply for M astering Design Thinking , a 3-month online certificate course taught by Eppinger and MIT Sloan senior lecturers Renée Richardson Gosline and David Robertson.
Steve Eppinger is a professor of management science and innovation at MIT Sloan. He holds the General Motors Leaders for Global Operations Chair and has a PhD from MIT in engineering. He is the faculty co-director of MIT's System Design and Management program and Integrated Design and Management program, both master’s degrees joint between the MIT Sloan and Engineering schools. His research focuses on product development and technical project management, and has been applied to improving complex engineering processes in many industries.
Read next: 10 agile ideas worth sharing
Related Articles

Great Questions Lead to Great Design: A Guide to the Design-thinking Process
Great designers help teams and stakeholders make better decisions by using questions to identify opportunities, reveal underlying needs, and understand user context—all of which lead to better designs.

By Jorge Juan Perales
Jorge Juan has designed successful digital products for over a decade. He loves fast-moving teams and delivering great value to users.
PREVIOUSLY AT
Listen to the audio version of this article
Great designers help teams and stakeholders make better decisions by using questions to identify opportunities, reveal underlying needs, and understand user context.
James Dyson, having been inspired by a centrifuge used to separate paint particles from the air, came up with the world’s first bagless vacuum cleaner in 1983 after famously going through 5,127 prototypes —the epitome of design thinking . He must have asked a lot of questions along the way…
Designers face tough problems every day—problems that require them to find design solutions that deal with business and technical constraints while also addressing user needs. At the same time, the urge to find solutions quickly shouldn’t preclude designers from thoroughly understanding the heart of the problem, as well as the user context, from the outset.
The critical “investigative phase” should not be bypassed—it is a vital component in the design-thinking process. It is where carefully formulated design thinking questions reveal themselves as a great way to approach a design problem even before designers start “designing.”
Questions are a genuine expression of our curiosity and interest in something. They are the means by which people seek meaning in the surrounding world and often trigger our willingness to explore.

When designers are faced with a problem, their brain is programmed to find a good enough solution right away and act upon it. However, it is important to note that those willing to deliver successful products and services must face the problems and build a deeper understanding of them in order to come up with valuable insights.
By knowing how questions on design work and how to use them cleverly, designers can unleash the potential of good questions to build understanding, trigger the imagination, and foster collaboration.
Why Designers Don’t Ask Questions
Designers typically operate in fast-moving environments which demand focusing on quick solutions and delivery . In that context, questions like “Why do we need to solve that problem?” or “How did you notice this problem?” which may lead to a better understanding of the underlying causes and needs, are seen as interruptions that slow down the process.
While quick wins are OK in some situations, designers also have the responsibility to help teams establish direction and not waste valuable resources working—no matter how fast—on the wrong problems.
Designers are like detectives; they need information from many different sources in order to resolve their cases. And what is a key skill that good detectives have? Asking smart questions that help them clarify the case, solve the puzzle and find the truth.

Why Don’t Designers Ask Questions as Often as They Should?
Some designers are afraid of annoying people . When someone presents a new idea or solution to the team, questions that reveal weaknesses or uncovered areas can make owners feel uncomfortable. They thought they had it all figured out, and suddenly, there’s an element of uncertainty introduced into the picture.
They realize there is more to think about than they had expected, so they look at the designer as an “annoyance.” Designers should make it clear that they are not there to annoy people or slow down the process unnecessarily but to help the team build better products; consequently, their feedback should be seen as a valuable contribution and a crucial part of a prudent design process.
A lot of people think of designers at an execution level —decisions are made by technology, business, and marketing teams while designers are there to simply execute commands. But designers also have the responsibility to expose the value of design at a strategic level.
Some designers lack the confidence and training —both to ask good questions and to do it in a way that clearly reveals their will to help and collaborate. As everything in life, asking good questions is a matter of training. The more you do it, the better you get at it. One of the purposes of this article is to provide designers with some ideas that will help them get started in the art of asking good questions.

Types of Effective Design Thinking Process Questions
A good question is the one that lets you obtain the type , quality , and quantity of information you need. In order to do so, designers have to decide both the type of questions they use and the way they formulate them.
Here are some basic but very effective design thinking prompts:
Open-ended questions encourage people to reflect and reveal what’s important for them. They allow people to freely expand on what is comfortable for them, rather than justifying their thoughts. Open-ended questions tend to explore possibilities, feelings, and the reasons why. Michael J. Marquardt, author of Leading with questions , describes some types of open-ended questions:
- Explorative questions force expansion on new points of view and uncovered areas. Have you thought of…?
- Affective questions reveal people’s feelings about something. How do you feel about…?
- Reflective questions encourage more elaboration. What do you think causes…?
- Probing questions invite a deeper examination. Can you describe how…?
- Analytical questions look for the roots of a problem. What are the causes of…?
- Clarifying questions help align and avoid misunderstandings. So, you mean that..?
Closed questions call for specific answers—usually yes or no—or they force the respondent to select an answer from a given set, or to agree or disagree with a statement. Closed questions tend to focus on facts—what, when, where—and are usually easy to answer. For example: “Where were you born? How many miles do you drive a month?”

The Anatomy of a Good Question
A good question doesn’t depend just on the type of question it is, but also on how you frame it. The form of a question is part of its function. Good questions should be framed under these principles:
Good questions should empower. Disempowering questions focus on why the person did not succeed, which puts that person in a defensive mode. Empowering questions are asked from trust—they get people to think and find their own answers, which transfers ownership and develops self-responsibility.
For example, when giving feedback, instead of just saying “I don’t think this would work,” you could ask, “What other options have you explored, and why did you choose this one?”
Good questions should challenge assumptions. They should help clarify the situation and cause individuals, teams, and organizations to explore the methods, processes, and conventions that drive their actions.
Good questions should cause the person to stretch. They should encourage reflection and help people go beyond the obvious. Good questions motivate people to take things to the next level. For example, when discussing with technology teams, instead of asking, “Can you do this?” you could ask, “Supposing this is the way to go, what would you need to have or eliminate in order to accomplish this?”
Good questions should encourage breakthrough thinking. Good questions open up new possibilities. They involve people in divergent thought processes that lead to new perspectives. For example, when designing a new login screen, instead of just asking, “How could we make the login process faster?” you could ask, “How could we deliver value to our users without them having to log in?”

The Setup for Good Questions
Even if you choose the right type of question and you frame it correctly, you need to set the stage in order for others to understand why you are asking questions and what for. Designers are not judges—they are facilitators that provide a context for the information to flow as part of the design thinking framework and help everyone make informed decisions.
Here is a process that helps accomplish that:
Adopt a learner mindset. Our mindset frames how we see the world. A learner is optimistic and seeks understanding as a way to guide their actions. Be curious, attentive, and receptive. You are not a judge, you are a designer who needs to investigate the problem more deeply in order to make decisions, so let people know that.
Find the right people to ask. Learn who can help you the most and be sure you can count on them: adapt to their schedule, look for the best moment to get them on board and engage them in your project.
Set the stage. Warm up. Provide context and get people to feel comfortable in order for them to be open and ready.
Ask your questions. Sometimes, you just want people to express their thoughts on something. Other times, you want to ask specific questions even if you know it will be unpleasant for them. If you really need answers to those, set the stage properly and ask them anyway.
Dig deeper. Ask follow-up questions in order to get deeper information and clarify that everyone understands the same thing. Use the power of silence—just keep silent, look people in the eye, and nod—so they can expand on their thoughts and ideas without interruption.
How Can Asking Good Questions Build Understanding?
Good questions challenge the status quo, forcing people to pay attention to what’s really going on. They help discover how things work, who’s involved, and how everything relates. Questions help create a clear map of the situation.
Find the root of the problem. Some designers focus on symptoms and simply provide solutions for them. Great designers focus on understanding the origin of those symptoms in order to make a good diagnosis.
Challenge assumptions. Individuals, teams, and organizations have their own habits and processes. Good questions help detect their biases and find new perspectives and points of view.
Understanding context. Designers use different mapping techniques in order to get a clear picture of how the whole system works. They use ethnography and empathy to understand people’s behaviors and mental models. Good questions help gain valuable insights and uncover social, economic, or cultural patterns that take place in a particular context.
Questioning Techniques That Build a Deeper Understanding
This method helps you get a deeper understanding of the root causes and underlying beliefs and motivations of people. It’s at the heart of a proper design thinking process. Sakichi Toyoda, one of the fathers of the Japanese industrial revolution, developed the technique in the 1930s. Here’s how to apply it:
- People don’t buy products in our online store. – Why?
- Because they don’t complete the purchase, they drop off. – Why?
- Because they tend to abandon the shopping cart. – Why?
- Because the cart is where we show shipping details and they think 10 days is too long. – Why?
- Because people buy our product as a gift to someone just a couple of days before the gifting date. 10 days is too long for shipping.
By question five, product designers most likely got closer to the root of the problem and shed light on new approaches to consider that weren’t necessarily the original, “assumed” problem. For a deeper description on the 5 Whys Method , visit Mindtools .
Who, What, Where, When, Why, and How
This is another framework that can be used in order to analyze and get a deeper understanding of the situation and context. Whenever you face a problem, asking these questions will help you get a clear view of the current situation, map critical pain points, and come up with possible ways of taking concrete action that will solve the problem:
- Who interferes with the process in the situation? Users, stakeholders, suppliers, clients, team…
- What elements compose the situation? Actions, behaviors, elements, tools…
- Where does it happen? Geographically, culturally, socially, economically…
- When does this occur? Past, present, future, situational context (when I’m in a rush), frequency…
- Why does this happen? Causes, constraints, needs, motivations…
- How is the situation created? Processes, metrics, results…

How Can Designers Trigger the Imagination by Asking Great Questions?
Great questions have the power to transport us to unimagined scenarios and transform the way we see reality. Questions like, “How would this be in 2050?” lead us to a mindset where our current constraints and biases are no longer valid, forcing us to operate under new paradigms.
When we reframe a situation with questions like, “What would happen if all humans were blind?” we are challenging the set of beliefs and values that we use when inferring meaning, so our view of the situation can change dramatically. When people see things from new perspectives, innovation happens.
Questioning Techniques That Can Trigger the Imagination
There are some question starters that will help you frame your questions in a way that encourages imagination and causes people to develop new perspectives:
- How would it be different if…?
- Suppose that…?
- What if we knew…?
- What would change if…?
- What other way could we…?

Design Question Examples that Foster Collaboration
Questions are also a good way to help teammates identify critical points in their designs and find stronger arguments for their decisions. Through intelligent and constructive feedback , the whole team can benefit from everyone’s point of view and area of expertise.
Instead of asking “Isn’t that interaction a bit awkward?” which could make people defensive, great designers ask questions like, “What were other options you considered, and why did you choose this one?” You’ll help people reflect on their work, explain the reasons why, and see questions as a gift.
Questions build respect and show interest in others’ feelings and thoughts. They help align team members , clarify goals, and give people a sense of responsibility and ownership.
Questions also improve self-awareness and develop better listening and greater understanding capabilities. When you ask your teammates questions, you learn about how they think, what they believe in, how they feel in certain situations, etc. It helps build solid links with the team.
Questioning Techniques That Foster Collaboration
As part of a design thinking exercise, there are some question starters that will help frame questions in a way that builds trust and encourages team collaboration:
- How do you feel about…?
- How would you describe…?
- How could we…?
- What help do we need in order to…?
The Design Thinking Process Using Great Questions
Questioning is a powerful tool that every designer should be able to use fluently. As part of a design thinking process, questions can help understand a situation and get valuable insights. They can also foster creativity and innovation within an organization, and can help teams align and unite.
Asking questions and letting the information flow is essential for growth as an individual and as an organization. But a questioning culture also requires an atmosphere of trust and responsibility, where everyone’s wisdom and capabilities are respected and promoted.
As a designer, ask questions and make sure everyone understands that they come from genuine curiosity and a desire to explore product design more deeply, with the aim of coming up with the best design solution.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- UI Design Best Practices and Common Mistakes
- Empty States: The Most Overlooked Aspect of UX
- Simplicity Is Key: Exploring Minimal Web Design
- Heuristic Principles for Mobile Interfaces
- Designing for Readability: A Guide to Web Typography (With Infographic)
Jorge Juan Perales
Madrid, Spain
Member since April 5, 2016
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
By entering your email, you are agreeing to our privacy policy .
Toptal Designers
- Adobe Creative Suite Experts
- Agile Designers
- AI Designers
- Art Direction Experts
- Augmented Reality Designers
- Axure Experts
- Brand Designers
- Creative Directors
- Dashboard Designers
- Digital Product Designers
- E-commerce Website Designers
- Full-Stack Designers
- Information Architecture Experts
- Interactive Designers
- Mobile App Designers
- Mockup Designers
- Presentation Designers
- Prototype Designers
- SaaS Designers
- Sketch Experts
- Squarespace Designers
- User Flow Designers
- User Research Designers
- Virtual Reality Designers
- Visual Designers
- Wireframing Experts
- View More Freelance Designers
Join the Toptal ® community.
How to solve problems with design thinking
May 18, 2023 Is it time to throw out the standard playbook when it comes to problem solving? Uniquely challenging times call for unique approaches, write Michael Birshan , Ben Sheppard , and coauthors in a recent article , and design thinking offers a much-needed fresh perspective for leaders navigating volatility. Design thinking is a systemic, intuitive, customer-focused problem-solving approach that can create significant value and boost organizational resilience. The proof is in the pudding: From 2013 to 2018, companies that embraced the business value of design had TSR that were 56 percentage points higher than that of their industry peers. Check out these insights to understand how to use design thinking to unleash the power of creativity in strategy and problem solving.
Designing out of difficult times
What is design thinking?
The power of design thinking
Leading by design
Author Talks: Don Norman designs a better world
Are you asking enough from your design leaders?
Tapping into the business value of design
Redesigning the design department
Author Talks: Design your future
A design-led approach to embracing an ecosystem strategy
More than a feeling: Ten design practices to deliver business value
MORE FROM MCKINSEY
How design helps incumbents build new businesses
What Is Design Thinking and Why Is It Important?
It all starts with understanding the problem you’re solving.
Design thinking involves human-centric approaches used to solve problems throughout the design process. It is applied in user experience (UX) design and user interface (UI) design to create products specifically with user needs in mind, and focuses on being solution-based rather than being problem-based.
Design Thinking Definition
Design thinking describes creative problem-solving approaches used to innovate user-centric products and services, as well as develop effective solutions in the design process.
What Is Design Thinking?
Design thinking refers to procedures applied in the design process that help make decisions and address roadblocks in a user-centric manner. It puts a focus on finding design solutions that get to the root of why a user or product problem occurs, rather than focusing on fixing the problem alone. Design thinking tends to be non-linear and iterative in its process to identify areas for improvement at each step of design. UX, UI and product designers may utilize design thinking to develop products and services that effectively address user needs.
Tim Brown, chair of the design consultancy IDEO , describes design thinking as “a human-centered approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.”
The design thinking method grew to prominence after being taught in Stanford University’s design school in 2003. Today, design thinking is applied as a product development and brand positioning strategy by high-profile software firms like Intuit, Samsung and Google to build and test new ideas efficiently.
Why Is Design Thinking Important?
Offers flexibility .
While design thinking is associated with creative design, its practices can be applied to solve various types of problems, especially those requiring an understanding of human needs. Its application can also vary widely depending on the company and its customers, making it a flexible approach to product development or overcoming business obstacles.
Can Help Startups and Early Businesses Launch
Startups may use design learning to gain a deeper understanding about their users and guide prototype development. Legacy companies may apply it to launch new product lines, reframe their value propositions or fundamentally reinvent themselves.
Zack Onisko, CEO of Dribbble , calls design thinking the yin to lean startup ’s yang. The lean startup approach relies heavily on user analytics and A/B testing. Each approach has its advantages, he said, but starting with design thinking may be easier for younger, smaller firms not yet at the scale to adopt a lean methodology in earnest.
Embraces Creativity
In an article for the Harvard Business Review , Jeanne Liedtka, a professor in the University of Virginia’s Darden School of Business, cited a seven-year study of 50 projects from business, healthcare and social services sectors, in which she found “design thinking has the potential to unleash people’s full creative energies, win their commitment, and radically improve processes.”
Design thinking’s focus on assembling diverse teams to reframe problems and experiment helps “get around the human biases or attachments to specific behavioral norms that time and again block the exercise of imagination,” she added.
Phases of Design Thinking
Design thinking is an iterative, early-stage framework for creating products or building and structuring a business. For software companies , it often moves in step with a five-stage development cycle.
These stages are modular and do not have to occur in sequence — or even at all — and tend to work best at early stages of product development.
Design Thinking Process
- Test and implement
1. Empathize
This stage asks, “What is the problem you’re trying to solve?” It is an attempt to empathize with the needs and desires of current or potential users through in-depth interviews and close observation.
This step usually involves a succinct problem statement. The statement describes a product or feature that can realistically be built and assessed against strategic goals for growth.
During ideation, the product team, designers and software engineers brainstorm possible solutions to the problem. It is largely about prioritization and the ordering of ideas and intentions.
4. Prototype
This phase brings the idea into the world through the creation of physical models or digital wireframes and prototypes. By visualizing solutions on paper, teams can better identify potential issues or determine if the solution properly meets user needs.
5. Test and Implement
Product models are tested with users to see where the product is addressing problems and where it still might need improvement. Once a working prototype meets an agreed-upon standard, it is released into the wild. As user feedback is collected, the product is continuously improved to better meet customers’ needs.
Benefits of Design Thinking
Encourages empathy and customer focus.
Design thinking encourages practicing empathy and understanding a target user’s lived experience, which helps identify true user needs and avoid unintentional prejudice that might color decision-making. It also helps clarify how to talk about a product to potential customers, said Anders Wallace, a user experience and user interface designer at NBC.
At the early stages of the customer discovery process, gathering qualitative insights and “walking in users’ shoes” can form an organic understanding of a product problem from customer eyes.
Getting to know a customer and their concerns first-hand “translates into, strategically, what is the product we should make to help them,” said Jon Kolko, chief operating officer at design consultancy Modernist Studio (acquired by Gorilla Logic).
Fosters Creativity and Innovation
Design thinking leverages a flexible approach to problem solving, where solutions don’t have to be designed in a linear fashion. This allows teams to complete steps in any order they choose or delegate more time to certain steps over others based on their needs, making for possibly unique or innovative solutions. Additionally, design thinking encourages the sharing of ideas from multiple perspectives like designers, users and stakeholders to solve problems, making for various creative solutions that can arise.
Can Improve Return on Investment
Design thinking lets designers discover what solutions are most effective early on in a product’s development, reducing mistakes and making for a possibly higher ROI down the line. Without design thinking, a designer may make a product decision based only on quantitative data or perceived user wants, which can make for increased risk of product dissatisfaction upon release. Plus, design thinking’s ability to test multiple decisions before release means designers can invest properly into what their users need, instead of applying quick fixes or guessing on how to make a product succeed.
Challenges of Design Thinking
Lack of structure or focus.
While design thinking’s nonlinear nature can open the door for increased creativity, this can also lead to a lack of focused product vision and development structure. Utilizing design thinking for teams that aren’t already familiar with its practices can cause confusion or disorganization, which may result in unclear time and resource delegation, and even delay a product’s release entirely.
Can Be Time- and Resource-Intensive
Accounting for each step of the design thinking process can require extensive time, resources and expertise, making it possibly less-than-ideal for fast-paced business environments. Design thinking prioritizes gathering qualitative, often-interview based data in the ‘empathize’ phase of its process, which can take more effort to accomplish than using quantitative insights. Repeating prototyping and testing phases until finding the best solution can also demand more time than only carrying out one testing stage.
Can Be Difficult to Implement in Hierarchical Organizations
Design thinking can necessitate some upfront risk, creativity and increased collaboration amongst teams and users to make the practice effective. As such, this makes it potentially difficult to adopt for businesses with a hierarchical culture. A hierarchical organizational culture tends to be risk-averse and sticks to known procedures, which can restrict the innovative endeavors encouraged by design thinking.
Related Reading Decolonizing Design, Explained
How to Get Started With Design Thinking
Design thinking can be applied to almost any project to tackle a problem. To start, here’s a few ways to implement design thinking in product development or beyond.
Balance Customer, Client and User Needs
Design thinking as it ought to be practiced goes beyond the present-day functionality of a website or mobile OS, said Michael Schrage, a research fellow in MIT Sloan School’s Initiative on the Digital Economy who has consulted with Prudential, Pfizer, Microsoft, Amazon and Google on innovation and performance management. It looks to the future and asks the question: “Who do you want your customer to become?”
Schrage calls design thinking an “investment in the customer and clients’ capabilities, their creativity, their competence and their human capital.” He takes a broad, somewhat architectural view of who is equipped to be a designer and what their role is.
“What does architecture do? It balances the aesthetic with functionality. You can have ugly, brutalist buildings that stand up. And you can have beautiful, gorgeous buildings that fall down. To me, design thinking is about the balance you want to strike in the service of transforming your customer, transforming your client and transforming your user.”
Identify Staffing Needs
If you’re going to adopt a design thinking framework, it’s wise to do an internal audit of your staffing needs, said Marcello Magalhaes, founder and chief design officer at brand design firm Speakeasy . His firm helps clients like Coca-Cola, Fanta, McDonald’s and Burger King find the right creative talent for special product launches and branding campaigns — roles that often don’t exist in-house.
Design consultancies may offer firms this advantage, Magalhaes said: identifying unserved markets and acting as knowledge brokers who can keep costs down by leveraging their networks to recruit non-salaried talent with specialized skills.
“Instead of being in the cockpit, you want to be on the lookout for those who can sit in the cockpit,” he said.
Use Prototypes
Prototypes are key to striking balance between customer and client needs, Schrage said, but not in the way you might expect.
“The prototype is used not just to discover the functionality of the product, but the temperament and the typology and the preferences of the users,” he said. “In economics, we call this revealed preference. We don’t care what people say. We care what people do.”
Leverage User Insights and Personalization
Design thinking at its best happens at companies that leverage user insight to encourage customers to behave the way customers want, Schrage told Built In.
“In 2015, how many design thinkers said, ‘How do we want our user experience to learn about the customer?’ You can be sure they were asking that question at Amazon, at Facebook, at Google and, of course, at Netflix and Alibaba Group and TikTok,” Schrage said. “Everyone’s asking it now.”
Now recommendation engines are beginning to perform a similar function: learning about users and serving up customized features, advertisements and tooling options. This may be the direction design thinking is heading, converging with machine learning to influence customer behavior.
“That’s why we care about personalization,” he continued. “It’s wonderful to have software that learns about you. We don’t have to build a custom product for everyone. We build a product that learns about you better, and, through customization, you train the product for us.”
Frequently Asked Questions
What is design thinking.
Design thinking refers to human-centric approaches used to solve problems and address roadblocks in the design process. It can be applied to various types of problems inside and outside product design, and works to be solution-based rather than problem-based.
What are the 5 stages of design thinking?
The 5 stages of the design thinking process include:
What is an example of design thinking?
An example of design thinking is UberEats' app development, where the company has conducted interviews with partners during deliveries, restaurant workers during a rush and customers when ordering a meal to understand the needs of each party and implement features accordingly in its app.
Jessica Powers contributed reporting to this story.
Recent Visual Design Articles

New NPM integration: design with fully interactive components from top libraries!
22 Creative Design Thinking Exercises to Bring Your Team Closer Together

Design thinking exercises are crucial in fostering creative problem-solving, collaboration, and innovation. These exercises engage participants in a structured and iterative problem-solving approach, enabling them to explore, understand, and address complex challenges effectively.
Key takeaways:
- Design thinking exercises are structured activities or methods used to encourage and facilitate collaboration.
- These exercises foster creativity providing structured but open-ended frameworks for problem-solving.
- The list of design thinking exercises is huge; in this article, we elaborate on 22 of them.
Streamline design operations and enhance designer-developer collaboration with UXPin Merge. Visit our Merge page for more details and how to request access.
Reach a new level of prototyping
Design with interactive components coming from your team’s design system.
What is the Purpose of Design Thinking Exercises?
The primary purpose of design thinking exercises is to cultivate empathy and a deep understanding of users’ needs and perspectives. By encouraging participants to step into users’ shoes through empathy mapping and user interviews, design thinking helps uncover valuable insights that inform the design process.
These design thinking workshops create a user-centered environment that encourages collaboration and creativity. These activities empower design teams to challenge assumptions, explore diverse perspectives, and approach problems from multiple angles.
Design Thinking Exercises for Empathy and User Research
These design thinking activities enable teams to gain empathy and a user-centric perspective during the research phase, informing the design process and ensuring solutions align with user needs.
- Empathy mapping : Create visual representations of user perspectives by capturing their thoughts, feelings, actions, and aspirations. This exercise helps teams develop a deeper understanding of users’ experiences.
- Persona development : Create fictional user personas representing different user segments based on research and insights. Personas humanize user data, making it easier for teams to empathize and design for specific user groups.
- Customer journey mapping : Visualize users’ end-to-end experience as they interact with a product or service. This exercise helps identify pain points, opportunities, and moments of delight throughout the user journey.
Ideation and Brainstorming Exercises
Ideation and brainstorming exercises are essential to the design thinking process , aiming to generate a range of ideas and possible solutions. Designers use these exercises to foster creativity, drive collaboration , and explore new possibilities.
SCAMPER is an acronym that stands for S ubstitute, C ombine, A dapt, M odify, P ut to another use, E liminate, and R everse. This technique prompts designers to creatively explore different dimensions of a concept or problem, encouraging alternative perspectives and generating fresh ideas.
Brainstorming sessions
Brainstorming is a group activity that encourages free thinking and the rapid generation of ideas. Participants share their thoughts, build on each other’s suggestions, and explore various possibilities without judgment or criticism.
Crazy 8s is a fast-paced exercise that challenges participants to sketch eight ideas in eight minutes. This time-constrained activity encourages rapid ideation and pushes participants to think outside the box, resulting in diverse concepts.
Mind mapping and concept mapping
Mind mapping and concept mapping are visual techniques that help organize thoughts and ideas. By creating diagrams or visual frameworks, designers can explore connections, relationships, and associations between different concepts, stimulating further ideation.
Design studio workshops
Design studio workshops unite cross-functional team members to generate ideas and potential solutions collaboratively. Participants share their perspectives, expertise, and insights through structured exercises and facilitated discussions, resulting in more comprehensive and well-rounded concepts.
Worst possible idea
This exercise challenges participants to devise the worst possible ideas or solutions deliberately. By exploring extreme and unconventional concepts, designers can break free from conventional thinking and uncover unexpected insights or alternative paths.
The 5 Ws and H ( W ho, W hat, W hen, W here, W hy, and H ow) is a questioning technique that prompts participants to analyze and explore different aspects of a design challenge. By systematically considering these elements, designers can uncover new perspectives, identify potential gaps, and generate innovative solutions.
Prototyping and Testing Exercises
These prototyping and testing exercises offer valuable opportunities for designers to gather feedback, iterate on ideas, and validate design concepts.
Paper prototyping
Paper prototyping is a low-fidelity technique where designers create rough sketches or wireframe mockups on paper. This exercise lets designers quickly iterate and gather feedback on a design concept’s overall layout, content, and flow.
Designers can use paper prototypes to simulate user interactions and test usability, compiling valuable insights before investing time and resources into digital prototypes.
Role-playing and simulation
Role-playing and simulation exercises involve participants acting out specific scenarios or user personas to understand user needs and behaviors better. By immersing themselves in the end user’s perspective, designers can empathize with their experiences, identify pain points, and uncover opportunities for improvement.
Wizard of Oz testing
Wizard of Oz testing is a technique where designers simulate the functionality of an interactive system while manually controlling it behind the scenes. This methodology allows designers to test user interactions and gather feedback without investing time and resources in developing a fully functional prototype.
By creating the illusion of an automated system, designers can observe user behavior, validate assumptions, and refine the design based on real-time feedback.
Collaborative Exercises for Teamwork and Co-creation
Collaborative prototyping
Collaborative prototyping involves creating prototypes to test and validate design concepts within a day. Team members work in parallel on a single digital whiteboard and then collaborate using a design tool to build a prototype. By the end of the day, the team has a basic prototype to start the iterative process of prototyping and testing .
Co-design sessions
Co-design sessions bring together multidisciplinary team members and stakeholders to actively participate in the design process. These collaborative exercises foster teamwork and co-creation by leveraging the diverse perspectives and expertise of the participants.
By involving various stakeholders in the design process, co-design sessions facilitate shared understanding, generate innovative ideas, and ensure that the final design reflects the collective input and insights of the team.
Collaborative sketching
Collaborative sketching involves team members collectively sketching ideas and concepts on a shared surface or whiteboard. This exercise encourages open collaboration and rapid idea generation.
By visually expressing their thoughts, team members can communicate ideas more effectively, stimulate creativity, and spark discussions. Collaborative sketching promotes a sense of ownership while fostering teamwork.
Storyboarding and visual storytelling
Storyboarding and visual storytelling exercises help teams convey design ideas and concepts in a narrative format. This technique involves creating illustrations or images that depict user interactions, scenarios, or journeys.
Storyboarding allows teams to visualize the user experience and identify gaps or opportunities in the design. Teams can communicate complex ideas, align design directions, and create engaging user experiences.
Design charrettes
Design charrettes are intensive collaborative workshops where team members solve design challenges within a set timeframe. These super-efficient sessions encourage active participation, foster creativity, and promote collective problem-solving.
Design charrettes often involve brainstorming, rapid prototyping, and iterative design exercises. By engaging in focused and time-constrained collaborative activities, teams can generate ideas, explore design alternatives, and make significant progress in a short period.
Design Thinking Exercises for Reflection and Learning
Rose, Thorn, Bud
The Rose, Thorn, Bud exercise is a reflection activity that encourages participants to share positive aspects (roses), areas for improvement (thorns), and potential opportunities (buds) in a given project or experience.
Rose, Bud, Thorn helps teams identify strengths, address challenges, and explore new possibilities with a structured framework for reflection. The exercise enables team members to learn from past experiences and apply those insights to future iterations or projects.
Post-it voting
Post-it voting is a simple and effective technique to gather insights and prioritize ideas within a group. Participants write their ideas or suggestions on individual sticky notes and then vote on the most valuable or relevant ones.
This exercise promotes active participation and empowers team members to have a voice in decision-making. Post-it voting helps teams identify popular ideas, build consensus, and focus efforts on the most impactful concepts.
The Four Ls exercise ( L iked, L earned, L acked, and L onged for) provides a structured framework for reflection and feedback gathering. Participants share what they liked, learned, lacked, and longed for in a project or experience.
The Four Ls encourages constructive feedback, helps identify areas of improvement, and uncovers growth opportunities. The exercise promotes open dialogue and creates a safe space for team members to reflect on their collective experiences and identify ways to enhance future outcomes .
Retrospective exercises
Retrospective exercises are reflective activities conducted at the end of a project or iteration to evaluate the team’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
These exercises include team discussions, storytelling, timeline mapping, or even gamified approaches like “sailboat retrospective” or “stop, start, continue.”
Retrospectives foster a culture of continuous improvement by providing a dedicated space for teams to reflect on their successes, challenges, and lessons learned. These exercises enable teams to optimize processes, enhance collaboration, and evolve their practices.
Scale DesignOps With UXPin Merge
One of DesignOps’ biggest challenges is Merging design and development. These teams use different tools, speak different languages, and work with different constraints.
UXPin Merge aims to bridge that gap by bringing code components into the design process to create a Code-to-Design workflow . Designers and developers work with one component library from a single repository, creating a single source of truth across the organization.
This single source of truth eliminates many design system challenges , requiring fewer resources for product teams to scale and deliver products faster and with minimal errors or rework.
Scale your DesignOps– not your design team –with the world’s most advanced end-to-end design tool. Visit our Merge page to request access.
Use a single source of truth for design and development. Discover Merge
by UXPin on 24th July, 2023
UXPin is a web-based design collaboration tool. We’re pleased to share our knowledge here.
UXPin is a product design platform used by the best designers on the planet. Let your team easily design, collaborate, and present from low-fidelity wireframes to fully-interactive prototypes.
No credit card required.
These e-Books might interest you

Design Systems & DesignOps in the Enterprise
Spot opportunities and challenges for increasing the impact of design systems and DesignOps in enterprises.


DesignOps Pillar: How We Work Together
Get tips on hiring, onboarding, and structuring a design team with insights from DesignOps leaders.
We use cookies to improve performance and enhance your experience. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our cookie policy.

How To Run an Awesome Design Thinking Workshop

Design Thinking has become an extremely popular approach to problem-solving—not only among designers, but across all areas of business . A Design Thinking workshop will spark innovation, foster a user-centric mindset, and get cross-functional teams working together to design a great product .
Workshop facilitation is an important skill for any designer, but it can be tricky to master. In this guide, we’ll show you how to run an effective design thinking workshop.
By the end, you’ll be ready to take your colleagues (or clients) through the entire Design Thinking process , equipping them with the tools they need to come up with innovative strategies and ideas.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- What is a Design Thinking workshop?
- Why run a Design Thinking workshop?
- How to run a Design Thinking workshop (step-by-step)
Ready to run an unforgettable Design Thinking workshop? Let’s go!
1. What is a Design Thinking workshop?
A Design Thinking workshop is a hands-on, activity-based session built around the Design Thinking process. Most often, these are conducted in person, but you can certainly adapt and conduct a remote Design Thinking workshop .
It can last two hours, two days, or even a full week—it all depends on the context and the goals at hand.
Based on the five phases of Design Thinking, a Design Thinking workshop focuses on:
- Empathy: Getting to grips with a real user problem and building empathy for the target users / customers.
- Ideation, innovation, and problem-solving: Generating as many ideas and potential solutions as possible.
- Prototyping and testing: Building low-fidelity prototypes of the ideas generated, ready for testing on real or representative users.
Design Thinking workshops are all about collaboration and problem-solving. As a designer, you might hold a Design Thinking workshop with your direct team in order to tackle a tough design challenge you’ve been struggling with. However, Design Thinking workshops aren’t just for designers; they are also increasingly used to teach professionals how to innovate and problem-solve. Throughout your design career, you might find yourself running Design Thinking workshops for clients—going into different organizations and showing them how they can apply Design Thinking to their own business challenges.
Indeed, Design Thinking can be applied to all areas of business, and a Design Thinking workshop can therefore be useful for everyone—from marketing, product, and sales, right through to the C-level. Let’s consider the benefits of a Design Thinking workshop in more detail.

2. Why run a Design Thinking workshop?
As a designer, incorporating Design Thinking into your process will help you to quickly come up with viable, user-centric solutions—ultimately resulting in a quicker time-to-market, improved customer retention, significant cost savings, and a great ROI.
Design Thinking workshops enable you to spread this value across your organization (or your client’s organization). Here are some of the benefits at a glance:
- Teach people how to problem-solve: Problem solving is a key skill that everyone should master. A Design Thinking workshop teaches problem solving in action, giving the workshop participants an approach they can apply to almost any challenge in any area of their lives.
- Foster innovation and teamwork: The very essence of Design Thinking lies in collaboration and thinking outside the box. As a designer, these things are second nature to you; for others, it might not come so easily. A Design Thinking workshop breaks down silos and shows participants how to challenge their assumptions—a recipe for innovation!
- Secure a competitive advantage: A Design Thinking workshop may result in groundbreaking solutions that ultimately set the company apart—but competitive products aren’t the only takeaway. Design Thinking workshops teach creative thinking, which is increasingly seen as a competitive advantage when applied at a strategic level.
“Most companies today have innovation envy. They yearn to come up with a game-changing innovation like Apple’s iPod, or create an entirely new category like Facebook. Many make genuine efforts to be innovative—they spend on R&D, bring in creative designers, hire innovation consultants. But they get disappointing results. Why? We rely far too exclusively on analytical thinking, which merely refines current knowledge, producing small improvements to the status quo. To innovate and win, companies need design thinking .” —Roger L. Martin, The Design of Business: Why Design Thinking is the Next Competitive Advantage (2009)
All these benefits aside, Design Thinking workshops are incredibly fun and engaging. They bring together a diverse group of people from different departments and provide a rare opportunity to get hands-on with the problem.
So how do you go about setting up and facilitating a Design Thinking workshop? Let’s find out.

3. How to run a Design Thinking workshop: Step-by-step
Now we’ll go through all the necessary steps for running a Design Thinking workshop. We’ve divided this guide into two phases: how to plan and prepare for your Design Thinking workshop, followed by how to actually conduct the workshop .
Phase 1: Planning and preparation
To help with the preparation phase, we’ve put together a pre-workshop checklist (below). Further down, you’ll find more information to help you with each checklist item.
Pre-workshop checklist:
- Scope out the challenge and set workshop objective(s)
- Find a suitable location
- Plan the agenda (including time slots for each activity)
- Gather all necessary materials
1. Scope out the challenge and set objectives
There are many reasons you might hold a Design Thinking workshop; perhaps you need ideas for a new product, or maybe you’re looking for ways to improve an existing one. It could be that you need to come up with a drastic strategy for regaining consumer trust after a PR disaster! If you’re running a workshop for a client, perhaps the main purpose is to teach them about Design Thinking and how it can be applied to their business. In this case, you can still solve a real-world problem based on their product and industry.
Whatever the context, be clear on what the workshop should achieve. Let’s imagine you’re working for LoveFoundry, an online dating service. The goal of the workshop might be to come up with ways to improve the user experience for LoveFoundry customers.
For the purpose of your workshop, you’ll frame the challenge as a “how might we” question: How might we improve the user experience for LoveFoundry customers?
At the moment, this is a rather broad question. However, you’ve established the purpose of your Design Thinking workshop: to generate ideas for how to improve an existing digital product. Later on, you’ll narrow the design challenge down as part of the workshop itself.
2. Prepare the workshop location
Next, you need to create the optimal space for your workshop.
Design Thinking workshops should be dynamic and interactive, so it’s important that participants have plenty of room—especially when it comes to the prototyping stage. Ideally, you’ll have a separate table for all the materials and equipment (more on that in step three!).
Aside from comfortable seating and good lighting, you can create a relaxed environment by playing some background music. Another simple yet powerful touch is to position some thought-provoking artifacts around the room. If you’re running a workshop for a client, you might print display advertising campaigns from three of their biggest competitors, for example.
The purpose of a Design Thinking workshop is to get people thinking outside the box, so be sure to set up a space that invites creativity.
3. Plan your agenda
Now for the most crucial part: planning your workshop agenda. When tackling this somewhat tricky task, there are two golden rules to bear in mind:
- Don’t overfill your agenda.
- Keep it activity-based.
It might be tempting to cram in as much as possible, but the workshop will just end up feeling rushed—which is not conducive to creativity! Think about the time you have available and divide it up logically. Ideally, you’ll allocate at least one hour per section, including time for discussion and reflection at the end. You’ll also need to incorporate an introduction, an ice-breaker activity to get the group warmed up, and sufficient breaks throughout.
Another common error is to focus too heavily on presentations. A Design Thinking workshop should be largely activity-based; your participants need to be hands-on and engaged. The key is to deliver interesting, relevant content, followed by a practical exercise and then group discussion.
We’ll look at what to include in your workshop agenda in phase two of this guide a little further down.
4. Gather all necessary materials
With your agenda in place, you should now have a good idea of what you’ll need for the workshop.
Part of the workshop will be dedicated to building low-fidelity prototypes, for which you’ll need a good selection of materials. Opt for simple, everyday materials that everyone is familiar with—such as white copy paper, colored construction paper, sticky tape, marker pens, and Post-it notes.
It’s also a good idea to have a camera on-hand so you can document the workshop. This is extremely helpful when it comes to reviewing your workshop, and, if you’re running your workshop with clients, photos also make for a great souvenir.
With general preparation out of the way, let’s move on to phase two of our guide. In this section, we’ll explore your Design Thinking workshop agenda in more detail.
Phase 2: Executing your Design Thinking workshop
In phase one, we went through some general pointers to consider when devising the workshop agenda. Now we’re going to consider the agenda in more detail, going through all the elements that make up a successful Design Thinking workshop! We’ve also included time slots based on a 1-day workshop.
1. Introduction and briefing (15 minutes)
Start by welcoming everybody to the workshop and setting expectations. Some key points to include in your introduction are:
- Who you are (if you’re conducting a workshop with a client).
- The workshop objectives and the design challenge: e.g. To introduce the process of Design Thinking using a real-world design challenge: How might we improve the user experience for LoveFoundry customers?
- The workshop schedule.
This is also a good time to mention that you’d like to document the workshop by taking photos.
2. Ice-breaker activity (20 minutes)
It’s always a good idea to kick off the workshop with an ice-breaker. This will put everybody at ease before the real work begins!
Here are some fun ice-breaker activities you might like to use:
- One truth, two lies: Get everybody up on their feet and standing in a circle. Each person takes it in turns to tell one truth about themselves together with two lies. The rest of the group votes on which statement they think is true.
- One-word relay: The aim of the one-word relay is to construct a story as a group. You’ll all stand in a circle and take it in turns to add a few words to what the previous person has said. You should end up with a grammatically sensical yet completely random (and hilarious) story.
- Five-minute portraits: Give each participant a piece of paper and a felt-tip pen. The group has five minutes to doodle a portrait of another workshop participant of their choice. At the end, each person presents their portrait; can the rest of the group guess who it’s supposed to be?
For more inspiration, check out this list of 26 ice-breaker games and activities .

3. Introduction to Design Thinking (20 minutes)
If you’re conducting a Design Thinking workshop with clients or colleagues from other departments, you’ll need to get everybody up to speed on what Design Thinking actually is.
This can be a brief presentation covering the following points:
- A definition of what Design Thinking is. We’ve covered the fundamentals of Design Thinking in this guide .
- The five phases of Design Thinking, together with a quick explanation of each: Empathise, define, ideate, prototype, and test.
- The benefits of Design Thinking. This might be a good time to share some interesting stats—for example: teams that are applying IBM’s Design Thinking practices have calculated an ROI of up to 300% .
- A real-world Design Thinking case study, such as the Rotterdam Eye Hospital case .
By now, you’ve set the scene and put everybody at ease. This is a good point to break for ten minutes before diving into the first activity.
4. Building empathy for the user (1 hour)
Understanding your end user’s needs is the first step towards innovation—and that’s the first message you’ll deliver in your Design Thinking workshop.
For the empathise phase of the workshop, you’ll encourage participants to step into the user’s shoes and really think about what they need from the product. Continuing with the example of LoveFoundry, our imaginary online dating service, let’s consider how you might construct the empathise phase.
- Presentation (10 minutes): What is empathy? Why is it so important to design for the user first? You can find lots of information about empathy in Design Thinking here .
- Activity—conduct user research (10 minutes): Normally, the empathise phase consists of conducting research with actual users. For your Design Thinking workshop, ask your participants to pair up and take it in turns to play the user. Provide them with some starter questions, such as: How would you describe your most recent experience with online dating? How did the experience make you feel?
- Activity—create an empathy map (10 minutes): Each participant divides their page into four quadrants: “says”, “thinks”, “does”, and “feels”. Based on what they observed in the previous activity, they’ll fill in each quadrant with hypothetical (or direct) quotes and observations.
- Presentation of empathy maps (20 minutes): Ask each participant to briefly present their empathy map to the rest of the group.
- Reflection and discussion (10 minutes): As a group, discuss what you’ve learned so far. This is also a good time for questions.
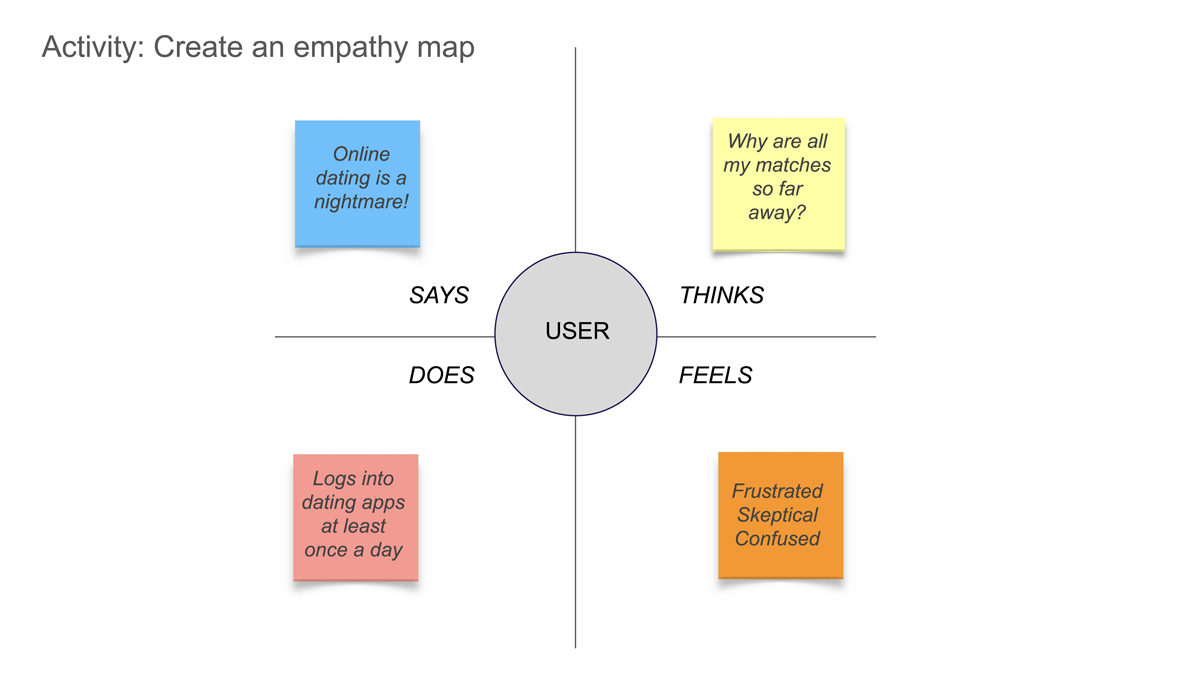
5. Define a problem statement (1 hour)
Next, you’ll move onto the define phase. This is where your participants will narrow down the broader design challenge (how might we improve the user experience for LoveFoundry customers?) to something more specific.
The define phase of your Design Thinking workshop might look something like this:
- Presentation (10 minutes): What is the define stage and why is it necessary? What is a meaningful problem statement? You can learn all about how to define a problem statement in this guide .
- Activity—craft a point of view (10 minutes): Based on their empathy maps from the empathise phase, ask participants to create a point of view statement. The point of view statement should include a specific user, a need, and an insight. For example: “A busy, middle-aged professional needs an easy way of meeting like-minded people in the local area. Safety is also an important factor.”
- Activity—reframe the problem as a “how might we” question (10 minutes): Now, participants will turn the user’s needs into a “how might we” question. For example: “How might we provide an easy, safe, online dating experience?”
- Presentation of problem statements (20 minutes): Ask each participant to share their problem statements and “how might we” questions, with a brief explanation as to why they decided to focus on this particular problem. You, the facilitator, will write each problem statement up on the board.
- Reflection and discussion (10 minutes): As a group, discuss what you’ve learned so far. Has everybody identified similar user needs, or is there lots of variety?
6. Ideation part 1: Generate ideas and potential solutions (1 hour)
The third phase in the Design Thinking process consists of ideation—coming up with ideas and potential solutions to solve the user’s problem.
Start by introducing an ideation technique of your choice. For this example, we’ll use the worst possible idea technique followed by a simple brainstorm. You can learn about different ideation techniques in this comprehensive guide to ideation in Design Thinking .
You might break the ideation phase up as follows:
- Presentation (5 minutes): What is ideation? What ideation technique will the group be using today, and how does it work? Provide a few examples to help them get started.
- Activity—worst possible idea (10 minutes): Using the “worst possible idea” technique, ask the group to spend around ten minutes coming up with “anti-solutions” to the problem they’re trying to solve.
- Activity—coming up with solutions (10 minutes): Having explored the opposite of what would be helpful to the user, it should now be easier to find potential solutions. Get the group to spend another ten minutes brainstorming as many ideas as possible. They can use words or sketches.
- Activity—sharing ideas and getting feedback (10 minutes): Ask participants to pair up and share their ideas. This step is all about gathering useful feedback: Are the ideas good? Why, or why not?
- Activity—refining your solution (10 minutes): Incorporating what they’ve learned about the user and the feedback they received on their initial ideas, it’s time for the Design Thinkers to pull everything into one single solution. For this activity, encourage participants to sketch out their solution rather than using words.
- Reflection and discussion (5 minutes): As a group, discuss what you’ve learned from the ideation phase so far.
7. Ideation part 2: User journey mapping (1 hour)
Now you’ll introduce a key UX design tool into the mix: user journey maps.
As explained by the Nielsen Norman Group , a journey map is a visualization of the process that a person goes through in order to accomplish a goal. In the second part of the ideation phase, you’ll get your participants to compile a series of user actions into a timeline. Then they’ll add desires and pain-points for each step in the user’s journey, based on the one solution they decided on previously. For this part of the workshop, participants will need plenty of Post-it notes and a large surface to work on—such as a table, wall, or whiteboard.
You can divide the journey mapping phase of your Design Thinking workshop into the following activities:
- Presentation (10 minutes): What is a user journey map? Why do we need to create one, and what steps are involved?
- Activity—define the activities and steps in the customer’s experience (15 minutes): Ask participants to write down all the steps they can think of that make up the user’s journey. For example: Downloads the app, creates an account, uploads a profile photo, browses through potential matches, receives a match, sends a message. For the last 5 minutes, participants should combine any steps that are too similar, narrowing it down to 8-15 steps.
- Activity—group the steps into phases (10 minutes): Participants will now group the steps from the last activity into phases, aiming for 3-7 phases in total. Phases should be labelled from the user’s perspective. For example: Getting started, browsing the app, interacting with other users , etc.
- Activity—adding goals and pain-points (15 minutes): Ask participants to come up with goals and pain-points that relate to each step in the user journey. Goals are what propel the user from one step to the next, while pain-points prevent the user from moving forward. For example: The step “browses through potential matches” could be propelled by the user goal of wanting to meet new people. A pain-point could be that they don’t find any suitable matches in the local area.
- Sharing user journey maps, reflection and discussion (10 minutes): At the end of the ideation phase, put ten minutes aside for presenting and reflecting on all the user journey maps created.
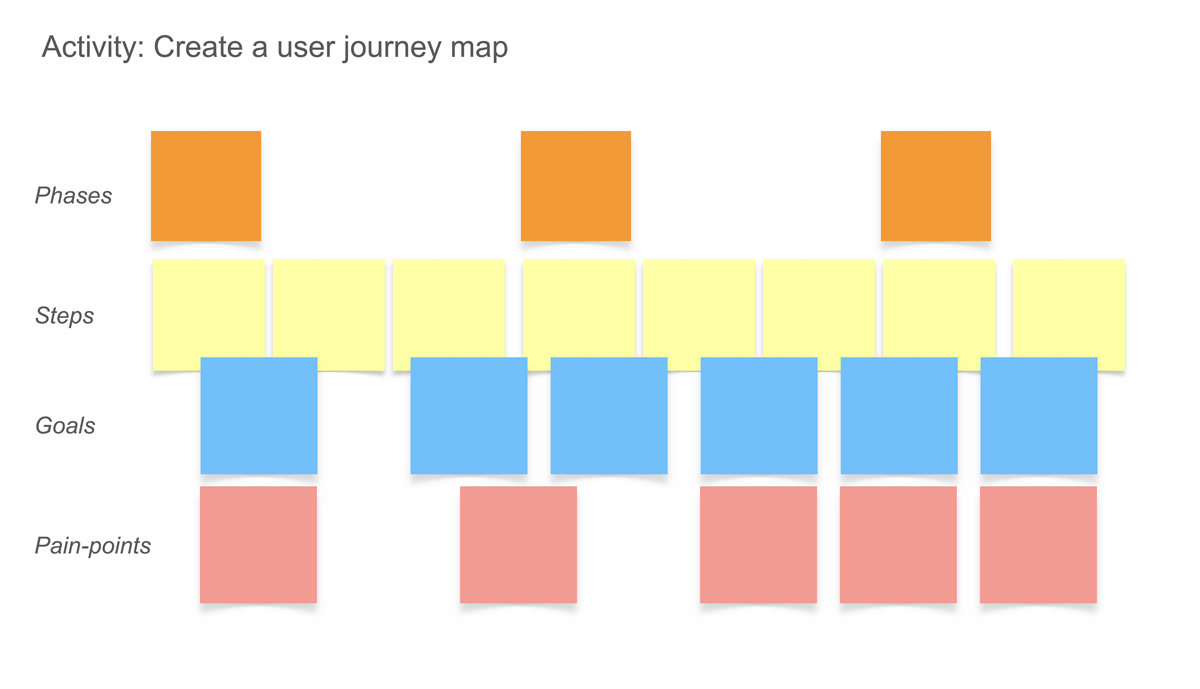
8. Prototype and test ideas (1 hour)
Now for the fun part: building prototypes and testing ideas!
In this section of the workshop, participants will turn the steps from their user journey maps into digital screens for an app. They’ll then gather feedback from the rest of the group. Here’s an example of how you might run the prototyping and testing phase:
- Presentation (5 minutes): A brief introduction to prototyping and the materials needed for the following activities.
- Activity—create mobile screens (15 minutes): For each step in the user journey, participants will sketch out the user interface (i.e. the mobile screen) that would be needed for this step. Encourage participants to use one piece of paper per screen; this way, they won’t need to start over completely if one goes slightly wrong.
- Activity—add functionality to mobile screens (15 minutes): Now participants will turn their sketches into low-fidelity paper prototypes by adding functionality. Using Post-it notes, they’ll describe the functionality of each button; for example “adds item to basket”.
- Activity—user testing (15 minutes): Ask participants to spend some time with each member of the group, walking them through their designs and gathering feedback . Recommend using a feedback grid with the following quadrants: what worked, what could be improved, questions, and ideas.
- Activity—decide on a winning approach (10 minutes): Once the user testing round is complete, stick all design solutions up on the wall. As a group, you’ll now decide on a winning approach. Ask each participant to place a sticker on the idea they think is best.
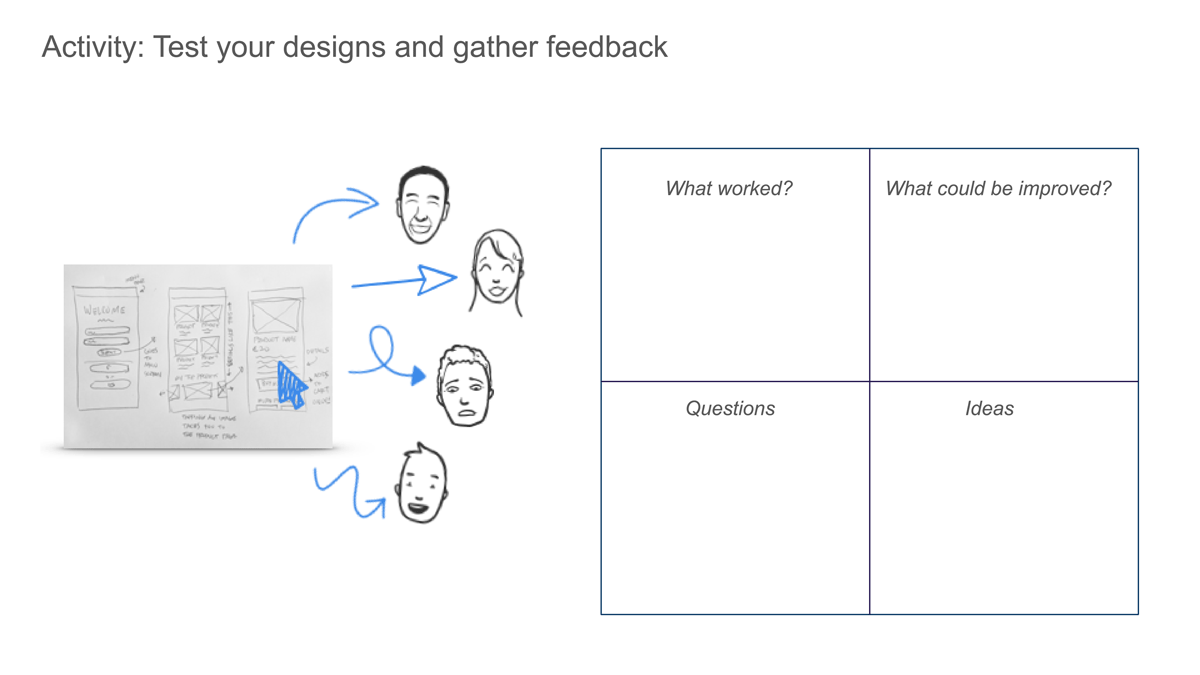
9. Debrief and outline next steps (15 minutes)
Round off your Design Thinking workshop with a quick debrief. Participants should come away with an understanding of how Design Thinking can be used in the real world, so explain what would usually happen next—turning paper prototypes into wireframes and, eventually, clickable prototypes to be tested on real users, for example.
Dedicate the last ten minutes or so to reflection and discussion. Ask your Design Thinkers how they enjoyed the workshop and what they’ve learned. Was there anything that surprised them? What will they take away with them?
4. Running a Design Thinking workshop: What next?
Congratulations: you’ve just conducted an engaging, informative, and extremely valuable Design Thinking workshop! So what next?
If you are new to the world of workshop facilitation, you can apply some Design Thinking principles to the process itself. Take a user-centered approach and ask your participants for feedback. A great way of gathering feedback is to send a “thank you for taking part!” email together with a survey link. You can also include any good photos you took of the workshop.
Like any design project, be sure to continuously iterate and improve upon your Design Thinking workshop. If you’d like some examples of design thinking in the real world, check this out: 5 Game-Changing Examples of Design Thinking .
For a video overview of how to run a design thinking workshop remotely , be sure to check out this guide:
And for further reading, check out the following resources:
- How to Run a Remote Design Thinking Workshop (with Brittni Bowering)
- A Guide To User Testing In Design Thinking
- What Is Human-Centered Design? A Beginner’s Guide
- A Comprehensive Guide To Lean UX
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

- Colleges & Degrees
- Academic Calendar
- International Education
- Graduate Studies
- Accreditation
- Tuition and Fees
- Parking & Maps
- Careers with CSULB
- Alumni Home
- Alumni Volunteering
- Alumni Giving
Campus Life
- Centers & Organizations
- Commencement
- Student Life
- Office of the President
- Office of the Provost
- Administration & Finance
- Student Affairs
- University Relations & Development
- Information Technology
- Beach Shops
- Campus Directory
- Enrollment Services
- Financial Aid
- Schedule of Classes
- Student Records
- 49er Foundation
- Research Foundation

1250 BELLFLOWER BOULEVARD LONG BEACH, CALIFORNIA 90840 562.985.4111
David Teubner 2024 Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award Recipient
Associate Professor David Teubner is the 2024 recipient of the CSULB Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award. Dave has been an influential leader in the Design Department and a dedicated leader in the Industrial Design program. He is passionate about design and has worked in the field since 1980 in animation, film production, advertising, and industrial design. Dave instills design thinking and problem-solving in all his courses, the use of technology, and is now incorporating AI into his curriculum.
The University Achievement Awards were held on Wednesday, April 24, 2024, at The Pointe on CSULB campus with Dr. Karyn Scissum Gunn, Provost & Senior Vice President; Simon Kim, AVP, Research and Development; and Pei-Fang Hung, Chair, Academic Senate presiding. Our sincere congratulations go to Associate Professor David Teubner on receiving the prestigious award. For the full story: https://www.csulb.edu/office-of-the-provost/university-achievement-awards

- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

Obstacles to Problem Solving and Innovation in Design Thinking
Understanding the obstacles that prevent teams from reaching innovative solutions that solve underlying problems is a very important aspect of the Design Thinking process. When we ignore a major influencing factor while trying to develop a solution, we are setting ourselves up for a potentially negative result, or may even be creating an even more problematic situation than the one we are trying to resolve. To ensure your team has the optimum working environment for problem solving, let us look at the most common obstacles to problem solving and innovation — as well as a few simple steps you can take to prevent them.
Obstacles to Problem Solving
The following list of factors, though not exhaustive, represents some of the obstacles to achieving innovative solutions to the challenges we face. The more obstacles we encounter within a problem space , the more difficult the path to innovation. Our goal should always be to create a space where obstacles are understood and removed or neutralised while exploring solutions.
- Individual people
- Impulsive reactions
- Man with a hammer syndrome
- Team construction
- Power structures
- Organisational constraints and power structures
- Environment
- Sustainability
If the list above seems long and broad, that’s the whole point . Hundreds of factors can influence how conducive a team can be when solving problems, so it is extremely important to be cognizant of how small and seemingly unimportant factors can adversely affect your team’s progress. While it is not efficient to consider and analyse each and every factor in full, you should nevertheless put them at the back of your mind when working on a project.
Let us elaborate further on the most common obstacles teams face when trying to solve a problem.
Impulsive Reactions
When confronted with a challenging situation, we tend to want to be spontaneous in our reactions. The instinctive mentality is that we should strike, and strike fast, if we want to solve a challenging problem. We tend to pinpoint obvious superficial factors and attack them directly, without reviewing subtle and perhaps more influential factors. We might individually attack symptoms of problems, when the more appropriate solution would be to understand the situation as a group before attempting to apply a solution. Similarly, any one problem may comprise a tangled complex of sub-problems; striking at one of these may ‘seem’ to solve it, but doing so may have deep-reaching effects that can complicate tangent sub-problems and make the whole thing even more problematic. This impulsive urge to jump into a problem and quickly solve it can be a stumbling block in your project, because a truly useful and impactful solution requires a deep, empathic understanding of the problem. Consequently, it takes insight and restraint to overcome this impulse. While it feels good to be doing something about a problem, remember that “doing something” doesn’t have to mean taking a potentially brash action. The danger here is to mistake careful analysis for wasting time, as it seems to be far less proactive-looking and lacks the glory of a good, quick strike back that shows the problem solver can think on his feet.
Indeed, the very first reaction is rarely the most appropriate in problem solving, unless the problem is so familiar and frequent that one has become an expert in patching it quickly. Its reoccurrence may, however, indicate that the root has not been addressed — but that is another issue. Regarding being impulsive and diving in too soon, it prevents us from taking a bigger-picture view, from gaining deeper insight and from understanding how others view and experience the same problem.
Best practice: In order to solve a complex, wicked problem, you and your team need to resist the urge to react impulsively — whether it’s to solve the obvious, superficial factors quickly, or to develop the very first idea into a full product directly — and learn to dive deep and develop a holistic understanding of the problem, before starting to ideate the possible solutions to it.

In order to solve a complex, wicked problem, you and your team need to resist the urge to react impulsively and learn to dive deep and develop a holistic understanding of the problem, before starting to ideate the possible solutions to it.
Egos Get in the Way
At times, we can be our own worst enemies when it comes to working in teams trying to solve problems. If we're focused on ourselves, showing off, on egos and asserting ourselves over others, we will most likely run into issues. Not only will there almost definitely be conflicts within the team, we will also tend to fall in love with our own ideas and refuse to accept it when tests indicate that the solution is not working with the target users.
Solving problems with others requires a sincere desire to achieve the objectives together. It requires a degree of humility and excellent people skills as well. When individuals are more interested in asserting themselves over others, flexing their authority, experience or creative muscles and proving a personal point, the group will suffer and the solutions or ideas that are being forced through may not be the most appropriate. Someone’s vanity will therefore dilute the team’s effectiveness.
Best practice: The most successful problem-solving spaces provide room for each player or actor to present his/her views, thoughts, feelings and experiences, thereby allowing a more holistic approach to solving the problem. There should be no room for egos in an innovative design project.
As you may have noticed, the word “holistic” has popped up quite a few times already — and will likely appear many more times in any Design Thinking article you read. That’s because it’s one of the core aspects of the Design Thinking mindset. It's one of the words you should definitely stick up on the wall close to your thinking and working space if you want to apply Design Thinking. HOLISTIC!

We all agree, so it must be right... right? Wrong!
Groupthink is a phenomenon that occurs when the desire for harmony or conformity in the group results in a dysfunctional or irrational decision-making outcome. When working in groups, we find in many cases that people will agree with group decisions due to self-confidence issues, a kind of group peer pressure, or fear of having an opposing view rejected. But groupthink does not only occur due to negative reasoning. It may result from the desire towards a more cohesive group dynamic by avoiding conflict or controversy. Individuals consider expressing loyalty to the group to require avoiding views which may be out of sync with what the group has achieved consensus on.
Groupthink is especially dangerous when it comes to a Design Thinking project, where the team is focused on creating an innovative solution to combat a tricky problem. In Design Thinking, it is crucial to iterate and to base your decisions on user testing and understanding; with groupthink, your team might suppress dissenting viewpoints and be less critical when evaluating ideas.
Best practice: In order to avoid this scenario, team managers need to create a safe and playful space for individuals to express themselves, throw ideas out there, and not feel targeted. No-one must be allowed to dominate while ideas are being brainstormed. The right mentality must be adopted at the beginning of the project, where critiques of ideas are never made personal (and should never feel personal). Of course, during later stages where ideas are evaluated and chosen for their appropriateness, a more critical approach should be taken rather than adopting a conforming mindset.
Man with a Hammer Syndrome
As the saying goes, “to the man with a hammer, every problem looks like a nail.”
We approach problems based on the toolset which we feel most comfortable with and most skilled at. Engineers, doctors, teachers, developers, and politicians may all have tendencies to want to exercise their core skills or experience within their own field. This may not be the correct approach to solve a specific problem, and it may not be a means to achieve the desired objective, especially when the problem has multiple influencing factors which require, wait for it, Holistic thinking. At times, we need to look outside of our core tendencies, skills and experiences and approach the problem on its own level of need.
We tend to try to solve problems which appear similar to previously solved problems, using the same methods even though simpler or more optimal solutions may exist. It's part of how the human brain works in following familiar patterns, thereby reducing cognitive load . But when embarking on a Design Thinking project, it is important to abandon our tendencies to follow patterns, because the way the brain tries to help us reduce cognitive load is the very same one in which it inhibits our ability to think outside of the box!
Best practice: Creating cross-disciplinary teams will help solve this issue, as there will be many men with different kinds of hammers looking for different kinds of nails. It’s of course crucial that the team leader illuminates to all team members that all skills and mindsets are equally important so as to avoid power struggles. In this context the manager’s skills and ideas are as important as the newly employed designer’s are. Likewise, the web designer ’s, architect’s, and developer’s skills and ideas are equally important in a Design Thinking process.

As the saying goes, “to the man with a hammer, every problem looks like a nail.” We tend to try to solve problems which appear similar to previously solved problems, using the same methods even though simpler or more optimal solutions may exist. It's part of how the human brain works in following familiar patterns, thereby reducing cognitive load. 'Hammering Man' (1994) is a sculpture which is located in various cities.
It's a Bird; it's a Plane – Misdiagnosing Problems
We need to be sure we are diagnosing problems correctly, as treating symptoms may — as in the case of illnesses — not result in a cure but only temporary relief. In some cases, prescribing the incorrect medication to tackle a symptom may even cause a deepening of the root illness. As part of any human-centred design approach, digging deep into human experience uncovers more about the problems we face than if we only scrutinised things on a superficial level.
Best practice: It is when we immerse ourselves in all the factors that influence a situation that we gain a deeper understanding of the way forward. We need to be vigilant, fully focused and aware of the obstacles which could derail our progress while keeping our focus squarely on the destination.
The Take Away
Before we take on a Design Thinking project, it is important, firstly, to take note of the various obstacles that can prevent us from reaching a solution that really works. From our impulsive tendencies to react to problems quickly and solve them just as fast, to the threat of egos and groupthink, there are many potential pitfalls that teams should learn to avoid. Developing a holistic understanding of the problems that the target users face is a key element of Design Thinking, which is typically adopted to solve complex, wicked problems where multiple spheres and fields collide.
Creativity: Methods to Design Better Products and Services

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, what is design thinking and why is it so popular.
- 1.6k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

Stage 3 in the Design Thinking Process: Ideate

- 4 years ago
Stage 4 in the Design Thinking Process: Prototype

- 3 years ago
Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
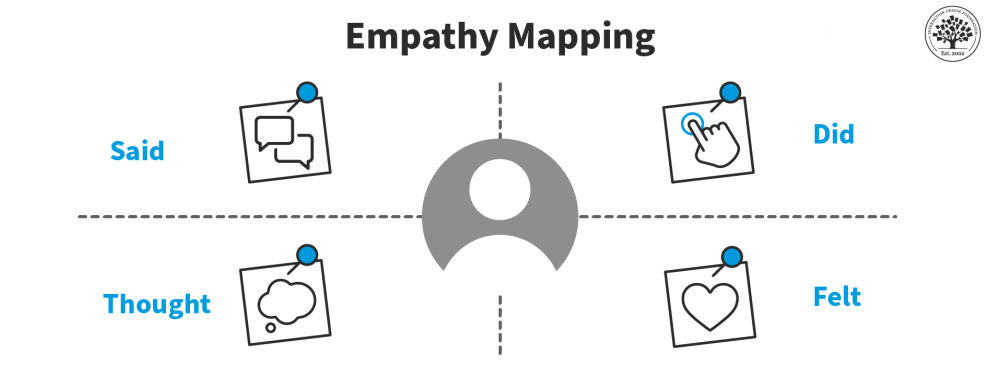
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- April 26, 2024 • 21:50 Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
- April 25, 2024 • 40:33 The Crackdown on Student Protesters
- April 24, 2024 • 32:18 Is $60 Billion Enough to Save Ukraine?
- April 23, 2024 • 30:30 A Salacious Conspiracy or Just 34 Pieces of Paper?
- April 22, 2024 • 24:30 The Evolving Danger of the New Bird Flu
- April 19, 2024 • 30:42 The Supreme Court Takes Up Homelessness
- April 18, 2024 • 30:07 The Opening Days of Trump’s First Criminal Trial
- April 17, 2024 • 24:52 Are ‘Forever Chemicals’ a Forever Problem?
- April 16, 2024 • 29:29 A.I.’s Original Sin
- April 15, 2024 • 24:07 Iran’s Unprecedented Attack on Israel
- April 14, 2024 • 46:17 The Sunday Read: ‘What I Saw Working at The National Enquirer During Donald Trump’s Rise’
- April 12, 2024 • 34:23 How One Family Lost $900,000 in a Timeshare Scam
Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out
New york’s highest appeals court has overturned the movie producer’s 2020 conviction for sex crimes, which was a landmark in the #metoo movement..
Hosted by Katrin Bennhold
Featuring Jodi Kantor
Produced by Nina Feldman , Rikki Novetsky and Carlos Prieto
Edited by M.J. Davis Lin and Liz O. Baylen
Original music by Dan Powell and Elisheba Ittoop
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
When the Hollywood producer Harvey Weinstein was convicted of sex crimes four years ago, it was celebrated as a watershed moment for the #MeToo movement. Yesterday, New York’s highest court of appeals overturned that conviction.
Jodi Kantor, one of the reporters who broke the story of the abuse allegations against Mr. Weinstein in 2017, explains what this ruling means for him and for #MeToo.
On today’s episode

Jodi Kantor , an investigative reporter for The New York Times.

Background reading
The verdict against Harvey Weinstein was overturned by the New York Court of Appeals.
Here’s why the conviction was fragile from the start .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Katrin Bennhold is the Berlin bureau chief. A former Nieman fellow at Harvard University, she previously reported from London and Paris, covering a range of topics from the rise of populism to gender. More about Katrin Bennhold
Jodi Kantor is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative reporter and co-author of “She Said,” which recounts how she and Megan Twohey broke the story of sexual abuse allegations against Harvey Weinstein, helping to ignite the #MeToo movement. Instagram • More about Jodi Kantor
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
— whether you work in team efforts like product development, service design, or program management, or individual pursuits like technical problem-solving in the stack or personal development. Questions don't DO the work, but they are critical to ensuring we're doing better and more impactful things along the way: doing the right work.
Questions guide you through these iterations. Problem Framing: Before diving into solutions, design thinking encourages an in-depth understanding of the problem itself. Your questions should focus on framing the issue from multiple perspectives. Collaboration: Design thinking is a collaborative effort.
It is the concept of Framing and Reframing the design problem. In short, problem framing is about uncovering the actual problem worth solving - which is often hidden to everyone when the design process begins. Framing and reframing are essential elements of design because "it is often not at all clear what 'the problem' is, it may have ...
The term "Design Thinking" dates back to the 1987 book by Peter Rowe; "Design Thinking." In that book he describes the way that architects and urban planners would approach design problems. However, the idea that there was a specific pattern of problem solving in "design thought" came much earlier in Herbert A Simon's book, "The Science of the Artificial" which was published ...
The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you develop solutions in a human-focused way. Initially designed at Stanford's d.school, the five stage design thinking method can help solve ambiguous questions, or more open-ended problems. Learn how these five steps can help your team create innovative solutions ...
Design thinking is an innovative problem-solving process rooted in a set of skills.The approach has been around for decades, but it only started gaining traction outside of the design community after the 2008 Harvard Business Review article [subscription required] titled "Design Thinking" by Tim Brown, CEO and president of design company IDEO.
Great Questions Lead to Great Design: A Guide to the Design-thinking Process. Great designers help teams and stakeholders make better decisions by using questions to identify opportunities, reveal underlying needs, and understand user context—all of which lead to better designs. authors are vetted experts in their fields and write on topics ...
Table of contents. What are the 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process. Stage 1: Empathize—Research Your Users' Needs. Stage 2: Define—State Your Users' Needs and Problems. Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas. Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions. Stage 5: Test—Try Your Solutions Out.
The proof is in the pudding: From 2013 to 2018, companies that embraced the business value of design had TSR that were 56 percentage points higher than that of their industry peers. Check out these insights to understand how to use design thinking to unleash the power of creativity in strategy and problem solving. Designing out of difficult times.
To solve these new, complex problems, Design Thinking steps in with a bold and newly systematised, non-linear human-centred approach. Design Thinking allows us to adopt a human-centred perspective in creating innovative solutions while also integrating logic and research. In order to embrace Design Thinking and innovation, we need to ensure ...
Design Thinking is a problem-solving framework. Unlike other brainstorming methods, design thinking uses empathetic observation to focus on human-centered needs first before diving into ideation. The process of design thinking is derived from the methods that designers, architects, and engineers all use to do their work.
In the Design Thinking process, this step is what's known as the "define" stage. As the second step in the Design Thinking process, the define stage is where you'll establish a clear idea of exactly which problem you will solve for the user. You'll then shape this into a problem statement which will act as your northern star ...
Design thinking involves human-centric approaches used to solve problems throughout the design process. It is applied in user experience (UX) design and user interface (UI) design to create products specifically with user needs in mind, and focuses on being solution-based rather than being problem-based.
These exercises foster creativity providing structured but open-ended frameworks for problem-solving. The list of design thinking exercises is huge; in this article, we elaborate on 22 of them. Streamline design operations and enhance designer-developer collaboration with UXPin Merge. Visit our Merge page for more details and how to request access.
6. Ideation part 1: Generate ideas and potential solutions (1 hour) The third phase in the Design Thinking process consists of ideation—coming up with ideas and potential solutions to solve the user's problem. Start by introducing an ideation technique of your choice.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Defining your design challenge is probably one of the most important steps in the Design Thinking process, as it sets the tone and guides all of the activities that follow. In the Define mode, you should end up creating an actionable problem statement which is commonly known as the Point of View (POV) in Design Thinking. You should always base your Point Of View on a deeper understanding of ...
If you get stuck you can read my two-part articles (part1 and part 2) about solving these classical system design questions. 2. How do you design a URL Shortening service like goo.gl or bit.ly ...
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues.You may face challenges around growth, design, user engagement, and even team culture and happiness.In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team's skillset.
2. Tell me about a time when you faced an unexpected challenge at work. Tip: For this question, you'll want to choose a specific example from your work history to demonstrate your ability to be flexible while solving problems. To stay focused, you can use the STAR method to answer this question.
Demonstrating your ability to tackle challenges effectively can set you apart from other applicants. Here are five tips to help you showcase your problem-solving skills during an interview: 1. Use the STAR Method. Structure your responses using the Situation, Task, Action, and Result (STAR) method.
Rabbit R1 design. The Rabbit R1 is a compact, cute, pocketable gadget with a 2.88-inch screen. ... Identify objects and answer questions about them. ... Problem solving with the 'Rabbit Eye'
Associate Professor David Teubner is the 2024 recipient of the CSULB Distinguished Faculty Teaching Award. Dave has been an influential leader in the Design Department and a dedicated leader in the Industrial Design program. He is passionate about design and has worked in the field since 1980 in animation, film production, advertising, and industrial design. Dave instills design thinking and ...
Understanding the obstacles that prevent teams from reaching innovative solutions that solve underlying problems is a very important aspect of the Design Thinking process. When we ignore a major influencing factor while trying to develop a solution, we are setting ourselves up for a potentially negative result, or may even be creating an even more problematic situation than the one we are ...
January 31, 2022. Once again, Musk announces that Cybertruck production is delayed again to late 2022 due to various design and manufacturing challenges.. November 1, 2022. Unsurprisingly, Tesla ...
Harvey Weinstein Conviction Thrown Out New York's highest appeals court has overturned the movie producer's 2020 conviction for sex crimes, which was a landmark in the #MeToo movement.