IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address

Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
- Technologies
- Privacy Policy
Latest Research topics in vlsi design
Latest research topics in vlsi design.
If we narrow down our discussion to research in areas like electronics, electrical, computer science, artificial intelligence , wireless communication and related fields, which are the base of everything in this high-tech world. In these fields researchers have developed applications (aided with technology) for every field ranging from biomedical to aerospace and construction, which were nowhere related to electronics or even current.
As the research fields we are talking about are providing base to the developing world and providing it with reliable technologies which are being used in real time, the work of researcher becomes more wide starting with an idea to the realization of the idea in the real world in form of application or product.
To make a reliable and working model the idea of the VLSI design project ( i.e speech processing application, biomedical monitoring system etc) needs to be implemented and re-implemented, re-tested and improvised. The there are many development cycles and techniques available which eases up the implementation like:
- Behavioral simulation
- Software based model
- Hardware Implementation (ASIC)
- Programmable hardware (FPGA)
- Co-simulation
Behavioral simulation is used at initial phase and it is not appropriate for testing the real time behavior of the system in actual environment as it is more close to systems behavior in ideal environment.
We can simulate the actual environment by using different software models (more like software models of channels used to test communication systems) but its capabilities are also limited to human capability to model the environmental conditions in mathematical equations and models.
All of us are familiar with ASIC, their high performance and hardwired implementation. These are good for final implementation but not for intermediate stages of implementation and testing. Nothing is better than ASIC for real time testing of analog VLSI circuits. But for digital circuits and DSP applications we have a better option of FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array).
The hardware co-simulation is a good idea to test and monitor systems in real time. To get more details about PhD thesis in VLSI you can do online research or contact us.
latest Low power research topics in vlsi design
The Research Support Centre provides expert advice and support across the whole Engineering and Technical research lifecycle, from discovery through exploitation of technical and translational research. The centre has two primary functions:
- i) to facilitate the delivery of the Engineering Sciences research strategy and to build partnerships andii) to bring together all the technical research management and support services for Students.
To achieve these goals the centre is made up of two inter-relating components. The Academic Research Support Centre consists of the Research Coordination Office, Platform Technologies team and a Translational Research Office. The Technical Research Support Centre is made up of the Joint Research Office.
The Research Support Centre encompasses a wide range of expertise and facilities. By coordinating these resources, we can provide researchers with a package of support that is integrated, high quality and streamlined – and clearly accountable.
Once a researcher has a proposal for high quality research that will benefit, they can access all the help and resources they need through one gateway. This includes support with the approval process and funding applications and help setting up technical trials.
VLSI PHD Projects
Our research interests cover low power processor architectures, low power circuit design techniques, analog and mixed signal circuit design, rapid prototyping of digital systems, reconfigurable processors, Digital arithmetic, advanced processor architectures, vlsi implementation of signal and image processing algorithms, testing verification, memory design, Embedded vlsi and asynchronous circuits.
Organization engaged with embedded commodity development and serving various business solutions such as
- Embedded System Product Development,
- Software services,
- Android development,
- Web development.
Description for “Ph.d guidance with project assitance” Ph.d/ M.Phil PROJECT ASSISTANCE We look forward to welcoming you to one of our “Research and Development Division” for all Ph.D., Research scholars. We will arrange you the following details for completing your Ph.d Degree
- Any University Admission- We provides a step-to-step guide to completing the application form, and will help make the process as straight forward as possible.
- Guide Arrangement
- Survey Paper Preparation
- Problem Identification –Problem Identification of Existing System.
- Implementation in all domains
- Mobile Ad hoc Networks
- Wireless Networks
- Image Processing
- Grid Computing
- Distributed Computing
- Natural Language Processing
- Cloud Computing
- Soft Computing
- Data Mining
- Wireless Senor Networks
Delivering effective support on your Ph. D work:
Companies represents a simple and practical advice on the problems of getting started, getting organized with the working on Ph.D projects.
We make you understand the practicalities of surviving the ordeal. We just make you divide the huge task into less challenging pieces. The training includes a suggested structure and a guide to what should go in each section.
We afford complete support with real-time exposure in your Ph.D works in the field of VLSI. Our Mission drives us in the way of delivering applications as well as products with complete integrity, innovative & interesting ideas with 100% accuracy.
- Assistance in ALL Stages of your PhD Research in VLSI from Topic Selection to Thesis Submission.
- Creating 100% confident in submitting your thesis work.
- Our experienced professionals support you in your research works.
- Providing complete solutions for the Research Scholars in many advanced domains.
Technologies used in VLSI:
- Modelsim 6.5b Simulator
- Xilinx ISE 10.1 System generator
III. Quartus 11.1
- Tanner v7 EDA tool
iii. W-Edit
- Microwind & DSCH v2
VII. P-spice
VIII. LT-spice
. Spartan IIIe
- Hardware Description Language
. Verilog HDL
CORE AREA OF GUIDANCE:
- Digital signal processing Vlsi
- Image processing Vlsi
III. Wireless Vlsi
- Communication Vlsi
- Testing Vlsi
- Digital cmos Vlsi
VII. low power Vlsi
VIII. Core Vlsi
- Memory Designs
PROJECT SUPPORT:
- Confirmation Letter
- Attendance Certificate
III. Completion Certificate
Preprocessing Work:
- Paper Selection
Identifying the problem:
- Screenshots
III. Simulation Report
- Synthesize Report
Report Materials:
- Block Diagrams
- Review Details
III. Relevant Materials
- Presentation
- Supporting Documents
- Software E-Books
VII. Software Development Standards & Procedure – E-Book
Learning Exposure:
VIII. Programming classes
- Practical training
- Project Design & Implementation
Publishing Support:
XII. Conference Support
XIII. Journal Support
XIV. Guide Arrangements
Vlsi based projects like image processing projects, low power projects, matlab with vlsi projects , cryptography projects, OFDM projects, SDR projects, communication projects, zigbee projects, digital signal processing projects, and also protocol interfacing projects like uart ,i2c,spi projects.
Signal and Image processing projects can be simulated by using Modelsim 6.5b and synthesized by Xilinx 10.1 using Spartan IIIe fpga and by Quartus 11.1using altera de2 fpga. In image processing projects, the input image or video can be converted to coefficients using Matlab. Low power projects can be designed using Tanner, Microwind and spice tools.
We spotlights on imparting an overall exposure to the concept and design methodologies of all major aspects of vlsi engineering relevant to industry needs and ground-breaking thoughts with 100% pure accuracy.
latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design low power testing bist latest research topics in vlsi design latest latest research topics in vlsi design area latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design

- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Implementation of NOR Gate from NAND Gate
- Implementation of NOT Gate using NOR Gate
- Digital Modulation Techniques
- How To Find Voltage In A Series Circuit
- Implementation of NAND Gate using 2 : 1 MUX
- Fermi Level
- Carson's Rule for Bandwidth Calculation
- Implementation of AND Gate from NAND Gate
- Truth Table
- Types of Rectifier
- NPN Transistor
- Series and Parallel Inductor
- Implementation of AND Gate from NOR Gate
- What is Noise Factor?
- N channel MOSFET
- Electronics and Communication Engineering
- Half Wave Rectifier
- Solid-State Lighting
- Implementation of OR Gate from NOR Gate
What is VLSI ?
VLSI (Very large scale integration) is a process of integrating hundreds or thousands of transistors onto a single silicon semiconductor microchip. In present years, contemporary VLSI technology Complex digital systems can now be realized on a single silicon chip. Designers of Custom systems find this technology, particularly attractive since it allows for significant cost reductions by compressing a large amount of digital logic complexity into a single chip.
The number of uses for integrated circuits (ICs) in high performance computing, telecommunications, image and video processing, and consumer electronics has been growing quickly since the introduction of very large scale integration (VLSI) designs. Silicon CMOS technology has emerged as the fabrication process within the last few years. The quick increase in transistors integrated into a single chip’s circuit illustrates the revolutionary significance of these developments.
Table of Content
Does VLSI need coding?
Vlsi design process.
- Design and Implementation
- Applications
- Disadvantages
VLSI stands for Very Large Scale Integration. It signifies the process of producing integrated circuits (ICs) by integrating thousands, millions, or even billions of transistors on a single chip. In VLSI, the technology has allowed progressive growth with composite and secure devices, beginning from microprocessors and chips of memory to processors of digital signal and application specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
The integrated circuits ICs are used in VLSI as a broad range of devices, from fundamental devices to advanced supercomputers . In VLSI design, Designers test and design the electronic integrated circuits at a very limited scale, so generally, it is in the range of 0.1 to 0.01 micrometres.
Design Specification, Architectural Design, RTL Design, Functional Verification, Logic Synthesis and verification, Physical Design and verification, sign-off and Fabrication of ICs are methods that are used in the VLSI design process. The layout of transistors and interconnections needs to be constructed and optimized on the chip, designers use authorized software tools to follow the layout of IC design to conserve the performance, power consumption, efficiency, and manufacturability into account.

Let’s understand the need of VLSI coding with different tools and techniques involved in VLSI:
- Yes, VLSI needs coding because it is used to make different complicated designs that are used in the IC’s which are enhanced in today’s life.
- Some circuits that are needed to make digital designs like simulation tools and verification are involved in the broad range of digital IC design tools.
- To ensure the digital design works properly, designers make use of IC design to test the circuits when devices of IC are fabricated.
- Designers make use of VLSI coding by using programming languages and tools involved in VLSI designing.
- HDLs (Hardware Description languages) such as Verilog and VHDL are involved for use in digital circuits by checking the behavior and functionality of digital devices.
- Some EDA tools like Cadence, Synopsys and Mentor Graphics are involved for the purpose to use in VLSI circuits for simulation the digital design.
- Some verification tools like emulation and simulation are involved for the purpose to make use of testing the functionality of VLSI circuits to make sure that they functions properly when the digital ICs are fabricated.
- In conclusion, VLSI technology involves the high number of transistors and other devices components on a single chip that is used for the design and fabrication.
- Y chart is developed by Gajski Kuhn that he developed a model named as Y chart that is used to checking the digital semiconductor devices.
- Gajski Kuhn Y chart has three domains that has to be put on radial axes.
- Various domains are divided into different areas like levels of abstraction using centered rings.
- The top level named as a outer ring, that explains the chip architecture, and the low levels named as a inner rings, to make the design and implementation in a better way by following techniques:
- The process of high-level synthesis or logical synthesis is involved for making a structural description from a behavioral description.
- The layout synthesis is involved for making a physical description from a structural description.

Gajski Kuhn Y Chart
A VLSI chip goes through several stages of VLSI design , from the chip’s specification to the final product’s fabrication. The following steps are involved in the design process:

VLSI design process
Design Specification
- Some specifications involved in VLSI design are power consumption, performance, and functionality and area of chip that are make used in the design specifications.
- Digital devices has some specifications in VLSI design like abstract description of the architecture that must to be designed.
Architectural Design
- After design specification, the architecture of chip is designed. So, to make the architecture of the design by some requirements of the functionality, performance, or general system requirements.
- In this design, all the connections and functions are specified by the component of the chip.
- Using integrated circuits (ICs), designing of electronic circuits is the Register Transfer Level (RTL) design at a high level description.
- The RTL description of the digital circuit is written in hardware description language ( HDL ) such as VHDL or Verilog, works as the input. The RTL description expresses the functionality and behavior of the circuit at a high level description.
Functional Verification
- Using simulation tools, It simulates the behavior and functionality of the integrated circuit in unique input cases and to meet the specified requirements by design verification to test the ASIC design .
- Our goal is to make sure that chip functions correctly by ensuring to test the ASIC design by verification so it’s behavior is managed by checking specifications and requirements of functionality of design.
Logic Synthesis
- Logic Synthesis defines the RTL code that transforms into a gate-level netlist by using synthesis tool, which represents the logical architecture of the circuit in terms of standard cells.
- Using HDL ( Verilog /VHDL), it produces a gate-level netlist that is a description of logic cells and their interconnections. These tools map the functionality described in the HDL to a set of standard cells or library elements.
- Performance, size, and power consumption of the design are all optimized during the synthesis process.
Logical Verification
- A verification is required to be performed to verify whether the synthesis tool produced the gate-level netlist accurately.
- The output of Logic synthesis are gate-level netlist that is given as input to the Physical design after verification and testing.
Physical Design
- In this step, gate-level netlist is converted into a physical layout. Layout is a representation of an IC in terms of planar geometric shapes which correspond to the patterns of metal-oxide or semiconductor layers that make up the components of the IC. A design tool like Cadence Virtuoso is used to create layouts.
- In physical design step, it is divided into sub-steps such as Partitioning, floorplanning, placement, clock-tree synthesis, routing, timing closure are formed.
Given below are the Steps for Physical Design:
- Partitioning: It is the process of dividing a system on chip (SoC) into small blocks. As a result, you can effectively manage semiconductor designs as a group of connected functional blocks. The best way to handle semiconductor designs is as related groups of functional blocks.
- Floorplanning: Floorplanning is a process of placing the various blocks and I/O ports across the chip area based on the design constraints. Floorplanning involves determining the physical layout of the IC on the semiconductor wafer or die.
- Placement : Placement involves assigning physical locations to the standard cells and other components on the chip according to the floorplan.
- Clock Tree Synthesis: It is the process of connecting the clocks to all clock pin of sequential circuits by using inverters/buffers in order to balance the skew and to minimize the insertion delay. A single clock source powers each and every clock pin. Clock Tree Synthesis is used to minimize delay and skew.
- Routing: Once every element is positioned, a detailed and global routing is started to establish connections between all the elements. It involves physically connecting metal traces to macros, standard cells, I/O ports, power, and the clock.
- Timing Closure: It is the process that determines a chip’s speed by satisfying the timing constraints. For a smoother chip operation, it makes sure that all of the signals arrive at the appropriate time. Timing closure involves ensuring that the circuit meets timing requirements, such as setup and hold times, clock frequency, and maximum propagation delays .
Physical Verification and Sign off
- This stage undergoes 3 steps of physical verification known as sign off checks.
- It helps to check whether the layout is working correctly the way it was designed to.
Given below are the Steps for Physical Verification:
- Layout v/s Schematic (LVS) :It is the process of verifying the layout is compared with the schematic whether their functionality matches or not.
- Design Rule check (DRC): It is the process of verifying whether the given layout follows the design rules given by the fabrication team. DRC checks implies to physical checks of spacing rules between metals, minimum width rules, etc.
- Logic equivalence checking (LEC): It is a formal verification technique used in VLSI design to verify that two different representations of a digital circuit, often an RTL description and a gate-level netlist, exhibit functional equivalence.
Fabrication
- Output of Layout is GDS-II (Graphical Data Stream Information Interchange) file produced and used by the semiconductor foundries to fabricate the silicon.
- After physical verification step, the design is ready for fabrication. Tape out is the final result of the design process for ICs before they are sent for manufacturing.
- The Tape out is specifically the point at which the graphic for photo-mask of the circuit is sent to foundry.
- Fabrication process consists of several steps involving wafer growth, epitaxial growth, etching, doping, deposition, and diffusion of various materials on the wafer. One mask is used during every step.
Packaging and Testing
- Each of the wafers contains hundreds of chips. The technique of “scribing and cleaving” is used to divide and package these chips. Chips that don’t pass an electrical test are discarded.
- Every chip is tested and packed to make sure it satisfies all design requirements and operates as intended.
Design and Implementation of VLSI
Let’s discuss the Design and Implementation of VLSI by learning the different aspects of IC design in various fields of digital circuit that comes under the VLSI domain:
Digital VLSI Design
- Transistors, logic gates and other electronic components are made by designing of digital circuits known as Digital VLSI design.
- Microprocessors, memory devices, controllers are the digital devices that comes in digital VLSI domain.
Analog VLSI Design
- Analog devices are involved in the process of processing continuous signals by designing and implementation of the analog circuits .
- Analog VLSI domain includes some devices like digital-to-analog converters (DACs), filters, oscillators, amplifiers, etc.
Mixed-Signal VLSI Design
- In mixed-signal VLSI, both analog and digital VLSI techniques are combined on a single chip.
- Both analog and digital VLSI techniques are combined oftenly in SoCs (System on Chip) so to ensure that both analog and digital devices are needed by complex system that is created for the mixed-signal VLSI.
RF (Radio Frequency) VLSI Design
- RF VLSI design involves the main aim of making the integrated circuits for wireless communication devices such as radios, transceivers, etc.
- For the aspect of applications, it involves the designing of circuits that has increased the efficiency for devices like Bluetooth, RFID, Wi-Fi, etc. that works at radio frequencies.
Low-Power VLSI Design
- Low power VLSI design is used to reduce the power consumption of integrated circuits that used in various applications like Internet of Things, battery operated devices and devices which are energy efficient.
- Some methods that are used to make use of low power VLSI operation are voltage scaling, power gating, clock gating, some devices which are energy efficient.
ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) Design
- The process of designing specialized integrated circuits for specific tasks or objectives is known as ASIC design.
- ASICs are suitable for specific applications including image processing, sensor interfaces, cryptographic algorithms, and automotive electronics as they improve performance, power economy, and area usage.
FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) Design
- FPGA involves some digital logic devices which needs to be configured and programming the FPGA design so to make the digital circuits by make use of configured digital logic devices.
- In FPGA design, some specific applications like prototyping, etc. are used for fast growth of FPGA design.
Applications of VLSI Technology
There are several applications for VLSI technology across numerous sectors and firms. These are some important fields in which VLSI is extremely significant.

Applications of VLSI technology
Consumer Electronics
- The creation of smartphones, tablets, gaming consoles, and smartwatches has been made possible by VLSI technology, which has completely changed the industry of consumer electronics.
- These products improve user experiences and productivity with their cutting-edge features, quick processing, and energy-saving technologies.
Automotive Industry
- VLSI technology has transformed vehicle functionality and safety in the automobile industry.
- VLSI chips are used by electronics systems, Engine Control Units (ECUs), and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) to provide functions including real-time vehicle diagnostics, autonomous driving, and object, lane, and sign detection.
Telecommunications
- The telecommunications sector has profited tremendously from VLSI technology. It has made it easier to construct 5G wireless communication, high-speed network infrastructure, and cutting-edge mobile devices.
- To provide dependable and quick data transfer, VLSI-based chips are utilized in network switches, routers, modems, and base stations.
- The development of medical imaging equipment, wearable health monitors, and implanted medical devices has been made possible by VLSI technology, which has had a substantial impact on the healthcare industry.
- Accurate diagnosis, real-time monitoring, and enhanced patient care are all provided by these electronic devices.
The Advantages of VLSI technology
- Compact Size: Traditional circuits are significantly greater than VLSI circuits because of electronic circuits are created to ensure the computation of digital logic circuits.
- Consumes less Power: VLSI circuits are better than Traditional circuits because VLSI circuits are eco-friendly. This is necessary for the battery life saving.
- High performance: By adding the high number of transistors on a chip so to accomplish VLSI circuits are high speeds with they perform complex tasks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By using VLSI technology, electronic circuits which are complicated that they are executed in large quantity. All the features and various components are implemented on a single chip. Electronic circuits are used and implemented because of their easy accessibility.
- Increased Reliability: Comparing to discrete devices, some short link and better manufacturing capabilities used by VLSI circuits because of their better reliability in terms of errors and failures.
The Disadvantages of VLSI technology
- Inflexible: Once fabricated, it is not easy to be modified and is not flexible.
- High Cost of Development: Design tools, development platforms, and testing equipment must be obtained in large quantities throughout the time-consuming and expensive process of developing VLSI devices. It can be challenging and expensive to alter the design since the circuits are specially designed and cannot be readily modified.
- Manufacturing Challenges: The quality and functionality of the finished product may be impacted by a number of manufacturing difficulties that VLSI devices are susceptible to, including yield loss, variability, and reliability problems.
- Time to Market: Longer time to market for new goods might result from the longer design, verification, and manufacturing cycles associated with VLSI devices.
- Short Product Life Cycle: VLSI design perceives rapid technological innovation, which may result in short product life cycles as new technology and products age quickly.
A crucial component of VLSI design is design flow, which offers an efficient and structured process for creating intricate integrated circuits. Designers can successfully navigate through the many stages of the VLSI design process and ensure the successful production of dependable and high-performing electronic systems by adhering to a clearly defined design flow. The design process needs to change as technology develops to be able to address the opportunities and difficulties of the future and produce creative and effective VLSI designs.
Electronics are revolutionized by the development of VLSI, which combines several transistors into a single chip. It makes gadgets faster, smaller, and more efficient viable. Commonly employed technologies comprise BJT, FET, and CMOS. Applications for VLSI can be found in consumer electronics, automotive, industrial automation, telecommunications, and healthcare. Power consumption and chip complexity are constraints. The research and development of new materials like graphene, embedded memory, and 3D integration are among the upcoming trends. As VLSI technology develops, new opportunities arise across a range of industries.
What is VLSI ? – FAQs
What is vlsi used for.
Millions of transistors are needed for manufacturing electronic components like memory chips and microprocessors, which are the primary uses for VLSI.
Is VLSI digital or analog?
VLSI technology includes both digital and analog design elements. Digital circuits are superior at carrying out intricate calculations and logical processes, but analog circuits are excellent at processing continuous signals precisely.
Which HDLs are utilized in VLSI?
Hardware description languages (HDLs) such as Verilog, System Verilog and VHDL, are used to describe the behavior and functionality of digital circuits.
Why Gate array design in VLSI is usually faster than prototype full-custom design?
Predefined standard cells, or pre-designed and pre-characterized building components like flip-flops, multiplexers, and logic gates, make up gate arrays. Because these standard cells have previously been produced and validated, designers can utilize them as the foundation of their ideas instead of needing to create unique transistor-level designs.
Why clock tree synthesis is done before routing?
Clock tree synthesis is performed before signal routing, to prevent congestion to the clock nets and to obtain an optimal timing skew.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Electronics Engineering - Verilog/VLSI
- Verilog-HDL
- Analog and Digital Electronics
- Electronics Engineering
- Google Releases ‘Prompting Guide’ With Tips For Gemini In Workspace
- Google Cloud Next 24 | Gmail Voice Input, Gemini for Google Chat, Meet ‘Translate for me,’ & More
- 10 Best Viber Alternatives for Better Communication
- 12 Best Database Management Software in 2024
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

HILTON HAWAIIAN VILLAGE HONOLULU, HAWAII JUNE 16-20, 2024
BRIDGING THE DIGITAL & PHYSICAL WORLDS with efficiency & intelligence
Add this year’s event to your calendar:
Microsoft Outlook Calendar | Google Calendar | Apple Calendar
The five-day event will include:
- Plenary Sessions, Technical Sessions
- Evening Panels
- Short Courses
- Demo Session for Outstanding Papers
- SSCS / EDS Women in Engineering & Young Professionals events
- Traditional Luau Celebration
The Symposium will feature selected presentations and panel sessions as well as advanced VLSI technology developments, innovative circuit designs, and the applications they enable, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, wearable/implantable biomedical applications, big data, cloud / edge computing, virtual reality (VR) / augmented reality (AR), robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
Hotel Reservation Open
COMING SOON!
April 17, 2024 Full Program & Registration

SYMPOSIUM CHAIRS
Gosia Jurczak, Lam Research
Borivoje Nikolic, University of California, Berkeley
SYMPOSIUM CO-CHAIR
Takaaki Tsunomura, Tokyo Electron Ltd.
Mototsugu Hamada, The Univ. of Tokyo
PROGRAM CHAIRS
Vijay Narayanan, IBM T. J. Watson Research Center
Ron Kapusta, Analog Devices
PROGRAM CO-CHAIRS
Kazuhiko Endo, Tohoku University
Sugako Otani, Renesas Electronics
CONTACT INFO
VLSI Secretariat North America and Europe
VLSI Secretariat Japan and Far East
CONFERENCE POLICIES
Notifications & Policies
Accessibility
Non-discrimination Policy
IEEE Ethics Reporting
IEEE Privacy Policy
Call for Papers
Ca ll for Workshops
Symposium Archive
© 2024 Copyright IEEE. All rights reserved. A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world’s largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity.
VLSI System and Computation Lab
WE ENGINEER EXCELLENCE
EE 260 Spring 2020: Advanced VLSI Design for Machine Learning and AI
Sheldon Tan ([email protected])
Office Hours: Thursday 3:00 to 4:00pm (better by appointment).
Office: WCH 424
Tuesday and Thursday from 11am to 12:20pm
Location:
Zoom meeting ID: https://ucr.zoom.us/j/983426494
Meeting ID: 983 426 494
One tap mobile +16699006833,,983426494# US (San Jose) +16468769923,,983426494# US (New York)
Dial by your location +1 669 900 6833 US (San Jose) +1 646 876 9923 US (New York) Meeting ID: 983 426 494
Teaching assistants
Sheriff Sadiqbatcha ([email protected])
Office Hour: Thursday 2:00pm to 3:00 pm (TA will attend each course, so better by appointment right after class)
TA Office Room: WCB 361
Prerequisite
Basic background in machine learning, VLSI designs
Course description
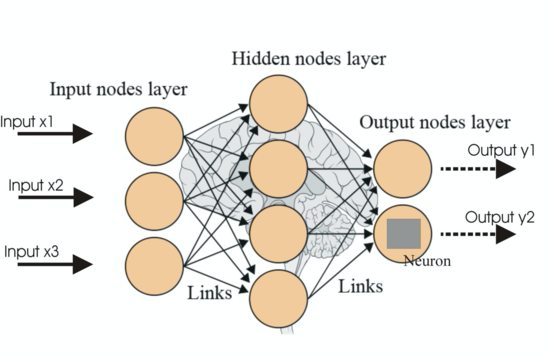
The course will introduce the advanced topics in modern VLSI IC design techniques and methodologies for emerging applications. Topic includes VLSI/FPGA design and optimization techniques for deep neutral network, approximate/stochastic computing, computing in memory, ML/AI-based approaches to VLSI design methodologies and emerging quantum/Ising computing.
Course background and description
The first working silicon transistor was invented at Bell lab in 1954 by Morris Tanenbaum and commercially produced by Texas Instrument in 1954 and it has been 62th anniversary of the invention. Recently machine learning, especially deep neutral networks (DNN) take us by storm as they propelled an evolution in machine learning fields and redefined many existing applications with new human-level AI capabilities. DNNs such as convolution neural networks (CNN) have recently been applied to many cognitive applications such as visual object recognition, object detection, speech recognition, natural language understanding, etc. due to dramatic accuracy improvements in those tasks. In this course, we will focus on recent advances in DNNs and how to design fast and power efficient DNN networks for many emerging applications and computing platforms. We also cover important topics such as approximate/stochastic computing, novel compute architectures and computing in/near memory techniques. We will also cover emerging machine learning design techniques for VLSI digital and analog circuit design. Important emerging topics such as quantum/Ising computing will be also covered. This course has a large emphasis on paper survey and seminar presentations of many important techniques.
Who can take the course?
Both EE and CS undergraduate and graduate students are welcome as VLSI design are fundamental knowledge and skills for hardware implementation of today's complicated systems.
Course topics and calendars
- Approximate and stochastic computing for machine learning
- VLSI architecture for deep neutral networks
- Computing in/near memory techniques
- Advanced design techniques for deep neutral networks
- Emerging adiabatic Ising and quantum computing
- Machine learning or AI of Thing (AIOT)
- VLSI architecture and circuit design for machine/deep learning
- Machine learning based techniques for Electronic Design Automation (EDA)
- Machine learning-based thermal modeling, analysis and control
- Machine learning-based reliability analysis and modeling
Reference book
Lecture notes and related papers.
Paper survey and presentations : 50%
Final project, project report and project presentation: 50%
All of them will be graded on the scale of 0 to 100 with 100 being the maximum score.
Each student (can form a team with no more than 2 people) need to work on a project in this course. The topics need to be approved by instructor.
VLSI Design Tutorial
https://github.com/sheldonucr/ee260_lab
Home works assignment will be issued through iLearn

VLSI Research Topics Ideas [MS PhD]
List of Research Topics and Ideas of VLSI for MS and Ph.D. Thesis.
- High-throughput VLSI architecture for soft-decision decoding with ORBGRAND
- Approximate Pruned and Truncated Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform VLSI Hardware for Energy-Efficient ECG Signal Processing
- ADMM-Based Infinity-Norm Detection for Massive MIMO: Algorithm and VLSI Architecture
- Evaluating the Performances of Memristor, FinFET, and Graphene TFET in VLSI Circuit Design
- VLSI mask optimization: From shallow to deep learning
- Area-Delay-Power Efficient VLSI Architecture of FIR Filter for Processing Seismic Signal
- A Novel High-Performance Hybrid Full Adder for VLSI Circuits
- PGOpt: Multi-objective design space exploration framework for large-Scale on-chip power grid design in VLSI SoC using evolutionary computing technique
- Testing single via related defectsin digital VLSI designs
- An Improved Impulse Noise Removal VLSI Architecture Using DTBDM Method
- VLSI Implementation of Multi-channel ECG Lossless Compression System
- A Scalable VLSI Architecture for Illumination-Invariant Heterogeneous Face Recognition
- Speed-area optimized VLSI architecture of multi-bit cellular automaton cell based random number generator on FPGA with testable logic support
- Compact 3D Thermal Model for VLSI and ULSI Interconnect Network Reliability Verification
- Simultaneous Parametric and Functional Testing of Digital VLSI During Radiation Experiments
- A New 4-2 Compressor for VLSI Circuits and Systems
- An ultra-low-power CNFET-based improved Schmitt trigger design for VLSI sensor applications
- Performance Analysis of Clock Gating Designs in Low Power Vlsi Circuits
- Flexible scheme for reconfiguring 2D mesh-connected VLSI subarrays under row and column rerouting
- A Survey on VLSI Implementation of AES Algorithm with Dynamic S-Box
- High-Throughput VLSI architecture for Soft-Decision decoding with ORBGRAND
- Methods for Ensuring Full Traceability of the Production Testing Results of the Digital VLSI
- Low Power Circuit Design for Footed Quasi Resistance Scheme In 45NM VLSI Technology
- Fast Auto-Correction algorithm for Digital VLSI Circuits
- Review of VLSI Architecture of Cryptography Algorithm for IOT Security
- The VLSI Realization of Sign-Magnitude Decimal Multiplication Efficiency
- Gate-Overlap Tunnel Field-Effect Transistors (GOTFETs) for Ultra-Low-Voltage and Ultra-Low-Power VLSI Applications
- VLSI design of a fast one-stage independent component extracting system based on ICA-R algorithm
- Fully Reused VLSI Architectu Encoding for DSRC Applica
- VLSI Architecture for DWT using 5/3 Wavelet Coefficient using Vedic Math’s
- Design and vlsi implementation of a decimation filter for hearing aid applications
- Analysis and Comparison of Leakage Power Reduction Techniques for VLSI Design
- A low area VLSI implementation of extended tiny encryption algorithm using Lorenz chaotic system
- Study and Analysis of Digital Counters for VLSI Applications
- Synthesis of VLSI Structural Cell Partitioning Using Genetic Algorithm
- VLSI Architecture for 8-bit Reversible Arithmetic Logic Unit based on Programmable Gate
- Features of Designing Digital Processing Systems for Radiolocation Systems Based on Microprocessor VLSI Sets
- Multiple-Criteria Decision Analysis Using VLSI Global Routing
- Performance Evaluation of VLSI Implemented WSN Algorithms
- Soft Error Rate Estimation of VLSI Circuits
- Wave pipelined VLSI architecture for a Viterbi decoder using self reset logic with 0.65 nm technology
- Efficient Band Offset Calculation Method for HEVC and Its VLSI Implementation
- 2021 IEEE 39th VLSI Test Symposium (VTS)
- A spike based learning neuron in analog VLSI
- Computing Orientation of an Image by Projection Method and its VLSI Implementation
- A Greedy Iterative Algorithm and VLSI Implementation Strategy for Multiuser Detection
- The First Ge Nanosheets GAAFET CMOS Inverters Fabricated by 2D Ge/Si Multilayer Epitaxy, Ge/Si Selective Etching
- Novel Architecture for Lifting Discrete Wavelet Packet Transform With Arbitrary Tree Structure
- Back-Gate Network Extraction Free from Dynamic Self-Heating in FD SOI
- Improvement of Nanotwinned Copper Thermal Stability for High Temperature Heterogeneous Integration
- DFT Models of Ferroelectric Hafnium-Zirconium Oxide Stacks With and Without Dielectric Interlayers
- Selective Area Epitaxy of Axial Wurtzite-InAs Nanowire on InGaAs NW by MOCVD
- Calculation of Field Dependent Mobility in MoS2 and WS2 with Multi-Valley Monte Carlo Method
- Ultra-thin Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 Ferroelectric Tunnel Junction with High Current Density
- Alleviation of Charge Trapping and Flicker Noise in HfZrO2-Based Ferroelectric Capacitors by Thermal Engineering
- On-Wafer Electronic Layer Detectors Array (ELDA) for e-beam Imaging in Advanced Lithographic Systems
- Contact engineered charge plasma junctionless transistor for suppressing tunneling leakage
- Quantum Tunneling PUF: A Chip Fingerprint for Hardware Security
- Ferroelectric and Antiferroelectric Hf/Zr oxide films: past, present and future
- An Approach to Diminish the Leakage Power in Complementary MOS VLSI Circuits
- Benchmarking the Performance of Heterogeneous Stacked RRAM with CFETSRAM and MRAM for Deep Neural Network Application Amidst Variation and Noise
- Multi-bit cryogenic flash memory on Si/SiGe and Ge/GeSi heterostructures
- Tensor-Centric Processor Architecture for Applications in Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
- Evaluation de la complexit d’implantation en VLSI par la synth se architecturale: une exp rience en filtrage adaptatif
- A precise debugging method and defect diagnosis with mass big-data analysis in the designed high-dense array for rapid yield improvement in a logic platform
- Dynamic Mapping Mechanism to Compute DNN Models on a Resource-limited NoC Platform
- Bandgap-Engineered Tunneling Layer on Operation Characteristics of Poly-Ge Charge-Trapping Flash Memory Devices
- Reconfigurable Database Processor for Query Acceleration on FPGA
- Holistic and In-Context Design Flow for 2.5 D Chiplet-Package Interaction Co-Optimization
- ONNC Compiler Used in Fault-Mitigating Mechanisms Analysis on NVDLA-Based and ReRAM-Based Edge AI Chip Design
- Quantum dot celluar automata-based encoder and priority encoder circuits: Low latency and area efficient design
- Shutdown mode implementation for Boost and Inverting Buck-Boost converter
- AN ELEGANCE OF A NOVEL DIGITAL FILTER USING MAJORITY LOGIC FOR SNR IMPROVEMENT IN SIGNAL PROCESSING
- Recent Progress on Flexible Capacitive Pressure Sensors: From Design and Materials to Applications
- Prototypage d’algorithmes adaptatifs par un outil de synthèse d’architectures VLSI.
- ALGORITMOS PARA PROBLEMAS DE STEINER COM APLICAÇÕES EM PROJETO DE CIRCUITOS VLSI
- An Energy-Efficient Conditional Biasing Write Assist With Built-In Time-Based Write-Margin-Tracking for Low-Voltage SRAM
- Prospective incorporation of booster in carbon interconnects for high-speed integrated circuits
- Laser beam testing of finished integrated circuits
- A survey of in-spin transfer torque mram computing
- Oxytocin modulates neural processing of mitral/tufted cells in the olfactory bulb
- Power Efficient Bit Lines: A Succinct Study
- Introduction: Soft Error Modeling
- Functional Constraints in the Selection of Two-Cycle Gate-Exhaustive Faults for Test Generation
- Adiabatic Logic-Based Area-and Energy-Efficient Full Adder Design
- Improved Noise Margin and Reduced Power Consumption in Subthreshold Adiabatic Logic Using Dual Rail Power Supply
- IMPROVING SIZE-BOUNDS FOR SUBCASES OF SQUARE-SHAPED SWITCHBOX ROUTING
- Design and Performance Evaluation of Highly Efficient Adders in Nanometer Technology
- Qualitative and quantitative analysis of parallel-prefix adders
- 4-Bit Ripple Carry Adder Using Area-Efficient Full Adder in CMOS Technology
- Systolic-Architecture-Based Matrix Multiplications and Its Realization for Multi-Sensor Bias Estimation Algorithms
- BiPart: a parallel and deterministic hypergraph partitioner
- Dealing with Aging and Yield in Scaled Technologies
- Ultraefficient imprecise multipliers based on innovative 4: 2 approximate compressors
- A Low Power Approach for Designing 12-Bit Current Steering DAC
- Structure Fortification of Mixed CNT Bundle Interconnects for Nano Integrated Circuits Using Constraint-Based Particle Swarm Optimization
- Gain-Cell Embedded DRAM Under Cryogenic Operation–A First Study
- Communication and performance evaluation of 3-ary n-cubes onto network-on-chips
- A New Function Mapping Approach in Defective Nanocrossbar Array Using Unique Number Sequence
- Design, Simulation and Comparative Analysis of Performance Parameters of a 4-bit CMOS based Full Adder Circuit using Microwind and DSch at Various …
- A Conversion Mode Reconfigurable SAR ADC for Multistandard Systems
- Leakage-Tolerant Low-Power Wide Fan-in OR Logic Domino Circuit
- Carver Mead:” It’s All About Thinking,” A Personal Account Leading up to the First Microwave Transistor
- Reusable Delay Path Synthesis for Lightening Asynchronous Pipeline Controller
- An ultra-low-power CNFET based dual VDD ternary dynamic Half Adder
- Advanced Silicon & Semiconducting Silicon-Alloy Based Materials & Devices
- A Novel Modeling-Attack Resilient Arbiter-PUF Design
- Fast and Accurate Estimation of Statistical Eye Diagram for Nonlinear High-Speed Links
- Parallel algorithms
- Transistor self-heating: The rising challenge for semiconductor testing
- Adaptive Forward Body Bias Voltage Generator
- PVT Aware Analysis of ISCAS C17 Benchmark Circuit
- Hard-to-Detect Fault Analysis in FinFET SRAMs
- Design and comparative analysis of on-chip sigma delta ADC for signal processing applications
- Cost-Effective Test Screening Method on 40-nm Embedded SRAMs for Low-Power MCUs
- Passivity-based non-fragile control of a class of uncertain fractional-order nonlinear systems
- Impact of Spacers in Raised Source/Drain 14 nm Technology Node InGaAs-nFinFET on Short Channel Effects
- High Speed Energy Efficient Multiplier Using 20nm FinFET Technology
- Data Flow Obfuscation: A New Paradigm for Obfuscating Circuits
- Design and Analysis of 10T SRAM Cell with Stability Characterizations
- Evaluation of Real-Time Embedded Systems in HILS and Delay Issues
- Implementation and Analysis of Low Power Consumption Full Swing GDI Full Adders
- A Comprehensive Framework for Analysis of Time-Dependent Performance-Reliability Degradation of SRAM Cache Memory
- [HTML][HTML] X-architecture Steiner minimal tree algorithm based on multi-strategy optimization discrete differential evolution
- A New Improved V-Square-Controlled Buck Converter With Rail-to-Rail OTA-Based Current-Sensing Circuits
- A Very-Low-Voltage Frequency Divider in Folded MOS Current Mode Logic With Complementary n-and p-type Flip-Flops
- Variability Analysis of On-Chip Interconnect System Using Prospective Neural Network
- Low Power NAND Gate–based Half and Full Adder/Subtractor Using CMOS Technique
- Synchronization of mutual coupled fractional order one-sided lipschitz systems
- Novel Ternary Adder and Multiplier Designs Without Using Decoders or Encoders
- Reconfigurable Binary Neural Network Accelerator with Adaptive Parallelism Scheme
- High-Performance Spintronic Nonvolatile Ternary Flip-Flop and Universal Shift Register
- High Voltage Receiver Using Low Voltage Devices With Reduced Dead-zone
- Fast and High-Performing 1-Bit Full Adder Circuit Based on Input Switching Activity Patterns and Gate Diffusion Input Technique
- Training Neural Network for Machine Intelligence in Automatic Test Pattern Generator
- Evaluation of Bit Manipulation Instructions in Optimization of Size and Speed in RISC-V
- Machine-learning-based self-tunable design of approximate computing
- A novel current-controlled memristor-based chaotic circuit
- Performance Analysis of MoS2FET for Electronic and Spintronic Application
- Asynchronous Four-Phase and Two-Phase Circuits: Testing and Design for Testability
- Controlling GIDL Using Core–Shell Technique in Conventional Nano-Wire
- New FDNR and FDNC Simulation Configurations Using Inverted VDDIBAs
- Optimal Mappings of the Spectrum of BPSK/QPSK Sequences to Finite Polynomial Fields and Rings
- Impact of Multi-Metal Gate Stacks on the Performance of ß-Ga2O3 MOS Structure
- On the Reliability of In-Memory Computing: Impact of Temperature on Ferroelectric TCAM
- Design of Prominent Single-Precision 32-Bit Floating-Point Adder Using Single-Electron Transistor Operating at Room Temperature
- HIPER: Low Power, High Performance and Area-Efficient Hardware Accelerators for Hidden Periodicity Detection using Ramanujan Filter Banks
- A 13-bit 312.5-MS/s Pipelined SAR ADC With Open-Loop Integrator-Based Residue Amplifier and Gain-Stabilized Integration Time Generation
- Design of a new BUS for low power reversible computation
- Controlling Mode Transition Noise Occurred at Ground Rail in Data Preserving MTCMOS Shift Register
- Diversity Schemes in Multi-hop Visible Light Communications for 6G Networks
- Fabrication of Micro-Compliant Mechanisms Using Micro-Stereolithography
- A 27S/32S DC-balanced line coding scheme for PAM-4 signaling
- Game Theory-based Parameter-Tuning for Path Planning of UAVs
- A Low Latency Stochastic Square Root Circuit
- New Resistorless FDNR Simulation Configuration Employing CDDITAs
- An Energy-Efficient Level Shifter Using Time Borrowing Technique for Ultra Wide Voltage Conversion from Sub-200mV to 3.0 V
- Improved Store-Carry-Forward Scheme for Information Dissemination in Unfavorable Vehicular Distribution
- Effect of surface modification treatment on top-pinned MTJ with perpendicular easy axis
- Design and Implementation of an Efficient Mixed Parallel-Pipeline SAD Architecture for HEVC Motion Estimation
- Negative Voltage Generator and Current DAC Based Regulator For Flash Memory
- A non-autonomous chaotic system with no equilibrium
- SIXOR: Single-Cycle In-Memristor XOR
- Accelerated Addition in Resistive RAM Array Using Parallel-Friendly Majority Gates
- Towards energy-efficient STT-MRAM design with multi-modes reconfiguration
- HT-IWT-DCT-Based Hybrid Technique of Robust Image Watermarking
- GPU-Accelerated Soft Error Rate Analysis of Large-Scale Integrated Circuits
- Performance Evaluation of Sub 5 nm GAA NWMBCFET using Silicon Carbide Source/Drain Material
- A novel ultra-low power 7T full adder design using mixed logic
- Reversible Fade Gate as Decoder, Encoder and Full Adder
- A novel parallel prefix adder for optimized Radix-2 FFT processor
- Smart Soldier Health Monitoring System Incorporating Embedded Electronics
- Theoretical Analysis of Defected Ground Multiband Rectangular Shape Microstrip Patch Antenna
- Design of Efficient Ternary Subtractor
- Novel CDDITA-Based-Grounded Inductance Simulation Circuits
- Trim Time Reduction in Analog/RF ICs Based on Inter-Trim Correlation
- Ferroelectric HfO2 Memory Transistors with High-? Interfacial Layer and Write Endurance Exceeding 1010 Cycles
- Design and Analysis of Low-Power SRAM
- High-speed and low-cost carry select adders utilizing new optimized add-one circuit and multiplexer-based logic
- Selective Flip-Flop Optimization for Circuit Reliability
- Effect of Developer Temperature on Photoresist Contrast in Grayscale Lithography
- Power Series Representation Op logical Functions and its Applications to Error Detection and Error Correction Codes.(Dept. E)
- Creating Fastest Self timing Reference Path for High Speed Memory Designs
- Blockchain-enabled traceable, transparent transportation system for blood bank
- Reliability Evaluation and Analysis of FPGA-Based Neural Network Acceleration System
- Enhancement of ovonic threshold switching characteristics using nanometer-scale virtual electrode formed within ultrathin hafnium dioxide interlayer
- Neural networks integrated circuit with switchable gait pattern for insect-type microrobot
- Analog and Radio-Frequency Performance of Hetero-Gate-Dielectric FD SOI MOSFET in Re-S/D Technology
- Stumped nature hyperjerk system with fractional order and exponential nonlinearity: Analog simulation, bifurcation analysis and cryptographic applications
- Field-free and sub-ns magnetization switching of magnetic tunnel junctions by combining spin-transfer torque and spin–orbit torque
- Fundamentals of microelectronics
- Comparative Analysis of Channel Estimation Techniques in Vehicular Communication
- Statistical analysis of vehicle detection in the ITS application for monitoring the traffic and road accident using internet of things
- 3-D CMOS chip stacking for security ICs featuring backside buried metal power delivery networks with distributed capacitance
- Sensor Localization in WSNs Using Rotating Directional-Antenna at the Base Station
- A 6-Bit 1.5-GS/s SAR ADC With Smart Speculative Two-Tap Embedded DFE in 130-nm CMOS for Wireline Receiver Applications
- FPGA implementation of fast digital FIR and IIR filters
- Uniform 4-Stacked Ge0.9Sn0.1 Nanosheets Using Double Ge0.95Sn0.05 Caps by Highly Selective Isotropic Dry Etch
- A 3–7 GHz CMOS Power Amplifier Design for Ultra-Wide-Band Applications
- Fault-tolerant hamiltonian cycles and paths embedding into locally exchanged twisted cubes
- Error-Controlling Technique in Wireless Communication
- Human Action Recognition Using a New Hybrid Descriptor
- Minimization of Peak-to-Average Power Ratio in DHT Precoded OFDM System by A-Law Companding
- Machine Learning Oriented Dynamic Cost Factors-Based Routing in Communication Networks
- Digital/Analog Performance Optimization of Vertical Nanowire FETs Using Machine Learning
- Physical synthesis for advanced neural network processors
- A low latency modular-level deeply integrated MFCC feature extraction architecture for speech recognition
- On the Best-Partition Communication Complexity
- IMPLEMENTATION OF DIVISION AND SQUARE ROOT: MODELING AND EVALUATIONS
- Structural and Optical Analysis of Bulk-Hetero Interface Between MoS2: Pentacene
- Realization of a Low Profile, Wideband Omni-directional Antenna for Ku-band Airborne Applications
- Ultracompact channel add-drop filter based on single multimode nanobeam photonic crystal cavity
- Structural and Optical Characterization of EZO Thin Film for Application in Optical Waveguide
- Design-technology co-optimization of sequential and monolithic CFET as enabler of technology node beyond 2nm
- A Survey of Semantic Segmentation on Biomedical Images Using Deep Learning
- PAPR Reduction in OFDM for VLC System
- A Survey on Proactive and Reactive Channel Switching Techniques in Cognitive Radios
- FPGA-based Hardware Acceleration for SVM Machine Learning Algorithm
- Cross-Layer Approximate Hardware Synthesis for Runtime Configurable Accuracy
- A Multichannel Link-Layer Cooperation Protocol (MLCP) for Cognitive Radio Ad Hoc Network
- AdaTrust: Combinational Hardware Trojan Detection Through Adaptive Test Pattern Construction
- Performance Evaluation of Negative Capacitance Junctionless FinFET under Extreme Length Scaling
- A PVT aware differential delay circuit and its performance variation due to power supply noise
- A Survey on Methodologies and Database Used for Facial Emotion Recognition
- A Survey Study of Diseases Diagnosed Through Imaging Methodology Using Ultrasonography
- Special Session: Physical Attacks through the Chip Backside: Threats, Challenges, and Opportunities
- MOS based pseudo-resistors exhibiting Tera Ohms of Incremental Resistance for biomedical applications: Analysis and proof of concept
- Automated Simulator for the Validation of Bio-Impedance Devices
- The Architectural Optimizations of a Low-Complexity and Low-Latency FFT Processor for MIMO-OFDM Communication Systems
- An Optimal Design of 16 Bit ALU
- Analysis of Power Adaptation Techniques Over Beaulieu-Xie Fading Model
- Design and Analysis of Wearable Step-Shaped Sierpinski Fractal Antenna for WBAN Applications
- ASSURE: RTL Locking Against an Untrusted Foundry
- Design of Dynamic Induction Charging Vehicle for Glimpse of Future: Cutting Down the Need for High-Capacity Batteries and Charging Stations
- Performance Analysis of Speck Cipher Using Different Adder Architectures
- A Comparative Analysis of Statistical Model and Spectral Subtractive Speech Enhancement Algorithms
- Dimensionality Reduction Using Principal Component Analysis for Lecture Attendance Management System
- Design and implementation of current mode circuit for digital modulation
- SWM: A High-Performance Sparse-Winograd Matrix Multiplication CNN Accelerator
- A Compact IPD Based on-Chip Bandpass Filter for 5G Radio Applications
- An automated parallel simulation flow for cyber-physical system design
- Conformal Omni Directional Antenna for GPS Applications
- Recognition of Natural and Computer-Generated Images Using Convolutional Neural Network
- SPIDER-based out-of-order execution scheme for Ht-MPSOC
- Fast Encoding Using X-Search Pattern and Coded Block Flag Fast Method
- Design and Simulation of a Dual-Band Radiometer for Humidity and Temperature Profiling
- Voice Controlled IoT Based Grass Cutter Powered by Solar Energy
- Periodic Octagon Split Ring Slot Defected Ground Structure for MIMO Microstrip Antenna
- COPRICSI: COnstraint-PRogrammed Initial Circuit SIzing
- Design of Electronic Instrumentation for Isotope Processing
- Fluid-to-cell assignment and fluid loading on programmable microfluidic devices for bioprotocol execution
- Design and analysis of improved high-speed adaptive filter architectures for ECG signal denoising
- Compact and efficient structure of 8-bit S-box for lightweight cryptography
- Virtually Doped Silicon-on-Insulator Junctionless Transistor for Reduced OFF-State Leakage Current
- Reliability-Driven Voltage Optimization for NCFET-based SRAM Memory Banks
- [HTML][HTML] Design and simulation of high-performance 2: 1 multiplexer based on side-contacted FED
- Special Session–Machine Learning in Test: A Survey of Analog, Digital, Memory, and RF Integrated Circuits
- Enhancement of magnetic coupling and magnetic anisotropy in MTJs with multiple CoFeB/MgO interfaces for high thermal stability
- Nonlinear Circuits and Systems with Memristors: Nonlinear Dynamics and Analogue Computing via the Flux-Charge Analysis Method
- The Vedic Design-Carry Look Ahead (VD-CLA): A Smart and Hardware-Friendly Implementation of the FIR Filter for ECG Signal Denoising
- Information Theory-Based Defense Mechanism Against DDOS Attacks for WSAN
- TxSim: Modeling training of deep neural networks on resistive crossbar systems
- Automated Observability Analysis for Mixed-Signal Circuits
- Silicon-on-nothing electrostatically doped junctionless tunnel field effect transistor (son-ed-jltfet): A short channel effect resilient design
- Fault Detection and Classification in Microgrid Using Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network
- [HTML][HTML] Development of neural networks chip generating driving waveform for electrostatic motor
- Computer Laboratory
- Soft Error Tolerant Circuit Design Using Partitioning-Based Gate Sizing
- Recent Development in Analytical Model for Graphene Field Effect Transistors for RF Circuit Applications
- Phenomenological CNN model of a somatosensory effects
- Reusability and Scalability of an SoC Testbench in Mixed-Signal Verification—The Inevitable Necessity
- Power-and area-optimized high-level synthesis implementation of a digital down converter for software-defined radio applications
- 3–21 GHz broadband and high linearity distributed low noise amplifier
- 64-GHz datapath demonstration for bit-parallel SFQ microprocessors based on a gate-level-pipeline structure
- Resynthesize Technique for Soft Error-Tolerant Design of Combinational Circuits
- FPGA implementations for data encryption and decryption via concurrent and parallel computation: A review
- Vertically integrated computing labs using open-source hardware generators and cloud-hosted FPGAs
- Fast shared-memory streaming multilevel graph partitioning
- Comparison of NMOS and PMOS Input Driving Dynamic Comparator in 45nm Technology
- Hybrid Forecasting Model Based on Nonlinear Auto-Regressive Exogenous Network, Fourier Transform, Self-organizing Map and Pattern Recognition Model for Hour …
- Design and Implementation of Fast Locking All-Digital Duty Cycle Corrector Circuit with Wide Range Input Frequency
- Design of Low Power Barrel Shifter Architecture by Using Proposed MUX Based CORDIC in CMOS Logic
- Adaptive filtering algorithms in acoustic echo cancellation: a case study in architecure complexity evaluation
- Performance improvement of elliptic curve cryptography system using low power, high speed 16× 16 Vedic multiplier based on reversible logic
- Density Gradient Study on Junctionless Stack Nano-Sheet with Stack Gate Oxide for Low Power Application
- All-digital built-in self-test scheme for charge-pump phase-locked loops
- FPGA Hardware Acceleration of Soft Error Rate Estimation of Digital Circuits
- Power-aware hold optimization for ASIC physical synthesis
- Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor (CNTFET) and Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM) Based Ternary Combinational Logic Circuits
- New LMI Criterion to the Robust Stability of Discrete-Time Systems with Time-Varying Delays and Generalized Overflow Nonlinearities
- A dual-mode successive approximation register analog to digital converter to detect malicious off-chip power noise measurement attacks
- FPGA Design of SAR Type ADC Based Analog Input Module for Industrial Applications
- Secure energy efficient network priority routing protocol for effective data collection and key management in dynamic WSNs
- A Highly Linear SAW-Less Noise-Canceling Receiver With Shared TIAs Architecture
- Monolithic 3D stacked multiply-accumulate units
- Guidance-based improved depth upsampling with better initial estimate
- Circuit and system-level aspects of phase change memory
- An Active, Low-Power, 10Gbps, Current-based Transimpedance Amplifier in a Broadband Optical Receiver Front-End
- Conception de deux points mémoire statiques CMOS durcis contre l’effet des aléas logiques provoqués par l’environnement radiatif spatial
- Carbon Nanotube Field Effect Transistor (CNTFET) and Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM) Based Ternary Combinational Logic Circuits. Electronics 2021, 10 …
- A CMOS-integrated compute-in-memory macro based on resistive random-access memory for AI edge devices
- Design and Fabrication of a Polymer Microring Resonator: Polymer Microring Resonator
- Design for Testability of Low Dropout Regulators
- Magnonic band structure in CoFeB/Ta/NiFe meander-shaped magnetic bilayers
- Novel Circuit Model of Multi-walled CNT Bundle Interconnects Using Multi-valued Ternary Logic
- Higher-order Network Analysis Takes Off, Fueled by Classical Ideas and New Data
- High-Level Synthesis of Custom DSP Blocks using Distributed Arithmetic
- Enhancement-Mode Atomic-Layer-Deposited In2O3 Transistors With Maximum Drain Current of 2.2 A/mm at Drain Voltage of 0.7 V by Low-Temperature Annealing …
- Design of High-Speed Binary Counter Architecture for Low-Power Applications
- A Systematic Review on an Embedded Web Server Architecture
- Build-in compact and efficient temperature sensor array on field programmable gate array
- SAIF: Automated Asset Identification for Security Verification at the Register Transfer Level
- Low power, high-performance reversible logic enabled CNTFET SRAM cell with improved stability
- Design and Verification of Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture-Advanced Peripheral Bus (AMBA-APB) Protocol
- A Reconfigurable Architecture to Implement Linear Transforms of Image Processing Applications
- Etude du bruit électrique en 1/f et des fluctuations RTS aux basses fréquences dans le transistor MOS submicronique
- sonal communication, June 16, 1994.
- In-memory realization of SHA-2 using ReVAMP architecture
- Enabling Write-Reduction Multiversion Scheme With Efficient Dual-Range Query Over NVRAM
- Design and validation of an artificial neural network based on analog circuits
- Insight into threshold voltage and drain induced barrier lowering in negative capacitance field effect transistor
- The past and future of multi-gate field-effect transistors: Process challenges and reliability issues
- A 96-MB 3D-Stacked SRAM Using Inductive Coupling With 0.4-V Transmitter, Termination Scheme and 12: 1 SerDes in 40-nm CMOS……………….. K. Shiba …
- [HTML][HTML] A Survey on Application Specific Processor Architectures for Digital Hearing Aids
- A Review on Performance Evaluation of Different Low Power SRAM Cells in Nano-Scale Era
- Multilevel Hypergraph Partitioning with Vertex Weights Revisited
- [HTML][HTML] The involution tool for accurate digital timing and power analysis
- Design and Implementation of Fast Locking All-Digital Duty Cycle Corrector Circuit with Wide Range Input Frequency. Electronics 2021, 10, 71
- Memristor based high speed and low power consumption memory design using deep search method
- Comparative Analysis of Adder for Various CMOS Technologies
- Design of Parallel Sorting System Using Discrete-Time Neural Circuit Model
- Via-Minimization-Oriented Region Routing Under Length-Matching Constraints in Rapid Single-Flux-Quantum Circuits
- Process Variation-Aware Soft Error Rate Estimation Method for Integrated Circuits
- Global placement with deep learning-enabled explicit routability optimization
- Microcomputer Application in Motion Control
- Fault-Tolerant Application Mapping on Mesh-of-Tree based Network-on-Chip
- Capacitance-to-Digital Converter for Operation under Uncertain Harvested Voltage down to 0.3 V with No Trimming, Reference and Voltage Regulation
- Mixed-radix, virtually scaling-free CORDIC algorithm based rotator for DSP applications
- A Theoretical Study of Design Rewiring Using ATPG
- FPGA Implementation of Bio-inspired Computing Based Deep Learning Model
- Toward Functional Safety of Systolic Array-Based Deep Learning Hardware Accelerators
- Employing the Empirical Mode Decomposition to Denoise the Random Telegraph Noise
- Dependence of metal gate work function variation for various ferroelectric thickness on electrical parameters in NC-FinFET
- [HTML][HTML] A comparison of modeling approaches for current transport in polysilicon-channel nanowire and macaroni GAA MOSFETs
- Electronically tunable third-order dual-mode quadrature sinusoidal oscillators employing VDCCs and all grounded components
- FPGA Implementation of Radix-4-Based Two-Dimensional FFT with and Without Pipelining Using Efficient Data Reordering Scheme
- TRENDS IN DISTRIBUTED OBJECT COM-PUTING
- Designing a New 4: 2 compressor using an efficient multi-layer full-adder based on nanoscale quantum-Dot cellular automata
- Introduction to Dual Mode Logic (DML)
- 3-D IC: An Overview of Technologies, Design Methodology, and Test Strategies
- A Novel Plaintext-Related Color Image Encryption Scheme Based on Cellular Neural Network and Chen’s Chaotic System
- Spatial Coverage of FM Radio Signal Variation Measurement and Comparison of two Major Radio Stations within Akwa Ibom State
- Fabrication and selective wet etching of Si0. 2Ge0. 8/Ge multilayer for Si0. 2Ge0. 8 channel gate-all-around MOSFETs
- High-performance area-efficient polynomial ring processor for CRYSTALS-Kyber on FPGAs
- Dynamic workload allocation for edge computing
- Non-volatile memory behavior of interfacial InOx layer in InAs nano-wire field-effect transistor for neuromorphic application
- A Case Study on FPGA Implementation of Parts Counting Orientation Recognition Method for Industrial Vision System
- A Survey of FIR Filter Design Techniques: Low-complexity, Narrow Transition-band and Variable Bandwidth
- A low-power dynamic ternary full adder using carbon nanotube field-effect transistors
- Design and analysis of (5, 10) regular LDPC encoder using MRP technique
- Low-Voltage DML
- Efficient Ternary Compressor Design Using Capacitive Threshold Logic in CNTFET Technology
- Realization of 8 x 4 Barrel shifter with 4-bit binary to Gray converter using FinFET for Low Power Digital Applications
- Performance Efficient Floating-Point Multiplication Using Unified Adder–Subtractor-Based Karatsuba Algorithm
- High-speed programmable photonic circuits in a cryogenically compatible, visible-NIR 200 mm CMOS architecture
- S ntese de Alto N vel de Protocolos para a Abordagem IP sobre ATM
- A Systematic Review of Approximate Adders: Accuracy and Performance Analysis
- Evaluation of low power consumption network on chip routing architecture
- Tiny robots and sensors need tiny batteries—here’s how to do it
- Planarized Nb 4-Layer Fabrication Process for Superconducting Integrated Circuits and Its Fabricated Device Evaluation
- Efficient FPGA architecture of optimized Haar wavelet transform for image and video processing applications
- Gradual magnetization switching via domain nucleation driven by spin–orbit torque
- TEM studies during development of a 4-megabit DRAM
- Circuit Design Using Genetic Programming: An Illustrative Study
- Machine Learning for Electronic Design Automation: A Survey
- Design optimization of sub-5 nm node nanosheet field effect transistors to minimize self-heating effects
- Suppression of ambipolar behavior and simultaneous improvement in RF performance of gate-overlap tunnel field effect transistor (GOTFET) devices
- Analysis on High-Performance Full Adders
- Features of Organizing the Process of Designing Radar Microcircuits
- Magnetoresistive Circuits and Systems: Embedded Non-Volatile Memory to Crossbar Arrays
- On the role of system software in energy management of neuromorphic computing
- Introduction to nanowires: types, proprieties, and application of nanowires
- Unveiling the impact of the bias dependent charge neutrality point on graphene based multi transistor applications
- True Random Number Generation using Latency Variations of Commercial MRAM Chips
- Online Test Strategies and Optimizations for Reliable Reconfigurable Architectures
- Impact of the SiO2 interface layer on the crystallographic texture of ferroelectric hafnium oxide
- Voltage-gate assisted spin-orbit torque magnetic random access memory for high-density and low-power embedded application
- 1 A Programmable Neural-Network Inference Accelerator Based on Scalable In-Memory Computing
- Shift Left Trends for Design Convergence in SOC: An EDA Perspective
- Domain wall mobility engineering by a perpendicular magnetic field in microwires with a gradient of perpendicular anisotropy
- Characterization of QUBO reformulations for the maximum -colorable subgraph problem
- State of charge estimation of lithium batteries in electric vehicles using IndRNN
- Design of AES-Based Encryption Chip for IoT Security
- A 15-bit, 5 MSPS SAR ADC with on-chip digital calibration
- Optimization of Low Power LNA Using PSO for UWB Application
- Amorphous InGaZnO Thin-Film Transistors With Sub-10-nm Channel Thickness and Ultrascaled Channel Length
- Digital Implementation of Sigmoid Function in Artificial Neural Network Using VHDL
- Performance Analysis for Tri-Gate Junction-Less FET by Employing Trioxide and Rectangular Core Shell (RCS) Architecture
- Design of dopingless GaN nanowire FET with Low ‘Q’for high switching and RF applications
- Circuit Design for Non-volatile Magnetic Memory
- Post-Moore Memory Technology: Sneak Path Current (SPC) Phenomena on RRAM Crossbar Array and Solutions
- An Energy-Efficient UWB Transmitter with Wireless Injection Locking for RF Energy-Harvesting Sensors
- A Novel Structure and Operation Scheme of Vertical Channel NAND Flash with Ferroelectric Memory for Multi String Operations
- Approximate Multipliers Using Bio-Inspired Algorithm
- Fault-Tolerant Implementation of Quantum Arithmetic and Logical Unit (QALU) Using Clifford+T-Group
- WADE: A Web-based Automated electronic Design Environment
- Hybrid memristor-CMOS implementation of logic gates design using LTSpice.
- Towards Scalable Spectral Embedding and Data Visualization via Spectral Coarsening
- Half-Select Disturb-Free 10T Tunnel FET SRAM Cell with Improved Noise Margin and Low Power Consumption
- Impact of Trapped-Charge Variations on Scaled Ferroelectric FET Nonvolatile Memories
- A 4-GS/s 10-ENOB 75-mW ringamp ADC in 16-nm CMOS with background monitoring of distortion
- Realization with fabrication of double-gate MOSFET based buck regulator
- Two-dimensional transistors with reconfigurable polarities for secure circuits
- A NEW DESIGN OF TANGENT HYPERBOLIC FUNCTION GENERATOR WITH APPLICATION TO THE NEURAL NETWORK IMPLEMENTATIONS
- A Power-Efficient SAR ADC with Optimized Timing-Redistribution Asynchronous SAR Logic in 40-nm CMOS
- Klessydra-T: Designing Vector Coprocessors for Multithreaded Edge-Computing Cores
- Electromigration in solder joints: A cross-sectioned model system for real-time observation
- Design of Soft-Error-Aware SRAM With Multi-Node Upset Recovery for Aerospace Applications
- M3DSSD: Monocular 3D single stage object detector
- A ring oscillator with very low phase noise and wide frequency range using carbon nanotube technology for PLL applications
- Towards Next Generation Robust Cryptosystems
- Design and FPGA Synthesis of an Efficient Synchronous Counter with Clock-Gating Techniques
- Layout dependence of total-ionizing-dose response in 65-nm bulk Si pMOSFET
- Soft-error resilient read decoupled SRAM with multi-node upset recovery for space applications
- On-Fly-TOD: an efficient mechanism for crosstalk fault reduction in WNoC
- Experimental Examination of Component-Differentially-Challenged XOR PUF Circuits
- Implementation of Neuro-Memristive Synapse for Long-and Short-Term Bio-Synaptic Plasticity
- BiFeO3 clad modified fiber optic gas sensor for room temperature applications
- AutoBridge: Coupling Coarse-Grained Floorplanning and Pipelining for High-Frequency HLS Design on Multi-Die FPGAs
- Macrolide Biosensor Optimization through Cellular Substrate Sequestration
- A design towards an energy-efficient and lightweight data security model in Fog Networks
- Security of Neural Networks from Hardware Perspective: A Survey and Beyond
- An Empirical Study of the Reliability of High-Level Synthesis Tools
- Design of low-power coupled chopper instrumentation amplifier using pin pong ripple reduction for biomedical applications
- Low Powered Self-Testable ALU
- Nanopower multiple-input DTMOS OTA and its applications to high-order filters for biomedical systems
- EM Lifetime Constrained Optimization for Multi-Segment Power Grid Networks
- Approximate Array Multipliers
- Linear k-arboricity of Caylay graphs on Abelian groups with given degree
- ObfusX: routing obfuscation with explanatory analysis of a machine learning attack
- FPGA-based architecture for bi-cubic interpolation: the best trade-off between precision and hardware resource consumption
- Hardware Verification: Theory and Practice
- Decomposition Methods of FSM Implementation
- Word Length Selection Method for HIL power converter models
- Review on performance analysis of P3HT: PCBM-based bulk heterojunction organic solar cells
- Silico-Algorithmes et Arithm etique des Ordinateurs
- Post-Moore Memory Technology: Sneak Path Current (SPC) Phenomena on RRAM Crossbar Array and Solutions. Micromachines 2021, 12, 50
- On the Design of a Fault-Tolerant Scalable Three Dimensional NoC-Based Digital Neuromorphic System With On-Chip Learning
- Electric Propulsion Methods for Small Satellites: A Review
- Multi-Ferroic Properties on BiFeO3/BaTiO3 Multi-Layer Thin-Film Structures with the Strong Magneto-Electric Effect for the Application of Magneto-Electric Devices
- A Systematic Review on Various Types of Full Adders
- Superconducting neural networks with disordered Josephson junction array synaptic networks and leaky integrate-and-fire loop neurons
- Benchmarking Machine Learning: How Fast Can Your Algorithms Go?
- Optimization of zero-level interlayer dielectric materials for gate-all-around silicon nanowire channel fabrication in a replacement metal gate process
- Multilevel Acyclic Hypergraph Partitioning*
- Robust circuit implementation of 4-bit 4-tube CNFET based ALU at 16-nm technology node
- Process validation test of CNTFET using Stanford model
- Energy-aware routing considering load balancing for SDN: a minimum graph-based Ant Colony Optimization
- Traffic sign detection optimization using color and shape segmentation as pre-processing system
- Neuromorphic vision sensors: Principle, progress and perspectives
- Binary Decision Diagrams
- [HTML][HTML] Fast simulations of highly-connected spiking cortical models using GPUs
- Dual Mode Logic in FD-SOI Technology
- Spin–orbit torque and Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction in perpendicularly magnetized heterostructures with iridium
- On the Origin of Wake-Up and Antiferroelectric-Like Behavior in Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxide
- Website Development for Trading Between Farmers and Government
- Modeling and experimental analysis of an internally-cooled vapor chamber
- Logic Synthesis of Sequential Logic Circuits for Adiabatic Quantum-Flux-Parametron Logic
- Further stability analysis of neutral-type Cohen-Grossberg neural networks with multiple delays
- Perspective on ferroelectric, hafnium oxide based transistors for digital beyond von-Neumann computing
- Verilog Implementation of Biometric-Based Transmission of Fused Images Using Data Encryption Standards Algorithm
- Learned smartphone isp on mobile npus with deep learning, mobile ai 2021 challenge: Report
- Domain wall-magnetic tunnel junction spin–orbit torque devices and circuits for in-memory computing
- Comparing bulk-Si FinFET and gate-all-around FETs for the 5 nm technology node
- Enhancing Security and Trust of IoT Devices–Internet of Secured Things (IoST)
- Dual Metal Double Gate Ge-Pocket TFET (DMG-DG-Ge-Pocket TFET) with Hetero Dielectric: DC & Analog Performance Projections
- DML Energy-Delay Tradeoffs and Optimization
- Analysis and Design of On-Chip RF Interconnect Line for Wideband True-Time Delay Line Application
- RECON: Resource-efficient CORDIC-based neuron architecture
- A compensation textures dehazing method for water alike area
- An Efficient Hardware Architecture for Deblocking Filter in HEVC
- Toward novel designs of reversible ternary 6: 2 Compressor using efficient reversible ternary full-adders
- 3D-aCortex: An ultra-compact energy-efficient neurocomputing platform based on commercial 3D-NAND flash memories
- Study and Implementation of Ladder Logic Conversion to VHDL for Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)-Based Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)
- Enhanced Lubrication Ability of Polyalphaolefin and Polypropylene Glycol by COOH-Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes as an Additive
- A reliable, multi-bit error tolerant 11T SRAM memory design for wireless sensor nodes
- [HTML][HTML] Mathematical optimization approach for facility layout on several rows
- Mobility enhancement techniques for Ge and GeSn MOSFETs
- Towards the development of backing layer for piezoelectric micromachined ultrasound transducers
- EN SYNTHESE D’ARCHITECTURE
- Implementation of Autoencoders with Systolic Arrays through OpenCL
- Ultra-high-performance magnetic nonvolatile level converter flip-flop with spin-hall assistance for dual-supply systems with power gating architecture
- Adaptive Deconvolution-based stereo matching Net for Local Stereo Matching
- Investigation of thick GaAs: Cr pixel sensors for X-ray imaging applications
- Damage in silicon after reactive ion etching
- Unraveling the optical contrast in Sb2Te and AgInSbTe phase-change materials
- Emerging technologies and the security of western Europe
- An overview of biological applications and fundamentals of new inlet and vacuum ionization technologies
- Realization of a self-powered ZnSnO MSM UV photodetector that uses surface state controlled photovoltaic effect
- Ultra-Low Power and High-Throughput SRAM Design to Enhance AI Computing Ability in Autonomous Vehicles
- Lowering the Schottky Barrier Height by Titanium Contact for High-Drain Current in Mono-layer MoS 2 Transistor
- Power-Oriented Monitoring of Clock Signals in FPGA Systems for Critical Application
- On the crossing numbers of join products of W_ {4}+ P_ {n} and W_ {4}+ C_ {n}
- A Crystal-Less BLE Transmitter With Clock Recovery From GFSK-Modulated BLE Packets
- Visibilidade em Poligonos utilizando algoritmos paralelos
- Um Protocolo SR ARQ Ponto-a-Multiponto com Reconhecimento Acumulativo para Comunica cões a Altas Velocidades
- Deep-Learning Assisted Compact Modeling of Nanoscale Transistor
- Proposed pipeline clocking scheme for microarchitecture data propagation delay minimization
- Ultralow-loss silicon nitride waveguides for nonlinear optics
- [HTML][HTML] Benchmarking monolayer MoS 2 and WS 2 field-effect transistors
- Phase Change Random Access Memory for Neuro-Inspired Computing
- Security of Emerging Memory Chips
- Study on Power Minimization techniques in SAR ADC Devices by Using Comparators Circuits
- Built-In Self-Test (BIST) Methods for MEMS: A Review
- AXON: NETWORK VIRTUAL STORAGE DESIGNz
- IOT-HARPSECA: A Secure Design and Development System of Roadmap for Devices and Technologies in IOT Space
- [HTML][HTML] High performance IIR filter implementation on FPGA
- Terrestrial precise positioning system using carrier phase from burst signals and optically distributed time and frequency reference
- Generation of Pseudorandom Sequence Using Regula-Falsi Method
- A fractional-order CNN hyperchaotic system for image encryption algorithm
- Genfloor: Interactive generative space layout system via encoded tree graphs
- Our Perspectives
- Transformations of Rectangular Dualizable Graphs
- High-speed CMOS-compatible III-V on Si membrane photodetectors
- Configurable DSI partitioned approximate multiplier
- Stacking faults and precipitates in annealed and co-sputtered C49 TiSi2 films
- Trading-o Power versus Area through a Parameterizable Model for Virtual Memory Manage
- Reconfigurable Carry Look-Ahead Adder Trading Accuracy for Energy Efficiency
- Internet Rescue Robots for Disaster Management [J]
- Reliable advanced encryption standard hardware implementation: 32-bit and 64-bit data-paths
- A new opportunity for the emerging tellurium semiconductor: resistive switching device implementation
- [HTML][HTML] Simulation and experimental verification of modified sinusoidal pulse width modulation technique for torque ripple attenuation in Brushless DC motor drive
- Ordered Binary Decision Diagrams, Gaussian Elimination and Graph Theory
- Monitor Circuits for Cross-Layer Resiliency
- TSV Fault Contactless Testing Method Based on Group Delay
- [HTML][HTML] An Efficient Design of QCA Full-Adder-Subtractor with Low Power Dissipation
- EBIC diffusion length of dislocated silicon
- A 1-MS/s to 1-GS/s ringamp-based pipelined ADC with fully dynamic reference regulation and stochastic scope-on-chip background monitoring in 16 nm
- A 1.93-pJ/Bit PCI Express Gen4 PHY Transmitter with On-Chip Supply Regulators in 28 nm CMOS
- Influence of High-Pressure Annealing Conditions on Ferroelectric and Interfacial Properties of Zr-Rich Hf?Zr1??O2Capacitors
- Fault-based Built-in Self-test and Evaluation of Phase Locked Loops
- Field-programmable gate arrays in a low power vision system
- On undirected two-commodity integral flow, disjoint paths and strict terminal connection problems
- Scheduling Conditional Nested Loops in a Resource Constrained ASIC Design
- Reliability-Aware Multipath Routing of Time-Triggered Traffic in Time-Sensitive Networks
- Time-domain computing in memory using spintronics for energy-efficient convolutional neural network
- End-to-End Data Architecture Considerations for IoT
- Covering problem on fuzzy graphs and its application in disaster management system
- A Time-Frequency Measurement and Evaluation Approach for Body Channel Characteristics in Galvanic Coupling Intrabody Communication
- Crosstalk minimization in network on chip (NoC) links with dual binary weighted code CODEC
- A physical model for bulk gate insulator trap generation during bias-temperature stress in differently processed p-channel FETs
- On the capabilities of Cellular Automata-based MapReduce model in Industry 4.0
- Rail-to-rail dynamic voltage comparator scalable down to pw-range power and 0.15-v supply
- In situ microsectioning and imaging of semiconductor devices using a scanning ion microscope
- Estimation Probabiliste des Ressources, pour la synth ese d’Architectures
- Improved design debugging architecture using low power serial communication protocols for signal processing applications
- An enhanced cost-aware mapping algorithm based on improved shuffled frog leaping in network on chips
- Single Event Transient (SET) Mitigation Circuits With Immune Leaf Nodes
- A Period-Aware Routing Method for IEEE 802.1 Qbv TSN Networks
- Special session: Reliability analysis for ML/AI hardware
- The Japanese fifth generation computing project: curricular applications
- Proposal for ultrafast all-optical pseudo random binary sequence generator using microring resonator-based switches
- Hardware/Software Codesign for Energy Efficiency and Robustness: From Error-Tolerant Computing to Approximate Computing
- TAAL: tampering attack on any key-based logic locked circuits
- Hardware Trojan Prevention and Detection by Filling Unused Space Using Shift registers, Gate-chain and Extra Routing.
- Quiet 2-Level Adiabatic Logic
- Towards a DML Library Characterization and Design with Standard Flow
- Sedenionic formulation for the field equations of multifluid plasma
- Design and analysis of double-gate junctionless vertical TFET for gas sensing applications
- Shared-Memory n-level Hypergraph Partitioning
- An Improved Adaptive Genetic Algorithm for Two-Dimensional Rectangular Packing Problem
- [HTML][HTML] Neuromorphic model of reflex for realtime human-like compliant control of prosthetic hand
- Memory applications from 2D materials
- Fast multipole method for 3-D Laplace equation in layered media
- Dielectric spectroscopy and electrical conductivity measurements of a series of orthoconic antiferroelectric liquid crystalline esters
- The unified modeling language reference manual
- Design of a 2–30 GHz Low-Noise Amplifier: A Review
- Compact Modeling of Multidomain Ferroelectric FETs: Charge Trapping, Channel Percolation, and Nucleation-Growth Domain Dynamics
- Early Detection of Prediabetes and T2DM Using Wearable Sensors and Internet-of-Things-Based Monitoring Applications
- Road surface detection and differentiation considering surface damages
- Deep learning-based feature extraction and optimizing pattern matching for intrusion detection using finite state machine
- 2 An EM/Power SCA-Resilient AES-256 with Synthesizable Signature Attenuation Using Digital-Friendly Current Source and RO-Bleed-Based Integrated Local …
- Uniform Crystal Formation and Electrical Variability Reduction in Hafnium-Oxide-Based Ferroelectric Memory by Thermal Engineering
- REVIEW ON RUDIMENTS OF DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
- Computer simulation of X-ray topographs of curved silicon crystals
- The analog/RF performance of a strained-Si graded-channel dual-material double-gate MOSFET with interface charges
- Detecting Signature of Virus Using Metamaterial-Based One-Dimensional Multi-layer Photonic Crystal Structure Under Polarized Incidence
- A DTMOS-based power efficient recycling folded cascode operational transconductance amplifier
- Block coordinate descent based algorithm for computational complexity reduction in multichannel active noise control system
- RRAM-Based Neuromorphic Computing Systems
- analysis and Simulation of Schottky tunneling using Schottky barrier FET with 2-D analytical modeling
- Investigation of Multiple-valued Logic Technologies for Beyond-binary Era
- Structure and substructure connectivity of alternating group graphs
- Power and area efficient stochastic artificial neural networks using spin–orbit torque-based true random number generator
- Improvised hierarchy of Floating Point Multiplication using 5: 3 Compressor
- Research on digital image watermark encryption based on hyperchaos
- Calibration of WLI Lateral Indication Error with 2D Micro/Nano Pitch Standard
- Implementation of Autoencoders with Systolic Arrays through OpenCL. Electronics 2021, 10, 70
- State-of-the-Art TFET Devices
- 1 A 6.2 GHz Single Ended Current Sense Amplifier (CSA) Based Compileable 8T SRAM in 7nm FinFET Technology
- Resilient and Secure Hardware Devices Using ASL
- 6 A 5-to-6GHz Current-Mode Subharmonic Switching Digital Power Amplifier for Enhancing Power Back-Off Efficiency
- Comparative Analysis of Rapid Single Flux Quantum (RSFQ) Circuit Technique Multipliers
- BiCoSS: toward large-scale cognition brain with multigranular neuromorphic architecture
- Analysis of subthreshold swing in junctionless double gate MOSFET using stacked high-k gate oxide.
- TAN modelling of HH-shape microstrip interconnect tree
- Improving efficiency in neural network accelerator using operands hamming distance optimization
- Thickness of the subgroup intersection graph of a finite group [J]
- A 189×600 Back-Illuminated Stacked SPAD Direct Time-of-Flight Depth Sensor for Automotive LiDAR Systems
- A Fully Integrated 2.7 µW-70.2 dBm-Sensitivity Wake-Up Receiver with Charge-Domain Analog Front-End,-16.5 dB-SIR, FEC and Cryptographic Checksum
- Learning complexity of simulated annealing
- General Efficient TMR for Combinational Circuit Hardening Against Soft Errors and Improved Multi-Objective Optimization Framework
- High Current Density in Monolayer MoS2 Doped by AlOx
- A general semantics for logics of affirmation and negation
- Symmetric-Mapping LUT-Based Method and Architecture for Computing XY-Like Functions
- Modelling and Design of 5T, 6T and 7T SRAM Cell Using Deep Submicron CMOS Technology
- [HTML][HTML] Coupled VO2 oscillators circuit as analog first layer filter in convolutional neural networks
- Design of CMOS 6T and 8T SRAM for Memory Applications
- Brain-inspired golden chip free hardware trojan detection
- S ntese L ogica do Protocolo IPv6: Resultado de uma Metodologia visando o Projeto de Protocolos em Hardware
- Influence of exposure energy and heat treatment conditions on through-glass via metallization of photoetchable glass interposers
- A 0.8 V multimode vision sensor for motion and saliency detection with ping-pong PWM pixel
- Machine Learning for Statistical Modeling: The Case of Perpendicular Spin-Transfer-Torque Random Access Memory
- A 22nm 4Mb 8b-Precision ReRAM Computing-in-Memory Macro with 11.91 to 195.7 TOPS/W for Tiny AI Edge Devices
- Electron beam induced artefact during TEM and Auger analysis of multilayer dielectrics
- Binary precision neural network manycore accelerator
- Deep learning-driven simultaneous layout decomposition and mask optimization
Computer Science Research Topics – MS PhD
Related posts:.
- VLSI Design MCQs
- How many transistors are in LSI, VLSI, ULSI?
- information visualization Research Topics Ideas [MS PhD]
- Molecular Computing Research Topics Ideas [MS PhD]
- Software Security Research Topics Ideas [MS PhD]
- Stochastic Networks Research Topics Ideas [MS PhD]
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Group Discussion Topics for Engineering Students in VLSI
- Rahul David
- August 3, 2023
VLSI is a crucial domain within the field of engineering, focusing on the design and implementation of integrated circuits. With the rapid advancements in technology, VLSI plays a pivotal role in various sectors such as electronics, communication, healthcare, and automotive industries. As an engineering student specializing in VLSI, it is essential to stay updated with the latest trends and developments in the field. Participating in group discussion topics for engineering students can facilitate knowledge enhancement, foster better communication skills, and encourage the exchange of ideas among peers.
Also read: What is design for testability and why is it important ?
Engaging Group Discussion Topics for Engineering Students
Here are some engaging group discussion topics for engineering students in VLSI:
The Impact of VLSI Design on Modern Electronic Devices
Discuss how VLSI design has revolutionized electronic devices such as smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices. Analyze the challenges faced by VLSI designers in meeting the increasing demand for smaller, faster, and energy-efficient devices.
Future Trends in VLSI Technology
Explore emerging trends in VLSI technology such as 3D IC integration, neuromorphic computing, quantum computing, and nanotechnology. Discuss their potential applications, advantages, and challenges.

Role of VLSI Physical Design in Integrated Circuit Manufacturing
Delve into the significance of VLSI physical design in optimizing chip performance, power consumption, and area utilization. Discuss the methodologies and tools employed in physical design and their impact on manufacturing yield.
Introduction to DFT (Design for Testability) in VLSI
Explain the concept of DFT and its importance in ensuring the quality and reliability of integrated circuits. Discuss various DFT techniques such as scan chains, built-in self-test (BIST), and boundary scans.
Overview of VLSI Companies in Bangalore
Explore the prominent VLSI companies in Bangalore , India’s Silicon Valley. Discuss their contributions to the VLSI industry, the nature of their work, and the career opportunities they offer to VLSI engineers.
Choosing the Right VLSI Training Institute in Bangalore
Discuss the factors to consider when selecting a VLSI training institute in Bangalore . Analyze the curriculum, faculty expertise, industry collaborations, hands-on projects, and placement assistance offered by different institutes.
VLSI Companies in Hyderabad and Their Specializations
Explore the VLSI companies in Hyderabad and their specific areas of expertise, such as FPGA design, ASIC development, verification, or physical design. Discuss the opportunities available for VLSI professionals in Hyderabad.
Read more on what is an FPGA in VLSI .
Advantages of Pursuing a VLSI Online Course

Comparison of VLSI Courses Online
Compare different VLSI courses online in terms of their syllabus, teaching methodology, hands-on projects, certification, and industry recognition. Discuss the factors to consider while choosing an online course.
By engaging in group discussions on these topics, engineering students specializing in VLSI can broaden their understanding of the field, exchange ideas, and gain valuable insights from their peers. These discussions will not only enhance their technical knowledge but also improve their communication and critical thinking skills, preparing them for a successful career in the dynamic field of VLSI.
Share This Post:

8 Common Mistakes to Avoid in VLSI Job Applications

What is SystemVerilog: The Language for Modern Hardware Design and verification

VLSI Basics: Unveiling the Microworld
Exploring the Nexus of VLSI vs Embedded Systems: Unraveling the Intricacies
Best Practices for the Physical Design of IoT Solutions

Power Dissipation in CMOS Circuits
Trending blogs, what is an fpga in vlsi.

Know The Difference Between Verilog And System Verilog
Everything you need to know about synthesis in vlsi, benefits of opting vlsi electronic courses, what is eco in vlsi physical design, blog categories.
- Analog Layout (9)
- ASIC Design Flow (2)
- Design for Test (29)
- Design Verification (27)
- General (67)
- Internship (18)
- Physical Design (39)
- RTL Design – Lint & CDC (7)
- SOC Design (1)
- Synthesis & STA (2)

Course Categories

VLSI Courses for Professionals

VLSI Courses for Freshers

Online VLSI Courses (Self Paced)

VLSI Programs for Enterprises
Subscribe to our blog.
- Hiring Companies
- Placement Details
Associate With Us
- Refer & Earn
- Be Our Trainer
- Be Our Guest Blogger
For Enterprises
- Corporate Training
Programs Offered
- Formal Verification
- ASIC Design Verification
- Design For Test
- Physical Design
VLSI Courses for Students & Freshers (UG/PG)
- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- Terms & conditions
Get Upto 40% OFF

Best VLSI based IEEE project topics for engineering students
Long gone are the days wherein computers are as large as rooms with large vacuum tubes. They no longer take up an entire room or make loud humming noises. All these operations have scaled-down in size and multiplied in application. Nowadays, we see products that occupy very little space but offer abundant functionality. Modern-day machines get smaller in size and larger in an application, every single day. So, what pushed this technology forward by such a large extent? The art of computing brought in a wave of electronic miniaturization thanks to the semiconductor transistor. One of the most important fields that work closely with this is VLSI technology. If you are a budding EEE engineer, then VLSI projects are something you need to invest time and energy in. Here’s a look at some great VLSI IEEE projects to help you get started on your journey
Have you checked out our projects on VLSI yet? VLSI Kit will be shipped to you and you can build using tutorials. You can start with a free demo today!
1. VLSI Starter
2. VLSI Explorer
3. VLSI Champion
4. VLSI (Career Building Course)
Discover more IEEE VLSI projects
What is a VLSI design?
VLSI stands for Very Large-Scale Integration. Essentially, this involves the creation of integrated circuits by combining thousands of MOS transistors and other electrical components onto a single chip. These MOS IC chips are a staple within the electronics industry and enabled complex semiconductor, signal processing and communication technologies to come up. VLSI design consists of all the different processes that go into creating these IC chips.
Explore more IEEE VLSI projects
Processes Involved in Designing a VLSI IC
Front End Steps:
- Problem Specification - Represent the system in a mainframe by defining the performance characteristics and other definitions.
- Architecture Definition - Define what architecture you will use, number of floating point units, RISC or CISC, and what cache size.
- Functional Design - Once the architecture is chosen, decide the facilitates to be provided. Also, functionalities it should have, and the specifications of the functional units.
- Logic Design - Integrate boolean expressions, control flow, register allocation and RTL description.
- Circuit Design - Create a circuit as a netlist, containing gates, transistors and other important components.
- Physical Design - Convert the netlist into a physical body as a layout. This is done by the following protocol called the lambda rules which details the size, ratio and spacing of components.
Latest projects on VLSI
Want to develop practical skills on VLSI? Checkout our latest projects and start learning for free
Back end Steps:
- Wafer processing - Melting of silicon and then inserting the crystal orientation is called wafer processing. After this, the polishing of the ingot and crystal orientation occurs.
- Lithography - Mask with a photographic mask and highlight tracks on it by exposing it to UV lights.
- Etching - This step helps in removing material selectively so as to create patterns, by using additional chemicals or plasma.
- Ion implantation - Add the necessary dopants as ions in a targeted manner.
- Metallization - Deposit a thin layer of aluminum over the wafer to act as a good conductor.
- Assembly and Packaging - Cut the wafer into single chips, separate them and then test them individually. After ascertaining that they are of high quality, package them as needed.
Explore more about VLSI design
Skyfi Labs helps students develop skills in a hands-on manner through VLSI Online Courses where you learn by building real-world projects.
You can enrol with friends and receive kits at your doorstep.
You can learn from experts, build working projects, showcase skills to the world and grab the best jobs. Start Learning VLSI today!
What is VLSI and its applications?
VLSI chips are used in all kinds of fields. Some examples include;
- Personal computers, cell phones, digital cameras
- Consumer electronic gadgets.
- Automobiles and Anti-Lock Braking Systems
- Medical field, medical equipment
- Digital signal processing
- Speech identification and translation
- Switching telephone circuits
- Voice communication networks
- Data networks
Advantages of VLSI Technology
- Smaller sized components as circuit elements form single chips
- Lower cost thanks to the power of mass production
- Lower power consumption due to smaller size
- Higher reliability as there are fewer interconnections
- Additional functionality
- Efficient use of space
- Reduced weight and easier packaging
- Easily replaceable
- High operating speeds
- Significant career and growth opportunities
Online VLSI design courses for engineering students
VLSI Starter online course for engineers
Everything from smartphones to complicated aircraft makes use of VLSI technology in some way or the other. This VLSI design course will serve as the best introductory course, as it opens you to the subject. Since the VLSI industry is worth 1.75 trillion dollars, this is a great opportunity for you to further your career. In this online course, students will learn how to work with industry-wide tools, such as Xilinx ISE and to program in Verilog. The students will also be working with Logic Gates, comparators, encoders and decoders.
Explore more about this course
VLSI Explorer online course for engineers
This is the perfect VLSI IEEE project if you are a medium-level user of VLSI technology. This course will help you understand more about how the technology works. It is perfect for understanding the widespread applications of technology. Furthermore, this course gives students an opportunity for hands-on experience. They get to work with the actual codes and simulations and get a solid introduction to VLSI. They also learn Verilog Programming, work with logic gates and build circuits with the help of this course.
Learn more about this course
VLSI Champion online course for engineers
In case you already know about the basics of VLSI, this is the course to take to improve your knowledge. By the end of this VLSI IEEE project, students will gain experience with tools like Xilinx ISE. They will also gain exposure to the creation and development of combinational and sequential circuits. Students will model electronic systems, and design in the Xilinx Design Suite. They will gain an insight into Verilog Programming, optimization and learn how to build a Static RAM Design.
Discover more about this VLSI course
Best VLSI-based IEEE projects for engineering students
1. Real-time Traffic Light Control
In this VLSI design IEEE project, students will learn how to build an FPGA-based traffic light controller. Not only does this help regulate traffic, but it also reduces the average waiting time of drivers. Since VHDL can help simulate the working of circuits, it is used to build this interface. A model of the controller is created using VHDL, and to verify the design, a timing simulation is done. By taking part and completing this project, students will gain a thorough understanding of how VLSI technology works.
Learn more about this project
2. Fuzzy-based PID controller
This VLSI IEEE project is extremely useful and has many applications in the transportation industry. In order to create this system, we interface Fuzzy Logic Controllers, MATLAB and the VLSI system. The programming is done in the VHDL language. In effect, the PID controller works as a great feedback control mechanism. It finds use in flight controllers, high-speed trains, motor drivers, and even for water regulation. Therefore, this project brings EEE engineers the best of both worlds. It has equal parts of fuzzy logic, and VLSI technology, making it a great project to learn a lot of new skills.
Learn more about this IEEE project
3. Design and VLSI implementation of Anti-collision robot processor
Robots are occupying this world faster than ever. In manufacturing industries multiple robots have to work in the same environment this IEEE project helps you to design a robot processor that detects and avoids the other robots with the help of RFID technology. As part of this VLSI project, you will be introduced into the VLSI design process.
Find more IEEE VLSI projects from the following list:
- Behavioural synthesis of Asynchronous circuits
- Design of FPGA based 32-bit Floating-point Arithmetic unit
- Design and synthesis of QPSK
- Design of CAN protocol
- Fuzzy based mobile robot controller designing using VHDL
- Implementation of Highspeed pipeline VLSI Architecture
- Implementation of overlap based logic cell and its power analysis
- Design of data encryption standard for data encryption
- ASIC Design of complex multiplier
The field of engineering is extremely competitive. Therefore, to differentiate yourself from the crowd and really enhance your value, you need to constantly upskill. When you look at the field of EEE, VLSI technology is a very impactful and useful area. By taking part in these VLSI IEEE projects, you get to build experience and learn valuable concepts to come out as a better engineer.
Explore more VLSI project ideas
Join 250,000+ students from 36+ countries & develop practical skills by building projects
Get kits shipped in 24 hours. Build using online tutorials.
Blogs you might like on VLSI
Subscribe to our blog.
Stay up-to-date and build projects on latest technologies
☎ Have a Query?
Emerging VLSI Trends in 2023
- by Maven Silicon
- July 19, 2023
- 3 minutes read
Looking for the latest VLSI trends and VLSI jobs in 2023? Maven Silicon, a leading VLSI training institute, is here to guide you. VLSI is revolutionizing industries with its ability to integrate millions of transistors onto a single chip. In this blog post, we’ll explore the emerging VLSI trends in 2023 that are shaping the future and highlight the exciting job openings in this field. Discover the benefits of pursuing a career in VLSI and how Maven Silicon can help you kick-start your journey.
VLSI Application & Trends in 2023
The applications of VLSI span across various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, healthcare, and artificial intelligence. As we move into 2023, several VLSI trends are making waves:
AI-driven VLSI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has merged with VLSI, opening up endless possibilities. AI-driven VLSI solutions have gained significant traction in industries like autonomous vehicles, robotics, smart homes, and beyond. The integration of AI algorithms directly into VLSI chips allows for the real-time processing of massive amounts of data, leading to intelligent decision-making and unprecedented levels of efficiency. This trend empowers autonomous vehicles to analyze complex surroundings, robots to navigate dynamically changing environments, and smart homes to adapt to residents’ preferences seamlessly. The synergy between AI and VLSI has propelled us toward a new era of intelligent and responsive technologies.
IoT and VLSI
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution is in full swing, and VLSI plays a pivotal role in shaping this interconnected ecosystem. Emerging trends in VLSI focus on designing chips optimized for IoT-enabled devices, ensuring efficient data communication, low power consumption, and enhanced security. These specialized VLSI chips enable IoT devices to communicate seamlessly over the internet, exchanging data with other devices and cloud services. Moreover, with advancements in low-power design techniques, IoT devices can operate for extended periods on battery power, making them more practical and environmentally friendly. VLSI’s contribution to IoT is driving the proliferation of smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation, transforming the way we interact with our surroundings.
Edge Computing and VLSI
Edge computing has emerged as a game-changer in handling real-time data processing and analysis. VLSI’s role in this trend is crucial, as it enables the development of high-performance, energy-efficient chips tailored for edge devices. By processing data locally at the edge, these VLSI chips significantly reduce latency and response times, making them ideal for applications that demand immediate results. Edge devices, such as sensors and cameras, benefit from low-power VLSI solutions that allow for prolonged operation without compromising performance. The combination of edge computing and VLSI has unlocked a new realm of possibilities, from responsive AI applications to smart infrastructure like traffic management and environmental monitoring.
Benefits of VLSI
Exciting and challenging work.
The field of VLSI indeed provides a dynamic and intellectually stimulating work environment for engineers and professionals. As a VLSI engineer, you get the opportunity to be at the forefront of designing complex integrated circuits that power a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones and computers to IoT devices and automotive electronics.
Also read: Why VLSI is Used?
Lucrative Job Opportunities
The demand for VLSI professionals is on the rise, making it a highly sought-after field with numerous job opportunities across various industries. As technology continues to advance and electronic devices become an integral part of our lives, the need for skilled VLSI engineers has grown significantly.
Positions such as VLSI Design Engineer, Verification Engineer, and Physical Design Engineer are in high demand. VLSI Design Engineers are responsible for designing and architecting integrated circuits, while Verification Engineers focus on validating and testing chip designs. Physical Design Engineers, on the other hand, play a crucial role in implementing the circuit layout to optimize performance and power consumption.
Also read: Skills required to become a VLSI engineer?
Job Openings
If you’re eager to embark on a VLSI career, numerous job openings await you. Maven Silicon is renowned for its VLSI training with 100% placement assistance. Explore exciting roles like VLSI Design Engineer, Verification Engineer, Physical Design Engineer, FPGA Engineer, and Analog/Mixed-Signal Design Engineer.
Also read: Salary of VLSI Engineers in India
As we step into 2023, the world of VLSI presents abundant opportunities. Stay updated with the latest VLSI trends, leverage the benefits of this field, and secure a rewarding career in VLSI. Maven Silicon can equip you with the necessary skills to excel in the ever-evolving VLSI landscape. Start your journey towards a successful VLSI career today with our job-oriented courses .
Share This Post:
[…] Discover the emerging VLSI trends in 2023, from groundbreaking innovations to cutting-edge advancements. Stay ahead in the world of technology. […]
Comments are closed.
Related Post
What is Metastability in VLSI?
What is Skew in VLSI?
VLSI Role in Advancing Sensors and Smart Devices
Refer your friends to Maven, you'll get 20% off once they enroll in out course.
Your friends name
Your friends email id
Have Doubts?
Why should i do vlsi training.
All the Integrated Chips we use in mobiles, TVs, computers, satellites, and automobiles, etc. are designed with VLSI technology. Hence, there is a huge scope and growth in the VLSI Industry and it is full of job opportunities. Since there is a huge gap between what the college education offers and the industry expectation, it is recommended to go for the VLSI training which bridges that gap and gives you a great hands-on experience.
What is chip designing?
Steps involved in Chip design Chip’s architecture: Create circuit designs, Run simulations, Supervise layout, Tape out the chip to the foundry and Evaluate the prototype once the chip comes back from the laboratory. Chip designers work to make faster, cheaper and more innovative chips that can automate parts or the entire function of electronic devices. A chip design engineer’s job involves architecture, logic design, circuit design and physical design of the chip, testing, and verification of the final product.
Is VLSI a good career?
VLSI is a very good domain to build a career with a huge number of opportunities. There is a demand for chips in every sector, be it automobiles, consumer electronics or high-end servers. You should have good command on Verilog, SystemVerilog, and UVM to start your career as VLSI Design or VLSI Verification Engineer
What is the eligibility for VLSI Chip Designing Courses?
The undergraduates, graduates, or postgraduates from below streams can take up VLSI Chip Design Course and make a career in VLSI Industry. BE/BTech in EEE/ECE/TE or ME/MTech/MS in Electronics/MSc Electronics
To join the industry as a VLSI verification engineer, you must have hands-on experience of below topics: SystemVerilog, Universal Verification Methodologies UVM, Assertion based Verification SVA
Maven Silicon provides the best quality VLSI training through a variety of design and verification courses to suit your need and demand. We offer online VLSI courses, Job-oriented fulltime and Blended VLSI courses, Internship programs, part time courses and corporate training.Explore our offerings at https://www.maven-silicon.com/
Every course has a different admission procedure: 1. For Advanced VLSI Design and Verification course at Maven Silicon, you can apply while you are in the final semester, graduation or post-graduation. 2. For the Internship program, you can apply in your pre-final/final year. Advise you to book your seats in advance, pertaining to limited admissions and increased demand. 3. You can subscribe to our online courses directly from our elearn portal https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ You can apply for our Online, Job-oriented, Part-time and Corporate courses on https://www.maven-silicon.com/application
We do have an entrance exam for our job-oriented courses VLSI RN and VLSI VM. After you meet the eligibility criteria you have to undergo an Online Entrance Test which would check you on the concepts of Basic Electronics and Digital Electronics. Post scoring 60% in this test, you are processed for the technical interview with our technical experts. Based on your performance during the interview, you will be selected for the Advanced VLSI Design and Verification course. For our online VLSI courses, we do not have any entrance exams. You can directly subscribe the courses from our elearn portal https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/
Yes, we do provide the scholarship on our job-oriented courses VLSI RN and VLSI VM based on your performance in the technical interview. To excel in the Online entrance test and the technical interview, we suggest you take our Online Digital electronics course at https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/digital-electronics This online Digital electronics course will help you to learn and refresh the complete fundamentals of digital electronics, highly needed for any VLSI course. Contact us for more details.
We provide 100% placement assistance with our job-oriented course until you get placed. You can refer the link for the placement updates and know more about our hiring partners: https://www.maven-silicon.com/placement
VLSI Frontend course imparts training in the Design and Verification of a chip which mostly includes RTL(Register Transfer Level) coding using either VHDL/Verilog/SystemVerilog and the verification of the DUT(can be an IP or SOC) by building verification Environment or Testbench using SystemVerilog/UVM/.You also learn to meet the timing constraints of the chip using STA(Static Timing Analysis) and Synthesizing the design using synthesizable constructs. The maximum number of VLSI job opportunities are available in the Verification segment. Backend courses mostly deal with the physical design part of the chip which includes Floorplan, Map, Place and route and DFT and ATPG scan insertion and checks for the flip flops. It also includes the physical verification part of the chip, memory characterization, analog layout, and design.
Yes. VLSI is a high growth domain with huge job opportunities. Electronics is the basic knowledge required to get into the VLSI industry. Engineers with Electronics background can enter into VLSI Industry easily. The VLSI Course is helpful for ECE/EEE students to learn and build up the skill set as per the Industry requirement to enter the Chip/IC Design and Verification Domain.
Inexpensive courses with the utmost quality are our unique selling points. You can explore our courses at https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/
We help you with support material to enhance your basic knowledge of Digital electronics and perform your best. Our online Digital electronics course will help you to learn and refresh the complete fundamentals of digital electronics, which are highly needed for any VLSI course. Contact us for more details.
We do have online VLSI courses for engineers like you. You can start learning with our hands-on online VLSI courses which comes with labs, project, reference material. We also connect with live Q&A, doubt clarification sessions and Whatsapp support group. Click here to explore and subscribe https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ . If you are looking for online VLSI course with Placement support, then you refer our Blended VLSI learning program at https://www.maven-silicon.com/blended-vlsi-design-asic-verification
We always encourage you to join the course along with friends because it motivates you to learn and finish the course at a fast pace. Contact us to know about group discount options.
Yes. It is good to start early. You can explore and subscribe to our online VLSI design methodologies course or our Internship Program. It is a front-end VLSI course that imparts the VLSI Design Flow, Digital Design and RTL programming using Verilog HDL. After completing the online VLSI DM course/Internship Program, you can easily crack college campus interviews or you can also take up our Advanced ASIC Verification course with 100% placement assistance and can avail up to 100% scholarship based on your grades in our Online VLSI Design Course and the scores of technical interview with our experts.
Yes, we have part-time/Weekend VLSI courses for working professionals. They are specially designed to help you strike a balance between your job and learning. Explore VLSI DM and VM part-time course under Part-time VLSI course in Program offerings at our website https://www.maven-silicon.com/systemverilog-uvm-functional-verification-course
Our Job oriented VLSI courses are highly effective and rigorous programs and follow a continuous evaluation scheme. Candidates are evaluated in the courses through lab reports, project reports, practice tests, assignments, technical presentations, and mock interviews. We also have an evaluation program in our Online VLSI courses through quizzes, tests, and assignments.
You do not need to pay extra for the requisite learning material. We do provide free library access and free online VLSI Courses to our trainees enrolled for job oriented courses for reference and support.
Once you complete your online VLSI course you can upgrade to job oriented VLSI Courses with a very good scholarship. We provide 100% placement assistance for the job oriented VLSI Courses. Advanced VLSI Design and Verification [VLSI – RN ] and Advanced ASIC Verification [ VLSI-VM ] are the job oriented VLSI Courses.
Maven Silicon offers customized in-house and onsite corporate VLSI training courses. This program is specially designed for engineers keeping in view the ever-changing demands of the industry. The participants are equipped with the latest tools, techniques, and skills needed to excel as Verification Engineers. Some of our Corporate training VLSI Courses are SystemVerilog HVL, Verilog HDL, Universal Verification Methodology and Assertion based Verification. Click here for more details: https://www.maven-silicon.com/corporate-training
Yes. Our courses will be very useful. We have had many students taking up our course before going to foreign universities for their Master’s program in VLSI. The practical approach of the courses could help them get campus job opportunities and assistantships..
You can opt for online or offline course but you must choose the right mode considering the time you can spend and the flexibility you need. The online course also provides you Live Q&A, doubt clarification, handy technical support and reference material. So, it is a great offering with best of both worlds. You can learn on the go along with your college studies/ regular office hours and upskill yourself. With Maven Silicon’s Online Verification course, you can master VLSI even if you stay in a remote corner of the world.
Steps involved in Chip design Chip’s architecture: Create circuit designs, Run simulations, Supervise layout, Tape out the chip to the foundry and Evaluate the prototype once the chip comes back from the laboratory. Chip designers work to make faster, cheaper and more innovative chips that can automate parts or the entire function of electronic devices. A chip design engineer’s job involves architecture, logic design, circuit design and physical design of the chip, testing, and verification of the final product.
We do have online VLSI courses for engineers like you. You can start learning with our hands-on online VLSI courses which comes with labs, project, reference material. We also connect with live Q&A, doubt clarification sessions and Whatsapp support group. Click here to explore and subscribe https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ . If you are looking for online VLSI course with Placement support, then you refer our Blended VLSI learning program at https://www.maven-silicon.com/blended-vlsi-design-asic-verification
Once you complete your online VLSI course you can upgrade to job oriented VLSI Courses with a very good scholarship. We provide 100% placement assistance for the job oriented VLSI Courses. Advanced VLSI Design and Verification [VLSI – RN ] and Advanced ASIC Verification [ VLSI-VM ] are the job oriented VLSI Courses.
You can opt for online or offline course but you must choose the right mode considering the time you can spend and the flexibility you need. The online course also provides you Live Q&A, doubt clarification, handy technical support and reference material. So, it is a great offering with best of both worlds. You can learn on the go along with your college studies/ regular office hours and upskill yourself. With Maven Silicon’s Online Verification course, you can master VLSI even if you stay in a remote corner of the world.
- Why Maven Silicon
- Success Stories
- Training Calender
- Advanced VLSI Design and Verification Course – [VLSI RN]
- Advanced ASIC Verification Course – [VLSI VM]
- Advanced VLSI Design and DFT Course – [VLSI DFT]
- Advanced Physical Design Course – [VLSI PD] NEW
- Online VLSI Design Course
- Online VLSI Verification Course
- Advanced ASIC Verification Course – [VLSI VM-PT]
- VLSI Design Course – [VLSI DM-PT]
- Free VLSI Courses
- VLSI jobs for freshers
- Free VLSI Projects
- Free VLSI Workshop
- Maven Podcast
- Hire Talent
- Corporate Training
Download the Maven Learning App
South Taluk, 21/1A, III Floor, MS Plaza, Gottigere Uttarahalli Hobli, Bannerghatta Main Rd, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560076
© Copyright 2023 Maven Silicon, All Rights Reserved. Privacy and Terms
- Physical Design Interview Questions
- Physical Design Course
- VLSI Physical Design Flow
- VLSI Training Institute in Hyderabad
- SystemVerilog Assertions
- Verilog Interview Questions
- DFT interview question
- VLSI interview questions
- SystemVerilog Interview Questions
- SystemVerilog Course
- VLSI courses online
- ASIC Verification
- UVM Verification
- Systemverilog Tutorial
- Internship in electronics
- VLSI Design
- VLSI projects
- VLSI System Design
- VLSI Internship in Bangalore
- Preferences

Vlsi Topics PowerPoint PPT Presentations


VLSI Technology
Jul 10, 2014
2.63k likes | 6.48k Views
VLSI Technology. Introduction Typical Applications Moore’s Law The cost of fabrication Technology Background What is a chip Fabrication Technology CMOS Technology. VLSI Technology. VLSI is an implementation technology for electronic circuitry – analog or digital
Share Presentation
- individual chips
- automobile dr vp dubey
- cmos fabrication
- critically important
- type silicon

Presentation Transcript
VLSI Technology • Introduction • Typical Applications • Moore’s Law • The cost of fabrication • Technology Background • What is a chip • Fabrication Technology • CMOS Technology Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
VLSI Technology • VLSI is an implementation technology for electronic circuitry – analog or digital • It is concerned with forming a pattern of interconnected switches and gates on the surface of a crystal of semiconductor • Microprocessors • personal computers • microcontrollers • Memory - DRAM / SRAM • Special Purpose Processors - ASICS (CD players, DSP applications) • Optical Switches • Has made highly sophisticated control systems mass-producable and therefore cheap Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Moore’s Law • Gordon Moore: co-founder of Intel • Predicted that the number of transistors per chip would grow exponentially (double every 18 months) • Exponential improvement in technology is a natural trend: • e.g. Steam Engines - Dynamo - Automobile Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
What is a Silicon Chip? • A pattern of interconnected switches and gates on the surface of a crystal of semiconductor (typically Si) • These switches and gates are made of • -areas of n-type silicon • -areas of p-type silicon • -areas of insulator • -lines of conductor (interconnects) joining areas together • Aluminium, Copper, Titanium, Molybdenum, polysilicon, tungsten • The geometry of these areas is known as the layout of the chip • Connections from the chip to the outside world are made around the edge of the chip to facilitate connections to other devices Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication Technology • Silicon of extremely high purity • chemically purified then grown into large crystals • Wafers • crystals are sliced into wafers • wafer diameter is currently 150mm, 200mm, 300mm • wafer thickness <1mm • surface is polished to optical smoothness • Wafer is then ready for processing • Each wafer will yield many chips • chip die size varies from about 5mmx5mm to 15mmx15mm • A whole wafer is processed at a time Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Different parts of each die will be made P-type or N-type (small amount of other atoms intentionally introduced - doping -implant) • Interconnections are made with metal • Insulation used is typically SiO2. SiN is also used. New materials being investigated (low-k dielectrics) Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication Technology • NMOS Fabrication • CMOS Fabrication • -n-well process • -p-well process • -twin-tub process • BiCMOS Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication Technology • All the devices on the wafer are made at the same time • After the circuitry has been placed on the chip • the chip is overglassed (with a passivation layer) to protect it • only those areas which connect to the outside world will be left uncovered (the pads) • The wafer finally passes to a test station • test probes send test signal patterns to the chip and monitor the output of the chip • The yield of a process is the percentage of die which pass this testing • The wafer is then scribed and separated up into the individual chips. These are then packaged • Chips are ‘binned’ according to their performance Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
CMOS Technology • First proposed in the 1960s. Was not seriously considered until the severe limitations in power density and dissipation occurred in NMOS circuits • Now the dominant technology in IC manufacturing • Employs both pMOS and nMOS transistors to form logic elements • The advantage of CMOS is that its logic elements draw significant current only during the transition from one state to another and very little current between transitions - hence power is conserved. • In the case of an inverter, in either logic state one of the transistors is off. Since the transistors are in series, (~ no) current flows. • See twin-well cross sections Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
BiCMOS • A known deficiency of MOS technology is its limited load driving capabilities (due to limited current sourcing and sinking abilities of pMOS and nMOS transistors. • Bipolar transistors have • higher gain • better noise characteristics • better high frequency characteristics • BiCMOS gates can be an efficient way of speeding up VLSI circuits • See table for comparison between CMOS and BiCMOS • CMOS fabrication process can be extended for BiCMOS • Example Applications • CMOS - Logic • BiCMOS - I/O and driver circuits • ECL - critical high speed parts of the system Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Classification of Silicon Technology Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
BASIC CMOS TECHNOLOGY FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSING STEPS Basic steps • Oxide growth • Thermal diffusion • Ion implantation • Deposition • Etching • Epitaxy Photolithography Photolithography is the means by which the above steps are applied to selected areas of the silicon wafer. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Diffusion is typically done at high temperatures: 800 to 1400°C Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Ion Implantation Ion implantation is the process by which impurity ions are accelerated to a high velocity and physically lodged into the target material. • Annealing is required to activate the impurity atoms and repair the physical damage to the crystal lattice. This step is done at 500 to 800°C. • Ion implantation is a lower temperature process • compared to diffusion. • • Can implant through surface layers, thus it is useful for • field-threshold adjustment. • • Can achieve unique doping profile such as buried • concentration peak Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Properties of Silicon Dioxide • Silicon dioxide (SiO2) is a critically important material in Integrated Circuit (IC) processing because • It is an excellent electrical insulator • It adheres well to most materials • it can be “grown” on a silicon wafer or deposited on top of the wafer • SiO2 is generally known as quartz glass or simply glass and is used for the gate oxide in a MOSFET. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Silicon Nitride (Si3 N4) • Silicon nitride is another useful material, which is often called nitride. • 3SiH4 (gas) + 4NH3 (gas) = Si3N4 (solid) + 12H2 (gas) • Nitrides are unique in that they acts as strong barriers to most atoms. This makes them ideal for use as an overglass layer, which is final protective coating on a chip, since it keeps contaminants from reaching the sensitive silicon circuits. • Silicon nitride is used in fabrication sequence that electrically isolates adjacent FETS and they have a relatively high dielectric constants =7.80 Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Deposition Deposition is the means by which various materials are deposited on the silicon wafer. Examples: • Silicon nitride (Si3N4) • Silicon dioxide (SiO2) • Aluminum • Polysilicon There are various ways to deposit a material on a substrate: • Chemical-vapor deposition (CVD) • Low-pressure chemical-vapor deposition (LPCVD) • Plasma-assisted chemical-vapor deposition (PECVD Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Etching Etching is the process of selectively removing a layer of material. When etching is performed, the etchant may remove portions or all of: • The desired material • The underlying layer • The masking layer Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Photolithography Components • Photo-resist material • Mask • Material to be patterned (e.g., oxide) Positive photo-resist: Areas exposed to UV light are soluble in the developer Negative photo-resist:Areas not exposed to UV light are soluble in the developer Steps 1. Apply photo-resist 2. Soft bake (drives off solvents in the photo-resist) 3. Expose the photo-resist to UV light through a mask 4. Develop (remove unwanted photo-resist using solvents) 5. Hard bake ( ≈ 100°C) 6. Remove photo-resist (solvents) Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
The process of exposing selective areas to light through a photo-mask is called printing. Types of printing include: • Contact printing • Proximity printing • Projection printing Illustration of Positive Photo-resist Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Photolithographic Process Sequence Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Photolithographic Process Sequence----cont. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Patterning of Poly-silicon gate Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication of NMOS Transistor The process starts with the oxidation of the silicon substrate (Fig.(a)), in which a relatively thick silicon dioxide layer, also called field oxide, is created on the surface (Fig.(b)). Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Then, the field oxide is selectively etched to expose the silicon surface on which the MOS transistor will be created (Fig.(c)). Following the above step, the surface is covered with a thin, high-quality oxide layer, which will eventually form the gate oxide Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication of NMOS Transistor------Contd. On top of the thin oxide layer, a layer of polysilicon is deposited (Fig. (e)). Polysilicon is used both as gate electrode material for MOS transistors and also as an interconnect medium in silicon integrated circuits. Undopedpolysilicon has relatively high resistivity. The-resistivity of polysilicon can be reduced, however, by doping it with impurity atoms. ysilicon can be reduced, however, by doping it with impurity atoms. After deposition, the polysilicon layer is patterned and etched to form the intercon-nects and the MOS transistor gates (Fig. (f)) Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Fabrication of NMOS Transistor------Contd. The thin gate oxide not covered by polysilicon is also etched away, which exposes the bare silicon surface on which the source and drainjunctions are to be formed (Fig. 2.4(g)). The entire silicon surface is then doped with a high concentration of impurities, either through diffusion or ion implanta-tion (in this case with donor atoms to produce n-type doping). Figure (h) shows that the doping penetrates the exposed areas on the silicon surface, ultimately creating two n-type regions (source and drain junctions) in the p-type substrate. The impurity doping also penetrates the polysilicon on the surface, reducing its resistivity Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Once the source and drain regions are completed, the entire surface is again covered with an insulating layer of silicon dioxide (Fig. (i)). The insulating oxide layer is then patterned in order to provide contact windows for the drain and source junctions (Fig.(j)). Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
The surface is covered with evaporated aluminum which will form the intercon-nects (Fig. (k)). Finally, the metal layer is patterned and etched, completing the interconnection of the MOS transistors on the surface (Fig. (1)). Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Device Isolation Techniques • The MOS transistors that comprise an integrated circuit must be electrically isolated from each other during fabrication. • Isolation is required to prevent unwanted conduction paths between the devices, to avoid creation of inversion layers outside the channel regions of transistors, and to reduce leakage currents. • To achieve a sufficient level of electrical isolation between neighboring transistors on a chip surface, the devices are typically created in dedicated regions called active areas, where each active area is surrounded by a relatively thick oxide barrier called the field oxide. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Disadvantage of field oxide: The most significant disadvantage is that the thickness of the field oxide leads to rather large oxide steps at the boundaries between active areas and isolation Fabrication (field) regions. When polysilicon and metal layers are deposited over such boundaries in of MOSFETs subsequent process steps, the sheer height difference at the boundary can cause cracking of deposited layers, leading to chip failure. To prevent this, most manufacturers prefer isolation techniques that partially recess the field oxide into the silicon surface, resulting in a more planar surface topology. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
Local Oxidation of Silicon (LOCOS) The local oxidation of silicon (LOCOS) technique is based on the principle of selectively growing the field oxide in certain regions, instead of selectively etching away the active areas after oxide growth. Selective oxide growth is achieved by shielding the active areas with silicon nitride (Si3 N4) during oxidation, which effectively inhibits oxide growth. The basic steps of the LOCOS process are illustrated in Fig. . Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
LOCOS process flow----Contd. Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
CMOS Process Flow Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
TYPICAL CMOS FABRICATION PROCESS N-Well CMOS Fabrication Major Steps 1.) Implant and diffuse the n-well 2.) Deposition of silicon nitride 3.) n-type field (channel stop) implant 4.) p-type field (channel stop) implant 5.) Grow a thick field oxide (FOX) 6.) Grow a thin oxide and deposit polysilicon 7.) Remove poly and form LDD spacers 8.) Implantation of NMOS S/D and n-material contacts 9.) Remove spacers and implant NMOS LDDs 10.) Repeat steps 8.) and 9.) for PMOS 11.) Anneal to activate the implanted ions 12.) Deposit a thick oxide layer (BPSG - borophosphosilicate glass) 13.) Open contacts, deposit first level metal and etch unwanted metal 14.) Deposit another interlayer dielectric (CVD SiO2), open vias, deposit 2nd level metal 15.) Etch unwanted metal, deposit a passivation layer and open over bonding pads Dr VP Dubey VLSI Technology
- More by User

VLSI Testing
VLSI Testing. Dr. Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Alabama 36849, USA [email protected] http://www.eng.auburn.edu/~vagrawal August 7-13, 2010. Course Description.
508 views • 20 slides

VLSI. Prof. Vojin G. Oklobdzija References (used for creation of the presentation material): [1] Mead, Conway, “ Introduction to VLSI Systems ”, Addison Wesley Publishing. [2] Glasser, Dobberpuhl, “ The Design and Analysis of VLSI Circuits ”, Addison Wesley Publishing.
1.14k views • 35 slides

VLSI Trends
VLSI Trends. A Brief History. 1958: First integrated circuit Flip-flop using two transistors From Texas Instruments 2011 Intel 10 Core Xeon Westmere-EX 2.6 billion transistors 32 nm process. Courtesy Texas Instruments. Courtesy Intel. Moore’s Law. Growth rate
1.25k views • 18 slides

VLSI Technology. Scaling Moore’s Law 3D VLSI.
814 views • 32 slides

VLSI Testing. Design error and fault simulation. 304-649. Jean-François Boland. Presentation Plan. Project Overview Design error and fault models ESIM Software Future work. Project Overview. Simulation Design error Logical fault ESIM software, [Al-Asaad 00], [Hayes 00]
236 views • 7 slides

VLSI Devices
VLSI Devices. Intuitive understanding of device operation Fundamental analytic models Manual Models Spice Models Secondary and deep-sub-micron effects Junction Diode and FET Resistor and Capacitor. B. A. Al. SiO. 2. p. n. Cross-section of . pn. -junction in an IC process . A.
733 views • 54 slides

VLSI Design
VLSI Design. Rehan Azmat Lecture 2 Semiconductor Theory. Previous Lecture. Introduction History Market Trends. Lecture 2. Semiconductor. Transistor Revolution. First Integrated Circuit. Intel 4004 Microprocessor. Intel Pentium IV Microprocessor. Moore’s Law. Die Size. Frequency.
598 views • 13 slides
Fluid “VLSI”
Fluid “VLSI”. System of Channels. Fluidic Systems Ensure Supply and Transport. Bioreactor. Channels. Cross-section: nm to mm range Materials: Glass, silicon, oxide, diamond, polymers Permanently bonded or reversely bondable. PDMS Channels. PDMS is porous and has a hydrophobic
610 views • 43 slides

VLSI Design. Third Year Standard Project - SB1 Second Mini Lecture Web page: https://camtools.cam.ac.uk. David M Holburn David Chuah Jiming Jiang. 12th May - 6th June 2009. Summary of progress so far. Developed ring oscillator (RO) concept Confirmed using VHDL & ModelSim
639 views • 35 slides

VLSI Design. Rehan Azmat Lecture 4 Devices. Previous Lecture. Semiconductor Theory Diode BJTs FETs MOSFETs. Lecture 4. MOSFET Static Behavior. N-MOS Transistor. MOS Symbols. MOS Static Behavior. The Threshold Voltage Resistive Operation The Saturation Region
652 views • 17 slides

VLSI Placement
VLSI Placement. Prof. Shiyan Hu [email protected] Office: EERC 731. Problem formulation. Input: Blocks (standard cells and macros) B 1 , ... , B n Shapes and Pin Positions for each block B i Nets N 1 , ... , N m Output: Coordinates (x i , y i ) for block B i .
444 views • 29 slides

vlsi. very large scale integration. vlsi the process of creating INTEGRATED circuits by packing many transistors on a single chip. VLSI began in the 1970s when complex SEMICONDUCTER & COMMUNICATION technologies were being developed. The microprocessor is a VLSI device.
537 views • 16 slides

VLSI. Acronym of VLSI V ery- L arge- S cale I ntegration A VLSI contains more than a million or so switching devices or logic gates Early in the first decade of the 21 st century, the actual number of transistors has exceeded 100 million
452 views • 14 slides

VLSI Testing. 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee 06-2757575 X 62371 [email protected] September 13, 2005. IC Design & Production Flow. 1. Design House 2. Foundry 3. Foundry or Testing House 4. Packaging House 5. Testing House. IC Design & Design-for-Test. Wafer Manufacturing. Wafer Testing.
381 views • 6 slides

255 views • 18 slides

Chapter 2: VLSI Technology
Chapter 2: VLSI Technology. Tahir Muhammad Lecture 2 FPGA-Based System Design. Topics. Basic fabrication steps. Transistor structures. Basic transistor behavior. Latch up. Fabrication processes. IC built on silicon substrate: some structures diffused into substrate;
279 views • 22 slides

VLSI Devices. Intuitive understanding of device operation Fundamental analytic models Manual Models Spice Models Secondary and deep-sub-micron effects Junction Diode and FET Resistor and Capacitor. B. A. Al. SiO. 2. p. n. Cross-section of. pn. -junction in an IC process. A. Al.
590 views • 54 slides

VLSI Fabrication Technology
VLSI Fabrication Technology. 1. Figure A.1 Silicon ingot and wafer slices. Figure A.2 (a) An 8-pin plastic dual-in-line IC package, (b) A 16-pin surface mount package. (e) n + diffusion (mask #4). (a) Define n -well diffusion (mask #1). (f) p + diffusion (mask #5).
295 views • 16 slides

Call for Paper - Upcoming Issues Upcoming Conferences 2024 -->
List of topics.
SSRG International Journal of VLSI & Signal Processing (SSRG-IJVSP) is a journal that publishes articles which contribute new novel experimentation and theoretical work in in all areas of VLSI & Signal Processing and its applications. The journal welcomes publications of high quality papers on theoretical developments and practical VLSI & Signal Processing.
- VLSI Circuits
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
- Low Power and Power Aware Design
- Testing, Reliability, Fault-Tolerance
- Emerging Technologies
- Post-CMOS VLSI
- VLSI Applications (communications, video, security, sensor networks, etc.)
- Nano electronics, Molecular, Biological and Quantum Computing.
- Intellectual property creating and sharing.
- Wireless communications.
- Custom, semi-custom, ASIC, programmable circuit design.
- Performance-driven, reliability-driven, thermally-driven, radiation hardening design.
- Processor, co-processor, multi-processor, memory design.
- Digital, analog, RF, mixed, asynchronous circuit design.
- Transducer design.
- Design for testability, built-in self-test.
- Adaptive Computing Systems with FPGA components.
- Mixed Analog / Digital Systems.
- Technology-related design, interconnect design, very deep submicron design
- Signal processing theory, algorithms, architecture, design, and implementation.
- Image / video processing, coding, compression, restoration, analysis, understanding, and communications.
- Speech processing, coding, compression, and recognition.
- Audio signal processing, coding, and compression.
- Image/video processing, coding, compression, restoration, analysis and understanding, and communications.
- Multimedia signal processing and technology.
Any other topics relevant to latest trends in VLSI & Signal Processing.
Engineers World
" Where engineers speak "
(vlsi seminar ,latest vlsi seminar topics, vlsi seminar list , vlsi research center , vlsi seminar , vlsi seminar projects, vlsi projects training, m.tech vlsi seminar)
Simulation of power grid networks considering wires and lognormal leakage current variations
Highly Parallel FPGA emulation for LPDC error floor characterization in perpendicular magnetic recording channel
VLSI Projects For M.tech 2021
Seminar Topics For M tech in VLSI
Electronics & Communication Engineering Seminar Topics
Applied Electronics & Instrumentation Seminar Topics
Seminar Topics for Electronics based on Microcontroller
Seminar Topics for ECE based on Matlab
Seminar Topics for ECE based on VLSI
Seminar Topics for Electronics based on Embedded Systems
Seminar Topics for Electronics Final Year Students based on Artificial Intelligence
Seminar Presentation Topics for Electrical & Electronics Engineering
Seminar Presentation Topics for Mechatronics Engineering
M.Tech Seminar Topics for Electronics Engineering
Viva Questions For Electronics and Communication Engineering (new)
Electronics Engineering Projects
Students Corner
- 1.Aeronautical Click for New Ideas >>
- 2.Aerospace Click for New Ideas >>
- 3.Agriculture Click for New Ideas >>
- 4.Aquaculture Click for New Ideas >>
- 5.Automobile Click for New Ideas >>
- 6.Applied Electronics & Instrumentation
- 7.Automation Click for New Ideas >>
- 8.Bio Chemical Click for New Ideas >>
- 9.Bio Medical Click for New Ideas >>
- 10.BioTechnology Click here >>
- 11.Ceramic Click for New Ideas >>
- 12.Chemical Click for New Ideas >>
- 13.Civil Click for New Ideas >>
- 14.Communication System
- 15.Computer Science
- 16.Computer Aided Design
- 17.Electrical Click for New Ideas >>
- 18.Electronics Click for New Ideas >>
- 19.Engineering Design
- 20.Environmental
- 21.Food Technology Click here >>
- 22.Genetics Click for New Ideas >>
- 23. Hacking Will be uploaded soon
- 24.Industrial Click here >>
- 25.Information Technology
- 26.Instrumentation & Control
- 27.Leather Technology
- 28.Marine Click here >>
- 29.Material Science Click here >>
- 30.Metallurgical Click here >>
- 31.Mechanical Click for New Ideas >>
- 32.Mechatronics >>
- 33.Mining Click for New Ideas >>
- 34.Naval Architecure Click here >>
- 35.Nanotechnology Click here >>
- 36.Ocean Click here >>
- 37.Oil & Paint Click here >>
- 38.Petroleum Click for New Ideas>>
- 39.Polymer Click for New Ideas >>
- 40.Polymer Electronics Click here >>
- 41.Printing Technology Click here >>
- 42.Production Click here >>
- 43.Pulp & Paper Technology
- 44.Railway Click here >>
- 45.Robotics Click here >>
- 46.Steel Click here >>
- 47.Sugar Technology Click here >>
- 48.Tele Communication Click here>>
- 49.Textile Click here >>
- 50.Transportation Click here >>
Copyright (c) 2021 engineers world All rights reserved. Powered by EW
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
QS World University Rankings rates MIT No. 1 in 11 subjects for 2024
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
QS World University Rankings has placed MIT in the No. 1 spot in 11 subject areas for 2024, the organization announced today.
The Institute received a No. 1 ranking in the following QS subject areas: Chemical Engineering; Civil and Structural Engineering; Computer Science and Information Systems; Data Science and Artificial Intelligence; Electrical and Electronic Engineering; Linguistics; Materials Science; Mechanical, Aeronautical, and Manufacturing Engineering; Mathematics; Physics and Astronomy; and Statistics and Operational Research.
MIT also placed second in five subject areas: Accounting and Finance; Architecture/Built Environment; Biological Sciences; Chemistry; and Economics and Econometrics.
For 2024, universities were evaluated in 55 specific subjects and five broader subject areas. MIT was ranked No. 1 in the broader subject area of Engineering and Technology and No. 2 in Natural Sciences.
Quacquarelli Symonds Limited subject rankings, published annually, are designed to help prospective students find the leading schools in their field of interest. Rankings are based on research quality and accomplishments, academic reputation, and graduate employment.
MIT has been ranked as the No. 1 university in the world by QS World University Rankings for 12 straight years.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- 2024 QS World University Rankings
Related Topics
- Computer science and technology
- Linguistics
- Chemical engineering
- Civil and environmental engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Materials science
- Mathematics
- Business and management
- School of Architecture and Planning
- MIT Sloan School of Management
- School of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
- Aeronautical and astronautical engineering
Related Articles

QS World University Rankings rates MIT No. 1 in 11 subjects for 2023

QS ranks MIT the world’s No. 1 university for 2023-24
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

A biomedical engineer pivots from human movement to women’s health
Read full story →

MIT tops among single-campus universities in US patents granted

A new way to detect radiation involving cheap ceramics

A crossroads for computing at MIT

Growing our donated organ supply
New AI method captures uncertainty in medical images
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Challenges in Architecting System-on-Chips - Elmore Family School of Electrical and Computer Engineering - Purdue University

Challenges in Architecting System-on-Chips
This presentation discusses some of the challenges involved in architecting System on Chips. A brief introduction to SoC is provided in the beginning. Furthermore, a sample SoC architecture is discussed with some of the key modules and interfaces highlighted. The presentation discusses various topics such as Pad multiplexing, Multiple Clocks, Internal Buses, Memory Sub system, Mixed Signal, Debug Facilities, IP block integration, Low Power design, Verification phases etc. along with the challenges faced by the architects/designers when these are being incorporated in an SoC. The presentation utilizes analogies to explain some of the concepts.
Dr. Pramod Govindan received his Bachelor of Technology in electronics and communication engineering from Government Engineering College in India, a Master of Science in VLSI and microelectronics and a Doctor of Philosophy in electrical engineering from the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT), Chicago. He had held technical/managerial positions at Analog Devices Inc. (ADI), California, and Rambus Chip technologies (India), and served as Assistant Professor at the University of North Florida (UNF), and Teaching Faculty at Oregon Institute of Technology (OIT) and University of Maryland (UMD). His research interest and effort primarily include reconfigurable hardware system-on-chip based digital system design and hardware realizations of Cryptographic algorithms on application specific integrated circuits (ASIC) and field programmable gate arrays (FPGA).
Professor David Janes, [email protected]
2024-04-16 08:00:00 2024-04-16 17:00:00 America/Indiana/Indianapolis Challenges in Architecting System-on-Chips Pramod Govindan Rambus Chip Technologies 11:15 am
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Research-Backed Benefits of Daily Rituals
- Michael I. Norton

A survey of more than 130 HBR readers asked how they use rituals to start their days, psych themselves up for stressful challenges, and transition when the workday is done.
While some may cringe at forced corporate rituals, research shows that personal and team rituals can actually benefit the way we work. The authors’ expertise on the topic over the past decade, plus a survey of nearly 140 HBR readers, explores the ways rituals can set us up for success before work, get us psyched up for important presentations, foster a strong team culture, and help us wind down at the end of the day.
“Give me a W ! Give me an A ! Give me an L ! Give me a squiggly! Give me an M ! Give me an A ! Give me an R ! Give me a T !”
- Michael I. Norton is the Harold M. Brierley Professor of Business Administration at the Harvard Business School. He is the author of The Ritual Effect and co-author of Happy Money: The Science of Happier Spending . His research focuses on happiness, well-being, rituals, and inequality. See his faculty page here .
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Need Help? US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333 Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060 Contact & Support
latest research topics in vlsi design. latest research topics in vlsi design - Doctor of philosophy is the final degree in any area. It requires a lot of efforts and hard work to achieve this.It starts with selection of a topic which should be recent and lies in your area of interest. If we talk specifically about research in technology then ...
VLSI. VLSI stands for Very Large Scale Integration. It signifies the process of producing integrated circuits (ICs) by integrating thousands, millions, or even billions of transistors on a single chip. In VLSI, the technology has allowed progressive growth with composite and secure devices, beginning from microprocessors and chips of memory to processors of digital signal and application ...
The five-day event will include: The Symposium will feature selected presentations and panel sessions as well as advanced VLSI technology developments, innovative circuit designs, and the applications they enable, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, IoT, wearable/implantable biomedical applications, big data, cloud / edge ...
VLSI-1 Class Notes Work required by this course §Lectures -Read sections in text and slides before class §Homework problems -8 homework assignments §Laboratory exercises -Three major exercises dealing with various aspects of VLSI design -Complete each section before the deadline §Project (EE 382M)
The 2023 Symposium on VLSI Technology & Circuits, ... In addition to the technical presentations, the Symposium program will feature a demonstration session, joint focus sessions, evening panels, short courses, workshops, and a special ... • This Forum is devoted to topics that extend the scope of the Symposia by suggesting the future ...
Class Presentations . Summary: Each person in class will be asked to give a 30-minute presentation on the topic of their choice, relevant to advanced VLSI design. Basically anything not covered in this course or CpE311 in VLSI design is fair game. See below for some ideas if you have trouble.
PRESENTATION I NSTRUCTIONS. All authors whether presenting in-person at the Symposium or on-demand need to provide an MP4 file, a 2-minute video, 2-slide summary along with a pdf of your slide deck, each of these items will be available for the OnDemand / Virtual attendees beginning June 17. Click each item below for instructions to help you.
We will also cover emerging machine learning design techniques for VLSI digital and analog circuit design. Important emerging topics such as quantum/Ising computing will be also covered. This course has a large emphasis on paper survey and seminar presentations of many important techniques. Who can take the course?
16 likes • 21,517 views. Kalyan Acharjya. Introduction of VLSI Design, Chip Development, Moore's Law. Its gives you the basic development overview of VLSI Technology.
List of Research Topics and Ideas of VLSI for MS and Ph.D. Thesis. High-throughput VLSI architecture for soft-decision decoding with ORBGRAND. Approximate Pruned and Truncated Haar Discrete Wavelet Transform VLSI Hardware for Energy-Efficient ECG Signal Processing. ADMM-Based Infinity-Norm Detection for Massive MIMO: Algorithm and VLSI ...
Group Discussion Topics for Engineering Students in VLSI. Rahul David. August 3, 2023. 11:18 am. 387. VLSI is a crucial domain within the field of engineering, focusing on the design and implementation of integrated circuits. With the rapid advancements in technology, VLSI plays a pivotal role in various sectors such as electronics ...
œtä€> Z |Œ ^¡E±)Ëk ¿3x5a²½-îõ gõ1àÿØÂ" ¡|ÄUˆy:'É»° b‹$¹öê!—Ó˜(2™‹y¡Íi…¨ ì³ ÓϨ|öŠ—€íOBë¿ ù¦1 ï¼ ,:šóš&¾œB "¦\ ÓK7tuJ!5$òö—' 3KJ—§T ¡Ó¨—¥ „ #1ù,Õ;ÿÿ PK !º¡ öÕ l ppt/presentation.xmlì˜ÛŽã( †ïWÚw°|»r;àsÔÉÈéLV+õîF"ž 'Xƒ Ò ...
Best VLSI-based IEEE projects for engineering students. 1. Real-time Traffic Light Control. In this VLSI design IEEE project, students will learn how to build an FPGA-based traffic light controller. Not only does this help regulate traffic, but it also reduces the average waiting time of drivers.
VLSI. May 9, 2014 •. 30 likes • 30,421 views. So Ma. I made this presentation for you , I hope its useful for you all, and I hate Plagiarism please, I also used some slides here but I mentioned all in the last slide :) Hope you can get benefits from it. Read more.
Technical Seminar Topics For M Tech Vlsi Design. (Electronics Engineering,Electronics & Communication Engineering,Communication Engineering) Low power tunable analog circuit blocks based on. Statistical design optimization of F in FET SRAM using back gate voltage. Integration and implementation of secured IP based Surveillance networks.
Emerging trends in VLSI focus on designing chips optimized for IoT-enabled devices, ensuring efficient data communication, low power consumption, and enhanced security. These specialized VLSI chips enable IoT devices to communicate seamlessly over the internet, exchanging data with other devices and cloud services.
ELEC 5970-003/6970-003 (Fall 2004) Advanced Topics in Electrical Engineering Designing VLSI for Low-Power and Self-Test Power Consumption in a CMOS Circuit - Designing VLSI for Low-Power and Self-Test. Power ... James J. Danaher Professor. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Presentation Transcript. Selected Topics in VLSI Design Results of Phase 1: First working FIR filter Design by Christoph Niemann and Vincent Wiese 30.10.2013 Institute MD, University of Rostock. Content • Adder • Multiplier • Architecture • Implementation • Metric • Future Improvements.
VLSI Technology. VLSI is an implementation technology for electronic circuitry - analog or digital Slideshow 1586527 by sarai ... to download presentation Download Policy: ... Topics. Basic fabrication steps. Transistor structures. Basic transistor behavior. Latch up. Fabrication processes. IC built on silicon substrate: some structures ...
The journal welcomes publications of high quality papers on theoretical developments and practical VLSI & Signal Processing. Papers are solicited from, but not limited to the following topics: PCB Design. VLSI Circuits. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Low Power and Power Aware Design. Testing, Reliability, Fault-Tolerance. Emerging Technologies.
VLSI Seminar Topics (vlsi seminar ,latest vlsi seminar topics, vlsi seminar list , vlsi research center , vlsi seminar , vlsi seminar projects, vlsi projects training, m.tech vlsi seminar) Data rendition flip-flops for power down applications On chip ESD protection sgategics for RF circuits in CMOS technologies
QS World University Rankings has placed MIT in the No. 1 spot in 11 subject areas for 2024, the organization announced today. The Institute received a No. 1 ranking in the following QS subject areas: Chemical Engineering; Civil and Structural Engineering; Computer Science and Information Systems; Data Science and Artificial Intelligence; Electrical and Electronic Engineering; Linguistics ...
The presentation utilizes analogies to explain some of the concepts. Bio Dr. Pramod Govindan received his Bachelor of Technology in electronics and communication engineering from Government Engineering College in India, a Master of Science in VLSI and microelectronics and a Doctor of Philosophy in electrical engineering from the Illinois ...
Presentation by Corey Geiger, CoBank. 15 Cheese consumption now double 1982's 20 pounds 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 1970 1974 1978 1982 1986 1990 1994 1998 2002 2006 2010 2014 2018 2022. What's the future for U.S. cheese consumption? Countries above 60 pounds •Denmark - 62 pounds
Summary. A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you're pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing ...
The Genesis of GitHub Copilot . Burke began the presentation by thanking the hosts and expressing enthusiasm for the transformative potential of GitHub Copilot.GitHub Copilot is the original and most widely used AI tool in the developer community, and with AI becoming an integral part of the development process, its ability to significantly increase productivity and happiness among developers ...
The authors' expertise on the topic over the past decade, plus a survey of nearly 140 HBR readers, explores the ways rituals can set us up for success before work, get us psyched up for ...