
Practice With Order of Operations Problems and Answers
I see it happen all the time in my math classroom: students attempt math problems and get the wrong answer even though they are performing each math operation correctly. How can this be!? Isn’t math supposed to have a single correct answer?
Well, as it turns out, there is a set of rules that tells us the right order and wrong order that operations can be performed in a mathematical expression. And without knowing this very important set of rules, you can’t be sure that you will always get the correct answer! Let’s take a look at this set of rules and dig into some practice with order of operations problems and answers so that you can make sure this doesn’t happen to you!
What is the Correct Order of Operations?
In math and algebra, the order of operations is an important set of rules that tell us the correct order that arithmetic operations should be performed in when working with a numerical expression. Performing operations in the right order using a standard method makes it so that two people will always get the same correct answer when solving a given problem.
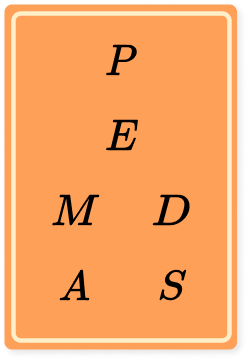
In order to help remember the standard order of operations, we can use the acronym PEMDAS.
The PEMDAS rule (sometimes known as BEDMAS or the BODMAS rule) works by matching the first letter of each operation to each of the mathematical operations.
- P (Parentheses) – We start by performing the operations inside any set of parentheses first. It is important to start with any expressions within innermost parentheses and work outward.
- E (Exponents) – The next step is to evaluate or simplify any expressions involving exponents or powers. It is important to remember that this step also includes any square root.
- MD (Multiplication and Division) – It is important to perform multiplication and division from left to right in the order that they appear in the expression. This is a common place where students make mistakes!
- AS (Addition and Subtraction) – Finally, we perform addition and subtraction from left to right as they appear in the expression. Like multiplication and division, these operations have the same priority and are performed from left to right.
To help my students, I have told them to think of the acronym PEMDAS as standing for “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally”. There are many different ways to remember the PEMDAS acronym, but I have found that this mnemonic device is a great way to help my students remember the order of the PEMDAS acronym.
If you follow the rules of the order of operations, you should find that arriving at the correct answer isn’t as hard as you once thought!
Why Does Order of Operations Matter?
In order to understand when order of operations matters, take a look at this simple 2-step order of operations problem. Consider the following expression:
$$2 + 4 \times 3$$
There are two approaches that you could take here, and only one of them will give you the correct answer! Which one do you think is correct?
As you can see, each strategy results in different answers. The strategy on the left adds 2 + 4 first, while the strategy on the right multiplies 4 x 3 first. Remember that we use the PEMDAS rule to help us identify the right order.
PEMDAS tells us that multiplication must be performed before addition. This tells us that the second solution is correct!
Order of Operations Problems and Answers
Let’s take a look at a few more examples of order of operations problems and answers! I’ll start by introducing you to some simpler problems with two basic operations, and we’ll work our way up to more complex 4-step order of operations problems! Just be sure to review the answer key for each problem to make sure you get the same answer!
2-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #1: \(5 – 3 \times 2\)
In this first example, following order of operations tells us to perform multiplication before subtraction. Taking a look at the given values, we know that this will result in:
\begin{split} &5 – 3 \times 2 \\ \\ =&5 – 6 \\ \\ =& -1 \end{split}
Remember, performing subtraction first is a common mistake that will prevent you from obtaining the correct answer!
Example #2: \((4 \div 2) + 7\)
The first step of the PEMDAS rule is to tackle any math expressions inside parentheses. After that, we can add 7 to the result.
\begin{split} &(4 \div 2) + 7 \\ \\ =&2 + 7 \\ \\ =& 9 \end{split}
Example #3: \(3^3 – 4\)
The first step in this example is to work out our exponent. After that, we can subtract 4 from the result.
\begin{split} &3^3 – 4 \\ \\ =&27 – 4 \\ \\ =&23 \end{split}
3-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #4: \(\sqrt{4} \times 3 – 5\)
Remember that the ‘E’ in the PEMDAS acronym also includes the square root operation. As such, we need to evaluate the square root of 4 before multiplying by 3 and subtracting 5.
\begin{split} &\sqrt{4} \times 3 – 5 \\ \\ =&2 \times 3 – 5 \\ \\ =&6 – 5 \\ \\ =&1 \end{split}
Example #5: \((6 ÷ 2) + 3 × 2\)
In this example we must remember to tackle the parentheses first. While your instinct may be to add the 3 next, remember that you need to multiply 3 times 2 first!
\begin{split} &(6 ÷ 2) + 3 × 2 \\ \\ =&3 + 3 × 2 \\ \\ =&3 + 6\\ \\ =&9 \end{split}
Example #6: \(7 – 2 × 3 ÷ 2\)
In this example, we multiply 2 by 3 first, then divide the result by 2. Remember that multiplication and division operations are performed in the order in which they appear from left to right.
\begin{split} &7 – 2 × 3 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&7 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&7 – 3 \\ \\ =&4 \end{split}
4-Step Order of Operations Problems
Example #7: \(2 + 4 × 3 – 4 ÷ 2\)
\begin{split} &2 + 4 × 3 – 4 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2 + 12 – 4 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2 + 12 – 2 \\ \\ =&12 \end{split}
Example #8: \(2^3 + (4 × 3) – 6 ÷ 2\)
\begin{split} &2^3 + (4 × 3) – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&2^3 + 12 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&8 + 12 – 6 ÷ 2 \\ \\ =&8 + 12 – 3 \\ \\ =&17 \end{split}
Using Order of Operations to Solve Math Problems
When I teach order of operations in my classes, I always encourage my students to keep the PEMDAS rule handy for every problem. Sometimes these problems can seem very simple, but may actually require more thinking. In particular, problems with both multiplication and division operations tend to confuse students!
Take the time that you need to fully understand this very important concept. You will find it comes up often in your studies of math, particularly when working with algebraic formulas !
Like all math concepts, mastering the use of order of operations takes practice and critical thinking. I am hopeful that these order of operations problems and answers have helped you feel more comfortable with this very important algebra skill!
Did you find these order of operations problems and answers helpful? Share this post and subscribe to Math By The Pixel on YouTube for more helpful mathematics content!
RECOMMENDED FOR YOU
Examples of One Solution Equations, Zero, and Infinite
Linear Equations Word Problems Worksheet with Solutions
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Order of op
Order of operations
Here you will learn about order of operations , including what it means and how to calculate and solve order of operations problems using PEMDAS .
Students will first learn about order of operations as a part of operations and algebraic thinking in elementary school.
What is the order of operations?
Order of operations refers to the rule that explains the sequence of steps necessary for correctly evaluating a mathematical expression or math problem.
You will use the acronym PEMDAS to help recall the correct order, or priority, in which you complete mathematical operations.
Mathematical operations such as multiplication and addition have to be completed in a specific order. This sequence of steps helps us to evaluate any mathematical expression, both with numerical values and algebraic expressions.
To evaluate an expression using PEMDAS, you need to understand what PEMDAS represents and be able to apply the PEMDAS rule to any calculation.
PEMDAS stands for:
P arentheses, E xponents, M ultiplication and D ivision, A ddition and S ubtraction
Parentheses have a higher priority than exponents, so we calculate what is inside a pair of parentheses first. Exponents have a higher priority than division and multiplication, so any exponent that can be evaluated is calculated next, and so on.
The order can be remembered using the mnemonic device for PEMDAS, ‘Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally.’
It is important to note that multiplication and division are given equal priority , and addition and subtraction are given equal priority.
When completing calculations that involve multiplication and division or addition and subtraction, you work from left to right.
For example,
Consider the following expression 12-7+6.
12-7=5 and then 5+6=11
Consider the following expression 10 \div 5 \times 2.
10 \div 5=2 and then calculate 2 \times 2=4.
Visually you could represent PEMDAS as:
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 5th grade math and 6th grade math?
- Grade 5: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (5.OA.1) Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
- Grade 5: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (5.OA.2) Write simple expressions that record calculations with numbers, and interpret numerical expressions without evaluating them.
- Grade 6: Expressions and Equations (6.EE.1) Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents.
How to evaluate using order of operations
In order to evaluate expressions using order of operations , you would use PEMDAS :
Solve any calculations within parentheses.
Solve for any exponents.
Solve any division and multiplication calculations.
Solve any addition and subtraction calculations.
![order of operations critical thinking questions [FREE] Properties of Equality Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 3 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/properties-of-equality-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Properties of Equality Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 3 to 6)
Use this quiz to check your grade 3 to 6 students’ understanding of properties of equality. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 3rd, 5th and 6th grade properties of equality topics to identify areas of strength and support!
Order of operations examples
Example 1: pemdas with addition and multiplication.
Evaluate 3+6\times{7}.
There are no parentheses.
2 Solve for any exponents.
There are no exponents.
3 Solve any division and multiplication calculations.
The multiplication that we need to calculate is 6\times{7}=42.
Replacing 6\times{7} with 42 gives us the calculation 3+42.
4 Solve any addition and subtraction calculations.
So 3+6\times{7}=45
Example 2: PEMDAS with division and subtraction
Evaluate 12-8\div{2}.
The division you need to calculate is 8\div{2}=4.
Replacing 8\div{2} with 4 gives us the calculation 12-4.
So 12-8\div{4}=8
Example 3: PEMDAS with parentheses and multiplication
Evaluate 3(2+4\times{6}-3).
You have a pair of parentheses and so you need to resolve what is inside the set of parentheses first. This is the calculation 2+4\times{6}-3.
Using PEMDAS, multiplication comes before addition and subtraction so you need to solve the multiplication 4\times{6}=24.
Replacing 4\times{6} with 24 in the calculation, you have 2+24-3.
Addition and subtraction should be completed from left to right and so you have 2+24=26 and 26-3=23. Therefore 2+24-3=23.
As 2+4\times{6}-3=23 and 3(2+4\times{6}-3) means 3\times(2+4\times{6}-3), you have the updated calculation 3\times{23}.
3\times{23}=69
There is nothing else to solve, so the final answer is:
3(2+4\times{6}-3)=69
Example 4: PEMDAS with an exponent and multiplication
Evaluate 4\times{3}^{2}.
Here you have to resolve 3^{2}=3\times{3}=9.
Replacing 3^{2} with 9 in the calculation, you now have:
The final step needed is to calculate 4\times{9}=36
4\times{3}^{2}=36
Example 5: PEMDAS with brackets, an exponent and division
Evaluate 3+(10\div{4}\times{20})^{2}.
Within the set of parentheses, you have the calculation 10\div{4}\times{20}.
You need to work from left to right.
Completing the division, you have 10\div{4}=2.5
Next, 2.5\times{20}=50
Therefore, 10\div{4}\times{20}=50.
Replacing 10\div{4}\times{20} with 50, you now have the updated calculation,
You now have to solve 50^{2}=50\times{50}=2500.
Updating the calculation, you now have 3+2500.
There are no divisions or multiplications to solve.
3+2500=2503 which gives us the final answer:
3+(10\div{4}\times{20})^{2}=2503
Example 6: PEMDAS with everything
Evaluate 4^{2}+2(14-8)\div{3}.
Within the brackets is the calculation 14-8=6.
Updating the calculation by changing the value in the bracket to 6, you have
4^{2}+2\times{6}\div{3}
As 4^2=4 \times 4=16, you now have
16+2\times{6}\div{3}
Here you have to calculate 2\times{6}\div{3}. Working from left to right, you calculate 2\times{6} and then divide the solution by 3.
2\times{6}=12
12\div{3}=4
Updating the calculation, you now have 16+4.
As 16+4=20, our final answer is:
4^{2}+2(14-8)\div{3}=20
Teaching tips for order of operations
- While PEMDAS is a great way for students to remember the order of operations, it’s important that the students understand how to solve for each of the operations required, not simply giving them the acronym to memorize.
- It is important to find a way for students to practice outside of order of operations worksheets. The more practice a student gets, the better. For example you can physically separate word problems from the answer choices in the classroom. Students would have to walk around to discuss and solve the problem and then find the answer that matches.
- Students could be given an expression without the symbols. They would have to then decide which operations/symbols would make the expression true.
Easy mistakes to make
- Multiplication/division and addition/subtraction in the incorrect order When you have a chain of multiplication and division calculations or a chain of addition and subtraction calculations, you work from left to right. For example, If you put parentheses into the calculation 12\div{4}\times{3} with the purpose of keeping the calculation exactly the same, you must place the parentheses around 12\div{4}. This is because 12\div{4}\times{3}=9, and (12\div{4})\times{3}=3\times{3}=9. If you placed parentheses around 4\times{3} you would have 12\div{(4\times{3})}=12\div{12}=1 which is a different answer that you would get without the parenthesis.
- Exponents as multiplying a number by 2 When introducing exponents, some students will interpret 4^2 as 4 \times 2 instead of 4 \times 4. The use of a number line to represent this expression or using expanded notation when introducing the concept can help students internalize the learning.
- Multiplying before exponents Take 2\times{3}^{4}. Because you would perform exponents before you perform multiplication within PEMDAS, you need to calculate the exponent term first, and then multiply the solution by 2. Inserting a pair of parentheses with the purpose of keeping the calculation exactly the same, 2\times{3}^{4}=2\times(3^{4})=162. A common misconception is that the multiplication is carried out first, and then the value is raised to the power; here this would look like (2\times{3})^{4} and is equal to 6^{4}=1296 which is the wrong answer.
Related properties of equality lessons
- Properties of equality
- Associative property
- Commutative property
- Distributive property
Practice order of operations questions
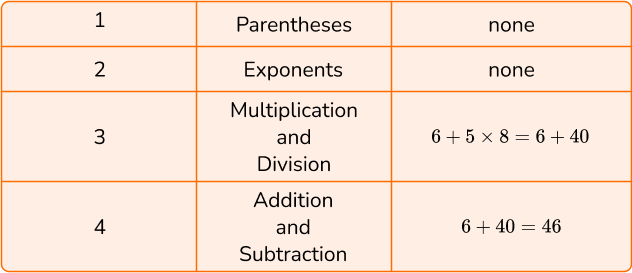
1. Calculate 6+5 \times 8.

To solve, follow the order of operations by using PEMDAS.
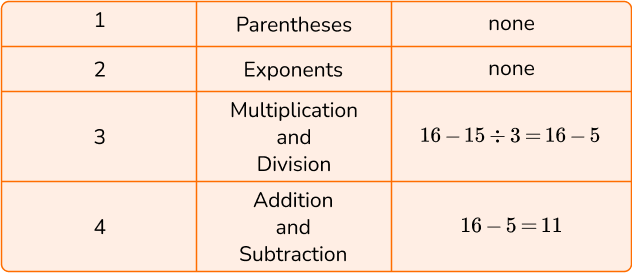
2. Calculate 16-15 \div 3.
To solve, follow the order of operations by using PEMDAS .
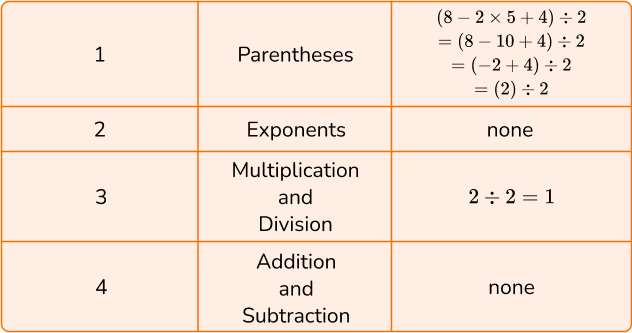
3. Calculate (8-2 \times 5+4) \div 2.
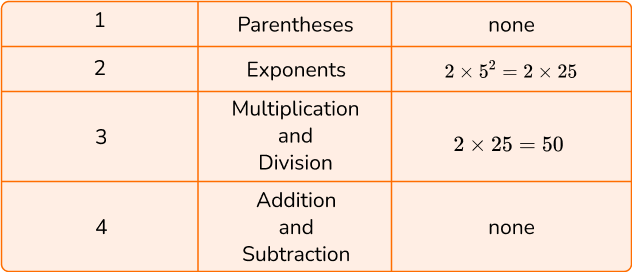
4. Calculate 2 \times 5^2.
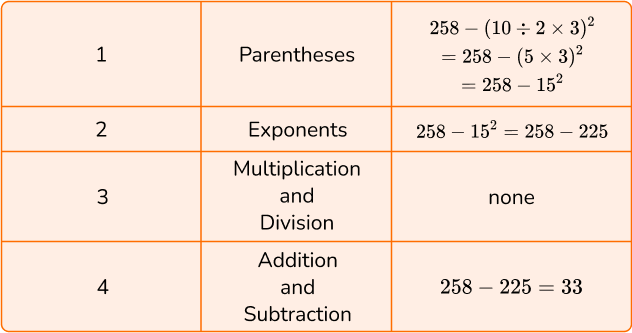
5. Calculate 258-(10 \div 2 \times 3)^2.
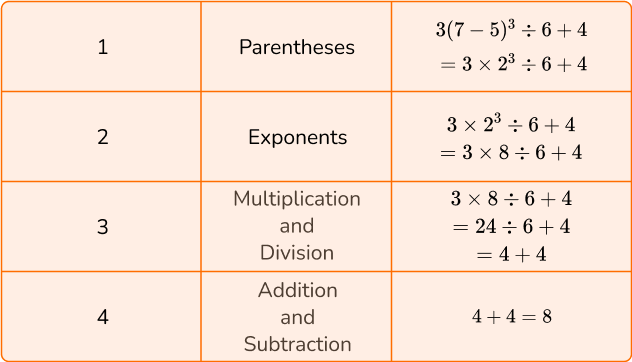
6. Calculate 3(7-5)^3 \div 6+4.
Order of operations FAQs
In the order of operations, multiplication and division are seen as equal and would be performed as they are stated within the expression, starting from left to right. The same is true with addition and subtraction.
Both PEMDAS and BODMAS are correct. The acronym BODMAS is the UK version of the same rules. It can also be referred to as BIDMAS or BEDMAS . The acronym in the UK would read as: B rackets, I ndices, D ivision and M ultiplication, A ddition and S ubtraction.
An exponent refers to the number of times a number is multiplied by itself. For example 7^2 = 7 \times 7 or 4^3 = 4 \times 4 \times 4.
Parentheses are used within mathematical expressions to note a modification is the normal order of operations. In the expression, (3+4) \times 3, because the addition is within parentheses, it is solved before the multiplication.
The next lessons are
- Addition and subtraction
- Multiplication and division
- Types of numbers
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
Privacy Overview

Teaching Order of Operations: No-fail Strategies that Work!
Order of operations can be frustrating to teach, but it doesn’t have to be. There’s no question that this is an extremely challenging topic for elementary students. Fortunately, there are loads of strategies for teaching order of operations that are both fun and effective.
One reason kids struggle with this concept is that there are so many rules to learn and follow. Even worse, rules that appear to be simple often prove to be deceptively complex.
For example, most kids can easily remember that multiplication and division are always performed before addition and subtraction, especially after they learn to follow the order described by “PEMDAS.”
However, they tend to get stuck when an equation includes both multiplication AND division. Most kids automatically multiply before dividing, but order of operations tells us to perform the operation that comes first when reading the problem from left to right. No wonder kids find order of operations to be super confusing!
Another reason kids struggle is that even when they understand how to use order of operations correctly, they don’t apply the rules systematically. Because the problems look easy, students try to rely on mental math alone to solve them. This may work with the easy problems, but mental math isn’t effective with more complex problems that include multiple operations, parentheses, exponents.
Order of Operations Lesson
The lesson begins with a quick activity to get students thinking about why we need rules for solving equations. This lesson “hook” is followed by an order of operations mini-lesson, a guided practice session, and a fast-paced game that doubles as a formative assessment activity.
To get the most from the activities, each student will need a dry erase board or tablet where they can work out the problems. You’ll also need at least one calculator for the class that uses order of operations correctly. A physical calculator is fine if displayed under a document camera, or you can use an online calculator. Be sure to test the calculator prior to the lesson to be sure it can handle order of operations problems. To find out, enter 1 + 2 x 3 and press the = sign. The correct answer is 7, so if your calculator displays 9 as the answer, it does NOT use order of operations correctly.

Before you teach PEMDAS or any other strategy, challenge your students to solve a simple equation such as this one: 3 + 8 x 2 = ? Ask your students to write the equation on a dry erase board or tablet, and then solve it and show you the answer.
You’re likely to see two different answers, but resist the urge to reveal the correct answer at this point. Most students will say the answer is 22 because they added 3 and 8 and then multiplied the sum by 2. However, who have studied order of operations in the past will say the answer is 19 because they multiplied 8 times 2 and added 3 to the product. Your students might be a bit confused when they notice that some of their classmates have different answers, but they are about to become even more confused!
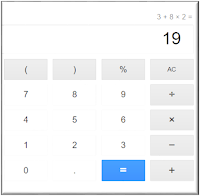
Tell your students that you’re going to use a calculator to check the answer, and as they watch, enter the problem above. When the calculator displays 19 as the answer, act surprised and say you must have entered the problem wrong. Enter it carefully again, and when you get the same answer, try a different calculator. When you get the same answer yet again, ask your students to pair up with a partner to discuss why the calculator keeps giving the “wrong” answer. After they talk it over for a few minutes, tell them that 19 is actually the correct answer, and that you’re going to teach them some important rules for solving problems that involve more than one operation.
This activity is a great way to start your order of operations lesson because it creates a feeling of “cognitive dissonance,” a state of mind in which we struggle to assimilate new facts that don’t match what we thought we knew about a topic. When students experience cognitive dissonance, they become eager to learn and open to new ideas, so it’s the perfect time to start the actual instruction.
2. Direct Instruction: Introduce Order of Operations
How you introduce order of operations will depend on your students’ readiness and their prior experiences with algebraic concepts. You might want to start by teaching your students how to use parentheses to indicate which part of an equation should be solved first. Write an equation two different ways, keeping the numbers the same but placing the parentheses around different pairs of numbers like this: (5 + 3) x 2 = ? and 5 + (3 x 2) = ?
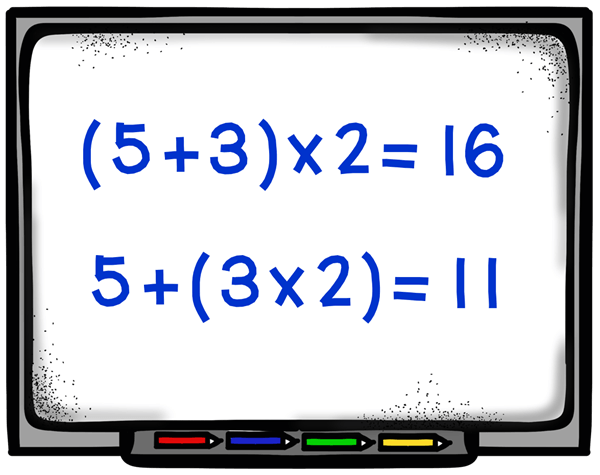
Show your students how to solve both problems, and point out that even though the numbers used in the equations are the same, the solutions are different. Give your students several more pairs of problems that have the same numbers and the parentheses in different locations. Stop after each problem to discuss the solution and clear up misunderstandings.
Next, display an equation that doesn’t have parentheses, like 15 – 5 x 2 = x. Point out that it’s not clear which part of the problem should be solved first, and as they’ve seen with the previous example, the order in which you perform the operations DOES matter.
Tell your students that mathematicians have agreed upon a set of rules called the “order of operations” that must be followed when solving problems. If your students have already studied exponents, you can teach the acronym PEMDAS which stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. The phrase “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” will help them remember the order of those letters. If your students haven’t studied exponents, you can substitute the acronym PMDAS and the phrase “Pass My Dad a Sandwich.”

3. Guided Practice: Teaching the Step-by-Step Method for Solving Problems
For the next part of the lesson, you’ll need to download the Order of Operations Freebie shown above. This freebie consists of three pages from Order of Operations Bingo Level 1 . Exponents are not mentioned on these pages, and the acronym PMDAS is used instead of PEMDAS.
After using the Order of Operations Review to explain the PMDAS acronym, display a copy of the practice page or give each student a paper copy. Introduce the step-by-step method for evaluating algebraic expressions by explaining the example at the top of the page. Using this strategy, each step is written on a separate line.
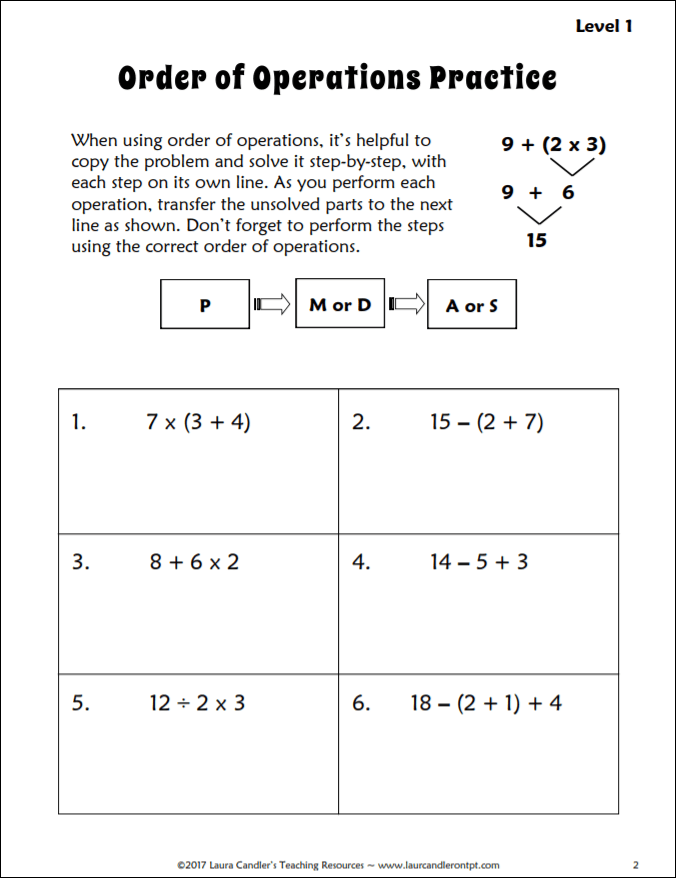
Guide your students through the process of solving the 6 practice problems one at a time. Check and discuss the solutions after each problem, and be sure to have them show you their work. If needed, refer to the answer key on page 3 of the freebie for step-by-step solutions.
If you have not taught this step-by step-method of solving order of operations problems, you might be tempted to skip it and let your students use mental math. Most of the problems are so easy that your students may be able to solve them without writing out each step.
However, relying on mental math to solve more challenging problems results in a lot of careless mistakes, so I recommending teaching your students to follow this step-by-step strategy with EVERY problem. If they get in the habit of using this systematic approach, they will be able to solve more complex problems with ease later. Trust me on this!
4. Play an Order of Operations Game
After your students understand how to solve order of operations problems, they’ll need lots of practice while the concepts are fresh in their minds. Games are far more effective for practice than worksheets because they are fast-pace and fun, motivating students to solve dozens of problems in a short time.
If you play the game as a class and discuss the answers after each problem, your students will know within a few round of the game if they are solving the problems correctly. If they aren’t, they will be motivated to ask questions and seek help to improve. Furthermore, many games can serve as formative assessment activities if you walk around while students are solving each problem to observe their work. Without having to administer a formal test, you’ll be able to see who understands the concepts and who needs more help.

Order of Operations Bingo is my favorite activity for practicing this skill because players can’t win without using order of operations correctly. To foster math skill development, ask your students to work out each problem on a dry erase board or tablet, using the step-by-step method. Stop after each problem to discuss each solution before presenting the next task card. Remind your students that they can only cover the answer on their Bingo boards with a chip if they had the correct answer BEFORE you revealed the solution to the class. If you enforce this rule, I can guarantee a huge drop in careless errors after the first round of the game!
5. Review and Practice with Order of Operations Task Cards or digital Boom Cards
The first four strategies are extremely effective for teaching kids how to use order of operations correctly. However, in order to retain what they’ve learned, your students will need opportunities for more review and practice throughout the year.
Whether you’re teaching students remotely or in the classroom, the Order of Operations Boom Cards below will meet this need perfectly! Boom Cards are self-checking, interactive, digital task cards that can be played on almost any device with Internet access. They are hosted on the Boom Learning platform, but free accounts are available. My Boom Cards also include optional audio directions; students can click the sound icon in the corner of each card to hear the words on the card read aloud! Kids love these interactive task cards because they’re fun, and teachers love them because they’re so effective!

If you prefer printable task cards, the Order of Operations Task Cards below will make it easy for your students keep these skills fresh. You can use the task cards shown below in math centers and with cooperative learning activities like Showdown or Team Scoot .
Differentiating Instruction is Easy
Differentiating instruction is easy because there are two levels of instructional materials, including the task cards, bingo game, and assessments. Level 1 includes basic problems like the ones used in the freebie. The materials for Level 2 have more complex problems and some of the problems include exponents. Both sets of bingo games, the printable task cards, and the assessments are included in one cost-saving bundle. If your curriculum includes exponents, the Order of Operations Games and Tests Bundle is your best option. If you use both levels in your classroom, you might want to print the task cards and game materials for each level on different colored card stock to keep them separate. (Boom Cards must be purchased separately.)
Classroom-Tested: Teacher and Student Approved
I love having teachers field test my products with their students. Several teachers tested Order of Operations Bingo with their students, and two of them sent pictures of their students playing the game. I love to see photos of kids using my lessons and activities, and I couldn’t resist sharing a few of them with you!
Fourth grade teacher Christina Ashburn tested Order of Operations Bingo and had her students solve the problems on dry erase boards as described in the lesson. She didn’t have bingo chips, so she laminated the game boards and had her students color over the answers with dry erase markers. I honestly never thought of doing that, but it’s a brilliant idea! For one thing, if kids are solving problems on dry erase boards, their markers should be handy. Also, you don’t have to worry about plastic Bingo chips ending up all over the classroom floor!
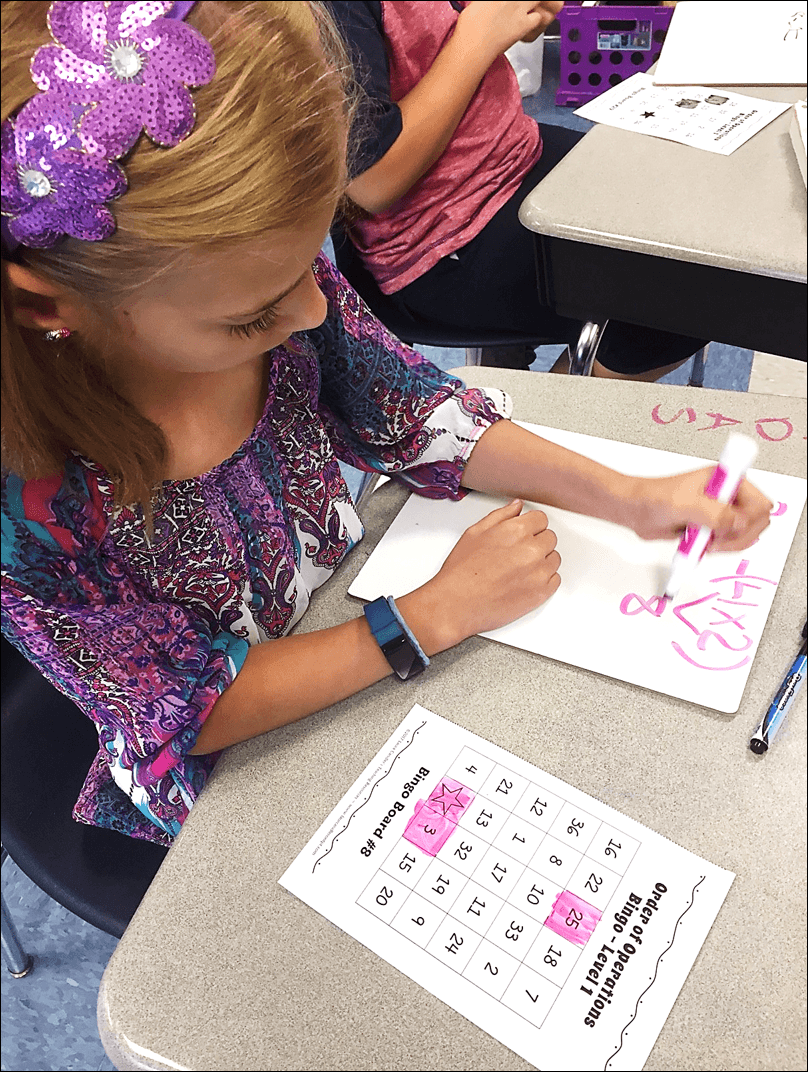
Fifth grade teacher Sheryl Nicholas also tested the game in her class. After observing her students play Order of Operations Bingo , she discovered an unexpected benefit. Sheryl explained, “My favorite part was how my non-English speakers immediately felt involved in the review. So much lately is ‘drill and test,’ but this made it a lot more interesting for the students. All were engaged in the activity and there was quite a bit of math talk as well as individual practicing of skills.”

After they played the game, Sheryl interviewed her students to get their feedback and shared some of their comments with me. I especially loved reading two comments about having to write out the steps of each problem. One student said, “I liked that you wouldn’t let me do them in my head but made me write the problems on the iPad and do them.” Another student wasn’t quite as enthusiastic about that part of the lesson, stating, “I wish you would have let me do these problems in my head. But then again, I always work too fast so I probably did better since I had to write them down.”
I just laughed when I read that last comment because it’s exactly the sort of thing some of my students would have said! This “no-fail” order of operations lesson is fun for students, and the step-by-step strategies make it highly effective, too. After playing the game, even kids recognize the importance of writing out the steps when solving order of operations problems, whether they like it or not!

Candler's Classroom Connections
- Growth Mindset
- Literature Circles
- Cooperative Learning


Order of Operations Exercises
Order of operations practice problems with answers.
There are nine (9) problems below that can help you practice your skills in applying the order of operations to simplify numerical expressions. The exercises have varying levels of difficulty which are designed to challenge you to be more extra careful in every step while you apply the rules of the Order of Operations. Good luck!
Part 1: Order of Operations problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
Problem 1: Simplify the numerical expression below.
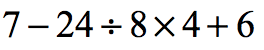
Problem 2: Simplify the numerical expression below.
Problem 3: Simplify the numerical expression below.
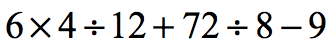
Part 2: Order of Operations problems involving the four arithmetic operations and parenthesis (or nested grouping symbols)
Problem 4: Simplify the numerical expression below.
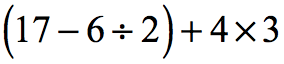
Problem 5: Simplify the numerical expression below.
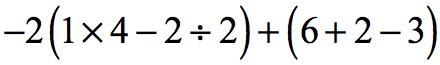
Problem 6: Simplify the numerical expression below.
![order of operations critical thinking questions -1×[(3-4×7)➗5]-2×24➗6](https://www.chilimath.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/order-of-operations-prob6.png)
Part 3: Order of Operations problems involving the four arithmetic operations, parentheses and exponents
Problem 7: Simplify using the Order of Operations.
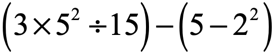
Problem 8: Simplify using the Order of Operations.
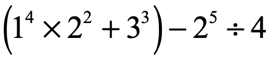
Problem 9: Simplify using the Order of Operations.
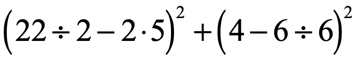
Take a Quiz
Order of Operations Quiz
You may also be interested in these related math lessons or tutorials:
Order of Operations
PEMDAS Rule
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy
12 Fun Activities To Teach And Practice Order Of Operations
December 19, 2023 // by Josilyn Markel
When students start to learn the order of operations, it marks a big leap in the development of their math skills. They’re going from doing one operation at a time to performing a whole series of operations, and this can be a bit difficult to teach and grasp. That’s why it’s important to teach the topic using several different methods and activities so that the concept can really stick and be correctly applied with plenty of practice. Here, we’ve compiled a list of twelve fun activities to help your students learn, practice, and master the order of operations!
1. Video Lesson: Intro to Order of Operations
This video is a great introduction to any order of operations lesson. The video is engaging, and the concepts are explained with just the right amount of detail. Plus, the language in the video is age and level-appropriate for fifth and sixth-grade students.
Learn More: YouTube
2. “Talking Calculators” Worksheet
With this worksheet activity in class, students solve a series of PEMDAS problems. Then, based on their answers, they fill in the blanks to tell a story. So, the story acts as the answer key, and students can easily monitor their own progress and mastery with this order of operations fun activity.
Learn More: The Mail Box
3. Order of Operations Puzzle: Three Challenge
This critical thinking activity requires students to put the correct signs of operations into the sequence of operations, but every number in every sequence is three! Students play around with PEMDAS in order to find the right sign of operation for each spot so that they can come up with the indicated answer.
Learn More: Math Equals Love
4. Order of Operations Error Analysis Task
In this error analysis activity, students have to find and correct the mistakes in the given expressions. Then, they should change the expression around to show the correct answer instead of the incorrect answer. This works well as a review activity right before the exam, or as practice for more advanced students.
Learn More: Math Geek Mama
5. PEMDAS Music Video
When it comes to order of operations activities, this one has got to be the catchiest! Simply play this groovy music video for your kiddos that explains the order of operations and that will also help them remember the correct sequence.
6. Order of Operations Football Board Game
In this fun partner activity, students play one-on-one football. You give each pair a deck of cards, and they have to maximize the yards that they can travel along the printable football field game board. It’s an exciting activity since kids take turns moving the “ball” up and down the “field”; the first one to score a “touchdown” is the winner!
7. Foldable Notes and Study Guide
Students can create their own order of operation resources with these interactive notebook sequences of operations activities. Printable and foldable note-taking guides help students build a whole repository of review materials that they can use to understand the topic at a deeper level and to keep the concepts fresh in their minds throughout the whole semester.
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers

8. Classroom Poster
This classroom poster is the perfect way to present the order of operations concept for students in a clear and concise way. It’s also beneficial for students to be able to see and remember the PEMDAS sequence; especially as the level of complexity of the equations and expressions increases throughout the semester.
Learn More: Amazon
9. Order Ops Royal Rescue Online Game
This is an activity students will love playing at home. Each learner becomes a knight in the “Order of Operations”, and they must rescue a princess by solving a series of questions about PEMDAS. The questions get more challenging as the quest progresses, and the plethora of questions offers a lot of great practice with the topic.
Learn More: Mr. Nuss Baum
10. Order of Operations Ladder Activity
In this individual activity, students cut and paste colorful paper to make a chain of correct answers. The order of operations steps must be followed carefully so that all of the ladder’s rungs end up in the correct position. You simply print the “rungs” on one piece of paper, and then students get to have all the fun with cutting, pasting, and solving the expressions.
11. Martian Hoverboards Online Game
In this fast-paced game, students have to quickly give the correct answer to the given order of operations problem. If not, their martian character falls down! It’s a race that relies on mental math and a solid understanding of PEMDAS.
Learn More: Math Nook
12. Online Traditional Worksheet: Order of Operations
This is a self-checking worksheet that students complete online. It includes operations without exponents as well as expressions with exponents, so it forms a comprehensive review and/or assessment of the topic. Plus, it marks the incorrect solutions, so students can benefit from immediate feedback.
Learn More: Online Math Learning
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Miss Glitter Teaches
Bringing a dash of sparkle to tired teachers
in Math · March 7, 2023
How To Teach Problems with Order of Operations
The good old order of operations…Actually, I totally remember learning how to solve problems with order of operations when I was in middle school. I liked the clear-cut sort of rules and directions to follow. Unlike in language arts, the order of operations had rules that didn’t get broken. My little organized self loved the simplicity of just following the rules.
However, as a teacher, I’ve learned that not everybody likes clear-cut rules like problems with order of operations have. Some kids prefer the more open-ended critical thinking type questions, like how to solve word problems. Some kids like rules, but only when it benefits them. Oh wait, I’m talking about the order of operations, not classroom behaviors…
Problems with order of operations can be fun for kids, no matter if they like following rules or not! So let’s dive in!

Definition for Order of Operations
First up, let’s talk about the definition for order of operations. The definition for order of operations is a set of steps needed to solve an expression with multiple operations. This means that students are given an expression and have to simplify it using the operations in a certain order.
These operations are multiplication, division, adding, and subtracting, as well as having parentheses and exponents. Problems with order of operations can have a few or all of these operations!
Acronym for Order of Operations
There’s an acronym for order of operations most commonly PEMDAS that is used for keeping track of the rules. The letters stand for parentheses, exponents, multiply, divide, add, and subtract.
There are other acronyms as well such as:
- GEMDAS (grouping, exponents, multiply, divide, add, subtract)
- GEMORDSORA (grouping, exponents, multiply OR divided, Subtract OR add)
No matter the acronym for order of operations that you chose to teach with, be sure to explain that multiply/divide happens as you read the problem from left to right. Same thing with adding and subtracting, we read from left to right. This is important when problems with order of operations have both adding and subtracting.
I usually use a hopscotch type of math poster idea to help students get the point across. I draw the arrows going from left to right to remind students that these steps of the order of operations happen in a different order depending on the problem.

Order of Operations and Exponents
Depending on if you teach 5th grade or 6th grade, you might have order of operations and exponents. According to the Common Core State Standards:
Problems with Order of Operations for 5th Grade
5.OA.A.1 Use parentheses, brackets, or braces in numerical expressions, and evaluate expressions with these symbols.
In 5th grade, students solve problems with order of operations with parentheses, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction. For an extension, you can always teach order of operations and exponents, but it is not in the Common Core Standard for 5th Grade.
Problems with Order of Operations for 6th Grade
6.EE.A.1 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents.
In 6th grade, students solve problems with order of operations with all of the components. This is an extension from the 5th-grade standard and if students need scaffolding, removing the exponents for a time might provide that.
Resources to Teach Order of Operations in Math Problems
I’ve rounded up some of my favorite resources to teach order of operations in math problems, whether you teach 5th or 6th grade.
I use a hands-on approach to teaching and practicing math and that is no different from teaching problems with order of operations. So, I love using math stations in my 6th-grade classroom and it helps with differentiation and creating a more engaged class. I talk all about how to set up math stations, how to stay organized, and different math station rotation ideas in my 5 part video series. Inside this free video series, you gain access to everything you need to set up math stations in under a week. Turn your math block from frustrating to fun! Drop your email below and you’ll get the 5 videos sent to your inbox ready whenever you are!
Digital Task Cards
A holdover from the digital era of teaching but is still a go-to in my classroom. This set of task cards can be used digitally with Google Forms or using TPT’s Easel Platform. A paper version is also included along with a recording form if you want to use the tasks card that way.
I share a bunch of ways how to use task cards in this blog post so if you are looking for creative ideas be sure to check it out .

Creative Math Posters
I love looking for ideas for math posters and order of operations is such a fun topic. I included my personal favorite, the hopscotch method as well as a few others.

Sure you can look up ideas for math posters and create your own. Or you can trace them and use fun fonts and layouts to keep yourself organized. But my favorite way to use math posters is using them as student reference sheets. I print fill-in-the-blank style anchor charts for my math interactive notebooks. Then as I am creating the full-size chart, students can fill in their own. This then stays in their notebook or math folder as a reference.
Inside my 5th grade math equations anchor chart bundle I include colorful options for you to print, black and white to make tracing easier and a fill-in-the-blanks copy for students to fill in with you. If you are interested in picking up the 5th grade math equations anchor chart pack click the picture below to learn more.

Math Games 2 Player
Want more of a gamified approach to practicing problems with order of operations? This math games 2 player option is perfect for partners or during math stations.
Students simply take a board and solve an order of operations math problem. Then they check their answer with their partner who has the answer. Partner A has Partner B’s answers and vice versa. This gives the games for mathematics a self-checking aspect. If the answer is correct, students take a turn at Tic Tac Toe.
My students love this game and usually set up a whole class competition to determine overall winners. The low-prep, print & play game is easy for me to prepare ahead of time and set out for math stations.
Want to try out the problems with order of operations game? Click here to learn more !

More Problems with Order of Operations
Want to learn more about problems with order of operations? Be sure to check out these blog posts and videos to help brainstorm new ways to teach order of operations in your upper elementary classroom!
- Math Antics- Order of Operations Video
- 12 Fun Activities to Teach and Practice Order of Operations
- 8 Ideas for Teaching Order of Operations
- Free Order of Operations Activity
- Three Order of Operations Activities to Keep Your Students Engaged
- Top 5 Order of Operation Resources for 5th Grade
- Mastering Order of Operations
I’d love to know how you teach problems with order of operations! Drop your ideas and hints in the comments!

Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest on Instagram

Have Questions?
Please let me know !
Privacy Policy
Miss Glitter
on Teachers Pay Teachers
- Organization
- Tips & Tricks
The Order of Operations and Variables:
Order of operations.
A good idea when working with many operations at a time is to do a little portion of the equation at a time, rewriting frequently. For example, do the portion within the parentheses and then rewrite the equation. Trying to do the entire equation at once can often lead to mistakes. Break it down into parts using the order of operations and do a little at a time.
What is the order of operations?
Operations are things like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. When you add two numbers together, you are performing the operation of addition on them. Similarly, when you multiply numbers together, you are performing the operation of multiplication.
The order of operations is the rule for what operations should be done first when there are several operations within the same equation.
The order of operations is like grammar rules for the language of math. It explains how to interpret an equation to mean what it is supposed to mean.
Applying the Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
The order of operations says that operations must be done in the following order: parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction.
Parentheses
When there are parentheses, whatever is inside must be done first. The stuff inside the parentheses may also need to be broken down according to the order of operations as well. It is even possible to have parentheses within parentheses. In cases like this, work from the inside out.
If there are exponents in the equation, these would be done next.
Multiplication and Division
Multiplication and division can be done together. In other words, it doesn’t matter if you do division or multiplication first, but they must be done after parentheses and exponents and before addition and subtraction.
Addition and Subtraction
Addition and subtraction also work together. You can do subtraction first, or you can do addition first. They are part of the same step, however, they can only be done after items in parentheses, exponents, and any multiplication and division.
A frequently used expression in English to help students remember the order of operations is PEMDAS.
Another way to remember this is the phrase “ Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally. ”
Critical Thinking Challenge
Can you think of another phrase that could help you remember the order of operations?
Video Source (04:50 mins) | Transcript
Video Source (01:07 mins) | Transcript
Video Source (05:49 mins) | Transcript
Video Source (04:21 mins) | Transcript
Remember to take it one step at a time and rewrite your equation after completing an operation. Doing this will help you keep track of what you’ve already done and make sure you don’t skip any steps.
Remember to continue to work on memorizing your single digit multiplication if they aren’t memorized yet. As you are beginning to see, we are using multiplication a lot in these lessons and they will be easier if you know your multiplication.
Additional Resources
- Khan Academy: Intro to order of operations (09:39 mins, Transcript )
- Khan Academy: Order of operations example (04:26 mins, Transcript )
- Khan Academy: Order of operations (PEMDAS) (05:19 mins, Transcript )
Practice Problems
Evaluate the following expression:
- \(0\div4\times7+5^{2}\div5\times5 = ?\)
- \(6 - 4 ^{2} \div 2 - 2^{3} + 3 = ?\)
- \(6 \div 1 - \lgroup 7 - 5 \rgroup \times 3^{2} \times 7 = ?\)
- \(7 + 2 \times 3^{3} + 12 \div 2 = ?\)
- \(2^{3} \times 5 \div \lgroup 5 - 1 \rgroup \div \lgroup 2 - 1 \rgroup \times 6 = ?\)
- \(5^{3} - \lgroup 5 \times 2 \rgroup^{2} - 2^{4} - 2^{3} = ?\)
There are various steps in the order of operations. Use only the steps required to solve this problem.
First, solve exponents. The 5 is the only number with an exponent.
\(0 \div 4 \times 7 + 5^{2} \div 5 \times 5\)
Solve the exponent by multiplying 5 × 5. Replace the exponent with the answer 25.
\(0 \div 4 \times 7 + 25 \div 5 \times 5\)
Now, solve any multiplication or division from left to right. Divide 0 by 4.
Now, replace the division of 0 by 4 with 0.
\(0\times 7 + 25 \div 5 \times 5\)
Solve any multiplication or division from left to right. Solve 0 × 7 and 25 divided by 5.
Replace 0 × 7 and 25 divided by 5 with their respective answers, 0 and 5.
\(0 + 5 \times 5\)
Continue solving the multiplication of 5 × 5.
Replace the 5 × 5 with the answer 25. The final step is to solve any addition.
Add 0 + 25. The answer is 25.
There are various steps in the Order of Operations. Use only the steps required to solve this particular problem.
First, resolve any exponents. There are two numbers with exponents, the 4 and 2.
\(6 - 4^{2} \div 2 - 2^{3} + 3\)
Solve the exponents by multiplying 4 × 4 and 2 × 2 × 2. Replace the previous exponents in the problem with the answers 16 and 8 respectively.
\(6 - 16 \div 2 - 8 + 3\)
Now, solve any multiplication or division from left to right. The division of 16 by 2 is the next step.
The solution to the division of 16 by 2 is 8. Replace the division of 16 by 2 with the number 8.
\(6 - 8 - 8 + 3\)
The last step in the Order of Operations is to solve any addition or subtraction from left to right. Solve the subtraction 6 − 8.
The difference between 6 − 8 is \(-2\). Replace the subtraction of 6 − 8 with a \(-2\).
\(- 2 - 8 + 3\)
Now subtract \(-2-8\).
The answer is \(-10\). Replace the subtraction with \(-10\). Proceed to the last step, add \(-10\) and 3.
\(- 10 + 3\)
Replace \(-10+3\) with the answer, which is \(-7\).
- \(-120\) ( Solution Video | Transcript )
- 60 ( Solution Video | Transcript )

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Algebra Topics - Order of Operations
Algebra topics -, order of operations, algebra topics order of operations.

Algebra Topics: Order of Operations
Lesson 1: order of operations, introduction to the order of operations.
How would you solve this problem?
12 - 2 ⋅ 5 + 1
The answer you get will depend largely on the order in which you solve the problem. For example, if you work the problem from left to right —12-2, then 10⋅5, then add 1—you'll get 51 .
12 - 2 ⋅ 5 + 1 10 ⋅ 5 + 1 50 + 1 51
On the other hand, if you solve the problem in the opposite direction—from right to left —the answer will be 0 .
12 - 2 ⋅ 5 + 1 12 - 2 ⋅ 6 12 - 12 0
Finally, what if you did the math in a slightly different order? If you multiply first, then add , the answer is 3 .
12 - 2 ⋅ 5 + 1 12 - 10 + 1 2 + 1 3
It turns out that 3 actually is the correct answer because it's the answer you get when you follow the standard order of operations . The order of operations is a rule that tells you the right order in which to solve different parts of a math problem. ( Operation is just another way of saying calculation. Subtraction, multiplication, and division are all examples of operations.)
The order of operations is important because it guarantees that people can all read and solve a problem in the same way. Without a standard order of operations, formulas for real-world calculations in finance and science would be pretty useless—and it would be difficult to know if you were getting the right answer on a math test!
Using the order of operations
The standard order of operations is:
Parentheses
Multiplication and division, addition and subtraction.
In other words, in any math problem you must start by calculating the parentheses first, then the exponents , then multiplication and division , then addition and subtraction . For operations on the same level, solve from left to right . For instance, if your problem contains more than one exponent, you'd solve the leftmost one first, then work right.
Let's look at the order of operations more closely and try another problem. This one might look complicated, but it's mainly simple arithmetic. You can solve it using the order of operations and some skills you already have.
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + (4 + 6 ⋅ 2) + 18 / 3 2 - 8
Always start with operations contained within parentheses. Parentheses are used to group parts of an expression.
If there is more than one set of parentheses, first solve for the ones on the left. In this problem, we only have one set:
In any parentheses, you follow the order of operations just like you do with any other part of a math problem.
Here, we have two operations: addition and multiplication . Because multiplication always comes first, we'll start by multiplying 6 ⋅ 2 .
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + (4 + 6 ⋅ 2 ) + 18 / 3 2 - 8
6 ⋅2 is 12. Next, we'll add 4 .
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + ( 4 + 12 ) + 18 / 3 2 - 8
4+12 is 16 . So we've simplified our parentheses to 16 . Since we just have a single number in the parentheses, we can get rid of them all together—they're not grouping together anything now.
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + 16 + 18 / 3 2 - 8
Second, solve any exponents . Exponents are a way of multiplying a number by itself. For instance, 2 3 is 2 multiplied by itself three times, so you would solve it by multiplying 2 ⋅2 ⋅2 . (To learn more about exponents, review our lesson here ).
There's only one exponent in this problem : 3 2 . 3 2 is 3 multiplied by itself twice —in other words, 3 ⋅ 3 .
3 ⋅ 3 is 9 , so 3 2 can be simplified as 9 .
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + 16 + 18 / 9 - 8
Next, look for any multiplication or division operations. Remember, multiplication doesn't necessarily come before division—instead, these operations are solved from left to right .
Starting from the left means that we need to solve 4 / 2 first.
4 divided by 2 is 2 . That makes our next problem 2 ⋅ 3 .
2 ⋅ 3 + 16 + 18 / 9 - 8
2 ⋅ 3 is 6 . Finally, there's only one multiplication or division problem left: 18 / 9 .
6 + 16 + 18 / 9 - 8
18 / 9 is 2 . There's nothing left to multiply or divide, so we can move on to the next and final part of the Order of Operations: addition and subtraction .
6 + 16 + 2 - 8
Our problem looks a lot simpler to solve now. All that's left is addition and subtraction.
Just like we did with multiplication and division, we'll add and subtract from left to right . That means that first we'll add 6 and 16 .
6 + 16 is 22 . Next, we need to add 22 to 2 .
22 + 2 is 24 . Only one operation left: 24 - 8 .
24-8 is 16 . That's it!
We're done! We've solved the entire problem, and the answer is 16 . In other words, 4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + ( 4 + 6 ⋅ 2 ) + 18 / 3 2 - 8 equals 16 .
4 / 2 ⋅ 3 + (4 + 6 ⋅ 2) + 18 / 3 2 - 8 = 16
Whew! That was a lot to say, but once we broke it down into the right order it really wasn't that complicated to solve. When you're first learning the order of operations, it might take you a while to solve a problem like this. With enough practice, though, you'll get used to solving problems in the right order.
Remembering the order of operations
If you use it a lot, you'll eventually get the hang of the order of operations. Until then, it can be helpful to use a word or phrase to remember it. Two popular ones are the nonsense word PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, Addition and Subtraction) and the phrase Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally .
/en/algebra-topics/exponents/content/
- Reading/Writing Topics
- Math Topics
Critical Thinking with Order of Operations Review FREEBIE

Of course I "ran" right over and downloaded this at TpT. Thanks for sharing. I know my kids will adore this! :) Finding JOY in 6th Grade
I am very thankful first grade math is easy :) Not sure I could cut it in the big grades! Ha! Thanks for sharing the freebie! Hope you have a fab week, Michele! Molly Lucky to Be in First
Thanks for sharing. We will using order of operations soon and this will be perfect to include in my math workshop.
This is a great game! I can't wait to share with my 5th graders! Anything with dice makes them happy!
Thank you for taking the time to comment. I will make every effort to respond back to you!
Keep in Touch
Popular posts.

Blog Archive
- ► January (1)
- ► August (1)
- ► January (2)
- ► September (1)
- ► June (3)
- ► May (3)
- ► April (4)
- ► March (1)
- ► February (2)
- ► December (1)
- ► July (2)
- ► May (5)
- ► April (5)
- ► March (3)
- ► February (6)
- ► January (6)
- ► December (2)
- ► November (2)
- ► October (5)
- ► August (7)
- ► July (6)
- ► June (5)
- ► April (2)
- ► March (4)
- ► February (4)
- ► January (5)
- ► December (3)
- ► November (6)
- ► October (4)
- ► September (3)
- ► August (5)
- ► July (9)
- ► June (21)
- ► May (9)
- ► April (7)
- ► March (10)
- ► February (8)
- ► January (11)
- ► December (11)
- ► November (10)
- ► October (10)
- One More Day to Win a Sharpener!
- September Swap: Interactive Reading Literature No...
- Today is the Day! Pencil Sharpener Giveaway!
- Otzi the Iceman
- Open House and Curriculum Night
- Tried it Tuesday: Quiet Classroom Pencil Sharpene...
- Critical Thinking with Order of Operations Review ...
- Group Problem Solving is 31-Wonderful!
- Monday Made It September Edition Getting My Back ...
- Mentor Text Sunday: Prime Numbers Anyone?
- Thursday Throwdown: Sending Students Off With a Fe...
- Blog Hopping for a 1000 Follower Giveaway!
- ► August (13)
- ► July (17)
- ► June (13)
- ► May (8)
- ► April (10)
- ► March (9)
- ► February (11)
- ► January (13)
- ► December (9)
- ► September (7)
- ► August (8)
Find it Fast
- Back to School
- Interactive
- Interactive Notebook
- Mentor Texts
- Mid-Week Math
- Notice and Note
- Organization
- Spark Student Motivation
FLORIDA BLOGGER
Blogs i follow.
© 2015 Coffee Cups and Lesson Plans . Victoria Template designed by Georgia Lou Studios All rights reserved.

Order of Operations Questions

Primary Study Cards

- 5-a-day Answers
- Worksheet Answers


Order of Operations Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers.
BODMAS, BIDMAS, bodmas,
GCSE Revision Cards

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
24 Card Game - Order of Operations & Critical Thinking - Math

Description
Questions & answers.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
3-Step Order of Operations Problems. Example #4: 4-√ × 3- 5. Remember that the 'E' in the PEMDAS acronym also includes the square root operation. As such, we need to evaluate the square root of 4 before multiplying by 3 and subtracting 5. = = = 4-√ × 3- 5 2 × 3- 5 6- 5 1. Example #5: (6 ÷ 2) + 3 × 2.
Free order of operations math school topic guide, including step-by-step examples, free practice questions, teaching tips, and more! ... Grade 5: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (5.OA.2) ... Practice order of operations questions. 1. Calculate 6+5 \times 8. 88 . 46 . 640 . 118 .
The phrase "Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally" will help them remember the order of those letters. If your students haven't studied exponents, you can substitute the acronym PMDAS and the phrase "Pass My Dad a Sandwich.". 3. Guided Practice: Teaching the Step-by-Step Method for Solving Problems.
This engaging resource activates critical thinking and problem-solving skills, all while building a true understanding of the order of operations.Each sheet has 12 to 30 problems with varied orders of operations. Level 1 problems are shorter. Level 2 problems are longer, involve multiple steps. These order of operations worksheets are great
Order of Operations Practice Problems with Answers. There are nine (9) problems below that can help you practice your skills in applying the order of operations to simplify numerical expressions. The exercises have varying levels of difficulty which are designed to challenge you to be more extra careful in every step while you apply the rules ...
Here, we've compiled a list of twelve fun activities to help your students learn, practice, and master the order of operations! 1. Video Lesson: Intro to Order of Operations. Math Antics - Order Of Operations. Watch on. This video is a great introduction to any order of operations lesson.
Some kids prefer the more open-ended critical thinking type questions, like how to solve word problems. Some kids like rules, but only when it benefits them. Oh wait, I'm talking about the order of operations, not classroom behaviors… Problems with order of operations can be fun for kids, no matter if they like following rules or not!
This activity is great for the hundredth day of school, for enrichment, or for a morning math warm-up.Drag and drop the numbers and operations on the Google Slides in a specific order to create 100!For example, make 100: using these numbers: 3, 2, 33, 1and these operations: +, x, Subjects: Critical Thinking, Math, Mental Math. Grades: 4 th - 6 th.
The order of operations is like grammar rules for the language of math. It explains how to interpret an equation to mean what it is supposed to mean. Applying the Order of Operations (PEMDAS) The order of operations says that operations must be done in the following order: parentheses, exponents, multiplication, division, addition, and subtraction.
The standard order of operations is: Parentheses. Exponents. Multiplication and division. Addition and subtraction. In other words, in any math problem you must start by calculating the parentheses first, then the exponents, then multiplication and division, then addition and subtraction. For operations on the same level, solve from left to right.
Description. Help students deepen their understanding of the order of operations as they critically think through solving these task cards. Whether in a small group, game of skoot, or a daily challenge question, these cards can help expand your scholars thinking. Total Pages. 6 pages. Answer Key.
At. 5:40. Sal says that you have to do things from left to right when you have multiple operations at the same level. At this point in the video, the problem is: 10 x 4 / 2 - 5 x 6. Sal solves left to right: 40 / 2 - 5 x 6 = 20 - 30 = -10. But if I don't do it in the same order I get the same answer: 10 x 2 - 5 x 6 = 20 - 30 = -10.
a simplified improperfraction, like 7/4. a mixed number, like 1 3/4. an exactdecimal, like 0.75. a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2/3 pi. Related content. Video 9 minutes 40 seconds9:40. Intro to order of operations. Video 3 minutes 34 seconds3:34. Order of operations examples: exponents.
I was able to begin a little of my Math Workshop concept using a launch, mini lesson, work time and reflection model. It will be slow going for awhile. I was also able to teach my smarties to play 31-Wonderful, and an Order of Operations Game. This Order of Operations Game is quick and really reinforced critical math thinking.
Order of Operations Questions. Previous: Primary 5-a-day, videos, worksheets and more.
The order of operations is a crucial math concept that ensures consistent results when solving problems with multiple operations. By following PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division, and Addition and Subtraction), students can accurately evaluate expressions and avoid common mistakes. Mastering this skill is essential for ...
Solving problems that have multiple operations can be difficult. This activity will teach students the tricks that will make these kinds of problems easier.
This 'Correct the Order of Operations Questions' resource is a great way for learners to check their deeper understanding of BIDMAS/BODMAS. The activity would be great as an assessment tool since it requires the learners to challenge their knowledge of the order of operations. It would also be useful as an early finisher extension task for a ...
36. Products. $257.00 $397.00 Save $140.00. View Bundle. Pre-Algebra Logic Puzzle Bundle. These group activities could be done in the physical classroom or in breakout sessions on Zoom or Google classroom. Each student will be responsible for a set of 6 problems applying the concepts you have taught in class. Together, the group will solve the ...
BODMAS, BIDMAS, bodmas, Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on the Order of Operations.
Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process ...
Order of Operations Task Cards. Created by. Maneuvering the Middle. This set includes 48 cards (24 on level, 24 higher level) that require students to evaluate expressions with parentheses. Common Core Standards 5.OA.1 and TEKS 6.5E. Included: 48 task cards (2 differentiated sets) recording sheet (used for both sets) answer keys ideas of ...
This HM Government advice outlines the importance of sharing information about children, young people and their families in order to safeguard children. It should be read alongside the statutory guidance Working together to safeguard children 20236. The advice is non-statutory and replaces the HM Government Information sharing: advice for ...
A fun way in which students can choose four digits, 0-9, and create a number problem in which the answer is 24. They may use any of the 4 operations to solve the problem, however, each number may only be used once, no limit on operations. This is a great activity to supplement lessons on order of operations, math properties, and critical thinking.