
Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

Top 7 Research Budget Templates with Samples and Examples

Tejas Prasanna
There is no magic formula for creating a research budget. Depending on the kind of research and the potential changes it can bring about, careful planning and allocation is necessary. Budgets can, thus, vary depending on the sponsors, besides other factors. However, every research budget has some essential guidelines.
Research budgets depend on the project deliverables, timelines, and milestones. The resources required also depend on the scope of the projects and sponsors.
Best Templates for Planning Your Research Budget
Designing a research budget is not easy. You will need to consider the resources required and categorize them according to guidelines to ensure funding is not a problem. The categories may include the project’s necessary supplies and equipment and the wages you must pay your assistants. Research budgets are allocated for a year, but you can also plan for a quarter, depending on the project.
At SlideTeam, we have taken care of all these pain points and designed content-ready presentation templates that address each of these points. You save the time, the resources, and the tedium in having to make these presentations from scratch.
What is even better is that each of the templates is 100% editable and customizable. The content-ready nature means you get a starting point and a structure to guide your presentation; the editability feature means you can customize the template to audience profile.
Let’s explore these templates now.
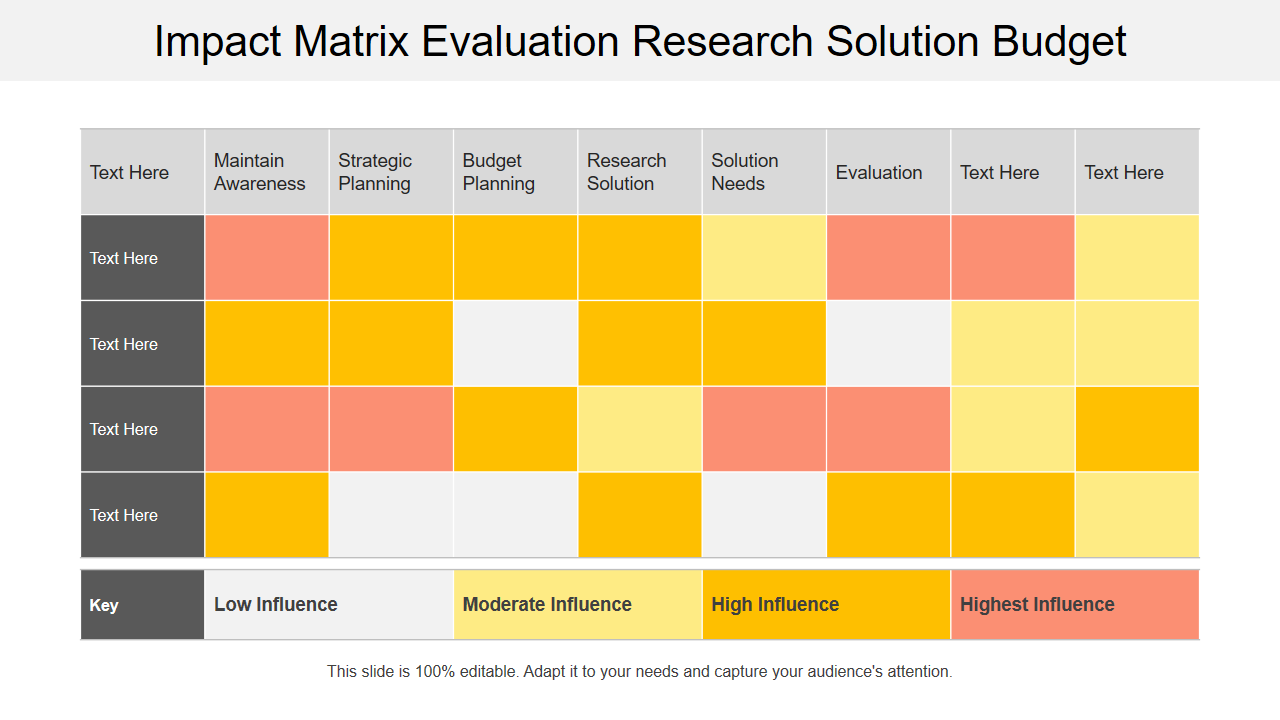
Template 1 - Impact matrix evaluation research solution budget
This PPT Template is the perfect solution for your research budgeting needs. The matrix suggests what solutions are essential with the help of relevant keys that assign priority levels. Priorities go from low to highest influence with increasing importance. They are color-coded, with white being the lowest and red being the highest influence. For instance, Maintain Awareness and Evaluation are red in many cases, as shown in the slide. So, that means that they bear a significant impact on the research budget. Similarly, Strategic and Budget Planning are color-coded white, which means they don't impact the research budget as much in some cases.
With the impact matrix and heatmap, mapping out your research budget will be a breeze.
Get it now!
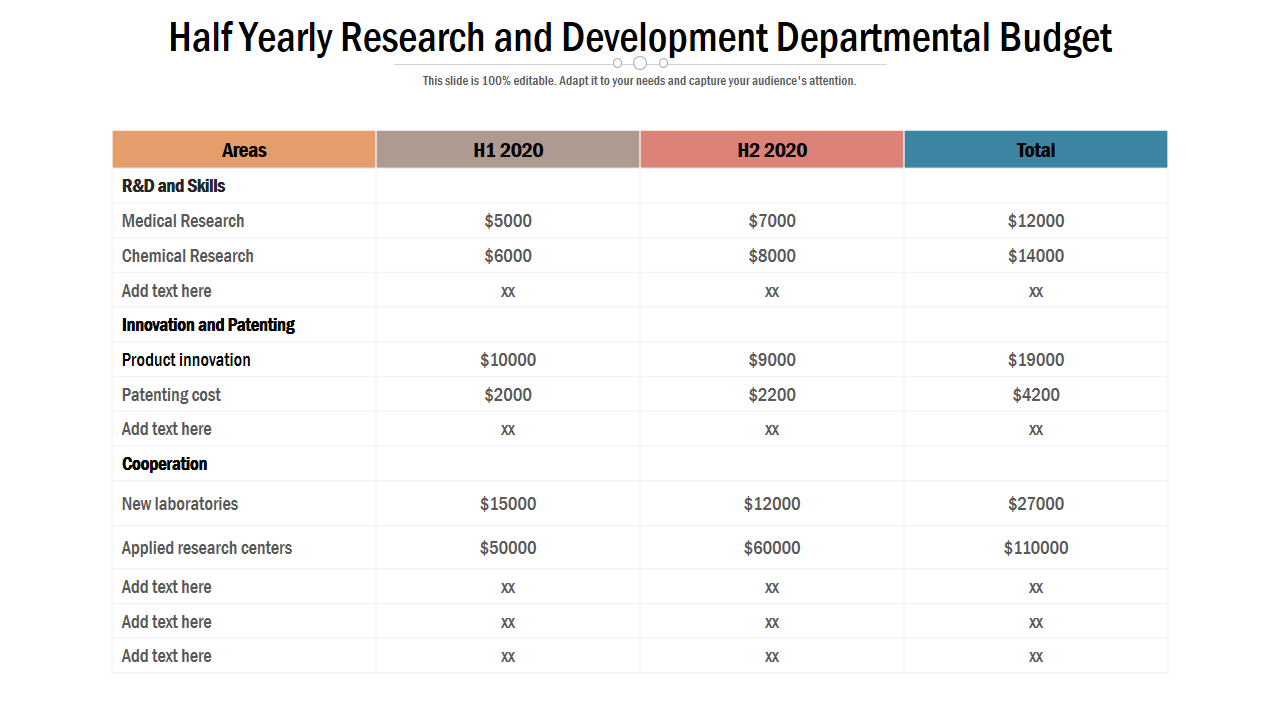
Template 2 Half-yearly research and development departmental budget
Research and Development departments can plan the budget required for projects for the two halves of the year using this PPT Template. The presentation template highlights areas for which you will need funding such as research and development, skills, innovation and patenting, and cooperation. You can also list your requirements for each area. For instance, under R&D and skills, you may need funding for medical research, chemical research, etc. Similarly, for innovation and patenting, you may need funding for product innovation and to cover patenting costs. Likewise, cooperation may involve setting up new laboratories and research centers. With this outlined, you can split the budget required for your research project for the two halves of the year.
Download now!
Template 3 - Budget Estimate for Research and Development Project
This presentation template for the budget estimate for your research and development project is apt for arriving at the calculation for the four quarters in a year. You can define and assign tasks as per the requirements of the project and allocate a set budget for each. The tasks may involve conducting market research and competitive analysis or be innovative or developmental. In either case, you can use this template to set a fixed budget for each task in the research project.

Get it today!
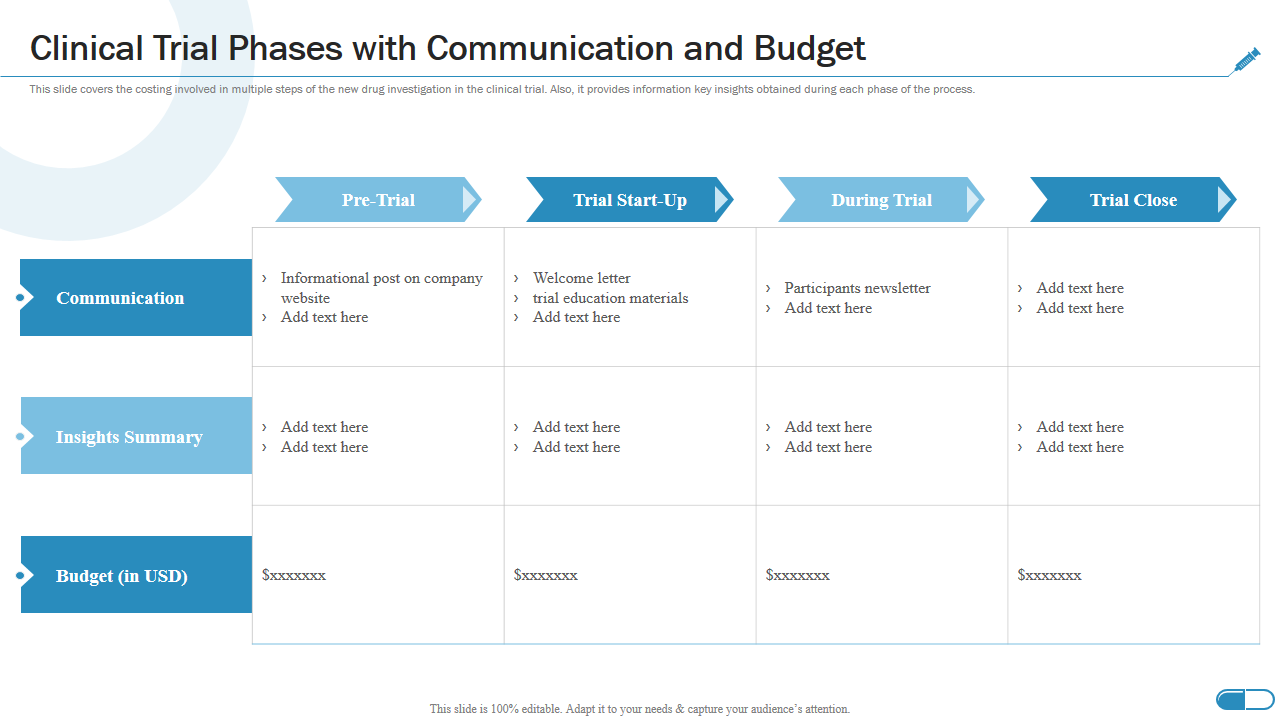
Template 4 Clinical Trial Phases with Communication and Budget Research Design for Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve many phases, and you should let your research associates know about each step. For instance, you could post the information on the company website and provide relevant insights during the pre-trial phase. Similarly, you can offer the welcome letter and training materials during the trial start-up. During the trial, you can send newsletters to your associates, giving them relevant information and other valuable insights. All this requires funding, and you will need to allocate a budget. However, you don't need to worry, as this PPT Preset has you sorted, with dedicated sections for the pre-trial, trial start-up, during-trial, and trial-end phases. It also has communication, insights summary, and budget sections. You can use the budget section in the matrix to allot a budget for each trial phase and each section, including communication and insights.
Download here!
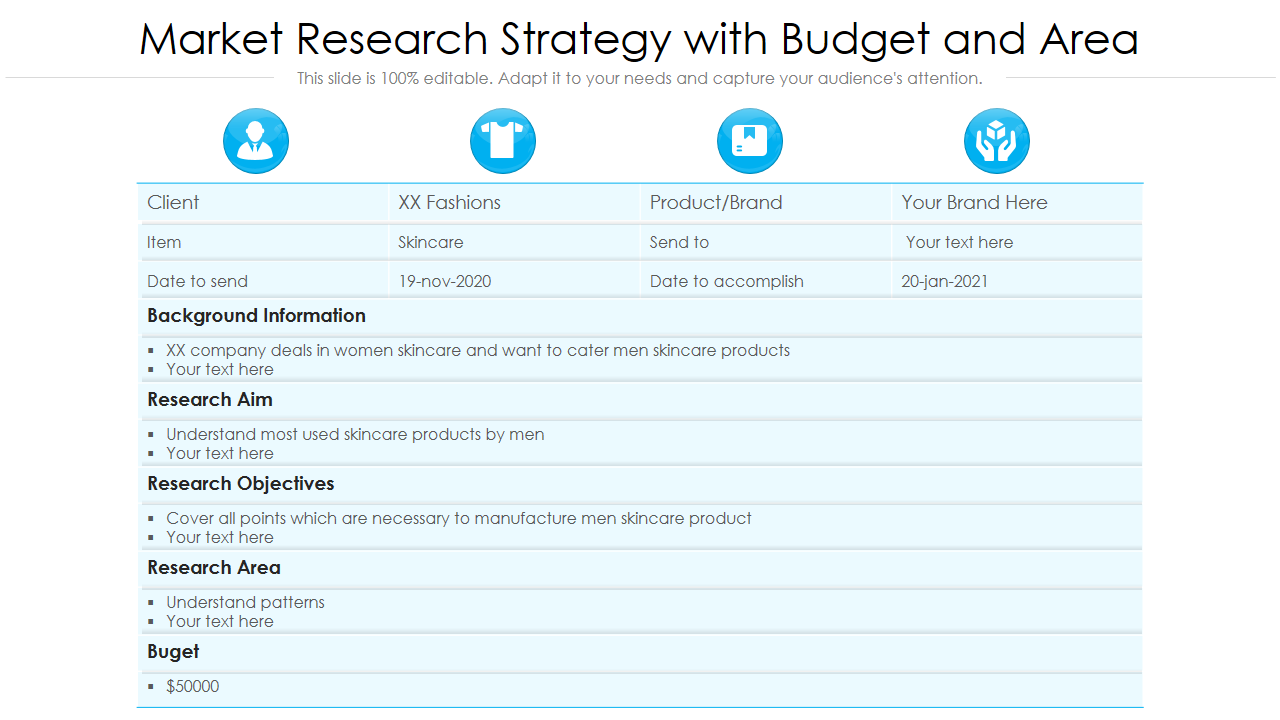
Template 5 Market research strategy with budget and area
The PPT Template has all the core elements required for your market research strategy, including the budget and area. This slide lets you list your clients, the items, and when to send them. You can also list background information related to your research, the aim and objectives of the project, the areas covered, and the budget.
The presentation template also provides a dedicated space to list your brands and products and a timeline for completing the research.
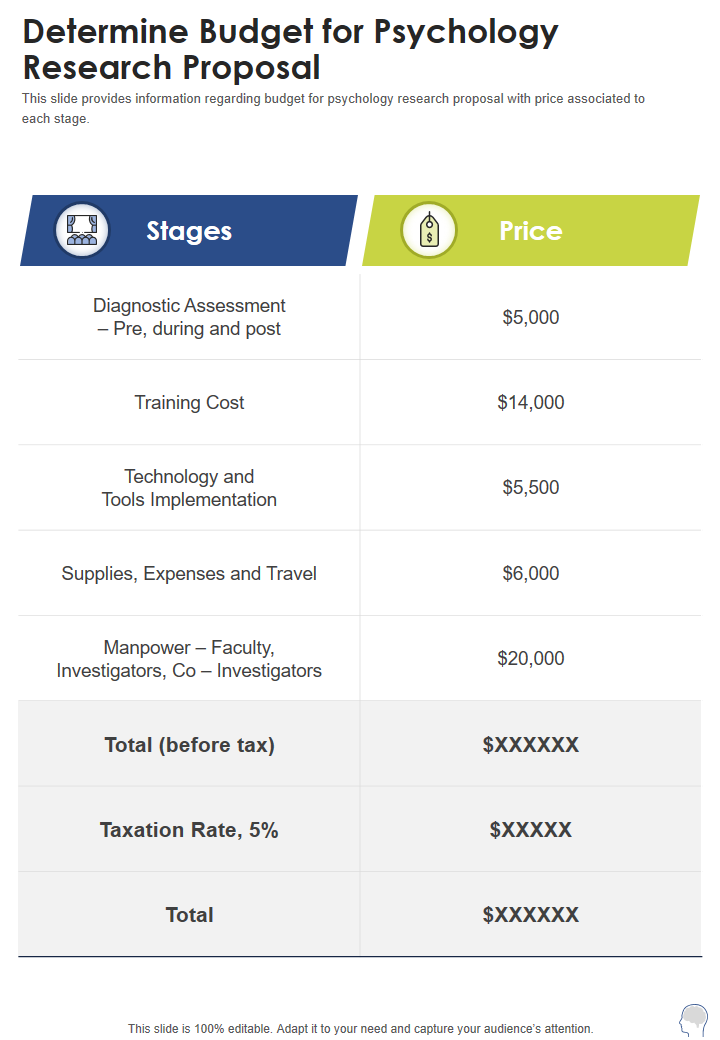
Template 6 - Determine Budget for Psychology Research Proposal One-Pager Sample Example Document
This presentation template is an easy-to-use tool for determining the budget required for psychology research. With this slide, you can allocate a budget for each area, including diagnostic assessment, training, technology and tools, supplies, travel, and workforce. It is a practical, hands-on template with information required to plan the budget for conducting psychological tests and evaluations. Please note that depending on your geography, taxes might or might not deserve a separate column.
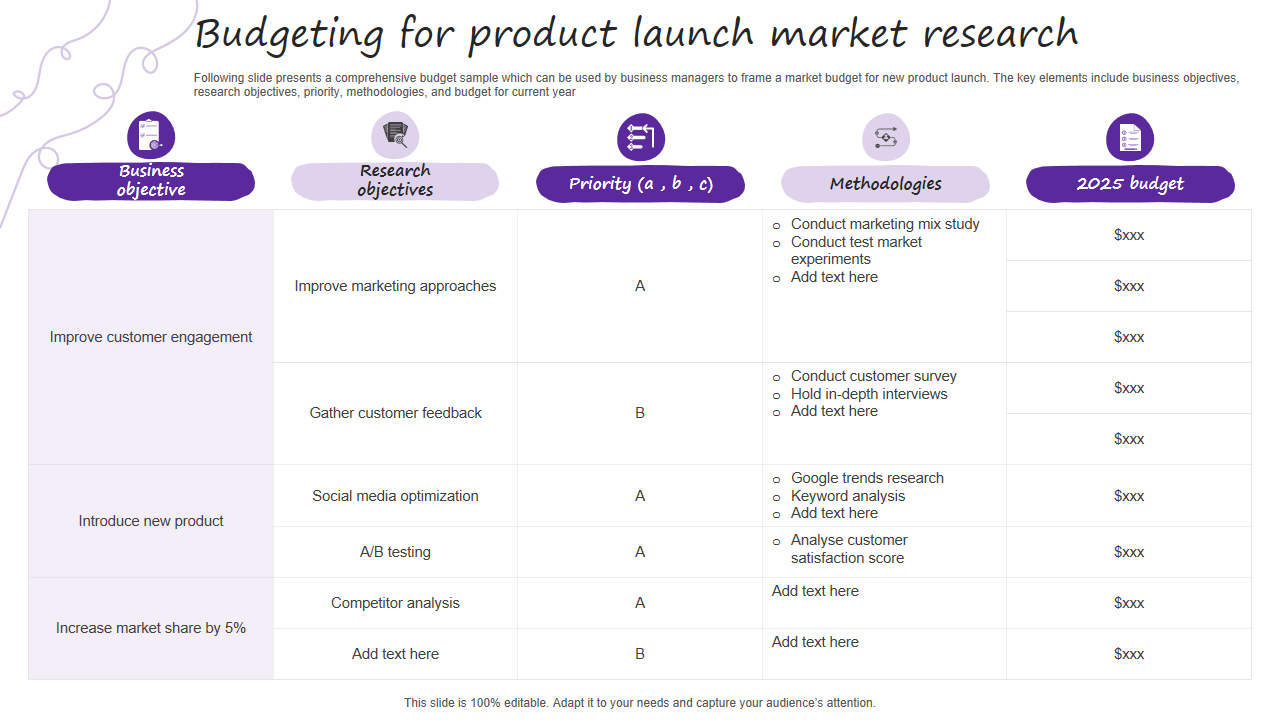
Template 7 - Budgeting for Product Launch Market Research
Every company needs to conduct market research before launching a new product. The PowerPoint Presentation that you have here can help you plan the budget required for conducting such market research. It includes necessary information, including business and research objectives, priorities, methodologies, and forecasts. The presentation template also has the metrics required for the research, such as improving customer engagement, introducing new products, and increasing market share. For example, to improve customer engagement, you may be looking to improve marketing approaches and gather customer feedback. The methods you may use include conducting marketing mix studies and tests. Similarly, you may want to optimize your social media posts and profiles and conduct A/B tests when introducing new products. Improving your market share may involve analyzing the competition. You may even use this handy template for conducting market research, estimating, and forecasting budgets.
RESEARCH IS IMPORTANT BUSINESS
You can plan your research and the budget required using these templates. Remember that each new product launch has lots of research behind it. When going for a new launch, don’t just research the products and its uses, but also the markets – particularly, your target audience and how they will benefit from your brands. When allocating the budget for your research, don't forget to note your total resources and try to be as cost-effective as possible. You must consider the expected costs that you may incur and use these templates to work out a research budget that fits within your resources.
FAQs on Research Budget
What should be included in a research budget.
Research budgets should include all direct costs, and facilities and administrative costs (F&A). The facilities and administrative expenses are needed to achieve the primary objectives of the research. The project description should state the proposed budget and serve as a financial expression for the research. The idea is to ensure that the budget is comprehensive.
How do you create a research budget?
You can create a simple research budget by following these steps:
- List activities that will help you carry out the research.
- Check the rules for getting the funding required.
- Check all costs involved.
- Lay out the costs using a spreadsheet.
- Justify your budget by asking why and for what you need the money and where you got your figures.
What is the role of budget in research?
A budget can provide a detailed and clear picture of the structure of the research project, not to mention that it also lets you know how well it can be managed. The research project budget usually lets you see whether it will go according to plan and if it is feasible. So, it must be complete and reasonable.
What is the average budget for a research project?
The budget for a research project depends on the type of research and the proposed difference it could make to a field of study. For instance, the average budget for a market research project may vary between $20,000 and $50,000. Similarly, larger scientific research projects may cost millions or even billions of dollars, as in pharmaceuticals.
Related posts:
- Top 5 Startup Budget Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 5 Construction Project Budget Templates With Examples And Samples
- Top 10 Cost Comparison Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 5 Budget Planner Templates with Examples and Samples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Purchasing Process Example Templates with Samples

Top 10 Banking Company Profile Templates for Crafting a Profile that Makes Money Talk!
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Ayurveda Integr Med
- v.10(2); Apr-Jun 2019
How to plan and write a budget for research grant proposal?
Medical research can have an enormous positive impact on human health. Health research improves the quality of human lives and society which plays a vital role in social and economic development of the nation. Financial support is crucial for research. However, winning a research grant is a difficult task. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: one is an innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies providing funding for health research including traditional Indian medicine (from an Indian perspective) and key points for planning and writing budget section of a grant application.
1. Introduction
Why health science research is important and why should it to be funded? Science and technology innovations and health research can have an enormous impact on human health. They improve public health, quality of human lives, longevity and have made society better [1] , [2] . Healthy humans with better quality of life are crucial for the social and economical development of the nation [3] . Medical research led to the expansion of knowledge about health problems/conditions and their mechanism, risk factors, outcomes of treatments or interventions, preventive measures and proper management. Clinical studies or trials provide important information about the safety and efficacy of a drug/intervention. Innovative basic science research had led to the discovery of new technology, efficient diagnostic and therapeutic devices. So, currently, an effort with multidisciplinary approach is a demand for better understanding of clinical conditions and providing safest health care to the community [2] , [4] .
Whether it is basic or applied, clinical or non-clinical, all research needs financial support. Considering the importance of research in economic growth of a nation, many countries are increasing their budget for research and development in science. A study on impact of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) on research and development in science among Asian countries has found that one who spends more on research has more research outcomes in the form of total number of research documents, citations per documents and h-index [5] . About 95% of the NIH (National Institutes of Health, USA), budget goes directly to research awards, programs, and centers; training programs; and research and development contracts [6] . Total expenditure carried out for research in India is too less than USA and China. Percentage of GDP for research and development in India is 0.88%, while South Korea, USA and China have 4.292%, 2.742 and 2.1% respectively [7] .
Owing to the increasing competition among the researchers, especially the young ones, for their academic growth, preparing and planning a winning research proposal becomes very essential. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: (1) innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and (2) appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies (from an Indian perspective) and key points for planning and writing budget section of a grant application.
2. What is the purpose of the budget plan in a grant application?
A budget is the quantitative expression of a financial plan for future expenses on the project in a given period of time [8] . Budget plan is a key element of a grant application. It demonstrates the required cost for the proposed project. It is a prediction of expenses and serves a plan for funders on how the organization will operate the project, spend the money in a given set of period and where their money will go. It shows the funders exactly what they can support and also helps the institution and investigating team in management of the project. Moreover, budget plan requires for accountability [9] .
3. Which are the funding agencies that sponsor health research in India?
Various national and international sponsoring agencies have identified health problems of priority for funding a research. Some of the leading funding agencies providing grant for health research including alternative systems of medicine in India are given in Table 1 . State Universities/deemed Universities also have a provision of funding for medical research.
Table 1
List of funding agencies those promote health research.
4. What constitutes a research project budget?
Proforma of the research grant applications and presentation of budget section may vary among the sponsoring agencies. However, major parts of budget plan in the applications of the above mentioned funding agencies are quite similar. The budget section is broadly divided into two categories: direct and indirect costs.
4.1. Direct costs:
These are the costs incurred specifically to carry out a project [10] . Direct costs include expenses towards personnel, materials, equipments, consumables and travel. These particulars are further categorized into recurring and non-recurring expenses on the basis of their occurrence during the study period. A brief description of the sub-sections under direct cost is given below:
4.1.1. Personnel:
Budget for personnel can be mentioned in this section in case human resources are required for the study and as per funding agency guidelines. Salaries with allowances can be budgeted for human resources such as site manager, research assistant, junior research fellow (JRF), senior research fellow (SRF), research associate, technician, data entry operator and attender. Most of the Indian funding agencies do not have a provision for salaries for the principal investigator (PI) and co-investigators (Co-PI). Ministry of AYUSH [11] and Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Science (RGUHS), Karnataka [12] provide one-time minimal fees for investigators and supporting staff respectively. There is a provision for salaries of investigators in Wellcome trust-DBT India alliance grants [13] .
4.1.2. Recurring expenses:
Recurring expenses are those which are variable and which keep on occurring throughout the entire project duration. Particulars categorized in this category are consumables, chemicals, glasswares, laboratory test charges, diagnostic kits, stationery, prints, photocopies, communication, postage, telephone charges, survey tools, questionnaires, publication charges, reprints, binding etc. Other expenses could be allowances for patients/participants, food charges and physician fees.
4.1.3. Non-recurring expenses:
Non-recurring expenses are those which are one-time in nature or which do not recur at regular intervals. Particulars included in this category are equipments or instruments with its accessories, software's, computer, printer, electrical and electronic items and accessories of the existing instrument in your lab. Percentage of budget allocated for equipment varies among the funding agencies from 25% to 90% of the entire budget. Some of the agencies do not have provision for equipment in budget. Vision Group on Science and Technology allocated their maximum grant (up to 90%) for development of infrastructure of laboratories [14] .
4.1.4. Traveling expenses:
Budget allocated for traveling can be used for attending meetings, conferences, workshops and training programs. Foreign travel is not allowed by any Indian funding agency. Traveling expenses for collection of data, survey and visit to other centers in multicentric study can be budgeted in this sub-section.
4.2. Indirect costs:
These are the costs which cannot be directly attributed to specific expenses of a project, but are required to run a project. It is also termed as overhead charges. Laboratory, electricity, water, library and other facilities are provided by the institution to run a proposed research project. Therefore, a fixed cost (usually) of about 5–15% of the total budget is provisioned as institutional overhead charges which goes to the institution directly. The range may, however, be flexible on the basis of the type of funding agency.
5. Budget justification
Most of the funding agencies require submission of a budget justification with all the items described above. Sometimes it is also called as budget narrative. Explanation of need for each line item in the budget with item-wise and year-wise breakdown has to be provided. Quantification of total costs of each line-item and document cost calculation should be done. When writing a budget justification, it is important to follow the same order as that in an itemized budget. For example, if equipment such as color doppler is required, then justify the need of a device with respect to the proposed methodology of the study. Similarly, for non-recurring expenses, breakdown the consumables item-wise and year-wise with its cost and calculation according to the protocol of the study and justify accordingly.
6. Budget summary
An item-wise and year wise summary of the total budget is usually required in most of the applications. Budget summary outlines the proposed grant and often (most of the format) appears at the beginning of the proposal. It should always be prepared at the end, after the grant proposal has been completely developed. A sample budget summary (as an example) for a proposed study for the duration of three years is shown in Table 2 . In the personnel section, a research fellow salary with allowances is budgeted year-wise. The salary of the research fellow for the first and second year is Rs. 2,30,000 per year (JRF) with an enhancement to Rs 2, 59,000 for the third year (SRF) as per the guidelines of the funding agency. As non-recurring expenses are one time in nature, a budget for equipment was budgeted only for the first year. Under the section of recurring expenses, more budgets are allocated in the second year for consumables because recruitment of subjects in large number will be done during the second year of the proposed study. Similarly, expenses toward travel, investigator fee and other miscellaneous costs year-wise have been budgeted. The emoluments and guidelines on service conditions for research personnel employed in research project by ICMR has been given in reference section [15] , [16] .
Table 2
Sample budget summary (year wise).
7. How to plan a simple research budget?
Planning of the research budget begins with an innovative research question, objectives and design of the study. Before starting to write a budget plan, it is essential to understand the expectations of funding agencies, University/Institute and the team of researchers. It is imperative to keep in mind that the research proposal will be reviewed by both scientific and financial (non-scientific) experts. Hence, the proposal should be prepared in such a way that it can be easily understood by even non-scientific experts.
Firstly, a list of what is essential and would add value for research such as focus of research, primary and secondary outcomes of the study, the source of the sample, study setting, sample design and sample size, techniques used to collect data, method of data analysis and available resources should be made [17] .
Secondly, the instructions, format of the application and rules of the funding agency should be read thoroughly. Budget specifications, limitations of recurring and non-recurring costs, and necessity of budget justification with cost breakdown should be checked. Note that one should not deviate or modify the proforma of the funding agency.
Thirdly, a list of items should be made and categorized into recurring and non-recurring expenses. Breakdown of the budget into item-wise and year-wise with cost calculation should be done. It should be ensured that costs are reasonable, allowable and related to the research proposal, so that the budget appears realistic. Travel expenses should be calculated as per the rules of the funding agency.
Fourthly, item-wise and year-wise justification of the requirement in a same sequence of format should be provided. A well-justified budget can enhance the evaluation of the research proposal by reviewers and funding body.
The last most important part is to review the budget and verify the costs and calculation. It is better, if other research team members can review the budget plan and re-calculate the costs thoroughly. Remember, too high budget and too low budget with respect to the research proposal are suspicious and chances of receiving a grant are less.
Sources of funding
Conflict of interest.
Peer review under responsibility of Transdisciplinary University, Bangalore.
The Research Whisperer
Just like the thesis whisperer – but with more money, how to make a simple research budget.

Every research project needs a budget*.
If you are applying for funding, you must say what you are planning to spend that funding on. More than that, you need to show how spending that money will help you to answer your research question .
So, developing the budget is the perfect time to plan your project clearly . A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project.
Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project.
1. List your activities
Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is going to do it.
Take your methodology and turn it into a step-by-step plan. Have you said that you will interview 50 people? Write it on your list.
Are you performing statistical analysis on your sample? Write it down.
Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.
What about travel? Write down each trip separately. Be specific. You can’t just go to ‘South East Asia’ to do fieldwork. You need to go to Kuala Lumpur to interview X number of people over Y weeks, then the same again for Singapore and Jakarta.
Your budget list might look like this:
- I’m going to do 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- I’ll need teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- I’ll need Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- I’ll need Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem.
- The transcription service will transcribe the 30 interviews.
- I’ll analysis the transcribed results. (No teaching release required – I’ll do it in my meagre research time allowance.)
- I’ll need a Thingatron X32C to do the trials.
- Thing Inc will need to install the Thingatron. (I wonder how long that will take.)
- The research assistant will do three trials a month with the Thingatron.
- I’ll need to hire a research assistant (1 day per week for a year at Level B1.)
- The research assistant will do the statistical analysis of the Thingatron results.
- I’ll do the writing up in my research allowance time.
By the end, you should feel like you have thought through the entire project in detail. You should be able to walk someone else through the project, so grab a critical friend and read the list to them. If they ask questions, write down the answers.
This will help you to get to the level of specificity you need for the next step.
2. Check the rules again
You’ve already read the funding rules, right? If not, go and read them now – I’ll wait right here until you get back.
Once you’ve listed everything you want to do, go back and read the specific rules for budgets again. What is and isn’t allowed? The funding scheme won’t pay for equipment – you’ll need to fund your Thingatron from somewhere else. Cross it off.
Some schemes won’t fund people. Others won’t fund travel. It is important to know what you need for your project. It is just as important to know what you can include in the application that you are writing right now.
Most funding schemes won’t fund infrastructure (like building costs) and other things that aren’t directly related to the project. Some will, though. If they do, you should include overheads (i.e. the general costs that your organisation needs to keep running). This includes the cost of basics like power and lighting; desks and chairs; and cleaners and security staff. It also includes service areas like the university library. Ask your finance officer for help with this. Often, it is a percentage of the overall cost of the project.
If you are hiring people, don’t forget to use the right salary rate and include salary on-costs. These are the extra costs that an organisation has to pay for an employee, but that doesn’t appear in their pay check. This might include things like superannuation, leave loading, insurance, and payroll tax. Once again, your finance officer can help with this.
Your budget list might now look like this:
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem, plus travel insurance (rule 3F).
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required.
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C . Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project.
- Three trials a month with Thingatron, by research assistant.
- Statistical analysis of Thingatron results, by research assistant.
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs.
- Overheads at 125% of total cash request, as per rule 3H.
3. Cost each item
For each item on your list, find a reasonable cost for it . Are you going to interview the fifty people and do the statistical analysis yourself? If so, do you need time release from teaching? How much time? What is your salary for that period of time, or how much will it cost to hire a replacement? Don’t forget any hidden costs, like salary on-costs.
If you aren’t going to do the work yourself, work out how long you need a research assistant for. Be realistic. Work out what level you want to employ them at, and find out how much that costs.
How much is your Thingatron going to cost? Sometimes, you can just look that stuff up on the web. Other times, you’ll need to ring a supplier, particularly if there are delivery and installation costs.
Jump on a travel website and find reasonable costs for travel to Kuala Lumpur and the other places. Find accommodation costs for the period that you are planning to stay, and work out living expenses. Your university, or your government, may have per diem rates for travel like this.
Make a note of where you got each of your estimates from. This will be handy later, when you write the budget justification.
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me (see below for travel costs).
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork = $25,342 – advice from finance officer.
- Flights to KL ($775), Singapore ($564), Jakarta ($726), Melbourne ($535) – Blue Sky airlines, return economy.
- Accommodation for a month in each place (KL: $3,500; Sing: $4,245; Jak: $2,750 – long stay, three star accommodation as per TripAdviser).
- Per diem for three months (60 days x $125 per day – University travel rules).
- Travel insurance (rule 3F): $145 – University travel insurance calculator .
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service: 30 interviews x 60 minutes per interview x $2.75 per minute – Quote from transcription service, accented voices rate.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required. (In-kind contribution of university worth $2,112 for one week of my time – advice from finance officer ).
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C. Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project. ($2,435 in-kind – quote from partner organisation, at ‘favoured client’ rate.)
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs. $12,456 – advice from finance officer.
Things are getting messy, but the next step will tidy it up.
4. Put it in a spreadsheet
Some people work naturally in spreadsheets (like Excel). Others don’t. If you don’t like Excel, tough. You are going to be doing research budgets for the rest of your research life.
When you are working with budgets, a spreadsheet is the right tool for the job, so learn to use it! Learn enough to construct a simple budget – adding things up and multiplying things together will get you through most of it. Go and do a course if you have to.
For a start, your spreadsheet will multiply things like 7 days in Kuala Lumpur at $89.52 per day, and it will also add up all of your sub-totals for you.
If your budget doesn’t add up properly (because, for example, you constructed it as a table in Word), two things will happen. First, you will look foolish. Secondly, and more importantly, people will lose confidence in all your other numbers, too. If your total is wrong, they will start to question the validity of the rest of your budget. You don’t want that.
If you are shy of maths, then Excel is your friend. It will do most of the heavy lifting for you.
For this exercise, the trick is to put each number on a new line. Here is how it might look.
5. Justify it
Accompanying every budget is a budget justification. For each item in your budget, you need to answer two questions:
- Why do you need this money?
- Where did you get your figures from?
The budget justification links your budget to your project plan and back again. Everything item in your budget should be listed in your budget justification, so take the list from your budget and paste it into your budget justification.
For each item, give a short paragraph that says why you need it. Refer back to the project plan and expand on what is there. For example, if you have listed a research assistant in your application, this is a perfect opportunity to say what the research assistant will be doing.
Also, for each item, show where you got your figures from. For a research assistant, this might mean talking about the level of responsibility required, so people can understand why you chose the salary level. For a flight, it might be as easy as saying: “Blue Sky airlines economy return flight.”
Here is an example for just one aspect of the budget:
Fieldwork: Kuala Lumpur
Past experience has shown that one month allows enough time to refine and localise interview questions with research partners at University of Malaya, test interview instrument, recruit participants, conduct ten x one-hour interviews with field notes. In addition, the novel methodology will be presented at CONF2015, to be held in Malaysia in February 2015.
Melbourne – Kuala Lumpur economy airfare is based on current Blue Sky Airlines rates. Note that airfares have been kept to a minimum by travelling from country to country, rather than returning to Australia.
1 month accommodation is based on three star, long stay accommodation rates provided by TripAdvisor.
30 days per diem rate is based on standard university rates for South-East Asia.
Pro tip: Use the same nomenclature everywhere. If you list a Thingatron X32C in your budget, then call it a Thingatron X32C in your budget justification and project plan. In an ideal world, someone should be able to flip from the project plan, to the budget and to the budget justification and back again and always know exactly where they are.
- Project plan: “Doing fieldwork in Malaysia? Whereabouts?” Flips to budget.
- Budget: “A month in Kuala Lumpur – OK. Why a month?” Flips to budget justification.
- Budget justification: “Ah, the field work happens at the same time as the conference. Now I get it. So, what are they presenting at the conference?” Flips back to the project description…
So, there you have it: Make a list; check the rules; cost everything; spreadsheet it; and then justify it. Budget done. Good job, team!
This article builds on several previous articles. I have shamelessly stolen from them.
- Constructing your budget – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- What makes a winning budget ? – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- How NOT to pad your budget – Tseen Khoo.
- Conquer the budget, conquer the project – Tseen Khoo.
- Research on a shoestring – Emily Kothe.
- How to make a simple Gantt chart – Jonathan O’Donnell.
* Actually, there are some grant schemes that give you a fixed amount of money, which I think is a really great idea . However, you will still need to work out what you are going to spend the money on, so you will still need a budget at some stage, even if you don’t need it for the application.
Also in the ‘simple grant’ series:
- How to write a simple research methods section .
- How to make a simple Gantt chart .
Share this:
28 comments.
This has saved my day!
Happy to help, Malba.
Like Liked by 1 person
[…] you be putting in a bid for funding? Are there costs involved, such as travel or equipment costs? Research Whisperer’s post on research budgets may help you […]
I’ve posted a link to this article of Jonathan’s in the Australasian Research Management Society LinkedIn group as well, as I’m sure lots of other people will want to share this.
Thanks, Miriam.
This is great! Humorous way to talk explain a serious subject and could be helpful in designing budgets for outreach grants, as well. Thanks!
Thanks, Jackie
If you are interested, I have another one on how to do a timeline: https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2011/09/13/gantt-chart/
[…] really useful information regarding budget development can be found on the Research Whisperer Blog here. Any other thoughts and suggestions are welcome – what are your tips to developing a good […]
[…] it gets you to the level of specificity that you need for a detailed methods section. Similarly, working out a budget for your workshops will force you to be specific about how many people will be attending (venue […]
A friend of mine recently commented by e-mail:
I was interested in your blog “How to make a simple research budget”, particularly the statement: “Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.”
From my limited experience so far, I’d think you could add:
“Who else is nearby who might share the costs of the Thingatron? If it’s a big capital outlay, and you’re only going to use it to 34% of it’s capacity, sharing can make the new purchase much easier to justify. But how will this fit into your grant? And then it’s got to be maintained – the little old chap who used to just do all that odd mix of electrickery and persuasion to every machine in the lab got retrenched in the last round. You can run it into the ground. But that means you won’t have a reliable, stable Thingatron all ready to run when you apply for the follow-on grant in two years.”
[…] (For more on this process, take a look at How to Write a Simple Project Budget.) […]
[…] Source: How to make a simple research budget […]
This is such a big help! Thank You!
No worries, Claudine. Happy to help.
Would you like to share the link of the article which was wrote about funding rules? I can’t find it. Many thanks!
Hello there – do you mean this post? https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2012/02/14/reading-guidelines
Thank @tseen khoo, very useful tips. I also want to understand more about 3C 3F 3H. What do they stand for? Can you help me find out which posts talk about that. Thank again.
[…] mount up rapidly, even if you are in a remote and developing part of the world. Putting together a half decent budget early on and being aware of funding opportunities can help to avoid financial disaster half way […]
This is so amazing, it really helpful and educative. Happy unread this last week before my proposal was drafted.
Happy to help, Babayomi. Glad you liked it.
really useful! thanks kate
[…] “How to Make a Simple Research Budget,” by Jonathan O’Donnell on The Research Whisperer […]
[…] offering services that ran pretty expensive. until I found this one. It guided me through making a simple budget. The information feels sort of like a university graduate research paper but having analysed […]
[…] Advice on writing research proposals for industry […]
[…] research serves as the bedrock of informed budgeting. Explore the average costs of accommodation, transportation, meals, and activities in your chosen […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Sample Budget Justifications
Sponsor requirements differ, and sample budget justifications should be seen only as a starting point. Guidelines for sponsor requirements are in the annotated budget justifications. Read the solicitation and the sponsor’s proposal preparation guidelines for each proposal's requirements.
For Research Sponsors
- Sample Budget Justification for Non-Federal Research [DOCX] - April 6, 2023
- Annotated Budget Justification - Non-Federal Research
- Sample Budget Justification for Federal Research [DOCX] - April 6, 2023
- Annotated Budget Justification - Federal Research
For Non-Research Sponsors:
- Sample Budget Justification for Non-Federal Non-Research [DOCX] - July 29, 2022
- Annotated Budget Justification - Non-Federal Non-Research
- Sample Budget Justification for Federal Non-Research [DOCX] - July 29, 2022
- Annotated Budget Justification - Federal Non-Research
- Uniform Guidance Fixed Rate Requirements
- F&A Methodology
- F&A Components
- MIT Use of a de minimis Rate
- Fund Account Overhead Rates
- Allocation Rates
- Determination of On-Campus and Off-Campus Rates
- Employee Benefits (EB) Rates
- Vacation Accrual Rates
- Graduate Research Assistant Tuition Subsidy
- Historical RA Salary Levels
- MIT Facts and Profile Information
- Classification of Sponsored Projects
- Types of Sponsored Awards
- How Are Sponsored Projects Generated?
- Cost Principles and Unallowable Costs
- Direct and Indirect Costs
- Pre-Proposals / Letters of Intent
- MIT Investigator Status
- Components of a Proposal
- Special Reviews
- Applying Through Workspace
- Proposal Preparation Checklist
- Proposals and Confidential Information
- Personnel Costs
- Subcontracts and Consultants
- Kuali Coeus Approval Mapping
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Submission of Revised Budgets
- Standard Contract Terms and Conditions
- Contractual Obligations and Problematic Terms and Conditions
- Review and Negotiation of Federal Contract and Grant Terms and Conditions
- Industrial Collaboration
- International Activities
- MIT Export Control - Export Policies
- Nondisclosure and Confidentiality Agreements
- Negative Confirmation On Award Notices
- Routing and Acceptance of the Award Notice
- COI and Special Review Hold Notice Definitions
- Limiting Long-Term WBS Account Structures
- SAP Project WBS Element Conditions
- Kuali Coeus Electronic Document Storage (EDS)
- Billing Agreements
- PI Absence from Project
- Cost Transfers
- Equipment Threshold
- Uniform Guidance and the FAR
- MIT Standard Terms and Policies
- Guidelines for Charging Faculty Summer Salary
- Key Personnel
- Limitations on Funds - Federal Contracts
- Managing Salary Costs
- Monitoring Project Budgets
- Monthly Reconciliation and Review
- No-Cost Extensions
- Reporting Requirements
- Return of Unexpended Funds to Foundations
- Determining the Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB)
- Working With the Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB)
- Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB) and Child Account Budgets
- Sponsor Approved Budget (SAB) and Prior Approvals
- Submitting an SAB Change Request
- When a PI Leaves MIT
- Research Performance Progress Reports
- Closing Out Fixed Price Awards
- Closeout of Subawards
- Record Retention
- Early Termination
- Reporting FAQs
- Using SciENcv
- AFOSR No-Cost Extension Process
- Terms and Conditions
- New ONR Account Set Ups
- Department of Defense Disclosure Guidance
- Department of Energy / Office of Science Disclosure Guidance
- Introduction to Industrial Sponsors
- General Considerations for Industrial Proposals
- SRC Guidance to Faculty Considering Applying for SRC Funding
- Find Specific RFP Information
- Industrial Proposal Checklist
- Proposal Formats
- Special Requirements
- Deadline Cycles
- Model Proposals
- Non-Competitive Industrial Proposals
- Master and Alliance Agreements With Non-Standard Proposal Processes
- Template Agreements
- New Consortium Agreements
- Competitive Industrial Proposals
- Collaborative (No-cost) Research Agreements
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration Disclosure Guidance
- NASA Graduate Research Fellowship Programs
- NASA PI Status and Definitions
- NIH Checklists and Preparation Guides
- National Institutes of Health Disclosure Guidance
- Human Subjects and NIH Proposals
- NIH Data Management and Sharing
- NIH Research Performance Progress Reports
- Grant Opportunities for Academic Liaison with Industry (GOALI) proposals
- MIT Guidance Regarding the NSF CAREER Program
- Research Experiences for Undergraduates (REU) Supplements
- National Science Foundation Disclosure Guidance
- NSF Proposals: Administrative Review Stage
- NSF Collaborations
- NSF Pre-Award and Post-Award Actions
- NSF Reporting
- NSF Frequently Asked Questions
- NSF Safe and Inclusive Working Environment
- Process, Roles and Responsibilities
- What Is Allowable/Eligible Cost Sharing?
- MIT’s Preferred Cost Sharing Funds
- Third-Party Cost Sharing
- Showing Cost Sharing in a Proposal Budget
- Sponsor Specific Instructions Regarding Location in the Proposal
- Funding F&A Costs as Cost Sharing
- Using Faculty Effort for Cost Sharing
- Information about Completing the Cost Sharing Template
- NSF Cost Sharing Policy
- Tracking/Reporting Cost Sharing
- Special Cost Sharing Topics
- International Activities Examples
- Rubicon Fellowships
- Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellowships
- Criteria for Subrecipients
- Subawards at Proposal
- Requesting New Subawards
- Managing Subawards
- RAS Subaward Team Contacts
- Funding and Approval
- Proposal Phase
- Award Set-up
- Monitoring Research During Project Period
- Closeout Phase
- Voluntary Cost Sharing
- Sponsor-Specific Guidance
- Audits and Auditors
- Upcoming Trainings and Events
- Research Administration Practices (RAP)
- NCURA Virtual Workshops and Webinars
- Guide to RA Resources and Training
- Career Paths
- Newsletters
- Tools and Systems
- Award Closeout & Audits
- Award Setup
- Cost Sharing
- Export Control
- Financial Conflict of Interest
- Kuali Coeus
- Project Monitoring
- Proposal Preparation & Submission
- Research Sub Awards
- Research Administration Email Lists
- RAS Operations
- VPR Research Administration Organization Chart
- By department
- By administrator
- Research Administrator Day
- News & Announcements
- Onsite searching on the VPR public websites
Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .

How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
10 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Find My GCO
- IACUC applications (Cayuse Animal Management System)
- IBC Applications (eMUA)
- IRB Applications (RASS-IRB) External
- Institutional Profile & DUNS
- Rates and budgets
- Report external interests (COI)
- Join List Servs
- Ask EHS External
- Research Development Services
- Cornell Data Services External
- Find Your Next Funding Opportunity
- Travel Registry External
- RASS (Formerly Form 10 and NFA) External
- International research activities External
- Register for Federal and Non-Federal Systems
- Disclose Foreign Collaborations and Support
- Web Financials (WebFin2) External
- PI Dashboard External
- Research metrics & executive dashboards
- Research Financials (formerly RA Dashboard) External
- Subawards in a Proposal
- Proposal Development, Review, and Submission
- Planning for Animals, Human Participants, r/sNA, Hazardous Materials, Radiation
- Budgets, Costs, and Rates
- Collaborate with Weill Cornell Medicine
- Award Negotiation and Finalization
- Travel and International Activities
- Project Finances
- Project Modifications
- Research Project Staffing
- Get Confidential Info, Data, Equipment, or Materials
- Managing Subawards
- Animals, Human Participants, r/sNA, Hazardous Materials, Radiation
- Project Closeout Financials
- Project Closeout
- End a Project Early
- Protecting an Invention, Creation, Discovery
- Entrepreneurial and Startup Company Resources
- Gateway to Partnership Program
- Engaging with Industry
- Responsible Conduct of Research (RCR)
- Export Controls
- Research with Human Participants
- Research Security
- Work with Live Vertebrate Animals
- Research Safety
- Regulated Biological Materials in Research
- Financial Management
- Conflicts of Interest
- Search
Budget Templates and Budget Justification Templates
The Sponsored Budget Template is an Excel-based tool, with Cornell-relevant equations already saved into over a dozen worksheets.
Worksheets include:
- General Expense
- Cost-Sharing
- Salary 9 month
- F&A Detail
- Other typical budget categories
The "Quicktips" tab contains instructions.
Navigate among the worksheets using the arrows on the bottom left of your screen, or click on the tabs.
Download the Sponsored Budget Template (.xlsx) | Download the Sponsored Budget Justification Template (.docx)
The sample budget template was conceived and created by a team of department administrative managers and OSP staff with the goal of helping researchers and support staff develop sponsored project proposal budgets.
For more information about developing budgets see the Overview of Costs for Project Budget page.
Budget, Costs, and Rates
Overview of costs for project budgets (budget and costing guide), employee benefit (fringe) rates, escalation rates, facilities & administrative (f&a) rates, postdoctoral associate minimum salary, grad student tuition, health benefits, and stipend, nih salary cap, per diem rates for travel, weill cornell medicine f&a and benefits rates, proposing cost share.
Join us for a discussion on Cornell’s Research Administration Support System (RASS) new proposal budgeting functionality.
At this session attendees will learn about:
- Streamlining proposal budgets with RASS
- General updates and new RASS features
- Resources available
Presenters:
- About Grants
- How to Apply - Application Guide
- Write Application
Develop Your Budget
Cost considerations, budgets: getting started.
- Allowable direct vs. allowable F&A costs
- Modular vs. Detailed Budgets
Modular Budgets
- Detailed Budget: Personnel (Sec A & B)
- Detailed Budget: Equipment, Travel, and Trainee Costs (Sec C, D, and E)
- Detailed Budget: Other Direct Costs (Sec F)
Consortiums/Subawards
Understanding the out years.
- Other resources
As you begin to develop a budget for your research grant application and put all of the relevant costs down on paper, many questions may arise. Your best resources for answering these questions are the grants or sponsored programs office within your own institution, your departmental administrative officials, and your peers. They can answer questions such as:
- What should be considered a direct cost or indirect cost?
- What is the fringe benefit rate?
- What is the graduate student stipend rate?
- What Facilities and Administrative (F&A) costs rate should I use?
Below are some additional tips and reminders we have found to be helpful for preparing a research grant application, mainly geared towards the SF424 (R&R) application. (Note: these tips do not supersede the budget instructions found in the relevant application instruction guide found on the How to Apply - Application Guide page.
An applicant's budget request is reviewed for compliance with the governing cost principles and other requirements and policies applicable to the type of recipient and the type of award. Any resulting award will include a budget that is consistent with these requirements. Information on the applicable cost principles and on allowable and unallowable costs under NIH grants is provided in the NIH Grants Policy Statement, Section 7.2 The Cost Principles Statement under Cost Considerations /grants/policy/nihgps/HTML5/section_7/7_cost_consideration.htm . In general, NIH grant awards provide for reimbursement of actual, allowable costs incurred and are subject to Federal cost principles /grants/policy/nihgps/HTML5/section_7/7.2_the_cost_principles.htm .
The cost principles address four tests that NIH follows in determining the allowability of costs. Costs charged to awards must be allowable, allocable, reasonable, necessary, and consistently applied regardless of the source of funds. NIH may disallow the costs if it determines, through audit or otherwise, that the costs do not meet the tests of allowability, allocability, reasonableness, necessity, and consistency.
- II.1 (Mechanism of Support),
- II.2 (Funds Available),
- III.2 (Cost Sharing or Matching), and
- IV.5 (Funding Restrictions).
- Identify all the costs that are necessary and reasonable to complete the work described in your proposal.
- Throughout the budgeting process, round to whole dollars and use only U.S. dollars.
- Reviewers look for reasonable costs and will judge whether your request is justified by your aims and methods.
- Reviewers will consider the person months you've listed for each of the senior/key personnel and will judge whether the figures are in sync with reviewer expectations, based on the research proposed.
- Significant over- or under-estimating suggests you may not understand the scope of the work. Despite popular myth, proposing a cost-sharing (matching) arrangement where you only request that NIH support some of the funding while your organization funds the remainder does not normally impact the evaluation of your proposal. Only a few select programs require cost-sharing, and these programs will address cost-sharing in the funding opportunity.
Direct Costs: Costs that can be identified specifically with a particular sponsored project, an instructional activity, or any other institutional activity, or that can be directly assigned to such activities relatively easily with a high degree of accuracy.
F&A Costs: Necessary costs incurred by a recipient for a common or joint purpose benefitting more than one cost objective, and not readily assignable to the cost objectives specifically benefitted, without effort disproportionate to the results achieved. To facilitate equitable distribution of indirect expenses to the cost objectives served, it may be necessary to establish a number of pools of F&A (indirect) costs. F&A (indirect) cost pools must be distributed to benefitted cost objectives on bases that will produce an equitable result in consideration of relative benefits derived.
- The total costs requested in your budget will include allowable direct costs (related to the performance of the grant) plus allowable F&A costs. If awarded, each budget period of the Notice of Award will reflect direct costs, applicable F&A, and in the case of SBIR or STTR awards, a "profit" or fee .
- For most institutions the negotiated F&A rate will use a modified total direct cost base, which excludes items such as: equipment, student tuition, research patient care costs, rent, and sub-recipient charges (after the first $25,000). Check with your sponsored programs office to find out your negotiated direct cost base.
- When calculating whether your direct cost per year is $500,000 or greater, do not include any sub-recipient F&A in the base but do include all other direct costs as well as any equipment costs. NOTE: Direct cost requests equal to or greater than $500,000 require prior approval from the NIH Institute/Center before application submission. For more information, see NIH Guide Notice NOT-OD-02-004 .
- For many SBIR/STTR recipients, 40% of modified total direct costs is a common F&A rate, although rates at organizations may vary.
Modular versus Detailed Budgets
The NIH uses 2 different formats for budget submission depending on the total direct costs requested and the activity code used.
The application forms package associated with most NIH funding opportunities includes two optional budget forms—(1) R&R Budget Form; and, (2) PHS 398 Modular Budget Form. NIH applications will include either the R&R Budget Form or the PHS 398 Modular Budget Form, but not both. To determine whether to use a detailed versus modular budget for your NIH application, see the flowchart below.

NIH uses a modular budget format to request up to a total of $250,000 of direct costs per year (in modules of $25,000, excluding consortium F&A costs) for some applications, rather than requiring a full detailed budget. The modular budget format is NOT accepted for
- SBIR and STTR grant applications,
- applications from foreign (non-U.S.) institutions (must use detailed budget even when modular option is available), or
- applications that propose the use of human fetal tissue (HFT) obtained from elective abortions (as defined in NOT-OD-19-128 for HFT) whether or not costs are incurred.
Creating a modular budget
- Select the PHS398 Modular Budget form for your submission package, and use the appropriate set of instructions from the electronic application user's guide. You do not need to submit the SF424 (R&R) Budget form if you submit the PHS398 Modular Budget form.
- Consider creating a detailed budget for your own institution's use including salaries, equipment, supplies, graduate student tuition, etc. for every year of funds requested. While the NIH will not ask for these details, they are important for you to have on hand when calculating your F&A costs base and writing your justification, and for audit purposes.
- In order to determine how many modules you should request, subtract any consortium F&A from the total direct costs, and then round to the nearest $25,000 increment.
A modular budget justification should include:
- Personnel Justification: The Personnel Justification should include the name, role, and number of person-months devoted to this project for every person on the project. Do not include salary and fringe benefit rate in the justification, but keep in mind the legislatively mandated salary cap when calculating your budget. [When preparing a modular budget, you are instructed to use the current cap when determining the appropriate number of modules.]
- Consortium Justification: If you have a consortium/subcontract, include the total costs (direct costs plus F&A costs), rounded to the nearest $1,000, for each consortium/subcontract. Additionally, any personnel should include their roles and person months; if the consortium is foreign, that should be stated as well.
- Additional Narrative Justification: Additional justification should include explanations for any variations in the number of modules requested annually. Also, this section should describe any direct costs that were excluded from the total direct costs (such as equipment, tuition remission) and any work being conducted off-site, especially if it involves a foreign study site or an off-site F&A rate.
See the NIH Modular Research Grant Applications page and the NIH Grants Policy Statement for more information.
Detailed Budget: Personnel (Sections A & B)
Personnel make up sections A and B of the SF424 (R&R) Budget form. All personnel from the applicant organization dedicating effort to the project should be listed on the personnel budget with their base salary and effort, even if they are not requesting salary support.
- Effort : Effort must be reported in person months. For help converting percent effort to person months, see: /grants/policy/person_months_faqs.htm .
- Salary Caps: NIH will not pay requested salary above the annual salary cap, which can be found at /grants/policy/salcap_summary.htm . If salary is requested above the salary cap, NIH will reduce that line item to the salary cap, resulting in a reduced total award amount. In future years, if the salary cap increases, recipients may rebudget to pay investigator salaries up to the new salary cap, but NIH will not increase the total award amount. If you are preparing a detailed budget, you are instructed to base your request on actual institutional base salaries (not the cap) so that NIH staff has the most current information in hand at the time of award and can apply the appropriate salary cap at that time.
- Fringe Benefits: The fringe benefits rate is based on your institution's policy; the NIH does not have a pre-set limit on fringe benefits. More information on what is included as fringe benefits can be found in the Grants Policy Statement at /grants/policy/nihgps/HTML5/section_12/12.8.1_salaries_and_fringe_benefits.htm . If you have questions about what rate to use, consult your institution's sponsored programs office.
- Senior/Key Personnel: The Senior/Key Personnel section should include any senior or key personnel from the applicant organization who are dedicating effort to this project. "Other Significant Contributors" who dedicate negligible effort should not be included. Some common significant contributors include: 1) CEOs of companies who provide overall leadership, but no direct contribution to the research; and 2) mentors for K awardees, who provide advice and guidance to the candidate but do not work on the project. Likewise, any consultants or collaborators who are not employed by the applicant organization should not be included in section A, but rather should be included in section F.3 of the budget (for consultants) or in section A of the consortium/subaward budget page (for collaborators).
- Postdoctoral Associates: Postdocs can be listed in either section A or B depending on their level of involvement in project design and execution. If listed in section B, include the individuals' names and level of effort in the budget justification section.
- Other Personnel: Other personnel can be listed by project role. If multiple people share the same role such as "lab technician", indicate the number of personnel to the left of the role description, add their person months together, and add their requested salaries together. The salaries of secretarial/clerical staff should normally be treated as F&A costs. Direct charging of these costs may be appropriate where a major project or activity explicitly budgets for administrative or clerical services and individuals involved can be specifically identified with the project or activity [see Exhibit C of OMB Circular A-21 (relocated to 2 CFR, Part 220)]. Be specific in your budget justifications when describing other personnel's roles and responsibilities.
Detailed Budget: Equipment, Travel, and Trainee Costs (Sections C, D, and E)
- Generally equipment is excluded from the F&A base, so if you have something with a short service life (< 1 year), even if it costs more than $5,000, you are better off including it under "supplies".
- If you request equipment that is already available (listed in the Facilities & Other Resources section, for example), the narrative justification must explain why the current equipment is insufficient to accomplish the proposed research and how the new equipment's use will be allocated specifically to the proposed research. Otherwise, NIH may disallow this cost.
- General purpose equipment, such as desktop computers and laptops, that will be used on multiple projects or for personal use should not be listed as a direct cost but should come out of the F&A costs, unless primarily or exclusively used in the actual conduct of the proposed scientific research.
- While the application does not require you to have a price quote for new equipment, including price quotes in your budget justification can aid in the evaluation of the equipment cost to support the project.
- Trainee Costs: Leave this section blank unless otherwise stated in the funding opportunity. Graduate student tuition remission can be entered in section F.8.
Detailed Budget: Other Direct Costs (Section F)
- Materials and Supplies: In the budget justification, indicate general categories such as glassware, chemicals, animal costs, including an amount for each category. Categories that include costs less than $1,000 do not have to be itemized.
- Animal Costs: While included under "materials and supplies", it is often helpful to include more specific details about how you developed your estimate for animal costs. Include the number of animals you expect to use, the purchase price for the animals (if you need to purchase any), and your animal facility's per diem care rate, if available. Details are especially helpful if your animal care costs are unusually large or small. For example, if you plan to follow your animals for an abnormally long time period and do not include per diem rates, the reviewers may think you have budgeted too much for animal costs and may recommend a budget cut.
- Publication Costs: You may include the costs associated with helping you disseminate your research findings from the proposed research. If this is a new application, you may want to delay publication costs until the later budget periods, once you have actually obtained data to share.
- Consultant Services: Consultants differ from Consortiums in that they may provide advice, but should not be making decisions for the direction of the research. Typically, consultants will charge a fixed rate for their services that includes both their direct and F&A costs. You do not need to report separate direct and F&A costs for consultants; however, you should report how much of the total estimated costs will be spent on travel. Consultants are not subject to the salary cap restriction; however, any consultant charges should meet your institution's definition of "reasonableness".
- ADP/Computer Services: The services you include here should be research specific computer services- such as reserving computing time on supercomputers or getting specialized software to help run your statistics. This section should not include your standard desktop office computer, laptop, or the standard tech support provided by your institution. Those types of charges should come out of the F&A costs.
- Justify basis for costs, itemize by category.
- Enter the total funds requested for alterations and renovations. Where applicable, provide the square footage and costs.
- If A&R costs are in excess of $300,000 further limitations apply and additional documentation will be required.
- The names of any hospitals and/or clinics and the amounts requested for each.
- If both inpatient and outpatient costs are requested, provide information for each separately.
- Provide cost breakdown, number of days, number of patients, costs of tests/treatments.
- Justify the costs associated with standard care or research care. (Note: If these costs are associated with patient accrual, restrictions may be justified in the Notice of Award.) (See NIH Grants Policy Statement NIH Grants Policy Statement, Research Patient Care Costs )
- Tuition: In your budget justification, for any graduate students on your project, include what your school's tuition rates are. You may have to report both an in-state and out-of-state tuition rate. Depending on your school stipend and tuition levels, you may have to budget less than your school's full tuition rate in order to meet the graduate student compensation limit (equivalent to the NRSA zero-level postdoctorate stipend level).
- Human Fetal Tissue (HFT) from elective abortions: If your application proposes the use of human fetal tissue obtained from elective abortions (as defined in NOT-OD-19-128 ), you must include a line item titled “Human Fetal Tissue Costs” on the budget form and an explanation of those costs in the budget justification.
- Other: Some types of costs, such as entertainment costs, are not allowed under federal grants. NIH has included a list of the most common questionable items in the NIH Grants Policy Statement ( /grants/policy/nihgps/HTML5/section_7/7_cost_consideration.htm ). If NIH discovers an unallowable cost in your budget, generally we will discount that cost from your total award amount, so it is in your best interest to avoid requesting unallowable costs. If you have any question over whether a cost is allowable, contact your sponsored programs office or the grants management specialist listed on the funding opportunity.
If you are using the detailed budget format, each consortium you include must have an independent budget form filled out.
- In the rare case of third tier subawards, section F.5 "subawards/consortium/contractual" costs should include the total cost of the subaward, and the entire third tier award is considered part of the direct costs of the consortium for the purposes of calculating the primary applicant's direct costs.
- Cost Principles. Regardless of what cost principles apply to the parent recipient, the consortium is held to the standards of their respective set of cost principles.
- Consortium F&A costs are NOT included as part of the direct cost base when determining whether the application can use the modular format (direct costs < $250,000 per year), or determining whether prior approval is needed to submit an application (direct costs $500,000 or more for any year). NOTE: The $500K prior approval policy does not apply to applications submitted in response to RFAs or in response to other funding opportunities including specific budgetary limits above $500K.
- F&A costs for the first $25,000 of each consortium may be included in the modified total direct cost base, when calculating the overall F&A rate, as long as your institution's negotiated F&A rate agreement does not express prohibit it.
- If the consortium is a foreign institution or international organization, F&A for the consortium is limited to 8%.
- Consortiums should each provide a budget justification following their detailed budget. The justification should be separate from the primary recipient's justification and address just those items that pertain to the consortium.
- We do not expect your budget to predict perfectly how you will spend your money five years down the road. However, we do expect a reasonable approximation of what you intend to spend. Be thorough enough to convince the reviewers that you have a good sense of the overall costs.
- In general, NIH does not have policy on salary escalation submitted in an application. We advise applicants to request in the application the actual costs needed for the budget period and to request cost escalations only if the escalation is consistent with institutional policy. See /grants/policy/salcap_summary.htm and /grants/policy/fy2012_salary_cap_faqs.htm .
- Any large year-to-year variation should be described in your budget justification. For example, if you have money set aside for consultants only in the final year of your budget, be sure to explain why in your justification (e.g. the consultants are intended to help you with the statistical interpretation of the data and therefore are not needed before the final year).
- In general, NIH recipients are allowed a certain degree of latitude to rebudget within and between budget categories to meet unanticipated needs and to make other types of post-award changes. Some changes may be made at the recipient's discretion as long as they are within the limits established by NIH. In other cases, NIH prior written approval may be required before a recipient makes certain budget modifications or undertakes particular activities (such as change in scope). See NIH Grants Policy Statement - Changes in Project and Budget .
Other resources to help you create your budget
<--- Previous Topic | Next Topic --->
This page last updated on: September 11, 2019
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
- UBC Research + Innovation
- Support for Researchers
- Attracting Funding
- Budgeting and Indirect Costs
Budget Templates
All funded research grants, contracts and agreements are required to include indirect cost recovery.
The required indirect cost recovery for research projects is:
- 25% on all non-industry funding (governemnt and non-profits)
- 40% of all direct costs on industry funding (any projects initiated before May 1, 2015 may continue to charge the previous rate of 25%)
The only exceptions to these rates are funds from any of the Tri-Council funding agencies (UBC recovers indirect costs for Tri-Council funds through the Federal Research Support Fund formerly the Indirect Costs Program. The only exception is the SSHRC-administered Tri-Agency New Frontiers in Research Fund. Applicants to this fund should contact ORS about building indirect cost recovery into their application.) and funds through grant applications which specify an alternate rate.
Many of the verified exceptions to the standard UBC rate of recovery are listed in the Indirect Costs of Research Verified Rates Table .
Since May 1, 2015, all discretionary powers for the recovery rate of indirect costs (for projects not covered by the standard or published verified rates) has rested with the Deans of the Faculties and not with the Vice-President, Research & Innovation Office.
Below is a sample budget development process.
A researcher creates a proposal for a research project with a government or non-profit partner with the following direct costs:
Direct Costs
The following models below demonstrate how to present to the sponsor a budget for this project utilizing the 25% recovery rate for government and non-profit projects.
Unless the sponsor specifies in writing that they require the indirect costs of research to be presented as a separate line item, the indirect cost should be built into each budget line item, as is customary for budgets.
Preferred “Price” Model
(25% Indirect Cost Built Into Pricing)
Alternative “Cost” Model
(only if required by Sponsor) (25% Indirect Cost Separated)
Tri-Council Matching or Partnered Grants
For Tri-Council grants requiring funding from one or more funding partners, the Tri-Council agency matches only the direct costs of the partners. Examples of these programs include, NSERC Collaborative Research and Development Grants, NSERC Idea to Innovation Grants, SSHRC Partnership Grants, CIHR Industry Partnered Collaborative Research Program, CIHR Proof of Principle Grants. In these cases, the agency may require that direct and indirect costs be shown separately in the budget submitted to the Tri-council agency. In all cases, an indirect cost recovery rate of 25% (for projects initiated after May 1, 2015, this rate will be 40% for industry partners) must be applied to the matching funds provided by the partner. Indirect costs should not be applied to the funds requested from the Tri-council agency. The only exception is the SSHRC-administered Tri-Agency New Frontiers in Research Fund. Applicants to this fund should contact ORS about building indirect cost recovery into their application
Departmental, Unit and Faculty-Specific Fees
Some departments or units require that an “administrative fee” be charged to each project. It’s expected that consistent recovery of indirect costs of research will alleviate the need for these additional fees. If these additional fees are required, however, indirect cost recovery must still be applied at the standard rate to all direct costs, including the administrative fee.
Sub-Awards to UBC
In multi-site projects, it’s the responsibility of the main site to apply on behalf of each sub-site the appropriate indirect cost recovery for that institution. As a sub-awardee, UBC requires 25% indirect costs recovery to be included in funds from the main site. The only exceptions to this are sub-awards from other academic institutions who’ve received grant funding (e.g. from Tri-Council agencies or NIH), in which UBC has approved the alternate rate. All industry projects must recover indirect costs at the standard rate of 40% , irrespective of where the industry sponsor receives its funding.
Machine and Equipment Purchase Grants
Grants for which 100% of the funds are to be applied toward the purchase of equipment, and not directly connected with a specific research project, are exempt from indirect-cost recovery.

Research Budget

Research is highly necessary for a business simply because it helps the company understand the customers, competitors, and the market, in general. The data that the project’s processes bring can make way for the development of company operations. However, all these benefits do not come cheap. Most companies, especially the startups, would even submit proposals to request grants from federal agencies, loans from banks, and investments from other fund sources. To successfully acquire financial assistance for their quantitative or qualitative research , it is necessary to produce a research budget document. If by any chance, you are planning to create such a document, our article and variety of examples can assist you! Check them out below!
11+ Research Budget Examples
1. research budget template.

- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
Size: A4, US
2. Research Project Budget Template

3. Research Budget Proposal Template

- Apple Pages
Size: 52 KB
4. Research Budget Proposal

Size: 60 KB
5. Marketing Research Budget
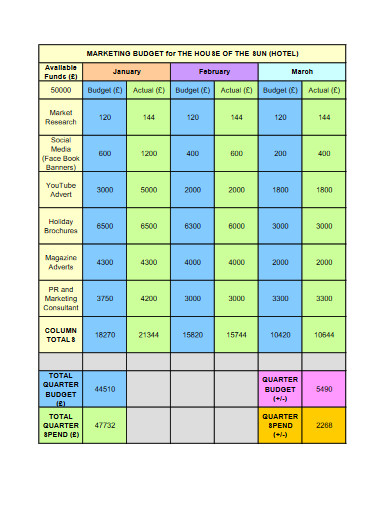
6. Research Budget Estimate Form
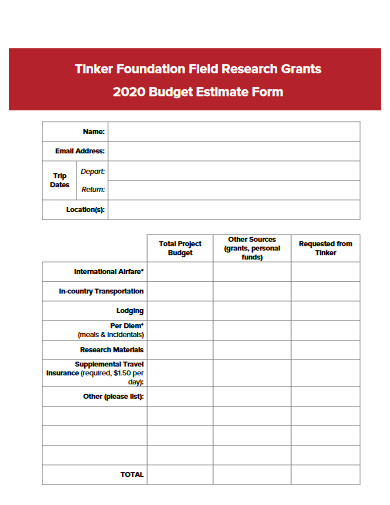
Size: 54 KB
7. Sample Research Budget
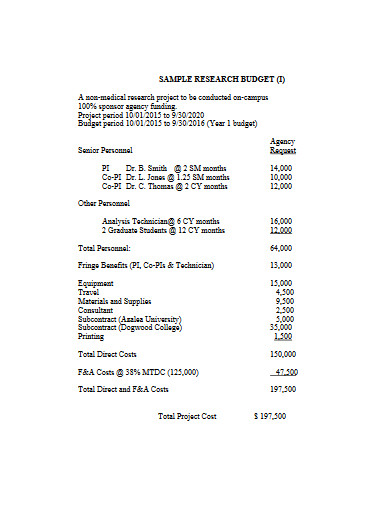
Size: 71 KB
8. Budget Research Proposal
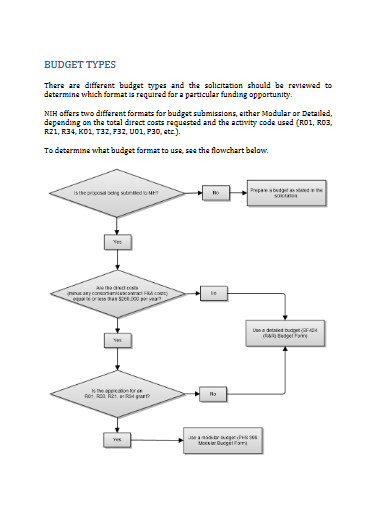
Size: 37 KB
9. Research Budget Format

Size: 90 KB
10. Simple Research Budget Template

Size: 313 KB
11. Project Research Budget Template
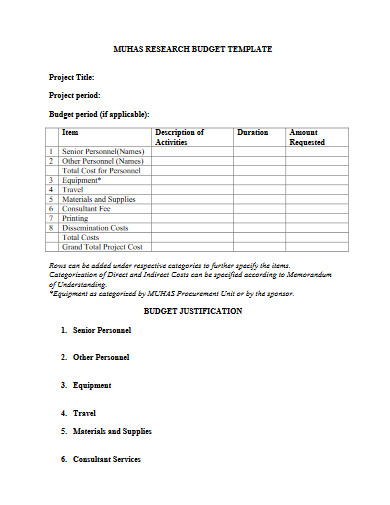
Size: 12 KB
12. Research Budget in PDF

Size: 124 KB
What Is a Research Budget?
A research budget is the breakdown of the estimated income and expenses of a certain research project. According to MyMoneyCoach, budgeting lets individuals and organizations ascertain whether the financial resources are enough to complete a project . Additionally, if the said resources fall short, the process will help them prioritize the much-needed things or activities. Often, people use the term budgets for estimates . Unarguably, most of their elements are alike. The only difference is that budgets highlight how much money is up for spending. At the same time, estimates are predictions of how much money is needed to buy certain things or perform certain activities.
Research: Expensive or Not?
Some entrepreneurs do not know how advantageous research is for their businesses. Upon hearing about business research, the most common question that comes to their mind is whether such an undertaking is expensive or not. Sad to say, the answer is indefinite because its cost will vary depending on your expertise about the subject.
Firms who are not confident enough of their knowledge and experience in business research can hire research companies that can do the job for them. Doing so will approximately cost them USD 1,500 to $30,000, depending on how big the job is. On the contrary, corporate entities who are knowledgeable about the idea of business research can do it by themselves with a little guidance of online sources and other sorts of reference. The cost for it can go down from USD 100 up to USD 5,000.
How To Create a Research Budget
Considering that budgeting involves numbers and figures, you have to be delicate not just to them but also to the itemized entries. Moreover, each of its sections has to comply with the standards to ensure its completeness. By our own research, we are confident that our outline of the necessary guidelines below can help you in making your research budget without any hassle.
1. Describe Research Goals and Objectives
Generally, the research’s main function is to help improve an organization’s workplace operation and the company’s market standing. To effectively set and acquire the necessities for the undertaking, you need to have a better understanding of its specific goals and objectives . Hence, you have to describe them first and foremost.
2. Set the Research Methodology
There are many ways to gather and interpret data for your research. Each of them requires specific materials and equipment, which obviously have a monetary value. Most researchers commonly utilize participant observation, survey methodology , in-person interviews , focus groups, experimental research , secondary data analysis, and mixed methods as their techniques.
3. Specify Target Audience
The target audience is a good basis for your budget . Its volume and demographic can determine how much money you will need for the provision of research materials, such as survey questionnaires and survey forms . For example, if you’re targeting an audience of 10 to 15 people aged 50 to 60, the cost is surely expensive. Most of these people are probably in a nursing home. Aside from preparing them tokens for their participation, you also have to spend some dimes getting into the nursing home, like transportation and the creation of permission slips .
4. Calculate Income
After specifying your target audience, calculate your research’s overall income. Include in your calculations the allotment of your research’s financial assistance. Also, you have to indicate where these funds come from. The total income will be the very foundation of your budget .
5. Reckon Expenditures
Now that you have your income already set, create a list of all the items that you need to spend on. With your income as your basis, distribute the funds according to your priorities to ensure the inclusion of important things or activities, while delaying or eliminating the unnecessary ones.
Once you have successfully set every detail, don’t forget to review each of them one more time. With money at stake, misspellings, miscalculations, and other faults should have no room in your budget . By reviewing your budget before finalizing, you allow yourself to make your data accurate, which is a very crucial quality for research.
What do you mean by the direct and indirect costs of budgeting?
Direct costs refer to the expenses to produce goods or provide services, while indirect costs describe the necessary expenditures for the continuity of business operations.
What are some of the biggest disadvantages of business research?
1. Just like any other type of research, business research is time-consuming.
2. Due to the fast-changing markets, the results of business research can easily become out of date.
3. The business research’s respondents have chances of becoming biased, putting your entire project at risk of having inaccurate information.
What are the phases of budgeting?
Budgeting has five phases. They include preparation and formulation, approval, execution, revision, and control.
American filmmaker, anthropologist, and author Zora Neale Hurston once said, “Research is formalized curiosity. It is poking and prying with a purpose”, and she is right. Through it, we unravel things we never knew we had, whether they’re good news or bad ones. Either way, the discovery of these things can lead to improvement. Funding research is, absolutely, a good idea. However, businesses can only give so much. Some don’t even have anything to offer at all, risking themselves to rely on loans. Because of these facts, researchers have to learn the process of budgeting, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Sample budgets
Justification.
Bumblebee colonies will be obtained from Koppert Biological Systems (MI, USA) and shipped overnight to Nevada. An emerging standard for publication is the utilization of three to five colonies for testing so as to minimize individual colony biases and to acquire a sufficient data set. In order to maintain the colonies I will need pollen to feed them on a daily basis. Additionally I will use the chemical octopamine hydrochloride to explore neuroendocrine relationships between gustatory responsiveness, learning, and octopamine.
I estimated shipping costs to the best of my knowledge.
* Costs are estimated based on average costs of the material; final cost may be slightly different.
17 Research Proposal Examples

A research proposal systematically and transparently outlines a proposed research project.
The purpose of a research proposal is to demonstrate a project’s viability and the researcher’s preparedness to conduct an academic study. It serves as a roadmap for the researcher.
The process holds value both externally (for accountability purposes and often as a requirement for a grant application) and intrinsic value (for helping the researcher to clarify the mechanics, purpose, and potential signficance of the study).
Key sections of a research proposal include: the title, abstract, introduction, literature review, research design and methods, timeline, budget, outcomes and implications, references, and appendix. Each is briefly explained below.
Watch my Guide: How to Write a Research Proposal
Get your Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
Research Proposal Sample Structure
Title: The title should present a concise and descriptive statement that clearly conveys the core idea of the research projects. Make it as specific as possible. The reader should immediately be able to grasp the core idea of the intended research project. Often, the title is left too vague and does not help give an understanding of what exactly the study looks at.
Abstract: Abstracts are usually around 250-300 words and provide an overview of what is to follow – including the research problem , objectives, methods, expected outcomes, and significance of the study. Use it as a roadmap and ensure that, if the abstract is the only thing someone reads, they’ll get a good fly-by of what will be discussed in the peice.
Introduction: Introductions are all about contextualization. They often set the background information with a statement of the problem. At the end of the introduction, the reader should understand what the rationale for the study truly is. I like to see the research questions or hypotheses included in the introduction and I like to get a good understanding of what the significance of the research will be. It’s often easiest to write the introduction last
Literature Review: The literature review dives deep into the existing literature on the topic, demosntrating your thorough understanding of the existing literature including themes, strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in the literature. It serves both to demonstrate your knowledge of the field and, to demonstrate how the proposed study will fit alongside the literature on the topic. A good literature review concludes by clearly demonstrating how your research will contribute something new and innovative to the conversation in the literature.
Research Design and Methods: This section needs to clearly demonstrate how the data will be gathered and analyzed in a systematic and academically sound manner. Here, you need to demonstrate that the conclusions of your research will be both valid and reliable. Common points discussed in the research design and methods section include highlighting the research paradigm, methodologies, intended population or sample to be studied, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures . Toward the end of this section, you are encouraged to also address ethical considerations and limitations of the research process , but also to explain why you chose your research design and how you are mitigating the identified risks and limitations.
Timeline: Provide an outline of the anticipated timeline for the study. Break it down into its various stages (including data collection, data analysis, and report writing). The goal of this section is firstly to establish a reasonable breakdown of steps for you to follow and secondly to demonstrate to the assessors that your project is practicable and feasible.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. When applying for a scholarship, the budget should demonstrate that you are being responsible with your expensive and that your funding application is reasonable.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: A discussion of the anticipated findings or results of the research, as well as the potential contributions to the existing knowledge, theory, or practice in the field. This section should also address the potential impact of the research on relevant stakeholders and any broader implications for policy or practice.
References: A complete list of all the sources cited in the research proposal, formatted according to the required citation style. This demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the relevant literature and ensures proper attribution of ideas and information.
Appendices (if applicable): Any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview guides, or consent forms, that provide further information or support for the research proposal. These materials should be included as appendices at the end of the document.
Research Proposal Examples
Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples designed to briefly demonstrate what might be discussed in each section.
1. Education Studies Research Proposals
See some real sample pieces:
- Assessment of the perceptions of teachers towards a new grading system
- Does ICT use in secondary classrooms help or hinder student learning?
- Digital technologies in focus project
- Urban Middle School Teachers’ Experiences of the Implementation of
- Restorative Justice Practices
- Experiences of students of color in service learning
Consider this hypothetical education research proposal:
The Impact of Game-Based Learning on Student Engagement and Academic Performance in Middle School Mathematics
Abstract: The proposed study will explore multiplayer game-based learning techniques in middle school mathematics curricula and their effects on student engagement. The study aims to contribute to the current literature on game-based learning by examining the effects of multiplayer gaming in learning.
Introduction: Digital game-based learning has long been shunned within mathematics education for fears that it may distract students or lower the academic integrity of the classrooms. However, there is emerging evidence that digital games in math have emerging benefits not only for engagement but also academic skill development. Contributing to this discourse, this study seeks to explore the potential benefits of multiplayer digital game-based learning by examining its impact on middle school students’ engagement and academic performance in a mathematics class.
Literature Review: The literature review has identified gaps in the current knowledge, namely, while game-based learning has been extensively explored, the role of multiplayer games in supporting learning has not been studied.
Research Design and Methods: This study will employ a mixed-methods research design based upon action research in the classroom. A quasi-experimental pre-test/post-test control group design will first be used to compare the academic performance and engagement of middle school students exposed to game-based learning techniques with those in a control group receiving instruction without the aid of technology. Students will also be observed and interviewed in regard to the effect of communication and collaboration during gameplay on their learning.
Timeline: The study will take place across the second term of the school year with a pre-test taking place on the first day of the term and the post-test taking place on Wednesday in Week 10.
Budget: The key budgetary requirements will be the technologies required, including the subscription cost for the identified games and computers.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: It is expected that the findings will contribute to the current literature on game-based learning and inform educational practices, providing educators and policymakers with insights into how to better support student achievement in mathematics.
2. Psychology Research Proposals
See some real examples:
- A situational analysis of shared leadership in a self-managing team
- The effect of musical preference on running performance
- Relationship between self-esteem and disordered eating amongst adolescent females
Consider this hypothetical psychology research proposal:
The Effects of Mindfulness-Based Interventions on Stress Reduction in College Students
Abstract: This research proposal examines the impact of mindfulness-based interventions on stress reduction among college students, using a pre-test/post-test experimental design with both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods .
Introduction: College students face heightened stress levels during exam weeks. This can affect both mental health and test performance. This study explores the potential benefits of mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation as a way to mediate stress levels in the weeks leading up to exam time.
Literature Review: Existing research on mindfulness-based meditation has shown the ability for mindfulness to increase metacognition, decrease anxiety levels, and decrease stress. Existing literature has looked at workplace, high school and general college-level applications. This study will contribute to the corpus of literature by exploring the effects of mindfulness directly in the context of exam weeks.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n= 234 ) will be randomly assigned to either an experimental group, receiving 5 days per week of 10-minute mindfulness-based interventions, or a control group, receiving no intervention. Data will be collected through self-report questionnaires, measuring stress levels, semi-structured interviews exploring participants’ experiences, and students’ test scores.
Timeline: The study will begin three weeks before the students’ exam week and conclude after each student’s final exam. Data collection will occur at the beginning (pre-test of self-reported stress levels) and end (post-test) of the three weeks.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: The study aims to provide evidence supporting the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing stress among college students in the lead up to exams, with potential implications for mental health support and stress management programs on college campuses.
3. Sociology Research Proposals
- Understanding emerging social movements: A case study of ‘Jersey in Transition’
- The interaction of health, education and employment in Western China
- Can we preserve lower-income affordable neighbourhoods in the face of rising costs?
Consider this hypothetical sociology research proposal:
The Impact of Social Media Usage on Interpersonal Relationships among Young Adults
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effects of social media usage on interpersonal relationships among young adults, using a longitudinal mixed-methods approach with ongoing semi-structured interviews to collect qualitative data.
Introduction: Social media platforms have become a key medium for the development of interpersonal relationships, particularly for young adults. This study examines the potential positive and negative effects of social media usage on young adults’ relationships and development over time.
Literature Review: A preliminary review of relevant literature has demonstrated that social media usage is central to development of a personal identity and relationships with others with similar subcultural interests. However, it has also been accompanied by data on mental health deline and deteriorating off-screen relationships. The literature is to-date lacking important longitudinal data on these topics.
Research Design and Methods: Participants ( n = 454 ) will be young adults aged 18-24. Ongoing self-report surveys will assess participants’ social media usage, relationship satisfaction, and communication patterns. A subset of participants will be selected for longitudinal in-depth interviews starting at age 18 and continuing for 5 years.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of five years, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide insights into the complex relationship between social media usage and interpersonal relationships among young adults, potentially informing social policies and mental health support related to social media use.
4. Nursing Research Proposals
- Does Orthopaedic Pre-assessment clinic prepare the patient for admission to hospital?
- Nurses’ perceptions and experiences of providing psychological care to burns patients
- Registered psychiatric nurse’s practice with mentally ill parents and their children
Consider this hypothetical nursing research proposal:
The Influence of Nurse-Patient Communication on Patient Satisfaction and Health Outcomes following Emergency Cesarians
Abstract: This research will examines the impact of effective nurse-patient communication on patient satisfaction and health outcomes for women following c-sections, utilizing a mixed-methods approach with patient surveys and semi-structured interviews.
Introduction: It has long been known that effective communication between nurses and patients is crucial for quality care. However, additional complications arise following emergency c-sections due to the interaction between new mother’s changing roles and recovery from surgery.
Literature Review: A review of the literature demonstrates the importance of nurse-patient communication, its impact on patient satisfaction, and potential links to health outcomes. However, communication between nurses and new mothers is less examined, and the specific experiences of those who have given birth via emergency c-section are to date unexamined.
Research Design and Methods: Participants will be patients in a hospital setting who have recently had an emergency c-section. A self-report survey will assess their satisfaction with nurse-patient communication and perceived health outcomes. A subset of participants will be selected for in-depth interviews to explore their experiences and perceptions of the communication with their nurses.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including rolling recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing within the hospital.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the significance of nurse-patient communication in supporting new mothers who have had an emergency c-section. Recommendations will be presented for supporting nurses and midwives in improving outcomes for new mothers who had complications during birth.
5. Social Work Research Proposals
- Experiences of negotiating employment and caring responsibilities of fathers post-divorce
- Exploring kinship care in the north region of British Columbia
Consider this hypothetical social work research proposal:
The Role of a Family-Centered Intervention in Preventing Homelessness Among At-Risk Youthin a working-class town in Northern England
Abstract: This research proposal investigates the effectiveness of a family-centered intervention provided by a local council area in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth. This case study will use a mixed-methods approach with program evaluation data and semi-structured interviews to collect quantitative and qualitative data .
Introduction: Homelessness among youth remains a significant social issue. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in addressing this problem and identify factors that contribute to successful prevention strategies.
Literature Review: A review of the literature has demonstrated several key factors contributing to youth homelessness including lack of parental support, lack of social support, and low levels of family involvement. It also demonstrates the important role of family-centered interventions in addressing this issue. Drawing on current evidence, this study explores the effectiveness of one such intervention in preventing homelessness among at-risk youth in a working-class town in Northern England.
Research Design and Methods: The study will evaluate a new family-centered intervention program targeting at-risk youth and their families. Quantitative data on program outcomes, including housing stability and family functioning, will be collected through program records and evaluation reports. Semi-structured interviews with program staff, participants, and relevant stakeholders will provide qualitative insights into the factors contributing to program success or failure.
Timeline: The study will be conducted over a period of six months, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and report writing.
Budget: Expenses include access to program evaluation data, interview materials, data analysis software, and any related travel costs for in-person interviews.
Expected Outcomes and Implications: This study aims to provide evidence for the effectiveness of family-centered interventions in preventing youth homelessness, potentially informing the expansion of or necessary changes to social work practices in Northern England.
Research Proposal Template
Get your Detailed Template for Writing your Research Proposal Here (With AI Prompts!)
This is a template for a 2500-word research proposal. You may find it difficult to squeeze everything into this wordcount, but it’s a common wordcount for Honors and MA-level dissertations.
Your research proposal is where you really get going with your study. I’d strongly recommend working closely with your teacher in developing a research proposal that’s consistent with the requirements and culture of your institution, as in my experience it varies considerably. The above template is from my own courses that walk students through research proposals in a British School of Education.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
8 thoughts on “17 Research Proposal Examples”
Very excellent research proposals
very helpful
Very helpful
Dear Sir, I need some help to write an educational research proposal. Thank you.

Hi Levi, use the site search bar to ask a question and I’ll likely have a guide already written for your specific question. Thanks for reading!
very good research proposal
Thank you so much sir! ❤️
Very helpful 👌
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
same page about what a budget actually is. A budget is a financial proposal that reflects the work proposed. It outlines the expected project costs in detail, and should mirror the project description. A budget is presented as a categorical list of anticipated project costs that represent the
Template 4 Clinical Trial Phases with Communication and Budget Research Design for Clinical Trials. Clinical trials involve many phases, and you should let your research associates know about each step. ... Determine Budget for Psychology Research Proposal One-Pager Sample Example Document. This presentation template is an easy-to-use tool for ...
Budget summary outlines the proposed grant and often (most of the format) appears at the beginning of the proposal. It should always be prepared at the end, after the grant proposal has been completely developed. A sample budget summary (as an example) for a proposed study for the duration of three years is shown in Table 2. In the personnel ...
A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project. Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project. 1. List your activities. Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is ...
1. Title Page. Start your research proposal with a title page that clearly states your research. The title page is like a book cover, giving the first impression of your project. Therefore, you must ensure the design is engaging enough to attract your audience at first glance.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Sample Budget Justifications. Sponsor requirements differ, and sample budget justifications should be seen only as a starting point. Guidelines for sponsor requirements are in the annotated budget justifications. Read the solicitation and the sponsor's proposal preparation guidelines for each proposal's requirements.
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
The sample budget template was conceived and created by a team of department administrative managers and OSP staff with the goal of helping researchers and support staff develop sponsored project proposal budgets. For more information about developing budgets see the Overview of Costs for Project Budget page.
Abstract. Novice investigators may be intimidated by the task of proposal budget preparation. Often a basic understanding of the mechanics of budgeting, paired with a good working relationship with the institution's sponsored programs office, can alleviate much of the stress investigators encounter in developing budgets.
Develop Your Budget. As you begin to develop a budget for your research grant application and put all of the relevant costs down on paper, many questions may arise. Your best resources for answering these questions are the grants or sponsored programs office within your own institution, your departmental administrative officials, and your peers.
The template includes sample project proposal budget data with task-by-task budget specifics, which you can use to compare your projects' proposed budget figures against actual budgeting, to arrive at a precise under/over balance. ... Expedite the process of obtaining funding with this research proposal budget template, which includes a line ...
Proposal Budgets. The budget should list all cost details for the year or another appropriate period of time. It should include any applicable salaries & wages, fringe benefits, services, supplies, equipment, publications, travel, other direct expenses, and any facility and administrative costs. A brief outline for developing a budget is ...
Below is a sample budget development process. A researcher creates a proposal for a research project with a government or non-profit partner with the following direct costs: ... Examples of these programs include, NSERC Collaborative Research and Development Grants, NSERC Idea to Innovation Grants, SSHRC Partnership Grants, CIHR Industry ...
3. Specify Target Audience. The target audience is a good basis for your budget. Its volume and demographic can determine how much money you will need for the provision of research materials, such as survey questionnaires and survey forms. For example, if you're targeting an audience of 10 to 15 people aged 50 to 60, the cost is surely ...
research proposal budget template project name date created research organization last updated fy1 rate fy1 hrs fy2 rate fy2 hrs fy3 rate fy3 hrs fy4 hrs fy4 rate
This document provides a sample project proposal and sample budget from a previous year's GME research grant program. Please note: These sample documents should be ... learners, and can serve as one of the unique tools for future research in skill acquisition, competency assessment, and quality improvement in the neonatal intubation. The Food and
Misc. funding is for unexpected expenses. $60. Total. $987.94. I estimated shipping costs to the best of my knowledge. * Costs are estimated based on average costs of the material; final cost may be slightly different. View examples of budgets for undergraduate research proposals at the University of Nevada, Reno.
Budget: Estimate the costs associated with the research project and include evidence for your estimations. Typical costs include staffing costs, equipment, travel, and data collection tools. ... Research Proposal Examples. Research proposals often extend anywhere between 2,000 and 15,000 words in length. The following snippets are samples ...
To enter a budget on a Research.gov . proposal initiated by a Principal Investigator (PI), access the Budget(s) landing page either by clicking the Budget(s) link on the proposal main page or by clicking the Budget(s) link on the proposal menu. Refer to the Budget Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on the Research.gov About Proposal Preparation and
Medical Research Budget Template. researchamerica.org. Download. A research proposal budget sample is in many ways similar to the research budget sample, only that at this stage, it is still a proposal. This sample is often written in a linear or tabular format and it details all the expenses that are associated with the proposal project.