Martin Luther King Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on martin luter king.
Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D. After that, he joined the American Civil Right Movement. He was among one of the great men who dedicated their life for the community.


Reason for Martin Luther King to be famous
There are two reasons for someone to be famous either he is a good man or a very bad person. Martin Luther King was among the good one who dedicated his life to the community. Martin Luther King was also known as MLK Jr. He gained popularity after he became the leader and spokesperson of the Civil Rights Movement in the 1950s and 1960s.
Martin Luther King was an American activist, minister, and humanitarian. Also, he had worked for several other causes and actively participated in many protests and boycotts. He was a peaceful man that has faith in Christian beliefs and non-violence. Also, his inspiration for them was the work of Mahatma Gandhi and Nelson Mandela. For his work in the field of civil rights, the Nobel Committee awarded him the Nobel Peace Prize.
He was a great speaker that motivated the blacks to protest using non-violence. Also, he uses peaceful strategies like a boycott, protest march , and sit-ins, etc. for protests against the government.
Impact of King
King is one of the renowned leaders of the African-American who worked for the welfare of his community throughout his life. He was very famous among the community and is the strongest voice of the community. King and his fellow companies and peaceful protesters forced the government several times to bend their laws. Also, kings’ life made a seismic impact on life and thinking of the blacks. He was among one of the great leaders of the era.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Humanitarian and civil rights work
As we know that King was a civic leader . Also, he has taken part in many civil right campaigns and boycotts like the Bus Boycott, Voting Rights and the most famous March on Washington. In this march along with more than 200,000 people, he marched towards Washington for human right. Also, it’s the largest human right campaign in U.S.A. history. During the protest, he gave a speech named “I Have a Dream” which is history’s one of the renowned speeches.
Death and memorial
During his life working as a leader of the Civil Rights Movement he makes many enemies. Also, the government and plans do everything to hurt his reputation. Martin Luther King was assassinated in 1968. Every year the US celebrates his anniversary as Martin Luther King Jr. day in the US. Also, they honored kings’ memory by naming school and building after him and a Memorial at Independence Mall.
Martin Luther King was a great man who dedicated his whole life for his community. Also, he was an active leader and a great spokesperson that not only served his people but also humanity. It was due to his contribution that the African-American got their civil rights.
Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- This Day In History
- History Classics
- HISTORY Podcasts
HISTORY Vault
- Link HISTORY on facebook
- Link HISTORY on twitter
- Link HISTORY on youtube
- Link HISTORY on instagram
- Link HISTORY on tiktok
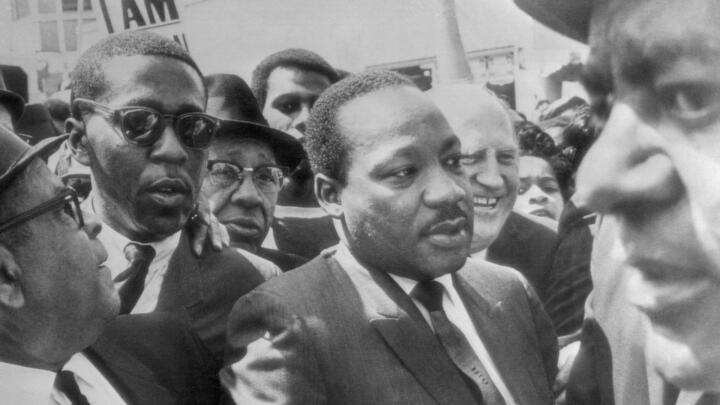
✯ ✯ ✯ Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. ✯ ✯ ✯ His Life and Legacy
Martin Luther King Jr. dedicated his life to the nonviolent struggle for civil rights in the United States. King's leadership played a pivotal role in ending entrenched segregation for African Americans and to the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, considered a crowning achievement of the civil rights era. King was assassinated in 1968, but his words and legacy continue to resonate for all those seeking justice in the United States and around the world. As King said at the Washington National Cathedral on March 31, 1968, "Darkness cannot drive out darkness; only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate; only love can do that."

10 Things You May Not Know About Martin Luther King Jr.

An Intimate View of MLK Through the Lens of a Friend
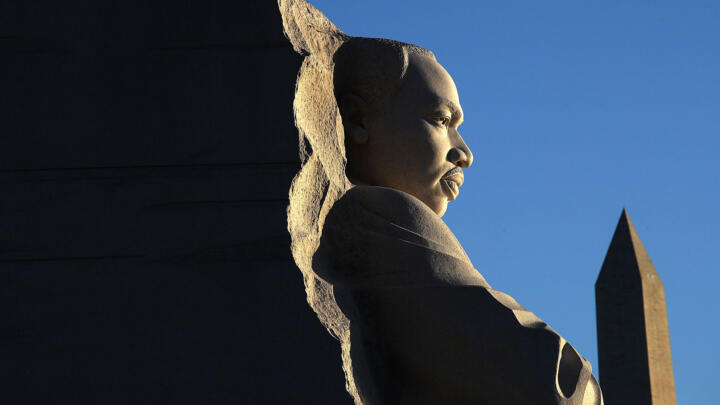

The Fight for Martin Luther King Jr. Day
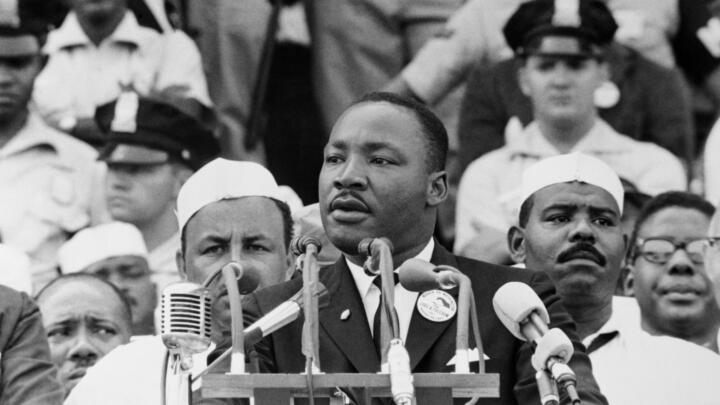

7 of Martin Luther King Jr.'s Most Notable Speeches
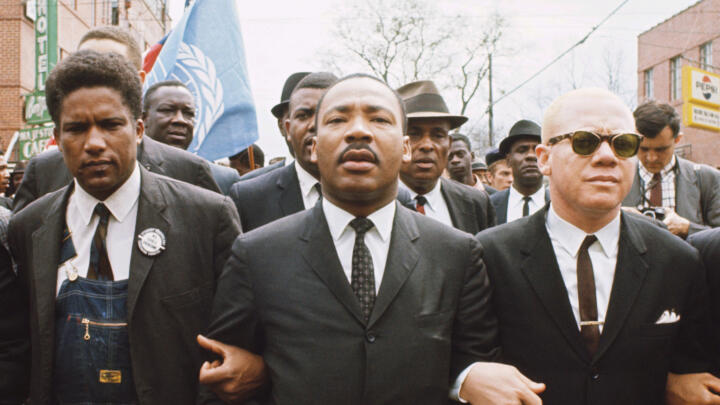

Martin Luther King Jr.

7 Things You May Not Know About MLK’s 'I Have a Dream' Speech
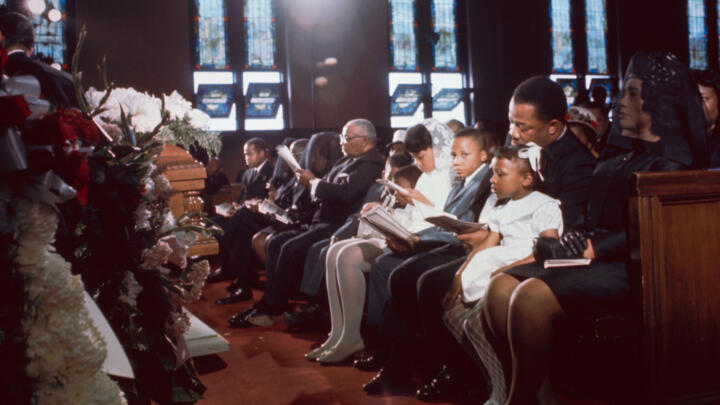

America in Mourning After MLK's Shocking Assassination: Photos

For Martin Luther King Jr., Nonviolent Protest Never Meant ‘Wait and See’

How an Assassination Attempt Affirmed MLK’s Faith in Nonviolence

Jesse Jackson on M.L.K.: One Bullet Couldn’t Kill the Movement

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Final Speech

MLK's Poor People's Campaign Demanded Economic Justice

Martin Luther King Jr.’s Famous Speech Almost Didn’t Have the Phrase 'I Have a Dream'

How Selma's 'Bloody Sunday' Became a Turning Point in the Civil Rights Movement

Playlist: Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.

Watch the Black History collection on HISTORY Vault to look back on the history of African American achievements.
Get instant access to free updates.
Don’t Miss Out on HISTORY news, behind the scenes content, and more.
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
Need help with the site?
Create a profile to add this show to your list.
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and major leader of the Civil Rights Movement. After his assassination, he was memorialized by Martin Luther King Jr. Day.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
In Focus: Martin Luther King Jr. Day
Days after his 1968 assassination , a campaign for a holiday in King’s honor began. U.S. Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan first proposed a bill on April 8, 1968, but the first vote on the legislation didn’t happen until 1979. King’s widow, Coretta Scott King , led the lobbying effort to drum up public support. Fifteen years after its introduction, the bill finally became law.
In 1983, President Ronald Reagan ’s signature created Martin Luther King Jr. Day of Service as a federal holiday. It’s celebrated annually on the third Monday in January. The only national day of service, Martin Luther King Jr. Day was first celebrated in 1986. The first time all 50 states recognized the holiday was in 2000.
See Martin Luther King Jr.’s life depicted onscreen in the 2018 documentary I Am MLK Jr. or the Oscar-winning movie Selma .
Quick Facts
Where did martin luther king jr. go to school, philosophy of nonviolence, civil rights accomplishments, "i have a dream" and other famous speeches, wife and kids, fbi surveillance, later activism, assassination, who was martin luther king jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. was a Baptist minister and civil rights activist who had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States, beginning in the mid-1950s. Among his many efforts, King headed the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC). Through his nonviolent activism and inspirational speeches , he played a pivotal role in ending legal segregation of Black Americans, as well as the creation of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . King won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964, among several other honors. He was assassinated by James Earl Ray and died on April 4, 1968, at age 39. King continues to be remembered as one of the most influential and inspirational Black leaders in history.
FULL NAME: Martin Luther King Jr. BIRTHDAY: January 15, 1929 DIED: April 4, 1968 BIRTHPLACE: Atlanta, Georgia SPOUSE: Coretta Scott King (1953-1968) CHILDREN: Yolanda, Martin III, Dexter, and Bernice King ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Capricorn
Martin Luther King Jr. was born as Michael Luther King Jr. in Atlanta. His birthday was January 15, 1929.
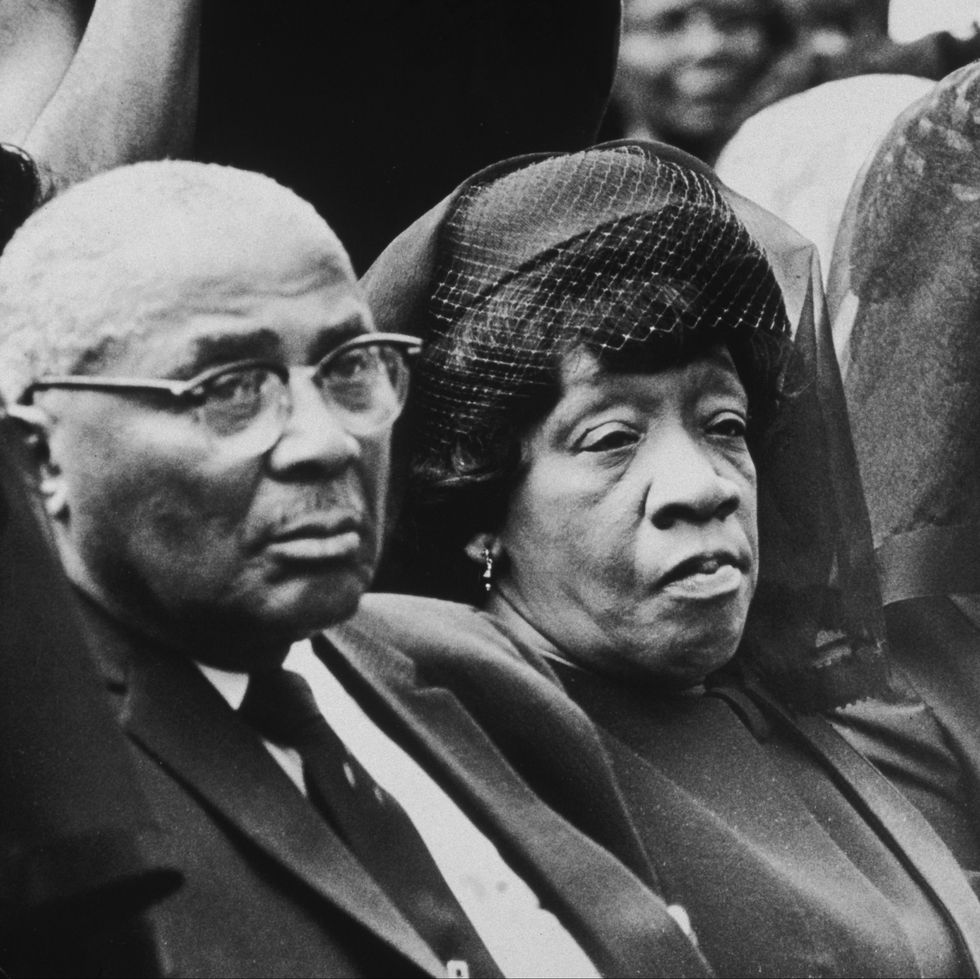

His parents were Michael Luther King Sr. and Alberta Williams King. The Williams and King families had roots in rural Georgia. Martin’s maternal grandfather, A.D. Williams, was a rural minister for years and then moved to Atlanta in 1893. He took over the small, struggling Ebenezer Baptist Church with around 13 members and made it into a forceful congregation. He married Jennie Celeste Parks, and they had one child who survived, Alberta.
Michael Sr. came from a family of sharecroppers in a poor farming community. He married Alberta in 1926 after an eight-year courtship. The newlyweds moved to A.D.’s home in Atlanta. Michael stepped in as pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church upon the death of his father-in-law in 1931. He, too, became a successful minister and adopted the name Martin Luther King Sr. in honor of the German Protestant religious leader Martin Luther . In due time, Michael Jr. followed his father’s lead and adopt the name himself to become Martin Luther King Jr.
A middle child, Martin Jr. had an older sister, Willie, and a younger brother, Alfred. The King children grew up in a secure and loving environment. Martin Sr. was more the disciplinarian, while Alberta’s gentleness easily balanced out their father’s strict hand.
Although they undoubtedly tried, Martin Jr.’s parents couldn’t shield him completely from racism. His father fought against racial prejudice, not just because his race suffered, but also because he considered racism and segregation to be an affront to God’s will. He strongly discouraged any sense of class superiority in his children, which left a lasting impression on Martin Jr.
Growing up in Atlanta, King entered public school at age 5. In May 1936, he was baptized, but the event made little impression on him.
In May 1941, King was 12 years old when his grandmother Jennie died of a heart attack. The event was traumatic for the boy, more so because he was out watching a parade against his parents’ wishes when she died. Distraught at the news, young King jumped from a second-story window at the family home, allegedly attempting suicide.
King attended Booker T. Washington High School, where he was said to be a precocious student. He skipped both the ninth and eleventh grades and, at age 15, entered Morehouse College in Atlanta in 1944. He was a popular student, especially with his female classmates, but largely unmotivated, floating through his first two years.
Influenced by his experiences with racism, King began planting the seeds for a future as a social activist early in his time at Morehouse. “I was at the point where I was deeply interested in political matters and social ills,” he recalled in The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr . “I could envision myself playing a part in breaking down the legal barriers to Negro rights.”
The Autobiography of Martin Luther King, Jr.

At the time, King felt that the best way to serve that purpose was as a lawyer or a doctor. Although his family was deeply involved in the church and worship, King questioned religion in general and felt uncomfortable with overly emotional displays of religious worship. This discomfort had continued through much of his adolescence, initially leading him to decide against entering the ministry, much to his father’s dismay.
But in his junior year, King took a Bible class, renewed his faith, and began to envision a career in the ministry. In the fall of his senior year, he told his father of his decision, and he was ordained at Ebenezer Baptist Church in February 1948.
Later that year, King earned a sociology degree from Morehouse College and began attended the liberal Crozer Theological Seminary in Chester, Pennsylvania. He thrived in all his studies, was elected student body president, and was valedictorian of his class in 1951. He also earned a fellowship for graduate study.
Even though King was following his father’s footsteps, he rebelled against Martin Sr.’s more conservative influence by drinking beer and playing pool while at college. He became romantically involved with a white woman and went through a difficult time before he could break off the relationship.
During his last year in seminary, King came under the guidance of Morehouse College President Benjamin E. Mays, who influenced King’s spiritual development. Mays was an outspoken advocate for racial equality and encouraged King to view Christianity as a potential force for social change.

After being accepted at several colleges for his doctoral study, King enrolled at Boston University. In 1954, while still working on his dissertation, King became pastor of the Dexter Avenue Baptist Church of Montgomery, Alabama. He completed his doctorate and earned his degree in 1955 at age 25.
Decades after King’s death, in the late 1980s, researchers at Stanford University’s King Papers Project began to note similarities between passages of King’s doctoral dissertation and those of another student’s work. A committee of scholars appointed by Boston University determined that King was guilty of plagiarism in 1991, though it also recommended against the revocation of his degree.
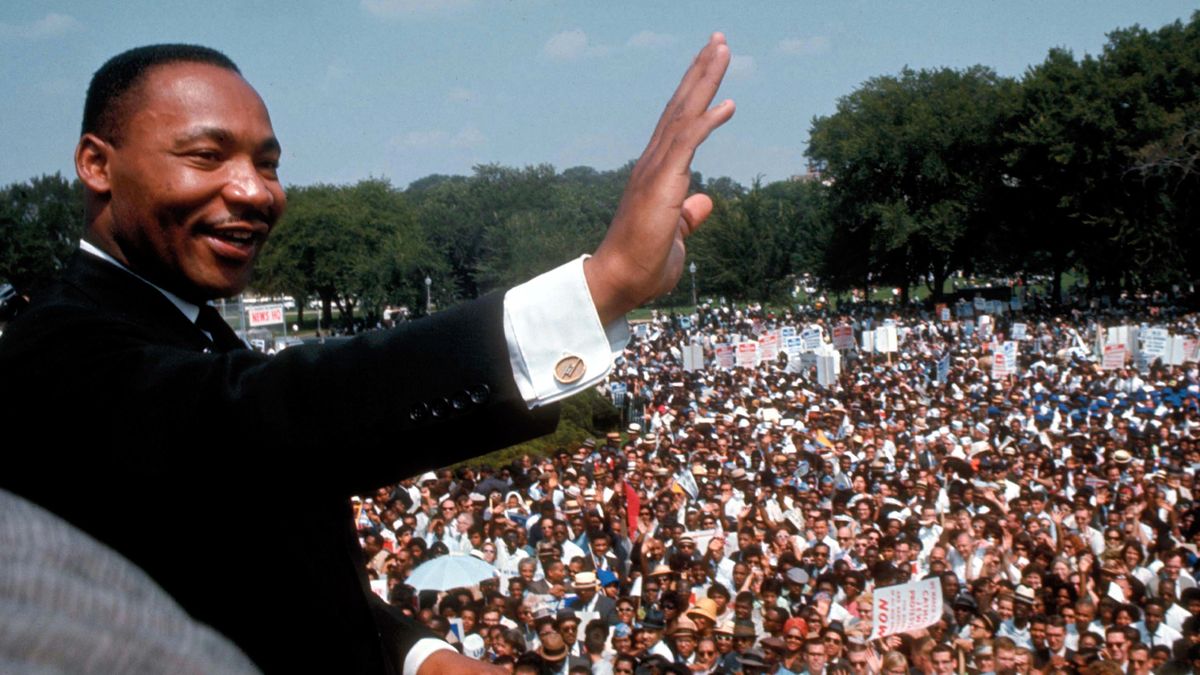

First exposed to the concept of nonviolent resistance while reading Henry David Thoreau ’s On Civil Disobedience at Morehouse, King later discovered a powerful exemplar of the method’s possibilities through his research into the life of Mahatma Gandhi . Fellow civil rights activist Bayard Rustin , who had also studied Gandhi’s teachings, became one of King’s associates in the 1950s and counseled him to dedicate himself to the principles of nonviolence.
As explained in his autobiography , King previously felt that the peaceful teachings of Jesus applied mainly to individual relationships, not large-scale confrontations. But he came to realize: “Love for Gandhi was a potent instrument for social and collective transformation. It was in this Gandhian emphasis on love and nonviolence that I discovered the method for social reform that I had been seeking.”
It led to the formation of King’s six principles of nonviolence :
- Nonviolence is a way of life for courageous people.
- Nonviolence seeks to win friendship and understanding.
- Nonviolence seeks to defeat injustice, not people.
- Nonviolence holds that suffering for a just cause can educate and transform.
- Nonviolence chooses love instead of hate.
- Nonviolence believes that the universe is on the side of justice.
In the years to come, King also frequently cited the “ Beloved Community ”—a world in which a shared spirit of compassion brings an end to the evils of racism, poverty, inequality, and violence—as the end goal of his activist efforts.

Led by his religious convictions and philosophy of nonviolence, King became one of the most prominent figures of the Civil Rights Movement . He was a founding member of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference and played key roles in several major demonstrations that transformed society. This included the Montgomery Bus Boycott that integrated Alabama’s public transit, the Greensboro Sit-In movement that desegregated lunch counters across the South, the March on Washington that led to the passage of the 1964 Civil Rights Act, and the Selma-to-Montgomery marches in Alabama that culminated in the 1965 Voting Rights Act.
King’s efforts earned him the Nobel Peace Prize in 1964 when he was 35.
Montgomery Bus Boycott
King’s first leadership role within the Civil Rights Movement was during the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955–1956. The 381-day protest integrated the Alabama city’s public transit in one of the largest and most successful mass movements against racial segregation in history.
The effort began on December 1, 1955, when 42-year-old Rosa Parks boarded the Cleveland Avenue bus to go home after an exhausting day at work. She sat in the first row of the “colored” section in the middle of the bus. As the bus traveled its route, all the seats in the white section filled up, then several more white passengers boarded the bus.
The bus driver noted that there were several white men standing and demanded that Parks and several other African Americans give up their seats. Three other Black passengers reluctantly gave up their places, but Parks remained seated.
The driver asked her again to give up her seat, and again she refused. Parks was arrested and booked for violating the Montgomery City Code. At her trial a week later, in a 30-minute hearing, Parks was found guilty and fined $10 and assessed $4 court fee.
The local NAACP chapter had been looking to challenge Montgomery’s segregated bus policy and had almost made 15-year-old Claudette Colvin the face of the campaign months earlier. She similarly refused to give up her bus seat to a white man on March 2, 1955, but after organizers learned Colvin was pregnant, they feared it would scandalize the deeply religious Black community and make Colvin, along with the group’s efforts, less credible in the eyes of sympathetic white people. Parks’ experience of discrimination provided another opportunity.
On the night Parks was arrested, E.D. Nixon , head of the local NAACP chapter, met with King and other local civil rights leaders to plan a Montgomery Bus Boycott. King was elected to lead the boycott because he was young, well-trained, and had solid family connections and professional standing. He was also new to the community and had few enemies, so organizers felt he would have strong credibility with the Black community.
In his first speech as the group’s president, King declared:
“We have no alternative but to protest. For many years, we have shown an amazing patience. We have sometimes given our white brothers the feeling that we liked the way we were being treated. But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.”
King’s skillful rhetoric put new energy into the civil rights struggle in Alabama. The Montgomery Bus Boycott began December 5, 1955, and for more than a year, the local Black community walked to work, coordinated ride sharing, and faced harassment, violence, and intimidation. Both King’s and Nixon’s homes were attacked.
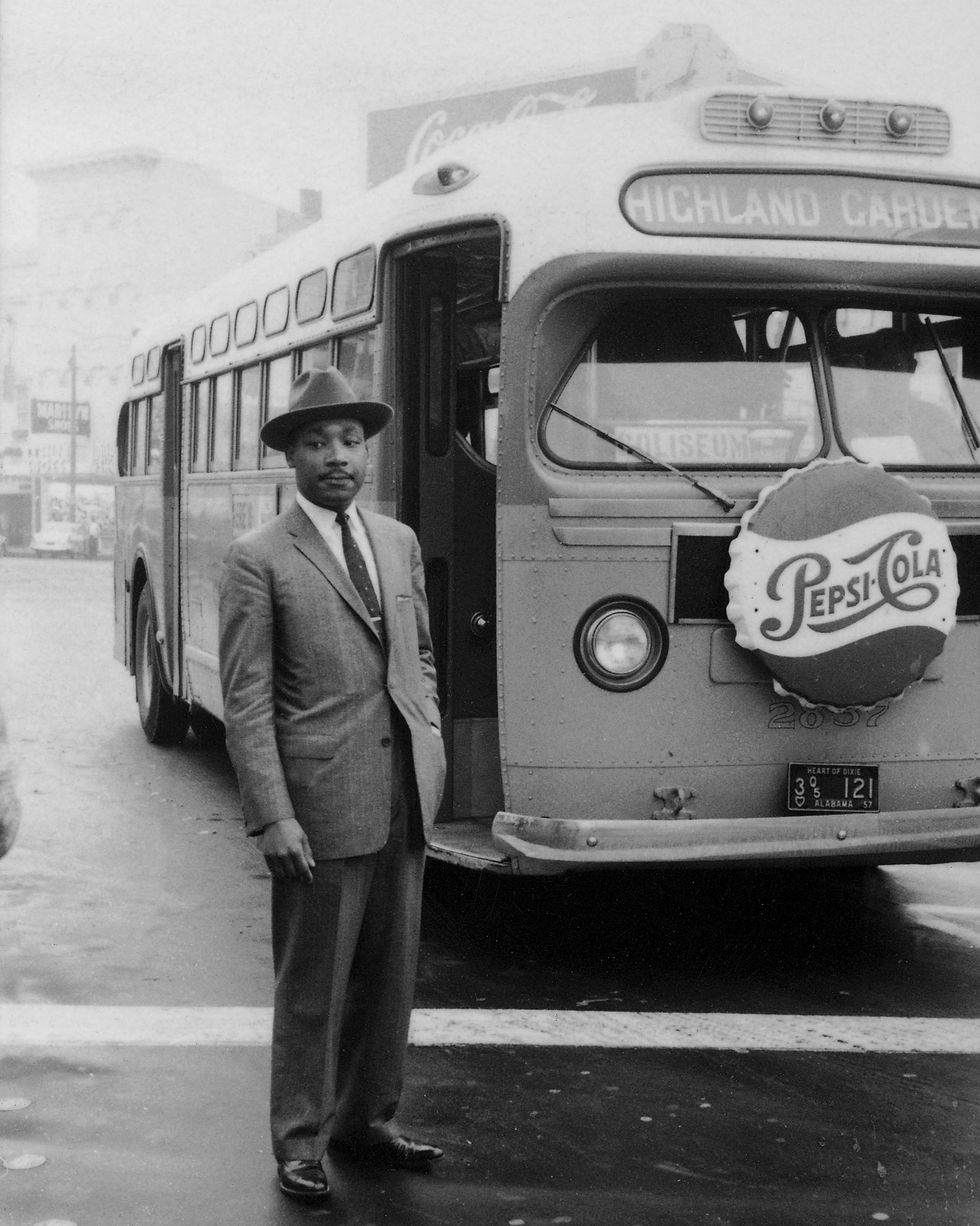
In addition to the boycott, members of the Black community took legal action against the city ordinance that outlined the segregated transit system. They argued it was unconstitutional based on the U.S. Supreme Court ’s “separate is never equal” decision in Brown v. Board of Education (1954). Several lower courts agreed, and the nation’s Supreme Court upheld the ruling in a November 13, 1956, decision that also ruled the state of Alabama’s bus segregation laws were unconstitutional.
After the legal defeats and large financial losses, the city of Montgomery lifted the law that mandated segregated public transportation. The boycott ended on December 20, 1956.
Southern Christian Leadership Conference
Flush with victory, African American civil rights leaders recognized the need for a national organization to help coordinate their efforts. In January 1957, King, Ralph Abernathy , and 60 ministers and civil rights activists founded the Southern Christian Leadership Conference to harness the moral authority and organizing power of Black churches. The SCLC helped conduct nonviolent protests to promote civil rights reform.
King’s participation in the organization gave him a base of operation throughout the South, as well as a national platform. The SCLC felt the best place to start to give African Americans a voice was to enfranchise them in the voting process. In February 1958, the SCLC sponsored more than 20 mass meetings in key southern cities to register Black voters. King met with religious and civil rights leaders and lectured all over the country on race-related issues.
Stride Toward Freedom: The Montgomery Story

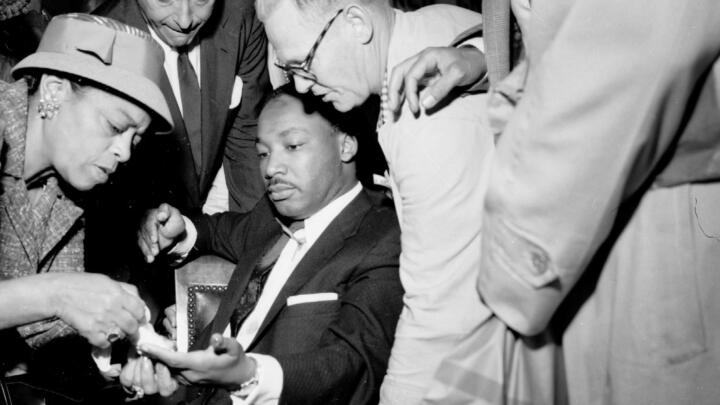
That September, King survived an attempt on his life when a woman with mental illness stabbed him in the chest as he signed copies of his book Stride Toward Freedom in a New York City department store. Saved by quick medical attention, King expressed sympathy for his assailant’s condition in the aftermath .
In 1959, with the help of the American Friends Service Committee, King visited Gandhi ’s birthplace in India. The trip affected him in a profound way, increasing his commitment to America’s civil rights struggle.
Greensboro Sit-In
By 1960, King was gaining national exposure. He returned to Atlanta to become co-pastor with his father at Ebenezer Baptist Church but also continued his civil rights efforts. His next activist campaign was the student-led Greensboro Sit-In movement.
In February 1960, a group of Black students in Greensboro, North Carolina , began sitting at racially segregated lunch counters in the city’s stores. When asked to leave or sit in the “colored” section, they just remained seated, subjecting themselves to verbal and sometimes physical abuse.
The movement quickly gained traction in several other cities. That April, the SCLC held a conference at Shaw University in Raleigh, North Carolina, with local sit-in leaders. King encouraged students to continue to use nonviolent methods during their protests. Out of this meeting, the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC) formed and, for a time, worked closely with the SCLC. By August 1960, the sit-ins had successfully ended segregation at lunch counters in 27 southern cities. But the movement wasn’t done yet.
On October 19, 1960, King and 75 students entered a local department store and requested lunch-counter service but were denied. When they refused to leave the counter area, King and 36 others were arrested. Realizing the incident would hurt the city’s reputation, Atlanta’s mayor negotiated a truce, and charges were eventually dropped.
Soon after, King was imprisoned for violating his probation on a traffic conviction. The news of his imprisonment entered the 1960 presidential campaign when candidate John F. Kennedy made a phone call to Martin’s wife, Coretta Scott King . Kennedy expressed his concern over the harsh treatment Martin received for the traffic ticket, and political pressure was quickly set in motion. King was soon released.

Letter from Birmingham Jail
In the spring of 1963, King organized a demonstration in downtown Birmingham, Alabama. With entire families in attendance, city police turned dogs and fire hoses on demonstrators. King was jailed, along with large numbers of his supporters.
The event drew nationwide attention. However, King was personally criticized by Black and white clergy alike for taking risks and endangering the children who attended the demonstration.
In his famous Letter from Birmingham Jail , King eloquently spelled out his theory of nonviolence: “Nonviolent direct action seeks to create such a crisis and foster such a tension that a community, which has constantly refused to negotiate, is forced to confront the issue.”
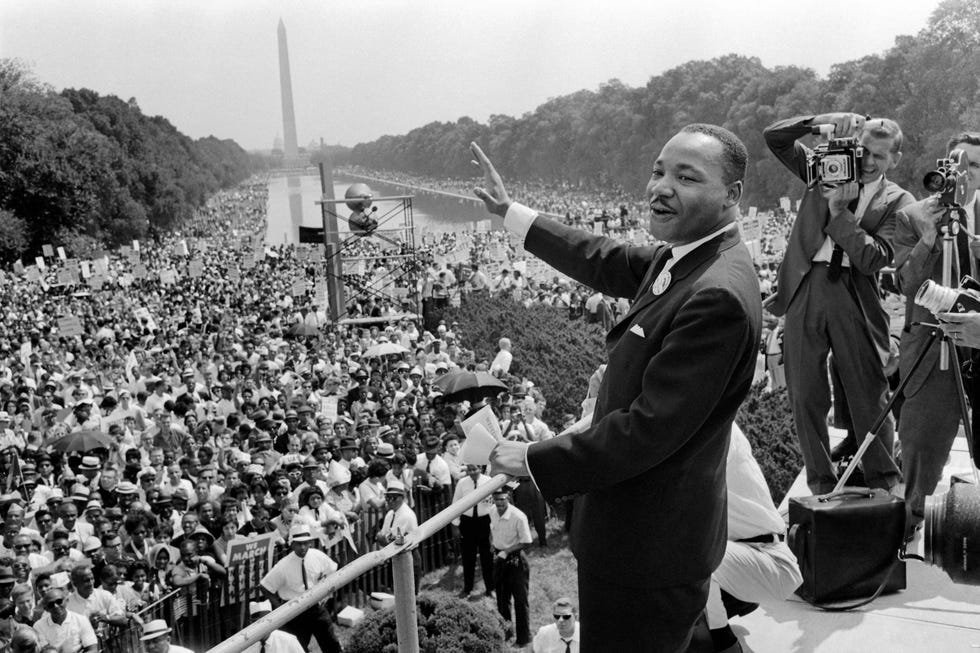
1963 March on Washington
By the end of the Birmingham campaign, King and his supporters were making plans for a massive demonstration on the nation’s capital composed of multiple organizations, all asking for peaceful change. The demonstration was the brainchild of labor leader A. Philip Randolph and King’s one-time mentor Bayard Rustin .
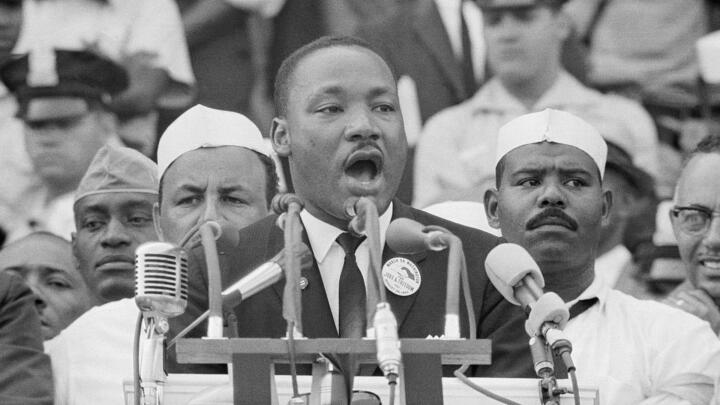
On August 28, 1963, the historic March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom drew an estimated 250,000 people in the shadow of the Lincoln Memorial. It remains one of the largest peaceful demonstrations in American history. During the demonstration, King delivered his famed “I Have a Dream” speech .
The rising tide of civil rights agitation that had culminated in the March on Washington produced a strong effect on public opinion. Many people in cities not experiencing racial tension began to question the nation’s Jim Crow laws and the near-century of second-class treatment of African American citizens since the end of slavery. This resulted in the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 , authorizing the federal government to enforce desegregation of public accommodations and outlawing discrimination in publicly owned facilities.
Selma March
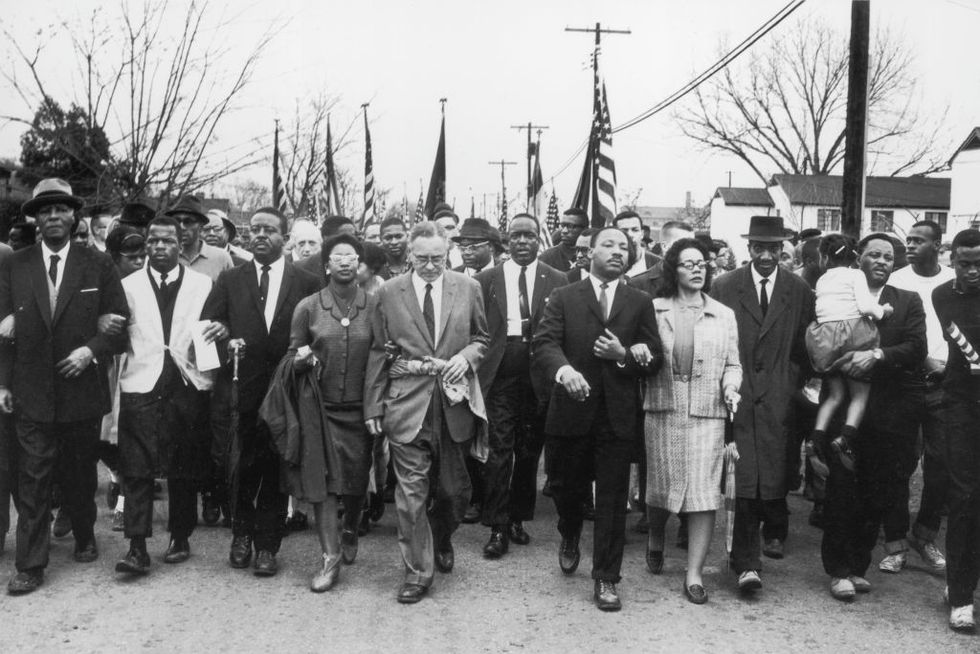

Continuing to focus on voting rights, King, the SCLC, SNCC, and local organizers planned to march peacefully from Selma, Alabama, to the state’s capital, Montgomery.
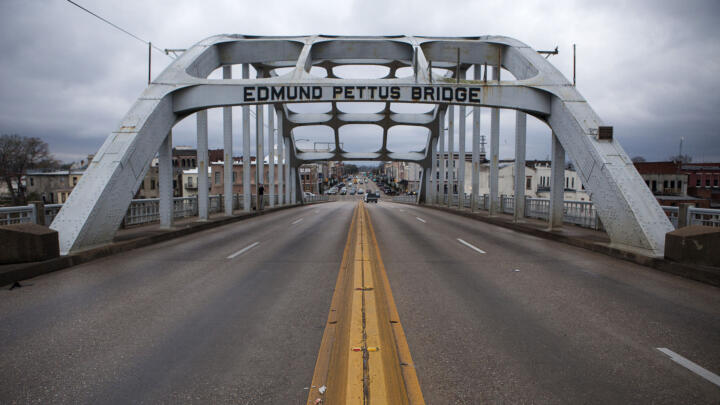
Led by John Lewis and Hosea Williams , demonstrators set out on March 7, 1965. But the Selma march quickly turned violent as police with nightsticks and tear gas met the demonstrators as they tried to cross the Edmund Pettus Bridge in Selma. The attack was televised, broadcasting the horrifying images of marchers being bloodied and severely injured to a wide audience. Of the 600 demonstrators, 58 were hospitalized in a day that became known as “ Bloody Sunday .” King, however, was spared because he was in Atlanta.
Not to be deterred, activists attempted the Selma-to-Montgomery march again. This time, King made sure he was part of it. Because a federal judge had issued a temporary restraining order on another march, a different approach was taken.
On March 9, 1965, a procession of 2,500 marchers, both Black and white, set out once again to cross the Pettus Bridge and confronted barricades and state troopers. Instead of forcing a confrontation, King led his followers to kneel in prayer, then they turned back. This became known as “Turnaround Tuesday.”
Alabama Governor George Wallace continued to try to prevent another march until President Lyndon B. Johnson pledged his support and ordered U.S. Army troops and the Alabama National Guard to protect the protestors.
On March 21, 1965, approximately 2,000 people began a march from Selma to Montgomery. On March 25, the number of marchers, which had grown to an estimated 25,000 gathered in front of the state capitol where King delivered a televised speech. Five months after the historic peaceful protest, President Johnson signed the 1965 Voting Rights Act .

Along with his “I Have a Dream” and “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” speeches, King delivered several acclaimed addresses over the course of his life in the public eye.
“I Have A Dream” Speech
Date: august 28, 1963.
King gave his famous “I Have a Dream” speech during the 1963 March on Washington. Standing at the Lincoln Memorial, he emphasized his belief that someday all men could be brothers to the 250,000-strong crowd.
Notable Quote: “I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.”
“Give Us the Ballot” Speech
Date: may 17, 1957.
Six years before he told the world of his dream, King stood at the same Lincoln Memorial steps as the final speaker of the Prayer Pilgrimage for Freedom. Dismayed by the ongoing obstacles to registering Black voters, King urged leaders from various backgrounds—Republican and Democrat, Black and white—to work together in the name of justice.
Notable Quote: “Give us the ballot, and we will no longer have to worry the federal government about our basic rights. Give us the ballot, and we will no longer plead to the federal government for passage of an anti-lynching law... Give us the ballot, and we will transform the salient misdeeds of bloodthirsty mobs into the calculated good deeds of orderly citizens.”
Nobel Peace Prize Acceptance Speech
Date: december 10, 1964.
Speaking at the University of Oslo in Norway, King pondered why he was receiving the Nobel Prize when the battle for racial justice was far from over, before acknowledging that it was in recognition of the power of nonviolent resistance. He then compared the foot soldiers of the Civil Rights Movement to the ground crew at an airport who do the unheralded-yet-necessary work to keep planes running on schedule.
Notable Quote: “I think Alfred Nobel would know what I mean when I say that I accept this award in the spirit of a curator of some precious heirloom which he holds in trust for its true owners—all those to whom beauty is truth and truth, beauty—and in whose eyes the beauty of genuine brotherhood and peace is more precious than diamonds or silver or gold.”
“Our God is Marching On (How Long? Not Long)” Speech
Date: march 25, 1965.
At the end of the bitterly fought Selma-to-Montgomery march, King addressed a crowd of 25,000 supporters from the Alabama State Capitol. Offering a brief history lesson on the roots of segregation, King emphasized that there would be no stopping the effort to secure full voting rights, while suggesting a more expansive agenda to come with a call to march on poverty.
Notable Quote: “I come to say to you this afternoon, however difficult the moment, however frustrating the hour, it will not be long, because ‘truth crushed to earth will rise again.’ How long? Not long, because ‘no lie can live forever.’... How long? Not long, because the arc of the moral universe is long, but it bends toward justice.”
“Beyond Vietnam: A Time to Break Silence” Speech
Date: april 4, 1967.
One year before his assassination, King delivered a controversial sermon at New York City’s Riverside Church in which he condemned the Vietnam War. Explaining why his conscience had forced him to speak up, King expressed concern for the poor American soldiers pressed into conflict thousands of miles from home, while pointedly faulting the U.S. government’s role in escalating the war.
Notable Quote: “We still have a choice today: nonviolent coexistence or violent co-annihilation. We must move past indecision to action. We must find new ways to speak for peace in Vietnam and justice throughout the developing world, a world that borders on our doors. If we do not act, we shall surely be dragged down the long, dark, and shameful corridors of time reserved for those who possess power without compassion, might without morality, and strength without sight.”
“I’ve Been to the Mountaintop” Speech
Date: april 3, 1968.
The well-known orator delivered his final speech the day before he died at the Mason Temple in Memphis, Tennessee. King reflected on major moments of progress in history and his own life, in addition to encouraging the city’s striking sanitation workers.
Notable Quote: “I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.”
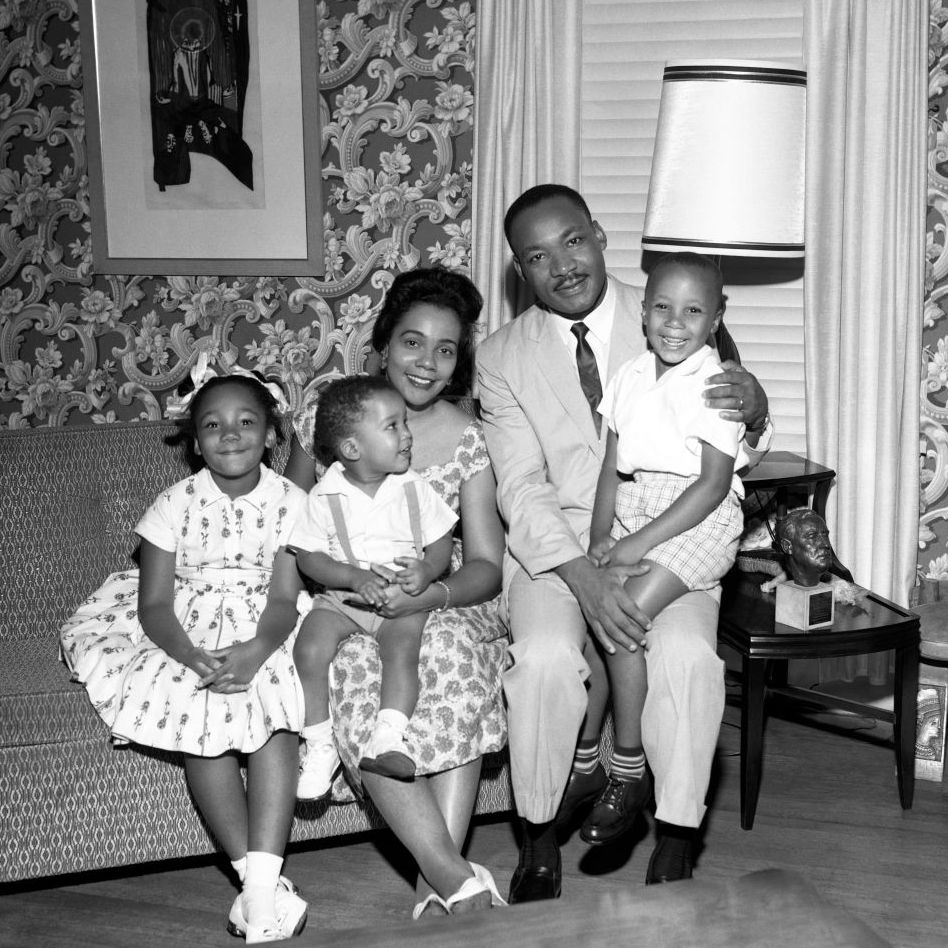
While working on his doctorate at Boston University, King met Coretta Scott , an aspiring singer and musician at the New England Conservatory school in Boston. They were married on June 18, 1953, and had four children—two daughters and two sons—over the next decade. Their oldest, Yolanda, was born in 1955, followed by sons Martin Luther King III in 1957 and Dexter in 1961. The couple welcomed Bernice King in 1963.
Although she accepted the responsibility to raise the children while King travelled the country, Coretta opened their home to organizational meetings and served as an advisor and sounding board for her husband. “I am convinced that if I had not had a wife with the fortitude, strength, and calmness of Corrie, I could not have withstood the ordeals and tensions surrounding the movement,” King wrote in his autobiography.
His lengthy absences became a way of life for their children, but Martin III remembered his father returning from the road to join the kids playing in the yard or bring them to the local YMCA for swimming. King also fostered discussions at mealtimes to make sure everyone understood the important issues he was seeking to resolve.
Leery of accumulating wealth as a high-profile figure, King insisted his family live off his salary as a pastor. However, he was known to splurge on good suits and fine dining, while contrasting his serious public image with a lively sense of humor among friends and family.
Due to his relationships with alleged Communists, King became a target of FBI surveillance and, from late 1963 until his death, a campaign to discredit the civil rights activist. While FBI wiretaps failed to produce evidence of Communist sympathies, they captured the civil rights leader’s engagement in extramarital dalliances. This led to the infamous “suicide letter” of 1964, later confirmed to be from the FBI and authorized by then-Director J. Edgar Hoover , which urged King to kill himself if he wanted to prevent news of his affairs from going public.
In 2019, historian David Garrow wrote of explosive new allegations against King following his review of recently released FBI documents. Among the discoveries was a memo suggesting that King had encouraged the rape of a parishioner in a hotel room, as well as evidence that he might have fathered a daughter with a mistress. Other historians questioned the veracity of the documentation, especially given the FBI’s known attempts to damage King’s reputation. The original surveillance tapes regarding these allegations are under judicial seal until 2027.
From late 1965 through 1967, King expanded his civil rights efforts into other larger American cities, including Chicago and Los Angeles. But he met with increasing criticism and public challenges from young Black power leaders. King’s patient, non-violent approach and appeal to white middle-class citizens alienated many Black militants who considered his methods too weak, too late, and ineffective.
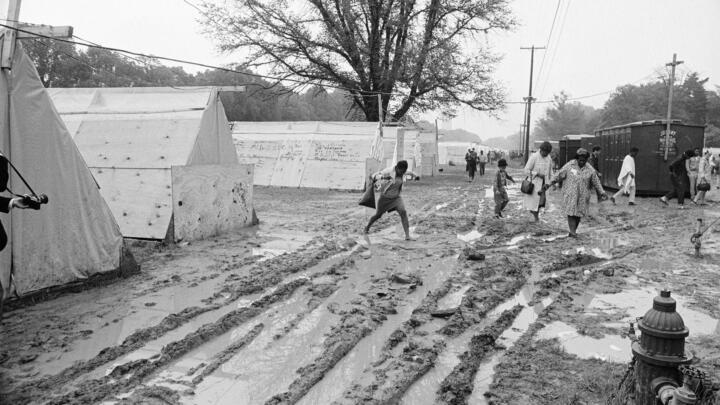
To address this criticism, King began making a link between discrimination and poverty, and he began to speak out against the Vietnam War . He felt America’s involvement in Vietnam was politically untenable and the government’s conduct in the war was discriminatory to the poor. He sought to broaden his base by forming a multiracial coalition to address the economic and unemployment problems of all disadvantaged people. To that end, plans were in the works for another march on Washington to highlight the Poor People’s Campaign, a movement intended to pressure the government into improving living and working conditions for the economically disadvantaged.
By 1968, the years of demonstrations and confrontations were beginning to wear on King. He had grown tired of marches, going to jail, and living under the constant threat of death. He was becoming discouraged at the slow progress of civil rights in America and the increasing criticism from other African American leaders.
In the spring of 1968, a labor strike by Memphis, Tennessee, sanitation workers drew King to one last crusade. On April 3, 1968, he gave his final and what proved to be an eerily prophetic speech, “I’ve Been to the Mountaintop,” in which he told supporters, “Like anybody, I would like to live a long life. Longevity has its place. But I’m not concerned about that now… I’m not worried about anything. I’m not fearing any man. Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord.”

While standing on a balcony outside his room at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee, Martin Luther King Jr. was killed by a sniper’s bullet on April 4, 1968. King died at age 39. The shocking assassination sparked riots and demonstrations in more than 100 cities across the country.
The shooter was James Earl Ray , a malcontent drifter and former convict. He initially escaped authorities but was apprehended after a two-month international manhunt. In 1969, Ray pleaded guilty to assassinating King and was sentenced to 99 years in prison.
The identity of King’s assassin has been the source of some controversy. Ray recanted his confession shortly after he was sentenced, and King’s son Dexter publicly defended Ray’s innocence after meeting with the convicted gunman in 1997. Another complicating factor is the 1993 confession of tavern owner Loyd Jowers, who said he contracted a different hit man to kill King. In June 2000, the U.S. Justice Department released a report that dismissed the alternative theories of King’s death. Ray died in prison on April 23, 1998.
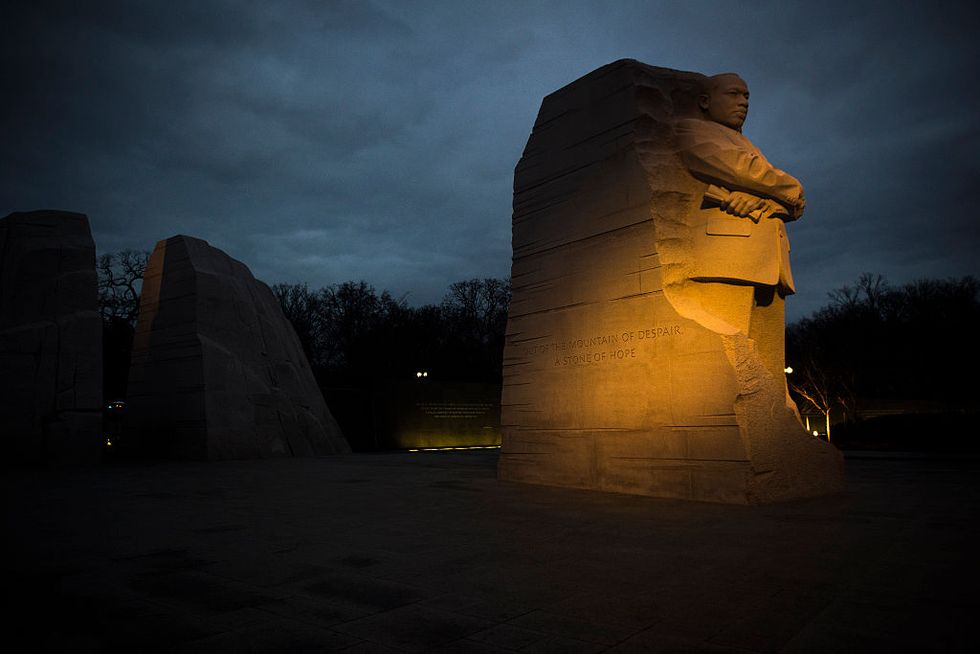

King’s life had a seismic impact on race relations in the United States. Years after his death, he is the most widely known Black leader of his era.
His life and work have been honored with a national holiday, schools and public buildings named after him, and a memorial on Independence Mall in Washington, D.C.
Over the years, extensive archival studies have led to a more balanced and comprehensive assessment of his life, portraying him as a complex figure: flawed, fallible, and limited in his control over the mass movements with which he was associated, yet a visionary leader who was deeply committed to achieving social justice through nonviolent means.
- But we come here tonight to be saved from that patience that makes us patient with anything less than freedom and justice.
- There comes a time when the cup of endurance runs over and men are no longer willing to be plunged into an abyss of injustice where they experience the bleakness of corroding despair.
- Any law that uplifts human personality is just. Any law that degrades human personality is unjust.
- The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.
- Let us not seek to satisfy our thirst for freedom by drinking from the cup of bitterness and hatred.
- Darkness cannot drive out darkness: only light can do that. Hate cannot drive out hate: only love can do that.
- The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy. The true neighbor will risk his position, his prestige, and even his life for the welfare of others.
- We must all learn to live together as brothers, or we will all perish together as fools.
- Forgiveness is not an occasional act; it is a permanent attitude.
- I have a dream that my four children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
- The function of education, therefore, is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. But education which stops with efficiency may prove the greatest menace to society. The most dangerous criminal may be the man gifted with reason but with no morals.
- I’ve seen the promised land. I may not get there with you. But I want you to know tonight that we, as a people, will get to the promised land.
- Power at its best is love implementing the demands of justice. Justice at its best is love correcting everything that stands against love.
- A man who won’t die for something is not fit to live.
- At the center of non-violence stands the principle of love.
- Right, temporarily defeated, is stronger than evil triumphant.
- In the end, we will remember not the words of our enemies, but the silence of our friends.
- Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere.
- Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.
Fact Check: We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn’t look right, contact us !
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us
Civil Rights Activists

5 Crowning Achievements of Maya Angelou

30 Civil Rights Leaders of the Past and Present

Benjamin Banneker

Marcus Garvey

Madam C.J. Walker

Maya Angelou

17 Inspiring Martin Luther King Quotes

Bayard Rustin

Colin Kaepernick

About Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.
Dr. king jr..

Drawing inspiration from both his Christian faith and the peaceful teachings of Mahatma Gandhi, Dr. King led a nonviolent movement in the late 1950s and ‘ 60s to achieve legal equality for African-Americans in the United States. While others were advocating for freedom by “any means necessary,” including violence, Martin Luther King, Jr. used the power of words and acts of nonviolent resistance, such as protests, grassroots organizing, and civil disobedience to achieve seemingly-impossible goals. He went on to lead similar campaigns against poverty and international conflict, always maintaining fidelity to his principles that men and women everywhere, regardless of color or creed, are equal members of the human family.
Dr. King’s “I Have a Dream” speech, Nobel Peace Prize lecture and “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” are among the most revered orations and writings in the English language. His accomplishments are now taught to American children of all races, and his teachings are studied by scholars and students worldwide. He is the only non-president to have a national holiday dedicated in his honor and is the only non-president memorialized on the Great Mall in the nation’s capital. He is memorialized in hundreds of statues, parks, streets, squares, churches and other public facilities around the world as a leader whose teachings are increasingly-relevant to the progress of humankind.
Some of Dr. King’s Most Important Achievements

In 1957 , Dr. King was elected president of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC), an organization designed to provide new leadership for the now burgeoning civil rights movement. He would serve as head of the SCLC until his assassination in 1968, a period during which he would emerge as the most important social leader of the modern American civil rights movement.
In 1963 , he led a coalition of numerous civil rights groups in a nonviolent campaign aimed at Birmingham, Alabama, which at the time was described as the “most segregated city in America.” The subsequent brutality of the city’s police, illustrated most vividly by television images of young blacks being assaulted by dogs and water hoses, led to a national outrage resulting in a push for unprecedented civil rights legislation. It was during this campaign that Dr. King drafted the “Letter from a Birmingham Jail,” the manifesto of Dr. King’s philosophy and tactics, which is today required-reading in universities worldwide.
Later in 1963 , Dr. King was one of the driving forces behind the March for Jobs and Freedom, more commonly known as the “March on Washington,” which drew over a quarter-million people to the national mall. It was at this march that Dr. King delivered his famous “I Have a Dream” speech, which cemented his status as a social change leader and helped inspire the nation to act on civil rights. Dr. King was later named Time magazine’s “Man of the Year.”

Also in 1964 , partly due to the March on Washington, Congress passed the landmark Civil Rights Act, essentially eliminating legalized racial segregation in the United States. The legislation made it illegal to discriminate against blacks or other minorities in hiring, public accommodations, education or transportation, areas which at the time were still very segregated in many places.
The next year, 1965 , Congress went on to pass the Voting Rights Act, which was an equally-important set of laws that eliminated the remaining barriers to voting for African-Americans, who in some locales had been almost completely disenfranchised. This legislation resulted directly from the Selma to Montgomery, AL March for Voting Rights lead by Dr. King.
Between 1965 and 1968, Dr. King shifted his focus toward economic justice – which he highlighted by leading several campaigns in Chicago, Illinois – and international peace – which he championed by speaking out strongly against the Vietnam War. His work in these years culminated in the “Poor Peoples Campaign,” which was a broad effort to assemble a multiracial coalition of impoverished Americans who would advocate for economic change.
Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.’s less than thirteen years of nonviolent leadership ended abruptly and tragically on April 4th, 1968 , when he was assassinated at the Lorraine Motel in Memphis, Tennessee. Dr. King’s body was returned to his hometown of Atlanta, Georgia, where his funeral ceremony was attended by high-level leaders of all races and political stripes.
- For more information regarding the Transcription of the King Family Press Conference on the MLK Assassination Trial Verdict December 9, 1999, Atlanta, GA. Click Here
- For more information regarding the Civil Case: King family versus Jowers. Click here .
- Later in 1968, Dr. King’s wife, Mrs. Coretta Scott King, officially founded the Martin Luther King, Jr. Center for Nonviolent Social Change, which she dedicated to being a “living memorial” aimed at continuing Dr. King’s work on important social ills around the world.
We envision the Beloved Community where injustice ceases and love prevails.
Contact Info
449 Auburn Avenue, NE Atlanta, Georgia 30312
404.526.8900
Quick Links
- History Timeline
- King Holiday
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Latest News
- Spotlight on Women’s History Month with The King Center
- The King Center Joins the King Family in Mourning the Loss of Naomi Barber King, wife of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr’s Late Brother
Stay Connected
Cross Cultural Solidarity

MLK: Speeches, Sermons, Essays, & Interviews
Below are King’s most essential speeches, sermons, and short writings, with links to audio and video when available. When dates are uncertain, a likely range of when a work was composed or performed is given. See also this collection of articles by MLK scholars about nearly every conceivable dimension of King’s life and thought, and this resource on books by and about King.
November, 1954: Transformed Nonconformist.
December 5, 1955: Address to the first mass meeting of the Montgomery bus boycott. Audio .
1956: The Violence of Desperate Men .
April 1956: Our Struggle.
March 18, 1956: When Peace Becomes Obnoxious.
May 7, 1956: The Death of Evil upon the Seashore .
November 1956: Paul’s Letter to American Christians . Audio.
January 1, 1957: Facing the Challenge of a New Age , Address Delivered at NAACP Emancipation Day Rally.
February 6, 1957: Nonviolence and Racial Justice.
April 7, 1957: The Birth of a New Nation . (On King’s travels to Ghana.) Audio .
May 17, 1957: Give Us the Ballot . Audio.
September 2, 1957: “A Look to the Future,” Address Delivered at Highlander Folk School’s Twenty-fifth Anniversary Meeting.
November, 1957: Loving Your Enemies . Audio.
March 9, 1959: Farewell Statement for All India Radio. Audio.
March 22, 1959: Palm Sunday Sermon on Mohandas K. Gandhi.
July 1959: My Trip to the Land of Gandhi.
October 1959: The Social Organization of Nonviolence . (A response to Robert Williams call for Black people to take up arms.)
April, 1960: Pilgrimage to Nonviolence.
March 1961: The Man Who Was a Fool .
1961: Interview on BBC’s “Face to Face.” Video.
September 1962: Can A Christian Be a Communist?
July 1962 – March 1963: Shattered Dreams .
July 1962 – March 1963: Love In Action .
July 1962 – March 31, 1963: A Tough Mind and a Tender Heart .
July 1962 – March 1963: On Being a Good Neighbor.
July 1962 – March 1963: Our God is Able .
July 1962 – March 1963: Antidotes for Fear .
July 1962 – March 1963: The Answer to a Perplexing Question .
June, 1963: A Knock at Midnight . Audio .
June 23, 1963: Great March to Freedom Rally, Detroit. Audio .
August 28, 1963: I Have a Dream . Video . Audio .
September 18, 1963: Eulogy for the Martyred Children . (Funeral service for the children killed in the Birmingham bombing.) Audio.
December 10, 1964: Acceptance Address for the Nobel Peace Prize . Video.
January, 1965: MLK Playboy interview . (The interviewer is Alex Hayley.)
March 25, 1965: Address at the Conclusion of the Selma to Montgomery March . Audio.
March 28, 1965: Interview on Meet the Press , immediately following the Selma to Montgomery March. Video.
June, 1965: The Bravest Man I Ever Met .
July 4, 1965: The American Dream . Audio (different version.)
May 31, 1966: “Buddhists and Martyrs of the Civil Rights Movement”: Joint statement by Martin Luther King, Jr., and Thich Nhat Hanh, International Committee of Conscience on Vietnam.
June 5, 1966: Guidelines for a Constructive Church . Audio.
January 25, 1967: Letter from Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. nominating Thich Nhat Hanh for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1967 .
April 4, 1967: Beyond Vietnam . Audio.
April 9, 1967: The Three Dimensions of a Complete Life. Audio.
April 14, 1967: The Other America. Video.
August 27, 1967: Why Jesus Called a Man a Fool. Audio.
August 16, 1967: “Where Do We Go From Here?,” Address Delivered at the Eleventh Annual SCLC Convention . Audio.
September 1, 1967: The Role of the Behavioral Scientist in the Civil Rights Movement .
October 26, 1967: What is Your Life’s Blueprint? Video. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: The Impasse in Race Relations. Audio . (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Conscience and the War in Vietnam. Audio. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Youth and Social Action. Audio. (No text version available.)
November/December 1967: Nonviolence and Social Change . Audio.
December 24, 1967: A Christmas Sermon on Peace (text incomplete.) Audio .
1967: Racism and the World House.
1967: King interviewed on NBC. Video.
1967: King interviewed on the Merv Griffin Show. Video ( Part 1 on civil rights, part two on Vietnam and Communism.)
February 4, 1968: The Drum Major Instinct. Audio.
February 23, 1968: Honoring Dr. Du Bois .
March 3, 1968: Unfulfilled Dreams . Audio (incomplete.)
March 18, 1968: All Labor Has Dignity.
March 31, 1968: Remaining Awake Through a Great Revolution . Audio.
April 3, 1968 (the day before King’s assassination): “ I’ve Been to the Mountaintop .” Audio .
128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples
Looking for Martin Luther King topics to research? Being one of the most prominent human rights activists in the 20th century, MLK is definitely worth writing about!
🔝 Top Martin Luther King topics to Write about
🏆 best martin luther king essay examples, 👨🏿 martin luther king essay titles, 🎓 creative titles for mlk essay, ❓ research questions about martin luther king.
Martin Luther King Jr. was an American Baptist minister and a civil rights defender who rose to fame in 1955. In his iconic “I have a dream” speech, he talked about civil and economic rights for people of color in the US.
In your Martin Luther King essay, you might want to focus on his ideas and philosophy. Why is MLK considered a hero? How did he change the world? In your paper, you can answer these questions. Another option is to look at the main themes Martin Luther King touched upon in his speeches. One more idea is to analyze the key quotes of MLK. Whether you are assigned an argumentative essay or a research paper, this article will be helpful. It contains a list of catchy MLK essay titles, best Martin Luther King topics, and research questions. Martin Luther King essay examples are added to inspire you even more.
- Martin Luther King: ideas and philosophy
- Why is MLK considered a hero?
- The Montgomery bus boycott: the significance
- I have a dream: rhetorical analysis
- MLK and the idea of peaceful protest
- Assassination of Martin Luther King
- Martin Luther King Jr. and Christian ideas
- Martin Luther King and his views on the Vietnam war
- MLK: the role in popular culture
- MLK assassination: conspiracy theories
- Essay on Martin Luther King’s I Have a Dream Speech One hundred years later, the life of the Negro is still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination…….
- I Have a Dream Speech Analysis The speech has become a symbol of a new era of freedom and symbol of the American civil rights movement.”I Have a Dream” is a representation of the “America Dream” about a free and equal […]
- The Comparison of the Speeches by Martin Luther King and Alicia Garza Both speeches address the same issue that concerns the inequality that exists in the US society when it comes to the rights of black and white people.
- How could King be more upset with moderate whites than violent extremists like clansmen? In his letter, King is trying to persuade and win the authority of the white man who in the real sense had acted as a hindrance to the attainment of the various goals of the […]
- “Letter From Birmingham Jail” Rhetorical Analysis Essay He supports his argument in the next paragraph, where he puts it across that they have been governed by a combination of unjust and just law whereby there is a need to separate the two.
- Martin Luther King Jr. vs. Nelson Mandela Letter from Birmingham jail was directed to the people and the eight white clergy members in Birmingham who condemned the actions of Martin Luther in public.
- Martin Luther King’s Speech: A Summary King noted that the constitution and the Declaration of Independence guaranteed the freedom and equality of all the citizens of the country.
- Use of Pathos: Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” During his lifetime, Martin Luther King Junior had the privilege of giving several speeches whose main theme in almost all was on the freedom of the black Americans.’I have a dream’ was among the many […]
- Ethical Leadership: Martin Luther King All individuals were expected to consider his actions and embrace the idea of morality. Through the use of a positive community culture and empowerment tactics, King managed to model such desirable behaviors.
- Analysis of “I Have a Dream “, by Martin Luther King, Jr. They are used in the speech to capture the attention of the audience. Repetition is used throughout the speech to put an emphasis on the main idea of the message.
- Martin Luther King Jr’s “I Have a Dream” Speech Critique The purpose of the king’s speech was to motivate the endorsement of change within the Americans, and the state, in relation to Americans’ inappropriate views towards unlike races or tribal groups in America.
- Martin Luther King Jr. as a Born Leader King was a trait leader, as he was able to translate his vision or his dream to others and make them enthusiastic about it.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s and Alicia Garza’s Speeches Comparison He demonstrates inspiration and magnetism, explaining the history of the issues affecting the audience. Garza is passionate about leaving her home and joining the movements on the streets to pass the message of freedom.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s and Malcolm X’s Leadership Styles Thesis: Martin Luther King and Malcolm X were both charismatic leaders, but the latter was more of a transformational leader as well because of his idealistic views and his ability to inspire his followers to […]
- Speech Evaluation: Martin Luther King, Jr. The analysis of the speech helps to understand various tools and techniques, which he implemented to find the way to reach the audience.
- Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. and Steve Jobs: Comparison In the case of Martin Luther King Jr, his commitment to non-violent resistance as a way of effecting social change was informed by his Christian upbringing and study of Mohandas Gandhi’s philosophy.
- Comparing the Oratory Styles and Impact of Martin Luther King Jr. and Alicia Garza On the other hand, Alicia Garza also displays a level of passion and charisma that captures the attention of her audience.
- Rhetorical Techniques in “Letter From Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King His flawless use of metaphors and parallelism allows the reader or the audience to empathize with King and support him in his fight against racial injustice.
- Rousseau’s the Social Contract vs. Martin Luther King His “Social Contract” is one of the most intriguing writings of Rousseau because he defends man, though being part of the society has its own right in terms of privacy.
- Martin Luther King and Winston Churchill’s Leadership Styles This move that paved the way for his growth in the military career later led to his emergence as a renowned leader in Britain and across the world.
- Martin Luther King and Thomas Hobbes on the Subject of Justice This paper discusses the subject of justice and specifically holds the view that justice is to follow one’s consciousness, and not to obey the unjust law.
- Martin Luther King and Malcolm X Although Malcolm X did not favor violence, he had a strong objection on the subject of nonviolence philosophy on the blacks.
- Comparing Views on the Feminism of Wollstonecraft and Martin Luther King This means that if women are given and encouraged to have the same level of education as the men than the society would be a much better place as both the female and male genders […]
- “Why We can’t Wait” by Martin Luther King (Jr) He was quick to emphasize confidently that the reason for writing the letter was not in response to criticism but to the injustice, which was persistent in Birmingham. The letter is a strong response in […]
- “The Quest for Peace and Justice” by Martin Luther King King states that poverty is one of the main problems for the global community, both in developing and economically developed countries.
- Analysis of the Kings Letter From Birmingham Jail From the biblical stand, the king was justified to move in the hope that his contributions would bring change in the destined world.
- Analyzing Martin Luther Speech “I Have a Dream” It is also imperative to note that Luther is addressing all Americans, both white and black, and hence the use of words “we” and “our”.
- The Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial of Honor The design of the memorial refers to the line about a stone of hope in Dr. The creative expression in the monument thoroughly captures the people’s perception of Dr.King.
- “Letter From Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr. King that supports his position is that protests began after multiple attempts by the representatives of the Black community to regulate disagreements peacefully and attract White authorities’ attention to the inappropriateness of segregation. Thus, the […]
- Elvis Presley and Martin Luther King’s Shared Dream The similarities between the song and the speech concern both the form and content of the test, with the key message being the desire for a better world in which everyone can exist in harmony […]
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s Legacy and Modern-Day Criticism King was linked to the development of the civil rights movement as it was considered to cause a lot of revolution in the country through the use of peaceful demonstrations, which succeeded in the attainment […]
- Martin Luther King’s and Alicia Garza’s Speeches A master of words, a preacher, and a fighter for the equality of people before God and the law, King speaks with hope for a better future for the world and the nation.
- Martin Luther King’s Leadership Approach Moreover, King was part of the change and provided a good example to the people making the crowd trust the idea of equality in the country.
- The Impact of Martin Luther King’s Death Luther King’s personality, his life, and his death caused more significant changes in expanding the rights of the African American people.
- The Speeches by Martin Luther King and Malcolm X I want to thank you for this interesting and properly built discussion about how justice and the law are combined in the speeches by Martin Luther King and Malcolm X. The indefatigable aggressiveness of the […]
- Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. Assassination The assassination of Martin Luther King Jr.dealt a blow to the ideology of nonviolence and love that underpinned King’s philosophy and which he sought to make basic ideas for the civil rights movement.
- Analysis of “I Have a Dream” Speech of Martin Luther King He could explain what was happening to the African Americans of that times and how its was affecting the lives of millions of people in the country.
- Martin Luther King Jr. as an Equality Activist At one time, Martin doubted which profession to give preference to medicine or law, everything was decided in favor of the ministry of the church, which influenced the education and literacy of the future leader.
- Martin Luther King Jr: American Civil Rights Leader This was an act of defiance against the laws which segregated the buses based on the color of the people.Dr. King led to the abolishment of the laws which were oppressive to the African-Americans.
- Martin Luther King’s Speech “I Have a Dream” In conclusion, it is necessary to note that King’s speech is still relevant as nowadays, African Americans, immigrants, and females do not have opportunities that they would have in the world of justice.
- John Kennedy, Martin Luther King, and Abraham Lincoln: Principles of Leadership In this regard, John Kennedy stated in general that, “We have the power to make this the best generation of mankind in the history of the world or make it the last”.
- Martin Luther King and His Trace in Chicago History The campaign targeted to improve the situation in the black neighborhoods and make stress the discrimination practices of realtors and housing officials of the city.
- Martin Luther King Jr.: A Great Pastor King’s life was a continuation of the commitment his family had made to advance the ministry and mission of the Christian church.
- The Martin Luther King Assassination Martin Luther King is often regarded as one of the most courageous leaders of the Civil Rights Movement in the history of the USA.
- Martin Luther King, Jr. and Malcolm X Under the leadership of Martin Luther King, whom the activists chose as their representative and leader, they protested the arrest with a bus boycott that put a strain on the town’s economy.
- Historical Figures: Martin Luther King Jr. In his speeches, he also addressed controversial and urgent topics like the war in Vietnam and poverty opposing the policies that instigated it.’Freedom’ the word that he often used had the central place in his […]
- Life of Martin Luther King and Modern Life Martin Luther King lived in the middle of the 20th century facing the problems of the American society of that time.
- Martin Luther King Junior, Great American Leader I have always been aware of the fact that if I were to succeed in my life and become a great person, then I would have to develop a solid personality and character.
- Kennedy’s and Martin Luther King’s Assassination in 1960’s The American history of assassinations in the 1960’s left an indelible mark in the minds of many people. Similar to the assassination of John F.
- “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King: What Has Changed The constitution was drafted by the framers in such a manner that only White men who owned acres of land and property would be given the right to voice their opinion and decide the functioning […]
- Martin Luther King Argument From Birmingham Jail King provides a clear background of the real reasons of his arrestment and his desire to grab attention of the Christian society of Birmingham’s clergymen in Alabama.Dr.
- A Short Biography of Martin Luther King, Jr The aim of the proposed study is to explore the factors between the occurrence of King’s principles in a world of racial discrimination and the impact of non-violence and civil disobedience in the world of […]
- Social Ethics. Letter from Martin Luther King Jr. The Letter that Martin Luther King wrote to eight ministers in Birmingham, Alabama, in 1963 was in response to their published appeal to their congregations to stop demonstrating against the unjust segregation laws that had […]
- Martin Luther King, Jr.: Leadership Analysis By studying the activity of prominent activists of the past and the key prerequisites to their success, it is possible to learn more about the art of leading others.
- Leadership Lessons From Martin Luther King Jr. Born in 1929, Luther King Jr.lived during World War I and in the post-war era of the United States, which was characterized by the severe oppression and segregation of African-Americans within the country. Lessons to […]
- Martin Luther King’s Public Speech In terms of strength and persuasive characteristics, the part of the speech, where King, makes an appeal to the Declaration of Independence is the most effective because he uses all three modes of appeal and […]
- Martin Luther King and Malcolm X: Who Is Closer to Success? Martin Luther King Jr.and Malcolm X are remembered for their outstanding fight for civil rights in the United States at a time when the black community faced oppression and inequality in different ways.
- Martin Luther King and His Impact on Society The ability of people to refuse to follow the regime is a major way how Martin Luther King accomplished change and respect towards the African American population.
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s Social and Political Philosophy C: “An unjust law is a code that is out of harmony with the moral law”. C: “An unjust law is a human law that is not rooted in eternal law and natural law”.
- Martin Luther King’s Psychological Portrait Martin Luther King is one of the most prominent figures in the history of the United States who had a profound impact on the development of the country.
- “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King: What We Already Achieved Martin Luther King is a figure of world significance whose famous speech influenced millions of people and led to significant reforms in the U.S. Yet, there are still certain areas in which the U.S.and would […]
- “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King The fact that the word segregation was used in the second half of the 20th century is astonishing. In 1963, the city of Birmingham was considered a fortress of segregation.
- The Speech “I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King It could be said that the primary goal of the paper is to examine the effectiveness of the speech while evaluating the impact on the audience, occasion, speaker, and the lines of the speech.
- The Civil Rights Movement: Martin King and Malcolm X’s Views King also stressed that the major concepts he adopted were taken from the “Sermon on the Mount and the Gandhian method of nonviolent resistance”.
- Dr. Martin Luther King’s Speech I Have a Dream For example, at the beginning of the speech where he began by lamenting on the precarious justice system in the United States that was tilted against the Negros, he figuratively used the terms “promissory note,” […]
- Martin Luther King’s Leadership in Historical Context The ideological commitment, articulation of the values, and the goals of the civil rights movements made King one of the leaders of all time.
- “Letter from a Birmingham Jail” by Luther King Throughout, however, he refers back to the notion of time, the moment, and in this, he is addressing the concept of Kairos.
- “I Have a Dream” Speech by Martin Luther King Jr Unlike previous presentations, the speech had an influence on the overall realization and implementation of statutory provisions that were critical to the sustenance of equality and justice in society.
- Martin Luther King Theory: Issue of Power The letter teaches people of faith that they should use peaceful means in demanding for their rights. In conclusion, them letter by Martin Luther advocated for the respect of human rights.
- Malcolm X and Martin Luther King Comparison In the entire history of the United States, Malcolm X and Martin Luther King were the greatest advocators of freedom and civil rights. He believed that the whites were not to be allowed to misbehave […]
- Martin Luther King Jr.’s Letter From Birmingham Jail He raises the stakes in his letter by pointing out “…the intent of our peaceful, active action is to generate a crisis-filled situation that will certainly necessitate commencement of negotiations”. King’s letter reveal a man […]
- Martin Luther King, Jr. Civil Rights Movement Martin Luther King noticed the negative trend and he took his stand to make people see the devastating effects of the war.
- Loury, Douglass, and King Jr. Loury addressed the challenge to liberals and conservatives that was in the spirit of Martin Luther King, Jr. Loury found it difficult to sell the idea of self help and reliance among the black because […]
- The Life and Work of Martin Luther King Jr. In this case, he can be boldly referred to as one of the best orators that the country has ever had. As a matter of fact, this march was done to demand for freedom and […]
- Martin Luther King Junior Other clauses repeated in the speech include; ‘Now is the time’ found in the sixth paragraph of the speech, where Martin was emphasizing that the time of freedom had come.’Let freedom ring’ is another clause […]
- Martin Luther King’s Last Speech He says that just like the biblical Jews who suffered in the wilderness, but their descendants finally reached the Promised Land, so will the descendants of the black people in the United States.
- Obtaining Objective Truth in Regards to Martin Luther King’s Role in the Fight for Equality in the United States Historians and Scholar’s View of Martin Luther King’s Role in the Fight for Equality in the United States Historians and scholars have made a lot of contributions to discovering the life of Martin Luther King […]
- Martin Luther King, Jr. He observed that the Whites had continually segregated and oppressed the Negroes despite the fact that, the latter had tried to emancipate themselves from the demeaning chains of racial prejudice and segregation that clouded the […]
- Why the Philosophy of King is More Effective in Fighting Racism than Malcolm’s? The idea of harmony and respect of all human beings is a result of his Christian foundation as well as the philosophy of Gandhi that he encountered later on in his life.
- Martin Luther King Jr. “I Have a Dream“ Martin Luther King is optimistic that African Americans will have basic rights including voting and other social rights in the future.
- Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. National Memorial Foundation The Memorial is located in the South West region of the National Mall. It is believed that Martin Luther King, Jr.influenced and continues to influence every visitor in the museum.
- Martin Luther King and The March on Washington To elaborate his point of view he refers to the Constitution which stated that people were equal in terms of their political rights, and shows how African-Americans were disfranchised by the government.
- Forgiveness in Martin Luther’s Movement for Rights Blacks The bible teachings tell us that God exists in the holy trinity and the only way to forgive others is for us to be able to forgive our own transgressions.
- The Fight for Equality in Martin Luther King’s Life and Writings The south was defeated and as such one of the effects of the war was to help reconstruct this region by putting in democratic laws.
- Changing the Unjust Laws: “Letter From Birmingham Jail” Therefore, the main aim of the letter was to push for the changing of the unjust laws as well as upholding the Supreme Court ruling of the year 1954.
- The Dangers of Dogmatism With Approaches Adopted by Martin Luther King Jr and Plato Moreover, King justified his pursuit of justice on the streets from the fact that the protests he organized were essentially peaceful and nonviolent; meaning that all he was trying to do was get his message […]
- Reliability of King’s arguments The major conclusion of the part of Martin Luther King’s speech touching upon the issue of Ho Chi Min’s land reform is that this reform was benevolent for the peasants, and can be categorized as […]
- The Black Arts Era: Contributions of Malcolm X & Martin Luther King Jr. The era was heralded by the establishment of the Black Arts Movement in Harlem in the decade of the 1960s. Many historians view this movement as the artistic arm of the Black Power movement, representing […]
- Motivation Evaluation: Martin Luther King Jr. This enables us to understand the humanistic and diversity views of motivation in King. A diversity view of motivation points out the fact that King was a realist and pragmatic in his approaches.
- Separate but Equal: “Letter From Birmingham Jail” by Martin Luther King Jr. In particular, it is necessary to analyze this work in terms of ethos, pathos, and logos and the way in which King balances these three appeals in order to convince the readers.
- Political Theories of Malcolm X and Martin Luther King, Jr. The struggle reached a climax in the mid 1960s, and in the midst of it all were two charismatic and articulate leaders, Martin Luther King, Jr.and Malcolm X.
- Martin Luther King’s “Letter From a Birmingham Jail” This letter from Birmingham Jail analysis essay shall highlight some of the issues discussed in the historic letter including King’s reason for being in Birmingham and why he felt compelled to break the law.
- “Why We Can’t Wait” a Historical Document by Martin Luther King Jr. Many of the exceptional leaders in the past have spent some time in detention centers due to their aspiration to transform the society.
- Was Martin Luther King Vital to the Gaining of Civil Rights for African Americans?
- Does Martin Luther King Junior’s Life Affect His Children’s Lives?
- Has Dr. Martin Luther King’s Dream Become Reality?
- How Did Gandhi Influence Martin Luther King?
- Why the Martin Luther King Jr. Holiday Should Be Repealed?
- How Did Martin Luther King Affect the Civil Rights Movement?
- How Did Religion Influence Martin Luther King?
- How Far Did Martin Luther King Further the Cause of Civil Rights?
- How Important Was Martin Luther King Compared to Malcolm X?
- How Martin Luther King Predicted the Decline of the Mainline Church?
- How Martin Luther King Would Have Viewed Comments about Hurricane Katrina?
- How Much Impact Did Martin Luther King Have in Black Rights?
- Why Does Martin Luther King Have a Public Holiday but Not Malcolm X?
- Why Martin Luther King Jr Is a Machiavellian Leader?
- Why Some Activists Rejected the Approach of Martin Luther King to Civil Rights?
- What Are the Three Important Facts about Martin Luther King?
- How Did Martin Luther King Change the World?
- What Are the Five Accomplishments of Martin Luther King Jr?
- How Racism Experience Shaped Martin Luther King?
- Do All States Recognize Martin Luther King Day?
- What Did Martin Luther King Speak Out Against?
- What Is the Main Purpose of Martin Luther King’s Speeches?
- For What Was Martin Luther King Imprisoned?
- Who Inspired Martin Luther King on Nonviolence Fight?
- How Martin Luther King’s Ideas Represented in “Conscience for Change”?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/martin-luther-king-essay-examples/
"128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/martin-luther-king-essay-examples/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/martin-luther-king-essay-examples/.
1. IvyPanda . "128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/martin-luther-king-essay-examples/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "128 Martin Luther King Topics & Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/martin-luther-king-essay-examples/.
- Nelson Mandela Topics
- Apartheid Essay Topics
- John F. Kennedy Questions
- Leadership Qualities Research Ideas
- Abraham Lincoln Topics
- Social Justice Essay Ideas
- Franklin Roosevelt Questions
- Barack Obama Topics
Martin Luther King Jr.: a Legacy of Achievements
This essay about Martin Luther King Jr.’s pivotal role in the American civil rights movement. It highlights his leadership in significant events such as the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the founding of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference, and the historic March on Washington. King’s advocacy led to key legislative victories, including the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. His legacy extends globally, inspiring movements for social justice and nonviolent resistance. Despite facing opposition and personal sacrifices, King’s unwavering commitment to equality continues to shape the fight against injustice today.
How it works
Martin Luther King Jr., a luminary whose utterances and endeavors echo across epochs, endures as one of the most consequential figures of the American civil rights crusade. Born on January 15, 1929, in Atlanta, Georgia, King etched an enduring impression on American society through his relentless activism, commanding rhetoric, and steadfast dedication to justice. His achievements facilitated the emergence of a fresh paradigm for the United States and the world, anchored in parity and nonviolent opposition.
One of King’s nascent triumphs was his leadership role in the Montgomery Bus Boycott of 1955-1956.
Provoked by the apprehension of Rosa Parks for declining to relinquish her bus seat to a Caucasian, the boycott signified a pivotal juncture in the civil rights tussle. King, then a youthful clergyman in Montgomery, Alabama, was tasked with leading the Montgomery Improvement Association and orchestrating the boycott. For over a year, the African American community in Montgomery eschewed public bus transportation, evincing remarkable resilience and solidarity. Their exertions culminated in a seminal Supreme Court decree that invalidated segregation on public buses, thereby solidifying King’s reputation as a dynamic leader.
King proceeded to co-establish the Southern Christian Leadership Conference (SCLC) in 1957, an entity dedicated to harnessing the potency of nonviolent dissent to effect societal metamorphosis. The SCLC emerged as a potent force in the civil rights campaign, amplifying King’s message of peaceful resistance and broadening the struggle for racial equality across the American South. Under King’s tutelage, the SCLC orchestrated marches, voter registration initiatives, and other manifestations of nonviolent protest, advocating for integration and rectitude.
One of King’s most conspicuous accomplishments was his role in orchestrating the historic 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Over 250,000 individuals congregated at the Lincoln Memorial to advocate for civil and economic rights for African Americans. It was during this march that King delivered his seminal “I Have a Dream” address, expounding a compelling vision of a future where individuals would “not be evaluated by the color of their skin but by the essence of their character.” This address galvanized support for the civil rights movement and left an enduring impression on the American psyche.
King’s advocacy also played a pivotal role in the enactment of seminal civil rights legislation. His leadership and activism facilitated the momentum requisite for the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which proscribed discrimination predicated on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. The Voting Rights Act of 1965, another epochal triumph, ensued shortly thereafter and sought to eradicate racial bias in voting, notably in the South.
Beyond these legal victories, King championed economic equity and dissented against the Vietnam War. He discerned the interwoven nature of racial and economic disparities and inaugurated the Poor People’s Campaign in 1968 to advocate for economic entitlements for all marginalized factions. This campaign, which aspired to establish a multiracial alliance of disadvantaged individuals, underscored the imperative to redress systemic impoverishment through governmental intervention.
King’s vision transcended geographical confines. In 1964, he attained the distinction of being the youngest recipient of the Nobel Peace Prize for his steadfast commitment to nonviolent resistance. His doctrine of nonviolent protest, influenced by the precepts of Mahatma Gandhi, emerged as a potent archetype for social movements globally. His legacy inspired activists combating apartheid in South Africa, advocating for civil rights in Northern Ireland, and beyond.
Despite encountering vehement opposition and personal sacrifices, King remained unwavering in his quest for equity and parity until his assassination on April 4, 1968. He bequeathed a legacy of achievements that persistently mold the contemporary struggle for civil rights. His endeavors propelled the cause of equity for African Americans and underscored the significance of nonviolent opposition in contesting injustice. King’s accomplishments endure as a testimonial to the transformative potency of fortitude and benevolence, reminding us that substantive metamorphosis can emanate from resolute conviction in a brighter world.
Cite this page
Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/
"Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/ [Accessed: 15 May. 2024]
"Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 15, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/
"Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/. [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Martin Luther King Jr.: A Legacy of Achievements . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/martin-luther-king-jr-a-legacy-of-achievements/ [Accessed: 15-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Celebrate the legacy of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. with the University Libraries

This year University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill honors the legacy of Martin Luther King Jr. with the theme “The Time is Now.” To coincide with this celebration, the University Libraries has gathered this list of books, films and other materials to help you learn about King’s impact and engage with his ideals.
E-books and Audiobooks
Throughout January, the University Libraries’ Honoring Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. OverDrive collection will highlight dozens of books on topics related to King’s legacy. From King’s own Where Do We Go from Here to John Lewis’s co-authored graphic novel March , you can engage with the history and impact of King’s work and the movement he helped lead.
Films
The Media & Design Center has created a list of films about King and his legacy, which can be accessed via streaming, DVD or VHS. (The center can also provide devices to play physical media). Films include Selma , Tony Brown’s essay on Martin Luther King Jr. and In Remembrance of Martin .
Selected Materials from the Wilson Special Collections Library
Collections in Wilson Library contain materials related to Martin Luther King Jr., including MLK buttons, a vintage church hand fan bearing King’s image and recordings of King’s speeches.
There are also some materials that you can access online. For example, have you ever wondered how the University reacted to news about the assassination of King? What happened at Carolina’s first MLK celebration in 1982? Blog posts from the University Archives take a look back at these moments in University history.
Wilson Library also holds recordings featuring Dr. King. For example, you can hear him in a 1963 mass meeting along with Ralph Abernathy in this recording from the Guy and Candie Carawan Collection . King discusses the historical significance of the civil rights movement in Birmingham, the importance of perseverance and unity, and jailing of children and other participants in the civil rights movement, among other topics.
The Carawan Collection also includes a press conference from the same year featuring King, Abernathy and Fred Shuttlesworth. The three address questions about the details of negotiations between leaders of the civil rights movement and business leaders and public officials, as well as specific developments in the civil rights movement in the preceding weeks. ( Part 1 ; Part 2 ; Part 3.)
This collection of resources was first published in January of 2023. It was updated in January 2024.
Chapter 1: Early Years
Main navigation.
Of course I was religious. I grew up in the church. My father is a preacher, my grandfather was a preacher, my great-grandfather was a preacher, my only brother is a preacher, my daddy's brother is a preacher. So I didn't have much choice.
- November 25, 1926 – Michael (later Martin) Luther King, Sr., marries Alberta Williams, daughter of A.D. Williams, pastor of Ebenezer Baptist Church
- January 15, 1929 – Michael (later Martin) Luther King, Jr., born at Williams/King family home at 501 Auburn Avenue in Atlanta
- March 21, 1931 – A. D. Williams dies and is succeeded as pastor of Ebenezer by King Sr.
- May 18, 1941 – King Jr.'s grandmother Jennie Celeste Williams dies and family moves to 193 Boulevard in Atlanta
I was born in the late twenties on the verge of the Great Depression, which was to spread its disastrous arms into every corner of this nation for over a decade. I was much too young to remember the beginning of this depression, but I do recall, when I was about five years of age, how I questioned my parents about the numerous people standing in breadlines. I can see the effects of this early childhood experience on my present anticapitalistic feelings.
My birthplace was Atlanta, Georgia, the capital of the state and the so-called "gateway to the South." Atlanta is home for me. I was born on Auburn Avenue. Our church, Ebenezer Baptist, is on Auburn Avenue. I'm now co-pastor of that church, and my office in the Southern Christian Leadership Conference is on Auburn Avenue.
I went through the public schools of Atlanta for a period, and then I went to what was then known as the Atlanta University Laboratory High School for two years. After that school closed, I went to Booker T. Washington High School.
The community in which I was born was quite ordinary in terms of social status. No one in our community had attained any great wealth. Most of the Negroes in my hometown who had attained wealth lived in a section of town known as "Hunter Hills." The community was characterized with a sort of unsophisticated simplicity. No one was in the extremely poor class. It is probably fair to class the people of this community as those of average income. It was a wholesome community, notwithstanding the fact that none of us were ever considered members of the "upper-upper class." Crime was at a minimum, and most of our neighbors were deeply religious.
From the very beginning I was an extraordinarily healthy child. It is said that at my birth the doctors pronounced me a one hundred percent perfect child, from a physical point of view. I hardly know how an ill moment feels. I guess the same thing would apply to my mental life. I have always been somewhat precocious, both physically and mentally. So it seems that from a hereditary point of view, nature was very kind to me.
My home situation was very congenial. I have a marvelous mother and father. I can hardly remember a time that they ever argued (my father happens to be the kind who just won't argue) or had any great falling out. These factors were highly significant in determining my religious attitudes. It is quite easy for me to think of a God of love mainly because I grew up in a family where love was central and where lovely relationships were ever present. It is quite easy for me to think of the universe as basically friendly mainly because of my uplifting hereditary and environmental circumstances. It is quite easy for me to lean more toward optimism than pessimism about human nature mainly because of my childhood experiences.
In my own life and in the life of a person who is seeking to be strong, you combine in your character antitheses strongly marked. You are both militant and moderate; you are both idealistic and realistic. And I think that my strong determination for justice comes from the very strong, dynamic personality of my father, and I would hope that the gentle aspect comes from a mother who is very gentle and sweet.
Mother Dear
My mother, Alberta Williams King, has been behind the scene setting forth those motherly cares, the lack of which leaves a missing link in life. She is a very devout person with a deep commitment to the Christian faith. Unlike my father, she is soft-spoken and easygoing. Although possessed of a rather recessive personality, she is warm and easily approachable.
The daughter of A. D. Williams, a successful minister, Alberta Williams grew up in comparative comfort. She was sent to the best available schools and college and was, in general, protected from the worst blights of discrimination. An only child, she was provided with all of the conveniences that any high school and college student could expect. In spite of her relatively comfortable circumstances, my mother never complacently adjusted herself to the system of segregation. She instilled a sense of self-respect in all of her children from the very beginning.
My mother confronted the age-old problem of the Negro parent in America: how to explain discrimination and segregation to a small child. She taught me that I should feel a sense of "somebodiness" but that on the other hand I had to go out and face a system that stared me in the face every day saying you are "less than," you are "not equal to." She told me about slavery and how it ended with the Civil War. She tried to explain the divided system of the South—the segregated schools, restaurants, theaters, housing; the white and colored signs on drinking fountains, waiting rooms, lavatories—as a social condition rather than a natural order. She made it clear that she opposed this system and that I must never allow it to make me feel inferior. Then she said the words that almost every Negro hears before he can yet understand the injustice that makes them necessary: "You are as good as anyone." At this time Mother had no idea that the little boy in her arms would years later be involved in a struggle against the system she was speaking of.
Martin Luther King, Sr., is as strong in his will as he is in his body. He has a dynamic personality, and his very physical presence (weighing about 220 pounds) commands attention. He has always been a very strong and self-confident person. I have rarely ever met a person more fearless and courageous than my father, notwithstanding the fact that he feared for me. He never feared the autocratic and brutal person in the white community. If they said something to him that was insulting, he made it clear in no uncertain terms that he didn't like it.
A sharecropper's son, he had met brutalities at firsthand, and had begun to strike back at an early age. His family lived in a little town named Stockbridge, Georgia, about eighteen miles from Atlanta. One day, while working on the plantation, he keenly observed that the boss was cheating his father out of some hard-earned money. He revealed this to his father right in the presence of the plantation owner. When his happened the boss angrily and furiously shouted, "Jim, if you don't keep this nigger boy of yours in his place, I am going to slap him down." Grandfather, being almost totally dependent on the boss for economic security, urged Dad to keep quiet.
My dad, looking back over that experience, says that at that moment he became determined to leave the farm. He often says humorously, "I ain't going to plough a mule anymore." After a few months he left Stockbridge and went to Atlanta determined to get an education. Although he was then eighteen—a year older than most persons finishing high school—he started out getting a high school education and did not stop until he had finished Atlanta's Morehouse College.
The thing that I admire most about my dad is his genuine Christian character. He is a man of real integrity, deeply committed to moral and ethical principles. He is conscientious in all of his undertakings. Even the person who disagrees with his frankness has to admit that his motives and actions are sincere. He never hesitates to tell the truth and speak his mind, however cutting it may be. This quality of frankness has often caused people to actually fear him. I have had young and old alike say to me, "I'm scared to death of your dad." Indeed, he is stern at many points.
My father has always had quite an interest in civil rights. He has been president of the NAACP in Atlanta, and he always stood out in social reform. From before I was born, he had refused to ride the city buses after witnessing a brutal attack on a load of Negro passengers. He led the fight in Atlanta to equalize teachers' salaries and was instrumental in the elimination of Jim Crow elevators in the courthouse.
As pastor of the Ebenezer Baptist Church, my father wielded great influence in the Negro community and perhaps won the grudging respect of the whites. At any rate, they never attacked him physically, a fact that filled my brother and sister and me with wonder as we grew up in this tension-packed atmosphere. With this heritage, it is not surprising that I also learned to abhor segregation, considering it both rationally inexplicable and morally unjustifiable.
I have never experienced the feeling of not having the basic necessities of life. These things were always provided by a father who always put his family first. My father never made more than an ordinary salary, but the secret was that he knew the art of saving and budgeting. He has always had sense enough not to live beyond his means. So for this reason he was able to provide us with the basic necessities of life with little strain. I went right on through school and never had to drop out to work or anything.
The first twenty-five years of my life were very comfortable years. If I had a problem I could always call Daddy. Things were solved. Life had been wrapped up for me in a Christmas package. This is not to say that I was born with a silver spoon in my mouth; far from it. I always had a desire to work, and I would spend my summers working.
Doubts spring forth unrelentingly
I joined the church at the age of five. I well remember how this event occurred. Our church was in the midst of the spring revival, and a guest evangelist had come down from Virginia. On Sunday morning the evangelist came into our Sunday school to talk to us about salvation, and after a short talk on this point he extended an invitation to any of us who wanted to join the church. My sister was the first one to join the church that morning, and after seeing her join I decided that I would not let her get ahead of me, so I was the next. I had never given this matter a thought, and even at the time of my baptism I was unaware of what was taking place. From this it seems quite clear that I joined the church not out of any dynamic conviction, but out of a childhood desire to keep up with my sister.
The church has always been a second home for me. As far back as I can remember I was in church every Sunday. My best friends were in Sunday school, and it was the Sunday school that helped me to build the capacity for getting along with people. I guess this was inevitable since my father was the pastor of my church, but I never regretted going to church until I passed through a state of skepticism in my second year of college.
The lessons which I was taught in Sunday school were quite in the fundamentalist line. None of my teachers ever doubted the infallibility of the Scriptures. Most of them were unlettered and had never heard of biblical criticism. Naturally, I accepted the teachings as they were being given to me. I never felt any need to doubt them—at least at that time I didn't. I guess I accepted biblical studies uncritically until I was about twelve years old. But this uncritical attitude could not last long, for it was contrary to the very nature of my being. I had always been the questioning and precocious type. At the age of thirteen, I shocked my Sunday school class by denying the bodily resurrection of Jesus. Doubts began to spring forth unrelentingly.
How could I love a race of people who hated me?
Two incidents happened in my late childhood and early adolescence that had a tremendous effect on my development. The first was the death of my grandmother. She was very dear to each of us, but especially to me. I sometimes think I was her favorite grandchild. I was particularly hurt by her death mainly because of the extreme love I had for her. She assisted greatly in raising all of us. It was after this incident that for the first time I talked at any length on the doctrine of immortality. My parents attempted to explain it to me, and I was assured that somehow my grandmother still lived. I guess this is why today I am such a strong believer in personal immortality.
The second incident happened when I was about six years of age. From the age of three I had a white playmate who was about my age. We always felt free to play our childhood games together. He did not live in our community, but he was usually around every day; his father owned a store across the street from our home. At the age of six we both entered school—separate schools, of course. I remember how our friendship began to break as soon as we entered school; this was not my desire but his. The climax came when he told me one day that his father had demanded that he would play with me no more. I never will forget what a great shock this was to me. I immediately asked my parents about the motive behind such a statement.
We were at the dinner table when the situation was discussed, and here for the first time I was made aware of the existence of a race problem. I had never been conscious of it before. As my parents discussed some of the tragedies that had resulted from this problem and some of the insults they themselves had confronted on account of it, I was greatly shocked, and from that moment on I was determined to hate every white person. As I grew older and older this feeling continued to grow.
My parents would always tell me that I should not hate the white man, but that it was my duty as a Christian to love him. The question arose in my mind: How could I love a race of people who hated me and who had been responsible for breaking me up with one of my best childhood friends? This was a great question in my mind for a number of years.
I always had a resentment towards the system of segregation and felt that it was a grave injustice. I remember a trip to a downtown shoe store with Father when I was still small. We had sat down in the first empty seats at the front of the store. A young white clerk came up and murmured politely:
"I'll be happy to wait on you if you'll just move to those seats in the rear."
Dad immediately retorted, "There's nothing wrong with these seats. We're quite comfortable here."
"Sorry," said the clerk, "but you'll have to move."
"We'll either buy shoes sitting here," my father retorted, "or we won't buy shoes at all."
Whereupon he took me by the hand and walked out of the store. This was the first time I had seen Dad so furious. That experience revealed to me at a very early age that my father had not adjusted to the system, and he played a great part in shaping my conscience. I still remember walking down the street beside him as he muttered, "I don't care how long I have to live with this system, I will never accept it."
And he never has. I remember riding with him another day when he accidentally drove past a stop sign. A policeman pulled up to the car and said:
"All right, boy, pull over and let me see your license."
My father instantly retorted: "Let me make it clear to you that you aren't talking to a boy. If you persist in referring to me as boy, I will be forced to act as if I don't hear a word you are saying."
The policeman was so shocked in hearing a Negro talk to him so forthrightly that he didn't quite know how to respond. He nervously wrote the ticket and left the scene as quickly as possible.
The angriest I have ever been
There was a pretty strict system of segregation in Atlanta. For a long, long time I could not go swimming, until there was a Negro YMCA. A Negro child in Atlanta could not go to any public park. I could not go to the so-called white schools. In many of the stores downtown, I couldn't go to a lunch counter to buy a hamburger or a cup of coffee. I could not attend any of the theaters. There were one or two Negro theaters, but they didn't get any of the main pictures. If they did get them, they got them two or three years later.
When I was about eight years old, I was in one of the downtown stores of Atlanta and all of a sudden someone slapped me, and the only thing I heard was somebody saying, "You are that nigger that stepped on my foot." And it turned out to be a white lady. Of course I didn't retaliate at any point; I wouldn't dare retaliate when a white person was involved. I think some of it was part of my native structure—that is, that I have never been one to hit back. I finally told my mother what had happened, and she was very upset about it. But the lady who slapped me had gone, and my mother and I left the store almost immediately.
I remember another experience I used to have in Atlanta. I went to high school on the other side of town—to the Booker T. Washington High School. I had to get the bus in what was known as the Fourth Ward and ride over to the West Side. In those days, rigid patterns of segregation existed on the buses, so that Negroes had to sit in the backs of buses. Whites were seated in the front, and often if whites didn't get on the buses, those seats were still reserved for whites only, so Negroes had to stand over empty seats. I would end up having to go to the back of that bus with my body, but every time I got on that bus I left my mind up on the front seat. And I said to myself, "One of these days, I'm going to put my body up there where my mind is."
When I was fourteen, I traveled from Atlanta to Dublin, Georgia, with a dear teacher of mine, Mrs. Bradley. I participated in an oratorical contest there and I succeeded in winning the contest.
My subject, ironically enough, was "The Negro and the Constitution."
We cannot have an enlightened democracy with one great group living in ignorance. We cannot have a healthy nation with one-tenth of the people ill-nourished, sick, harboring germs of disease which recognize no color lines—obey no Jim Crow laws. We cannot have a nation orderly and sound with one group so ground down and thwarted that it is almost forced into unsocial attitudes and crime. We cannot be truly Christian people so long as we flout the central teachings of Jesus: brotherly love and the Golden Rule. We cannot come to full prosperity with one great group so ill-delayed that it cannot buy goods. So as we gird ourselves to defend democracy from foreign attack, let us see to it that increasingly at home we give fair play and free opportunity for all people.
Today thirteen million black sons and daughters of our forefathers continue the fight for the translation of the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth Amendments from writing on the printed page to an actuality. We believe with them that "if freedom is good for any it is good for all," that we may conquer Southern armies by the sword, but it is another thing to conquer Southern hate, that if the franchise is given to Negroes, they will be vigilant and defend, even with their arms, the ark of federal liberty from treason and destruction by her enemies.
That night, Mrs. Bradley and I were on a bus returning to Atlanta. Along the way, some white passengers boarded the bus, and the white driver ordered us to get up and give the whites our seats. We didn't move quickly enough to suit him, so he began cursing us. I intended to stay right in that seat, but Mrs. Bradley urged me up, saying we had to obey the law. We stood up in the aisle for ninety miles to Atlanta. That night will never leave my memory. It was the angriest I have ever been in my life.
I had grown up abhorring not only segregation but also the oppressive and barbarous acts that grew out of it. I had seen police brutality with my own eyes, and watched Negroes receive the most tragic injustice in the courts. I can remember the organization known as the Ku Klux Klan. It stands on white supremacy, and it was an organization that in those days even used violent methods to preserve segregation and to keep the Negro in his place, so to speak. I remember seeing the Klan actually beat a Negro. I had passed spots where Negroes had been savagely lynched. All of these things did something to my growing personality.
I had also learned that the inseparable twin of racial injustice was economic injustice. Although I came from a home of economic security and relative comfort, I could never get out of my mind the economic insecurity of many of my playmates and the tragic poverty of those living around me. During my late teens I worked two summers (against my father's wishes—he never wanted my brother and me to work around white people because of the oppressive conditions) in a plant that hired both Negroes and whites. Here I saw economic injustice firsthand, and realized that the poor white was exploited just as much as the Negro. Through these early experiences I grew up deeply conscious of the varieties of injustice in our society.
As if the curtain had been dropped on my selfhood
Just before going to college I went to Simsbury, Connecticut, and worked for a whole summer on a tobacco farm to earn a little school money to supplement what my parents were doing. One Sunday, we went to church in Simsbury, and we were the only Negroes there. On Sunday mornings I was the religious leader and spoke on any text I wanted to 107 boys. I had never thought that a person of my race could eat anywhere, but we ate in one of the finest restaurants in Hartford.
After that summer in Connecticut, it was a bitter feeling going back to segregation. It was hard to understand why I could ride wherever I pleased on the train from New York to Washington and then had to change to a Jim Crow car at the nation's capital in order to continue the trip to Atlanta. The first time that I was seated behind a curtain in a dining car, I felt as if the curtain had been dropped on my selfhood. I could never adjust to the separate waiting rooms, separate eating places, separate rest rooms, partly because the separate was always unequal, and partly because the very idea of separation did something to my sense of dignity and self-respect.
NEXT Chapter 2: Morehouse College

Dreams and Declarations: Five Powerful Quotes from Dr. Martin Luther King Jr.
F rom the middle of the 1950s until his passing in 1968, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., a Baptist clergyman and civil rights activist, played a significant role in the American civil rights movement. Atlanta, Georgia, was the place of his birth on January 15, 1929. Because of his Christian views, he is well-recognized for using nonviolent civil disobedience to advance civil rights. His lectures and sermons are still studied and appreciated today since he is considered one of America's best orators.
One of King's most famous speeches, the "I Have a Dream" speech, was delivered on August 28, 1963, during the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. In the speech, he called for an end to racism in the United States and for civil and economic rights for African Americans . The speech was a defining moment of the civil rights movement and is considered to be one of the greatest speeches in American history.
After King's assassination in 1968, a campaign was launched to make his birthday, January 15, a national holiday . Civil rights organizations, labor unions, and religious groups led the campaign. However, the campaign faced significant opposition, with many lawmakers arguing that King's holiday would be too costly and that he did not deserve the honor. Despite this opposition, the campaign continued, and on November 2, 1983, President Ronald Reagan signed a bill making Martin Luther King Jr. Day a federal holiday, which was first observed on January 20, 1986.
The holiday is now celebrated across the United States and is seen as a day to honor the legacy of Martin Luther King Jr. and his fight for civil rights. Many people take the day to reflect on his teachings and to volunteer in their communities in honor of his service and dedication to social justice. It is a day to remember the sacrifices he made for the rights and freedom of African Americans and to honor his legacy by continuing the fight for equality and civil rights for all people.
Martin Luther King Jr. was an incredible leader and an influential figure in American history. His sermons and speeches inspire people to this day, and his birthday, January 15, has become a national holiday to commemorate his life and legacy. His teachings and nonviolent approach to civil rights have impacted American society and the world. His birthday serves as a reminder of the ongoing struggle for civil rights and equality and the importance of continuing to work toward a just and equitable society. Below are five impactful quotes from Martin Luther King Jr.
- "We will have to repent in this generation not merely for the hateful words and actions of the bad people but for the appalling silence of the good people."
- "The ultimate measure of a man is not where he stands in moments of comfort and convenience, but where he stands at times of challenge and controversy."
- "A nation that continues year after year to spend more money on military defense than on programs of social uplift is approaching spiritual death."
- "The function of education is to teach one to think intensively and to think critically. Intelligence plus character - that is the goal of true education."
- "I submit to you that if a man hasn't discovered something that he will die for, he isn't fit to live."
More from My Money Chronicles
Little Known Black History Facts
Greek Picnics Across America

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Trump Knows Dominance Wins. Someone Tell Democrats.

By M. Steven Fish
Mr. Fish is the author of “Comeback: Routing Trumpism, Reclaiming the Nation, and Restoring Democracy’s Edge.”
Donald Trump once called Bill Barr, his former attorney general, “Weak, Slow Moving, Lethargic, Gutless, and Lazy.” When Mr. Barr recently endorsed Mr. Trump, rather than express gratitude or graciousness, the former president said , “Based on the fact that I greatly appreciate his wholehearted Endorsement, I am removing the word ‘Lethargic’ from my statement. Thank you Bill. MAGA2024!”
This is the sort of thing Mr. Trump is known for, even with people who came around and bent the knee . It is a critical part of his politics — and it’s an area that pollsters aren’t fully measuring and Democratic strategists rarely take into consideration.
Politics is a dominance competition, and Mr. Trump is an avid and ruthless practitioner of it . He offers a striking contrast with most Democrats, who are more likely to fret over focus-group data and issue ever more solemn pledges to control prescription drug prices .
What these Democrats seem to have forgotten is that they have their own liberal tradition of dominance politics — and if they embrace it, they would improve their chances of defeating Trumpism. But unlike Mr. Trump, whose lies and conduct after the 2020 election were damaging to democracy, leaders like Franklin Roosevelt, John F. Kennedy, Lyndon Johnson and the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. exerted dominance in liberal ways and to prodemocratic ends. They obeyed the law, told the truth, and honored liberal values.
Psychologists have noted the effectiveness of dominance in elections and governing . My recent research also finds that what I call Mr. Trump’s “high-dominance strategy” is far and away his most formidable asset.
High-dominance leaders shape reality. They embrace conflict, chafe at playing defense and exhibit self-assurance even in pursuit of unpopular goals . By contrast, low-dominance leaders accept reality as it is and shun conflict. They tell people what they think they want to hear and prefer mollification to confrontation.
Today’s Republicans are all about dominance. They embrace us-versus-them framing, double down on controversial statements and take risks . Today’s Democrats often recoil from “othering” opponents and back down after ruffling feathers . They have grown obsessively risk-averse , poll-driven , allergic to engaging on hot-button issues (except perhaps abortion) — and more than a little boring.
Polling even dictates whether Democrats proclaim their own good news. Republicans never quit crowing about the economy on their watch. Democrats tend to fear doing so unless surveys show that everyone is already feeling the benefits. So in defiance of much of the evidence , voters think Mr. Trump’s economy was better than Barack Obama’s and Mr. Biden’s.
Politicians’ language reflects their dominance orientations. Mr. Trump uses entertaining and provocative parlance and calls opponents — and even allies — weak , gutless and pathetic . Still, neuroscientists monitoring listeners’ brain activity while they watched televised debates found that audiences — not just Mr. Trump’s followers — delighted in the belittling nicknames he uses for his opponents. His boldness and provocations held audience attention at a much higher level than his opponents’ play-it-safe recitations of their policy stances and résumés.
Mr. Trump is also often crude and regularly injects falsehoods into his comments. But these are not in and of themselves signs of dominance; it’s just that the Democrats’ inability to effectively respond makes them appear weak by comparison.
For their own part, Democrats typically refrain from transgressive language and often present themselves as vulnerable and menaced . When Kamala Harris was asked in January if she was scared of a second Trump term, she said , “I am scared as heck!” and added that “we should all be scared.”
To voters, that fear smells like weakness. In a 2022 CBS News survey on parties’ traits, the most frequently cited description of the Democratic Party was “weak.” In a recent Gallup poll , 38 percent regarded Mr. Biden as “a strong and decisive leader,” compared with 57 percent for Mr. Trump.
A reputation for weakness may be a singularly damaging liability. In a 2016 exit poll , more than twice as many voters said they wanted a “strong leader” than one who “shares my values” or “cares about people like me.” In another poll, Mr. Trump was regarded as the “ stronger leader .”
The American National Elections Studies has polled voters on presidential candidates’ traits since the 1980s, and the candidate who rated higher on “strong leadership” has never lost. The one who more people agree “really cares about people like you” loses about half the time.
High-dominance messaging necessitates unfailingly asserting your side’s moral superiority. But the psychologists John Jost and Orsolya Hunyady find that liberals feel compelled to give equal credence to conservative intuitions. They struggle to adopt the us-versus-them framing that is crucial to rousing supporters and confronting opponents who decidedly do not honor the legitimacy of liberals’ opinions — or even necessarily the results of free elections. Psychologists have also shown that Democrats are conflicted about the appropriate use of aggression.
Such crippling qualms are recent problems. Roosevelt, Kennedy, Johnson and King owned the Republicans. Their high-dominance styles enabled the creation of every progressive program their low-dominance successors are struggling to salvage today.
On the eve of his first re-election, Roosevelt thundered : “I should like to have it said of my first administration that in it the forces of selfishness and of lust for power met their match. I should like to have it said of my second administration that in it these forces met their master.” Kennedy hammered home that the Republicans’ limp social welfare policies and tepid approach to civil rights failed to show the world what America was made of , and he never hesitated to aggressively trumpet triumphs .
Johnson mixed bigot-busting rhetoric with ferocious arm-twisting to muscle voting rights , colorblind immigration policy and Medicare into law. He did enjoy Democratic congressional majorities, but he also faced the necessity of bringing around the segregationist wing of his party, and his high-dominance style was key to his legislative victories.
Few were less solicitous of prevailing opinion than King. With reference to the 1964 Republican presidential nominee, Barry Goldwater, King said that he could “go halfway with Brother Goldwater” on the idea that legislation couldn’t solve racism. With tongue planted firmly in cheek, he then smoothly eviscerated Goldwater’s stance: “It may be true that the law can’t make a man love me, but it can restrain him from lynching me.” King’s reference to “Brother Goldwater,” who opposed all manner of civil rights legislation, bore no hint of sarcasm. But he also knew that he was owning his opponent by wielding what he always called “the weapon of love” and using language that expressed self-assurance and faith in the nation to establish moral superiority.
There are contemporary Democrats with a high-dominance style. Gov. Andy Beshear of Kentucky stands up for trans and abortion rights , proclaimed June Pride Month in the state, and chided the unvaccinated during the pandemic. When a Republican lawmaker displayed a photo of Mr. Beshear with drag queens at a gay rights rally and accused him of corrupting kids, the governor shot back that the participants “are as much Kentuckians as anybody else.”
The Republican tucked his tail between his legs, whimpering: “My problem is not with the gay movement. I didn’t say anything about the ‘Pride Celebration.’” Mr. Beshear won re-election by five points in a state Mr. Trump carried by 26 points in 2020.
Mr. Biden’s Republican-owning 2024 State of the Union address and the briny language he uses to describe Mr. Trump in private delighted the Democrats — and won rare kudos from Republican strategists. But these are just flashes of dominance — and flashes aren’t nearly enough.
A dominance advantage is no guarantee of victory, as Mr. Trump’s 2020 loss to Mr. Biden showed. What’s more, Mr. Trump may sometimes pay a price for his extreme dominance style, whether it’s by turning off some voters or incurring the wrath of impatient judges in his seemingly endless court cases.
Still, Mr. Trump’s high-dominance style remains the most formidable tool in his arsenal. Taking on Mr. Trump’s party in its area of greatest strength would leave it beatable in national elections.
Mr. Biden could even counter the perception that his age has rendered him feeble by taking a page from his higher-dominance predecessors, the mighty leaders who mobilized dominance to promote freedom, equality and progress.
M. Steven Fish, a political scientist at the University of California, Berkeley, is the author of “Comeback: Routing Trumpism, Reclaiming the Nation, and Restoring Democracy’s Edge.”
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Martin Luther King, Jr. (born January 15, 1929, Atlanta, Georgia, U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tennessee) was a Baptist minister and social activist who led the civil rights movement in the United States from the mid-1950s until his death by assassination in 1968. His leadership was fundamental to that movement's success in ending the ...
Stephen F. Somerstein/Getty Images. Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his ...
500+ Words Essay on Martin Luter King. Martin Luther King Jr. was an African-American leader in the U.S. He lost his life while performing a peaceful protest for the betterment of blacks in America. His real name was Michael King Jr. He completed his studies and attained a Ph.D.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 - April 4, 1968) was an American Christian minister, activist, and political philosopher who was one of the most prominent leaders in the civil rights movement from 1955 until his assassination in 1968. A black church leader and a son of early civil rights activist and minister Martin Luther King Sr., King advanced civil rights ...
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr., made history, but he was also transformed by his deep family roots in the African-American Baptist church, his formative experiences in his hometown of Atlanta, his theological studies, his varied models of religious and political leadership, and his extensive network of contacts in the peace and social ...
Martin Luther King, Jr. - Political and Social Views Martin Luther King, Jr. - Travels ... 4:473-481). A revised version of King's essay was later reprinted in a collected volume edited by Fey (How My Mind Has Changed [Cleveland: Meridian Books, 1961], pp. 105-115). 2. In notes that King may have written in preparation for this article, he ...
To Shape a New World is a milestone in the study of Martin Luther King, Jr., essentially a sanctified figure in American life, whose actual ideas are rarely interrogated in any depth, either in the public realm or in academic circles. What makes this volume particularly striking is the exceptionally high quality of the essays, which are analytically rigorous, impressively researched, and often ...
Martin Luther King Jr. was a social activist and Baptist minister who played a key role in the American civil rights movement from the mid-1950s until his assassination in 1968. Explore his life ...
Explore the first volume of the papers of Martin Luther King, Jr., covering his early life and education, his call to serve as a pastor, and his involvement in the civil rights movement. Learn about his personal and professional achievements, his challenges and struggles, and his vision for a more just and peaceful world.
This year's Martin Luther King Jr. Day, on January 15, coincides with the late civil rights leader 's birthday. Had he lived, King would be turning 95 years old. Days after his 1968 ...
Martin Luther King, Jr., (born Jan. 15, 1929, Atlanta, Ga., U.S.—died April 4, 1968, Memphis, Tenn.), U.S. civil rights leader. The son and grandson of Baptist preachers, King became an adherent of nonviolence while in college. Ordained a Baptist minister himself in 1954, he became pastor of a church in Montgomery, Ala.; the following year he received a doctorate from Boston University.
During the less than 13 years of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.'s leadership of the modern American Civil Rights Movement, from December 1955 until April 4, 1968, African Americans achieved more genuine progress toward racial equality in America than the previous 350 years had produced. Dr. King is widely regarded as America's pre-eminent advocate of nonviolence and one of the greatest ...
Introduction. Martin Luther King, Jr. 1929-1968. American orator and essayist. The following entry provides an overview of King's career. King was the leader of the civil rights movement in the ...
I Have a Dream: Essay Introduction. One of the finest explanations of American's dream is the powerful speech of Martin Luther King, Jr. He delivered the speech at the Lincoln Memorial on August 28, 1963, in Washington D.C. The speech is mainly centered on racial equality and stoppage of discrimination. We will write a custom essay on your topic.
Martin Luther King, Jr., may be America's most revered politicalfigure, commemorated in statues, celebrations, and street namesaround the world. On the fif...
January 25, 1967: Letter from Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. nominating Thich Nhat Hanh for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1967. April 4, 1967: Beyond Vietnam. Audio. April 9, 1967: The Three Dimensions of a Complete Life. Audio. April 14, 1967: The Other America. Video. August 27, 1967: Why Jesus Called a Man a Fool. Audio.
Martin Luther King Jr: American Civil Rights Leader. This was an act of defiance against the laws which segregated the buses based on the color of the people.Dr. King led to the abolishment of the laws which were oppressive to the African-Americans. Martin Luther King's Speech "I Have a Dream".
Genre: Essay. Topic: Martin Luther King, Jr. - Education. Details. In the following three essays, King wrestles with the role of religion in modern society. In the first assignment, he calls science and religion "different though converging truths" that both "spring from the same seeds of vital human needs." King emphasizes an awareness ...
Essays and criticism on Martin Luther King Jr. - Criticism. An objective assessment of Martin Luther King, Jr.: If the world is at all capable of candor, if the need by blacks and whites to ...
This essay about Martin Luther King Jr.'s pivotal role in the American civil rights movement. It highlights his leadership in significant events such as the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the founding of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference, and the historic March on Washington. King's advocacy led to key legislative victories, including ...
Martin Luther King Jr Essay: Martin Luther King Junior, born as Michael King Jr was an American activist who became one of the most famous American spokespersons of all time. He was an advocate of civil rights through non-violence and civil disobedience. He was mostly influenced by the Indian freedom fighter Mahatma Gandhi who is known to be the flag-bearer of "Ahimsa" or "Non-violence ...
The Media & Design Center has created a list of films about King and his legacy, which can be accessed via streaming, DVD or VHS. (The center can also provide devices to play physical media). Films include Selma, Tony Brown's essay on Martin Luther King Jr. and In Remembrance of Martin. Selected Materials from the Wilson Special Collections ...
January 15, 1929 - Michael (later Martin) Luther King, Jr., born at Williams/King family home at 501 Auburn Avenue in Atlanta. March 21, 1931 - A. D. Williams dies and is succeeded as pastor of Ebenezer by King Sr. May 18, 1941 - King Jr.'s grandmother Jennie Celeste Williams dies and family moves to 193 Boulevard in Atlanta.
F rom the middle of the 1950s until his passing in 1968, Dr. Martin Luther King Jr., a Baptist clergyman and civil rights activist, played a significant role in the American civil rights movement ...
Guest Essay. Trump Knows Dominance Wins. Someone Tell Democrats. May 6, 2024. ... Lyndon Johnson and the Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. exerted dominance in liberal ways and to prodemocratic ends ...
Martin Luther King, Jr. wrote, "Education must enable one to sift and weigh evidence, to discern the true from the false, the real from the unreal, and the facts from the fiction."