- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription

Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – Light
Chapter 16 of Class 8 Science is about Light. The chapter Light starts with the concepts and meaning of light and the laws of reflection. Students might have already heard the word reflection in the previous chapter. In this unit, students learn what reflection is and what laws are associated with it. This chapter will answer the most common questions in students’ minds, like how can a visually impaired person read. How can an owl see only at night but not during daylight? What is the braille system? And other such questions. In this chapter, you will also study the human eye and the construction of the human eye. Students will also learn fun experiments for explaining reflections, such as how to build a kaleidoscope. By completing this chapter, students will be capable of understanding many interesting concepts
Quick Links
Extramarks is an online learning platform providing educational resources to lakhs of students. One of the important features of our study material is that we provide a lot of questions and solutions. Students can master any subject or topic with the practice of relevant questions. Students can refer to our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 to gain a better understanding of the concepts covered in Chapter ‘Light’. The Important Questions: Class 8 Science Chapter 16 will boost students’ confidence and preparation for the exam. The question bank covers all varieties of questions that are helpful for the students to understand the concepts in the best way.
Our in-house experienced Science faculty members prepare our question bank Chapter 16 Class 8 Science Important Questions and all of its solutions. The questions are taken from different authentic sources such as the NCERT textbook, past year’s question papers, and NCERT exemplar books. It includes MCQ types of questions, and short and long-answer questions based on the CBSE exam pattern. Students are advised to register on the Extramarks website and access unlimited and extended study materials on the desired topics.
Get Access to CBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions 2022-23 with Chapter-Wise Solutions
You can also find CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-by-Chapter Important Questions here:
| 1 | Chapter 1 | |
| 2 | Chapter 2 | |
| 3 | Chapter 3 | |
| 4 | Chapter 4 | |
| 5 | Chapter 5 | |
| 6 | Chapter 6 | |
| 7 | Chapter 7 | |
| 8 | Chapter 8 | |
| 9 | Chapter 9 | |
| 10 | Chapter 10 | |
| 11 | Chapter 11 | |
| 12 | Chapter 12 | |
| 13 | Chapter 13 | |
| 14 | Chapter 14 | |
| 15 | Chapter 15 | |
| 16 | Chapter 16 | Light |
| 17 | Chapter 17 | |
| 18 | Chapter 18 | |
Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – With Solutions
Considering that our team has collated questions from different sources in one place, our question bank of Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Important Questions has proven helpful for a lot of students. Our Science expert faculty members have prepared detailed and step-by-step instruction-based answers for each of the questions covered in our question bank. Students will be able to fully revise the chapter while they are solving questions.
Below are a few questions and their solutions from our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16.
Question 1. Image formed in a plane mirror undergoes _______________.
Answer 1. lateral inversion.
The reversal of a mirror image, where the object’s right side appears on the left side behind the mirror, is known as lateral inversion.
Question 2. Name the part of the eye that gives a distinctive colour.
Answer 2. Iris is the part of our eye that gives us distinctive colour. The iris is a coloured ring that surrounds our pupils and gives our eyes their distinct colour.
Question 3. The lens that focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called___________.
Answer 3. Retina.
Several thousand light-sensitive cells (rods and cones) and some other nerve cells make up the retina, which receives and organises visual data. Through our optic nerve, retina sends this information to brain, allowing us to see.
Question 4. What is a blind spot?
Answer 4. There are no sensory cells at the optic nerve and the retina intersection. Hence, vision is not possible there. This is known as the blind spot.
Question 5. ____________ are sensitive to bright light in eye.
Answer 5. Cones.
In the retina, cones are a kind of photoreceptor cell. They are responsible for our colour perception. Cones are concentrated in the macula, located in the centre of our retina and help us see small details.
Question 6. Lack of which nutrient element is responsible for eye troubles?
Answer 6. The deficiency of Vitamin A causes eye troubles. Xerophthalmia is a progressive eye problem caused by a lack of vitamin A. Xerophthalmia can progress to night blindness or more serious damage to the cornea, the outer layer of the eye.
Question 7. Some persons may lose their vision because of a _________ or an __________.
Answer 7. Disease, injury.
Question 8. Who developed a system for visually impaired people and published it in 1821?
Answer 8. The Braille system was developed in the 1820s by Louis Braille and is the most commonly used resource for visually challenged people. Blind individuals read and write using the Braille system. A set of raised bumps or dots can be sensed with the help of a finger in the Braille system.
Question 9. Do you think a light ray is an idealisation? Why?
Answer 9. Yes, a ray of light is an idealisation. A narrow beam of light is made up of several rays. For simplicity, the word ray is used for a little light beam.
Question 10. Give any two uses of the periscope.
Answer 10. Tanks, submarines, and soldiers in bunkers use periscopes to see things outside.
Question 11. List the food items that contain vitamin A.
Answer 11. Vitamin A is abundant in raw carrots, broccoli, green vegetables (such as spinach), and cod liver oil. Vitamin A is found in eggs, milk, curd, cheese, butter, and fruits like papaya and mango.
Question 12. State laws of reflection.
Answer 12. ‘The incidence angle is equal to the reflection angle,’ says the first law of reflection.
The incident reflected, and normal rays drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface lie in the same plane, per the second law of reflection.
Question 13. Give any four examples of luminous objects.
Answer 13. The sun, fire, candle flame, and an electric lamp are luminous objects.
Question 14. Explain regular reflection with the help of a diagram.
Answer 14. A regular reflection is a reflection made from a smooth surface like a mirror. Regular reflection creates images.
Question 15. What is the function of the retina?
Answer 15. The lens directs incident light to the retina, which includes several nerve cells. The nerve cells’ sensations are then transferred to the brain through the optic nerve.
Question 16. Give an example to show that reflected light can be reflected again.
Answer 16. Stand in front of a mirror and ask a friend to hold a mirror behind you so you can see your haircut; your hair image will appear in the mirror in front of you; this is the best example of reflected light returning to the source.
Question 17. Can we see objects in the dark? Why?
Answer 17. When the incident light is reflected by the object and reaches our eyes, we can see it. However, when the object reflects no light, we cannot see it.
Question 18. How do you make a kaleidoscope?
Answer 18. Make three small rectangular mirror strips, each about 15 cm long and 4 cm wide, to make a kaleidoscope. Connect them together to make a prism. Place these mirrors in a circular cardboard tube or a tube made of thick chart paper. Assemble the tube such that it is slightly bigger than the mirror strips. Close one end of this tube with cardboard with a hole in the middle that you can see through. Put a piece of the transparent plastic sheet under the cardboard to make it more durable. Fix a round plate glass on the opposite end, touching the mirrors. Place numerous pieces of coloured glass on this glass plate (broken pieces of coloured bangles). A round glass plate is used to close this end of the tube. Make sure there’s enough space for the coloured pieces to move around. Now the kaleidoscope is ready to be used.
Question 19. Write any five ways to take care of your eyes.
Answer 19. Some common measures to take care of the eyes are as follows-
- Use suitable eyewear if advised.
- It is not good for the eyes to have too little or too much light. Eye strain and headaches are caused by insufficient light. The retina can be impaired by too much light, such as sunlight, a strong lamp, or a laser torch.
- Do not look directly at the sun or bright light.
- Do not rub your eyes. If dust particles enter your eyes, rinse them with clean water. If your condition does not improve, go to the doctor.
- Always read books at a comfortable distance for your eyes. Avoid reading the book too close to your eyes or keeping it too far away when reading.
Question 20. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
Answer 20. If a person is inside a room with no light, it is impossible to see the object inside the dark room, but the object outside the room is seen easily.
When light falls on the eyes after reflecting from the object, it becomes visible. If the room is dark, the objects in the room reflect no light. Hence, the person cannot see the objects in the room without light.
Question 21. Mention the following, whether regular or diffused reflection, which will occur when a light beam strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
(a) A Polished wooden table.
(b) Chalk powder.
(c) A Cardboard surface.
(d) A Marble floor with some water spread over it.
(e) A Mirror.
(f) A Piece of paper.
Answer 21. a) A wooden table that has been polished-regular reflection.
A surface polished recently is an example of a smooth surface. A wooden table that has been polished has a smooth surface.
b) White chalk powder used in school- diffused reflection
chalk powder spread over a surface is a good example of an irregular surface. Hence, it is rough. Therefore, the diffused reflection will appear from the chalk powder.
c) Cardboard surface- diffused reflection.
The cardboard surface is a type of irregular surface.Hence, the diffused reflection will occur from a cardboard surface.
d) Marble floor – regular reflection.
A marble floor can be a good example of a stable surface. Since water makes the ceramic shiny, , the reflections are regular occurrences on this surface.
e) Mirror- regular reflection
A mirror has a very smooth surface, giving a regular reflection.
f) Piece of paper- diffused reflection
Although a piece of paper looks smooth, it has many irregularities on its surface. Due to this, it will give a diffused reflection.
Question 22. State the laws of reflection.
Answer 22. The law of reflection states that
- a) The angle of incidence and angle of reflection are always equal.
- b) At the point of incidence, the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal to the reflective surface all lie in the same plane.
Question 23. Describe that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Answer 23. On a table, place a plane mirror normal to the plane of the table. Make a small hole in a piece of paper and hold it perpendicular to the table. Try this experiment in a dark room. Put one more piece of paper on the table to make contact with the mirror. Draw a perpendicular line to the mirror on the piece of paper on the table. Now beam light rays with the help of a torch will pass through the small hole so that the light beam hits the normal at the lower part of the mirror. The light rays from the hole incident on the mirror will reflect the ray of light. Looking at the paper on the table, we can simply show that the incident ray, normal ray, and reflected ray at the incidence point lie in the same plane.
Question 24. What will be the angle of incidence of a ray when the reflected ray is perpendicular to the incident ray?
Answer 24. If the reflected ray lies perpendicular to the incident ray, then the angle of incidence is 45 degrees. According to the laws of reflection, the incidence angle and the angle of reflection are equal. Hence, the incidence ray and angle of reflection are 90/2=45 degrees.
Question 25. How many images of the candle will be seen if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by a distance of 40 cm?
Answer 25. When a candle is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm, multiple and infinite images will be seen due to the multiple reflections between the mirrors. An unlimited number of images are formed when two mirrors are placed parallel to each other.
Question 26. The part of the eye which controls the light entering is called –
Answer 26. The answer is option (a) iris.
Explanation – Iris is a dark, muscular part behind the cornea. Its function is to regulate the entry of light.
Question 27. We can see a non-luminous object when light-
(a) completely passes through the object.
(b) gets completely absorbed by the object.
(c) emitted by the object falls on our eye.
(d) is reflected from the object towards the eye.
Answer 27. The answer is option (d) is reflected from the object towards the eye.
Question 28. A light ray incident on mirror A at an angle of 25 degrees falls on mirror B after reflection. The angle of reflection for the reflected ray from mirror B would be-
(a) 25 degrees.
(b) 50 degrees.
(c) 65 degrees.
(d) 115 degrees.
Answer 28. The answer is option (c) 65 degrees.
Explanation- The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B will be 65° because the reflected ray from mirror A forms an incident ray on mirror 6 and is then reflected by an angle of 65°.
Question 29. Which statements are correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
(a) Cones are sensitive to dim light.
(b) Cones are sensitive to bright light.
(c) Rods are sensitive to bright light.
(d) Rods can sense colour.
Answer 29. The answer is option (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light.
Explanation- Cones are sensitive to bright light; hence, they sense colour, whereas rods are sensitive to dim light and cannot sense colour.
Question 30. Which part of the eye gives colour to our eyes?
Answer 30. Iris of the eye gives colour to the eyes.
Question 31. While waving his hand fastly in front of his eyes, Boojho observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it?
Answer 31. The persistence of vision is the reason for the blurred vision of Boojho; while waving his hand fastly in front of his eyes, he observes that his fingers appear blurred.
Question 32. How often is a ray of light reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other?
Answer 32. Two plane mirrors reflect an infinite number of times, a ray of light placed parallel and facing each other.
Question 33. The angle between the ray of incidence and the reflected ray is 60°. What is the angle of incidence?
Answer 33. The answer is 30°.
Explanation- The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
Since, the Angle of incident ray+ Angle of reflected ray is 60°.
The angle of incidence = 30°
Question 34. What happens to the light when it gets dispersed? Give an example.
Answer 34. When the light gets dispersed, it gets split into its constituent colours. Ex: rainbow.
Question 35. The eyes of nocturnal animals have large corneas and large pupils. How does this structure help them?
Answer 35. They can see objects even in low light. A large pupil and a large cornea help lighter enter their eyes.
Question 36. What type of lens is found in our eyes? Where does it form the image of the object?
Answer 36. Our eyes have a convex lens, forming the image on the retina.
Question 37. Which part of the eye gets affected when someone suffers from a cataract? How is it treated?
Answer 37. If a person suffers from a cataract, their eye lens will become cloudy. Cataracts can be cured by replacing the opaque lens with an artificial lens.
Question 38. Explain the process which enables us to recognise motion in a cartoon film.
Answer 38.A Carton movie is a projection of a static picture. 24 pictures are shown in one second in a specific order, giving us the perception of movement.
Question 39. How is the phenomenon of light reflection used in making a kaleidoscope? What are the uses of a kaleidoscope?
Answer 39. The kaleidoscope gives several images formed by reflection from the mirrors inclined towards one another. Designers and artists use a kaleidoscope to get ideas for new patterns to design wallpapers, jewellery, and fabrics.
Question 40. What is a periscope? How many mirrors are there in a periscope?
Answer 40. A periscope is an instrument that reflects the reflected ray again. It is made of a tube attached to a set of mirrors. There are two mirrors in a periscope.
Question 41. State the various uses of a periscope.
Answer 41. Uses of periscope-
- It is used to see over and around an object.
- It is used to see over a wall.
- Used in warfare.
Question 42. Can you see your image in a plane mirror? Write two characteristics of the image so formed.
Answer 42. Yes, we can see our image in a plane mirror. The image formed will be-
- Virtual and erect.
- The same size as the object
Question 43. Explain why a book lying on the table in a room can be seen from all parts of the room.
Answer 43. A book lying on the table in a room can be seen from all parts of the room because of the light reflection falling on it.
Question 44. We can see the sun because it is glowing. How can we see the moon?
Answer 44. We see the moon because the light from the sun falls on the moon and is reflected on the earth.
Question 45. Write the two types of reflection of light. What kind of reflection makes us see an object from all directions?
Answer 45. The two types of light reflection are- regular reflection of light and diffuse reflection of light.
The regular reflection of light makes us see an object from all directions.
Question 46. A wall reflects light and a mirror also reflects light. What is the difference in the way they
reflect light?
Answer 46. Reflection of light from the wall is a diffused reflection, and reflection of light from a mirror is a regular reflection.
Question 47. What are the main parts of the human eye?
Answer 47. The main parts of the human eye are-
Iris, Lens, Pupil, Cornea, Retina, Ciliary muscles, and Optic nerve.
Question 48. What is the vision range of a normal person?
Answer 48. A normal human eye’s vision range is from 25cm to infinity.
Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Our question bank of Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Important Questions covers questions from different topics covered in the Light chapter.
Students can face difficulty understanding complex topics in Science. One way to resolve this is to practise Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16. The question bank covers all the important topics, and these questions are created from an exam point of view and are most likely to be asked in the exam. Practising Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 gives students a competitive edge.
Here are some benefits of solving questions from our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16.
- The comprehensive question guide puts together important questions from different sources. So it’s easy for students to refer only to our question bank instead of referring to multiple sources and wasting time in searching for them. The answers to each question are prepared by experienced science teachers. They provide step-by-step answers with deep conceptual explanations which helps students prepare for exams in a balanced manner.
- The series of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 consists of objective types, short answers, and long answers. These questions adhere to the latest CBSE syllabus and are based on the exam format as prescribed by NCERT. So, students can confidently rely on our question patterns and solutions for their exam preparation.
- The solutions provide details required in clearing the question paper, which can benefit students during final exam preparation and their future career paths and achievements.
Extramarks is a leading online learning website that offers comprehensive learning solutions to students in Classes 1-12. We also provide extra study and course materials. Students can also click the links below to access all the most important resources.
NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Answer the following questions:
- What primarily distinguishes unicellular organisms from multicellular organisms?
- State the function of pseudopodia in Amoeba .
- Give an example of a single cell in humans which can change its shape.
Marks: 3 Ans
- Cell number primarily distinguishes unicellular organisms from multicellular organisms. Unicellular organisms are made up of a single cell, while multicellular organisms are made up of multiple cells.
- Pseudopodia are the projections that protrude out of the body of Amoeba and help in movement and capturing of food.
- White blood cells in humans are single-celled and can change their shape.
Q.2 What is the need of staining a section of tissue, before observing it under the microscope? Name a stain.
Marks: 2 Ans
Staining with coloured dyes makes the cellular parts clearly visible. The dyes react with cellular components to give colour to the components. Methylene blue is a blue dye that is often used to stain onion peel cells.
Q.3 Read the following functions of a certain part of cells. i. Protection against abiotic factors ii. Providing shape and rigidity to the cells iii. Selective diffusion of the materials across it iv. Site of photosynthesis Which of the following function(s) are carried out by the cell wall?
A. i and ii
B. ii and iii
C. iii and iv
D. i and iv
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 8 science important questions, chapter 1 - crop production and management.

Chapter 2 - Microorganisms : Friend and Foe
Chapter 3 - synthetic fibres and plastics, chapter 4 - materials : metals and non-metals, chapter 5 - coal and petroleum, chapter 6 - combustion and flame, chapter 7 - conservation of plants and animals, chapter 8 - cell - structure and functions, chapter 9 - reproduction in animals, chapter 10 - reaching the age of adolescence, chapter 11 - force and pressure, chapter 12 - friction, chapter 13 - sound, chapter 14 - chemical effects of electric current, chapter 15 - some natural phenomena, chapter 17 - stars and the solar system, chapter 18 - pollution of air and water, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. where can students easily get important questions class 8 science chapter 16.
To make it simpler for students to learn, revise, and prepare for their examinations, Extramarks provides a list of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16. With this comprehensive series of questions prepared by experts, topics from every nook and corner of the chapters are covered, thus ensuring that the students achieve better grades in their examinations. You can rely completely upon it as you get authentic and correct solutions to the Science Class 8 Chapter 16 Important Questions.
2. Is the series of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 enough to score good marks?
The solutions we provide here at Extramarks are concise and written from an examination point of view. The answers to the exercise questions are clearly explained with examples. They are completely accurate. These solutions will help students prepare for their exams as we follow the guidelines provided by the NCERT book and the CBSE Science syllabus. These solutions will help students develop a conceptual foundation that explains all key concepts in an easy-to-get language. This exercise will cover all the topics and subtopics that your Class 8 Science exams could be expected to cover.
Along with this, we recommend students first start their studies with NCERT study materials, including the NCERT textbook and NCERT exemplar books.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light
- Class 8 Important Question
- Chapter 16: Light

CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-16 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
The important questions for class 8 science chapter 16 PDF available on the Vedantu website for easy access and students can download the PDF anytime. The important questions for Class 8 Science chapter 16 PDF cover every topic from chapter 16 of class 8 science. It will be helpful for students for fetching a good score in their academic exams. The Class 8 Science chapter 16 important questions are designed for the students in such a way that they will be able to understand the concepts with clear understanding. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for better solutions can download Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Study Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – Light
1. When all the parallel rays reflected from a rough or irregular surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as ___________.
A. multiple reflections B. regular reflection
C. lateral inversion D. diffused reflection
Ans: D. diffused reflection.
2. The angle between normal and incident rays is called the ___________________.
A. angle of incidence B. angle of reflection
C. angle of refraction D. normal
Ans: A. angle of incidence
3. Which part of the eye protects the interior from accidents?
A. pupil B. retina
C. cornea D. rods
Ans: C. Cornea protects the eye's sensitive components from dirt, bacteria, and other foreign particles.
4. Which one of the following works on the basis of multiple reflections?
A. kaleidoscope B. microscope C. telescope D. periscope
Ans: A. Kaleidoscope. A kaleidoscope is an optical device containing two or more reflecting surfaces that are angled at an angle to each other.
5. Angle of incidence is __________equal to the angle of reflection
A. Sometimes B. Never
C. always D. almost
Ans: C. Always
6. White light consist of ___________ colours
A. six B. seven
C. eight D. nine
Ans: B. Seven. Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet are the colors that make up white light.
7. Image formed in a plane mirror undergoes _______________.
Ans: lateral inversion. The reversal of a mirror image, where the right side of the object appears on the left side behind the mirror, is known as lateral inversion.
8. Name the part of the eye which gives distinctive color.
Ans: Iris is the part of the eye that gives distinctive color. The iris is a colored ring that surrounds our pupils and gives our eyes their distinct color.
9. The lens focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called___________.
Ans: Retina. Thousands of light-sensitive cells (rods and cones) and other nerve cells make up the retina, which receives and organizes visual data. Through your optic nerve, your retina conveys this information to your brain, allowing you to see.
10. What is a blind spot?
Ans: There are no sensory cells at the intersection of the optic nerve and the retina, hence vision is impossible there. This is referred to as the blind spot.
11. ____________ are sensitive to bright light in eye.
Ans: Cones. In the retina, cones are a type of photoreceptor cell. They are responsible for our color perception. Cones are concentrated in the macula, which is located in the center of our retina and helps us see small details.
12. Lack of which nutrient is responsible for eye troubles?
Ans: Deficiency of Vitamin A causes eye troubles. Xerophthalmia is a progressive eye disease caused by a lack of vitamin A. Xerophthalmia can progress to night blindness or more serious damage to the cornea, the outer layer of the eye.
13. Some persons may lose their eyesight because of a _________ or an __________. Ans: Disease, injury.
14. Who developed a system for visually challenged persons and published it in 1821? Ans: Braille was developed in the 1820s by Louis Braille and is the most widely used resource for visually impaired people. Louis Braille. Blind individuals read and write using the Braille system. A set of raised bumps or dots can be sensed with a finger in the Braille system.
15. Do you think a ray of light is an idealization? Why?
Ans: Yes a ray of light is an idealization. In reality, there is a narrow beam of light that is made up of several rays. For simplicity, the term ray is used for a narrow beam of light.
16. Give any two uses of periscope.
Ans: Submarines, tanks, and soldiers in bunkers use periscopes to see things outside.
17. ___________ system helps visually challenged persons to read and write.
Ans: Braille. Braille is a written language for the blind in which characters are represented by patterns of raised dots that can be felt with their fingertips.
18. The impression of an image does not vanish immediately from the retina. It persists there for about ___________of a second.
Ans: 1/16 th
19. a. Define dispersion of light.
Ans: Dispersion of light is referred to as splitting of light into its constituent colors.
b. Give an example of dispersion.
Ans: Rainbow is a natural phenomenon that shows dispersion.
20. Define the following,
a. Incident ray
Ans: a. Incident ray is defined as a light ray, which strikes any surface.
b. reflected ray.
Ans: The ray that returns from the surface after it has been reflected is known as the reflected ray.
The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, according to the law of reflection.
21. List the food items which contain vitamin A.
Ans: Vitamin A is abundant in raw carrots, broccoli, and green vegetables (such as spinach) as well as cod liver oil. Vitamin A is found in foods including eggs, milk, curd, cheese, butter, and fruits like papaya and mango.
22. State laws of reflection.
Ans: ‘The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection,' says the first law of reflection.
The incident rays reflected rays, and normal rays are drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface all lie in the same plane, according to the second law of reflection.
23. Give any four examples of luminous objects.
Ans: The Sun, fire, the flame of a candle, and an electric lamp are examples of luminous objects.
24. Describe regular reflection with the help of a diagram.
Ans: Regular reflection is a reflection from a smooth surface such as a mirror. Regular reflection creates images.
25. What is the function of the retina?
Ans: The lens directs light to the retina, which includes a number of nerve cells. The nerve cells' sensations are subsequently transferred to the brain via the optic nerve.
26. Given an example to show that reflected light can be reflected again.
Ans: Stand in front of a mirror and tell a friend to hold a mirror behind you so you can see your haircut; your hair picture will appear in the mirror in front of you; this is the best example of reflected light returning to the source.
27. Can we see objects in dark? Why?
Ans : When light reflected by an object reaches our eyes, we can see it. However, when there is no light reflected by the object, we cannot see it.
28. How does the braille system work?
Ans: There are 63 dot patterns or characters in the Braille system. A letter, a combination of letters, a common word, or a grammatical sign is represented by each character. Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of three dots each. Below are various dot patterns that symbolize English letters and common words.
When embossed on Braille sheets, these patterns assist visually impaired people in recognizing words by touch. The dots have been slightly right to make them easier to touch.
29. Explain the structure of the eye with a neat labeled diagram.
Ans: The shape of the eye is generally spherical. The eye's outer layer is white. It is tough in order to protect the interior of the eye from damage. The cornea is the translucent front section of the eye. The iris is a dark muscular tissue that lies behind the cornea. The pupil is a tiny aperture in the iris that allows light to pass through. The iris regulates the size of the pupil. The iris is the colored portion of the eye.

30. How do you make a kaleidoscope?
Ans: Get three rectangular mirror strips, each about 15 cm long and 4 cm broad, to build a kaleidoscope. To make a prism, join them together. Place the mirrors in a circular cardboard tube or a tube made of thick chart paper. Assemble the tube so that it is slightly longer than the mirror strips. Close one end of the tube with a cardboard disc with a hole in the middle that you can see through. Put a piece of the transparent plastic sheet under the cardboard disc to make it more durable. Fix a round plane glass plate at the opposite end, touching the mirrors. Place numerous little pieces of colored glass on this glass plate (broken pieces of colored bangles). A ground glass plate is used to close this end of the tube. Make sure there's enough space for the color pieces to move around. Now, the kaleidoscope is ready to use.
31. Demonstrate an activity to show that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Ans: On the paper, draw lines to illustrate the position of the plane mirror, incident ray, and reflected ray. At the place where the incident ray reaches the mirror, draw a line at a 90o angle to the line representing the mirror. The normal to the reflecting surface at that location is this line. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection should be measured. Change the angle of incidence and repeat the activity multiple times. The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection when the experiment is accurately carried out.
32. Write any five ways to take care of your eyes.
Ans: Some possible measures to take care of the eyes are as follows:
Use appropriate eyewear if advised.
It is harmful to the eyes to have too little or too much light. Eye strain and headaches are caused by insufficient light. The retina can be damaged by too much light, such as that of the Sun, a strong lamp, or a laser torch.
Do not look directly at the Sun or bright light.
Do not rub your eyes. If dust particles get into your eyes, rinse them out with clean water. If your condition does not improve, see a doctor.
Always read at a comfortable distance for your eyes. Avoid bringing the book too close to your eyes or keeping it too far away when reading.
Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16
Class 8 science ch 16 extra questions.
The class 8 science ch 16 extra questions cover all the important concepts from chapter 16 of class 8 science. Chapter 16 of class 8 deals with the concepts of light and given an introduction to the world of physics. Physics is a branch of science that deals with the study of nature. When we study the concepts of physics we must keep in mind that we are going to study what we will be experiencing in our day-to-day lives. For understanding chapter 16 students are suggested to prepare with quality material and reliable content like class 8 science chapter 16 important questions. The important questions class 8 science chapter 16 Pdf material provided here gives a deep insight into the class 8 science chapter 16.
Students can master any difficult subject or topic with the practice of relevant questions. The class 8 science ch 16 extra questions provided here will boost students’ confidence and their exam preparation. The class 8 science chapter 16 important questions incorporated all kinds of questions that will be helpful for the students in understanding the concepts in a better way. Before going through class 8 science ch 16 extra questions let us have a look at what this chapter includes and what we are going to learn from chapter 16 of class 8 science.
The class 8 science chapter 16 deals with the concepts of light. We know that Light is an important natural phenomenon in our lives, we can say it is one of the important senses of human life. Everything we are able to see is only because of the presence of light. Chapter 16 has given a detailed description of the concept of light and the laws of physics. It explains why the sense of sight is an essential part of every living thing. Because of the light, we are able to see what is happening around us, we are able to witness the beauty of our nature because of the sight. The content you are going through on the screen can be read-only because of the light. Thus sight is an essential sense among all the senses.
The chapter Light begins with the concepts and meaning of the light and laws of reflections. Students might have already come across the word like the reflection in the previous chapter, in this unit students learn what is reflection and what are the laws associated with the reflection. This chapter will give answers to the most common questions that arise in students like how can a visually disabled person read? How an owl can see only in the night but not during the daylight? What is a braille system is also explained in chapter 16 of class 8 physics. These questions can find the detailed solution from the class 8 science ch 16 extra questions.
In this chapter students will also learn about the human eye, the construction of the human eye. Students will also learn some interesting experiments for explaining the reflection such as the construction of a kaleidoscope. By the end of the chapter, students will be capable of answering many interesting concepts, and in addition to their preparation, important questions for class 8 science chapter 16 Pdf will be a brownie point.
What are the Benefits of Important Questions from Vedantu for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light
Explore the advantages of Vedantu's Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light. These curated questions provide a strategic approach to mastering key concepts, ensuring comprehensive understanding and effective exam preparation. Here are few points that describe the Benefits of Important Questions from Vedantu for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light:
Focus on key topics for efficient studying.
Prepares students for exams and reduces anxiety.
Reinforces understanding of fundamental concepts.
Teaches effective time management.
Enables self-assessment and progress tracking.
Strategic approach for higher scores.
Covers a wide range of topics for comprehensive understanding.
Supports exam preparation and boosts confidence.
The study material provided here is important questions class 8 science chapter 16 Pdf is prepared by the experts according to the prescribed syllabus. It includes MCQ types of questions, diagram-oriented questions, short and long answer questions, along with class 8 science ch 16 extra questions. Students are advised to register to the Vedantu today and get access to the unlimited and extended study materials of the desired topics.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light
1. What is the way to take care of your eyes?
Ans: Eyes are very important and proper care should be taken for protection.
If you are advised to use the spectacles make sure to use the suitable and the correct spectacles.
Keep the spectacles always clean.
Don’t let your eyes be exposed to too much light. This will lead to damage to the retina.
Never look directly to the sunlight or any powerful dazzling light. It will be harmful.
While reading a book keep it at a proper distance, don’t get too close to the eyes.
If the dust particles go inside your eyes do not rub them, just wash with clean water.
2. Mention the function of the parts of the eye.
Ans: The main parts of the human eye are Cornea, Iris, Pupil, Lens, Retina and Optic nerve. The thin layer where the light enters the eye and which forms a transparent bulge is called Cornea. A dark muscular diaphragm whose function is to control the size of the pupil is called Iris. The function of the lens is to adjust the focal length which is required to focus on the object according to the distances.
A Retina is a very sensitive and delicate membrane where the images are formed and has many photosensitive cells called rods and cones. Rods are sensitive to dim lights and cones are sensitive to bright lights.
The function of the optic nerve is to transmit the electric signals from the eye to the brain.
3. What do you understand about the Braille System?
Ans: Certain people are affected usually whom we say as visually impaired due to many reasons. The term Braille system is used to help visually impaired persons to read and write. This contains 63 dot patterns or we can say as the characters. These characters are on the Braille sheets which can be easily recognized by the touch. These characters slightly bulge so the persons can feel the characters.
4. What are the laws of reflection?
Ans: The definition of the law of reflection is when the light falls on any smooth surface the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence and the incident ray, the normal to the surface and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
The laws of reflection state that
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of the incident to the line perpendicular to the surface of the point of contact.
The reflected ray is always in the plane which is defined by the ray of the incident to the surface of the point of contact.
5. Define regular and irregular reflection?
Ans: Regular reflections are produced by the plane mirrors with smooth surfaces. The image produced by the regular reflection is always clear and visible. The images are virtual and we cannot collect the image on the screen.
Irregular reflections are produced by the rough surfaces. In this reflection, the illuminated objects are seen from any position. In this type of reflection, the parallel incident light rays are reflected irregularly in many directions.
To know more about Chapter 16 - Light of Class 8 Science refer to the notes provided by Vedantu . They are available on the website of Vedantu and their App and that too free of cost.
Chapterwise Important Questions for CBSE Class 8 Science
Cbse study materials.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 16 Class 8 - Light
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Check out the NCERT Solutions, Notes, Experiments, Activities and some Extra Questions for Chapter 16 Class 8 Science - Light.
Everything is provided free of cost, and is the best education material available for Light Class 8.
In this chapter, we will study -
- How do we see objects?
- What are visible and invisible objects?
What are Luminous and Non-Luminous Objects?
and the Difference between them
- What is Incident Ray, Reflected Ray and Normal
- What is Angle of Incidence and Angle of Reflection
What are Laws of Reflection
Regular and Diffused Reflection
Image formed a Plane Mirror and its characteristics
What exactly is Lateral Inversion
Multiple Reflections of Light
and its applications like Periscope
What is a Kaleidoscope ?
How can we construct a Kaleidoscope
What is Dispersion of Light
The Human Eye - and its different parts
What is the function of Iris and Pupil?
What is a blind spot ?
Other Important Points about Human Eye like Eyelids, Range of Vision, How do we see moving objects
What is Visual Impairment?
What is Braille System
How to take proper care of eyes?
In addition to this, we have also provided some Practice Problems - both 1 mark and 2+ Marks. They are in the Extra Question link given below.
Click on a link below to get started
Note : When you click on a link below, the first question will open. To open other questions, scroll down to the bottom. You will get a list with arrows. It has everything you will need
NCERT Questions
Teachoo questions.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Class 8 - NCERT Science Solutions
Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room? Explain.
No, we cannot see objects in a dark room because there is no light to illuminate the objects in the room. When light falls on the eyes after reflecting from the object, it becomes visible. If the light is available outside the room, then the objects present would reflect it and hence we would be able to see objects.
Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
| S. No. | Regular Reflection | Diffused Reflection |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It occurs when the surface is smooth. | It occurs when the surface is rough. |
| 2. | Reflected rays move in a particular direction. | Reflected rays scatter in random directions. |
| 3. | Example: Reflection by plane mirror | Example: Reflection by cardboard. |
Diffused reflection is not due to the failure of the laws of reflection. It is caused by the irregularities in the reflecting surface, like that of a cardboard.
Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
(a) Polished wooden table
(b) Chalk powder
(c) Cardboard surface
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it
(f) Piece of paper
(a) Polished wooden table — Regular reflection Reason — The polished wooden table has a smooth surface, hence, the reflections are regular.
(b) Chalk powder — Diffused reflection Reason — Chalk powder spread on a surface will form an irregular surface, hence, the reflections are diffused.
(c) Cardboard surface — Diffused reflection Reason — The surface of the cardboard is irregular, hence, the reflections are diffused.
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it — Regular reflection Reason — Marble floor with water spread over it is a smooth surface, hence, the reflections are regular.
(e) Mirror — Regular reflection Reason — A mirror has a very smooth surface, hence, the reflections are regular.
(f) Piece of paper — Diffused reflection Reason — Piece of paper has many irregularities, hence, the reflections are diffused.
State the laws of reflection.
Two laws of reflection are :
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) Incident ray, reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to the reflecting surface, lie in the same plane.
Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Take a sheet of stiff paper or a chart paper. Let the sheet project a little beyond the edge of the table. Cut the projecting portion of the sheet in the middle. Look at the reflected ray. Make sure that the reflected ray extends to the projected portion of the paper. Bend that part of the projected portion on which the reflected ray falls.
When the whole sheet of paper is spread on the table, it represents one plane. The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray are all in this plane.
When we bend the paper we create a plane different from the plane in which the incident ray and the normal lie. Then we do not see the reflected ray.
Hence, the above activity indicates that the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Fill in the blanks in the following.
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be ............... m away from his image.
(b) If you touch your ............... ear with your right hand in front of a plane mirror, it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with ...............
(c) The size of the pupil becomes ............... when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have ............... cones than rods in their eyes.
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be 2 m away from his image.
Reason — When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, their image appears to be as far behind the mirror as the person is in front of it. So, when the person is 1 m away from the mirror. His image will be formed at 1 m from the mirror on the other side, hence, his image will be 1 + 1 = 2 m from the person himself.
(b) If you touch your left ear with your right hand in front of a plane mirror, it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with your left hand.
Reason — The image formed by a mirror is laterally inverted hence, when we touch our left ear with our right hand in front of a plane mirror, it will be seen in the mirror that our right ear is touched with our left hand.
(c) The size of the pupil becomes large when you see in dim light.
Reason — In dim light conditions, there's less available light for vision. To allow more light to enter the eye and improve visibility in low-light environments, the iris dilates the pupil. When the pupil dilates, it enlarges in size, allowing more light to pass through the eye and reach the retina at the back of the eye.
(d) Night birds have fewer cones than rods in their eyes.
Reason — Having fewer cones and more rods allows night birds to have better night vision. Rods are more sensitive to low levels of light, making them ideal for detecting prey and navigating in the dark. Additionally, having fewer cones means that night birds likely have reduced color vision or even monochromatic vision, which is less important for hunting in low-light conditions.
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- Under special conditions
Reason — According to the laws of reflection :
Image formed by a plane mirror is
- virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
- real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
- real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Reason — Image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
To make a kaleidoscope, we will take three rectangular mirror strips each about 15 cm long and 4 cm wide. We will join them together to form a prism as shown in the figure below:
After that, we will fix the arrangement of mirrors in a circular cardboard tube or tube of a thick chart paper. It should be slightly longer than the mirror strips. Close one end of the tube by a cardboard disc having a hole in the centre, through which we can see.
In order to make the disc durable, we will paste a piece of transparent plastic sheet under the cardboard disc. At the other end, touching the mirrors, we will fix a circular plane glass plate.
After that, we will place on this glass plate several small pieces of coloured glass (broken pieces of coloured bangles). Close this end of the tube by a ground glass plate. Allow enough space for the colour pieces to move around.
Our kaleidoscope is ready.
Question 10
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.
Labelled sketch of the human eye is shown below:
Question 11
Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 13.8 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teacher's advice?
Intensity of laser light is very high. It can cause damage to the retina and lead to blindness. Hence, Gurmit's teacher advised her not to use a laser light for the activity as she was concerned about the risk of accidental exposure to the laser beam, which could potentially cause damage to Gurmit's eyes or the eyes of others nearby.
Question 12
Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
In order to take care of our eyes we should do the following:
- We should always read at the normal distance for vision. We should not bring the book too close to our eyes or keep it too far.
- We should not look at the Sun or a powerful light directly.
- Too little or too much light is bad for eyes. Insufficient light causes eyestrain and headaches. Too much light, like that of the Sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina.
- We should never rub our eyes. If particles of dust go into our eyes, we should wash our eyes with clean water or visit the doctor if need be.
- If advised, we should use suitable spectacles.
Question 13
What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
∠i + ∠r = 90° where
∠i = angle of incident.
∠r = angle of reflection
According to the law of reflection,
Substituting the above law in the given condition we get,
∠i = 90 2 \dfrac{90}{2} 2 90 = 45°
Therefore, angle of incidence = 45°.
Question 14
How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
When a candle is placed between two parallel plane mirrors, infinite images are formed due to repeated reflections between the mirrors.
Question 15
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in Fig. 13.19. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
Let MM' and M'M'' be the two plane mirrors at right angles.
The reflected ray from the second mirror is shown in the figure below:
Given that the ray is incident on mirror MM' at 30°,
∴ ∠AOX = 30°
∴ ∠XOO' = ∠AOX = 30°
As OX ⊥ MM' and O'X ⊥ M'M''
∴ ∠OXO' = 90°
In ΔOXO', by angle sum property.
∠XOO' + ∠OXO' + ∠XO'O = 180°
⇒ 30° + 90° + ∠XO'O = 180°
⇒ ∠XO'O = 180° - 90° - 30°
⇒ ∠XO'O = 60°
∴ Angle of incidence of the ray on M'M'' = 60°
∴ Angle of reflection of the ray from M'M'' = 60° [∵ ∠i = ∠r]
Question 16
Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror, as shown in Fig. 13.20. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also, can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R?
Boojho cannot see himself in the mirror because light rays originating from him do not reach his eyes after reflection.
He can see the image of objects situated at P and Q because the light rays coming from P and Q get reflected by the mirror and reach his eyes.
Boojho can't see the image of object situated at R because the light rays from object R do not reach his eyes after reflection.
Question 17
(a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (Fig. 13.21).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
(a) Image of the object placed at A is formed behind the mirror and distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the distance of A from the mirror.
(b) Yes, Paheli at B can see this image.
(c) Yes, Boojho at C can see this image.
(d) Image of the object at A will not move, hence, it will remain in the same position when Paheli moves from B to C.
A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 8 science case study question, case study question class 8 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 8 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 8 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 8 Science.
There are total 18 chapter Crop Production and Management, Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
, Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Materials: Metals and Non-Metals, Coal and Petroleum, Combustion and Flame, Conservation of Plants and Animals, Cell – Structure and Functions, Reproduction in Animals, Reaching the Age of Adolescence, Force and Pressure, Friction, Sound, Chemical Effects of Electric Current, Some Natural Phenomena, Light, Stars and the Solar System, Pollution of Air and Water
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Case Study Question
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Case Study Question
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Case Study Question
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence Case Study Question
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure Case Study Question
- Chapter 12 Friction Case Study Question
- Chapter 13 Sound Case Study Question
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Case Study Question
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Case Study Question
- Chapter 16 Light Case Study Question
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Case Study Question
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Chapter 16: Light for Class 8

- Updated on
- Jan 4, 2022

In chapter 16 of Class 8 NCERT Science book, we find the topic of ‘Light’. The chapter explains light, its properties and its uses. It is another enjoyable chapter that is informative as well. In this blog, we will read some of the important notes on Class 8 Light.
Also Read: Class 8 Science
This Blog Includes:
Laws of reflection, types of reflection, types of objects, the human eye, care of the eyes, class 8 light ncert solutions, class 8 light mcqs.
Download the Full Class 8 Light Chapter PDF Here

- The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection . It is the law of reflection.
- The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane . This is another law of reflection.
- On striking a mirror or any other object light generally is reflected in another direction. The light ray which strikes any surface is called the incident ray . The ray that comes back from the surface after the reflection is known as the reflected ray .
- The line making an angle of 90º to the line representing the mirror or surface of the object at the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror is known as the normal to the reflecting surface at that point.
- The angle between the normal and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence (∠i). The angle between normal and the reflected ray is known as the angle of reflection (∠r).
Lateral Inversion
The image formed by a mirror where the left of the object appears on the right and the right appears on the left is known as lateral inversion.
When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection . The diffused reflection is caused by the irregularities in the reflecting surface not due to the failure of the Law of reflection.
Reflection from a smooth surface like that of a mirror is called regular reflection. Images are formed by regular reflections .
NCERT Class 8 Maths Syllabus
Illuminated Objects
The objects which shine in the light of other objects are called illuminated objects.

Luminous Objects
The objects which give their own light such as the sun, fire, flame of a candle and an electric lamp are known as luminous objects.
Color of Sunlight
Sunlight is referred to as white light. It consists of 7 colours. These are the same 7 colours as that of the rainbow. The splitting of light into its colours is known as dispersion of light . Rainbow is a natural phenomenon showing dispersion and if sunlight is dispersed using a prism it shows these 7 colours on dispersion.
Also Read: Science Projects for Class 8

The eye is roughly structured in a spherical shape. The outer coat of the eye is white. It is tough so that it can protect the interior of the eye from accidents. It also is covered by the eyelid so that it can block out the excess light when needed. The eye has many parts which are described below –
Its transparent front part is called cornea
Behind the cornea is a dark muscular structure called the iris. The size of the pupil is controlled by the iris. The iris controls the amount of light entering the eye. Iris gives the eye its distinctive colour. For example – blue eyes, green eyes, brown eyes etc.
In the iris is a small opening called the Pupil
The lens focuses light on a layer on the back of the eye called the retina. The retina contains several nerve cells.
Optic Nerve
Sensations felt by the nerve cells are then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. There are 2 kinds of cells– cones – which are sensitive to bright light and sense colour. Rods are sensitive to dim light.
The junction of the optic nerve and the retina has no sensory cells so no vision is possible at that spot. Therefore it is called the blind spot.
Sometimes, particularly in old age eyesight becomes foggy due to the eye lens becoming cloudy. When this happens the person is said to have a cataract. There is a loss of vision but it is possible to treat this defect. The opaque lens is removed and a new artificial lens is inserted through technology. You may also be aware of eye problems like myopia and hypermetropia which are problems in seeing farther objects and the closer ones respectively.
Eyes are very important sense organs and therefore it is necessary that you take proper care of your eyes. Given below are some tips on how to take care of your eyes –
- Have a regular checkup. If there is a problem with your eyes you should go to an eye specialist.
- If advised use suitable spectacles.
- Too little or too much light is bad for the eyes. Insufficient light causes strain in the eyes and headaches. Too much light, like that of the sun, a powerful lamp or a laser torch can injure the retina. Therefore do not look at the sun or a powerful light directly.
- Never rub your eyes. If particles of dust go into your eyes wash them gently with clean water. If there is no improvement go to a doctor.
- Wash your eyes with clean water frequently.
- Always read at the normal distance. Do not read by bringing the book too close to your face or keeping it too far.
- Eat a balanced diet. Lack of vitamin A in food is responsible for many eye troubles like night blindness. One should include food like raw carrots, broccoli and green vegetables (such as spinach) and cod liver oil are rich in vitamin A in the diet. Eggs, milk, curd, cheese, butter and fruits such as papaya and mango are also a rich source of vitamin A.
Visually challenged people can also learn to read and write through a special language and other helpful resources. Braille is the most popular language and resources for visually challenged people. It was invented by Louis Braille who was visually challenged himself and published in 1821. The present system was adopted in 1932. There is Braille code for common languages, mathematics and scientific notation and even many Indian languages can be read using this system.
Q1. Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room?
Answer: When we’re in a dark room, we can’t see what’s around us. We can see the objects outside the room because the light is accessible outside the room and rays of light can reach our eyes after being reflected by the objects.
Q2. Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection?
Answer:
| All the reflected rays are parallel | The reflected rays are not parallel |
| It occurs on a smooth and polished surface | 2. It appears on the rough surface |
| Reflected rays are in one direction | 3. Reflected rays are scattered in diverse directions |
No, diffuse reflection does not mean the failure of the laws of reflection.
Q3. Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
- Polished wooden table
- Chalk powder
- Cardboard surface
- Marble floor with water spread over it
- Piece of paper
- Regular Reflection. This is because the surface is flat and polished.
- Diffused Reflection. This is because the surface is rough.
- Diffused Reflection. This is because the surface is rough.
Q4. State the laws of reflection.
Answer: The laws of reflection are:
- The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Q5. Fill in the following blanks:
- A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be _____ m away from his image.
- If you touch your _____ ear with a right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with _____.
- The size of the pupil becomes ______ when you see in dim light.
- Night birds have _____ cones than rods in their eyes.
Answer: (a) 2
(b) Left, Left hand
(c) Larger
(d) Lesser
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Q1. A smooth shining surface, which rebounds the light back in the same or in a different direction, is called
- Reflection of light
- Point of Incidence
Answer: (i) A mirror
Q2. The beam of light striking the reflecting surface is called
- Reflecting ray
- Incident ray
- Refracted ray
- Normal ray
Answer: (ii) Incident ray
Q3. The front bulged part of the eyeball is called
- Choroid
- Pupil
Answer: (i) Cornea
Q4. Band of seven colours is called
- VIBGYOR
- Spectrum
Answer: (ii) Spectrum
Q5. Which of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
- Cones are sensitive to dim light
- Cones are sensitive to bright light
- Rods are sensitive to bright light
- Rods can sense color
Answer: (ii) Cones are sensitive to bright light
Class 8 English
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see our surroundings when it gets reflected from objects around us.
The change in the direction of light when it strikes the surface of an object is called reflection. This sending back of the light is called reflecting of light. Smooth surfaces create good regular reflections.
There are two types of reflection: regular and irregular reflections. When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as diffused or irregular reflection. The diffused reflection is caused by the irregularities in the reflecting surface not due to the failure of the Law of reflection. Reflection from a smooth surface like that of a mirror is called regular reflection. Images are formed by regular reflections.
The angle between the normal and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence .
List of NCERT Books Class 8
Hope these notes on Class 8 Light helped clear your doubts and explain the chapter to you properly. If you need guidance with any other chapters or with any other subjects check our other blogs on Leverage Edu for help. Hope we will be able to help you get better marks in your exams.
Kritika is a thinker, dedicated Content Writer, and Ms. know-it-all for Study Abroad universities. She has done her graduation in Journalism and holds 3 years of experience in Social Media and Content Marketing. She is a provider who loves dogs, cooks delicious dinners, and is passionate about designing. If she’s on a break, you will most likely find her in an animal shelter, at the beach or searching for new designs for her outfits.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
June 20, 2022 by Sastry CBSE
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1 Part of the eye which controls the entering of light is called (a) iris (b) cornea (c) lens (d) retina Answer. (a) Iris is a dark muscular structure behind the cornea, which controls the amount of light entering into the eye.
Question 2 We can see a non-luminous object when the light (a) emitted by the object falls on the eye (b) is reflected from the object towards our eye (c) completely passes through the object (d) gets completely absorbed by the object Answer. (b) We can see a non-luminous object (object that does not produce its own light), when light reflected by the object enters our eyes.
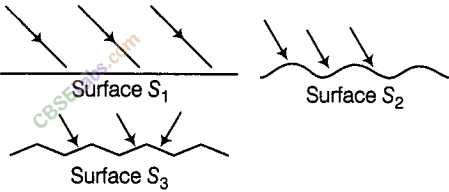
Question 7 Which of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye? (a) Cones are sensitive to dim light. (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light (c) Rods are sensitive to bright light (d) Rods can sense colour Answer. (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light and they sense colour. However, rods are sensitive dim light.
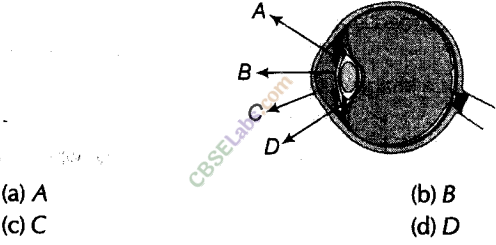
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 9 Name the part of the eye which gives colour to the eyes. Answer. Iris is the part of the eye which gives its distinctive colour. e.g. If a person is said to have blue eyes, then that actually refers to the blue colour of the iris.
Question 10 Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it? Answer. The impression of an image persists for about 1/16th of a second on the retina. This is known as persistence of vision. If still images of a moving object are flashed on the eye at a rate faster than 16 per second, then the eye perceives this object as moving. So, in case by waving hand very fast in front of eyes, the rate of movement of hand becomes very large (much faster than 16 per second), therefore, the fingers appear blurred.
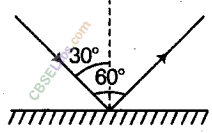
So, distance between the mirror and the object = 12 cm
Question 14 What happens to light when it gets dispersed? Give an example. Answer. Light is splitted into its constituent colours, when it gets dispersed, e.g. Rainbow formation is due to the dispersion of white light after passing through water droplets.
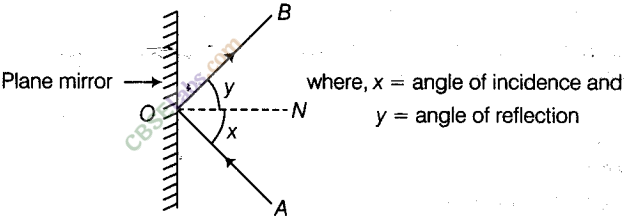
Question 17 Eyes of the nocturnal birds have large cornea and a large pupil. How does this structure help them? Answer. The size of the eyes of nocturnal bird is large. Eyes of the nocturnal birds having large cornea with a wider pupil, can collect more ambient light which help them to see the objects even at night.
Question 18 What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object? Answer. Convex lens is present in our eyes, which focuses light on the back of the eye, on a layer called retina. So, it forms the image of an object at retina.
Question 19 Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from ‘ cataract? How is it treated? Answer. In people (particularly old aged) suffering from cataract, the eye lens becomes clouded. Cataract is treated by replacing the opaque lens with a new artificial lens.
Long Answer Type Questions
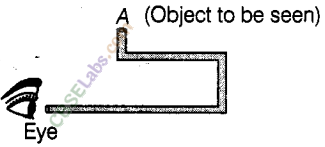
Question 22 Explain the process which enables us to perceive motion in a cartoon film. Answer. In a cartoon film, we see the projection of static pictures on the screen in a specific order. Generally, the static pictures are made to move across the eye in a sequence at the rate of 24 pictures per second (faster than 16 per second) giving us the perception of a moving picture. ‘
Question 23 How is the phenomenon of reflection used in making a kaleidoscope. What are the applications of a kaleidoscope? Answer. Kaleidoscope is a cylinder with three mirrors containing loose, coloured objects such as beads or pebbles and bits of glass. As the viewer looks into one end, light entering the other end, creates a colourful pattern due to reflection. It works on the principle of multiple reflection, where several mirrors are placed at an angle (usually 60°) to one another. Typically, these are three rectangular mirrors set at 60° to each other so that they form an equilateral triangle. The 60° angle creates seven duplicate images of the objects, 5 at 60° and 2 at 90°. As the tube is rotated, the tumbling of the coloured objects present varying colours and patterns. Its applications are given below: (i) It is used for decoration purposes, toys, etc. (ii)Kaleidoscope is also useful for designers and artists to get idea for new patterns to design wallpapers, jwellery and fabrics.

NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Chapter 4 Materials : Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
- Chapter 12 Friction
- Chapter 13 Sound
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena
- Chapter 16 Light
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water
NCERT Exemplar Solutions NCERT Exemplar Maths NCERT Exemplar Science
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Learn Insta
RD Sharma Solutions , RS Aggarwal Solutions and NCERT Solutions
Light Class 8 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 16
September 7, 2020 by Prasanna
In this page, we are providing Light Class 8 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 16 pdf download. NCERT Extra Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light will help to score more marks in your CBSE Board Exams.
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Extra Questions and Answers Light
Extra Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light with Answers Solutions
Light Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. Why fingers appear blurred when we move our hand very fast in front of our eyes? Answer: This is due to persistence of vision 1/16th of a second.
Question 2. What makes things visible? Answer: When light reaches our eyes after striking an object, we are able to see an object.
Question 3. Which element is used at the back of plane mirror? Answer: Silver
Question 4. The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 18 cm. What is the distance between mirror and the object? Answer: 9 cm
Question 5. How is hypermetropia corrected? Answer: It is corrected by using convex lens.
Question 6. How is myopia corrected? Answer: It is corrected by using concave lens.
Question 7. A ray of light is incident on a mirror at an angle of 40°. What is the angle of reflection ? Answer: 40°
Question 8. Name a device which works on the principle of multiple reflection. Answer: Periscope
Question 9. Can we see an object in the dark? Answer: No
Question 10. What is the nature of the image formed by the plane mirror? Answer: Virtual and erect
Question 11. Where is the image formed in a plane mirror? Answer: Behind the mirror
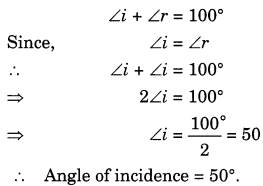
Question 13. What is yellow spot? Answer: It is highly light sensitive spot for seeing things with highest clearness.
Question 14. Give an example of night bird. Answer: Owl
Question 15. What do we call the image that cannot be obtained on a screen? Answer: Virtual
Question 16. Show mathematically, the first law of reflection. Answer: ∠i = ∠r

Question 19. How many colours are there in a spectrum of white light? Answer: Seven
Question 20. Name the scientist who studied that if a white light is passed through a prism, it splits into different colours. Answer: Sir Issac Newton
Question 21. Name the spot inside the human eye where the image is not visible. Answer: Blind spot
Question 22. Name the liquid found between the cornea and lens. Answer: Aqueous humour
Question 23. Name the liquid found between the lens and the retina. Answer: Vitreous humour
Question 24. Define the incident ray. Answer: The ray of light striking the surface is called an incident ray.
Question 25. Define angle of reflection. Answer: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle of reflection.
Light Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1. Define light. Answer: Light is defined as a form of energy that stimulates sight and makes things visible.
Question 2. What is reflection? Answer: The bouncing back of light into the same medium after it falls on a surface is called reflection.
Question 3. What is a mirror? Answer: A piece of glass with a shiny metal-covered at back, that reflects light, producing an image of the object in front of it is known as mirror.
Question 4. State the two laws of reflection. Answer: The two laws of reflection are:
- The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal all lie in the same plane.
Question 5. How do we see various objects? Answer: We see various objects due to reflection. As we know all surface reflect light, when light falls on any object, it reflects the light. The reflected light reaches our eyes and we are able to see the object.
Question 6. What do you mean by reflected ray? Answer: The ray of light which is returned back into the same medium after the incident ray strikes the surface ’ is called reflected ray.
Question 7. What is irregular reflection? Answer: Irregular reflection is defined as the reflection of light from an uneven surface. In irregular reflection, the reflected beam is not parallel.
Question 8. List the characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror. Answer: The characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror are:
- It is virtual.
- It is erect.
- It is of same size as the object.
Question 9. What is lateral inversion? Answer: The phenomenon of changing left side to right and right side to left by the mirror while forming image is called lateral inversion.
Question 10. What is the far point and near point of the human eye with normal vision? Answer: In optics, the farthest and closest point at which an object can be brought into focus by the eye are called far point and near point of the eye respectively. The far point of the human eye with normal vision is infinity. The near point of the human eye with normal vision is 25 cm.
Question 11. What is aqueous humour? Answer: The space between the cornea and lens is filled with a liquid called the aqueous humour.
Question 12. Differentiate between rod and cone cells. Answer: Rods are the rod-shaped cells present in the retina of an eye which are sensitive to dim light whereas cones are the cone-shaped cells present in the retina of the eye which are sensitive to bright light.
Light Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Type
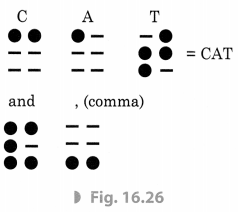
Braille system has 63 dot patterns or characters. Each character represents a letter, a combination of letters, a common word or a grammatical sign. Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of three dots each. Patterns of dots to represent some English letters and some common words are shown in Fig. 16.26.
These patterns when embossed on Braille sheets help visually challenged persons to recognise words by touching. To make them easier to touch, the dots are raised slightly. Visually challenged people learn the Braille system by beginning with letters, then special characters and letter combinations. Methods depend upon recognition by touching. Each character has to be memorised. Braille texts can be produced by hand or by machine. Typewriter-like devices and printing machines have now been developed.
Question 2. Explain the phenomenon of dispersion of light. Answer: Dispersion is defined as the phenomenon of splitting of white light into different colours on passing through a transparent medium such as prism. When white light is passed through a prism, it splits into seven colours. It is observed that the colours are in the following order: Violet (V), Indigo (I), Blue (B), Green (G), Yellow (Y), Orange (O) and Red (R). The order of colours can be remembered by the acronym VIBGYOR. This coloured band is called spectrum of white light.
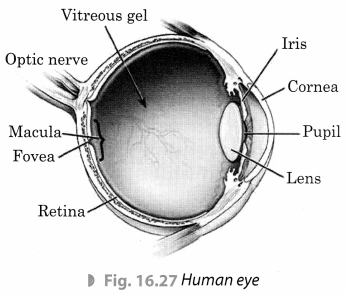
- The first part that is bulged outward is called ‘cornea. It protects the eye.
- Behind the cornea, the coloured part of the eye, iris is present. It controls the size of the pupil.
- Pupil is a small opening in the cornea which allows the light to enter the eye.
- Behind the iris, eye lens is present which is a convex lens. It focus the image on retina, by bending the light rays.
- Retina is the inner back surface of the eye which acts as a screen to form image. It is sensitive to light.
- The sensation of the image formed on the retina is carried to the brain by the optic nerve.
- Optic nerve is connection between the eye and the
Question 4. Write the ways to protect your eyes. Answer: Eyes are very delicate organ that enable us to see this colourful world. Thus, we must protect our eyes and take proper care of them. Following are the ways to protect the eye:
- Always sit straight while reading or writing.
- Never read while walking or lying down.
- Wash your eyes frequently with clean water.
- Never read in the dim or too much bright light.
- Never rub your eyes with hands.
- Never bring the book too close to your eyes.
- Eat foods rich in vitamin A.
Question 5. Explain some common eye defects in human. Answer: Some eye diseases are: (i) Cataract: A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognising faces. Cataracts are the cause of half of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataract is treated by replacing the opaque lens with a new artificial lens.
(ii) Myopia: Near-sightedness or myopia, is the most common refractive error of the eye. Myopia occurs when the eyeball is too long, relative to the focusing power of the cornea and lens of the eye. This causes light rays to focus at a point in front of the retina, rather than directly on its surface. It can be corrected using spectacles made of concave lens.
(iii) Hypermetropia: Hypermetropia or long-sightedness occurs when eyeball is too short or the cornea or crystalline lens does not refract the light enough. This lead to formation of the image of a nearby object behind the retina. A hypermetropic person may have blurred vision when looking at objects close to them, and clearer vision when looking at objects in the distance. By placing a convex (plus powered) lens in front of a hypermetropic eye, the image is moved forward and focuses correctly on the retina.
(iv) Astigmatism: It is a defect in the eye or in a lens caused by a deviation from spherical curvature, which results in distorted images, as light rays are prevented from meeting at a common focus. It can be corrected by using a convex lens or concave lens or both.
Light Class 8 Extra Questions HOTS
Question 1. What is power of accommodation? Answer: The process by which the ciliary muscles change the focal length of an eye lens to focus distant or near objects clearly on the retina is called power of accommodation.
Question 2. How does large cornea and a large pupil in the eyes of the nocturnal birds help them? Answer: Large cornea and a large pupil allow more light to enter their eyes and they can see objects even in faint light.
Question 3. What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object? Answer: Convex lens is there in our eyes. It forms image of an object on the retina.
Question 4. Boojho planned an activity to observe an object A through pipes A (Object to be seen) as shown in the given figure, so that he could see objects which he could not directly see.
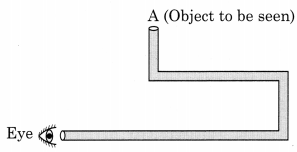
Light Class 8 Extra Questions Value Based (VBQs)
Question 1. While playing, something entered into Somya’s eye. She immediately washed her eye with cold water. But as the irritation persisted, she immediately reported to her class teacher. Her class teacher took her to an eye doctor.
(a) What should be done if some foreign particles enter your eyes? (b) Why is it not advised to rub your eyes when there is an eye irritation due to foreign particles? (c) Do you think Somya was right in her action? (d) What value of Somya is seen here? Answer: (a) We must do the following things:
- Restrict eye movement
- Shut the eyelid
- Do not rub eyes
- Try to clean it with splash of clear water
- Contact eye doctor immediately.
(b) Foreign object may cause abrasions or scratches on our cornea or rubbing. It may also cause bleeding of cornea. (c) Yes. (d) She is intelligent, knowledgeable and aware of such kind of small accidents.

PhysicsTeacher.in
High School Physics + more
Light Class 8 Numericals – solved numerical questions
Last updated on July 4th, 2023 at 02:07 pm
In this post, we will solve Numerical problems based on the Light chapter of class 8 science . Here, first, we will go through the law of reflection & related formulas, and then attempt the numerical questions. Solution & answer is given for all the numerical questions.
Formulas Used
1 ] According to the law of reflection , Angle of incidence <i = Angle of reflection <r 2] Angle of incidence = angle between the normal and incident ray 3] Angle of reflection = angle between the normal and reflected ray 4] Angle between Normal and plane mirror = 90 0
Light Class 8 Numericals – Questions and Answers
1. If the reflected ray makes an angle of 600 with the normal, what angle must the incident ray make with the normal?
The angle of reflection = <r = 60 0 . The angle of incidence = <i =?
According to the law of reflection, <i = <r But r = 60 0 Hence, <i= 60 0 The incident ray will make an angle of 60 0 with the normal.
2. If the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 90 0 , what are the values of the angle of incidence and angle of reflection?
Given: The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 90 0 . i.e. <i + <r = 90 0 ………….(1) According to the law of reflection, <i = <r ………….(2)
<i + <i = 90 0 =>2 <i = 90 0 So, <i= 45 0 The angle of incidence is 45 0 and hence, the angle of reflection is also 45 0 .
3. The angle between the plane mirror and incident ray is 35 0 , what is the angle of incidence and angle of reflection?

To solve this numerical the above figure will be helpful.
The angle between the plane mirror and the incident ray is 35 0 So, the angle between the normal and incident ray is = 90 0 – 35 0 = 55 0 This is actually the angle of incidence. According to the law of reflection, the angle of reflection = angle of incidence = 55 0 Answer: angle of reflection = angle of incidence = 55 0
4. What angle will the reflected ray make with the mirror if the angle of incidence is 40 0 ?
The angle of incidence = 40 0 So, the angle of reflection = 40 0 The angle of reflection = angle between the reflected ray and the normal = 40 0 So, the angle between the reflected ray and the mirror = 90 0 – 40 0 = 50 0
Related Posts:
- Lens Numericals class 10 | Thin lens numerical solved
- Numericals of Light Class 10
- List of Tutorials on Light (class 9 and 10 Physics-chapters on Light )
- Harder Numerical problems based on SNELL’S LAW - in Light chapter physics
- Real and Apparent depth Numerical problem - solved
- Numerical based on Lens Makers' equation - solved

Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light MCQ with Answers
Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Answers is available here in PDF format. CBSE Class 8 Science Light Objective Questions helps the students to understand the concepts thoroughly and to score good marks. Practising these MCQs will help you to answer every question that is being asked in the exams.
At Study Path, you can download PDF of Multiple Choice Questions for Class 8 Chapter 16 Light with Answers. We prepared these MCQs on the basis latest exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 8 Science Light MCQs before the exam to know their preparation level.

Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Question 1. A smooth shining surface, which rebounds the light back in same or in different direction, is called
(a) a mirror (b) a lens (c) reflection of light (d) point of incidence
Answer: (a) a mirror
Question 2. Beam of light striking the reflecting surface is called
(a) reflecting ray (b) incident ray (c) refracted ray (d) normal ray
Answer: (b) incident ray
Question 3. Band of seven colours is called
(a) VIBGYOR (b) spectrum (c) dispersion (d) reflection
Answer: (b) spectrum
Question 4. Front bulged part of the eyeball is called
(a) cornea (b) choroid (c) pupil (d) retina
Answer: (a) cornea
Question 5. Which one of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
(a) Cones are sensitive to dim light (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light (c) Rods are sensitive to bright light (d) Rods can sense colour
Answer: (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light
Question 6. In case of reflection of light, the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of reflection (r) are related as
(a) i = r (b) i < r (c) i > r (d) no definite relation
Answer: (a) i = r
Question 7. Name the type of mirror used as a backview mirror.
(a) Plane mirror (b) Concave mirror (c) Convex mirror (d) Any of these
Answer: (c) Convex mirror
Question 8. Visually impaired people can read and write using
(a) electronic writer (b) digital pens (c) braille system (d) hearing aids
Answer: (c) braille system
Question 9. The image formed by a camera and a simple microscope are respectively
(a) real and real (b) real and virtual (c) virtual and virtual (d) virtual and real
Answer: (b) real and virtual
Question 10. What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90° to the incident ray?
(a) 60° (b) 45° (c) 90° (d) 180°
Answer: (b) 45°
Question 11. The splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours is called
(a) refraction (b) dispersion (c) deviation (d) reflection
Answer: (b) dispersion
Question 12. The defect due to which a person is not able to see the distant objects clearly:
(a) Myopia (b) Hypermetropia (c) Cornea (d) Cataract
Answer: (a) Myopia
Question 13. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by
(a) eye lens (b) cornea (c) iris (d) ciliary muscle
Answer: (c) iris
Question 14. Myopia can be corrected by using a
(a) concave lens (b) convex lens (c) opaque lens (d) micro lens
Answer: (a) concave lens
Question 15. Light enters the eye through
(a) eye lens (b) pupil (c) cornea (d) retina
Answer: (c) cornea
Question 16. If the angle of incidence of light falling on a plane mirror is 30°, what will be the angle of reflection?
(a) 90° (b) 60° (c) 30° (d) 0°
Answer: (c) 30°
Question 17. When we stand in front of our dressing table, our left hand seems to be right and right seems to be left. This is called
(a) Left-right confusion (b) Lateral inversion (c) Up -side down phenomenon (d) mirage
Answer: (b) Lateral inversion
Question 18. Light passing through a prism splits into seven colours. This is called
(a) Dispersion (b) Dissolution (c) Division (d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Dispersion
Question 19. Rainbow is a natural phenomenon showing
(a) Reflection (b) Deflection (c) Dispersion (d) Diversion
Answer: (c) Dispersion
Question 20. In the retina of the eye, the area having no sensory cells is called
(a) iris (b) Blind spot (c) cornea (d) Dark spot
Answer: (b) Blind spot
Question 21. If light falls perpendicularly on a plane mirror, what will be the angle in which it will be reflected?
(a) 45° (b) 90° (c) 180° (d) 360°
Answer: (c) 180 degrees
Question 22. Which of the following is not a luminous object?
(a) sun (b) candle (c) moon (d) Tube light
Answer: (c) moon
Question 23. To make a kaleidoscope we require
(a) Three plane mirrors (b) Four plane mirrors (c) Three glass sheets (d) Four glass sheets
Answer: (a) Three plane mirrors
Question 24. In our eye _______ cells can sense colour
(a) Rod (b) Cone (c) Both rod and cone (d) Neither rod nor cone
Answer: (b) Cone
Question 25. An owl can see clearly at night but not day time because it has
(a) More rods and few cones (b) Less rod and more cones (c) More rods and more cone (d) Less rods and less cones
Answer: (a) More rods and few cones
At Study Path, you can also learn more about science chapter 16 Light by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Important Questions and Extra Questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT 8 Science Exemplar
- Chapter 16: Light
NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions for Chapter 16 - Light
Ncert exemplar solutions class 8 science chapter 16 – free pdf download.
The NCERT Exemplar Solution for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light provides you with details on the types and the level of difficulty of questions that are usually asked in the CBSE Class 8 examination and other competitive examinations. Hence, it is important for students to refer to the NCERT Exemplar Solution . The exemplar has a variety of questions like multiple-choice questions, match the following, fill in the blanks, short answer questions, very short answer questions, long answer questions and numerical problems.
Light is electromagnetic radiation within a certain portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. In this chapter, students will learn about the different properties of light and their sources. Along with these, they will be introduced to the laws of reflection and how a human eye works or how eyes see images. Solve and practise higher-order thinking questions of this chapter from NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light.
Download the PDF of the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions for Chapter 16 – Light

Access Answers to the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 – Light
Multiple choice questions.
1. Part of the eye which controls the light entering is called
Answer is (a) iris
Explanation:
Iris is a dark muscular structure exists behind the cornea. Its function is to control the entry of light.
2. We can see a non-luminous object when light:
(a) emitted by the object falls on the eye.
(b) is reflected from the object towards our eye.
(c) completely passes through the object.
(d) gets completely absorbed by the object.
The answer is (b) is reflected from the object towards our eye.
3. Light is falling on surface S1, S2, S3 as shown in Fig.16.1.

Surfaces on which the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection is/are
(a) S1 only
(b) S1 and S2 only
(c) S2 and S3
(d) all the three surfaces
The answer is (d) all the three surfaces
Laws of reflection are always followed irrespective of the surface of the object hence the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
4. A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of the eye with respect to the position of the bulb is shown in Fig.16.2 as A, B, C and D. In which position mirror will be visible?

Answer is (a) A
In case of A ray of light from A strikes mirror and gets reflected back to make an angle of incidence and angle of reflection equal.
5. A small hole P is made in a piece of cardboard. The hole is illuminated by a torch as shown in Fig. 16.3. The pencil of light coming out of the hole falls on a mirror.

At which point should the eye be placed so that the hole can be seen?
The eye should be placed at position A because the hole can be seen only when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
6. Two mirrors A and B are placed at right angles to each other as shown in Fig.16.4.

A ray of light incident on mirror A at an angle of 25 0 falls on mirror B after reflection. The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B would be
Answer is (c) 65 0
The angle of reflection for the ray reflected from mirror B will be 65° because reflected ray from mirror A forms incident ray on mirror 6 and then reflected back by an angle of 65°.
7. Which of the following statements is correct regarding rods and cones in the human eye?
(a) Cones are sensitive to dim light.
(b) Cones are sensitive to bright light.
(c) Rods are sensitive to bright light.
(d) Rods can sense colour.
The answer is (b) Cones are sensitive to bright light.
Cones are sensitive to bright light hence they sense the colour whereas rods are sensitive to dim light and they cannot sense colour.
8. In the figure of the human eye (Fig.16.5), the cornea is represented by the letter

Answer is (c) C
Very Short Answer Questions
9. Name the part of the eye which gives colour to the eyes
Iris the part of the eye which gives colour to the eyes.
10. Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred. What could be the reason for it?
Persistence of vision is the reason for the blurred vision of Boojho while waving his hand very fast in front of his eyes, observes that his fingers appear blurred.
11. How many times is a ray of light reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other?
An infinite number of times a ray of light reflected by two plane mirrors placed parallel and facing each other.
12. The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is 60°. What is the value of the angle of incidence?
Answer is 30°.
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Since Angle of incident ray+ Angle of reflected ray is 60°.
The angle of incidence = 30°
13. The distance between the object and its image formed by a plane mirror appears to be 24 cm. What is the distance between the mirror and the object?
The distance will be 12 cm
Object +image formed =24 cm
Object +mirror =12 cm
Short Answer Questions
14. What happens to light when it gets dispersed? Give an example.
When the light gets dispersed it is split into its constituent colours. Ex: rainbow.
15. Draw Fig.16.6 showing the position of the plane mirror. Also, label the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it.

16. Look at Fig.16.7. Can the image of the child in it be obtained on a screen?

No, the image of the child cannot be obtained on a screen because the image is a virtual image.
17. Eyes of the nocturnal birds have large cornea and a large pupil. How does this structure help them?
They can see objects even in the faint light. As a large pupil and large cornea allow more light to enter their eyes.
18. What kind of lens is there in our eyes? Where does it form the image of an object?
Our eyes have a convex type of lens and the image is formed on the retina.
19. Which part of the eye gets affected if someone is suffering from cataract? How is it treated?
If a person is suffering from cataract their eye lens will be cloudy. Cataract can be treated by replacing the opaque lens by an artificial lens.
Long Answer Questions
20. Boojho planned activity to observe an object A through pipes as shown in Fig. 16.8, so that he could see objects which he could not directly see.
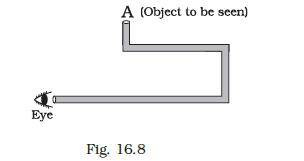
(a) How many mirrors should he use to see the objects?
(b) Indicate the positions of the mirrors in the figure.
(c) What must be the angle with respect to the incident light at which he should place the mirrors?
(d) Indicate the direction of the rays in the figure.
(e) If any of the mirrors are removed, will he be able to see the objects?
a) Three mirrors should he use to see the objects.
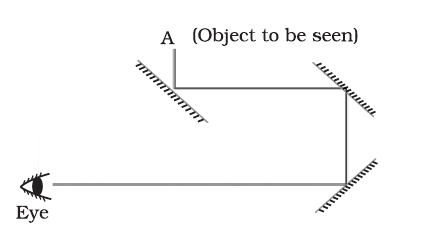
e) He will not be able to see the objects.
21. There is a mistake in each of the following ray diagrams given as Fig. 16.9 a, b, and c. Make the necessary correction (s).

The Fig. in all the three cases after correction should be as in the given figure

22. Explain the process which enables us to perceive motion in a cartoon film.
Carton movie is actually a projection of a static picture. 24 pictures per second are shown in a specific order which gives us the perception of movement.
23. How is the phenomenon of reflection used in making a kaleidoscope? What are the applications of a kaleidoscope?
The kaleidoscope gives a number of images formed by reflection from the mirrors inclined to one another. Designers and artists use kaleidoscope to get ideas for new patterns to design wallpapers, Jewellery and fabrics.
24. Fig. 16.10 shows the word REST written in two ways in front of a mirror. Show how the word would appear in the mirror.

25. Write down the names of parts of the eye in the blank spaces shown in Fig. 16.10.

1. Ciliary muscle
6. Optic Nerve
The Important Topics of the NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light
- What Makes Things Visible
- Laws of Reflection
- Regular and Diffused Reflection
- Reflected Light Can be Reflected Again
- Multiple Images
- Sunlight – White or Coloured
- What Is Inside Our Eyes
- Care of the Eyes
- Visually Challenged Persons Can Read and Write
- What Is the Braille System?
BYJU’S provides comprehensive study materials , notes, video and animation lessons, sample papers and books for CBSE students of all classes. We also keep track of the progress each student makes. After assessing the situation, regular feedback is given. We also have a responsive support team to clear all doubts. Students can raise all their queries on any subject.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16
How is the phenomenon of reflection used in making a kaleidoscope what are the applications of a kaleidoscope covered in chapter 16 of ncert exemplar solutions for class 8 science, what are the important topics covered in chapter 16 of ncert exemplar solutions for class 8 science, are ncert exemplar solutions for class 8 science chapter 16 sufficient for the exam preparation.
| NCERT EXEMPLAR Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Notes of Ch 16 Light| Class 8th Science
Study material and notes of ch 16 light class 8th science.

Contact Form

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Very Short Answer Type Question. Question 1: Name a device which works on the reflection of reflected light. Answer: Periscope. Question 2: Name the point inside the human eye where no vision is possible. Answer: Blind spot. Question 3: Name an eye disease caused by the deficiency of vitamin A in the diet.
Short Answer Type Questions. 1: Define light. Discuss its importance. Answer: Light is an electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has a wavelength in the range of about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm between the invisible infrared.
Light Class 8 Notes - Chapter 16. Introduction to Light Laws of Reflection Regular and Diffused Reflection Dispersion Human Eye Visual Defects Seeing Sans Eyes Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light. According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 13.
Below are a few questions and their solutions from our question bank of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 16. Question 1. Image formed in a plane mirror undergoes _______________. Answer 1. lateral inversion. The reversal of a mirror image, where the object's right side appears on the left side behind the mirror, is known as lateral ...
Name the liquid found between the cornea and lens. Answer: Aqueous humour. Question 23. Name the liquid found between the lens and the retina. Answer: Vitreous humour. Question 24. Define the incident ray. Answer: The ray of light striking the surface is called an incident ray. Question 25.
Study Important Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Light. 1. When all the parallel rays reflected from a rough or irregular surface are not parallel, the reflection is known as ___________. A. multiple reflections B. regular reflection.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light are given below. Here we have provided the best and error-free answers to all the exercise questions that will strengthen your foundation in science. Solving NCERT questions will assist you in grasping the content in the Crop Production and Management chapter in a better way.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - 1 Mark Questions and Answers. Question 1. Define dispersion of light. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007] Answer: Splitting up of white light into seven colours when it passes through a glass prism is known as dispersion of light. Question 2.
It has everything you will need. Check out the NCERT Solutions, Notes, Experiments, Activities and some Extra Questions for Chapter 16 Class 8 Science - Light.Everything is provided free of cost, and is the best education material available for Light Class 8.In this chapter, we will study -How do weseeobjects?What arevisible and in.
Chapter 16 Light Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions will prepare yourself well before examinations and help in improving the student's experience. These are helpful in building a great foundation of concepts and make easy for the students to understand basics. It can be used to enrich knowledge and make lessons for learners more exciting.
Chapter 13 Light Class 8 - NCERT Science Solutions. Exercises Question 1. ... Justify your answer in each case. (a) Polished wooden table (b) Chalk powder (c) Cardboard surface ... Question 8. Image formed by a plane mirror is. virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged. virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object. ...
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question.
8 minute read. In chapter 16 of Class 8 NCERT Science book, we find the topic of 'Light'. The chapter explains light, its properties and its uses. It is another enjoyable chapter that is informative as well. In this blog, we will read some of the important notes on Class 8 Light. Also Read: Class 8 Science.
1. What is the Band of seven colours? 2. ______ is not a source of light. 3. If light falls perpendicularly on a plane mirror, at what angle will it be reflected? 4. The difference in colour of the eye is caused by the difference in____. Important Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light are provided here which can help the students to ...
Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light. NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) Question 1 ... Following the laws of reflection of light, in case A, when a ray of light from the bulb strikes the mirror M, it will get reflected back such that the angle of incidence is equal to ...
Class 8 Science NCERT Solutions for Chapter 16 Light - Summary The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 are created by subject experts according to the latest CBSE syllabus. It consists of answers to the textbook questions, extra questions, exemplary problems, worksheets and questions from the previous years' question papers.
Answer: Irregular reflection is defined as the reflection of light from an uneven surface. In irregular reflection, the reflected beam is not parallel. Question 8. List the characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror. Answer: The characteristics of an image formed in a plane mirror are: It is virtual.
On this page, you will find notes, questions, and answers to class 8 science chapter 13 Light. These Light class 8 notes, explanations, examples, and questions and answers are according to CBSE and the NCERT textbook. If you like the study material, feel free to share the link as much as possible.
Solution: The angle of incidence = 40 0. So, the angle of reflection = 40 0. The angle of reflection = angle between the reflected ray and the normal = 40 0. So, the angle between the reflected ray and the mirror = 90 0 - 40 0 = 50 0. In this post, we will solve Numerical problems & questions based on the Light chapter of class 8 science ...
Question 1. A smooth shining surface, which rebounds the light back in same or in different direction, is called. Answer: (a) a mirror. Question 2. Beam of light striking the reflecting surface is called. Answer: (b) incident ray. Question 3. Band of seven colours is called. Answer: (b) spectrum.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 16 - Free PDF Download. The NCERT Exemplar Solution for Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light provides you with details on the types and the level of difficulty of questions that are usually asked in the CBSE Class 8 examination and other competitive examinations. Hence, it is important for students to refer to the NCERT Exemplar Solution.
10 Nov, 2017. Study Material and Notes of Ch 16 Light Class 8th Science. Topics in the chapter. • Introduction. • Laws of reflection. • Types of reflections. • Image formation by a plane mirror. → Multiple Reflections.