Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
User Experience
- User Experience Research

See how XM for Customer Frontlines works
User experience (ux) research: definition and methodology.
17 min read To build outstanding products and services for your customers, you need a thorough understanding of who they are, what they need and where their pain points and priorities lie. UX research helps you fully step into your customers’ shoes.
What do we mean by user experience?
User experience (UX) is a customer’s-eye view of your business as it relates to completing tasks and using interactive platforms and services.
It’s closely tied to the idea of customer experience (CX) , but rather than being a holistic view of your brand, it’s more focused on utility and usability testing – the hands-on side of things. You can think of UX as a sub-discipline of CX .
For example, CX research might consider how customers perceive a company’s customer service levels and how confident they feel in having their issues resolved. Meanwhile, UX research would focus on how successfully those customers navigate a self-service website, whether the language on that site is clear and how easy it is to use.
Free eBook: The essential website experience & UX playbook
What is user experience (UX) research?
User experience (UX) research is about diving deep into how customers interact with your brand on a practical, functional level, and observing how easily they can complete their tasks and meet their goals.
User research is the process of discovering the behaviors , motivations, and needs of your customers through observation, task analysis, and other types of user feedback . It can involve working directly with members of your target audience through UX testing sessions, remote session observation using digital tools, surveys to collect user feedback, and many more UX research methods and techniques.
Why is UX research important?
So what exactly is the value of user experience research? After all, you understand your business and its workings better than anyone. How can uninformed external users help you learn more?
The fresh perspective of your end-users is exactly why UX research is so valuable. Because they’re not already immersed in your language, processes, and systems, user testing participants are in the best position to help you see where things might be confusing to a newcomer who isn’t involved with your business.
Better yet, they can show you where confusion or frustration might lead a new or potential customer to miss out on product benefits, fail to convert, or even give up and look toward your competitors instead.
In areas like new product design and development , user research allows you to head off potential issues with products and services before they even hit the shelves. You can design the product correctly the first time, instead of having to fix it later when customers are unhappy.
Simply put, UX research is critical because it keeps you from wasting time, money, and effort designing the wrong product or solution. It’s valuable for all areas of your business and yields clear benefits for your product, your users, and your bottom line.
- Product benefits By asking your customers for direct feedback about a potential product, you can discover how and when customers prefer to use a product, what pain points your product will solve, and how to improve your product design .
- User benefits UX research is unbiased feedback, straight from the most valuable source: your customers. Because this type of research is not biased by investors, company leaders, or outside influences, it is the best resource for getting actionable product feedback.
- Business benefits Knowing what your users value helps you spend less time and money fixing flawed designs, speeds up the product development process , and increases customer satisfaction.
UX research helps brands and organizations to:
- Understand how users experience products, websites, mobile apps, and prototypes
- Evaluate and optimize prototypes and ideas based on UX research discoveries – and nail the design and experience early in a product’s life cycle
- Unearth new customer needs and business opportunities
- Find and fix hidden problems with products and services that arise in real-world use cases
- Make informed decisions through the product development process by testing various aspects of product designs
- Provide user experiences that outperform other businesses in your sector ( UX competitor research )
- Understand each user interaction across complete customer journeys
- Build a richer, more useful picture of your target audiences for better marketing and advertising
What’s the ROI of performing UX research?
The ROI of UX research is tricky to pin down because there often isn’t a direct, easy-to-spot correlation between time spent on it and resulting revenue. UX research can and does drive revenue, but it more directly influences metrics that show customer satisfaction, customer retention, and behavioral goals like user signups.
A simple way to draw a straight (if basic) line between UX research and its associated ROI is to calculate your conversion rate, where ‘conversion’ simply means completing the action you had in mind:
Number of people who took your desired action
————————————————————— x 100
Total visitors/users
That percentage can be calculated and revisited over time to see how UX changes resulting from your research are having an effect.
Generally, when we talk about ROI, we’re talking about the highest possible rates of return you can attribute to an investment. But – while PWC research suggests that ROI on UX research can rise to as high as 301% – it’s better not to get caught up in absolutes with operational data like revenue.
Instead, it’s worth thinking more about the benefits that come out of tracking human behavior associated with improving your UX in general.
For example, IBM research states that 3 out of 5 users think that a positive user experience is more influential than strong advertising, while Forrester Research estimates that as many as 50% of potential sales fall through because users can’t find the information they need.
Thorough UX research can also cut a project’s development time by up to 50% .
Ultimately, when trying to track the ROI of your time spent doing quantitative and qualitative research on UX, you want to look at behavior and sentiment. If your main goal is website use, you should notice a decline in bounce rate as a sign of positive ROI. If you sell services, run regular CSAT surveys to determine how satisfied customers are with everything.
You might also find that data in unusual places. For example, if you spot a decline in chatbot requests around how to do or perform certain actions, or for information, then you know your new UX implementations are working as desired.
Those kinds of behavioral data points will shine a light on how worthwhile your UX research has been more readily than changes in revenue.
User experience research methods
The type of UX research techniques you choose will depend on the type of research question you’re tackling, your deadline, the size of your UX research team, and your environment.
There are three research dimensions to consider as you decide which methods are best for your project:
Attitudinal and behavioral
“Attitudinal” refers to what people say, while “ behavioral ” refers to what people actually do – and these are often very different. Attitudinal research is often used in marketing because it measures people’s stated beliefs and needs. However, in product design and user experience research, what people do tends to be more relevant.
For example, A/B testing shows visitors different versions of a site at random to track the effect of site design on conversion and behavior.
Another behavioral method is eye tracking, which helps researchers understand how users interact and visually engage with the design of an interface by following their gaze.
Qualitative and quantitative methods
Quantitative UX research studies collect and analyze results, then generalize findings from a sample to a population. They typically require large numbers of representative cases to work with and are structured in their approach.
Quantitative research uses measurement tools like surveys or analytics to gather data about how subjects use a product and are generally more mathematical in nature. This type of inquiry aims to answer questions like ‘what,’ ‘where’ and ‘when’.
Qualitative research methods, on the other hand, gather information about users by observing them directly, as in focus groups or field studies.
Qualitative research aims to understand the human side of data by gaining a sense of the underlying reasons and motivations surrounding consumer behavior. It tends to use small numbers of diverse (rather than representative) cases, and the data collection approach is less structured. Qualitative methods are best suited to address the ‘how’ or ‘why’ of consumer behavior.
Qualitative UX research methods
Several UX research methodologies can help UX researchers answer those big ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions, and influence the design process of any product or service you’ve got cooking. Here are just a few …
1. Participatory design
In participatory design, people are asked to draw or design their own best-case version of the tool, product, or service in question. This gives UX researchers the ability to ask qualitative questions about why specific choices have been made. If multiple participants make similar choices, it’s easy to spot patterns that should be adopted.
You might ask participants how they would redesign your website. While their responses will naturally vary, you might spot that several of them have moved your site’s navigation to a more prominent spot, or have moved the checkout from the left of the screen to the right.
2. Card sorting
Card sorting involves giving participants a range of cards that represent business-specific topics and asking them how they would sort them into groups. UX researchers are then able to probe into why their audience might group certain things, and make changes to existing offerings as a result.
If you have a wide range of products and solutions, card sorting would be a useful way to gauge how your target audience would naturally bucket them on your website. A furniture seller, for example, might use this technique to find that people are naturally inclined to group items by room, rather than by furniture type.
3. Diary studies
If you’d like to know how the UX of your product or service varies over time or throughout the length of its use, a diary study can help. Here, participants are given a way to record their thoughts as they set about using the product or service in question, noting things that occur to them as they go. This is useful as it provides real-world insight over a longer period than a one-off focus group.
Giving people access to an early build of an app and asking them to keep usability testing notes can highlight pain points in the user interface. In a one-off focus group, having to tap three times to get to an oft-used screen might seem fine – whereas participants are more likely to find it annoying in the day-to-day. This kind of longer-term usability test can provide really valuable insights.
Both quantitative and qualitative UX research methodologies can be useful when planning the design and development of your brand presence, as well as for usability testing when it comes to product and service design.
Context-of-use
By collecting and analyzing information about users, the intended use of the application, the tasks they perform with the application, and the technical constraints presented by the application, context-of-use analysis allow UX researchers to better understand the overall experience.
Typically, context-of-use analysis data is collected through research surveys, focus groups, interviews, site visits, and observational studies.
Context-of use-analysis is one method for identifying the most important elements of an application or product in the context of using that application or product. This type of UX research is typically done early in the product lifecycle and continued as data identifies which components of the product and UX are most critical.
Types of user research tools
There are many types of user research methods for discovering data useful for product design and development. Below are some common examples of tools user experience researchers may use to gather information and draw insights into mental models, or users’ thought processes.
UX research surveys or questionnaires can discover data at scale through in-person or remote polling, with specific questions designed to collate useful information about user experience.
User groups or focus groups are a form of a structured interview that consults members of a target audience on their experience, views, and attitudes towards the product or solution. They usually involve neutral parties, such as a moderator and note-taker, and are led by a researcher who asks open-ended questions focused on specific aspects of an investigation.
User interviews are one-on-one structured interviews with a target audience member, led by a UX researcher to understand more about personal experiences with the product. These user interviews can be directed to compare and contrast answers between users, or non-directed, where users lead the conversation.
Ethnographic interviews take place within the target users’ typical environment to get a better context-of-use view. Field studies and site visits are similarly observational in nature, and take place in situ where the product or service is used, but may involve larger groups.
This is not a comprehensive list of research techniques but represents some of the main ways UX researchers might perform usability testing or trial UX design.
When to conduct user experience research
Before launching a new product or service, understanding user preferences that could impact your design or development is key to success. The earlier user experience research is performed, the more effective the end product or service will be, as it should encompass the insights learned about your target audience.
As a product and service’s use and value evolve over its lifecycle, the user experience will change over time. User research should be undertaken on an ongoing basis to determine how to adapt to users’ new needs and preferences.
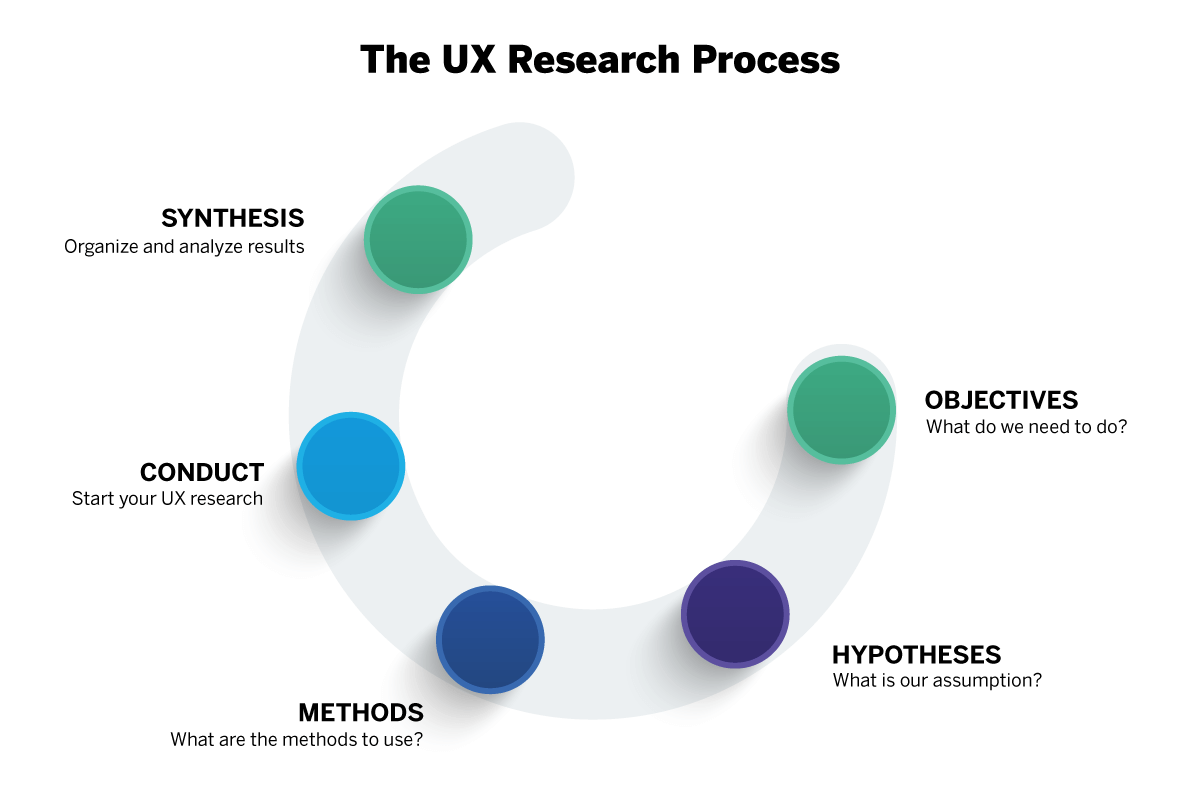
Five basic steps to conducting UX research
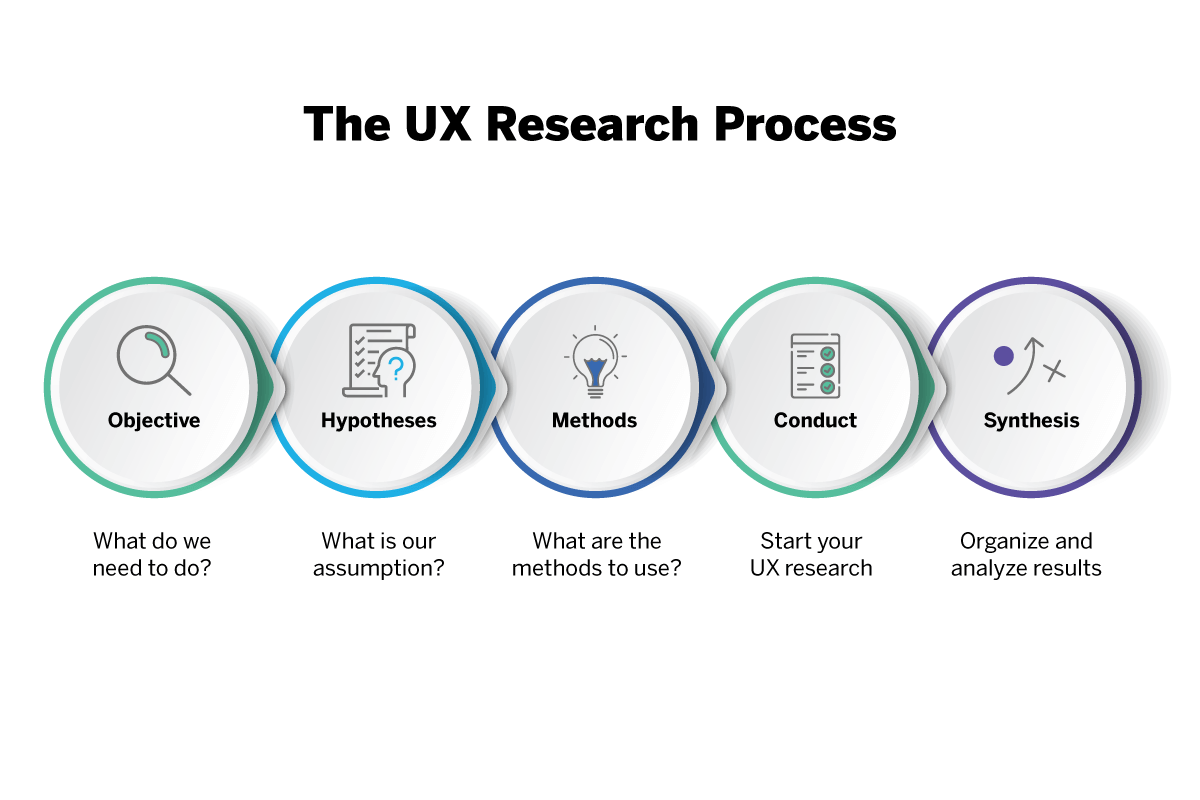
If you’re new to UX research, here’s a step-by-step list of what to consider before you begin your UX testing program:
- Objectives What do you need to find out about your users and their needs?
- Hypothesis What do you think you already know about your users?
- Methods Based on your deadline, project type, and the size of your research team, what UX research methods should you use?
- Process Using your selected UX research method(s), begin collecting data about your users, their preferences, and their needs.
- Synthesis Analyze the data you collected to fill in your knowledge gaps, address your hypothesis and create a plan to improve your product based on user feedback.
Qualtrics makes UX research simple and easy
User experience research and user testing are multifaceted and can involve a lot of both quantitative and qualitative data. To ease the process and make sure it is efficient and scalable, it’s best conducted using a highly responsive platform that allows you to collect data, analyze trends and draw conclusions all in one place.
Whether you need attitudinal or behavioral insights, Qualtrics is your go-to solution for collecting all kinds of UX data and making use of it in the context of your wider CX program .
Conduct in-person studies or send beautifully designed surveys easily and quickly, and view your results via custom dashboards and reports using the most sophisticated research platform on the planet.
Free eBook: The essential website experience & UX playbook
Related resources
User experience 20 min read, user experience surveys 9 min read, ux research tools 8 min read, user analytics 11 min read, rage clicks 11 min read, user experience analytics 10 min read, website user experience 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
The Complete Guide to UX Research Methods
UX research provides invaluable insight into product users and what they need and value. Not only will research reduce the risk of a miscalculated guess, it will uncover new opportunities for innovation.
By Miklos Philips
Miklos is a UX designer, product design strategist, author, and speaker with more than 18 years of experience in the design field.
PREVIOUSLY AT
“Empathy is at the heart of design. Without the understanding of what others see, feel, and experience, design is a pointless task.” —Tim Brown, CEO of the innovation and design firm IDEO
User experience (UX) design is the process of designing products that are useful, easy to use, and a pleasure to engage. It’s about enhancing the entire experience people have while interacting with a product and making sure they find value, satisfaction, and delight. If a mountain peak represents that goal, employing various types of UX research is the path UX designers use to get to the top of the mountain.
User experience research is one of the most misunderstood yet critical steps in UX design. Sometimes treated as an afterthought or an unaffordable luxury, UX research, and user testing should inform every design decision.
Every product, service, or user interface designers create in the safety and comfort of their workplaces has to survive and prosper in the real world. Countless people will engage our creations in an unpredictable environment over which designers have no control. UX research is the key to grounding ideas in reality and improving the odds of success, but research can be a scary word. It may sound like money we don’t have, time we can’t spare, and expertise we have to seek.
In order to do UX research effectively—to get a clear picture of what users think and why they do what they do—e.g., to “walk a mile in the user’s shoes” as a favorite UX maxim goes, it is essential that user experience designers and product teams conduct user research often and regularly. Contingent upon time, resources, and budget, the deeper they can dive the better.

What Is UX Research?
There is a long, comprehensive list of UX design research methods employed by user researchers , but at its center is the user and how they think and behave —their needs and motivations. Typically, UX research does this through observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies.
There are two main types of user research: quantitative (statistics: can be calculated and computed; focuses on numbers and mathematical calculations) and qualitative (insights: concerned with descriptions, which can be observed but cannot be computed).
Quantitative research is primarily exploratory research and is used to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. Some common data collection methods include various forms of surveys – online surveys , paper surveys , mobile surveys and kiosk surveys , longitudinal studies, website interceptors, online polls, and systematic observations.
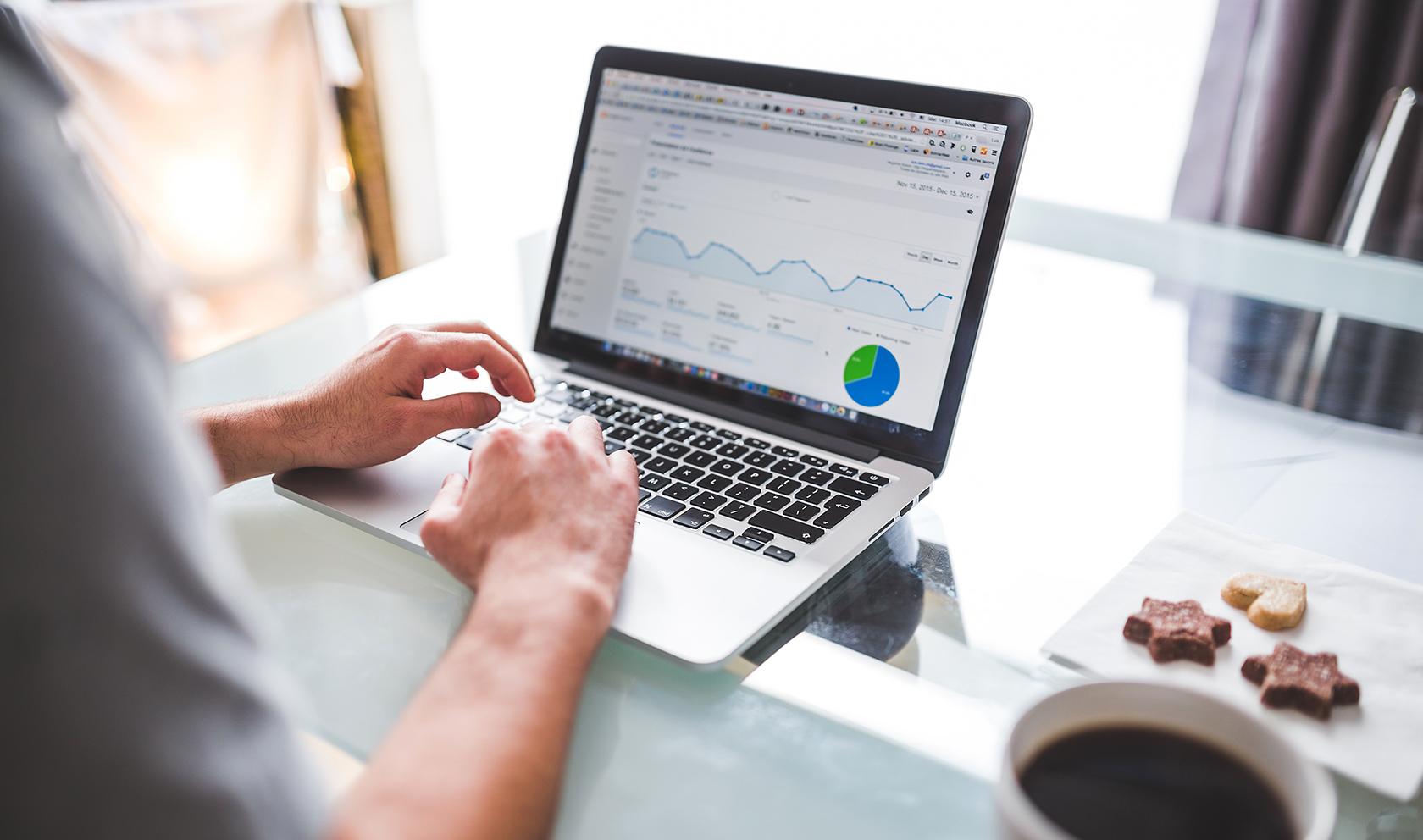
This user research method may also include analytics, such as Google Analytics .
Google Analytics is part of a suite of interconnected tools that help interpret data on your site’s visitors including Data Studio , a powerful data-visualization tool, and Google Optimize, for running and analyzing dynamic A/B testing.
Quantitative data from analytics platforms should ideally be balanced with qualitative insights gathered from other UX testing methods , such as focus groups or usability testing. The analytical data will show patterns that may be useful for deciding what assumptions to test further.
Qualitative user research is a direct assessment of behavior based on observation. It’s about understanding people’s beliefs and practices on their terms. It can involve several different methods including contextual observation, ethnographic studies, interviews, field studies, and moderated usability tests.

Jakob Nielsen of the Nielsen Norman Group feels that in the case of UX research, it is better to emphasize insights (qualitative research) and that although quant has some advantages, qualitative research breaks down complicated information so it’s easy to understand, and overall delivers better results more cost effectively—in other words, it is much cheaper to find and fix problems during the design phase before you start to build. Often the most important information is not quantifiable, and he goes on to suggest that “quantitative studies are often too narrow to be useful and are sometimes directly misleading.”
Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted. William Bruce Cameron
Design research is not typical of traditional science with ethnography being its closest equivalent—effective usability is contextual and depends on a broad understanding of human behavior if it is going to work.
Nevertheless, the types of user research you can or should perform will depend on the type of site, system or app you are developing, your timeline, and your environment.
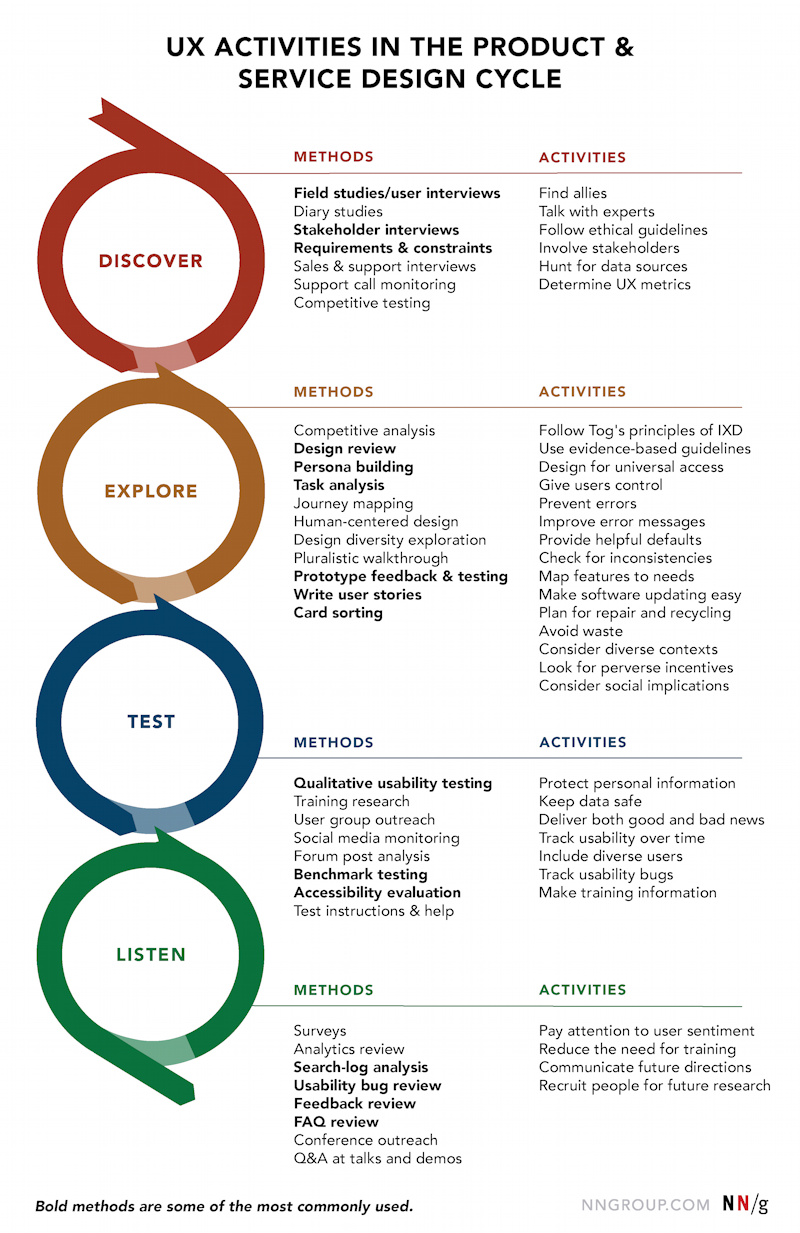
Top UX Research Methods and When to Use Them
Here are some examples of the types of user research performed at each phase of a project.
Card Sorting : Allows users to group and sort a site’s information into a logical structure that will typically drive navigation and the site’s information architecture. This helps ensure that the site structure matches the way users think.
Contextual Interviews : Enables the observation of users in their natural environment, giving you a better understanding of the way users work.
First Click Testing : A testing method focused on navigation, which can be performed on a functioning website, a prototype, or a wireframe.
Focus Groups : Moderated discussion with a group of users, allowing insight into user attitudes, ideas, and desires.
Heuristic Evaluation/Expert Review : A group of usability experts evaluating a website against a list of established guidelines .
Interviews : One-on-one discussions with users show how a particular user works. They enable you to get detailed information about a user’s attitudes, desires, and experiences.
Parallel Design : A design methodology that involves several designers pursuing the same effort simultaneously but independently, with the intention to combine the best aspects of each for the ultimate solution.
Personas : The creation of a representative user based on available data and user interviews. Though the personal details of the persona may be fictional, the information used to create the user type is not.
Prototyping : Allows the design team to explore ideas before implementing them by creating a mock-up of the site. A prototype can range from a paper mock-up to interactive HTML pages.
Surveys : A series of questions asked to multiple users of your website that help you learn about the people who visit your site.
System Usability Scale (SUS) : SUS is a technology-independent ten-item scale for subjective evaluation of the usability.
Task Analysis : Involves learning about user goals, including what users want to do on your website, and helps you understand the tasks that users will perform on your site.
Usability Testing : Identifies user frustrations and problems with a site through one-on-one sessions where a “real-life” user performs tasks on the site being studied.
Use Cases : Provide a description of how users use a particular feature of your website. They provide a detailed look at how users interact with the site, including the steps users take to accomplish each task.

You can do user research at all stages or whatever stage you are in currently. However, the Nielsen Norman Group advises that most of it be done during the earlier phases when it will have the biggest impact. They also suggest it’s a good idea to save some of your budget for additional research that may become necessary (or helpful) later in the project.
Here is a diagram listing recommended options that can be done as a project moves through the design stages. The process will vary, and may only include a few things on the list during each phase. The most frequently used methods are shown in bold.
Reasons for Doing UX Research
Here are three great reasons for doing user research :
To create a product that is truly relevant to users
- If you don’t have a clear understanding of your users and their mental models, you have no way of knowing whether your design will be relevant. A design that is not relevant to its target audience will never be a success.
To create a product that is easy and pleasurable to use
- A favorite quote from Steve Jobs: “ If the user is having a problem, it’s our problem .” If your user experience is not optimal, chances are that people will move on to another product.
To have the return on investment (ROI) of user experience design validated and be able to show:
- An improvement in performance and credibility
- Increased exposure and sales—growth in customer base
- A reduced burden on resources—more efficient work processes
Aside from the reasons mentioned above, doing user research gives insight into which features to prioritize, and in general, helps develop clarity around a project.

What Results Can I Expect from UX Research?
In the words of Mike Kuniaysky, user research is “ the process of understanding the impact of design on an audience. ”
User research has been essential to the success of behemoths like USAA and Amazon ; Joe Gebbia, CEO of Airbnb is an enthusiastic proponent, testifying that its implementation helped turn things around for the company when it was floundering as an early startup.
Some of the results generated through UX research confirm that improving the usability of a site or app will:
- Increase conversion rates
- Increase sign-ups
- Increase NPS (net promoter score)
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Increase purchase rates
- Boost loyalty to the brand
- Reduce customer service calls
Additionally, and aside from benefiting the overall user experience, the integration of UX research into the development process can:
- Minimize development time
- Reduce production costs
- Uncover valuable insights about your audience
- Give an in-depth view into users’ mental models, pain points, and goals
User research is at the core of every exceptional user experience. As the name suggests, UX is subjective—the experience that a person goes through while using a product. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the needs and goals of potential users, the context, and their tasks which are unique for each product. By selecting appropriate UX research methods and applying them rigorously, designers can shape a product’s design and can come up with products that serve both customers and businesses more effectively.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- How to Conduct Effective UX Research: A Guide
- The Value of User Research
- UX Research Methods and the Path to User Empathy
- Design Talks: Research in Action with UX Researcher Caitria O'Neill
- Swipe Right: 3 Ways to Boost Safety in Dating App Design
- How to Avoid 5 Types of Cognitive Bias in User Research
Understanding the basics
How do you do user research in ux.
UX research includes two main types: quantitative (statistical data) and qualitative (insights that can be observed but not computed), done through observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies. The UX research methods used depend on the type of site, system, or app being developed.
What are UX methods?
There is a long list of methods employed by user research, but at its center is the user and how they think, behave—their needs and motivations. Typically, UX research does this through observation techniques, task analysis, and other UX methodologies.
What is the best research methodology for user experience design?
The type of UX methodology depends on the type of site, system or app being developed, its timeline, and environment. There are 2 main types: quantitative (statistics) and qualitative (insights).
What does a UX researcher do?
A user researcher removes the need for false assumptions and guesswork by using observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies to understand a user’s motivation, behavior, and needs.
Why is UX research important?
UX research will help create a product that is relevant to users and is easy and pleasurable to use while boosting a product’s ROI. Aside from these reasons, user research gives insight into which features to prioritize, and in general, helps develop clarity around a project.
- UserResearch
Miklos Philips
London, United Kingdom
Member since May 20, 2016
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
By entering your email, you are agreeing to our privacy policy .
Toptal Designers
- Adobe Creative Suite Experts
- Agile Designers
- AI Designers
- Art Direction Experts
- Augmented Reality Designers
- Axure Experts
- Brand Designers
- Creative Directors
- Dashboard Designers
- Digital Product Designers
- E-commerce Website Designers
- Full-Stack Designers
- Information Architecture Experts
- Interactive Designers
- Mobile App Designers
- Mockup Designers
- Presentation Designers
- Prototype Designers
- SaaS Designers
- Sketch Experts
- Squarespace Designers
- User Flow Designers
- User Research Designers
- Virtual Reality Designers
- Visual Designers
- Wireframing Experts
- View More Freelance Designers
Join the Toptal ® community.
Integrations
What's new?
Prototype Testing
Live Website Testing
Feedback Surveys
Interview Studies
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Research Maturity Model
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub
What is UX Research: The Ultimate Guide for UX Researchers
0% complete
User experience research is a crucial component of the human-centered design process and an essential part of creating solutions that meet user expectations and deliver value to customers. This comprehensive guide to UX research dives into the fundamentals of research and its various methods and includes tips and best practices from leading industry experts.
Make informed design decisions with user research
Validate ideas, test prototypes, assess usability, and deliver real, actionable insights to your product team.
UX research: Your ultimate guide to nailing user experience and exceeding expectation
User experience research, or UX research , is the process of gathering insights about users' behaviors, needs, and pain points through observation techniques and feedback methodologies. It’s a form of user research that looks at how users interact with your product, helping bridge the gaps between what you think users need, what users say they need—and what they actually need.
The goal of UX research is to understand your users and gain context and perspectives to help make informed decisions and build user-centered products. It’s an essential part of designing, developing, and launching a product that will be an instant hit—but it should also be used throughout the product’s lifecycle post-launch to keep updated, and ensure new features are relevant to your audience.
As Sinéad Davis Cochrane , UX Manager at Workday, explains: “UX research represents insights gathered directly from users and customers, that helps you make product decisions at every stage of the development process.”
Is UX research the same as user research?
The terms ‘user research’ and ‘UX research’ are often used interchangeably, but they do differ. User research is the parent of UX research; it’s a broader research effort that aims to understand the demographics, behaviors, and sentiments of your users and personas.
UX research, on the other hand, is a type of user research that’s specific to your product or platform. Where user research focuses on the user as a whole, UX research considers how they interact with, respond to, and feel about your product or concept itself.
In both cases, the overarching goal is to get to know your users, understand what they need from your product, gain context to help make informed decisions, and build human-centered experiences.
Involve your users at every stage of your design process
Create research projects with Maze using customizable templates, and start making data-informed product decisions
Why is conducting UX research important?
In an ideal world, users would find your product easy to navigate, your net promoter score (NPS) would be off the charts, and you’d see adoption and activation rates skyrocket. In reality, however, this can be a challenging dream to achieve—but it is possible. The only way to build a product that users really resonate with is by involving them throughout the development process and building with them.
UX research is more than just a single ‘step’ in the development process: it should happen continuously, throughout the product lifecycle—so whether you’re building new products or iterating on existing ones, every decision is informed by user insights.
Here’s what you can achieve with continuous UX research:
Make informed decisions based on data
Our 2023 Continuous Research Report shows that 74% of people who do research (PWDR) believe research is crucial to guiding product decisions. Plus, 60% of respondents find that user recommendations inspire new product ideas.
Getting stakeholder buy-in to product decisions can be challenging, but when you suggest changes based on UX research, you have data to back up your suggestions. Your users inform your product, becoming the decision-makers as well as the customer.
UX research helps reduce and mitigate the risk of building the wrong thing—or building the right thing in the wrong way.

Sinéad Davis Cochrane , UX Manager at Workday
Reduce bias in the UX design process
There are hundreds of cognitive biases identified by psychologists, many of which unknowingly influence our decisions and the products we build. But a key principle of great UX design is to put aside existing beliefs, and learn from your users.
“You have to be humble, optimistic, and open-minded,” says Bertrand Berlureau , Senior Product Designer at iMSA. Using effective UX research, you can root out bias or assumptions, and follow real human behavior to inform product decisions.
According to Sinéad, you should consider these questions early in the design process:
- “What are your assumptions?”
- “What are some of the assumptions you’ve been making about your end-users and product without any evidence?”
- “What are the anecdotes or coincidental pieces of information that you hold, and how can you challenge them?”
Biases can subconsciously affect research and UX design, and it can be tricky to identify them. The first step to overcoming cognitive biases is by being aware of them. Head to chapter three of our cognitive biases guide to discover how.
Test and validate concepts
The power of UX research is that it can prove you right or wrong—but either way, you’ll end up knowing more and creating a product that provides a better user experience. For Bertrand, an idea without a test is just an idea. So, before the design process, his team starts with these user research methods:
- Face-to-face and remote user interviews
- Focus groups
- Co-creativity sessions through design sprints, quick prototyping, and hypothesis concepts
- User testing
UX research is the only way to unequivocally confirm your product is solving the right problem, in the right way. By speaking directly to real users, you can pinpoint what ideas to focus on, then validate your proposed solution, before investing too much time or money into the wrong concept.
Work on solutions that bring real value to customers
Another main benefit of UX research is that it allows product teams to mitigate risk and come up with products users want to use. “One of the main risks we need to control is whether users actually want to use a solution we've implemented,” explains Luke Vella , Group Product Manager at Maze. “UX research helps us reduce this risk, allowing us to build solutions that our customers see as valuable and make sure that they know how to unlock that value.”
Luke works on pricing and packaging, an area that requires constant user research. On one hand, he and his team want to understand which problems their users are facing and come up with plans to satisfy those different needs. On the other hand, they need to make sure they can monetize in a sustainable way to further invest in the product. You can only get this perfect balance by speaking to users to inform each step of the decision.
Market your product internally and externally
UX research also plays a crucial role in helping product marketers understand the customer and effectively communicate a product's value to the market—after all, a product can only help those who know about it.
For example, Naomi Francis , Senior Product Marketing Manager at Maze, uses different research methods to inform marketing strategy. Naomi conducts user interviews to build personas, using user research to collect insights on messaging drafts, product naming, and running surveys to gather user feedback on beta products and onboarding.
Understanding how and why customers need and use our product pushes marketing launches to the next level—you can get a steer on everything from messaging to language and approach.

Naomi Francis , Senior Product Marketing Manager at Maze
Types of UX research
All UX research methods fit into broader UX research techniques that drive different goals, and provide different types of insight. You can skip to chapter seven for a rundown of the top 9 UX research methods , or keep reading for a deep dive on the main types of UX research:
- Moderated and unmoderated
- Remote and in-person
- Generate and evaluate
- Qualitative and quantitative
- Behavioral and attitudinal
Where moderated/unmoderated and remote/in-person refer to the way research is conducted , the other types of UX research reflect the type of data they gather.
The most powerful insights come from a mixture of testing types—e.g. attitudinal and behavioral, generative and evaluative, and quantitative and qualitative. You don’t need to run all types of research at all times, but you’ll benefit from gathering multiple types of data throughout different stages of product development.
Moderated research
Moderated research is any research conducted with a facilitator or researcher present. A moderator may observe research sessions and take notes, ask questions, or provide instruction to participants where needed.
Like all research, it’s crucial a moderator doesn’t overly guide participants or influence results. Due to certain types of cognitive biases , people may behave differently while being observed, so researchers often opt for unmoderated methods to avoid results being impacted.
UX research methods for moderated research
- User interviews to speak directly with your target user face-to-face
- Focus groups to gather feedback on a variety of topics
- Moderated usability testing to hear the thought process behind the actions
Unmoderated research
As the name suggests, unmoderated research refers to the lack of a moderator. Often used in tandem with remote research , users complete tasks independently, guided by pre-written instructions.
Unmoderated research is helpful to ensure users are acting entirely of their own volition, and it has a lower cost and quicker turnaround than moderated research—however it does require efficient planning and preparation, to ensure users can navigate the tasks unaided.
UX research methods for unmoderated research
- Unmoderated usability testing to see how easily users navigate your product
- Live website testing to witness users interacting with your product in real time
- Surveys to have users answer specific questions and rate design elements
Remote research
An incredibly flexible approach, remote research is often favored due to its time-to-results and cost savings. Remote research can be moderated or unmoderated, and is conducted using UX research tools which record user behavior, feedback, and screen recordings.
Another key benefit is its reach and accessibility—by moving research to a virtual platform, you can access users from anywhere in the world, and ensure research is inclusive of those with different abilities or requirements, who may otherwise be unable to take part in traditional in-person research.
UX research methods for remote research
- Usability testing to evaluate how accessible your product is
- Card sorting to understand how users categorize and group topics
- Concept testing to assess what ideas users are drawn to
- Wireframe or prototype testing to invite users to test a rough version of the design
In-person research
Research conducted in-person is typically more expensive, as it may require travel, accommodation, or equipment. Many traditionally in-person research methods can easily be performed remotely, so in-person research is often reserved for if there’s additional needs for accessibility, or if your product requires physical testing, safety considerations or supervision while being tested.
UX research methods for in-person research
- Guerrilla research to speak to random users and gather feedback
- User interviews to connect with users and read body language
- Field studies to gauge how your product fits into a real world environment
Generative research
Generative research provides a deep understanding of your target audience’s motivations, challenges, and behaviors. Broadly speaking, it pinpoints a problem statement, identifies the problem to be solved, and collects enough data to move forward.
It should happen before you even begin designing, as it helps you identify what to build, the types of problems your user is facing, and how you can solve them with your product or service.
UX research methods for generative research
- Field studies to get familiar with users in their authentic environment
- User interviews to ask open-ended questions about pain points
- Diary research to keep a log of users’ behaviors, activities, and beliefs over time
- Open card sorting to have users define and name their own categories
Evaluative research
Evaluative research focuses on evaluating a product or concept in order to collect data that will improve the solution. Evaluative research usually happens early on and is used in a continuous, iterative way throughout the design process and following launch. You can use this type of UX research to assess an idea, check navigation, or see if your prototype meets your user’s needs.
UX research methods for evaluative research
- Usability testing to see if your platform is easy and intuitive to use
- A/B testing two versions of a design to see which one works best
- Tree testing to assess if your website’s information architecture (IA) makes sense
- Five-second tests to collect first impressions
Behavioral research
This type of research refers to observation—it’s human nature that sometimes what we say, or what we think we’ll do doesn’t match up to what we actually do in a situation. Behavioral research is about observing how users interact with your product or how they behave in certain situations, without any intervention.
UX research methods for behavioral research
- Observation in labs or real environments to witness behavior in real time
- Tree testing to view which paths users take on a website
- Diary research to see how users interact with your product in real life
Attitudinal research
Attitudinal research is the companion to behavioral research—it’s about what people say, and how they feel. In attitudinal research, you ask users to share their own experiences and opinions; this may be about your product, a concept, or specific design element. With a mix of attitudinal and behavioral research, you can get a broader picture of what your user truly needs.
UX research methods for attitudinal research
- Focus groups to understand users’ perspectives on your product
- User interviews to ask people questions about your product directly
- Surveys to gather insights on user preferences and opinions
Quantitative research
Quantitative and qualitative research methods are two types of research that can be used in unison or separately. Quantitative research comes from data and statistics, and results in numerical data.
It allows you to identify patterns, make predictions, and generalize findings about a target audience or topic. “[At iMSA] We analyze a lot of metrics and specific data like traffic analytics, chatbot feedback, user surveys, user testing, etc. to make decisions,” explains Bertrand. “The convergence of all the data, our user’s needs, governs the choices we make.”
Types of quantitative results you can find through UX research include:
- Time spent on tasks
- Net promoter score (NPS)
- System usability score (SUS)
- Number of clicks taken to complete a task
- Preference percentage on A/B tests
UX research methods for quantitative research
- A/B testing to see which option your users likes best
- Tree testing to get data on which paths users follow on your website
- Usability testing to get a score on system usability
- Heatmaps to spot where users spend most of their session time
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is about understanding the why behind the data. It comes from comments, opinions, and observations—this type of research answers why and how users think or act in a certain way. Qualitative data helps you understand the underlying motivations, thoughts, and attitudes of target users. For this reason, attitudinal research is often qualitative (though not always).
UX research methods for qualitative research
- Interviews to discover your users’ motivations and frustrations
- Open question surveys to learn users’ pain points in their own words
- Focus groups to observe users’ interacting with your product
- Think aloud usability tests to hear commentary behind each user decision
💡 Product tip:
Maze allows you to record your participants' screen, audio, and video with Clips, so you can collect qualitative and quantitative insights simultaneously.
When should you conduct UX research?
The truth is, you should always be researching. When NASA wants to send a new shuttle into space, they don't build a rocket and launch it right away. They develop a design, test it in simulations and lab environments, and iterate between each stage. Only once they’ve run all the foreseeable scenarios do they put a person on the ship. Why should your product be any different?
With an overwhelming 83% of product professionals surveyed in our 2023 Continuous Research Report believing research should happen at all stages, it’s surprising that just 36% run tests after launch. While time and budget can make continuous research a challenge, testing at different stages gives you access to unique insights about your users and how they interact with your product.

That being said, if you can only afford to research a few times throughout the development process , here are some key moments to focus on:
Before developing the product
This is when you need to conduct the most extensive and detailed part of your research. During this phase, you’ll want to conduct generative research to get to know exactly:
- Who your user is
- The types of problems they’re facing (and what kind of product they want to solve them)
- What their expectations on a product or service like yours are
- What they like or dislike about your competitors
- Where they currently go to solve the mentioned problems
- What needs to happen for them to change companies (if they’re using a different product)
You can use a variety of UX research methods like focus groups and surveys to gather insights during this stage.
Remember: This step applies even if your product is already live, if you’re thinking of introducing a new feature. Validate your idea and investigate potential alternatives before you spend time and money developing and designing new functionality.
When you want to validate your decisions
This is the point where you’ll run through a few cycles of researching, building, and iterating, before launching your product. The Maze Product team does this through continuous product discovery, via a dual-track habit:
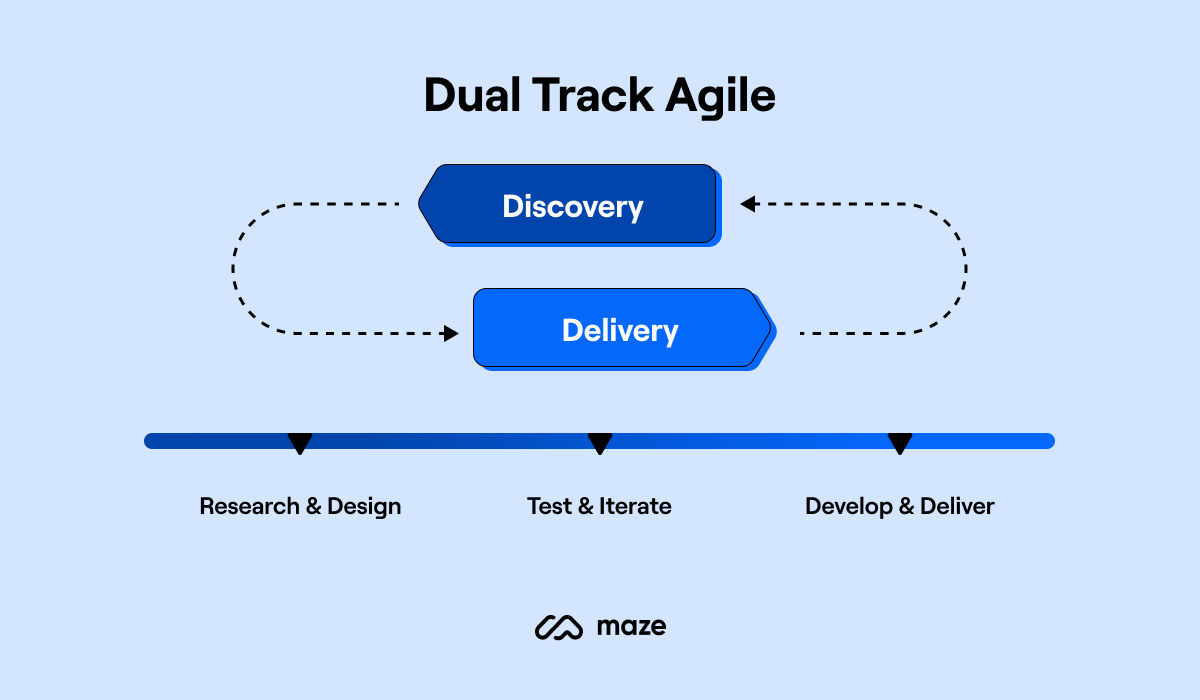
Conduct research regularly while developing and building your product to see if you’re headed in the right direction. Let the research findings feed your deliverables.
Gather qualitative insights on user sentiment through surveys or focus groups. Test your wireframe or sketches to get quantitative answers in the form of clicks, heatmaps, or SUS. Use card sorting to generate ideas, tree testing to assess IA, or prototype testing to assess the usability of a beta version. The options are endless, so there’s no reason to miss maximizing your research at this stage and gather insights to power product decisions.
To evaluate product accessibility
Your product will be used by a multitude of diverse, unique users. Your research participants should be representative of your real audience, which means including all usage scenarios and user personas. Usability testing is one form of UX research that can be used here to ensure your product works for all its users, regardless of ability or need.
There are many ways to ensure your design is inclusive and accessible , including:
- Testing alt-texts, screen-reading capabilities, and color combinations
- Avoiding screen flashes or sudden pop-ups that may be triggering for certain conditions
- Being intentional in what language and imagery is used
Once your product is live
Research doesn’t end once you push your platform to production. Conduct Live Website Testing to evaluate how well your product is meeting your users' expectations and needs. This type of research invites you to answer the question: did we nail it?
Testing your live website also allows you to see how your users interact with your design in a real environment, so you can identify and solve mistakes fast. Pay close attention to loading times, error messages, and other quantitative data that may indicate bugs. You can also conduct regular sentiment checks by embedding feedback surveys into your product itself, to assess user satisfaction and NPS in a few clicks.
TL;DR: Why, how, and when to conduct UX research
The more you understand your customers, the better you can create products that meet expectations, tailor your strategy to their specific needs, and increase your chances for success. Plus, UX research allows you to create unbiased products that put your customers at the center of your business.
To conduct UX research, you’ll need to mix the stage of your product lifecycle with the right research type and methods. Meaning, while you need to conduct UX research continuously, you should look for different types of insights depending on the development stage you’re at and what your current objective is.
For example, if you want to test your live product, you should conduct a mix of quantitative and qualitative evaluative research. That means you might want to perform:
- Usability tests
- Feedback surveys
- Five-second tests
- Prototype testing
Now we’ve covered the what and why of UX research, let’s get into the how. Continue to the next chapter to learn how to create a UX research strategy that blows your competitors away.
Frequently asked questions
What are some examples of UX research?
Some examples of UX research include:
- A/B testing
- Prototype or wireframe testing
- Card sorting
- User interviews
- Tree testing
- 5-second testing
- Usability testing
What are the basics of UX research?
The basics of UX research are simple: you just need a clear goal in mind and a mix of quantitative and qualitative tests. Then, it's a case of:
- Determining the right testing methods
- Testing on an audience that’s an accurate representation of your real users
- Doing continuous product discovery
- Performing unbiased research to build an unbiased design
- Iterating and building user-centric products
UX research gets easier when you use a product discovery platform like Maze. This tool allows you to run multiple types of product research such as usability, prototype, card sorting, and wireframe tests—and get answers within hours.
Is UX research hard?
UX research isn’t hard, especially when you use an intuitive tool for product discovery—like Maze. Maze allows you to build tests using its multiple available templates. It also lets you bring your own users or recruit from its panel and creates an automated, ready-to-share metrics report. Maze gives you answers to tests within hours so you can improve your UX based on real user feedback fast.
Building a UX research strategy
What is UX Research? Methods, Process, Tools, Examples
Appinio Research · 15.02.2024 · 40min read

Ever wondered how successful products and services are meticulously crafted to cater to your needs and preferences? User Experience (UX) research is the key that unlocks the secrets behind creating user-centered designs. In this guide, we will delve deep into UX research, uncovering its methods, strategies, and practical applications. Whether you're a designer, developer, product manager, or simply curious about the science of user satisfaction, this guide will empower you with the knowledge and tools to understand, implement, and benefit from UX research principles.
What is UX Research?
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the design and functionality of products and services to enhance user satisfaction and usability.
Importance of UX Research
Effective UX research plays a pivotal role in shaping user-centered design and development processes. Its significance can be understood through several key points:
- User-Centered Design : UX research places users at the forefront of design decisions, ensuring that products and services are tailored to meet their needs and preferences.
- Enhanced Usability : Research findings lead to improvements that enhance the overall usability of products, reducing user frustration and increasing engagement.
- Cost Reduction : Identifying and addressing usability issues early in the design process can save time and resources by avoiding costly redesigns or post-launch fixes.
- Competitive Advantage : Organizations prioritizing UX research gain a competitive edge by delivering superior user experiences that attract and retain customers.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction : User satisfaction is closely linked to loyalty and positive word-of-mouth, making UX research an investment in long-term customer relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making : Research data provides valuable insights that inform strategic decisions, reducing the guesswork and subjectivity in design choices.
UX Research Goals and Objectives
The primary goals and objectives of UX research revolve around understanding user needs, improving usability, and driving user-centered design. Here are the key objectives that guide UX research efforts:
- User Understanding : Gain a deep understanding of the target audience, including their demographics, behaviors, motivations, and pain points.
- Usability Evaluation : Identify usability issues and challenges users encounter during interactions with a product or service.
- Task Efficiency : Determine how efficiently users can accomplish tasks within a system, with a focus on minimizing friction and errors.
- User Satisfaction : Measure user satisfaction and gather feedback to uncover areas where improvements can enhance overall user experience.
- Feature Prioritization : Assess which features or functionalities are most valuable to users, guiding feature prioritization in development.
- Validation and Iteration : Validate design decisions through testing and iteration, ensuring that changes align with user expectations and preferences.
- Benchmarking : Establish benchmarks to track improvements over time and compare performance to industry standards.
- Evidence-Based Design : Base design decisions on empirical data and user insights, fostering a user-centered and data-driven design culture.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity : Ensure that products and services are accessible to a diverse range of users, including those with disabilities.
- Risk Mitigation : Identify and mitigate potential risks and challenges early in the design process, reducing the likelihood of post-launch issues.
- Continuous Improvement : Embrace a culture of constant improvement, where UX research is an ongoing process that informs product enhancements and updates.
By aligning research efforts with these objectives, organizations can create products and services that resonate with users, leading to increased user satisfaction and business success.
How to Plan UX Research?
Planning is the foundation of any successful UX research project. It sets the direction, defines your objectives, and ensures that your efforts are focused on achieving meaningful outcomes.
Setting Clear Objectives
Setting clear objectives is the first and most crucial step in planning UX research. Your objectives guide the entire research process, helping you stay on track and measure success effectively. When defining objectives, consider the following:
- Specificity : Objectives should be clear and specific. Vague goals can lead to ambiguous research outcomes.
- Relevance : Ensure that your objectives align with the overall goals of your product or project. How will the research contribute to the success of the endeavor?
- Measurability : Define objectives that are measurable. You should be able to determine whether you've achieved them or not.
- Timeframe : Consider the timeline for your research. Are your objectives achievable within the given time frame?
A well-defined objective might look something like this: "To identify pain points in our mobile app's onboarding process by conducting usability testing with 15 participants, with the aim of reducing drop-off rates by 20% within the next quarter."
Identifying Target Audience
Understanding your target audience is fundamental to effective UX research. Your product or service is designed for specific users, and knowing them intimately is essential. When identifying your target audience, keep the following in mind:
- Demographics : Who are your users? What are their age, gender, location, and other relevant demographics?
- Psychographics : Dig deeper into their lifestyles, values, interests, and behaviors. What motivates them, and what are their pain points?
- User Personas : Create user personas to visualize your target audience. Personas help in humanizing and empathizing with your users.
- User Journeys : Map out the typical user journeys to understand the various touchpoints and interactions users have with your product.
Defining Research Questions
Research questions act as the compass that guides your journey through the UX research landscape. They should be well-crafted and directly tied to your objectives. When defining research questions, consider the following:
- Open-Endedness : Craft questions that allow for open-ended responses . Closed-ended questions with yes/no answers can limit the depth of insights.
- Unbiased Language : Ensure that your questions are phrased in a neutral and impartial manner. Biased questions can lead to skewed results.
- Relevance : Are your research questions directly related to your objectives? Avoid asking questions that do not contribute to your research goals.
- User-Centered : Frame questions from the user's perspective. What would users want to know or share about their experience?
For instance, if your objective is to improve the checkout process of an e-commerce website, a research question could be: "What challenges do users encounter during the checkout process, and how can we simplify it to enhance their experience?"
Budgeting and Resource Allocation
Effective UX research requires proper allocation of resources, both in terms of budget and personnel. Before embarking on your research journey:
- Financial Resources : Determine the budget available for your research project. This budget should cover participant incentives, research tools, and any other associated costs.
- Time Allocation : Allocate time appropriately for each phase of the research process, including recruitment, data collection, analysis, and reporting.
- Human Resources : Identify the team members or researchers responsible for conducting the research. Ensure they have the necessary skills and expertise.
- Tools and Software : Assess whether you have access to the required research tools, such as usability testing software, survey platforms, or analytics tools.
Proper budgeting and resource allocation prevent unexpected obstacles and ensure a seamless research process. Remember that investing in UX research is an investment in the overall success of your product or service.
Types of UX Research
When it comes to User Experience (UX) research, understanding the different types of research methodologies is crucial. Each type has its own strengths and applications, allowing you to gather specific insights into user behavior, preferences, and interactions. These are the three primary types of UX research.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on collecting numerical data to quantify user behaviors, preferences, or attitudes. It involves systematic data collection and statistical analysis. Here's a deeper look into quantitative research:
- Data Collection : Quantitative research relies on structured data collection methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, or data analytics tools. These methods yield data in numerical form.
- Objective Measurement : It aims to provide objective and measurable data. This is particularly useful for answering questions like "How many users performed a specific action?" or "What percentage of users prefer feature A over feature B?"
- Large Sample Sizes : Quantitative research often involves larger sample sizes to ensure statistical significance. This allows for generalizable findings.
- Statistical Analysis : Statistical analysis plays a central role in quantitative research. It helps identify trends, correlations, and patterns within the data.
- A/B Testing : A common application of quantitative research is A/B testing, where two versions of a design or feature are compared to determine which performs better based on quantifiable metrics.
Quantitative research provides valuable insights when you need to make data-driven decisions and understand the broader user trends and preferences within your target audience.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research dives deep into the subjective aspects of the user experience. It seeks to understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations. Here's a closer look at qualitative research:
- Data Collection : Qualitative research relies on methods such as user interviews, usability testing, focus groups , and ethnographic studies. These methods capture rich, non-numerical data.
- Subjective Insights : Qualitative research aims to uncover subjective insights. It helps answer questions like "Why do users find a particular feature frustrating?" or "What emotions do users experience during a specific interaction?"
- Small Sample Sizes : Qualitative research typically involves smaller sample sizes but offers in-depth insights into individual experiences.
- Contextual Understanding : Researchers often engage with users in their natural environment or within the context of product use. This provides a holistic understanding of user behaviors.
- Thematic Analysis : Qualitative data is analyzed through techniques like thematic coding, where common themes and patterns in user feedback are identified.
Qualitative research is particularly valuable when you want to gain a deeper understanding of user needs, pain points, and the emotional aspects of their interactions with your product or service.
Mixed-Methods Research
Mixed-methods research combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research approaches. It offers a comprehensive view of the user experience by leveraging the strengths of both methodologies. Here's what you need to know about mixed-methods research:
- Data Variety : Mixed-methods research involves collecting both numerical and non-numerical data. This includes quantitative data from surveys and qualitative data from interviews or observations.
- Holistic Insights : By combining quantitative and qualitative data, researchers can gain a more complete and nuanced understanding of user behavior and preferences.
- Sequential or Concurrent : Mixed-methods research can be conducted sequentially (first quantitative, then qualitative) or concurrently (simultaneously collecting both types of data).
- Data Integration : Researchers must carefully integrate and analyze the data from both sources to draw comprehensive conclusions.
- Complementary Insights : The aim is to complement the strengths of one method with the weaknesses of the other, providing a more well-rounded perspective.
Mixed-methods research is valuable when you want to explore complex user experiences, understand the reasons behind quantitative trends, or validate findings from one method with the other. It offers a holistic approach to UX research that can lead to more informed design decisions.
How to Conduct UX Research?
Now that you've laid the groundwork and explored the types of UX research, it's time to delve into the practical aspects of conducting UX research.
Recruitment: Finding the Right Participants
Recruiting participants is a crucial step in UX research. The quality of your research outcomes depends on selecting the right participants who represent your target audience. Here's how to do it effectively:
- Define Participant Criteria : Begin by defining specific criteria for your participants. These criteria should align with your research objectives. For instance, if you're testing a healthcare app, you might require participants who have experience with healthcare services.
- Recruitment Channels : Determine where and how you will find participants. Common recruitment channels include online platforms, user testing services, or in-house databases.
- Incentives : Consider offering incentives to motivate participants. This could be monetary compensation, gift cards, or access to your product or service.
- Screening : Screen potential participants to ensure they meet your criteria. Conducting a screening interview or questionnaire can help filter out inappropriate candidates.
Sampling: Choosing the Right Sample Size
Sampling involves selecting a subset of your target audience for research. The size and representativeness of your sample are critical for obtaining reliable results:
- Sample Size : Determine the appropriate sample size based on your research goals and statistical requirements. Larger samples enhance the reliability of your findings.
- Random Sampling : Whenever possible, aim for random sampling to reduce bias. Randomly selecting participants from your target population increases the likelihood of obtaining a representative sample.
- Stratified Sampling : In cases where certain user segments are essential, consider stratified sampling. This ensures that each segment is adequately represented in your sample.
Recruitment and sampling are foundational elements of UX research, ensuring that the data collected accurately reflects the perspectives of your intended user base.
Choosing the Right Data Collection Methods
Selecting the most suitable data collection methods is vital for gathering relevant and meaningful information. Depending on your research objectives, you can utilize various methods:
- Usability Testing : Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It provides direct insights into how users navigate and use your design.
- Surveys and Questionnaires : Surveys are useful for gathering structured, quantitative data. They allow you to collect responses from a large number of participants quickly.
- Interviews : Interviews offer a deeper understanding of user experiences by engaging participants in open-ended conversations. They are particularly effective for uncovering motivations and pain points.
- Observations : Observational studies involve watching users in their natural context, providing insights into real-world behavior.
- Eye-Tracking : Eye-tracking technology can reveal where users focus their attention within your design, helping to optimize layouts and content placement.
- Heatmaps : Heatmaps display aggregated user interactions, highlighting areas of interest and interaction intensity within your design.
- Card Sorting : Card sorting exercises help organize information and navigation structures based on how users group and label items.
Choosing the proper data collection methods depends on your research goals, the type of insights you seek, and the available resources. When it comes to data collection, Appinio offers a streamlined solution that simplifies the process and ensures actionable results.
With Appinio , you can effortlessly design surveys, target specific demographics, and gather insights from a diverse pool of respondents. Whether you're conducting usability testing, administering surveys, or conducting interviews, Appinio provides the tools you need to make informed decisions quickly and efficiently.
Ready to elevate your UX research? Book a demo with Appinio today and experience the power of real-time consumer insights firsthand!
Book a Demo
Making Sense of Collected Data
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze it effectively. Proper data analysis is critical for drawing meaningful insights and conclusions:
- Quantitative Analysis : For quantitative data collected through surveys or analytics, use statistical analysis techniques to identify patterns, correlations, and statistically significant findings.
- Qualitative Analysis : Qualitative data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses, requires thematic coding and content analysis to uncover themes, trends, and user sentiments.
- Mixed-Methods Integration : In mixed-methods research, integrate both quantitative and qualitative data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the user experience.
- Usability Metrics : When conducting usability testing, use established usability metrics such as task completion rates, time on task, and error rates to evaluate user performance.
- Data Visualization : Visualize your data using charts, graphs, and diagrams to make complex information more accessible and understandable.
Data analysis transforms raw data into actionable insights that inform design improvements and decision-making.
Improving User Experience Through Testing
Usability testing is a fundamental UX research method that involves observing users as they interact with your product or prototype. It helps identify usability issues and gather direct feedback for improvement:
- Test Planning : Begin by creating test scenarios and tasks that align with your research objectives. Determine what you want participants to accomplish during the test.
- Recruitment : Recruit participants who match your target audience and meet your criteria. Ensure they represent the diversity of your user base.
- Moderated vs. Unmoderated Testing : Choose between moderated (where a facilitator guides participants) and unmoderated (participants complete tasks independently) usability testing, depending on your needs and resources.
- Task Observation : Observe participants as they navigate your design, paying attention to their interactions, struggles, and feedback.
- Think-Aloud Protocol : Encourage participants to vocalize their thoughts and feelings during the test. This provides insights into their cognitive processes.
- Post-Test Interviews : Conduct post-test interviews to gather deeper insights. Ask participants about their overall experience, pain points, and suggestions for improvement.
- Iterative Testing : Usability testing is often an iterative process. After making design changes based on feedback, conduct additional tests to validate improvements.
Usability testing helps uncover issues that may not be apparent through other research methods, leading to improved user satisfaction and product usability.
Collecting Quantitative Insights
Surveys and questionnaires are valuable tools for collecting structured, quantitative data from a large number of participants. They can provide insights into user preferences, satisfaction, and demographics:
- Survey Design : Carefully design your survey or questionnaire , ensuring questions are clear, concise, and relevant to your research objectives.
- Sampling : Distribute your survey to a representative sample of your target audience to obtain meaningful results.
- Response Scale : Choose an appropriate response scale, such as Likert scales or multiple-choice questions, depending on the type of data you want to collect.
- Pre-Testing : Before launching your survey, conduct pre-testing to identify and address any potential issues with question wording or survey flow.
- Data Analysis : Once survey responses are collected, perform statistical analysis to uncover patterns and correlations within the data.
Surveys and questionnaires are efficient tools for gathering quantitative data, making them ideal for measuring user satisfaction, preferences, and trends.
Interviews and Observations
Interviews and observations provide qualitative insights that can help you understand the "why" behind user behaviors and motivations:
- Interview Types : Choose between structured, semi-structured, or unstructured interviews, depending on your research goals. Structured interviews use predefined questions, while unstructured interviews allow for open-ended conversations.
- Participant Selection : Select participants who represent your target audience and can provide diverse perspectives.
- Interview Moderation : During interviews, create a comfortable environment for participants to share their thoughts openly. Encourage them to expand on their responses.
- Observations : When conducting observational research, carefully observe users in their natural context or during product use. Take notes on their actions, gestures, and expressions.
- Contextual Inquiry : Contextual inquiries involve observing users while they perform specific tasks related to your product or service. This approach provides insights into real-world behavior.
- Data Interpretation : Analyze interview transcripts and observational notes using thematic coding or content analysis to identify recurring themes and patterns.
Interviews and observations allow you to gain a deep understanding of user experiences, uncover pain points, and inform design decisions from a user-centered perspective.
With these data collection methods at your disposal, you can tailor your approach to gather the most relevant insights for your specific UX research objectives. Whether you choose to observe user interactions, administer surveys, conduct interviews, or run usability tests , each method offers unique advantages for understanding and improving the user experience.
How to Interpret UX Research Data?
As you gather data through various UX research methods, the next critical step is to analyze and interpret this data effectively. This process involves transforming raw information into actionable insights that can drive design improvements and strategic decisions.
Visualizing Insights for Clarity
Data visualization is a powerful technique for making complex data more accessible and understandable. It involves representing data graphically through charts, graphs, and diagrams. Here's why data visualization matters and how to use it effectively:
- Simplify Complex Data : Data visualization simplifies large datasets and helps users quickly grasp trends and patterns.
- Enhance Communication : Visual representations of data are often more effective in conveying information than raw numbers or text.
- Choose the Right Visualization : Select the appropriate type of visualization based on the data and the story you want to tell. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and heatmaps.
- Labels and Legends : Ensure that your visualizations have clear labels, legends, and scales. This makes it easier for viewers to understand and interpret the data.
- Interactivity : In digital formats, consider adding interactivity to allow users to explore data further by hovering, clicking, or filtering.
- Data Storytelling : Use data visualizations to tell a compelling story. Explain the context, highlight key findings, and guide viewers through the insights.
Data visualization aids in identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies within your data, helping you make informed decisions based on a visual representation of your research findings.
Identifying Patterns and Trends
Identifying patterns and trends within your data is essential for understanding user behavior and preferences. Here's how to effectively uncover these insights:
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) : Begin with an exploratory analysis of your data. Visualizations, such as histograms, box plots, and scatterplots, can reveal patterns and outliers.
- Segmentation : Segment your data by relevant variables (e.g., demographics , psychographic , user behaviors) to identify patterns within specific groups.
- Statistical Analysis : Use statistical methods to analyze your data quantitatively. Techniques like regression analysis, correlation, and hypothesis testing can uncover relationships and trends.
- Time Series Analysis : If your data includes time-based information, such as user interactions over time, use time series analysis to identify temporal trends and seasonality.
- Qualitative Data : For qualitative data from interviews or open-ended survey responses, use thematic coding to identify recurring themes and insights.
- Comparative Analysis : Compare data before and after design changes or between different user groups to assess the impact of interventions.
Identifying patterns and trends in your data allows you to deeply understand user behaviors, preferences, and pain points, enabling data-driven decision-making.
Turning Data into Actionable Knowledge
Drawing insights and conclusions from your data is the ultimate goal of UX research. It's the stage where you transform data into actionable knowledge that informs design improvements and strategic decisions:
- Hypothesis Validation : Determine whether your research findings align with your initial hypotheses and objectives.
- Prioritization : Prioritize the most significant insights and findings. Focus on those that have the most substantial impact on the user experience.
- User-Centered Recommendations : Frame your insights in a user-centered manner. Consider how the findings can benefit users and enhance their interactions with your product or service.
- Iterative Design : Use insights to inform iterative design improvements. Test and validate changes based on research findings to ensure they address identified issues.
- Communicate Effectively : Communicate your insights and conclusions clearly to stakeholders, designers, and developers. Use data-driven evidence to support your recommendations.
- Continuous Learning : UX research is an ongoing process. Continue to learn and adapt based on user feedback and new research findings.
Ultimately, the ability to draw meaningful insights and conclusions from your UX research data is what drives the improvement of user experiences and the success of your products and services. It's the bridge between data collection and impactful action.
Examples of UX Research
To gain a deeper understanding of how UX research is applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore some concrete examples that illustrate its importance and impact.
E-Commerce Website Optimization
Scenario : An e-commerce company notices a high cart abandonment rate on their website, with users frequently leaving before completing their purchases.
UX Research Approach : The company conducts usability testing with a group of participants. They observe users as they navigate the website, add products to their carts, and attempt to complete the checkout process.
Findings : Through usability testing, the research team identifies several issues contributing to cart abandonment. Users struggle with unclear product descriptions, a complex checkout process, and a lack of payment options. Additionally, users express concerns about data security during the payment phase.
Impact : Armed with these insights, the company makes a series of improvements. They streamline the checkout process, improve product descriptions, add multiple payment options, and prominently display security certifications. As a result, cart abandonment rates decrease significantly, leading to a notable increase in completed purchases and revenue.
Mobile App Redesign
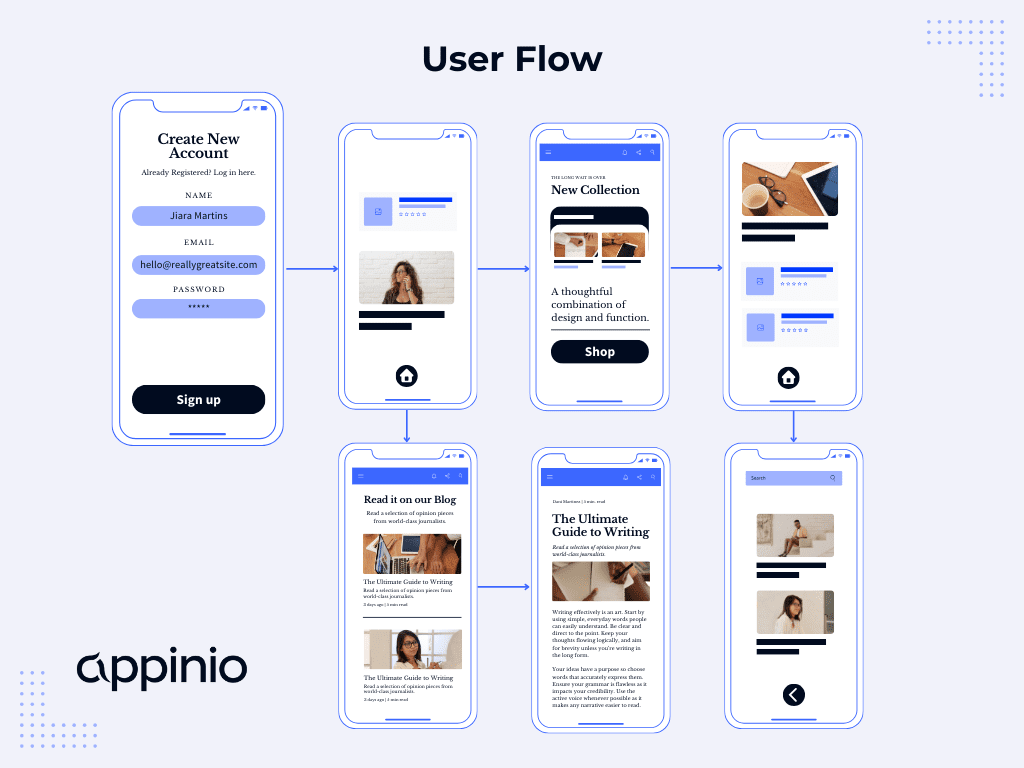
Scenario : A mobile app development company receives user feedback indicating that their app is challenging to navigate and lacks key features.
UX Research Approach : The company initiates a comprehensive research effort that includes user interviews, surveys, and competitor analysis. They aim to understand user expectations, pain points, and the strengths of competing apps.
Findings : User interviews reveal that users desire a more intuitive navigation structure and specific features that rival apps offer. Surveys confirm these preferences and competitor analysis uncovers successful design patterns.
Impact : The company embarks on a redesign project based on user feedback and industry best practices. They restructure the app's interface, add requested features, and enhance the overall user experience. As a result, user satisfaction increases, app ratings improve, and user engagement metrics rise.
Healthcare Information Portal Enhancement
Scenario : A healthcare organization operates an online portal where patients access medical records and communicate with healthcare providers. Users report difficulties in finding information and engaging with the portal.
UX Research Approach : The organization employs a mixed-methods research approach, combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative research. They analyze user interactions and survey responses while also conducting in-depth interviews with patients.
Findings : Quantitative data analysis reveals that users frequently abandon tasks without completion, such as accessing test results. Surveys and interviews uncover confusion related to navigation, terminology, and information layout.
Impact : Armed with a comprehensive understanding of user challenges, the organization revamps the portal's navigation, rewrites content in plain language, and introduces user-friendly features such as task wizards. User engagement with the portal increases, and patients report improved satisfaction with the online experience, leading to enhanced patient-provider interactions.
Social Media Platform Feature Expansion
Scenario : A popular social media platform aims to expand its feature set to stay competitive and retain users. However, the platform's leadership wants to ensure that any new features align with user preferences.
UX Research Approach : The social media platform initiates a series of surveys and user feedback sessions. They present users with potential feature concepts and gather their opinions, expectations, and concerns.
Findings : Through surveys and user feedback sessions, the platform discovers that users desire enhanced privacy controls, a more user-friendly post creation process, and better content filtering options. Additionally, users express concerns about the potential impact of new features on their data privacy.
Impact : Armed with user insights, the platform introduces new features while addressing user concerns. They implement robust privacy settings, simplify post creation, and provide users with customizable content filters. User engagement increases as users appreciate the platform's responsiveness to their needs, and user satisfaction remains high.
These examples highlight how UX research methods, such as usability testing, interviews, surveys, and data analysis, can identify specific issues, inform design improvements, and ultimately enhance the user experience. By investing in UX research, organizations can address user pain points, improve product offerings, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
How to Report UX Research Findings?
After conducting UX research and drawing valuable insights, the next crucial step is effectively communicating your findings to stakeholders and team members.
Creating Research Reports
Research reports are comprehensive documents that encapsulate your entire UX research process and findings. They serve as a valuable reference for team members and stakeholders. Here's how to create effective research reports:
- Structured Format : Organize your report in a structured format that includes sections such as an executive summary, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
- Visual Aids : Use visuals such as charts, graphs, and screenshots to illustrate your findings. Visual aids make complex data more accessible.
- Clear Language : Write in clear, concise language that is easily understandable by both technical and non-technical readers.
- Methodology Details : Provide a detailed account of your research methodology, including participant recruitment, data collection methods, and analysis techniques.
- Key Insights : Summarize the most critical findings and insights that emerged from your research. Highlight what these findings mean for the user experience.
- Actionable Recommendations : Include actionable recommendations for improving the product or service based on your research insights.
Creating a well-structured research report ensures that your findings are documented comprehensively and can be referred to as a reference for future decision-making.
Presenting to Stakeholders
Presenting your research findings to stakeholders is essential in the UX research process. It's an opportunity to convey the significance of your insights and garner support for implementing changes.
- Know Your Audience : Understand the background and interests of your audience. Tailor your presentation to their level of expertise and concerns.
- Storytelling : Craft a compelling narrative around your research. Use storytelling techniques to engage your audience and convey the user experience effectively.
- Visuals : Incorporate visuals, such as charts, graphs, and user personas, to illustrate key points and findings.
- Interactive Demonstrations : If possible, demonstrate user interactions or showcase usability improvements through interactive prototypes.
- Key Takeaways : Summarize the main takeaways and actionable recommendations. Highlight how implementing these changes can benefit the organization and users.
- Address Questions : Be prepared to answer questions and provide additional context during the presentation.
Effective presentations not only convey the value of your research but also foster collaboration and support for user-centered improvements.
Making Recommendations
One of the most critical aspects of UX research is translating findings into actionable recommendations that drive improvements in the user experience. Here's how to make recommendations effectively:
- Prioritize Recommendations : Identify and prioritize recommendations based on their potential impact and feasibility. Consider short-term and long-term goals.
- User-Centered Focus : Frame recommendations in a user-centered manner. Explain how implementing each recommendation will directly benefit users.
- Specificity : Make recommendations specific and actionable. Avoid vague suggestions. For example, instead of saying "improve navigation," specify "simplify the main menu structure."
- Data-Backed Evidence : Support recommendations with data-backed evidence from your research. Reference specific findings or user feedback that led to each recommendation.
- Collaboration : Collaborate with designers, developers, and other stakeholders to implement recommendations effectively. Provide guidance and support during the implementation phase.
- Iterative Approach : Recognize that UX research is an ongoing process. Encourage an iterative approach where recommendations are tested, refined, and re-evaluated over time.
Effective recommendations bridge the gap between research findings and meaningful changes that enhance the user experience. They guide product development efforts toward user-centered design and improved satisfaction.
Iterative UX Research
Iterative UX research is a fundamental practice that involves continuous feedback and improvement throughout the product development lifecycle. It emphasizes the importance of ongoing research, testing, and refinement to create user-centered designs.
Here's how it works:
- Feedback Loops : Establish feedback loops where user feedback and insights are collected continuously, not just at specific project phases.
- Regular Testing : Conduct regular usability testing, user interviews, or surveys to gather insights and validate design decisions.
- A/B Testing : Implement A/B testing to compare different design variations and make data-driven decisions on feature implementations.
- Prototyping : Create prototypes and gather user feedback early in the design process. Use this feedback to refine and iterate on designs.
- Monitoring Metrics : Continuously monitor key performance metrics, such as user engagement and conversion rates, to identify areas for improvement.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration : Promote collaboration between UX researchers, designers, developers, and product managers to ensure that research findings inform design and development decisions.
Iterative UX research ensures that user feedback is integrated into the design and development process, leading to products and services that continually evolve to meet user needs and preferences.
Ethical Considerations in UX Research
Ethical considerations in UX research are paramount to protect the rights and well-being of participants and ensure the integrity of the research process. Here are some ethical principles to adhere to:
- Informed Consent : Obtain informed consent from participants, clearly explaining the research purpose, procedures, and any potential risks involved.
- Privacy and Data Security : Safeguard participant privacy by anonymizing and securely storing sensitive data. Follow data protection regulations, such as GDPR.
- Transparency : Be transparent about the research objectives, methodologies, and the use of collected data. Avoid misleading or deceptive practices.
- Avoiding Harm : Ensure that research activities do not harm participants physically or emotionally. Minimize any potential discomfort or stress.
- Respect and Dignity : Treat participants with respect and dignity. Avoid any form of discrimination, bias, or exploitation.
- Bias Awareness : Be aware of potential biases in research design and analysis . Strive for inclusivity and fairness in participant selection and interpretation of findings.
- Debriefing : Provide participants with a debriefing session after their involvement in research, explaining the purpose of the study and addressing any questions or concerns.
Ethical UX research practices uphold the principles of integrity, transparency, and respect, fostering trust between researchers and participants and ensuring the ethical integrity of the research process.
Conclusion for UX Research
UX research is the compass that guides the creation of products and services with you, the user, at the center. By understanding your needs, preferences, and challenges, organizations can craft experiences that truly resonate with you. From setting clear objectives and conducting research to analyzing data and making improvements, the journey of UX research is a continuous cycle of enhancement, ensuring that the digital world becomes more user-friendly with each iteration. Remember, UX research is a powerful tool that empowers teams to create products that delight users and drive success. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just beginning your journey into UX, the principles and practices outlined in this guide can help you make a positive impact in the ever-evolving landscape of user experience.
How to Conduct UX Research in Minutes?
Introducing Appinio , the ultimate solution for lightning-fast UX research! As a real-time market research platform, Appinio specializes in providing companies with instantaneous consumer insights, revolutionizing the way businesses make data-driven decisions.
With our intuitive platform, conducting your own market research becomes a breeze, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: swift, informed choices for your business. Say goodbye to lengthy research processes and hello to quick, reliable results with Appinio.
Here's why you should choose Appinio:
- Instant Insights : From questions to actionable insights in a matter of minutes, empowering you to make decisions on the fly.
- User-Friendly Interface : No need for a research degree; our platform is designed for simplicity and ease of use, making it accessible to everyone.
- Global Reach : Reach your target audience anywhere in the world, with the ability to define precise demographics and survey respondents across over 90 countries.
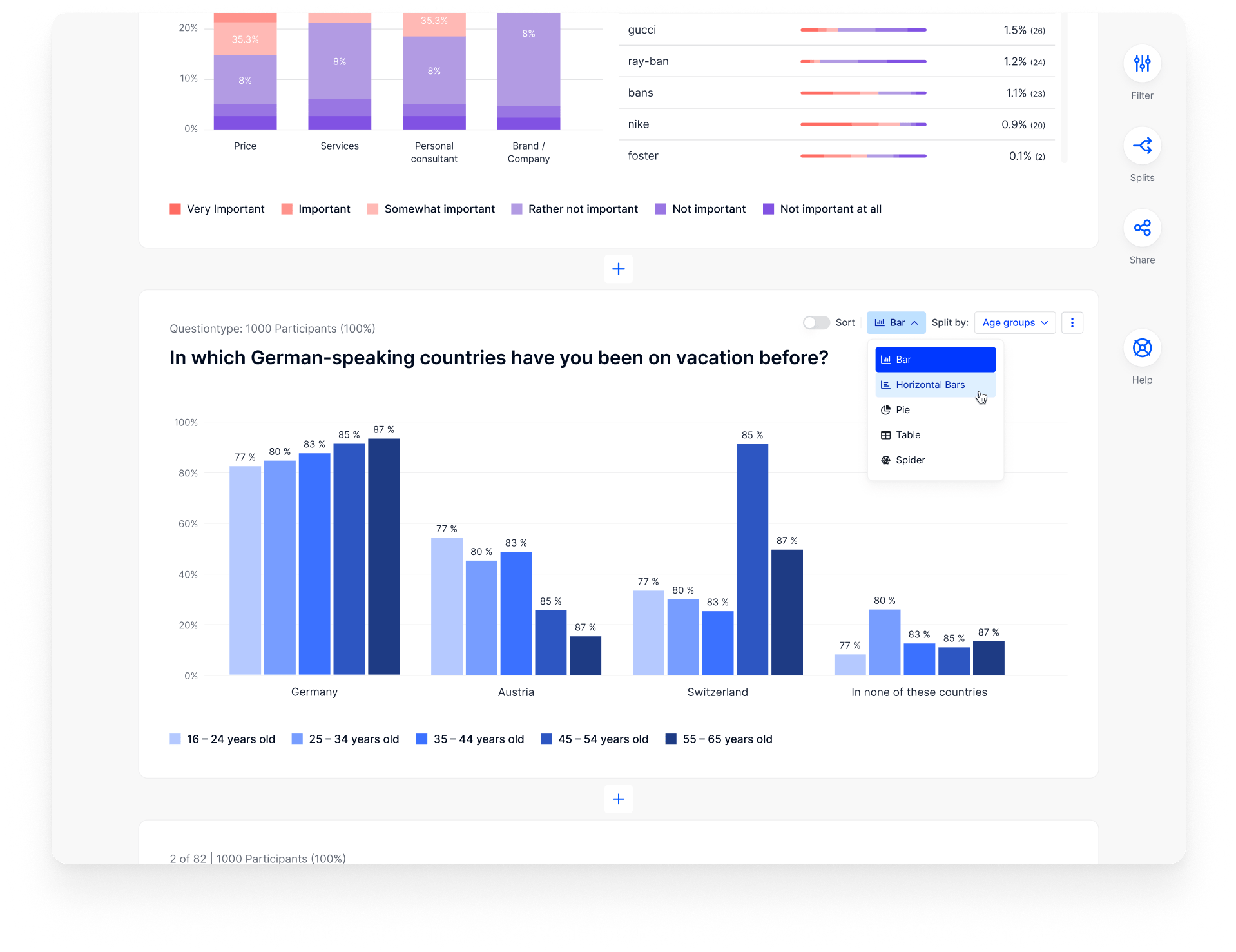
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more
30.05.2024 | 29min read
Pareto Analysis: Definition, Pareto Chart, Examples
28.05.2024 | 32min read
What is Systematic Sampling? Definition, Types, Examples

16.05.2024 | 30min read
Time Series Analysis: Definition, Types, Techniques, Examples
Market Research vs. UX Research: How to Decide?

Posted by Julia Marks on Mar 20, 2023
It’s an exciting time to be in UX research – a rapidly, evolving world means an increasingly important need to understand it. Where do you start, you ask? When to turn to market research, UX research – or both – to answer your company’s most burning questions isn’t always black and white, so let’s unpack the differences and similarities between the two.
The line between market research & UX research can be blurry at times. When speaking with fellow colleagues who’ve transitioned from dedicated market research to UX research roles over the years, you'll hear there’s a lot of overlap. Some argue:
- UX research is a subset of market research
- Both research types can occur at any point along the company and/or product lifecycle
- Both researchers advocate for and/or act as the voice of the consumers
While both market researchers and UX researchers conduct research with many different purposes, in general, market research champions who your target is, while user experience research champions that target’s ideal experience. Ask these three questions to decide which expertise, UX or Market, to invest in:
What questions are you trying to answer?
- What’s the desired delivery of insights timeline?
What impact will this research have?
Research objective:.
In market research , the questions usually stem from any team focused on trying to make business decisions related to the brand, its product or service offerings, or its mission. These teams will ask questions to understand consumer purchase behaviors, ensure business strategies are intact, and competitiveness is maintained in the industry. Here are some example questions:
- What demographic targets and market niches hold the most sales potential?
- What impact does an advertising campaign have on the audience’s brand perceptions and purchase interest?
- How does the target audience feel about the brand’s overall mission?
UX research explores the optimization of product design and interaction. So whereas market research often focuses more broadly on the sales of a product or service, UX research narrows in on how people engage and interact with the products or services. In most cases, UX research is geared towards solutions-based insights because it stems from the idea that there is a problem to be identified, solved for, and/or prevented. Here are some example questions:
- How do people use or interact with the product on a daily basis, and what frustrations or delights do they have?
- How do product features impact the user’s ability to effectively complete a task?
- How will users feel about a redesign of a product or service, and what are the key watch-outs?
- What groups of people use the product differently or have different expectations than others?
- What current solutions and behaviors exist that unearth the white space for new product development?
Every company within every industry can benefit from both types of research to thrive – ensuring your target audiences are offered the right products that work optimally for their needs. Although the questions vary, the reality is that a research study can include aspects from both research types. For example, studies we’ve conducted at AnswerLab have assessed how users currently use products, as well as their interest in new products the team was considering, which included profiling the potential target. Here are some example questions that overlap:
- Who is the target audience – what do they think, feel, see, and do…and what are their unique needs and desires?
- How do people comprehend and resonate with elements of marketing programs and platforms, such as websites, social media messaging, content marketing, etc.?
Study Design:
What’s the desired delivery timeline for insights.
How quickly do these insights need to be shared with stakeholders? The answer will not always help you discern which research is best but in many cases, certainly not always, UX research can be better for quicker turnaround times. This is often because the questions and decisions needed to be made tend to be more pointed toward a specific product, service, or need.
Although UX research is historically associated with qualitative studies and market research with quantitative studies, both types of research can involve quantitative and qualitative methodologies and span any length of time to meet a deadline. In fact, both types of research can be conducted using most of the same types of quantitative or qualitative methodologies.
So if the methodologies and the insights delivery timelines can overlap between the research practices, why are they often conducted by different researchers in dedicated agencies or departments? Although not drastically different, there’s a level of expertise and skill in asking UX-type questions and conducting impactful UX studies. For instance, UX researchers are often deeply embedded and knowledgeable in engineering and design team terminology. That said, those that transition between the two disciplines either for a specific project or in their larger career, usually feel really comfortable diving in. At its core, consumer research is consumer research.
Research Impact:
Last but not least, the impact of this research will determine if market or UX research should be the main focus. How will the answer to this research question affect the company’s next move? If the answer will impact the trajectory of the user’s engagement with the product or future product’s design, UX research is key. However, if the answer will impact the trajectory of the overall strategy that the product will thrive in, market research is necessary.
Regardless of the intended impact, it’s important to remember why we’re here. The center of all research questions is what the impact will have on the business. Making users [insert goal: happier, more successful, etc.] will ultimately drive them to continue coming back to what your company has to offer. A holistic approach to research ensures users’ sign-off on every touchpoint with your product and brand overall.
Understanding your audience and their experiences are dependent on each other’s success, which is why one research type is not more important than the other. Knowing which type of research to employ based on these three factors – research objective, study design and research impact – will help your team decide which route to take.
Need help building your research program? Get in touch with a UX strategist to get started.
Julia marks, related insights.
We’re continuing the conversation on research with teens. Last week, we shared why you should conduct research with teen...
You’re a UX Researcher. It’s a Tuesday morning and you have some agile ceremony to go to. Your product owner has changed...
Qualitative researchers are often asked to supplement their research with quantitative methods, and for many, it’s easy ...
stay connected with AnswerLab
Keep up with the latest in UX research. Our monthly newsletter offers useful UX insights and tips, relevant research, and news from our team.
Learn / Blog / Article
Back to blog
How to do market research in 4 steps: a lean approach to marketing research
From pinpointing your target audience and assessing your competitive advantage, to ongoing product development and customer satisfaction efforts, market research is a practice your business can only benefit from.
Learn how to conduct quick and effective market research using a lean approach in this article full of strategies and practical examples.

Last updated
Reading time.
A comprehensive (and successful) business strategy is not complete without some form of market research—you can’t make informed and profitable business decisions without truly understanding your customer base and the current market trends that drive your business.
In this article, you’ll learn how to conduct quick, effective market research using an approach called 'lean market research'. It’s easier than you might think, and it can be done at any stage in a product’s lifecycle.
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps
What is market research, why is market research so valuable, advantages of lean market research, 4 common market research methods, 5 common market research questions, market research faqs.
We’ll jump right into our 4-step approach to lean market research. To show you how it’s done in the real world, each step includes a practical example from Smallpdf , a Swiss company that used lean market research to reduce their tool’s error rate by 75% and boost their Net Promoter Score® (NPS) by 1%.
Research your market the lean way...
From on-page surveys to user interviews, Hotjar has the tools to help you scope out your market and get to know your customers—without breaking the bank.
The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours.
1. Create simple user personas
A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data from people who use websites and products similar to your own. Start by defining broad user categories, then elaborate on them later to further segment your customer base and determine your ideal customer profile .
How to get the data: use on-page or emailed surveys and interviews to understand your users and what drives them to your business.
How to do it right: whatever survey or interview questions you ask, they should answer the following questions about the customer:
Who are they?
What is their main goal?
What is their main barrier to achieving this goal?
Pitfalls to avoid:
Don’t ask too many questions! Keep it to five or less, otherwise you’ll inundate them and they’ll stop answering thoughtfully.
Don’t worry too much about typical demographic questions like age or background. Instead, focus on the role these people play (as it relates to your product) and their goals.
How Smallpdf did it: Smallpdf ran an on-page survey for a couple of weeks and received 1,000 replies. They learned that many of their users were administrative assistants, students, and teachers.
Next, they used the survey results to create simple user personas like this one for admins:
Who are they? Administrative Assistants.
What is their main goal? Creating Word documents from a scanned, hard-copy document or a PDF where the source file was lost.
What is their main barrier to achieving it? Converting a scanned PDF doc to a Word file.
💡Pro tip: Smallpdf used Hotjar Surveys to run their user persona survey. Our survey tool helped them avoid the pitfalls of guesswork and find out who their users really are, in their own words.
You can design a survey and start running it in minutes with our easy-to-use drag and drop builder. Customize your survey to fit your needs, from a sleek one-question pop-up survey to a fully branded questionnaire sent via email.
We've also created 40+ free survey templates that you can start collecting data with, including a user persona survey like the one Smallpdf used.
2. Conduct observational research
Observational research involves taking notes while watching someone use your product (or a similar product).
Overt vs. covert observation
Overt observation involves asking customers if they’ll let you watch them use your product. This method is often used for user testing and it provides a great opportunity for collecting live product or customer feedback .
Covert observation means studying users ‘in the wild’ without them knowing. This method works well if you sell a type of product that people use regularly, and it offers the purest observational data because people often behave differently when they know they’re being watched.
Tips to do it right:
Record an entry in your field notes, along with a timestamp, each time an action or event occurs.
Make note of the users' workflow, capturing the ‘what,’ ‘why,’ and ‘for whom’ of each action.

Don’t record identifiable video or audio data without consent. If recording people using your product is helpful for achieving your research goal, make sure all participants are informed and agree to the terms.
Don’t forget to explain why you’d like to observe them (for overt observation). People are more likely to cooperate if you tell them you want to improve the product.
💡Pro tip: while conducting field research out in the wild can wield rewarding results, you can also conduct observational research remotely. Hotjar Recordings is a tool that lets you capture anonymized user sessions of real people interacting with your website.
Observe how customers navigate your pages and products to gain an inside look into their user behavior . This method is great for conducting exploratory research with the purpose of identifying more specific issues to investigate further, like pain points along the customer journey and opportunities for optimizing conversion .
With Hotjar Recordings you can observe real people using your site without capturing their sensitive information
How Smallpdf did it: here’s how Smallpdf observed two different user personas both covertly and overtly.
Observing students (covert): Kristina Wagner, Principle Product Manager at Smallpdf, went to cafes and libraries at two local universities and waited until she saw students doing PDF-related activities. Then she watched and took notes from a distance. One thing that struck her was the difference between how students self-reported their activities vs. how they behaved (i.e, the self-reporting bias). Students, she found, spent hours talking, listening to music, or simply staring at a blank screen rather than working. When she did find students who were working, she recorded the task they were performing and the software they were using (if she recognized it).
Observing administrative assistants (overt): Kristina sent emails to admins explaining that she’d like to observe them at work, and she asked those who agreed to try to batch their PDF work for her observation day. While watching admins work, she learned that they frequently needed to scan documents into PDF-format and then convert those PDFs into Word docs. By observing the challenges admins faced, Smallpdf knew which products to target for improvement.
“Data is really good for discovery and validation, but there is a bit in the middle where you have to go and find the human.”
3. Conduct individual interviews
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. They allow you to dig deep and explore their concerns, which can lead to all sorts of revelations.
Listen more, talk less. Be curious.
Act like a journalist, not a salesperson. Rather than trying to talk your company up, ask people about their lives, their needs, their frustrations, and how a product like yours could help.
Ask "why?" so you can dig deeper. Get into the specifics and learn about their past behavior.
Record the conversation. Focus on the conversation and avoid relying solely on notes by recording the interview. There are plenty of services that will transcribe recorded conversations for a good price (including Hotjar!).
Avoid asking leading questions , which reveal bias on your part and pushes respondents to answer in a certain direction (e.g. “Have you taken advantage of the amazing new features we just released?).
Don't ask loaded questions , which sneak in an assumption which, if untrue, would make it impossible to answer honestly. For example, we can’t ask you, “What did you find most useful about this article?” without asking whether you found the article useful in the first place.
Be cautious when asking opinions about the future (or predictions of future behavior). Studies suggest that people aren’t very good at predicting their future behavior. This is due to several cognitive biases, from the misguided exceptionalism bias (we’re good at guessing what others will do, but we somehow think we’re different), to the optimism bias (which makes us see things with rose-colored glasses), to the ‘illusion of control’ (which makes us forget the role of randomness in future events).
How Smallpdf did it: Kristina explored her teacher user persona by speaking with university professors at a local graduate school. She learned that the school was mostly paperless and rarely used PDFs, so for the sake of time, she moved on to the admins.
A bit of a letdown? Sure. But this story highlights an important lesson: sometimes you follow a lead and come up short, so you have to make adjustments on the fly. Lean market research is about getting solid, actionable insights quickly so you can tweak things and see what works.
💡Pro tip: to save even more time, conduct remote interviews using an online user research service like Hotjar Engage , which automates the entire interview process, from recruitment and scheduling to hosting and recording.
You can interview your own customers or connect with people from our diverse pool of 200,000+ participants from 130+ countries and 25 industries. And no need to fret about taking meticulous notes—Engage will automatically transcribe the interview for you.
4. Analyze the data (without drowning in it)
The following techniques will help you wrap your head around the market data you collect without losing yourself in it. Remember, the point of lean market research is to find quick, actionable insights.
A flow model is a diagram that tracks the flow of information within a system. By creating a simple visual representation of how users interact with your product and each other, you can better assess their needs.
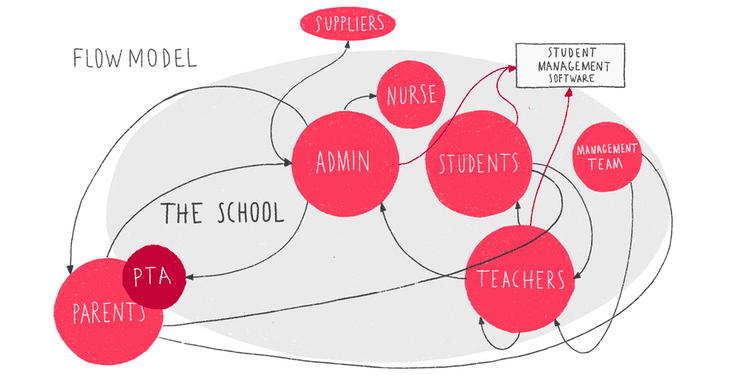
You’ll notice that admins are at the center of Smallpdf’s flow model, which represents the flow of PDF-related documents throughout a school. This flow model shows the challenges that admins face as they work to satisfy their own internal and external customers.
Affinity diagram
An affinity diagram is a way of sorting large amounts of data into groups to better understand the big picture. For example, if you ask your users about their profession, you’ll notice some general themes start to form, even though the individual responses differ. Depending on your needs, you could group them by profession, or more generally by industry.
We wrote a guide about how to analyze open-ended questions to help you sort through and categorize large volumes of response data. You can also do this by hand by clipping up survey responses or interview notes and grouping them (which is what Kristina does).
“For an interview, you will have somewhere between 30 and 60 notes, and those notes are usually direct phrases. And when you literally cut them up into separate pieces of paper and group them, they should make sense by themselves.”
Pro tip: if you’re conducting an online survey with Hotjar, keep your team in the loop by sharing survey responses automatically via our Slack and Microsoft Team integrations. Reading answers as they come in lets you digest the data in pieces and can help prepare you for identifying common themes when it comes time for analysis.
Hotjar lets you easily share survey responses with your team
Customer journey map
A customer journey map is a diagram that shows the way a typical prospect becomes a paying customer. It outlines their first interaction with your brand and every step in the sales cycle, from awareness to repurchase (and hopefully advocacy).
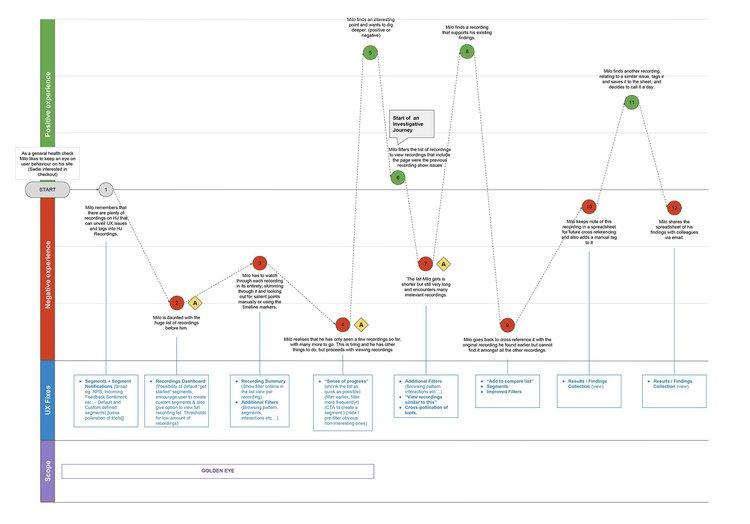
The above customer journey map , created by our team at Hotjar, shows many ways a customer might engage with our tool. Your map will be based on your own data and business model.
📚 Read more: if you’re new to customer journey maps, we wrote this step-by-step guide to creating your first customer journey map in 2 and 1/2 days with free templates you can download and start using immediately.
Next steps: from research to results
So, how do you turn market research insights into tangible business results? Let’s look at the actions Smallpdf took after conducting their lean market research: first they implemented changes, then measured the impact.

Implement changes
Based on what Smallpdf learned about the challenges that one key user segment (admins) face when trying to convert PDFs into Word files, they improved their ‘PDF to Word’ conversion tool.
We won’t go into the details here because it involves a lot of technical jargon, but they made the entire process simpler and more straightforward for users. Plus, they made it so that their system recognized when you drop a PDF file into their ‘Word to PDF’ converter instead of the ‘PDF to Word’ converter, so users wouldn’t have to redo the task when they made that mistake.
In other words: simple market segmentation for admins showed a business need that had to be accounted for, and customers are happier overall after Smallpdf implemented an informed change to their product.
Measure results
According to the Lean UX model, product and UX changes aren’t retained unless they achieve results.
Smallpdf’s changes produced:
A 75% reduction in error rate for the ‘PDF to Word’ converter
A 1% increase in NPS
Greater confidence in the team’s marketing efforts
"With all the changes said and done, we've cut our original error rate in four, which is huge. We increased our NPS by +1%, which isn't huge, but it means that of the users who received a file, they were still slightly happier than before, even if they didn't notice that anything special happened at all.”
Subscribe to fresh and free monthly insights.
Over 50,000 people interested in UX, product, digital empathy, and beyond, receive our newsletter every month. No spam, just thoughtful perspectives from a range of experts, new approaches to remote work, and loads more valuable insights. If that floats your boat, why not become a subscriber?
I have read and accepted the message outlined here: Hotjar uses the information you provide to us to send you relevant content, updates and offers from time to time. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any email.
Market research (or marketing research) is any set of techniques used to gather information and better understand a company’s target market. This might include primary research on brand awareness and customer satisfaction or secondary market research on market size and competitive analysis. Businesses use this information to design better products, improve user experience, and craft a marketing strategy that attracts quality leads and improves conversion rates.
David Darmanin, one of Hotjar’s founders, launched two startups before Hotjar took off—but both companies crashed and burned. Each time, he and his team spent months trying to design an amazing new product and user experience, but they failed because they didn’t have a clear understanding of what the market demanded.
With Hotjar, they did things differently . Long story short, they conducted market research in the early stages to figure out what consumers really wanted, and the team made (and continues to make) constant improvements based on market and user research.
Without market research, it’s impossible to understand your users. Sure, you might have a general idea of who they are and what they need, but you have to dig deep if you want to win their loyalty.
Here’s why research matters:
Obsessing over your users is the only way to win. If you don’t care deeply about them, you’ll lose potential customers to someone who does.
Analytics gives you the ‘what’, while research gives you the ‘why’. Big data, user analytics , and dashboards can tell you what people do at scale, but only research can tell you what they’re thinking and why they do what they do. For example, analytics can tell you that customers leave when they reach your pricing page, but only research can explain why.
Research beats assumptions, trends, and so-called best practices. Have you ever watched your colleagues rally behind a terrible decision? Bad ideas are often the result of guesswork, emotional reasoning, death by best practices , and defaulting to the Highest Paid Person’s Opinion (HiPPO). By listening to your users and focusing on their customer experience , you’re less likely to get pulled in the wrong direction.
Research keeps you from planning in a vacuum. Your team might be amazing, but you and your colleagues simply can’t experience your product the way your customers do. Customers might use your product in a way that surprises you, and product features that seem obvious to you might confuse them. Over-planning and refusing to test your assumptions is a waste of time, money, and effort because you’ll likely need to make changes once your untested business plan gets put into practice.
Lean User Experience (UX) design is a model for continuous improvement that relies on quick, efficient research to understand customer needs and test new product features.
Lean market research can help you become more...
Efficient: it gets you closer to your customers, faster.
Cost-effective: no need to hire an expensive marketing firm to get things started.
Competitive: quick, powerful insights can place your products on the cutting edge.
As a small business or sole proprietor, conducting lean market research is an attractive option when investing in a full-blown research project might seem out of scope or budget.
There are lots of different ways you could conduct market research and collect customer data, but you don’t have to limit yourself to just one research method. Four common types of market research techniques include surveys, interviews, focus groups, and customer observation.
Which method you use may vary based on your business type: ecommerce business owners have different goals from SaaS businesses, so it’s typically prudent to mix and match these methods based on your particular goals and what you need to know.
1. Surveys: the most commonly used
Surveys are a form of qualitative research that ask respondents a short series of open- or closed-ended questions, which can be delivered as an on-screen questionnaire or via email. When we asked 2,000 Customer Experience (CX) professionals about their company’s approach to research , surveys proved to be the most commonly used market research technique.
What makes online surveys so popular?
They’re easy and inexpensive to conduct, and you can do a lot of data collection quickly. Plus, the data is pretty straightforward to analyze, even when you have to analyze open-ended questions whose answers might initially appear difficult to categorize.
We've built a number of survey templates ready and waiting for you. Grab a template and share with your customers in just a few clicks.
💡 Pro tip: you can also get started with Hotjar AI for Surveys to create a survey in mere seconds . Just enter your market research goal and watch as the AI generates a survey and populates it with relevant questions.
Once you’re ready for data analysis, the AI will prepare an automated research report that succinctly summarizes key findings, quotes, and suggested next steps.
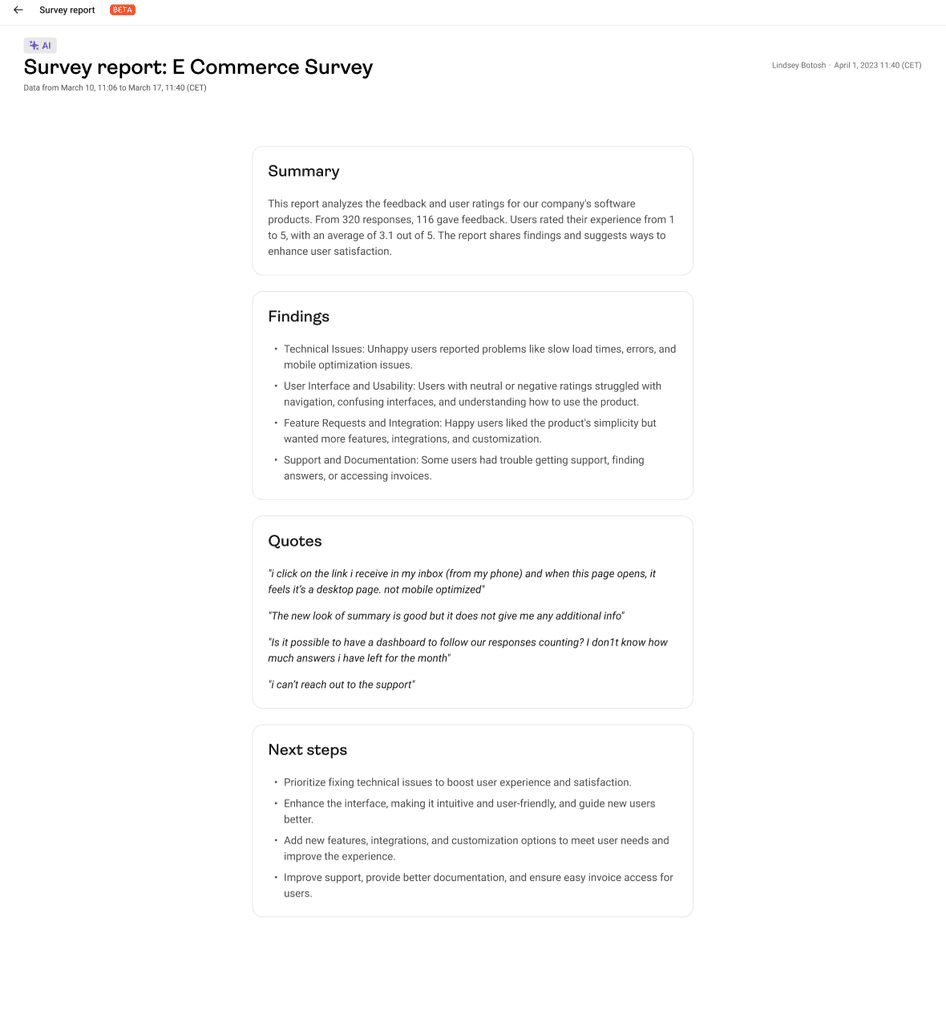
An example research report generated by Hotjar AI for Surveys
2. Interviews: the most insightful
Interviews are one-on-one conversations with members of your target market. Nothing beats a face-to-face interview for diving deep (and reading non-verbal cues), but if an in-person meeting isn’t possible, video conferencing is a solid second choice.
Regardless of how you conduct it, any type of in-depth interview will produce big benefits in understanding your target customers.
What makes interviews so insightful?
By speaking directly with an ideal customer, you’ll gain greater empathy for their experience , and you can follow insightful threads that can produce plenty of 'Aha!' moments.
3. Focus groups: the most unreliable
Focus groups bring together a carefully selected group of people who fit a company’s target market. A trained moderator leads a conversation surrounding the product, user experience, or marketing message to gain deeper insights.
What makes focus groups so unreliable?
If you’re new to market research, we wouldn’t recommend starting with focus groups. Doing it right is expensive , and if you cut corners, your research could fall victim to all kinds of errors. Dominance bias (when a forceful participant influences the group) and moderator style bias (when different moderator personalities bring about different results in the same study) are two of the many ways your focus group data could get skewed.
4. Observation: the most powerful
During a customer observation session, someone from the company takes notes while they watch an ideal user engage with their product (or a similar product from a competitor).
What makes observation so clever and powerful?
‘Fly-on-the-wall’ observation is a great alternative to focus groups. It’s not only less expensive, but you’ll see people interact with your product in a natural setting without influencing each other. The only downside is that you can’t get inside their heads, so observation still isn't a recommended replacement for customer surveys and interviews.
The following questions will help you get to know your users on a deeper level when you interview them. They’re general questions, of course, so don’t be afraid to make them your own.
1. Who are you and what do you do?
How you ask this question, and what you want to know, will vary depending on your business model (e.g. business-to-business marketing is usually more focused on someone’s profession than business-to-consumer marketing).
It’s a great question to start with, and it’ll help you understand what’s relevant about your user demographics (age, race, gender, profession, education, etc.), but it’s not the be-all-end-all of market research. The more specific questions come later.
2. What does your day look like?
This question helps you understand your users’ day-to-day life and the challenges they face. It will help you gain empathy for them, and you may stumble across something relevant to their buying habits.
3. Do you ever purchase [product/service type]?
This is a ‘yes or no’ question. A ‘yes’ will lead you to the next question.
4. What problem were you trying to solve or what goal were you trying to achieve?
This question strikes to the core of what someone’s trying to accomplish and why they might be willing to pay for your solution.
5. Take me back to the day when you first decided you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this goal.
This is the golden question, and it comes from Adele Revella, Founder and CEO of Buyer Persona Institute . It helps you get in the heads of your users and figure out what they were thinking the day they decided to spend money to solve a problem.
If you take your time with this question, digging deeper where it makes sense, you should be able to answer all the relevant information you need to understand their perspective.
“The only scripted question I want you to ask them is this one: take me back to the day when you first decided that you needed to solve this kind of problem or achieve this kind of a goal. Not to buy my product, that’s not the day. We want to go back to the day that when you thought it was urgent and compelling to go spend money to solve a particular problem or achieve a goal. Just tell me what happened.”
— Adele Revella , Founder/CEO at Buyer Persona Institute
Bonus question: is there anything else you’d like to tell me?
This question isn’t just a nice way to wrap it up—it might just give participants the opportunity they need to tell you something you really need to know.
That’s why Sarah Doody, author of UX Notebook , adds it to the end of her written surveys.
“I always have a last question, which is just open-ended: “Is there anything else you would like to tell me?” And sometimes, that’s where you get four paragraphs of amazing content that you would never have gotten if it was just a Net Promoter Score [survey] or something like that.”
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research asks questions that can’t be reduced to a number, such as, “What is your job title?” or “What did you like most about your customer service experience?”
Quantitative research asks questions that can be answered with a numeric value, such as, “What is your annual salary?” or “How was your customer service experience on a scale of 1-5?”
→ Read more about the differences between qualitative and quantitative user research .
How do I do my own market research?
You can do your own quick and effective market research by
Surveying your customers
Building user personas
Studying your users through interviews and observation
Wrapping your head around your data with tools like flow models, affinity diagrams, and customer journey maps
What is the difference between market research and user research?
Market research takes a broad look at potential customers—what problems they’re trying to solve, their buying experience, and overall demand. User research, on the other hand, is more narrowly focused on the use (and usability ) of specific products.
What are the main criticisms of market research?
Many marketing professionals are critical of market research because it can be expensive and time-consuming. It’s often easier to convince your CEO or CMO to let you do lean market research rather than something more extensive because you can do it yourself. It also gives you quick answers so you can stay ahead of the competition.
Do I need a market research firm to get reliable data?
Absolutely not! In fact, we recommend that you start small and do it yourself in the beginning. By following a lean market research strategy, you can uncover some solid insights about your clients. Then you can make changes, test them out, and see whether the results are positive. This is an excellent strategy for making quick changes and remaining competitive.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Related articles

6 traits of top marketing leaders (and how to cultivate them in yourself)
Stepping into a marketing leadership role can stir up a mix of emotions: excitement, optimism, and, often, a gnawing doubt. "Do I have the right skills to truly lead and inspire?" If you've ever wrestled with these uncertainties, you're not alone.
Hotjar team

The 7 best BI tools for marketers in 2024 (and how to use them)
Whether you're sifting through campaign attribution data or reviewing performance reports from different sources, extracting meaningful business insights from vast amounts of data is an often daunting—yet critical—task many marketers face. So how do you efficiently evaluate your results and communicate key learnings?
This is where business intelligence (BI) tools come in, transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive informed, customer-centric decisions.

6 marketing trends that will shape the future of ecommerce in 2023
Today, marketing trends evolve at the speed of technology. Ecommerce businesses that fail to update their marketing strategies to meet consumers where they are in 2023 will be left out of the conversations that drive brand success.

Geoff Whiting
- Artificial Intelligence
- Product Management
- UX Research
Market Research vs User Research: How To Overcome Uncertainty

Creating a digital product from scratch can make for an exciting process but never a smooth ride. But by doing the right research at the right time, you can get the information you need to advance. Easier said than done... Is it not just a question of market research vs user research?
We wrote this to help you choose the right research methods more easily.
In this article we answer:
- How do we distinguish between types of research?
- What characteristics define market research vs user research?
- How do we combine market research and user research?
Whether a product manager working in a big company or the owner of a startup, you face a multitude of uncertainties along the way. When taking on the challenge of converting an idea into a real product, you identify the target users and their pain points.
You also find out if your solution works for them and analyze how they use it. How do we decide then which way to go whenever we come to a crossroads?
At UX studio , we strongly believe that research provides the answer! But choosing the right type of research for the right questions at the right time doesn’t come so straightforwardly. It is not just about market research vs user research anymore.
So how should you do it then? Let’s take a look at some of the questions you might have along the way.

So many questions regarding research. What should I do?
- Does the need for our product exist? How big of a potential market has it got?
- What competing products have already entered the market? What market shares have they gained?
- Who would we see as the customers for our product? What are they trying to accomplish? What pain points and motivations have they got?
- How do potential users currently solve their problems?
- How likely will they buy our product? How much would they pay?
- What features do they find the most important?
- Does our product solve their problems? How intuitively can they use the product?
- How do they use it? How satisfied does it leave them?
- How can we get more of them?
We know that questions like these keep coming and they can overwhelm us sometimes. Don’t panic. Doing the right research can give the answers you need to move on and create a great product. However, things could look a bit fuzzy. So, what type of research do you need and when?
In a previous post about UX research , my colleague Alexandra explored the kinds of user research methods product managers have at hand at each step of the product development life cycle in order to make informed decisions.
Now I want to take a step back and think of research in general. Some questions might not find the best answers applying user research methods. Sometimes we need to turn to market research to get the relevant and reliable answers we need. And use other tools as well.
So not all research works the same?

Exactly. The type of research depends on the questions you want to answer and the kind of information you need. Take two of the most important questions we face at the beginning of a project: Does the market have the need for a product like we want to build and how much ?
The user research approach
A UX researcher would try to find answers by conducting interviews with potential users. Ideally, they would spend time observing them in their environment ( ethnography ). They would pay special attention to user behavior observing the problems they face and how they solve them.
The interviews should provide information on:
- What the people want to achieve;
- How they currently do it;
- What problems they face along the way; and
- What motivates them to keep going.
The research should indicate if a need for a product like we envision exists. However, it wouldn’t say anything about how much need exists (how many people have the problem, with what frequency, etc.).

The market research approach
A market researcher would also try to conduct interviews with potential users. This is where the question market research vs user research comes in. Market researchers would concentrate on the product idea’s appeal, key purchasing factors and other possible solutions.
They would follow the interviews with a survey on a representative sample from the target group. It would find out the product’s occurrence and frequency, the current solution, the likelihood of using the new product, and user demographic characteristics.
The survey results would add a quantitative dimension to the qualitative insights. Consequently, they give an idea about the amount of need on the market, and in turn an estimate of the new product’s potential.
This example shows how user research and market research clearly differ in strategy. It also indicates that the insights they provide complement each other.
User research aims to find people’s true pain points and motivations based on their behavior. However, market research aims to find people’s attitudes towards a product and estimate the size of the potential market .

So how exactly do user research and market research differ?
Market research: broad insights focused on attitudes.
Market research primarily involves getting the broad picture , uncovering high-level information regarding a specific industry. Market researchers use mainly quantitative methods , meaning they focus on numbers. They run studies on large representative samples so to infer results for the whole population.
The results of surveys reflect the situation in the whole population within an acceptable margin of error. This can make us quite sure of the average potential user’s age, income level, level of education and other general characteristics.
Market research tends to give more weight to attitudinal data (what people say about themselves or about what they would do) rather than to concrete behaviors in a certain context. They use insights from market research primarily to inform marketing decisions .
User Research: Detailed insights focused on behavior
User research employs a very different strategy. It has nothing to do with market size and shares, trends, market segments, demographics, and less to do with attitudinal responses. Instead, it looks at people’s behavior , how they solve everyday problems, use a product, etc. It does not deal with broad data, but rather very specific, deep insights regarding users.
User research provides a direction about how to design a product, and to what extent it meets user needs. We can use significantly smaller sample sizes because the results don’t need statistical accuracy.
User research focuses on producing qualitative data about what lies behind what people say. It looks specifically at what they literally do while using a product. Also, it prioritizes design guidance and improves the user experience.
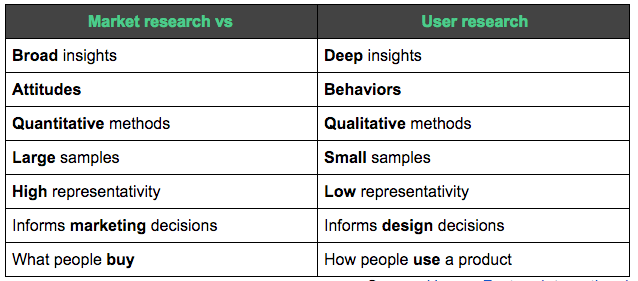
Can’t I just choose one and adapt the results to fit my needs?
Not really. Both research methods play an important role, and you must avoid using one in the wrong place. Relying on market research insights to inform UX design decisions works equally as bad as relying on user research insights to derive market size.
UX design requires different information from what market research delivers. It also estimates market size, and market shares require different information.
Also, a UX researcher or a market researcher requires different knowledge and skill sets. All-rounders who can equally master both come along a lot less often.
When do I apply user research and when market research?
Apply market research early in the product development cycle.
Market research plays an important role during the product development cycle’s early stages for analyzing the potential to make money. Here we need business insights on market size, trends and competition, and to identify product/service areas that interest people.
Apply user research to understand users and guide the design process
After the initial market research, user research will take over and dive into one of the focus areas we want to understand more deeply.
User research brings useful insights for building an innovative product: validating specific design decisions, deriving features and testing product ideas.
Once we have some concrete product ideas, market research again plays an important role. It helps in evaluating which of these concepts will most likely sell successfully and also in identifying approximate price points.
Combine market and user research to make better decisions
For making the best decisions, understand when to use both market research and user research. See below how to combine user research and market research throughout the product development cycle.
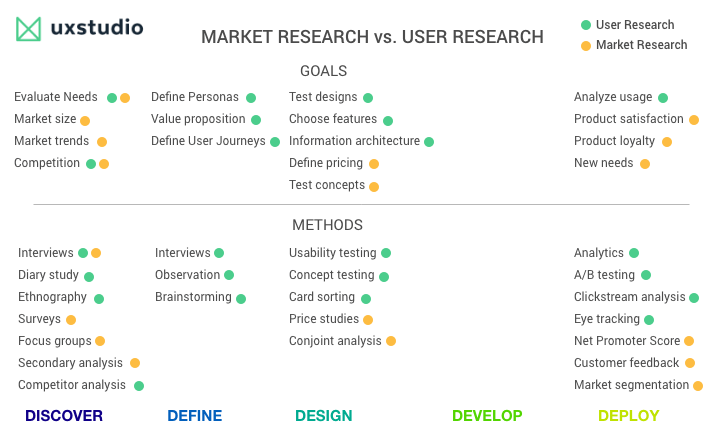
“ The most important thing for user experience professionals to know is when marketing research is needed, and when user experience research is needed. If you understand how these two methodologies work together through a product lifecycle, you will be able to work effectively with marketing departments. You can demonstrate the value of including user experience research in their projects because you are able to explain how it complements the market research they are already conducting .”
Apala Lahiri Chavan Chief Oracle and Innovator Human Factors International
Summary: Market Research vs User Research: Overcoming Uncertainty
#1 Research methods don’t all work the same. Think of the kind of information you need and choose a method that can provide the relevant answers.
#2 Although the line between and user research and market research looks quite blurred, don’t confuse the two or use them interchangeably!
#3 Market research mainly provides broad, quantitative insights about people’s attitudes and their willingness to buy a product. This, in turn, informs marketing decisions.
#4 User research mainly provides deep, focused qualitative insights about people’s behavior and how they would use a product. As a result, this informs design decisions.
#5 Used together, user research and market research can help product managers make better decisions and provide a clear roadmap to create successful products.
Want to read more?
What is beyond market research vs user research? Read more related articles to research on our blog: Product Manager’s Guide To UX Research and Nine UX Research Methods Product People Should Know .
Want to know more about the UX process? Download our free ebook Product Manager’s Guide To UX Design to read our UX case studies and learn about tools and tricks.
We also have additional reading for you, an actual hardcover Product Design book as well! And we ship it worldwide!
More into in-person learning. Reach out to us if you are thinking about organizing an in-house UX training for your team. We sure have some ideas! 😉
Let's talk
Building a bridge between UX research and market research
Table of contents.
1. Survalyzer provides answers and TestingTime test users 2. Methodological approach to market research and UX research 3. Quality in the offer, quality in the experience 4. Clients from market research, user experience and customer experience, as well as innovation departments 5. Templates for quantitative UX research to measure UX KPIs 6. UX Toolbox for free quantitative UX research
1. Survalyzer provides answers and TestingTime test users
Christian Hyka has been Managing Director of Survalyzer for almost 10 years. He is responsible for strategic product development and corporate strategy, but also supports sales. With its intuitive survey software, Survalyzer supports market researchers in survey creation, sampling and evaluation. The software has great features such as reports in the form of a ready-made PowerPoint presentation at the push of a button, as well as an online dashboard with various filtering options. The product covers all needs concerning the online data collection process to provide the desired insights fast and in an agile manner.
Reto Lämmler , Co-Founder and CEO of TestingTime, created the company in early 2015, together with Oliver Ganz, who acts as Chief Technical Officer. The idea behind TestingTime is to simplify the lives of UX and user researchers. For this purpose, TestingTime takes over the entire test user recruiting effort, thus pursuing the vision of creating a world full of happy users. As CEO, Reto ensures that TestingTime progresses in the right direction.
This is also the topic of the conversation between the two thought leaders from market research and UX. What is the next step in these fields? What is the next step for these companies? Christian and Reto appear to be at home in two different worlds, but actually they are extremely similar. Why? Read on and find out.
2. Methodological approach to market research and UX research
In general, market research is directed at understanding purchasing behaviour and preferences related to products and messages. Its aim is to understand and interpret the factors that lead to achieving a sale. UX, on the other hand, focuses on the interaction between customers and products. Market research reveals the target group and trends for a product or service. UX, on the other hand, explores how to achieve a more desirable user experience for the target group. When reading this, the immediate question that arises concerns the potentials that could be derived from a combination of both fields. And considering their development, could there be a merger sooner or later?
2.1 Quantitative or qualitative market research
Classic market research is a traditional field, while UX research is considered agile and modern. The differentiation between quantitative and qualitative market research has existed for several decades. And user experience research, which is now available in a wide variety of facets, historically originates in qualitative market research.
The quantitative market research that Survalyzer is doing, traditionally sneers a little at qualitative market research, according to Christian. Because when it comes to hard facts for a broad mass of people, quantitative market research, with its big sampling, is required. In this case, a qualitative study with just a few participants is simply not sufficient.
Christian believes that digitisation is a major game changer in connection with a possible combination of both methods. Research tools can bridge the gap, because some of their functions are the same. For example, the way a screener for test users is created is technically very similar to that of an online survey. Hence, Christian feels certain that the boundaries between quantitative and qualitative research will tend to disappear. Because suddenly people are working with the same tools and sharing their experiences. Both domains still have different tools in use, but they will be able to benefit more and more from each other.
2.2 UX researcher or classic market researcher
Reto’s position is similar. In past times, market researchers used to sneer at UX researchers and their approach. Exaggerating a little, quantitative market researchers did not seriously believe that it is possible to tell everyone how tomorrow’s product should be designed with just five user tests. At that time it was a very agile way of working, while market researchers had to rely on methodical correctness following the waterfall principle.
In addition, market research has existed as a study path for several years, and the concept is still the same as it was years ago. UX courses, on the other hand, are something very new. Reto himself obtained a master’s degree in Human Computer Interaction Design (HCID), something that has not been around for very long.
In the meantime, the methods in the world of UX have changed and improved. No longer is there just the simple 5-people usability test—currently various study methods are used. In addition, these have been supplemented by quantitative UX methods. Qualitative results are supported with quantitative validation.
Reto therefore agrees that the worlds of market research and UX research are getting increasingly closer. Not only are some of the same tools used, but there are also parallels in the methods. Ultimately, both intend the same: to offer or develop products and services that customers love, and as a consequence thereof, use and buy them.
3. Quality in the offer, quality in the experience
Quality is a central issue for both Survalyzer and TestingTime—but in a slightly different context. It is a key factor for a great customer experience.
3.1 High-quality results in online surveys
Survalyzer focuses on ensuring quality for the integration of their solution. Quality checks for this purpose are basically carried out automatically and by machine. However, they are constantly faced with challenges, such as the time required to complete a survey. How long does it take to complete the survey? What is appropriate here and what could indicate an unsuitable participant? Another issue are the so-called “straightliners”. Straightlining occurs when survey participants select identical (or almost identical) answer options. This reduces the data quality of the survey results.
Another issue are “trap questions”. Survalyzer provides its clients with a list of questions to intercept such people. It is used to identify respondents who do not pay much attention to the questions in the survey and not only answer the “trap question” itself in a non-optimal manner, but also other questions included in it.
Finally there are the “bad open answers”. This is the biggest problem for Survalyzer and its clients. Because participants sometimes write letter sequences like “afds” in the answer field. Uncovering and eliminating precisely these behavioural patterns is extremely crucial for Survalyzer and its clients to achieve quality.
3.2 High-quality panel with reliable test users
What TestingTime often hears from its clients is how they have had bad experiences with quantitative research panel providers in the past. They wished to use some of them for qualitative research purposes and were disappointed with the results. For Survalyzer, the above problems are a major challenge, and if unsuitable test users are added to the process, it has an even more negative effect on the result.
TestingTime, on the other hand, comes from the world of qualitative research, and it was necessary to make sure from the start that reliable test users were recruited. There was no way around checking people carefully beforehand. Because they have to appear personally for interviews—regardless of whether on site at the customer’s, at a research lab or remotely. When doing so, these people must match exactly the profile requested by the client. In addition, they have to be exactly what they said about themselves during the screening process.
TestingTime has always made the effort to carry out careful quality checks. However, at some point a database size was reached where it was no longer possible to do manual checks, for example, by calling the candidate in person. For this reason and to be able to continue to scale, machine learning was invested in. The team checked whether it was possible to use past responses and data to determine whether they could be rated correctly. You can find out more about this process in the blog posts “ Pool quality at scale with the help of artificial intelligence “ and “ Great quality and reliability are no coincidence “.
3.3 Survalyzer and TestingTime as a power duo
TestingTime has the same mechanisms in the screener as Survalyzer’s trap questions, response speed, etc. But the algorithm is based on all the information that the test users have provided so far. It automatically calculates whether a test user is reliable and suitable for the respective study.
Our offer would solve the problem for Survalyzer and its clients. If only well-rated and quality-tested people were used for studies, there would be no problem with the quality of the survey results and no time would be lost in sorting out straightliners, etc. The advantage of using Survalyzer in combination with TestingTime is that market researchers can access a qualitative panel like the one provided by TestingTime and use high-end survey software.
4. Clients from market research, user experience and customer experience, as well as innovation departments
Survalyzer serves clients from various industries in the DACH region as well as in the Netherlands. The company boasts a large number of clients from the banking industry, which has high requirements concerning compliance guidelines and Survalyzer specialises in these. Most of Survalyzer’s clients are still market researchers, but this is something the company wishes to change.
TestingTime is active across Europe, with a focus on the DACH region, France and the United Kingdom. At TestingTime, clients can be divided into three different fields: classic market research (the main focus of Survalyzer), user and customer experience, and innovation departments.
Six years ago, there was only the UX designer. Some time later, the UX researcher split off. The UX designer creates the experience and the UX researcher checks the experience. Or even before the UX designer creates the experience, the UX researcher checks what the experience should be like. Therefore, there was also a change at TestingTime, and the focus, although mainly on UX researchers, now also is on product managers, because these are often concerned with product-market fit.
However, innovation specialists and market researchers are also increasingly among TestingTime’s clients. People working in UX and innovation do small and regular projects with us. Market researchers, on the other hand, come with very big projects, but not so often. Agility has always been in the DNA of UX professionals, and market researchers are becoming increasingly aware of agility. For this reason, they also approach TestingTime, as we include agile practices in our offer.
Specialists from the three areas are looking for slightly different answers, and we are very excited about all of them at TestingTime. They have one thing in common though: they are looking for people to validate their idea, product or service. And they all need a survey tool to find answers.
5. Templates for quantitative UX research to measure UX KPIs
With its technology platform, Survalyzer provides easy-to-use templates as an option. This template approach requires application purposes. Last summer, Christian and Reto came up with the idea of creating standardised templates for UX.
5.1 System Usability Scale (SUS)
When evaluating the most important KPIs that are common in the world of UX, they quickly came up with the System Usability Scale (SUS). It offers a fast and reliable method for assessing the usability of design solutions. After a deep dive, Christian realized that it fits Survalyzer’s approach very well. Among other things, he read our various blog posts on how to measure UX (see the blog post in German Make UX measurable & strengthen the UX culture in the company ).
5.2 Single Ease Question (SEQ)
After doing some further brainstorming, Christian and Reto decided to build together a UX toolbox with various measuring tools. Thus, the Single Ease Question (SEQ) was added to the SUS. It checks how easily a tool can be used and how easy it is to complete a task. As the name suggests, the SEQ focuses on just a single question.
5.3 Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Finally, they decided on the Net Promoter Score (NPS). The Net Promoter Score uses a standardised survey to determine the satisfaction of a company’s customers. It’s origins can be found in the world of marketing, but surprisingly, it is often used in the world of UX. The SUS is superior to the NPS for the purposes of UX research, but the NPS has become an industry standard because it allows a better communication with stakeholders outside the world of UX.
6. UX Toolbox for free quantitative UX research
With these three tools mentioned above, Survalyzer and TestingTime launched the UX Toolbox. Its purpose is to build the bridge between market research and UX research. We wish to give our customers an advantage by using Survalyzer and TestingTime in combination, thus getting the best out of their studies.
UX has matured extremely from a methodological viewpoint in recent years, and UX measurability is a topic increasingly focused on. The toolbox helps its users to measure UX and to show to their supervisors and other stakeholders that progress and investment in UX is important.
The UX Toolbox with its evaluation convenience feature can now be used free of charge.
Toolbox with templates for measuring UX KPIs
The free toolbox reliably supports UX researchers with user experience evaluations. It allows a valid, trustworthy and objective measurement of user perception. The three relevant KPIs—Single Ease Question (SEQ), Net Promoter Score (NPS) and System Usability Scale (SUS)—help you to better assess risks and derive improvements based on them.
Use the UX Toolbox now for free.
Ines Misura
As a longtime marketer, Ines gained in-depth marketing knowledge within different industries and in companies of different sizes. She has always been at the forefront of testing new marketing trends, even in private projects. Ines always puts the customer’s expectations, needs and wishes at the centre of her work in order to provide a positive customer experience.
Related UX resources
Receive UX tips directly to your inbox.
UX tip of the week
Receive UX tips directly to your inbox. Max one email per week, we promise.

How to Conduct User Experience Research Like a Professional
Whether you’re looking to develop a broad UX design skillset, or you’re exploring UX research as a design specialization , here’s your complete introduction to conducting user research like a pro.
Hello, I’m Raven, a mentor for aspiring UX designers enrolled in the CareerFoundry UX Design Course . I also work as a UX Research Assistant at IBM and studied behavioral science at the University of Texas. I have 10 years of experience studying and analyzing human behavior—user research is definitely my thing.
During the past few years, I’ve worked with major companies, academic institutions, and non-profit organizations to develop and improve impactful products and applications. I’ve moderated focus groups, designed and administered surveys, carried out usability testing, and conducted user interviews. I also know a thing or two about creating a good persona!
In this guide, we’re going to cover the basics of UX research. We’ll start with exactly what it is, and then move on to discuss the various steps and associated terminology of UX research , as well as its role and value within the broader design process . We’ll then review the most common UX research methods, diving into how they’re conducted and a few best practices.
If you’re particularly interested in one of these topics, simply select it from the list below to jump straight to it. I’ve also added videos throughout the guide for those of you who prefer to learn with both eyes and ears—and I recommend you save this set of free UX research tutorials for later, too. Sound good? Let’s get started!
Introduction To User Experience (UX) Research
- What is UX research?
- What’s the difference between good and bad UX research?
- What are the five steps of UX research?
- What’s the role of research in the UX design process?
- Whats the value of UX research?
Introduction To User Experience Research Methods
- User Groups
- Usability Testing
- User Interviews
- Online Surveys
- User Personas
- What Next? User Research Analysis
1. What is UX research?
You read my bio in the introduction. Using only this information, could you explain why I recently switched from one time management app to another? Probably not. In order to answer this question, you need more context. UX research provides that context. So, what is UX research and what is its purpose ?
“User research is how you will know your product or service will work in the real world, with real people. It’s where you will uncover or validate the user needs which should form the basis of what you are designing.”
— Chris Mears, UXr
According to Design Modo , UX research is; “The process of understanding user behaviors, needs, and attitudes using different observation and feedback collection methods.” One of the other benefits of user experience research is that it helps us understand how people live their lives so that we can respond to their needs with informed design solutions. Good UX research involves using the right method at the right time during the development of a product.
Maria Arvidsson, Head of Product and UX at Usabilla , describes UX research as:
“The means through which you try to understand your users’ needs, behaviors and motivations and validate your assumptions and solutions.”
2. What’s the difference between good and bad UX research?
The biggest sign of an amateur UX designer is excluding end users from the design process. At the very start of my career I held the attitude that I could test any app, website, or product on myself, replacing the act of speaking with users. Never a good idea. It took time for me to learn a more professional approach, which is to start the design process by listening to the end user. Overall, UX research helps us avoid our biases since we are required to design solutions for people who are not like us.
“Insights that are received directly from user experience research are like muscle memory; the more you do research, the more insights you build up. But just like muscle memory, YOU have to be a part of the hard work in order to enjoy the lasting benefits of it that are specific to you. While it may be tempting to outsource research to a specialized team (and sometimes you can’t avoid it), you should try your utmost best to engage in at least a little bit of the research so that the insights grow under your skin instead of being handed to you from someone else who has sweated it.”
—UX designer Ali Rushdan Tariq from ARTariq
A quick plug before we continue: If you’re looking to become a professional in this subdomain of UX, be sure to take a look at our guide to becoming a UX researcher
3. What are the five steps of UX research?
Created by Erin Sanders , the Research Learning Spiral provides five main steps for conducting UX research. The first two steps are about forming questions and hypotheses, and the last three steps are about gathering knowledge through selected UX research methods.
- Objectives: What are the knowledge gaps we need to fill?
- Hypotheses: What do we think we understand about our users?
- Methods: Based on time and manpower, what methods should we select?
- Conduct: Gather data through the selected methods.
- Synthesize: Fill in the knowledge gaps, prove or disprove our hypotheses, and discover opportunities for our design efforts.
4. What’s the role of research in the UX design process?
UX research is the starting point for a project . Research helps us learn about the users and their behavior, goals, motivations, and needs. It also shows us how they currently navigate a system, where they have problems and, most importantly, how they feel when interacting with our product.
UX research comes first in the UX design process because without it, our work can only be based on our own experiences and assumptions, which is not objective. As Neil Turner, founder of UX for the Masses told us, a good foundation is key to successful design:
“Good user research is key to designing a great user experience. Designing without good user research is like building a house without solid foundations—your design will soon start to crumble and eventually fall apart.”
5. What’s the value of UX research?
In the current digital product landscape, the real value of UX research is its ability to reduce uncertainty in terms of what users want and need , which yields benefits for the product, the business, and, of course, the users themselves.
1. Product Benefits
UX research provides data about the end user of the product, how and when the user will use the product, and the main problems the product will solve. UX research is also helpful when UX designers and the rest of the team (and stakeholders) have to decide between multiple design solutions.
2. Business Benefits
UX research brings a lot of a value to businesses. By knowing the end users and incorporating design requirements upfront, businesses can speed up the product development process, eliminate redesign costs, and increase user satisfaction.
3. User Benefits
One of the greatest values of user experience research is that it’s unbiased user feedback. Simply put, UX research speaks the user’s thoughts—without any influence from outside authority. It also serves as a bridge between users and the company.
“User experience research provides powerful insights that allow companies to humanize their customers and insert their needs, intentions, and behaviors into the design and development process. In turn, these insights enable companies to create experiences that meet—and sometimes exceed—customer needs and expectations. User experience research should be conducted well before the first sketch is drawn and integrated throughout the concept, iterative design, and launch phases of a product.”
—Janelle Estes, Director of Research Strategy at UserTesting
UX research is based on observation, understanding, and analysis. With the help of various UX research techniques, you will:
- O bserve your users , keeping an eye out for non-verbal clues as to how they are feeling;
- Develop an understanding of the user’s mental model : what does the user anticipate when using a certain product? Based on their previous experience, how do they expect this particular product to work?
- A nalyze the insights you’ve gathered and try to identify patterns and trends. Eventually, these insights will inform the decisions you make about the product and how it is designed.
With that in mind, let’s consider some of the most valuable user research techniques.
1. User Groups
User groups—also called “focus group discussions” or “focus groups”—are structured interviews that quickly and inexpensively reveal the desires, experiences, and attitudes of a target audience. User groups are a helpful user experience research method when a company needs a lot of insight in a short amount of time. If you are unsure when to use a user experience research method, user groups can be a good one to start with.
Why Do We Conduct User Groups?
User groups can help your company better understand:
1) How users perceive a product
2) What users believe are a product’s most important features
3) What problems users experience with the product
4) Where users feel the product fails to meet expectations
User groups can also be used to generate ideas of what users want to see in the future.
What people say and what people do are often very different, therefore user groups do not provide an accurate measurement of behavior . And because user groups are conducted with more than one user at a time, participants may influence each other’s opinions and preferences (aka “groupthink”), thus introducing bias and producing inaccurate data.
Best Practices For User Groups
Getting the most out of your user group is straightforward if you consider the following best practices when conducting this particular user research technique.
- Ask good questions: Make sure your questions are clear, open-ended, and focused on the topics you’re investigating.
- Choose a few topics: On average, plan to discuss 3-5 topics during a 90-minute focus group.
- Include the right amount of people: A good focus group should include 3-6 users—large enough to include a variety of perspectives, but small enough so everyone has a chance to speak.
“Conducting user research allows you to dive deep beneath the surface of what your users say they want, to instead uncover what they actually need. It’s the key to ensuring that your products and features will actually solve the problems that your clients face on a day to day basis. User research is imperative if you want to create a successful, habit forming product.”
— Jennifer Aldrich, UX and Content Strategist at InVisionApp
How To Conduct User Experience Research With User Groups
Conducting user groups can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Create a schedule that provides enough time for recruiting, testing, analyzing, and integrating results.
- Assemble your team, and establish roles: choose a moderator, note-taker, and discussion leader.
- Define the scope of your research: what questions will you ask? And how in-depth do you want to explore the answers? This will determine the number of people and the number of groups that need to be tested.
- Create a discussion guide that includes 3-5 topics for discussion.
- Recruit potential or existing users who are likely to provide good feedback.
- Conduct user group testing, and record data.
- Analyze and report findings.
“It’s really hard to design products by user groups. A lot of times, people don’t know what they want until you show it to them.”
—Steve Jobs
2. Usability Testing
According to the usability.gov website, usability testing refers to “evaluating a product or service by testing it with representative users.” During a test, participants will be asked to complete specific tasks while one or more observers watch, listen, and record notes. The main goal of this user experience testing method is to identify usability problems, collect qualitative data, and determine participants’ overall satisfaction with the product.
Why Do We Perform Usability Testing?
Usability testing helps identify problems before they are coded. When development issues are identified early on, it is typically less expensive to fix them. Usability testing also reveals how satisfied users are with the product , as well as what changes are required to improve user satisfaction and performance .
Unfortunately, usability testing is not 100% representative of the real life scenario in which a user will engage with your product. Also, because the data is qualitative, this kind of UX testing method doesn’t provide the large samples of feedback a questionnaire might. The good news it that the qualitative feedback you receive can be far more accurate and insightful.
Best Practices For Usability Testing
- Test with five users: Testing five users is typically enough to identify a design’s most important usability problems.
- Invite your team to the testing sessions: Anyone who is involved with how fast and how well problems are addressed should be invited to the usability testing sessions. These stakeholders may include the executive team, and lead developers or designers.
- Keep the findings brief and to-the-point: When you report the findings of a usability test, limit the comments to the ones that are really important. One good rule of thumb is to include the top three positive comments and the top three problems. The overall report should be no more than approximately 50 comments and 30 pages.
How to Conduct UX Research with Usability Testing
Usability testing can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Identify what needs to be tested and why (e.g. a new product, feature, etc.)
- Identify the target audience (or your desired customers).
- Create a list of tasks for the participants to work through.
- Recruit the right participants for the test.
- Involve the right stakeholders.
- Apply what you learn.
“One of usability’s most hard-earned lessons is that ‘you are not the user.’ If you work on a development project, you’re atypical by definition. Design to optimize the user experience for outsiders, not insiders.”
– Jakob Nielsen
3. User Interviews
A well-known user experience methodology is an interview. An interview is a user experience research method used to discover the attitudes, beliefs, and experiences of users (and potential users) of a product. Interviews are typically conducted by one interviewer speaking to one user at a time for 30 minutes to an hour. Interviews can take place face-to-face, over the phone, or via video streaming.
Why Do We Conduct Interviews?
Of all the user experience design methods, interviews are typically conducted at the beginning of the product development cycle when reviewing product goals. Because of the one-to-one nature of the interview, individual concerns and misunderstandings can be directly addressed and cleared up.
Face-to-face interviews also allow you to capture verbal and nonverbal cues, such as emotions and body language, which may identify enthusiasm for the product or discomfort with the questions.
When thinking about what research methodology to use, bear in mind that interviews are also a good supplement to online surveys: conducting an interview beforehand helps you refine questions for the survey, while conducting an interview afterwards allows you to gain explanations for survey answers.
There are a few drawbacks, however. First, because interviews require a team of people to conduct them, personnel costs are usually difficult to keep low. Sample size is also limited to the size of the interviewing staff.
Best Practices For User Interviews
- Hire a skilled interviewer: A skilled interviewer asks questions in a neutral manner, listens well, makes users feel comfortable, and knows when and how to probe for more details.
- Create a discussion guide: Write up a discussion guide (or an interview protocol) for all interviewers to follow. This guide should include questions and follow-up questions.
- Get informed consent: Before conducting the interview, make sure to get permission or consent to record the session. It’s also good to have one or two note takers on hand.
How To Conduct User Experience Research With User Interviews
Conducting an interview can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Prepare a discussion guide, or a list of questions to ask participants.
- Select a recording method (e.g. written notes, tape recorder, video).
- Conduct at least one trial run of the interview.
- Recruit the right participants for the interview.
- Conduct the interview.
- Analyze and report the results.
“Curiosity is a natural outcome of caring, and it is the single greatest contributor to effective user research … Caring and curiosity engender personal investment, and investment motivates a researcher to develop a deep understanding of users.”
– Demetrius Madrigal
4. Online Surveys
A survey is a research tool that typically includes a set of questions used to find out the preferences, attitudes, and opinions of your users on a given topic. Today, surveys are generally conducted online and in various lengths and formats. Data collected from surveys is received automatically, and the survey tool selected generally provides some level of analysis, the data from which can then be used for user experience studies further down the line to inform your product.
“It is so important to avoid using leading questions when it comes to surveys. It’s a common mistake that many people make. For example phrasing a question like “What do you dislike about Uber?” assumes the user has a negative preference for the service off the bat. A more neutral phrase would be “Tell us about your experience getting around town.” – this elicits more natural user feedback and behavior instead of forcing them down a funnel.”
– Top tip from UXBeginner
Why Do We Conduct Online Surveys?
Unlike traditional surveys, online surveys enable companies to quickly collect data from a broad (and sometimes remote) audience for free—or a low price. Surveys also help you discover who your users are , what your users want to accomplish, and what information your users are looking for.
Unfortunately, what users say versus what they do are two different things and can often yield inaccurate results. Furthermore, poorly worded questions can negatively influence how users respond. Length can also be an issue—many people hate taking long surveys. This is why it’s important to create short surveys so users are more likely to complete them and participate in future research efforts.
Best Practices For Online Surveys
- Keep it short: Keep your surveys brief, especially if participants will be compensated little or not at all. Only focus on what is truly important.
- Keep it simple: Make sure questions can be easily understood: ambiguous or complex wording can make questions more difficult to understand, which can bring the data into question.
- Keep it engaging: Include a mix of both multiple choice questions and open-ended questions (or questions in which users complete the answer).
How To Conduct User Experience Research With Online Surveys
Conducting an online survey can be broken down into a few major steps:
- Identify goals and objectives of the survey.
- Create survey questions.
Note: Consider collecting information about how satisfied users are with your product, what users like/dislike, and if they have suggestions for improvement.
- Select an online survey tool (e.g. SurveyMonkey, Qualtrics).
- Recruit participants.
- Conduct the survey.
“We have to arm ourselves with data, research … and a clear understanding of our users so our decisions are not made out of fear but out of real, actionable information. Although our clients may not have articulated reasons for why they want what they want, it is our responsibility to have an ironclad rationale to support our design decisions.”
– Debra Levin Gelman
5. User Personas
A user persona is a fictional representation of your ideal customer. A persona is generally based on user research and includes the needs, goals, and observed behavior patterns of your target audience. You can find out how to create a user persona in this detailed guide .
Why Do We Create User Personas?
Whether you’re developing a smartphone app or a mobile-responsive website, any user experience research job will require you to understand who will be using the product. Knowing your audience will help influence the features and design elements you choose, thus making your product more useful. A persona clarifies who is in your target audience by answering the following questions:
- Who is my ideal customer?
- What are the current behavior patterns of my users?
- What are the needs and goals of my users?
Understanding the needs of your users is vital to developing a successful product. Well-defined personas will enable you to efficiently identify and communicate user needs. Personas will also help you describe the individuals who use your product, which is essential to your overall value proposition.
Unfortunately, creating personas can be expensive — it all depends on how deep into user research your organization is willing to go. There is also no real “scientific logic” behind persona building, which makes some people a little more hesitant to accept them.
Best Practices For User Personas
- Create a well-defined user persona: A great persona contains four key pieces of information: header, demographic profile, end goal(s), scenario.
- Keep personas brief: As a rule of thumb, avoid adding extra details that cannot be used to influence the design. If it does not affect the final design or help make any decisions easier: omit it.
- Make personas specific and realistic: Avoid exaggerated caricatures, and include enough detail to help you find real-life representation.
How To Conduct User Experience Research By Creating Personas
Creating user personas can be broken down into these main steps:
- Discuss and identify who your target users are with stakeholders (e.g. UX team, marketing team, product manager).
- Survey and/or interview real users to get their demographic information, pain points, and preferences.
- Condense the research, and look for themes to define your groups.
- Organize your groups into personas.
- Test your personas.
“Be someone else. It takes great empathy to create a good experience. To create relevant experiences, you have to forget everything you know and design for others. Align with the expected patience, level of interest, and depth of knowledge of your users. Talk in the user’s language.”
– Niko Nyman
Which User Experience Research Method Should You Use?
Now that you know more about the various user experience research methods, which one do you choose? Well, it all depends on your overall research goals.
You’ll also need to consider what stage you’re at in the design process. If you’re just starting out, you’ll want to focus on understanding your users and the underlying problem . What are you trying to solve? Who are you trying to solve it for? At this early stage in the design process, you’ll typically use a mixture of both qualitative and quantitative methods such as field studies, diary studies, surveys, and data mining.
Once you’ve established a direction for your design, you’ll start to think about actually building your product. Your UX research will now focus on evaluating your designs and making sure that they adequately address your users’ needs . So, you’ll choose research methods that can help you to optimize your designs and improve usability—such as card sorting and usability testing.
Eventually, you’ll have finalized your design and developed a working product—but this doesn’t mean your research is done! This is the ideal time to investigate how well the product performs in the real world. At this point, you’ll focus mainly on quantitative research methods , such as usability benchmarking, surveys, and A/B testing.
To help you with the task of choosing your research methods, let’s explore some important distinctions between the various techniques.
Behavioral vs. Attitudinal Research
As mentioned before, there is a big difference between “what people do” versus “what people say.” Attitudinal research is used to understand or measure attitudes and beliefs, whereas behavioral research is used to measure behaviors. For example, usability testing is a behavioral user research method that focuses on action and performance. By contrast, user research methods like user groups, interviews, and persona creation focus on how people think about a product.
UX designers often conduct task analysis to see not how users say they complete tasks in a user flow, but how they actually do.
Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
When conducting UX research and choosing a suitable method, it’s important to understand the difference between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research gathers data that is measurable. It gives you clear-cut figures to work with, such as how many users purchased an item via your e-commerce app, or what percentage of visitors added an item to their wishlist. “Quant methods”, as they’re sometimes called in the industry, help you to put a number on the usability of your product. They also allow you to compare different designs and determine if one version performs significantly better than another.
Qualitative research explores the reasons or motivations behind these actions. Why did the user bounce from your website? What made them “wishlist” an item instead of purchasing it? While quantitative data is fixed, qualitative data is more descriptive and open-ended. You can learn all about qualitative research in the video guide below, in which CareerFoundry graduate and professional UX designer Maureen Herben takes you through the most common qualitative user research processes and tools.
A further distinction to make is between how qualitative and quantitative studies go about collecting data. Studies that are qualitative in nature are based on direct observation. For example, you’ll gather data about the user’s behaviours or attitudes by observing them directly in action. Quantitative studies gather this data indirectly—through an online survey, for example.
Qualitative research methods (e.g. usability testing, user groups, interviews) are better for answering questions about why or how to fix a problem, whereas quantitative methods (e.g. online surveys) are great for answering questions about how many and how much.
Ideally, you’ll use a mixture of both qualitative and quantitative methods throughout your user research, and work hard to ensure that the UX research you conduct is inclusive !
6. What Next? Conducting User Research Analysis
Once you’ve conducted extensive user research, you’ll move on to the analysis phase. This is where you’ll turn the raw data you’ve gathered into valuable insights. The purpose of UX research analysis is to interpret what the data means; what does it tell you about the product you’re designing, and the people you’re designing it for? How can you use the data you’ve gathered to inform the design process?
Watch this video to learn how to conduct user research analysis in five simple steps:
Final thoughts
“User experience research is the work that uncovers and articulates the needs of individuals and/or groups in order to inform the design of products and services in a structured manner.”
—Nick Remis, Adaptive Path
Overall, the purpose of user experience research is simple: to discover patterns and reveal unknown insights and preferences from the people who use your product. It basically provides the context for our design. Research also helps us fight the tendency to design for ourselves (or our stakeholders)—and returns the focus on designing for the user.
If you’d like to learn more about UX research, check out these articles:
- What Does a UX Researcher Actually Do? The Ultimate Career Guide
- The Ultimate Guide to UX Research Bootcamps
- Top 5 Mistakes to Avoid in Your UX Research Portfolio
- Interview Toolkit: Top 5 UX Research Questions to Prepare For
And to get inspired, check out these 15 quotes from influential designers in the industry.
.webp)
Market Research vs User Research: What’s the Difference?

The more you understand about our customers and the market at large, the better you can tailor our products, services, and strategies to meet their needs and expectations.
Two critical tools in this quest for insights are market research and user research . While they might seem similar at first glance, each serves a distinct purpose and offers unique insights that can significantly impact a business's trajectory.
So, what exactly makes them different? How do they each contribute to a successful business strategy ? Read on to learn their unique benefits and the ways you can effectively utilize them in tandem to maximize business success.

What is market research?
Market research, as the term implies, involves researching the market you want to target with your product or service.
It involves gathering information about the current state of the market, your competitors, and customers' trends, with the fundamental purpose of making educated decisions about the viability of your products and services for the intended market.
Some of the most common methods used in market research include surveys, focus groups, interviews, and observation.
Surveys, such as the template below, are effective for collecting large amounts of data from a wide demographic.
On the other hand, focus groups and interviews provide more in-depth qualitative insights , but usually from a smaller group of people.
You should conduct market research whenever you need to make strategic decisions related to your products or services. This can range from entering a new market, launching a new product, rebranding, or assessing the impact of marketing campaigns.
What is user research?
User research, in contrast, is a more focused type of research that delves deep into understanding the behaviors, needs, and motivations of your users.
The aim here is to gain insights into the end-user's mindset, which can help you improve your product's user experience and usability .
Some of the most commonly used user research methods include surveys , usability testing, user interviews , and contextual inquiries.
User research is an important step at any point throughout the product development cycle, from conceptualization and prototyping to continuous product improvements.
Below is a Usability Metric for User Experience (UMUX) survey template, one of the many standardized surveys you can use as part of your user research:
Market research vs user research: the key differences
While both market research and user research play integral roles in the strategic decision-making process, they serve distinct purposes and have unique methodologies.
The primary goal of market research is to gather information about the market landscape, including competitors, customer demographics, and market trends . This information can guide your businesses in making strategic decisions.
On the other hand, user research focuses on understanding the end users of a product or service. It seeks to delve into users' behaviors, needs, and motivations to ensure a product or service meets its intended audience's expectations and improves the overall user experience.
Market research typically has a larger scope as it aims to gather data about the entire market. This research often involves large sample sizes to provide a broader view of market dynamics.
Although it can involve a substantial number of participants, user research often delves into qualitative data , meaning its scope can be narrower and more depth-focused. It explores the interactions of a smaller, more specific group of users with a product or service, allowing for a deeper understanding of user behavior.
Researchers
Market research is usually conducted by marketing or business development teams looking to understand the dynamics of a given market. User research, in contrast, is often carried out by design and product development teams aiming to enhance the product's usability and user experience.

The benefits of market research
Here are some of the primary advantages of utilizing market research in business operations.
Discover customer preferences
The ability to understand customer preferences and behaviors with market research will give you a significant competitive edge. You’ll discover insights into what your customers want, their purchasing habits, and their perception of your brand so that you can tailor your products, services, and marketing efforts to match customer expectations.
Unveil market trends
Market trends change rapidly. Staying up-to-date with these shifts is critical to ensure your business remains relevant. Market research can help you identify emerging trends, technological advancements, and changes in consumer behavior so that you can ensure your products and services continue to meet market demand.
Identify business opportunities
By understanding the market landscape, including unmet customer needs and gaps in the market, you can identify potential areas for growth or expansion. This could mean diversifying your product line, entering a new market, or offering new services to fulfill unmet customer needs.
The B2B market research survey below can help you uncover your customers’ unmet essential needs and get ahead of the competition:
Reduce business risks
Investing in a new business venture or launching a new product always involves a certain level of risk. Market research can significantly mitigate these risks by providing valuable data about the market conditions and potential challenges.
Conduct competitive analysis
With market research, you’ll gain insights into your competitors’ strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. You can analyze their pricing, marketing strategies, customer base, and product offerings. This understanding can help you differentiate your products and services, develop effective marketing strategies, and ultimately gain a competitive edge.
The benefits of user research
User research is not just about improving your product; it also helps create a user-centered strategy that can have profound effects on your entire business.
Boost user experience
The key objective of user research is to optimize user experience. By studying user behaviors, needs, and motivations, you can design products and services that align with user expectations, leading to increased user satisfaction and improved product engagement.
Use the survey template below to measure user satisfaction with the key aspects of your product:
Guide product development
Without understanding what your users truly need, product development can be a shot in the dark. User research illuminates the path, offering insights that can inform every stage of product development. It ensures that the product design is intuitive, features are relevant, and that overall, the product addresses user needs effectively.
Facilitate user-centric decision making
User research shifts the business decision-making process from being assumption-based to being user-centered . This user-centric approach ensures that your business decisions, from marketing strategies to product features, are aligned with what your users want and need.
Use the survey template below to conduct a quick UX audit and collect insights on user needs:
Uncover user pain points
User research is like a magnifying glass that allows your business to identify and understand user pain points . These could be areas in your product or service where users struggle or face difficulties. Identifying these pain points is the first step towards improving your product or service and enhancing user satisfaction.
Increase ROI
While user research requires an investment of time and resources, the return on investment can be substantial in the form of reduced costs associated with product revisions, increased user engagement, and improved customer retention rates.
Integrating market research and user research
Although it might not always be possible to conduct both types of research, the combination can help you stay relevant and responsive to changing market conditions and user expectations.
While market research will inform your high-level strategic decisions, such as entering a new market or developing a new product line, user research can provide insights into the tactical aspects, such as product design and user experience.
Market trends and user needs change over time, so make both types of research an ongoing, iterative process to get a macro perspective of the market dynamics and a micro perspective of individual user interactions.

Supercharge your research with customized surveys
Despite their distinct objectives and methodologies, both market research and user research play pivotal roles in the success of your product or service.
Interestingly, there is a common thread between these two types of research - surveys. As a versatile tool, surveys can be used to gather data on customer preferences, buying habits, and overall market trends, providing a snapshot of the market at large as well as individual end user needs.
With Survicate, you get access to 300+ survey templates you can use right away to take your research to the next level. However, if you’d like to create one from scratch, you can do so in just a few clicks. Simply sign up , integrate with your favorite third-party tool , and start collecting invaluable user and customer data today.

We’re also there

- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
User Experience (UX) Surveys: The Ultimate Guide
Imagine you're a business owner eager to improve your website's user experience. You want to know what's working, what's not, and where you need improvements. While you have various research methods (such as user interviews , usability tests, A/B testing , etc.) available, a user experience (UX) survey helps gather valuable insights and pinpoint the areas for enhancement.
UX surveys can offer actionable insights , presenting qualitative data that informs decisions.
- Transcript loading…
Through this piece, you'll learn everything about user experience surveys. From market research professionals and business owners to website developers, anyone aiming for customer satisfaction will find this helpful.
You'll learn about UX survey best practices and the right questions to help identify pain points and understand different question types.
What are UX Surveys?
UX Surveys, or User Experience Surveys, gather information about users' feelings, thoughts, and behaviors related to UX design , product, or service. These online surveys form a part of the broader field of usability surveys. They focus on understanding how users interact with a system, application, or website to create a user-centered design .
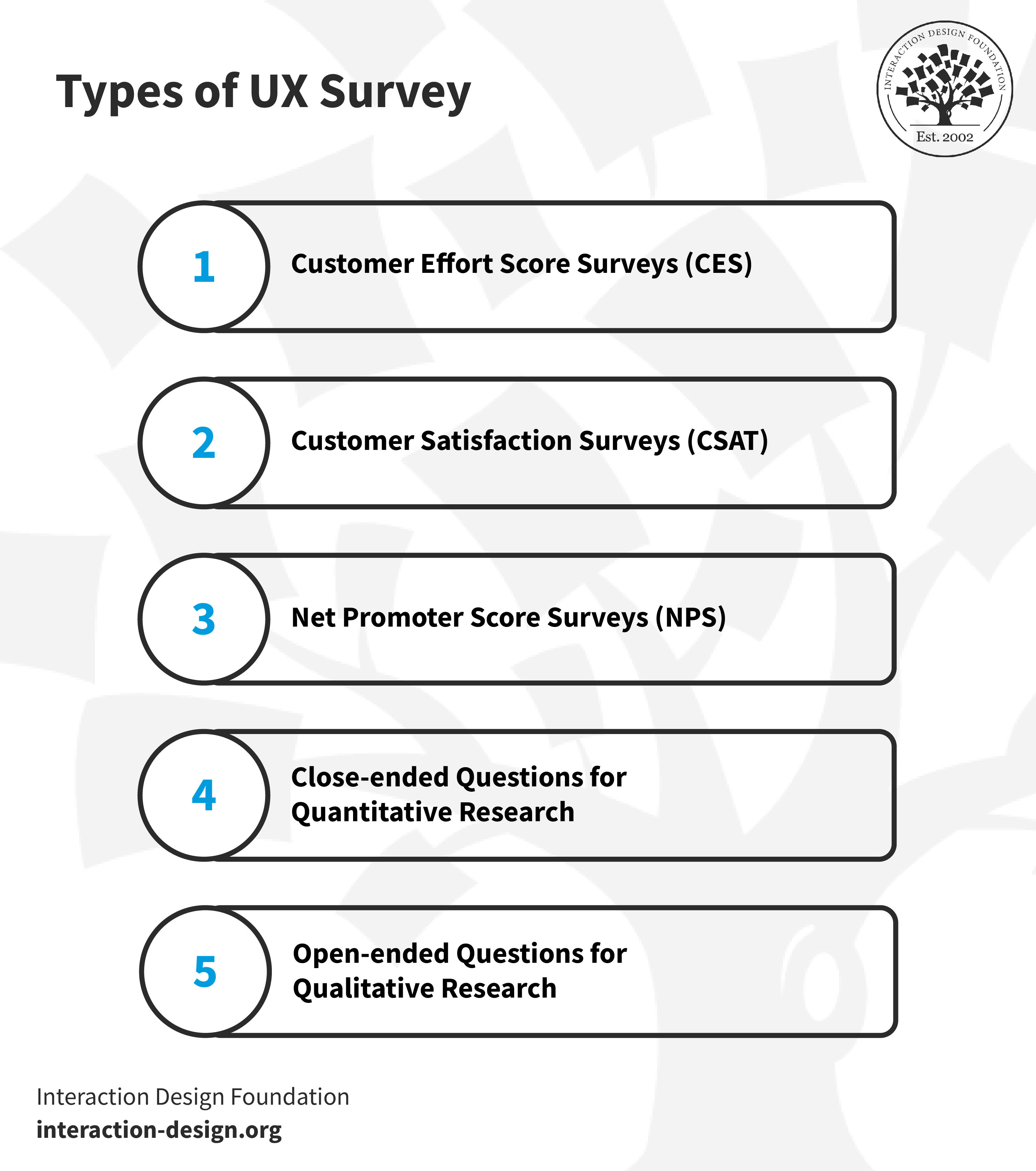
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
1. Customer Effort Score Surveys (CES)
CES surveys assess how simple it is for customers to complete tasks with your company. Think of it like this: It's a score that tells you if using your product or getting help from your service team was a breeze or a struggle for the customer.
Many people value quick, straightforward answers to their questions. Time is precious, so spending less effort resolving issues is better. Ease of experience can be more revealing than overall satisfaction. Experts now use the Customer Effort Score.
For instance, after a customer service interaction, the question could be:
"How easy was resolving your issue with our customer support?"
Very Difficult
This format helps companies understand the ease of interaction from the customer's viewpoint. It can be an excellent tool for identifying areas for improvement.
2. Customer Satisfaction Surveys (CSAT)
A CSAT survey measures how happy customers are with your company.
The main question is, "How satisfied are you with our service?"
Answers range from 1, meaning "very dissatisfied," to 5, indicating "very satisfied."
CSAT surveys focus on individual interactions, like purchasing or using customer support. They use numeric scales to track satisfaction levels over time. These surveys help you understand your customers’ needs and pinpoint issues with your products or services. They also allow you to categorize customers based on their satisfaction levels, which helps with targeted improvements.
3.Net Promoter Score Surveys (NPS)
NPS surveys are simple and quick since they use just one question: “On a scale from 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product/company to a friend or colleague?”. Based on the score, you can do respondent segmentation into one of three categories:
Promoters (Score 9-10): These are your biggest fans, and they are likely to recommend your product.
Passives (Score 7-8): These folks find your product/service satisfactory but could easily switch to competitors.
Detractors (Score 0-6): These unhappy customers could harm your brand through negative word-of-mouth.
You can calculate the NPS score by subtracting the Detractors' percentage from the Promoters'. This gives a snapshot of customer loyalty and areas for improvement.
4. Close-ended Questions for Quantitative Research
Well-designed, close-ended questions are easy to answer. Users pick from predefined options like checkboxes, scales, or radio buttons. These surveys are suitable for gathering data. You'll see these in exit surveys asking users about their shopping experience. The answers provide actionable data, like customer preferences or standard problems.
Get more insights on quantitative research in this course on Data-driven Design .
You may ask,
"How satisfied are you with our delivery speed?"
The options could be:
Very Satisfied
Dissatisfied
Very Dissatisfied
Here, users don't need to type out their thoughts. They select an option that best describes their feelings. It's quick for the user and easy for the company to analyze.
5. Open-ended Questions for Qualitative User Research
While closed-ended questions offer fixed options for quick responses, open-ended questions allow for more detailed, free-form answers. These questions ask for written responses. They dig deeper into how users feel and what they expect.
It may take more time to analyze the responses you gather from this type of survey. But they're valuable because they offer nuanced insights.
For example, questions like "What feature do you wish we had?" can lead to ideas for product enhancements that meet users' needs .
When and Why Should One Conduct a UX Survey?
Conducting a UX survey is a strategic decision to understand various aspects of user interaction with a product or service. Here are vital scenarios and reasons for implementing them:
1. Feature Evaluation and Enhancement
You may find UX surveys better suited to assess existing products than development ones. These surveys can gather insights on how well your target audience receives a feature or service. Feedback from such surveys can guide adjustments or additions to your product.
For instance, if customers believe an existing feature lacks functionality, you can focus on enhancing it. UX surveys offer valuable data to refine a product to better align with customer needs and expectations.
2. Identifying Pain Points
Spotting pain points is essential for creating a user-friendly experience. UX surveys provide direct feedback from users about what's troubling them. These could be issues you're unaware of that make the customer experience less enjoyable or efficient.
For example, users might point out that they find your checkout process too complicated or that they have trouble finding specific information on your website. These insights are like gold; they give you specific areas to focus your improvement efforts. Addressing these issues helps you fix problems and show users you value and act upon their feedback.
3. Assessing Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is crucial for any business. A well-timed UX survey can gauge how well you meet customer expectations after a critical interaction, such as a purchase or customer service call.
Positive feedback helps identify vital areas, while negative feedback highlights issues that need attention.

4. Evaluating Customer Loyalty
Long-term success hinges on customer loyalty. NPS surveys, a type of UX survey, help gauge this.
Identifying promoters, passives, and detractors can help you tailor customer retention and referral strategies. If you see a dip in loyalty scores, it's an alert to dig deeper into potential issues.
5. Journey Mapping
Journey mapping visually represents a user's interactions with your product or service. It tracks the entire experience, from the first touchpoint to the final interaction. A well-designed UX survey can provide insights at multiple stages of this journey.
For example, you can use CES surveys at various checkpoints to measure ease of use . Are customers finding it simple to navigate from one section of your website to another? CSAT surveys can check satisfaction at critical touchpoints like purchase or support.
Open-ended questions can offer qualitative insights into why users make specific choices. These answers fill gaps in the journey map that analytics data might lack.
6. During Major Transitions or Updates
If you're planning a significant change, such as a rebrand or major update, a UX survey becomes invaluable. It helps assess customer sentiment and expectations before you roll out the differences.
Collecting survey data allows for adjustments that align with customer needs. This way, you can reduce the risk of negative backlash.
7. Continuous Improvement
The need for improvement never stops. Regular UX surveys create a feedback loop to help you track user sentiment and performance metrics. They allow for ongoing adjustments based on real-world usage.
For example, if you notice a slight dip in satisfaction scores related to app usability, you can investigate and make adjustments before it becomes a significant issue.
Continuous improvement through regular UX surveys keeps your product aligned with users’ needs and expectations. It helps you sustain your success.
6 UX Survey Best Practices From Experts
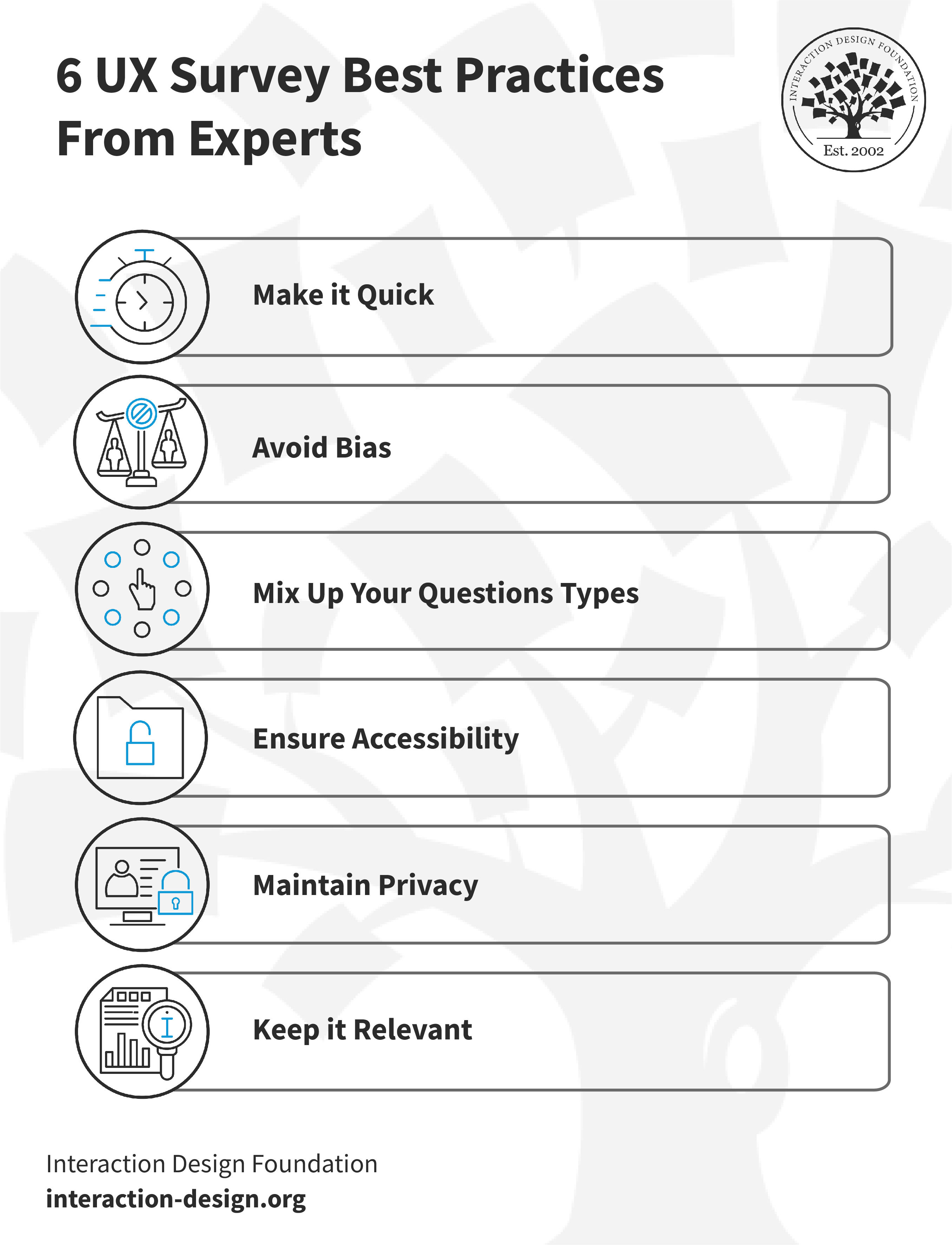
Conducting a UX survey requires careful planning and execution to achieve actionable insights. Here are five best practices from experts in the field:
1. Make it Quick
People value their time, and long surveys can deter participation. A quick and concise survey ensures that the participant remains engaged. Focus on the essential questions and remove any unnecessary ones.
Steps you can take:
Limit your survey to 5-10 essential questions
Use clear and concise language
Preview the survey with a friend or colleague to get feedback on the length.
2. Keep It Relevant
Ensuring relevance in your survey questions is crucial for collecting valuable data. If questions stray off-topic, they risk irritating or baffling participants. Keep questions focused to ensure you get the insights for your goals.
Define your target audience and goals before writing questions
Avoid generic questions that don't relate to the product or service
Focus on specific user experiences that align with your objectives.
Provide not applicable/don’t know answers for all closed questions.
3. Avoid Bias
Bias can distort the results and lead to misguided conclusions. The objective framing of questions helps in collecting unbiased responses. Some of the common biases include:
Question order bias: Affects responses based on the sequence of questions.
Confirmation bias: Only ask questions that affirm what you already believe.
Primacy bias: People choose the first options given.
Recency bias: People are more influenced by their last experience.
Hindsight bias: Respondents say events were foreseeable.
Assumption bias: Assumes respondents know certain information.
Clustering bias: People see patterns where none exist.
Avoid leading questions
Use neutral language
Consider asking an expert to review your questions for potential bias
Test the survey on a small group before launching it.
4. Mix Up Your Question Types
While multiple-choice and rating scales excel at gathering numerical data, open-ended questions offer rich, qualitative insights. The blend can give you a more comprehensive view of customer sentiment.
Use a mixture of types of questions according to the information you need
Utilize open-ended questions for in-depth insights and multiple-choice for quick feedback
Consider using scale questions to gauge user satisfaction or preferences
5. Ensure Accessibility
Making your survey accessible helps you capture a wide range of perspectives. If you create an accessible survey for everyone, including those with reduced abilities, you'll get a more complete and diverse set of insights. This comprehensive view can enhance the quality of your data and decision-making.
Utilize easy-to-read fonts and adequate color contrast
Provide alternative text for images
Ensure that users can navigate the survey using keyboard controls
Test the survey's accessibility features
Avoid complex layouts and matrix-style questions
See the W3’s Web Content Accessibility Guidelines for more details.
6.Maintain Privacy
Prioritizing participants' privacy is critical to building trust. When people feel confident that their data is safe, they're more likely to engage fully in your survey. A strong privacy policy meets legal standards and boosts participation rates. It enriches the quality of your insights.
State your privacy policy at the start of the survey
Use secure platforms for conducting the survey
Assure participants that their responses will remain confidential
Put sensitive or personal questions towards the end
Following these best practices, you can make UX surveys effective for gathering insights and improving the user experience. The actionable steps outlined above make creating an engaging, unbiased, and insightful survey possible.
The Ultimate Guide to Conduct a UX Survey
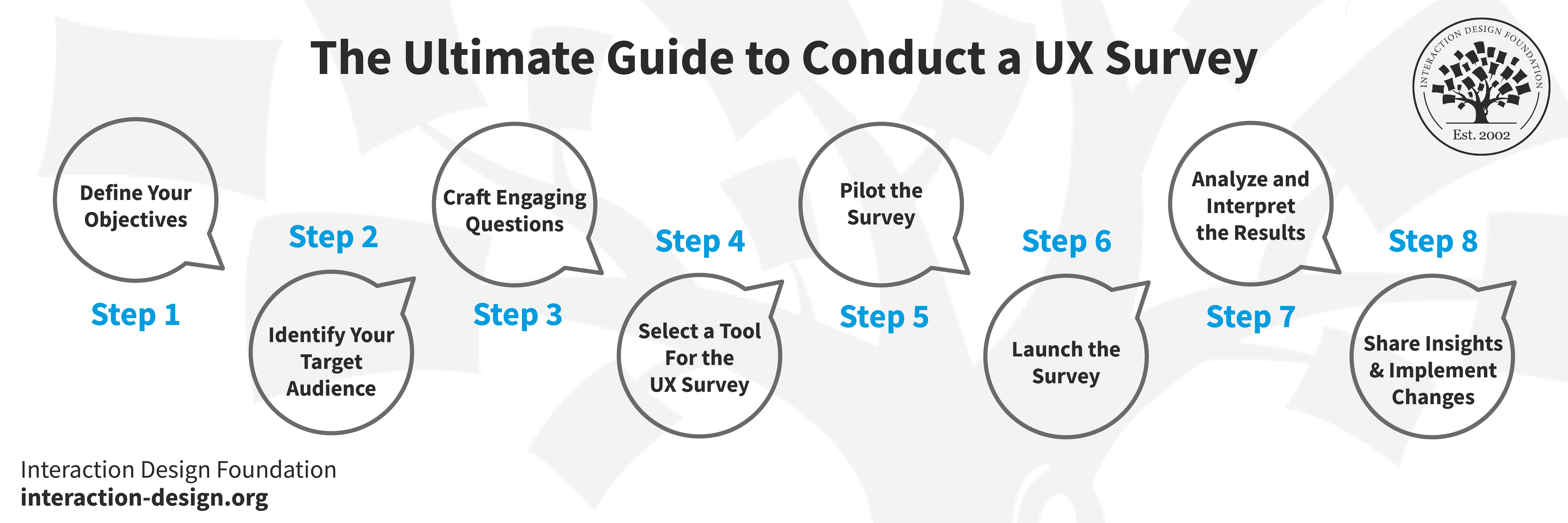
Conducting UX surveys is essential for understanding user interaction with your product. Follow these steps to design, distribute, and analyze surveys for actionable insights.
Step 1: Define Your Objectives
Defining clear objectives sets the stage for a successful UX survey. It helps you understand the key insights you are seeking. To zero in on what you're aiming to discover, consider these questions:
What is the main goal? Understand if you want to measure user satisfaction or you want to focus on something else.
Which user behaviors are relevant? Is the survey targeting frequent users, new users, or both?
What are the key metrics? Do you want to look at completion rates, time spent, or other indicators?
New feature opinions : Are you seeking input on new rolled-out features?
Pain points : Are you trying to identify user frustrations and roadblocks?
Clarity in the objectives will guide every next step and ensure you align the results with your project goals. Well-defined goals will streamline the survey's structure and help craft relevant questions. The sharper focus also helps in analyzing the data you collect later on.
Step 2: Identify Your Target Audience
Identifying your target audience is a pivotal step in creating a survey. Here's why:
Product awareness: Gauge how much your audience knows about your product. This shapes the depth and detail of questions.
Interests : Understand what topics engage your audience. Use that insight to make questions interesting.
Language : A professional audience may understand industry jargon. A general audience may not. Choose words carefully.
Region : Geography can affect preferences and opinions. Localize questions if needed.
Understanding your target audience helps you write questions that they can relate to. It leads to higher engagement and more accurate data in user research . You can also create customer personas and a user journey around them.
Step 3: Craft Engaging Questions for the Questionnaire
Questions are the heart of your survey. Writing engaging, clear, and unbiased questions will provide the insights you need.
Learn the art of writing good questions for surveys
So, here’s what you can do to craft engaging questions:
Use different types, such as multiple-choice for quick feedback or open-ended for deeper insights.
Use simple language, avoid jargon, and ensure each question serves a clear purpose.
Be mindful of potential biases and keep the questions neutral.
Your questions must captivate the user's interest and guide them through the survey.
Step 4: Select a Tool For the UX Research Survey
Selecting the right tool for your UX survey is crucial for data collection and analysis. A Google Form provides a quicker way to get started with UX surveys. Here’s why:
Ease of use : Google Forms is user-friendly. Even if you're not tech-savvy, you can create a survey quickly.
Customization : It offers various themes and allows question branching based on prior answers.
Integration : Google Forms integrates with other Google services like Google Sheets for real-time data tracking.
Free : For basic features, it's free of charge.
Data analysis : Offers basic analytics like pie charts and bar graphs for quick insights.
You can also use specialized UX research tools like SurveyMonkey with more advanced features. Consider what your objectives and target audience need. Then, choose a tool that best serves those needs.
Step 5: Pilot the Survey
Pilot testing is an invaluable step in refining the UX survey. It provides an opportunity to uncover unforeseen issues with the survey design, questions, or technology.
Recruit participants in small numbers to test the survey. You can ask internal team members for help or contact professionals via LinkedIn. Use this test survey to understand their experience and make necessary adjustments. This can make the difference between a good survey and a great one. It helps iron out the kinks and ensures a smoother product experience for the primary audience.
Step 6: Launch the Survey
Launching the survey is more than making it live. It involves choosing the proper channels, timing, and even incentives. Promoting the survey ensures that it reaches your intended audience and encourages participation.
Consider the time of day, week, and even platform that aligns with your audience. You must plan every aspect of the launch to maximize participation.
Step 7: Analyze and Interpret the Results
Data analysis transforms raw data into valuable insights. Use analytical tools to sort, filter, and interpret the data in the context of your objectives. Look for patterns and correlations but also for unexpected discoveries.
Your interpretation should lead to actionable insights that guide product or service improvement. This step transforms the effort of surveying real value for your project.
Step 8: Share Insights and Implement Changes
Finally, sharing your findings and implementing changes completes the process. Create comprehensive reports and engage stakeholders with the insights. Sharing fosters a shared understanding and sets the stage for informed decisions.
Plan and iterate on improvements based on the insights and use the learnings for continuous enhancement.
Each step is a building block that contributes to a successful and insightful user experience survey. Following this roadmap helps ensure that you create an engaging, relevant, and actionable UX research survey.
The 20 Best User Experience Survey Questions
These questions form a comprehensive framework for understanding various aspects of the user experience. Remember to use only a few of these to keep response rates high.
How did you find our website/app?
This question helps assess the effectiveness of your marketing channels. It shows you where people first encounter your brand. While Google Analytics reveals traffic from specific sources like AdWords or Facebook, it needs to track direct traffic. Knowing this can fine-tune your marketing strategy.
What was your primary goal in visiting our site today? Did you achieve it?
Focuses on why users visit and if the site meets their needs. It helps identify gaps in content or functionality.
How easy was it to navigate our site?
This question examines the effectiveness of your website. You're on the right track if people find it easy to navigate. If not, it's a red flag. Your site's layout or functionality may need tweaks.
What features did you use most?
This question identifies which parts of your product or service are most valuable to customers. If the majority say they often use a specific feature, that's a pivotal strength to highlight in marketing.
Were there any features that needed to be clarified or easier to use?
This question zeroes in on potential weak spots in your product design or functionality. A feature consistently labeled as confusing or complicated to use needs improvement.
How would you rate your overall experience?
Provides a general impression of user satisfaction.
What would you change about our website or app?
This question invites suggestions for improving your digital solution. It gives users a voice in the development process.
How likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or colleague?
Recommendations measure customer satisfaction and loyalty. Pop-up surveys commonly use this question based on a widely used metric called the Net Promoter Score (NPS). A high likelihood to recommend means customers are happy and likely to become brand advocates.
What other products or services would you like us to offer?
This question taps into unmet customer needs and wants. Responses can reveal gaps in your current offerings and inspire new products or services.
Did you encounter any technical issues?
Technical issues, like bugs, error messages, or crashes, can affect customer satisfaction.
What is your preferred payment/delivery method?
It may seem trivial, but some customers will only buy if their preferred payment method is available. So, you must understand the popular payment options that resonate with your target audience.
What is your preferred method of contact for support?
This question seeks to know how customers prefer to reach out for help. Understanding this helps businesses optimize their customer service channels.
How would you describe our product in one sentence?
This question aims to capture a concise customer impression of your product. The one-sentence descriptions can reveal key strengths or weaknesses.
How does our product compare to similar ones in the market?
This question seeks to understand your product's competitive edge or shortcomings. Responses can tell you where you excel or lag behind rivals.
Were our support resources (FAQs, live chat) helpful?
You need to understand the effectiveness of your customer support tools, like FAQs and live chat. If most people find these resources helpful, they validate your support strategy. If not, it's a cue to improve these areas. Understanding this aspect ensures that you offer assistance that benefits your customers.
How could our product better meet your needs in the future?
This question aims to collect suggestions for future improvements. Whether adding new features or refining existing ones, the feedback helps roadmap planning. If multiple customers highlight the same issue (like with pricing), that's a vital sign that needs attention.
How did you find the speed of the site?
This question evaluates how site speed impacts user satisfaction. Slow loading can frustrate users and may even lead them to abandon the site. If multiple people report this issue, it signals a need for optimization.
What language options would you prefer for our website/app?
This question identifies the language preferences of your user base. If a significant portion prefers another language, it makes sense to offer that option. Adding new languages can broaden your reach and make your platform more inclusive.
Would you like a follow-up from our team regarding your feedback?
This question gauges interest in further communication. A 'yes' suggests the respondent is engaged and open to dialogue, indicating higher loyalty or interest. A 'no 'means they provided feedback but aren't looking for a discussion.
Would you be interested in future updates or newsletters?
This question gauges customer interest in staying connected with your brand. A 'yes' indicates a satisfied customer likely to engage with future offerings. A 'no' could suggest they're not fully satisfied or not interested in long-term engagement.
UX Survey Templates
Here’s a list of the eight best user experience survey templates that are free to use:
Client Feedback Form
Find out what clients think about your business. Use this form as a case study to gather thoughts on customer service and more. Make changes to the template to focus on specific aspects of customer interaction
NPS-Enhanced Software Survey
Experts have made this ready-to-use template to improve your software's Net Promoter Score (NPS). Gather critical insights to elevate your product.
Basic NPS Inquiry Template
Easily gauge customer loyalty with this template. Customers rate their likelihood of recommending you from 0 to 10. Adapt the template to explore additional areas.
Support Team Feedback Form
Assess the performance of your customer service team. Adapt the survey to delve into aspects you are particularly interested in.
Quick Response Customer Survey
Send this brief survey to understand customer perceptions . It encourages customers to elaborate on their answers. Make adjustments to fit your needs.
Product Feedback Survey
Use this template to collect comments on your products. It aims to identify issues and suggest resolutions.
Snapshot Product Assessment
Collect rapid feedback on your products. Use this form to get concise and actionable comments from customers.
Comprehensive Client Feedback Form
Capture detailed information on how your customers feel about your products and services. This is useful for pinpointing specific areas for improvement.
Final Thoughts
And there you have it. We have provided an in-depth guide to creating a successful UX survey. It covers all the essential aspects, from defining objectives to crafting engaging questions, ensuring accessibility, analyzing results, and implementing changes.
We’ve included a curated list of 20 UX survey questions and eight templates, each serving a unique purpose in understanding the user experience.
Two major takeaways from this content include:
Align the survey with clear objectives : Understanding what you want to achieve with the survey sets the foundation for success. It guides every subsequent step.
Asking relevant and engaging questions : Crafting clear, interesting, and unbiased questions that cover various facets of the user experience is vital. It helps in capturing genuine feedback and insights.
You can follow these guidelines to uncover profound insights that drive success in your product or service.
Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX

Get Weekly Design Tips
Topics in this article, what you should read next, how to moderate user interviews.

- 4 years ago
Data Analysis: Techniques, Tools, and Processes
Writing Good Questions for Surveys
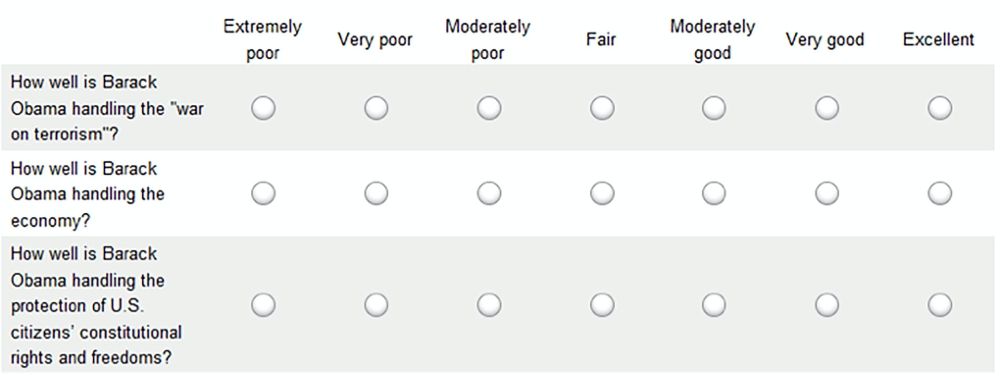
- 3 years ago
Why and When to Use Surveys

Ensuring Quality

Design for Virtual Reality: Top Learnings from the IxDF Course

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
What is Marketing Research? Examples and Best Practices
12 min read

Marketing research is essentially a method utilized by companies to collect valuable information regarding their target market. Through the common practice of conducting market research, companies gather essential information that enables them to make informed decisions and develop products that resonate with consumers. It encompasses the gathering, analysis, and interpretation of data, which aids in identifying consumer demands, anticipating market trends, and staying ahead of the competition.
Exploratory research is one of the initial steps in the marketing research process. It helps businesses gain broad insights when specific information is unknown. If you are seeking insight into how marketing research can influence the trajectory of your SaaS, then you have come to the right place!
- Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry.
- Primary market research gathers specific data directly from the target audience using tools like surveys and focus groups, while secondary market research utilizes existing data from various sources to provide broader market insights.
- Effective market research combines both qualitative methods, which explore consumer motivations, and quantitative methods, which provide measurable statistics, to create comprehensive insights that guide business strategy and decision-making.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Defining marketing research

Launching a product without knowing what your target audience wants is like walking in the dark. Market research lights the way, helping you collect, analyze, and understand information about your target market. This allows you to refine your business strategies and make decisions based on solid evidence.
Gone are the days when just intuition or subjective judgment was enough. Objective insights from market research help avoid costly mistakes and meet consumer needs by identifying trends and changes in the market. This is crucial for assessing a product’s potential success, optimizing marketing strategies, and preparing for market shifts.
Market research is a systematic approach that provides essential information, helping businesses navigate the complexities of the commercial world. Partnering with market research companies can offer additional benefits, leveraging their expertise in understanding market demands, trends, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing. Whether starting a new business, developing products, or updating marketing plans, understanding how to conduct effective market research is key to success.
To conduct market research effectively, businesses must determine study goals, identify target consumers, collect and analyze data, and use the findings to make informed decisions. This process is vital for evaluating past performance, measuring changes over time, and addressing specific business needs. It guides businesses in product development, marketing strategies, and overall decision-making, ensuring a better ROI and providing an eye-opening view of the market through various research methods, whether conducted in-house or outsourced.
The purpose of marketing research
Conducting marketing research is more than just gathering data; it’s about turning that data into actionable insights to refine your business strategies. This process helps you understand what motivates your customers, enabling you to tailor your products and services to minimize risks from the start. Importantly, market research plays a pivotal role in measuring and enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are critical for understanding key demographics, improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention. Customer satisfaction is measured as a key outcome, directly linked to the success of marketing strategies and business activities.
For SaaS product managers, market research, including competitive analysis, is crucial. It evaluates past strategies and gauges the potential success of new offerings. This research provides essential insights into brand strength, consumer behavior, and market position, which are vital for teams focused on sales, marketing, and product development.
A key aspect of market research is analyzing customer attitudes and usage. This analysis offers detailed insights into what customers want, the choices they make, and the challenges they face. It helps identify opportunities in the market and aids in formulating effective strategies for market entry.
Overall, market research equips SaaS entrepreneurs with the knowledge to meet their target audience’s needs effectively, guiding product adjustments and innovations based on informed decisions.
Key components of market research
Conducting market research is analogous to preparing a cake, requiring precise ingredients in specific quantities to achieve the intended outcome. Within this realm, necessary components consist of primary and secondary data gathering, thorough analysis, and insightful interpretation.
Primary research techniques such as exploratory studies, product evolution inquiries, estimations of market dimensions and shares, and consumer behavior examinations play a crucial role in collecting targeted information that can be directly applied. These methods afford a deeper understanding of your target demographic, allowing for customized strategy development.
In contrast, secondary research enriches the specificity of primary findings by adding wider context. It taps into external resources encompassing works from other investigators, sector-specific reports, and demographics data, which provide an expansive yet less particularized landscape view of the marketplace.
The subsequent phase involves meticulous analysis of collated data offering unbiased perspectives critical for identifying deficiencies while recognizing emerging patterns. Technological progress now facilitates examination efforts on both structured and unstructured datasets effectively addressing large-scale analytical complexities.
Ultimately, it’s through expert-led interpretation that value transcends raw figures, yielding strategies grounded in deep comprehension. Akin to decoding recipes using selected ingredients—this interpretative step enables crafting optimal business maneuvers just as one would bake their ideal confectionery creation utilizing proper culinary guidance.
Types of market research: primary and secondary
Now that you know the importance of clear research objectives, let’s explore the different types of market research and the techniques available to achieve these goals. Market research methods can be divided into two main categories: primary research and secondary research . The choice between these depends on factors like your budget, time constraints, and whether you need exploratory data or definitive answers.
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from sources. This process is like mining for precious metals, as it requires using various methods to gather fresh insights.
- Surveys (here – in-app survey templates from Userpilot ).
- Interviews.
- Focus groups.
- Product trials.
This approach gives you first-hand insight into your target audience.
Conversely, secondary research uses already established datasets of primary data – which can add depth and reinforcement to your firsthand findings.
Conducting your own market research using primary research tools can be a cost-effective strategy, allowing businesses to gather valuable insights directly and tailor their research to specific needs.
Let’s look a bit deeper into them now.
What is primary market research?
Market research uses primary market research as an essential tool. This involves collecting new data directly from your target audience using various methods, such as surveys , focus groups, and interviews.
Each method has its benefits. For example, observational studies allow you to see how consumers interact with your product.
There are many ways to conduct primary research.
Focus Groups : Hold discussions with small groups of 5 to 10 people from your target audience. These discussions can provide valuable feedback on products, perceptions of your company’s brand name, or opinions on competitors. Additionally, these discussions can help understand the characteristics, challenges, and buying habits of target customers, optimizing brand strategy.
Interviews : Have one-on-one conversations to gather detailed information from individuals in your target audience.
Surveys : These are a common tool in primary market research and can be used instead of focus groups to understand consumer attitudes. Surveys use structured questions and can reach a broad audience efficiently.
Navigating secondary market research
While marketing research using primary methods is like discovering precious metals, secondary market research technique is like using a treasure map. This approach uses data collected by others from various sources, providing a broad industry view. These sources include market analyses from agencies like Statista, historical data such as census records, and academic studies.
Secondary research provides the basic knowledge necessary for conducting primary market research goals but may lack detail on specific business questions and could also be accessible to competitors.
To make the most of secondary market research, it’s important to analyze summarized data to identify trends, rely on reputable sources for accurate data, and remain unbiased in data collection methods.
The effectiveness of secondary research depends significantly on how well the data is interpreted, ensuring that this information complements the insights from primary research.
Qualitative vs quantitative research
Market research employs both qualitative and quantitative methods, offering distinct insights that complement each other. Qualitative research aims to understand consumer behaviors and motivations through detailed analysis, while quantitative research collects measurable data for statistical analysis.
The selection of qualitative or quantitative methods should align with your research goals. If you need to uncover initial insights or explore deep consumer motivations, qualitative techniques like surveys or interviews are ideal.
On the other hand, if you need data that can be measured and analyzed for reliability, quantitative methods are more suitable.
However, these approaches don’t have to be used separately. Combining qualitative and quantitative methods in mixed-method studies allows you to capture both detailed exploratory responses and concrete numerical data. This integration offers a comprehensive view of the market, leveraging the strengths of both approaches to provide a fuller understanding of market conditions.
Implementing market research tools: Userpilot’s role
Similar to how a compass is essential for navigation at sea, businesses need appropriate instruments to carry out effective market research. Userpilot’s suite of product analytics and in-app engagement tools are critical components for this purpose.
Acting as a Buyer Persona Research instrument, Userpilot’s product analytics provide key quantitative research capabilities. This helps clearly define and comprehend the attributes and behaviors of potential customers, providing you with insights into your ICP (Ideal Customer Persona), user preferences, and product-market fit.
Beyond product analytics, Userpilot offers robust in-app engagement features such as modals and surveys that support real time collection of market research information. These interactive features work synergistically with the analytical tools to enable companies to gather detailed data and feedback crucial for informed business decision-making.
Marketing research process: Step-by-step guide
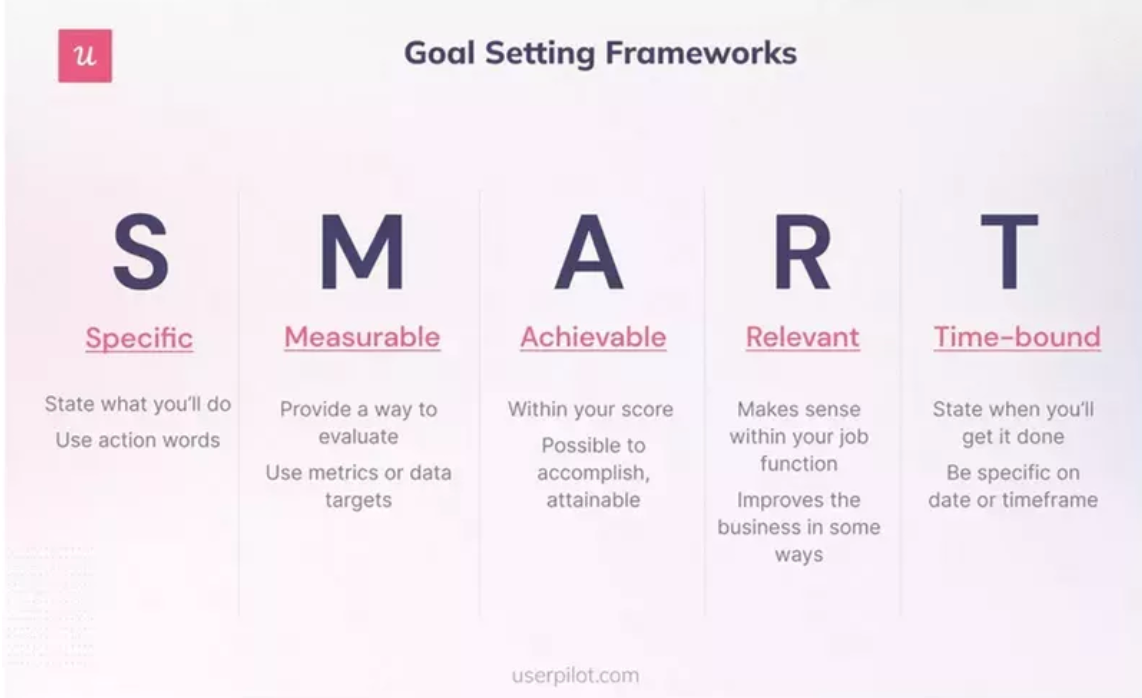
Marketing research conists of several critical stages:
- Defining precise goals.
- Delving into the knowledge of your target demographic.
- Collecting and scrutinizing data.
- Revealing insights that can be translated into tangible actions.
Following these steps allows you to gather critical information that guides business decisions.
An effective research strategy is crucial and involves:
- Properly allocating funds.
- Formulating testable hypotheses.
- Choosing appropriate methods for the study.
- Determining the number of study participants.
- Considering external variables.
A well-planned strategy ensures that your market research is focused, efficient, and produces useful outcomes.
After collecting data, the next step is to analyze it. This involves comparing the data to your initial questions to draw conclusions relevant to your business strategies.
Userpilot makes your data analysis easier by providing handy analytics dashboards for key user metrics such as activation, engagement, core feature adoption, and retention out of the box:
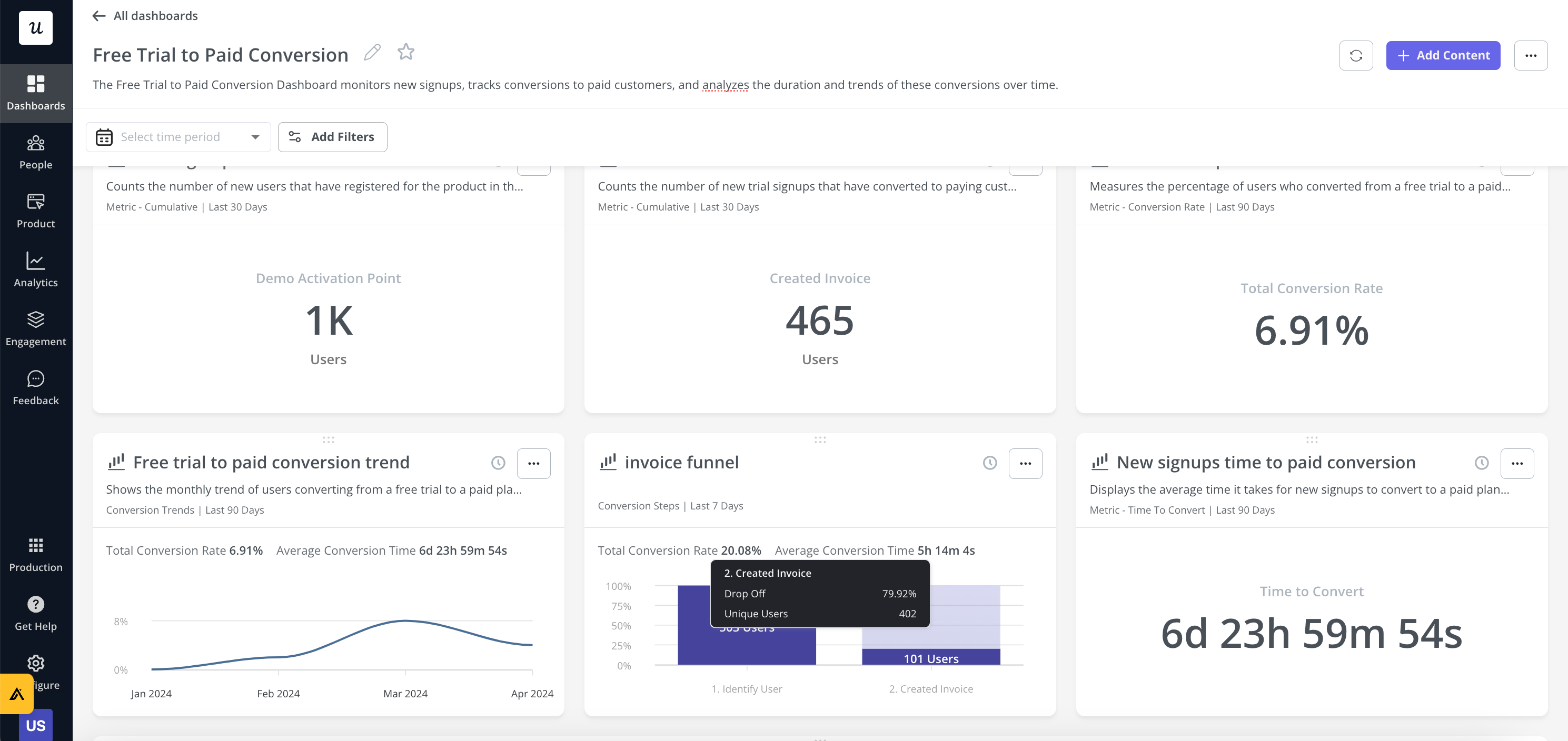
Finally, you report the findings and the process, providing recommendations based on the evidence. This is like solving a puzzle: each piece helps to complete the overall picture.
Challenges and best practices in market research
Delving into market research comes with its own set of hurdles. Those conducting the research must deliver more profound insights within increasingly shorter timespans, and they need to cultivate strategic, continuous research methods to stay abreast of an ever-changing business landscape.
Ensuring high-quality data can be demanding due to issues such as disjointed tools or insufficient analytical expertise. New solutions like Userpilot are surfacing that make these obstacles less daunting by offering accessible and user-friendly options. Maintaining clear lines of communication with your market research team is crucial for achieving both punctuality and quality in outcomes.
The advantages of engaging in marketing research cannot be overstated.
Real-life examples of successful market research
Real-life examples of market research in the SaaS industry often showcase innovative approaches to understanding customer needs and product-market fit.
For instance, Slack, the communication platform, utilized extensive market research to identify gaps in communication tools and understand the workflows of teams. This led to the development of features that seamlessly integrated with other tools and catered to the needs of various team sizes and structures.
Another example is HubSpot, which conducted market research to understand the pain points of small to medium-sized businesses in managing customer relationships. The insights gained helped shape their all-in-one inbound marketing, sales, and service platform, which has become integral to their users’ daily operations. These examples demonstrate how SaaS companies can employ market research to inform product development, improve user experience, and strategically position themselves in a competitive market.
Choosing the right market research tools
For B2B SaaS product managers aiming to do market research, having the right set of tools can make a significant difference. Here’s a list of valuable SaaS tools that can be leveraged for effective market research:
- Userpilot : A comprehensive Product Growth Platform offering in-depth product analytics, a code-free in-app experience builder, bespoke in-app survey capabilities, and robust integration options with platforms like Salesforce and Hubspot. This tool is particularly useful for understanding user behavior, enhancing user engagement, and gathering targeted feedback.
- Qualtrics : Known for its powerful survey tools, Qualtrics helps businesses gather and analyze customer feedback effectively. Its advanced analytics features are ideal for testing market hypotheses and understanding customer sentiments.
- SurveyMonkey : A versatile tool that enables product managers to create, send, and analyze surveys quickly and easily. SurveyMonkey is suitable for gauging customer satisfaction and collecting feedback on potential new features.
- Mixpanel : Specializes in user behavior analytics, offering detailed insights into how users interact with your product. This is essential for identifying patterns and optimizing product features.
- Hotjar : Combines analytics and feedback tools to give teams insights into user behavior and preferences. Hotjar’s heatmaps and session recordings are invaluable for understanding the user experience on a deeper level.
- Tableau : A leading platform for business intelligence and data visualization, Tableau allows product managers to create comprehensive visual reports that can inform strategic decisions based on user data analysis.
Each of these tools provides unique functionalities that can assist SaaS product managers in conducting thorough market research, thereby ensuring that their products are perfectly aligned with user needs and market demands.
Measuring the impact of market research
The pivotal challenge for market research lies in demonstrating its return on investment (ROI) and overall influence on corporate success sufficiently enough to justify regular financial commitment from company leaders. The worth attributed to a market research firm hinges not only on their ability to deliver relevant and high-caliber information, but also on their pricing structures and their contribution towards propelling organizational growth.
To gauge how effectively business choices made based on market research findings succeed, various metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are utilized. These numerical tools act as navigational aids directing enterprises toward achieving objectives while simultaneously verifying that efforts invested in conducting market analysis are yielding fruitful guidance.
Throughout our look at market research, we’ve seen its importance and impact. Our discussion covered the basics of market research, its key components, and different types, including both qualitative and quantitative methods, and the role of Userpilot’s tools. We’ve examined the details of the market research process, tackled challenges, identified best practices, and shared success stories. We also provided advice on choosing the right market research partner and how to measure the effectiveness of your market research.
In today’s data-driven world, comprehensive market research is crucial for companies that want to succeed. It acts like a guide, helping businesses navigate the complex market landscape. Start your own detailed research today, supported by insightful analytics to help you succeed.
Frequently asked questions
What is market research and why is it important.
Understanding your target market, honing business strategies, and making informed decisions are all essential components that depend heavily on effective market research. It offers objective insights to help avoid expensive errors and foresees the needs of customers .
What is the difference between primary and secondary market research?
Primary market research is characterized by the direct gathering of data, in contrast to secondary market research which leverages existing information from alternative sources for addressing research inquiries.
Such a distinction can guide you in selecting an approach that aligns with your precise needs for conducting specific research.
What are some examples of successful market research?
Examples of successful market research are evident in the operations of well-known companies such as Starbucks, Apple, and McDonald’s. They have harnessed this tool to fine-tune their business strategies and make decisions based on solid information.
By employing market research, these businesses have managed to gain insight into their customers’ desires and needs, which has contributed significantly to their success.
How can I choose the right market research partner?
Selecting an ideal market research ally involves identifying a firm that resonates with your project requirements, financial plan, and corporate goals while also verifying their track record of dependability and consistency via reviews from previous clients.
Best wishes on your endeavor!
How is the impact of market research measured?
The effectiveness of market research hinges on the precision, representativeness, and pertinence of its data, along with how successful business decisions are when they’re based on the findings from this research. These elements define the impact of the research conducted.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Product-led vs sales-led: what’s the difference, and which one is right for you.
Userpilot Content Team
What Are Marketing Funnels? A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Your User Journey
Best marketing analytics software for saas.
Skip to main content
COVID-19 update: Google is prioritizing everyone's health and safety, this may impact UX Research. Learn More
- English (United Kingdom)
- Español (Latinoamérica)
- Português (Brasil)
- Português (Portugal)
Jump to Content
Help shape the future of Google
Your feedback is important to us.
We’d love to know your thoughts, so we can keep making Google products that fit your needs. You’ll get to influence things millions of people use every day, from email and productivity apps to tools for developers and educators.
Even if you don’t currently use Google products, you can still sign up for a chance to participate in our research. If one of our studies is a good fit for you, we’ll get in touch with details and next steps. Most participants will get a thank-you gift.
Every study opportunity is:
Open - Whether you are a newbie or an experienced Google product user, anyone can sign up to participate.
Secure - You can trust us to never share your data with third parties.
Flexible - Participation can be remote or in person. It’s up to you.
Beneficial - After you participate you may receive a small gift, like a Visa or a retailer-specific gift card.
Valuable - Your feedback will help us build better products for everyone.
Tell us a little bit about yourself by filling out a form . It’ll help us determine if any of the upcoming UX research studies would be a good match.
Join a research session
If a study is a good fit for you, you’ll get a follow-up questionnaire and details about what the study involves, including next steps and location.
Accept our thanks
After completing the study, most participants will get a giftcard to thank them for their time.
Your feedback will make it possible for us to continue our mission of building a more helpful Google for everyone – no matter who they are, where they live, or what they want to accomplish.
For more information, take a look at our FAQ .
Search Markets
- Report Store
- Airport Systems Research
- Aviation Research
- CNS Systems Research
- Components Research
- Defence Platforms & Systems Research
- Defense Platforms & Systems Research
- Electronic Warfare Research
- Homeland Security Research
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Research
- Marine/Others Research
- Security Research
- Simulation & Training Research
- Space Research
- Unmanned Systems Research
- Agricultural Biologicals Research
- Agrochemicals & Fertilizers Research
- Animal Feed & Feed Additives Research
- Farm Equipment & Irrigations Research
- Feed & Animal Nutrition Research
- Life Sciences Research
- Precision Agriculture Research
- Seeds & Others Research
- Testing & Services Research
- Automotive Components Research
- Automotive Logistics Research
- Automotive Technology & Services Research
- Autonomous Vehicles Research
- Bikes And Motorcycles Research
- ICE, Electric, Hybrid, Autonomous Vehicles Research
- Off Road Vehicles, LCV, HCV Research
- Power Generation, Transmission & Distribution Research
- Railway Research
- Sensor And Control Research
- Telematics & Infotainment Research
- Testing, Inspection & Certification Research
- Tires & Wheels Research
- Banking Research
- FinTech Research
- Insurance Research
- Payments Research
- Accounting Services Research
- Architectural and Engineering Services Research
- Commercial Cleaning Services Research
- Corporate Training & Development Research
- Environmental Services Research
- Health and Safety Services Research
- Human Resources Services Research
- Information Technology Services Research
- Management Consulting Research
- Overhead, Consumables and Accessories Research
- Professional Services Research
- Real Estate Services Research
- Security Services Research
- Supply Chain Management Services Research
- Adhesives & Sealants Research
- Advanced Materials Research
- Basic Chemicals Research
- Disinfectants & Preservatives Research
- Inorganic Chemicals Research
- Metals & Alloys Research
- Nano Technology Research
- Organic Chemicals Research
- Packaging Research
- Petrochemicals Research
- Pharmaceutical Research
- Plastics, Polymers & Resins Research
- Polymers & Plastics Research
- Renewable Chemicals Research
- Specialty Chemicals Research
- Water Treatment Chemicals Research
- `Building Construction Research
- Construction Equipment & Machinery Research
- Construction Materials Research
- Engineering Services Research
- Green Construction Research
- Infrastructure Construction Research
- Machinery & Equipment Research
- Safety & Security Equipment Research
- Smart Infrastructure Research
- Specialty Construction Research
- Beauty & Personal Care Research
- Clothing, Footwear & Accessories Research
- Consumer Electronic Devices Research
- Consumer F&B Research
- Electronic & Electrical Research
- Electronics & Appliances Research
- Food & Beverage Research
- Food Packaging Research
- Homecare & Decor Research
- Luxury & Designer Research
- Sports & Leisure Research
- Sustainable Consumer Goods Research
- E-Learning & Online Education Research
- Higher Education Research
- K-12 Education Research
- Augmented/Virtual Reality Research
- Battery & Wireless Charging Research
- Camera, Display & Lighting Research
- Chipset And Processors Research
- Communication & Connectivity Technology Research
- Data Center & Networking Research
- Display Technology Research
- Drones & Robotics Research
- Electronics System & Components Research
- Energy Storage Research
- Industrial Automation Research
- Information System & Analytics Research
- Internet of Things & M2M Research
- Materials & Components Research
- Nanotechnology Research
- Next Generation Technologies Research
- Power & Energy Research
- Security, Access Control And Robotics Research
- Semiconductor Materials & Components Research
- Silicon, Wafer & Fabrication Research
- Wearable Technology Research
- Batteries Research
- Drilling, Intervention & Completion Research
- Industrial Motors, Pumps & Control Devices Research
- Offshore Oil & Gas Research
- Renewable Energy Research
- Smart Grid Research
- Alternative Food Sources Research
- Cold Chain Logistics Research
- Flavors, Colors & Fragrances Research
- Food Additives & Ingredients Research
- Food & Beverage Additives Research
- Food & Beverage Ingredients Research
- Food & Beverage Logistics Research
- Food & Beverage Logistics, Cold Chain & Packaging Research
- Food & Beverage Processing and Technology Research
- Food Processing Equipment & Technology Research
- Food Safety & Processing Research
- Food Safety & Standards Research
- Nutraceuticals & Dietary Supplements Research
- Nutraceuticals & Functional Foods Research
- Plant Based Alternatives/Ingredients Research
- Processed & Frozen Foods Research
- Proteins, Vitamins and Minerals Research
- Software & Services Research
- Analytics Research
- Application Software Research
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Research
- Cloud Computing Research
- Communication Services Research
- Cyber Security Research
- Digital Media Research
- Digitalization & IoT Research
- E-commerce Research
- Endpoint Security Research
- Healthcare IT Research
- Healthcare Services Research
- Maintenance and Repair Services Research
- Materials Research
- Medical Devices Research
- Mobility & Telecom Research
- Network Security Research
- Public Safety Research
- Building Construction Research
- Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Research
- Consumer Goods Research
- Electronics & Semiconductor Research
- Environmental Management Research
- Environmental & Safety Research
- Heavy Industry Research
- Recycling Research
- Recycling & Waste Management Research
- Safety Equipment Research
- Textiles & Apparel Research
- Valves & Actuators Research
- Metallic Minerals Research
- Metals Research Analysis
- Mining Equipment & Technology Research
- Mining Services Research
- Non-Metallic Minerals Research
- Biotechnology Research
- Cell Biology Research
- Medical Device Research
- Apparel & Footwear Research
- Brick And Mortar Research
- E-Commerce Research
- Home & Furniture Research
- Specialty Retail Research

Global User Experience (UX) Market Size By Deployment Mode(On-Premises, Cloud Based), By Organization Size(SMEs, and Large Enterprises), By Geographic Scope And Forecast
- Description
- Table of Contents
- Methodology
User Experience (UX) Market Size And Forecast
User Experience (UX) Market size was valued at USD 6,120.64 Million in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 20,058 Million by 2028 , growing at a CAGR of 16.24% from 2021 to 2028.
Dynamic businesses, increase in companies becoming consumer-centric and the want to understand consumer behaviour, and increasing in digitalization are some of the factors anticipated to foster market growth during the forecast period. The Global User Experience (UX) Market report provides a holistic evaluation of the market. The report offers a comprehensive analysis of key segments, trends, drivers, restraints, competitive landscape, and factors that are playing a substantial role in the market.
>>> Get | Download Sample Report @ – https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/download-sample/?rid=156869
What is User Experience (UX) Market?
User Experience (UX), as the name suggests, can be referred to as what a user feels, perceives, when they use or interact with a system. This system can be a website, an app, or a desktop software. User Experience (UX) is focused towards making users feel comfortable using the platform. The User Experience (UX) software understands how data exchange is taking place.
With more and more companies becoming user centric, the importance of understanding and enhancing User Experience (UX) has become of prime importance. Customer Satisfaction has become an indispensable element of an organization’s success. Improving the User Experience (UX) will guarantee just that and much more.
Apart from enhancing customer satisfaction, it’ll help reduce cost of ownership, it’ll create a better brand image among the customer, it’ll generate better sales which ultimately translates to increased revenue. In this age of increasing competition, an improved User Experience (UX) might give one the extra edge over competitors.
What's inside a VMR industry report?
Our reports include actionable data and forward-looking analysis that help you craft pitches, create business plans, build presentations and write proposals.
>>> Ask For Discount @ – https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/ask-for-discount/?rid=156869
Global User Experience (UX) Market Overview
Dynamic businesses, increase in companies becoming consumer-centric and the want to understand consumer behaviour, and increasing in digitalization are some of the major factors driving the market. Digitalization has made all sorts of activities-ranging from buying groceries to paying electricity and banking-online. This creates a need to design the web systems in such a way that makes users return to the platform and also delivers a flawless experience.
Moreover, with more and more companies becoming customer centric, satisfaction of customers becomes utmost important. These web systems are what the customers interact with, and if satisfied, they become the brand ambassadors of the organization by saying nice things in their circles and promoting the brand. Technological Developments have made the creation of such interface easier. These factors are expected to act as market drivers.
However, the training required to operate such tools and reluctance on the part of a certain set employees to learn about new technology are anticipated to restrain the market growth. There is a learning curve that comes with operating any new technology and some employees may be reluctant towards adopting such technology. Moreover, with the increasing number of players competing on a regional level offering specific products and solutions, gathering data can be a difficult task.
It becomes extremely difficult to make a customer think or feel something about a particular service because online activities have become so routine. In addition, being available for customer’s needs around the clock can become tricky. Furthermore, with the diverse pool of customers ranging in nationality to the languages they speak and their culture, formulating an interface that satisfies everyone can be a difficult task. These factors are expected to restrain the market.
Global User Experience (UX) Market: Segmentation Analysis
The Global User Experience (UX) Market is segmented based on Deployment Mode, Organization Size, and Geography.
User Experience (UX) Market, By Deployment Mode
• On-premise • Cloud Based
To Get Summarized Market Report By Deployment Mode:- Download Sample Report Now
Based on Deployment Mode, the market is bifurcated into On-Premises, Cloud Based. Cloud Based accounted for the largest market share of 77.54% in 2020, and is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 16.68% during the forecast period. On-Premises was the second-largest market in 2020.
User Experience (UX) Market, By Organization Size
• Large Enterprise • Small Enterprise
Based on the Organization Size, the global User Experience (UX) market has been segmented into SMEs, and Large Enterprises. Large Enterprises accounted for the largest market share of 67.43% in 2020, and is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 17.87% during the forecast period. SMEs was the second-largest market in 2020.
User Experience (UX) Market, By Geography
• North America • Europe • Asia Pacific • Rest of the world
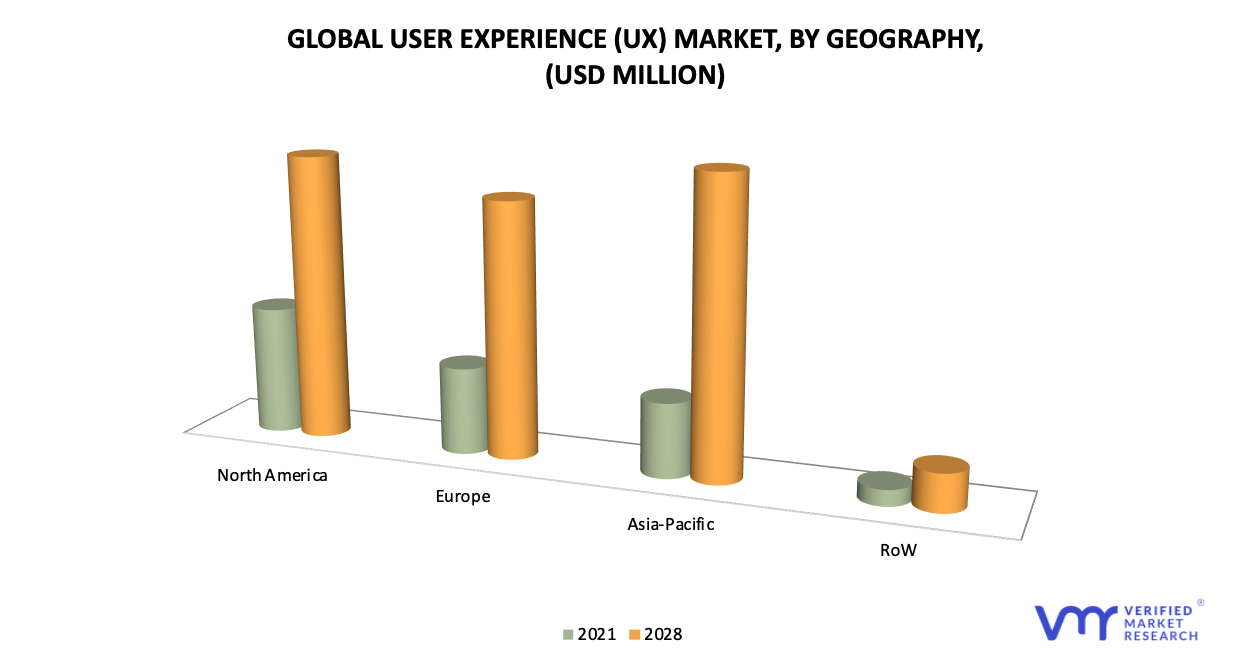
To Get Summarized Market Report By Geography:- Download Sample Report Now
On the basis of regional analysis, the Global User Experience (UX) Market is classified into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the world. North America accounted for the largest market share of 42.80% in 2020, and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.19% during the forecast period. Europe was the second-largest market in 2020; it is projected to grow at a CAGR of 16.69%. However, Asia-Pacific is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of 21.78%.
Key Players
The “Global User Experience (UX) Market” study report will provide valuable insight with an emphasis on the global market. The major players in the market are UserTesting, Hotjar, UserZoom, Userlytics, Lookback, USABILITYHUB, and Others.
The competitive landscape section also includes key development strategies, market share, and market ranking analysis of the above-mentioned players globally.
Report Scope
Top trending reports:.
Global Synthetic and Bio Based Polypropylene Market Size And Forecast
Global Syringaldehyde Market Size And Forecast
Research Methodology of Verified Market Research:

To know more about the Research Methodology and other aspects of the research study, kindly get in touch with our Sales Team at Verified Market Research .
Reasons to Purchase this Report
• Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the market based on segmentation involving both economic as well as non-economic factors • Provision of market value (USD Billion) data for each segment and sub-segment • Indicates the region and segment that is expected to witness the fastest growth as well as to dominate the market • Analysis by geography highlighting the consumption of the product/service in the region as well as indicating the factors that are affecting the market within each region • Competitive landscape which incorporates the market ranking of the major players, along with new service/product launches, partnerships, business expansions, and acquisitions in the past five years of companies profiled • Extensive company profiles comprising of company overview, company insights, product benchmarking, and SWOT analysis for the major market players • The current as well as the future market outlook of the industry with respect to recent developments which involve growth opportunities and drivers as well as challenges and restraints of both emerging as well as developed regions • Includes in-depth analysis of the market of various perspectives through Porter’s five forces analysis • Provides insight into the market through Value Chain • Market dynamics scenario, along with growth opportunities of the market in the years to come • 6-month post-sales analyst support
Customization of the Report
• In case of any Queries or Customization Requirements please connect with our sales team, who will ensure that your requirements are met.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the projected market size & growth rate of the user experience (ux) market, what are the key driving factors for the user experience (ux) market, what are the top players operating in the user experience (ux) market, what segments are covered in the user experience (ux) market report, how can i get a sample reports/company profiles for the user experience (ux) market.
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 MARKET DEFINITION 1.2 MARKET SEGMENTATION 1.3 RESEARCH TIMELINES 1.4 ASSUMPTIONS 1.5 LIMITATIONS
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 2.1 DATA MINING 2.2 SECONDARY RESEARCH 2.3 PRIMARY RESEARCH 2.4 SUBJECT MATTER EXPERT ADVICE 2.5 QUALITY CHECK 2.6 FINAL REVIEW 2.7 DATA TRIANGULATION 2.8 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH 2.9 TOP-DOWN APPROACH 2.1 RESEARCH FLOW
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 3.1 MARKET OVERVIEW 3.2 GLOBAL USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET GEOGRAPHICAL ANALYSIS (CAGR %) 3.3 GLOBALUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE (USD MILLION) 3.4 GLOBALUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE (USD MILLION) 3.5 FUTURE MARKET OPPORTUNITIES 3.6 GLOBAL MARKET SPLIT
4 MARKET OUTLOOK 4.1 GLOBAL USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET OUTLOOK 4.2 MARKET DRIVERS 4.2.1 GROWING NEED FOR USER EXPERIENCE IN DIGITAL WORLD 4.2.2 GROWING FOCUS OF BUSINESSES TO OPTIMIZE CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE 4.2.3 GROWING SMART PHONE USERS AND INTERNET PENETRATION 4.2.4 GROWING SIGNIFICANCE OF UX IN CONTENT MARKETING AND NATIVE ADVERTISING 4.3 RESTRAINTS 4.3.1 LOW LEVEL OF PROFICIENCY 4.4 OPPORTUNITIES 4.4.1 GROWING ADOPTION OF CLOUD COMPUTING 4.4.2 FIFTH-GENERATION WIRELESS NETWORKS TO DRIVE THE MARKET DEMAND 4.5 COVID- 19 IMPACT ANALYSIS
5 MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE 5.1 OVERVIEW 5.2 ON-PREMISES 5.3 CLOUD BASED
6 MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE 6.1 OVERVIEW 6.1 SMES 6.2 LARGE ENTERPRISES
7 MARKET, BY GEOGRAPHY 7.1 OVERVIEW 7.2 NORTH AMERICA 7.2.1 U.S. 7.2.2 CANADA 7.2.3 MEXICO 7.3 EUROPE 7.3.1 GERMANY 7.3.2 U.K. 7.3.3 FRANCE 7.3.4 REST OF EUROPE 7.4 ASIA PACIFIC 7.4.1 CHINA 7.4.2 INDIA 7.4.3 JAPAN 7.4.4 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC 7.5 REST OF WORLD 7.5.1 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICA 7.5.2 LATIN AMERICA
8 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE 8.1 OVERVIEW 8.2 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO 8.3 COMPANY MARKET RANKING ANALYSIS
9 COMPANY PROFILES 9.1 USERTESTING 9.1.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.1.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.1.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING 9.1.4 KEY DEVELOPMENT 9.1.5 SWOT ANALYSIS
9.2 HOTJAR 9.2.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.2.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.2.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING 9.2.4 SWOT ANALYSIS
9.3 USERZOOM 9.3.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.3.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.3.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING 9.3.4 KEY DEVELOPMENTS 9.3.5 SWOT ANALYSIS
9.4 USERLYTICS 9.4.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.4.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.4.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING 9.4.4 SWOT ANALYSIS
9.5 USABILITYHUB 9.5.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.5.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.5.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING 9.5.4 KEY DEVELOPMENTS 9.5.5 SWOT ANALYSIS
9.6 LOOKBACK 9.6.1 COMPANY OVERVIEW 9.6.2 COMPANY INSIGHTS 9.6.3 PRODUCT BENCHMARKING
LIST OF TABLES TABLE 1 GLOBAL USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 2 GLOBAL USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 3 GLOBAL USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY GEOGRAPHY, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 4 NORTH AMERICA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 5 NORTH AMERICA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 6 NORTH AMERICA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 7 U.S.USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 8 U.S. USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 9 CANADA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 10 CANADA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 11 MEXICO USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 12 MEXICO USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 13 EUROPE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 14 EUROPE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 15 EUROPE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 16 GERMANY USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 17 GERMANY USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 18 U.K. USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 19 U.K. USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 20 FRANCE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 21 FRANCE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 22 REST OF EUROPE USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 23 REST OF EUROPEUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 24 ASIA PACIFIC USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 25 ASIA PACIFIC USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 26 ASIA PACIFICUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 27 CHINA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 28 CHINA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 29 INDIA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 30 INDIAUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 31 JAPANUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 32 JAPANUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 33 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 34 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 35 REST OF WORLD USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY COUNTRY, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 36 REST OF WORLD USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 37 REST OF WORLD USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 38 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICAUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 39 MIDDLE EAST AND AFRICAUSER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 40 LATIN AMERICA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT MODE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 41 LATIN AMERICA USER EXPERIENCE (UX) MARKET, BY ORGANIZATION SIZE, 2021 – 2028 (USD MILLION) TABLE 42 COMPANY MARKET RANKING ANALYSIS TABLE 43 USERTESTING: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING TABLE 44 USERTESTING: KEY DEVELOPMENT TABLE 45 HOTJAR: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING TABLE 46 USERZOOM: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING TABLE 47 USERZOOM: KEY DEVELOPMENTS TABLE 48 USERLYTICS: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING TABLE 49 USABILITYHUB: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING TABLE 50 USABILITYHUB: KEY DEVELOPMENTS TABLE 51 LOOKBACK: PRODUCT BENCHMARKING
Report Research Methodology

Verified Market Research uses the latest researching tools to offer accurate data insights. Our experts deliver the best research reports that have revenue generating recommendations. Analysts carry out extensive research using both top-down and bottom up methods. This helps in exploring the market from different dimensions.
This additionally supports the market researchers in segmenting different segments of the market for analysing them individually.
We appoint data triangulation strategies to explore different areas of the market. This way, we ensure that all our clients get reliable insights associated with the market. Different elements of research methodology appointed by our experts include:
Exploratory data mining
Market is filled with data. All the data is collected in raw format that undergoes a strict filtering system to ensure that only the required data is left behind. The leftover data is properly validated and its authenticity (of source) is checked before using it further. We also collect and mix the data from our previous market research reports.
All the previous reports are stored in our large in-house data repository. Also, the experts gather reliable information from the paid databases.

For understanding the entire market landscape, we need to get details about the past and ongoing trends also. To achieve this, we collect data from different members of the market (distributors and suppliers) along with government websites.
Last piece of the ‘market research’ puzzle is done by going through the data collected from questionnaires, journals and surveys. VMR analysts also give emphasis to different industry dynamics such as market drivers, restraints and monetary trends. As a result, the final set of collected data is a combination of different forms of raw statistics. All of this data is carved into usable information by putting it through authentication procedures and by using best in-class cross-validation techniques.
Data Collection Matrix
Econometrics and data visualization model.

Our analysts offer market evaluations and forecasts using the industry-first simulation models. They utilize the BI-enabled dashboard to deliver real-time market statistics. With the help of embedded analytics, the clients can get details associated with brand analysis. They can also use the online reporting software to understand the different key performance indicators.
All the research models are customized to the prerequisites shared by the global clients.
The collected data includes market dynamics, technology landscape, application development and pricing trends. All of this is fed to the research model which then churns out the relevant data for market study.
Our market research experts offer both short-term (econometric models) and long-term analysis (technology market model) of the market in the same report. This way, the clients can achieve all their goals along with jumping on the emerging opportunities. Technological advancements, new product launches and money flow of the market is compared in different cases to showcase their impacts over the forecasted period.
Analysts use correlation, regression and time series analysis to deliver reliable business insights. Our experienced team of professionals diffuse the technology landscape, regulatory frameworks, economic outlook and business principles to share the details of external factors on the market under investigation.
Different demographics are analyzed individually to give appropriate details about the market. After this, all the region-wise data is joined together to serve the clients with glo-cal perspective. We ensure that all the data is accurate and all the actionable recommendations can be achieved in record time. We work with our clients in every step of the work, from exploring the market to implementing business plans. We largely focus on the following parameters for forecasting about the market under lens:
- Market drivers and restraints, along with their current and expected impact
- Raw material scenario and supply v/s price trends
- Regulatory scenario and expected developments
- Current capacity and expected capacity additions up to 2027
We assign different weights to the above parameters. This way, we are empowered to quantify their impact on the market’s momentum. Further, it helps us in delivering the evidence related to market growth rates.
Primary validation
The last step of the report making revolves around forecasting of the market. Exhaustive interviews of the industry experts and decision makers of the esteemed organizations are taken to validate the findings of our experts.
The assumptions that are made to obtain the statistics and data elements are cross-checked by interviewing managers over F2F discussions as well as over phone calls.

Different members of the market’s value chain such as suppliers, distributors, vendors and end consumers are also approached to deliver an unbiased market picture. All the interviews are conducted across the globe. There is no language barrier due to our experienced and multi-lingual team of professionals. Interviews have the capability to offer critical insights about the market. Current business scenarios and future market expectations escalate the quality of our five-star rated market research reports. Our highly trained team use the primary research with Key Industry Participants (KIPs) for validating the market forecasts:
- Established market players
- Raw data suppliers
- Network participants such as distributors
- End consumers
The aims of doing primary research are:
- Verifying the collected data in terms of accuracy and reliability.
- To understand the ongoing market trends and to foresee the future market growth patterns.
Industry Analysis Matrix
User Experience (UX) Market

Download Sample Report
Related Reports
Global sludge treatment chemicals market size by type (coagulants, flocculants, disinfectants), by application (oil and gas, automotive, paper and pulp), by geographic scope and forecast, metaverse market size by product type (mobile metaverse, desktop metaverse), by applications (game, social, conference, content creation, online shopping), by geographic scope and forecast for 2024-2031, global hybrid intelligence market size by organization (small& medium enterprises, large enterprises), by vertical (bfsi, entertainment), by geographic scope and forecast, north america 5g enterprise market size by technology (network function virtualization (nfv) and software-defined network (sdn)), by access equipment (radio node, service node and das), by end user (bfsi, media and entertainment, retail and ecommerce, transportation and logistics), by country and forecast, global 5g ntn market size by components, by application, by platform, by geographic scope and forecast, global edge computing market size by deployment type, by application, by industry vertical, by geographic scope and forecast, north america high-performance computing (hpc) market size by deployment models, by applications, by end-users, by geographic scope and forecast, global b2b data exchange market size by industry vertical, by data type, by data format, by geographic scope and forecast, global 5g services market size by industry verticals, by communication type, by geographic scope and forecast, global speech and voice recognition market size by deployment (cloud, on-premise), by end user (automotive, banking, telecommunication), by geographic scope and forecast.
View More Reports

- Our Solution
- Food & Beverage
- Chemical & Materials
- Semiconductors and Electronics
- Materials & packaging
- Agriculture & Animal Feed
- Industrial Automation
- OIL, GAS & ENERGY
- Cloud Solutions
- Procurement Consulting
- Company Profile Analysis
- Primary Research
- DBMR Market Position Grid
- Bulk Report
- Industry Subscription
- Annual Update
- Quarterly Update
- Pharma Insights
- Market Insights
- Press Release
- Infographics
- White Paper
- Case Studies
- Business Case Studies
- COVID-19 Resources
- Our Company
- Company News Room
- Investor Relations

- US: +1 614 591 3140 UK: +44 845 154 9652 APAC : +653 1251 975
- Database Cloud Login
Global User Experience (UX) Research Software Market – Industry Trends and Forecast to 2031

- Upcoming Report
- No of Tables: 220
- No of Figures: 60
- Report Description
- Table of Content
- List of Table
- List of Figure
- Request for TOC
- Speak to Analyst
- Inquire Before Buying
- Free Sample Report
Global User Experience (UX) Research Software Market, By Type (Cloud, On-Premises), Application (Large Enterprises, SMEs) - Industry Trends and Forecast to 2031.
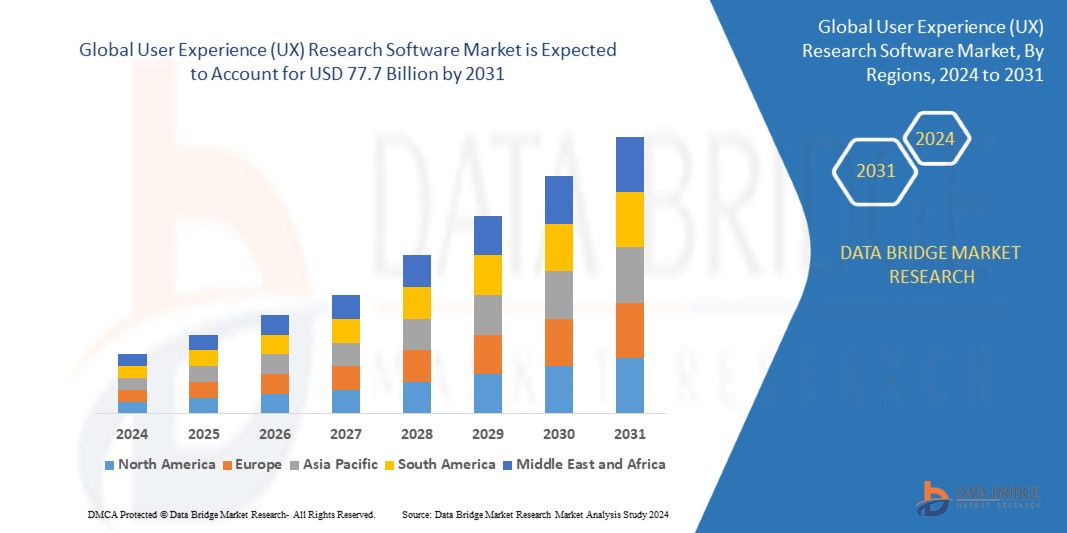
User Experience (UX) Research Software Market Analysis and Size
User Experience (UX) Research Software refers to tools designed to facilitate the systematic collection and analysis of data to enhance the understanding of user interactions with digital products. These platforms assist researchers in studying user behaviour, preferences, and feedback, contributing to the improvement of product design and functionality. UX research software often includes features for surveys, usability testing, heat maps, and analytics, streamlining the process of gathering valuable insights for optimizing user satisfaction and overall product performance.
Data Bridge Market Research analyzes that the global user experience (UX) research software market, which was USD 22.2 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 77.7 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 22.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2031. In addition to the market insights such as market value, growth rate, market segments, geographical coverage, market players, and market scenario, the market report curated by the Data Bridge Market Research team includes in-depth expert analysis, import/export analysis, pricing analysis, production consumption analysis, and pestle analysis.
Report Scope and Market Segmentation
Market Definition
The user experience (UX) research software refers to a comprehensive ecosystem of software solutions designed to evaluate and enhance the user experience in digital products and services. This market encompasses tools and platforms that facilitate the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of user feedback and behaviour. It plays a pivotal role in helping businesses and developers understand user preferences, identify pain points, and iteratively refine their digital offerings.
User Experience (UX) Research Software Market Dynamics
- Increasing Importance of UX Research
UX research is becoming increasingly important as businesses realize the need to create products and services that are user-friendly and meet the needs of their customers. UX research software helps businesses to conduct UX research more efficiently and effectively. This increasing importance is driving the market growth.
- Rise of Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is leading to a proliferation of new digital products and services. Businesses need to ensure that these products and services are well-designed and meet the needs of their users. UX research software can help businesses to do this, which is a driving factor of market.
Opportunities
- Growing Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is being used to develop new UX research tools and techniques. These AI-powered tools can help businesses to automate tasks such as data analysis and insights generation. This can free up UX researchers to focus on more strategic tasks, which is creating new opportunities for the market.
Restraints/Challenges
- High Cost of UX Research Software
UX research software can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. The high cost for research is a challenge for the market growth.
- Lack of Awareness
Many businesses are not aware of the benefits of UX research software or how to use it effectively. This can be due to a lack of understanding of UX research or because businesses are not aware of the software solutions that are available, which in turn can be restraining the markeat growth. This user experience (UX) research software market report provides details of new recent developments, trade regulations, import-export analysis, production analysis, value chain optimization, market share, impact of domestic and localized market players, analyses opportunities in terms of emerging revenue pockets, changes in market regulations, strategic market growth analysis, market size, category market growths, application niches and dominance, product approvals, product launches, geographic expansions, technological innovations in the market. To gain more info on the user experience (UX) research software market contact Data Bridge Market Research for an Analyst Brief, our team will help you take an informed market decision to achieve market growth.
Recent Developments
- In August 2023, UserTesting, a leading provider of human insights for digital product teams, has acquired SessionCam, a leader in session replay and heatmap analytics. The acquisition allowed UserTesting to offer its customers a more comprehensive suite of UX research tools, including the ability to record and analyze user sessions, track user behavior, and generate heatmaps
- In July 2023, UXPin, a leading provider of a UX design platform, has raised USD 60 million in Series D funding. The investment will be used to accelerate the growth of the company's platform and expand its global reach. UXPin's platform is used by over 250,000 designers at companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft to create and prototype user interfaces
Global User Experience (UX) Research Software Market Scope
The user experience (UX) research software market is segmented on the basis of type and application. The growth amongst these segments will help you analyze meagre growth segments in the industries and provide the users with a valuable market overview and market insights to help them make strategic decisions for identifying core market applications.
- On-Premises
- Application
- Large Enterprises
- SMEs Solutions
Global User Experience (UX) Research Software Market Regional Analysis/Insights
The user experience (UX) research software market is analyzed and market size insights and trends are provided by country, type, and application as referenced above.
The countries covered in the market report are U.S., Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, the rest of South America, Germany, Italy, U.K., France, Spain, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Turkey, Russia, rest of Europe, Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Philippines, rest of Asia-Pacific, Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., South Africa, Egypt, Israel, and rest of the Middle East and Africa.
North America is expected to dominate the market due to the increase in online commerce business with the increasing need for user experience analytics and growth in mobile marketing across industry verticals in this region. Asia-Pacific is expected to register the highest CAGR for this period due to the increasing number of social media platforms and rising adoption of mobile marketing for the promotion of products and services and advancements in digital platforms in the region.
The country section of the report also provides individual market impacting factors and changes in regulation in the market domestically that impacts the current and future trends of the market. Data points like down-stream and upstream value chain analysis, technical trends and porter's five forces analysis, case studies are some of the pointers used to forecast the market scenario for individual countries. Also, the presence and availability of global brands and their challenges faced due to large or scarce competition from local and domestic brands, impact of domestic tariffs and trade routes are considered while providing forecast analysis of the country data.
Competitive Landscape and Global User Experience (UX) Research Software Market Share Analysis
The user experience (UX) research software market competitive landscape provides details by competitor. Details included are company overview, company financials, revenue generated, market potential, investment in research and development, new market initiatives, global presence, production sites and facilities, production capacities, company strengths and weaknesses, product launch, product width and breadth, application dominance. The above data points provided are only related to the companies' focus related to user experience (UX) research software market.
Some of the major players operating in the user experience (UX) research software market are:
- IBM Corporation (U.S.)
- SAP SE (Germany)
- Oracle (U.S.)
- Broadcom (U.S.)
- Micro Focus (U.K.)
- AppDynamics (U.S.)
- Riverbed Technology (U.S.)
- BMC Software, Inc. (U.S.)
- Catchpoint Systems, Inc. (U.S.)
- Dynatrace LLC. (U.S.)
- New Relic, Inc. (U.S.)
- Lakeside Software, Inc. (U.S.)
- Nexthink (Switzerland)
- CenturyLink (U.S.)
- ControlUp Technologies LTD (U.S.)
- Bitbar (U.S.)
- eG Innovations (U.S.)
- SmartBear Software (U.S.)
- Stackify (U.S.)
- Würth Phoenix S.r.l (Italy)
- AppNeta (U.S.)
- Datadog (U.S.)
Please fill in the below form for detailed Table of Content
By clicking the "Submit" button, you are agreeing to the Data Bridge Market Research Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions
Please fill in the below form for detailed List of Table
Please fill in the below form for detailed list of figure, please fill in the below form for infographics, research methodology:.
Data collection and base year analysis are done using data collection modules with large sample sizes. The stage includes obtaining market information or related data through various sources and strategies. It includes examining and planning all the data acquired from the past in advance. It likewise envelops the examination of information inconsistencies seen across different information sources. The market data is analysed and estimated using market statistical and coherent models. Also, market share analysis and key trend analysis are the major success factors in the market report. To know more, please request an analyst call or drop down your inquiry.
The key research methodology used by DBMR research team is data triangulation which involves data mining, analysis of the impact of data variables on the market and primary (industry expert) validation. Data models include Vendor Positioning Grid, Market Time Line Analysis, Market Overview and Guide, Company Positioning Grid, Patent Analysis, Pricing Analysis, Company Market Share Analysis, Standards of Measurement, Global versus Regional and Vendor Share Analysis. To know more about the research methodology, drop in an inquiry to speak to our industry experts.
Please fill in the below form for Research Methodology
Customization available:.
Data Bridge Market Research is a leader in advanced formative research. We take pride in servicing our existing and new customers with data and analysis that match and suits their goal. The report can be customized to include price trend analysis of target brands understanding the market for additional countries (ask for the list of countries), clinical trial results data, literature review, refurbished market and product base analysis. Market analysis of target competitors can be analyzed from technology-based analysis to market portfolio strategies. We can add as many competitors that you require data about in the format and data style you are looking for. Our team of analysts can also provide you data in crude raw excel files pivot tables (Fact book) or can assist you in creating presentations from the data sets available in the report.
Please fill in the below form for Available Customization
Get online access to the report on the world's first market intelligence cloud.
- Interactive Data Analysis Dashboard
- Company Analysis Dashboard for high growth potential opportunities
- Research Analyst Access for customization & queries
- Competitor Analysis with Interactive dashboard
- Latest News, Updates & Trend analysis
- Harness the Power of Benchmark Analysis for Comprehensive Competitor Tracking
FREQUENTLY ASK QUESTIONS
- View Infographics...
- Research Methodology
- Available Customization
CHOOSE LICENCE TYPE
- Enterprise User 7000.00
- Single User 4800.00
- DBMR Factbook 3000.00
- DBMR Prime 8000.00
- DBMR Supreme 12000.00
Can be used by entire organization across the globe + Downloadable and Printable PDF + 30 + Countries
Why Choose Us
Industry coverage.
DBMR works across the globe in multiple industries which equip us with knowledge across verticals and provide our clients with insights not only from their industry but how other industries will impact their ecosystem.
Regional Coverage
Coverage of Data Bridge is not restricted to developed or emerging economies. We work across the globe covering the largest array of countries where no other market research or business consulting firm has ever conducted research; creating growth opportunities for our clients in areas which are still unknown.
Technology Coverage
In today’s world, technology drives the market sentiment, so our vision is to provide our clients insights not only for developed technologies but upcoming and disrupting technological changes throughout the product lifecycle by enabling them with unforeseen opportunities in the market which will create disruption in their industry. This leads to innovation and our clients to come out as winners.
Goal Oriented Solutions
DBMR goal is to help our clients achieve their goals through our solutions; hence we formatively create the most appropriate solutions for our client needs, saving time and efforts for them to drive their grand strategies.
Unparallel Analyst Support
Our analysts take pride in our clients’ success. Unlike others, we believe in working along our clients to achieve their goals with 24 hours analyst support determining the correct needs and inspire innovation through service.

Client Testimonials
David manning - thermo fisher scientific.
Dear Ricky, I want to thank you for the excellent market analysis (LIMS INSTALLED BASE DATA) that you and your team delivered, especially end of year on short notice. Sachin and Shraddha captured the requirements, determined their path forward and executed quickly. You, Sachin and Shraddha have been a pleasure to work with – very responsive, professional and thorough. Your work is much appreciated.

Manager - Market Analytics,
Thank you for all the assistance and the level of detail in the market report. We are very pleased with the results and the customization. We would like to continue to do business.
Business Development Manager,
DBMR was attentive and engaged while discussing the Global Nasal Spray Market. They understood what we were looking for and was able to provide some examples from the report as requested. DBMR Service team has been responsive as needed. Depending on what my colleagues were looking for, I will recommend your services and would be happy to stay connected in case we can utilize your research in the future.
Business Intelligence and Analytics,
We are impressed by the CENTRAL PRECOCIOUS PUBERTY (CPP) TREATMENT report - so a BIG thanks to you colleagues.

Competition Analyst,
I just wanted to share a quick note and let you know that you guys did a really good job. I’m glad I decided to work with you. I shall continue being associated with your company as long as we have market intelligence needs.

Marketing Director,
It was indeed a good experience, would definitely recommend and come back for future prospects.
DBMR did an outstanding job on the Global Drug Delivery project, We were extremely impressed by the simple but comprehensive presentation of the study and the quality of work done. This report really helped us to access untapped opportunities across the globe.

The study was customized to our targets and needs with well-defined milestones. We were impressed by the in-depth customization and inclusion of not only major but also minor players across the globe. The DBMR Market position grid helped us to analyze the market in different dimension which was very helpful for the team to get into the minute details.

Product manager,
Thankful to the team for the amazing coordination, and helping me at the last moment with my presentation. It was indeed a comprehensive report that gave us revenue impacting solution enabling us to plan the right move.

Investor relations,
Thank you for the report, and addressing our needs in such short time. DBMR has outdone themselves in this project with such short timeframe.

Market Analyst,
We found the results of this study compelling and will help our organization validate a market we are considering to enter. Thank you for a job well done.

Andrew - Senior Global Marketing Manager,
I want to thank you for your help with this report – It’s been very helpful in our business planning and it well organized.

Amarildo - Manager, Global Strategic Alignment
We believe the work done by Data Bridge Team for our requirements in the North America Loyalty Management Market was fantastic and would love to continue working with your team moving forward.
Thank you for your quick response to this unfortunate circumstance. Please extend my thanks to your reach team. I will be contacting you in the future with further projects
Tommaso Finocchiaro
I acknowledge the difficulty given by the very short warning for this report, and I think that its quality and your delivering time have been very satisfying. Obviously, as a provider Data Bridge Market Research will be considered as a plus for future needs of Nippon Gases.
Yuki Kopyl (Asian Business Development Department)
Xylose report was very useful for our team. Thank you very much & hope to work with you again in the future
Share Your Experience With Us
Avail PDF Sample Reports

By clicking the "Submit" button, you are agreeing to the Data Bridge Market Research Privacy Policy. and Terms and Conditions
Corporate Email ID Only (Avoid Using Generic mail ID such as Gmail)
Skip navigation

World Leaders in Research-Based User Experience
5 prioritization methods in ux roadmapping.

November 14, 2021 2021-11-14
- Email article
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Twitter
Prioritizing work into a roadmap can be daunting for UX practitioners. Prioritization methods base these important decisions on objective, relevant criteria instead of subjective opinions.
This article outlines 5 methods for prioritizing work into a UX roadmap :
- Impact–effort matrix
- Feasibility, desirability, and viability scorecard
- RICE method
- MoSCoW analysis
These prioritization methods can be used to prioritize a variety of “items,” ranging from research questions, user segments, and features to ideas, and tasks. This article focuses on using these methods within the context of roadmapping—prioritizing problems that need to be solved into a strategic timeline.
In This Article:
1. impact–effort matrix, 2. feasibility, desirability, and viability scorecard , 3. rice method, 4. moscow analysis, 5. kano model, 1.a. overview.
An impact–effort matrix is a 2D-visual that plots relative user value against implementation complexity. Variations of this matrix are used across various product-development approaches, including Six Sigma, design thinking, and Agile.

The resulting matrix captures the relative effort necessary to implement candidate features and their impact on the users. It can be subdivided into four quadrants:
- Quick wins include low-effort, high-impact items that are worth pursuing.
- Big bets include high-effort, high-value items; they should be carefully planned and prototyped, and, if executed, are likely to be differentiators against competitors.
- Money pit includes low-impact, high-effort items that are not worth the business investment; there are better places to spend time and resources.
- Fill-ins comprise low-effort, low-impact items that may be easy to implement but may not be worth the effort as their value is minimal.
A comparative matrix is a malleable tool. While we discuss impact–effort matrices in this article, you can easily replace each axis with other criteria or use multiple matrices to assess more than two criteria. When setting up multiple matrices, set up your axes so that the Quick Wins (or whatever the equivalent best-outcome quadrant is) is positioned in the same spot (for example, always in the bottom left position), in order to easily compare several matrices and identify the items that consistently fall in best-outcome quadrant.
1.B. Criteria
This prioritization method uses two primary criteria to rank features that are considered for implementation: the impact that the feature will have on the end user and the effort required to implement that feature.
- Impact is the value the item will bring to the end user. The level of impact an item will have on end users depends on the users’ need, their alternatives, and the severity of the pain point the item solves.
- Effort is the amount of labor and resources required to solve the problem. The more technically complex the item, the higher effort it will require.
1.C. Process
Items are gathered on a whiteboard and their relative scores on the impact and effort dimensions are established through voting. Team members are given colored dots (one color per dimension) to vote for those items that they consider to rate highly on one or both dimensions.
A general rule of thumb is that the number of votes per person is half the number of items being prioritized. It’s also possible that certain team members vote on a single dimension, according to their expertise — for example, UX professionals may rank impact, while developers may rank implementation effort.

After team members have silently voted on items, the items can be placed collaboratively on an effort–impact matrix (the x-axis represents effort, while the y-axis represents impact) according to the number of impact and effort votes received.
Once everything is placed onto the chart, discuss the results and compare items, prioritizing those in the quick-wins and big-bets quadrants. Feel free to use the artifact as a platform for negotiation — throughout discussion with the team, it’s okay to collaboratively move items. However, at the end, there should be agreement on the final placement and the artifact should be documented and saved so it can easily be referenced in the future.
1.D. Best for Quick, Collaborative Prioritization
An impact–effort matrix is best suited for quick, collaborative prioritizations. The method has a few advantages:
- The output is a shared visual that aligns mental models and builds common ground .
- It is democratic — each person can express their own opinion through a vote.
- It can be done relatively quickly due to its simplicity.
2.A. Overview
This method was developed by IDEO in the early 2000s. It ranks items based on a sum of individual scores across three criteria: feasibility, desirability, and viability.

2.B. Criteria
This prioritization method uses three criteria to rank items (i.e., features to be implemented):
- Feasibility : the degree to which the item can be technically built. Does the skillset and expertise exist to create this solution?
- Desirability : how much users want the item. What unique value proposition does it provide? Is the solution fundamentally needed, or are users otherwise able to accomplish their goals?
- Viability : if the item is functionally attainable for the business. Does pursuing the item benefit the business? What are the costs to the business and is the solution sustainable over time?
2.C. Process
Create a table, with one row for each possible item, and columns for the 3 criteria — feasibility, desirability, and viability. Then, determine a numeric scoring scale for each criterion. In the example above, we used a numeric scale from 1 to 10, with 1 being a low score.
Next, give each item a score across each criterion. Scoring should be as informed as possible — aim to include team members who have complementary expertise. Once each item is scored across each criterion, calculate its total score and force a rank. Sort the table from highest to lowest total score, then discuss the results with your team.
2.D. Best for Customized Criteria
This scorecard format is highly customizable. You can add columns to reflect criteria specific to your organization’s context and goals. You can also replace the criteria with others relevant to you. For example, the NUF Test , created by Dave Gray, uses the same scorecard format, but with New , Useful , Feasible as the criteria set.
Another common modification is assigning weights to the different criteria — with those that are very important weighing more heavily in the final score.
3.A. Overview
RICE is a prioritization framework developed by Intercom . It takes into account four factors: reach, impact, confidence, and effort to prioritize which features to implement.

3.B. Criteria
This RICE method is based on scoring each item on 4 different dimensions:
- Reach : the number of users the item affects within a given time period
- Impact : the value added to users
- Confidence : how confident you are in your estimates of the other criteria (for example, highly confident if multiple data sources support your evaluation)
- Effort : the amount of work necessary to implement the item
3.C. Process
Using the RICE method is straightforward. Separate scores are assigned for each criterion, then an overall score is calculated.
- A reach score is often estimated by looking at the number of users per time period (e.g., week, year); ideally, this number is pulled from digital analytics or frequency metrics .
- The impact score should reflect how much the item will increase delight or alleviate friction; it is hard to precisely calculate, and, thus, it’s usually assigned a score (for example, through voting, like in the previous methods) often on a scale from .25 (low) to 3 (high).
- The confidence score is a percentage that represents how much you and your team trust the reach and impact scores. 100% represents high confidence, while 25% represents wild guesses.
- The effort score is calculated as “person-months” — the amount of time it will take all team members to complete the item. For example, an item is 6 person-months if it would require 3 months of work from a designer and 1 month from 3 separate developers.
Once you have each of the 4 criterion scores, use the formula to calculate the final score for each item: multiply the reach, impact, and confidence scores and divide the result by the effort score. Then compare, discuss, and reevaluate all the items’ scores with your team.
3.D. Best for Technical-Oriented Teams
The RICE method works well for organizations that are more technical in nature (for example, when stakeholders are comfortable with equations or spreadsheets). The RICE method also works well when there are many items that need to be prioritized. Consider including peers with diverse domains of expertise in the RICE process and assign them the task of calculating the score for the criterion that relates to their expertise.
4.A. Overview
MoSCoW analysis is a method for clustering items into four primary groups: Must Have , Should Have , Could Have , and Will Not Have . It was created by Dai Clegg and is used in many Agile frameworks.

4.B. Criteria
This prioritization approach groups items into four buckets:
- Must have : items that are vital to the product or project. Think of these as required for anything else to happen. If these items aren’t delivered, there is no point in delivering the solution at all. Without them the product won’t work, a law will be broken, or the project becomes useless.
- Should have: items that are important to the project or context, but not absolutely mandatory. These items support core functionality (that will be painful to leave out), but the project or product will still work without them.
- Could haves : items that are not essential, but wanted and nice to have. They have a small impact if left out.
- Will not have: items that are not needed. They don’t present enough value and can be deprioritized or dropped.
4.C. Process
MoSCoW analysis can be applied to an entire project (start to finish) or to a project increment (a sprint or specific time horizon).
Begin by identifying the scope you are prioritizing items for. If your goal is to create a UX roadmap, you’ll usually have to prioritize for the first three time horizons: now (work occurring in the next 2 months), next (work occurring in the next 6 months), and future (work occurring in the next year).
Compile the items being prioritized and give each team member 3 weighted voting dots, (one dot with a 1 on it, the next with a 2 on it, and so forth). Ask team members to assign their dots to the items they believe most important, with 3 being weighed most heavily.

Add up each item’s score based on the ranked votes (3 = 3 points and so forth). Identify the items with the highest scores and make sure that everybody in the group agrees on their importance.
As each item is discussed and agreed upon as a Must Have , move it to a new dedicated space. Repeat this process for lower-priority items and assign them to the Should Have, Could Have , and Will Not Have groups based on their scores.
Once you have assigned each item to one of the four groups, establish the resources and bandwidth required for each group, starting with the Must Haves . Keep track of the total bandwidth and resources at your disposal, distributing and allocating your total amount across Must Haves (which should get the most resources), Should Haves (with the second most resources), and finally Could Haves (with few resources).
There is not a clear threshold for how many items should be in each group. To determine this number, return to the goal of the prioritization activity. For example, if you are prioritizing items in a backlog, there is only time for so many tasks to be achieved in one sprint. In this scenario, all Must Haves should be easily achieved within one sprint; this constraint will limit how many items cannot be placed within this group.

4.D. Best for Teams with Clear Time Boxes
MoSCoW is a good prioritization method for teams looking for a simplified approach (given the relatively vague prioritization criteria set) and with a clear time box identified for the work. Without a clearly scoped timeline for completing the work, teams run the risk of overloading the Must Haves (of course, everything will feel like a Must Have if the timeline is the next two years!).
5.A. Overview
The Kano model was published by Dr. Noriaki Kano in 1984 and is a primary prioritization method in the Six Sigma framework. Items are grouped into four categories according to user satisfaction and functionality and plotted on a 2D graph.

5.B. Criteria
This prioritization method uses two primary criterions to rank items: functionality and satisfaction.
- None (-2) : the solution cannot be implemented
- Some (-1) : the solution can be partly implemented
- Basic (0) : the solution’s primary functions can be implemented, but nothing more
- Good (1) : the solution can be implemented to an acceptable degree
- Best (2) : the solution can be implemented to its full potential
- Frustrated (-2) : the solution causes additional hardship for the user
- Dissatisfied (-1) : the solution does not meet users’ expectations
- Neutral (0)
- Satisfied (1) : the solution meets users’ expectations
- Delighted (2) : the solution exceeds users’ expectations
5.C. Process
Each item is first assigned a satisfaction score and a functionality score. The satisfaction score should be based on user data — for example, on existing user research or on a top-task user survey asking users to rate the importance of each feature; the functionality score can be rooted in the collective expertise of the team.
These scores are then used to plot items onto a 2D-graph, with the x-axis corresponding to functionality and the y-axis to satisfaction. Each axis goes from -2 to 2.

Based on their placement on their scores, items fall into one of four categories:
- The Attractive category (often called Excitement ) are items that are likely to bring a considerable increase in user delight. A characteristic of this category is the disproportionate increase in satisfaction to functionality. Your users may not even notice their absence (because they weren’t expectations in the first place), but with good-enough implementation, user excitement can grow exponentially. The items in the Attractive are those with a satisfaction score of 0 or better. These items appear above the blue Attractive line in the Kano illustration above.
- The Performance category contains items that are utilitarian. Unlike other categories, this group grows proportionately. The more you invest in items within this category, the more customer satisfaction they are likely to prompt. The items in the Performance category have equal satisfaction and performance scores and fall on the green line in the Kano illustration above.
- The Indifferent category contains items that users feel neutral towards — satisfaction does not significantly increase or decrease with their functionality and is always 0. Regardless of the amount of investment put into these items, users won’t care. These items are all placed on the dark blue Indifference line (which overlaps with the x-axis).
- The Must-be category are basic items that are expected by users. Users assume these capabilities exist. They are unlikely to make customers more satisfied, but without them, customers will be disproportionately dissatisfied. Items fall into the Must-be category when their satisfaction score is 0 or worse. These are the items in the purple area of the Kano diagram, below the purple Must Be line.
Once items are assigned to groups, make sure that everybody in the team agrees with the assignment. Items with scores of (0,0), (-2,0) and (+2,0) may initially belong to two groups. In these cases, discuss the item and ask yourself if user value will grow proportionately with your team’s investment. If the answer is yes, group the item with Performance . In cases this is false, group the item with Indifferent .
Move items as needed, then prioritize items into your roadmap. Items in the Performance category should have the highest priority, followed by Must be , Attractive , then Indifferent .
5.D. Best for Forcing a User-Centric Prioritization
The Kano model is a good approach for teams who have a hard time prioritizing based on the user — often due to politics or a traditional development-driven culture. The Kano model introduces user research directly into the prioritization process and mandates discussion around user expectations.
There are many more prioritization methods, aside from the five mentioned in this article. (It’s also easy to imagine variations on these 5.) One method is not better than another. Consider your project’s context, team culture, and success criteria when choosing a prioritization approach.
Once you find an approach that works, don’t be afraid to iterate — adjust and adapt it to fit to your needs or appeal to your team. Involve others in this process. The best prioritization methods are ones that everyone on your team, including stakeholders, buy into.
McBride, S. (2018). RICE: Simple prioritization for product managers. Intercom. https://www.intercom.com/blog/rice-simple-prioritization-for-product-managers/
What is the Kano Model? ProductPlan. https://www.productplan.com/glossary/kano-model/
Related Courses
Facilitating ux workshops.
Lead goal-based group activities to make decisions and establish alignment
Discovery: Building the Right Thing
Conduct successful discovery phases to ensure you build the best solution
UX Roadmaps
Plan what your team will work on when, from next quarter to multi-year UX strategy. Align, prioritize, & communicate future work
Related Topics
- Design Process Design Process
Learn More:
Please accept marketing cookies to view the embedded video. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gklsUyD6RPE
UX Design Prioritization Methods

Using a CSD Matrix in Discovery
Anna Kaley · 3 min

The Goldilocks Principle for Prototyping
Megan Brown · 3 min

Problem Space and Solution Space Research
Maria Rosala · 2 min
Related Articles:
Derailed Design Critiques: Tactics for Getting Back on Track
Rachel Krause · 6 min
Facilitating UX Workshops: Study Guide
Kate Kaplan · 5 min
How to Get Stakeholders to Sketch: A Magic Formula
Kate Kaplan · 8 min
Journey Mapping for Remote Teams: A Digital Template
Sarah Gibbons · 4 min
A Guide to Service-Blueprinting Workshops
Alita Joyce · 8 min
DesignOps 101
Kate Kaplan · 6 min

Reqi Systems Engineering Articles

Enhancing User Requirement Capture: User Stories, Mapping, and Use Cases
In the ever-evolving world of software development, the key to building successful applications lies in understanding and capturing user requirements. To accomplish this, developers and product teams employ powerful techniques such as User Stories, User Journey Mapping, and Use Cases. In this article, we will explore these methodologies and delve into their profound impact on comprehending user needs. Additionally, we will address critical challenges faced during the process and present insightful solutions to elevate the effectiveness of capturing user requirements.
Table of Contents
Understanding User Perspectives with User Stories
Gaining insight into user experiences with user journey mapping, capturing detailed interactions through use cases, overcoming key challenges.
At the heart of user-centric software development lies the concept of User Stories—succinct descriptions that encapsulate a user’s goal or requirement. By answering the fundamental questions of “who,” “what,” and “why,” User Stories enable teams to align their efforts with user expectations.
The following steps are crucial for leveraging the power of User Stories:
- Identifying User Roles: Recognize the diverse user roles or personas that interact with the system. This comprehensive understanding sets the stage for capturing user requirements effectively.
- Defining User Goals: Uncover the specific goals and objectives that each user role aims to achieve when utilizing the software. Employing the SMART criteria—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound—ensures goal effectiveness.
- Crafting User Story Statements: Compose concise and precise User Story statements using the format: “As a [user role], I want [goal] so that [reason].” These statements serve as a compass, guiding the prioritization of features based on user needs.
- Prioritizing User Stories: Collaborate with stakeholders to prioritize User Stories, placing emphasis on those with the greatest impact on user satisfaction. This approach enables teams to deliver value-driven solutions efficiently.
User Journey Mapping unlocks the door to profound insights into user experiences and interactions with the system. By visualizing their journey, teams can uncover pain points and identify opportunities for improvement. The following steps shed light on the power of User Journey Mapping:
- Identifying Key User Interactions: Pinpoint critical touchpoints where users engage with the system, including onboarding, feature usage, and support interactions.
- Mapping User Actions and Emotions: Capture user actions, thoughts, and emotions at each touchpoint. This holistic representation of their experience unveils motivations, frustrations, and expectations, guiding the development process.
- Identifying Pain Points and Opportunities: Carefully analyze the User Journey Map to identify pain points—areas where users face challenges—and opportunities for improvement. Addressing these requirements ensures an enhanced user experience.
- Collaborating for Effective Solutions: Engage stakeholders in collaborative discussions to ideate and define innovative solutions that address the identified requirements. By embracing diverse perspectives, teams can uncover groundbreaking approaches to user satisfaction.
To comprehend the intricacies of user requirements, software development teams rely on Use Cases. These detailed descriptions of interactions between users and the system cover both functional and non-functional requirements. Follow these steps to unlock the potential of Use Cases:
- Identifying Actors: Identify the various actors or entities involved in system interaction, ranging from primary users to secondary stakeholders. This comprehensive perspective ensures all aspects of user requirements are considered.
- Defining Use Case Scenarios: Craft detailed Use Case scenarios that outline the interactions between actors and the system. By encapsulating the steps, preconditions, and postconditions, teams can accurately address user expectations.
- Capturing System Responses: Document the system’s responses to each Use Case scenario, including outputs, notifications, and error handling. This level of detail ensures the software behaves as intended and meets user needs.
- Validating and Refining Use Cases: Collaborate with stakeholders to validate and refine the Use Cases, ensuring they accurately represent user requirements and align with the intended system behavior. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and fine-tuning.
- Challenge: Complexity and Time Consumption: Capturing user requirements can be a complex and time-consuming process, especially in large-scale projects. To address this challenge, it is essential to break down the process into manageable phases. By focusing on one user role or interaction at a time, teams can maintain clarity and ensure thoroughness without overwhelming themselves.
- Challenge: Limited User Input and Engagement: One common obstacle in requirement capture is obtaining sufficient user input and engagement. To overcome this challenge, it is crucial to actively involve users throughout the process. Conduct interviews, surveys, and usability testing sessions to gather valuable insights directly from the users. By incorporating their feedback and involving them in decision-making, teams can better understand their requirements and ensure alignment with user expectations.
- Challenge: Varying Interpretations and Miscommunication: Misinterpretation or miscommunication of user requirements can lead to significant challenges during the development process. To mitigate this risk, foster clear and open communication channels with users and stakeholders. Regularly seek feedback, clarify ambiguities, and document requirements in a precise and unambiguous manner. Visual aids such as diagrams, prototypes, and interactive mock-ups can further enhance understanding and minimize the potential for miscommunication.
Capturing user requirements is an essential step in building successful software applications. User Stories, User Journey Mapping, and Use Cases provide powerful techniques to comprehend user needs and align development efforts accordingly. By employing these methodologies and overcoming challenges through effective solutions, development teams can ensure the delivery of user-centric solutions that not only meet but exceed user expectations. Embrace these approaches, foster collaboration, and engage users throughout the process to create software that truly resonates with their needs and aspirations.
Related Posts

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
User Experience Is Make-or-Break for Resale Platforms

For secondhand goods marketplaces to function, they need to attract sellers, and those who want to resell items care about more than whether there are going to be buyers — they want it to be easy.
By the Numbers
The March edition of the PYMNTS Intelligence series “ New Reality Check: The Paycheck-to-Paycheck Report ,” titled “Tracking Consumer Use of Supplemental Income Sources,” drew from a survey of more than 4,200 U.S. consumers in February to understand their financial lifestyles.

Supplemental research from the study found that 54% of resellers consider how easy and intuitive the interface of a given online secondhand marketplace is when deciding where to sell their items. The share of consumers who care about usability is roughly equal to the share that cares about how large the platform’s user base is.
The Data in Context
Resale has been on the rise as consumers seek both supplemental income, on the sellers’ side, and less expensive purchasing options, on the buyers’ side.
European resale marketplace Vinted seems to have found the formula for success in the space by diversifying its platform to generate revenue from multiple aspects of the user experience. Last month, the company announced it achieved profitability for the first time.
“We have been deploying capital with high ROI for many years, constantly taking into account the financial sustainability of our investments, so I am pleased we are able to now share that we are operating profitably and posted positive EBITDA for 2023,” Vinted Group CEO Thomas Plantenga said in a statement at the time.
Plus, Faircado shared Tuesday (May 28) that it raised $3.3 million to advance its AI-enhanced reCommerce platform. The company expressed its aim to empower consumers to make environmentally and economically conscious purchasing decisions by facilitating the transition from new to secondhand goods.
For all PYMNTS retail coverage, subscribe to the daily Retail Newsletter .
Recommended
Trending news, the big story, featured news, partner with pymnts.
We’re always on the lookout for opportunities to partner with innovators and disruptors.
SmartScout Review and User Ratings
Darren DeMatas
June 6, 2024
[show_reviewed_by_link]
In addition to receiving commissions generated through affiliate marketing, we are able to fund our independent research and reviews at no extra cost to our readers. Learn more.
We examined 27 different aspects, including features, pricing, and customer service for the top Amazon keyword tools in the market.
To maintain a balanced perspective, we also compared SmartScout to other popular Amazon research tools. Our goal was to see how it stands up against alternatives like Jungle Scout, Helium 10, and Viral Launch.
Real-world experiences make any review better. If you’ve used SmartScout or its alternatives, please share your thoughts. Your feedback can help others make better choices.

SmartScout is a cutting-edge software solution specifically designed to assist Amazon sellers in enhancing their business operations. Scott Needham, the founder, knows the struggles Amazon sellers face. His experiences drive the ongoing improvements in SmartScout’s tools.
The platform offers a variety of pricing plans, including an Enterprise Plan tailored for larger organizations and a Free Trial for those who wish to test its capabilities before making a commitment. This flexibility ensures that businesses of all sizes can leverage SmartScout’s powerful features without significant upfront costs.
What Is SmartScout
SmartScout is a cloud-based software designed to help Amazon sellers and service providers research competitors, analyze products, and optimize their overall market strategy. It features an intuitive dashboard that makes it easy for users to navigate through various tools and datasets. Whether you are looking to dissect customer buying patterns or perform UPC scans, SmartScout provides the necessary resources to gain comprehensive insights.

SmartScout offers more than 20 specialized tools tailored for Amazon’s ecosystem. These tools enable users to research brands and products, estimate sales volumes, and identify shared keywords among competitors. Users can also generate custom reports and create unlimited custom markets, thus making their market research precise and exhaustive.
With its unique features, such as Brand Search, Traffic Graph, Seller Search Tools, and Ad Spy, SmartScout stands out in its ability to unveil hidden opportunities on Amazon. It offers unparalleled access to category, product, sales, and traffic data, allowing users to effectively identify potential suppliers and optimize their listing strategies. These capabilities make SmartScout a comprehensive and invaluable tool for Amazon sellers looking to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
SmartScout Pros
- Offers a free trial, allowing you to test out the features before committing.
- Founded by an experienced Amazon seller, ensuring industry relevance and practical insights.
- Unique features such as Traffic Graph and AdSpy provide advanced competitive analysis and product insights.
- Includes standard tools for keyword and product research, aligning with key competitor offerings while adding unique capabilities.
- Specialized metrics and analytics offer deeper insights into customer buying patterns and sales estimations.
SmartScout Cons
- Doesn’t offer refunds
- Lacks inventory management features, which can be crucial for sellers handling large volumes.
- Does not include review automation, limiting user ability to manage customer feedback efficiently.
- Can be pricey for small or new sellers with limited budgets.
- Occasional data discrepancies compared to other tools.
For those wondering about the cost-benefit scenario, the pricing tiers provided by SmartScout can cater to a wide array of businesses, from small startups to established enterprises. This flexibility ensures that you’re not overpaying for features you might not need, while still having room to scale up as your business grows.
Ultimately, the true value of SmartScout lies in its ability to turn complex datasets into actionable insights. Its potential to improve your business’s operational efficiency, strategic planning, and competitive edge makes it a substantial tool for any eCommerce venture looking to thrive in a crowded marketplace.
SmartScout Pricing
SmartScout offers a range of pricing plans designed to cater to businesses of various sizes and needs. The entry-level plan, known as the Basic plan, is priced at $49 per month, with the option to reduce this to $41 per month if you opt for an annual payment. This plan provides essential features suitable for new or small businesses starting on their journey.

The Essentials plan, priced at $97 per month, takes things a step further. It’s tailored for growing businesses that need more enhanced features and resources. For those needing even more advanced tools and support, the Business plan is $187 per month. This tier is ideal for established businesses aiming to scale their operations significantly.
In addition, SmartScout offers an enterprise plan for larger organizations that require personalized solutions. While the pricing for this plan isn’t listed, it provides a customized approach that includes advanced features and dedicated support tailored to the specific needs of larger enterprises.
All plans come with a free trial, allowing you to explore the platform and its capabilities before making a commitment. This is a valuable opportunity to ensure the platform meets your needs without any upfront investment.
Terms and Refunds
SmartScout offers a standard set of terms and conditions, which you can easily access on their website. When signing up for any of their plans, you should familiarize yourself with their terms regarding billing cycles, subscription renewals, and cancellations. It’s crucial to read these details to avoid any unexpected charges.

SmartScout provides a refund policy that is quite accommodating. If for any reason you are unsatisfied with the service during your first 7 days, you can request a full refund. This helps to mitigate the risk for new users who might be hesitant to commit to a long-term subscription without first evaluating the product.
For subscriptions beyond the trial period, SmartScout’s refund policy stipulates that partial refunds are not offered. Hence, if you cancel your plan midway through a billing cycle, you’ll retain access to the service until the end of that period but won’t receive a refund for the unused time. This makes it essential to monitor your subscription and plan any cancellations accordingly.
SmartScout offers a variety of features designed to enhance your ecommerce experience, particularly for Amazon sellers. These tools aim to streamline your product research and decision-making processes.
Research Features
Smartscout features.
Product Finder: SmartScout’s comprehensive product finder helps you discover new and trending items on Amazon. You can filter products by category, price range, and ratings to pinpoint high-potential opportunities.
Keyword Detective: Similar to Jungle Scout ‘s Keyword Scout , SmartScout provides robust keyword research capabilities. This tool helps you identify and optimize the most effective keywords for your listings, improving your product’s visibility in search results.
Sales Estimator: The Sales Estimator allows you to project potential sales for products based on historical data. It helps you gauge the market demand and make data-driven decisions.
Competitor Analysis: Understanding your competition is crucial. SmartScout’s competitor analysis feature lets you track your competitors’ products, pricing strategies, and sales performance, enabling you to stay one step ahead.
FBA Calculator: Much like the FBA Calculator from Jungle Scout, SmartScout’s version helps you calculate your Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) fees and potential profit margins . This tool ensures that you have a clear understanding of your costs before committing to a product.
AdSpy: SmartScout’s AdSpy feature is designed for Amazon PPC competitor research. It allows you to monitor and analyze your competitors’ ad campaigns, identifying their strategies and keywords. This insight can help you optimize your own campaigns and enhance your advertising effectiveness.
AI Listing Architect: The AI Listing Architect offers an innovative way to create high-converting Amazon listings. This feature uses AI technology to generate optimized content for your products, ensuring your listings are both compelling and search engine friendly, which can significantly boost your sales potential.
Overall, SmartScout combines a suite of powerful features to support your Amazon selling journey. Whether you are a newcomer or a seasoned seller, these tools can significantly enhance your ability to make informed decisions and optimize your operations.
When using a sophisticated tool like SmartScout, effective customer support becomes a crucial factor. SmartScout offers multiple support channels to cater to varying user needs. You can access their help through email, live chat, and resourceful online documentation. However, it’s important to note that they do not offer phone support or 24/7 support, and there is no dedicated account management available.
The live chat feature is particularly notable for its responsiveness. Users have reported quick and helpful responses, often resolving issues in real-time. Furthermore, email support also ranks high in customer satisfaction, with comprehensive answers provided within a reasonable timeframe.
In addition to direct support, SmartScout’s website is filled with a variety of resource materials including guides, tutorials, and FAQs. These resources are designed to help you navigate the platform efficiently and make the most out of its features.
Moreover, for those on the Enterprise Plan, SmartScout provides priority support and dedicated account representatives. This ensures that enterprise users receive tailored assistance and prompt resolutions to any queries, thereby ensuring seamless business operations.
Your experience with customer support might vary, and that’s where your feedback becomes invaluable. Whether you’ve had an outstanding support interaction or found areas for improvement, sharing your experiences can help others make informed decisions.
For growing businesses looking to expand their market research capabilities, SmartScout offers multiple pricing plans, including an Enterprise Plan, which caters specifically to extensive data needs and advanced features. This plan enhances your ability to scale effortlessly as your business demands increase.
Growth Features
While SmartScout offers robust tools for market analysis and competitor research, it’s important to note that some features essential for growing brands on Amazon are missing. For instance, SmartScout does not provide review generation or inventory management capabilities. These features can be critical for maintaining product quality and ensuring stock levels meet customer demand.
When exploring tools similar to SmartScout, you’ll find several alternatives that offer unique features tailored to different needs and budgets. Below, we’ve highlighted some key players in the market:
Jungle Scout
Overview: Jungle Scout is a veteran in the Amazon seller tool space, predominantly known for its comprehensive product research capabilities.
Features: It offers product tracking, keyword research, and sales analytics. Unique features include opportunity finder and supplier database.
Pros: User-friendly interface, extensive training resources, and an active community.
Cons: It can be pricey for new sellers.
Helium 10

Overview: Helium 10 stands out as an all-in-one suite, catering to the various needs of ecommerce sellers.
Features: It includes tools for product research, keyword tracking, listing optimization, and even refund management.
Pros: Wide array of tools and continuous feature updates.
Cons: The magnitude of features can be overwhelming for beginners.
Viral Launch

Overview: Viral Launch is designed to offer a robust solution for product and market intelligence, especially for new Amazon sellers looking to scale quickly.
Features: Product discovery, market intelligence, and listing optimization are core features. It also provides launch services to boost product rankings.
Pros: Detailed market insights and launch support.
Cons: Higher learning curve and premium pricing.
Share Your Experience With SmartScout
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and where you are in your ecommerce journey. Each alternative to SmartScout brings its own strengths and may serve different aspects of your business more effectively. We encourage you to explore these options and determine which one aligns best with your objectives. Have you tried any of these tools or others? Share your experiences and thoughts below!
About the author
User Reviews:
Write your review.
ZonGuru Review and User Ratings
AMZ Tracker Review & User Ratings
Product Reviews
Featured on.

Join 30K+ entrepreneurs already learning ecommerce.
Ecommerce ceo.
Partner With Us
Editorial Policy
Review Guidelines
Terms Of Use
Affiliate Disclosure
Privacy Policy
Guides & Resources
Ecommerce Learning Center
How To Start An Ecommerce Business
How To Make Money Online
What To Sell Online
How To Sell On Amazon
Online Business Ideas
Best Ecommerce Tools
Ecommerce Platforms
Fulfillment Services
Shipping Software
Inventory Management
Print On Demand
Dropshipping Companies
Amazon Research
Online Course Platforms
POS Systems
3PL Companies
BigCommerce
Shopify vs BigCommerce
2800 N 6th Street #5156 St. Augustine, FL 32084 United States
(904) 458-7077
Copyright © 2024 - Mission Demand LLC . All rights reserved.
Exclusive Member of Mediavine Finance
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Internet & Technology
6 facts about americans and tiktok.
62% of U.S. adults under 30 say they use TikTok, compared with 39% of those ages 30 to 49, 24% of those 50 to 64, and 10% of those 65 and older.
Many Americans think generative AI programs should credit the sources they rely on
Americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, whatsapp and facebook dominate the social media landscape in middle-income nations, sign up for our internet, science, and tech newsletter.
New findings, delivered monthly
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure in the U.S.
64% of Americans live within 2 miles of a public electric vehicle charging station, and those who live closest to chargers view EVs more positively.
When Online Content Disappears
A quarter of all webpages that existed at one point between 2013 and 2023 are no longer accessible.
A quarter of U.S. teachers say AI tools do more harm than good in K-12 education
High school teachers are more likely than elementary and middle school teachers to hold negative views about AI tools in education.
Teens and Video Games Today
85% of U.S. teens say they play video games. They see both positive and negative sides, from making friends to harassment and sleep loss.
Americans’ Views of Technology Companies
Most Americans are wary of social media’s role in politics and its overall impact on the country, and these concerns are ticking up among Democrats. Still, Republicans stand out on several measures, with a majority believing major technology companies are biased toward liberals.
22% of Americans say they interact with artificial intelligence almost constantly or several times a day. 27% say they do this about once a day or several times a week.
About one-in-five U.S. adults have used ChatGPT to learn something new (17%) or for entertainment (17%).
Across eight countries surveyed in Latin America, Africa and South Asia, a median of 73% of adults say they use WhatsApp and 62% say they use Facebook.
5 facts about Americans and sports
About half of Americans (48%) say they took part in organized, competitive sports in high school or college.
REFINE YOUR SELECTION
Research teams, signature reports.
The State of Online Harassment
Roughly four-in-ten Americans have experienced online harassment, with half of this group citing politics as the reason they think they were targeted. Growing shares face more severe online abuse such as sexual harassment or stalking
Parenting Children in the Age of Screens
Two-thirds of parents in the U.S. say parenting is harder today than it was 20 years ago, with many citing technologies – like social media or smartphones – as a reason.
Dating and Relationships in the Digital Age
From distractions to jealousy, how Americans navigate cellphones and social media in their romantic relationships.
Americans and Privacy: Concerned, Confused and Feeling Lack of Control Over Their Personal Information
Majorities of U.S. adults believe their personal data is less secure now, that data collection poses more risks than benefits, and that it is not possible to go through daily life without being tracked.
Americans and ‘Cancel Culture’: Where Some See Calls for Accountability, Others See Censorship, Punishment
Social media fact sheet, digital knowledge quiz, video: how do americans define online harassment.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Personal Finance Financial Advisors Credit Cards Taxes Retirement
- Insurance Auto Vision Life Dental Health Medicare Home Life Business Pet
- Investing Stocks Options ETFs Mutual Funds Futures IPOs Bonds Index Funds Forex Prop Trading
- Alternative investing Real Estate Startups Collectables
- Mortgage Rates Calculator Reviews Purchase Refinance Self-Employed
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges Price Action Apps Earn Crypto Wallets
Trading.com Review

Trading.com is a highly regulated counterparty designed for a new generation of traders, offering easy and intuitive access to forex trading. To excel in the forex market, you need access to diverse currency pairs, robust trading platforms, reliable execution and a competitive spread. Trading.com excels in all these criteria, offering 65+ forex pairs and real-time market execution on the cutting-edge MT5 platform.
As part of its commitment to providing the best forex trading conditions, Trading.com offers ultra-tight spreads, zero commissions and competitive leverage on major currency pairs. Beginner traders with little or no experience will find its comprehensive educational resources valuable. A practice account with $10,000 in virtual money is available to help traders build confidence before trading live.
Trading.com is the ideal counterparty for diverse traders, including beginners and experts seeking optimum trading conditions. In this Trading.com review, we analyze the trading conditions, platforms, core features and overall product offerings to help you decide if it is a suitable counterparty to kickstart your forex trading journey.
- Experienced forex traders seeking counterparties that provide commission-free real-time market execution on the MT5 platform with ultra-tight spreads, competitive leverage and access to a diverse market
- Pattern-day traders and scalpers looking to optimize trading performance by capitalizing on real-time market execution provided by Trading.com
- Beginner forex traders can also find Trading.com ideal due to the flexibility of its practice account, which gives them ample time to build confidence and gain mastery of the trading platform before trading live account
- Dedicated support 24 hours a day, 5 days a week
- Fast and hassle-free account setup and onboarding process
- Liquidity across 65+ currency pairs, including majors like EUR/USD, GBP/USD and USD/JPY
- Leverage available up to 50:1
- New customers can receive a $100 tradable promotional credit
- Customizable and intuitive web and mobile trading platform for seamless on-the-go trading
- Free practice accounts with $10,000 virtual funds and no expiry date
- Cutting-edge trading platform — MetaTrader 5 is available on desktop mobile platforms as well as a web terminal
- Robust technical indicators and advanced charting for in-depth market analysis
- Excellent research and educational resources, including well-crafted articles, video tutorials, forex glossaries and calculator
- Trading.com is regulated by Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and a member of the National Futures Association (NFA)
- Relatively new to the U.S. market
- No copy or social trading integration
- Promotional credit funds are not immediately withdrawable as certain terms & conditions apply
Trading.com Ratings at a Glance
- Trading.com Product Offering
- Tradable Instruments and Account Types
- Trading Platforms
- See All 17 Items
Trading.com Product Offering
Despite being relatively new compared to other well-established counterparties, Trading.com has already earned its spot among the best forex trading counterparties thanks to its diverse market, trading platform, low trading costs and more. Here’s a breakdown of its offerings.
Tradable Instruments and Account Types
Trading.com offers over 69 currency pairs, encompassing forex majors like EUR/USD, USD/JPY and GBP/USD, as well as minor pairs such as GBP/AUD, AUD/CAD and EUR/AUD. Additionally, you can trade various exotic currency pairs, including GBP/DKK, USD/TRY and EUR/ZAR. This extensive range of currency pairs provides opportunities for diversified trading strategies.
Besides the flexibility to choose your favorite currency, you can also capitalize on the company’s industry-leading leverage to amplify your positions while enjoying cost-effective trading execution thanks to its ultra-tight spreads. Note, trading in foreign currency contracts on margin carries a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. The high degree of leverage can work against you as well as for you. Before deciding to trade foreign exchange you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, and risk appetite. This comprehensive offering reflects Trading.com’s commitment to catering to the diverse needs and preferences of forex traders, fostering a dynamic and rewarding trading experience.
As an extension of its dedication to delivering a compelling trading experience, Trading.com offers only one account type — the T1 Account. Most forex counterparties offer multiple account options to accommodate diverse traders’ needs. However, it’s easy to confuse the various account types, and uncertainties may arise regarding what you can access and what you can’t.
Trading.com’s T1 Account is the ultimate package for an all-in-one forex trading experience. The account boasts every feature and tool you could need to trade the forex market without hassle.
These encompass a member area, news and research portal, advanced trading tools and learning center — all in a user-friendly portal. You can fund your account, plan your strategies, analyze the market and identify new opportunities — all within your portal. The T1 account makes sense if you seek a seamless trading experience.
Trading Platforms
Trading.com offers a cutting-edge and innovative MT5 trading platform. MT5 is the more sophisticated successor to the MT4. Both are versatile and well-recognized among traders in the financial market. However, MT5 boasts more extensive features and functionalities, making it the perfect online forex trading platform for traders seeking a more robust trading technology. These include over 38 pre-installed technical indicators, 44 analytical charting tools and 21 timeframes.
These basic features facilitate accurate technical analysis and fast decision-making in trading. However, the MT5 platform goes beyond that. It also offers detachable charts, depth-of-market (DoM), extra pending order types (sell stop limit and buy stop limit) and an integrated economic calendar. It is a reliable platform that boasts fully customizable charting options, multiple order types, advanced analytical capabilities and built-in copy trading systems.
MT5 supports one-click trading, automated trading via Expert Advisors (EAs), trading from charts and trailing stops. Trading.com provides MT5 on mobile devices (Android and iOS) and PCs (Windows). The platform supports the powerful MT5 WebTrader terminal, which grants you instant access to the global market directly from your browser on Mac and PC and requires no software download.
Trading.com offers a webtrader platform for U.S. users where you’ll be able to indulge in a full forex trading journey directly from your web browser—no downloads necessary. Featuring comprehensive charting, advanced tools, and a customizable interface, the platform offers everything essential for initiating currency trades on any web enabled device.
Additionally U.S. traders will have access to Trading.com’s mobile app where you’ll experience a seamless and user-friendly forex trading experience, regardless of your device. Take your trades with you wherever you go and relish in the platform’s convenience. By prioritizing mobile accessibility, they’ve optimized the platform’s strengths and incorporated numerous features similar to their webtrader, along with some extra functionalities all neatly tailored to fit in the palm of your hand.
Research Resources and Tools
Suppose you seek a deep dive into the market. In that case, Trading.com’s comprehensive research material can provide you with valuable market insights needed to make a more informed trading decision. It features daily updates, news and analysis on current market-moving events. Trading.com offers advanced tools on its research portal to help you plan your trades and capitalize on opportunities without hassles. For instance, you can directly assess expert analysis on the latest market movements from the in-house team.
Using the trading signal, you can discover potential currency pair movements with detailed trade signals based on the latest market data. The investor sentiment tool can help you gauge market sentiment by viewing the percentage of traders with buy or sell positions on specific currency pairs. And thanks to technical summaries, you can gain insights into the strength and direction of a currency pair’s underlying trend across multiple timeframes. All these tools can help you make more informed decisions that enhance your trading success.
There’s also an economic calendar with vital economic events and indicators, such as interest rate decisions, employment reports and GDP releases. This can help you anticipate market movements and adjust your trading strategies accordingly. Filtering out noise and focusing on events that could impact your trading are essential if you hope to excel in the market. The economic calendar enables you to utilize historical data and expected results to inform your trading decisions.
Educational Tools and Resources
Excellent educational resources empower traders with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the forex markets effectively. Trading.com provides extensive educational content to satisfy the needs of various traders, from beginners to intermediate and expert traders. These include short, well crafted tutorials designed to help traders discover the world of online forex trading one piece at a time. Overall, you can access up to 33 of such articles.
If you prefer learning via video format, Trading.com also offers video tutorials. This is more like breaking the written content into short, fun videos to enhance the learning experience. Trading.com provides a trading glossary to help you brush up on your trading terminologies. The firm even provides a walkthrough of the trading platforms via short videos. A forex calculator is also available to help you calculate position sizes, swaps and margins. Trading.com goes the extra mile to provide the essential tools needed to trade the forex market under optimal conditions.
Trading.com offers a Practice Account with $10,000 in virtual currency to help beginner traders develop confidence and build their strategy before trading with a live account. Unlike most brokers, Trading.com’s Practice Account does not expire, meaning you can use it for as long as you like, assuming you have a real account with Trading.com.
Customer Service
You can contact Trading.com’s support team via Live Chat, phone or email to ask questions about the platform and services, resolve account issues or make general inquiries. The dedicated support team is available 24/5. The phone and Live Chat channels grant you fast access to the support team, making them ideal for addressing complaints requiring immediate assistance.
We tested the Live Chat and received an instant response with no delay. The agent was professional, efficient and friendly when addressing questions. You can use the email channels for less urgent inquiries. A more efficient approach to assessing answers to your questions without contacting customer support is via the FAQ section. Trading.com’s FAQ section features a comprehensive collection of potential questions traders may have and their corresponding answers.
So, if you have queries, search the FAQ before contacting support. The firm also maintains an active presence on multiple social media channels, including Facebook, X, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn. This provides an alternative means of connecting to the support team. Trading.com has a 3.7-star rating on Trustpilot from 10 reviewers. All comments were positive except for one reviewer, who contributed to the average rating.
Trading.com Markets Inc. is licensed and regulated as a forex dealer in the United States by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA). Being authorized to operate under the regulatory oversight of such reputable organizations means Trading.com adheres to strict regulatory standards, ensuring a secure trading environment for its clients.
As part of its risk management strategy, the firm employs robust processes that regularly monitor their regulatory capital levels. Trading.com complies with all applicable data protection laws and utilizes the latest security technology to safeguard all personally identifiable information (PIS) at rest or in transit on its network.
Trading.com will not share or sell your PIS or other sensitive data to a third party without your consent except in line with a judicial order. You can review Trading.com’s Privacy Policy to fully understand the steps it takes to protect your data and your responsibilities. Additional measures the firm takes to protect your data and funds include:
- Providing a secure payment method with TLS technology for transfer security and privacy
- Partnering with multiple liquidity providers to keep the spread low
- Ensuring transparent trading conditions and costs
Minimum Investment and Pricing
The investment minimums and pricing can shape your trading strategy and determine your profitability. Here’s a breakdown of Trading.com’s pricing details.
Spread and Fees
Trading.com is committed to maintaining price transparency. The only applicable fee is the rollover fee for overnight positions. There are no currency transfers or hidden fees, and the platform is commission-free. The spread accounts for all applicable fees during trade execution. And since the spread is variable, your total trading cost can swing both sides depending on the market conditions.
It will be lower during normal trading conditions and higher during high volatility or liquidity. You can view your total trading cost or spread for each trade in the Order History section of the WebTrader or app and your daily and monthly account statements. You can also review the forex pricing page for the average spread per instrument.
Margin and Leverages
Trading.com also offers competitive leverage for margin trading, empowering you to increase your position size and seize potential opportunities with enhanced trading power. The leverage varies among the currency pairs and can be as high as 1:50 for forex majors like EURUSD. This means that with a $100 balance, you can increase your position size by up to $5,000, thereby boosting your profit.
Remember that leverage magnifies your losses the same way it does profits. Trading.com employs an automated trading system that monitors the overall utilization of your available collateral to limit your trading losses and prevent your total losses from exceeding your account balance. This system also requires you to maintain a margin level of at least 100%.
Deposit and Withdrawal
Trading.com offers two funding options: Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments and Bank Wire (BW) transfers. You can access both methods via your wallet. The minimum and maximum deposits via ACH are $50 and $10,000, respectively. There are no deposit charges; deposits take 2-5 business days to clear.
With Bank Wire transfers, there is no per-transaction limit on deposits, and like ACH, funds will also take 2-5 business days to clear. However, a fee of $13 applies to deposited amounts less than $250.
Your bank may also charge fees. Trading.com processes all withdrawals within 24 business hours of your initial request. However, it can take 2-5 business days for the money to appear in your account. A withdrawal fee of $13 applies for Bank Wire transfers less than $250. All other withdrawals are free. Your bank may also charge fees, so it’s best to check with them.
Trading.com also charges a monthly inactivity fee of $10 per month after you go 12 months without a trade. These inactivity fees end after you make a trade, close your account or your pre-funded account balance reaches 0.
Promotions
Trading.com currently offers two promos: a paper trading competition and a no-deposit bonus. Both involve opening and validating your live trading account. To join the paper trading competition, click the promotion icon on the top bar of your newly created real account and opt in. Then, validate your phone number and begin trading on your practice account. The top three monthly performing traders (based on ROI) are awarded $1,000, $3,000 or $6,000, respectively, in ascending order.
Like the paper trading competition, the no-deposit bonus does not require depositing funds. Once you’ve signed up for a live account and validated your phone number, you can claim your $100 bonus and start trading immediately. No deposit needed, all profits are withdrawable. Customers must maintain a verified account to qualify for one-time promotional credit. Credit is part of tradable equity but is not withdrawable until trading requirements are met. Trading Requirements: For every one lot traded, $5 credit vests into cash balance. Residual trade losses exceeding cash balance are deducted from credit until depleted.
If you make a living off the forex market like millions of people do, you shouldn’t limit your trading activities to your PC or MacBook. While they offer practicality, especially during technical analysis, major market-moving events can occur while you’re on the go.
Mobile trading becomes invaluable in such scenarios when you’re away from your computer. That’s the vision behind Trading.com’s sleek and intuitive mobile trading app — to facilitate seamless access to the forex markets on the go.
There’s no major difference between the app and Trading.com’s WebTrader or MT5 platform. It boasts the same features and functionality, including customizable watchlists, advanced charting, multiple order types, risk management tools, one-click trading, a research portal and expert news and analysis. Just think of it as the WebTrader adapted for mobile devices. However, you cannot request a transaction data report via the app.
User Experience
Trading.com delivers a seamless forex trading experience that appeals to beginners, intermediate and expert forex traders in the U.S. The platform’s impressive educational and research resources, innovative trading platform and advanced analytical tools have enabled it to captivate traders and forex investors.
The company also tries to maintain cost-efficient execution, with spreads as slow as 1.0 and zero commission. In addition to its WebTrader and MT5 platform, Trading.com offers a mobile trading app with a clean and user friendly interface.
The firm maintains full transparency on all aspects of its services, and thanks to its efficient support team, traders can easily get the answers to the questions they seek across multiple channels.
Trading.com seems on the right track to fulfilling its mission of leading online forex trading innovation through an unwavering commitment to its four guiding principles: simplicity, reliability, transparency and support. Benzinga considers Trading.com highly reliable.
Trading.com vs. Competitors
Trading.com has a few competitors, such as Forex.com and OANDA, in the U.S. market. Despite being new in the U.S. market, Trading.com is already head-to-head with these well-established counterparties regarding a wide range of forex markets, cutting-edge trading technology, analytical tools, comprehensive research and educational resources.
Trading.com’s most tangible competitive advantage is its unwavering commitment to providing its clients with a transparent and seamless online forex trading experience by ensuring the best possible trading conditions.

CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 69% to 77.7% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider . You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
The products and services available to you at FOREX.com will depend on your location and on which of its regulated entities holds your account

Trading.com Overall
Whether you’re a beginner or forex trading veteran seeking a new trading experience, Trading.com boasts all the features and tools to ensure that you excel in your trading journey. Its comprehensive forex market, innovative trading platform, easy-to-use analytical tools, research and educational resources are just what any dedicated trader needs to take advantage of the immense opportunities available in the forex market. Trading.com also offers excellent customer support, meaning you can ask technical and general questions anytime during your trade and get feedback without delays.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is trading.com safe.
Yes, Trading.com prioritizes security and regulatory compliance to ensure a safe trading environment for its clients. The firm is regulated by Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and member of the National Futures Association (NFA) in the U.S.
How do I start trading?
To start trading, you typically need to open an account with a platform like Trading.com, deposit funds, conduct research, develop a trading strategy and execute trades based on your strategy.
What type of trading is best for beginners?
For beginners, it’s often recommended to start with long-term investing or swing trading. These strategies typically require less active monitoring compared to day trading or options trading. However, it’s important to understand that all forms of trading involve risks, including the risk of significant losses. Beginners should carefully consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and the time they can commit to monitoring their investments. It is also advisable to seek education and potentially consult with a financial advisor before starting to trade.
Submit Your One Minute Opinion
How do you like trading.com, get a forex pro on your side.
FOREX.com , registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), lets you trade a wide range of forex markets with low pricing and fast, quality execution on every trade.
You can also tap into:
- EUR/USD as low as 0.2 with fixed $5 commissions per 100,000
- Powerful, purpose-built currency trading platforms
- Monthly cash rebates of up to $9 per million dollars traded with FOREX.com’s Active Trader Program
Learn more about FOREX.com ’s low pricing and how you can get started trading with FOREX.com.

Generative AI
Artificial intelligence isn’t going anywhere.
Create once. Distribute forever.
Saas seo: why alternative pages are a great investment, how calm business is using content & seo to win in b2b, about us overview.
- Software Companies
- Manufacturing Companies
- “Boring” Industries
- Link Building
- Content Creation
- Content Distribution
- Content Repurposing
- Search Engine Optimization
- Content Marketing Strategies
- Technical Search Engine Optimization
- Conversion Rate Optimization Services
- Case Studies
- Training & Development
- Our Leadership
Subscribe For Exclusive Trends, Research & Data
Gain access to exclusive research, training, trends and support from the best marketers in the world.
Foundation Labs provides you with timely, meaningful, and relevant data that enables you to grow your company in a meaningful way. The world’s top SaaS companies subscribe to Foundation Labs to receive industry news and data driven insights to create a marketing culture that drives results.
We have two different plans:
→ Exclusive B2B SaaS growth, SEO & content case studies → Quarterly reports on data-backed B2B SaaS trends, correlations & more → Weekly Insiders-only email on trends, data & research → Insiders-only webinars on B2B SaaS content marketing → Two weekly newsletters with case studies & SaaS stories
→ Exclusive B2B SaaS growth, SEO & content case studies → Quarterly reports on data-backed B2B SaaS trends, correlations & more → Weekly Insiders-only email on trends, data & research → Insiders-only webinars on B2B SaaS content marketing → Two weekly newsletters with case studies & SaaS stories → Invite-only fireside chats with marketing leaders at B2B SaaS giants → SaaS reports breaking down what’s working across industries today
Learn How The Best B2B SaaS Companies Do Marketing.
- Name * First Last
- Enter your email address
Last updated on June 6th, 2024
How to Write SEO Content According to the Google Leaks
Article's Content
We’re covering what the recent Google leaks mean for marketers and how you should structure your content based on these findings.
There are lots of fantastic explanations of what’s in the recent Google leaks and why they matter. Personally, I’d highly recommend this article and this article for the technical explanations.
But here, we’re going to explain what those leaks mean for marketers. We’re focused on giving you the executive summary and key takeaways, not all the technical details.
So, let’s dive in and find out how this is going to change the way you build your content strategy.
What the Leaks Actually Are
Let’s not get ahead of ourselves. As pointed out by Ahrefs , some SEOs are making wild assumptions about what these leaks mean. What we know is that they reflect a wealth of data stored by Google.
But not every data point Google collects influences search rankings; some might be used minimally or not at all. For example, while Google tracks the number of visitors using Chrome, this metric is unlikely to be a direct ranking factor. The documents mostly highlight storage details and internal processes rather than specific ranking algorithms. SEOs should critically evaluate the information, avoiding assumptions based on incomplete or misleading data, and always consider the broader context before jumping to conclusions.
For the factors that we do believe are ranking factors, the documents provide nothing to indicate how they are weighted. That means that Google could consider some factors, such as backlink quality, to be critical while considering others, such as the font size of the anchor text of a backlink, to be very minor.
Or, it could be the opposite! Maybe the font size of your backlinks’ anchor text is the most important ranking factor. We don’t think so, and the experience and experimentation of SEOs bear that out, but it’s important to recognize that when this article says we believe these ranking factors matter more than others, that isn’t based on the content of the document.
Instead, we’re using our expertise and experience to evaluate which of the more than 14,000 data points described in the documents seem to be the key ones you should pay attention to. So, with that disclaimer out of the way, let’s dig in.
1. Content Quality
Google’s leaked documents suggest a heavy emphasis on content quality as a ranking factor. This aligns with Google’s longstanding public guidance, but the leaks provide additional insight into the specific aspects of content quality that matter most.
Focusing on relevance, originality, and comprehensiveness can significantly boost your content’s performance in search rankings. Here’s how you can ensure your content meets these criteria:
The primary goal of your content should be to answer the user’s query. As you can imagine, there are several features in the API leaks that seem to track the relevance of a keyword to an article. This means you need to understand what your audience is searching for and tailor your content accordingly.
Use tools like Google’s Keyword Planner to identify popular search terms and questions related to your topic. Ensure that your content provides clear and direct answers to these queries, addressing the user’s intent.
Originality
Google’s algorithms seem to favour unique content over duplicated material. To stand out, create original content that offers a new perspective or additional value compared to what’s already available.
This doesn’t mean you can’t cover the same topics as other sites, but your approach should add something new — whether it’s new data, a fresh take, or a more comprehensive guide. One great way to add authority and authenticity is by interviewing a subject matter expert and including some quotes from them.
Comprehensiveness
Depth of content is crucial. Google prefers pages that thoroughly cover a topic, providing comprehensive information that leaves no question unanswered. Structure your content with clear subheadings, bullet points, and tables where appropriate to enhance readability and make it easier for users (and search engines) to find the information they need.
Including related keywords and subtopics can also help to signal the thoroughness of your content to search engines. For example, if you’re writing an article about flathead screwdrivers, don’t just include information about them. A lot of people will want to know the differences and comparisons between flathead and Phillips screwdrivers, so even information that may not seem immediately relevant is important for a fully comprehensive article.
2. User Experience (UX)
Improving user experience is important for achieving higher search rankings and ensuring user satisfaction. According to the leaked Google ranking factors, Google does track quite a few UX factors, and it’s likely they play a role in how your page ranks.
Page Load Speed
First, page load speed is important. Faster-loading pages not only enhance user satisfaction but also likely rank higher in search results. It also affects other possible ranking factors, such as mobile bounce rate . Here’s an example that Google gave themselves:

To improve this, optimize images by compressing them without sacrificing quality, leverage browser caching to reduce load times for repeat visitors, and use a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute content efficiently across multiple servers, reducing latency.
Responsiveness
A responsive page is one that responds to the device it’s being accessed from — essentially, if you’re on a phone, it goes to a mobile version of the website. It looks like this is a factor Google may consider in their rankings.
Ensure your website is optimized for mobile by implementing responsive design, which adjusts content to fit various screen sizes seamlessly. Simplify navigation on mobile devices by using clear, easy-to-tap buttons and streamlined menus.
Regularly testing your site’s mobile performance using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test can help identify and address any issues promptly, maintaining a smooth mobile user experience.
Site Architecture
Lastly, site architecture plays a vital role in good UX, and it almost certainly affects how your pages rank. A clear and intuitive navigation structure helps users and search engines find information quickly and easily.
Organize your site’s content into logical categories and subcategories using descriptive labels. Ensure that important pages are accessible within a few clicks from the homepage, improving both user experience and search engine indexing.
By focusing on these aspects — page load speed, mobile-friendliness, and site architecture — you can create a user-friendly website that ranks well and keeps visitors engaged.
3. Backlinks
Backlinks seem to be a key part of Google’s ranking algorithm, reflecting a site’s credibility and authority. However, not all backlinks are created equal. Understanding the nuances of backlink quality, quantity, and anchor text can significantly enhance your SEO strategy.
Backlink Quality
Quality may trump quantity when it comes to backlinks. High-quality backlinks are those that come from reputable, authoritative sites within your niche. Google’s algorithm likely uses these backlinks as votes of confidence, signalling that your content is valuable and trustworthy. Walk through this process to make sure your backlinks are high quality:

To secure high-quality backlinks, focus on creating exceptional, shareable content that industry leaders will naturally link to. Building relationships with influencers and authoritative sites in your field can also lead to valuable backlinks. Guest posting on reputable blogs and participating in industry forums can further bolster your backlink profile. Tools like Ahrefs and Moz can help you identify the quality of your backlinks, allowing you to target high-authority domains.
Quantity of Backlinks
While quality is paramount, quantity still matters. A healthy backlink profile includes a diverse range of backlinks from various sources. This diversity indicates to Google that your site is popular and relevant across a broad spectrum of the web.
However, acquiring backlinks should be a natural process. Avoid black-hat SEO techniques like buying links or participating in link farms, as these can lead to penalties. Instead, focus on earning backlinks through consistent, high-quality content creation; strategic outreach; and social media promotion. Regularly monitor your backlink profile using tools like SEMrush to ensure you maintain a balance of quality and quantity.
Anchor Text
Anchor text — the clickable text in a hyperlink — plays a significant role in how Google interprets the context of your backlinks. Effective anchor text should be relevant to the linked content and incorporate your target keywords naturally.
However, over-optimization of anchor text can lead to penalties. A diverse anchor text profile, including branded, generic, and exact match anchors, may appear more natural to Google’s algorithms. For instance, if your target keyword is “SEO strategies”, the anchor text of backlinks to your article should vary between “SEO strategies”, “click here”, “this guide”, and your brand name. Using tools like Majestic can help analyze and diversify your anchor text profile, ensuring it supports your SEO efforts without risking over-optimization.
4. User Engagement
For a long time, SEOs have wondered whether engagement factors matter for how Google ranks articles. It still isn’t certain, but given that we now Google tracks each of the factors below, it seems more likely than ever that they matter.
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR measures the percentage of users who click on your link after seeing it in the search results. A higher CTR indicates that users find your site relevant to their search queries.
We’ve always known that high-ranking pages have higher CTRs, but it’s always been a bit of a chicken-and-egg question: Is the CTR high because they rank high, or does Google rank them higher when the CTR goes up? The answer is probably both.

To boost your CTR, optimize your titles and meta descriptions to be compelling and relevant. Use action-oriented language, and include your primary keyword to attract users’ attention. For example, instead of a generic title like “SEO Tips”, use “10 Proven SEO Tips to Boost Your Rankings”. This approach makes your content stand out and encourages users to click through.
Bounce Rate
This refers to the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page. A lower bounce rate suggests that users are engaging with your site content and finding it valuable.
To reduce bounce rate, ensure your page content is engaging and highly relevant to the user’s query. Use clear headings, bullet points, and visual elements to make your content easily digestible. Additionally, include internal links to related articles to encourage users to explore more of your site. Offering a seamless user experience keeps visitors engaged and reduces bounce rates.
Dwell time is the amount of time users spend on your site after clicking through from the search results. Longer dwell times indicate that your content is informative and engaging.
Create content that is both engaging and informative to increase dwell time. Use multimedia elements like videos, infographics, and interactive content to keep users interested. Ensure your content is well-structured and covers the topic comprehensively. Engaging storytelling, practical examples, and actionable advice can also encourage users to stay on your site longer.
By focusing on improving CTR, reducing bounce rates, and increasing dwell time, you can make users more engaged, which in turn can positively impact your search rankings. These metrics provide valuable insights into how users interact with your site and can guide your efforts to create more effective, user-focused content.
5. Local SEO
Local SEO focuses on optimizing your online presence to attract more business from relevant local searches. Key factors include your Google My Business listing, local keywords, and reviews and ratings.
Google My Business Listing
A complete and accurate Google My Business listing is vital for local SEO, helping your business appear in local search results and Google Maps.
Ensure your Google My Business profile is fully optimized with accurate information, photos, and regular updates. Include essential details like your business name, address, phone number, and business hours. Adding high-quality photos and regularly updating your profile with posts and offers can enhance your visibility and attract more local customers.
Local Keywords
Using keywords relevant to your local area helps search engines connect your business with local search queries.
Incorporate local keywords naturally into your content, titles, and meta descriptions. For instance, if you run a bakery in Austin, use phrases like “best bakery in Austin” or “Austin artisan breads”. Including local landmarks or neighbourhoods in your keywords can further boost your local SEO efforts.
Reviews and Ratings
Positive reviews and high ratings are crucial for building trust and credibility with potential customers and search engines.
Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on your Google My Business profile and other review platforms. Respond to all reviews, both positive and negative, to show that you value customer feedback and are engaged with your audience. Promptly addressing any issues raised in negative reviews can also demonstrate your commitment to customer service and improve your reputation.

6. On-Page SEO
You’re welcome to explore our full guide to on-page SEO , but in general, it involves optimizing individual pages on your website to improve their search engine rankings and attract more organic traffic. Key components include title tags, meta descriptions, and header tags.
Title tags are important since they are the first impression users and search engines have of your page. They need to be relevant and compelling, including target keywords.

Craft unique, keyword-rich titles for each page. Ensure that the title accurately reflects the content of the page while incorporating your primary keyword. For example, if your page is about “SEO Best Practices”, a good title could be “Top 10 SEO Best Practices to Improve Your Rankings”. Keep your titles within 50–60 characters to ensure they display properly in search results.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions provide a brief summary of your page’s content and are essential for encouraging clicks from search results.
Write concise and persuasive meta descriptions that include target keywords. Aim for around 150–160 characters, and ensure your description provides a clear, enticing overview of what users can expect from the page. For instance, use something like, “Learn the top SEO best practices that can help improve your search rankings and drive more traffic to your site.”
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Header tags help structure your content, making it easier for search engines and users to understand how you’ve organized it. It could be that putting keywords in header tags makes them more effective.
Use header tags to organize content logically. The H1 tag should represent the main title of the page and include your primary keyword. Use H2 and H3 tags to break down the content into sections and subsections, respectively.
This not only improves readability but also helps search engines understand the hierarchy and context of your content. For example, under an H1 title like “SEO Best Practices”, you might use H2 tags for sections such as “Keyword Research”, “On-Page Optimization”, and “Link Building”. Make sure to include keywords frequently but naturally — H2s and H3s can be great places to target secondary keywords.
7. Technical SEO
Look, this is basic, but that’s what makes it so important. Technical SEO is the backbone of a well-optimized website, ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and understand your site. The Google leaks highlight several technical factors that can influence your rankings. Here’s how to address these critical areas:
Crawlability
If you don’t know, crawlability refers to how easily search engine bots can access and index the content on your site. If search engines can’t crawl your site effectively, your content won’t appear in search results.
Use a robots.txt file to guide search engines on which pages to crawl and which to avoid. This file should also prevent bots from accessing irrelevant or duplicate content that could dilute your SEO efforts.
Additionally, create an XML sitemap that lists all your important pages, helping search engines find and index them efficiently. Ensure no critical pages are inadvertently blocked by regularly reviewing your robots.txt file and sitemap.
You’re probably already doing this, but it’s good to have the confirmation from the Google documents that it matters.
Secure Connection (HTTPS)
Google almost certainly prefers a secure connection (HTTPS) over a non-secure one (HTTP). HTTPS protects user data and signals to Google that your site is trustworthy.
Obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority to secure your site. Once installed, ensure your site uses HTTPS across all pages. You can verify this by checking for a padlock icon in your browser’s address bar. Also, update any internal links, canonical tags, and redirects to use HTTPS to avoid mixed content issues. Tools like the ones made by SSL Labs can help you identify and fix any security gaps.
Structured Data
Structured data, or schema markup, helps search engines understand the content on your site and present it in a richer format in search results, such as rich snippets.
Implement structured data using schema.org vocabulary. This can include adding markup for articles, products, reviews, FAQs, and more. Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to validate your markup and ensure it’s correctly implemented. By doing so, you can enhance your search listings with additional information, making them more attractive and informative to users. This can lead to higher click-through rates and improved visibility.
By focusing on crawlability, secure connections, and structured data, you can ensure that your site is technically sound and optimized for search engines. These factors not only improve your chances of ranking higher but also enhance the user experience by providing a secure and informative browsing environment.
How to Apply These Tips
Much of this article has been theoretical. But it’s important to reiterate that we’ve picked these factors out of the 14,000 data points based on our practical experience doing SEO and seeing what works and what doesn’t. Fortunately, this leak has confirmed that Google tracks many of the factors we’ve always thought mattered.
In fact, we’ve been breaking down how B2B leaders have been executing these exact strategies for years. For example, if you want to see fantastic local SEO efforts, check out how Dialpad is dominating area codes . If you want to see excellent content quality, look no further than our breakdown of Stripe’s content . Finally, you can also check out an amazing backlink strategy in our Buffer breakdown .
Did you enjoy this post?
Other reads on this topic, how b2b tech companies can publish 100+ articles per year, how rippling boosted their blog traffic by 10x in one year, the “why” behind major serp traffic dips in saas and beyond.
Ensure Secure & Frictionless User Experiences with Passkeys

Presented by
Pedro Martinez, Business Owner Digital Banking Authentication, Thales & Megan Shamas, CMO, FIDO Alliance
About this talk
More from this channel.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
UX research helps brands and organizations to: Understand how users experience products, websites, mobile apps, and prototypes. Evaluate and optimize prototypes and ideas based on UX research discoveries - and nail the design and experience early in a product's life cycle. Unearth new customer needs and business opportunities.
User research is at the core of every exceptional user experience. As the name suggests, UX is subjective—the experience that a person goes through while using a product. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the needs and goals of potential users, the context, and their tasks which are unique for each product.
User experience research, or UX research, is the process of gathering insights about users' behaviors, needs, and pain points through observation techniques and feedback methodologies. It's a form of user research that looks at how users interact with your product, helping bridge the gaps between what you think users need, what users say they ...
UX (user experience) research is the systematic study of target users and their requirements, to add realistic contexts and insights to design processes. UX researchers adopt various methods to uncover problems and design opportunities. Doing so, they reveal valuable information which can be fed into the design process.
User Experience (UX) Research is a systematic process of understanding and evaluating how users interact with a product, service, or system. It encompasses a wide range of research methods and techniques to gain insights into user behaviors, preferences, needs, and pain points. The ultimate goal of UX research is to inform and improve the ...
UX research explores the optimization of product design and interaction. So whereas market research often focuses more broadly on the sales of a product or service, UX research narrows in on how people engage and interact with the products or services. In most cases, UX research is geared towards solutions-based insights because it stems from ...
How to conduct lean market research in 4 steps. The following four steps and practical examples will give you a solid market research plan for understanding who your users are and what they want from a company like yours. 1. Create simple user personas. A user persona is a semi-fictional character based on psychographic and demographic data ...
UX Research Cheat Sheet. Susan Farrell. February 12, 2017. Summary: User research can be done at any point in the design cycle. This list of methods and activities can help you decide which to use when. User-experience research methods are great at producing data and insights, while ongoing activities help get the right things done.
See below how to combine user research and market research throughout the product development cycle. Market Research vs User Research: They answer different questions and come up in different stages " The most important thing for user experience professionals to know is when marketing research is needed, and when user experience research is ...
2.1 Quantitative or qualitative market research. Classic market research is a traditional field, while UX research is considered agile and modern. The differentiation between quantitative and qualitative market research has existed for several decades. And user experience research, which is now available in a wide variety of facets ...
How to Conduct UX Research with Usability Testing. Usability testing can be broken down into a few major steps: Identify what needs to be tested and why (e.g. a new product, feature, etc.) Identify the target audience (or your desired customers). Create a list of tasks for the participants to work through.
Researchers. Market research is usually conducted by marketing or business development teams looking to understand the dynamics of a given market. User research, in contrast, is often carried out by design and product development teams aiming to enhance the product's usability and user experience.
Through this piece, you'll learn everything about user experience surveys. From market research professionals and business owners to website developers, anyone aiming for customer satisfaction will find this helpful.. You'll learn about UX survey best practices and the right questions to help identify pain points and understand different question types.
Attitudinal research looks at a user's feelings and attitudes toward an experience. UX research methods. One aspect of your role as a UX designer will be deciding which research method is appropriate for answering which questions. The UX research tool chest contains a variety of options to help you glean information from your users.
Market research is a systematic and objective process crucial for understanding target markets, refining business strategies, and informing decisions, which includes collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data on customers, competitors, and the industry. ... improving user experience, designing better products, and driving customer retention ...
You'll get to influence things millions of people use every day, from email and productivity apps to tools for developers and educators. Even if you don't currently use Google products, you can still sign up for a chance to participate in our research. If one of our studies is a good fit for you, we'll get in touch with details and next ...
User Experience (UX) Market Size And Forecast. User Experience (UX) Market size was valued at USD 6,120.64 Million in 2020 and is projected to reach USD 20,058 Million by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 16.24% from 2021 to 2028.. Dynamic businesses, increase in companies becoming consumer-centric and the want to understand consumer behaviour, and increasing in digitalization are some of the factors ...
Data Bridge Market Research analyzes that the global user experience (UX) research software market, which was USD 22.2 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 77.7 billion by 2031, at a CAGR of 22.5% during the forecast period 2024 to 2031.
Through feature prioritization, we can avoid a glut of features, the condition called featuritis. Use a MoSCoW as you finalize research or start with your design phase. As your design phase ...
In the U.S. and Canada, Coursera charges $49 per month after the initial 7-day free trial period. The Google UX Design Certificate can be completed in less than 6 months at under 10 hours per week of part-time study, so most learners can complete the certificate for less than $300 USD.
This article outlines 5 methods for prioritizing work into a UX roadmap: Impact-effort matrix. Feasibility, desirability, and viability scorecard. RICE method. MoSCoW analysis. Kano model. These prioritization methods can be used to prioritize a variety of "items," ranging from research questions, user segments, and features to ideas, and ...
Capturing user requirements is an essential step in building successful software applications. User Stories, User Journey Mapping, and Use Cases provide powerful techniques to comprehend user needs and align development efforts accordingly. By employing these methodologies and overcoming challenges through effective solutions, development teams ...
User research is a relatively new field on the Russian market. Only several years ago, sponsors mainly requested user interface design services, but during the past few years interest in user research has significantly piqued. Also, the fast-growing Russian market has attracted international attention as a part of global user research projects.
Supplemental research from the study found that 54% of resellers consider how easy and intuitive the interface of a given online secondhand marketplace is when deciding where to sell their items.
We examined 27 different aspects, including features, pricing, and customer service for the top Amazon keyword tools in the market. To maintain a balanced perspective, we also compared SmartScout to other popular Amazon research tools. Our goal was to see how it stands up against alternatives like Jungle Scout, Helium 10, and Viral Launch.
Americans' Views of Technology Companies. Most Americans are wary of social media's role in politics and its overall impact on the country, and these concerns are ticking up among Democrats. Still, Republicans stand out on several measures, with a majority believing major technology companies are biased toward liberals. short readsApr 3, 2024.
Robust technical indicators and advanced charting for in-depth market analysis; Excellent research and educational resources, including well-crafted articles, video tutorials, forex glossaries and ...
The answer is probably both. To boost your CTR, optimize your titles and meta descriptions to be compelling and relevant. Use action-oriented language, and include your primary keyword to attract users' attention. For example, instead of a generic title like "SEO Tips", use "10 Proven SEO Tips to Boost Your Rankings".
In this episode, Pedro Martinez from Thales and Megan Shamas from FIDO Alliance will delve into best practices and real-world examples for implementing passkeys and Strong Customer Authentication (SCA). Join us for insights from industry leaders on enhancing security and user experience. Key takeaways: - MFA and friction: The end consumer's ...