Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456

Essay on Gautam Buddha

An Introduction
Gautam Buddha is popularly called Lord Buddha or The Buddha. He was a great and religious leader of ancient India. He is regarded as the founder of Buddhism, which is one of the most followed religions in the world today.
The followers of Buddha are now called Buddhists which means the enlightened beings, the ones who have rediscovered the path to freedom starting from ignorance, craving to the cycle of rebirth and suffering. Buddha himself propagated it for nearly 45 years.
His teachings are based on his insights of suffering and dissatisfaction ending in a state called Nirvana.
Gautam Buddha is considered to be one of the greatest religious preachers in the world. He was the preacher of peace and harmony. In this Gautam Buddha essay, you will find one long and one short piece about the epic religious guru followed by many. Studying this piece will help you learn who Gautama Buddha was and what made him choose the path of spirituality. The long and short essay on Gautam Buddha will help students of Class 5 and above to write one on their own. These essays are specially designed so that you can have all the needed information about Gautam Buddha. This essay will help you to understand the life of Gautam Buddha in minimum words. Basically in a few words, this essay gives you a brief detail about Buddha.
Gautam Buddha, the messenger of peace, equality, and fraternity, was born in Lumbini in the 6th Century BC, the Terai region of Nepal. His real name was Siddhartha Gautam. He belonged to the royal family of Kapilavastu. His father was Suddhodhana, the ruler. Maya Devi, Gautam’s mother, died soon after giving birth to him. He was a thoughtful child with a broad mind. He was very disciplined and liked to question contemporary concepts to understand and gather more knowledge.
He wanted to devote his life to spirituality and meditation. This was what his father did not like about him. He went against his father’s wishes to find spirituality. His father was worried that someday, Gautam will leave his family to pursue his wishes. For this, Suddhodhana always guarded his son against the harshness surrounding him. He never let his son leave the palace anytime. When he was 18 years of age, Gautam was married to Yashodhara, a princess with magnificent beauty. They had a son named ‘Rahul’. Even though Siddhartha’s family was complete and happy, he did not find peace. His mind always urged him intending to find the truth beyond the walls.
As per the Buddhist manuscripts, when Siddhartha saw an old man, an ailing person, and a corpse, he understood that nothing in this material world is permanent. All the pleasures he enjoyed were temporary and someday, he had to leave them behind. His mind startled from the realization. He left his family, the throne, and the kingdom behind and started roaming in the forests and places aimlessly. All he wanted was to find the real truth and purpose of life. In his journey, he met with scholars and saints but nobody was able to quench his thirst for truth.
He then commenced meditation with the aim to suffer and then realized the ultimate truth sitting under a huge banyan tree after 6 years. It was in Bodh Gaya in Bihar. He turned 35 and was enlightened. His wisdom knew no boundaries. The tree was named Bodhi Vriksha. He was very satisfied with his newly found knowledge and gave his first speech on enlightenment in Sarnath. He found the ultimate truth behind the sorrows and troubles people face in the world. It was all due to their desires and attraction to earthly things.
A couple of centuries after he died, he came to be known as the Buddha which means the enlightened one. All the teachings of Buddha were compiled in the Vinaya. His teachings were passed to the Indo-Aryan community through oral traditions.
In his lecture, he mentioned the Noble Eightfold Path to conquer desires and attain full control. The first 3 paths described how one can gain physical control. The next 2 paths showed us how to achieve the fullest mental control. The last 2 paths were described to help people attain the highest level of intellect. These paths are described as Right Understanding, Right Thought, Right Speech, Right Action, Right Livelihood, Right Effort, Right Mindfulness, and Right Concentration synchronously.
The title “Buddha” was used by several ancient groups and for each group, it had its meaning. The word Buddhism refers to a living being who has got enlightened and just got up from his phase of ignorance. Buddhism believes that there have been Buddhas in the past before Gautam Buddha and there will be Buddhas in the future also. The Buddhists celebrate the life of Gautam Buddha starting from his birth to his enlightenment and passage into Nirvana stage as well.
In his life, Gautam Buddha had done a lot of spiritual things and lived his life by going through so much. Each suffering and each liberation of his has turned into teachings.
Some of them are explained below:
Finding Liberation: the ultimate motive of our soul is to find liberation.
The Noble truth of Life: for salvation, you need to know about all the four Noble truths of your life.
Suffering is not a Joke: each suffering leads you to experience a new you.
There are noble eightfold paths that you need to follow.
Death is final, the one who has taken birth will die surely and everything in life is impermeable, you are not going to have anything that will be permanent so focus on salvation rather than pleasing others.
He preached that only sacrifice cannot make a person happy and free from all the bonds he has in the world. He also defined the final goal as Nirvana. Even to this day, his preaching finds meaning and can be related to our sorrows. According to his teachings, the right way of thinking, acting, living, concentrating, etc can lead to such a state. He never asked anyone to sacrifice or pray all day to achieve such a state. This is not the way to gain such a mindful state.
He didn’t mention any god or an almighty controlling our fate. His teachings are the best philosophical thoughts one can follow. Gautam Buddha was his new name after gaining Nirvana and knowing the truth. He was sure that no religion can lead to Nirvana. Only the Noble Eightfold Path can be the way to achieve such a state. He breathed last in 483 BC in Kushinagar, now situated in Uttar Pradesh and his life became an inspiration.
Even after being in a happy family with a loving wife and son, he left his royal kingdom in search of the truth. No one was able to satisfy him with knowledge. He then attained his enlightenment under a banyan tree in Bodh Gaya. He described the Noble Eightfold Path that everyone should follow to get rid of sorrow and unhappiness. He died in 483 BC but his preaching is found to be still relevant to this date. This tells us how Siddhartha became Gautam Buddha. It also tells us about his valuable preaching and shows us the way to achieve Nirvana.

FAQs on Essay on Gautam Buddha
1. What made Siddhartha realize pleasures are Temporary?
When he first saw an ailing person, a corpse, and an old man, he realized worldly pleasures are temporary. He realized that all the pleasures that this world is running behind are fake. Nothing will stay forever, even the ones whom you love the most will leave you sooner or later, so you should not run behind these material pleasures. Focus on attaining salvation. Everyone who has taken birth will definitely leave one day, the thing that you have today will not be there tomorrow. There is only one soul for yourself. The body or the material things that you are proud of today will leave you tomorrow. Everything is not going to be the same.
2. What did he do to achieve Knowledge and Peace?
Gautam Buddha was more focused on achieving salvation, he wanted to know the truth of life. He wanted to have knowledge of all the things and peace along with Moksha. To receive knowledge and peace, Gautam Buddha left his home and his family behind. He wandered here and there aimlessly just to find peace in his life. Not only this, he talked with many scholars and saints so that he could receive the knowledge of everything that he was searching for.
3. What did he Preach?
Gautam Buddha was the preacher of peace. In this essay, we are introduced to the preaching of Gautam Buddha. He has taught all about how to receive salvation and attain Nirvana without following any particular religion. Some of his preachings are :
Have respect for your life.
No lying and respect for honesty.
No sexual misconduct and at least you should respect the people of the same community and respect women as well.
The path of sufferings, truth of causes; these factors will create a path of salvation for you. You need to believe in the reality of life and then move towards attaining the ultimate.
4. Does Gautam Buddha believe in God?
Buddhists actually don't believe in any dainty figure or God but according to them, there are some supernatural powers present in this universe that can help people or they can even encourage people to move toward enlightenment. Gautam Buddha, on seeing people dying and crying, realized that human life is nothing but suffering and all you need to do is get over this materialistic world and lead your life towards attaining salvation. Nothing is permanent nor even this body, so enlighten yourself towards the path of salvation.

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
The Buddha (fl. circa 450 BCE) is the individual whose teachings form the basis of the Buddhist tradition. These teachings, preserved in texts known as the Nikāyas or Āgamas , concern the quest for liberation from suffering. While the ultimate aim of the Buddha’s teachings is thus to help individuals attain the good life, his analysis of the source of suffering centrally involves claims concerning the nature of persons, as well as how we acquire knowledge about the world and our place in it. These teachings formed the basis of a philosophical tradition that developed and defended a variety of sophisticated theories in metaphysics and epistemology.
1. Buddha as Philosopher
2. core teachings, 3. non-self, 4. karma and rebirth, 5. attitude toward reason, primary sources, secondary sources, other internet resources, related entries.
This entry concerns the historical individual, traditionally called Gautama, who is identified by modern scholars as the founder of Buddhism. According to Buddhist teachings, there have been other buddhas in the past, and there will be yet more in the future. The title ‘Buddha’, which literally means ‘awakened’, is conferred on an individual who discovers the path to nirvana, the cessation of suffering, and propagates that discovery so that others may also achieve nirvana. This entry will follow modern scholarship in taking an agnostic stance on the question of whether there have been other buddhas, and likewise for questions concerning the superhuman status and powers that some Buddhists attribute to buddhas. The concern of this entry is just those aspects of the thought of the historical individual Gautama that bear on the development of the Buddhist philosophical tradition.
The Buddha will here be treated as a philosopher. To so treat him is controversial, but before coming to why that should be so, let us first rehearse those basic aspects of the Buddha’s life and teachings that are relatively non-controversial. Tradition has it that Gautama lived to age 80. Up until recently his dates were thought to be approximately 560–480 BCE, but many scholars now hold that he must have died around 405 BCE. He was born into a family of some wealth and power, members of the Śākya clan, in the area of the present border between India and Nepal. The story is that in early adulthood he abandoned his comfortable life as a householder (as well as his wife and young son) in order to seek a solution to the problem of existential suffering. He first took up with a number of different wandering ascetics ( śramanas ) who claimed to know the path to liberation from suffering. Finding their teachings unsatisfactory, he struck out on his own, and through a combination of insight and meditational practice attained the state of enlightenment ( bodhi ) which is said to represent the cessation of all further suffering. He then devoted the remaining 45 years of his life to teaching others the insights and techniques that had led him to this achievement.
Gautama could himself be classified as one of the śramanas . That there existed such a phenomenon as the śramanas tells us that there was some degree of dissatisfaction with the customary religious practices then prevailing in the Gangetic basin of North India. These practices consisted largely in the rituals and sacrifices prescribed in the Vedas. Among the śramanas there were many, including the Buddha, who rejected the authority of the Vedas as definitive pronouncements on the nature of the world and our place in it (and for this reason are called ‘heterodox’). But within the Vedic canon itself there is a stratum of (comparatively late) texts, the Upaniṣads , that likewise displays disaffection with Brahmin ritualism. Among the new ideas that figure in these (‘orthodox’) texts, as well as in the teachings of those heterodox śramanas whose doctrines are known to us, are the following: that sentient beings (including humans, non-human animals, gods, and the inhabitants of various hells) undergo rebirth; that rebirth is governed by the causal laws of karma (good actions cause pleasant fruit for the agent, evil actions cause unpleasant fruit, etc.); that continual rebirth is inherently unsatisfactory; that there is an ideal state for sentient beings involving liberation from the cycle of rebirth; and that attaining this state requires overcoming ignorance concerning one’s true identity. Various views are offered concerning this ignorance and how to overcome it. The Bhagavad Gītā (classified by some orthodox schools as an Upaniṣad ) lists four such methods, and discusses at least two separate views concerning our identity: that there is a plurality of distinct selves, each being the true agent of a person’s actions and the bearer of karmic merit and demerit but existing separately from the body and its associated states; and that there is just one self, of the nature of pure consciousness (a ‘witness’) and identical with the essence of the cosmos, Brahman or pure undifferentiated Being.
The Buddha agreed with those of his contemporaries embarked on the same soteriological project that it is ignorance about our identity that is responsible for suffering. What sets his teachings apart (at this level of analysis) lies in what he says that ignorance consists in: the conceit that there is an ‘I’ and a ‘mine’. This is the famous Buddhist teaching of non-self ( anātman ). And it is with this teaching that the controversy begins concerning whether Gautama may legitimately be represented as a philosopher. First there are those (e.g. Albahari 2006) who (correctly) point out that the Buddha never categorically denies the existence of a self that transcends what is empirically given, namely the five skandhas or psychophysical elements. While the Buddha does deny that any of the psychophysical elements is a self, these interpreters claim that he at least leaves open the possibility that there is a self that is transcendent in the sense of being non-empirical. To this it may be objected that all of classical Indian philosophy—Buddhist and orthodox alike—understood the Buddha to have denied the self tout court . To this it is sometimes replied that the later philosophical tradition simply got the Buddha wrong, at least in part because the Buddha sought to indicate something that cannot be grasped through the exercise of philosophical rationality. On this interpretation, the Buddha should be seen not as a proponent of the philosophical methods of analysis and argumentation, but rather as one who sees those methods as obstacles to final release.
Another reason one sometimes encounters for denying that the Buddha is a philosopher is that he rejects the characteristically philosophical activity of theorizing about matters that lack evident practical application. On this interpretation as well, those later Buddhist thinkers who did go in for the construction of theories about the ultimate nature of everything simply failed to heed or properly appreciate the Buddha’s advice that we avoid theorizing for its own sake and confine our attention to those matters that are directly relevant to liberation from suffering. On this view the teaching of non-self is not a bit of metaphysics, just some practical advice to the effect that we should avoid identifying with things that are transitory and so bound to yield dissatisfaction. What both interpretations share is the assumption that it is possible to arrive at what the Buddha himself thought without relying on the understanding of his teachings developed in the subsequent Buddhist philosophical tradition.
This assumption may be questioned. Our knowledge of the Buddha’s teachings comes by way of texts that were not written down until several centuries after his death, are in languages (Pāli, and Chinese translations of Sanskrit) other than the one he is likely to have spoken, and disagree in important respects. The first difficulty may not be as serious as it seems, given that the Buddha’s discourses were probably rehearsed shortly after his death and preserved through oral transmission until the time they were committed to writing. And the second need not be insuperable either. (See, e.g., Cousins 2022.) But the third is troubling, in that it suggests textual transmission involved processes of insertion and deletion in aid of one side or another in sectarian disputes. Our ancient sources attest to this: one will encounter a dispute among Buddhist thinkers where one side cites some utterance of the Buddha in support of their position, only to have the other side respond that the text from which the quotation is taken is not universally recognized as authoritatively the word of the Buddha. This suggests that our record of the Buddha’s teaching may be colored by the philosophical elaboration of those teachings propounded by later thinkers in the Buddhist tradition.
Some scholars (e.g., Gombrich 2009, Shulman 2014) are more sanguine than others about the possibility of overcoming this difficulty, and thereby getting at what the Buddha himself had thought, as opposed to what later Buddhist philosophers thought he had thought. No position will be taken on this dispute here. We will be treating the Buddha’s thought as it was understood within the later philosophical tradition that he had inspired. The resulting interpretation may or may not be faithful to his intentions. It is at least logically possible that he believed there to be a transcendent self that can only be known by mystical intuition, or that the exercise of philosophical rationality leads only to sterile theorizing and away from real emancipation. What we can say with some assurance is that this is not how the Buddhist philosophical tradition understood him. It is their understanding that will be the subject of this essay.
The Buddha’s basic teachings are usually summarized using the device of the Four Nobles’ Truths:
- There is suffering.
- There is the origination of suffering.
- There is the cessation of suffering.
- There is a path to the cessation of suffering.
The first of these claims might seem obvious, even when ‘suffering’ is understood to mean not mere pain but existential suffering, the sort of frustration, alienation and despair that arise out of our experience of transitoriness. But there are said to be different levels of appreciation of this truth, some quite subtle and difficult to attain; the highest of these is said to involve the realization that everything is of the nature of suffering. Perhaps it is sufficient for present purposes to point out that while this is not the implausible claim that all of life’s states and events are necessarily experienced as unsatisfactory, still the realization that all (oneself included) is impermanent can undermine a precondition for real enjoyment of the events in a life: that such events are meaningful by virtue of their having a place in an open-ended narrative.
It is with the development and elaboration of (2) that substantive philosophical controversy begins. (2) is the simple claim that there are causes and conditions for the arising of suffering. (3) then makes the obvious point that if the origination of suffering depends on causes, future suffering can be prevented by bringing about the cessation of those causes. (4) specifies a set of techniques that are said to be effective in such cessation. Much then hangs on the correct identification of the causes of suffering. The answer is traditionally spelled out in a list consisting of twelve links in a causal chain that begins with ignorance and ends with suffering (represented by the states of old age, disease and death). Modern scholarship has established that this list is a later compilation. For the texts that claim to convey the Buddha’s own teachings give two slightly different formulations of this list, and shorter formulations containing only some of the twelve items are also found in the texts. But it seems safe to say that the Buddha taught an analysis of the origins of suffering roughly along the following lines: given the existence of a fully functioning assemblage of psychophysical elements (the parts that make up a sentient being), ignorance concerning the three characteristics of sentient existence—suffering, impermanence and non-self—will lead, in the course of normal interactions with the environment, to appropriation (the identification of certain elements as ‘I’ and ‘mine’). This leads in turn to the formation of attachments, in the form of desire and aversion, and the strengthening of ignorance concerning the true nature of sentient existence. These ensure future rebirth, and thus future instances of old age, disease and death, in a potentially unending cycle.
The key to escape from this cycle is said to lie in realization of the truth about sentient existence—that it is characterized by suffering, impermanence and non-self. But this realization is not easily achieved, since acts of appropriation have already made desire, aversion and ignorance deeply entrenched habits of mind. Thus the measures specified in (4) include various forms of training designed to replace such habits with others that are more conducive to seeing things as they are. Among these is training in meditation, which serves among other things as a way of enhancing one’s observational abilities with respect to one’s own psychological states. Insight is cultivated through the use of these newly developed observational powers, as informed by knowledge acquired through the exercise of philosophical rationality. There is a debate in the later tradition as to whether final release can be attained through theoretical insight alone, through meditation alone, or only by using both techniques. Ch’an, for instance, is based on the premise that enlightenment can be attained through meditation alone, whereas Theravāda advocates using both but also holds that analysis alone may be sufficient for some. (This disagreement begins with a dispute over how to interpret D I.77–84; see Cousins 2022, 81–6.) The third option seems the most plausible, but the first is certainly of some interest given its suggestion that one can attain the ideal state for humans just by doing philosophy.
The Buddha seems to have held (2) to constitute the core of his discovery. He calls his teachings a ‘middle path’ between two extreme views, and it is this claim concerning the causal origins of suffering that he identifies as the key to avoiding those extremes. The extremes are eternalism, the view that persons are eternal, and annihilationism, the view that persons go utterly out of existence (usually understood to mean at death, though a term still shorter than one lifetime is not ruled out). It will be apparent that eternalism requires the existence of the sort of self that the Buddha denies. What is not immediately evident is why the denial of such a self is not tantamount to the claim that the person is annihilated at death (or even sooner, depending on just how impermanent one takes the psychophysical elements to be). The solution to this puzzle lies in the fact that eternalism and annihilationism both share the presupposition that there is an ‘I’ whose existence might either extend beyond death or terminate at death. The idea of the ‘middle path’ is that all of life’s continuities can be explained in terms of facts about a causal series of psychophysical elements. There being nothing more than a succession of these impermanent, impersonal events and states, the question of the ultimate fate of this ‘I’, the supposed owner of these elements, simply does not arise.
This reductionist view of sentient beings was later articulated in terms of the distinction between two kinds of truth, conventional and ultimate. Each kind of truth has its own domain of objects, the things that are only conventionally real and the things that are ultimately real respectively. Conventionally real entities are those things that are accepted as real by common sense, but that turn out on further analysis to be wholes compounded out of simpler entities and thus not strictly speaking real at all. The stock example of a conventionally real entity is the chariot, which we take to be real only because it is more convenient, given our interests and cognitive limitations, to have a single name for the parts when assembled in the right way. Since our belief that there are chariots is thus due to our having a certain useful concept, the chariot is said to be a mere conceptual fiction. (This does not, however, mean that all conceptualization is falsification; only concepts that allow of reductive analysis lead to this artificial inflation of our ontology, and thus to a kind of error.) Ultimately real entities are those ultimate parts into which conceptual fictions are analyzable. An ultimately true statement is one that correctly describes how certain ultimately real entities are arranged. A conventionally true statement is one that, given how the ultimately real entities are arranged, would correctly describe certain conceptual fictions if they also existed. The ultimate truth concerning the relevant ultimately real entities helps explain why it should turn out to be useful to accept conventionally true statements (such as ‘King Milinda rode in a chariot’) when the objects described in those statements are mere fictions.
Using this distinction between the two truths, the key insight of the ‘middle path’ may be expressed as follows. The ultimate truth about sentient beings is just that there is a causal series of impermanent, impersonal psychophysical elements. Since these are all impermanent, and lack other properties that would be required of an essence of the person, none of them is a self. But given the right arrangement of such entities in a causal series, it is useful to think of them as making up one thing, a person. It is thus conventionally true that there are persons, things that endure for a lifetime and possibly (if there is rebirth) longer. This is conventionally true because generally speaking there is more overall happiness and less overall pain and suffering when one part of such a series identifies with other parts of the same series. For instance, when the present set of psychophysical elements identifies with future elements, it is less likely to engage in behavior (such as smoking) that results in present pleasure but far greater future pain. The utility of this convention is, however, limited. Past a certain point—namely the point at which we take it too seriously, as more than just a useful fiction—it results in existential suffering. The cessation of suffering is attained by extirpating all sense of an ‘I’ that serves as agent and owner.
The Buddha’s ‘middle path’ strategy can be seen as one of first arguing that since the word ‘I’ is a mere enumerative term like ‘pair’, there is nothing that it genuinely denotes; and then explaining that our erroneous sense of an ‘I’ stems from our employment of the useful fiction represented by the concept of the person. While the second part of this strategy only receives its full articulation in the later development of the theory of two truths, the first part can be found in the Buddha’s own teachings, in the form of several philosophical arguments for non-self. Best known among these is the argument from impermanence (S III.66–8), which has this basic structure:
It is the fact that this argument does not contain a premise explicitly asserting that the five skandhas (classes of psychophysical element) are exhaustive of the constituents of persons, plus the fact that these are all said to be empirically observable, that leads some to claim that the Buddha did not intend to deny the existence of a self tout court . There is, however, evidence that the Buddha was generally hostile toward attempts to establish the existence of unobservable entities. In the Pohapāda Sutta (D I.178–203), for instance, the Buddha compares someone who posits an unseen seer in order to explain our introspective awareness of cognitions, to a man who has conceived a longing for the most beautiful woman in the world based solely on the thought that such a woman must surely exist. And in the Tevijja Sutta (D I.235–52), the Buddha rejects the claim of certain Brahmins to know the path to oneness with Brahman, on the grounds that no one has actually observed this Brahman. This makes more plausible the assumption that the argument has as an implicit premise the claim that there is no more to the person than the five skandhas .
Premise (1) appears to be based on the assumption that persons undergo rebirth, together with the thought that one function of a self would be to account for diachronic personal identity. By ‘permanent’ is here meant continued existence over at least several lives. This is shown by the fact that the Buddha rules out the body as a self on the grounds that the body exists for just one lifetime. (This also demonstrates that the Buddha did not mean by ‘impermanent’ what some later Buddhist philosophers meant, viz., existing for just a moment; the Buddhist doctrine of momentariness represents a later development.) The mental entities that make up the remaining four types of psychophysical element might seem like more promising candidates, but these are ruled out on the grounds that these all originate in dependence on contact between sense faculty and object, and last no longer than a particular sense-object-contact event. That he listed five kinds of psychophysical element, and not just one, shows that the Buddha embraced a kind of dualism. But this strategy for demonstrating the impermanence of the psychological elements shows that his dualism was not the sort of mind-body dualism familiar from substance ontologies like those of Descartes and of the Nyāya school of orthodox Indian philosophy. Instead of seeing the mind as the persisting bearer of such transient events as occurrences of cognition, feeling and volition, he treats ‘mind’ as a kind of aggregate term for bundles of transient mental events. These events being impermanent, they too fail to account for diachronic personal identity in the way in which a self might be expected to.
Another argument for non-self, which might be called the argument from control (S III.66–8), has this structure:
Premise (1) is puzzling. It appears to presuppose that the self should have complete control over itself, so that it would effortlessly adjust its state to its desires. That the self should be thought of as the locus of control is certainly plausible. Those Indian self-theorists who claim that the self is a mere passive witness recognize that the burden of proof is on them to show that the self is not an agent. But it seems implausibly demanding to require of the self that it have complete control over itself. We do not require that vision see itself if it is to see other things. The case of vision suggests an alternative interpretation, however. We might hold that vision does not see itself for the reason that this would violate an irreflexivity principle, to the effect that an entity cannot operate on itself. Indian philosophers who accept this principle cite supportive instances such as the knife that cannot cut itself and the finger-tip that cannot touch itself. If this principle is accepted, then if the self were the locus of control it would follow that it could never exercise this function on itself. A self that was the controller could never find itself in the position of seeking to change its state to one that it deemed more desirable. On this interpretation, the first premise seems to be true. And there is ample evidence that (2) is true: it is difficult to imagine a bodily or psychological state over which one might not wish to exercise control. Consequently, given the assumption that the person is wholly composed of the psychophysical elements, it appears to follow that a self of this description does not exist.
These two arguments appear, then, to give good reason to deny a self that might ground diachronic personal identity and serve as locus of control, given the assumption that there is no more to the person than the empirically given psychophysical elements. But it now becomes something of a puzzle how one is to explain diachronic personal identity and agency. To start with the latter, does the argument from control not suggest that control must be exercised by something other than the psychophysical elements? This was precisely the conclusion of the Sāṃkhya school of orthodox Indian philosophy. One of their arguments for the existence of a self was that it is possible to exercise control over all the empirically given constituents of the person; while they agree with the Buddha that a self is never observed, they take the phenomena of agency to be grounds for positing a self that transcends all possible experience.
This line of objection to the Buddha’s teaching of non-self is more commonly formulated in response to the argument from impermanence, however. Perhaps its most dramatic form is aimed at the Buddha’s acceptance of the doctrines of karma and rebirth. It is clear that the body ceases to exist at death. And given the Buddha’s argument that mental states all originate in dependence on sense-object contact events, it seems no psychological constituent of the person can transmigrate either. Yet the Buddha claims that persons who have not yet achieved enlightenment will be reborn as sentient beings of some sort after they die. If there is no constituent whatever that moves from one life to the next, how could the being in the next life be the same person as the being in this life? This question becomes all the more pointed when it is added that rebirth is governed by karma, something that functions as a kind of cosmic justice: those born into fortunate circumstances do so as a result of good deeds in prior lives, while unpleasant births result from evil past deeds. Such a system of reward and punishment could be just only if the recipient of pleasant or unpleasant karmic fruit is the same person as the agent of the good or evil action. And the opponent finds it incomprehensible how this could be so in the absence of a persisting self.
It is not just classical Indian self-theorists who have found this objection persuasive. Some Buddhists have as well. Among these Buddhists, however, this has led to the rejection not of non-self but of rebirth. (Historically this response was not unknown among East Asian Buddhists, and it is not rare among Western Buddhists today.) The evidence that the Buddha himself accepted rebirth and karma seems quite strong, however. The later tradition would distinguish between two types of discourse in the body of the Buddha’s teachings: those intended for an audience of householders seeking instruction from a sage, and those intended for an audience of monastic renunciates already versed in his teachings. And it would be one thing if his use of the concepts of karma and rebirth were limited to the former. For then such appeals could be explained away as another instance of the Buddha’s pedagogical skill (commonly referred to as upāya ). The idea would be that householders who fail to comply with the most basic demands of morality are not likely (for reasons to be discussed shortly) to make significant progress toward the cessation of suffering, and the teaching of karma and rebirth, even if not strictly speaking true, does give those who accept it a (prudential) reason to be moral. But this sort of ‘noble lie’ justification for the Buddha teaching a doctrine he does not accept fails in the face of the evidence that he also taught it to quite advanced monastics (e.g., A III.33). And what he taught is not the version of karma popular in certain circles today, according to which, for instance, an act done out of hatred makes the agent somewhat more disposed to perform similar actions out of similar motives in the future, which in turn makes negative experiences more likely for the agent. What the Buddha teaches is instead the far stricter view that each action has its own specific consequence for the agent, the hedonic nature of which is determined in accordance with causal laws and in such a way as to require rebirth as long as action continues. So if there is a conflict between the doctrine of non-self and the teaching of karma and rebirth, it is not to be resolved by weakening the Buddha’s commitment to the latter.
The Sanskrit term karma literally means ‘action’. What is nowadays referred to somewhat loosely as the theory of karma is, speaking more strictly, the view that there is a causal relationship between action ( karma ) and ‘fruit’ ( phala ), the latter being an experience of pleasure, pain or indifference for the agent of the action. This is the view that the Buddha appears to have accepted in its most straightforward form. Actions are said to be of three types: bodily, verbal and mental. The Buddha insists, however, that by action is meant not the movement or change involved, but rather the volition or intention that brought about the change. As Gombrich (2009) points out, the Buddha’s insistence on this point reflects the transition from an earlier ritualistic view of action to a view that brings action within the purview of ethics. For it is when actions are seen as subject to moral assessment that intention becomes relevant. One does not, for instance, perform the morally blameworthy action of speaking insultingly to an elder just by making sounds that approximate to the pronunciation of profanities in the presence of an elder; parrots and prelinguistic children can do as much. What matters for moral assessment is the mental state (if any) that produced the bodily, verbal or mental change. And it is the occurrence of these mental states that is said to cause the subsequent occurrence of hedonically good, bad and neutral experiences. More specifically, it is the occurrence of the three ‘defiled’ mental states that brings about karmic fruit. The three defilements ( kleśa s) are desire, aversion and ignorance. And we are told quite specifically (A III.33) that actions performed by an agent in whom these three defilements have been destroyed do not have karmic consequences; such an agent is experiencing their last birth.
Some caution is required in understanding this claim about the defilements. The Buddha seems to be saying that it is possible to act not only without ignorance, but also in the absence of desire or aversion, yet it is difficult to see how there could be intentional action without some positive or negative motivation. To see one’s way around this difficulty, one must realize that by ‘desire’ and ‘aversion’ are meant those positive and negative motives respectively that are colored by ignorance, viz. ignorance concerning suffering, impermanence and non-self. Presumably the enlightened person, while knowing the truth about these matters, can still engage in motivated action. Their actions are not based on the presupposition that there is an ‘I’ for which those actions can have significance. Ignorance concerning these matters perpetuates rebirth, and thus further occasions for existential suffering, by facilitating a motivational structure that reinforces one’s ignorance. We can now see how compliance with common-sense morality could be seen as an initial step on the path to the cessation of suffering. While the presence of ignorance makes all action—even that deemed morally good—karmically potent, those actions commonly considered morally evil are especially powerful reinforcers of ignorance, in that they stem from the assumption that the agent’s welfare is of paramount importance. While recognition of the moral value of others may still involve the conceit that there is an ‘I’, it can nonetheless constitute progress toward dissolution of the sense of self.
This excursus into what the Buddha meant by karma may help us see how his middle path strategy could be used to reply to the objection to non-self from rebirth. That objection was that the reward and punishment generated by karma across lives could never be deserved in the absence of a transmigrating self. The middle path strategy generally involves locating and rejecting an assumption shared by a pair of extreme views. In this case the views will be (1) that the person in the later life deserves the fruit generated by the action in the earlier life, and (2) that this person does not deserve the fruit. One assumption shared by (1) and (2) is that persons deserve reward and punishment depending on the moral character of their actions, and one might deny this assumption. But that would be tantamount to moral nihilism, and a middle path is said to avoid nihilisms (such as annihilationism). A more promising alternative might be to deny that there are ultimately such things as persons that could bear moral properties like desert. This is what the Buddha seems to mean when he asserts that the earlier and the later person are neither the same nor different (S II.62; S II.76; S II.113). Since any two existing things must be either identical or distinct, to say of the two persons that they are neither is to say that strictly speaking they do not exist.
This alternative is more promising because it avoids moral nihilism. For it allows one to assert that persons and their moral properties are conventionally real. To say this is to say that given our interests and cognitive limitations, we do better at achieving our aim—minimizing overall pain and suffering—by acting as though there are persons with morally significant properties. Ultimately there are just impersonal entities and events in causal sequence: ignorance, the sorts of desires that ignorance facilitates, an intention formed on the basis of such a desire, a bodily, verbal or mental action, a feeling of pleasure, pain or indifference, and an occasion of suffering. The claim is that this situation is usefully thought of as, for instance, a person who performs an evil deed due to their ignorance of the true nature of things, receives the unpleasant fruit they deserve in the next life, and suffers through their continuing on the wheel of saṃsāra. It is useful to think of the situation in this way because it helps us locate the appropriate places to intervene to prevent future pain (the evil deed) and future suffering (ignorance).
It is no doubt quite difficult to believe that karma and rebirth exist in the form that the Buddha claims. It is said that their existence can be confirmed by those who have developed the power of retrocognition through advanced yogic technique. But this is of little help to those not already convinced that meditation is a reliable means of knowledge. What can be said with some assurance is that karma and rebirth are not inconsistent with non-self. Rebirth without transmigration is logically possible.
When the Buddha says that a person in one life and the person in another life are neither the same nor different, one’s first response might be to take ‘different’ to mean something other than ‘not the same’. But while this is possible in English given the ambiguity of ‘the same’, it is not possible in the Pāli source, where the Buddha is represented as unambiguously denying both numerical identity and numerical distinctness. This has led some to wonder whether the Buddha does not employ a deviant logic. Such suspicions are strengthened by those cases where the options are not two but four, cases of the so-called tetralemma ( catuṣkoṭi ). For instance, when the Buddha is questioned about the post-mortem status of the enlightened person or arhat (e.g., at M I.483–8) the possibilities are listed as: (1) the arhat continues to exist after death, (2) does not exist after death, (3) both exists and does not exist after death, and (4) neither exists nor does not exist after death. When the Buddha rejects both (1) and (2) we get a repetition of ‘neither the same nor different’. But when he goes on to entertain, and then reject, (3) and (4) the logical difficulties are compounded. Since each of (3) and (4) appears to be formally contradictory, to entertain either is to entertain the possibility that a contradiction might be true. And their denial seems tantamount to affirmation of excluded middle, which is prima facie incompatible with the denial of both (1) and (2). One might wonder whether we are here in the presence of the mystical.
There were some Buddhist philosophers who took ‘neither the same nor different’ in this way. These were the Personalists ( Pudgalavādins ), who were so called because they affirmed the ultimate existence of the person as something named and conceptualized in dependence on the psychophysical elements. They claimed that the person is neither identical with nor distinct from the psychophysical elements. They were prepared to accept, as a consequence, that nothing whatever can be said about the relation between person and elements. But their view was rejected by most Buddhist philosophers, in part on the grounds that it quickly leads to an ineffability paradox: one can say neither that the person’s relation to the elements is inexpressible, nor that it is not inexpressible. The consensus view was instead that the fact that the person can be said to be neither identical with nor distinct from the elements is grounds for taking the person to be a mere conceptual fiction. Concerning the persons in the two lives, they understood the negations involved in ‘neither the same nor different’ to be of the commitmentless variety, i.e., to function like illocutionary negation. If we agree that the statement ‘7 is green’ is semantically ill-formed, on the grounds that abstract objects such as numbers do not have colors, then we might go on to say, ‘Do not say that 7 is green, and do not say that it is not green either’. There is no contradiction here, since the illocutionary negation operator ‘do not say’ generates no commitment to an alternative characterization.
There is also evidence that claims of type (3) involve parameterization. For instance, the claim about the arhat would be that there is some respect in which they can be said to exist after death, and some other respect in which they can be said to no longer exist after death. Entertaining such a proposition does not require that one believe there might be true contradictions. And while claims of type (4) would seem to be logically equivalent to those of type (3) (regardless of whether or not they involve parameterization), the tradition treated this type as asserting that the subject is beyond all conceptualization. To reject the type (4) claim about the arhat is to close off one natural response to the rejections of the first three claims: that the status of the arhat after death transcends rational understanding. That the Buddha rejected all four possibilities concerning this and related questions is not evidence that he employed a deviant logic.
The Buddha’s response to questions like those concerning the arhat is sometimes cited in defense of a different claim about his attitude toward rationality. This is the claim that the Buddha was essentially a pragmatist, someone who rejects philosophical theorizing for its own sake and employs philosophical rationality only to the extent that doing so can help solve the practical problem of eliminating suffering. The Buddha does seem to be embracing something like this attitude when he defends his refusal to answer questions like that about the arhat , or whether the series of lives has a beginning, or whether the living principle ( jīva ) is identical with the body. He calls all the possible views with respect to such questions distractions insofar as answering them would not lead to the cessation of the defilements and thus to the end of suffering. And in a famous simile (M I.429) he compares someone who insists that the Buddha answer these questions to someone who has been wounded by an arrow but will not have the wound treated until they are told who shot the arrow, what sort of wood the arrow is made of, and the like.
Passages such as these surely attest to the great importance the Buddha placed on sharing his insights to help others overcome suffering. But this is consistent with the belief that philosophical rationality may be used to answer questions that lack evident connection with pressing practical concerns. And on at least one occasion the Buddha does just this. Pressed to give his answers to the questions about the arhat and the like, the Buddha first rejects all the possibilities of the tetralemma, and defends his refusal on the grounds that such theories are not conducive to liberation from saṃsāra . But when his questioner shows signs of thereby losing confidence in the value of the Buddha’s teachings about the path to the cessation of suffering, the Buddha responds with the example of a fire that goes out after exhausting its fuel. If one were asked where this fire has gone, the Buddha points out, one could consistently deny that it has gone to the north, to the south, or in any other direction. This is so for the simple reason that the questions ‘Has it gone to the north?’, ‘Has it gone to the south?’, etc., all share the false presupposition that the fire continues to exist. Likewise the questions about the arhat and the like all share the false presupposition that there is such a thing as a person who might either continue to exist after death, cease to exist at death, etc. (Anālayo 2018, 41) The difficulty with these questions is not that they try to extend philosophical rationality beyond its legitimate domain, as the handmaiden of soteriologically useful practice. It is rather that they rest on a false presupposition—something that is disclosed through the employment of philosophical rationality.
A different sort of challenge to the claim that the Buddha valued philosophical rationality for its own sake comes from the role played by authority in Buddhist soteriology. For instance, in the Buddhist tradition one sometimes encounters the claim that only enlightened persons such as the Buddha can know all the details of karmic causation. And to the extent that the moral rules are thought to be determined by the details of karmic causation, this might be taken to mean that our knowledge of the moral rules is dependent on the authority of the Buddha. Again, the subsequent development of Buddhist philosophy seems to have been constrained by the need to make theory compatible with certain key claims of the Buddha. For instance, one school developed an elaborate form of four-dimensionalism, not because of any deep dissatisfaction with presentism, but because they believed the non-existence of the past and the future to be incompatible with the Buddha’s alleged ability to cognize past and future events. And some modern scholars go so far as to wonder whether non-self functions as anything more than a sort of linguistic taboo against the use of words like ‘I’ and ‘self’ in the Buddhist tradition (Collins 1982: 183). The suggestion is that just as in some other religious traditions the views of the founder or the statements of scripture trump all other considerations, including any views arrived at through the free exercise of rational inquiry, so in Buddhism as well there can be at best only a highly constrained arena for the deployment of philosophical rationality.
Now it could be that while this is true of the tradition that developed out of the Buddha’s teachings, the Buddha himself held the unfettered use of rationality in quite high esteem. This would seem to conflict with what he is represented as saying in response to the report that he arrived at his conclusions through reasoning and analysis alone: that such a report is libelous, since he possesses a number of superhuman cognitive powers (M I.68). But at least some scholars take this passage to be not the Buddha’s own words but an expression of later devotionalist concerns (Gombrich 2009: 164). Indeed one does find a spirited discussion within the tradition concerning the question whether the Buddha is omniscient, a discussion that may well reflect competition between Buddhism and those Brahmanical schools that posit an omniscient creator. And at least for the most part the Buddhist tradition is careful not to attribute to the Buddha the sort of omniscience usually ascribed to an all-perfect being: the actual cognition, at any one time, of all truths. Instead a Buddha is said to be omniscient only in the much weaker sense of always having the ability to cognize any individual fact relevant to the soteriological project, viz. the details of their own past lives, the workings of the karmic causal laws, and whether a given individual’s defilements have been extirpated. Moreover, these abilities are said to be ones that a Buddha acquires through a specific course of training, and thus ones that others may reasonably aspire to as well. The attitude of the later tradition seems to be that while one could discover the relevant facts on one’s own, it would be more reasonable to take advantage of the fact that the Buddha has already done all the epistemic labor involved. When we arrive in a new town we could always find our final destination through trial and error, but it would make more sense to ask someone who already knows their way about.
The Buddhist philosophical tradition grew out of earlier efforts to systematize the Buddha’s teachings. Within a century or two of the death of the Buddha, exegetical differences led to debates concerning the Buddha’s true intention on some matter, such as that between the Personalists and others over the status of the person. While the parties to these debates use many of the standard tools and techniques of philosophy, they were still circumscribed by the assumption that the Buddha’s views on the matter at hand are authoritative. In time, however, the discussion widened to include interlocutors representing various Brahmanical systems. Since the latter did not take the Buddha’s word as authoritative, Buddhist thinkers were required to defend their positions in other ways. The resulting debate (which continued for about nine centuries) touched on most of the topics now considered standard in metaphysics, epistemology and philosophy of language, and was characterized by considerable sophistication in philosophical methodology. What the Buddha would have thought of these developments we cannot say with any certainty. What we can say is that many Buddhists have believed that the unfettered exercise of philosophical rationality is quite consistent with his teachings.
- Albahari, Miri, 2006, Analytical Buddhism , Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
- –––, 2014, ‘Insight Knowledge of No Self in Buddhism: An Epistemic Analysis,’ Philosophers’ Imprint , 14(1), available online .
- Anālayo, Bhikkhu, 2018, Rebirth in Early Buddhism and Current research , Cambridge, MA: Wisdom.
- Collins, Stephen, 1982, Selfless Persons , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Cousins, L. S., 2022, Meditations of the Pali Tradition: Illuminating Buddhist Doctrine, History, and Practice, edited by Sarah Shaw, Boulder, CO: Shambala.
- Gethin, Rupert, 1998, The Foun dations of Buddhism , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Gombrich, Richard F., 1996, How Buddhism Began , London: Athlone.
- –––, 2009, What the Buddha Thought , London: Equinox.
- Gowans, Christopher, 2003, Philosophy of the Buddha , London: Routledge.
- Harvey, Peter, 1995, The Selfless Mind , Richmond, UK: Curzon.
- Jayatilleke, K.N., 1963, Early Buddhist Theory of Knowledge , London: George Allen and Unwin.
- Rahula, Walpola, 1967, What the Buddha Taught , 2 nd ed., London: Unwin.
- Ronkin, Noa, 2005, Early Buddhist Metaphysics , London: Routledge.
- Ruegg, David Seyfort, 1977, ‘The Uses of the Four Positions of the Catuṣkoṭi and the Problem of the Description of Reality in Mahāyāna Buddhism,’ Journal of Indian Philosophy , 5: 1–71.
- Siderits, Mark, 2021, Buddhism As Philosophy , 2nd edition, Indianapolis: Hackett.
- Smith, Douglass and Justin Whitaker, 2016, ‘Reading the Buddha as a Philosopher,’ Philosophy East and West , 66: 515–538.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- The Pali Tipitaka , Pali texts
- Ten Philosophical Questions to Ask About Buddhism , a series of talks by Richard P. Hayes
- Access to Insight , Readings in Theravada Buddhism
- Buddhanet , Buddha Dharma Education Association
Abhidharma | Chinese Philosophy: Chan Buddhism | Chinese Philosophy: Huayan Buddhism | Chinese Philosophy: Tiantai Buddhism | ethics: in Indian Buddhism | Japanese Philosophy: Pure Land | Japanese Philosophy: Zen Buddhism | -->Korean Philosophy: Buddhism --> | Madhyamaka | Nāgārjuna | two truths in India, theory of | two truths in Tibet, theory of | -->yogaacaara -->
Copyright © 2023 by Mark Siderits < msideri @ ilstu . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
The life of the Buddha

Although born a prince, he realized that conditioned experiences could not provide lasting happiness or protection from suffering. After a long spiritual search he went into deep meditation, where he realized the nature of mind. He achieved the state of unconditional and lasting happiness: the state of enlightenment, of buddhahood. This state of mind is free from disturbing emotions and expresses itself through fearlessness, joy and active compassion. For the rest of his life, the Buddha taught anyone who asked how they could reach the same state.
Buddha’s early life

India at the time of the Buddha was very spiritually open. Every major philosophical view was present in society, and people expected spirituality to influence their daily lives in positive ways.
At this time of great potential, Siddhartha Gautama, the future Buddha, was born into a royal family in what is now Nepal, close to the border with India. Growing up, the Buddha was exceptionally intelligent and compassionate. Tall, strong, and handsome, the Buddha belonged to the Warrior caste. It was predicted that he would become either a great king or spiritual leader. Since his parents wanted a powerful ruler for their kingdom, they tried to prevent Siddharta from seeing the unsatisfactory nature of the world. They surrounded him with every kind of pleasure. He was given five hundred attractive ladies and every opportunity for sports and excitement. He completely mastered the important combat training, even winning his wife, Yasodhara, in an archery contest.
Suddenly, at age 29, he was confronted with impermanence and suffering. On a rare outing from his luxurious palace, he saw someone desperately sick. The next day, he saw a decrepit old man, and finally a dead person. He was very upset to realize that old age, sickness and death would come to everyone he loved. Siddharta had no refuge to offer them.
The next morning the prince walked past a meditator who sat in deep absorption. When their eyes met and their minds linked, Siddhartha stopped, mesmerized. In a flash, he realized that the perfection he had been seeking outside must be within mind itself. Meeting that man gave the future Buddha a first and enticing taste of mind, a true and lasting refuge, which he knew he had to experience himself for the good of all.
Buddha’s enlightenment

The Buddha decided he had to leave his royal responsibilities and his family in order to realize full enlightenment. He left the palace secretly, and set off alone into the forest. Over the next six years, he met many talented meditation teachers and mastered their techniques. Always he found that they showed him mind’s potential but not mind itself. Finally, at a place called Bodhgaya, the future Buddha decided to remain in meditation until he knew mind’s true nature and could benefit all beings. After spending six days and nights cutting through mind’s most subtle obstacles, he reached enlightenment on the full moon morning of May, a week before he turned thirty-five.
At the moment of full realization, all veils of mixed feelings and stiff ideas dissolved and Buddha experienced the all-encompassing here and now. All separation in time and space disappeared. Past, present, and future, near and far, melted into one radiant state of intuitive bliss. He became timeless, all-pervading awareness. Through every cell in his body he knew and was everything. He became Buddha , the Awakened One.
After his enlightenment, Buddha traveled on foot throughout northern India. He taught constantly for forty-five years. People of all castes and professions, from kings to courtesans, were drawn to him. He answered their questions, always pointing towards that which is ultimately real.
Throughout his life, Buddha encouraged his students to question his teachings and confirm them through their own experience. This non-dogmatic attitude still characterizes Buddhism today.
Visiting Sleeping Beauties: Reawakening Fashion?
You must join the virtual exhibition queue when you arrive. If capacity has been reached for the day, the queue will close early.
Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History Essays
Buddhism and buddhist art.
Portrait of Shun'oku Myōha
Unidentified artist Japanese
Fasting Buddha Shakyamuni
Reliquary in the Shape of a Stupa
Standing Buddha Offering Protection
Buddha Maitreya (Mile)
Buddha Maitreya (Mile) Altarpiece
Buddha Offering Protection
Head of Buddha
Buddha, probably Amitabha
Pensive bodhisattva
Avalokiteshvara, the Bodhisattva of Infinite Compassion
Buddha Shakyamuni or Akshobhya, the Buddha of the East
Enthroned Buddha Attended by the Bodhisattvas Avalokiteshvara and Vajrapani
The Bodhisattva Padmapani Lokeshvara
Buddha Vairocana (Dari)
Buddha Amoghasiddhi with Eight Bodhisattvas
Death of the Historical Buddha (Nehan-zu)
Cup Stand with the Eight Buddhist Treasures
Seated Buddha
Vidya Dehejia Department of Art History and Archaeology, Columbia University
February 2007
The fifth and fourth centuries B.C. were a time of worldwide intellectual ferment. It was an age of great thinkers, such as Socrates and Plato, Confucius and Laozi. In India , it was the age of the Buddha, after whose death a religion developed that eventually spread far beyond its homeland.
Siddhartha, the prince who was to become the Buddha, was born into the royal family of Kapilavastu, a small kingdom in the Himalayan foothills. His was a divine conception and miraculous birth, at which sages predicted that he would become a universal conqueror, either of the physical world or of men’s minds. It was the latter conquest that came to pass. Giving up the pleasures of the palace to seek the true purpose of life, Siddhartha first tried the path of severe asceticism, only to abandon it after six years as a futile exercise. He then sat down in yogic meditation beneath a bodhi tree until he achieved enlightenment. He was known henceforth as the Buddha , or “Enlightened One.”
His is the Middle Path, rejecting both luxury and asceticism. Buddhism proposes a life of good thoughts, good intentions, and straight living, all with the ultimate aim of achieving nirvana, release from earthly existence. For most beings, nirvana lies in the distant future, because Buddhism, like other faiths of India, believes in a cycle of rebirth. Humans are born many times on earth, each time with the opportunity to perfect themselves further. And it is their own karma—the sum total of deeds, good and bad—that determines the circumstances of a future birth. The Buddha spent the remaining forty years of his life preaching his faith and making vast numbers of converts. When he died, his body was cremated, as was customary in India.
The cremated relics of the Buddha were divided into several portions and placed in relic caskets that were interred within large hemispherical mounds known as stupas. Such stupas constitute the central monument of Buddhist monastic complexes. They attract pilgrims from far and wide who come to experience the unseen presence of the Buddha. Stupas are enclosed by a railing that provides a path for ritual circumambulation. The sacred area is entered through gateways at the four cardinal points.
In the first century B.C., India’s artists, who had worked in the perishable media of brick, wood, thatch, and bamboo, adopted stone on a very wide scale. Stone railings and gateways, covered with relief sculptures, were added to stupas. Favorite themes were events from the historic life of the Buddha, as well as from his previous lives, which were believed to number 550. The latter tales are called jatakas and often include popular legends adapted to Buddhist teachings.
In the earliest Buddhist art of India, the Buddha was not represented in human form. His presence was indicated instead by a sign, such as a pair of footprints, an empty seat, or an empty space beneath a parasol.
In the first century A.D., the human image of one Buddha came to dominate the artistic scene, and one of the first sites at which this occurred was along India’s northwestern frontier. In the area known as Gandhara , artistic elements from the Hellenistic world combined with the symbolism needed to express Indian Buddhism to create a unique style. Youthful Buddhas with hair arranged in wavy curls resemble Roman statues of Apollo; the monastic robe covering both shoulders and arranged in heavy classical folds is reminiscent of a Roman toga. There are also many representations of Siddhartha as a princely bejeweled figure prior to his renunciation of palace life. Buddhism evolved the concept of a Buddha of the Future, Maitreya, depicted in art both as a Buddha clad in a monastic robe and as a princely bodhisattva before enlightenment. Gandharan artists made use of both stone and stucco to produce such images, which were placed in nichelike shrines around the stupa of a monastery. Contemporaneously, the Kushan-period artists in Mathura, India, produced a different image of the Buddha. His body was expanded by sacred breath ( prana ), and his clinging monastic robe was draped to leave the right shoulder bare.
A third influential Buddha type evolved in Andhra Pradesh, in southern India, where images of substantial proportions, with serious, unsmiling faces, were clad in robes that created a heavy swag at the hem and revealed the left shoulder. These southern sites provided artistic inspiration for the Buddhist land of Sri Lanka, off the southern tip of India, and Sri Lankan monks regularly visited the area. A number of statues in this style have been found as well throughout Southeast Asia.
The succeeding Gupta period, from the fourth to the sixth century A.D., in northern India, sometimes referred to as a Golden Age, witnessed the creation of an “ideal image” of the Buddha. This was achieved by combining selected traits from the Gandharan region with the sensuous form created by Mathura artists. Gupta Buddhas have their hair arranged in tiny individual curls, and the robes have a network of strings to suggest drapery folds (as at Mathura) or are transparent sheaths (as at Sarnath). With their downward glance and spiritual aura, Gupta Buddhas became the model for future generations of artists, whether in post-Gupta and Pala India or in Nepal , Thailand , and Indonesia. Gupta metal images of the Buddha were also taken by pilgrims along the Silk Road to China .
Over the following centuries there emerged a new form of Buddhism that involved an expanding pantheon and more elaborate rituals. This later Buddhism introduced the concept of heavenly bodhisattvas as well as goddesses, of whom the most popular was Tara. In Nepal and Tibet , where exquisite metal images and paintings were produced, new divinities were created and portrayed in both sculpture and painted scrolls. Ferocious deities were introduced in the role of protectors of Buddhism and its believers. Images of a more esoteric nature , depicting god and goddess in embrace, were produced to demonstrate the metaphysical concept that salvation resulted from the union of wisdom (female) and compassion (male). Buddhism had traveled a long way from its simple beginnings.
Dehejia, Vidya. “Buddhism and Buddhist Art.” In Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History . New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2000–. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/budd/hd_budd.htm (February 2007)
Further Reading
Dehejia, Vidya. Indian Art . London: Phaidon, 1997.
Mitter, Partha. Indian Art . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001.
Additional Essays by Vidya Dehejia
- Dehejia, Vidya. “ Hinduism and Hindu Art .” (February 2007)
- Dehejia, Vidya. “ Recognizing the Gods .” (February 2007)
- Dehejia, Vidya. “ South Asian Art and Culture .” (February 2007)
Related Essays
- Chinese Buddhist Sculpture
- Cosmic Buddhas in the Himalayas
- Life of the Buddha
- Tibetan Buddhist Art
- Zen Buddhism
- Chinese Hardstone Carvings
- Daoism and Daoist Art
- East Asian Cultural Exchange in Tiger and Dragon Paintings
- Hinduism and Hindu Art
- Internationalism in the Tang Dynasty (618–907)
- Jain Sculpture
- Japanese Illustrated Handscrolls
- Kings of Brightness in Japanese Esoteric Buddhist Art
- Korean Buddhist Sculpture (5th–9th Century)
- Kushan Empire (ca. Second Century B.C.–Third Century A.D.)
- Mauryan Empire (ca. 323–185 B.C.)
- The Mon-Dvaravati Tradition of Early North-Central Thailand
- Music and Art of China
- Nepalese Painting
- Nepalese Sculpture
- Pre-Angkor Traditions: The Mekong Delta and Peninsular Thailand
- Recognizing the Gods
- Shunga Dynasty (ca. Second–First Century B.C.)
- Tang Dynasty (618–907)
- Tibetan Arms and Armor
- Wang Hui (1632–1717)
- China, 1000–1400 A.D.
- China, 1–500 A.D.
- China, 500–1000 A.D.
- Himalayan Region, 1000–1400 A.D.
- Himalayan Region, 500–1000 A.D.
- Japan, 1000–1400 A.D.
- Korea, 500–1000 A.D.
- South Asia, 1–500 A.D.
- South Asia: North, 500–1000 A.D.
- South Asia: South, 500–1000 A.D.
- Southeast Asia, 1400–1600 A.D.
- Southeast Asia, 500–1000 A.D.
- 10th Century A.D.
- 11th Century A.D.
- 12th Century A.D.
- 13th Century A.D.
- 14th Century A.D.
- 15th Century A.D.
- 16th Century A.D.
- 17th Century A.D.
- 18th Century A.D.
- 19th Century A.D.
- 1st Century A.D.
- 1st Century B.C.
- 20th Century A.D.
- 21st Century A.D.
- 2nd Century A.D.
- 2nd Century B.C.
- 3rd Century A.D.
- 3rd Century B.C.
- 4th Century A.D.
- 4th Century B.C.
- 5th Century A.D.
- 5th Century B.C.
- 6th Century A.D.
- 7th Century A.D.
- 8th Century A.D.
- 9th Century A.D.
- Amoghasiddhi
- Ancient Greek Art
- Ancient Roman Art
- Andhra Pradesh
- Avalokiteshvara
- Cartography
- Deity / Religious Figure
- Gilt Bronze
- Gilt Copper
- Gupta Period
- Hellenistic Period
- Himalayan Region
- Kushan Period
- Monasticism
- Relic / Reliquary
- Relief Sculpture
- Religious Art
- Sancai Glaze
- Sculpture in the Round
- Southeast Asia
- Uttar Pradesh
Online Features
- 82nd & Fifth: “Divinity” by Denise Leidy
- 82nd & Fifth: “Pensive” by Soyoung Lee
- The Artist Project: “Thomas Struth on Chinese Buddhist sculpture”
- Connections: “Relics” by John Guy
- Growth & Development
- Play & Activities
- Life Skills
- Play & Learning
- Learning & Education
- Rhymes & Songs
- Preschool Locator

Essay On Gautam Buddha – 10 Lines, Short And Long Essay For Children
Key Points To Note: Essay On Gautam Buddha For Lower Primary Classes
10 lines on gautam buddha in english for kids, short essay on gautam buddha for kids, long essay on gautam buddha for children, interesting facts about gautam buddha for kids, what will your child learn from this essay.
Everybody knows Gautam Buddha as the embodiment of peace, serenity, wisdom and enlightenment. The Buddha figurines and statues are popular as a reminder in homes and offices to maintain calmness and focus. From a moral and philosophical perspective, children have much to gain by writing an essay on Gautam Buddha. Their research on the topic will familiarise them with one of the most loved and respected spiritual leaders. This article will show you how to write an essay for classes 1, 2 and 3 on Gautam Buddha.
Here are some important points to remember when writing an essay on Gautam Buddha:
- Essays on Gautam Buddha should have basic facts about him, such as his place of birth, the names of his family, and his early life.
- Long and short-form essays should have introductory and concluding lines.
- The narrative of the events of his life should be chronological to keep the readers engaged.
- Avoid including exaggerated content in the essay, and stick to simple facts.
One-line essays are a great place to start essay writing for children. Here is an example of an essay for classes 1 and 2 on Gautam Buddha:
- Gautam Buddha is the founder of Buddhism.
- He was born to a royal family in 623 BC in Lumbini, Nepal.
- His father was King Shuddhodan, and his mother was Queen Maya.
- His mother died soon after he was born, so he was raised by a stepmother Mahaprajapati.
- In his childhood, he was also called Siddharta.
- Gautam was given all the material pleasures to stop him from leaving the palace.
- He fell into deep contemplation at first sight of illness and death, and decided to find a way to end the suffering.
- Gautam left his wife, kingdom and son Rahula to find the solution to suffering.
- After six long years of penance and meditation, he finally attained enlightenment under the bodhi tree.
- Gautama taught the noble eight-fold path to free oneself from suffering until he died.
A short paragraph on Gautam Buddha is a good exercise for the narration of a story in brief. Children can learn from this 150-word essay on Gautama Buddha:
Gautam Buddha is one of the most well-known spiritual leaders in history who started the religion of Buddhism. He was born in Lumbini, near the Indo-Nepal border, in the 6th century BC. He belonged to a wealthy family. His mother died shortly after his birth, and he was raised as a prince with every imaginable comfort and luxury.
Not knowing suffering or death, Gautama was touring his kingdom one day when he came across sick and dead people. Deeply disturbed by the existence of suffering in the world, he decided to find a way out of it. He left his wife and child to live an ascetic life and find answers to existential problems.
Wandering in search of truth, he reached Gaya, where he sat in penance under a peepal tree. Having meditated for years under the tree, he finally attained enlightenment one morning under the very tree. The enlightened Gautam Buddha then set out to teach what he had learned to the rest of the world. His teachings eventually became the basis of the religion of Buddhism.

A long composition should have a good narrative to keep the reader engaged. Here is an example of an essay for class 3 on Gautam Buddha:
Born in the 6th century BC, Siddharta Gautama was a prince of a small kingdom in the Terai region of Nepal. His mother dreamed that the boy would grow up to become a great king or saint but died soon after his birth. His father, king Suddhodhana, was worried that he might leave the kingdom to become a saint and changed the environment of the palace to be one of endless comforts and pleasures. As Gautam grew into a young man, he was kept away from anything that would provoke spiritual thoughts. He was married to Yashodhara, a beautiful princess with whom he had a son named Rahula.
While on a tour of the kingdom one day, Gautam saw an ailing person and a corpse. He was disturbed by it as he had never known suffering in his lavish life. He soon worried that his life of pleasure also had a timeline and nothing was permanent. Deeply troubled by the thought, he looked for answers but found none that satisfied him. Gautam then decided to find the answers for himself and left behind his family and kingdom.
Gautam searched for answers and studied under many gurus but never felt satisfied with the answers. He tried meditation techniques and every trick in the books. Finally, when nothing came to fruition, he starved himself thinking his physical being was the problem. A kind woman offered him rice to eat, and it suddenly rejuvenated him that punishing himself was not the way.
Recovering from starvation, he sat under the bodhi tree and vowed not to leave until he experienced an awakening. His effort paid off, and after six long years of searching, he finally attained enlightenment under the same tree. Gautam Buddha went ahead to teach what he had learned and become a great leader. His teachings eventually became central to Buddhism, one of the most respected religions in the world.
Here are some interesting facts about Gautam Buddha:
- Gautama Buddha left home in search of spirituality.
- He gave up his palace life after seeing four things – a corpse, an old man, a sick man, and a wandering ascetic.
- To stop him from becoming a sage, he was married at 16.
- He left his palace at 29 and attained enlightenment at 35.
- He died at the age of 80.
The Gautam Buddha essay is a source of good information on the topic for children. By studying the long and short-form articles written above, they can learn how to write an essay on Buddha.
1. What Did Gautam Buddha Do To Attain Knowledge And Peace?
Gautam Buddha gave up his family, kingdom and lavish life to live and wander as an ascetic for years. He learnt various important things through his journey, including meditation, which finally blossomed as his enlightenment. With his awakening, he was liberated from the cycles of birth and death and instantly at peace.
2. What Does Buddhism Teach Us?
Buddhism teaches us the most basic truths about existence:
- The fact of suffering in reality
- The reason behind suffering
- The end of suffering
- The path one should take to end suffering
Gautam Buddha was an enlightened teacher who led many to the path of righteous life and out of suffering. The above essays are a snapshot of his life and some events, teaching a great deal about him.
Mother Teresa Essay for Class 1, 2 & 3 Children Essay On Swami Vivekananda for Class 1, 2 and 3 Kids APJ Abdul Kalam Essay for Classes 1, 2 and 3 Children
- Essays for Class 1
- Essays for Class 2
- Essays for Class 3
5 Recommended Books To Add To Your Child’s Reading List and Why
5 absolute must-watch movies and shows for kids, 15 indoor toys that have multiple uses and benefits, leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment

Most Popular
The best toys for newborns according to developmental paediatricians, the best toys for three-month-old baby brain development, recent comments.

FirstCry Intelli Education is an Early Learning brand, with products and services designed by educators with decades of experience, to equip children with skills that will help them succeed in the world of tomorrow.

The FirstCry Intellikit `Learn With Stories` kits for ages 2-6 brings home classic children`s stories, as well as fun activities, specially created by our Early Learning Educators.

For children 6 years and up, explore a world of STEAM learning, while engaging in project-based play to keep growing minds busy!

Build a love for reading through engaging book sets and get the latest in brain-boosting toys, recommended by the educators at FirstCry Intellitots.

Our Comprehensive 2-year Baby Brain Development Program brings to you doctor-approved toys for your baby`s developing brain.

Our Preschool Chain offers the best in education across India, for children ages 2 and up.
©2024 All rights reserved
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use

Welcome to the world of Intelli!
We have some FREE Activity E-books waiting for you. Fill in your details below so we can send you tailor- made activities for you and your little one.
Parent/Guardian's Name
Child's DOB
What would you like to receive other than your Free E-book? I would like information, discounts and offers on toys, books and products I want to find a FirstCry Intellitots Preschool near me I want access to resources for my child's development and/or education

Welcome to the world of intelli!
FREE guides and worksheets coming your way on whatsapp. Subscribe Below !!
THANK YOU!!!
Here are your free guides and worksheets.

Friday essay: how the West discovered the Buddha
Emeritus Professor in the History of Religious Thought, The University of Queensland
Disclosure statement
Philip C. Almond does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Queensland provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Buddhism is the third largest (and fastest growing) religion in Australia with approximately half a million adherents .
The celebration of the Buddha’s birthday here (on or around May 15) has become a major cultural event and the Buddhist doctrine of “mindfulness” is now a part of mainstream culture . But how and when did the West discover the Buddha?
The facts about the Buddha’s life are opaque but we can assume he was born no earlier than 500 BCE and died no later than 400 BCE. He was said to be the son of an Indian king, so distressed by the sight of suffering that he spent years searching for the answer to it, finally attaining enlightenment while sitting under a bodhi (sacred fig) tree.
The Buddha’s family name was Gotama (in the Pali language) or Gautama (in Sanskrit). Although it does not appear in the earliest traditions, his personal name was later said to be Siddhartha, which means “one who has achieved his purpose”. (This name was retrofitted by later believers.)
According to Buddhist tradition, the Buddha spent 45 years teaching the path to enlightenment, gathering followers, and creating the Buddhist monastic community. According to the legend, upon his death at the age of 80, he entered Nirvana.
In India during the 3rd century BCE, the emperor Ashoka first promoted Buddhism. From this time on, it spread south, flourishing in Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia, then moving through Central Asia including Tibet, and on to China, Korea, and Japan. Ironically, the appeal of Buddhism declined in India in succeeding centuries. It was virtually extinct there by the 13th century.

In that same century, the Venetian merchant Marco Polo gave the West its first account of Buddha’s life. Between 1292 and 1295, journeying home from China, Marco Polo arrived in Sri Lanka. There he heard the story of the life of Sergamoni Borcan whom we now know as the Buddha.

Marco wrote about Sergamoni Borcan, a name he had heard at the court of Kublai Khan, in his book The Description of the World . This was the Mongolian name for the Buddha: Sergamoni for Shakyamuni – the sage of the Shakya clan, and Borcan for Buddha – the “divine” one. (He was also known as Bhagavan – the Blessed One, or Lord.)
According to Marco, Sergamoni Borcan was the son of a great king who wished to renounce the world. The king moved Sergamoni into a palace, tempting him with the sensual delights of 30,000 maidens.
But Sergamoni was unmoved in his resolve. When his father allowed him to leave the palace for the first time, he encountered a dead man, and an infirm old man. He returned to the palace frightened and astonished , “saying to himself that he would not remain in this bad world but would go seeking the one who had made it and did not die.”
Sergamoni then left the palace permanently and lived the abstinent life of a celibate recluse. “Certainly,” Marco declared , “had he been Christian, he would have been a great saint with our Lord Jesus Christ”.
Read more: How the Buddha became a Christian saint
Jesuits and authors
Little more was known about the Buddha for the next 300 years in the West. Nevertheless, from the mid-16th century, information accumulated, primarily as a result of the Jesuit missions to Japan and China.

By 1700, it was increasingly assumed by those familiar with the Jesuit missions that the Buddha was the common link in an array of religious practitioners they were encountering.
For example, Louis le Comte (1655-1728), writing his memoir of his travels through China on a mission inspired by the Sun King Louis XIV declared, “all the Indies have been poisoned with his pernicious Doctrine. Those of Siam call them Talapoins, the Tartars call them Lamas or Lama sem, the Japoners Bonzes, and the Chinese Hocham.”

The writings of the English author Daniel Defoe (c.1660-1731) show what the educated English reader might have known of the Buddha in the early 18th century.
In his Dictionary of all Religions (1704), Defoe tells us of an idol of Fe (the Buddha) on an island near the Red Sea, said to represent an atheistic philosopher who lived 500 years before Confucius, that is, around 1,000 BCE.
This idol was carried to China
with Instructions concerning the Worship paid to it, and so introduced a Superstition, that in several things abolish’d the Maxims of Confucius, who always condemned Atheism and idolatry.
A quite different Buddha was to be encountered by the British in the later 1700s as they achieved economic, military, and political dominance in India. Initially, the British were reliant on their Hindu informants. They told them the Buddha was an incarnation of their god Vishnu who had come to lead the people astray with false teaching.

More confusion reigned. It was often argued in the West that there were two Buddhas – one whom Hindus believed to be the ninth incarnation of Vishnu (appearing around 1000 BCE), the other (Gautama) appearing around 1000 years later.
And yet more confusion. For there was a tradition in the West since the mid-17th century that the Buddha came from Africa.
Well into the 19th century, it was thought that representations of the Buddha, particularly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, depicted with woolly hair and thick “Ethiopian lips” (as one writer put it ) were evidence of his African origins.
Such observers were mistaking traditional representations of the Buddha with his hair tightly coiled into tiny cones as a sign of his African origins.
First use of the term ‘Buddhism’
Two major turning points eventually sorted out these confusions. The first was the invention of the term “Buddhism”.
Its first use in English was in 1800 in a translation of a work entitled Lectures on History by Count Constantine de Volney . A politician and orientalist, de Volney coined the term “Buddhism” to identify the pan-Asian religion that he believed was based on a mythical figure called “Buddha”.
Only then did Buddhism begin to emerge from the array of “heathen idolatries” with which it had been identified, becoming identified as a religion, alongside Christianity, Judaism, and Islam.
The second turning point was the arrival in the West of Buddhist texts. The decade from 1824 was decisive. For centuries, not a single original document of the Buddhist religion had been accessible to the scholars of Europe.
But in the space of ten years, four complete Buddhist literatures were discovered – in Sanskrit, Tibetan, Mongolian, and Pāli. Collections from Japan and China were to follow.
With the Buddhist texts in front of them, Western scholars were able to determine Buddhism was a tradition that had arisen in India around 400-500 years BCE.
And among these texts was the Lalitavistara (written around the 4th century CE), which contained a biography of the Buddha. For the first time Westerners came to read an account of his life.
The Lalitavistara and other biographies depicted a highly magical and enchanted world – of the Buddha’s heavenly life before his birth, of his conception via an elephant, of his mother’s transparent womb, of his miraculous powers at his birth, of the many miracles he performed, of gods, demons, and water spirits.
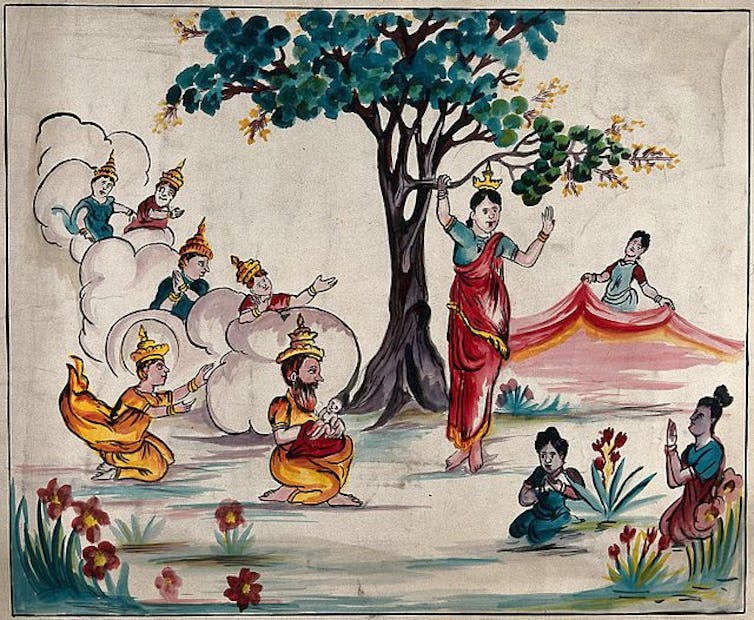

But within these enchanted texts, there remained the story of the life of the Buddha with which we are familiar. Of the Indian King Shuddhodana who, fearing Gautama would reject the world, keeps his son sheltered from any sights of suffering. When Gautama finally leaves the palace he encounters an old man, a diseased man, and a dead man. He then decides to search for the answer to suffering.
For the Buddha, the cause of suffering lies in attachment to the things of the world. The path to liberation from it thus lies in the rejection of attachment.
The Buddha’s way to the cessation of attachment was eventually summarised in the Holy Eightfold Path – right views, right resolve, right speech, right conduct, right livelihood, right effort, right mindfulness, right meditation. The outcome of this path was the attainment of Nirvana when the self at the time of death escaped from rebirth and was extinguished like the flame of a candle.
This selfless Buddha, who was said to have died in the groves of trees near the Indian town of Kusinagara , was the one the West soon came to admire. As the Unitarian minister Richard Armstrong, put it in 1870,
his personality has endured for centuries, and is as fresh and beautiful as now when displayed to European eyes, as when Siddharta [sic] himself breathed his dying breath in the shades of (the forest of) Kusinagara.
History versus legend
But is the Buddha of the legend also the Buddha of history? That the tradition we call Buddhism was founded by an Indian sage named Gautama around the 5th century BCE is very likely.
That he preached a middle way to liberation between worldly indulgence and extreme asceticism is highly probable. That he cultivated practices of mindfulness and meditation, which led to peace and serenity, is almost certain.
That said, the earliest Buddhist traditions showed little interest in the details of the life of the Buddha. It was, after all, his teachings – the Dharma as Buddhists call it – rather than his person that mattered.
But we can discern a growing interest in the life of the Buddha from the first century BCE until the second or third centuries of the common era as the Buddha transitions within Buddhism from a teacher to a saviour, from human to divine.
It was from the first to the fifth centuries CE that there developed a number of Buddhist texts giving full accounts of the life of the Buddha , from his birth (and before) to his renunciation of the world, his enlightenment, his teachings, and finally to his death.
Thus, there is a long period of at least 500-900 years between the death of the Buddha and these biographies of him. Can we rely upon these very late lives of the Buddha for accurate information about the events of his life? Probably not.
Nevertheless, the legend of his life and teachings still provide an answer to the meaning of human life for some 500 million followers in the modern world.
- Friday essay
- Western civilisation

Compliance Lead

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)
An Overview of Buddhism’s Core Beliefs
This essay about the foundational beliefs and teachings of Buddhism, tracing its origins to ancient India and the profound impact of Siddhartha Gautama’s enlightenment. It explores the Four Noble Truths, the Noble Eightfold Path, karma, and the Three Marks of Existence as central to understanding Buddhist philosophy. Despite variations in interpretation, Buddhism emphasizes individual practice, compassion, and the pursuit of liberation from suffering.
How it works
The ancient inception of Buddhism, an esteemed and impactful faith, can be traced back to ancient India during the 6th century BCE. Initiated by Siddhartha Gautama, revered as the Buddha or the “Enlightened One,” its teachings propagated across Asia, profoundly shaping diverse cultures, philosophies, and spiritual customs throughout epochs. Grasping the fundamental tenets of Buddhism offers insight into how this profound legacy interprets existence, suffering, and the quest for enlightenment.
At the essence of Buddhism are the Four Noble Truths, delineating the quintessential comprehension of being.
The primary truth, Dukkha, acknowledges the inherent presence of suffering and discontent in life. Whether stemming from ailment, aging, mortality, or unfulfilled yearnings, humanity inevitably encounters tribulation. The second truth, Samudaya, discerns the origin of suffering in Tanha, or craving. According to the Buddha, it is the attachment to desires and worldly possessions that perpetuates the cycle of suffering.
The third truth, Nirodha, instills hope by affirming the prospect of ending suffering. Through transcending attachment and craving, one can attain Nirvana, a state of emancipation from suffering. Lastly, the fourth truth, Magga, elucidates the route to achieve this liberation. This journey is known as the Noble Eightfold Path, a manual for moral and intellectual cultivation that facilitates individuals in reaching Nirvana.
The Noble Eightfold Path encompasses eight practices categorized into three domains: wisdom, ethical conduct, and mental refinement. Under wisdom, Right View fosters a profound comprehension of the Four Noble Truths, while Right Intention underscores the significance of dedication and affirmative resolve. Ethical conduct encompasses Right Speech (eschewing falsehoods and injurious language), Right Action (upholding moral conduct), and Right Livelihood (sustaining a livelihood without causing harm). Lastly, mental refinement comprises Right Effort (cultivating positive mental states), Right Mindfulness (maintaining awareness and presence in each moment), and Right Concentration (developing the ability to focus through meditation).
Another cardinal belief in Buddhism is the doctrine of karma. In Buddhism, karma denotes the moral law of causality, wherein one’s actions exert influence on future outcomes. Positive intentions and actions yield favorable consequences, whereas negative actions yield unfavorable repercussions. Karma not only impacts the present life but also influences subsequent rebirths in the cycle known as samsara. The ultimate aspiration is to transcend this cycle by attaining enlightenment.
Buddhists also adhere to the Three Marks of Existence: impermanence (anicca), suffering (dukkha), and non-self (anatta). Impermanence recognizes the transient nature of all phenomena, including human lives. Embracing this notion can facilitate acceptance of change and reduction of attachment. Suffering reaffirms the First Noble Truth, while non-self challenges the notion of a fixed, unchanging identity, emphasizing that the self is instead an amalgamation of perpetually changing elements.
In Buddhism, there exists no omnipotent creator deity. Instead, the emphasis lies on individual practice and personal metamorphosis. Although various branches of Buddhism espouse diverse interpretations and practices, most share a commitment to the Buddha’s fundamental teachings of compassion, wisdom, and the pursuit of liberation from suffering.
In summation, Buddhism’s foundational beliefs are rooted in comprehending the nature of suffering and the path to liberation through the Four Noble Truths and the Noble Eightfold Path. The principles of karma and the Three Marks of Existence further guide adherents in their spiritual odyssey. While the teachings of the Buddha are ancient, their insights endure as a framework for leading a life of mindfulness, compassion, and purpose.
Cite this page
An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs. (2024, May 12). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/
"An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs." PapersOwl.com , 12 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/ [Accessed: 17 May. 2024]
"An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs." PapersOwl.com, May 12, 2024. Accessed May 17, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/
"An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs," PapersOwl.com , 12-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/. [Accessed: 17-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). An Overview of Buddhism's Core Beliefs . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/an-overview-of-buddhisms-core-beliefs/ [Accessed: 17-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Academic Test Guide
Essay on Gautam Buddha in English For Students and Children
We are Sharing Essay on Gautam Buddha in English for students and children- In this article, we have tried our best to give the best essay about Gautama Buddha for Classes 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12 and Graduation in 200, 300, 400, 500, 800 1000 words, a Short essay on Gautam Buddha.

Essay on Gautam Buddha in 150 to 250 words
Gautama Buddha who started Buddhism is known as the Rational Prophet and Philosopher. It is so because he believes, not in blind faith but in reason, inquiry, test, analysis, research, and insight.
He is said to have been born in 563 BC at Lumbini in the Kapilvastu state. He was the son of Shudhodhana, the king of Kapilvastu and his childhood name was Siddhartha.
He was very compassionate by nature from his very childhood and loved solitude. He was not fond of a luxurious life as was available in the palace.
In order to draw his attention to the pursuit of worldly pleasures, the king married him to a beautiful Princess Yashodhara. She bore him a charming son, Rahul. But Siddhartha still could not give up the unworldly outlook.
He wanted to move out of the palace and reach out to the people to know their real position, but he was forbidden to do so by the king.
Also Read- 10 Lines on Gautam Buddha
One day he disguised himself as a merchant and went out of the palace with his charioteer who was disguised as a clerk.
He was greatly pained to see an old man, a sick man, and a dead man. He is known to have uttered: “Either, there is no God or if He is there, He is too cruel or indifferent to allow so much misery in the world.”
One night, he kissed his sleeping wife and child for the last time and left the palace never to return again. He went out in search of truth and in his endeavor to find out some means for mitigating the misery of the world.
He attained enlightenment as he was sitting under the Bodhi Tree at Gaya. Thereafter, he traveled far and wide to spread his message and to make known to the people the truth that he had discovered.
The people gave him the title “Gautam Buddha.” He preached the Middle course, Eightfold Path for Truth, non-violence, and service to human beings and animals.
His message which assumed the shape of Buddhism spread far and wide in India and later to several countries including Sri Lanka, China, Japan, Thailand, Korea, etc.
Buddhism spread in full fury after Emperor Ashoka embraced it and sent his missionaries, including his son, Mahendra, and daughter, Sanghmitra to several countries to spread it.
The Buddha attained salvation in 483 BC at Kushinagar in Deoria (Uttar Pradesh).
Gautam Buddha Essay in 500 to 600 words
Gautam Buddha is among the greatest religious teachers of the world. He gave the message of truth, peace, humanity, and equality. He founded Buddhism. It is followed in China, Japan, Burma, and the countries of Southeast Asia.
Gautam Buddha was born in 563 BC in the Lumbini forests in Nepalese Terai. His father, Suddhodana was the ruler of Kapilavastu and the chief of the Sakya clan. His mother’s name was Mahamaya. Gautam Buddha’s childhood name was Siddhartha.
Buddha was a child with a contemplative bent of mind. His father always worried that his son might leave home to become a wandering ascetic’ as the Brahmans had predicted. So, he took every care to influence him in favour of worldly life. Gautam Buddha was married at the age of 16, to a beautiful princess Yashodhara. He lived in luxury and comfort. A son, Rahul, was born to him.
A turning point in prince Siddhartha’s life came when he was 29 years old. Driving with his charioteer, one day he saw an old man, as bent as a roof gable. Another day he saw a sick man, suffering and very ill. On a third occasion, he saw a dead body. All these produced a profound effect on his mind. Miseries of old age, the dying Sickman, and mysteries of death puzzled and haunted Buddha’s thoughts. He felt that life was an imitation cover only.
The actual was missing and he must look for the real. He departed from the palace quietly leaving his wife, infant son, and all the royal comforts in search of peace and truth.
He visited many places, met many scholars and saints but was not satisfied. After six years of wandering and meditation, at the age of 35, Siddhartha got enlightenment at Bodh Gaya. Siddhartha got transformed into ‘Buddha’ or ‘enlightened’. The pipal tree under which he got enlightenment came to be known as the ‘Bodhi Tree’.
Buddha delivered his first sermon at Sarnath called ‘Turning of the Wheel of Law’. Buddha taught that the root cause of suffering is desire. The essence of Buddha’s early preaching are the Four Noble Truths :
1. Life is fundamentally disappointment and suffering; 2. Suffering is a result of one’s desires for pleasure, power, and continued existence; 3. In order to stop disappointment and suffering, one must stop desiring; 4. The way to stop desiring and thus suffering is by following the Noble Eightfold Path (ashtangika marg). The Eightfold Path is right views, right intention, right speech, right action, right livelihood, right effort, right awareness, and right concentration.
Buddha also attacked some religious and social practices of his times. He refused to recognize the religious significance of the caste system. But he recognized the connection between economic welfare and moral development. According to Buddha, trying to suppress crime through punishment is futile4. Poverty is the cause of immorality and crime. Therefore, he laid stress on the improvement of the economic condition of the people.
Buddha was a man of great wisdom and great compassion. He spent his life spreading his teachings, making converts to the religious truths and beliefs he propounded, and training large numbers of learned, well-disciplined followers to continue the work after his death.
Buddha attained nirvana in Kushinagar (Uttar Pradesh) in 483 BC. Before his soul rested in peace, he uttered his famous last words: ‘Be you lamps unto yourselves. Hold fast to the Truth as a lamp, look not for refuge to anyone besides yourselves.’
# Essay on Gautam Buddha for Kids | Students # Speech on Gautam Buddha # Buddha essay # Short Note on Gautam Buddha
Dear viewers, Hope you like this article Essay on Gautam Buddha in English, please let us know by commenting below.
Essay on Guru Nanak Dev Ji
Essay on Mahatma Gandhi
Essay on Bhagat Singh
Essay on Rabindranath Tagore
Essay on Raja Ram Mohan Roy
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Basic Buddhist Teachings – II
The four noble truths.
In Buddhism, the four noble truths (Pāli: cattāri ariyasaccāni) are recognized as the first teaching given by the Buddha and are considered one of his most important teachings.
They are called “Noble Truths” because, as the Buddha says, they are real (tathāni), infallible (avitathāni), and do not change (anaññathāni). (SN Tatha Sutta).
It is because of the complete understanding of these four noble truths, as they really are, that the Buddha is called “Worthy” (Arahant), and “Perfectly Enlightened by Himself ” (Sammā Sambuddho). (SN Sammā sambuddha Sutta).
Besides, the word “Buddhism” comes from the word “buddha”, which in turn comes from the word “buddhi” and “bodhi”. These words literally mean “intellect”, “intelligence”, “wisdom” or “supreme knowledge”. They refer more specifically to the intelligence and supreme knowledge that a Buddha possesses due to the understanding of the four noble truths. But metaphorically they are usually translated as “enlightenment” or “awakening”, and the word “Buddha” as “enlightened” or “awakened”.
Whether a Buddha appears in the world or not, the four noble truths exist. However, a Buddha is needed to reveal them, bring them to light and teach them to the “deceived” world. As formulated by the Buddha, the four noble truths are central and universal events regardless of time and space. These are:
- All beings experience pain and misery (dukkha) during their lifetime: “ Birth is pain, old age is pain, sickness is pain, death is pain; sorrow, grief, sorrow, grief, and anxiety is pain. Contact with the unpleasant is pain. Separating from the pleasant is pain. Not getting what one wants is pain. In short, the five assemblies of mind and matter that are subject to attachment are pain “.
- The origin (samudaya) of pain and misery is due to a specific cause: “ It is the desire that leads to rebirth, accompanied by pleasure and passion, seeking pleasure here and there; that is, the desire for pleasures, the desire for existence, the desire for non-existence “.
- The cessation (nirodha) of pain and misery can be achieved as follows: “ With the complete non-passion and cessation of this very desire, with its abandonment and renunciation, with its liberation and detachment from it “.
- The method we must follow to stop pain and misery is that of the Noble Eightfold Path .
These truths do not exist in external things such as grass, wood and stones; they do exist though, in our body, which is composed of material elements and mental elements, such as consciousness and perception. As the Buddha says, “ In this body with its perception and consciousness I declare the world of pain, the origin, the cessation, and the practice that leads to its cessation “.
Of the four truths, the first identifies the innate physical and psychological pain or the innate misery, pain and suffering intertwined in the essence of life; the second identifies the origin and cause of the pain; the third recognizes the state in which the pain and its cause cease and are thus absent; and the fourth formulates a course of practice towards this state of pause.
This teaching begins with the analysis of the concept of pain that we all experience and the source of it, i.e., the desire we have within us. Due to our desire and in order to feel safe and secure, we constantly strive to gain experiences and objects that create pleasant emotions. We avoid anything that causes us pain and try to manipulate situations and people around to achieve what we want. In reality, the rest of the unstable world seldom matches what we want, and thus, we are often hurt and frustrated.
If we manage to overcome our desire we will feel greater harmony with ourselves and the world around us and the pain will be eliminated. The way to achieve this is through the Noble Eightfold Path .
Subscribe here! We will be informing you about our free lessons and we will send you as a gift, one of the most popular discourses of the Buddha, Karaṇīya Metta Sutta, in e-book, in English.
Your subscription has been completed!
Contact Info
5 apostolou pavlou st., ag. paraskevi, 15342, athens, greece, [email protected], +30 213 088 9977, monday – friday 09:00 – 17:00, contact athens theravada centre.
Your Name (required)
Your Email (required)
Your Message
Privacy Overview
500 Words Essay on GAUTAM BUDDHA and Buddhism
Gautam Buddha was one of the greatest religious teachers of the world. He gave the message of truth, peace, humanity and equality. His teachings and sayings became the basis of Buddhism, one of world’s leading religions which are followed in some countries like Japan, China, and Burma etc.
He is believed to have been born in Lumbini forests in Nepalese Terai in the sixth century B.C. Before he became the Buddha (the Enlightened), he was called Siddharth. His father’s name was Suddhodana, who was the ruler of Kapilvastu. His mother’s name was Maya Devi, who died soon after Siddharth’s birth.
Siddharth was a child with a contemplative bent of mind. He was inclined towards meditation and spiritual pursuits much against the wishes of his father. His father feared that Siddharth might leave home, and so, kept tried to insulate him from the harsh realities of the world outside by keeping him inside the palace all the time.
He even arranged his marriage with a beautiful princess Yashodhara when he was 18. They had a son named Rahul. But all these could not change the mind of young Siddharth.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The Buddhist traditions mention that when Siddharth encountered an old man, a sick person and a dead body, he realized how short lived is worldly passions and pleasures. Soon after he left his family and Kingdom and went into the forest in search of peace and truth. He wandered from place to place to gain knowledge. He met many scholars and saints but he was not satisfied.
At last he started hard meditation bearing great physical suffering. After six years of wandering and meditation Siddharth got enlightment when he was sitting in meditation under a pipal tree in the town of Ganges (Bihar).
Siddharth now got transformed into Buddha or the enlightened one at the age of the thirty five. The pipal tree under which he got Enlightment came to be known as Bodhi Vriksha.
Buddha attained what he wished for. He preached his first sermon in Sarnath, near Varanasi. He taught that the world is full of sorrows and people suffer on account of desire. Hence desires needed to be conquered by following Eightfold Path. Of these eight paths, the first three would ensure physical control, the next two ensures mental control, and the last two would ensure intellectual development.
Buddha taught that the final goal of every Buddhist is the attainment of ‘Nirvana’. ‘Nirvana’ could be attained neither by prayer nor by sacrifice. It can be achieved by right kind of living and thinking. Buddha did not speak of God and his teachings constitute more of a philosophy and system of ethics than a religion. Buddhism affirms the law of Karma by which a person’s action in life determines his status in future incarnations.
Buddhism is identified with the principles of non-violence. The Tripitika’ is a collection of Buddha’s teachings, life and philosophical discourses on the teachings and the commentaries. Buddha attained his Nirvana in Khushinagar (U.P.) in 483 B.C.
Related Articles:
- 41 Important questions on Buddhism
- Here is your free essay on Buddhism
- The Buddha system of philosophy arose out of the teachings of Gautama Buddha (Buddhism)
- Words of wisdom by Buddha on Karma and Nirvana and Non-Violence
SILENT COURSE
Essay Writing, Letter Writing, Notice Writing, Report Writing, Speech, Interview Questions and answers, government exam, school speeches, 10 lines essay, 10 lines speech
- Hindi Essay
- Eng. Speech
- Hindi Speech
- Notice Writing
- Report Writing
Friday, June 10, 2022
Essay on gautam buddha in english for school students, essay on gautam buddha (500 words).

3 comments:
This is broadly known as Spokane Teachers Credit Union Bank was founded in 1934 in Spokane, Washington, and the bank is currently providing its services to the citizens of Washington state along with residents of Kootenai and Bonner in Idaho. STCU Online STCU has a total asset value of 1.5 billion dollars with a total of 91,000 members, which makes its third-largest credit union bank from Washington. Spokane Teachers Credit Union Bank does offer online banking services which enable a customer to utilize their mobile banking as well in different mobile operating systems.
Buddhism is a realy complex and interesting topic.
28 फरवरी ➤ राष्ट्रीय विज्ञान दिवस - National Science Day
- ➤ राष्ट्रीय विज्ञान दिवस पर निबंध
- ➤ सी.वी रमन जी पर निबंध
- ➤ राष्ट्रीय विज्ञान दिवस पर 10 वाक्य
- ➤ Essay on National Science Day In English
- ➤ Essay on C.V. Raman In English
- ➤ 10 Lines on National Science Day
- ➤ 10 Lines on National Science Day In English
एक देश, एक चुनाव / One Nation One Election
- - एक देश एक चुनाव पर निबंध
- - एक देश, एक चुनाव पर 10 वाक्य
- - Essay on One Nation, One Election In English
- - 10 Lines on One Nation, One Election In English
आदित्य एल1 मिशन / Aditya-L1 Mission
- - आदित्य एल1 मिशन पर निबंध
- - आदित्य एल1 मिशन पर 10 पंक्ति
- - Essay on Aditya-L1 Mission In English
- - 10 Lines on Aditya-L1 Mission In English
चंद्रयान 3 / Chandrayaan-3
- - चंद्रयान 3 पर निबंध
- - चंद्रयान 3 पर 10 पंक्ति
- - Essay on Chandrayaan 3
- - 10 Lines on Chandryaan-3
Popular Posts
- Write A Letter To Your Friend Congratulating Him On His Success In The Examination Q. Write A Letter To Your Friend Congratulating Him On His Success In The Examination. Ans : RZH-333, Street-9 Bangalore Road Mysore - 570...
- Write An Application To The Principal For Fee Concession Q. Write An Application To The Principal For Fee Concession. Ans : Letter Writing To The Principal Adarsh School Dwarka Sec - 7 Delhi :...
- Write A Letter To Your Friend Inviting Him To Spend Summer Vacation With You Q. Write A Letter To Your Friend Inviting Him To Spend Summer Vacation With You. Examination Hall Palika Road, Delhi 17th May...
- अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस पर निबंध - Essay on International Yoga Day In Hindi - 21st June Essay on International Yoga Day In Hindi (300 Words) अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस पर निबंध अंतर्राष्ट्रीय योग दिवस हर साल 21 जून को पुरे विश्व मे...
- Essay on Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam In 300 Words Essay on Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam In English | 300 Words Father of India Missile Programmed Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam is the 11 th president of...
- How To Write An Application to The Principal For Sick Leave (How To Write An Application To The Principal For Sick Leave) To The Principal Delhi Convent School Subject : Application...
- दो दिन की छुट्टी / अवकाश के लिए प्रधानाचार्य जी को आवेदन पत्र या प्रार्थना पत्र - Write An Application To The Principal For Leave Two Days Question : Write An Application To The Principal For Leave Two Days दो दिन की छुट्टी / अवकाश के लिए प्रधानाचार्य जी को आवेदन पत्र या ...
- स्कूल छोड़ने के लिए प्रधानाचार्य जी को प्रार्थनापत्र - Write An Application To The Principal For School Leaving Certificate In Hindi Question : Write An Application To The Principal For School Leaving Certificate प्रश्न : स्कूल छोड़ने के लिए प्रधानाचार्य जी को प्रार्थ...
- Fee Installment के लिए आवेदन - Application For Fee Installment In School In Hindi Fee Installment के लिए आवेदन | Application For Fee Installment In School In Hindi दिनांक :- सेवा में प्रधानाचार्य / प्रधानाचा...
- Write An Application To The Principal For A School Picnic Q. Write An Application To The Principal For A Picnic Q. Application to the principal to arrange for school picnic Q. Application for Per...
- - Road Accident Report Writing
- - Fire Accident Report Writing
- - Kerala Flood Report Writing
- - Pulwama Attack Report Writing
- - Blood Donation Camp Report Writing
- - Lost Wrist Watch Notice Writing
- - Lost Water Bottle Notice Writing
- - Lost Pencil Box Notice Writing
- - Fancy Dress Competition Notice Writing
- - Sick Leave Application
- - School Leaving Certificate
- - For Scholarship
- - Fee Concession
- - Congratulation Letter (Exam)
- - Application for Picnic
- English-Essay (120)
- Hindi-Essay (120)
- 10-Lines-English (31)
- 10-Lines-Hindi (31)
- English-Festival-Essay (25)
- Hindi-Festival-Essay (25)
- Hindi-Speech (19)
- Hindi-Letter (18)
- 10-Lines-Speech (15)
- English-Speech (14)
- English-Letter (13)
- Freedom-Fighter-Hindi-Essay (13)
- Freedom-Fighter-Essay (12)
- 10-Lines-Hindi-Speech (8)
- 10-lines-hindi-essay (8)
- 10-Lines-Essay (5)
- English-Notice (5)
- English-Report (5)
- 10-Lines-Domestic-Animal (4)
- 10-Lines-Historical-Monuments (2)
- 10-Lines-Wild-Animal (2)
- Freshers-Interview (2)
- Experienced-Interview (1)
Site Information
- Privacy Policy
Contact Form
Total pageviews.

Essay on Buddha Purnima in English 2020
Buddha Purnima is a Buddhist festival which celebrates the birth of Gautam Buddha. He was the founder of Buddhism. His real name was Siddhartha Gautam and he was born in Lumbini. Buddhism is a major religion in the world.
This festival is celebrated in different countries in different ways. In India, Buddhist people go to a monastery, include prayer meets, sermons, recitation of Buddhist scriptures, group meditation etc. They wear white clothes and eat sweet rice kheer.
In China, people remember Buddha by lighting incense and offering food to the monks. They also wash the statue of Buddha in temples and light lanterns. In Japan, this festival is celebrated on 8th April every year. People pour ama-cha (herbal tea) on small statues of Buddha and decorate it with flowers. Those small statues are known as baby Buddha.
Buddha Purnima is a festival which celebrates the teachings of Gautam Buddha. His birthday reminds us of his philosophy which was to live a pure and simple life. It reminds us of non- violence which influenced Gandhiji very much.
Table of Contents
Question on Buddha Purnima
What happens on buddha purnima, why is buddha purnima important.
Buddha Purnima commemorates the birth, death and the enlightenment of Lord Buddha on the same day. Budhha is the symbol of peace and non- violence. He was born in Lumbini in Nepal and died in Khushinagar, India known as Parinirvana .
Related Posts:
- Random Harry Potter Character Generator
- Random Compound Word Generator
- Goblin Market Poem by Christina Rossetti Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- Random Phrase Generator [English]
- Michael Poem by William Wordsworth Summary, Notes and Line by Line Explanation in English
- The Happy Prince Summary by Oscar Wilde


- Forums New posts Search Forums
- Members Registered members Current visitors Recent Activity
- Free Assessment
Material for WAEC 2024 Lit-in English (Prose, OBJ/ESSAY Questions and Answers
- Thread starter Steadygist
- Start date Today at 2:35 AM
GET STUDY MATERIAL FOR WAEC MAY/JUNE 2024 LITERATURE IN ENGLISH (PROSE, OBJ, DRAMA & POETRY FREE MATERIAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS [SCHOOL CANDIDATES] Friday, 17th May 2024 Literature-In-English 2 (Prose) 9:30am – 10:45am Literature-In-English 1 (Objective) 10:45am – 11:45am Get Complete Study Material For Verified 2024 Waec Literature In English 2 (Prose & Obj Essay) Questions And Answers Click Here To Get Full Answers material On WhatsApp
Jump to navigation
War and Trauma Literature
We seek papers/article-length write-ups/essays/commentaries/causeries on war and representations in literature and allied subjects, exploring the trauma of psychological, physiological, socio-emotional, somatic, eco-environmental, financial, fiscal consequences on the subjects, economies. Papers across disciplines, dealing with the trauma/post-trauma in war literature will be undertaken for consideration. The twentieth-century war climate will particularly be the case in point. Articles/papers on novel ideations, unheard dimensions of wars of the past, in the nineteenth century or the troubled or strained nationalities/borders of the current world order, will also be considered. Battle-field horrors, fear-mongering, policy negotiations, imaginary lands, utopias/dystopias, failed social architecture, distorted political visions, destructive civil or military actions, revolutions, falling stocks, crippling economies, troubled poetic psyche, expansive prose critique etc are some of the thematic ambits for deliberation and review. For the summer issue 1.1, we encourage praxis-based, pragmatic, conceptual manuscripts from scholars and practitioners across social sciences and humanities. Prospective submitting authors should consult the manuscript guidelines below and submit a proposal that includes:
· An abstract of 250 words with 1-2 sentences on each of the following:
- Essential points of literature review (which underline the introduction to the study)
- Problem or research questions and research objectives clearly stated
- Brief description of (research) methods/Methodology
- Praxis, Concept, or Results/findings
- Implications/Relevance in Future
Manuscript Guidelines:
00001. Manuscripts must be in both Microsoft Word.Doc. Do not send your files as pdf.
00002. Manuscripts should not exceed 3500-5000 words, including abstracts and work cited
00003. Manuscripts should be written in English, should be single- spaced, including quotations and references and in 12-point Times New Roman font. Follow MLA ninth style formatting. More can be read from- https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formattin...
00004. Titles must be in bold, 14-point Times New Roman font while sub-titles remain 12-point, bold, and initial letter cap. All abbreviations and acronyms should be written in full at first appearance in the manuscript text.
00005. All manuscripts must include a brief but captivating abstract which should not exceed 200 words and should describe the scope of the work, methodology, theoretical framework, and the findings. The abstract should also include a set of 5 keywords (preferably in pairs) listed in order of importance to assist in indexing the article.
00006. Manuscripts must not have been published or submitted for publication elsewhere.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay on Gautam Buddha. Gautam Buddha, the messenger of peace, equality, and fraternity, was born in Lumbini in the 6th Century BC, the Terai region of Nepal. His real name was Siddhartha Gautam. He belonged to the royal family of Kapilavastu. His father was Suddhodhana, the ruler.
Buddha (born c. 6th-4th century bce, Lumbini, near Kapilavastu, Shakya republic, Kosala kingdom [now in Nepal]—died, Kusinara, Malla republic, Magadha kingdom [now Kasia, India]) was the founder of Buddhism, one of the major religions and philosophical systems of southern and eastern Asia and of the world. Buddha is one of the many epithets of a teacher who lived in northern India sometime ...
Gautama Buddha. Siddhartha Gautama (c. 563 BC - c. 483 BC [1]) was the founder of Buddhism. He is best known by the title the Buddha. The title means "Fully Awakened One". He was born as a prince in a region of what is now the country Nepal in a Shakya Kingdom in Lumbini. He is also called Shakyamuni Buddha. This is because he was a member of ...
October 2003. According to tradition, the historical Buddha lived from 563 to 483 B.C., although scholars postulate that he may have lived as much as a century later. He was born to the rulers of the Shakya clan, hence his appellation Shakyamuni, which means "sage of the Shakya clan.". The legends that grew up around him hold that both his ...
The Buddha (fl. circa 450 BCE) is the individual whose teachings form the basis of the Buddhist tradition. These teachings, preserved in texts known as the Nikāyas or Āgamas, concern the quest for liberation from suffering.While the ultimate aim of the Buddha's teachings is thus to help individuals attain the good life, his analysis of the source of suffering centrally involves claims ...
After spending six days and nights cutting through mind's most subtle obstacles, he reached enlightenment on the full moon morning of May, a week before he turned thirty-five. At the moment of full realization, all veils of mixed feelings and stiff ideas dissolved and Buddha experienced the all-encompassing here and now.
The life of the Buddha. The teacher known as the Buddha lived in northern India sometime between the mid-6th and the mid-4th centuries before the Common Era. In ancient India the title buddha referred to an enlightened being who has awakened from the sleep of ignorance and achieved freedom from suffering. According to the various traditions of Buddhism, buddhas have existed in the past and ...
Buddha (c. 500s B.C.E.) The historical Buddha, also known as Gotama Buddha, Siddhārtha Gautama, and Buddha Śākyamuni, was born in Lumbini, in the Nepalese region of Terai, near the Indian border. He is one of the most important Asian thinkers and spiritual masters of all time, and he contributed to many areas of philosophy, including ...
Buddhism, religion and philosophy that developed from the teachings of the Buddha (Sanskrit: "Awakened One"), a teacher who lived in northern India between the mid-6th and mid-4th centuries bce (before the Common Era). Spreading from India to Central and Southeast Asia, China, Korea, and Japan, Buddhism has played a central role in the spiritual, cultural, and social life of Asia, and ...
The Buddha spent the remaining forty years of his life preaching his faith and making vast numbers of converts. When he died, his body was cremated, as was customary in India. The cremated relics of the Buddha were divided into several portions and placed in relic caskets that were interred within large hemispherical mounds known as stupas.
Children can learn from this 150-word essay on Gautama Buddha: Gautam Buddha is one of the most well-known spiritual leaders in history who started the religion of Buddhism. He was born in Lumbini, near the Indo-Nepal border, in the 6th century BC. He belonged to a wealthy family.
Buddhism (/ ˈ b ʊ d ɪ z əm / BUUD-ih-zəm, US also / ˈ b uː d-/ BOOD-), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise seven percent of the global population. ...
Thailand. Wikimedia Commons. In that same century, the Venetian merchant Marco Polo gave the West its first account of Buddha's life. Between 1292 and 1295, journeying home from China, Marco ...
Essay Example: The ancient inception of Buddhism, an esteemed and impactful faith, can be traced back to ancient India during the 6th century BCE. Initiated by Siddhartha Gautama, revered as the Buddha or the "Enlightened One," its teachings propagated across Asia, profoundly shaping diverse. Essay Example: The ancient inception of Buddhism, an ...
Buddha Purnima, also known as Vesak, is a festival that commemorates the birth, enlightenment, and passing away of the Lord Buddha. The origin of Buddha Purnima can be traced back to over 2500 years ago, to ancient India when the Buddha was born as Prince Siddhartha Gautama in Lumbini, Nepal. According to Buddhist scriptures, Queen Mayadevi ...
Essay on Gautam Buddha in 150 to 250 words. Gautama Buddha who started Buddhism is known as the Rational Prophet and Philosopher. It is so because he believes, not in blind faith but in reason, inquiry, test, analysis, research, and insight. He is said to have been born in 563 BC at Lumbini in the Kapilvastu state.
Dhamma means discipline, law or religion; pada the path or way, and together Dhammapada is the 'path of virtue'. This founding text of Buddhist teaching is here presented in both Pali and English by one of India's foremost philosophers and religious authorities, S. Radhakrishnan. The verses of the Dhammapada were believed from very early times to have been the utterances of Gautama the Buddha ...
As formulated by the Buddha, the four noble truths are central and universal events regardless of time and space. These are: All beings experience pain and misery (dukkha) during their lifetime: " Birth is pain, old age is pain, sickness is pain, death is pain; sorrow, grief, sorrow, grief, and anxiety is pain. Contact with the unpleasant is ...
English alone several translations are available, including editions by such noted scholars as Max Mul-ler and Dr. S. Radhakrishnan. However, when pre-sented from a non-Buddhist frame of reference, the teachings of the Buddha inevitably suffer some dis-tortion. This, in fact, has already happened with our
Buddhism is identified with the principles of non-violence. The Tripitika' is a collection of Buddha's teachings, life and philosophical discourses on the teachings and the commentaries. Buddha attained his Nirvana in Khushinagar (U.P.) in 483 B.C. Home; Essay In English Language
Essay on Gautam Buddha (500 Words) Introduction: Gautam Buddha was a great man, who is considered to be an incarnation of God. Gautam Buddha is also known as Lord Buddha or Mahatma Buddha. His real or childhood name was Siddharth Gautam. He showed the whole world the path of peace and non-violence.
Essay on Buddha Purnima in English 2020. Buddha Purnima is a Buddhist festival which celebrates the birth of Gautam Buddha. He was the founder of Buddhism. His real name was Siddhartha Gautam and he was born in Lumbini. Buddhism is a major religion in the world.
In Japan, Buddha's birthday is observed on April 8 and celebrated in Buddhist temples as Hana Matsuri, which means flower festival. On this day, a small "flower hall" is set up on the temple ...
10 LINES ESSAY ON GAUTAM BUDDHA IN ENGLISH/Gautam Buddha ESSAY 10 Lines #gautambuddha #englishessay#10linesessay #buddha #lordbuddha #buddhism #essay #shorte...
Fiscal consolidation and the reintroduction of the WAEMU fiscal framework is crucial for maintaining debt sustainability, external viability, and financial stability. The 3 and 70 percent of GDP deficit and debt ceilings envisaged by the expired rule remain appropriate, while addressing the stock-flow adjustments will help rebuild fiscal buffers. Convergence to a fiscal deficit of 3 percent of ...
WAEC May/June study 2024 FREE ENGLISH LANGUAGE ANSWER ROOM [School Candidates] Study Material for WAEC English Language Questions and Answers 2024 Wednesday, 15th May, 2024 English Language 2 (Essay) - 09:30am - 11:30am. English Language 1 (Objective) - 11:30am - 12:30pm English Language 3 (Test of Orals) ** /**** - 2:00pm - 4:45pm
GET STUDY MATERIAL FOR WAEC MAY/JUNE 2024 LITERATURE IN ENGLISH (PROSE, OBJ, DRAMA & POETRY FREE MATERIAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS [SCHOOL CANDIDATES] Friday, 17th May 2024 Literature-In-English 2 (Prose) 9:30am - 10:45am Literature-In-English 1 (Objective) 10:45am - 11:45am Get Complete Study...
contact email: [email protected]. Call for Papers for a Special Issue of Studies in the Novel: Disability and Disease in the Novel. Editors: Dr. Lydia R. Cooper (University of Seattle) and Dr. Matthew L. Reznicek (University of Minnesota) In this Special Issue, we are looking for scholars engaged with the question of how the novel ...
Papers across disciplines, dealing with the trauma/post-trauma in war literature will be undertaken for consideration. The twentieth-century war climate will particularly be the case in point. Articles/papers on novel ideations, unheard dimensions of wars of the past, in the nineteenth century or the troubled or strained nationalities/borders ...