Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods

What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations.
Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research , which involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g. text, video, or audio).
Quantitative research is widely used in the natural and social sciences: biology, chemistry, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc.
- What is the demographic makeup of Singapore in 2020?
- How has the average temperature changed globally over the last century?
- Does environmental pollution affect the prevalence of honey bees?
- Does working from home increase productivity for people with long commutes?
Table of contents
Quantitative research methods, quantitative data analysis, advantages of quantitative research, disadvantages of quantitative research, frequently asked questions about quantitative research.
You can use quantitative research methods for descriptive, correlational or experimental research.
- In descriptive research , you simply seek an overall summary of your study variables.
- In correlational research , you investigate relationships between your study variables.
- In experimental research , you systematically examine whether there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables.
Correlational and experimental research can both be used to formally test hypotheses , or predictions, using statistics. The results may be generalised to broader populations based on the sampling method used.
To collect quantitative data, you will often need to use operational definitions that translate abstract concepts (e.g., mood) into observable and quantifiable measures (e.g., self-ratings of feelings and energy levels).
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once data is collected, you may need to process it before it can be analysed. For example, survey and test data may need to be transformed from words to numbers. Then, you can use statistical analysis to answer your research questions .
Descriptive statistics will give you a summary of your data and include measures of averages and variability. You can also use graphs, scatter plots and frequency tables to visualise your data and check for any trends or outliers.
Using inferential statistics , you can make predictions or generalisations based on your data. You can test your hypothesis or use your sample data to estimate the population parameter .
You can also assess the reliability and validity of your data collection methods to indicate how consistently and accurately your methods actually measured what you wanted them to.
Quantitative research is often used to standardise data collection and generalise findings . Strengths of this approach include:
- Replication
Repeating the study is possible because of standardised data collection protocols and tangible definitions of abstract concepts.
- Direct comparisons of results
The study can be reproduced in other cultural settings, times or with different groups of participants. Results can be compared statistically.
- Large samples
Data from large samples can be processed and analysed using reliable and consistent procedures through quantitative data analysis.
- Hypothesis testing
Using formalised and established hypothesis testing procedures means that you have to carefully consider and report your research variables, predictions, data collection and testing methods before coming to a conclusion.
Despite the benefits of quantitative research, it is sometimes inadequate in explaining complex research topics. Its limitations include:
- Superficiality
Using precise and restrictive operational definitions may inadequately represent complex concepts. For example, the concept of mood may be represented with just a number in quantitative research, but explained with elaboration in qualitative research.
- Narrow focus
Predetermined variables and measurement procedures can mean that you ignore other relevant observations.
- Structural bias
Despite standardised procedures, structural biases can still affect quantitative research. Missing data , imprecise measurements or inappropriate sampling methods are biases that can lead to the wrong conclusions.
- Lack of context
Quantitative research often uses unnatural settings like laboratories or fails to consider historical and cultural contexts that may affect data collection and results.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research , you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific predictions, called hypotheses , by calculating how likely it is that a pattern or relationship between variables could have arisen by chance.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari

Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- I NEED TO . . .
What is Quantitative Research?
- What is Qualitative Research?
- Quantitative vs Qualitative
- Step 1: Accessing CINAHL
- Step 2: Create a Keyword Search
- Step 3: Create a Subject Heading Search
- Step 4: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Second Concept
- Step 5: Repeat Steps 1-3 for Quantitative Terms
- Step 6: Combining All Searches
- Step 7: Adding Limiters
- Step 8: Save Your Search!
- What Kind of Article is This?
- More Research Help This link opens in a new window
Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns . Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data. Some of the numeric data is intrinsically quantitative (e.g. personal income), while in other cases the numeric structure is imposed (e.g. ‘On a scale from 1 to 10, how depressed did you feel last week?’). The collection of quantitative information allows researchers to conduct simple to extremely sophisticated statistical analyses that aggregate the data (e.g. averages, percentages), show relationships among the data (e.g. ‘Students with lower grade point averages tend to score lower on a depression scale’) or compare across aggregated data (e.g. the USA has a higher gross domestic product than Spain). Quantitative research includes methodologies such as questionnaires, structured observations or experiments and stands in contrast to qualitative research. Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of narratives and/or open-ended observations through methodologies such as interviews, focus groups or ethnographies.
Coghlan, D., Brydon-Miller, M. (2014). The SAGE encyclopedia of action research (Vols. 1-2). London, : SAGE Publications Ltd doi: 10.4135/9781446294406
What is the purpose of quantitative research?
The purpose of quantitative research is to generate knowledge and create understanding about the social world. Quantitative research is used by social scientists, including communication researchers, to observe phenomena or occurrences affecting individuals. Social scientists are concerned with the study of people. Quantitative research is a way to learn about a particular group of people, known as a sample population. Using scientific inquiry, quantitative research relies on data that are observed or measured to examine questions about the sample population.
Allen, M. (2017). The SAGE encyclopedia of communication research methods (Vols. 1-4). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc doi: 10.4135/9781483381411
How do I know if the study is a quantitative design? What type of quantitative study is it?
Quantitative Research Designs: Descriptive non-experimental, Quasi-experimental or Experimental?
Studies do not always explicitly state what kind of research design is being used. You will need to know how to decipher which design type is used. The following video will help you determine the quantitative design type.
- << Previous: I NEED TO . . .
- Next: What is Qualitative Research? >>
- Last Updated: Dec 8, 2023 10:05 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/quantitative_and_qualitative_research
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.

Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences pp 27–49 Cite as
Quantitative Research
- Leigh A. Wilson 2 , 3
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
4072 Accesses
4 Citations
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. High-quality quantitative research is characterized by the attention given to the methods and the reliability of the tools used to collect the data. The ability to critique research in a systematic way is an essential component of a health professional’s role in order to deliver high quality, evidence-based healthcare. This chapter is intended to provide a simple overview of the way new researchers and health practitioners can understand and employ quantitative methods. The chapter offers practical, realistic guidance in a learner-friendly way and uses a logical sequence to understand the process of hypothesis development, study design, data collection and handling, and finally data analysis and interpretation.
- Quantitative
- Epidemiology
- Data analysis
- Methodology
- Interpretation
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Babbie ER. The practice of social research. 14th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth Cengage; 2016.
Google Scholar
Descartes. Cited in Halverston, W. (1976). In: A concise introduction to philosophy, 3rd ed. New York: Random House; 1637.
Doll R, Hill AB. The mortality of doctors in relation to their smoking habits. BMJ. 1954;328(7455):1529–33. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529 .
Article Google Scholar
Liamputtong P. Research methods in health: foundations for evidence-based practice. 3rd ed. Melbourne: Oxford University Press; 2017.
McNabb DE. Research methods in public administration and nonprofit management: quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2nd ed. New York: Armonk; 2007.
Merriam-Webster. Dictionary. http://www.merriam-webster.com . Accessed 20th December 2017.
Olesen Larsen P, von Ins M. The rate of growth in scientific publication and the decline in coverage provided by Science Citation Index. Scientometrics. 2010;84(3):575–603.
Pannucci CJ, Wilkins EG. Identifying and avoiding bias in research. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):619–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181de24bc .
Petrie A, Sabin C. Medical statistics at a glance. 2nd ed. London: Blackwell Publishing; 2005.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. 3rd ed. New Jersey: Pearson Publishing; 2009.
Sheehan J. Aspects of research methodology. Nurse Educ Today. 1986;6:193–203.
Wilson LA, Black DA. Health, science research and research methods. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2013.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Leigh A. Wilson
Faculty of Health Science, Discipline of Behavioural and Social Sciences in Health, University of Sydney, Lidcombe, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leigh A. Wilson .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Wilson, L.A. (2019). Quantitative Research. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Statistical Analysis | 5 Steps & Examples
Statistical analysis means investigating trends, patterns, and relationships using quantitative data . It is an important research tool used by scientists, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
To draw valid conclusions, statistical analysis requires careful planning from the very start of the research process . You need to specify your hypotheses and make decisions about your research design, sample size, and sampling procedure.
After collecting data from your sample, you can organize and summarize the data using descriptive statistics . Then, you can use inferential statistics to formally test hypotheses and make estimates about the population. Finally, you can interpret and generalize your findings.
This article is a practical introduction to statistical analysis for students and researchers. We’ll walk you through the steps using two research examples. The first investigates a potential cause-and-effect relationship, while the second investigates a potential correlation between variables.
Table of contents
Step 1: write your hypotheses and plan your research design, step 2: collect data from a sample, step 3: summarize your data with descriptive statistics, step 4: test hypotheses or make estimates with inferential statistics, step 5: interpret your results, other interesting articles.
To collect valid data for statistical analysis, you first need to specify your hypotheses and plan out your research design.
Writing statistical hypotheses
The goal of research is often to investigate a relationship between variables within a population . You start with a prediction, and use statistical analysis to test that prediction.
A statistical hypothesis is a formal way of writing a prediction about a population. Every research prediction is rephrased into null and alternative hypotheses that can be tested using sample data.
While the null hypothesis always predicts no effect or no relationship between variables, the alternative hypothesis states your research prediction of an effect or relationship.
- Null hypothesis: A 5-minute meditation exercise will have no effect on math test scores in teenagers.
- Alternative hypothesis: A 5-minute meditation exercise will improve math test scores in teenagers.
- Null hypothesis: Parental income and GPA have no relationship with each other in college students.
- Alternative hypothesis: Parental income and GPA are positively correlated in college students.
Planning your research design
A research design is your overall strategy for data collection and analysis. It determines the statistical tests you can use to test your hypothesis later on.
First, decide whether your research will use a descriptive, correlational, or experimental design. Experiments directly influence variables, whereas descriptive and correlational studies only measure variables.
- In an experimental design , you can assess a cause-and-effect relationship (e.g., the effect of meditation on test scores) using statistical tests of comparison or regression.
- In a correlational design , you can explore relationships between variables (e.g., parental income and GPA) without any assumption of causality using correlation coefficients and significance tests.
- In a descriptive design , you can study the characteristics of a population or phenomenon (e.g., the prevalence of anxiety in U.S. college students) using statistical tests to draw inferences from sample data.
Your research design also concerns whether you’ll compare participants at the group level or individual level, or both.
- In a between-subjects design , you compare the group-level outcomes of participants who have been exposed to different treatments (e.g., those who performed a meditation exercise vs those who didn’t).
- In a within-subjects design , you compare repeated measures from participants who have participated in all treatments of a study (e.g., scores from before and after performing a meditation exercise).
- In a mixed (factorial) design , one variable is altered between subjects and another is altered within subjects (e.g., pretest and posttest scores from participants who either did or didn’t do a meditation exercise).
- Experimental
- Correlational
First, you’ll take baseline test scores from participants. Then, your participants will undergo a 5-minute meditation exercise. Finally, you’ll record participants’ scores from a second math test.
In this experiment, the independent variable is the 5-minute meditation exercise, and the dependent variable is the math test score from before and after the intervention. Example: Correlational research design In a correlational study, you test whether there is a relationship between parental income and GPA in graduating college students. To collect your data, you will ask participants to fill in a survey and self-report their parents’ incomes and their own GPA.
Measuring variables
When planning a research design, you should operationalize your variables and decide exactly how you will measure them.
For statistical analysis, it’s important to consider the level of measurement of your variables, which tells you what kind of data they contain:
- Categorical data represents groupings. These may be nominal (e.g., gender) or ordinal (e.g. level of language ability).
- Quantitative data represents amounts. These may be on an interval scale (e.g. test score) or a ratio scale (e.g. age).
Many variables can be measured at different levels of precision. For example, age data can be quantitative (8 years old) or categorical (young). If a variable is coded numerically (e.g., level of agreement from 1–5), it doesn’t automatically mean that it’s quantitative instead of categorical.
Identifying the measurement level is important for choosing appropriate statistics and hypothesis tests. For example, you can calculate a mean score with quantitative data, but not with categorical data.
In a research study, along with measures of your variables of interest, you’ll often collect data on relevant participant characteristics.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

In most cases, it’s too difficult or expensive to collect data from every member of the population you’re interested in studying. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
Statistical analysis allows you to apply your findings beyond your own sample as long as you use appropriate sampling procedures . You should aim for a sample that is representative of the population.
Sampling for statistical analysis
There are two main approaches to selecting a sample.
- Probability sampling: every member of the population has a chance of being selected for the study through random selection.
- Non-probability sampling: some members of the population are more likely than others to be selected for the study because of criteria such as convenience or voluntary self-selection.
In theory, for highly generalizable findings, you should use a probability sampling method. Random selection reduces several types of research bias , like sampling bias , and ensures that data from your sample is actually typical of the population. Parametric tests can be used to make strong statistical inferences when data are collected using probability sampling.
But in practice, it’s rarely possible to gather the ideal sample. While non-probability samples are more likely to at risk for biases like self-selection bias , they are much easier to recruit and collect data from. Non-parametric tests are more appropriate for non-probability samples, but they result in weaker inferences about the population.
If you want to use parametric tests for non-probability samples, you have to make the case that:
- your sample is representative of the population you’re generalizing your findings to.
- your sample lacks systematic bias.
Keep in mind that external validity means that you can only generalize your conclusions to others who share the characteristics of your sample. For instance, results from Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic samples (e.g., college students in the US) aren’t automatically applicable to all non-WEIRD populations.
If you apply parametric tests to data from non-probability samples, be sure to elaborate on the limitations of how far your results can be generalized in your discussion section .
Create an appropriate sampling procedure
Based on the resources available for your research, decide on how you’ll recruit participants.
- Will you have resources to advertise your study widely, including outside of your university setting?
- Will you have the means to recruit a diverse sample that represents a broad population?
- Do you have time to contact and follow up with members of hard-to-reach groups?
Your participants are self-selected by their schools. Although you’re using a non-probability sample, you aim for a diverse and representative sample. Example: Sampling (correlational study) Your main population of interest is male college students in the US. Using social media advertising, you recruit senior-year male college students from a smaller subpopulation: seven universities in the Boston area.
Calculate sufficient sample size
Before recruiting participants, decide on your sample size either by looking at other studies in your field or using statistics. A sample that’s too small may be unrepresentative of the sample, while a sample that’s too large will be more costly than necessary.
There are many sample size calculators online. Different formulas are used depending on whether you have subgroups or how rigorous your study should be (e.g., in clinical research). As a rule of thumb, a minimum of 30 units or more per subgroup is necessary.
To use these calculators, you have to understand and input these key components:
- Significance level (alpha): the risk of rejecting a true null hypothesis that you are willing to take, usually set at 5%.
- Statistical power : the probability of your study detecting an effect of a certain size if there is one, usually 80% or higher.
- Expected effect size : a standardized indication of how large the expected result of your study will be, usually based on other similar studies.
- Population standard deviation: an estimate of the population parameter based on a previous study or a pilot study of your own.
Once you’ve collected all of your data, you can inspect them and calculate descriptive statistics that summarize them.
Inspect your data
There are various ways to inspect your data, including the following:
- Organizing data from each variable in frequency distribution tables .
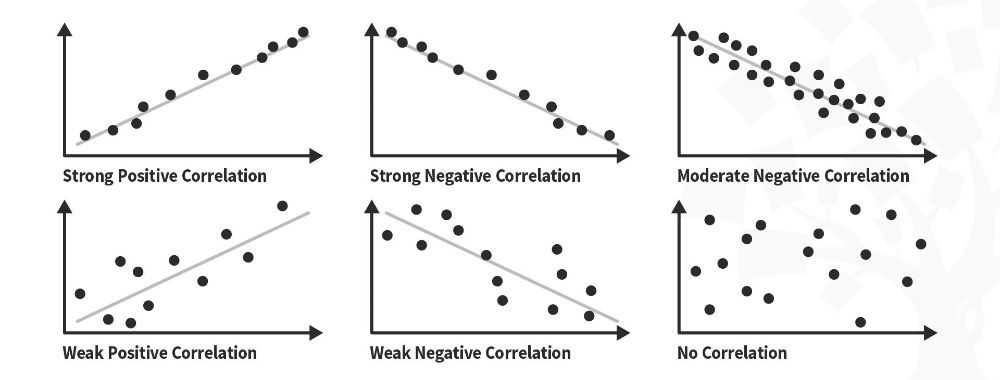
- Displaying data from a key variable in a bar chart to view the distribution of responses.
- Visualizing the relationship between two variables using a scatter plot .
By visualizing your data in tables and graphs, you can assess whether your data follow a skewed or normal distribution and whether there are any outliers or missing data.
A normal distribution means that your data are symmetrically distributed around a center where most values lie, with the values tapering off at the tail ends.
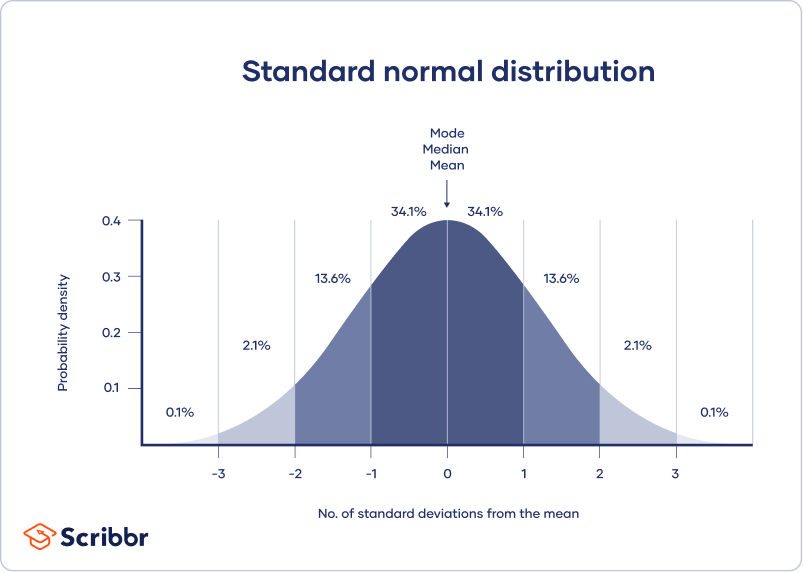
In contrast, a skewed distribution is asymmetric and has more values on one end than the other. The shape of the distribution is important to keep in mind because only some descriptive statistics should be used with skewed distributions.
Extreme outliers can also produce misleading statistics, so you may need a systematic approach to dealing with these values.
Calculate measures of central tendency
Measures of central tendency describe where most of the values in a data set lie. Three main measures of central tendency are often reported:
- Mode : the most popular response or value in the data set.
- Median : the value in the exact middle of the data set when ordered from low to high.
- Mean : the sum of all values divided by the number of values.
However, depending on the shape of the distribution and level of measurement, only one or two of these measures may be appropriate. For example, many demographic characteristics can only be described using the mode or proportions, while a variable like reaction time may not have a mode at all.
Calculate measures of variability
Measures of variability tell you how spread out the values in a data set are. Four main measures of variability are often reported:
- Range : the highest value minus the lowest value of the data set.
- Interquartile range : the range of the middle half of the data set.
- Standard deviation : the average distance between each value in your data set and the mean.
- Variance : the square of the standard deviation.
Once again, the shape of the distribution and level of measurement should guide your choice of variability statistics. The interquartile range is the best measure for skewed distributions, while standard deviation and variance provide the best information for normal distributions.
Using your table, you should check whether the units of the descriptive statistics are comparable for pretest and posttest scores. For example, are the variance levels similar across the groups? Are there any extreme values? If there are, you may need to identify and remove extreme outliers in your data set or transform your data before performing a statistical test.
From this table, we can see that the mean score increased after the meditation exercise, and the variances of the two scores are comparable. Next, we can perform a statistical test to find out if this improvement in test scores is statistically significant in the population. Example: Descriptive statistics (correlational study) After collecting data from 653 students, you tabulate descriptive statistics for annual parental income and GPA.
It’s important to check whether you have a broad range of data points. If you don’t, your data may be skewed towards some groups more than others (e.g., high academic achievers), and only limited inferences can be made about a relationship.
A number that describes a sample is called a statistic , while a number describing a population is called a parameter . Using inferential statistics , you can make conclusions about population parameters based on sample statistics.
Researchers often use two main methods (simultaneously) to make inferences in statistics.
- Estimation: calculating population parameters based on sample statistics.
- Hypothesis testing: a formal process for testing research predictions about the population using samples.
You can make two types of estimates of population parameters from sample statistics:
- A point estimate : a value that represents your best guess of the exact parameter.
- An interval estimate : a range of values that represent your best guess of where the parameter lies.
If your aim is to infer and report population characteristics from sample data, it’s best to use both point and interval estimates in your paper.
You can consider a sample statistic a point estimate for the population parameter when you have a representative sample (e.g., in a wide public opinion poll, the proportion of a sample that supports the current government is taken as the population proportion of government supporters).
There’s always error involved in estimation, so you should also provide a confidence interval as an interval estimate to show the variability around a point estimate.
A confidence interval uses the standard error and the z score from the standard normal distribution to convey where you’d generally expect to find the population parameter most of the time.
Hypothesis testing
Using data from a sample, you can test hypotheses about relationships between variables in the population. Hypothesis testing starts with the assumption that the null hypothesis is true in the population, and you use statistical tests to assess whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not.
Statistical tests determine where your sample data would lie on an expected distribution of sample data if the null hypothesis were true. These tests give two main outputs:
- A test statistic tells you how much your data differs from the null hypothesis of the test.
- A p value tells you the likelihood of obtaining your results if the null hypothesis is actually true in the population.
Statistical tests come in three main varieties:
- Comparison tests assess group differences in outcomes.
- Regression tests assess cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
- Correlation tests assess relationships between variables without assuming causation.
Your choice of statistical test depends on your research questions, research design, sampling method, and data characteristics.
Parametric tests
Parametric tests make powerful inferences about the population based on sample data. But to use them, some assumptions must be met, and only some types of variables can be used. If your data violate these assumptions, you can perform appropriate data transformations or use alternative non-parametric tests instead.
A regression models the extent to which changes in a predictor variable results in changes in outcome variable(s).
- A simple linear regression includes one predictor variable and one outcome variable.
- A multiple linear regression includes two or more predictor variables and one outcome variable.
Comparison tests usually compare the means of groups. These may be the means of different groups within a sample (e.g., a treatment and control group), the means of one sample group taken at different times (e.g., pretest and posttest scores), or a sample mean and a population mean.
- A t test is for exactly 1 or 2 groups when the sample is small (30 or less).
- A z test is for exactly 1 or 2 groups when the sample is large.
- An ANOVA is for 3 or more groups.
The z and t tests have subtypes based on the number and types of samples and the hypotheses:
- If you have only one sample that you want to compare to a population mean, use a one-sample test .
- If you have paired measurements (within-subjects design), use a dependent (paired) samples test .
- If you have completely separate measurements from two unmatched groups (between-subjects design), use an independent (unpaired) samples test .
- If you expect a difference between groups in a specific direction, use a one-tailed test .
- If you don’t have any expectations for the direction of a difference between groups, use a two-tailed test .
The only parametric correlation test is Pearson’s r . The correlation coefficient ( r ) tells you the strength of a linear relationship between two quantitative variables.
However, to test whether the correlation in the sample is strong enough to be important in the population, you also need to perform a significance test of the correlation coefficient, usually a t test, to obtain a p value. This test uses your sample size to calculate how much the correlation coefficient differs from zero in the population.
You use a dependent-samples, one-tailed t test to assess whether the meditation exercise significantly improved math test scores. The test gives you:
- a t value (test statistic) of 3.00
- a p value of 0.0028
Although Pearson’s r is a test statistic, it doesn’t tell you anything about how significant the correlation is in the population. You also need to test whether this sample correlation coefficient is large enough to demonstrate a correlation in the population.
A t test can also determine how significantly a correlation coefficient differs from zero based on sample size. Since you expect a positive correlation between parental income and GPA, you use a one-sample, one-tailed t test. The t test gives you:
- a t value of 3.08
- a p value of 0.001
The final step of statistical analysis is interpreting your results.
Statistical significance
In hypothesis testing, statistical significance is the main criterion for forming conclusions. You compare your p value to a set significance level (usually 0.05) to decide whether your results are statistically significant or non-significant.
Statistically significant results are considered unlikely to have arisen solely due to chance. There is only a very low chance of such a result occurring if the null hypothesis is true in the population.
This means that you believe the meditation intervention, rather than random factors, directly caused the increase in test scores. Example: Interpret your results (correlational study) You compare your p value of 0.001 to your significance threshold of 0.05. With a p value under this threshold, you can reject the null hypothesis. This indicates a statistically significant correlation between parental income and GPA in male college students.
Note that correlation doesn’t always mean causation, because there are often many underlying factors contributing to a complex variable like GPA. Even if one variable is related to another, this may be because of a third variable influencing both of them, or indirect links between the two variables.
Effect size
A statistically significant result doesn’t necessarily mean that there are important real life applications or clinical outcomes for a finding.
In contrast, the effect size indicates the practical significance of your results. It’s important to report effect sizes along with your inferential statistics for a complete picture of your results. You should also report interval estimates of effect sizes if you’re writing an APA style paper .
With a Cohen’s d of 0.72, there’s medium to high practical significance to your finding that the meditation exercise improved test scores. Example: Effect size (correlational study) To determine the effect size of the correlation coefficient, you compare your Pearson’s r value to Cohen’s effect size criteria.
Decision errors
Type I and Type II errors are mistakes made in research conclusions. A Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s false.
You can aim to minimize the risk of these errors by selecting an optimal significance level and ensuring high power . However, there’s a trade-off between the two errors, so a fine balance is necessary.
Frequentist versus Bayesian statistics
Traditionally, frequentist statistics emphasizes null hypothesis significance testing and always starts with the assumption of a true null hypothesis.
However, Bayesian statistics has grown in popularity as an alternative approach in the last few decades. In this approach, you use previous research to continually update your hypotheses based on your expectations and observations.
Bayes factor compares the relative strength of evidence for the null versus the alternative hypothesis rather than making a conclusion about rejecting the null hypothesis or not.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Likert scale
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Framing effect
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hostile attribution bias
- Affect heuristic
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Descriptive Statistics | Definitions, Types, Examples
- Inferential Statistics | An Easy Introduction & Examples
- Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Akaike Information Criterion | When & How to Use It (Example)
- An Easy Introduction to Statistical Significance (With Examples)
- An Introduction to t Tests | Definitions, Formula and Examples
- ANOVA in R | A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Central Limit Theorem | Formula, Definition & Examples
- Central Tendency | Understanding the Mean, Median & Mode
- Chi-Square (Χ²) Distributions | Definition & Examples
- Chi-Square (Χ²) Table | Examples & Downloadable Table
- Chi-Square (Χ²) Tests | Types, Formula & Examples
- Chi-Square Goodness of Fit Test | Formula, Guide & Examples
- Chi-Square Test of Independence | Formula, Guide & Examples
- Coefficient of Determination (R²) | Calculation & Interpretation
- Correlation Coefficient | Types, Formulas & Examples
- Frequency Distribution | Tables, Types & Examples
- How to Calculate Standard Deviation (Guide) | Calculator & Examples
- How to Calculate Variance | Calculator, Analysis & Examples
- How to Find Degrees of Freedom | Definition & Formula
- How to Find Interquartile Range (IQR) | Calculator & Examples
- How to Find Outliers | 4 Ways with Examples & Explanation
- How to Find the Geometric Mean | Calculator & Formula
- How to Find the Mean | Definition, Examples & Calculator
- How to Find the Median | Definition, Examples & Calculator
- How to Find the Mode | Definition, Examples & Calculator
- How to Find the Range of a Data Set | Calculator & Formula
- Hypothesis Testing | A Step-by-Step Guide with Easy Examples
- Interval Data and How to Analyze It | Definitions & Examples
- Levels of Measurement | Nominal, Ordinal, Interval and Ratio
- Linear Regression in R | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Missing Data | Types, Explanation, & Imputation
- Multiple Linear Regression | A Quick Guide (Examples)
- Nominal Data | Definition, Examples, Data Collection & Analysis
- Normal Distribution | Examples, Formulas, & Uses
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses | Definitions & Examples
- One-way ANOVA | When and How to Use It (With Examples)
- Ordinal Data | Definition, Examples, Data Collection & Analysis
- Parameter vs Statistic | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) | Guide & Examples
- Poisson Distributions | Definition, Formula & Examples
- Probability Distribution | Formula, Types, & Examples
- Quartiles & Quantiles | Calculation, Definition & Interpretation
- Ratio Scales | Definition, Examples, & Data Analysis
- Simple Linear Regression | An Easy Introduction & Examples
- Skewness | Definition, Examples & Formula
- Statistical Power and Why It Matters | A Simple Introduction
- Student's t Table (Free Download) | Guide & Examples
- T-distribution: What it is and how to use it
- Test statistics | Definition, Interpretation, and Examples
- The Standard Normal Distribution | Calculator, Examples & Uses
- Two-Way ANOVA | Examples & When To Use It
- Type I & Type II Errors | Differences, Examples, Visualizations
- Understanding Confidence Intervals | Easy Examples & Formulas
- Understanding P values | Definition and Examples
- Variability | Calculating Range, IQR, Variance, Standard Deviation
- What is Effect Size and Why Does It Matter? (Examples)
- What Is Kurtosis? | Definition, Examples & Formula
- What Is Standard Error? | How to Calculate (Guide with Examples)
What is your plagiarism score?
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Quantitative Research
What is quantitative research.
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people’s attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
“Quantification clarifies issues which qualitative analysis leaves fuzzy. It is more readily contestable and likely to be contested. It sharpens scholarly discussion, sparks off rival hypotheses, and contributes to the dynamics of the research process.” — Angus Maddison, Notable scholar of quantitative macro-economic history
- Transcript loading…
See how quantitative research helps reveal cold, hard facts about users which you can interpret and use to improve your designs.
Use Quantitative Research to Find Mathematical Facts about Users
Quantitative research is a subset of user experience (UX) research . Unlike its softer, more individual-oriented “counterpart”, qualitative research , quantitative research means you collect statistical/numerical data to draw generalized conclusions about users’ attitudes and behaviors . Compare and contrast quantitative with qualitative research, below:
Quantitative research is often best done from early on in projects since it helps teams to optimally direct product development and avoid costly design mistakes later. As you typically get user data from a distance—i.e., without close physical contact with users—also applying qualitative research will help you investigate why users think and feel the ways they do. Indeed, in an iterative design process quantitative research helps you test the assumptions you and your design team develop from your qualitative research. Regardless of the method you use, with proper care you can gather objective and unbiased data – information which you can complement with qualitative approaches to build a fuller understanding of your target users. From there, you can work towards firmer conclusions and drive your design process towards a more realistic picture of how target users will ultimately receive your product.

Quantitative analysis helps you test your assumptions and establish clearer views of your users in their various contexts.
Quantitative Research Methods You Can Use to Guide Optimal Designs
There are many quantitative research methods, and they help uncover different types of information on users. Some methods, such as A/B testing, are typically done on finished products, while others such as surveys could be done throughout a project’s design process. Here are some of the most helpful methods:
A/B testing – You test two or more versions of your design on users to find the most effective. Each variation differs by just one feature and may or may not affect how users respond. A/B testing is especially valuable for testing assumptions you’ve drawn from qualitative research. The only potential concerns here are scale—in that you’ll typically need to conduct it on thousands of users—and arguably more complexity in terms of considering the statistical significance involved.
Analytics – With tools such as Google Analytics, you measure metrics (e.g., page views, click-through rates) to build a picture (e.g., “How many users take how long to complete a task?”).
Desirability Studies – You measure an aspect of your product (e.g., aesthetic appeal) by typically showing it to participants and asking them to select from a menu of descriptive words. Their responses can reveal powerful insights (e.g., 78% associate the product/brand with “fashionable”).
Surveys and Questionnaires – When you ask for many users’ opinions, you will gain massive amounts of information. Keep in mind that you’ll have data about what users say they do, as opposed to insights into what they do . You can get more reliable results if you incentivize your participants well and use the right format.
Tree Testing – You remove the user interface so users must navigate the site and complete tasks using links alone. This helps you see if an issue is related to the user interface or information architecture.
Another powerful benefit of conducting quantitative research is that you can keep your stakeholders’ support with hard facts and statistics about your design’s performance—which can show what works well and what needs improvement—and prove a good return on investment. You can also produce reports to check statistics against different versions of your product and your competitors’ products.
Most quantitative research methods are relatively cheap. Since no single research method can help you answer all your questions, it’s vital to judge which method suits your project at the time/stage. Remember, it’s best to spend appropriately on a combination of quantitative and qualitative research from early on in development. Design improvements can be costly, and so you can estimate the value of implementing changes when you get the statistics to suggest that these changes will improve usability. Overall, you want to gather measurements objectively, where your personality, presence and theories won’t create bias.
Learn More about Quantitative Research
Take our User Research course to see how to get the most from quantitative research.
See how quantitative research methods fit into your design research landscape .
This insightful piece shows the value of pairing quantitative with qualitative research .
Find helpful tips on combining quantitative research methods in mixed methods research .
Questions related to Quantitative Research
Qualitative and quantitative research differ primarily in the data they produce. Quantitative research yields numerical data to test hypotheses and quantify patterns. It's precise and generalizable. Qualitative research, on the other hand, generates non-numerical data and explores meanings, interpretations, and deeper insights. Watch our video featuring Professor Alan Dix on different types of research methods.
This video elucidates the nuances and applications of both research types in the design field.
In quantitative research, determining a good sample size is crucial for the reliability of the results. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, emphasizes the importance of statistical significance with an example in our video.
He illustrates that even with varying results between design choices, we need to discern whether the differences are statistically significant or products of chance. This ensures the validity of the results, allowing for more accurate interpretations. Statistical tools like chi-square tests can aid in analyzing the results effectively. To delve deeper into these concepts, take William Hudson’s Data-Driven Design: Quantitative UX Research Course .
Quantitative research is crucial as it provides precise, numerical data that allows for high levels of statistical inference. Our video from William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, highlights the importance of analytics in examining existing solutions.
Quantitative methods, like analytics and A/B testing, are pivotal for identifying areas for improvement, understanding user behaviors, and optimizing user experiences based on solid, empirical evidence. This empirical nature ensures that the insights derived are reliable, allowing for practical improvements and innovations. Perhaps most importantly, numerical data is useful to secure stakeholder buy-in and defend design decisions and proposals. Explore this approach in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX Research course and learn from William Hudson’s detailed explanations of when and why to use analytics in the research process.
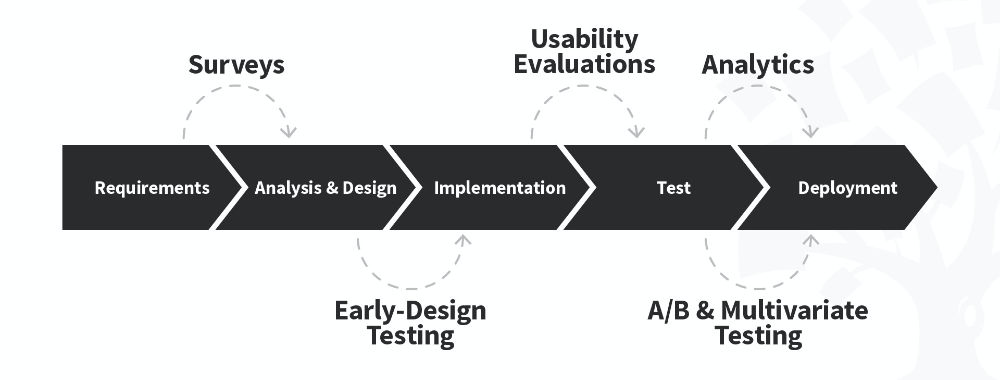
After establishing initial requirements, statistical data is crucial for informed decisions through quantitative research. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, sheds light on the role of quantitative research throughout a typical project lifecycle in this video:
During the analysis and design phases, quantitative research helps validate user requirements and understand user behaviors. Surveys and analytics are standard tools, offering insights into user preferences and design efficacy. Quantitative research can also be used in early design testing, allowing for optimal design modifications based on user interactions and feedback, and it’s fundamental for A/B and multivariate testing once live solutions are available.
To write a compelling quantitative research question:
Create clear, concise, and unambiguous questions that address one aspect at a time.
Use common, short terms and provide explanations for unusual words.
Avoid leading, compound, and overlapping queries and ensure that questions are not vague or broad.
According to our video by William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, quality and respondent understanding are vital in forming good questions.
He emphasizes the importance of addressing specific aspects and avoiding intimidating and confusing elements, such as extensive question grids or ranking questions, to ensure participant engagement and accurate responses. For more insights, see the article Writing Good Questions for Surveys .
Survey research is typically quantitative, collecting numerical data and statistical analysis to make generalizable conclusions. However, it can also have qualitative elements, mainly when it includes open-ended questions, allowing for expressive responses. Our video featuring the CEO of Syntagm, William Hudson, provides in-depth insights into when and how to effectively utilize surveys in the product or service lifecycle, focusing on user satisfaction and potential improvements.
He emphasizes the importance of surveys in triangulating data to back up qualitative research findings, ensuring we have a complete understanding of the user's requirements and preferences.
Descriptive research focuses on describing the subject being studied and getting answers to questions like what, where, when, and who of the research question. However, it doesn’t include the answers to the underlying reasons, or the “why” behind the answers obtained from the research. We can use both f qualitative and quantitative methods to conduct descriptive research. Descriptive research does not describe the methods, but rather the data gathered through the research (regardless of the methods used).
When we use quantitative research and gather numerical data, we can use statistical analysis to understand relationships between different variables. Here’s William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm with more on correlation and how we can apply tests such as Pearson’s r and Spearman Rank Coefficient to our data.
This helps interpret phenomena such as user experience by analyzing session lengths and conversion values, revealing whether variables like time spent on a page affect checkout values, for example.
Random Sampling: Each individual in the population has an equitable opportunity to be chosen, which minimizes biases and simplifies analysis.
Systematic Sampling: Selecting every k-th item from a list after a random start. It's simpler and faster than random sampling when dealing with large populations.
Stratified Sampling: Segregate the population into subgroups or strata according to comparable characteristics. Then, samples are taken randomly from each stratum.
Cluster Sampling: Divide the population into clusters and choose a random sample.
Multistage Sampling: Various sampling techniques are used at different stages to collect detailed information from diverse populations.
Convenience Sampling: The researcher selects the sample based on availability and willingness to participate, which may only represent part of the population.
Quota Sampling: Segment the population into subgroups, and samples are non-randomly selected to fulfill a predetermined quota from each subset.
These are just a few techniques, and choosing the right one depends on your research question, discipline, resource availability, and the level of accuracy required. In quantitative research, there isn't a one-size-fits-all sampling technique; choosing a method that aligns with your research goals and population is critical. However, a well-planned strategy is essential to avoid wasting resources and time, as highlighted in our video featuring William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm.
He emphasizes the importance of recruiting participants meticulously, ensuring their engagement and the quality of their responses. Accurate and thoughtful participant responses are crucial for obtaining reliable results. William also sheds light on dealing with failing participants and scrutinizing response quality to refine the outcomes.
The 4 types of quantitative research are Descriptive, Correlational, Causal-Comparative/Quasi-Experimental, and Experimental Research. Descriptive research aims to depict ‘what exists’ clearly and precisely. Correlational research examines relationships between variables. Causal-comparative research investigates the cause-effect relationship between variables. Experimental research explores causal relationships by manipulating independent variables. To gain deeper insights into quantitative research methods in UX, consider enrolling in our Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX course.
The strength of quantitative research is its ability to provide precise numerical data for analyzing target variables.This allows for generalized conclusions and predictions about future occurrences, proving invaluable in various fields, including user experience. William Hudson, CEO of Syntagm, discusses the role of surveys, analytics, and testing in providing objective insights in our video on quantitative research methods, highlighting the significance of structured methodologies in eliciting reliable results.
To master quantitative research methods, enroll in our comprehensive course, Data-Driven Design: Quantitative Research for UX .
This course empowers you to leverage quantitative data to make informed design decisions, providing a deep dive into methods like surveys and analytics. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned professional, this course at Interaction Design Foundation offers valuable insights and practical knowledge, ensuring you acquire the skills necessary to excel in user experience research. Explore our diverse topics to elevate your understanding of quantitative research methods.
Literature on Quantitative Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on Quantitative Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Quantitative Research
Take a deep dive into Quantitative Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on Quantitative Research
Best practices for qualitative user research.

- 3 years ago
Card Sorting

Understand the User’s Perspective through Research for Mobile UX

- 10 mths ago
7 Simple Ways to Get Better Results From Ethnographic Research

Question Everything

Tree Testing
Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
- 8 years ago
How to Fit Quantitative Research into the Project Lifecycle
Why and When to Use Surveys

Correlation in User Experience
First-Click Testing

What to Test

Rating Scales in UX Research: The Ultimate Guide

Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
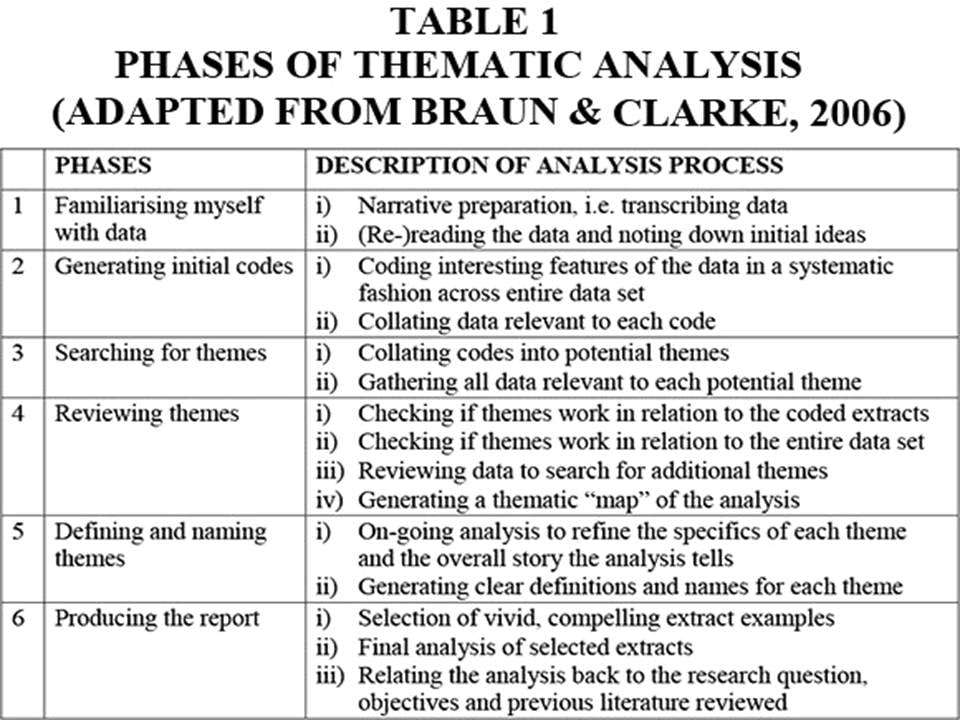
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded.
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis
What Is Quantitative Data?
- Statistics Tutorials
- Probability & Games
- Descriptive Statistics
- Inferential Statistics
- Applications Of Statistics
- Math Tutorials
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
- Ph.D., Mathematics, Purdue University
- M.S., Mathematics, Purdue University
- B.A., Mathematics, Physics, and Chemistry, Anderson University
In statistics, quantitative data is numerical and acquired through counting or measuring and contrasted with qualitative data sets, which describe attributes of objects but do not contain numbers. There are a variety of ways that quantitative data arises in statistics. Each of the following is an example of quantitative data:
- The heights of players on a football team
- The number of cars in each row of a parking lot
- The percent grade of students in a classroom
- The values of homes in a neighborhood
- The lifetime of a batch of a certain electronic component.
- The time spent waiting in line for shoppers at a supermarket.
- The number of years in school for individuals at a particular location.
- The weight of eggs taken from a chicken coop on a certain day of the week.
Additionally, quantitative data can further be broken down and analyzed according to the level of measurement involved including nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio levels of measurement or whether or not the data sets are continuous or discrete.
Levels of Measurement
In statistics, there's a variety of ways in which quantities or attributes of objects can be measured and calculated, all of which involve numbers in quantitative data sets. These datasets do not always involve numbers that can be calculated, which is determined by each datasets' level of measurement :
- Nominal: Any numerical values at the nominal level of measurement should not be treated as a quantitative variable. An example of this would be a jersey number or student ID number. It makes no sense to do any calculation upon these types of numbers.
- Ordinal: Quantitative data at the ordinal level of measurement can be ordered, however, differences between values are meaningless. An example of data at this level of measurement is any form of ranking.
- Interval: Data at the interval level can be ordered and differences can be meaningfully calculated. However, data at this level typically lacks a starting point. Moreover, ratios between data values are meaningless. For example, 90 degrees Fahrenheit is not three times as hot as when it is 30 degrees.
- Ratio: Data at the ratio level of measurement can not only be ordered and subtracted, but it may also be divided. The reason for this is that this data does have a zero value or starting point. For example, the Kelvin temperature scale does have an absolute zero .
Determining which of these levels of measurement a data set falls under will help statisticians determine whether or not the data is useful in making calculations or observing a set of data as it stands.
Discrete and Continuous
Another way that quantitative data can be classified is whether the data sets are discrete or continuous -- each of these terms has entire subfields of mathematics dedicated to studying them; it is important to distinguish between discrete and continuous data because different techniques are used.
A data set is discrete if the values can be separated from each other. The main example of this is the set of natural numbers . There is no way that a value can be a fraction or between any of the whole numbers. This set very naturally arises when we are counting objects that are only useful while whole like chairs or books.
Continuous data arises when individuals represented in the data set can take on any real number in a range of values. For example, weights may be reported not just in kilograms, but also grams, and milligrams, micrograms and so on. Our data is limited only by the precision of our measuring devices.
- The Levels of Measurement in Statistics
- Levels of Measurement Worksheet With Solutions
- Paired Data in Statistics
- Understanding Levels and Scales of Measurement in Sociology
- What Is a Histogram?
- What Is a Range in Statistics?
- Relative Frequency Histograms
- What Is Skewness in Statistics?
- A Review of Software Tools for Quantitative Data Analysis
- The Difference Between Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
- Degrees of Freedom in Statistics and Mathematics
- What Are the Maximum and Minimum?
- What Is the Plural of Data?
- What You Should Know About Econometrics
- Definition of a Percentile in Statistics and How to Calculate It
- What Is the Midhinge?
Quantitative Data Analysis 101
The lingo, methods and techniques, explained simply.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) and Kerryn Warren (PhD) | December 2020
Quantitative data analysis is one of those things that often strikes fear in students. It’s totally understandable – quantitative analysis is a complex topic, full of daunting lingo , like medians, modes, correlation and regression. Suddenly we’re all wishing we’d paid a little more attention in math class…
The good news is that while quantitative data analysis is a mammoth topic, gaining a working understanding of the basics isn’t that hard , even for those of us who avoid numbers and math . In this post, we’ll break quantitative analysis down into simple , bite-sized chunks so you can approach your research with confidence.

Overview: Quantitative Data Analysis 101
- What (exactly) is quantitative data analysis?
- When to use quantitative analysis
- How quantitative analysis works
The two “branches” of quantitative analysis
- Descriptive statistics 101
- Inferential statistics 101
- How to choose the right quantitative methods
- Recap & summary
What is quantitative data analysis?
Despite being a mouthful, quantitative data analysis simply means analysing data that is numbers-based – or data that can be easily “converted” into numbers without losing any meaning.
For example, category-based variables like gender, ethnicity, or native language could all be “converted” into numbers without losing meaning – for example, English could equal 1, French 2, etc.
This contrasts against qualitative data analysis, where the focus is on words, phrases and expressions that can’t be reduced to numbers. If you’re interested in learning about qualitative analysis, check out our post and video here .
What is quantitative analysis used for?
Quantitative analysis is generally used for three purposes.
- Firstly, it’s used to measure differences between groups . For example, the popularity of different clothing colours or brands.
- Secondly, it’s used to assess relationships between variables . For example, the relationship between weather temperature and voter turnout.
- And third, it’s used to test hypotheses in a scientifically rigorous way. For example, a hypothesis about the impact of a certain vaccine.
Again, this contrasts with qualitative analysis , which can be used to analyse people’s perceptions and feelings about an event or situation. In other words, things that can’t be reduced to numbers.
How does quantitative analysis work?
Well, since quantitative data analysis is all about analysing numbers , it’s no surprise that it involves statistics . Statistical analysis methods form the engine that powers quantitative analysis, and these methods can vary from pretty basic calculations (for example, averages and medians) to more sophisticated analyses (for example, correlations and regressions).
Sounds like gibberish? Don’t worry. We’ll explain all of that in this post. Importantly, you don’t need to be a statistician or math wiz to pull off a good quantitative analysis. We’ll break down all the technical mumbo jumbo in this post.

Need a helping hand?
As I mentioned, quantitative analysis is powered by statistical analysis methods . There are two main “branches” of statistical methods that are used – descriptive statistics and inferential statistics . In your research, you might only use descriptive statistics, or you might use a mix of both , depending on what you’re trying to figure out. In other words, depending on your research questions, aims and objectives . I’ll explain how to choose your methods later.
So, what are descriptive and inferential statistics?
Well, before I can explain that, we need to take a quick detour to explain some lingo. To understand the difference between these two branches of statistics, you need to understand two important words. These words are population and sample .
First up, population . In statistics, the population is the entire group of people (or animals or organisations or whatever) that you’re interested in researching. For example, if you were interested in researching Tesla owners in the US, then the population would be all Tesla owners in the US.
However, it’s extremely unlikely that you’re going to be able to interview or survey every single Tesla owner in the US. Realistically, you’ll likely only get access to a few hundred, or maybe a few thousand owners using an online survey. This smaller group of accessible people whose data you actually collect is called your sample .
So, to recap – the population is the entire group of people you’re interested in, and the sample is the subset of the population that you can actually get access to. In other words, the population is the full chocolate cake , whereas the sample is a slice of that cake.
So, why is this sample-population thing important?
Well, descriptive statistics focus on describing the sample , while inferential statistics aim to make predictions about the population, based on the findings within the sample. In other words, we use one group of statistical methods – descriptive statistics – to investigate the slice of cake, and another group of methods – inferential statistics – to draw conclusions about the entire cake. There I go with the cake analogy again…
With that out the way, let’s take a closer look at each of these branches in more detail.
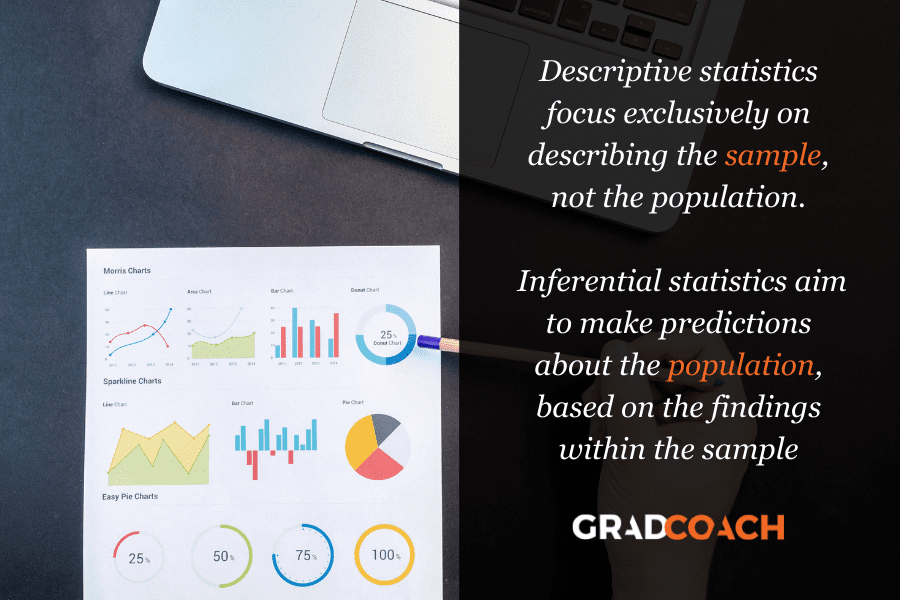
Branch 1: Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics serve a simple but critically important role in your research – to describe your data set – hence the name. In other words, they help you understand the details of your sample . Unlike inferential statistics (which we’ll get to soon), descriptive statistics don’t aim to make inferences or predictions about the entire population – they’re purely interested in the details of your specific sample .
When you’re writing up your analysis, descriptive statistics are the first set of stats you’ll cover, before moving on to inferential statistics. But, that said, depending on your research objectives and research questions , they may be the only type of statistics you use. We’ll explore that a little later.
So, what kind of statistics are usually covered in this section?
Some common statistical tests used in this branch include the following:
- Mean – this is simply the mathematical average of a range of numbers.
- Median – this is the midpoint in a range of numbers when the numbers are arranged in numerical order. If the data set makes up an odd number, then the median is the number right in the middle of the set. If the data set makes up an even number, then the median is the midpoint between the two middle numbers.
- Mode – this is simply the most commonly occurring number in the data set.
- In cases where most of the numbers are quite close to the average, the standard deviation will be relatively low.
- Conversely, in cases where the numbers are scattered all over the place, the standard deviation will be relatively high.
- Skewness . As the name suggests, skewness indicates how symmetrical a range of numbers is. In other words, do they tend to cluster into a smooth bell curve shape in the middle of the graph, or do they skew to the left or right?
Feeling a bit confused? Let’s look at a practical example using a small data set.
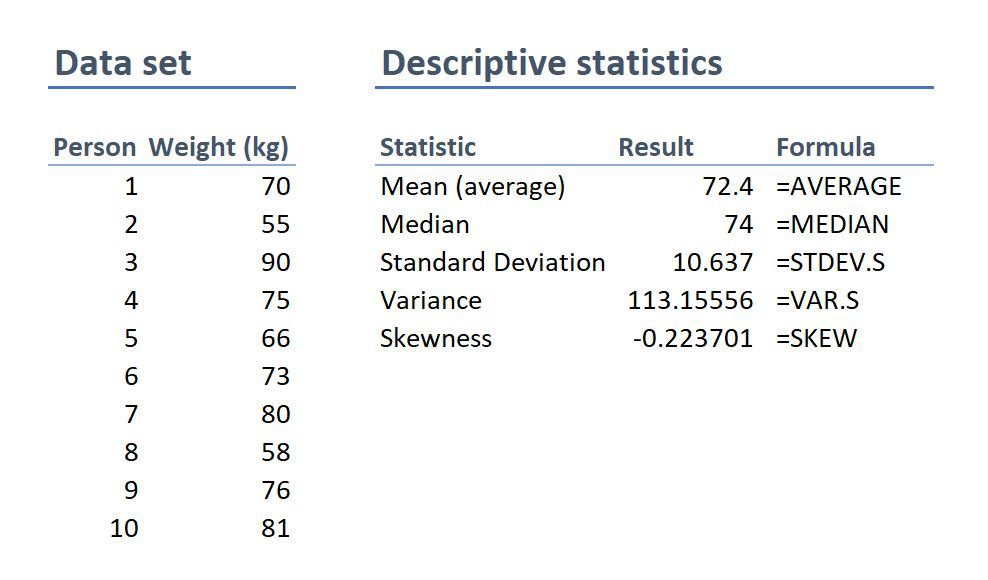
On the left-hand side is the data set. This details the bodyweight of a sample of 10 people. On the right-hand side, we have the descriptive statistics. Let’s take a look at each of them.
First, we can see that the mean weight is 72.4 kilograms. In other words, the average weight across the sample is 72.4 kilograms. Straightforward.
Next, we can see that the median is very similar to the mean (the average). This suggests that this data set has a reasonably symmetrical distribution (in other words, a relatively smooth, centred distribution of weights, clustered towards the centre).
In terms of the mode , there is no mode in this data set. This is because each number is present only once and so there cannot be a “most common number”. If there were two people who were both 65 kilograms, for example, then the mode would be 65.
Next up is the standard deviation . 10.6 indicates that there’s quite a wide spread of numbers. We can see this quite easily by looking at the numbers themselves, which range from 55 to 90, which is quite a stretch from the mean of 72.4.
And lastly, the skewness of -0.2 tells us that the data is very slightly negatively skewed. This makes sense since the mean and the median are slightly different.
As you can see, these descriptive statistics give us some useful insight into the data set. Of course, this is a very small data set (only 10 records), so we can’t read into these statistics too much. Also, keep in mind that this is not a list of all possible descriptive statistics – just the most common ones.
But why do all of these numbers matter?
While these descriptive statistics are all fairly basic, they’re important for a few reasons:
- Firstly, they help you get both a macro and micro-level view of your data. In other words, they help you understand both the big picture and the finer details.
- Secondly, they help you spot potential errors in the data – for example, if an average is way higher than you’d expect, or responses to a question are highly varied, this can act as a warning sign that you need to double-check the data.
- And lastly, these descriptive statistics help inform which inferential statistical techniques you can use, as those techniques depend on the skewness (in other words, the symmetry and normality) of the data.
Simply put, descriptive statistics are really important , even though the statistical techniques used are fairly basic. All too often at Grad Coach, we see students skimming over the descriptives in their eagerness to get to the more exciting inferential methods, and then landing up with some very flawed results.
Don’t be a sucker – give your descriptive statistics the love and attention they deserve!
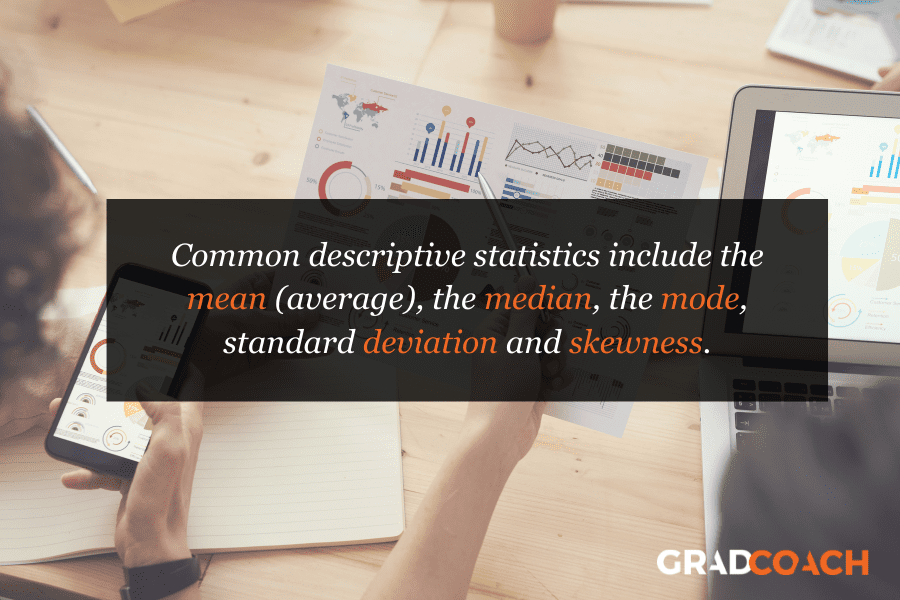
Branch 2: Inferential Statistics
As I mentioned, while descriptive statistics are all about the details of your specific data set – your sample – inferential statistics aim to make inferences about the population . In other words, you’ll use inferential statistics to make predictions about what you’d expect to find in the full population.
What kind of predictions, you ask? Well, there are two common types of predictions that researchers try to make using inferential stats:
- Firstly, predictions about differences between groups – for example, height differences between children grouped by their favourite meal or gender.
- And secondly, relationships between variables – for example, the relationship between body weight and the number of hours a week a person does yoga.
In other words, inferential statistics (when done correctly), allow you to connect the dots and make predictions about what you expect to see in the real world population, based on what you observe in your sample data. For this reason, inferential statistics are used for hypothesis testing – in other words, to test hypotheses that predict changes or differences.

Of course, when you’re working with inferential statistics, the composition of your sample is really important. In other words, if your sample doesn’t accurately represent the population you’re researching, then your findings won’t necessarily be very useful.
For example, if your population of interest is a mix of 50% male and 50% female , but your sample is 80% male , you can’t make inferences about the population based on your sample, since it’s not representative. This area of statistics is called sampling, but we won’t go down that rabbit hole here (it’s a deep one!) – we’ll save that for another post .
What statistics are usually used in this branch?
There are many, many different statistical analysis methods within the inferential branch and it’d be impossible for us to discuss them all here. So we’ll just take a look at some of the most common inferential statistical methods so that you have a solid starting point.
First up are T-Tests . T-tests compare the means (the averages) of two groups of data to assess whether they’re statistically significantly different. In other words, do they have significantly different means, standard deviations and skewness.
This type of testing is very useful for understanding just how similar or different two groups of data are. For example, you might want to compare the mean blood pressure between two groups of people – one that has taken a new medication and one that hasn’t – to assess whether they are significantly different.
Kicking things up a level, we have ANOVA, which stands for “analysis of variance”. This test is similar to a T-test in that it compares the means of various groups, but ANOVA allows you to analyse multiple groups , not just two groups So it’s basically a t-test on steroids…
Next, we have correlation analysis . This type of analysis assesses the relationship between two variables. In other words, if one variable increases, does the other variable also increase, decrease or stay the same. For example, if the average temperature goes up, do average ice creams sales increase too? We’d expect some sort of relationship between these two variables intuitively , but correlation analysis allows us to measure that relationship scientifically .
Lastly, we have regression analysis – this is quite similar to correlation in that it assesses the relationship between variables, but it goes a step further to understand cause and effect between variables, not just whether they move together. In other words, does the one variable actually cause the other one to move, or do they just happen to move together naturally thanks to another force? Just because two variables correlate doesn’t necessarily mean that one causes the other.
Stats overload…
I hear you. To make this all a little more tangible, let’s take a look at an example of a correlation in action.
Here’s a scatter plot demonstrating the correlation (relationship) between weight and height. Intuitively, we’d expect there to be some relationship between these two variables, which is what we see in this scatter plot. In other words, the results tend to cluster together in a diagonal line from bottom left to top right.
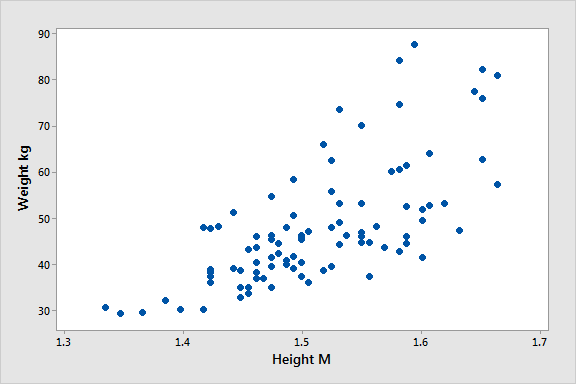
As I mentioned, these are are just a handful of inferential techniques – there are many, many more. Importantly, each statistical method has its own assumptions and limitations.
For example, some methods only work with normally distributed (parametric) data, while other methods are designed specifically for non-parametric data. And that’s exactly why descriptive statistics are so important – they’re the first step to knowing which inferential techniques you can and can’t use.

How to choose the right analysis method
To choose the right statistical methods, you need to think about two important factors :
- The type of quantitative data you have (specifically, level of measurement and the shape of the data). And,
- Your research questions and hypotheses
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
Factor 1 – Data type
The first thing you need to consider is the type of data you’ve collected (or the type of data you will collect). By data types, I’m referring to the four levels of measurement – namely, nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. If you’re not familiar with this lingo, check out the video below.
Why does this matter?
Well, because different statistical methods and techniques require different types of data. This is one of the “assumptions” I mentioned earlier – every method has its assumptions regarding the type of data.
For example, some techniques work with categorical data (for example, yes/no type questions, or gender or ethnicity), while others work with continuous numerical data (for example, age, weight or income) – and, of course, some work with multiple data types.
If you try to use a statistical method that doesn’t support the data type you have, your results will be largely meaningless . So, make sure that you have a clear understanding of what types of data you’ve collected (or will collect). Once you have this, you can then check which statistical methods would support your data types here .
If you haven’t collected your data yet, you can work in reverse and look at which statistical method would give you the most useful insights, and then design your data collection strategy to collect the correct data types.
Another important factor to consider is the shape of your data . Specifically, does it have a normal distribution (in other words, is it a bell-shaped curve, centred in the middle) or is it very skewed to the left or the right? Again, different statistical techniques work for different shapes of data – some are designed for symmetrical data while others are designed for skewed data.
This is another reminder of why descriptive statistics are so important – they tell you all about the shape of your data.
Factor 2: Your research questions
The next thing you need to consider is your specific research questions, as well as your hypotheses (if you have some). The nature of your research questions and research hypotheses will heavily influence which statistical methods and techniques you should use.
If you’re just interested in understanding the attributes of your sample (as opposed to the entire population), then descriptive statistics are probably all you need. For example, if you just want to assess the means (averages) and medians (centre points) of variables in a group of people.
On the other hand, if you aim to understand differences between groups or relationships between variables and to infer or predict outcomes in the population, then you’ll likely need both descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
So, it’s really important to get very clear about your research aims and research questions, as well your hypotheses – before you start looking at which statistical techniques to use.
Never shoehorn a specific statistical technique into your research just because you like it or have some experience with it. Your choice of methods must align with all the factors we’ve covered here.
Time to recap…
You’re still with me? That’s impressive. We’ve covered a lot of ground here, so let’s recap on the key points:
- Quantitative data analysis is all about analysing number-based data (which includes categorical and numerical data) using various statistical techniques.
- The two main branches of statistics are descriptive statistics and inferential statistics . Descriptives describe your sample, whereas inferentials make predictions about what you’ll find in the population.
- Common descriptive statistical methods include mean (average), median , standard deviation and skewness .
- Common inferential statistical methods include t-tests , ANOVA , correlation and regression analysis.
- To choose the right statistical methods and techniques, you need to consider the type of data you’re working with , as well as your research questions and hypotheses.

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

74 Comments
Hi, I have read your article. Such a brilliant post you have created.
Thank you for the feedback. Good luck with your quantitative analysis.
Thank you so much.
Thank you so much. I learnt much well. I love your summaries of the concepts. I had love you to explain how to input data using SPSS
Amazing and simple way of breaking down quantitative methods.
This is beautiful….especially for non-statisticians. I have skimmed through but I wish to read again. and please include me in other articles of the same nature when you do post. I am interested. I am sure, I could easily learn from you and get off the fear that I have had in the past. Thank you sincerely.
Send me every new information you might have.
i need every new information
Thank you for the blog. It is quite informative. Dr Peter Nemaenzhe PhD
It is wonderful. l’ve understood some of the concepts in a more compréhensive manner
Your article is so good! However, I am still a bit lost. I am doing a secondary research on Gun control in the US and increase in crime rates and I am not sure which analysis method I should use?
Based on the given learning points, this is inferential analysis, thus, use ‘t-tests, ANOVA, correlation and regression analysis’
Well explained notes. Am an MPH student and currently working on my thesis proposal, this has really helped me understand some of the things I didn’t know.
I like your page..helpful
wonderful i got my concept crystal clear. thankyou!!
This is really helpful , thank you
Thank you so much this helped
Wonderfully explained
thank u so much, it was so informative
THANKYOU, this was very informative and very helpful
This is great GRADACOACH I am not a statistician but I require more of this in my thesis
Include me in your posts.
This is so great and fully useful. I would like to thank you again and again.
Glad to read this article. I’ve read lot of articles but this article is clear on all concepts. Thanks for sharing.
Thank you so much. This is a very good foundation and intro into quantitative data analysis. Appreciate!
You have a very impressive, simple but concise explanation of data analysis for Quantitative Research here. This is a God-send link for me to appreciate research more. Thank you so much!
Avery good presentation followed by the write up. yes you simplified statistics to make sense even to a layman like me. Thank so much keep it up. The presenter did ell too. i would like more of this for Qualitative and exhaust more of the test example like the Anova.
This is a very helpful article, couldn’t have been clearer. Thank you.
Awesome and phenomenal information.Well done
The video with the accompanying article is super helpful to demystify this topic. Very well done. Thank you so much.
thank you so much, your presentation helped me a lot
I don’t know how should I express that ur article is saviour for me 🥺😍
It is well defined information and thanks for sharing. It helps me a lot in understanding the statistical data.
I gain a lot and thanks for sharing brilliant ideas, so wish to be linked on your email update.
Very helpful and clear .Thank you Gradcoach.
Thank for sharing this article, well organized and information presented are very clear.
VERY INTERESTING AND SUPPORTIVE TO NEW RESEARCHERS LIKE ME. AT LEAST SOME BASICS ABOUT QUANTITATIVE.
An outstanding, well explained and helpful article. This will help me so much with my data analysis for my research project. Thank you!
wow this has just simplified everything i was scared of how i am gonna analyse my data but thanks to you i will be able to do so
simple and constant direction to research. thanks
This is helpful
Great writing!! Comprehensive and very helpful.
Do you provide any assistance for other steps of research methodology like making research problem testing hypothesis report and thesis writing?
Thank you so much for such useful article!
Amazing article. So nicely explained. Wow
Very insightfull. Thanks
I am doing a quality improvement project to determine if the implementation of a protocol will change prescribing habits. Would this be a t-test?
The is a very helpful blog, however, I’m still not sure how to analyze my data collected. I’m doing a research on “Free Education at the University of Guyana”
tnx. fruitful blog!
So I am writing exams and would like to know how do establish which method of data analysis to use from the below research questions: I am a bit lost as to how I determine the data analysis method from the research questions.
Do female employees report higher job satisfaction than male employees with similar job descriptions across the South African telecommunications sector? – I though that maybe Chi Square could be used here. – Is there a gender difference in talented employees’ actual turnover decisions across the South African telecommunications sector? T-tests or Correlation in this one. – Is there a gender difference in the cost of actual turnover decisions across the South African telecommunications sector? T-tests or Correlation in this one. – What practical recommendations can be made to the management of South African telecommunications companies on leveraging gender to mitigate employee turnover decisions?
Your assistance will be appreciated if I could get a response as early as possible tomorrow
This was quite helpful. Thank you so much.
wow I got a lot from this article, thank you very much, keep it up
Thanks for yhe guidance. Can you send me this guidance on my email? To enable offline reading?
Thank you very much, this service is very helpful.
Every novice researcher needs to read this article as it puts things so clear and easy to follow. Its been very helpful.
Wonderful!!!! you explained everything in a way that anyone can learn. Thank you!!
I really enjoyed reading though this. Very easy to follow. Thank you
Many thanks for your useful lecture, I would be really appreciated if you could possibly share with me the PPT of presentation related to Data type?
Thank you very much for sharing, I got much from this article
This is a very informative write-up. Kindly include me in your latest posts.
Very interesting mostly for social scientists
Thank you so much, very helpfull
You’re welcome 🙂
woow, its great, its very informative and well understood because of your way of writing like teaching in front of me in simple languages.
I have been struggling to understand a lot of these concepts. Thank you for the informative piece which is written with outstanding clarity.
very informative article. Easy to understand
Beautiful read, much needed.
Always greet intro and summary. I learn so much from GradCoach
Quite informative. Simple and clear summary.
I thoroughly enjoyed reading your informative and inspiring piece. Your profound insights into this topic truly provide a better understanding of its complexity. I agree with the points you raised, especially when you delved into the specifics of the article. In my opinion, that aspect is often overlooked and deserves further attention.
Absolutely!!! Thank you
Thank you very much for this post. It made me to understand how to do my data analysis.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis
Zulfiqar ali.
Department of Anaesthesiology, Division of Neuroanaesthesiology, Sheri Kashmir Institute of Medical Sciences, Soura, Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
S Bala Bhaskar
1 Department of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care, Vijayanagar Institute of Medical Sciences, Bellary, Karnataka, India
Statistical methods involved in carrying out a study include planning, designing, collecting data, analysing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of the research findings. The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. The results and inferences are precise only if proper statistical tests are used. This article will try to acquaint the reader with the basic research tools that are utilised while conducting various studies. The article covers a brief outline of the variables, an understanding of quantitative and qualitative variables and the measures of central tendency. An idea of the sample size estimation, power analysis and the statistical errors is given. Finally, there is a summary of parametric and non-parametric tests used for data analysis.
INTRODUCTION
Statistics is a branch of science that deals with the collection, organisation, analysis of data and drawing of inferences from the samples to the whole population.[ 1 ] This requires a proper design of the study, an appropriate selection of the study sample and choice of a suitable statistical test. An adequate knowledge of statistics is necessary for proper designing of an epidemiological study or a clinical trial. Improper statistical methods may result in erroneous conclusions which may lead to unethical practice.[ 2 ]
Variable is a characteristic that varies from one individual member of population to another individual.[ 3 ] Variables such as height and weight are measured by some type of scale, convey quantitative information and are called as quantitative variables. Sex and eye colour give qualitative information and are called as qualitative variables[ 3 ] [ Figure 1 ].

Classification of variables
Quantitative variables
Quantitative or numerical data are subdivided into discrete and continuous measurements. Discrete numerical data are recorded as a whole number such as 0, 1, 2, 3,… (integer), whereas continuous data can assume any value. Observations that can be counted constitute the discrete data and observations that can be measured constitute the continuous data. Examples of discrete data are number of episodes of respiratory arrests or the number of re-intubations in an intensive care unit. Similarly, examples of continuous data are the serial serum glucose levels, partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood and the oesophageal temperature.
A hierarchical scale of increasing precision can be used for observing and recording the data which is based on categorical, ordinal, interval and ratio scales [ Figure 1 ].
Categorical or nominal variables are unordered. The data are merely classified into categories and cannot be arranged in any particular order. If only two categories exist (as in gender male and female), it is called as a dichotomous (or binary) data. The various causes of re-intubation in an intensive care unit due to upper airway obstruction, impaired clearance of secretions, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, pulmonary oedema and neurological impairment are examples of categorical variables.
Ordinal variables have a clear ordering between the variables. However, the ordered data may not have equal intervals. Examples are the American Society of Anesthesiologists status or Richmond agitation-sedation scale.
Interval variables are similar to an ordinal variable, except that the intervals between the values of the interval variable are equally spaced. A good example of an interval scale is the Fahrenheit degree scale used to measure temperature. With the Fahrenheit scale, the difference between 70° and 75° is equal to the difference between 80° and 85°: The units of measurement are equal throughout the full range of the scale.
Ratio scales are similar to interval scales, in that equal differences between scale values have equal quantitative meaning. However, ratio scales also have a true zero point, which gives them an additional property. For example, the system of centimetres is an example of a ratio scale. There is a true zero point and the value of 0 cm means a complete absence of length. The thyromental distance of 6 cm in an adult may be twice that of a child in whom it may be 3 cm.
STATISTICS: DESCRIPTIVE AND INFERENTIAL STATISTICS
Descriptive statistics[ 4 ] try to describe the relationship between variables in a sample or population. Descriptive statistics provide a summary of data in the form of mean, median and mode. Inferential statistics[ 4 ] use a random sample of data taken from a population to describe and make inferences about the whole population. It is valuable when it is not possible to examine each member of an entire population. The examples if descriptive and inferential statistics are illustrated in Table 1 .
Example of descriptive and inferential statistics

Descriptive statistics
The extent to which the observations cluster around a central location is described by the central tendency and the spread towards the extremes is described by the degree of dispersion.
Measures of central tendency
The measures of central tendency are mean, median and mode.[ 6 ] Mean (or the arithmetic average) is the sum of all the scores divided by the number of scores. Mean may be influenced profoundly by the extreme variables. For example, the average stay of organophosphorus poisoning patients in ICU may be influenced by a single patient who stays in ICU for around 5 months because of septicaemia. The extreme values are called outliers. The formula for the mean is

where x = each observation and n = number of observations. Median[ 6 ] is defined as the middle of a distribution in a ranked data (with half of the variables in the sample above and half below the median value) while mode is the most frequently occurring variable in a distribution. Range defines the spread, or variability, of a sample.[ 7 ] It is described by the minimum and maximum values of the variables. If we rank the data and after ranking, group the observations into percentiles, we can get better information of the pattern of spread of the variables. In percentiles, we rank the observations into 100 equal parts. We can then describe 25%, 50%, 75% or any other percentile amount. The median is the 50 th percentile. The interquartile range will be the observations in the middle 50% of the observations about the median (25 th -75 th percentile). Variance[ 7 ] is a measure of how spread out is the distribution. It gives an indication of how close an individual observation clusters about the mean value. The variance of a population is defined by the following formula:

where σ 2 is the population variance, X is the population mean, X i is the i th element from the population and N is the number of elements in the population. The variance of a sample is defined by slightly different formula:

where s 2 is the sample variance, x is the sample mean, x i is the i th element from the sample and n is the number of elements in the sample. The formula for the variance of a population has the value ‘ n ’ as the denominator. The expression ‘ n −1’ is known as the degrees of freedom and is one less than the number of parameters. Each observation is free to vary, except the last one which must be a defined value. The variance is measured in squared units. To make the interpretation of the data simple and to retain the basic unit of observation, the square root of variance is used. The square root of the variance is the standard deviation (SD).[ 8 ] The SD of a population is defined by the following formula:

where σ is the population SD, X is the population mean, X i is the i th element from the population and N is the number of elements in the population. The SD of a sample is defined by slightly different formula:

where s is the sample SD, x is the sample mean, x i is the i th element from the sample and n is the number of elements in the sample. An example for calculation of variation and SD is illustrated in Table 2 .
Example of mean, variance, standard deviation

Normal distribution or Gaussian distribution
Most of the biological variables usually cluster around a central value, with symmetrical positive and negative deviations about this point.[ 1 ] The standard normal distribution curve is a symmetrical bell-shaped. In a normal distribution curve, about 68% of the scores are within 1 SD of the mean. Around 95% of the scores are within 2 SDs of the mean and 99% within 3 SDs of the mean [ Figure 2 ].

Normal distribution curve
Skewed distribution
It is a distribution with an asymmetry of the variables about its mean. In a negatively skewed distribution [ Figure 3 ], the mass of the distribution is concentrated on the right of Figure 1 . In a positively skewed distribution [ Figure 3 ], the mass of the distribution is concentrated on the left of the figure leading to a longer right tail.

Curves showing negatively skewed and positively skewed distribution
Inferential statistics
In inferential statistics, data are analysed from a sample to make inferences in the larger collection of the population. The purpose is to answer or test the hypotheses. A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. Hypothesis tests are thus procedures for making rational decisions about the reality of observed effects.
Probability is the measure of the likelihood that an event will occur. Probability is quantified as a number between 0 and 1 (where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty).
In inferential statistics, the term ‘null hypothesis’ ( H 0 ‘ H-naught ,’ ‘ H-null ’) denotes that there is no relationship (difference) between the population variables in question.[ 9 ]
Alternative hypothesis ( H 1 and H a ) denotes that a statement between the variables is expected to be true.[ 9 ]
The P value (or the calculated probability) is the probability of the event occurring by chance if the null hypothesis is true. The P value is a numerical between 0 and 1 and is interpreted by researchers in deciding whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis [ Table 3 ].
P values with interpretation

If P value is less than the arbitrarily chosen value (known as α or the significance level), the null hypothesis (H0) is rejected [ Table 4 ]. However, if null hypotheses (H0) is incorrectly rejected, this is known as a Type I error.[ 11 ] Further details regarding alpha error, beta error and sample size calculation and factors influencing them are dealt with in another section of this issue by Das S et al .[ 12 ]
Illustration for null hypothesis

PARAMETRIC AND NON-PARAMETRIC TESTS
Numerical data (quantitative variables) that are normally distributed are analysed with parametric tests.[ 13 ]
Two most basic prerequisites for parametric statistical analysis are:
- The assumption of normality which specifies that the means of the sample group are normally distributed
- The assumption of equal variance which specifies that the variances of the samples and of their corresponding population are equal.
However, if the distribution of the sample is skewed towards one side or the distribution is unknown due to the small sample size, non-parametric[ 14 ] statistical techniques are used. Non-parametric tests are used to analyse ordinal and categorical data.
Parametric tests
The parametric tests assume that the data are on a quantitative (numerical) scale, with a normal distribution of the underlying population. The samples have the same variance (homogeneity of variances). The samples are randomly drawn from the population, and the observations within a group are independent of each other. The commonly used parametric tests are the Student's t -test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and repeated measures ANOVA.
Student's t -test
Student's t -test is used to test the null hypothesis that there is no difference between the means of the two groups. It is used in three circumstances:

where X = sample mean, u = population mean and SE = standard error of mean

where X 1 − X 2 is the difference between the means of the two groups and SE denotes the standard error of the difference.
- To test if the population means estimated by two dependent samples differ significantly (the paired t -test). A usual setting for paired t -test is when measurements are made on the same subjects before and after a treatment.
The formula for paired t -test is:

where d is the mean difference and SE denotes the standard error of this difference.
The group variances can be compared using the F -test. The F -test is the ratio of variances (var l/var 2). If F differs significantly from 1.0, then it is concluded that the group variances differ significantly.
Analysis of variance
The Student's t -test cannot be used for comparison of three or more groups. The purpose of ANOVA is to test if there is any significant difference between the means of two or more groups.
In ANOVA, we study two variances – (a) between-group variability and (b) within-group variability. The within-group variability (error variance) is the variation that cannot be accounted for in the study design. It is based on random differences present in our samples.
However, the between-group (or effect variance) is the result of our treatment. These two estimates of variances are compared using the F-test.
A simplified formula for the F statistic is:

where MS b is the mean squares between the groups and MS w is the mean squares within groups.
Repeated measures analysis of variance
As with ANOVA, repeated measures ANOVA analyses the equality of means of three or more groups. However, a repeated measure ANOVA is used when all variables of a sample are measured under different conditions or at different points in time.
As the variables are measured from a sample at different points of time, the measurement of the dependent variable is repeated. Using a standard ANOVA in this case is not appropriate because it fails to model the correlation between the repeated measures: The data violate the ANOVA assumption of independence. Hence, in the measurement of repeated dependent variables, repeated measures ANOVA should be used.
Non-parametric tests
When the assumptions of normality are not met, and the sample means are not normally, distributed parametric tests can lead to erroneous results. Non-parametric tests (distribution-free test) are used in such situation as they do not require the normality assumption.[ 15 ] Non-parametric tests may fail to detect a significant difference when compared with a parametric test. That is, they usually have less power.
As is done for the parametric tests, the test statistic is compared with known values for the sampling distribution of that statistic and the null hypothesis is accepted or rejected. The types of non-parametric analysis techniques and the corresponding parametric analysis techniques are delineated in Table 5 .
Analogue of parametric and non-parametric tests

Median test for one sample: The sign test and Wilcoxon's signed rank test
The sign test and Wilcoxon's signed rank test are used for median tests of one sample. These tests examine whether one instance of sample data is greater or smaller than the median reference value.
This test examines the hypothesis about the median θ0 of a population. It tests the null hypothesis H0 = θ0. When the observed value (Xi) is greater than the reference value (θ0), it is marked as+. If the observed value is smaller than the reference value, it is marked as − sign. If the observed value is equal to the reference value (θ0), it is eliminated from the sample.
If the null hypothesis is true, there will be an equal number of + signs and − signs.
The sign test ignores the actual values of the data and only uses + or − signs. Therefore, it is useful when it is difficult to measure the values.
Wilcoxon's signed rank test
There is a major limitation of sign test as we lose the quantitative information of the given data and merely use the + or – signs. Wilcoxon's signed rank test not only examines the observed values in comparison with θ0 but also takes into consideration the relative sizes, adding more statistical power to the test. As in the sign test, if there is an observed value that is equal to the reference value θ0, this observed value is eliminated from the sample.
Wilcoxon's rank sum test ranks all data points in order, calculates the rank sum of each sample and compares the difference in the rank sums.
Mann-Whitney test
It is used to test the null hypothesis that two samples have the same median or, alternatively, whether observations in one sample tend to be larger than observations in the other.
Mann–Whitney test compares all data (xi) belonging to the X group and all data (yi) belonging to the Y group and calculates the probability of xi being greater than yi: P (xi > yi). The null hypothesis states that P (xi > yi) = P (xi < yi) =1/2 while the alternative hypothesis states that P (xi > yi) ≠1/2.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
The two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test was designed as a generic method to test whether two random samples are drawn from the same distribution. The null hypothesis of the KS test is that both distributions are identical. The statistic of the KS test is a distance between the two empirical distributions, computed as the maximum absolute difference between their cumulative curves.
Kruskal-Wallis test
The Kruskal–Wallis test is a non-parametric test to analyse the variance.[ 14 ] It analyses if there is any difference in the median values of three or more independent samples. The data values are ranked in an increasing order, and the rank sums calculated followed by calculation of the test statistic.
Jonckheere test
In contrast to Kruskal–Wallis test, in Jonckheere test, there is an a priori ordering that gives it a more statistical power than the Kruskal–Wallis test.[ 14 ]
Friedman test
The Friedman test is a non-parametric test for testing the difference between several related samples. The Friedman test is an alternative for repeated measures ANOVAs which is used when the same parameter has been measured under different conditions on the same subjects.[ 13 ]
Tests to analyse the categorical data
Chi-square test, Fischer's exact test and McNemar's test are used to analyse the categorical or nominal variables. The Chi-square test compares the frequencies and tests whether the observed data differ significantly from that of the expected data if there were no differences between groups (i.e., the null hypothesis). It is calculated by the sum of the squared difference between observed ( O ) and the expected ( E ) data (or the deviation, d ) divided by the expected data by the following formula:

A Yates correction factor is used when the sample size is small. Fischer's exact test is used to determine if there are non-random associations between two categorical variables. It does not assume random sampling, and instead of referring a calculated statistic to a sampling distribution, it calculates an exact probability. McNemar's test is used for paired nominal data. It is applied to 2 × 2 table with paired-dependent samples. It is used to determine whether the row and column frequencies are equal (that is, whether there is ‘marginal homogeneity’). The null hypothesis is that the paired proportions are equal. The Mantel-Haenszel Chi-square test is a multivariate test as it analyses multiple grouping variables. It stratifies according to the nominated confounding variables and identifies any that affects the primary outcome variable. If the outcome variable is dichotomous, then logistic regression is used.
SOFTWARES AVAILABLE FOR STATISTICS, SAMPLE SIZE CALCULATION AND POWER ANALYSIS
Numerous statistical software systems are available currently. The commonly used software systems are Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS – manufactured by IBM corporation), Statistical Analysis System ((SAS – developed by SAS Institute North Carolina, United States of America), R (designed by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman from R core team), Minitab (developed by Minitab Inc), Stata (developed by StataCorp) and the MS Excel (developed by Microsoft).
There are a number of web resources which are related to statistical power analyses. A few are:
- StatPages.net – provides links to a number of online power calculators
- G-Power – provides a downloadable power analysis program that runs under DOS
- Power analysis for ANOVA designs an interactive site that calculates power or sample size needed to attain a given power for one effect in a factorial ANOVA design
- SPSS makes a program called SamplePower. It gives an output of a complete report on the computer screen which can be cut and paste into another document.
It is important that a researcher knows the concepts of the basic statistical methods used for conduct of a research study. This will help to conduct an appropriately well-designed study leading to valid and reliable results. Inappropriate use of statistical techniques may lead to faulty conclusions, inducing errors and undermining the significance of the article. Bad statistics may lead to bad research, and bad research may lead to unethical practice. Hence, an adequate knowledge of statistics and the appropriate use of statistical tests are important. An appropriate knowledge about the basic statistical methods will go a long way in improving the research designs and producing quality medical research which can be utilised for formulating the evidence-based guidelines.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

Effective Use of Statistics in Research – Methods and Tools for Data Analysis
Remember that impending feeling you get when you are asked to analyze your data! Now that you have all the required raw data, you need to statistically prove your hypothesis. Representing your numerical data as part of statistics in research will also help in breaking the stereotype of being a biology student who can’t do math.
Statistical methods are essential for scientific research. In fact, statistical methods dominate the scientific research as they include planning, designing, collecting data, analyzing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of research findings. Furthermore, the results acquired from research project are meaningless raw data unless analyzed with statistical tools. Therefore, determining statistics in research is of utmost necessity to justify research findings. In this article, we will discuss how using statistical methods for biology could help draw meaningful conclusion to analyze biological studies.
Table of Contents
Role of Statistics in Biological Research
Statistics is a branch of science that deals with collection, organization and analysis of data from the sample to the whole population. Moreover, it aids in designing a study more meticulously and also give a logical reasoning in concluding the hypothesis. Furthermore, biology study focuses on study of living organisms and their complex living pathways, which are very dynamic and cannot be explained with logical reasoning. However, statistics is more complex a field of study that defines and explains study patterns based on the sample sizes used. To be precise, statistics provides a trend in the conducted study.
Biological researchers often disregard the use of statistics in their research planning, and mainly use statistical tools at the end of their experiment. Therefore, giving rise to a complicated set of results which are not easily analyzed from statistical tools in research. Statistics in research can help a researcher approach the study in a stepwise manner, wherein the statistical analysis in research follows –
1. Establishing a Sample Size
Usually, a biological experiment starts with choosing samples and selecting the right number of repetitive experiments. Statistics in research deals with basics in statistics that provides statistical randomness and law of using large samples. Statistics teaches how choosing a sample size from a random large pool of sample helps extrapolate statistical findings and reduce experimental bias and errors.
2. Testing of Hypothesis
When conducting a statistical study with large sample pool, biological researchers must make sure that a conclusion is statistically significant. To achieve this, a researcher must create a hypothesis before examining the distribution of data. Furthermore, statistics in research helps interpret the data clustered near the mean of distributed data or spread across the distribution. These trends help analyze the sample and signify the hypothesis.
3. Data Interpretation Through Analysis
When dealing with large data, statistics in research assist in data analysis. This helps researchers to draw an effective conclusion from their experiment and observations. Concluding the study manually or from visual observation may give erroneous results; therefore, thorough statistical analysis will take into consideration all the other statistical measures and variance in the sample to provide a detailed interpretation of the data. Therefore, researchers produce a detailed and important data to support the conclusion.
Types of Statistical Research Methods That Aid in Data Analysis
Statistical analysis is the process of analyzing samples of data into patterns or trends that help researchers anticipate situations and make appropriate research conclusions. Based on the type of data, statistical analyses are of the following type:
1. Descriptive Analysis
The descriptive statistical analysis allows organizing and summarizing the large data into graphs and tables . Descriptive analysis involves various processes such as tabulation, measure of central tendency, measure of dispersion or variance, skewness measurements etc.
2. Inferential Analysis
The inferential statistical analysis allows to extrapolate the data acquired from a small sample size to the complete population. This analysis helps draw conclusions and make decisions about the whole population on the basis of sample data. It is a highly recommended statistical method for research projects that work with smaller sample size and meaning to extrapolate conclusion for large population.
3. Predictive Analysis
Predictive analysis is used to make a prediction of future events. This analysis is approached by marketing companies, insurance organizations, online service providers, data-driven marketing, and financial corporations.
4. Prescriptive Analysis
Prescriptive analysis examines data to find out what can be done next. It is widely used in business analysis for finding out the best possible outcome for a situation. It is nearly related to descriptive and predictive analysis. However, prescriptive analysis deals with giving appropriate suggestions among the available preferences.
5. Exploratory Data Analysis
EDA is generally the first step of the data analysis process that is conducted before performing any other statistical analysis technique. It completely focuses on analyzing patterns in the data to recognize potential relationships. EDA is used to discover unknown associations within data, inspect missing data from collected data and obtain maximum insights.
6. Causal Analysis
Causal analysis assists in understanding and determining the reasons behind “why” things happen in a certain way, as they appear. This analysis helps identify root cause of failures or simply find the basic reason why something could happen. For example, causal analysis is used to understand what will happen to the provided variable if another variable changes.
7. Mechanistic Analysis
This is a least common type of statistical analysis. The mechanistic analysis is used in the process of big data analytics and biological science. It uses the concept of understanding individual changes in variables that cause changes in other variables correspondingly while excluding external influences.
Important Statistical Tools In Research
Researchers in the biological field find statistical analysis in research as the scariest aspect of completing research. However, statistical tools in research can help researchers understand what to do with data and how to interpret the results, making this process as easy as possible.
1. Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS)
It is a widely used software package for human behavior research. SPSS can compile descriptive statistics, as well as graphical depictions of result. Moreover, it includes the option to create scripts that automate analysis or carry out more advanced statistical processing.
2. R Foundation for Statistical Computing
This software package is used among human behavior research and other fields. R is a powerful tool and has a steep learning curve. However, it requires a certain level of coding. Furthermore, it comes with an active community that is engaged in building and enhancing the software and the associated plugins.
3. MATLAB (The Mathworks)
It is an analytical platform and a programming language. Researchers and engineers use this software and create their own code and help answer their research question. While MatLab can be a difficult tool to use for novices, it offers flexibility in terms of what the researcher needs.
4. Microsoft Excel
Not the best solution for statistical analysis in research, but MS Excel offers wide variety of tools for data visualization and simple statistics. It is easy to generate summary and customizable graphs and figures. MS Excel is the most accessible option for those wanting to start with statistics.
5. Statistical Analysis Software (SAS)
It is a statistical platform used in business, healthcare, and human behavior research alike. It can carry out advanced analyzes and produce publication-worthy figures, tables and charts .
6. GraphPad Prism
It is a premium software that is primarily used among biology researchers. But, it offers a range of variety to be used in various other fields. Similar to SPSS, GraphPad gives scripting option to automate analyses to carry out complex statistical calculations.
This software offers basic as well as advanced statistical tools for data analysis. However, similar to GraphPad and SPSS, minitab needs command over coding and can offer automated analyses.
Use of Statistical Tools In Research and Data Analysis
Statistical tools manage the large data. Many biological studies use large data to analyze the trends and patterns in studies. Therefore, using statistical tools becomes essential, as they manage the large data sets, making data processing more convenient.
Following these steps will help biological researchers to showcase the statistics in research in detail, and develop accurate hypothesis and use correct tools for it.
There are a range of statistical tools in research which can help researchers manage their research data and improve the outcome of their research by better interpretation of data. You could use statistics in research by understanding the research question, knowledge of statistics and your personal experience in coding.
Have you faced challenges while using statistics in research? How did you manage it? Did you use any of the statistical tools to help you with your research data? Do write to us or comment below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Statistics in research can help a researcher approach the study in a stepwise manner: 1. Establishing a sample size 2. Testing of hypothesis 3. Data interpretation through analysis
Statistical methods are essential for scientific research. In fact, statistical methods dominate the scientific research as they include planning, designing, collecting data, analyzing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of research findings. Furthermore, the results acquired from research project are meaningless raw data unless analyzed with statistical tools. Therefore, determining statistics in research is of utmost necessity to justify research findings.
Statistical tools in research can help researchers understand what to do with data and how to interpret the results, making this process as easy as possible. They can manage large data sets, making data processing more convenient. A great number of tools are available to carry out statistical analysis of data like SPSS, SAS (Statistical Analysis Software), and Minitab.
nice article to read
Holistic but delineating. A very good read.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional…

Planning Your Data Collection: Designing methods for effective research
Planning your research is very important to obtain desirable results. In research, the relevance of…
- Language & Grammar
Best Plagiarism Checker Tool for Researchers — Top 4 to choose from!
While common writing issues like language enhancement, punctuation errors, grammatical errors, etc. can be dealt…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats were achieved!
It’s beginning to look a lot like success! Some of the greatest opportunities to research…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Qualitative Vs. Quantitative Research — A step-wise guide to conduct research
A research study includes the collection and analysis of data. In quantitative research, the data…
2022 in a Nutshell — Reminiscing the year when opportunities were seized and feats…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

Statistics Made Easy
The Importance of Statistics in Research (With Examples)
The field of statistics is concerned with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data.
In the field of research, statistics is important for the following reasons:
Reason 1 : Statistics allows researchers to design studies such that the findings from the studies can be extrapolated to a larger population.
Reason 2 : Statistics allows researchers to perform hypothesis tests to determine if some claim about a new drug, new procedure, new manufacturing method, etc. is true.
Reason 3 : Statistics allows researchers to create confidence intervals to capture uncertainty around population estimates.
In the rest of this article, we elaborate on each of these reasons.
Reason 1: Statistics Allows Researchers to Design Studies
Researchers are often interested in answering questions about populations like:
- What is the average weight of a certain species of bird?
- What is the average height of a certain species of plant?
- What percentage of citizens in a certain city support a certain law?
One way to answer these questions is to go around and collect data on every single individual in the population of interest.
However, this is typically too costly and time-consuming which is why researchers instead take a sample of the population and use the data from the sample to draw conclusions about the population as a whole.

There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. These are known as sampling methods .
There are two classes of sampling methods:
- Probability sampling methods : Every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample.
- Non-probability sampling methods : Not every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample.
By using probability sampling methods, researchers can maximize the chances that they obtain a sample that is representative of the overall population.
This allows researchers to extrapolate the findings from the sample to the overall population.
Read more about the two classes of sampling methods here .
Reason 2: Statistics Allows Researchers to Perform Hypothesis Tests
Another way that statistics is used in research is in the form of hypothesis tests .
These are tests that researchers can use to determine if there is a statistical significance between different medical procedures or treatments.
For example, suppose a scientist believes that a new drug is able to reduce blood pressure in obese patients. To test this, he measures the blood pressure of 30 patients before and after using the new drug for one month.
He then performs a paired samples t- test using the following hypotheses:
- H 0 : μ after = μ before (the mean blood pressure is the same before and after using the drug)
- H A : μ after < μ before (the mean blood pressure is less after using the drug)
If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05), then he can reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the new drug leads to reduced blood pressure.
Note : This is just one example of a hypothesis test that is used in research. Other common tests include a one sample t-test , two sample t-test , one-way ANOVA , and two-way ANOVA .
Reason 3: Statistics Allows Researchers to Create Confidence Intervals
Another way that statistics is used in research is in the form of confidence intervals .
A confidence interval is a range of values that is likely to contain a population parameter with a certain level of confidence.
For example, suppose researchers are interested in estimating the mean weight of a certain species of turtle.
Instead of going around and weighing every single turtle in the population, researchers may instead take a simple random sample of turtles with the following information:
- Sample size n = 25
- Sample mean weight x = 300
- Sample standard deviation s = 18.5
Using the confidence interval for a mean formula , researchers may then construct the following 95% confidence interval:
95% Confidence Interval: 300 +/- 1.96*(18.5/√ 25 ) = [292.75, 307.25]
The researchers would then claim that they’re 95% confident that the true mean weight for this population of turtles is between 292.75 pounds and 307.25 pounds.
Additional Resources
The following articles explain the importance of statistics in other fields:
The Importance of Statistics in Healthcare The Importance of Statistics in Nursing The Importance of Statistics in Business The Importance of Statistics in Economics The Importance of Statistics in Education
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 26 March 2024
Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning
- Michiel Schreurs ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9449-5619 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Supinya Piampongsant 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Miguel Roncoroni ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7461-1427 1 , 2 , 3 na1 ,
- Lloyd Cool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9936-3124 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ,
- Beatriz Herrera-Malaver ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5096-9974 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Christophe Vanderaa ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7443-5427 4 ,
- Florian A. Theßeling 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Łukasz Kreft ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7620-4657 5 ,
- Alexander Botzki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6691-4233 5 ,
- Philippe Malcorps 6 ,
- Luk Daenen 6 ,
- Tom Wenseleers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1434-861X 4 &
- Kevin J. Verstrepen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3077-6219 1 , 2 , 3
Nature Communications volume 15 , Article number: 2368 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
49k Accesses
847 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Chemical engineering
- Gas chromatography
- Machine learning
- Metabolomics
- Taste receptors
The perception and appreciation of food flavor depends on many interacting chemical compounds and external factors, and therefore proves challenging to understand and predict. Here, we combine extensive chemical and sensory analyses of 250 different beers to train machine learning models that allow predicting flavor and consumer appreciation. For each beer, we measure over 200 chemical properties, perform quantitative descriptive sensory analysis with a trained tasting panel and map data from over 180,000 consumer reviews to train 10 different machine learning models. The best-performing algorithm, Gradient Boosting, yields models that significantly outperform predictions based on conventional statistics and accurately predict complex food features and consumer appreciation from chemical profiles. Model dissection allows identifying specific and unexpected compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Adding these compounds results in variants of commercial alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers with improved consumer appreciation. Together, our study reveals how big data and machine learning uncover complex links between food chemistry, flavor and consumer perception, and lays the foundation to develop novel, tailored foods with superior flavors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Sensory lexicon and aroma volatiles analysis of brewing malt
Xiaoxia Su, Miao Yu, … Tianyi Du
Predicting odor from molecular structure: a multi-label classification approach
Kushagra Saini & Venkatnarayan Ramanathan
Toward a general and interpretable umami taste predictor using a multi-objective machine learning approach
Lorenzo Pallante, Aigli Korfiati, … Marco A. Deriu
Introduction
Predicting and understanding food perception and appreciation is one of the major challenges in food science. Accurate modeling of food flavor and appreciation could yield important opportunities for both producers and consumers, including quality control, product fingerprinting, counterfeit detection, spoilage detection, and the development of new products and product combinations (food pairing) 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 . Accurate models for flavor and consumer appreciation would contribute greatly to our scientific understanding of how humans perceive and appreciate flavor. Moreover, accurate predictive models would also facilitate and standardize existing food assessment methods and could supplement or replace assessments by trained and consumer tasting panels, which are variable, expensive and time-consuming 7 , 8 , 9 . Lastly, apart from providing objective, quantitative, accurate and contextual information that can help producers, models can also guide consumers in understanding their personal preferences 10 .
Despite the myriad of applications, predicting food flavor and appreciation from its chemical properties remains a largely elusive goal in sensory science, especially for complex food and beverages 11 , 12 . A key obstacle is the immense number of flavor-active chemicals underlying food flavor. Flavor compounds can vary widely in chemical structure and concentration, making them technically challenging and labor-intensive to quantify, even in the face of innovations in metabolomics, such as non-targeted metabolic fingerprinting 13 , 14 . Moreover, sensory analysis is perhaps even more complicated. Flavor perception is highly complex, resulting from hundreds of different molecules interacting at the physiochemical and sensorial level. Sensory perception is often non-linear, characterized by complex and concentration-dependent synergistic and antagonistic effects 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 that are further convoluted by the genetics, environment, culture and psychology of consumers 22 , 23 , 24 . Perceived flavor is therefore difficult to measure, with problems of sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility that can only be resolved by gathering sufficiently large datasets 25 . Trained tasting panels are considered the prime source of quality sensory data, but require meticulous training, are low throughput and high cost. Public databases containing consumer reviews of food products could provide a valuable alternative, especially for studying appreciation scores, which do not require formal training 25 . Public databases offer the advantage of amassing large amounts of data, increasing the statistical power to identify potential drivers of appreciation. However, public datasets suffer from biases, including a bias in the volunteers that contribute to the database, as well as confounding factors such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of the product.
Classical multivariate statistics and machine learning methods have been used to predict flavor of specific compounds by, for example, linking structural properties of a compound to its potential biological activities or linking concentrations of specific compounds to sensory profiles 1 , 26 . Importantly, most previous studies focused on predicting organoleptic properties of single compounds (often based on their chemical structure) 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , thus ignoring the fact that these compounds are present in a complex matrix in food or beverages and excluding complex interactions between compounds. Moreover, the classical statistics commonly used in sensory science 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 require a large sample size and sufficient variance amongst predictors to create accurate models. They are not fit for studying an extensive set of hundreds of interacting flavor compounds, since they are sensitive to outliers, have a high tendency to overfit and are less suited for non-linear and discontinuous relationships 40 .
In this study, we combine extensive chemical analyses and sensory data of a set of different commercial beers with machine learning approaches to develop models that predict taste, smell, mouthfeel and appreciation from compound concentrations. Beer is particularly suited to model the relationship between chemistry, flavor and appreciation. First, beer is a complex product, consisting of thousands of flavor compounds that partake in complex sensory interactions 41 , 42 , 43 . This chemical diversity arises from the raw materials (malt, yeast, hops, water and spices) and biochemical conversions during the brewing process (kilning, mashing, boiling, fermentation, maturation and aging) 44 , 45 . Second, the advent of the internet saw beer consumers embrace online review platforms, such as RateBeer (ZX Ventures, Anheuser-Busch InBev SA/NV) and BeerAdvocate (Next Glass, inc.). In this way, the beer community provides massive data sets of beer flavor and appreciation scores, creating extraordinarily large sensory databases to complement the analyses of our professional sensory panel. Specifically, we characterize over 200 chemical properties of 250 commercial beers, spread across 22 beer styles, and link these to the descriptive sensory profiling data of a 16-person in-house trained tasting panel and data acquired from over 180,000 public consumer reviews. These unique and extensive datasets enable us to train a suite of machine learning models to predict flavor and appreciation from a beer’s chemical profile. Dissection of the best-performing models allows us to pinpoint specific compounds as potential drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Follow-up experiments confirm the importance of these compounds and ultimately allow us to significantly improve the flavor and appreciation of selected commercial beers. Together, our study represents a significant step towards understanding complex flavors and reinforces the value of machine learning to develop and refine complex foods. In this way, it represents a stepping stone for further computer-aided food engineering applications 46 .
To generate a comprehensive dataset on beer flavor, we selected 250 commercial Belgian beers across 22 different beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S1 ). Beers with ≤ 4.2% alcohol by volume (ABV) were classified as non-alcoholic and low-alcoholic. Blonds and Tripels constitute a significant portion of the dataset (12.4% and 11.2%, respectively) reflecting their presence on the Belgian beer market and the heterogeneity of beers within these styles. By contrast, lager beers are less diverse and dominated by a handful of brands. Rare styles such as Brut or Faro make up only a small fraction of the dataset (2% and 1%, respectively) because fewer of these beers are produced and because they are dominated by distinct characteristics in terms of flavor and chemical composition.
Extensive analysis identifies relationships between chemical compounds in beer
For each beer, we measured 226 different chemical properties, including common brewing parameters such as alcohol content, iso-alpha acids, pH, sugar concentration 47 , and over 200 flavor compounds (Methods, Supplementary Table S1 ). A large portion (37.2%) are terpenoids arising from hopping, responsible for herbal and fruity flavors 16 , 48 . A second major category are yeast metabolites, such as esters and alcohols, that result in fruity and solvent notes 48 , 49 , 50 . Other measured compounds are primarily derived from malt, or other microbes such as non- Saccharomyces yeasts and bacteria (‘wild flora’). Compounds that arise from spices or staling are labeled under ‘Others’. Five attributes (caloric value, total acids and total ester, hop aroma and sulfur compounds) are calculated from multiple individually measured compounds.
As a first step in identifying relationships between chemical properties, we determined correlations between the concentrations of the compounds (Fig. 1 , upper panel, Supplementary Data 1 and 2 , and Supplementary Fig. S2 . For the sake of clarity, only a subset of the measured compounds is shown in Fig. 1 ). Compounds of the same origin typically show a positive correlation, while absence of correlation hints at parameters varying independently. For example, the hop aroma compounds citronellol, and alpha-terpineol show moderate correlations with each other (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.57), but not with the bittering hop component iso-alpha acids (Spearman’s rho=0.16 and −0.07). This illustrates how brewers can independently modify hop aroma and bitterness by selecting hop varieties and dosage time. If hops are added early in the boiling phase, chemical conversions increase bitterness while aromas evaporate, conversely, late addition of hops preserves aroma but limits bitterness 51 . Similarly, hop-derived iso-alpha acids show a strong anti-correlation with lactic acid and acetic acid, likely reflecting growth inhibition of lactic acid and acetic acid bacteria, or the consequent use of fewer hops in sour beer styles, such as West Flanders ales and Fruit beers, that rely on these bacteria for their distinct flavors 52 . Finally, yeast-derived esters (ethyl acetate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate) and alcohols (ethanol, isoamyl alcohol, isobutanol, and glycerol), correlate with Spearman coefficients above 0.5, suggesting that these secondary metabolites are correlated with the yeast genetic background and/or fermentation parameters and may be difficult to influence individually, although the choice of yeast strain may offer some control 53 .

Spearman rank correlations are shown. Descriptors are grouped according to their origin (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)), and sensory aspect (aroma, taste, palate, and overall appreciation). Please note that for the chemical compounds, for the sake of clarity, only a subset of the total number of measured compounds is shown, with an emphasis on the key compounds for each source. For more details, see the main text and Methods section. Chemical data can be found in Supplementary Data 1 , correlations between all chemical compounds are depicted in Supplementary Fig. S2 and correlation values can be found in Supplementary Data 2 . See Supplementary Data 4 for sensory panel assessments and Supplementary Data 5 for correlation values between all sensory descriptors.
Interestingly, different beer styles show distinct patterns for some flavor compounds (Supplementary Fig. S3 ). These observations agree with expectations for key beer styles, and serve as a control for our measurements. For instance, Stouts generally show high values for color (darker), while hoppy beers contain elevated levels of iso-alpha acids, compounds associated with bitter hop taste. Acetic and lactic acid are not prevalent in most beers, with notable exceptions such as Kriek, Lambic, Faro, West Flanders ales and Flanders Old Brown, which use acid-producing bacteria ( Lactobacillus and Pediococcus ) or unconventional yeast ( Brettanomyces ) 54 , 55 . Glycerol, ethanol and esters show similar distributions across all beer styles, reflecting their common origin as products of yeast metabolism during fermentation 45 , 53 . Finally, low/no-alcohol beers contain low concentrations of glycerol and esters. This is in line with the production process for most of the low/no-alcohol beers in our dataset, which are produced through limiting fermentation or by stripping away alcohol via evaporation or dialysis, with both methods having the unintended side-effect of reducing the amount of flavor compounds in the final beer 56 , 57 .
Besides expected associations, our data also reveals less trivial associations between beer styles and specific parameters. For example, geraniol and citronellol, two monoterpenoids responsible for citrus, floral and rose flavors and characteristic of Citra hops, are found in relatively high amounts in Christmas, Saison, and Brett/co-fermented beers, where they may originate from terpenoid-rich spices such as coriander seeds instead of hops 58 .
Tasting panel assessments reveal sensorial relationships in beer
To assess the sensory profile of each beer, a trained tasting panel evaluated each of the 250 beers for 50 sensory attributes, including different hop, malt and yeast flavors, off-flavors and spices. Panelists used a tasting sheet (Supplementary Data 3 ) to score the different attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating 12 samples across different sessions and performing ANOVA. In 95% of cases no significant difference was found across sessions ( p > 0.05), indicating good panel consistency (Supplementary Table S2 ).
Aroma and taste perception reported by the trained panel are often linked (Fig. 1 , bottom left panel and Supplementary Data 4 and 5 ), with high correlations between hops aroma and taste (Spearman’s rho=0.83). Bitter taste was found to correlate with hop aroma and taste in general (Spearman’s rho=0.80 and 0.69), and particularly with “grassy” noble hops (Spearman’s rho=0.75). Barnyard flavor, most often associated with sour beers, is identified together with stale hops (Spearman’s rho=0.97) that are used in these beers. Lactic and acetic acid, which often co-occur, are correlated (Spearman’s rho=0.66). Interestingly, sweetness and bitterness are anti-correlated (Spearman’s rho = −0.48), confirming the hypothesis that they mask each other 59 , 60 . Beer body is highly correlated with alcohol (Spearman’s rho = 0.79), and overall appreciation is found to correlate with multiple aspects that describe beer mouthfeel (alcohol, carbonation; Spearman’s rho= 0.32, 0.39), as well as with hop and ester aroma intensity (Spearman’s rho=0.39 and 0.35).
Similar to the chemical analyses, sensorial analyses confirmed typical features of specific beer styles (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). For example, sour beers (Faro, Flanders Old Brown, Fruit beer, Kriek, Lambic, West Flanders ale) were rated acidic, with flavors of both acetic and lactic acid. Hoppy beers were found to be bitter and showed hop-associated aromas like citrus and tropical fruit. Malt taste is most detected among scotch, stout/porters, and strong ales, while low/no-alcohol beers, which often have a reputation for being ‘worty’ (reminiscent of unfermented, sweet malt extract) appear in the middle. Unsurprisingly, hop aromas are most strongly detected among hoppy beers. Like its chemical counterpart (Supplementary Fig. S3 ), acidity shows a right-skewed distribution, with the most acidic beers being Krieks, Lambics, and West Flanders ales.
Tasting panel assessments of specific flavors correlate with chemical composition
We find that the concentrations of several chemical compounds strongly correlate with specific aroma or taste, as evaluated by the tasting panel (Fig. 2 , Supplementary Fig. S5 , Supplementary Data 6 ). In some cases, these correlations confirm expectations and serve as a useful control for data quality. For example, iso-alpha acids, the bittering compounds in hops, strongly correlate with bitterness (Spearman’s rho=0.68), while ethanol and glycerol correlate with tasters’ perceptions of alcohol and body, the mouthfeel sensation of fullness (Spearman’s rho=0.82/0.62 and 0.72/0.57 respectively) and darker color from roasted malts is a good indication of malt perception (Spearman’s rho=0.54).

Heatmap colors indicate Spearman’s Rho. Axes are organized according to sensory categories (aroma, taste, mouthfeel, overall), chemical categories and chemical sources in beer (malt (blue), hops (green), yeast (red), wild flora (yellow), Others (black)). See Supplementary Data 6 for all correlation values.
Interestingly, for some relationships between chemical compounds and perceived flavor, correlations are weaker than expected. For example, the rose-smelling phenethyl acetate only weakly correlates with floral aroma. This hints at more complex relationships and interactions between compounds and suggests a need for a more complex model than simple correlations. Lastly, we uncovered unexpected correlations. For instance, the esters ethyl decanoate and ethyl octanoate appear to correlate slightly with hop perception and bitterness, possibly due to their fruity flavor. Iron is anti-correlated with hop aromas and bitterness, most likely because it is also anti-correlated with iso-alpha acids. This could be a sign of metal chelation of hop acids 61 , given that our analyses measure unbound hop acids and total iron content, or could result from the higher iron content in dark and Fruit beers, which typically have less hoppy and bitter flavors 62 .
Public consumer reviews complement expert panel data
To complement and expand the sensory data of our trained tasting panel, we collected 180,000 reviews of our 250 beers from the online consumer review platform RateBeer. This provided numerical scores for beer appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality as well as the average overall score.
Public datasets are known to suffer from biases, such as price, cult status and psychological conformity towards previous ratings of a product. For example, prices correlate with appreciation scores for these online consumer reviews (rho=0.49, Supplementary Fig. S6 ), but not for our trained tasting panel (rho=0.19). This suggests that prices affect consumer appreciation, which has been reported in wine 63 , while blind tastings are unaffected. Moreover, we observe that some beer styles, like lagers and non-alcoholic beers, generally receive lower scores, reflecting that online reviewers are mostly beer aficionados with a preference for specialty beers over lager beers. In general, we find a modest correlation between our trained panel’s overall appreciation score and the online consumer appreciation scores (Fig. 3 , rho=0.29). Apart from the aforementioned biases in the online datasets, serving temperature, sample freshness and surroundings, which are all tightly controlled during the tasting panel sessions, can vary tremendously across online consumers and can further contribute to (among others, appreciation) differences between the two categories of tasters. Importantly, in contrast to the overall appreciation scores, for many sensory aspects the results from the professional panel correlated well with results obtained from RateBeer reviews. Correlations were highest for features that are relatively easy to recognize even for untrained tasters, like bitterness, sweetness, alcohol and malt aroma (Fig. 3 and below).
RateBeer text mining results can be found in Supplementary Data 7 . Rho values shown are Spearman correlation values, with asterisks indicating significant correlations ( p < 0.05, two-sided). All p values were smaller than 0.001, except for Esters aroma (0.0553), Esters taste (0.3275), Esters aroma—banana (0.0019), Coriander (0.0508) and Diacetyl (0.0134).
Besides collecting consumer appreciation from these online reviews, we developed automated text analysis tools to gather additional data from review texts (Supplementary Data 7 ). Processing review texts on the RateBeer database yielded comparable results to the scores given by the trained panel for many common sensory aspects, including acidity, bitterness, sweetness, alcohol, malt, and hop tastes (Fig. 3 ). This is in line with what would be expected, since these attributes require less training for accurate assessment and are less influenced by environmental factors such as temperature, serving glass and odors in the environment. Consumer reviews also correlate well with our trained panel for 4-vinyl guaiacol, a compound associated with a very characteristic aroma. By contrast, correlations for more specific aromas like ester, coriander or diacetyl are underrepresented in the online reviews, underscoring the importance of using a trained tasting panel and standardized tasting sheets with explicit factors to be scored for evaluating specific aspects of a beer. Taken together, our results suggest that public reviews are trustworthy for some, but not all, flavor features and can complement or substitute taste panel data for these sensory aspects.
Models can predict beer sensory profiles from chemical data
The rich datasets of chemical analyses, tasting panel assessments and public reviews gathered in the first part of this study provided us with a unique opportunity to develop predictive models that link chemical data to sensorial features. Given the complexity of beer flavor, basic statistical tools such as correlations or linear regression may not always be the most suitable for making accurate predictions. Instead, we applied different machine learning models that can model both simple linear and complex interactive relationships. Specifically, we constructed a set of regression models to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavor and quality and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. We trained and tested 10 different models (Methods), 3 linear regression-based models (simple linear regression with first-order interactions (LR), lasso regression with first-order interactions (Lasso), partial least squares regressor (PLSR)), 5 decision tree models (AdaBoost regressor (ABR), extra trees (ET), gradient boosting regressor (GBR), random forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR)), 1 support vector regression (SVR), and 1 artificial neural network (ANN) model.
To compare the performance of our machine learning models, the dataset was randomly split into a training and test set, stratified by beer style. After a model was trained on data in the training set, its performance was evaluated on its ability to predict the test dataset obtained from multi-output models (based on the coefficient of determination, see Methods). Additionally, individual-attribute models were ranked per descriptor and the average rank was calculated, as proposed by Korneva et al. 64 . Importantly, both ways of evaluating the models’ performance agreed in general. Performance of the different models varied (Table 1 ). It should be noted that all models perform better at predicting RateBeer results than results from our trained tasting panel. One reason could be that sensory data is inherently variable, and this variability is averaged out with the large number of public reviews from RateBeer. Additionally, all tree-based models perform better at predicting taste than aroma. Linear models (LR) performed particularly poorly, with negative R 2 values, due to severe overfitting (training set R 2 = 1). Overfitting is a common issue in linear models with many parameters and limited samples, especially with interaction terms further amplifying the number of parameters. L1 regularization (Lasso) successfully overcomes this overfitting, out-competing multiple tree-based models on the RateBeer dataset. Similarly, the dimensionality reduction of PLSR avoids overfitting and improves performance, to some extent. Still, tree-based models (ABR, ET, GBR, RF and XGBR) show the best performance, out-competing the linear models (LR, Lasso, PLSR) commonly used in sensory science 65 .
GBR models showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, with R 2 values up to 0.75 depending on the predicted sensory feature (Supplementary Table S4 ). The GBR models predict consumer appreciation (RateBeer) better than our trained panel’s appreciation (R 2 value of 0.67 compared to R 2 value of 0.09) (Supplementary Table S3 and Supplementary Table S4 ). ANN models showed intermediate performance, likely because neural networks typically perform best with larger datasets 66 . The SVR shows intermediate performance, mostly due to the weak predictions of specific attributes that lower the overall performance (Supplementary Table S4 ).
Model dissection identifies specific, unexpected compounds as drivers of consumer appreciation
Next, we leveraged our models to infer important contributors to sensory perception and consumer appreciation. Consumer preference is a crucial sensory aspects, because a product that shows low consumer appreciation scores often does not succeed commercially 25 . Additionally, the requirement for a large number of representative evaluators makes consumer trials one of the more costly and time-consuming aspects of product development. Hence, a model for predicting chemical drivers of overall appreciation would be a welcome addition to the available toolbox for food development and optimization.
Since GBR models on our RateBeer dataset showed the best overall performance, we focused on these models. Specifically, we used two approaches to identify important contributors. First, rankings of the most important predictors for each sensorial trait in the GBR models were obtained based on impurity-based feature importance (mean decrease in impurity). High-ranked parameters were hypothesized to be either the true causal chemical properties underlying the trait, to correlate with the actual causal properties, or to take part in sensory interactions affecting the trait 67 (Fig. 4A ). In a second approach, we used SHAP 68 to determine which parameters contributed most to the model for making predictions of consumer appreciation (Fig. 4B ). SHAP calculates parameter contributions to model predictions on a per-sample basis, which can be aggregated into an importance score.
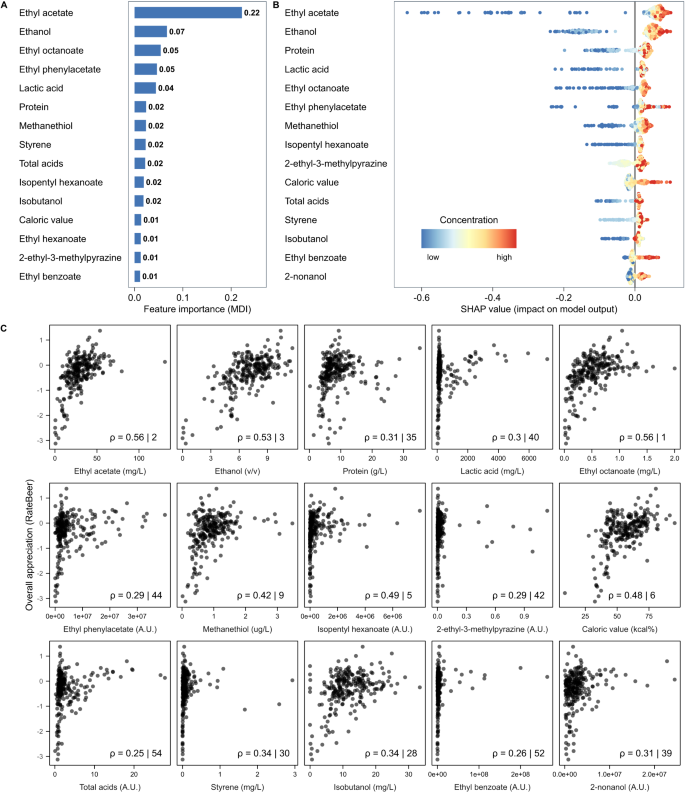
A The impurity-based feature importance (mean deviance in impurity, MDI) calculated from the Gradient Boosting Regression (GBR) model predicting RateBeer appreciation scores. The top 15 highest ranked chemical properties are shown. B SHAP summary plot for the top 15 parameters contributing to our GBR model. Each point on the graph represents a sample from our dataset. The color represents the concentration of that parameter, with bluer colors representing low values and redder colors representing higher values. Greater absolute values on the horizontal axis indicate a higher impact of the parameter on the prediction of the model. C Spearman correlations between the 15 most important chemical properties and consumer overall appreciation. Numbers indicate the Spearman Rho correlation coefficient, and the rank of this correlation compared to all other correlations. The top 15 important compounds were determined using SHAP (panel B).
Both approaches identified ethyl acetate as the most predictive parameter for beer appreciation (Fig. 4 ). Ethyl acetate is the most abundant ester in beer with a typical ‘fruity’, ‘solvent’ and ‘alcoholic’ flavor, but is often considered less important than other esters like isoamyl acetate. The second most important parameter identified by SHAP is ethanol, the most abundant beer compound after water. Apart from directly contributing to beer flavor and mouthfeel, ethanol drastically influences the physical properties of beer, dictating how easily volatile compounds escape the beer matrix to contribute to beer aroma 69 . Importantly, it should also be noted that the importance of ethanol for appreciation is likely inflated by the very low appreciation scores of non-alcoholic beers (Supplementary Fig. S4 ). Despite not often being considered a driver of beer appreciation, protein level also ranks highly in both approaches, possibly due to its effect on mouthfeel and body 70 . Lactic acid, which contributes to the tart taste of sour beers, is the fourth most important parameter identified by SHAP, possibly due to the generally high appreciation of sour beers in our dataset.
Interestingly, some of the most important predictive parameters for our model are not well-established as beer flavors or are even commonly regarded as being negative for beer quality. For example, our models identify methanethiol and ethyl phenyl acetate, an ester commonly linked to beer staling 71 , as a key factor contributing to beer appreciation. Although there is no doubt that high concentrations of these compounds are considered unpleasant, the positive effects of modest concentrations are not yet known 72 , 73 .
To compare our approach to conventional statistics, we evaluated how well the 15 most important SHAP-derived parameters correlate with consumer appreciation (Fig. 4C ). Interestingly, only 6 of the properties derived by SHAP rank amongst the top 15 most correlated parameters. For some chemical compounds, the correlations are so low that they would have likely been considered unimportant. For example, lactic acid, the fourth most important parameter, shows a bimodal distribution for appreciation, with sour beers forming a separate cluster, that is missed entirely by the Spearman correlation. Additionally, the correlation plots reveal outliers, emphasizing the need for robust analysis tools. Together, this highlights the need for alternative models, like the Gradient Boosting model, that better grasp the complexity of (beer) flavor.
Finally, to observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 , 76 (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). One-way partial dependence plots show how a change in concentration affects the predicted appreciation. These plots reveal an important limitation of our models: appreciation predictions remain constant at ever-increasing concentrations. This implies that once a threshold concentration is reached, further increasing the concentration does not affect appreciation. This is false, as it is well-documented that certain compounds become unpleasant at high concentrations, including ethyl acetate (‘nail polish’) 77 and methanethiol (‘sulfury’ and ‘rotten cabbage’) 78 . The inability of our models to grasp that flavor compounds have optimal levels, above which they become negative, is a consequence of working with commercial beer brands where (off-)flavors are rarely too high to negatively impact the product. The two-way partial dependence plots show how changing the concentration of two compounds influences predicted appreciation, visualizing their interactions (Supplementary Fig. S7 ). In our case, the top 5 parameters are dominated by additive or synergistic interactions, with high concentrations for both compounds resulting in the highest predicted appreciation.
To assess the robustness of our best-performing models and model predictions, we performed 100 iterations of the GBR, RF and ET models. In general, all iterations of the models yielded similar performance (Supplementary Fig. S8 ). Moreover, the main predictors (including the top predictors ethanol and ethyl acetate) remained virtually the same, especially for GBR and RF. For the iterations of the ET model, we did observe more variation in the top predictors, which is likely a consequence of the model’s inherent random architecture in combination with co-correlations between certain predictors. However, even in this case, several of the top predictors (ethanol and ethyl acetate) remain unchanged, although their rank in importance changes (Supplementary Fig. S8 ).
Next, we investigated if a combination of RateBeer and trained panel data into one consolidated dataset would lead to stronger models, under the hypothesis that such a model would suffer less from bias in the datasets. A GBR model was trained to predict appreciation on the combined dataset. This model underperformed compared to the RateBeer model, both in the native case and when including a dataset identifier (R 2 = 0.67, 0.26 and 0.42 respectively). For the latter, the dataset identifier is the most important feature (Supplementary Fig. S9 ), while most of the feature importance remains unchanged, with ethyl acetate and ethanol ranking highest, like in the original model trained only on RateBeer data. It seems that the large variation in the panel dataset introduces noise, weakening the models’ performances and reliability. In addition, it seems reasonable to assume that both datasets are fundamentally different, with the panel dataset obtained by blind tastings by a trained professional panel.
Lastly, we evaluated whether beer style identifiers would further enhance the model’s performance. A GBR model was trained with parameters that explicitly encoded the styles of the samples. This did not improve model performance (R2 = 0.66 with style information vs R2 = 0.67). The most important chemical features are consistent with the model trained without style information (eg. ethanol and ethyl acetate), and with the exception of the most preferred (strong ale) and least preferred (low/no-alcohol) styles, none of the styles were among the most important features (Supplementary Fig. S9 , Supplementary Table S5 and S6 ). This is likely due to a combination of style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original models, as well as the low number of samples belonging to some styles, making it difficult for the model to learn style-specific patterns. Moreover, beer styles are not rigorously defined, with some styles overlapping in features and some beers being misattributed to a specific style, all of which leads to more noise in models that use style parameters.
Model validation
To test if our predictive models give insight into beer appreciation, we set up experiments aimed at improving existing commercial beers. We specifically selected overall appreciation as the trait to be examined because of its complexity and commercial relevance. Beer flavor comprises a complex bouquet rather than single aromas and tastes 53 . Hence, adding a single compound to the extent that a difference is noticeable may lead to an unbalanced, artificial flavor. Therefore, we evaluated the effect of combinations of compounds. Because Blond beers represent the most extensive style in our dataset, we selected a beer from this style as the starting material for these experiments (Beer 64 in Supplementary Data 1 ).
In the first set of experiments, we adjusted the concentrations of compounds that made up the most important predictors of overall appreciation (ethyl acetate, ethanol, lactic acid, ethyl phenyl acetate) together with correlated compounds (ethyl hexanoate, isoamyl acetate, glycerol), bringing them up to 95 th percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations (Methods) within the Blond group (‘Spiked’ concentration in Fig. 5A ). Compared to controls, the spiked beers were found to have significantly improved overall appreciation among trained panelists, with panelist noting increased intensity of ester flavors, sweetness, alcohol, and body fullness (Fig. 5B ). To disentangle the contribution of ethanol to these results, a second experiment was performed without the addition of ethanol. This resulted in a similar outcome, including increased perception of alcohol and overall appreciation.
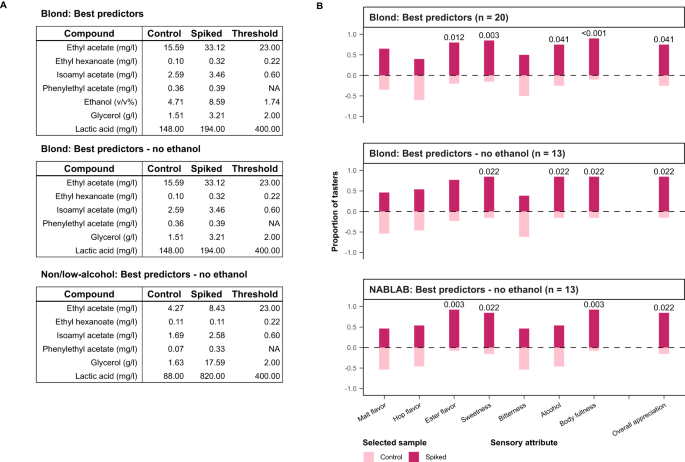
Adding the top chemical compounds, identified as best predictors of appreciation by our model, into poorly appreciated beers results in increased appreciation from our trained panel. Results of sensory tests between base beers and those spiked with compounds identified as the best predictors by the model. A Blond and Non/Low-alcohol (0.0% ABV) base beers were brought up to 95th-percentile ethanol-normalized concentrations within each style. B For each sensory attribute, tasters indicated the more intense sample and selected the sample they preferred. The numbers above the bars correspond to the p values that indicate significant changes in perceived flavor (two-sided binomial test: alpha 0.05, n = 20 or 13).
In a last experiment, we tested whether using the model’s predictions can boost the appreciation of a non-alcoholic beer (beer 223 in Supplementary Data 1 ). Again, the addition of a mixture of predicted compounds (omitting ethanol, in this case) resulted in a significant increase in appreciation, body, ester flavor and sweetness.
Predicting flavor and consumer appreciation from chemical composition is one of the ultimate goals of sensory science. A reliable, systematic and unbiased way to link chemical profiles to flavor and food appreciation would be a significant asset to the food and beverage industry. Such tools would substantially aid in quality control and recipe development, offer an efficient and cost-effective alternative to pilot studies and consumer trials and would ultimately allow food manufacturers to produce superior, tailor-made products that better meet the demands of specific consumer groups more efficiently.
A limited set of studies have previously tried, to varying degrees of success, to predict beer flavor and beer popularity based on (a limited set of) chemical compounds and flavors 79 , 80 . Current sensitive, high-throughput technologies allow measuring an unprecedented number of chemical compounds and properties in a large set of samples, yielding a dataset that can train models that help close the gaps between chemistry and flavor, even for a complex natural product like beer. To our knowledge, no previous research gathered data at this scale (250 samples, 226 chemical parameters, 50 sensory attributes and 5 consumer scores) to disentangle and validate the chemical aspects driving beer preference using various machine-learning techniques. We find that modern machine learning models outperform conventional statistical tools, such as correlations and linear models, and can successfully predict flavor appreciation from chemical composition. This could be attributed to the natural incorporation of interactions and non-linear or discontinuous effects in machine learning models, which are not easily grasped by the linear model architecture. While linear models and partial least squares regression represent the most widespread statistical approaches in sensory science, in part because they allow interpretation 65 , 81 , 82 , modern machine learning methods allow for building better predictive models while preserving the possibility to dissect and exploit the underlying patterns. Of the 10 different models we trained, tree-based models, such as our best performing GBR, showed the best overall performance in predicting sensory responses from chemical information, outcompeting artificial neural networks. This agrees with previous reports for models trained on tabular data 83 . Our results are in line with the findings of Colantonio et al. who also identified the gradient boosting architecture as performing best at predicting appreciation and flavor (of tomatoes and blueberries, in their specific study) 26 . Importantly, besides our larger experimental scale, we were able to directly confirm our models’ predictions in vivo.
Our study confirms that flavor compound concentration does not always correlate with perception, suggesting complex interactions that are often missed by more conventional statistics and simple models. Specifically, we find that tree-based algorithms may perform best in developing models that link complex food chemistry with aroma. Furthermore, we show that massive datasets of untrained consumer reviews provide a valuable source of data, that can complement or even replace trained tasting panels, especially for appreciation and basic flavors, such as sweetness and bitterness. This holds despite biases that are known to occur in such datasets, such as price or conformity bias. Moreover, GBR models predict taste better than aroma. This is likely because taste (e.g. bitterness) often directly relates to the corresponding chemical measurements (e.g., iso-alpha acids), whereas such a link is less clear for aromas, which often result from the interplay between multiple volatile compounds. We also find that our models are best at predicting acidity and alcohol, likely because there is a direct relation between the measured chemical compounds (acids and ethanol) and the corresponding perceived sensorial attribute (acidity and alcohol), and because even untrained consumers are generally able to recognize these flavors and aromas.
The predictions of our final models, trained on review data, hold even for blind tastings with small groups of trained tasters, as demonstrated by our ability to validate specific compounds as drivers of beer flavor and appreciation. Since adding a single compound to the extent of a noticeable difference may result in an unbalanced flavor profile, we specifically tested our identified key drivers as a combination of compounds. While this approach does not allow us to validate if a particular single compound would affect flavor and/or appreciation, our experiments do show that this combination of compounds increases consumer appreciation.
It is important to stress that, while it represents an important step forward, our approach still has several major limitations. A key weakness of the GBR model architecture is that amongst co-correlating variables, the largest main effect is consistently preferred for model building. As a result, co-correlating variables often have artificially low importance scores, both for impurity and SHAP-based methods, like we observed in the comparison to the more randomized Extra Trees models. This implies that chemicals identified as key drivers of a specific sensory feature by GBR might not be the true causative compounds, but rather co-correlate with the actual causative chemical. For example, the high importance of ethyl acetate could be (partially) attributed to the total ester content, ethanol or ethyl hexanoate (rho=0.77, rho=0.72 and rho=0.68), while ethyl phenylacetate could hide the importance of prenyl isobutyrate and ethyl benzoate (rho=0.77 and rho=0.76). Expanding our GBR model to include beer style as a parameter did not yield additional power or insight. This is likely due to style-specific chemical signatures, such as iso-alpha acids and lactic acid, that implicitly convey style information to the original model, as well as the smaller sample size per style, limiting the power to uncover style-specific patterns. This can be partly attributed to the curse of dimensionality, where the high number of parameters results in the models mainly incorporating single parameter effects, rather than complex interactions such as style-dependent effects 67 . A larger number of samples may overcome some of these limitations and offer more insight into style-specific effects. On the other hand, beer style is not a rigid scientific classification, and beers within one style often differ a lot, which further complicates the analysis of style as a model factor.
Our study is limited to beers from Belgian breweries. Although these beers cover a large portion of the beer styles available globally, some beer styles and consumer patterns may be missing, while other features might be overrepresented. For example, many Belgian ales exhibit yeast-driven flavor profiles, which is reflected in the chemical drivers of appreciation discovered by this study. In future work, expanding the scope to include diverse markets and beer styles could lead to the identification of even more drivers of appreciation and better models for special niche products that were not present in our beer set.
In addition to inherent limitations of GBR models, there are also some limitations associated with studying food aroma. Even if our chemical analyses measured most of the known aroma compounds, the total number of flavor compounds in complex foods like beer is still larger than the subset we were able to measure in this study. For example, hop-derived thiols, that influence flavor at very low concentrations, are notoriously difficult to measure in a high-throughput experiment. Moreover, consumer perception remains subjective and prone to biases that are difficult to avoid. It is also important to stress that the models are still immature and that more extensive datasets will be crucial for developing more complete models in the future. Besides more samples and parameters, our dataset does not include any demographic information about the tasters. Including such data could lead to better models that grasp external factors like age and culture. Another limitation is that our set of beers consists of high-quality end-products and lacks beers that are unfit for sale, which limits the current model in accurately predicting products that are appreciated very badly. Finally, while models could be readily applied in quality control, their use in sensory science and product development is restrained by their inability to discern causal relationships. Given that the models cannot distinguish compounds that genuinely drive consumer perception from those that merely correlate, validation experiments are essential to identify true causative compounds.
Despite the inherent limitations, dissection of our models enabled us to pinpoint specific molecules as potential drivers of beer aroma and consumer appreciation, including compounds that were unexpected and would not have been identified using standard approaches. Important drivers of beer appreciation uncovered by our models include protein levels, ethyl acetate, ethyl phenyl acetate and lactic acid. Currently, many brewers already use lactic acid to acidify their brewing water and ensure optimal pH for enzymatic activity during the mashing process. Our results suggest that adding lactic acid can also improve beer appreciation, although its individual effect remains to be tested. Interestingly, ethanol appears to be unnecessary to improve beer appreciation, both for blond beer and alcohol-free beer. Given the growing consumer interest in alcohol-free beer, with a predicted annual market growth of >7% 84 , it is relevant for brewers to know what compounds can further increase consumer appreciation of these beers. Hence, our model may readily provide avenues to further improve the flavor and consumer appreciation of both alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers, which is generally considered one of the key challenges for future beer production.
Whereas we see a direct implementation of our results for the development of superior alcohol-free beverages and other food products, our study can also serve as a stepping stone for the development of novel alcohol-containing beverages. We want to echo the growing body of scientific evidence for the negative effects of alcohol consumption, both on the individual level by the mutagenic, teratogenic and carcinogenic effects of ethanol 85 , 86 , as well as the burden on society caused by alcohol abuse and addiction. We encourage the use of our results for the production of healthier, tastier products, including novel and improved beverages with lower alcohol contents. Furthermore, we strongly discourage the use of these technologies to improve the appreciation or addictive properties of harmful substances.
The present work demonstrates that despite some important remaining hurdles, combining the latest developments in chemical analyses, sensory analysis and modern machine learning methods offers exciting avenues for food chemistry and engineering. Soon, these tools may provide solutions in quality control and recipe development, as well as new approaches to sensory science and flavor research.
Beer selection
250 commercial Belgian beers were selected to cover the broad diversity of beer styles and corresponding diversity in chemical composition and aroma. See Supplementary Fig. S1 .
Chemical dataset
Sample preparation.
Beers within their expiration date were purchased from commercial retailers. Samples were prepared in biological duplicates at room temperature, unless explicitly stated otherwise. Bottle pressure was measured with a manual pressure device (Steinfurth Mess-Systeme GmbH) and used to calculate CO 2 concentration. The beer was poured through two filter papers (Macherey-Nagel, 500713032 MN 713 ¼) to remove carbon dioxide and prevent spontaneous foaming. Samples were then prepared for measurements by targeted Headspace-Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector/Flame Photometric Detector (HS-GC-FID/FPD), Headspace-Solid Phase Microextraction-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), colorimetric analysis, enzymatic analysis, Near-Infrared (NIR) analysis, as described in the sections below. The mean values of biological duplicates are reported for each compound.
HS-GC-FID/FPD
HS-GC-FID/FPD (Shimadzu GC 2010 Plus) was used to measure higher alcohols, acetaldehyde, esters, 4-vinyl guaicol, and sulfur compounds. Each measurement comprised 5 ml of sample pipetted into a 20 ml glass vial containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 100 µl of 2-heptanol (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003) (internal standard) solution in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17) was added for a final concentration of 2.44 mg/L. Samples were flushed with nitrogen for 10 s, sealed with a silicone septum, stored at −80 °C and analyzed in batches of 20.
The GC was equipped with a DB-WAXetr column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.32 mm; layer thickness, 0.50 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FID and an HP-5 column (length, 30 m; internal diameter, 0.25 mm; layer thickness, 0.25 µm; Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to the FPD. N 2 was used as the carrier gas. Samples were incubated for 20 min at 70 °C in the headspace autosampler (Flow rate, 35 cm/s; Injection volume, 1000 µL; Injection mode, split; Combi PAL autosampler, CTC analytics, Switzerland). The injector, FID and FPD temperatures were kept at 250 °C. The GC oven temperature was first held at 50 °C for 5 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 5 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 4 °C/min until 200 °C kept for 3 min and a final ramp of (4 °C/min) until 230 °C for 1 min. Results were analyzed with the GCSolution software version 2.4 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The GC was calibrated with a 5% EtOH solution (VWR International) containing the volatiles under study (Supplementary Table S7 ).
HS-SPME-GC-MS
HS-SPME-GC-MS (Shimadzu GCMS-QP-2010 Ultra) was used to measure additional volatile compounds, mainly comprising terpenoids and esters. Samples were analyzed by HS-SPME using a triphase DVB/Carboxen/PDMS 50/30 μm SPME fiber (Supelco Co., Bellefonte, PA, USA) followed by gas chromatography (Thermo Fisher Scientific Trace 1300 series, USA) coupled to a mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific ISQ series MS) equipped with a TriPlus RSH autosampler. 5 ml of degassed beer sample was placed in 20 ml vials containing 1.75 g NaCl (VWR, 27810.295). 5 µl internal standard mix was added, containing 2-heptanol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, H3003), 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 128376), 2,3-hexanedione (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, 144169) and guaiacol (1 g/L) (Sigma-Aldrich, W253200) in ethanol (Fisher Chemical, E/0650DF/C17). Each sample was incubated at 60 °C in the autosampler oven with constant agitation. After 5 min equilibration, the SPME fiber was exposed to the sample headspace for 30 min. The compounds trapped on the fiber were thermally desorbed in the injection port of the chromatograph by heating the fiber for 15 min at 270 °C.
The GC-MS was equipped with a low polarity RXi-5Sil MS column (length, 20 m; internal diameter, 0.18 mm; layer thickness, 0.18 µm; Restek, Bellefonte, PA, USA). Injection was performed in splitless mode at 320 °C, a split flow of 9 ml/min, a purge flow of 5 ml/min and an open valve time of 3 min. To obtain a pulsed injection, a programmed gas flow was used whereby the helium gas flow was set at 2.7 mL/min for 0.1 min, followed by a decrease in flow of 20 ml/min to the normal 0.9 mL/min. The temperature was first held at 30 °C for 3 min and then allowed to rise to 80 °C at a rate of 7 °C/min, followed by a second ramp of 2 °C/min till 125 °C and a final ramp of 8 °C/min with a final temperature of 270 °C.
Mass acquisition range was 33 to 550 amu at a scan rate of 5 scans/s. Electron impact ionization energy was 70 eV. The interface and ion source were kept at 275 °C and 250 °C, respectively. A mix of linear n-alkanes (from C7 to C40, Supelco Co.) was injected into the GC-MS under identical conditions to serve as external retention index markers. Identification and quantification of the compounds were performed using an in-house developed R script as described in Goelen et al. and Reher et al. 87 , 88 (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). Briefly, chromatograms were analyzed using AMDIS (v2.71) 89 to separate overlapping peaks and obtain pure compound spectra. The NIST MS Search software (v2.0 g) in combination with the NIST2017, FFNSC3 and Adams4 libraries were used to manually identify the empirical spectra, taking into account the expected retention time. After background subtraction and correcting for retention time shifts between samples run on different days based on alkane ladders, compound elution profiles were extracted and integrated using a file with 284 target compounds of interest, which were either recovered in our identified AMDIS list of spectra or were known to occur in beer. Compound elution profiles were estimated for every peak in every chromatogram over a time-restricted window using weighted non-negative least square analysis after which peak areas were integrated 87 , 88 . Batch effect correction was performed by normalizing against the most stable internal standard compound, 4-fluorobenzaldehyde. Out of all 284 target compounds that were analyzed, 167 were visually judged to have reliable elution profiles and were used for final analysis.
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis
Discrete photometric and enzymatic analysis (Thermo Scientific TM Gallery TM Plus Beermaster Discrete Analyzer) was used to measure acetic acid, ammonia, beta-glucan, iso-alpha acids, color, sugars, glycerol, iron, pH, protein, and sulfite. 2 ml of sample volume was used for the analyses. Information regarding the reagents and standard solutions used for analyses and calibrations is included in Supplementary Table S7 and Supplementary Table S9 .
NIR analyses
NIR analysis (Anton Paar Alcolyzer Beer ME System) was used to measure ethanol. Measurements comprised 50 ml of sample, and a 10% EtOH solution was used for calibration.
Correlation calculations
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all chemical properties.
Sensory dataset
Trained panel.
Our trained tasting panel consisted of volunteers who gave prior verbal informed consent. All compounds used for the validation experiment were of food-grade quality. The tasting sessions were approved by the Social and Societal Ethics Committee of the KU Leuven (G-2022-5677-R2(MAR)). All online reviewers agreed to the Terms and Conditions of the RateBeer website.
Sensory analysis was performed according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) Sensory Analysis Methods 90 . 30 volunteers were screened through a series of triangle tests. The sixteen most sensitive and consistent tasters were retained as taste panel members. The resulting panel was diverse in age [22–42, mean: 29], sex [56% male] and nationality [7 different countries]. The panel developed a consensus vocabulary to describe beer aroma, taste and mouthfeel. Panelists were trained to identify and score 50 different attributes, using a 7-point scale to rate attributes’ intensity. The scoring sheet is included as Supplementary Data 3 . Sensory assessments took place between 10–12 a.m. The beers were served in black-colored glasses. Per session, between 5 and 12 beers of the same style were tasted at 12 °C to 16 °C. Two reference beers were added to each set and indicated as ‘Reference 1 & 2’, allowing panel members to calibrate their ratings. Not all panelists were present at every tasting. Scores were scaled by standard deviation and mean-centered per taster. Values are represented as z-scores and clustered by Euclidean distance. Pairwise Spearman correlations were calculated between taste and aroma sensory attributes. Panel consistency was evaluated by repeating samples on different sessions and performing ANOVA to identify differences, using the ‘stats’ package (v4.2.2) in R (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ).
Online reviews from a public database
The ‘scrapy’ package in Python (v3.6) (for package information, see Supplementary Table S8 ). was used to collect 232,288 online reviews (mean=922, min=6, max=5343) from RateBeer, an online beer review database. Each review entry comprised 5 numerical scores (appearance, aroma, taste, palate and overall quality) and an optional review text. The total number of reviews per reviewer was collected separately. Numerical scores were scaled and centered per rater, and mean scores were calculated per beer.
For the review texts, the language was estimated using the packages ‘langdetect’ and ‘langid’ in Python. Reviews that were classified as English by both packages were kept. Reviewers with fewer than 100 entries overall were discarded. 181,025 reviews from >6000 reviewers from >40 countries remained. Text processing was done using the ‘nltk’ package in Python. Texts were corrected for slang and misspellings; proper nouns and rare words that are relevant to the beer context were specified and kept as-is (‘Chimay’,’Lambic’, etc.). A dictionary of semantically similar sensorial terms, for example ‘floral’ and ‘flower’, was created and collapsed together into one term. Words were stemmed and lemmatized to avoid identifying words such as ‘acid’ and ‘acidity’ as separate terms. Numbers and punctuation were removed.
Sentences from up to 50 randomly chosen reviews per beer were manually categorized according to the aspect of beer they describe (appearance, aroma, taste, palate, overall quality—not to be confused with the 5 numerical scores described above) or flagged as irrelevant if they contained no useful information. If a beer contained fewer than 50 reviews, all reviews were manually classified. This labeled data set was used to train a model that classified the rest of the sentences for all beers 91 . Sentences describing taste and aroma were extracted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency (TFIDF) was implemented to calculate enrichment scores for sensorial words per beer.
The sex of the tasting subject was not considered when building our sensory database. Instead, results from different panelists were averaged, both for our trained panel (56% male, 44% female) and the RateBeer reviews (70% male, 30% female for RateBeer as a whole).
Beer price collection and processing
Beer prices were collected from the following stores: Colruyt, Delhaize, Total Wine, BeerHawk, The Belgian Beer Shop, The Belgian Shop, and Beer of Belgium. Where applicable, prices were converted to Euros and normalized per liter. Spearman correlations were calculated between these prices and mean overall appreciation scores from RateBeer and the taste panel, respectively.
Pairwise Spearman Rank correlations were calculated between all sensory properties.
Machine learning models
Predictive modeling of sensory profiles from chemical data.
Regression models were constructed to predict (a) trained panel scores for beer flavors and quality from beer chemical profiles and (b) public reviews’ appreciation scores from beer chemical profiles. Z-scores were used to represent sensory attributes in both data sets. Chemical properties with log-normal distributions (Shapiro-Wilk test, p < 0.05 ) were log-transformed. Missing chemical measurements (0.1% of all data) were replaced with mean values per attribute. Observations from 250 beers were randomly separated into a training set (70%, 175 beers) and a test set (30%, 75 beers), stratified per beer style. Chemical measurements (p = 231) were normalized based on the training set average and standard deviation. In total, three linear regression-based models: linear regression with first-order interaction terms (LR), lasso regression with first-order interaction terms (Lasso) and partial least squares regression (PLSR); five decision tree models, Adaboost regressor (ABR), Extra Trees (ET), Gradient Boosting regressor (GBR), Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost regressor (XGBR); one support vector machine model (SVR) and one artificial neural network model (ANN) were trained. The models were implemented using the ‘scikit-learn’ package (v1.2.2) and ‘xgboost’ package (v1.7.3) in Python (v3.9.16). Models were trained, and hyperparameters optimized, using five-fold cross-validated grid search with the coefficient of determination (R 2 ) as the evaluation metric. The ANN (scikit-learn’s MLPRegressor) was optimized using Bayesian Tree-Structured Parzen Estimator optimization with the ‘Optuna’ Python package (v3.2.0). Individual models were trained per attribute, and a multi-output model was trained on all attributes simultaneously.
Model dissection
GBR was found to outperform other methods, resulting in models with the highest average R 2 values in both trained panel and public review data sets. Impurity-based rankings of the most important predictors for each predicted sensorial trait were obtained using the ‘scikit-learn’ package. To observe the relationships between these chemical properties and their predicted targets, partial dependence plots (PDP) were constructed for the six most important predictors of consumer appreciation 74 , 75 .
The ‘SHAP’ package in Python (v0.41.0) was implemented to provide an alternative ranking of predictor importance and to visualize the predictors’ effects as a function of their concentration 68 .
Validation of causal chemical properties
To validate the effects of the most important model features on predicted sensory attributes, beers were spiked with the chemical compounds identified by the models and descriptive sensory analyses were carried out according to the American Society of Brewing Chemists (ASBC) protocol 90 .
Compound spiking was done 30 min before tasting. Compounds were spiked into fresh beer bottles, that were immediately resealed and inverted three times. Fresh bottles of beer were opened for the same duration, resealed, and inverted thrice, to serve as controls. Pairs of spiked samples and controls were served simultaneously, chilled and in dark glasses as outlined in the Trained panel section above. Tasters were instructed to select the glass with the higher flavor intensity for each attribute (directional difference test 92 ) and to select the glass they prefer.
The final concentration after spiking was equal to the within-style average, after normalizing by ethanol concentration. This was done to ensure balanced flavor profiles in the final spiked beer. The same methods were applied to improve a non-alcoholic beer. Compounds were the following: ethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W241415), ethyl hexanoate (Merck KGaA, W243906), isoamyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W205508), phenethyl acetate (Merck KGaA, W285706), ethanol (96%, Colruyt), glycerol (Merck KGaA, W252506), lactic acid (Merck KGaA, 261106).
Significant differences in preference or perceived intensity were determined by performing the two-sided binomial test on each attribute.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this work are available in the Supplementary Data files and have been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 . The RateBeer scores data are under restricted access, they are not publicly available as they are property of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Access can be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of RateBeer (ZX Ventures, USA). Source data are provided with this paper.
Code availability
The code for training the machine learning models, analyzing the models, and generating the figures has been deposited to Zenodo under accession code 10653704 93 .
Tieman, D. et al. A chemical genetic roadmap to improved tomato flavor. Science 355 , 391–394 (2017).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Plutowska, B. & Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography–olfactometry (GC–O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages – A review. Food Chem. 107 , 449–463 (2008).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Legin, A., Rudnitskaya, A., Seleznev, B. & Vlasov, Y. Electronic tongue for quality assessment of ethanol, vodka and eau-de-vie. Anal. Chim. Acta 534 , 129–135 (2005).
Loutfi, A., Coradeschi, S., Mani, G. K., Shankar, P. & Rayappan, J. B. B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 144 , 103–111 (2015).
Ahn, Y.-Y., Ahnert, S. E., Bagrow, J. P. & Barabási, A.-L. Flavor network and the principles of food pairing. Sci. Rep. 1 , 196 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bartoshuk, L. M. & Klee, H. J. Better fruits and vegetables through sensory analysis. Curr. Biol. 23 , R374–R378 (2013).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Piggott, J. R. Design questions in sensory and consumer science. Food Qual. Prefer. 3293 , 217–220 (1995).
Article Google Scholar
Kermit, M. & Lengard, V. Assessing the performance of a sensory panel-panellist monitoring and tracking. J. Chemom. 19 , 154–161 (2005).
Cook, D. J., Hollowood, T. A., Linforth, R. S. T. & Taylor, A. J. Correlating instrumental measurements of texture and flavour release with human perception. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 40 , 631–641 (2005).
Chinchanachokchai, S., Thontirawong, P. & Chinchanachokchai, P. A tale of two recommender systems: The moderating role of consumer expertise on artificial intelligence based product recommendations. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 61 , 1–12 (2021).
Ross, C. F. Sensory science at the human-machine interface. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20 , 63–72 (2009).
Chambers, E. IV & Koppel, K. Associations of volatile compounds with sensory aroma and flavor: The complex nature of flavor. Molecules 18 , 4887–4905 (2013).
Pinu, F. R. Metabolomics—The new frontier in food safety and quality research. Food Res. Int. 72 , 80–81 (2015).
Danezis, G. P., Tsagkaris, A. S., Brusic, V. & Georgiou, C. A. Food authentication: state of the art and prospects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 10 , 22–31 (2016).
Shepherd, G. M. Smell images and the flavour system in the human brain. Nature 444 , 316–321 (2006).
Meilgaard, M. C. Prediction of flavor differences between beers from their chemical composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 30 , 1009–1017 (1982).
Xu, L. et al. Widespread receptor-driven modulation in peripheral olfactory coding. Science 368 , eaaz5390 (2020).
Kupferschmidt, K. Following the flavor. Science 340 , 808–809 (2013).
Billesbølle, C. B. et al. Structural basis of odorant recognition by a human odorant receptor. Nature 615 , 742–749 (2023).
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Smith, B. Perspective: Complexities of flavour. Nature 486 , S6–S6 (2012).
Pfister, P. et al. Odorant receptor inhibition is fundamental to odor encoding. Curr. Biol. 30 , 2574–2587 (2020).
Moskowitz, H. W., Kumaraiah, V., Sharma, K. N., Jacobs, H. L. & Sharma, S. D. Cross-cultural differences in simple taste preferences. Science 190 , 1217–1218 (1975).
Eriksson, N. et al. A genetic variant near olfactory receptor genes influences cilantro preference. Flavour 1 , 22 (2012).
Ferdenzi, C. et al. Variability of affective responses to odors: Culture, gender, and olfactory knowledge. Chem. Senses 38 , 175–186 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lawless, H. T. & Heymann, H. Sensory evaluation of food: Principles and practices. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-6488-5 (2010).
Colantonio, V. et al. Metabolomic selection for enhanced fruit flavor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2115865119 (2022).
Fritz, F., Preissner, R. & Banerjee, P. VirtualTaste: a web server for the prediction of organoleptic properties of chemical compounds. Nucleic Acids Res 49 , W679–W684 (2021).
Tuwani, R., Wadhwa, S. & Bagler, G. BitterSweet: Building machine learning models for predicting the bitter and sweet taste of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 9 , 1–13 (2019).
Dagan-Wiener, A. et al. Bitter or not? BitterPredict, a tool for predicting taste from chemical structure. Sci. Rep. 7 , 1–13 (2017).
Pallante, L. et al. Toward a general and interpretable umami taste predictor using a multi-objective machine learning approach. Sci. Rep. 12 , 1–11 (2022).
Malavolta, M. et al. A survey on computational taste predictors. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 248 , 2215–2235 (2022).
Lee, B. K. et al. A principal odor map unifies diverse tasks in olfactory perception. Science 381 , 999–1006 (2023).
Mayhew, E. J. et al. Transport features predict if a molecule is odorous. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 119 , e2116576119 (2022).
Niu, Y. et al. Sensory evaluation of the synergism among ester odorants in light aroma-type liquor by odor threshold, aroma intensity and flash GC electronic nose. Food Res. Int. 113 , 102–114 (2018).
Yu, P., Low, M. Y. & Zhou, W. Design of experiments and regression modelling in food flavour and sensory analysis: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 71 , 202–215 (2018).
Oladokun, O. et al. The impact of hop bitter acid and polyphenol profiles on the perceived bitterness of beer. Food Chem. 205 , 212–220 (2016).
Linforth, R., Cabannes, M., Hewson, L., Yang, N. & Taylor, A. Effect of fat content on flavor delivery during consumption: An in vivo model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58 , 6905–6911 (2010).
Guo, S., Na Jom, K. & Ge, Y. Influence of roasting condition on flavor profile of sunflower seeds: A flavoromics approach. Sci. Rep. 9 , 11295 (2019).
Ren, Q. et al. The changes of microbial community and flavor compound in the fermentation process of Chinese rice wine using Fagopyrum tataricum grain as feedstock. Sci. Rep. 9 , 3365 (2019).
Hastie, T., Friedman, J. & Tibshirani, R. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, New York, NY). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-21606-5 (2001).
Dietz, C., Cook, D., Huismann, M., Wilson, C. & Ford, R. The multisensory perception of hop essential oil: a review. J. Inst. Brew. 126 , 320–342 (2020).
CAS Google Scholar
Roncoroni, Miguel & Verstrepen, Kevin Joan. Belgian Beer: Tested and Tasted. (Lannoo, 2018).
Meilgaard, M. Flavor chemistry of beer: Part II: Flavor and threshold of 239 aroma volatiles. in (1975).
Bokulich, N. A. & Bamforth, C. W. The microbiology of malting and brewing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 77 , 157–172 (2013).
Dzialo, M. C., Park, R., Steensels, J., Lievens, B. & Verstrepen, K. J. Physiology, ecology and industrial applications of aroma formation in yeast. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 41 , S95–S128 (2017).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Datta, A. et al. Computer-aided food engineering. Nat. Food 3 , 894–904 (2022).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Beer Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.).
Olaniran, A. O., Hiralal, L., Mokoena, M. P. & Pillay, B. Flavour-active volatile compounds in beer: production, regulation and control. J. Inst. Brew. 123 , 13–23 (2017).
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor-active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Meilgaard, M. C. Flavour chemistry of beer. part I: flavour interaction between principal volatiles. Master Brew. Assoc. Am. Tech. Q 12 , 107–117 (1975).
Briggs, D. E., Boulton, C. A., Brookes, P. A. & Stevens, R. Brewing 227–254. (Woodhead Publishing). https://doi.org/10.1533/9781855739062.227 (2004).
Bossaert, S., Crauwels, S., De Rouck, G. & Lievens, B. The power of sour - A review: Old traditions, new opportunities. BrewingScience 72 , 78–88 (2019).
Google Scholar
Verstrepen, K. J. et al. Flavor active esters: Adding fruitiness to beer. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96 , 110–118 (2003).
Snauwaert, I. et al. Microbial diversity and metabolite composition of Belgian red-brown acidic ales. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 221 , 1–11 (2016).
Spitaels, F. et al. The microbial diversity of traditional spontaneously fermented lambic beer. PLoS ONE 9 , e95384 (2014).
Blanco, C. A., Andrés-Iglesias, C. & Montero, O. Low-alcohol Beers: Flavor Compounds, Defects, and Improvement Strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 56 , 1379–1388 (2016).
Jackowski, M. & Trusek, A. Non-Alcohol. beer Prod. – Overv. 20 , 32–38 (2018).
Takoi, K. et al. The contribution of geraniol metabolism to the citrus flavour of beer: Synergy of geraniol and β-citronellol under coexistence with excess linalool. J. Inst. Brew. 116 , 251–260 (2010).
Kroeze, J. H. & Bartoshuk, L. M. Bitterness suppression as revealed by split-tongue taste stimulation in humans. Physiol. Behav. 35 , 779–783 (1985).
Mennella, J. A. et al. A spoonful of sugar helps the medicine go down”: Bitter masking bysucrose among children and adults. Chem. Senses 40 , 17–25 (2015).
Wietstock, P., Kunz, T., Perreira, F. & Methner, F.-J. Metal chelation behavior of hop acids in buffered model systems. BrewingScience 69 , 56–63 (2016).
Sancho, D., Blanco, C. A., Caballero, I. & Pascual, A. Free iron in pale, dark and alcohol-free commercial lager beers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 91 , 1142–1147 (2011).
Rodrigues, H. & Parr, W. V. Contribution of cross-cultural studies to understanding wine appreciation: A review. Food Res. Int. 115 , 251–258 (2019).
Korneva, E. & Blockeel, H. Towards better evaluation of multi-target regression models. in ECML PKDD 2020 Workshops (eds. Koprinska, I. et al.) 353–362 (Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-65965-3_23 .
Gastón Ares. Mathematical and Statistical Methods in Food Science and Technology. (Wiley, 2013).
Grinsztajn, L., Oyallon, E. & Varoquaux, G. Why do tree-based models still outperform deep learning on tabular data? Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2207.08815 (2022).
Gries, S. T. Statistics for Linguistics with R: A Practical Introduction. in Statistics for Linguistics with R (De Gruyter Mouton, 2021). https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110718256 .
Lundberg, S. M. et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2 , 56–67 (2020).
Ickes, C. M. & Cadwallader, K. R. Effects of ethanol on flavor perception in alcoholic beverages. Chemosens. Percept. 10 , 119–134 (2017).
Kato, M. et al. Influence of high molecular weight polypeptides on the mouthfeel of commercial beer. J. Inst. Brew. 127 , 27–40 (2021).
Wauters, R. et al. Novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae variants slow down the accumulation of staling aldehydes and improve beer shelf-life. Food Chem. 398 , 1–11 (2023).
Li, H., Jia, S. & Zhang, W. Rapid determination of low-level sulfur compounds in beer by headspace gas chromatography with a pulsed flame photometric detector. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 66 , 188–191 (2008).
Dercksen, A., Laurens, J., Torline, P., Axcell, B. C. & Rohwer, E. Quantitative analysis of volatile sulfur compounds in beer using a membrane extraction interface. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 54 , 228–233 (1996).
Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black-Box Models Interpretable. (2020).
Zhao, Q. & Hastie, T. Causal interpretations of black-box models. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. Publ. Am. Stat. Assoc. 39 , 272–281 (2019).
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R. & Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning. (Springer, 2019).
Labrado, D. et al. Identification by NMR of key compounds present in beer distillates and residual phases after dealcoholization by vacuum distillation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 100 , 3971–3978 (2020).
Lusk, L. T., Kay, S. B., Porubcan, A. & Ryder, D. S. Key olfactory cues for beer oxidation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 70 , 257–261 (2012).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Torrico, D. D., Dunshea, F. R. & Fuentes, S. Development of artificial neural network models to assess beer acceptability based on sensory properties using a robotic pourer: A comparative model approach to achieve an artificial intelligence system. Beverages 5 , 33 (2019).
Gonzalez Viejo, C., Fuentes, S., Torrico, D. D., Godbole, A. & Dunshea, F. R. Chemical characterization of aromas in beer and their effect on consumers liking. Food Chem. 293 , 479–485 (2019).
Gilbert, J. L. et al. Identifying breeding priorities for blueberry flavor using biochemical, sensory, and genotype by environment analyses. PLOS ONE 10 , 1–21 (2015).
Goulet, C. et al. Role of an esterase in flavor volatile variation within the tomato clade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 109 , 19009–19014 (2012).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Borisov, V. et al. Deep Neural Networks and Tabular Data: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 1–21 https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3229161 (2022).
Statista. Statista Consumer Market Outlook: Beer - Worldwide.
Seitz, H. K. & Stickel, F. Molecular mechanisms of alcoholmediated carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7 , 599–612 (2007).
Voordeckers, K. et al. Ethanol exposure increases mutation rate through error-prone polymerases. Nat. Commun. 11 , 3664 (2020).
Goelen, T. et al. Bacterial phylogeny predicts volatile organic compound composition and olfactory response of an aphid parasitoid. Oikos 129 , 1415–1428 (2020).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Reher, T. et al. Evaluation of hop (Humulus lupulus) as a repellent for the management of Drosophila suzukii. Crop Prot. 124 , 104839 (2019).
Stein, S. E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 10 , 770–781 (1999).
American Society of Brewing Chemists. Sensory Analysis Methods. (American Society of Brewing Chemists, St. Paul, MN, U.S.A., 1992).
McAuley, J., Leskovec, J. & Jurafsky, D. Learning Attitudes and Attributes from Multi-Aspect Reviews. Preprint at https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1210.3926 (2012).
Meilgaard, M. C., Carr, B. T. & Carr, B. T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques. (CRC Press, Boca Raton). https://doi.org/10.1201/b16452 (2014).
Schreurs, M. et al. Data from: Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10653704 (2024).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank all lab members for their discussions and thank all tasting panel members for their contributions. Special thanks go out to Dr. Karin Voordeckers for her tremendous help in proofreading and improving the manuscript. M.S. was supported by a Baillet-Latour fellowship, L.C. acknowledges financial support from KU Leuven (C16/17/006), F.A.T. was supported by a PhD fellowship from FWO (1S08821N). Research in the lab of K.J.V. is supported by KU Leuven, FWO, VIB, VLAIO and the Brewing Science Serves Health Fund. Research in the lab of T.W. is supported by FWO (G.0A51.15) and KU Leuven (C16/17/006).
Author information
These authors contributed equally: Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni.
Authors and Affiliations
VIB—KU Leuven Center for Microbiology, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Michiel Schreurs, Supinya Piampongsant, Miguel Roncoroni, Lloyd Cool, Beatriz Herrera-Malaver, Florian A. Theßeling & Kevin J. Verstrepen
CMPG Laboratory of Genetics and Genomics, KU Leuven, Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Leuven Institute for Beer Research (LIBR), Gaston Geenslaan 1, B-3001, Leuven, Belgium
Laboratory of Socioecology and Social Evolution, KU Leuven, Naamsestraat 59, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Lloyd Cool, Christophe Vanderaa & Tom Wenseleers
VIB Bioinformatics Core, VIB, Rijvisschestraat 120, B-9052, Ghent, Belgium
Łukasz Kreft & Alexander Botzki
AB InBev SA/NV, Brouwerijplein 1, B-3000, Leuven, Belgium
Philippe Malcorps & Luk Daenen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. conceived the experiments. S.P., M.S. and K.J.V. designed the experiments. S.P., M.S., M.R., B.H. and F.A.T. performed the experiments. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., L.K., A.B., P.M., L.D., T.W. and K.J.V. contributed analysis ideas. S.P., M.S., L.C., C.V., T.W. and K.J.V. analyzed the data. All authors contributed to writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kevin J. Verstrepen .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
K.J.V. is affiliated with bar.on. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information.
Nature Communications thanks Florian Bauer, Andrew John Macintosh and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. A peer review file is available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, peer review file, description of additional supplementary files, supplementary data 1, supplementary data 2, supplementary data 3, supplementary data 4, supplementary data 5, supplementary data 6, supplementary data 7, reporting summary, source data, source data, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Schreurs, M., Piampongsant, S., Roncoroni, M. et al. Predicting and improving complex beer flavor through machine learning. Nat Commun 15 , 2368 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Download citation
Received : 30 October 2023
Accepted : 21 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46346-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analysing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalise results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
What is Quantitative Research? Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns.Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations. The purpose of quantitative research is to test a predefined ...
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies.. Associated with the natural, applied, formal, and social sciences this research strategy promotes the objective empirical investigation of ...
Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions.This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected.
The following definition, taken from Aliaga and Gunderson (2000), describes what we mean by quantitative research methods very well: Quantitative research is 'Explaining phenomena by collecting numerical data that are analysed using mathematically based methods (in particu- lar statistics)'. Let's go through this definition step by step.
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
Introduction. Quantitative research, in contrast to qualitative research, deals with data that are numerical or that can be converted into numbers. The basic methods used to investigate numerical data are called 'statistics'. Statistical techniques are concerned with the organisation, analysis, interpretation and presentation of numerical data.
Identifying the measurement level is important for choosing appropriate statistics and hypothesis tests. For example, you can calculate a mean score with quantitative data, but not with categorical data. In a research study, along with measures of your variables of interest, you'll often collect data on relevant participant characteristics.
Introduction. Statistical analysis is necessary for any research project seeking to make quantitative conclusions. The following is a primer for research-based statistical analysis. It is intended to be a high-level overview of appropriate statistical testing, while not diving too deep into any specific methodology.
Quantitative research is the methodology which researchers use to test theories about people's attitudes and behaviors based on numerical and statistical evidence. Researchers sample a large number of users (e.g., through surveys) to indirectly obtain measurable, bias-free data about users in relevant situations.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings. Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
In statistics, quantitative data is numerical and acquired through counting or measuring and contrasted with qualitative data sets, which describe attributes of objects but do not contain numbers. There are a variety of ways that quantitative data arises in statistics. Each of the following is an example of quantitative data: The heights of ...
The two "branches" of quantitative analysis. As I mentioned, quantitative analysis is powered by statistical analysis methods.There are two main "branches" of statistical methods that are used - descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.In your research, you might only use descriptive statistics, or you might use a mix of both, depending on what you're trying to figure out.
Abstract. Statistical methods involved in carrying out a study include planning, designing, collecting data, analysing, drawing meaningful interpretation and reporting of the research findings. The statistical analysis gives meaning to the meaningless numbers, thereby breathing life into a lifeless data. The results and inferences are precise ...
Quantitative variables must use numbers. Think QUANTITY. A critical difference between qualitative vs quantitative data is that you can order the quantitative observations but not the qualitative observations. Quantitative variables can be continuous measurements on a scale or discrete counts. Learn more about continuous vs. discrete data.
Role of Statistics in Biological Research. Statistics is a branch of science that deals with collection, organization and analysis of data from the sample to the whole population. Moreover, it aids in designing a study more meticulously and also give a logical reasoning in concluding the hypothesis.
Descriptive statistics: Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and describe the basic features of the data, such as the mean, median, mode, ... Scientific research: Quantitative data is used extensively in scientific research to test hypotheses and draw conclusions. For example, in biology, researchers might use quantitative data to ...
The field of statistics is concerned with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data.. In the field of research, statistics is important for the following reasons: Reason 1: Statistics allows researchers to design studies such that the findings from the studies can be extrapolated to a larger population.. Reason 2: Statistics allows researchers to perform hypothesis tests to ...
2.0 Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is regarded as the organized inquiry about phenomenon through collection. of numer ical data and execution of statistical, mathematical or ...
Required Qualifications: Ph. D. in Data Science, Data Analytics, Statistics, Computational Mathematics, Computer Science, or closely related field; or an MS in one of the above fields, with industry experience in data science/analytics or at least three (3) years by the appointment date of teaching experience in one of the above mentioned fields.
For each beer, we measure over 200 chemical properties, perform quantitative descriptive sensory analysis with a trained tasting panel and map data from over 180,000 consumer reviews to train 10 ...