Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?

Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a business plan for inventions.
Attract investors and formalize processes by developing a roadmap for commercializing your innovation.

An inventor’s business plan is a framework for bringing a concept to market and achieving profitability. It’s similar to a regular business plan but adds details about intellectual property protection and prototypes. Ideally, a business plan for inventions builds upon a feasibility study. It should highlight your findings from a comprehensive competitive analysis and be tailored to its intended audience, such as investors.
An invention business plan is crucial for getting funding and securing strategic alliances. But you can also use it internally to guide operations, from marketing to hiring. Here’s how to craft an effective report.
Determine your audience and purpose
Although most business plans for a new invention follow a basic outline, you can tailor your approach to appeal to specific readers. Suppose you want to pitch your idea to investors or accelerator programs. In this case, it’s essential to mention funding requirements. But you should also emphasize the skills and experience your team brings to the table. According to Heer Law , “Often, investors and other stakeholders care as much or more about who the people are behind an invention than the potential of the invention on its own.”
However, if you’re looking for co-founders and employees, modify your document to clarify the skills required and long-term benefits for early joiners. Once you understand what drives your intended audience, you can write a business plan that excites them while answering their questions.
[ Read more: How These Innovation-Driven Startups Reached an Elusive Milestone: Profitability ]
Outline your invention business plan sections
The Small Business Association (SBA) said, “There’s no right or wrong way to write a business plan. What’s important is that your plan meets your needs.” You can use a basic template , take a free course , or start from scratch. Begin your process by outlining commonly used sections, then modify your document to include invention-specific content.
Often, investors and other stakeholders care as much or more about who the people are behind an invention than the potential of the invention on its own.
Christopher Heer, Annette Latoszewska, and Daryna Kutsyna, Heer Law
Consider adding the following components:
- Executive summary: Keep it concise but touch on each aspect of your plan. Remember to pique interest and compel your audience to read more.
- Company overview: Discuss your industry and niche, including what makes your invention and business stand out. Explain how you will commercialize your design (selling to consumers, wholesale, or retail).
- Organizational structure: This is where you describe your legal business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), or corporation). Provide details about inventors, executive team, and current or prospective employees.
- Market and competitive analysis: Share insights from your feasibility study, including an analysis of your industry, competitors, and market. Add statistics about market size and growth. Plus, offer a customer profile and explain what differentiates your invention from others.
- Invention: Tell readers about your design (features and functions) and how it benefits customers. Mention your product research, prototypes, and intellectual property registrations .
- Marketing and sales: Explain how you will apply competitive and market insights to earn a return. Topics may include sales, pricing, promotional strategies, positioning statements, and marketing campaigns.
- Financial information: Show how your invention will be profitable and use spreadsheets, charts, and graphs. Include projected revenue , profit and loss, cash flow, and a balance sheet. Also, detail any funding needs, how you’ll get the money, and what you’ll do with it.
- Appendix: Add all supporting evidence for your invention business plan. For instance, Chron.com said, “Investors respond well to business plans that include endorsements of the product from potential customers.
Add sections for your new invention
In addition to these regular sections, you can expand your business plan to include research and development, intellectual property protection , and owned or future IP assets. According to Heer Law, the research and development component helps readers understand “future products that can be commercially exploited.” Likewise, details about your intellectual property protection ensure investors that you’ve taken action to defend your innovation from unwanted duplication.
Provide information about any assets going through the application process and how various trademarks, patents , and copyrights will impact profitability. Also, discuss if you plan on developing new inventions or have prototypes available.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Applications are open for the CO—100! Now is your chance to join an exclusive group of outstanding small businesses. Share your story with us — apply today .
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .

Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
How to use ai to assess your competition, how startups contribute to innovation in emerging industries, how entrepreneurs can find a business mentor.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Business Plan Template for Innovation
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Do you have an innovative business idea that you're ready to bring to life? Look no further than ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Innovation! This template is specifically designed to help entrepreneurs and start-up companies outline their brilliant ideas, strategies, and goals, while also highlighting market opportunities, potential risks, and financial projections. With this template, you'll have everything you need to secure funding from investors and guide your path to success. So, why wait? Start planning your next big innovation with ClickUp today!
Business Plan Template for Innovation Benefits
When using the Business Plan Template for Innovation, you can expect the following benefits:
- Streamline the process of creating a comprehensive business plan for your innovative ideas
- Clearly define your unique selling proposition and competitive advantage to attract investors
- Identify potential obstacles and risks, allowing you to develop effective strategies for mitigating them
- Create realistic financial projections and forecasts to demonstrate the profitability of your innovation
- Guide your decision-making process and provide a roadmap for achieving your business goals
- Increase your chances of securing funding from investors by presenting a well-structured and compelling business plan
Main Elements of Innovation Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Innovation provides entrepreneurs and start-up companies with the essential tools to outline and execute their innovative business ideas. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do, ensuring that each task is properly categorized and accounted for.
- Custom Fields: Utilize 3 custom fields including Reference, Approved, and Section to add specific details and attributes to your business plan tasks, making it easier to track and manage the necessary information.
- Custom Views: Access 5 different views to effectively manage your business plan, including Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide. These views allow you to organize and visualize your business plan in different ways, ensuring clarity and facilitating collaboration.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with your team seamlessly using ClickUp's features such as real-time commenting, file attachments, and task assignments, ensuring effective communication and progress tracking.
- Integrations: Integrate ClickUp with other essential tools such as project management software, financial platforms, and communication tools to streamline your business plan process and enhance productivity.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Innovation
If you're ready to take your innovative ideas to the next level and create a business plan, follow these 5 steps using the Business Plan Template for Innovation in ClickUp:
1. Define your innovative idea
Start by clearly defining your innovative idea and how it solves a problem or meets a need in the market. Consider what makes your idea unique and how it provides value to customers. Be specific and focused in your description to ensure a clear understanding of your concept.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to brainstorm and outline your innovative idea, highlighting its key features and benefits.
2. Research your target market
Conduct thorough market research to understand your target audience and their needs. Identify the size of your target market, their demographics, behavior patterns, and purchasing habits. This information will help you tailor your product or service to meet their specific needs and preferences.
Utilize the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data, making it easy to identify trends and insights.
3. Develop your business model
Outline your business model, including your revenue streams, cost structure, and value proposition. Determine how you will generate revenue from your innovative idea and the resources required to bring it to market. Consider any partnerships or collaborations that may be necessary to support your business model.
Create custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze different aspects of your business model, such as revenue projections and cost estimates.
4. Create a marketing strategy
Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your innovative idea and attract customers. Identify the most effective channels to reach your target market and outline your messaging and positioning. Consider the unique selling points of your innovation and how to communicate them effectively.
Use tasks in ClickUp to create a timeline for your marketing activities and assign responsibilities to team members.
5. Set milestones and track progress
Establish key milestones and targets to track your progress and measure the success of your innovation. Break down your goals into smaller, achievable milestones that will keep you motivated and on track. Regularly review your progress and adjust your strategies as needed to ensure you're moving towards your ultimate vision.
Utilize Milestones in ClickUp to set and track your business plan milestones, ensuring that you stay focused and stay on track.
By following these steps and utilizing the Business Plan Template for Innovation in ClickUp, you'll be well-equipped to turn your innovative idea into a successful business venture. Good luck!
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Innovation
Entrepreneurs and start-up companies can use the Business Plan Template for Innovation in ClickUp to effectively outline their innovative business ideas and strategies, while also tracking progress and collaborating with team members.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize and outline different sections of your business plan, such as executive summary, market analysis, and financial projections
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and milestones for each section, ensuring timely completion of your business plan
- The Business Plan View provides a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate between sections and make necessary edits
- Create a Getting Started Guide View to provide instructions and guidelines for team members involved in the business plan creation process
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional context and track important information
- Collaborate with team members by assigning tasks, leaving comments, and attaching relevant files to ensure everyone is on the same page
With the ClickUp Business Plan Template for Innovation, you can streamline the process of creating a comprehensive and compelling business plan, setting your innovative ideas on the path to success.
- Business Plan Template for Colleges
- Business Plan Template for Press Agents
- Business Plan Template for Underwriters
- Business Plan Template for Importers
- Business Plan Template for Political Scientists
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
Ideas and insights from Harvard Business Publishing Corporate Learning

Five Steps to Implementing Innovation

We’re all familiar with stories about breakthrough products, services, and processes—the disruptors that grab the headlines and garner eye-popping valuations. And then there are the entrepreneurs who end up on the cover of Bloomberg Businessweek and write best-selling books about the keys to their success. The message seems to be that, through good timing or genius, innovation is the purview of a select few.
But at its core, innovation is simply a way to solve problems and create value in new ways. Overhauling an inefficient process, using customer feedback to breathe new life into a stale product—innovations don’t have to be splashy or game-changing to lead to sustained organizational success. These small but mighty initiatives seldom come from top management or an “idea lab,” but rather from individual contributors and frontline leaders who are closest to the customer and best positioned to understand their needs.
When employees from throughout the ranks learn to see themselves as innovators and take steps to make their ideas a reality, the results can be powerful. In addition to furthering a company’s purpose and bolstering its bottom line, employee-driven innovation engages people in ways that carrying out top-down directives never will.
Tips to get you started
Given the growing interest in innovation, it’s no surprise that organizations are looking for clear guidelines on how to implement it. Every innovation is unique. Even so, certain strategies and skills are useful across a range of projects and at all levels of an organization:
- Spot opportunities for innovation. As innovation expert Greg Satell puts it, “No matter what form innovation takes—short, agile sprints or long-term, grand-challenge investments—innovation is fundamentally about solving problems.” As you think about your organization, what problems need solving? Where do opportunities lie? Once you land on some promising ideas, continue to explore them from different angles. By doing so, you may discover even more exciting possibilities.
- Prioritize opportunities. You don’t have infinite time and resources, so prioritize potential innovations depending on where you think you’ll get the most bang for your buck. Narrow in on the two or three ideas you think are most worth digging into, testing, and refining. Then express them as hypotheses you can test through targeted experiments.
- Test your potential innovations. Keep your experiments modest in scope, especially when you’re starting out. You may want to begin with “paper prototypes,” or simple drawings of the new product or process that your end users can interact with to see what works and what doesn’t. They are quick and inexpensive, and they help you figure out where you need to tweak your concept. With each round of testing, move to progressively more complex experiments involving more users.
- Build support for your innovations. Don’t be shy. Make sure the time is right and tell your story to all your stakeholders, including those whose resource backing you need and those who’ll directly benefit from your innovation. You’ll want to tailor your approach based on what’s important to each person and what you need from them.
- Learn from your innovation efforts. You’ve probably heard the mantra “fail fast, learn fast.” After each innovation, list what you would do again and what you wouldn’t. And don’t overthink failure; the key is learn from it and apply those lessons to your next innovation.
We’ve seen these steps work at all levels in an organization. In fact, we even followed them when redesigning our Harvard ManageMentor® innovation-related topics. What process do you follow when implementing innovation in your organization?
Janice Molloy is senior manager, online learning at Harvard Business Publishing. Email her at [email protected] .
Let’s talk
Change isn’t easy, but we can help. Together we’ll create informed and inspired leaders ready to shape the future of your business.
© 2024 Harvard Business School Publishing. All rights reserved. Harvard Business Publishing is an affiliate of Harvard Business School.
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Information
- Terms of Use
- About Harvard Business Publishing
- Higher Education
- Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business School
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience. By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Cookie and Privacy Settings
We may request cookies to be set on your device. We use cookies to let us know when you visit our websites, how you interact with us, to enrich your user experience, and to customize your relationship with our website.
Click on the different category headings to find out more. You can also change some of your preferences. Note that blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience on our websites and the services we are able to offer.
These cookies are strictly necessary to provide you with services available through our website and to use some of its features.
Because these cookies are strictly necessary to deliver the website, refusing them will have impact how our site functions. You always can block or delete cookies by changing your browser settings and force blocking all cookies on this website. But this will always prompt you to accept/refuse cookies when revisiting our site.
We fully respect if you want to refuse cookies but to avoid asking you again and again kindly allow us to store a cookie for that. You are free to opt out any time or opt in for other cookies to get a better experience. If you refuse cookies we will remove all set cookies in our domain.
We provide you with a list of stored cookies on your computer in our domain so you can check what we stored. Due to security reasons we are not able to show or modify cookies from other domains. You can check these in your browser security settings.
We also use different external services like Google Webfonts, Google Maps, and external Video providers. Since these providers may collect personal data like your IP address we allow you to block them here. Please be aware that this might heavily reduce the functionality and appearance of our site. Changes will take effect once you reload the page.
Google Webfont Settings:
Google Map Settings:
Google reCaptcha Settings:
Vimeo and Youtube video embeds:
You can read about our cookies and privacy settings in detail on our Privacy Policy Page.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Planning, Startups, Stories
Tim berry on business planning, starting and growing your business, and having a life in the meantime., how does innovation fit into a business plan.
This is the third of four answers to questions I got in email last week from an MBA student asking my opinion as part of his research. The question is the title: how does innovation fit into a business plan?
Innovation changes a business plan pretty much as a reflection of how it changes a business. It adds risk, uncertainty, and interest too.
Funny thing about risk: we usually think of it as a negative, but in this case it isn’t. Risk has two sides to it: up and down.
- The upside risk in innovation is of course the benefits to a business when innovation leads to a more desirable offering: better product, suitable for a larger market, differentiated from competition, easier to build, and so forth. We get that immediately. It’s faster, cheaper, better; higher resolution, longer lasting, lighter, and so forth.
- The downside risk is there too. Live by innovation, die by innovation. The business that depends on innovation usually positions itself on innovation and loses big time when somebody else comes up with the next new bigger, faster, and better.
Uncertainty comes along with innovation because, by definition, what’s innovative is new; and new means it might not work, might have a fatal flaw, might not be accepted by the market, might never be finished. New also means it could take off very fast — more uncertainty — or not at all. It’s uncertainty about when the product (or service) is available, will it work, will enough people like it, are there competitors out there in the bushes where you can’t see them yet.
And interest comes with innovation too. Market makers are interested. Opinion leaders are interested. Competitors are interested. And investors are interested. To the investor, innovation means defensibility and market advantage.
So how does all of this fit into a business plan? It’s all over the plan. It’s in the forecasts, the schedules, the marketing plans, the financial strategy. It’s part of the business’ DNA.
It starts with strategy, the heart of a business plan. Innovation is part of your company’s identity, we would hope one of its strengths, and certainly a key element in business offering. It directly affects the market, both in the higher degree of guessing required (educated guessing, we hope) and in how it affects target market and message. And it affects strategy focus, too, because it turns a company towards it like plants growing towards the sun.
From there it flows easily into the flesh and bones of the plan, all of the concrete, specific, and measurable details about who does what, when, and how much it costs, and how much it brings in as revenue.
Conclusion: it’s an oblique question, in a way. Something like asking how courage fits in a novel, or color in a painting. How does direction fit into navigation?
[…] Sara Manela First mover advantage is great, except when it’s not. If your product is truly innovative, your biggest challenge is likely to be explaining what, exactly, your product is, what its […]
[…] *How Does Innovation Fit into a Business Plan? by Tim Berry […]
Thanks Joseph. And that, of course, is what my book The Plan-As-You-Go Business Plan (see the sidebar here, on this site) is about too. Tim.
If you know that innovation is part and parcel of your business, then select a planning methodology that is built innovation rather than one that merely accommodates it.
The Agile development approach is built for environments where the outcomes are not all clearly defined and innovation is required. In these environments it is clear that the ship will change course many times. If you know you are going to need to change directions often, especially in the early phases of the business, don't get on a Cruise ship, get on a Skidoo.
I never hear people telling entrepreneurs about the benefits of Agile development, so I am taking it on as my personal mission. See my website about it. http://www.Making-A-DREAM.com
Peace Joseph Flahiff, PMP [email protected]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
The eight essentials of innovation
Get the latest.
January 4, 2024
In the time since this article was first published, McKinsey has continued to explore the topics it covers. Read on for a summary of our latest insights.
Innovation may sound like a creative art: hard to quantify, dependent on lightning-bolt inspiration, subject to the availability of magic dust and luck. It’s true that innovation relies, to an extent, on the vagaries of ingenuity. But according to McKinsey research, innovation—and, crucially, the type of outperformance that innovation can spark in organizations—is much more likely to happen when there is a rigorous process in place to bring ideas to fruition.
The simple fact is that innovation translates to growth : innovation leaders generate almost twice as much revenue growth from innovation as their competitors. Our research in the years since the COVID-19 pandemic has found that these organizations, which we call “innovative growers,” do this by cultivating four best practices :
- Link innovation to growth aspirations and reinforce its importance in strategic and financial discussions.
- Pursue multiple pathways to growth, both in core businesses and when entering adjacent customer segments, industries, or geographies. Innovative growers also only enter markets where there are clear opportunities to create value.
- Invest productively in all innovation capabilities, including research and development, resourcing, and operational agility.
- Cultivate strong M&A capabilities, particularly programmatic dealmaking.
Innovation can be especially rewarding when deployed as a crisis-management measure . During periods of uncertainty, organizations that invest in innovation—contrary, perhaps, to the impulse to batten down the hatches—are also more likely to emerge ahead of competitors. More specifically, innovative organizations are more likely to find emerging pockets of growth in times of uncertainty.
Looking ahead, we expect innovative organizations to keep outpacing their peers. Our 2023 McKinsey Global Survey reveals a striking connection between organizations’ innovation capabilities and their abilities to increase value through the newest digital technologies, including generative AI. Everyone is talking about gen AI, but organizations with strong innovative cultures are walking the walk, too: thirty percent of top innovators we surveyed said they are already deploying gen AI at scale in their innovation and R&D functions, more than six times the rate of companies that are lagging on innovation. Top innovators are also already reaping significantly better business outcomes from their AI investments than slower-moving competitors.
Articles referenced:
- “ Companies with innovative cultures have a big edge with generative AI ,” August 2023
- “ Innovation: Your solution for weathering uncertainty ,” January 2023
- “ Committed innovators: How masters of essentials outperform ,” June 2022
- “ Innovation in a crisis: Why it is more critical than ever ,” June 2020
It’s no secret: innovation is difficult for well-established companies. By and large, they are better executors than innovators, and most succeed less through game-changing creativity than by optimizing their existing businesses.
Yet hard as it is for such organizations to innovate, large ones as diverse as Alcoa, the Discovery Group, and NASA’s Ames Research Center are actually doing so. What can other companies learn from their approaches and attributes? That question formed the core of a multiyear study comprising in-depth interviews, workshops, and surveys of more than 2,500 executives in over 300 companies, including both performance leaders and laggards, in a broad set of industries and countries (Exhibit 1). What we found were a set of eight essential attributes that are present, either in part or in full, at every big company that’s a high performer in product, process, or business-model innovation.
Since innovation is a complex, company-wide endeavor , it requires a set of crosscutting practices and processes to structure, organize, and encourage it. Taken together, the essentials described in this article constitute just such an operating system, as seen in Exhibit 2. These often overlapping, iterative, and nonsequential practices resist systematic categorization but can nonetheless be thought of in two groups. The first four, which are strategic and creative in nature, help set and prioritize the terms and conditions under which innovation is more likely to thrive. The next four essentials deal with how to deliver and organize for innovation repeatedly over time and with enough value to contribute meaningfully to overall performance.
To be sure, there’s no proven formula for success, particularly when it comes to innovation. While our years of client-service experience provide strong indicators for the existence of a causal relationship between the attributes that survey respondents reported and the innovations of the companies we studied, the statistics described here can only prove correlation. Yet we firmly believe that if companies assimilate and apply these essentials—in their own way, in accordance with their particular context, capabilities, organizational culture, and appetite for risk—they will improve the likelihood that they, too, can rekindle the lost spark of innovation. In the digital age, the pace of change has gone into hyperspeed, so companies must get these strategic, creative, executional, and organizational factors right to innovate successfully.
President John F. Kennedy’s bold aspiration, in 1962, to “go to the moon in this decade” motivated a nation to unprecedented levels of innovation. A far-reaching vision can be a compelling catalyst, provided it’s realistic enough to stimulate action today.
But in a corporate setting, as many CEOs have discovered, even the most inspiring words often are insufficient, no matter how many times they are repeated. It helps to combine high-level aspirations with estimates of the value that innovation should generate to meet financial-growth objectives. Quantifying an “innovation target for growth,” and making it an explicit part of future strategic plans, helps solidify the importance of and accountability for innovation. The target itself must be large enough to force managers to include innovation investments in their business plans. If they can make their numbers using other, less risky tactics, our experience suggests that they (quite rationally) will.
Establishing a quantitative innovation aspiration is not enough, however. The target value needs to be apportioned to relevant business “owners” and cascaded down to their organizations in the form of performance targets and timelines. Anything less risks encouraging inaction or the belief that innovation is someone else’s job.
For example, Lantmännen, a big Nordic agricultural cooperative, was challenged by flat organic growth and directionless innovation. Top executives created an aspirational vision and strategic plan linked to financial targets: 6 percent growth in the core business and 2 percent growth in new organic ventures. To encourage innovation projects, these quantitative targets were cascaded down to business units and, ultimately, to product groups. During the development of each innovation project, it had to show how it was helping to achieve the growth targets for its category and markets. As a result, Lantmännen went from 4 percent to 13 percent annual growth, underpinned by the successful launch of several new brands. Indeed, it became the market leader in premade food only four years after entry and created a new premium segment in this market.
Such performance parameters can seem painful to managers more accustomed to the traditional approach. In our experience, though, CEOs are likely just going through the motions if they don’t use evaluations and remuneration to assess and recognize the contribution that all top managers make to innovation.
Fresh, creative insights are invaluable, but in our experience many companies run into difficulty less from a scarcity of new ideas than from the struggle to determine which ideas to support and scale. At bigger companies, this can be particularly problematic during market discontinuities, when supporting the next wave of growth may seem too risky, at least until competitive dynamics force painful changes.
Innovation is inherently risky, to be sure, and getting the most from a portfolio of innovation initiatives is more about managing risk than eliminating it. Since no one knows exactly where valuable innovations will emerge, and searching everywhere is impractical, executives must create some boundary conditions for the opportunity spaces they want to explore. The process of identifying and bounding these spaces can run the gamut from intuitive visions of the future to carefully scrutinized strategic analyses. Thoughtfully prioritizing these spaces also allows companies to assess whether they have enough investment behind their most valuable opportunities.
During this process, companies should set in motion more projects than they will ultimately be able to finance, which makes it easier to kill those that prove less promising. RELX Group, for example, runs 10 to 15 experiments per major customer segment, each funded with a preliminary budget of around $200,000, through its innovation pipeline every year, choosing subsequently to invest more significant funds in one or two of them, and dropping the rest. “One of the hardest things to figure out is when to kill something,” says Kumsal Bayazit, RELX Group’s chief strategy officer. “It’s a heck of a lot easier if you have a portfolio of ideas.”
Once the opportunities are defined, companies need transparency into what people are working on and a governance process that constantly assesses not only the expected value, timing, and risk of the initiatives in the portfolio but also its overall composition. There’s no single mix that’s universally right. Most established companies err on the side of overloading their innovation pipelines with relatively safe, short-term, and incremental projects that have little chance of realizing their growth targets or staying within their risk parameters. Some spread themselves thinly across too many projects instead of focusing on those with the highest potential for success and resourcing them to win.
These tendencies get reinforced by a sluggish resource-reallocation process. Our research shows that a company typically reallocates only a tiny fraction of its resources from year to year, thereby sentencing innovation to a stagnating march of incrementalism. 1 1. See Stephen Hall, Dan Lovallo, and Reinier Musters, “ How to put your money where your strategy is ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 2012; and Vanessa Chan, Marc de Jong, and Vidyadhar Ranade, “ Finding the sweet spot for allocating innovation resources ,” McKinsey Quarterly , May 2014.
Innovation also requires actionable and differentiated insights—the kind that excite customers and bring new categories and markets into being. How do companies develop them? Genius is always an appealing approach, if you have or can get it. Fortunately, innovation yields to other approaches besides exceptional creativity.
The rest of us can look for insights by methodically and systematically scrutinizing three areas: a valuable problem to solve, a technology that enables a solution, and a business model that generates money from it. You could argue that nearly every successful innovation occurs at the intersection of these three elements. Companies that effectively collect, synthesize, and “collide” them stand the highest probability of success. “If you get the sweet spot of what the customer is struggling with, and at the same time get a deeper knowledge of the new technologies coming along and find a mechanism for how these two things can come together, then you are going to get good returns,” says Alcoa chairman and chief executive Klaus Kleinfeld.
The insight-discovery process, which extends beyond a company’s boundaries to include insight-generating partnerships, is the lifeblood of innovation. We won’t belabor the matter here, though, because it’s already the subject of countless articles and books. 2 2. See, for example, Marla M. Capozzi, Reneé Dye, and Amy Howe, “ Sparking creativity in teams: An executive’s guide ,” McKinsey Quarterly , April 2011; and Marla M. Capozzi, John Horn, and Ari Kellen, “ Battle-test your innovation strategy ,” McKinsey Quarterly , December 2012. One thing we can add is that discovery is iterative, and the active use of prototypes can help companies continue to learn as they develop, test, validate, and refine their innovations. Moreover, we firmly believe that without a fully developed innovation system encompassing the other elements described in this article, large organizations probably won’t innovate successfully, no matter how effective their insight-generation process is.

Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Business-model innovations—which change the economics of the value chain, diversify profit streams, and/or modify delivery models—have always been a vital part of a strong innovation portfolio. As smartphones and mobile apps threaten to upend oldline industries, business-model innovation has become all the more urgent: established companies must reinvent their businesses before technology-driven upstarts do. Why, then, do most innovation systems so squarely emphasize new products? The reason, of course, is that most big companies are reluctant to risk tampering with their core business model until it’s visibly under threat. At that point, they can only hope it’s not too late.
Leading companies combat this troubling tendency in a number of ways. They up their game in market intelligence, the better to separate signal from noise. They establish funding vehicles for new businesses that don’t fit into the current structure. They constantly reevaluate their position in the value chain, carefully considering business models that might deliver value to priority groups of new customers. They sponsor pilot projects and experiments away from the core business to help combat narrow conceptions of what they are and do. And they stress-test newly emerging value propositions and operating models against countermoves by competitors.
Amazon does a particularly strong job extending itself into new business models by addressing the emerging needs of its customers and suppliers. In fact, it has included many of its suppliers in its customer base by offering them an increasingly wide range of services, from hosted computing to warehouse management. Another strong performer, the Financial Times , was already experimenting with its business model in response to the increasing digitalization of media when, in 2007, it launched an innovative subscription model, upending its relationship with advertisers and readers. “We went against the received wisdom of popular strategies at the time,” says Caspar de Bono, FT board member and managing director of B2B. “We were very deliberate in getting ahead of the emerging structural change, and the decisions turned out to be very successful.” In print’s heyday, 80 percent of the FT ’s revenue came from print advertising. Now, more than half of it comes from content, and two-thirds of circulation comes from digital subscriptions.
Virulent antibodies undermine innovation at many large companies. Cautious governance processes make it easy for stifling bureaucracies in marketing, legal, IT, and other functions to find reasons to halt or slow approvals. Too often, companies simply get in the way of their own attempts to innovate. A surprising number of impressive innovations from companies were actually the fruit of their mavericks, who succeeded in bypassing their early-approval processes. Clearly, there’s a balance to be maintained: bureaucracy must be held in check, yet the rush to market should not undermine the cross-functional collaboration, continuous learning cycles, and clear decision pathways that help enable innovation. Are managers with the right knowledge, skills, and experience making the crucial decisions in a timely manner, so that innovation continually moves through an organization in a way that creates and maintains competitive advantage, without exposing a company to unnecessary risk?
Companies also thrive by testing their promising ideas with customers early in the process, before internal forces impose modifications that blur the original value proposition. To end up with the innovation initially envisioned, it’s necessary to knock down the barriers that stand between a great idea and the end user. Companies need a well-connected manager to take charge of a project and be responsible for the budget, time to market, and key specifications—a person who can say yes rather than no. In addition, the project team needs to be cross-functional in reality, not just on paper. This means locating its members in a single place and ensuring that they give the project a significant amount of their time (at least half) to support a culture that puts the innovation project’s success above the success of each function.
Cross-functional collaboration can help ensure end-user involvement throughout the development process. At many companies, marketing’s role is to champion the interests of end users as development teams evolve products and to help ensure that the final result is what everyone first envisioned. But this responsibility is honored more often in the breach than in the observance. Other companies, meanwhile, rationalize that consumers don’t necessarily know what they want until it becomes available. This may be true, but customers can certainly say what they don’t like. And the more quickly and frequently a project team gets—and uses—feedback, the more quickly it gets a great end result.
Some ideas, such as luxury goods and many smartphone apps, are destined for niche markets. Others, like social networks, work at global scale. Explicitly considering the appropriate magnitude and reach of a given idea is important to ensuring that the right resources and risks are involved in pursuing it. The seemingly safer option of scaling up over time can be a death sentence. Resources and capabilities must be marshaled to make sure a new product or service can be delivered quickly at the desired volume and quality. Manufacturing facilities, suppliers, distributors, and others must be prepared to execute a rapid and full rollout.
For example, when TomTom launched its first touch-screen navigational device, in 2004, the product flew off the shelves. By 2006, TomTom’s line of portable navigation devices reached sales of about 5 million units a year, and by 2008, yearly volume had jumped to more than 12 million. “That’s faster market penetration than mobile phones” had, says Harold Goddijn, TomTom’s CEO and cofounder. While TomTom’s initial accomplishment lay in combining a well-defined consumer problem with widely available technology components, rapid scaling was vital to the product’s continuing success. “We doubled down on managing our cash, our operations, maintaining quality, all the parts of the iceberg no one sees,” Goddijn adds. “We were hugely well organized.”
In the space of only a few years, companies in nearly every sector have conceded that innovation requires external collaborators. Flows of talent and knowledge increasingly transcend company and geographic boundaries. Successful innovators achieve significant multiples for every dollar invested in innovation by accessing the skills and talents of others. In this way, they speed up innovation and uncover new ways to create value for their customers and ecosystem partners.
Smart collaboration with external partners, though, goes beyond merely sourcing new ideas and insights; it can involve sharing costs and finding faster routes to market. Famously, the components of Apple’s first iPod were developed almost entirely outside the company; by efficiently managing these external partnerships, Apple was able to move from initial concept to marketable product in only nine months. NASA’s Ames Research Center teams up not just with international partners—launching joint satellites with nations as diverse as Lithuania, Saudi Arabia, and Sweden—but also with emerging companies, such as SpaceX.
High-performing innovators work hard to develop the ecosystems that help deliver these benefits. Indeed, they strive to become partners of choice, increasing the likelihood that the best ideas and people will come their way. That requires a systematic approach. First, these companies find out which partners they are already working with; surprisingly few companies know this. Then they decide which networks—say, four or five of them—they ideally need to support their innovation strategies. This step helps them to narrow and focus their collaboration efforts and to manage the flow of possibilities from outside the company. Strong innovators also regularly review their networks, extending and pruning them as appropriate and using sophisticated incentives and contractual structures to motivate high-performing business partners. Becoming a true partner of choice is, among other things, about clarifying what a partnership can offer the junior member: brand, reach, or access, perhaps. It is also about behavior. Partners of choice are fair and transparent in their dealings.
Moreover, companies that make the most of external networks have a good idea of what’s most useful at which stages of the innovation process. In general, they cast a relatively wide net in the early going. But as they come closer to commercializing a new product or service, they become narrower and more specific in their sourcing, since by then the new offering’s design is relatively set.
How do leading companies stimulate, encourage, support, and reward innovative behavior and thinking among the right groups of people? The best companies find ways to embed innovation into the fibers of their culture, from the core to the periphery.
They start back where we began: with aspirations that forge tight connections among innovation, strategy, and performance. When a company sets financial targets for innovation and defines market spaces, minds become far more focused. As those aspirations come to life through individual projects across the company, innovation leaders clarify responsibilities using the appropriate incentives and rewards.
The Discovery Group, for example, is upending the medical and life-insurance industries in its native South Africa and also has operations in the United Kingdom, the United States, and China, among other locations. Innovation is a standard measure in the company’s semiannual divisional scorecards—a process that helps mobilize the organization and affects roughly 1,000 of the company’s business leaders. “They are all required to innovate every year,” Discovery founder and CEO Adrian Gore says of the company’s business leaders. “They have no choice.”
Organizational changes may be necessary, not because structural silver bullets exist—we’ve looked hard for them and don’t think they do—but rather to promote collaboration, learning, and experimentation. Companies must help people to share ideas and knowledge freely, perhaps by locating teams working on different types of innovation in the same place, reviewing the structure of project teams to make sure they always have new blood, ensuring that lessons learned from success and failure are captured and assimilated, and recognizing innovation efforts even when they fall short of success.
Internal collaboration and experimentation can take years to establish, particularly in large, mature companies with strong cultures and ways of working that, in other respects, may have served them well. Some companies set up “innovation garages” where small groups can work on important projects unconstrained by the normal working environment while building new ways of working that can be scaled up and absorbed into the larger organization. NASA, for example, has ten field centers. But the space agency relies on the Ames Research Center, in Silicon Valley, to maintain what its former director, Dr. Pete Worden, calls “the character of rebels” to function as “a laboratory that’s part of a much larger organization.”
Big companies do not easily reinvent themselves as leading innovators. Too many fixed routines and cultural factors can get in the way. For those that do make the attempt, innovation excellence is often built in a multiyear effort that touches most, if not all, parts of the organization. Our experience and research suggest that any company looking to make this journey will maximize its probability of success by closely studying and appropriately assimilating the leading practices of high-performing innovators. Taken together, these form an essential operating system for innovation within a company’s organizational structure and culture.
Marc de Jong is a principal in McKinsey’s Amsterdam office, Nathan Marston is a principal in the London office, and Erik Roth is a principal in the Shanghai office.
The authors wish to thank Jill Hellman and McKinsey’s Peet van Biljon for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

The simple rules of disciplined innovation

How Discovery keeps innovating

Competition at the digital edge: ‘Hyperscale’ businesses
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Concept Map Note Taking
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
The Essential Guide to the Innovation Management Process

In today’s fast-paced business world, staying competitive requires more than just keeping up — it demands innovation. Organizations need to actively seek new solutions, improve processes, and anticipate future needs. In this guide we will walk you through the steps of the innovation management process helping you foster a culture of innovation within your organizations successfully.
What is Innovation Management
Innovation management is the systematic process of planning, organizing, controlling, and directing innovation within an organization. It helps foster and implement new ideas to improve the organization’s performance. It involves creating a culture that values creativity, identifying opportunities for innovation, and effectively executing those ideas. This encompasses activities like idea generation, research and development, testing, and the strategic deployment of innovative solutions.
The objective is to maintain a competitive edge, adapt to changing market demands, and continually upgrade the organization’s products or services. Successful innovation management requires leadership support, cross-functional collaboration, and a systematic approach to nurturing and implementing creative concepts.
The Key Pillars of Innovation Management
Together, these four aspects make up a holistic innovation management framework:
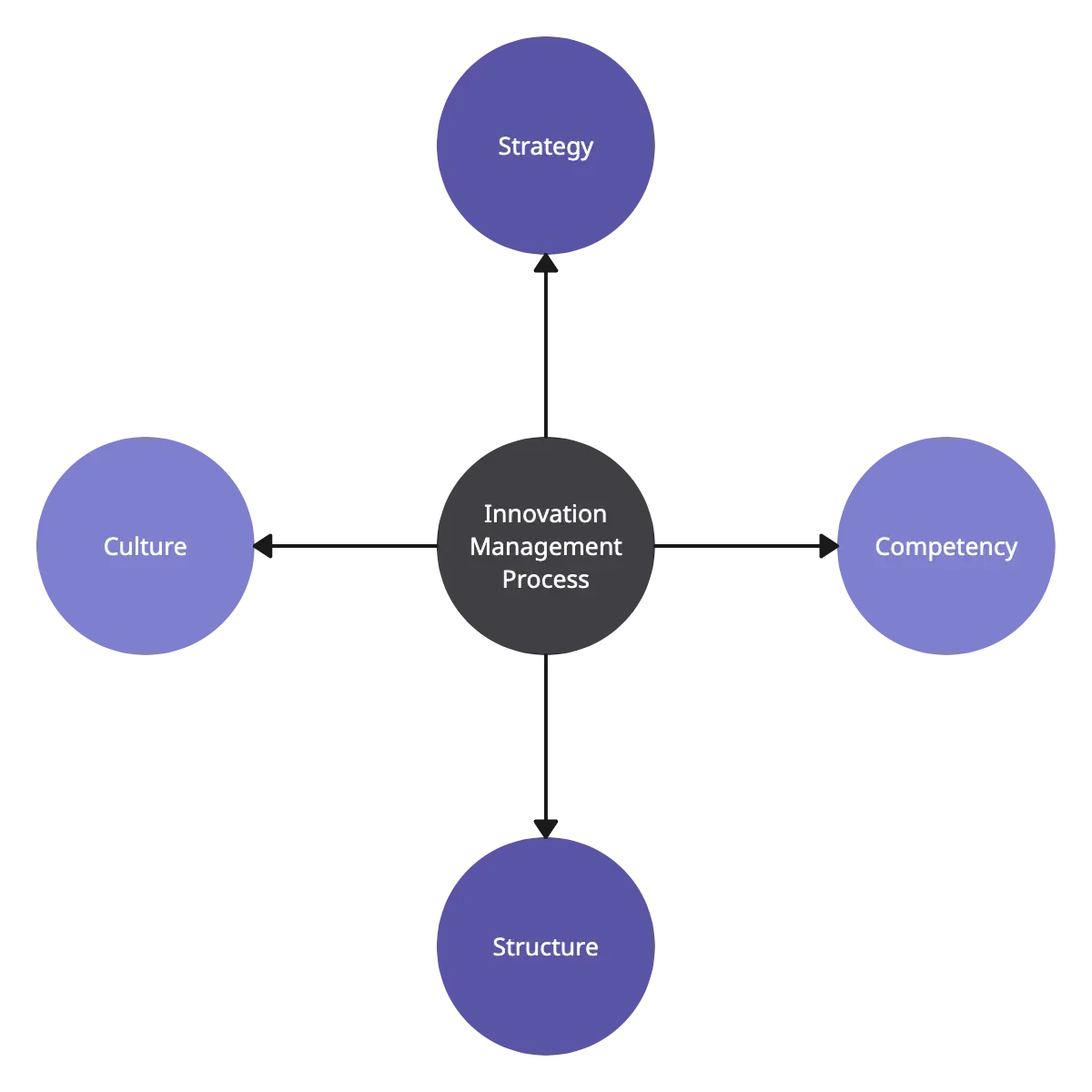
Competency : This refers to the skills, knowledge, and capabilities of individuals and teams involved in the innovation process. Competency encompasses both technical expertise and creative thinking, making sure that the organization has the right talent to drive innovation.
Structure : This includes how teams are organized, how information flows within the organization, and the existence of dedicated innovation teams or departments. A well-designed structure supports efficient communication and collaboration.
Culture : A culture that encourages risk-taking, values creativity, and embraces continuous learning creates an innovation-friendly environment. This includes promoting open communication, celebrating diverse perspectives, and recognizing the importance of experimentation.
Strategy : A clear innovation strategy aligns the organization’s innovation efforts with its overall business objectives. It involves defining goals, priorities, and the direction for innovation initiatives. A strategic approach ensures that innovation is not a random process but a targeted effort contributing to the organization’s long-term success.
Innovation Management Process
The innovation management process is a structured and systematic approach that organizations follow to foster, develop, and implement innovations. Organizations can use this process to navigate the complexities of innovation, transforming creative ideas into practical solutions that contribute to growth, competitiveness, and overall success.
The innovation management process is not just a linear series of steps but a cyclical and adaptive journey, creating a culture of learning and adaptation. This iterative approach helps organizations to stay agile, respond to market changes, and consistently drive meaningful innovation.

Innovation Management Process Steps
1. idea generation.
Idea generation is the initial phase where a diverse range of creative ideas is collected. This involves tapping into the collective intelligence of employees, engaging with customers, and staying attuned to emerging market trends. The goal is to create a pool of potential innovations that can address challenges or capitalize on opportunities.
2. Idea Screening
In the idea screening phase, the collected ideas undergo evaluation to identify those with the highest potential. Criteria such as feasibility, alignment with organizational goals, and market relevance are considered. This step helps prioritize and focus resources on the most promising concepts, filtering out ideas that may not be viable.
3. Concept Development and Testing
Once you have identified the promising ideas, you can move into the concept development phase. Here, ideas are translated into concrete concepts or prototypes. These concepts are then tested in real-world scenarios or through simulations to gather feedback and assess their practicality. Testing allows for refinement and improvement before moving to the next stage.
4. Implementation
The implementation phase involves turning the refined concept into a tangible product, service, or process. This stage requires coordinated effort, resource allocation, and effective project management to make sure a smooth transition from concept to reality. Implementation may occur within the organization or involve releasing the innovation to the broader market.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuously monitor and evaluate the progress of the product, service or process. This involves tracking the innovation’s performance against predefined metrics and assessing its impact on organizational goals. Regular evaluations help organizations adapt to changing circumstances and refine their innovation approach for the future. This step closes the loop in the innovation management process, creating a cycle of learning and improvement.
Innovation Management Toolkit
This innovation management toolkit is a collection of methodologies, processes, frameworks, and tools designed to facilitate, guide, and optimize the various stages of innovation within an organization.
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Why is Innovation Management Important
Innovation management is important for several key reasons:
Sustainable growth : Innovation is the key to sustainable business growth. Developing new ideas, products, and processes keeps organizations competitive and helps them adapt to market changes.
Competitive advantage : Innovation helps organizations to differentiate themselves by offering unique and valuable solutions, providing a competitive edge.
Adaptation to change : Innovation management helps organizations to adapt to market changes proactively, minimizing risks and capitalizing on new opportunities.
Efficiency and effectiveness : Through streamlined processes, new technologies, or creative problem-solving, innovation can boost performance.
Employee engagement : Fostering a culture of innovation can boost employee engagement and satisfaction.
Customer satisfaction : With new innovations, businesses can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to long-term relationships.
Risk mitigation : By experimenting with new ideas on a smaller scale, organizations can test their viability before making large-scale investments, reducing the risk of failure.
Innovation Management Best Practices
- Clear strategy : Develop a precise innovation strategy to guide goals, priorities, and align efforts with the organization’s vision.
- Open communication : Encourage open channels for idea sharing, fostering a collaborative environment where teams freely exchange insights and solutions.
- Cross-functional collaboration : Foster collaboration across diverse teams to leverage different skills and perspectives for comprehensive problem-solving.
- Continuous learning : Cultivate a culture of ongoing learning, emphasizing the importance of learning from both successes and failures.
- Dedicated resources : Allocate dedicated resources, including budget and time, to support innovation initiatives and ensure they receive the necessary attention.
- Encourage risk-taking : Create an environment that supports calculated risk-taking, empowering employees to think creatively and experiment without fear of repercussions.
- Customer-centric approach : Keep the end-user in mind throughout the innovation process to ensure the final products or services meet customer needs.
Effective Innovation Management Process Templates
Use: Idea generation and concept development
Mind maps visually represent interconnected ideas and concepts. They are effective for brainstorming sessions, capturing diverse thoughts, and organizing complex relationships, fostering creative thinking during the early stages of innovation.
Use: Idea generation and concept Development
SCAMPER is a creative thinking technique that stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. It encourages innovative thinking by prompting users to explore different ways of approaching a problem or idea.
Fishbone Diagrams (Ishikawa or Cause-and-Effect Diagrams)
Use: Problem analysis and root cause identification
Fishbone diagrams help identify potential causes of a problem influencing an outcome. In the innovation process, they are useful for analyzing challenges, understanding their root causes, and devising innovative solutions.
SWOT Analysis
Use: Strategic planning
SWOT analysis evaluates internal Strengths and Weaknesses, and external Opportunities and Threats. During the innovation management process, it can be used to identify areas for improvement, potential avenues for innovation, and understanding the external landscape.
Gantt Charts
Use: Project planning and implementation
Gantt charts visualize project timelines, tasks, and dependencies. They help innovation managers plan and track the progress of innovation initiatives, ensuring timely execution and efficient resource allocation.
Value Proposition Canvas
Use: Concept development and customer-centric innovation
The value proposition canvas illustrates how a product or service creates value for a customer. It guides innovation by aligning concepts with customer needs, ensuring that innovations resonate with target audiences.
Use: Business model innovation
Business model canvas provides a holistic view of a business model, covering key components like value proposition, customer segments, and revenue streams. It helps in innovating business models, assuring sustainability and profitability.
Design Thinking Template
Use: User-centric ideation and prototyping
A design thinking template typically follows key stages such as Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test. It guides teams through understanding user needs (Empathize), defining the problem (Define), generating ideas (Ideate), creating prototypes (Prototype), and testing and refining solutions (Test). This iterative process ensures a user-centric approach to innovation, encouraging empathy and creativity.
Use: Concept development and communication
Storyboards visually present the flow and user experience of a product or service. They help communicate concepts, user journeys, and the intended impact of innovations, so they’re helpful for internal understanding and external presentations.
Prototyping Templates
Use: Concept development and testing
Represents the visual or functional aspects of a product or service, crucial for testing and refining innovations before full-scale implementation.
Use: Strategic planning and implementation
Roadmaps visually represent the timeline and milestones of a project or initiative. In innovation management, they guide teams through the different stages of innovation, ensuring a structured and well-paced development process.
Learn about more methods and tools to streamline your innovation process with these resources;
- Top 6 Methods of Innovation to Come up with Unique Product Ideas
- 5 Effective Steps to Creating a Powerful Innovation Strategy
By fostering innovation, organizations not only stay competitive but also take a leading role in positive change. Embracing the iterative nature of innovation, learning from experiences, and adapting strategies ensures a forward-thinking and resilient approach. Innovative management process isn’t just about success; it’s about transforming organizations for sustainable growth and relevance.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.

Innovation Plan Template

What is an Innovation Plan?
An innovation plan is a detailed approach to help companies identify and pursue new ideas and opportunities. It is a strategic plan that defines focus areas and objectives, sets measurable targets (KPIs) and implements related projects to achieve those goals. This plan allows organizations to stay ahead of the competition and foster a culture of innovation.
What's included in this Innovation Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Innovation Plan template for?
This innovation plan template is designed for teams of any size and industry. It provides a framework for creating a strategic plan to develop new products, services, and processes. This template includes resources and guidance to help teams create actionable objectives, set achievable targets and plan for success.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a broad area of the business that needs to be addressed. It outlines the purpose and the desired impact of the innovation strategy. Examples of focus areas include Invest in Innovation, Improve Efficiency, and Strengthen Collaboration. When defining focus areas, it is important to keep them specific.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the specific goals that need to be achieved to meet the focus area. Examples of objectives include Identify new opportunities and Pursue new opportunities. Objectives should be actionable and measurable.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are metrics used to measure progress towards achieving the objectives. Examples of KPIs include Increase number of market opportunities identified, Decrease time to develop and test prototypes, and Increase percentage of processes automated. KPIs should be numerical, specific and measurable.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects are the actionable steps that need to be taken to achieve the KPIs. Examples of projects include Conduct market research, Develop and test prototypes, and Automate processes. Projects should be actionable and measurable.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade is a strategy execution platform that allows teams to create, manage, and track their strategy in one place. It helps teams to visualize their progress and measure success. With Cascade, teams can quickly implement their innovation plan and see tangible results faster.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Innovation in Business: What It Is & Why It’s Important

- 08 Mar 2022
Today’s competitive landscape heavily relies on innovation. Business leaders must constantly look for new ways to innovate because you can't solve many problems with old solutions.
Innovation is critical across all industries; however, it's important to avoid using it as a buzzword and instead take time to thoroughly understand the innovation process.
Here's an overview of innovation in business, why it's important, and how you can encourage it in the workplace.
What Is Innovation?
Innovation and creativity are often used synonymously. While similar, they're not the same. Using creativity in business is important because it fosters unique ideas . This novelty is a key component of innovation.
For an idea to be innovative, it must also be useful. Creative ideas don't always lead to innovations because they don't necessarily produce viable solutions to problems.
Simply put: Innovation is a product, service, business model, or strategy that's both novel and useful. Innovations don't have to be major breakthroughs in technology or new business models; they can be as simple as upgrades to a company's customer service or features added to an existing product.
Access your free e-book today.
Types of Innovation
Innovation in business can be grouped into two categories : sustaining and disruptive.
- Sustaining innovation: Sustaining innovation enhances an organization's processes and technologies to improve its product line for an existing customer base. It's typically pursued by incumbent businesses that want to stay atop their market.
- Disruptive innovation: Disruptive innovation occurs when smaller companies challenge larger businesses. It can be classified into groups depending on the markets those businesses compete in. Low-end disruption refers to companies entering and claiming a segment at the bottom of an existing market, while new-market disruption denotes companies creating an additional market segment to serve a customer base the existing market doesn't reach.
The most successful companies incorporate both types of innovation into their business strategies. While maintaining an existing position in the market is important, pursuing growth is essential to being competitive. It also helps protect a business against other companies affecting its standing.
Learn about the differences between sustaining and disruptive innovation in the video below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
The Importance of Innovation
Unforeseen challenges are inevitable in business. Innovation can help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company in the process. Here are three reasons innovation is crucial for your business:
- It allows adaptability: The recent COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business on a monumental scale. Routine operations were rendered obsolete over the course of a few months. Many businesses still sustain negative results from this world shift because they’ve stuck to the status quo. Innovation is often necessary for companies to adapt and overcome the challenges of change.
- It fosters growth: Stagnation can be extremely detrimental to your business. Achieving organizational and economic growth through innovation is key to staying afloat in today’s highly competitive world.
- It separates businesses from their competition: Most industries are populated with multiple competitors offering similar products or services. Innovation can distinguish your business from others.

Innovation & Design Thinking
Several tools encourage innovation in the workplace. For example, when a problem’s cause is difficult to pinpoint, you can turn to approaches like creative problem-solving . One of the best approaches to innovation is adopting a design thinking mentality.
Design thinking is a solutions-based, human-centric mindset. It's a practical way to strategize and design using insights from observations and research.
Four Phases of Innovation
Innovation's requirements for novelty and usefulness call for navigating between concrete and abstract thinking. Introducing structure to innovation can guide this process.
In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar teaches design thinking principles using a four-phase innovation framework : clarify, ideate, develop, and implement.

- Clarify: The first stage of the process is clarifying a problem. This involves conducting research to empathize with your target audience. The goal is to identify their key pain points and frame the problem in a way that allows you to solve it.
- Ideate: The ideation stage involves generating ideas to solve the problem identified during research. Ideation challenges assumptions and overcomes biases to produce innovative ideas.
- Develop: The development stage involves exploring solutions generated during ideation. It emphasizes rapid prototyping to answer questions about a solution's practicality and effectiveness.
- Implement: The final stage of the process is implementation. This stage involves communicating your developed idea to stakeholders to encourage its adoption.
Human-Centered Design
Innovation requires considering user needs. Design thinking promotes empathy by fostering human-centered design , which addresses explicit pain points and latent needs identified during innovation’s clarification stage.
There are three characteristics of human-centered design:
- Desirability: For a product or service to succeed, people must want it. Prosperous innovations are attractive to consumers and meet their needs.
- Feasibility: Innovative ideas won't go anywhere unless you have the resources to pursue them. You must consider whether ideas are possible given technological, economic, or regulatory barriers.
- Viability: Even if a design is desirable and feasible, it also needs to be sustainable. You must consistently produce or deliver designs over extended periods for them to be viable.
Consider these characteristics when problem-solving, as each is necessary for successful innovation.
The Operational and Innovative Worlds
Creativity and idea generation are vital to innovation, but you may encounter situations in which pursuing an idea isn't feasible. Such scenarios represent a conflict between the innovative and operational worlds.
The Operational World
The operational world reflects an organization's routine processes and procedures. Metrics and results are prioritized, and creativity isn't encouraged to the extent required for innovation. Endeavors that disrupt routine—such as risk-taking—are typically discouraged.
The Innovative World
The innovative world encourages creativity and experimentation. This side of business allows for open-endedly exploring ideas but tends to neglect the functional side.
Both worlds are necessary for innovation, as creativity must be grounded in reality. You should strive to balance them to produce human-centered solutions. Design thinking strikes this balance by guiding you between the concrete and abstract.

Learning the Ropes of Innovation
Innovation is easier said than done. It often requires you to collaborate with others, overcome resistance from stakeholders, and invest valuable time and resources into generating solutions. It can also be highly discouraging because many ideas generated during ideation may not go anywhere. But the end result can make the difference between your organization's success or failure.
The good news is that innovation can be learned. If you're interested in more effectively innovating, consider taking an online innovation course. Receiving practical guidance can increase your skills and teach you how to approach problem-solving with a human-centered mentality.
Eager to learn more about innovation? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation ,one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you're not sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What Your Innovation Process Should Look Like
- Steve Blank
- Pete Newell

Whether you’re a company or a government agency.
For innovation to contribute to a company or government agency, it needs to be designed as a process from start to deployment. When organizations lack a formal innovation pipeline process, project approvals tend to be based on who has the best demo or slides, or who lobbies the hardest. A canonical Lean Innovation process inside a company or government agency would include sourcing, curation, prioritization, hypothesis testing and exploration, incubation, and integration.
Companies and government agencies often make the mistake of viewing innovation as a set of unconstrained activities with no discipline. In reality, for innovation to contribute to a company or government agency, it needs to be designed as a process from start to deployment.
- SB Steve Blank is an adjunct professor at Stanford University, a senior fellow at Columbia University, and a lecturer at the University of California, Berkeley. He has been either a cofounder or an early employee at eight high-tech start-ups, and he helped start the National Science Foundation Innovation Corps and the Hacking for Defense and Hacking for Diplomacy programs. He blogs at www.steveblank.com .
- PN Pete Newell , Colonel (Retired), ran the U.S. Army’s Rapid Equipping Force and now runs BMNT, providing battlefield tested solutions to corporate and government problems.
Partner Center

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Must-Have Innovation Action Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

Taranjeet Singh
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, innovation isn't just a buzzword; it's a critical driving force behind growth and success. Picture this: You're seated at a strategy meeting, surrounded by enthusiastic minds, all brimming with ingenious ideas that could potentially reshape your company's future. The challenge lies in converting these innovative sparks into a structured action plan that propels your organization forward.
Enter the game-changer: Must-Have Innovation Action Plan Templates. These meticulously crafted templates serve as your strategic compass, guiding you through transforming innovative concepts into actionable steps.
Our Must-Have Technology Plan Templates will help you create a roadmap for your organization's technology needs so that you can achieve your business goals.
What sets these templates apart is their adaptability – a crucial element in today's ever-evolving business environment. These templates offer diverse frameworks, from product development to process optimization, and are designed to align with your unique vision seamlessly.
Achieve unparalleled growth in the digital age through our Must-have Digital Transformation Plan Templates .
Furthermore, these innovation action plan templates are 100% customizable, allowing you to customize them according to your requirements.
In this blog, we explore innovation frameworks, their significance and unveil the power of tailor-made solutions.
Let's begin!
Template 1: Action Plan for Innovation Techniques Categories Analysis PPT Template
This concise and comprehensive one-page PPT presentation is an invaluable guide for businesses and individuals seeking to enhance their innovation strategies. This power-packed PPT encompasses a structured approach to innovation, divided into four meticulously crafted sections.
The Methodology section lays out a systematic framework, offering insights into innovation techniques. Users can explore methodologies such as design thinking, brainstorming, and SWOT analysis, enabling them to approach innovation challenges with a well-defined strategy.
Under the Product Selection segment, users gain access to a curated selection process that aids in identifying the most promising ideas for development. This step ensures that only the most viable concepts move forward in the innovation pipeline, optimizing resources and maximizing the potential for success.
The Product Designing portion delves into the creative aspect of innovation, guiding translating concepts into tangible and marketable products. Users can explore tips and strategies for prototyping, iteration, and user-centric design, ensuring their innovative ideas are brought to life effectively.
In the Marketing section, users are equipped with tactics to propel their innovative products into the market. From target audience analysis to branding and promotion strategies, this segment empowers users to position their products for maximum impact and resonance.
An innovative layout places the user's perspective at the forefront, with the left side featuring three distinct categories: Need Seekers, Market Readers, and Technology Drivers. It allows users to tailor their approach based on their business focus and strategic goals.
Download the PPT to witness a transformative innovation journey.
Download Now!
Achieve goals every quarter with our Quarterly Action Plan Templates .
Template 2: Product Innovation Strategy and Action Plan PPT Template
This impactful one-page presentation and a strategically designed workflow diagram equip you with a winning approach to thrive in competitive markets.
The PPT unfolds a strategic journey in five pivotal steps:
- Determine Organizational Objectives and Product Goals : Start by aligning your innovation efforts with overarching organizational goals. Identify key product objectives harmonizing with your business mission, setting a solid foundation for your innovation strategy.
- Understand Competitors and Customers : Dive deep into the competitive landscape and analyze your potential rivals. Simultaneously, gain valuable insights into your customers' needs, preferences, and pain points. This holistic understanding guides formulating an innovation strategy familiar to your target audience and market dynamics.
- Develop a Unique Value Proposition : Forge a compelling value proposition that sets your product apart. Craft a narrative encapsulating your innovation's distinct benefits, positioning your brand as a frontrunner in meeting customer demands.
- Create a Realistic Strategy with Timeline, Budget, and Team Allocation : Build a pragmatic innovation roadmap. Define clear milestones, allocate budgetary resources judiciously, and assemble a dedicated team with the expertise to execute the strategy effectively and ensures a seamless and efficient implementation process.
- Execute and Measure Success : Put your strategy into action, closely monitoring its progress. Regularly assess key performance indicators against the predetermined goals, fine-tuning your approach as needed. A significant highlight of the plan is transitioning existing consumers seamlessly into new products or features, reducing user downtime by an impressive XX%.
Download the PPT to embark on a transformative journey to revolutionize your product development and market leadership approach.
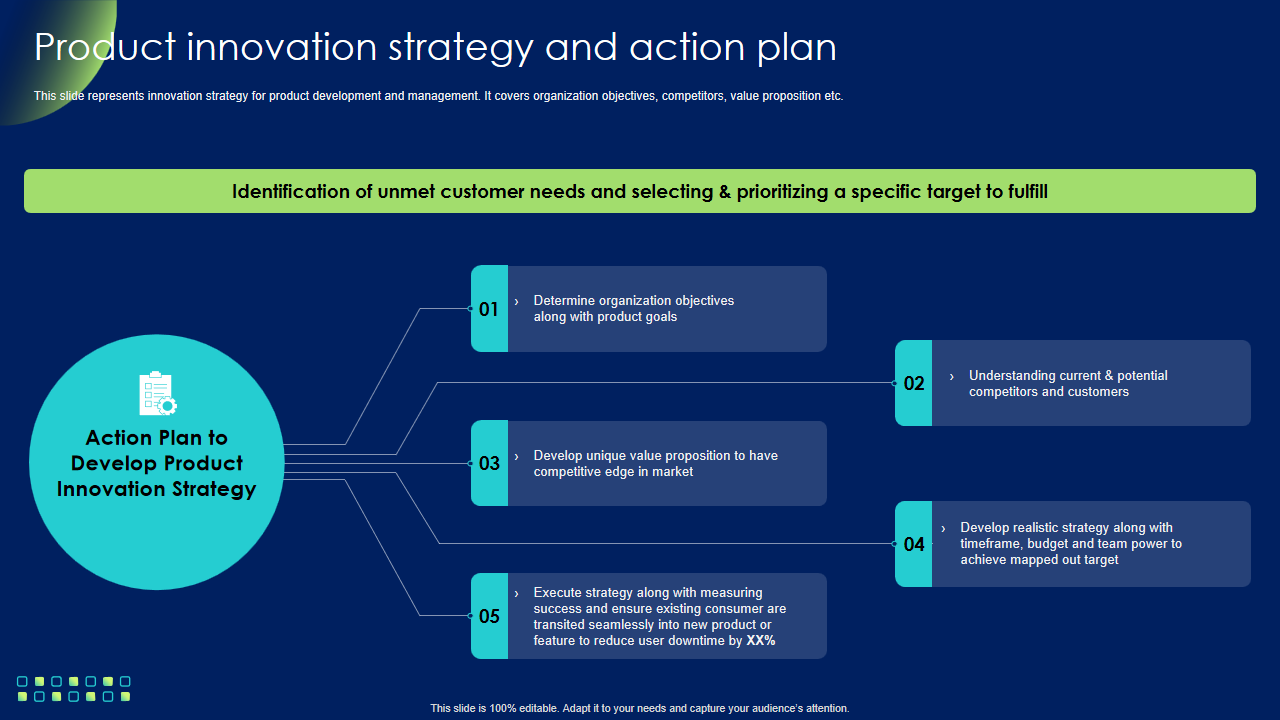
Template 3: Action Plan for Cross-Functional Product Teams PPT
Our one-page PowerPoint template provides
- a clear and concise overview of your project's progress,
- ensuring streamlined communication,
- effective delegation,
- successful goal attainment.
At the heart of this PPT lies a dynamic representation of your project's key components:
- Name of the Goal : Clearly stated at the top, your project's objective takes center stage, providing immediate context for all stakeholders involved.
- Number of Tasks Complete : Visualized through an intuitive bar percentage, track the completion of individual tasks, and gain insight into their status at a glance.
- Percent of Goal Complete : Another bar percentage dynamically showcases the overall progress towards achieving the set goal, aiding in real-time decision-making.
The template further extends into a detailed table that serves as your project's command center:
- Action : Each task is accompanied by a description of its activity, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of its purpose.
- Responsible : Assign specific team members to tasks, fostering accountability and promoting seamless collaboration.
- Start Date : Keep track of task initiation, enabling effective time management and progress assessment.
- Required Resources : Easily identify the resources needed for each task, minimizing delays and optimizing resource allocation.
- Status : A pie chart visualizes the task's current status, providing a holistic view of progress and bottlenecks.
With this template, you'll be equipped with a powerful tool that promotes clarity, accountability, and efficiency within your cross-functional product teams. Seamlessly manage tasks, allocate resources, and monitor progress while maintaining a concise and informative overview. Download the PPT and pave the way for successful project execution!
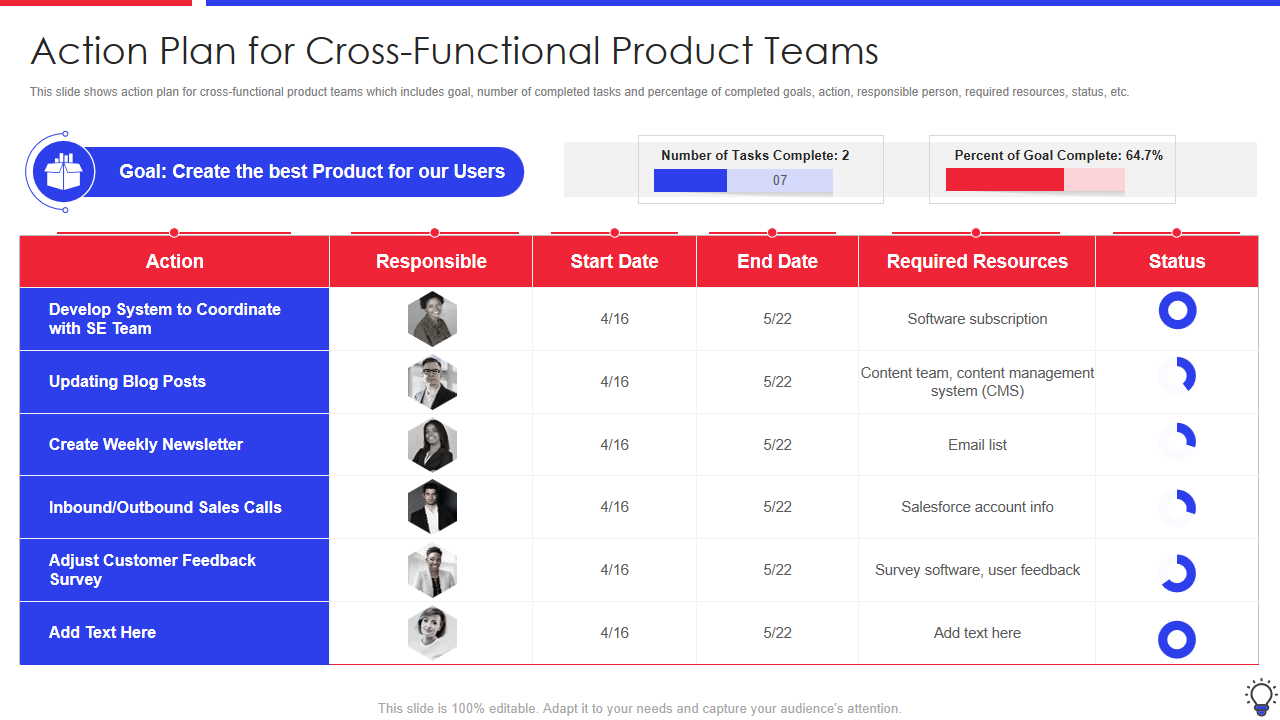
Innovation is the heartbeat of progress, and with these Innovation Action Plan Templates at your disposal, you hold the key to unlocking unprecedented growth. By harnessing the power of these customizable templates, you're poised to transform visionary concepts into tangible achievements. Embrace the future confidently, armed with strategic blueprints that transcend boundaries and redefine success. Your journey towards innovation begins now – carve your path and pioneer change like never before.
FAQs on Innovation Action Plan
How do you write an innovation plan.
To craft an effective innovation plan, follow these steps:
- Assessment : Understand current challenges, market trends, and competitor landscape.
- Goal Setting : Define clear objectives and align them with business strategy.
- Idea Generation : Encourage brainstorming, idea-sharing platforms, and cross-functional collaboration.
- Idea Selection : Evaluate ideas based on feasibility, potential impact, and goal alignment.
- Resource Allocation : Allocate budget, time, and personnel for implementation.
- Prototyping : Develop prototypes or concepts for testing and refinement.
- Testing : Assess prototypes through pilot programs or simulations, gathering feedback.
- Iterative Refinement : Continuously improve based on feedback and data.
- Implementation : Execute chosen ideas with well-defined project management.
- Measurement : Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track success.
- Communication : Regularly update stakeholders on progress and outcomes.
What is an innovation action?
An innovation action is a strategic endeavor to introduce novel ideas, processes, or technologies to drive positive change and advancement. It involves creatively addressing challenges, improving existing systems, or inventing new solutions, fostering progress and competitiveness across various fields. By fostering ingenuity and experimentation, innovation actions contribute to societal and economic development, encouraging growth and transformation in both established industries and emerging sectors.
What are the 4 types of innovation strategies?
The four types of innovation strategies are incremental, disruptive, architectural, and radical. Incremental innovation involves gradual improvements to existing products or processes. Disruptive innovation creates new markets by introducing simpler or more affordable solutions. Architectural innovation reconfigures existing components to create novel systems or products. Radical innovation entails groundbreaking advancements, often leading to entirely new industries. Each strategy offers distinct benefits and challenges, shaping how organizations approach innovation. By diversifying their approaches, businesses can balance short-term gains with long-term transformative potential, ensuring sustained growth and competitiveness in dynamic markets.
What is an innovation plan?
An innovation plan is a strategic roadmap that outlines a systematic approach for generating novel ideas, implementing creative solutions, and fostering organizational advancements. It encompasses a structured framework to identify areas of improvement, drive research and development, and introduce groundbreaking products, services, or processes. An effective innovation plan includes clear objectives, resource allocation, timelines, and metrics to measure progress and success. It encourages a culture of continuous learning, experimentation, and adaptation, aiming to stay competitive, address evolving customer needs, and drive growth. By fostering a collaborative environment and aligning innovation efforts with business goals, an innovation plan empowers companies to stay at the forefront of their industry and navigate ever-changing markets.
Related posts:
- Is Your Business Really Growing? Top 7 Business Metrics That’ll Prove You Right Or Wrong
- Human Resource Strategies to Prevent Your Growing Company From Imploding!
- Top 10 Free Business Google Slides Templates for Entrepreneurs
- [Updated 2023] Top 20 Innovation Strategy Templates to Churn Out Remarkable Products
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 7 SWOT Analysis Templates with Examples and Samples

Must-Have Tax Sheet Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


- Partners & Resources
- Business Attraction Team
- Business Development Team
- Cultural Development Team
- Global Trade Services Team
- Arts and Culture
- Expansion and Growth
- Export & Trade
- Internet Services
- Startup and Early Stage
- Webinar Recordings
- News & Program Updates
- Business Spotlights
- Upcoming Events
The Business Plan

Developing a Business Plan
The Business Plan is a written summary of what you hope to accomplish by being in business and how you intend to organize your resources to meet your goals. A business plan is a road map for operating your business and measures progress along the way. There are three major reasons for developing a business plan.
- It encourages realism: The process of putting a business plan together, including the thought you put into it before beginning to write it, forces you to take an objective, unemotional look at your business project in its entirety.
- It is an operating tool: When a business plan is properly used, it helps you to manage your business and work toward its success.
- It is a way to communicate ideas: it provides the basis for your financial proposal, and you can share additional details in conversation.
Click Here to view the Business Plan Template
The importance of proper planning cannot be overemphasized. By taking an objective look at your business, you can identify strengths and address weaknesses. Moreover, your business plan provides the information needed for lenders or investors to evaluate your venture.
Structure of the Business Plan
The business plan is divided into two main sections, with the first section being the written description of the entire project. This section should include explanations of the following topics:
- A description regarding the type, status, form and aims of your business, as well as what is unique about it
- A marketing strategy which identifies your target customers, their present and potential size and how you will satisfy them (see the “Developing a Marketing Strategy” article)
- A competition analysis including a list of all competitors, and the strengths and weaknesses of each
- A location analysis including where you will locate, the reasons for your site selection and the type of facility to be used
- A production analysis which will describe what and how you will produce/service and the type of equipment needed
- Management and personnel requirements which will list the background, experience, specific duties and wages and salaries of the staff
Section two of a business plan consists of financial data. It qualifies facts and assumptions laid out in section one and should include the following information:
- Sources and applications of funding which list where you will get your money and what you will use it for
- A capital equipment list that describes the equipment needed and what it will cost
- A balance sheet, a projected income statement and a projected cash flow analysis
- Historical records (if already operating)
The information contained in the financial data section of your business plan is critical to accurately evaluate the feasibility of your idea and to plan just how large an investment is required to bring your business to a stable level of operation. Remember to be realistic in your projections.
Before presenting your business plan to potential lenders/investors, you may want to have it reviewed by a consultant to ensure that all necessary information has been included. Next, use the business plan to map out the feasibility of your idea on paper. It is much cheaper to never start a business than it is to start one and fail early. Remember, your business plan is a tool for all parties, including lenders, investors, and you.
Ready to learn more?
Check out our New Business Checklist to find more helpful resources and considerations for starting a successful business.
Business Innovation Plan Template
About this template.
Design a powerful pitch deck using this easy-to-edit presentation template and showcase your innovation plan and long-term vision for the business. Use these slides to structure a presentation that walks your team members, investors, board of directors, and other stakeholders through your business plan in a way that is efficient, professional, and impactful.
Montserrat | Roboto
960 X 540 pixels

Title Slide
Start your business innovation plan with an eye-catching title. Add important details including the company tagline, sub-headline, logo, website, and other credentials.
Table of contents
Give your audience an outline of the agenda by listing the various topics covered in your business plan. This slide also has a text placeholder for you to add a short description about your company, product summary, timeline, feasibility, goals, or stage-wise plan.

Provide an overview of your business plan by summarizing products, services, target demographics, planned budget, goals, and other supporting data. Add icons, charts, or images to make it engaging and aesthetically appealing.
The problem
Identification of a problem is a crucial aspect in a pitch, so use this slide to encapsulate the challenges you're going to solve with this plan.

The solution
Now that you've outlined the problems, the next step is to talk about the different solutions that can be implemented to resolve them. Give insight into how your new project will add value to the business and emphasize key points using text effects and animation.
Product summary
Introduce your product with eye-catching visuals. Be clear, concise, and persuasive in explaining the benefits and the impact your product will have on the business.

The template offers different slides to capture information about the market, competitors, PEST, and SWOT. It also includes charts to represent data visually along with a brief interpretation. It offers visually pleasing layouts for each of these slides to keep the text minimal and engaging.
Financial highlights
Every project, idea, or business plan will have an annual budget allocated for different stages of a project. Showcase the different financial elements with tables and charts and highlight important data points with animation and text effects.
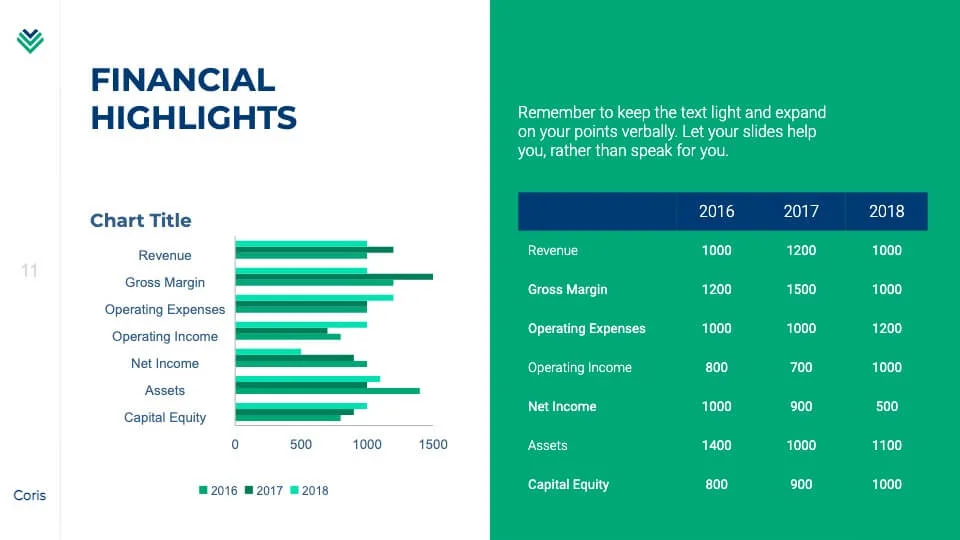
Use the timeline chart to demonstrate and breakdown your big goals and milestones for the project. Describe each of these by explaining what you're aiming to achieve, and make them compelling with icons and animation.
Business plan
Once the goals for the business plan have been set, break the various activities out into a stage-wise plan. List these activities with a brief description, and add supporting data to validate and enable an easier decision-making process.

Storytelling
Present your content in a narrative thread by outlining your problem statement and then defining the various possible solutions. Keep your text minimal and explain these points in detail during the session.
Vision, mission, and core values
This is an important title as it lays out what your company stands for, aspires to be, the impact it has on the community, and its core values. Explain in detail with a good headline, body text, and appealing icons, and elaborate each of these points while presenting.

Data at a glance
Use this slide to demonstrate your plan's important data with charts. Give insight into these numbers with your analysis, and emphasize key information using animation.
Meet the team
Introduce your team members who have worked on this project with their title, email address, and contact details. The slide has placeholders for photographs to include headshots of your speakers.

Demonstrate your content plan by displaying a collage of visuals to set a creative tone. Having a storyboard also helps in team coordination and speeds up the content creation process.
Zoho Show's business innovation plan template comes with ready-to-use and editable slides to structure your presentation from end to end with topics necessary to illustrate your plan. Modify the deck to suit your business needs and create a persuasive pitch experience for your investors and stakeholders that compels them to action.
These slides also contain pointers on how to use the slide to draft a compelling business innovation plan.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Innovation Business Plan and Collaboration

Related Papers
SSRN Electronic Journal
chintan shah
Strategic Alliances, Mergers and Acquisitions
Bob Walrave
Jana Krapez Trost
Elicia Maine
World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development
Robert Raeside
Tim Mazzarol
Where documents are made available* through records in La Trobe University Research Online they may be regarded as" open access" documents; interested readers may read, download or print them, but they remain protected by copyright, and many are subject to publishers' policies regarding use, reproduction or communication. Please check individual records for details of other permissible use. If you believe that any material has been made available without permission of the copyright owner please contact us with the details.
Ray Oakey, Aard Groen, …
Paul Benneworth
Hwan Jin Kim
Purpose – Entrepreneurial orientation (EO) and dynamic capabilities (DCs) are two important pillars of increasing performance in fast-changing environments. However, little is known about how the effects of EO and DCs on performance are reconciled, integrated and balanced in terms of contingency factors. In this study, the authors examine three contingencies – firm, market and product characteristics – that significantly affect the level of EO and DCs that firms pursue. Design/methodology/approach – Using survey data on 252 Korean manufacturing SMEs, this study analyzes the influence of EO and DCs on performance using hierarchical regression models. Findings – The results show that EO plays a critical role in small and young firms' performance but that DCs are more critical in incumbent firms. Further, both EO and DCs enhance performance in dynamic markets, and EO increases performance under radical product development, while DCs show negative effects. Originality/value – Given the importance of EO and DCs in increasing firm performance, a lack of empirical attempts have been made to reconcile the effects of EO and DCs in a single research setting. This study provides important and unique implications that can bridge the empirical gaps regarding the complementary roles of EO and DCs by exploring three contingency factors – firm, market and product characteristics – with respect to firm performance.
Ana Paula B S Etges
Innovation and risk are inseparable. In fact, literature on innovation management often recommends that innovation-oriented firms must actively monitor, evaluate, analyze and treat future events in order to mitigate risks whenever possible. This approach is particularly important in emergent economies characterized by unstructured national innovation systems and constant economic and market instability. However, there has been no systematic effort to identify and categorize risks that potentially impact businesses based on innovation. Thus, we propose an interpretative framework of risk events with potential financial impact in innovation-oriented firms constructed and tested by means of a mixed studies review. The risk events were identified through a comprehensive systematic search and review of the published literature on risk and innovation. From the 115 works that were analyzed, it was possible to identify nine categories of risk events frequently associated with innovation-oriented businesses that may generate financial impacts. The proposed interpretative framework was tested in an empirical study with 13 innovation-oriented firms located in six Brazilian technological parks. Results from the empirical study suggest that managers found the proposed interpretative framework complete and comprehensive. Moreover, the empirical study signaled which risk events are more relevant for the Brazilian context. The proposed framework is a first necessary step for future development of ERM models applicable in innovation-intensive contexts.
Gestão & Regionalidade
Mauricio Gómez Villegas , Enrique Ogliastri
In this introduction to the special issue of Gestão & Regionalidade entitled “Management and Innovation in Latin America,” we first review the published literature about the region, then introduce the ten new articles appearing in this issue, and finally reflect briefly on the current and future state of studies on innovation management and economics in the region. Latin America’s innovation performance remains far short of its economic relevance, despite increasing academic research on the issue. Future research should highlight interactive ways to promote innovation, social innova- tions, public innovation, innovations for sustainability, technological innovations associated with the fourth industrial revolution, and the very specific nature of Latin American entrepreneurship.
RELATED PAPERS
KINO - IKON
Jakub Čapek
Yan Prastyan
Escola Anna Nery
Margareth Zanchetta
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
Vaibhav Suryawanshi
Manuel Vilas
maximiliano Dias da Silva de Moraes
Ana Reyes Murillo
Intelligent Computing and Communication
Dr. Rajashekar B. Shettar
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical
JOSE ANTONIO " Z E T O " ALVES CORREIA
Journal of Advanced Nursing
Amy Mitchell
charles jebuni
Atif Siddique
Maximiliano E. Korstanje
Revista Tecnologia e Sociedade
Rejane Sartori
Critical Care
tatiana gutierrez
Agricultural Water Management
Atif Mahadeen
it - Information Technology
Transplantation
M Fajri Hidayat
The American Journal of Emergency Medicine
Brendon Hopgood
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Compliance Automation
- Blogs Benefits Realization Management Configuration Management Change Management Disaster and Recovery ( DR) Heatmap Meetings and Actions PMO Starter MS Project Templates Project Budget Project Closure Project Dashboards Project Implementation Project Initiation Project Management Concepts Project Risk Management Project Plans Project Status Reports Quality Management RAID Resource and Capacity Plans Stakeholder Management Task Management Testing Timeline and Roadmap
- All In One Pack
- Home icon-chevron
- icon-chevron Software
- Compliance Automation icon-chevron

- icon-chevron Blogs
- icon-chevron Benefits Realization Management
- Configuration Management icon-chevron
- Change Management icon-chevron
- Disaster and Recovery ( DR) icon-chevron
- Heatmap icon-chevron
- Meetings and Actions icon-chevron
- icon-chevron PMO Starter
- MS Project Templates icon-chevron
- Project Budget icon-chevron
- Project Closure icon-chevron
- Project Dashboards icon-chevron
- Project Implementation icon-chevron
- icon-chevron Project Initiation
- Project Management Concepts icon-chevron
- Project Risk Management icon-chevron
- Project Plans icon-chevron
- Project Status Reports icon-chevron
- Quality Management icon-chevron
- RAID icon-chevron
- icon-chevron Resource and Capacity Plans
- Stakeholder Management icon-chevron
- Task Management icon-chevron
- Testing icon-chevron
- Timeline and Roadmap icon-chevron
- All In One Pack icon-chevron
Implementing A Solid Change Management Framework
Introduction.
A change management framework is essential for organizations looking to successfully implement and navigate through transitions. It provides a structured approach to managing change, ensuring that all stakeholders are involved and informed throughout the process. By following a well-defined change management framework, organizations can effectively plan, communicate, and execute changes while minimizing resistance and maximizing adoption.

Key Components Of A Successful Change Management Framework
Here are the key components of a successful change management framework:
1. Clear Communication: Communication is crucial during any change process. Employees need to understand why the change is happening, how it will impact them, and what is expected of them during the transition. Transparent and timely communication helps build trust and understanding among employees.
2. Strong Leadership: Effective leadership is essential in driving change initiatives forward. Leaders need to clearly communicate the vision for change, motivate employees to embrace the changes, and provide the necessary support and resources to facilitate the transition.
3. Stakeholder Engagement: Involving key stakeholders in the change process is vital for successful implementation. Stakeholders may include employees, customers, suppliers, and other external parties who are impacted by the changes. By engaging stakeholders early on and soliciting their input, organizations can address concerns and gain buy-in for the proposed changes.
4. Comprehensive Planning: Change management requires a well-thought-out plan that outlines the objectives, scope, timeline, and resources needed for successful implementation. A detailed plan helps identify potential risks and challenges, allocate resources effectively, and track progress throughout the change process.
5. Training And Development: Providing employees with the necessary training and development opportunities is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition. By investing in employee development, organizations can equip their workforce with the skills and knowledge needed to adapt to the changes and thrive in the new environment.
6. Change Readiness Assessment: Before implementing any changes, organizations should assess their readiness for change. This involves evaluating factors such as organizational culture, employee attitudes, and existing processes to identify potential barriers to change and develop strategies to address them.
7. Continuous Feedback And Evaluation: Change management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. Organizations should solicit feedback from employees, stakeholders, and other relevant parties to gauge the effectiveness of the changes and make necessary adjustments to ensure success.
Measuring The Effectiveness Of The Change Management Framework
1. Key Performance Indicators: One of the ways to measure the effectiveness of a change management framework is through key performance indicators (KPIs). KPIs are specific metrics that can be used to assess the progress and impact of the change management process . Examples of KPIs in change management include employee engagement levels, adoption rates of new processes or technologies, and overall employee satisfaction.
2. Feedback And Surveys: Another effective way to measure the effectiveness of a change management framework is through feedback and surveys. Gathering feedback from employees who have undergone the change process can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the framework. Surveys can also help identify any gaps or areas of improvement in the change management process.
3. Data Analysis: Data analysis is also crucial in measuring the effectiveness of a change management framework. By analyzing quantitative data such as employee turnover rates, productivity levels, and financial performance, organizations can track the impact of the change management process on overall business success. Data analysis can provide concrete evidence of the effectiveness of the change management framework.
4. Continuous Improvement: Measuring the effectiveness of a change management framework is an ongoing process. Organizations should continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of the framework to identify areas for improvement. By collecting and analyzing data, gathering feedback, and using KPIs, organizations can ensure that their change management framework is achieving its desired outcomes.

The Benefits Of A Well-Structured Change Management Framework
1. Clarity And Focus: A well-structured change management framework provides clarity on the goals and objectives of the change initiative. It helps in setting clear expectations, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing a roadmap for the change process. This clarity and focus enable employees to stay aligned and motivated toward achieving the desired outcomes.
2. Minimize Resistance: Change often leads to resistance from employees who may be apprehensive about the unknown or fear losing their comfort zone. A well-structured change management framework helps in identifying potential sources of resistance and developing strategies to address them. By involving employees in the change process and addressing their concerns, organizations can minimize resistance and increase acceptance of the change.
3. Improve Communication: Effective communication is key to successful change management. A well-structured framework provides a structured communication plan that ensures information is disseminated in a timely and consistent manner. This helps in keeping employees informed, engaged, and motivated throughout the change process. Improved communication also fosters transparency and trust within the organization.
4. Enhance Employee Engagement: Change management is not just about implementing new processes or systems; it also involves managing the human aspect of change. A well-structured framework focuses on engaging employees throughout the change process by involving them in decision-making, providing opportunities for feedback, and recognizing their contributions. This helps in building a positive and supportive culture that encourages collaboration and innovation.
5. Increase Agility And Adaptability: In today's rapidly changing business environment, organizations need to be agile and adaptable to stay competitive. A well-structured change management framework equips organizations with the tools and processes to respond quickly to market changes, technological advancements, or regulatory requirements. This agility enables organizations to pivot and adapt to change efficiently, ensuring long-term success.
In summary, implementing a change management framework is crucial for successfully navigating through organizational transitions. This structured approach helps to effectively manage stakeholders, mitigate risks, and ensure the desired outcomes are achieved. By following a change management framework, organizations can minimize resistance to change and increase the likelihood of successful implementation. If you are looking to implement a change management framework in your organization, consider reaching out to our team for expert guidance and support.

Cost of living help and a future made in Australia
Investing in a future made in australia.
Investing in a Future Made in Australia and the skills to make it a reality
Print or save page
On this page
Attracting investment in key industries
Making Australians the beneficiaries of change
A Future Made in Australia is about creating new jobs and opportunities for every part of our country by maximising the economic and industrial benefits of the move to net zero and securing Australia’s place in a changing global economic and strategic landscape.
The Government’s $22.7 billion Future Made in Australia package will help facilitate the private sector investment required for Australia to be an indispensable part of the global economy.
For more information refer to the Future Made in Australia fact sheet [PDF 438KB]
Better deploying capital in priority areas
The Future Made in Australia package will realise Australia’s potential to become a renewable energy superpower, value‑add to our resources and strengthen economic security by better attracting and enabling investment in priority areas. The Government will create a Future Made in Australia Act and establish a National Interest Framework that identifies priority industries and ensures investments associated with them are responsible and targeted.
The Framework will have a focus on industries that contribute to the net zero transformation where Australia has a comparative advantage, and where Australia has national interest imperatives related to economic resilience and security.
Strengthening and streamlining approvals
This Budget provides a faster pathway to better decisions on environmental, energy, planning, cultural heritage and foreign investment approvals.
This includes:
- $134.2 million to better prioritise approvals for renewable energy projects of national significance, and support faster decisions on environment, cultural heritage and planning approvals.
- Working with the states and territories through the Energy and Climate Change Ministerial Council to accelerate electricity grid connections.
- $20.7 million to improve engagement with communities impacted by the energy transition and accelerate the delivery of key energy projects.
- $15.7 million to strengthen scrutiny of high‑risk foreign investment proposals, enhance monitoring and enforcement activities and support faster decisions.
The Government will also encourage foreign investment by providing refunds of 75 per cent of application fees for unsuccessful competitive bids.
Promoting sustainable finance
The Government is committing $17.3 million to mobilise private sector investment in sustainable activities. This includes extending Australia’s sustainable finance taxonomy to the agriculture sector and developing a labelling regime for financial products marketed as sustainable.
The Government will also examine opportunities to improve data quality and provide $1.3 million to develop and issue guidance for best practice transition plans.
Making Australia a renewable energy superpower
Powering australia with cheaper, cleaner, more reliable energy.
Australia’s potential to produce abundant renewable energy is a powerful source of comparative advantage. To realise this, the Government is unlocking more than $65 billion of investment in renewable capacity through the Capacity Investment Scheme by 2030.
This Budget helps Australians benefit from cheaper, cleaner energy sooner by investing $27.7 million to integrate consumer energy resources like batteries and solar into the grid.
The New Vehicle Efficiency Standard will save Australians around $95 billion at the bowser by 2050 and reduce transport emissions.
Unlocking investment in net zero industries and jobs
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
The Future Made in Australia package establishes time‑limited incentives to invest in new industries. The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia’s pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. This Budget also expands the Hydrogen Headstart program by $1.3 billion.
Boosting demand for Australia’s green exports
The Government is making it easier for businesses and trading partners to source low‑emissions products by building better markets and product standards for green products.
This Budget provides $32.2 million to fast‑track the initial phase of the Guarantee of Origin scheme, focused on renewable hydrogen, and bring forward the expansion of the scheme to accredit the emissions content of green metals and low‑carbon liquid fuels. The Government is also working closely with trading partners to identify opportunities to drive greater supply chain transparency and better market recognition of high environmental, social and governance standards in the critical minerals sector.
Realising the opportunities of the net zero transformation
Australia is committed to reaching net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and is developing six sector plans covering:
- electricity and energy
- agriculture and land
- the built environment.
This Budget continues investment in effective emissions abatement, including through $63.8 million to support emissions reduction efforts in the agriculture and land sector.
The Government is also investing $399 million to establish the Net Zero Economy Authority and support the economy‑wide net zero transformation. This Budget also invests an additional $48 million in reforms to the Australian Carbon Credit Unit scheme and $20.7 million to improve community engagement.
Strengthening resources and economic security
Backing a strong resources sector.
The Government is investing $8.8 billion over the decade to add more value to our resources and strengthen critical minerals supply chains. This Budget establishes a production tax incentive for processing and refining critical minerals at an estimated cost of $7 billion over the decade. It commits up to $1.2 billion in strategic critical minerals projects through the Critical Minerals Facility and the Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility, and pre‑feasibility studies for common user precincts.
This is in addition to $566.1 million to support Geoscience Australia to map all of Australia’s critical minerals, strategic materials, groundwater and other resources essential for the transition to net zero.
Manufacturing clean energy technologies
The Government is committing $1.5 billion to manufacturing clean energy technologies, including the $1 billion Solar Sunshot and $523.2 million Battery Breakthrough Initiative. These investments will be delivered by ARENA.
Strengthening supply chains
To support the delivery of the 82 per cent renewable energy target, the Government has formed the National Renewable Energy Supply Chain Action Plan with states and territories. The Government will invest an additional $14.3 million working with trade partners to support global rules on unfair trade practices and to negotiate benchmarks for trade in high quality critical minerals.
Digital, science and innovation
Investing in new technologies and capabilities.
The Government is investing $466.4 million to partner with PsiQuantum and the Queensland Government to build the world’s first commercial‑scale quantum computer in Brisbane.
The Government will undertake a strategic examination of Australia’s research and development (R&D) system with $38.2 million invested in a range of science, technology, engineering, and maths programs.
The Government is providing $448.7 million to partner with the United States in the Landsat Next satellite program to provide access to critical data to monitor the earth’s climate, agricultural production, and natural disasters.
Modernising and digitising industries
This Budget commits $288.1 million to support Australia’s Digital ID System. A National Robotics Strategy will also be released to promote the responsible production and adoption of robotics and automation technologies for advanced manufacturing in Australia.
Reforming tertiary education
The Government is committing $1.6 billion over 5 years, and an additional $2.7 billion from 2028–29 to 2034–35 to reform the tertiary education system and deliver Australia's future workforce.
This includes $1.1 billion for reforms to university funding and tertiary system governance.
Over $500 million will be provided for skills and training in priority industries and to support women’s participation in these sectors.
The Government will set a tertiary attainment target of 80 per cent of the working‑age population by 2050.
Supporting students on placements
The Government will establish Commonwealth Prac Payments (CPP) for students undertaking mandatory placements. From 1 July 2025, the payment will provide more than 73,000 eligible students, including teachers, nurses, midwives and social workers with $319.50 per week during their placements.
Felicity is a full‑time student receiving Youth Allowance, living by herself. She is studying a Bachelor of Nursing and must stop paid work during her mandatory prac placement. During her prac, Felicity receives $712.05 per week from the Government including: $319.50 of CPP, $285.55 of Youth Allowance (YA), $103.50 of Commonwealth Rent Assistance (CRA) and $3.50 of Energy Supplement.
Felicity receives $351.55 a week more than she would have in 2023 before indexation and the changes to YA, CRA and CPP in the current and 2023–24 Budget

Broadening access to university
From January 2026, needs‑based funding will provide per student funding contributions for under‑represented students. The Government will also provide $350.3 million to fully fund university enabling courses and increase pathways for prospective students to university.
Skills pipeline for priority industries
Skills and training for Future Made in Australia industries
The Government will expand eligibility to the New Energy Apprenticeships Program to include work in the clean energy sector, including in construction and advanced manufacturing. This will provide access to $10,000 incentive payments and support our target of 10,000 new energy apprentices.
The Government will commit $30 million to turbocharge the VET teaching workforce for clean energy courses and $50 million to upgrade and expand clean energy training facilities.
The Government will invest $55.6 million to establish the Building Women’s Careers program to support women’s participation in key industries including clean energy and advanced manufacturing.
Supporting apprentices and building the construction workforce
The $5,000 support payments to apprentices in priority occupations will be maintained for another 12 months to 1 July 2025, up from $3,000 in the absence of any changes. Employers of these apprentices will receive a $5,000 hiring incentive, up from $4,000 in the absence of changes. This will provide certainty to apprentices while the Strategic Review of the Apprenticeship Incentive System is underway.
The Government will also invest $88.8 million to deliver 20,000 new fee‑free TAFE places including pre‑apprenticeships in courses relevant to the construction sector. The Government will provide $1.8 million to deliver streamlined skills assessments for around 1,900 migrants from comparable countries to work in Australia’s housing construction industry.
Strengthening our defence industry capability
An integrated and focused approach to defending Australia
The Government is investing an additional $50.3 billion over ten years to implement the 2024 National Defence Strategy to meet Australia’s strategic needs.
Overall funding for Defence will reach $765 billion over the decade. Defence’s Integrated Investment Program has been rebuilt to create a focused Australian Defence Force, accelerate delivery of priority capabilities, and provide certainty to grow Australia’s defence industry. This includes funding for the Royal Australian Navy’s surface combatant fleet and establishing a guided weapons and explosive ordnance manufacturing capability earlier.
The Government is reforming Defence’s budget to support the National Defence Strategy and delivery of priority capabilities.
Developing defence industry and skills
Industry development grants funding of $165.7 million will also help businesses to scale up and deliver the Sovereign Defence Industrial Priorities, which include continuous naval shipbuilding and sustainment, and development and integration of autonomous systems.
The Government is providing $101.8 million to attract and retain the skilled industrial workforce to support Australian shipbuilding and delivery of conventionally armed, nuclear powered submarines. This includes a pilot apprenticeship program in shipbuilding trades and technologies.
Investing in civil maritime capabilities
The Government is providing $123.8 million to maintain and enhance civil maritime security capabilities. This includes $71.2 million to increase the Australian Border Force’s on‑water response and aerial surveillance capabilities.
Securing Australia’s place in the world
Strengthening relationships and simplifying trade
A stable, prosperous and resilient Pacific region
The Government is delivering over $2 billion in development assistance to the Pacific in 2024–25. This includes the Australia‑Tuvalu Falepili Union.
Investing in our relationship with Southeast Asia
Following the launch of Australia’s Southeast Asia Economic Strategy to 2040, the Government is committing $505.9 million to deepen ties with the region.
Australia recently celebrated 50 years of partnership with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). At the ASEAN‑Australia Special Summit, the Government announced a range of new and expanded initiatives, including a $2 billion Southeast Asia Investment Financing Facility to boost Australian trade and investment.
Simplifying trade
The Government will abolish 457 nuisance tariffs from 1 July 2024, streamlining $8.5 billion in annual trade and eliminating tariffs on goods such as toothbrushes, fridges, dishwashers, clothing and sanitary products.
The Government will provide $29.9 million to coordinate trade simplification and deliver the Digital Trade Accelerator program, and $10.9 million to enhance the Go Global Toolkit to support exporters.
The Government is expanding the Australia‑India Business Exchange, diversifying trade and helping more Australian businesses build commercial ties with India and across South Asia. There will be $2 million to support Australian agricultural exporters entering the Chinese markets.
Support for small businesses
Helping small businesses
This Budget’s Small Business Statement reaffirms the Government’s commitment to deliver a better deal for small businesses, with $641.4 million in targeted support.
For more information refer to the small business fact sheet [PDF 0.98MB]
Improving cash flow
The Government is providing $290 million to extend the $20,000 instant asset write‑off for 12 months. There will be $25.3 million to improve payment times to small businesses and $23.3 million to increase eInvoicing adoption.
Easing cost pressures and reducing the administrative burden
This Budget provides $3.5 billion of energy bill relief, including rebates of $325 to around one million small businesses.
The Government is reducing the administrative burden for small business by abolishing 457 nuisance tariffs and delivering $10 million to provide additional support for small business employers administering the Paid Parental Leave scheme.
Supporting confidence and resilience in the small business sector
This Budget invests a further $10.8 million in tailored, free and confidential financial and mental wellbeing supports for small business owners.
The Government is providing $20.5 million to the Fair Work Ombudsman to help small businesses understand and comply with recent workplace relations changes.
There will be $3 million to implement the Government’s response to the Review of the Franchising Code of Conduct, including remaking and enhancing the Code, and an additional $2.6 million to support more small businesses through alternative dispute resolution.
A more resilient Australia
Preparing for the future
The Government is preparing Australia for future droughts and heightened risk of natural disasters.
Disaster resilience and preparedness
The Government will provide $138.7 million to improve Australia’s response and resilience to natural hazards and disasters. Support includes: funding for the National Emergency Management Agency to supply communities with vital goods, equipment, and temporary accommodation during an emergency, aerial firefighting capability, and mental health support. This is in addition to the $11.4 billion previously committed for Disaster Recovery Funding Arrangements for the states and territories.
The Government is establishing a pilot program for Australia’s Strategic Fleet. These vessels will improve Australia’s capacity to respond and support communities and supply chains during crises.
Preparing for drought and climate change
This Budget provides $174.6 million from the National Water Grid Fund to deliver new water infrastructure projects that will enhance water security, boost agricultural production and help drought proof regional communities.
The Government will provide $519.1 million from its Future Drought Fund to help farmers and rural communities manage the impacts of climate change and prepare for future droughts.

This investment will build the drought resilience of more farmers like Victorian cropper Ed Rickard.
The Fund supported Ed in developing a better farm business plan, which identified his need for weather stations and soil moisture probes. It also helped him implement a succession plan that ensured his farm’s long-term viability.
Back to top
Neom axed a $1.5B project to make water for the city, report says — another blow to its grand ambition
- Neom canceled a desalination project worth $1.5 billion, according to a report.
- It comes as Saudi Arabia reportedly plans on scaling back part of the project.
- Enowa, a Neom subsidiary, told Meed it's water requirements had evolved.

A project to build a $1.5 billion water desalination plant in the Saudi Arabian desert city of Neom appears to have been scrapped.
A consortium made up of Neom subsidiary Enowa, Japan's Itochu, and France's Veolia had agreed to develop the plant in December 2022.
The plan was to create a desalination plant that ran on 100% renewable energy and delivered two million cubic meters of water a day to Neom, or about 30% of the city's projected needs.
The plant was to be based in Oxagon, Neom's industrial zone and the first phase was scheduled for completion next year.
However, sources familiar with the project told Middle East business-trade publication MEED that the joint development agreement for the project had expired and not been renewed.
Detailed reasons for the cancellation are unclear. BI contacted Enowa, Itochu and Veolia for comment.
Related stories
In a statement sent to MEED, Enowa said Neom's water requirements have evolved over the last year, "leading us to adopt a stepwise approach to expanding capacity."
Under the plans, the desalination plant would have diverted brine, the main waste product in desalination, toward industrial projects instead of discharging it into the sea.
Brine is one of the main pollutants caused by desalination plants.
Earlier in May, Malcolm Aw, a UK energy entrepreneur, said he canceled a $100 million contract to develop renewable energy desalination plants in Neom over human rights concerns.
It's a blow for the desert city. Neom is being built in deserts in the northwest of Saudi Arabia, one of the dryest and hottest parts of the world, meaning that desalination is key to the success of the project.
Planners have said Neom will be an eco-city, running without cars or roads and powered with 100% sustainable energy. It's part of Saudi ruler Mohammed bin Salman's Vision 2030 plan to reorient the country's economy away from the fossil fuels that are the source of its wealth and toward innovation, technology, and tourism.
But In April Bloomberg reported that Saudi Arabia had been forced to scale back plans for the project, which could cost as much as $1.5 trillion. According to the report, The Line, a planned mirrored "vertical skyscraper," may be reduced in size from more than 100 miles to just over one mile.
In an apparent effort to refute the report, the Saudi economy minister, Faisal Al Ibrahim, told CNBC last month that all Neom projects were continuing at the planned scale.
"There is no change in scale. It is a long-term project that's modular in design," he said.
Watch: Filling Cambodian lakes with sand creates pricey new land. It also displaces families.
- Main content
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and industry
- Charities and social enterprises
Charity Commission Business Plan 2024 to 2025

Published 24 May 2024
Applies to England and Wales

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/charity-commission-business-plan-2024-to-2025/charity-commission-business-plan-2024-to-2025
Introduction
April 2024 marked the start of a new five-year strategic period for the Charity Commission. This business plan sets out what we will do in the first year of that strategy towards achieving our aim to be an expert Charity Commission that is fair, balanced and independent.
Our business plan for 2024-25 is shaped around our five strategic priorities, through which we will:
- be fair and proportionate in our work and clear about our role
- support charities to get it right but take robust action where we see wrongdoing and harm
- speak with authority and credibility, free from the influence of others
- embrace technological innovation and strengthen how we use our data
- be the expert Commission - where our people are empowered and enabled to deliver excellence in regulation
Our Priorities
Priority 1 – we will be clear about our role and fair and proportionate in our work.
We will continue to refine our processes so that we focus on those issues that pose the greatest risk to the sector, ensuring these are handled consistently and that we reach the right outcomes. In parallel, we will pursue opportunities to increase the efficiency, quality and effectiveness of our casework processes and systems.
We will update our Regulatory and Risk Framework to provide clarity to the public on the Commission’s role and remit. We will ensure external understanding of our regulatory process is clear, particularly how we identify and assess risks and how we make fair and accurate decisions on the regulatory action we take.
We will take further steps to improve our communications with customers, ensuring we strike the right balance between being friendly and firm, reflecting the circumstances, while ongoing training and a focus on quality will lead to better customer experiences.
Priority 2 – We will support charities to get it right but take robust action where we see wrongdoing and harm
We will continue to publish improved trustee guidance that is easier to navigate and understand, further encouraging trustees to come to the Charity Commission as a valued source of support. This new guidance will help to improve governance and ultimately reduce problems.
Our programme of improvements to My Charity Commission Account (MCCA) will focus on delivering a better customer journey, as we work to onboard remaining charities onto the system.
We will run a pilot engagement exercise with a sample of new trustees to support them in taking on their responsibilities when joining or establishing a charity. A sample of trustees will receive a series of supportive emails throughout their first 12 months, pointing to our online guidance and support and providing insight to guide planning for future phases of MCCA.
Working closely with relevant stakeholders, we will continue to highlight the benefits a culture of philanthropic giving can deliver for charities, and the role of effective regulation in enabling philanthropists to give with confidence.
We will track and report our use of powers to address serious wrongdoing and harm, providing assurance that the Commission is deploying these effectively in those cases where robust action is required to protect people, assets and the charity. Service delivery will be measured against agreed operational performance standards.
Priority 3 – We will speak with authority and credibility, free from the influence of others
A new Communications Strategy will help bring our work to life and improve the way we engage with trustees, the public and stakeholders. Over time, we will achieve greater awareness and impact amongst our key audiences.
As part of this, our ongoing campaigns will support trustees and the public. Through our campaigns the public will be supported to give with confidence, making safer and more informed choices about the charities they support. This will contribute towards increased trust and confidence both in the wider Charity sector and the Commission Across the sector, trustees’ understanding of their responsiblities will improve, contributing to a longer-term reduction in unintentional harms caused by poor governance.
We will further improve how we measure public and trustee perspectives of charity as well as how we measure the Commission’s impact. This will allow us to better evaluate the effectiveness of our interventions.
The Commission will ensure it is ready for a General Election, to ensure consistent handling of casework and communications and ensure our staff have the information they need. We will also provide guidance to charities as they prepare for and navigate the general election period.
The Commission will share more of the data that it collects routinely, to provide commentary on key regulatory actions and trends, as well as making information about charities more accessible, building on the programme of quarterly releases commenced last year.
Priority 4 - We will embrace technological innovation and strengthen how we use our data
We will develop a five-year Information Strategy that sets out our data, information, technology and digital ambitions, with an underpinning aim of supporting the Commission to deliver its 2024-2029 Strategy.
Supporting this, we will deliver agreed priorities in an IT Roadmap, with the primary focus being on consolidating and driving continuous improvements to our services. This will ensure that our people have the tools they need and that our systems are accessible and reliable for those who engage with us.
We will aim to standardise how we capture information across the organisation, so that we are optimising the operational and strategic value of our data and further strengthening the Commission’s compliance with data protection requirements.
Following significant changes to the question set for 2023, we will consolidate these in the service for 2024 Annual Returns, , and meanwhile work on improvements to the user experience for the 2025 Return.
We will engage with other parts of government to make further progress towards the future digitalisation of accounts. And we will continue to work on upcoming changes to the Statement of Recommended Practice (SORP), expected to take effect in January 2026.
Priority 5 – We will be the expert Commission, where our people are empowered and enabled to deliver excellence in regulation
We will complete a review of our performance management approach ensuring that it is effective at supporting our people to deliver our strategic priorities and values.
We will explore how our people can develop their knowledge, skills and experience as part of a professional framework.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
Toyota mulls over $500 mln investment into Texas plant
- Medium Text

- Company Toyota Motor Corp Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Shivansh Tiwary and Nathan Gomes in Bengaluru; Editing by Shilpi Majumdar
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Oil rises 1% ahead of inflation data after downbeat week
Oil prices rose over 1% in muted trade owing to public holidays in Britain and the United States after a downbeat week characterised by the outlook for U.S. interest rates in the face of sticky inflation.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Consider adding the following components: Executive summary: Keep it concise but touch on each aspect of your plan. Remember to pique interest and compel your audience to read more. Company overview: Discuss your industry and niche, including what makes your invention and business stand out.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Innovation provides entrepreneurs and start-up companies with the essential tools to outline and execute their innovative business ideas. Here are the main elements of this template: Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
An innovation business plan will help you to: validate the feasibility of that idea. evaluate the market potential. verify that there is a real demand for your product. It can also help provide your innovation start-up with credibility and focus, which is vital if you want to attract investors for your innovation start-up.
Learn from your innovation efforts. You've probably heard the mantra "fail fast, learn fast." After each innovation, list what you would do again and what you wouldn't. And don't overthink failure; the key is learn from it and apply those lessons to your next innovation. We've seen these steps work at all levels in an organization.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A company's innovation strategy should specify how the different types of innovation fit into the business strategy and the resources that should be allocated to implement these innovations. An innovation strategy paves the way to. Improve the ability to retain customers. Reduce competitive intensity.
It starts with strategy, the heart of a business plan. Innovation is part of your company's identity, we would hope one of its strengths, and certainly a key element in business offering. It directly affects the market, both in the higher degree of guessing required (educated guessing, we hope) and in how it affects target market and message.
This is the real magic in creating an Innovation Plan — when it supports the vision and goals of the organization, it fits naturally into the daily activities of the business. Innovation Teams ...
Innovation management is the process of taking innovative ideas from their inception to implementation. A company's innovation capability rests in this system, and when done successfully can result in anything from a record-shattering new product to a revolutionary way to address customer needs. There are, generally, a few steps to innovation ...
1. Delivery Process. Your business idea doesn't have to be entirely new—it just has to fill a need. If you can identify a more convenient way of delivering an existing service, it could be an opportunity for your business. Uber is used as an example in Entrepreneurship Essentials.
Top executives created an aspirational vision and strategic plan linked to financial targets: 6 percent growth in the core business and 2 percent growth in new organic ventures. ... ultimately, to product groups. During the development of each innovation project, it had to show how it was helping to achieve the growth targets for its category ...
If you want to write a detailed business plan, follow this step-by-step guide: 1. Write an executive summary. An executive summary, also known as a company description, provides an overview of the organisation, including its objectives, partners and future expansion strategies. Start with the company's mission statement, then describe the ...
Innovation management is the systematic process of planning, organizing, controlling, and directing innovation within an organization. It helps foster and implement new ideas to improve the organization's performance. It involves creating a culture that values creativity, identifying opportunities for innovation, and effectively executing ...
This innovation plan template is designed for teams of any size and industry. It provides a framework for creating a strategic plan to develop new products, services, and processes. This template includes resources and guidance to help teams create actionable objectives, set achievable targets and plan for success. 1.
Innovation can help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company in the process. Here are three reasons innovation is crucial for your business: It allows adaptability: The recent COVID-19 pandemic disrupted business on a monumental scale. Routine operations were rendered obsolete over the course of a few months.
This article introduces a new tool to help leaders better align their innovation investments. The strategic innovation tool kit has two elements: a strategy summary framework and an innovation ...
A canonical Lean Innovation process inside a company or government agency would include sourcing, curation, prioritization, hypothesis testing and exploration, incubation, and integration. Post Share
control all intellectual property and profit within your organisation. maintain strong boundaries of a project. 4. Find support and guidance. Connect with a business adviser or find a grant or program to help drive innovation in your business. 5. Update your business plan. An innovation strategy is just one part of your business plan.
Template 1: Action Plan for Innovation Techniques Categories Analysis PPT Template. This concise and comprehensive one-page PPT presentation is an invaluable guide for businesses and individuals seeking to enhance their innovation strategies. This power-packed PPT encompasses a structured approach to innovation, divided into four meticulously ...
The Business Plan is a written summary of what you hope to accomplish by being in business and how you intend to organize your resources to meet your goals. A business plan is a road map for operating your business and measures progress along the way. There are three major reasons for developing a business plan.
Design a powerful pitch deck using this free and customizable presentation template and showcase your innovation plan for the business. ... Every project, idea, or business plan will have an annual budget allocated for different stages of a project. Showcase the different financial elements with tables and charts and highlight important data ...
All the above are important for the success of any business and must be Innovation Business Plan and Collaboration 4 decided and planned before the initiation of any project. Even though frameworks and guidelines for the development of a successful business plan are proposed by scholars and experts, a lot of problems are identified in the ...
Comprehensive Planning: Change management requires a well-thought-out plan that outlines the objectives, scope, timeline, and resources needed for successful implementation. A detailed plan helps identify potential risks and challenges, allocate resources effectively, and track progress throughout the change process. 5.
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
Neom canceled a desalination project worth $1.5 billion, according to a report. It comes as Saudi Arabia reportedly plans on scaling back part of the project. Enowa, a Neom subsidiary, told Meed ...
This business plan sets out what we will do in the first year of that strategy towards achieving our aim to be an expert Charity Commission that is fair, balanced and independent. Our business ...
New commitment brings company's total LEAP plans to $9 billion, 900 new jobs, to support current and future pipeline of medicines INDIANAPOLIS - Today during the Indiana Global Economic Summit, Governor Eric J. Holcomb joined Eli Lilly and Company (NYSE: LLY) Chair and CEO David A. Ricks to announce Lilly's plans to more than double its investment at the LEAP Research and Innovation ...
DENVER — Cracker Barrel is planning some major changes. The CEO announcedchanges May 16in a conference call with investors for the company known for its country food dishes and rustic décor ...
REUTERS/David 'Dee' Delgado/File Photo Purchase Licensing Rights. May 21 (Reuters) - Toyota Motor's (7203.T) North America arm is seeking tax relief for a potential project totaling $531.7 million ...