Random Assignment in Psychology: Definition & Examples
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
In psychology, random assignment refers to the practice of allocating participants to different experimental groups in a study in a completely unbiased way, ensuring each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group.
In experimental research, random assignment, or random placement, organizes participants from your sample into different groups using randomization.
Random assignment uses chance procedures to ensure that each participant has an equal opportunity of being assigned to either a control or experimental group.
The control group does not receive the treatment in question, whereas the experimental group does receive the treatment.
When using random assignment, neither the researcher nor the participant can choose the group to which the participant is assigned. This ensures that any differences between and within the groups are not systematic at the onset of the study.
In a study to test the success of a weight-loss program, investigators randomly assigned a pool of participants to one of two groups.
Group A participants participated in the weight-loss program for 10 weeks and took a class where they learned about the benefits of healthy eating and exercise.
Group B participants read a 200-page book that explains the benefits of weight loss. The investigator randomly assigned participants to one of the two groups.
The researchers found that those who participated in the program and took the class were more likely to lose weight than those in the other group that received only the book.

Importance
Random assignment ensures that each group in the experiment is identical before applying the independent variable.
In experiments , researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. Random assignment increases the likelihood that the treatment groups are the same at the onset of a study.
Thus, any changes that result from the independent variable can be assumed to be a result of the treatment of interest. This is particularly important for eliminating sources of bias and strengthening the internal validity of an experiment.
Random assignment is the best method for inferring a causal relationship between a treatment and an outcome.
Random Selection vs. Random Assignment
Random selection (also called probability sampling or random sampling) is a way of randomly selecting members of a population to be included in your study.
On the other hand, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and treatment groups.
Random selection ensures that everyone in the population has an equal chance of being selected for the study. Once the pool of participants has been chosen, experimenters use random assignment to assign participants into groups.
Random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs, while random selection can be used in a variety of study designs.
Random Assignment vs Random Sampling
Random sampling refers to selecting participants from a population so that each individual has an equal chance of being chosen. This method enhances the representativeness of the sample.
Random assignment, on the other hand, is used in experimental designs once participants are selected. It involves allocating these participants to different experimental groups or conditions randomly.
This helps ensure that any differences in results across groups are due to manipulating the independent variable, not preexisting differences among participants.
When to Use Random Assignment
Random assignment is used in experiments with a between-groups or independent measures design.
In these research designs, researchers will manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables.
There is usually a control group and one or more experimental groups. Random assignment helps ensure that the groups are comparable at the onset of the study.
How to Use Random Assignment
There are a variety of ways to assign participants into study groups randomly. Here are a handful of popular methods:
- Random Number Generator : Give each member of the sample a unique number; use a computer program to randomly generate a number from the list for each group.
- Lottery : Give each member of the sample a unique number. Place all numbers in a hat or bucket and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flipping a Coin : Flip a coin for each participant to decide if they will be in the control group or experimental group (this method can only be used when you have just two groups)
- Roll a Die : For each number on the list, roll a dice to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1, 2, or 3 places them in a control group and rolling 3, 4, 5 lands them in an experimental group.
When is Random Assignment not used?
- When it is not ethically permissible: Randomization is only ethical if the researcher has no evidence that one treatment is superior to the other or that one treatment might have harmful side effects.
- When answering non-causal questions : If the researcher is just interested in predicting the probability of an event, the causal relationship between the variables is not important and observational designs would be more suitable than random assignment.
- When studying the effect of variables that cannot be manipulated: Some risk factors cannot be manipulated and so it would not make any sense to study them in a randomized trial. For example, we cannot randomly assign participants into categories based on age, gender, or genetic factors.
Drawbacks of Random Assignment
While randomization assures an unbiased assignment of participants to groups, it does not guarantee the equality of these groups. There could still be extraneous variables that differ between groups or group differences that arise from chance. Additionally, there is still an element of luck with random assignments.
Thus, researchers can not produce perfectly equal groups for each specific study. Differences between the treatment group and control group might still exist, and the results of a randomized trial may sometimes be wrong, but this is absolutely okay.
Scientific evidence is a long and continuous process, and the groups will tend to be equal in the long run when data is aggregated in a meta-analysis.
Additionally, external validity (i.e., the extent to which the researcher can use the results of the study to generalize to the larger population) is compromised with random assignment.
Random assignment is challenging to implement outside of controlled laboratory conditions and might not represent what would happen in the real world at the population level.
Random assignment can also be more costly than simple observational studies, where an investigator is just observing events without intervening with the population.
Randomization also can be time-consuming and challenging, especially when participants refuse to receive the assigned treatment or do not adhere to recommendations.
What is the difference between random sampling and random assignment?
Random sampling refers to randomly selecting a sample of participants from a population. Random assignment refers to randomly assigning participants to treatment groups from the selected sample.
Does random assignment increase internal validity?
Yes, random assignment ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group, enhancing the study’s internal validity .
Does random assignment reduce sampling error?
Yes, with random assignment, participants have an equal chance of being assigned to either a control group or an experimental group, resulting in a sample that is, in theory, representative of the population.
Random assignment does not completely eliminate sampling error because a sample only approximates the population from which it is drawn. However, random sampling is a way to minimize sampling errors.
When is random assignment not possible?
Random assignment is not possible when the experimenters cannot control the treatment or independent variable.
For example, if you want to compare how men and women perform on a test, you cannot randomly assign subjects to these groups.
Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups in this study, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
Does random assignment eliminate confounding variables?
Yes, random assignment eliminates the influence of any confounding variables on the treatment because it distributes them at random among the study groups. Randomization invalidates any relationship between a confounding variable and the treatment.
Why is random assignment of participants to treatment conditions in an experiment used?
Random assignment is used to ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study. This allows researchers to conclude that the outcomes of the study can be attributed to the intervention at hand and to rule out alternative explanations for study results.
Further Reading
- Bogomolnaia, A., & Moulin, H. (2001). A new solution to the random assignment problem . Journal of Economic theory , 100 (2), 295-328.
- Krause, M. S., & Howard, K. I. (2003). What random assignment does and does not do . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 59 (7), 751-766.
Random Assignment in Psychology (Definition + 40 Examples)

Have you ever wondered how researchers discover new ways to help people learn, make decisions, or overcome challenges? A hidden hero in this adventure of discovery is a method called random assignment, a cornerstone in psychological research that helps scientists uncover the truths about the human mind and behavior.
Random Assignment is a process used in research where each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group within the study. This technique is essential in experiments as it helps to eliminate biases, ensuring that the different groups being compared are similar in all important aspects.
By doing so, researchers can be confident that any differences observed are likely due to the variable being tested, rather than other factors.
In this article, we’ll explore the intriguing world of random assignment, diving into its history, principles, real-world examples, and the impact it has had on the field of psychology.
History of Random Assignment
Stepping back in time, we delve into the origins of random assignment, which finds its roots in the early 20th century.
The pioneering mind behind this innovative technique was Sir Ronald A. Fisher , a British statistician and biologist. Fisher introduced the concept of random assignment in the 1920s, aiming to improve the quality and reliability of experimental research .
His contributions laid the groundwork for the method's evolution and its widespread adoption in various fields, particularly in psychology.
Fisher’s groundbreaking work on random assignment was motivated by his desire to control for confounding variables – those pesky factors that could muddy the waters of research findings.
By assigning participants to different groups purely by chance, he realized that the influence of these confounding variables could be minimized, paving the way for more accurate and trustworthy results.
Early Studies Utilizing Random Assignment
Following Fisher's initial development, random assignment started to gain traction in the research community. Early studies adopting this methodology focused on a variety of topics, from agriculture (which was Fisher’s primary field of interest) to medicine and psychology.
The approach allowed researchers to draw stronger conclusions from their experiments, bolstering the development of new theories and practices.
One notable early study utilizing random assignment was conducted in the field of educational psychology. Researchers were keen to understand the impact of different teaching methods on student outcomes.
By randomly assigning students to various instructional approaches, they were able to isolate the effects of the teaching methods, leading to valuable insights and recommendations for educators.
Evolution of the Methodology
As the decades rolled on, random assignment continued to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of research.
Advances in technology introduced new tools and techniques for implementing randomization, such as computerized random number generators, which offered greater precision and ease of use.
The application of random assignment expanded beyond the confines of the laboratory, finding its way into field studies and large-scale surveys.
Researchers across diverse disciplines embraced the methodology, recognizing its potential to enhance the validity of their findings and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
From its humble beginnings in the early 20th century to its widespread use today, random assignment has proven to be a cornerstone of scientific inquiry.
Its development and evolution have played a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of psychological research, driving discoveries that have improved lives and deepened our understanding of the human experience.
Principles of Random Assignment
Delving into the heart of random assignment, we uncover the theories and principles that form its foundation.
The method is steeped in the basics of probability theory and statistical inference, ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group, thus fostering fair and unbiased results.
Basic Principles of Random Assignment
Understanding the core principles of random assignment is key to grasping its significance in research. There are three principles: equal probability of selection, reduction of bias, and ensuring representativeness.
The first principle, equal probability of selection , ensures that every participant has an identical chance of being assigned to any group in the study. This randomness is crucial as it mitigates the risk of bias and establishes a level playing field.
The second principle focuses on the reduction of bias . Random assignment acts as a safeguard, ensuring that the groups being compared are alike in all essential aspects before the experiment begins.
This similarity between groups allows researchers to attribute any differences observed in the outcomes directly to the independent variable being studied.
Lastly, ensuring representativeness is a vital principle. When participants are assigned randomly, the resulting groups are more likely to be representative of the larger population.
This characteristic is crucial for the generalizability of the study’s findings, allowing researchers to apply their insights broadly.
Theoretical Foundation
The theoretical foundation of random assignment lies in probability theory and statistical inference .
Probability theory deals with the likelihood of different outcomes, providing a mathematical framework for analyzing random phenomena. In the context of random assignment, it helps in ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being placed in any group.
Statistical inference, on the other hand, allows researchers to draw conclusions about a population based on a sample of data drawn from that population. It is the mechanism through which the results of a study can be generalized to a broader context.
Random assignment enhances the reliability of statistical inferences by reducing biases and ensuring that the sample is representative.
Differentiating Random Assignment from Random Selection
It’s essential to distinguish between random assignment and random selection, as the two terms, while related, have distinct meanings in the realm of research.
Random assignment refers to how participants are placed into different groups in an experiment, aiming to control for confounding variables and help determine causes.
In contrast, random selection pertains to how individuals are chosen to participate in a study. This method is used to ensure that the sample of participants is representative of the larger population, which is vital for the external validity of the research.
While both methods are rooted in randomness and probability, they serve different purposes in the research process.
Understanding the theories, principles, and distinctions of random assignment illuminates its pivotal role in psychological research.
This method, anchored in probability theory and statistical inference, serves as a beacon of reliability, guiding researchers in their quest for knowledge and ensuring that their findings stand the test of validity and applicability.
Methodology of Random Assignment
Implementing random assignment in a study is a meticulous process that involves several crucial steps.
The initial step is participant selection, where individuals are chosen to partake in the study. This stage is critical to ensure that the pool of participants is diverse and representative of the population the study aims to generalize to.
Once the pool of participants has been established, the actual assignment process begins. In this step, each participant is allocated randomly to one of the groups in the study.
Researchers use various tools, such as random number generators or computerized methods, to ensure that this assignment is genuinely random and free from biases.
Monitoring and adjusting form the final step in the implementation of random assignment. Researchers need to continuously observe the groups to ensure that they remain comparable in all essential aspects throughout the study.
If any significant discrepancies arise, adjustments might be necessary to maintain the study’s integrity and validity.
Tools and Techniques Used
The evolution of technology has introduced a variety of tools and techniques to facilitate random assignment.
Random number generators, both manual and computerized, are commonly used to assign participants to different groups. These generators ensure that each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any group, upholding the principle of equal probability of selection.
In addition to random number generators, researchers often use specialized computer software designed for statistical analysis and experimental design.
These software programs offer advanced features that allow for precise and efficient random assignment, minimizing the risk of human error and enhancing the study’s reliability.
Ethical Considerations
The implementation of random assignment is not devoid of ethical considerations. Informed consent is a fundamental ethical principle that researchers must uphold.
Informed consent means that every participant should be fully informed about the nature of the study, the procedures involved, and any potential risks or benefits, ensuring that they voluntarily agree to participate.
Beyond informed consent, researchers must conduct a thorough risk and benefit analysis. The potential benefits of the study should outweigh any risks or harms to the participants.
Safeguarding the well-being of participants is paramount, and any study employing random assignment must adhere to established ethical guidelines and standards.
Conclusion of Methodology
The methodology of random assignment, while seemingly straightforward, is a multifaceted process that demands precision, fairness, and ethical integrity. From participant selection to assignment and monitoring, each step is crucial to ensure the validity of the study’s findings.
The tools and techniques employed, coupled with a steadfast commitment to ethical principles, underscore the significance of random assignment as a cornerstone of robust psychological research.
Benefits of Random Assignment in Psychological Research
The impact and importance of random assignment in psychological research cannot be overstated. It is fundamental for ensuring the study is accurate, allowing the researchers to determine if their study actually caused the results they saw, and making sure the findings can be applied to the real world.
Facilitating Causal Inferences
When participants are randomly assigned to different groups, researchers can be more confident that the observed effects are due to the independent variable being changed, and not other factors.
This ability to determine the cause is called causal inference .
This confidence allows for the drawing of causal relationships, which are foundational for theory development and application in psychology.
Ensuring Internal Validity
One of the foremost impacts of random assignment is its ability to enhance the internal validity of an experiment.
Internal validity refers to the extent to which a researcher can assert that changes in the dependent variable are solely due to manipulations of the independent variable , and not due to confounding variables.
By ensuring that each participant has an equal chance of being in any condition of the experiment, random assignment helps control for participant characteristics that could otherwise complicate the results.
Enhancing Generalizability
Beyond internal validity, random assignment also plays a crucial role in enhancing the generalizability of research findings.
When done correctly, it ensures that the sample groups are representative of the larger population, so can allow researchers to apply their findings more broadly.
This representative nature is essential for the practical application of research, impacting policy, interventions, and psychological therapies.
Limitations of Random Assignment
Potential for implementation issues.
While the principles of random assignment are robust, the method can face implementation issues.
One of the most common problems is logistical constraints. Some studies, due to their nature or the specific population being studied, find it challenging to implement random assignment effectively.
For instance, in educational settings, logistical issues such as class schedules and school policies might stop the random allocation of students to different teaching methods .
Ethical Dilemmas
Random assignment, while methodologically sound, can also present ethical dilemmas.
In some cases, withholding a potentially beneficial treatment from one of the groups of participants can raise serious ethical questions, especially in medical or clinical research where participants' well-being might be directly affected.
Researchers must navigate these ethical waters carefully, balancing the pursuit of knowledge with the well-being of participants.
Generalizability Concerns
Even when implemented correctly, random assignment does not always guarantee generalizable results.
The types of people in the participant pool, the specific context of the study, and the nature of the variables being studied can all influence the extent to which the findings can be applied to the broader population.
Researchers must be cautious in making broad generalizations from studies, even those employing strict random assignment.
Practical and Real-World Limitations
In the real world, many variables cannot be manipulated for ethical or practical reasons, limiting the applicability of random assignment.
For instance, researchers cannot randomly assign individuals to different levels of intelligence, socioeconomic status, or cultural backgrounds.
This limitation necessitates the use of other research designs, such as correlational or observational studies , when exploring relationships involving such variables.
Response to Critiques
In response to these critiques, people in favor of random assignment argue that the method, despite its limitations, remains one of the most reliable ways to establish cause and effect in experimental research.
They acknowledge the challenges and ethical considerations but emphasize the rigorous frameworks in place to address them.
The ongoing discussion around the limitations and critiques of random assignment contributes to the evolution of the method, making sure it is continuously relevant and applicable in psychological research.
While random assignment is a powerful tool in experimental research, it is not without its critiques and limitations. Implementation issues, ethical dilemmas, generalizability concerns, and real-world limitations can pose significant challenges.
However, the continued discourse and refinement around these issues underline the method's enduring significance in the pursuit of knowledge in psychology.
By being careful with how we do things and doing what's right, random assignment stays a really important part of studying how people act and think.
Real-World Applications and Examples

Random assignment has been employed in many studies across various fields of psychology, leading to significant discoveries and advancements.
Here are some real-world applications and examples illustrating the diversity and impact of this method:
- Medicine and Health Psychology: Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) are the gold standard in medical research. In these studies, participants are randomly assigned to either the treatment or control group to test the efficacy of new medications or interventions.
- Educational Psychology: Studies in this field have used random assignment to explore the effects of different teaching methods, classroom environments, and educational technologies on student learning and outcomes.
- Cognitive Psychology: Researchers have employed random assignment to investigate various aspects of human cognition, including memory, attention, and problem-solving, leading to a deeper understanding of how the mind works.
- Social Psychology: Random assignment has been instrumental in studying social phenomena, such as conformity, aggression, and prosocial behavior, shedding light on the intricate dynamics of human interaction.
Let's get into some specific examples. You'll need to know one term though, and that is "control group." A control group is a set of participants in a study who do not receive the treatment or intervention being tested , serving as a baseline to compare with the group that does, in order to assess the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Smoking Cessation Study: Researchers used random assignment to put participants into two groups. One group received a new anti-smoking program, while the other did not. This helped determine if the program was effective in helping people quit smoking.
- Math Tutoring Program: A study on students used random assignment to place them into two groups. One group received additional math tutoring, while the other continued with regular classes, to see if the extra help improved their grades.
- Exercise and Mental Health: Adults were randomly assigned to either an exercise group or a control group to study the impact of physical activity on mental health and mood.
- Diet and Weight Loss: A study randomly assigned participants to different diet plans to compare their effectiveness in promoting weight loss and improving health markers.
- Sleep and Learning: Researchers randomly assigned students to either a sleep extension group or a regular sleep group to study the impact of sleep on learning and memory.
- Classroom Seating Arrangement: Teachers used random assignment to place students in different seating arrangements to examine the effect on focus and academic performance.
- Music and Productivity: Employees were randomly assigned to listen to music or work in silence to investigate the effect of music on workplace productivity.
- Medication for ADHD: Children with ADHD were randomly assigned to receive either medication, behavioral therapy, or a placebo to compare treatment effectiveness.
- Mindfulness Meditation for Stress: Adults were randomly assigned to a mindfulness meditation group or a waitlist control group to study the impact on stress levels.
- Video Games and Aggression: A study randomly assigned participants to play either violent or non-violent video games and then measured their aggression levels.
- Online Learning Platforms: Students were randomly assigned to use different online learning platforms to evaluate their effectiveness in enhancing learning outcomes.
- Hand Sanitizers in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to use hand sanitizers or not to study the impact on student illness and absenteeism.
- Caffeine and Alertness: Participants were randomly assigned to consume caffeinated or decaffeinated beverages to measure the effects on alertness and cognitive performance.
- Green Spaces and Well-being: Neighborhoods were randomly assigned to receive green space interventions to study the impact on residents’ well-being and community connections.
- Pet Therapy for Hospital Patients: Patients were randomly assigned to receive pet therapy or standard care to assess the impact on recovery and mood.
- Yoga for Chronic Pain: Individuals with chronic pain were randomly assigned to a yoga intervention group or a control group to study the effect on pain levels and quality of life.
- Flu Vaccines Effectiveness: Different groups of people were randomly assigned to receive either the flu vaccine or a placebo to determine the vaccine’s effectiveness.
- Reading Strategies for Dyslexia: Children with dyslexia were randomly assigned to different reading intervention strategies to compare their effectiveness.
- Physical Environment and Creativity: Participants were randomly assigned to different room setups to study the impact of physical environment on creative thinking.
- Laughter Therapy for Depression: Individuals with depression were randomly assigned to laughter therapy sessions or control groups to assess the impact on mood.
- Financial Incentives for Exercise: Participants were randomly assigned to receive financial incentives for exercising to study the impact on physical activity levels.
- Art Therapy for Anxiety: Individuals with anxiety were randomly assigned to art therapy sessions or a waitlist control group to measure the effect on anxiety levels.
- Natural Light in Offices: Employees were randomly assigned to workspaces with natural or artificial light to study the impact on productivity and job satisfaction.
- School Start Times and Academic Performance: Schools were randomly assigned different start times to study the effect on student academic performance and well-being.
- Horticulture Therapy for Seniors: Older adults were randomly assigned to participate in horticulture therapy or traditional activities to study the impact on cognitive function and life satisfaction.
- Hydration and Cognitive Function: Participants were randomly assigned to different hydration levels to measure the impact on cognitive function and alertness.
- Intergenerational Programs: Seniors and young people were randomly assigned to intergenerational programs to study the effects on well-being and cross-generational understanding.
- Therapeutic Horseback Riding for Autism: Children with autism were randomly assigned to therapeutic horseback riding or traditional therapy to study the impact on social communication skills.
- Active Commuting and Health: Employees were randomly assigned to active commuting (cycling, walking) or passive commuting to study the effect on physical health.
- Mindful Eating for Weight Management: Individuals were randomly assigned to mindful eating workshops or control groups to study the impact on weight management and eating habits.
- Noise Levels and Learning: Students were randomly assigned to classrooms with different noise levels to study the effect on learning and concentration.
- Bilingual Education Methods: Schools were randomly assigned different bilingual education methods to compare their effectiveness in language acquisition.
- Outdoor Play and Child Development: Children were randomly assigned to different amounts of outdoor playtime to study the impact on physical and cognitive development.
- Social Media Detox: Participants were randomly assigned to a social media detox or regular usage to study the impact on mental health and well-being.
- Therapeutic Writing for Trauma Survivors: Individuals who experienced trauma were randomly assigned to therapeutic writing sessions or control groups to study the impact on psychological well-being.
- Mentoring Programs for At-risk Youth: At-risk youth were randomly assigned to mentoring programs or control groups to assess the impact on academic achievement and behavior.
- Dance Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: Individuals with Parkinson’s disease were randomly assigned to dance therapy or traditional exercise to study the effect on motor function and quality of life.
- Aquaponics in Schools: Schools were randomly assigned to implement aquaponics programs to study the impact on student engagement and environmental awareness.
- Virtual Reality for Phobia Treatment: Individuals with phobias were randomly assigned to virtual reality exposure therapy or traditional therapy to compare effectiveness.
- Gardening and Mental Health: Participants were randomly assigned to engage in gardening or other leisure activities to study the impact on mental health and stress reduction.
Each of these studies exemplifies how random assignment is utilized in various fields and settings, shedding light on the multitude of ways it can be applied to glean valuable insights and knowledge.
Real-world Impact of Random Assignment

Random assignment is like a key tool in the world of learning about people's minds and behaviors. It’s super important and helps in many different areas of our everyday lives. It helps make better rules, creates new ways to help people, and is used in lots of different fields.
Health and Medicine
In health and medicine, random assignment has helped doctors and scientists make lots of discoveries. It’s a big part of tests that help create new medicines and treatments.
By putting people into different groups by chance, scientists can really see if a medicine works.
This has led to new ways to help people with all sorts of health problems, like diabetes, heart disease, and mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
Schools and education have also learned a lot from random assignment. Researchers have used it to look at different ways of teaching, what kind of classrooms are best, and how technology can help learning.
This knowledge has helped make better school rules, develop what we learn in school, and find the best ways to teach students of all ages and backgrounds.
Workplace and Organizational Behavior
Random assignment helps us understand how people act at work and what makes a workplace good or bad.
Studies have looked at different kinds of workplaces, how bosses should act, and how teams should be put together. This has helped companies make better rules and create places to work that are helpful and make people happy.
Environmental and Social Changes
Random assignment is also used to see how changes in the community and environment affect people. Studies have looked at community projects, changes to the environment, and social programs to see how they help or hurt people’s well-being.
This has led to better community projects, efforts to protect the environment, and programs to help people in society.
Technology and Human Interaction
In our world where technology is always changing, studies with random assignment help us see how tech like social media, virtual reality, and online stuff affect how we act and feel.
This has helped make better and safer technology and rules about using it so that everyone can benefit.
The effects of random assignment go far and wide, way beyond just a science lab. It helps us understand lots of different things, leads to new and improved ways to do things, and really makes a difference in the world around us.
From making healthcare and schools better to creating positive changes in communities and the environment, the real-world impact of random assignment shows just how important it is in helping us learn and make the world a better place.
So, what have we learned? Random assignment is like a super tool in learning about how people think and act. It's like a detective helping us find clues and solve mysteries in many parts of our lives.
From creating new medicines to helping kids learn better in school, and from making workplaces happier to protecting the environment, it’s got a big job!
This method isn’t just something scientists use in labs; it reaches out and touches our everyday lives. It helps make positive changes and teaches us valuable lessons.
Whether we are talking about technology, health, education, or the environment, random assignment is there, working behind the scenes, making things better and safer for all of us.
In the end, the simple act of putting people into groups by chance helps us make big discoveries and improvements. It’s like throwing a small stone into a pond and watching the ripples spread out far and wide.
Thanks to random assignment, we are always learning, growing, and finding new ways to make our world a happier and healthier place for everyone!
Related posts:
- 19+ Experimental Design Examples (Methods + Types)
- Cluster Sampling vs Stratified Sampling
- 41+ White Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- 47+ Blue Collar Job Examples (Salary + Path)
- McDonaldization of Society (Definition + Examples)
Reference this article:
About The Author

Free Personality Test


Free Memory Test

Free IQ Test

PracticalPie.com is a participant in the Amazon Associates Program. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow Us On:
Youtube Facebook Instagram X/Twitter
Psychology Resources
Developmental
Personality
Relationships
Psychologists
Serial Killers
Psychology Tests
Personality Quiz
Memory Test
Depression test
Type A/B Personality Test
© PracticalPsychology. All rights reserved
Privacy Policy | Terms of Use
- Yale Directories
Institution for Social and Policy Studies
Advancing research • shaping policy • developing leaders, why randomize.
About Randomized Field Experiments Randomized field experiments allow researchers to scientifically measure the impact of an intervention on a particular outcome of interest.
What is a randomized field experiment? In a randomized experiment, a study sample is divided into one group that will receive the intervention being studied (the treatment group) and another group that will not receive the intervention (the control group). For instance, a study sample might consist of all registered voters in a particular city. This sample will then be randomly divided into treatment and control groups. Perhaps 40% of the sample will be on a campaign’s Get-Out-the-Vote (GOTV) mailing list and the other 60% of the sample will not receive the GOTV mailings. The outcome measured –voter turnout– can then be compared in the two groups. The difference in turnout will reflect the effectiveness of the intervention.
What does random assignment mean? The key to randomized experimental research design is in the random assignment of study subjects – for example, individual voters, precincts, media markets or some other group – into treatment or control groups. Randomization has a very specific meaning in this context. It does not refer to haphazard or casual choosing of some and not others. Randomization in this context means that care is taken to ensure that no pattern exists between the assignment of subjects into groups and any characteristics of those subjects. Every subject is as likely as any other to be assigned to the treatment (or control) group. Randomization is generally achieved by employing a computer program containing a random number generator. Randomization procedures differ based upon the research design of the experiment. Individuals or groups may be randomly assigned to treatment or control groups. Some research designs stratify subjects by geographic, demographic or other factors prior to random assignment in order to maximize the statistical power of the estimated effect of the treatment (e.g., GOTV intervention). Information about the randomization procedure is included in each experiment summary on the site.
What are the advantages of randomized experimental designs? Randomized experimental design yields the most accurate analysis of the effect of an intervention (e.g., a voter mobilization phone drive or a visit from a GOTV canvasser, on voter behavior). By randomly assigning subjects to be in the group that receives the treatment or to be in the control group, researchers can measure the effect of the mobilization method regardless of other factors that may make some people or groups more likely to participate in the political process. To provide a simple example, say we are testing the effectiveness of a voter education program on high school seniors. If we allow students from the class to volunteer to participate in the program, and we then compare the volunteers’ voting behavior against those who did not participate, our results will reflect something other than the effects of the voter education intervention. This is because there are, no doubt, qualities about those volunteers that make them different from students who do not volunteer. And, most important for our work, those differences may very well correlate with propensity to vote. Instead of letting students self-select, or even letting teachers select students (as teachers may have biases in who they choose), we could randomly assign all students in a given class to be in either a treatment or control group. This would ensure that those in the treatment and control groups differ solely due to chance. The value of randomization may also be seen in the use of walk lists for door-to-door canvassers. If canvassers choose which houses they will go to and which they will skip, they may choose houses that seem more inviting or they may choose houses that are placed closely together rather than those that are more spread out. These differences could conceivably correlate with voter turnout. Or if house numbers are chosen by selecting those on the first half of a ten page list, they may be clustered in neighborhoods that differ in important ways from neighborhoods in the second half of the list. Random assignment controls for both known and unknown variables that can creep in with other selection processes to confound analyses. Randomized experimental design is a powerful tool for drawing valid inferences about cause and effect. The use of randomized experimental design should allow a degree of certainty that the research findings cited in studies that employ this methodology reflect the effects of the interventions being measured and not some other underlying variable or variables.
Chapter 6: Experimental Research
Experimental design, learning objectives.
- Explain the difference between between-subjects and within-subjects experiments, list some of the pros and cons of each approach, and decide which approach to use to answer a particular research question.
- Define random assignment, distinguish it from random sampling, explain its purpose in experimental research, and use some simple strategies to implement it.
- Define what a control condition is, explain its purpose in research on treatment effectiveness, and describe some alternative types of control conditions.
- Define several types of carryover effect, give examples of each, and explain how counterbalancing helps to deal with them.
In this section, we look at some different ways to design an experiment. The primary distinction we will make is between approaches in which each participant experiences one level of the independent variable and approaches in which each participant experiences all levels of the independent variable. The former are called between-subjects experiments and the latter are called within-subjects experiments.
Between-Subjects Experiments
In a between-subjects experiment , each participant is tested in only one condition. For example, a researcher with a sample of 100 university students might assign half of them to write about a traumatic event and the other half write about a neutral event. Or a researcher with a sample of 60 people with severe agoraphobia (fear of open spaces) might assign 20 of them to receive each of three different treatments for that disorder. It is essential in a between-subjects experiment that the researcher assign participants to conditions so that the different groups are, on average, highly similar to each other. Those in a trauma condition and a neutral condition, for example, should include a similar proportion of men and women, and they should have similar average intelligence quotients (IQs), similar average levels of motivation, similar average numbers of health problems, and so on. This matching is a matter of controlling these extraneous participant variables across conditions so that they do not become confounding variables.
Random Assignment
The primary way that researchers accomplish this kind of control of extraneous variables across conditions is called random assignment , which means using a random process to decide which participants are tested in which conditions. Do not confuse random assignment with random sampling. Random sampling is a method for selecting a sample from a population, and it is rarely used in psychological research. Random assignment is a method for assigning participants in a sample to the different conditions, and it is an important element of all experimental research in psychology and other fields too.
In its strictest sense, random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being assigned to each of two conditions). The second is that each participant is assigned to a condition independently of other participants. Thus one way to assign participants to two conditions would be to flip a coin for each one. If the coin lands heads, the participant is assigned to Condition A, and if it lands tails, the participant is assigned to Condition B. For three conditions, one could use a computer to generate a random integer from 1 to 3 for each participant. If the integer is 1, the participant is assigned to Condition A; if it is 2, the participant is assigned to Condition B; and if it is 3, the participant is assigned to Condition C. In practice, a full sequence of conditions—one for each participant expected to be in the experiment—is usually created ahead of time, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence as he or she is tested. When the procedure is computerized, the computer program often handles the random assignment.
One problem with coin flipping and other strict procedures for random assignment is that they are likely to result in unequal sample sizes in the different conditions. Unequal sample sizes are generally not a serious problem, and you should never throw away data you have already collected to achieve equal sample sizes. However, for a fixed number of participants, it is statistically most efficient to divide them into equal-sized groups. It is standard practice, therefore, to use a kind of modified random assignment that keeps the number of participants in each group as similar as possible. One approach is block randomization . In block randomization, all the conditions occur once in the sequence before any of them is repeated. Then they all occur again before any of them is repeated again. Within each of these “blocks,” the conditions occur in a random order. Again, the sequence of conditions is usually generated before any participants are tested, and each new participant is assigned to the next condition in the sequence. Table 6.2 shows such a sequence for assigning nine participants to three conditions. The Research Randomizer website ( http://www.randomizer.org ) will generate block randomization sequences for any number of participants and conditions. Again, when the procedure is computerized, the computer program often handles the block randomization.
Random assignment is not guaranteed to control all extraneous variables across conditions. It is always possible that just by chance, the participants in one condition might turn out to be substantially older, less tired, more motivated, or less depressed on average than the participants in another condition. However, there are some reasons that this possibility is not a major concern. One is that random assignment works better than one might expect, especially for large samples. Another is that the inferential statistics that researchers use to decide whether a difference between groups reflects a difference in the population takes the “fallibility” of random assignment into account. Yet another reason is that even if random assignment does result in a confounding variable and therefore produces misleading results, this confound is likely to be detected when the experiment is replicated. The upshot is that random assignment to conditions—although not infallible in terms of controlling extraneous variables—is always considered a strength of a research design.
Treatment and Control Conditions
Between-subjects experiments are often used to determine whether a treatment works. In psychological research, a treatment is any intervention meant to change people’s behaviour for the better. This intervention includes psychotherapies and medical treatments for psychological disorders but also interventions designed to improve learning, promote conservation, reduce prejudice, and so on. To determine whether a treatment works, participants are randomly assigned to either a treatment condition , in which they receive the treatment, or a control condition , in which they do not receive the treatment. If participants in the treatment condition end up better off than participants in the control condition—for example, they are less depressed, learn faster, conserve more, express less prejudice—then the researcher can conclude that the treatment works. In research on the effectiveness of psychotherapies and medical treatments, this type of experiment is often called a randomized clinical trial .
There are different types of control conditions. In a no-treatment control condition , participants receive no treatment whatsoever. One problem with this approach, however, is the existence of placebo effects. A placebo is a simulated treatment that lacks any active ingredient or element that should make it effective, and a placebo effect is a positive effect of such a treatment. Many folk remedies that seem to work—such as eating chicken soup for a cold or placing soap under the bedsheets to stop nighttime leg cramps—are probably nothing more than placebos. Although placebo effects are not well understood, they are probably driven primarily by people’s expectations that they will improve. Having the expectation to improve can result in reduced stress, anxiety, and depression, which can alter perceptions and even improve immune system functioning (Price, Finniss, & Benedetti, 2008) [1] .
Placebo effects are interesting in their own right (see Note “The Powerful Placebo” ), but they also pose a serious problem for researchers who want to determine whether a treatment works. Figure 6.2 shows some hypothetical results in which participants in a treatment condition improved more on average than participants in a no-treatment control condition. If these conditions (the two leftmost bars in Figure 6.2 ) were the only conditions in this experiment, however, one could not conclude that the treatment worked. It could be instead that participants in the treatment group improved more because they expected to improve, while those in the no-treatment control condition did not.

Figure 6.2 Hypothetical Results From a Study Including Treatment, No-Treatment, and Placebo Conditions
Fortunately, there are several solutions to this problem. One is to include a placebo control condition , in which participants receive a placebo that looks much like the treatment but lacks the active ingredient or element thought to be responsible for the treatment’s effectiveness. When participants in a treatment condition take a pill, for example, then those in a placebo control condition would take an identical-looking pill that lacks the active ingredient in the treatment (a “sugar pill”). In research on psychotherapy effectiveness, the placebo might involve going to a psychotherapist and talking in an unstructured way about one’s problems. The idea is that if participants in both the treatment and the placebo control groups expect to improve, then any improvement in the treatment group over and above that in the placebo control group must have been caused by the treatment and not by participants’ expectations. This difference is what is shown by a comparison of the two outer bars in Figure 6.2 .
Of course, the principle of informed consent requires that participants be told that they will be assigned to either a treatment or a placebo control condition—even though they cannot be told which until the experiment ends. In many cases the participants who had been in the control condition are then offered an opportunity to have the real treatment. An alternative approach is to use a waitlist control condition , in which participants are told that they will receive the treatment but must wait until the participants in the treatment condition have already received it. This disclosure allows researchers to compare participants who have received the treatment with participants who are not currently receiving it but who still expect to improve (eventually). A final solution to the problem of placebo effects is to leave out the control condition completely and compare any new treatment with the best available alternative treatment. For example, a new treatment for simple phobia could be compared with standard exposure therapy. Because participants in both conditions receive a treatment, their expectations about improvement should be similar. This approach also makes sense because once there is an effective treatment, the interesting question about a new treatment is not simply “Does it work?” but “Does it work better than what is already available?
The Powerful Placebo
Many people are not surprised that placebos can have a positive effect on disorders that seem fundamentally psychological, including depression, anxiety, and insomnia. However, placebos can also have a positive effect on disorders that most people think of as fundamentally physiological. These include asthma, ulcers, and warts (Shapiro & Shapiro, 1999) [2] . There is even evidence that placebo surgery—also called “sham surgery”—can be as effective as actual surgery.
Medical researcher J. Bruce Moseley and his colleagues conducted a study on the effectiveness of two arthroscopic surgery procedures for osteoarthritis of the knee (Moseley et al., 2002) [3] . The control participants in this study were prepped for surgery, received a tranquilizer, and even received three small incisions in their knees. But they did not receive the actual arthroscopic surgical procedure. The surprising result was that all participants improved in terms of both knee pain and function, and the sham surgery group improved just as much as the treatment groups. According to the researchers, “This study provides strong evidence that arthroscopic lavage with or without débridement [the surgical procedures used] is not better than and appears to be equivalent to a placebo procedure in improving knee pain and self-reported function” (p. 85).
Within-Subjects Experiments
In a within-subjects experiment , each participant is tested under all conditions. Consider an experiment on the effect of a defendant’s physical attractiveness on judgments of his guilt. Again, in a between-subjects experiment, one group of participants would be shown an attractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt, and another group of participants would be shown an unattractive defendant and asked to judge his guilt. In a within-subjects experiment, however, the same group of participants would judge the guilt of both an attractive and an unattractive defendant.
The primary advantage of this approach is that it provides maximum control of extraneous participant variables. Participants in all conditions have the same mean IQ, same socioeconomic status, same number of siblings, and so on—because they are the very same people. Within-subjects experiments also make it possible to use statistical procedures that remove the effect of these extraneous participant variables on the dependent variable and therefore make the data less “noisy” and the effect of the independent variable easier to detect. We will look more closely at this idea later in the book . However, not all experiments can use a within-subjects design nor would it be desirable to.
Carryover Effects and Counterbalancing
The primary disadvantage of within-subjects designs is that they can result in carryover effects. A carryover effect is an effect of being tested in one condition on participants’ behaviour in later conditions. One type of carryover effect is a practice effect , where participants perform a task better in later conditions because they have had a chance to practice it. Another type is a fatigue effect , where participants perform a task worse in later conditions because they become tired or bored. Being tested in one condition can also change how participants perceive stimuli or interpret their task in later conditions. This type of effect is called a context effect . For example, an average-looking defendant might be judged more harshly when participants have just judged an attractive defendant than when they have just judged an unattractive defendant. Within-subjects experiments also make it easier for participants to guess the hypothesis. For example, a participant who is asked to judge the guilt of an attractive defendant and then is asked to judge the guilt of an unattractive defendant is likely to guess that the hypothesis is that defendant attractiveness affects judgments of guilt. This knowledge could lead the participant to judge the unattractive defendant more harshly because he thinks this is what he is expected to do. Or it could make participants judge the two defendants similarly in an effort to be “fair.”
Carryover effects can be interesting in their own right. (Does the attractiveness of one person depend on the attractiveness of other people that we have seen recently?) But when they are not the focus of the research, carryover effects can be problematic. Imagine, for example, that participants judge the guilt of an attractive defendant and then judge the guilt of an unattractive defendant. If they judge the unattractive defendant more harshly, this might be because of his unattractiveness. But it could be instead that they judge him more harshly because they are becoming bored or tired. In other words, the order of the conditions is a confounding variable. The attractive condition is always the first condition and the unattractive condition the second. Thus any difference between the conditions in terms of the dependent variable could be caused by the order of the conditions and not the independent variable itself.
There is a solution to the problem of order effects, however, that can be used in many situations. It is counterbalancing , which means testing different participants in different orders. For example, some participants would be tested in the attractive defendant condition followed by the unattractive defendant condition, and others would be tested in the unattractive condition followed by the attractive condition. With three conditions, there would be six different orders (ABC, ACB, BAC, BCA, CAB, and CBA), so some participants would be tested in each of the six orders. With counterbalancing, participants are assigned to orders randomly, using the techniques we have already discussed. Thus random assignment plays an important role in within-subjects designs just as in between-subjects designs. Here, instead of randomly assigning to conditions, they are randomly assigned to different orders of conditions. In fact, it can safely be said that if a study does not involve random assignment in one form or another, it is not an experiment.
An efficient way of counterbalancing is through a Latin square design which randomizes through having equal rows and columns. For example, if you have four treatments, you must have four versions. Like a Sudoku puzzle, no treatment can repeat in a row or column. For four versions of four treatments, the Latin square design would look like:
There are two ways to think about what counterbalancing accomplishes. One is that it controls the order of conditions so that it is no longer a confounding variable. Instead of the attractive condition always being first and the unattractive condition always being second, the attractive condition comes first for some participants and second for others. Likewise, the unattractive condition comes first for some participants and second for others. Thus any overall difference in the dependent variable between the two conditions cannot have been caused by the order of conditions. A second way to think about what counterbalancing accomplishes is that if there are carryover effects, it makes it possible to detect them. One can analyze the data separately for each order to see whether it had an effect.
When 9 Is “Larger” Than 221
Researcher Michael Birnbaum has argued that the lack of context provided by between-subjects designs is often a bigger problem than the context effects created by within-subjects designs. To demonstrate this problem, he asked participants to rate two numbers on how large they were on a scale of 1-to-10 where 1 was “very very small” and 10 was “very very large”. One group of participants were asked to rate the number 9 and another group was asked to rate the number 221 (Birnbaum, 1999) [4] . Participants in this between-subjects design gave the number 9 a mean rating of 5.13 and the number 221 a mean rating of 3.10. In other words, they rated 9 as larger than 221! According to Birnbaum, this difference is because participants spontaneously compared 9 with other one-digit numbers (in which case it is relatively large) and compared 221 with other three-digit numbers (in which case it is relatively small).
Simultaneous Within-Subjects Designs
So far, we have discussed an approach to within-subjects designs in which participants are tested in one condition at a time. There is another approach, however, that is often used when participants make multiple responses in each condition. Imagine, for example, that participants judge the guilt of 10 attractive defendants and 10 unattractive defendants. Instead of having people make judgments about all 10 defendants of one type followed by all 10 defendants of the other type, the researcher could present all 20 defendants in a sequence that mixed the two types. The researcher could then compute each participant’s mean rating for each type of defendant. Or imagine an experiment designed to see whether people with social anxiety disorder remember negative adjectives (e.g., “stupid,” “incompetent”) better than positive ones (e.g., “happy,” “productive”). The researcher could have participants study a single list that includes both kinds of words and then have them try to recall as many words as possible. The researcher could then count the number of each type of word that was recalled. There are many ways to determine the order in which the stimuli are presented, but one common way is to generate a different random order for each participant.
Between-Subjects or Within-Subjects?
Almost every experiment can be conducted using either a between-subjects design or a within-subjects design. This possibility means that researchers must choose between the two approaches based on their relative merits for the particular situation.
Between-subjects experiments have the advantage of being conceptually simpler and requiring less testing time per participant. They also avoid carryover effects without the need for counterbalancing. Within-subjects experiments have the advantage of controlling extraneous participant variables, which generally reduces noise in the data and makes it easier to detect a relationship between the independent and dependent variables.
A good rule of thumb, then, is that if it is possible to conduct a within-subjects experiment (with proper counterbalancing) in the time that is available per participant—and you have no serious concerns about carryover effects—this design is probably the best option. If a within-subjects design would be difficult or impossible to carry out, then you should consider a between-subjects design instead. For example, if you were testing participants in a doctor’s waiting room or shoppers in line at a grocery store, you might not have enough time to test each participant in all conditions and therefore would opt for a between-subjects design. Or imagine you were trying to reduce people’s level of prejudice by having them interact with someone of another race. A within-subjects design with counterbalancing would require testing some participants in the treatment condition first and then in a control condition. But if the treatment works and reduces people’s level of prejudice, then they would no longer be suitable for testing in the control condition. This difficulty is true for many designs that involve a treatment meant to produce long-term change in participants’ behaviour (e.g., studies testing the effectiveness of psychotherapy). Clearly, a between-subjects design would be necessary here.
Remember also that using one type of design does not preclude using the other type in a different study. There is no reason that a researcher could not use both a between-subjects design and a within-subjects design to answer the same research question. In fact, professional researchers often take exactly this type of mixed methods approach.
Key Takeaways
- Experiments can be conducted using either between-subjects or within-subjects designs. Deciding which to use in a particular situation requires careful consideration of the pros and cons of each approach.
- Random assignment to conditions in between-subjects experiments or to orders of conditions in within-subjects experiments is a fundamental element of experimental research. Its purpose is to control extraneous variables so that they do not become confounding variables.
- Experimental research on the effectiveness of a treatment requires both a treatment condition and a control condition, which can be a no-treatment control condition, a placebo control condition, or a waitlist control condition. Experimental treatments can also be compared with the best available alternative.
- You want to test the relative effectiveness of two training programs for running a marathon.
- Using photographs of people as stimuli, you want to see if smiling people are perceived as more intelligent than people who are not smiling.
- In a field experiment, you want to see if the way a panhandler is dressed (neatly vs. sloppily) affects whether or not passersby give him any money.
- You want to see if concrete nouns (e.g., dog ) are recalled better than abstract nouns (e.g., truth ).
- Discussion: Imagine that an experiment shows that participants who receive psychodynamic therapy for a dog phobia improve more than participants in a no-treatment control group. Explain a fundamental problem with this research design and at least two ways that it might be corrected.
- Price, D. D., Finniss, D. G., & Benedetti, F. (2008). A comprehensive review of the placebo effect: Recent advances and current thought. Annual Review of Psychology, 59 , 565–590. ↵
- Shapiro, A. K., & Shapiro, E. (1999). The powerful placebo: From ancient priest to modern physician . Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press. ↵
- Moseley, J. B., O’Malley, K., Petersen, N. J., Menke, T. J., Brody, B. A., Kuykendall, D. H., … Wray, N. P. (2002). A controlled trial of arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee. The New England Journal of Medicine, 347 , 81–88. ↵
- Birnbaum, M.H. (1999). How to show that 9>221: Collect judgments in a between-subjects design. Psychological Methods, 4 (3), 243-249. ↵
- Research Methods in Psychology. Authored by : Paul C. Price, Rajiv S. Jhangiani, and I-Chant A. Chiang. Provided by : BCCampus. Located at : https://opentextbc.ca/researchmethods/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy
1.4 Experimental Design and Ethics
Does aspirin reduce the risk of heart attacks? Is one brand of fertilizer more effective at growing roses than another? Is fatigue as dangerous to a driver as the influence of alcohol? Questions like these are answered using randomized experiments. In this module, you will learn important aspects of experimental design. Proper study design ensures the production of reliable, accurate data.
The purpose of an experiment is to investigate the relationship between two variables. When one variable causes change in another, we call the first variable the explanatory variable . The affected variable is called the response variable . In a randomized experiment, the researcher manipulates values of the explanatory variable and measures the resulting changes in the response variable. The different values of the explanatory variable are called treatments . An experimental unit is a single object or individual to be measured.
You want to investigate the effectiveness of vitamin E in preventing disease. You recruit a group of subjects and ask them if they regularly take vitamin E. You notice that the subjects who take vitamin E exhibit better health on average than those who do not. Does this prove that vitamin E is effective in disease prevention? It does not. There are many differences between the two groups compared in addition to vitamin E consumption. People who take vitamin E regularly often take other steps to improve their health: exercise, diet, other vitamin supplements, choosing not to smoke. Any one of these factors could be influencing health. As described, this study does not prove that vitamin E is the key to disease prevention.
Additional variables that can cloud a study are called lurking variables . In order to prove that the explanatory variable is causing a change in the response variable, it is necessary to isolate the explanatory variable. The researcher must design her experiment in such a way that there is only one difference between groups being compared: the planned treatments. This is accomplished by the random assignment of experimental units to treatment groups. When subjects are assigned treatments randomly, all of the potential lurking variables are spread equally among the groups. At this point the only difference between groups is the one imposed by the researcher. Different outcomes measured in the response variable, therefore, must be a direct result of the different treatments. In this way, an experiment can prove a cause-and-effect connection between the explanatory and response variables.
The power of suggestion can have an important influence on the outcome of an experiment. Studies have shown that the expectation of the study participant can be as important as the actual medication. In one study of performance-enhancing drugs, researchers noted:
Results showed that believing one had taken the substance resulted in [ performance ] times almost as fast as those associated with consuming the drug itself. In contrast, taking the drug without knowledge yielded no significant performance increment. 1
When participation in a study prompts a physical response from a participant, it is difficult to isolate the effects of the explanatory variable. To counter the power of suggestion, researchers set aside one treatment group as a control group . This group is given a placebo treatment–a treatment that cannot influence the response variable. The control group helps researchers balance the effects of being in an experiment with the effects of the active treatments. Of course, if you are participating in a study and you know that you are receiving a pill which contains no actual medication, then the power of suggestion is no longer a factor. Blinding in a randomized experiment preserves the power of suggestion. When a person involved in a research study is blinded, he does not know who is receiving the active treatment(s) and who is receiving the placebo treatment. A double-blind experiment is one in which both the subjects and the researchers involved with the subjects are blinded.
Example 1.19
Researchers want to investigate whether taking aspirin regularly reduces the risk of heart attack. Four hundred men between the ages of 50 and 84 are recruited as participants. The men are divided randomly into two groups: one group will take aspirin, and the other group will take a placebo. Each man takes one pill each day for three years, but he does not know whether he is taking aspirin or the placebo. At the end of the study, researchers count the number of men in each group who have had heart attacks.
Identify the following values for this study: population, sample, experimental units, explanatory variable, response variable, treatments.
The population is men aged 50 to 84. The sample is the 400 men who participated. The experimental units are the individual men in the study. The explanatory variable is oral medication. The treatments are aspirin and a placebo. The response variable is whether a subject had a heart attack.
Example 1.20
The Smell & Taste Treatment and Research Foundation conducted a study to investigate whether smell can affect learning. Subjects completed mazes multiple times while wearing masks. They completed the pencil and paper mazes three times wearing floral-scented masks, and three times with unscented masks. Participants were assigned at random to wear the floral mask during the first three trials or during the last three trials. For each trial, researchers recorded the time it took to complete the maze and the subject’s impression of the mask’s scent: positive, negative, or neutral.
- Describe the explanatory and response variables in this study.
- What are the treatments?
- Identify any lurking variables that could interfere with this study.
- Is it possible to use blinding in this study?
- The explanatory variable is scent, and the response variable is the time it takes to complete the maze.
- There are two treatments: a floral-scented mask and an unscented mask.
- All subjects experienced both treatments. The order of treatments was randomly assigned so there were no differences between the treatment groups. Random assignment eliminates the problem of lurking variables.
- Subjects will clearly know whether they can smell flowers or not, so subjects cannot be blinded in this study. Researchers timing the mazes can be blinded, though. The researcher who is observing a subject will not know which mask is being worn.
Example 1.21
A researcher wants to study the effects of birth order on personality. Explain why this study could not be conducted as a randomized experiment. What is the main problem in a study that cannot be designed as a randomized experiment?
The explanatory variable is birth order. You cannot randomly assign a person’s birth order. Random assignment eliminates the impact of lurking variables. When you cannot assign subjects to treatment groups at random, there will be differences between the groups other than the explanatory variable.
Try It 1.21
You are concerned about the effects of texting on driving performance. Design a study to test the response time of drivers while texting and while driving only. How many seconds does it take for a driver to respond when a leading car hits the brakes?
- Describe the explanatory and response variables in the study.
- What should you consider when selecting participants?
- Your research partner wants to divide participants randomly into two groups: one to drive without distraction and one to text and drive simultaneously. Is this a good idea? Why or why not?
- How can blinding be used in this study?
The widespread misuse and misrepresentation of statistical information often gives the field a bad name. Some say that “numbers don’t lie,” but the people who use numbers to support their claims often do.
A recent investigation of famous social psychologist, Diederik Stapel, has led to the retraction of his articles from some of the world’s top journals including Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, Social Psychology, Basic and Applied Social Psychology, British Journal of Social Psychology, and the magazine Science . Diederik Stapel is a former professor at Tilburg University in the Netherlands. Over the past two years, an extensive investigation involving three universities where Stapel has worked concluded that the psychologist is guilty of fraud on a colossal scale. Falsified data taints over 55 papers he authored and 10 Ph.D. dissertations that he supervised.
Stapel did not deny that his deceit was driven by ambition. But it was more complicated than that, he told me. He insisted that he loved social psychology but had been frustrated by the messiness of experimental data, which rarely led to clear conclusions. His lifelong obsession with elegance and order, he said, led him to concoct sexy results that journals found attractive. “It was a quest for aesthetics, for beauty—instead of the truth,” he said. He described his behavior as an addiction that drove him to carry out acts of increasingly daring fraud, like a junkie seeking a bigger and better high. 2
The committee investigating Stapel concluded that he is guilty of several practices including:
- creating datasets, which largely confirmed the prior expectations,
- altering data in existing datasets,
- changing measuring instruments without reporting the change, and
- misrepresenting the number of experimental subjects.
Clearly, it is never acceptable to falsify data the way this researcher did. Sometimes, however, violations of ethics are not as easy to spot.
Researchers have a responsibility to verify that proper methods are being followed. The report describing the investigation of Stapel’s fraud states that, “statistical flaws frequently revealed a lack of familiarity with elementary statistics.” 3 Many of Stapel’s co-authors should have spotted irregularities in his data. Unfortunately, they did not know very much about statistical analysis, and they simply trusted that he was collecting and reporting data properly.
Many types of statistical fraud are difficult to spot. Some researchers simply stop collecting data once they have just enough to prove what they had hoped to prove. They don’t want to take the chance that a more extensive study would complicate their lives by producing data contradicting their hypothesis.
Professional organizations, like the American Statistical Association, clearly define expectations for researchers. There are even laws in the federal code about the use of research data.
When a statistical study uses human participants, as in medical studies, both ethics and the law dictate that researchers should be mindful of the safety of their research subjects. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services oversees federal regulations of research studies with the aim of protecting participants. When a university or other research institution engages in research, it must ensure the safety of all human subjects. For this reason, research institutions establish oversight committees known as Institutional Review Boards (IRB) . All planned studies must be approved in advance by the IRB. Key protections that are mandated by law include the following:
- Risks to participants must be minimized and reasonable with respect to projected benefits.
- Participants must give informed consent . This means that the risks of participation must be clearly explained to the subjects of the study. Subjects must consent in writing, and researchers are required to keep documentation of their consent.
- Data collected from individuals must be guarded carefully to protect their privacy.
These ideas may seem fundamental, but they can be very difficult to verify in practice. Is removing a participant’s name from the data record sufficient to protect privacy? Perhaps the person’s identity could be discovered from the data that remains. What happens if the study does not proceed as planned and risks arise that were not anticipated? When is informed consent really necessary? Suppose your doctor wants a blood sample to check your cholesterol level. Once the sample has been tested, you expect the lab to dispose of the remaining blood. At that point the blood becomes biological waste. Does a researcher have the right to take it for use in a study?
It is important that students of statistics take time to consider the ethical questions that arise in statistical studies. How prevalent is fraud in statistical studies? You might be surprised—and disappointed. There is a website dedicated to cataloging retractions of study articles that have been proven fraudulent. A quick glance will show that the misuse of statistics is a bigger problem than most people realize.
Vigilance against fraud requires knowledge. Learning the basic theory of statistics will empower you to analyze statistical studies critically.
Example 1.22
Describe the unethical behavior in each example and describe how it could impact the reliability of the resulting data. Explain how the problem should be corrected.
A researcher is collecting data in a community.
- She selects a block where she is comfortable walking because she knows many of the people living on the street.
- No one seems to be home at four houses on her route. She does not record the addresses and does not return at a later time to try to find residents at home.
- She skips four houses on her route because she is running late for an appointment. When she gets home, she fills in the forms by selecting random answers from other residents in the neighborhood.
- By selecting a convenient sample, the researcher is intentionally selecting a sample that could be biased. Claiming that this sample represents the community is misleading. The researcher needs to select areas in the community at random.
- Intentionally omitting relevant data will create bias in the sample. Suppose the researcher is gathering information about jobs and child care. By ignoring people who are not home, she may be missing data from working families that are relevant to her study. She needs to make every effort to interview all members of the target sample.
- It is never acceptable to fake data. Even though the responses she uses are “real” responses provided by other participants, the duplication is fraudulent and can create bias in the data. She needs to work diligently to interview everyone on her route.
Try It 1.22
Describe the unethical behavior, if any, in each example and describe how it could impact the reliability of the resulting data. Explain how the problem should be corrected.
A study is commissioned to determine the favorite brand of fruit juice among teens in California.
- The survey is commissioned by the seller of a popular brand of apple juice.
- There are only two types of juice included in the study: apple juice and cranberry juice.
- Researchers allow participants to see the brand of juice as samples are poured for a taste test.
- Twenty-five percent of participants prefer Brand X, 33% prefer Brand Y and 42% have no preference between the two brands. Brand X references the study in a commercial saying “Most teens like Brand X as much as or more than Brand Y.”
- 1 McClung, M. Collins, D. “Because I know it will!”: placebo effects of an ergogenic aid on athletic performance. Journal of Sport & Exercise Psychology. 2007 Jun. 29(3):382-94. Web. April 30, 2013.
- 2 Yudhijit Bhattacharjee, “The Mind of a Con Man,” Magazine, New York Times, April 26, 2013. Available online at: http://www.nytimes.com/2013/04/28/magazine/diederik-stapels-audacious-academic-fraud.html?src=dayp&_r=2& (accessed May 1, 2013).
- 3 “Flawed Science: The Fraudulent Research Practices of Social Psychologist Diederik Stapel,” Tillburg University, November 28, 2012, http://www.tilburguniversity.edu/upload/064a10cd-bce5-4385-b9ff-05b840caeae6_120695_Rapp_nov_2012_UK_web.pdf (accessed May 1, 2013).
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Barbara Illowsky, Susan Dean
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introductory Statistics
- Publication date: Sep 19, 2013
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introductory-statistics/pages/1-4-experimental-design-and-ethics
© Jun 23, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Random Assignment in Psychology (Intro for Students)
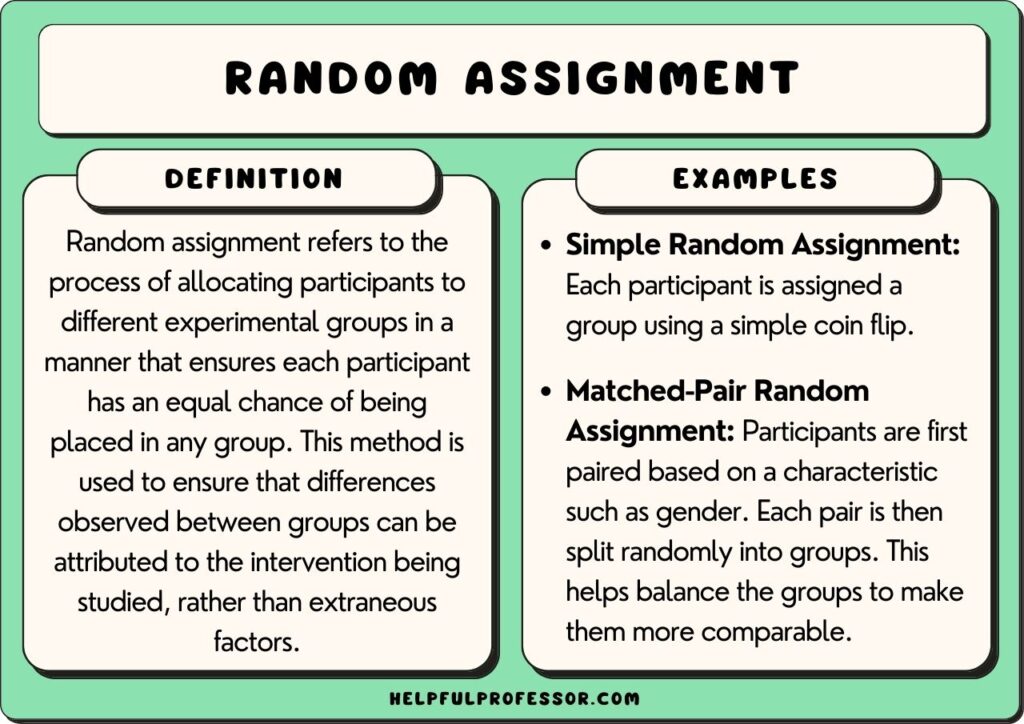
Random assignment is a research procedure used to randomly assign participants to different experimental conditions (or ‘groups’). This introduces the element of chance, ensuring that each participant has an equal likelihood of being placed in any condition group for the study.
It is absolutely essential that the treatment condition and the control condition are the same in all ways except for the variable being manipulated.
Using random assignment to place participants in different conditions helps to achieve this.
It ensures that those conditions are the same in regards to all potential confounding variables and extraneous factors .
Why Researchers Use Random Assignment
Researchers use random assignment to control for confounds in research.
Confounds refer to unwanted and often unaccounted-for variables that might affect the outcome of a study. These confounding variables can skew the results, rendering the experiment unreliable.
For example, below is a study with two groups. Note how there are more ‘red’ individuals in the first group than the second:
There is likely a confounding variable in this experiment explaining why more red people ended up in the treatment condition and less in the control condition. The red people might have self-selected, for example, leading to a skew of them in one group over the other.
Ideally, we’d want a more even distribution, like below:
To achieve better balance in our two conditions, we use randomized sampling.
Fact File: Experiments 101
Random assignment is used in the type of research called the experiment.
An experiment involves manipulating the level of one variable and examining how it affects another variable. These are the independent and dependent variables :
- Independent Variable: The variable manipulated is called the independent variable (IV)
- Dependent Variable: The variable that it is expected to affect is called the dependent variable (DV).
The most basic form of the experiment involves two conditions: the treatment and the control .
- The Treatment Condition: The treatment condition involves the participants being exposed to the IV.
- The Control Condition: The control condition involves the absence of the IV. Therefore, the IV has two levels: zero and some quantity.
Researchers utilize random assignment to determine which participants go into which conditions.
Methods of Random Assignment
There are several procedures that researchers can use to randomly assign participants to different conditions.
1. Random number generator
There are several websites that offer computer-generated random numbers. Simply indicate how many conditions are in the experiment and then click. If there are 4 conditions, the program will randomly generate a number between 1 and 4 each time it is clicked.
2. Flipping a coin
If there are two conditions in an experiment, then the simplest way to implement random assignment is to flip a coin for each participant. Heads means being assigned to the treatment and tails means being assigned to the control (or vice versa).
3. Rolling a die
Rolling a single die is another way to randomly assign participants. If the experiment has three conditions, then numbers 1 and 2 mean being assigned to the control; numbers 3 and 4 mean treatment condition one; and numbers 5 and 6 mean treatment condition two.
4. Condition names in a hat
In some studies, the researcher will write the name of the treatment condition(s) or control on slips of paper and place them in a hat. If there are 4 conditions and 1 control, then there are 5 slips of paper.
The researcher closes their eyes and selects one slip for each participant. That person is then assigned to one of the conditions in the study and that slip of paper is placed back in the hat. Repeat as necessary.
There are other ways of trying to ensure that the groups of participants are equal in all ways with the exception of the IV. However, random assignment is the most often used because it is so effective at reducing confounds.
Read About More Methods and Examples of Random Assignment Here
Potential Confounding Effects
Random assignment is all about minimizing confounding effects.
Here are six types of confounds that can be controlled for using random assignment:
- Individual Differences: Participants in a study will naturally vary in terms of personality, intelligence, mood, prior knowledge, and many other characteristics. If one group happens to have more people with a particular characteristic, this could affect the results. Random assignment ensures that these individual differences are spread out equally among the experimental groups, making it less likely that they will unduly influence the outcome.
- Temporal or Time-Related Confounds: Events or situations that occur at a particular time can influence the outcome of an experiment. For example, a participant might be tested after a stressful event, while another might be tested after a relaxing weekend. Random assignment ensures that such effects are equally distributed among groups, thus controlling for their potential influence.
- Order Effects: If participants are exposed to multiple treatments or tests, the order in which they experience them can influence their responses. Randomly assigning the order of treatments for different participants helps control for this.
- Location or Environmental Confounds: The environment in which the study is conducted can influence the results. One group might be tested in a noisy room, while another might be in a quiet room. Randomly assigning participants to different locations can control for these effects.
- Instrumentation Confounds: These occur when there are variations in the calibration or functioning of measurement instruments across conditions. If one group’s responses are being measured using a slightly different tool or scale, it can introduce a confound. Random assignment can ensure that any such potential inconsistencies in instrumentation are equally distributed among groups.
- Experimenter Effects: Sometimes, the behavior or expectations of the person administering the experiment can unintentionally influence the participants’ behavior or responses. For instance, if an experimenter believes one treatment is superior, they might unconsciously communicate this belief to participants. Randomly assigning experimenters or using a double-blind procedure (where neither the participant nor the experimenter knows the treatment being given) can help control for this.
Random assignment helps balance out these and other potential confounds across groups, ensuring that any observed differences are more likely due to the manipulated independent variable rather than some extraneous factor.
Limitations of the Random Assignment Procedure
Although random assignment is extremely effective at eliminating the presence of participant-related confounds, there are several scenarios in which it cannot be used.
- Ethics: The most obvious scenario is when it would be unethical. For example, if wanting to investigate the effects of emotional abuse on children, it would be unethical to randomly assign children to either received abuse or not. Even if a researcher were to propose such a study, it would not receive approval from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) which oversees research by university faculty.
- Practicality: Other scenarios involve matters of practicality. For example, randomly assigning people to specific types of diet over a 10-year period would be interesting, but it would be highly unlikely that participants would be diligent enough to make the study valid. This is why examining these types of subjects has to be carried out through observational studies . The data is correlational, which is informative, but falls short of the scientist’s ultimate goal of identifying causality.
- Small Sample Size: The smaller the sample size being assigned to conditions, the more likely it is that the two groups will be unequal. For example, if you flip a coin many times in a row then you will notice that sometimes there will be a string of heads or tails that come up consecutively. This means that one condition may have a build-up of participants that share the same characteristics. However, if you continue flipping the coin, over the long-term, there will be a balance of heads and tails. Unfortunately, how large a sample size is necessary has been the subject of considerable debate (Bloom, 2006; Shadish et al., 2002).
“It is well known that larger sample sizes reduce the probability that random assignment will result in conditions that are unequal” (Goldberg, 2019, p. 2).
Applications of Random Assignment
The importance of random assignment has been recognized in a wide range of scientific and applied disciplines (Bloom, 2006).
Random assignment began as a tool in agricultural research by Fisher (1925, 1935). After WWII, it became extensively used in medical research to test the effectiveness of new treatments and pharmaceuticals (Marks, 1997).
Today it is widely used in industrial engineering (Box, Hunter, and Hunter, 2005), educational research (Lindquist, 1953; Ong-Dean et al., 2011)), psychology (Myers, 1972), and social policy studies (Boruch, 1998; Orr, 1999).
One of the biggest obstacles to the validity of an experiment is the confound. If the group of participants in the treatment condition are substantially different from the group in the control condition, then it is impossible to determine if the IV has an affect or if the confound has an effect.
Thankfully, random assignment is highly effective at eliminating confounds that are known and unknown. Because each participant has an equal chance of being placed in each condition, they are equally distributed.
There are several ways of implementing random assignment, including flipping a coin or using a random number generator.
Random assignment has become an essential procedure in research in a wide range of subjects such as psychology, education, and social policy.
Alferes, V. R. (2012). Methods of randomization in experimental design . Sage Publications.
Bloom, H. S. (2008). The core analytics of randomized experiments for social research. The SAGE Handbook of Social Research Methods , 115-133.
Boruch, R. F. (1998). Randomized controlled experiments for evaluation and planning. Handbook of applied social research methods , 161-191.
Box, G. E., Hunter, W. G., & Hunter, J. S. (2005). Design of experiments: Statistics for Experimenters: Design, Innovation and Discovery.
Dehue, T. (1997). Deception, efficiency, and random groups: Psychology and the gradual origination of the random group design. Isis , 88 (4), 653-673.
Fisher, R.A. (1925). Statistical methods for research workers (11th ed. rev.). Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh.
Fisher, R. A. (1935). The Design of Experiments. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
Goldberg, M. H. (2019). How often does random assignment fail? Estimates and recommendations. Journal of Environmental Psychology , 66 , 101351.
Jamison, J. C. (2019). The entry of randomized assignment into the social sciences. Journal of Causal Inference , 7 (1), 20170025.
Lindquist, E. F. (1953). Design and analysis of experiments in psychology and education . Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Marks, H. M. (1997). The progress of experiment: Science and therapeutic reform in the United States, 1900-1990 . Cambridge University Press.
Myers, J. L. (1972). Fundamentals of experimental design (2nd ed.). Allyn & Bacon.
Ong-Dean, C., Huie Hofstetter, C., & Strick, B. R. (2011). Challenges and dilemmas in implementing random assignment in educational research. American Journal of Evaluation , 32 (1), 29-49.
Orr, L. L. (1999). Social experiments: Evaluating public programs with experimental methods . Sage.
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Quasi-experiments: interrupted time-series designs. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference , 171-205.
Stigler, S. M. (1992). A historical view of statistical concepts in psychology and educational research. American Journal of Education , 101 (1), 60-70.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Positive Punishment Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 25 Dissociation Examples (Psychology)
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Zone of Proximal Development Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link Perception Checking: 15 Examples and Definition
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Hum Reprod Sci
- v.4(1); Jan-Apr 2011
This article has been retracted.
An overview of randomization techniques: an unbiased assessment of outcome in clinical research.
Department of Biostatics, National Institute of Animal Nutrition & Physiology (NIANP), Adugodi, Bangalore, India
Randomization as a method of experimental control has been extensively used in human clinical trials and other biological experiments. It prevents the selection bias and insures against the accidental bias. It produces the comparable groups and eliminates the source of bias in treatment assignments. Finally, it permits the use of probability theory to express the likelihood of chance as a source for the difference of end outcome. This paper discusses the different methods of randomization and use of online statistical computing web programming ( www.graphpad.com /quickcalcs or www.randomization.com ) to generate the randomization schedule. Issues related to randomization are also discussed in this paper.
INTRODUCTION
A good experiment or trial minimizes the variability of the evaluation and provides unbiased evaluation of the intervention by avoiding confounding from other factors, which are known and unknown. Randomization ensures that each patient has an equal chance of receiving any of the treatments under study, generate comparable intervention groups, which are alike in all the important aspects except for the intervention each groups receives. It also provides a basis for the statistical methods used in analyzing the data. The basic benefits of randomization are as follows: it eliminates the selection bias, balances the groups with respect to many known and unknown confounding or prognostic variables, and forms the basis for statistical tests, a basis for an assumption of free statistical test of the equality of treatments. In general, a randomized experiment is an essential tool for testing the efficacy of the treatment.
In practice, randomization requires generating randomization schedules, which should be reproducible. Generation of a randomization schedule usually includes obtaining the random numbers and assigning random numbers to each subject or treatment conditions. Random numbers can be generated by computers or can come from random number tables found in the most statistical text books. For simple experiments with small number of subjects, randomization can be performed easily by assigning the random numbers from random number tables to the treatment conditions. However, in the large sample size situation or if restricted randomization or stratified randomization to be performed for an experiment or if an unbalanced allocation ratio will be used, it is better to use the computer programming to do the randomization such as SAS, R environment etc.[ 1 – 6 ]
REASON FOR RANDOMIZATION
Researchers in life science research demand randomization for several reasons. First, subjects in various groups should not differ in any systematic way. In a clinical research, if treatment groups are systematically different, research results will be biased. Suppose that subjects are assigned to control and treatment groups in a study examining the efficacy of a surgical intervention. If a greater proportion of older subjects are assigned to the treatment group, then the outcome of the surgical intervention may be influenced by this imbalance. The effects of the treatment would be indistinguishable from the influence of the imbalance of covariates, thereby requiring the researcher to control for the covariates in the analysis to obtain an unbiased result.[ 7 , 8 ]
Second, proper randomization ensures no a priori knowledge of group assignment (i.e., allocation concealment). That is, researchers, subject or patients or participants, and others should not know to which group the subject will be assigned. Knowledge of group assignment creates a layer of potential selection bias that may taint the data.[ 9 ] Schul and Grimes stated that trials with inadequate or unclear randomization tended to overestimate treatment effects up to 40% compared with those that used proper randomization. The outcome of the research can be negatively influenced by this inadequate randomization.
Statistical techniques such as analysis of covariance (ANCOVA), multivariate ANCOVA, or both, are often used to adjust for covariate imbalance in the analysis stage of the clinical research. However, the interpretation of this post adjustment approach is often difficult because imbalance of covariates frequently leads to unanticipated interaction effects, such as unequal slopes among subgroups of covariates.[ 1 ] One of the critical assumptions in ANCOVA is that the slopes of regression lines are the same for each group of covariates. The adjustment needed for each covariate group may vary, which is problematic because ANCOVA uses the average slope across the groups to adjust the outcome variable. Thus, the ideal way of balancing covariates among groups is to apply sound randomization in the design stage of a clinical research (before the adjustment procedure) instead of post data collection. In such instances, random assignment is necessary and guarantees validity for statistical tests of significance that are used to compare treatments.
TYPES OF RANDOMIZATION
Many procedures have been proposed for the random assignment of participants to treatment groups in clinical trials. In this article, common randomization techniques, including simple randomization, block randomization, stratified randomization, and covariate adaptive randomization, are reviewed. Each method is described along with its advantages and disadvantages. It is very important to select a method that will produce interpretable and valid results for your study. Use of online software to generate randomization code using block randomization procedure will be presented.
Simple randomization
Randomization based on a single sequence of random assignments is known as simple randomization.[ 3 ] This technique maintains complete randomness of the assignment of a subject to a particular group. The most common and basic method of simple randomization is flipping a coin. For example, with two treatment groups (control versus treatment), the side of the coin (i.e., heads - control, tails - treatment) determines the assignment of each subject. Other methods include using a shuffled deck of cards (e.g., even - control, odd - treatment) or throwing a dice (e.g., below and equal to 3 - control, over 3 - treatment). A random number table found in a statistics book or computer-generated random numbers can also be used for simple randomization of subjects.
This randomization approach is simple and easy to implement in a clinical research. In large clinical research, simple randomization can be trusted to generate similar numbers of subjects among groups. However, randomization results could be problematic in relatively small sample size clinical research, resulting in an unequal number of participants among groups.
Block randomization
The block randomization method is designed to randomize subjects into groups that result in equal sample sizes. This method is used to ensure a balance in sample size across groups over time. Blocks are small and balanced with predetermined group assignments, which keeps the numbers of subjects in each group similar at all times.[ 1 , 2 ] The block size is determined by the researcher and should be a multiple of the number of groups (i.e., with two treatment groups, block size of either 4, 6, or 8). Blocks are best used in smaller increments as researchers can more easily control balance.[ 10 ]
After block size has been determined, all possible balanced combinations of assignment within the block (i.e., equal number for all groups within the block) must be calculated. Blocks are then randomly chosen to determine the patients’ assignment into the groups.
Although balance in sample size may be achieved with this method, groups may be generated that are rarely comparable in terms of certain covariates. For example, one group may have more participants with secondary diseases (e.g., diabetes, multiple sclerosis, cancer, hypertension, etc.) that could confound the data and may negatively influence the results of the clinical trial.[ 11 ] Pocock and Simon stressed the importance of controlling for these covariates because of serious consequences to the interpretation of the results. Such an imbalance could introduce bias in the statistical analysis and reduce the power of the study. Hence, sample size and covariates must be balanced in clinical research.
Stratified randomization
The stratified randomization method addresses the need to control and balance the influence of covariates. This method can be used to achieve balance among groups in terms of subjects’ baseline characteristics (covariates). Specific covariates must be identified by the researcher who understands the potential influence each covariate has on the dependent variable. Stratified randomization is achieved by generating a separate block for each combination of covariates, and subjects are assigned to the appropriate block of covariates. After all subjects have been identified and assigned into blocks, simple randomization is performed within each block to assign subjects to one of the groups.
The stratified randomization method controls for the possible influence of covariates that would jeopardize the conclusions of the clinical research. For example, a clinical research of different rehabilitation techniques after a surgical procedure will have a number of covariates. It is well known that the age of the subject affects the rate of prognosis. Thus, age could be a confounding variable and influence the outcome of the clinical research. Stratified randomization can balance the control and treatment groups for age or other identified covariates. Although stratified randomization is a relatively simple and useful technique, especially for smaller clinical trials, it becomes complicated to implement if many covariates must be controlled.[ 12 ] Stratified randomization has another limitation; it works only when all subjects have been identified before group assignment. However, this method is rarely applicable because clinical research subjects are often enrolled one at a time on a continuous basis. When baseline characteristics of all subjects are not available before assignment, using stratified randomization is difficult.[ 10 ]
Covariate adaptive randomization
One potential problem with small to moderate size clinical research is that simple randomization (with or without taking stratification of prognostic variables into account) may result in imbalance of important covariates among treatment groups. Imbalance of covariates is important because of its potential to influence the interpretation of a research results. Covariate adaptive randomization has been recommended by many researchers as a valid alternative randomization method for clinical research.[ 8 , 13 ] In covariate adaptive randomization, a new participant is sequentially assigned to a particular treatment group by taking into account the specific covariates and previous assignments of participants.[ 7 ] Covariate adaptive randomization uses the method of minimization by assessing the imbalance of sample size among several covariates.
Using the online randomization http://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/index.cfm , researcher can generate randomization plan for treatment assignment to patients. This online software is very simple and easy to implement. Up to 10 treatments can be allocated to patients and the replication of treatment can also be performed up to 9 times. The major limitations of this software is that once the randomization plan is generated, same randomization plan cannot be generated as this uses the seed point of local computer clock and is not displayed for further use. Other limitation of this online software Maximum of only 10 treatments can be assigned to patients. Entering the web address http://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/index.cfm on address bar of any browser, the page of graphpad appears with number of options. Select the option of “Random Numbers” and then press continue, Random Number Calculator with three options appears. Select the tab “Randomly assign subjects to groups” and press continue. In the next page, enter the number of subjects in each group in the tab “Assign” and select the number of groups from the tab “Subjects to each group” and keep number 1 in repeat tab if there is no replication in the study. For example, the total number of patients in a three group experimental study is 30 and each group will assigned to 10 patients. Type 10 in the “Assign” tab and select 3 in the tab “Subjects to each group” and then press “do it” button. The results is obtained as shown as below (partial output is presented)
Another randomization online software, which can be used to generate randomization plan is http://www.randomization.com . The seed for the random number generator[ 14 , 15 ] (Wichmann and Hill, 1982, as modified by McLeod, 1985) is obtained from the clock of the local computer and is printed at the bottom of the randomization plan. If a seed is included in the request, it overrides the value obtained from the clock and can be used to reproduce or verify a particular plan. Up to 20 treatments can be specified. The randomization plan is not affected by the order in which the treatments are entered or the particular boxes left blank if not all are needed. The program begins by sorting treatment names internally. The sorting is case sensitive, however, so the same capitalization should be used when recreating an earlier plan. Example of 10 patients allocating to two groups (each with 5 patients), first the enter the treatment labels in the boxes, and enter the total number of patients that is 10 in the tab “Number of subjects per block” and enter the 1 in the tab “Number of blocks” for simple randomization or more than one for Block randomization. The output of this online software is presented as follows.
The benefits of randomization are numerous. It ensures against the accidental bias in the experiment and produces comparable groups in all the respect except the intervention each group received. The purpose of this paper is to introduce the randomization, including concept and significance and to review several randomization techniques to guide the researchers and practitioners to better design their randomized clinical trials. Use of online randomization was effectively demonstrated in this article for benefit of researchers. Simple randomization works well for the large clinical trails ( n >100) and for small to moderate clinical trials ( n <100) without covariates, use of block randomization helps to achieve the balance. For small to moderate size clinical trials with several prognostic factors or covariates, the adaptive randomization method could be more useful in providing a means to achieve treatment balance.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
An open portfolio of interoperable, industry leading products
The Dotmatics digital science platform provides the first true end-to-end solution for scientific R&D, combining an enterprise data platform with the most widely used applications for data analysis, biologics, flow cytometry, chemicals innovation, and more.

Statistical analysis and graphing software for scientists
Bioinformatics, cloning, and antibody discovery software
Plan, visualize, & document core molecular biology procedures
Electronic Lab Notebook to organize, search and share data
Proteomics software for analysis of mass spec data
Modern cytometry analysis platform
Analysis, statistics, graphing and reporting of flow cytometry data
Software to optimize designs of clinical trials
Randomly assign subjects to treatment groups
Randomly choose a group for each subject, randomly shuffle subjects within groups.
Analyze, graph and present your scientific work easily with GraphPad Prism. No coding required.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Published on March 8, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 22, 2023. In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization. With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control ...
If you assign subjects into two groups A and B, you assign subjects to each group purely randomly for every assignment. Even though this is the most basic way, if the total number of samples is small, sample numbers are likely to be assigned unequally. ... Random Allocation. An independent researcher makes random allocation cards using computer ...
The investigator randomly assigned participants to one of the two groups. The researchers found that those who participated in the program and took the class were more likely to lose weight than those in the other group that received only the book. ... experimenters use random assignment to assign participants into groups. Random assignment is ...
By Jim Frost 4 Comments. Random assignment uses chance to assign subjects to the control and treatment groups in an experiment. This process helps ensure that the groups are equivalent at the beginning of the study, which makes it safer to assume the treatments caused any differences between groups that the experimenters observe at the end of ...
Researchers used random assignment to put participants into two groups. One group received a new anti-smoking program, while the other did not. This helped determine if the program was effective in helping people quit smoking. Math Tutoring Program: A study on students used random assignment to place them into two groups.
by Zach Bobbitt February 9, 2021. In the field of statistics, randomization refers to the act of randomly assigning subjects in a study to different treatment groups. For example, suppose researchers recruit 100 subjects to participate in a study in which they hope to understand whether or not two different pills have different effects on blood ...
Random assignment in two-group experimental design is the method most researchers use to assign subjects to groups. With random assignment, subjects are put into groups using a random method.
The matched pairs experimental design is particularly advantageous for studies with limited sample sizes. When sample sizes are small, it can be challenging to achieve well-balanced groups through random assignment alone. To conduct this type of experiment, researchers must identify the characteristics they'll use to match the participants.
The outcome measured -voter turnout- can then be compared in the two groups. The difference in turnout will reflect the effectiveness of the intervention. ... By randomly assigning subjects to be in the group that receives the treatment or to be in the control group, researchers can measure the effect of the mobilization method regardless ...
It is essential in a between-subjects experiment that the researcher assign participants to conditions so that the different groups are, on average, highly similar to each other. ... random assignment should meet two criteria. One is that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each condition (e.g., a 50% chance of being ...
The control group helps researchers balance the effects of being in an experiment with the effects of the active treatments. ... The men are divided randomly into two groups: one group will take aspirin, and the other group will take a placebo. ... Random assignment eliminates the impact of lurking variables. When you cannot assign subjects to ...
Random assignment is a research procedure used to randomly assign participants to different experimental conditions (or 'groups'). This introduces the element of chance, ensuring that each participant has an equal likelihood of being placed in any condition group for the study. It is absolutely essential that the treatment condition and the ...
Control group: Does not consume vitamin supplements; Treatment group: Regularly consumes vitamin supplements.; In this experiment, we randomly assign subjects to the two groups. Because we use random assignment, the two groups start with similar characteristics, including healthy habits, physical attributes, medical conditions, and other factors affecting the outcome.
To test this claim, researchers randomly assign overweight subjects to two groups. Both groups eat the same amount of calories, but one group eats almost no carbs, and the other group includes carbs in their meals. After 2 months, the researchers test the claim that the no-carb diet is better than the usual diet.
Blocks are small and balanced with predetermined group assignments, which keeps the numbers of subjects in each group similar at all times.[1,2] The block size is determined by the researcher and should be a multiple of the number of groups (i.e., with two treatment groups, block size of either 4, 6, or 8).
Researchers randomly assign subjects to two groups, with each group receiving a different asthma medication. For one month, researchers record the number of asthma attacks suffered by each subject and compute the summary statistics as follows: x with bar on top subscript 1 equals 3.8 comma space s subscript 1 equals 1.7 comma space n subscript 1 equals 23 x with bar on top subscript 2 equals 4 ...
Researchers randomly assigned 38 subjects to two treatment groups, one taking a high dose of omega dash 3 fats and the other a placebo. a) Why was it important to randomize in assigning the subjects to the two groups?C. It should equalize the effects of unknown or uncontrollable sources of variation.
Web calculator to randomize. An open portfolio of interoperable, industry leading products. The Dotmatics digital science platform provides the first true end-to-end solution for scientific R&D, combining an enterprise data platform with the most widely used applications for data analysis, biologics, flow cytometry, chemicals innovation, and more.
Question: Researchers randomly assign subjects to two groups, with each group receiving a different asthma medication. For one month, researchers record the number of asthma attacks suffered by each subject. What's the correct formula for constructing a confidence interval for the difference between these two groups without pooling? i n2 O B. ni n2 O C. (x1-x2) ±t"s
Researchers randomly assign subjects to two groups, with each group receiving a different asthma medication. For one month, researchers record the number of asthma attacks suffered by each subject and compute the summary statistics as follows: = 3.8, s 1 = 1.7, n 1 = 23 = 4.2, s 2 = 1.5, n 2 = 24
Question: Researchers randomly assign subjects to two groups, with each group receiving a different asthma medication. For one month, researchers record the number of asthma attacks suffered by each subject. Which of these is the correct procedure for measuring the difference in the number of asthma attacks between the two groups? A.
Question: Researchers randomly assign subjects to two groups, with each group receiving a different asthma medication. For one month, researchers record the number of asthma attacks suffered by each subject and compute the summary statistics as follows: X_1 = 1 3.8, s_1 = 1.7, n_1 = 23 x_2 = 4.2, s_2 = 1.5, n_2 = 24 Which pair of hypotheses test whether the first