
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

10.2 Using Common Organizing Patterns
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the common speech organizational patterns: categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological.
- Understand how to choose the best organizational pattern, or combination of patterns, for a specific speech.

Twentyfour Students – Organization makes you flow – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this chapter we discussed how to make your main points flow logically. This section is going to provide you with a number of organization patterns to help you create a logically organized speech. The first organization pattern we’ll discuss is categorical/topical.
Categorical/Topical
By far the most common pattern for organizing a speech is by categories or topics. The categories function as a way to help the speaker organize the message in a consistent fashion. The goal of a categorical/topical speech pattern is to create categories (or chunks) of information that go together to help support your original specific purpose. Let’s look at an example.
In this case, we have a speaker trying to persuade a group of high school juniors to apply to attend Generic University. To persuade this group, the speaker has divided the information into three basic categories: what it’s like to live in the dorms, what classes are like, and what life is like on campus. Almost anyone could take this basic speech and specifically tailor the speech to fit her or his own university or college. The main points in this example could be rearranged and the organizational pattern would still be effective because there is no inherent logic to the sequence of points. Let’s look at a second example.
In this speech, the speaker is talking about how to find others online and date them. Specifically, the speaker starts by explaining what Internet dating is; then the speaker talks about how to make Internet dating better for her or his audience members; and finally, the speaker ends by discussing some negative aspects of Internet dating. Again, notice that the information is chunked into three categories or topics and that the second and third could be reversed and still provide a logical structure for your speech
Comparison/Contrast
Another method for organizing main points is the comparison/contrast speech pattern . While this pattern clearly lends itself easily to two main points, you can also create a third point by giving basic information about what is being compared and what is being contrasted. Let’s look at two examples; the first one will be a two-point example and the second a three-point example.
If you were using the comparison/contrast pattern for persuasive purposes, in the preceding examples, you’d want to make sure that when you show how Drug X and Drug Y differ, you clearly state why Drug X is clearly the better choice for physicians to adopt. In essence, you’d want to make sure that when you compare the two drugs, you show that Drug X has all the benefits of Drug Y, but when you contrast the two drugs, you show how Drug X is superior to Drug Y in some way.
The spatial speech pattern organizes information according to how things fit together in physical space. This pattern is best used when your main points are oriented to different locations that can exist independently. The basic reason to choose this format is to show that the main points have clear locations. We’ll look at two examples here, one involving physical geography and one involving a different spatial order.
If you look at a basic map of the United States, you’ll notice that these groupings of states were created because of their geographic location to one another. In essence, the states create three spatial territories to explain.
Now let’s look at a spatial speech unrelated to geography.
In this example, we still have three basic spatial areas. If you look at a model of the urinary system, the first step is the kidney, which then takes waste through the ureters to the bladder, which then relies on the sphincter muscle to excrete waste through the urethra. All we’ve done in this example is create a spatial speech order for discussing how waste is removed from the human body through the urinary system. It is spatial because the organization pattern is determined by the physical location of each body part in relation to the others discussed.
Chronological
The chronological speech pattern places the main idea in the time order in which items appear—whether backward or forward. Here’s a simple example.
In this example, we’re looking at the writings of Winston Churchill in relation to World War II (before, during, and after). By placing his writings into these three categories, we develop a system for understanding this material based on Churchill’s own life. Note that you could also use reverse chronological order and start with Churchill’s writings after World War II, progressing backward to his earliest writings.
Biographical
As you might guess, the biographical speech pattern is generally used when a speaker wants to describe a person’s life—either a speaker’s own life, the life of someone they know personally, or the life of a famous person. By the nature of this speech organizational pattern, these speeches tend to be informative or entertaining; they are usually not persuasive. Let’s look at an example.
In this example, we see how Brian Warner, through three major periods of his life, ultimately became the musician known as Marilyn Manson.
In this example, these three stages are presented in chronological order, but the biographical pattern does not have to be chronological. For example, it could compare and contrast different periods of the subject’s life, or it could focus topically on the subject’s different accomplishments.
The causal speech pattern is used to explain cause-and-effect relationships. When you use a causal speech pattern, your speech will have two basic main points: cause and effect. In the first main point, typically you will talk about the causes of a phenomenon, and in the second main point you will then show how the causes lead to either a specific effect or a small set of effects. Let’s look at an example.
In this case, the first main point is about the history and prevalence of drinking alcohol among Native Americans (the cause). The second point then examines the effects of Native American alcohol consumption and how it differs from other population groups.
However, a causal organizational pattern can also begin with an effect and then explore one or more causes. In the following example, the effect is the number of arrests for domestic violence.
In this example, the possible causes for the difference might include stricter law enforcement, greater likelihood of neighbors reporting an incident, and police training that emphasizes arrests as opposed to other outcomes. Examining these possible causes may suggest that despite the arrest statistic, the actual number of domestic violence incidents in your city may not be greater than in other cities of similar size.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing distinct main points in a clear manner is the problem-cause-solution speech pattern . In this format you describe a problem, identify what you believe is causing the problem, and then recommend a solution to correct the problem.
In this speech, the speaker wants to persuade people to pass a new curfew for people under eighteen. To help persuade the civic group members, the speaker first shows that vandalism and violence are problems in the community. Once the speaker has shown the problem, the speaker then explains to the audience that the cause of this problem is youth outside after 10:00 p.m. Lastly, the speaker provides the mandatory 10:00 p.m. curfew as a solution to the vandalism and violence problem within the community. The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution.
Psychological
A further way to organize your main ideas within a speech is through a psychological speech pattern in which “a” leads to “b” and “b” leads to “c.” This speech format is designed to follow a logical argument, so this format lends itself to persuasive speeches very easily. Let’s look at an example.
In this speech, the speaker starts by discussing how humor affects the body. If a patient is exposed to humor (a), then the patient’s body actually physiologically responds in ways that help healing (b—e.g., reduces stress, decreases blood pressure, bolsters one’s immune system, etc.). Because of these benefits, nurses should engage in humor use that helps with healing (c).
Selecting an Organizational Pattern
Each of the preceding organizational patterns is potentially useful for organizing the main points of your speech. However, not all organizational patterns work for all speeches. For example, as we mentioned earlier, the biographical pattern is useful when you are telling the story of someone’s life. Some other patterns, particularly comparison/contrast, problem-cause-solution, and psychological, are well suited for persuasive speaking. Your challenge is to choose the best pattern for the particular speech you are giving.
You will want to be aware that it is also possible to combine two or more organizational patterns to meet the goals of a specific speech. For example, you might wish to discuss a problem and then compare/contrast several different possible solutions for the audience. Such a speech would thus be combining elements of the comparison/contrast and problem-cause-solution patterns. When considering which organizational pattern to use, you need to keep in mind your specific purpose as well as your audience and the actual speech material itself to decide which pattern you think will work best.
Key Takeaway
- Speakers can use a variety of different organizational patterns, including categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological. Ultimately, speakers must really think about which organizational pattern best suits a specific speech topic.
- Imagine that you are giving an informative speech about your favorite book. Which organizational pattern do you think would be most useful? Why? Would your answer be different if your speech goal were persuasive? Why or why not?
- Working on your own or with a partner, develop three main points for a speech designed to persuade college students to attend your university. Work through the preceding organizational patterns and see which ones would be possible choices for your speech. Which organizational pattern seems to be the best choice? Why?
- Use one of the common organizational patterns to create three main points for your next speech.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Chapter 8: Organizing and Outlining
Victoria Leonard, College of the Canyons
Adapted by William Kelvin, Professor of Communication Studies, Katharine O’Connor, Ph.D., and Jamie C. Votraw, Professor of Communication Studies, Florida SouthWestern State College
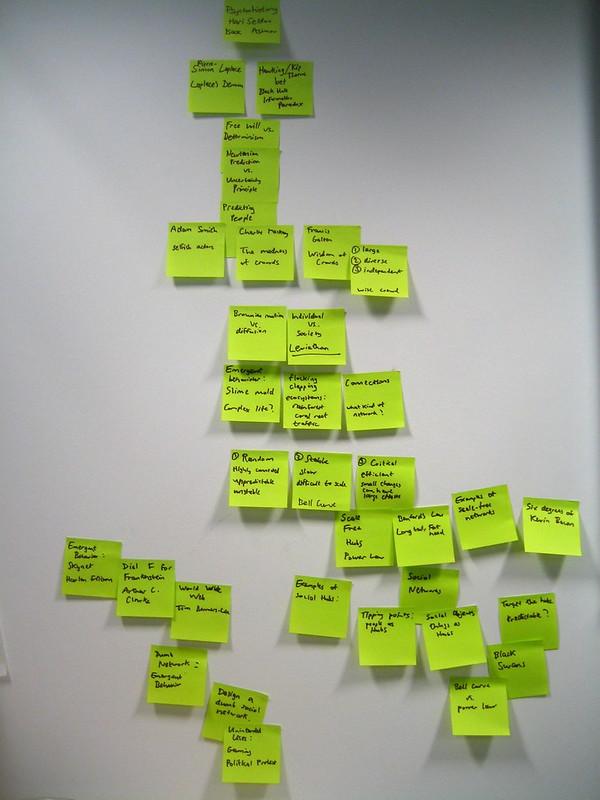

Figure 8.1: Outlining with Post it Notes 1
Introduction
One of your authors remembers taking an urban studies course in college. The professor was incredibly knowledgeable and passionate about the subject. Do you think that alone made her want to go to class? Unfortunately not. As great as this professor was in so many ways, the lectures were not organized. As much as she tried to take great notes and follow along, it felt like a hopeless task. Having a great topic that you are passionate about is important, but organizing your speech so that the audience can follow along is vital to the success of your speech.
When students are faced with developing a speech, they face the same challenges as a student asked to write an essay. Although the end product may be different in that you are not writing an essay or turning one in, you will go through much of the same process as you would in writing an essay.
Before you get too far into the writing process, it is important to know what steps you will have to take to write your speech. Note that the speech-writing process is formulaic: it is based on time-honored principles of rhetoric established thousands of years ago. Your initial preparation work will include the following:
- Selecting a topic
- Writing a general purpose
- Writing a specific purpose
- Writing a thesis statement
- Selecting main points
- Writing a preview statement
- Writing the body of the speech
This chapter will explain each of these steps so that you can create a thorough and well-written speech. As with anything we do that requires effort, the more you put in, the more you will get out of the writing process, in terms of both your education and your grade.
The Speech Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Selecting a topic.
We all want to know that our topics will be interesting to our audience. If you think back to Chapter 5, Identifying Topic, Purpose, and Audience, you will recall how important it is to be audience-centered. Does this mean that you cannot talk about a topic that your audience is unfamiliar with? No, what it does mean is that your goal as a speaker is to make that topic relevant to the audience. Whether you are writing an informative speech on earthquakes or the singer Jhené Aiko, you will need to make sure that you approach the speech in a way that helps your speech resonate with the audience. Although many of you would not have been alive when Hurricane Andrew hit Florida in 1992, this is an important topic to people who live in hurricane zones. Explaining hurricanes and hurricane preparation would be a great way to bring this topic alive for people who may not have lived through this event. Similarly, many audience members may be unfamiliar with Jhené Aiko, and that allows you to share information about her that might lead someone to want to check out her music.
If you are writing a persuasive speech, you might approach your topic selection differently. Think about what is happening in the world today. You can look at what affects you and your peers at a local, state, national, or global level. Whether you believe that gun violence is important to address because it is a problem at the national level, or you wish to address parking fees on your campus, you will have given thought to what is important to your audience. As Chapter 2 explained, your topics must fulfill the ethical goals of the speech. If you are ethical and select a topic you care about and make it relevant for the audience, you are on the right track.
Here are some questions that might help you select a topic:
- What are some current trends in music or fashion?
- What hobbies do I have that might be interesting to others?
- What objects or habits do I use every day that are beneficial to know about?
- What people are influencing the world in social media or politics?
- What authors, artists, or actors have made an impact on society?
- What events have shaped our nation or our world?
- What political debates are taking place today?
- What challenges do we face as a society or species?
- What health-related conditions should others be aware of?
- What is important for all people to be aware of in your community?
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. Now you must further narrow down the topic in your purpose statements.
Writing the Purpose Statements
Purpose statements allow you to do two things. First, they allow you to focus on whether you are fulfilling the assignment. Second, they allow you to narrow your topic so that you are not speaking too broadly. When creating an outline for your speech, you should include the general purpose and specific purpose statement at the beginning of your outline.
A general purpose statement is the overarching goal of a speech whether to inform, to persuade, to inspire, to celebrate, to mourn, or to entertain. It describes what your speech goal is, or what you hope to achieve. In public speaking classes, you will be asked to do any of the following: To inform, to persuade, or to entertain . Thus, your general purpose statement will be two words —the easiest points you will ever earn! But these two words are critical for you to keep in mind as you write the speech. Your authors have seen many persuasive speeches submitted inappropriately as informative speeches. Likewise, one author remembers a fascinating “persuasive speech” on the death penalty that never took a stance on the issue or asked the audience to—that would be an informative speech, right? You must always know your broad goal. Your audience should know it, too, and so should your instructor! Knowing your purpose is important because this is what you begin with to build your speech. It is also important to know your general purpose because this will determine your research approach. You might use different sources if you were writing a speech to inform versus to persuade.
A specific purpose statement is consistent with the general purpose of the speech, written according to assignment requirements, and clearly identifies desired audience outcomes. It is a declaration starting with the general purpose and then providing the topic with the precise objectives of the speech. It will be written according to your general purpose. For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: To inform my audience about the pros and cons of flipping houses.
Specific purpose statements are integral in knowing if your speech is narrowed enough or if you need to narrow it further. Consider these examples:
- To inform my audience about musical instruments
- To inform my audience about string instruments
- To inform my audience about the violin
As you can see, the first two examples are far too broad. But is the third purpose statement sufficiently narrow? Will the speaker be covering the violin’s design, physics, history, cost, or how to play it? What do you think about these possible topics?
- To inform my audience about the life and contributions of Patricia Bath
- To inform my audience about the invention of the wheelchair
- To inform my audience about the Biloxi Wade-Ins
- To inform my audience about how Fibromyalgia affects the body
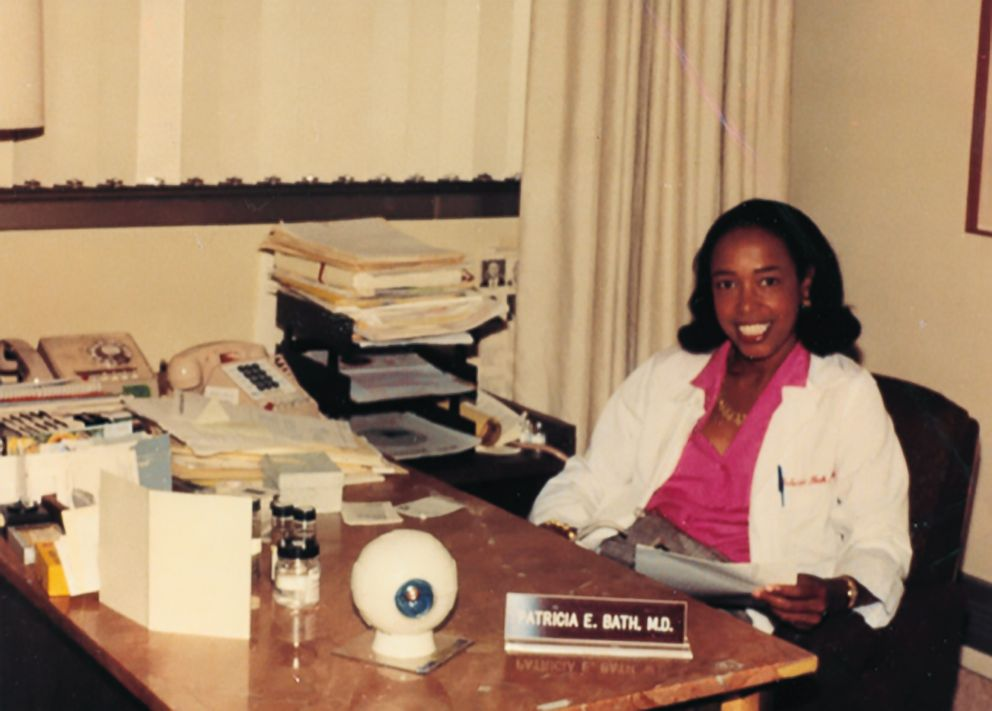

Figure 8.2: Dr. Patricia Bath 2
Hopefully, you can see that the examples above would work for an informative speech. They are specific and limited in their scope.
Your instructor will give you a time limit for your speech. Your specific purpose should help you see if you can stay within the time limit. You should put the purpose statements on your outline. Others may only ask you to put these on your topic submission. However, you do not state a general purpose or specific purpose during the delivery of your speech! These are simply guidelines for you as you write and for your instructor as they assess your writing.
Writing the Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a single, declarative statement that encapsulates the essence of your speech. Just like in essay writing, you want your thesis statement, or central idea, to reveal what your speech is about. Thesis statements can never be written as questions, nor can they include a research citation. The thesis statement is not a list of main points, it is an over-arching idea that encapsulates them all.
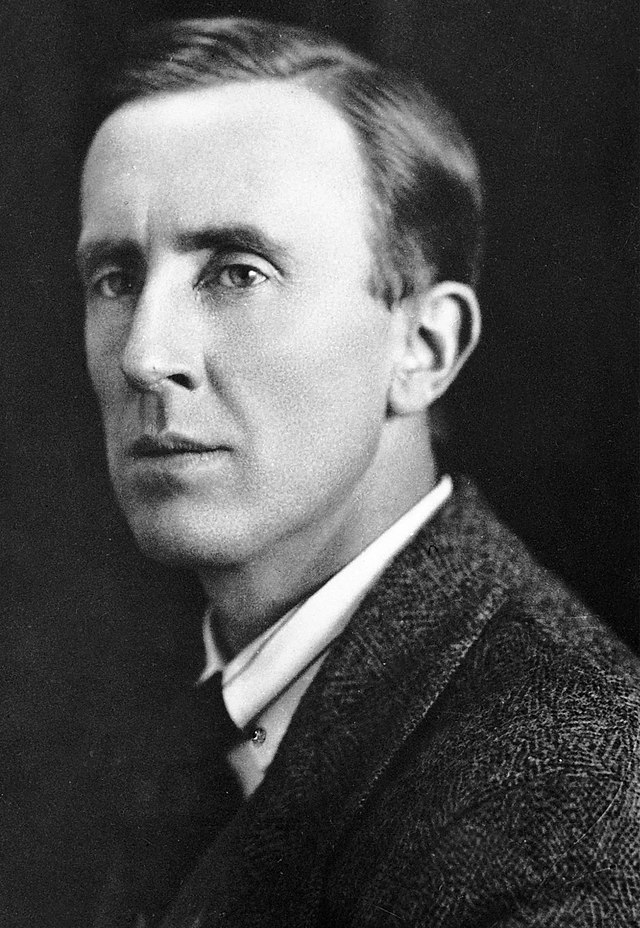

Figure 8.3: Portrait of Aut h or, J.R.R. Tolkien 3
As a Lord of the Rings enthusiast, I may choose to write a speech on author J.R.R. Tolkien. Here is an example of what a thesis statement may sound like:
J.R.R. Tolkien is known as the father of modern fantasy literature and became a pop culture icon after his death.
The thesis you just read provides the audience with just enough information to help them know what they will hear ahd learn from your speech.
Selecting Main Points
The main points are the major ideas you want to cover in your speech. Since speeches have time requirements, your outline will always be limited to two to three main points. Many instructors suggest that you have no more than three main points so you can do justice to each idea and stay within the time frame. You will also lose time on each main point describing it in the preview statement, internal transitions, and review of main points in the conclusion. Plus, it can be difficult for audiences to remember many points.
Let’s determine the main points for a short speech using the J.R.R. Tolkien thesis above. Having researched his life, you might come up with an initial list like this:
- Childhood and Background
- Military service
- Literary fame and honors
As interesting as all of these topics are, there is not enough time to speak about each idea. This is where the difficult decision of narrowing a speech comes in. Brainstorming all of the points you could cover would be your first step. Then, you need to determine which of the points would be the most interesting for your audience to hear. There are also creative ways to combine ideas and touch on key points within each main point. You will see how this can be achieved in the next section as we narrow down the number of topics we will discuss about J.R.R. Tolkein.
Writing the Preview Statement
A preview statement is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open an app on your phone to get directions to a location, you would be told exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for, such as landmarks. A preview statement in a speech fulfills the same goal. It is a roadmap for your speech. Let’s look at how a thesis and preview statement might look for a speech on J.R.R. Tolkien:
Thesis: J.R.R. Tolkien is known as the father of modern fantasy literature and became a pop culture icon after his death.
Preview: First, I will tell you about J.R.R. Tolkien’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe his rise to literary fame. Finally, I will explain his lasting cultural legacy.
Notice that the thesis statement captures the essence of the speech. The preview concisely names each main point that supports the thesis. You will want to refer to these main point names, or taglines , throughout the speech. This repetition will help audience members remember each main point; use variations of these taglines in your preview statement, when introducing each point, and again in the conclusion.
Always use your words to make the audience feel that they are part of the performance. This makes them feel included and on your side. Also, occasionally audience members will have more expertise than you. Imagine how an expert would feel when you begin your speech with “Today I will teach you about…” when they already know a lot about the subject. Use inclusive language in your preview statement–“Get ready to join me on a fantastic adventure…”
Organizing the Main Points
Once you know what your speech is about, you can begin developing the body of your speech. The body of the speech is the longest and most important part of your speech because it’s where the general purpose is executed, e.g., you inform or persuade with the main points that you listed in your preview statement. In general, the body of the speech comprises about 75% to 80% of the length of your speech. This is where you will present the bulk of your research, evidence, examples, and any other supporting material you have. Chapter 7 will provide you with specifics on how to do research and support your speech.
Several patterns of organization are available to choose from when writing a speech. You should keep in mind that some patterns work only for informative speeches and others for persuasive speeches. The topical, chronological, spatial, or causal patterns discussed here are best suited to informative speeches. The patterns of organization for persuasive speeches will be discussed in Chapter 10.
Topical Pattern
The chronological pattern needed main points ordered in a specific sequence, whereas the topical pattern arranges the information of the speech into different subtopics. For example, you are currently attending college. Within your college, various student services are important for you to use while you are there. You may visit the Richard H. Rush Library and its computer lab, Academic Support Centers, Career Services and the Office of Student Financial Aid.

Figure 8.6: Valencia Campus Library Stacks 6
To organize this speech topically, it doesn’t matter which area you speak about first, but here is how you could organize it:
Topic: Student Services at Florida SouthWestern State College
Thesis Statement: Florida SouthWestern State College has five important student services, which include the library, the library computer lab, Academic Support Centers, Career Services and the Financial Aid office.
Preview : This speech will discuss each of the five important student services that Florida SouthWestern State College offers.
Main Points:
I. The Richard H. Rush Library can be accessed five days a week and online and has a multitude of books, periodicals, and other resources to use.
II.The library’s computer lab is open for students to use for several hours a day, with reliable, high-speed internet connections and webcams.
III.The Academic Support Centers have subject tutors, computers, and study rooms.
IV.CareerSource offers career services both in-person and online, with counseling and access to job listings and networking opportunities.
V. The Office of Student Financial Aid is one of the busiest offices on campus, offering students a multitude of methods by which they can supplement their personal finances by paying for both tuition and books.
Note that many novices appreciate the topical pattern because of its simplicity. However, because there is no internal logic to the ordering of points, the speech writer loses an opportunity to include a mnemonic device (phrasing that helps people remember information) in their performance. Audience members are more likely to remember information if it hangs together in an ordered, logical way, such as the following patterns employ.
Chronological (Temporal) Pattern
When organizing a speech based on time or sequence, you would use a chronological (temporal) pattern of organization. Speeches that look at the history of someone or something, or the evolution of an object or a process could be organized chronologically. For example, you could use this pattern in speaking about President Barack Obama, the Holocaust, the evolution of the cell phone, or how to carve a pumpkin. The challenge of using this pattern is to make sure your speech has distinct main points and that it does not appear to be storytelling.
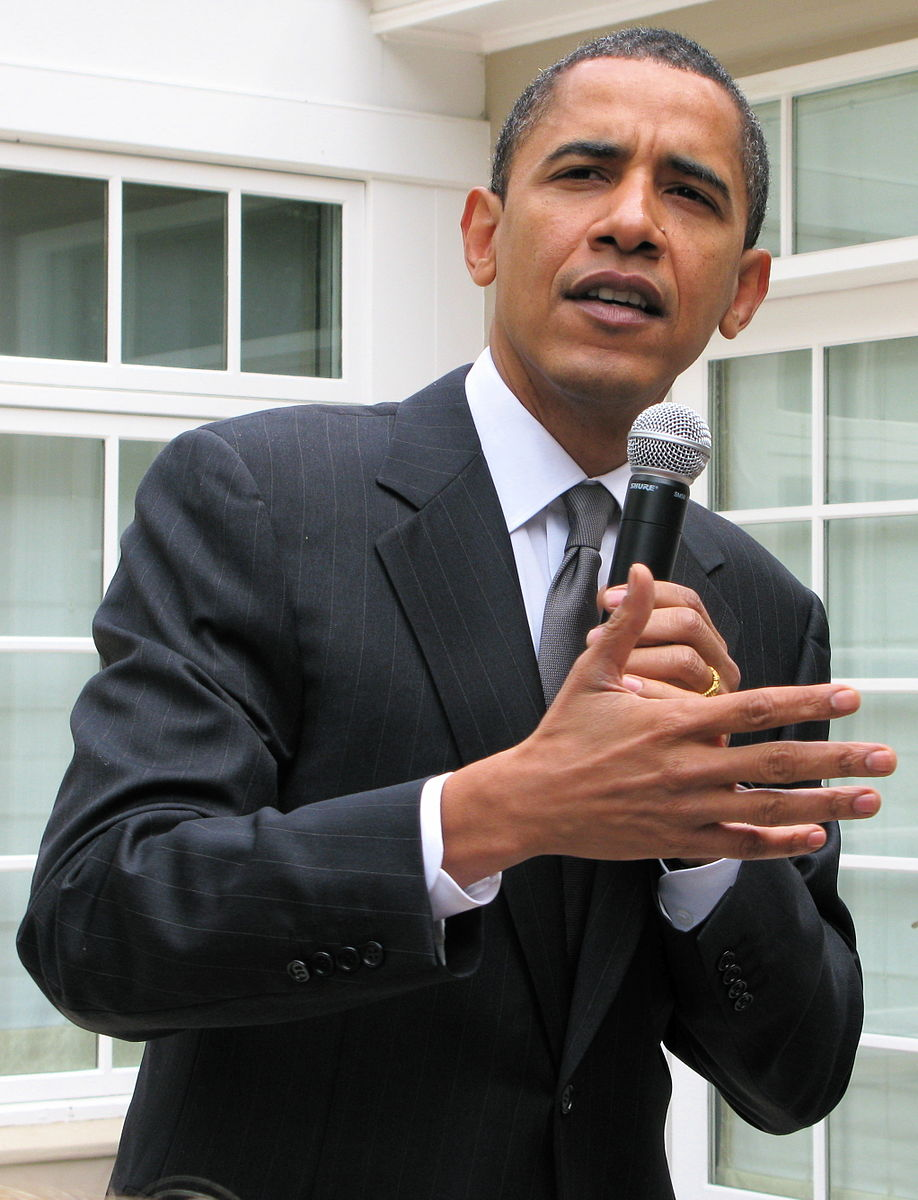

Figure 8.4: Barack Obama 4
Here is an example of how your main points will help you make sure that the points are clear and distinct:
Topic: President Barack Obama
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience about the life of President Barack Obama.
Thesis: From his humble beginnings, President Barack Obama succeeded in law and politics to become the first African-American president in U.S. history.
Preview: First, let’s look at Obama’s background and career in law. Then, we will look at his rise to the presidency of the United States. Finally, we will explore his accomplishments after leaving the White House.
I. First, let’s look at the early life of Obama and his career as a lawyer and advocate.
II. Second, let’s examine how Obama transitioned from law to becoming the first African-American President of the United States.
III. Finally, let’s explore all that Obama has achieved since he left the White House.
We hope that you can see that the main points clearly define and isolate different parts of Obama’s life so that each point is distinct. Using a chronological pattern can also help you with other types of informative speech topics.

Figure 8.5: Pumpkin Carving 5
Here is an additional example to help you see different ways to use this pattern:
Topic : How to Carve a Pumpkin
Specific Purpose: To inform my audience how to carve a pumpkin.
Thesis: Carving a pumpkin with special techniques and tools can result in amazing creations.
Preview: First, I will explain the process of gutting the pumpkin in preparation for carving. Then, I will describe the way you use your special tools to carve the face you hope to create. Finally, I will show you a variety of different designs that are unique to make your pumpkin memorable.
I. First, let me explain exactly how you open up the pumpkin, remove the seeds, and clean it so it is ready to carve.
II. Second, let me describe how the tools you have on hand are used to draw and carve the face of the pumpkin.
III. Finally, let me show you several unique designs that will make your pumpkin dazzle your friends and neighbors.
Note that some instructors prefer their students not give “how-to” speeches. Always clear your topic with your instructor early on in the speech-writing process.
Spatial Pattern
A spatial pattern arranges ideas according to their physical or geographic relationships. Typically, we can begin with a starting point and look at the main points of your speech directionally from top to bottom, inside to outside, left to right, north to south, and so on. A spatial pattern allows for creativity as well as clarity. For example, a speech about an automobile could be arranged using a spatial pattern and you might describe the car from the front end to the back end or the interior to the exterior. A speech on Disneyland might begin with your starting point at the entrance on Main Street, and each subsequent main point may be organized by going through each land in the park in a directional manner. Even a speech on the horrific tsunami off the Indonesian coast of Sumatra on December 26, 2004, could be discussed spatially as you use the starting point and describe the destruction as it traveled, killing 250,000 people.
If you have never heard of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, it is marine debris that is in the North Pacific Ocean. Just like the tsunami in the previous example, this mass could likewise be discussed using a spatial pattern.
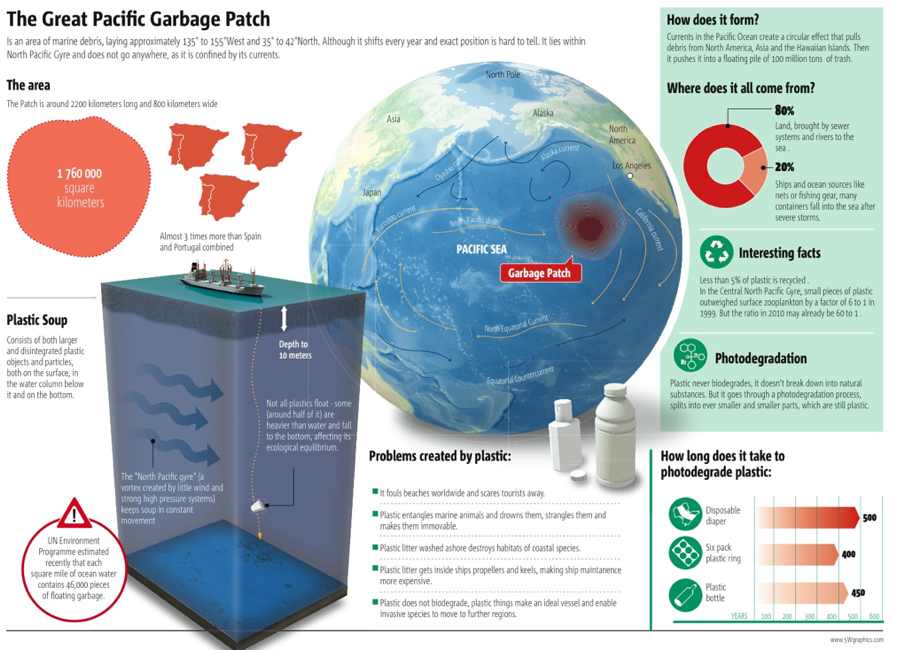
Figure 8.7: The Great Pacific Garbage Patch 7
In an informative speech, you could arrange your points spatially like this:
Topic: Great Pacific Garbage Patch
Thesis: The Great Pacific Garbage patch is not well known to most people; it consists of marine debris that is located in the North Pacific Ocean.
Preview: First, I will describe the Eastern Garbage Patch. Finally, I will explain the Western Patch.
I. The Eastern Garbage patch is located between the states of Hawaii and California.
II. The Western Garbage Patch is located near Japan.
Causal Pattern
A causal pattern of organization can be used to describe what occurred that caused something to happen, and what the effects were. Conversely, another approach is to begin with the effects and then talk about what caused them. For example, in 1994, there was a 6.7 magnitude earthquake that occurred in the San Fernando Valley in Northridge, California.
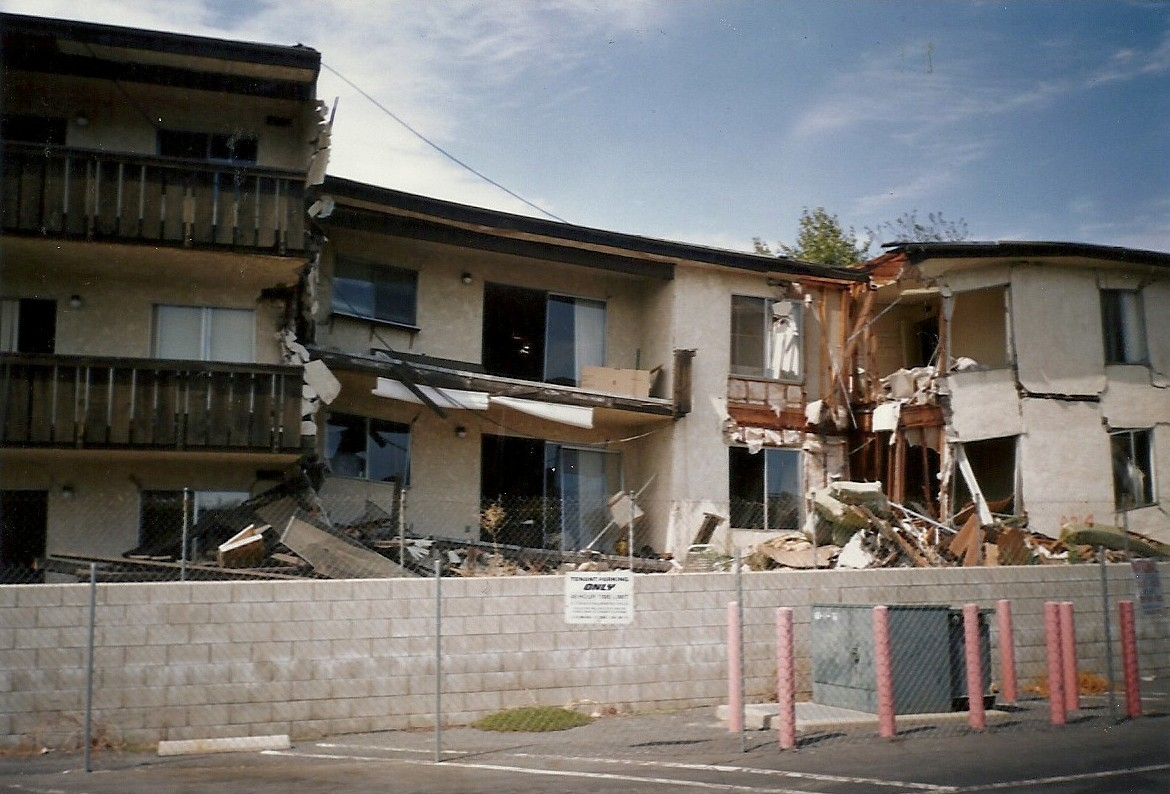

Figure 8.8: Northridge Meadows Apartment Building Collapse 8
Let’s look at how we can arrange this speech first by using a cause-effect pattern:
Topic: Northridge Earthquake
Thesis: The Northridge, California earthquake was a devastating event that was caused by an unknown fault and resulted in the loss of life and billions of dollars of damage.
I. The Northridge earthquake was caused by a fault that was previously unknown and located nine miles beneath Northridge.
II. The Northridge earthquake resulted in the loss of 57 lives and over 40 billion dollars of damage in Northridge and surrounding communities.
Depending on your topic, you may decide it is more impactful to start with the effects and work back to the causes ( effect-cause pattern ). Let’s take the same example and flip it around:
Thesis: The Northridge, California earthquake was a devastating event that resulted in the loss of life and billions of dollars in damage and was caused by an unknown fault below Northridge.
I. The Northridge earthquake resulted in the loss of 57 lives and over 40 billion dollars of damage in Northridge and surrounding communities.
II. The Northridge earthquake was caused by a fault that was previously unknown and located nine miles beneath Northridge.
Why might you decide to use an effect-cause approach rather than a cause-effect approach? In this particular example, the effects of the earthquake were truly horrible. If you heard all of that information first, you would be much more curious to hear about what caused such devastation. Sometimes natural disasters are not that exciting, even when they are horrible. Why? Unless they affect us directly, we may not have the same attachment to the topic. This is one example where an effect-cause approach may be very impactful.
One take-home idea for you about organizing patterns is that you can usually use any pattern with any topic. Could the Great Pacific Garbage Patch be explained using the chronological or causal patterns? Could the Northridge quake be discussed using the chronological or spatial patterns? Could a pumpkin-carving speech be spatially organized? The answer to all of the above is yes. The organizational pattern you select should be one that you think will best help the audience make sense of, and remember, your ideas.
Developing the Outline
Although students are often intimidated by the process of outlining a speech, you should know that it is a formulaic process. Once you understand the formula–the same one speech instructors have long taught and used to assess throughout the nation–speech writing should be a cinch. And remember, this process is what organizes your speech. A well-organized speech leads to better delivery. Simply, outlining is a method of organizing the introduction, body with main points, and conclusion of your speech. Outlines are NOT essays; they are properly formatted outlines! They use specific symbols in a specific order to help you break down your ideas in a clear way. There are two types of outlines: the preparation outline and the speaking outline.
Outline Types
When you begin the outlining process, you will create a preparation outline. A preparation outline consists of full, complete sentences, and thus, is void of awkward sentences and sentence fragments. In a full-sentence preparation outline, only one punctuated sentence should appear beside each symbol. In many cases, this type of outline will be used in preparing your speech, but will not be allowed to be used during your speech delivery. Remember that even though this outline requires complete sentences, it is still not an essay. The examples you saw earlier in this chapter were written in complete sentences, which is exactly what a preparation outline should look like.
A speaking outline is less detailed than the preparation outline and will include brief phrases or words that help you remember your key ideas. It is also called a “key word” outline because it is not written in complete sentences–only key words are present to jog your memory as needed. It should include elements of the introduction, body, and conclusion, as well as your transitions. Speaking outlines may be written on index cards to be used when you deliver your speech.
Confirm with your professor about specific submission requirements for preparation and speaking outlines.
Outline Components
Introduction and conclusion.
In Chapter 9, we identified the components of effective introductions and conclusions. Do you remember what they were? Your preparation outline should delineate the five elements of an introduction and the four elements of a conclusion . Recall, a complete introduction includes an attention-getter, relates the topic to the audience, establishes speaker credibility, states the thesis, and previews the main points. A quality conclusion will signal the speech is ending, restate the thesis, review the main points, and finish with a memorable ending.
Main Points
Main points are the main ideas in the speech. In other words, the main points are what your audience should remember from your talk, and they are phrased as single, declarative sentences. These are never phrased as a question, nor can they be a quote or form of citation. Any supporting material you have will be put in your outline as a subpoint. Since this is a public speaking class, your instructor will decide how long your speeches will be, but in general, you can assume that no speech will be longer than 10 minutes in length. Given that alone, we can make one assumption: All speeches will fall between 2 to 3 main points based simply on length. If you are working on an outline and you have ten main points, something is wrong, and you need to revisit your ideas to see how you need to reorganize your points.
All main points are preceded by Roman numerals (I, II, III, IV, V). Subpoints are preceded by capital letters (A, B, C, etc.), sub-sub points by Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.), then sub-sub-sub points by lowercase letters (a, b, c, etc.). You may expand further than this. Here is a short template:
I. First main point
- First subpoint
- Second subpoint
- First sub-subpoint
- First sub-sub-subpoint
- Second sub-sub-subpoint
- Second main point
- Third main point
References List
A quality speech requires a speaker to cite evidence to support their claims. Your professor will likely require that you incorporate evidence from your research in both your outline and speech. In Chapter 7, we reviewed how to gather information, incorporate the research into your speech, and cite your sources, both in your written outline and during oral delivery. An ethical and credible speaker gives credit where credit is due and shares source information with the audience. Accordingly, the last piece of your preparation outline is the References List. The references list will include full written citations for all resources used in the composition and presentation of your speech. The structure of the references list follows a specific format dictated by the American Psychological Association 7th Ed. (remember, the Communication Studies discipline uses this APA formatting). Since formatting varies by source type, it is useful to refer to a reference guide to determine the exact citation formatting when writing your references list.
Written Oral Citations
There is a good chance your professor will ask you to include oral citations in your speech delivery. If so, you should include these in your preparation outline. The written oral citation is where you share your evidence and details of how you plan to cite the source during the delivery. Often, this is written in a similar format as “According to an article titled [title], written by [author] in [year], [resource content].” You should include enough source-identifying information for your audience to verify the accuracy and credibility of the content. In your outline, write out the specific source-information you will use to orally cite the source in your speech. Discuss the required number of oral citations with your professor and include all of them in your written outline. At FSW, we require three oral citations.
Outlining Principles
Next, we will cover the principles of outline which are outlining “rules” that you want to follow to be most effective. (Your English teachers will thank us, too!). First, read through this example outline for a main point about dogs. We will recall this example as we move through the principles. Don’t skip this example. Read it now!

Figure 6.9: Big and Small Dog 9
Topic: Dogs
Thesis: There are many types of dogs that individuals can select from before deciding which would make the best family pet.
Preview: First, I will describe the characteristics of large breed dogs, then I will discuss the characteristics of small breed dogs.
- Some large breed dogs need daily activity.
- Some large breed dogs are dog friendly.
- After eating is one of the times drooling is bad.
- The drooling is horrible after they drink, so beware!
- Great Pyrenees Mountain dogs drool as well.
- If you live in an apartment, these breeds could pose a problem.
Transition statement: Now that we’ve explored the characteristics of large breed dogs, let’s contrast this with small breeds.
- Some small breed dogs need daily activity.
- Some small breed dogs are dog friendly.
- They will jump on people.
- They will wag their tails and nuzzle.
- Beagles love strangers.
- Cockapoos also love strangers.
This dog example will help us showcase the following outlining principles.
Subordination and Coordination
The example above helps us to explain the concepts of subordination and coordination . Subordination is used in outline organization so the content is in a hierarchical order. This means that your outline shows subordination by indention. All of the points that are “beneath” (indented in the format) are called subordinate points. For example, if you have a job with a supervisor, you are subordinate to the supervisor. The supervisor is subordinate to the owner of the company. Your outline content works in a similar way. Using the dog example outlined in the previous section of this chapter, subpoints A, B, and C described characteristics of large breed dogs, and those points are all subordinate to main point I. Similarly, subpoints i and ii beneath subpoint C.1. both described dogs that drool, so those are subordinate to subpoint C. If we had discussed “food” under point C, you would know that something didn’t make sense! Overall, to check your outline for coherence, think of the outline as a staircase; walking down the outline one step at a time.
Tech tip: You can use the Ruler function of word processing software such as Microsoft Word or Google Docs to create tabs that align subordinated points with each other and keep the following lines of text properly aligned. If you only use the tab key, text that flows beyond the first line will usually not align with the proper tab stop for a given sub-point. Some instructors may provide you with a template, but experiment with the Ruler function on your own. It’s very useful!
You will also see that there is a coordination of points. Coordination is used in outline organization so that all of the numbers or letters represent the same idea. You know they coordinate because they align vertically and there is no diagonal relationship between the symbols. In the dog example, A, B, and C were all characteristics of large breed dogs, so those are all coordinated and represent the same “idea.” Had C been “German Shepherd,” then the outline would have been incorrect because that is a type of dog, not a characteristic, therefore, breaking the rules of subordination and coordination.
Figure 8.10 below provides you with a visual graphic of the subordination and coordination process. You will see that the topic of this very brief outline is bread. The main point tells you that there are different types of bread: sourdough, wheat, white, and egg.
To check this brief outline for subordination, you would look to see what subpoints fall beneath the main point. Do all of the sub-points represent a type of bread? You will see that they do! Next, to check for coordination, you would look at all of the subpoints that have a vertical relationship to each other. Are the subpoints these four types of bread? They are. The image also allows you to see what happens when you make a mistake. The third example shows the subpoints as sourdough, wheat, white, and jelly. Clearly, jelly is not a type of bread. Thus, there is a lack of both subordination and coordination in this short example. Make sure you spend some time checking the subordination and coordination of your own subpoints all the way throughout the outline until you have reached your last level of subordination. Now, study the image so that these principles of outlining are crystal clear; please ask your professor questions about this because it is a major part of speechmaking.
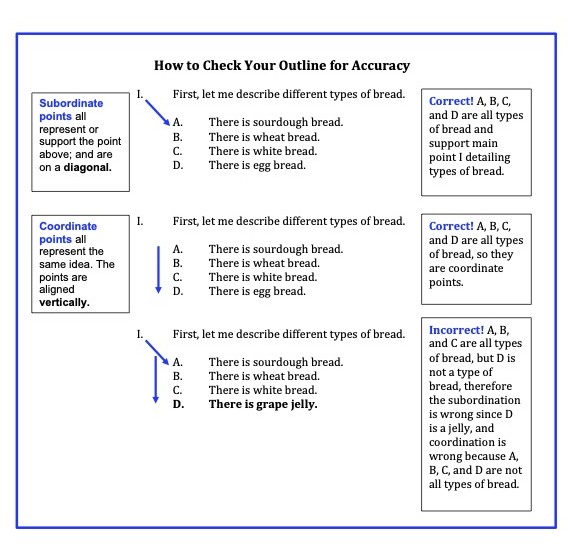
Figure 8.10: Checking Your Outline 10
You may be wondering why we bother with subordination and coordination. It actually helps both your listeners and your instructors. Listening is difficult. Any techniques that help audiences make sense of information are welcome. As soon as you begin talking, audiences listen for cues on how you are structuring information. If you organize clearly using logical relationships, your audience will be better able to follow your ideas. Further, for busy instructors examining many students’ outlines, when students’ grasp of subordination and coordination jump off the page due to their proper visual alignment, we know that students understand how to organize information for verbal delivery.
Parallelism
Another important rule in outlining is known as parallelism . This means that, when possible, you begin your sentences in a similar way, using a similar grammatical structure. For example, in the previous example on dogs, some of the sentences began with “some large breed dogs.” This type of structure adds clarity to your speech. Students often worry that parallelism will sound boring. It’s actually the opposite! It adds clarity. However, if you had ten sentences in a row, we would never recommend you begin them all the same way. That is where transitions come into the picture and break up any monotony that could occur.
The principle of division is an important part of outlining. Division is a principle of outlining that requires a balance between two subpoints in an outline. For each idea in your speech, you should have enough subordinate ideas to explain the point in detail and you must have enough meaningful information so that you can divide it into a minimum of two subpoints (A and B). If subpoint A has enough information that you can explain it, then it, too, should be able to be divided into two subpoints (1 and 2). So, in other words, division means this: If you have an A, then you need a B; if you have a 1, then you need a 2, and so on. What if you cannot divide the point? In a case like that, you would simply incorporate the information in the point above.
Connecting Your 2-3 Main Points
There are different types of transitions , which are words or phrases that help you connect all sections of your speech. To guarantee the flow of the speech, you will write transition statements to make connections between all sections of the outline. You will use these transitions throughout the outline, including between the introduction and the body, between the 2-3 main points, and between the body and the conclusion.
- Internal Reviews (Summaries) and Previews are short descriptions of what a speaker has said and will say that are delivered between main points.
Internal Reviews give your audience a cue that you have finished a main point and are moving on to the next main point. These also help remind the audience of what you have spoken about throughout your speech. For example, an internal review may sound like this, “So far, we have seen that the pencil has a long and interesting history. We also looked at the many uses the pencil has that you may not have known about previously.”
Internal Previews lay out what will occur next in your speech. They are longer than transitional words or signposts. For example, “Next, let us explore what types of pencils there are to pick from that will be best for your specific project.”
- Signposts are transitional words that are not full sentences, but connect ideas using words like “first,” “next,” “also,” “moreover,” etc. Signposts are used within the main point you are discussing, and they help the audience know when you are moving to a new idea.
- A nonverbal transition is a transition that does not use words. Rather, movement, such as pausing as you move from one point to another is one way to use a nonverbal transition. You can also use inflection by raising the pitch of your voice on a signpost to indicate that you are transitioning.
The most effective transitions typically combine many or all of the elements discussed here. Here is an example:
Now ( signpost ) that I have told you about the history of the pencil, as well as its many uses, ( internal review ) let’s look at what types of pencils you can pick from (mime picking up a pencil and moving a few steps for nonverbal transition ) that might be best for your project ( internal preview ).
Although this wasn’t the splashiest chapter in the text, it is one of the most critical chapters in speechmaking. Communicating your ideas in an organized and developed fashion means your audience will easily understand you. Each one of the principles and examples provided should be referenced as you work to develop your own speech. Remember that your speech will have a general purpose (typically to inform or persuade) and a specific purpose that details exactly what you hope to accomplish in the speech. Your speech’s thesis statement will be the central idea, what audiences most remember. The thesis is not just a list of main points, but it is a larger idea encompassing the two to three main points supporting it in the speech. Speeches should follow an organizational pattern, use standard formatting practices, and progress from full-sentence preparation outlines to key word speaking outlines before your performance. To see how all of these pieces come together, check out the sample preparation outline included at the bottom of the chapter. When writing your own preparation outline, use this sample as a guide. Consider each component a puzzle piece needed to make your outline complete.
Reflection Questions
- How has the information regarding general and specific purpose statements helped you to narrow your topic for your speech?
- Using brainstorming, can you generate a list of possible main points for your speech topic? Then, how will you decide which are the best choices to speak on?
- Which pattern(s) of organization do you think would be best for your informative speech? Why?
- Researchers say writing in small bursts is better. Do you agree that it is more effective to write your outline in small chunks of time rather than writing an entire speech in one day? Why or why not?
Body of the Speech
Coordination
General Purpose Statement
Internal Review (Summary)
Internal Preview
Nonverbal Transition
Preparation Outline
Preview Statement
Speaking Outline
Specific Purpose Statement
Subordination
Thesis Statement
Transitions
Written Oral Citation
Sample Speaking Outline
General Purpose: To inform
Specific Purpose: By the end of this speech, my audience will be able to explain bottle bricking, bottle brick benches, and their purposes.
Introduction —
I. Attention Getter: How many of you have thrown away a piece of plastic in the last 24 hours? Perhaps you pulled cellophane off a pack of gum or emptied out a produce bag. You probably don’t think about it, but those little pieces of plastic have two potential destinations – if they’re obedient, they go to a landfill. If they’re rogue, they can end up in waterways.
II. Thesis Statement: Today we will learn about a revolutionary way of dealing with plastic trash called bottle bricking.
III. Relevance Statement: As our planet’s ecological crises worsen, each of us should reflect on our impact on the environment. According to the Sea Education Society, a non-profit dedicated to reducing pollution through environmental education, there are more than one million pieces of plastic per square mile in the most polluted parts of the Atlantic Ocean, as Kirsten Silven of Earthtimes.org reported in (2011). If you want to take steps to preserve our world’s natural beauty for future generations, this speech is for you.
IV. Credibility Statement: When I first learned about bottle bricks I was incredulous. I thought “what is the point of stuffing plastic into plastic bottles?”. But soon the idea took hold of me and I was volunteering with local groups, eventually inspiring the creation of a Bottle Brick Bench at a high school I worked at.
V. Preview Main Points Statement: In this speech, we will learn how a bottle brick is made, how they are turned into benches, and the purpose behind this seemingly strange activity.
Transition: Before we go any further, let’s learn how to make a bottle brick.
Body —
- You will soon notice it everywhere.
- The trash must be clean and dry.
- Other hard-plastic bottles work, also.
- The bottles must be clean and dry.
- The stick should be long enough to reach the bottom of the bottle.
- Pick a smooth stick or give it a handle.
Transition: Now we know how to transform our trash into tools. But, what can bottle bricks be used for? One answer: a bench.
- Most creators argue you should use reclaimed stone (urbanite).
- Bricks make up the backrest.
- Cob is like mud.
- The benches make us realize how much plastic we toss, writes Brennan Blazer Bird on earthbench.org (2014) , home of the Peace on Earthbench Movement that the 25-year-old ecological educator founded.
- Later, people might think about it the plastic away they throw away
- Currently we have little use for soft plastic; most film plastics are not recyclable.
- Benches are a sign for change, and they are comfortable.
- Plastic “sequestered” in a bottle avoids landfills and the ocean.
- In landfills it gets into drinking water.
- All five subtropical ocean gyres have plastic “garbage patches,” according to 5gyres, a nonprofit dedicated to eliminating plastic pollution in the gyres (5gyres.org, 2014) .
- To have fun! The Harvest Collective called natural building such as earthbenches “incredibly fun and inspiring” on its website theharvestcollective.org (2014) .
Transition: So now that we understand why someone would make a bottle brick bench, let’s see if we’ve successfully “stuffed” this knowledge into our heads. [ I can make a bottle-stuffing motion to have fun during transition. ]
Conclusion —
- Signal end of the speech: I think it’s safe to say that every one of us throws away plastic on a regular basis has some degree of concern for the health of our planet.
- Review Main Points: Today we’ve learned how to make bottle bricks, how to put them into a bottle brick bench, and the reasons for doing so.
- Restate Thesis: Today we have seen that we can turn our seemingly useless, polluting trash into safe, useful technology. Maybe we can use such forward-thinking attitudes to promote sustainable cycles in all aspects of society.
- Specify desired audience response: I know that you aren’t all going to rush home and start bricking, but I’d like you to remember the basic premises underlying bottle bricks. But, by all means, if you’re interested in adding to the Peace on Earth Bench for Movement, visit earthbench.org or talk to me in class sometime.
- Strong closing (clincher): Who knows, maybe when you’re about to graduate you will be able to sit on a Bottle Brick Bench on campus reminding us all that we, through our individual choices, have the power to transform our species’ problems into solutions.
Introduction to Public Speaking Copyright © by Jamie C. Votraw, M.A.; Katharine O'Connor, Ph.D.; and William F. Kelvin, Ph.D.. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
Speech Structure: The Complete OBC Guide
What makes a great speech? The content, of course, but also the structure. All great speakers overlay their content on a well-known structure.
Your speech structure is the glue that binds your points together. Without it, you cannot really have the impact you desire to have on the audience.
The beauty of this is that a good structure is so subtle it is almost invisible. Its effectiveness is only evident in its impact.
Speech writing can be intimidating for some, however, we have incorporated plenty of speech examples to get a complete understanding. We aim to explain a proper structure that can be applied to any of your speeches.
There are four things you need to keep in mind about this:

Table of Contents
What is the purpose of your speech?
Can too much content be harmful, who is the audience, informative speech, persuasive speech, argumentative speech, demonstration speech, humorous speech, strong statement, visual prop or demonstration, personal anecdote, problem or strong statement, summary on writing your introduction:, credibility, cause and effect:, problems and solutions:, lucky number three, summary on writing your body:, call to action, inspirational, key takeaway, summary of writing your conclusion:, meta description:, picking the right topic.
The content of a speech can largely determine how the audience receives it. For this, you will need to accurately assess who is going to be listening to your speech. There are some questions you need to ask before sitting down to write this speech.
Do you intend to introduce a concept or argue on a controversial topic? Is your purpose of imparting knowledge or guiding the audience through a demonstration? It is essential to have your intentions cleared; otherwise, you can risk creating a speech with no direction.
We understand that as daunting as speaking can be, it is, at the same time, fascinating. When you pick a topic that you are passionate about, it is easy to find yourself packing the speech with all kinds of information. However, in doing so, you can overwhelm your audience.
There is such a thing as too much information. You need to make sure that whatever information you do include is impactful and influential. Aim for something short but memorable. Pick one takeaway message and gear your speech towards that objective.
While it is vital to pick a topic that interests you, it is equally important to make sure that it can grab the audience’s attention. What is the target demographic for your speech? What is the setting for this speech? Is it a particularly controversial topic?
This is important because as humans, most people are likely to be more interested in your presentation if it benefits them somehow. At the same time, you have to consider the setting.
For instance: an office setting would not be the right setting for a controversial social speech. If your speech includes demonstration and requires volunteers, you need to ensure that this is an audience willing to participate.
Do you understand the various types of speeches?
Before you pen down your presentation, stop to wonder whether you understand the different types of speeches. Understanding what kind of speech you are going for can help you better structure it for maximum efficiency:
An informative speech intends to explain complex topics to your audience by providing engaging information. This can include objects, events, procedures, and more. It is better if you pick a topic that you are interested in so that your enthusiasm shines through.
When you give an informative speech, you are merely trying to educate your audiences about a particular topic. You refrain from becoming too argumentative as it might come across too strong for your listeners. If this is the type of speech you intend to give, you can check out 100 Informative Speech Topics and Ideas to make your job easier.
A persuasive speech intends to convince the audiences of your viewpoint. It uses compelling points to sway the listener’s opinions. The primary purpose of this type of speech is to affect the audiences’ thought process and persuade them to think about changing how they feel about a topic.
Some examples of a persuasive speech can be a politician’s speech, an animal activist’s speech, and so on. As you can see, the goal here is to persuade and obtain something ultimately. A politician might want to sway your vote in their favor, whereas ani activist has a cause that they’d like to advocate for.
If this is the type of speech you intend to give, you can check out 237 Easy Persuasive Speech Topics and Guide to better plan your speech.
An argumentative speech is more or less a persuasive speech. However, a persuasive speech does not always have to be argumentative. The purpose of an argumentative is to alter how the audience views a subject.
Changing the audience’s opinion is not an easy job. This is why you need to not only pick a persuasive topic but also believe in it. You need a strong claim along with irrefutable points to support it.
The best argumentative speeches utilize issues relating to current events. You can see this in the media in the form of mostly social, ethical, political, or religious arguments. Your arguments should make use of logic and realistic examples. Some examples of this type of speech can be: Dress codes shouldn’t be mandatory, Space exploration is a waste of money, etc.
If you’d like to see more topic ideas for an argumentative speech, you can browse the 200 Argumentative Speech Topics and ideas: A Complete Guide .
A demonstration speech, true to its name, demonstrates to the audience how something works. This type of presentation is more common for high school or college students. It makes use of props and useful body language to properly guide the audience through an activity.
This type of speech can fall under informative speech as you are informing the listeners on a task. While this type of speech is considered a basic speech, it is an excellent way to practice your expository speaking.
If this is the type of speech you’d like to give, here’s a list of 279 Demonstration Speech Topics and Ideas: A Complete Guide , so that you can better perfect your speech.
A humorous speech is the perfect light-hearted solution for adding a fun twist to your speech. This type of presentation aims to entertain the audience. A humorous speech can incorporate any of the above examples. It is, thus, very versatile. And what’s more? You get to have just as much fun delivering it!
The thing to keep in mind with this kind of speech is that you need to pick a proper topic. You intend to garner a joyful response to its best not to pick a sensitive topic. To help you out, you can browse the 300 Funny Speech Topics to Tickle Some Funny Bones! to structure your humorous speech.
Writing the Introduction (Opening)
The introduction of your speech is vital to the success of your speech. It is what sets the tone of your entire speech. It determines whether or not you grab the attention of the listeners. You will get only one chance to charm your audience and make sure they follow the rest of your speech.
So, how can you make this happen? There are a few different ways you can approach this:
Asking a question is an excellent way to grab your audience’s attention. It piques their curiosity and ensures that they will listen to get an answer to said question. The question can be either rhetorical or literal. For instance, “Have you ever wondered what it’d be like to live in a world without technology?” or “Have you ever felt broken-hearted?”.
Either the audience resonates with your question, or it generates curiosity. This is also a great way to get some audience participation. If you say, “With a show of hands, how many of us here have tried to change our habits and failed?” you can not only garner interest but also physically get the audience invested in your speech.
A question is a great way to get your listeners thinking about your topic while introducing your topic, all in a matter of seconds!
A strong statement is also an excellent way to create a compelling introduction. You must know Martin Luther King’s iconic, “I have a dream.” The intensity that radiates from that sentence immediately captures an audiences’ attention and creates a commanding presence.
Similarly, an excellent example of this type of opening is from Larry Smith’s speech. “I want to discuss with you this afternoon why you’re going to fail to have a great career.” This immediately generates intrigue and curiosity. That’s what you’re going for.
This statement does not have to just be cold facts. It can be a part of a personal story as well. For instance, the statement “Last week, I found out that my childhood friend got in a car accident” is bound to create a powerful silence. If your speech has such a strong emotive statement, you can use it in your introduction to engage your audience better.
Another helpful tip that goes with a strong statement in silence. Give your listener’s a chance to absorb the statement that you have put in front of them with a couple of seconds of silence before diving in further.
A prop can be a fantastic addition to your speech. Not only does it help emphasize your point, but it also helps the audience stay focused on your speech. Props are especially good for a demonstrative speech. Or you can simply incorporate demonstrations as part of your speech.
Body language speaks much louder than words can for us humans. This is why using colorful bags, a deck of cards, colored papers, etc. can be so effective as an opener for your speech. Once, I attended a speech where the speaker brought a heavy bag and simply set it on the table, talking about the bag. The audience was hooked, waiting eagerly till the end to find out what was in the bag.
A quotation can be the perfect way to capture your audience’s attention. It also helps set a tone for the speech that is to come. The quote you pick can be a well-known saying such as “They say all that glitters is not gold, well I beg to differ.” Doing so, you can ignite curiosity.
Similarly, you can also quote a person or a publication and tie it to your speech. For instance, for a motivational speech, you can take the example of someone like Bill Gates- “Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning.” When you use a quote from a big name, you will definitely get people wanting to hear and learn more.
Humor is always a great tool to have in your arsenal. A good icebreaker can warm the listeners up to you and make them more receptive to the rest of your speech. Humor is a very endearing trait for a skilled speaker. Some ideas for your opening can be:
“It’s the funniest thing. As I was coming up to the stage, I began thinking we actually have quite a lot in common. None of us have a clue about what I’m going to say!”
“I know we are all busy, and I want to honor your time. So I will make sure to be accurate and brief, no matter long it takes me.”
The great thing about using humor is that it works on your audience subconsciously. You seem at ease with yourself and radiate confidence. You have to remember that for humor to be effective; it has to be effortless. If you seem unsure about your lines, the audience is sure to pick up on it.
A strong statistic will always add validity to your speeches. Presenting the audience with irrefutable facts backed up by a strong source is a surefire way to gain credibility. It can also add gravity to the scale of the issue that you want to draw attention to.
However, it is easy to overdo things when it comes to numbers. It can be tempting to add strong statistics to the rest of your speech as well. But remember, the strongest points are ones that linger in an audience’s mind. If you give them too many numbers, none of them will stick out in their heads, and they are bound to feel lost.
Some examples can be: “Look to your right. Now, look to your left. One in three women and one in four women are known to have suffered physical violence. A statement like this not only ignites awareness but also physically makes your listener feel involved in your speech.
An anecdote is a short story taken from your life itself. The story usually adds to the theme of your story. Short and light-hearted anecdotes can add a lot of enthusiasm and charm to your speech. However, you don’t have to make them humorous. Even more, touching stories can be equally, if not more engaging.
When used correctly, a personal anecdote makes for the perfect introduction that draws your listeners towards your central message. Not only does it create empathy, but it also sparks interest. If you don’t have a personal anecdote itself, you can go for a third-person anecdote that speaks to you as well.
Opening with a problem can make for a strong opening. This method generates interest and keeps the audience listening with the promise of an upcoming solution. Try to aim for a problem that caters to a wider demographic for a higher relatability.
Problems that relate to current events can have a better draw. For instance: “Why should remote working be implemented even after quarantine?”
In a similar vein, a powerful statement can be an excellent way to capture your audience’s attention. A statement, when paired with silence, can make for an effective tool. Example: “The top 20% of our society makes 80% of all the money. Would you like to be part of this 20%? If so, I’m going to give you some pointers on how you can align yourself in that direction. Does that sound like something you might be interested in?”
- Your opening plays a big role in whether or not you can grab your listener’s attention straight off the bat.
- Give your audience a reason to pay attention by clearly stating the purpose of your speech.
- If you are giving a speech regarding a field you have some experience with, remember to establish credibility early on.
- Give a short highlight reel of your main points.
- Quotations or powerful statements are a great way to catch the audience’s attention.
- Including current events or statistics will make your speech seem more relevant to a wider range of listeners.
- Asking a question will get your audience more involved and add intrigue to the rest of your presentation.
Structuring your content (Body)
The body of your speech will hold all of your main points. Since this is the longest section of your speech, you need to ensure that it is interesting enough to keep everyone’s attention. Depending on the objective of your speech, you will need to add examples, opinions, and facts to back up your points. What helps during this time is proper organization.
Here are some things you want to keep in mind while drafting the body of your speech:
No matter how much you believe in your point, you still need to give your audience a credible reason to take your word for it. This can be done by adding examples, detailed descriptions, statistics, and so on. Always remember to credit the source when using a statistic. You can also add a strong testimonial to add a touch of personalized support if that applies to your objective.
Transitions
When you have a lot of content packed into your speech, transitions become vital to the effectiveness of your speech. You can consider these as points of a refresh in your speech. Here, the audience can reengage and follow along more attentively.
The best transitions are always invisible. They can seamlessly add flow to your speech without giving any indication of such to your audience. There are many ways to incorporate this into your speech.
Some examples can be:
A connective transition is where you reiterate a previous point and introduce a connecting point. The way this method works is that it rehashes an important aspect while relating it to what’s next.
The most effective way to use this is in a problem/solution module. This is where you begin by stating a problem and transition towards a solution.
Example: Now that we’ve understood the various negative effects of junk food, let me tell you how we can plan a better diet to combat obesity.
When you do this, you are providing a summary of the problem and swiftly leading them towards a solution. If you jump straight to the next section, it can feel rushed. Besides, pauses are another important element of speech delivery.
Keywords, as the name suggests, have a certain draw to them. These are words that are central to the theme of your speech. Repetition is a very effective tool in conveying your message.
For instance: If your speech is about the scarcity of running water in rural communities, you can draw attention by repeating the factors that cause this issue. Doing so will also let you explain in better detail these factors while keeping your audience hooked to the main theme.
Content Approach
Depending on your speech, there are various ways to approach how you frame your content. We all know that content is king; however, without the right approach, it’s easy for your message to get lost along the way. This is why it’s so important to keep your subject matter relevant and interesting. Make sure the content is as compact and concise as you can make it. Some of the methods by which you can ensure this is as follows:
Cause and effect is a great way to present your ideas. This method works best for explaining events and consequences or results. Make sure to include all the appropriate details to add emphasis. The element of ‘what’s next’ is what keeps the audience hooked to your speech. As you unfold a cause and follow it with the effects, it will feel both interesting as well as rewarding to your audience.
Problem and solution is a speech method as old as time. But it is so because of its reliability. This approach works best for a motivational speech. This type of speech intends to address a problem and offer a systematic solution that benefits the listeners. It is also a common approach for pushing an audience to buy into a service or product. You pose a problem and then offer a solution, including a whole package. Make sure the solution you offer is versatile so that it applies to a wider range of people, thereby increasing appeal.
A narrative approach is excellent for anybody who wants to sharpen their storytelling skills. The important ingredients for a narrative speech are chronology and a simple organization pattern. Typically, any story will have a beginning, middle, and end. Going in order, with smooth transitions will make your story easy to follow.
This type of speech is most effective for presenting events, life lessons, experiences, rituals, and personal beliefs. Try to stick to the core of the story without too many unnecessary details. Just because a narrative includes storytelling does not mean it can’t have an end goal. For instance: a personal experience of failure might be a great story of caution for the listeners.
The most important thing for a successful narrative speech is build-up. You want your audience to be invested, to care about what comes next, to raise the stakes so that when you provide the conclusion, it is that much more effective. You must always ask yourself, “What do I want the audience to remember after this speech?”.
The best way to write this would be to outline a sketch of events that are relevant to your narrative. After that, you can think about the best way to escalate the stakes. Remember that eye contact is an important visual medium in a narrative speech. It will help your audience connect better to your story.
The number three is impactful. Even the general structure of a speech is divided into three parts: Opening, Body, and Conclusion. When you want to make a point that people remember, you should consider splitting it into three, where the first two act as a build-up while your final point brings the unexpected impact.
The best thing about this method is that you can apply it to just about any kind of speech. This, in fact, adds more structure to your speech and makes it more easily digestible. The key ingredient here becomes balance and transition. Make sure you focus on all three elements of your story equally, so it does not feel rushed. Add in a seamless transition to make your story structure seem effortless.
- Make sure you have designed your content to suit your audience.
- Divide your body into easily digestible sections so that your main points come across clearly.
- Stress on keywords and clever repetitions to drive your point home.
- Work on your transitions to establish clear sections but a seamless switch to keep your listeners hooked.
- When using facts or statistics, always back it up with a credible source.
Closing your speech (Conclusion)
The conclusion is vital to the success of your speech. This is the parting thought that you will be leaving your audience with, so you have to make sure that it’s a good one. The conclusion is where you reiterate your key point. This is why there is so much importance put on a conclusion to be powerful enough to stay in your memory.
Here are some possible ways you can approach your conclusion:
A call-to-action refers to a statement or material that intends to encourage the listener or viewer to take the initiative. It can also be considered as instruction as it usually directs the audience towards something.
The most effective way to approach this is to manage both your energy as well as your tempo. While it is essential to maintain a clear and well-enunciated speech throughout, when you reach a conclusion, you are going to want to speed up just a little bit.
What this does is add a sense of urgency to the message that you are giving. Similarly, higher energy makes the audience resonate and respond equally. They will associate this high energy with your message and remember your speech for longer.
Some examples of this can be: “As we can see, the effects of depression can be life-threatening. So I encourage each and every one of you to go home today and reach out to your friends, talk to them and open up a platform where they know they can come to talk to you for anything. Because you’d rather hear their problems than hear about their death.”
For speeches that are over 5-6 minutes long, the audience can sometimes lose track of the earlier points. This is why it is necessary to summarize your main points before you leave the stage. You don’t have to take them through the entire story, but make sure you include the keywords that trigger in them the memory of that portion.
You can do this by saying something along the lines of “Let me briefly run you through what we discussed” or “So, we talked about three main things today.” This not only does a great job of reiterating and reconfirming your main points but also signals to the audience that you are drawing towards the end of your presentation.
Repetition. Repetition. Repetition.
Even though you might be well familiarized with your speech, it is safe to assume that most of the audience is hearing it for the first time. For this reason, you need to drive your point home by essentially drilling it into their minds. Now, you can’t simply repeat the central theme over and over as that isn’t an effective strategy. But there can be an art to repetition as well.
You should aim to rephrase and reinforce your central idea as you conclude your speech. Don’t go for a word-for-word repetition, but aim to reframe your key themes and arguments. Paraphrasing, in this way, makes sure that you capture the essence of your speech without running the risk of boring your listeners with identical sentences.
We don’t even need to look too far for examples of this method. In Martin Luther King’s famous “I have a dream” speech at the Lincoln Memorial, he used this method of repetition paired with a rising momentum to create impact. Repetition works best when it is subtle and works on the listeners subconsciously.
Ending your speech on a light note is a great way to brighten moods and make sure the audience remembers your message. Your joke can also be a good way to repeat your central message. If you do decide to end with a humorous story, remember to carve out more time for it. Make sure your conclusion doesn’t distract from your main message.
Some people tend to get too excited and give away the upcoming punchline. Remember that the most effective humor approach is one you don’t see coming. How you can add the subtlety to your conclusion is by following this formula:
Set up – pause – Build up – pause – Punchline
Motivational conclusions are always an upbeat way to close your speech. You will be leaving the stage on high energy that is sure to be contagious. This also ensures that your audience will be taking a piece of your conclusion with them, making sure that it is not only memorable but also useful.
There are many ways to approach an inspirational closing. You can go with an anecdote, a quote, a poem, and so on. The purpose is to give a push, to add strength, to ignite a can-do attitude.
The trick to a powerful inspirational speech is emotion. Humans are excellent at empathizing. If you can adequately emote throughout your story, adding drama into your storytelling, then it is bound to have a more substantial effect. Vocal variety can also be an excellent element for this. Alter your tempo to weave excitement into your story. You can also use smart pauses to add more intrigue.
Your facial expressions play a significant role in how the audience receives your speech. Whether it is a sad or happy story, make sure that your face conveys it. It can be addictive to have the audience’s attention like this, but don’t get too greedy. Remember to end on your highest note, leaving a lasting impression.
There are many types of speeches out there. For instance: you might think that a humorous speech is just that: humorous. But think again. All the best speeches have at least one key takeaway.
A takeaway message is quite similar to an inspirational conclusion. The question you have to ask yourself is this: What is the purpose of my speech? Even if you’ve got a fantastic anecdotal story to share, you have to remember that the audience will always wonder what they are getting from the speech. That will be your takeaway.
For an effective conclusion, you have to step back and overview your speech. From your introduction to the body, what is the message you are trying to convey? Make sure your conclusion reflects it. For example: if your speech is about a drowning story, you can probably try to include what you could’ve done and how the audience can avoid being in a similar situation.
A call-back is a fun twist to add to your conclusion. There is a reason why a circle is one of the most pleasing shapes; it gives you a sense of completion. Even if you aren’t aware of it, it works on your mind subliminally. An effective way to conduct this method is to find a way to tie your ending to your introduction.
You can understand a call-back as a reference. It doesn’t have to be limited to just the introduction; you can reference the body of your speech as well. This not only makes for a great repetition tool but also adds a feeling of completion into your presentation.
However, you should pick something that the audience can connect to. This helps create a special and unique bond as if it were an inside joke just between you two.
- Signal your audience when you’re drawing to your conclusion.
- Add trigger transitions like “In conclusion,” “In summary,” “That brings us towards the end,” and so on.
- Try to end on a high note with something memorable.
- Write your conclusion last so that it complements your introduction.
- Try to paraphrase your words without repeating the same words over and over.
- Your audience is more likely to remember your speech if you end with something useful to them or with a call to action.
- Leave on an attention-grabbing note.
Wrapping Up:
A speech typically has one of four purposes: to inform, to entertain, to instruct, or to persuade. To deliver an effective speech, you need to first make sure you understand what your objective is. Then, you can follow our guidelines to construct a solid structure and deliver a well-rounded and impactful presentation. Now that you know how to create an effective speech structure, you are ready to dominate the stage!
The best speech structures are invisible and effective. Learn the tips and tricks to deliver the perfect opening, body, and conclusion and wow the stage.
Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech
Chronological, step-by-step, and spatial organization, learning objectives.
Explain the chronological, step-by-step, and spatial patterns for speeches and identify which topics work best for these types.
We can think of speeches organized chronologically, step by step, or spatially as following a “natural” or self-evident structure. When you’re talking about a process, for instance, walking the audience through the process step by step seems like a logical or natural choice.
Remember, though, that even if your speech is structured in a “natural” sequence, you still need an introduction that helps the listener understand why they’re listening to this story. Imagine that a friend is going to tell you a story about something that happened to them that day. First, let’s imagine that they start the story with “Something really funny happened to me . . . .” What are you listening for in the story? Now imagine if they started the story with “I’m really upset because of something that happened today.” Or “I really need your advice. Here’s what happened . . . .” With each of these different beginnings, we listen in a different way. In the first case, we’re primed to laugh; in the second, we get ready to offer comfort and sympathy; in the third, we’re prepared to problem solve. The same is true of the beginning of your speech: by setting the stage with the introduction or the “hook,” you’re letting the listener know what they’re listening for and how they should listen.
Chronological

A persuasive speech about Climate Change might describe the predicted effects of global warming in chronological order.
A chronologically organized speech pattern organizes its main points following a sequence of events or occurrences according to the time they took place. This structure works particularly well for informative and introductory speeches. For example, an introductory speech about the life events that lead you to attend your college could be organized chronologically starting with the first meeting with your guidance counselor, which lead to filling out an application a few weeks later to then drafting an essay, going on a campus tour a few months after that, having an interview with the department, and then finally getting the acceptance letter. Another example of a chronological speech topic would be a speech about a historical event, such as the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire, the Boxer Rebellion, or the Arab Spring, which covers the events that occurred in the order in which they happened.
The advantages of a chronological speech pattern are that it is very easy to follow and it creates a clean, clear order. The timeline does the organizational work for the speaker and makes it easy to use. The cons are that there may be many events that occurred, such as in a speech topic about women getting the right to vote, which may not fit into the speech delivery time limit. So, consider the time allotted in addition to whether the time sequence of events is the most effective way to present the material before selecting this pattern.
Step-by-Step

An informative speech about Salsa dancing might give step-by-step instructions.
This pattern presents the steps involved in doing something and is useful for “how-to” or demonstration speeches where you are teaching or showing how to do a task. It follows the order of a process. For example, the steps involved in baking a cake, a speech demonstrating the dance steps required to do the Macarena, or how to create a PowerPoint presentation would use a step-by-step structure.
The advantage of this organizational pattern is that it breaks the task into small pieces for the audience. It allows them to see the process of doing something so that they may be able to do it themselves. The disadvantage of this pattern is that it can be tedious or repetitious if listeners are already very familiar with some of the steps in the process. With this organizational pattern, it’s particularly important to know how much prior knowledge of the process your audience already has.

An informative speech about the International Space Station might use a spatial organization pattern, giving the listeners a tour of each part of the station as though they were moving through it.
A spatial pattern organizes each main point in a directional structure, connecting each main point to a whole. This structure is used for informative speeches where the topic is organized by location, geography, or moving through a space (“spatial” is the adjective form of “space”). For example, a speech about the parts of a resume might move in order from the top section to the bottom section. A speech about the regional cuisine of Germany might move from the Northwest region in a clockwise direction around the country. A speech about a building might start at the front doors and end on the roof. A speech about the pathway of Hurricane Sandy would include the geography showing the path moving from south to north east.
The spatial pattern is particularly useful if you want your listeners to be able to visualize an entire place or a complex object, since it moves between the part and the whole in a visual way. If you want your audience to visualize the Statue of Liberty, for instance, you might describe it spatially from top to bottom, rather than telling the story of its construction (chronological) or talking about the various things it has come to symbolize (topical).
To Watch: Beth Harris and Steven Zucker, “Diego Rivera, Man Controller of the Universe”
Spatial organizational patterns are often used to describe artworks and architecture. In this short video, art historians Dr. Beth Harris and Dr. Steven Zucker discuss Diego Rivera’s 1934 fresco mural Man, Controller of the Universe in the Palacio de Bellas Artes, Mexico City. The first part of the video is organized topically and chronologically, covering some of the major themes of the mural and the circumstances surrounding its creation. At around 3:25 in the video, Zucker says, “Let’s take a closer look at [the mural]”, and the two art historians discuss each part of the mural in sequence starting with the figure in the center. The spatial organization of their description is based on the visual structure of the painting; since the painting is largely symmetrical, Harris and Zucker describe the center, then the upper left and upper right, then the middle left and middle right, then the bottom left and bottom right.
You can view the transcript for “Diego Rivera, Man Controller of the Universe” here (opens in new window) .
What to watch for:
Note how Harris and Zucker end their tour of the artwork with broader thoughts about what we can learn from it: “We’re still very much at these crossroads. Technology is ever more important in our lives. What will technology bring us? A more egalitarian society, a world where everyone can be educated? Or will it bring greater inequality? These are still things debated today. We are still grappling with the increasing power of the tools that we have built, the power that technology has given us, and the choices that we make in terms of how we wield that power.” Whatever organizational pattern you use, it’s always crucial to bring the discussion around to something the audience can take away—a new insight, a new perspective, or a new way of framing a problem.
- ISS blueprint. Authored by : Daniel Molybdenum/NASA/Roscosmos, with the help of John Chryslar and others. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Space_Station#/media/File:ISS_blueprint.png . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- Salsa steps. Authored by : Florian Hoffmann. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salsa_(dance)#/media/File:Salsa_Basic_Steps,_LA-style.png . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Acqua alta in Piazza San Marco. Authored by : Wolfgang Moroder. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Climate_change#/media/File:Acqua_alta_in_Piazza_San_Marco-original.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Diego Rivera, Man Controller of the Universe. Authored by : Smarthistory. Located at : https://youtu.be/1mzQDfK3A5Q . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License
- Chronological, Step by Step, and Spatial Organization. Authored by : Susan Bagley-Koyle with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Chronological, Step by Step, and Spatial Organization. Authored by : Misti Wills with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


What this handout is about
This handout will help you create an effective speech by establishing the purpose of your speech and making it easily understandable. It will also help you to analyze your audience and keep the audience interested.
What’s different about a speech?
Writing for public speaking isn’t so different from other types of writing. You want to engage your audience’s attention, convey your ideas in a logical manner and use reliable evidence to support your point. But the conditions for public speaking favor some writing qualities over others. When you write a speech, your audience is made up of listeners. They have only one chance to comprehend the information as you read it, so your speech must be well-organized and easily understood. In addition, the content of the speech and your delivery must fit the audience.
What’s your purpose?
People have gathered to hear you speak on a specific issue, and they expect to get something out of it immediately. And you, the speaker, hope to have an immediate effect on your audience. The purpose of your speech is to get the response you want. Most speeches invite audiences to react in one of three ways: feeling, thinking, or acting. For example, eulogies encourage emotional response from the audience; college lectures stimulate listeners to think about a topic from a different perspective; protest speeches in the Pit recommend actions the audience can take.
As you establish your purpose, ask yourself these questions:
- What do you want the audience to learn or do?
- If you are making an argument, why do you want them to agree with you?
- If they already agree with you, why are you giving the speech?
- How can your audience benefit from what you have to say?
Audience analysis
If your purpose is to get a certain response from your audience, you must consider who they are (or who you’re pretending they are). If you can identify ways to connect with your listeners, you can make your speech interesting and useful.
As you think of ways to appeal to your audience, ask yourself:
- What do they have in common? Age? Interests? Ethnicity? Gender?
- Do they know as much about your topic as you, or will you be introducing them to new ideas?
- Why are these people listening to you? What are they looking for?
- What level of detail will be effective for them?
- What tone will be most effective in conveying your message?
- What might offend or alienate them?
For more help, see our handout on audience .
Creating an effective introduction
Get their attention, otherwise known as “the hook”.
Think about how you can relate to these listeners and get them to relate to you or your topic. Appealing to your audience on a personal level captures their attention and concern, increasing the chances of a successful speech. Speakers often begin with anecdotes to hook their audience’s attention. Other methods include presenting shocking statistics, asking direct questions of the audience, or enlisting audience participation.
Establish context and/or motive
Explain why your topic is important. Consider your purpose and how you came to speak to this audience. You may also want to connect the material to related or larger issues as well, especially those that may be important to your audience.
Get to the point
Tell your listeners your thesis right away and explain how you will support it. Don’t spend as much time developing your introductory paragraph and leading up to the thesis statement as you would in a research paper for a course. Moving from the intro into the body of the speech quickly will help keep your audience interested. You may be tempted to create suspense by keeping the audience guessing about your thesis until the end, then springing the implications of your discussion on them. But if you do so, they will most likely become bored or confused.
For more help, see our handout on introductions .
Making your speech easy to understand
Repeat crucial points and buzzwords.
Especially in longer speeches, it’s a good idea to keep reminding your audience of the main points you’ve made. For example, you could link an earlier main point or key term as you transition into or wrap up a new point. You could also address the relationship between earlier points and new points through discussion within a body paragraph. Using buzzwords or key terms throughout your paper is also a good idea. If your thesis says you’re going to expose unethical behavior of medical insurance companies, make sure the use of “ethics” recurs instead of switching to “immoral” or simply “wrong.” Repetition of key terms makes it easier for your audience to take in and connect information.
Incorporate previews and summaries into the speech
For example:
“I’m here today to talk to you about three issues that threaten our educational system: First, … Second, … Third,”
“I’ve talked to you today about such and such.”
These kinds of verbal cues permit the people in the audience to put together the pieces of your speech without thinking too hard, so they can spend more time paying attention to its content.
Use especially strong transitions
This will help your listeners see how new information relates to what they’ve heard so far. If you set up a counterargument in one paragraph so you can demolish it in the next, begin the demolition by saying something like,
“But this argument makes no sense when you consider that . . . .”
If you’re providing additional information to support your main point, you could say,
“Another fact that supports my main point is . . . .”
Helping your audience listen
Rely on shorter, simpler sentence structures.
Don’t get too complicated when you’re asking an audience to remember everything you say. Avoid using too many subordinate clauses, and place subjects and verbs close together.
Too complicated:
The product, which was invented in 1908 by Orville Z. McGillicuddy in Des Moines, Iowa, and which was on store shelves approximately one year later, still sells well.
Easier to understand:
Orville Z. McGillicuddy invented the product in 1908 and introduced it into stores shortly afterward. Almost a century later, the product still sells well.
Limit pronoun use
Listeners may have a hard time remembering or figuring out what “it,” “they,” or “this” refers to. Be specific by using a key noun instead of unclear pronouns.
Pronoun problem:
The U.S. government has failed to protect us from the scourge of so-called reality television, which exploits sex, violence, and petty conflict, and calls it human nature. This cannot continue.
Why the last sentence is unclear: “This” what? The government’s failure? Reality TV? Human nature?
More specific:
The U.S. government has failed to protect us from the scourge of so-called reality television, which exploits sex, violence, and petty conflict, and calls it human nature. This failure cannot continue.
Keeping audience interest
Incorporate the rhetorical strategies of ethos, pathos, and logos.
When arguing a point, using ethos, pathos, and logos can help convince your audience to believe you and make your argument stronger. Ethos refers to an appeal to your audience by establishing your authenticity and trustworthiness as a speaker. If you employ pathos, you appeal to your audience’s emotions. Using logos includes the support of hard facts, statistics, and logical argumentation. The most effective speeches usually present a combination these rhetorical strategies.
Use statistics and quotations sparingly
Include only the most striking factual material to support your perspective, things that would likely stick in the listeners’ minds long after you’ve finished speaking. Otherwise, you run the risk of overwhelming your listeners with too much information.
Watch your tone
Be careful not to talk over the heads of your audience. On the other hand, don’t be condescending either. And as for grabbing their attention, yelling, cursing, using inappropriate humor, or brandishing a potentially offensive prop (say, autopsy photos) will only make the audience tune you out.
Creating an effective conclusion
Restate your main points, but don’t repeat them.
“I asked earlier why we should care about the rain forest. Now I hope it’s clear that . . .” “Remember how Mrs. Smith couldn’t afford her prescriptions? Under our plan, . . .”
Call to action
Speeches often close with an appeal to the audience to take action based on their new knowledge or understanding. If you do this, be sure the action you recommend is specific and realistic. For example, although your audience may not be able to affect foreign policy directly, they can vote or work for candidates whose foreign policy views they support. Relating the purpose of your speech to their lives not only creates a connection with your audience, but also reiterates the importance of your topic to them in particular or “the bigger picture.”
Practicing for effective presentation
Once you’ve completed a draft, read your speech to a friend or in front of a mirror. When you’ve finished reading, ask the following questions:
- Which pieces of information are clearest?
- Where did I connect with the audience?
- Where might listeners lose the thread of my argument or description?
- Where might listeners become bored?
- Where did I have trouble speaking clearly and/or emphatically?
- Did I stay within my time limit?
Other resources
- Toastmasters International is a nonprofit group that provides communication and leadership training.
- Allyn & Bacon Publishing’s Essence of Public Speaking Series is an extensive treatment of speech writing and delivery, including books on using humor, motivating your audience, word choice and presentation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Boone, Louis E., David L. Kurtz, and Judy R. Block. 1997. Contemporary Business Communication . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Ehrlich, Henry. 1994. Writing Effective Speeches . New York: Marlowe.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.6: Speech Organization
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 9048

- Ganga S. Dhanesh@National University of Singapore
- Millersville University via Public Speaking Project
Members of different cultural groups have varying preferences for different organizational patterns such as linear and holistic.
linear pattern
Speakers from low-context cultures often use linear patterns, such as cause- and-effect, problem-solution, chronological and spatial. In these patterns the speaker develops the main idea step by step, relying on facts and data to support the main argument. The main points and sub-points are connected via transitions, internal previews and summaries. The speaker relies more on facts and data, rather than on stories and emotional appeals, and contextual understanding is not emphasized. However, other speakers, mostly from high-context cultures, use holistic and configural organizational patterns that are more indirect than the linear patterns (Lieberman, 1994).
We have no hope of solving our problems without harnessing the diversity, the energy, and the creativity of all our people. ~ Roger Wilkins

holistic pattern
In holistic patterns, instead of directly and explicitly presenting key ideas, the speaker uses examples and stories to convey the main idea and leaves it to the audience to interpret the message encoded in the examples and stories told. The main points and sub- points are connected through implication rather than by clear bridges and transitions. Cheryl Jorgensen Earp (1993; as cited in Jaffe, 2004) has identified three distinct types of holistic organizational patterns: wave, spiral and star.
wave pattern
In the wave pattern, speakers adopt a crest-trough wave pattern in which they use examples and stories to slowly build up to the main point at the crest of the wave. The speaker then winds down and repeats the pattern, reiterating main points or introducing new points at the peaks. Speeches that follow the wave pattern usually end dramatically, at the crest. Ceremonial speakers often employ this pattern, using repetitive phrases to build up to the crest.

spiral pattern
A speaker employing the spiral pattern builds up dramatic intensity by moving from smaller and less-intense scenarios to bigger and more-intense scenarios, in an upward spiral. A speech about disciplining a child might use a spiral pattern. First, the speaker could say that for a small transgression a child might be given a time-out. The next scenario could describe a larger transgression and a bigger punishment such as being grounded for a day. Subsequent scenarios could build further in intensity.
star pattern
A variation of the more linear topical pattern, the star pattern presents a set of main points connected by an underlying common theme. For different audiences, speakers will start with different main points, but all main points will be united by one theme. For instance, while delivering a speech on “save the dolphins” to primary school students, the speaker might start with a main point that appeals to children, such as the “born to be free” argument, and then cover the other main points. However, when addressing marine biologists, the speaker might start with the main point that keeping dolphins in captivity is harmful to their health. Then the speaker would cover the remaining points, all tied to the theme of saving dolphins.
All patterns, whether linear or holistic, require careful and skillful planning and organization. When addressing a diverse audience, public speakers should make an effort to adjust their organizational patterns to reflect their audiences’ preference.


25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Speech Writing
- Updated on
- Jan 16, 2024

The power of good, inspiring, motivating, and thought-provoking speeches can never be overlooked. If we retrospect, a good speech has not only won people’s hearts but also has been a verbal tool to conquer nations. For centuries, many leaders have used this instrument to charm audiences with their powerful speeches. Apart from vocalizing your speech perfectly, the words you choose in a speech carry immense weight, and practising speech writing begins with our school life. Speech writing is an important part of the English syllabus for Class 12th, Class 11th, and Class 8th to 10th. This blog brings you the Speech Writing format, samples, examples, tips, and tricks!
This Blog Includes:
What is speech writing, speech in english language writing, how do you begin an english-language speech, introduction, how to write a speech, speech writing samples, example of a great speech, english speech topics, practice time.
Must Read: Story Writing Format for Class 9 & 10
Speech writing is the art of using proper grammar and expression to convey a thought or message to a reader. Speech writing isn’t all that distinct from other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of certain distinct punctuation and writing style techniques. While writing the ideal speech might be challenging, sticking to the appropriate speech writing structure will ensure that you never fall short.
“There are three things to aim at in public speaking: first, to get into your subject, then to get your subject into yourself, and lastly, to get your subject into the heart of your audience.”- Alexander Gregg
The English language includes eight parts of speech i.e. nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives 410 , adverbs , prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Noun- A noun is a word that describes anything, such as an animal, a person, a place, or an emotion. Nouns are the building blocks for most sentences.
- Pronoun – Pronouns are words that can be used in place of nouns. They are used so that we don’t have to repeat words. This makes our writing and speaking much more natural.
- Verb – A verb is a term that implies activity or ‘doing.’ These are very vital for your children’s grammar studies, as a sentence cannot be complete without a verb.
- Adjective – An adjective is a term that describes something. An adjective is frequently used before a noun to add extra information or description.
- Prepositions- A preposition is a term that expresses the location or timing of something in relation to something else.
- Conjunction- Because every language has its own set of conjunctions, English conjunctions differ from those found in other languages. They’re typically used as a connecting word between two statements, concepts, or ideas.
- Interjections- Interjections are words that are used to describe a strong emotion or a sudden feeling.
Relevant Read: Speech on the Importance of English
The way you start your English speech can set the tone for the remainder of it. This semester, there are a variety of options for you to begin presentations in your classes. For example, try some of these engaging speech in English language starters.
- Rhetorical questions : A rhetorical question is a figure of speech that uses a question to convey a point rather than asking for a response. The answer to a rhetorical question may be clear, yet the questioner asks it to emphasize the point. Rhetorical questions may be a good method for students to start their English speeches. This method of introducing your material might be appealing to the viewers and encourage them to consider how they personally relate to your issue.
- Statistics: When making an instructive or persuasive speech in an English class, statistics can help to strengthen the speaker’s authority and understanding of the subject. To get your point over quickly and create an emotional response, try using an unexpected statistic or fact that will resonate with the audience.
- Set up an imaginary scene: Create an imaginary situation in your audience’s thoughts if you want to persuade them to agree with you with your speech. This method of starting your speech assists each member of the audience in visualizing a fantastic scenario that you wish to see come true.
Relevant Read: Reported Speech Rules With Exercises
Format of Speech Writing
Here is the format of Speech Writing:
- Introduction : Greet the audience, tell them about yourself and further introduce the topic.
- Body : Present the topic in an elaborate way, explaining its key features, pros and cons, if any and the like.
- Conclusion : Summary of your speech, wrap up the topic and leave your audience with a compelling reminder to think about!
Let’s further understand each element of the format of Speech Writing in further detail:
After the greetings, the Introduction has to be attention-getting. Quickly get people’s attention. The goal of a speech is to engage the audience and persuade them to think or act in your favour. The introduction must effectively include:
- A brief preview of your topic.
- Define the outlines of your speech. (For example, I’ll be talking about…First..Second…Third)
- Begin with a story, quote, fact, joke, or observation in the room. It shouldn’t be longer than 3-4 lines. (For Example: “Mahatma Gandhi said once…”, or “This topic reminds me of an incident/story…”)
This part is also important because that’s when your audience decides if the speech is worth their time. Keep your introduction factual, interesting, and convincing.
It is the most important part of any speech. You should provide a number of reasons and arguments to convince the audience to agree with you.
Handling objections is an important aspect of speech composition. There is no time for questions or concerns since a speech is a monologue. Any concerns that may occur during the speech will be addressed by a powerful speech. As a result, you’ll be able to respond to questions as they come in from the crowd. To make speech simpler you can prepare a flow chart of the details in a systematic way.
For example: If your speech is about waste management; distribute information and arrange it according to subparagraphs for your reference. It could include:
- What is Waste Management?
- Major techniques used to manage waste
- Advantages of Waste Management
- Importance of Waste Management
The conclusion should be something that the audience takes with them. It could be a reminder, a collective call to action, a summary of your speech, or a story. For example: “It is upon us to choose the fate of our home, the earth by choosing to begin waste management at our personal spaces.”
After concluding, add a few lines of gratitude to the audience for their time.
For example: “Thank you for being a wonderful audience and lending me your time. Hope this speech gave you something to take away.”

Practice Your Speech Writing with these English Speech topics for students !
A good speech is well-timed, informative, and thought-provoking. Here are the tips for writing a good school speech:
Speech Sandwich of Public Speaking
The introduction and conclusion must be crisp. People psychologically follow the primacy effect (tendency to remember the first part of the list/speech) and recency effect (tendency to recall the last part of the list/speech).
Use Concrete Facts
Make sure you thoroughly research your topic. Including facts appeals to the audience and makes your speech stronger. How much waste is managed? Give names of organisations and provide numerical data in one line.
Use Rhetorical Strategies and Humour
Include one or two open-ended or thought-provoking questions. For Example: “Would we want our future generation to face trouble due to global warming?” Also, make good use of humour and convenient jokes that engages your audience and keeps them listening.
Check Out: Message Writing
Know your Audience and Plan Accordingly
This is essential before writing your speech. To whom is it directed? The categorised audience on the basis of –
- Knowledge of the Topic (familiar or unfamiliar)
Use the information to formulate the speech accordingly, use information that they will understand, and a sentence that they can retain.
Timing Yourself is Important
An important aspect of your speech is to time yourself. Don’t write a speech that exceeds your word limit. Here’s how can decide the right timing for your speech writing:
- A one-minute speech roughly requires around 130-150 words
- A two-minute speech requires roughly around 250-300 words
Recommended Read: Letter Writing
Speech Writing Examples
Here are some examples to help you understand how to write a good speech. Read these to prepare for your next speech:
Write a speech to be delivered in the school assembly as Rahul/ Rubaina of Delhi Public School emphasises the importance of cleanliness, implying that the level of cleanliness represents the character of its residents. (150-200 words)
“Cleanliness is next to godliness,” said the great John Wesley. Hello, respected principal, instructors, and good friends. Today, I, Rahul/Rubaina, stand in front of you all to emphasise the significance of cleanliness.
Cleanliness is the condition or attribute of being or remaining clean. Everyone must learn about cleaning, hygiene, sanitation, and the different diseases that are produced by unsanitary circumstances. It is essential for physical well-being and the maintenance of a healthy atmosphere at home and at school. A filthy atmosphere invites a large number of mosquitos to grow and spread dangerous diseases. On the other side, poor personal cleanliness causes a variety of skin disorders as well as lowered immunity.
Habits formed at a young age become ingrained in one’s personality. Even if we teach our children to wash their hands before and after meals, brush their teeth and bathe on a regular basis, we are unconcerned about keeping public places clean. On October 2, 2014, the Indian Prime Minister began the “Swachh Bharat” programme to offer sanitation amenities to every family, including toilets, solid and liquid waste disposal systems, village cleanliness, and safe and appropriate drinking water supplies. Teachers and children in schools are actively participating in the ‘Clean India Campaign’ with zeal and excitement.
Good health ensures a healthy mind, which leads to better overall productivity, higher living standards, and economic development. It will improve India’s international standing. As a result, a clean environment is a green environment with fewer illnesses. Thus, cleanliness is defined as a symbol of mental purity.
Thank you very much.
Relevant Read: Speech on Corruption
You are Sahil/Sanya, the school’s Head Girl/Head Boy. You are greatly troubled by the increasing instances of aggressive behaviour among your students. You decide to speak about it during the morning assembly. Create a speech about “School Discipline.” (150 – 200 words)
INDISCIPLINE IN SCHOOLS,
It has been reported that the frequency of fights and incidences of bullying in our school has increased dramatically in the previous several months. Good morning to everyone present. Today, I, Sahil/Sanya, your head boy/girl, am here to shed light on the serious topic of “Increased Indiscipline in Schools.”
It has come to light that instructor disobedience, bullying, confrontations with students, truancy, and insults are becoming more widespread. Furthermore, there have been reports of parents noticing a shift in their children’s attitudes. As a result, many children are suffering emotionally, psychologically, and physically. The impact of this mindset on children at a young age is devastating and irreversible.
Not to mention the harm done to the school’s property. Theft of chalk, scribbling on desks, walls and lavatory doors, destruction of CCTV cameras and so forth. We are merely depriving ourselves of the comforts granted to us by doing so.
Following numerous meetings, it was determined that the main reasons for the problem were a lack of sufficient guidance, excessive use of social media, and peer pressure. The council is working to make things better. Everyone is required to take life skills classes. Counselling, motivating, and instilling friendly ideals will be part of the curriculum. Seminars for parents and students will be held on a regular basis.
A counsellor is being made available to help you all discuss your sentiments, grudges, and personal problems. We are doing everything we can and expect you to do the same.
So, let us work together to create an environment in which we encourage, motivate, assist, and be nice to one another because we are good and civilised humans capable of a great deal of love.
Relevant Read: How to Write a Speech on Discipline?
The current increase in incidences of violent student misbehaviour is cause for alarm for everyone. Students who learn how to manage their anger can help to alleviate the situation. Write a 150-200-word speech about the topic to be delivered at the school’s morning assembly. (10)
HOW TO CONTROL ANGER
Honourable Principal, Respected Teachers, and Dear Friends, I’d like to share a few “Ways to Manage Anger” with you today.
The growing intolerance among the younger generation, which is resulting in violence against teachers, is cause for severe concern. The guru-shishya parampara is losing its lustre. Aggressive behaviour in students can be provoked by a variety of factors, including self-defence, stressful circumstance, over-stimulation, or a lack of adult supervision.
It has become imperative to address the situation. Life skills workshops will be included in the curriculum. Teachers should be trained to deal with such stubborn and confrontational behaviours. Meditation and deep breathing are very beneficial and should be practised every morning. Students should be taught to count to ten before reacting angrily. Sessions on anger control and its importance must also be held.
Remember that Anger is one letter away from danger. It becomes much more crucial to be able to control one’s rage. It’s never too late to start, as a wise man once said.
“Every minute you stay angry, you lose sixty seconds of peace of mind.”
Relevant Read: English Speech Topics for Students
Martin Luther King Jr’s ‘I Have A Dream’ is one of his most famous speeches. Its impact has lasted through generations. The speech is written by utilising the techniques above. Here are some examples:
“still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination” – emotive Language
“In a sense, we’ve come to our nation’s capital to cash a check” – personalising the speech
“to stand up for freedom together” – a call to action.
Importantly, this is an example of how the listener comes first while drafting a speech. The language chosen appeals to a specific sort of audience and was widely utilised in 1963 when the speech was delivered.
- The Best Day of My Life
- Social Media: Bane or Boon?
- Pros and Cons of Online Learning
- Benefits of Yoga
- If I had a Superpower
- I wish I were ______
- Environment Conservation
- Women Should Rule the World!
- The Best Lesson I Have Learned
- Paperbacks vs E-books
- How to Tackle a Bad Habit?
- My Favorite Pastime/Hobby
- Understanding Feminism
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Is it real or not?
- Importance of Reading
- Importance of Books in Our Life
- My Favorite Fictional Character
- Introverts vs Extroverts
- Lessons to Learn from Sports
- Beauty is in the eye of the beholder
Also Read: How to Ace IELTS Writing Section?
Ans. Speech writing is the process of communicating a notion or message to a reader by employing proper punctuation and expression. Speech writing is similar to other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of some different punctuation and writing structure techniques.
Ans. Before beginning with the speech, choose an important topic. Create an outline; rehearse your speech, and adjust the outline based on comments from the rehearsal. This five-step strategy for speech planning serves as the foundation for both lessons and learning activities.
Ans. Writing down a speech is vital since it helps you better comprehend the issue, organises your thoughts, prevents errors in your speech, allows you to get more comfortable with it, and improves its overall quality.
Speech writing and public speaking are effective and influential. Hope this blog helped you know the various tips for writing the speech people would want to hear. If you need help in making the right career choices at any phase of your academic and professional journey, our Leverage Edu experts are here to guide you. Sign up for a free session now!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
14 comments
This site has been very helpful to me
Wow i have gained more knowledge
lt’s a nice One and l have loved it
Thank you for your feedback! Happy that you loved it.
Thank you for your feedback!
Very educating.
thanks for your valuable feedback
This is indeed very helpful
Thanks for your valuable feedback!
I have learned alot thank you
Hi, Thanks for your feedback!
Wow so reliable, thanks.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Rice Speechwriting
Beginners guide to what is a speech writing, what is a speech writing: a beginner’s guide, what is the purpose of speech writing.
The purpose of speech writing is to craft a compelling and effective speech that conveys a specific message or idea to an audience. It involves writing a script that is well-structured, engaging, and tailored to the speaker’s delivery style and the audience’s needs.
Have you ever been called upon to deliver a speech and didn’t know where to start? Or maybe you’re looking to improve your public speaking skills and wondering how speech writing can help. Whatever the case may be, this beginner’s guide on speech writing is just what you need. In this blog, we will cover everything from understanding the art of speech writing to key elements of an effective speech. We will also discuss techniques for engaging speech writing, the role of audience analysis in speech writing, time and length considerations, and how to practice and rehearse your speech. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how speech writing can improve your public speaking skills and make you feel confident when delivering your next big presentation.
Understanding the Art of Speech Writing
Crafting a speech involves melding spoken and written language. Tailoring the speech to the audience and occasion is crucial, as is captivating the audience and evoking emotion. Effective speeches utilize rhetorical devices, anecdotes, and a conversational tone. Structuring the speech with a compelling opener, clear points, and a strong conclusion is imperative. Additionally, employing persuasive language and maintaining simplicity are essential elements. The University of North Carolina’s writing center greatly emphasizes the importance of using these techniques.
The Importance of Speech Writing
Crafting a persuasive and impactful speech is essential for reaching your audience effectively. A well-crafted speech incorporates a central idea, main point, and a thesis statement to engage the audience. Whether it’s for a large audience or different ways of public speaking, good speech writing ensures that your message resonates with the audience. Incorporating engaging visual aids, an impactful introduction, and a strong start are key features of a compelling speech. Embracing these elements sets the stage for a successful speech delivery.
The Role of a Speech Writer
A speechwriter holds the responsibility of composing speeches for various occasions and specific points, employing a speechwriting process that includes audience analysis for both the United States and New York audiences. This written text is essential for delivering impactful and persuasive messages, often serving as a good start to a great speech. Utilizing NLP terms like ‘short sentences’ and ‘persuasion’ enhances the content’s quality and relevance.
Key Elements of Effective Speech Writing
Balancing shorter sentences with longer ones is essential for crafting an engaging speech. Including subordinate clauses and personal stories caters to the target audience and adds persuasion. The speechwriting process, including the thesis statement and a compelling introduction, ensures the content captures the audience’s attention. Effective speech writing involves research and the generation of new ideas. Toastmasters International and the Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill provide valuable resources for honing English and verbal skills.
Clarity and Purpose of the Speech
Achieving clarity, authenticity, and empathy defines a good speech. Whether to persuade, inform, or entertain, the purpose of a speech is crucial. It involves crafting persuasive content with rich vocabulary and clear repetition. Successful speechwriting demands a thorough understanding of the audience and a compelling introduction. Balancing short and long sentences is essential for holding the audience’s attention. This process is a fusion of linguistics, psychology, and rhetoric, making it an art form with a powerful impact.
Identifying Target Audience
Tailoring the speechwriting process hinges on identifying the target audience. Their attention is integral to the persuasive content, requiring adaptation of the speechwriting process. A speechwriter conducts audience analysis to capture the audience’s attention, employing new york audience analysis methods. Ensuring a good introduction and adapting the writing process for the target audience are key features of a great speech. Effective speechwriters prioritize the audience’s attention to craft compelling and persuasive speeches.
Structuring Your Speech
The speechwriting process relies on a well-defined structure, crucial to both the speech’s content and the writing process. It encompasses a compelling introduction, an informative body, and a strong conclusion. This process serves as a foundation for effective speeches, guiding the speaker through a series of reasons and a persuasive speechwriting definition. Furthermore, the structure, coupled with audience analysis, is integral to delivering a great speech that resonates with the intended listeners.
The Process of Writing a Speech
Crafting a speech involves composing the opening line, developing key points, and ensuring a strong start. Effective speech writing follows a structured approach, incorporating rhetorical questions and a compelling introduction. A speechwriter’s process includes formulating a thesis statement, leveraging rhetorical questions, and establishing a good start. This process entails careful consideration of the audience, persuasive language, and engaging content. The University of North Carolina’s writing center emphasizes the significance of persuasion, clarity, and concise sentences in speechwriting.
Starting with a Compelling Opener
A speechwriting process commences with a captivating opening line and a strong introduction, incorporating the right words and rhetorical questions. The opening line serves as both an introduction and a persuasive speech, laying the foundation for a great speechwriting definition. Additionally, the structure of the speechwriting process, along with audience analysis, plays a crucial role in crafting an effective opening. Considering these elements is imperative when aiming to start a speech with a compelling opener.
Developing the Body of the Speech
Crafting the body of a speech involves conveying the main points with persuasion and precision. It’s essential to outline the speechwriting process, ensuring a clear and impactful message. The body serves as a structured series of reasons, guiding the audience through the content. Through the use of short sentences and clear language, the body of the speech engages the audience, maintaining their attention. Crafting the body involves the art of persuasion, using the power of words to deliver a compelling message.
Crafting a Strong Conclusion
Crafting a strong conclusion involves reflecting the main points of the speech and summarizing key ideas, leaving the audience with a memorable statement. It’s the final chance to leave a lasting impression and challenge the audience to take action or consider new perspectives. A good conclusion can make the speech memorable and impactful, using persuasion and English language effectively to drive the desired response from the audience. Toastmasters International emphasizes the importance of a strong conclusion in speechwriting for maximum impact.
Techniques for Engaging Speech Writing
Engage the audience’s attention using rhetorical questions. Create a connection through anecdotes and personal stories. Emphasize key points with rhetorical devices to capture the audience’s attention. Maintain interest by varying sentence structure and length. Use visual aids to complement the spoken word and enhance understanding. Incorporate NLP terms such as “short sentences,” “writing center,” and “persuasion” to create engaging and informative speech writing.
Keeping the Content Engaging
Captivating the audience’s attention requires a conversational tone, alliteration, and repetition for effect. A strong introduction sets the tone, while emotional appeals evoke responses. Resonating with the target audience ensures engagement. Utilize short sentences, incorporate persuasion, and vary sentence structure to maintain interest. Infuse the speech with NLP terms like “writing center”, “University of North Carolina”, and “Toastmasters International” to enhance its appeal. Engaging content captivates the audience and compels them to listen attentively.
Maintaining Simplicity and Clarity
To ensure clarity and impact, express ideas in short sentences. Use a series of reasons and specific points to effectively convey the main idea. Enhance the speech with the right words for clarity and comprehension. Simplify complex concepts by incorporating anecdotes and personal stories. Subordinate clauses can provide structure and clarity in the speechwriting process.
The Power of Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal cues, such as body language and gestures, can add emphasis to your spoken words, enhancing the overall impact of your speech. By incorporating visual aids and handouts, you can further augment the audience’s understanding and retention of key points. Utilizing a conversational tone and appropriate body language is crucial for establishing a genuine connection with your audience. Visual aids and gestures not only aid comprehension but also help in creating a lasting impression, captivat**ing** the audience with compelling visual elements.
The Role of Audience Analysis in Speech Writing
Tailoring a speech to the audience’s needs is paramount. Demographics like age, gender, and cultural background must be considered. Understanding the audience’s interests and affiliation is crucial for delivering a resonating speech. Content should be tailored to specific audience points of interest, engaging and speaking to their concerns.
Understanding Audience Demographics
Understanding the varied demographics of the audience, including age and cultural diversity, is crucial. Adapting the speech content to resonate with a diverse audience involves tailoring it to the different ways audience members process and interpret information. This adaptation ensures that the speech can effectively engage with the audience, no matter their background or age. Recognizing the importance of understanding audience demographics is key for effective audience analysis. By considering these factors, the speech can be tailored to meet the needs and preferences of the audience, resulting in a more impactful delivery.
Considering the Audience Size and Affiliation
When tailoring a speech, consider the audience size and affiliation to influence the tone and content effectively. Adapt the speech content and delivery to resonate with a large audience and different occasions, addressing the specific points of the target audience’s affiliation. By delivering a speech tailored to the audience’s size and specific points of affiliation, you can ensure that your message is received and understood by all.
Time and Length Considerations in Speech Writing
Choosing the appropriate time for your speech and determining its ideal length are crucial factors influenced by the purpose and audience demographics. Tailoring the speech’s content and structure for different occasions ensures relevance and impact. Adapting the speech to specific points and the audience’s demographics is key to its effectiveness. Understanding these time and length considerations allows for effective persuasion and engagement, catering to the audience’s diverse processing styles.
Choosing the Right Time for Your Speech
Selecting the optimal start and opening line is crucial for capturing the audience’s attention right from the beginning. It’s essential to consider the timing and the audience’s focus to deliver a compelling and persuasive speech. The right choice of opening line and attention to the audience set the tone for the speech, influencing the emotional response. A good introduction and opening line not only captivate the audience but also establish the desired tone for the speech.
Determining the Ideal Length of Your Speech
When deciding the ideal length of your speech, it’s crucial to tailor it to your specific points and purpose. Consider the attention span of your audience and the nature of the event. Engage in audience analysis to understand the right words and structure for your speech. Ensure that the length is appropriate for the occasion and target audience. By assessing these factors, you can structure your speech effectively and deliver it with confidence and persuasion.
How to Practice and Rehearse Your Speech
Incorporating rhetorical questions and anecdotes can deeply engage your audience, evoking an emotional response that resonates. Utilize visual aids, alliteration, and repetition to enhance your speech and captivate the audience’s attention. Effective speechwriting techniques are essential for crafting a compelling introduction and persuasive main points. By practicing a conversational tone and prioritizing clarity, you establish authenticity and empathy with your audience. Develop a structured series of reasons and a solid thesis statement to ensure your speech truly resonates.
Techniques for Effective Speech Rehearsal
When practicing your speech, aim for clarity and emphasis by using purposeful repetition and shorter sentences. Connect with your audience by infusing personal stories and quotations to make your speech more relatable. Maximize the impact of your written speech when spoken by practicing subordinate clauses and shorter sentences. Focus on clarity and authenticity, rehearsing your content with a good introduction and a persuasive central idea. Employ rhetorical devices and a conversational tone, ensuring the right vocabulary and grammar.
How Can Speech Writing Improve Your Public Speaking Skills?
Enhancing your public speaking skills is possible through speech writing. By emphasizing key points and a clear thesis, you can capture the audience’s attention. Developing a strong start and central idea helps deliver effective speeches. Utilize speechwriting techniques and rhetorical devices to structure engaging speeches that connect with the audience. Focus on authenticity, empathy, and a conversational tone to improve your public speaking skills.
In conclusion, speech writing is an art that requires careful consideration of various elements such as clarity, audience analysis, and engagement. By understanding the importance of speech writing and the role of a speech writer, you can craft effective speeches that leave a lasting impact on your audience. Remember to start with a compelling opener, develop a strong body, and end with a memorable conclusion. Engaging techniques, simplicity, and nonverbal communication are key to keeping your audience captivated. Additionally, analyzing your audience demographics and considering time and length considerations are vital for a successful speech. Lastly, practicing and rehearsing your speech will help improve your public speaking skills and ensure a confident delivery.
Expert Tips for Choosing Good Speech Topics
Master the art of how to start a speech.

Popular Posts
How to write a retirement speech that wows: essential guide.
June 4, 2022
The Best Op Ed Format and Op Ed Examples: Hook, Teach, Ask (Part 2)
June 2, 2022
Inspiring Awards Ceremony Speech Examples
November 21, 2023
Mastering the Art of How to Give a Toast
Short award acceptance speech examples: inspiring examples, best giving an award speech examples.
November 22, 2023
Sentence Sense Newsletter

III.2 Varying one’s speech: Discourse patterns
2.1 introduction, 2.1.1 theoretical background: discourse patterns and registers, 2.1.2 research on linguistic variation in ancient greek drama, 2.1.3 methodology in this chapter, 2.2 distribution as input for interpretation, 2.2.1 δέ, 2.2.2 καί, 2.2.3 τε, 2.2.4 γάρ, 2.2.5 γε and δῆτα, 2.2.6 ἀλλά, 2.2.7 μέν, 2.2.8 δή, 2.2.9 οὖν, 2.3 conclusions, appendix: non-significant distributions.
- Fellowships
- Student Programs
- Self-Directed Study
- Faculty Development
Publications
- Browse all online
- Classics@ Journal
- Classical Inquiries⬀
- CHS Research Bulletin⬀
- Digital Humanities Projects
- Prospective Authors
Who We Are:
Forgot password.
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
- Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Get a free Grammar Adventure! Choose a single Adventure and add coupon code ADVENTURE during checkout. (All-Adventure licenses aren’t included.)
Sign up or login to use the bookmarking feature.
- 14 Understanding Writing Patterns

Start-Up Activity
Display the word “pattern.” Ask students to try to explain the term. Most students will explain it as a type of design as you would find in fabric. Inform them that the word has a second definition—a guide to making something.
Explain that people follow patterns to make many different things like clothes and models. Tell students that writing follows patterns, too, and they will learn about four writing patterns in this chapter. Read about the first pattern—time order—on page 66. Ask students if they have ever used this pattern.
Think About It
“Writing and tree houses have this in common: They both must have a strong frame.”
—Dave Kemper
Sequencing with a Time Line
Use time lines for critical thinking.

Using Time-Order Transitions
Teach about chronological transitions.

State Standards Covered in This Chapter
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.2.5
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.2.2
LAFS Covered in This Chapter
Lafs.2.w.2.5, lafs.2.w.1.2, teks covered in this chapter, 110.4.b.11.c, 110.4.b.11.d, 110.4.b.11.a, 110.4.b.11.b, 110.4.b.12.b, page 067 from write away.
This pattern helps organize the details in descriptions. Read and discuss the description of an igloo on this page. Then consider describing a topic as a class project, using location connecting words as needed.
Related Resource Tags
Click to view a list of tags that tie into other resources on our site
Page 068 from Write Away
The pattern helps organize details when giving examples, parts, or types. Read and discuss this explanation, which explains why big dogs are popular. Then consider developing an explanation as a class project, using example connection words as needed.
Page 069 from Write Away
Compare and contrast.
This pattern shows how two topics are the same and different. Read and discuss the example on this page, which compares grizzly and polar bears. The first part shows how the two bears are similar; the second part shows how they are different. Then consider developing a comparison of two other animals as a class project.
Comparing with a Venn Diagram
Analyze similarities and differences.

- 01 Starting to Write
- 02 Using the Writing Process
- 03 The Qualities of Writing
- 04 Keeping an Idea Notebook
- 05 Prewriting
- 06 Writing the First Draft
- 07 Revising Your Writing
- 08 Getting Help from a Partner
- 09 Checking for Errors
- 10 Publishing Your Writing
- 11 Writing Sentences
- 12 Combining Sentences
- 13 Writing Paragraphs
- 15 Writing in Journals
- 16 Writing Friendly Notes
- 17 Writing Friendly Letters and Emails
- 18 Writing All-About-Me Stories
- 19 Writing About Books
- 20 Making Counting Books
- 21 Writing News Stories
- 22 Writing Business Letters and Emails
- 23 How-To Writing
- 24 Making Posters
- 25 Making Picture Dictionaries
- 26 Writing Reports
- 27 Writing Circle Stories
- 28 Writing Add-On Stories
- 29 Writing Fables
- 30 Writing Mysteries
- 31 Writing Small Poems
- 32 Making Shape Poems
- 33 Rhyming Poems
- 34 Using the Library
- 35 Using a Computer
- 36 Reading Graphics
- 37 Reading New Words
- 38 Reading to Understand
- 39 Using Phonics
- 40 Making New Words
- 41 Making Contractions
- 42 Using a Glossary
- 43 Learning to View
- 44 Learning to Listen
- 45 Learning to Interview
- 46 Performing Stories
- 47 Telling Stories
- 48 Giving Oral Reports
- 49 Using Graphic Organizers
- 50 Thinking Clearly
- 51 Thinking Creatively
- 52 Working in Groups
- 53 Taking Tests
- 54 Proofreader's Guide
- 55 Student Almanac

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learning Objectives. Differentiate among the common speech organizational patterns: categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological. Understand how to choose the best organizational pattern, or combination of patterns, for a specific speech.
develop a thesis statement (central idea) that summarizes what you will talk about in your speech. select the best organizational pattern for the main points of your speech. develop a preparation outline and speaking outline for your speech. identify the elements of an outline. identify the principles of outlining.
The content, of course, but also the structure. All great speakers overlay their content on a well-known structure. Your speech structure is the glue that binds your points together. Without it, you cannot really have the impact you desire to have on the audience. The beauty of this is that a good structure is so subtle it is almost invisible.
The writing pattern called definition is used to explain the meaning of a word or phrase. 3:29: Words that signal this pattern are: is, refers to, means, is defined as, is called, is characterized by, and entails. 3:43: The structure of this writing pattern consists of a definition of the key word or phrase followed by examples or additional ...
A spatial pattern organizes each main point in a directional structure, connecting each main point to a whole. This structure is used for informative speeches where the topic is organized by location, geography, or moving through a space ("spatial" is the adjective form of "space"). For example, a speech about the parts of a resume ...
Ethos refers to an appeal to your audience by establishing your authenticity and trustworthiness as a speaker. If you employ pathos, you appeal to your audience's emotions. Using logos includes the support of hard facts, statistics, and logical argumentation. The most effective speeches usually present a combination these rhetorical strategies.
Introduction1. "Rhetoric," wrote Aristotle, "is the power of determining in a particular case what are the available means of persuasion.". This report reviews some effective means for the rhetoric of persuasive communication in speeches written by congressional staff for Senators and Representatives.
Patterns of organization. Rhetorical modes. Rhetorical styles. Writing Patterns Help You: • Focus your attention on a text and anticipate where it is going. Remember what you read. Develop your own writing. Analyze: break something down into its parts and examine them.
This publication about speech writing and types of speeches is the second of a three-part series about developing effective public speaking skills. This series also covers an introduction to public speaking and public speaking tools. ... Informative Speech. If the speech's purpose is to define, explain, describe, or demonstrate, it is an ...
spiral pattern. A speaker employing the spiral pattern builds up dramatic intensity by moving from smaller and less-intense scenarios to bigger and more-intense scenarios, in an upward spiral. A speech about disciplining a child might use a spiral pattern. First, the speaker could say that for a small transgression a child might be given a time ...
Speech organizational patterns, or methods of organization, refers to the way the information is arranged within the speech. That is to say, the writer chooses which main point to discuss first ...
Example 1. Write a speech to be delivered in the school assembly as Rahul/ Rubaina of Delhi Public School emphasises the importance of cleanliness, implying that the level of cleanliness represents the character of its residents. (150-200 words) "Cleanliness is next to godliness," said the great John Wesley.
The speechwriting process relies on a well-defined structure, crucial to both the speech's content and the writing process. It encompasses a compelling introduction, an informative body, and a strong conclusion. This process serves as a foundation for effective speeches, guiding the speaker through a series of reasons and a persuasive ...
The term "discourse pattern" was developed in Construction Grammar (CxG), a cognitive approach to language use. This approach assumes that all the linguistic knowledge of speakers and writers is stored in symbolic pairings of form and meaning, called "constructions.".
In this video, we'll go over eight of the most common writing patterns. They are definition, classification, generalization and example, cause and effect, comparison/contrast, list, sequence, and summary. We'll go over each one in turn. We'll describe the purpose of each pattern and list some signal words for them.
The ways you use language and vocabulary when writing the words of a speech will depend on the audience the purposeand you are writing for ; for example, in a speech to a group of teachers and parents giving your views on a recent proposal, formal language is most appropriate. Tips for writing a speech . Language - think about: •
Oct 7, 2018 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 101 likes • 165,420 views. JasonSumapig. Speech Writing. Education. 1 of 40. Download now. Principle of Speech Writing - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
In short, the physical and sensory modalities of speech and writing are as distinctly different as the physical processes of speaking and writing. And here too we have an intriguing borderline example: sign language is a kind of "speaking" that is visual-and-spatial, yet also temporal. Speech and writing as different linguistic products ...
The important phrases that learners don't often notice include the following: "First, it will consider …," "then it will take a look at …," and "in conclusion, the paper will explain ...
Writing Patterns Common Writing Patterns Type Description Signal Words Definition Explain the meaning of a word or phrase is, refers to, means, is defined as, is called, is characterized by, entails Classification Divide a topic into parts based on specific characteristics classified as, comprises, is comprised of, consists of, elements, kinds ...
Start-Up Activity. Display the word "pattern.". Ask students to try to explain the term. Most students will explain it as a type of design as you would find in fabric. Inform them that the word has a second definition—a guide to making something. Explain that people follow patterns to make many different things like clothes and models.