stylistic analysis Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords

Analysing Linguistic Stylistic Devices in The Adventures of Tom Sawyer and So Long a Letter: A Comparative Appraisal
This research work focuses on linguistic stylistic analysis of Mark Twain’s The Adventures of Tom Sawyer and Mariama Bâ’s So Long a Letter. It aims to identify the various translation procedures used in each novel in order to establish a comparison between the different translation procedures and style of each translator of modern and old English. A sampling method has been used to carry out this research work. Thus, one extract has been selected with its corresponding translation from the French and English versions of each novel. The results show that, in The Adventures of Tom Sawyer, the translator has used predominantly adaptation for his translation representing 32.32% in both selected extracts whereas in So Long a Letter, the translator has adopted predominantly literal translation representing a proportion of 28.48% in order to preserve the sustained register of the source text. However, both translators have also used other translation procedures in lower proportions depending on the context orientation. It has been noted that translation methods such as calque has been used only once whereas borrowing is nonexistent in the selected extracts from both literary works.
Religiosity and Romanticism in Mandar's Love Poem Text: Stylistic Analysis
The purpose of this study was to find the lexical form of religiosity and romanticism contained in the Mandar Sayang-sayang poetry. The type of research used is qualitative research, with qualitative descriptive methods. Sampling was done by using purposive sampling technique. The data collection procedure used a literature review procedure, listening method, note-taking technique, and reflective-introspective. The data analysis model used is an interactive model (interactive model). The results of the study found that the lexical containing the meaning of religiosity was found in the verse at the beginning of the text Sayang-sayang Mandar. Meanwhile, the lexical containing the expression of romanticism is found in almost all stanzas of the Mandar Sayang-Sayang text. The Mandar affectionate poetry is an expression of religiosity and the character of mutual love for fellow Mandar people and for all human beings in the world.
Ideological Manipulation in Twitter Communication: A Critical Stylistic Analysis of Donald Trump's Tweets
Donald Trump’s use of Twitter as a modality to defame opponents, antagonize media outlets and even glorify violence is an enduring legacy for political campaigns, presidential rhetoric and argumentative debates. This nontraditional use of social media as a political communication tool has invited Twitter’s fact-checking editorial decisions, alienated some of Trump’s supporters and attracted worldwide criticism. Using purposive sampling, the present paper employs the ten textual-conceptual functions of critical stylistics to analyze a dataset of Trump’s tweets on domestic and international political issues published between 2011 and 2020 and assembled from the monitor corpus Trump Twitter Archive. The critical stylistic analysis aims at uncovering Trump’s ideological outlook by identifying the extra layer of meaning in which the ideological evaluation is structured and exposing the way in which the resources of language are strategically deployed to influence and ideologically manipulate Trump’s followers’ experience of reality. Analysis reveals a network of lexical, syntactic, semantic and pragmatic choices underlying Trump’s seemingly simple rhetoric. It signposts his ideological evaluation and constructs a world for his followers to desire, believe or fear. The study extends the application of critical stylistics to microblogging channels, with implications both for the linguistic make-up of political communication in Web 2.0 contexts and for the explanatory power of critical stylistics.
Authors’ Figurative Expressions From Two Novels: A Comparative Analysis Between RTJNA Rosso and RTJNA Blu
Stylistic analysis of the novels Reisei To Jounetsu No Aida Rosso by Ekuni Kaori and Reisei To Jounetsu No Aida Bluu by Hitonari Tsuji is an analysis of metaphorical language style as a figurative language used to express the author's thoughts, personality, and perspectives. The use of distinctive language in a work shows the characteristics of individualism and the style of each author in conveying ideas through the medium of language. This study uses the metaphorical perspective of Michael C. Halley and Stephen Ullman. The results of the analysis show that the use of an author's language style provides information about the author's cultural background and the context in which they communicate. The metaphorical language style is used by the authors to express feelings and express different thoughts and each author has a uniqueness or specialty style which can be felt in a significant way by the readers of their works.
Representation of the Phenomenon “Trust” in Medical Advertising Discourse
The problem of creating institutional trust in modern Russian society is considered on the example of advertising activities of companies that produce and promote drugs on the consumer market. In order to identify techniques that contribute to the effective impact on the recipient – the formation of a trusting attitude towards the advertised product, the commercials shown on Russian television from 2010 to 2020 were analyzed. Using the methods of content analysis, discourse and stylistic analysis, elements of component and distributive analysis, it has been established that professional participants in medical advertising discourse use such techniques as the use of toponyms, lexical units borrowed from military discourse, terms, words with positive or negative connotations, presentation of statistical data, construction of a first-person statement, rhetorical questions. It was found that the mention of the country of origin of the drug, which is authoritative for the Russian consumer, has a positive effect on the confidence of patients in this drug; military vocabulary evokes associations with speed, accuracy, direction, strength and testifies to the effectiveness of the drug; medical, chemical, biological terms, statistical data objectify the transmitted information; rhetorical questions, self-narrative and others contribute to the establishment of close contact with the consumer.
A STUDY OF THE STYLISTIC FEATURES AND EFFECTS OF ENGLISH FOOTBALL NEWS
The study investigates the stylistic features of English football news from the perspective of general stylistics. Stylistics, as a discipline based on modern linguistic theories, turns to studying non-literary texts from the perspective of stylistics. The study examines English football news from the three levels of stylistic analysis, namely lexis, syntax and semantics. Compared with other news types, English football news are less attracted to linguistics, and most of the previous studies are focused on the research of the title. This study employs samples of English football news from the official website of the 2018 World Cup in Russia. The findings of this study suggest that at the lexical level, the use of technical terms, abbreviation, nicknames, neologism and numbers highlights the uniqueness of English football news in lexical use, thereby saving space, increasing readability and narrowing the distance between news editors and readers; at the syntactic level, the special stylistic features of English football news are mainly reflected in the unmarked theme and singular form of a plural concept; and the use of rhetorical devices such as metaphor, hyperbole and personification to achieve semantic variation reflects the stylistic features of English football news at the semantic level.
Stylistic Analysis of Milton’s Invocation of Paradise Lost Book 1
The process of changing the modern and contemporary name of stone seated bodhisattva from hansongsa temple site and its meaning.
This paper studies the changing process of the honorific name of the Stone Seated Bodhisattva from Hansongsa Temple Site according to the modern and contemporary political and social circumstances. The National Treasure no. 124, the stone image, was carried out to Japan in 1911, donated to Tokyo Imperial Museum, and got the honorific name, 'Tara Bodhisattva,' and the record of the remaining Treasure no. 81, the stone statue, considered as Manjusri, was discovered in Korea. Also, The return of National Treasure no. 124 in 1966 is considered to be the significant event for the change of the honorific name again. There was a disagreement between Korea and Japan on the significance of the image. Japanese academia agreed to return the image because it considered the treasure was not worth possession whilst Korean academic circle treated it as a sculpture that represents the return of Korean remains scattered in Japan. After the return of the National Treasure no. 124, Stone Seated Bodhisattva from Hansongsa Temple Site has been studied actively through the methodology of stylistic analysis in Korean academia. As a result, the overall opinion that Manjusri as the National Treasure no. 124 and Samantabhadra as the treasure no. 81 should be reconsidered because, at present, due to the impairment of animal-shaped pedestals which is considered as the clear evidence for two figures, there is no way to distinguish which stone is Manjusri and which Samantabhadra. Through the above discussion this paper tried to reflect on the significance of the stone seated statues of Hansongsa temple site by looking at the changes of the honorific name tracing the modern and contemporary research history of the stone seated images.
STYLISTIC ANALYSIS OF SURAKH AL-QUBUR: A SHORT STORY BY KAHLIL GIBRAN / ANALISIS STILISTIKA CERPEN SURAKH AL-QUBUR KARYA KAHLIL GIBRAN
This study aims to reveal the stylistic used in a short story written by Kahlil Gibran entitled “Surakh al-Qubur” and also to describe the effect of it toward meaning. This is a descriptive qualitative research that used stylistic analysis to show the aesthetics side found in the short story. Based on data analysis, it was found that there are five categories of language styles in short story Surakh al-Qubur, they are: first, lexical (synonym and typical words); second, grammatical (verb and noun); third, rhetorical (alliteration, asyndeton, assonance, chiasmus, polysyndeton, and hyperbole) and figure of speech (metaphor, personification, simile, and eponym); fourth, cohesion and connectors such as al-wawu, al-fa’u, tsumma, au, and am; and fifth, character speech that can be analyzed using narration and dialogue. The influence of stylistic on meaning is that readers get the information directly or indirectly, feels sadness, gives advice, gets a picture of injustice, makes readers curious and more focused.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Stylistic devices in news, as related to topic recognition

2012, Łódź (Lodz) Studies in Language
Related Papers
Loretta Innocenti
Philology matters
Feruza Khajieva
Тhe article discusses the problem of a stylistic device, its innate features and the literary, aesthetic, imagery functions, the example to stylistic convergence is also given. Moreover the classifications of stylistic devices are also investigated. The theories of ancient scholars as well as modern researchers are analyzed and predominant features of the criteria for classification are generalized. The article discusses such antique theories as Aristotle’s initial views on Stylistics, observations of the Hellenistic Roman rhetoric system, researches of Dionysius of Halicarnassus and the conclusions concerning the topic are also given. The article also deals with the review of the fundamental theories of modern researchers. I.R.Galperin’s, Yu.M. Skrebnyov’s, V.A.Kukharenko’s, Jochen Lüders’ classifications are investigated and the relevant conclusions are given. The research advances the idea of classifying the stylistic devices in the circle of language layers. The phenomenon of cr...
Stephen Melville
Fatima khudhair hassoon
Abstract: This study presents a stylistic analysis of newspaper stories. It is hypothesized that the language used in newspaper stories violates the rules of grammar and the norms of literary writing. Moreover their style tends to be very distinctive. This can be attributed to the limited space given to each article and the author as all journalists writes to an absent or imaginary reader that must be quickly attracted. The study aims at: 1. identifying some linguistic features of newspaper language. 2. shedding light on the style used in newspapers and how it differs from that used in literary writing. Six stories have been selected for the purpose of analysis. They are selected randomly from different English newspapers. All of them are written in the inverted pyramid style. Three models are adopted for the purpose of the analysis of the texts. The results show that the language and style used for writing newspaper stories deviates from the ordinary norms of writing. Key words: inverted pyramid, language of newspaper, stylistic analysis
Nordicom Review
Jørgen Lauridsen
Linguistic exposures are image constructions and some of the most distinctive mechanisms in the discourse community of journalism.By exposing the journalistic writers add focus, detail and substantiation to their stories. Linguistic exposures are tools that evoke images in the readers’ minds and help establish and improve the basis of interest and understanding.We are combining linguistic and statistical methods to investigate exposures in the news of five Danish national papers in order to determine how widespread it is, and with what force and impact the techniques are used.Our study contributes to existing knowledge by focusing on form rather than content. We investigate the creative use of specific structural elements of the language as the prevailing contact establishing tools of journalistic discourse. Our data are based on news from Berlingske Tidende, B.T., Politiken, Ekstra Bladet and Morgenavisen Jyllands-Posten.
The five centuries of expertise in use paper and ink to spread news assured some levels of communication that are behind the published texts. Inside the newspapers is a hidden speech, able to communicate ideas and even to guide or manipulate the reader’s attention to one or other article. This language configures the visual rhetoric of the newspapers and happened in two different levels: one more superficial, indicated by the typography, the images and all sort of the elements which ∗M.A. Digital Media. Bremen University / University of Arts Bremen – Germany
Marcel Broersma
World Journal of English Language
Valentyna Tryndiuk
The article analyzes the use of stylistic means in contemporary American novels about the challenges of postmodern society, such as terrorist attacks, loneliness in digital reality, and digital technologies. Descriptive, continuous sampling, dictionary definitions, and contextual and component analysis methods were used to analyze the language material from novels by Douglas Coupland and Don DeLillo. The analyzed stylistic units were diverse and characterized by an emotional and evaluative component, with negative assessments being the most common. The units were divided into thematic groups, such as drugs, money, human behavior, and success/failure. The place and role of stylistic units in the novels were related to their content and stylistic features, with colloquial lexical items playing a significant role in creating a special atmosphere. The study also identified prospects for analyzing current trends in the development of English spoken language based on the works of contempo...
Journal of Pragmatics
Débora Figueiredo
Zareen Gull
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Literary Devices & Terms
An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line, word, or paragraph—spells out a word or phrase with special significance to the text. Acrostics... (read full acrostic explanation with examples) An acrostic is a piece of writing in which a particular set of letters—typically the first letter of each line,... (read more)
An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and events. The story of "The Tortoise and The Hare" is a well-known allegory with a... (read full allegory explanation with examples) An allegory is a work that conveys a hidden meaning—usually moral, spiritual, or political—through the use of symbolic characters and... (read more)
Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the “b” sound in: “Bob brought the box of bricks to the basement.” The repeating sound... (read full alliteration explanation with examples) Alliteration is a figure of speech in which the same sound repeats in a group of words, such as the... (read more)
In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to other literary works, famous individuals, historical events, or philosophical ideas, and they do so in... (read full allusion explanation with examples) In literature, an allusion is an unexplained reference to someone or something outside of the text. Writers commonly allude to... (read more)
An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set in Medieval England featured a trip to a movie-theater, that would be an anachronism. Although... (read full anachronism explanation with examples) An anachronism is a person or a thing placed in the wrong time period. For instance, if a novel set... (read more)
Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one clause or sentence is repeated at or near the beginning of the following clause or... (read full anadiplosis explanation with examples) Anadiplosis is a figure of speech in which a word or group of words located at the end of one... (read more)
An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For example, a career coach might say, "Being the successful boss or CEO of a company... (read full analogy explanation with examples) An analogy is a comparison that aims to explain a thing or idea by likening it to something else. For... (read more)
An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable. The word "understand" is an anapest, with the unstressed syllables of "un" and "der" followed... (read full anapest explanation with examples) An anapest is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which two unstressed syllables are followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For example, Martin Luther King's famous "I Have a Dream" speech contains anaphora: "So let freedom... (read full anaphora explanation with examples) Anaphora is a figure of speech in which words repeat at the beginning of successive clauses, phrases, or sentences. For... (read more)
An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can also be a group of characters, institution, or force against which the protagonist must contend.... (read full antagonist explanation with examples) An antagonist is usually a character who opposes the protagonist (or main character) of a story, but the antagonist can... (read more)
Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word or phrase means something different each time it appears. A famous example of antanaclasis is... (read full antanaclasis explanation with examples) Antanaclasis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated within a sentence, but the word... (read more)
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous examples of anthropomorphism include Winnie the Pooh, the Little Engine that Could, and Simba from... (read full anthropomorphism explanation with examples) Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human characteristics, emotions, and behaviors to animals or other non-human things (including objects, plants, and supernatural beings). Some famous... (read more)
Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John F. Kennedy's words, "Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you... (read full antimetabole explanation with examples) Antimetabole is a figure of speech in which a phrase is repeated, but with the order of words reversed. John... (read more)
Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance, Neil Armstrong used antithesis when he stepped onto the surface of the moon in 1969... (read full antithesis explanation with examples) Antithesis is a figure of speech that juxtaposes two contrasting or opposing ideas, usually within parallel grammatical structures. For instance,... (read more)
An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as a general or universal truth. The Rolling Stones are responsible for penning one of the... (read full aphorism explanation with examples) An aphorism is a saying that concisely expresses a moral principle or an observation about the world, presenting it as... (read more)
Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is used not to question the meaning of a word, but whether it is actually appropriate... (read full aphorismus explanation with examples) Aphorismus is a type of figure of speech that calls into question the way a word is used. Aphorismus is... (read more)
Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as a way of proving a point. An example of aporia is the famous Elizabeth Barrett... (read full aporia explanation with examples) Aporia is a rhetorical device in which a speaker expresses uncertainty or doubt—often pretended uncertainty or doubt—about something, usually as... (read more)
Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or cannot respond in reality. The entity being addressed can be an absent, dead, or imaginary... (read full apostrophe explanation with examples) Apostrophe is a figure of speech in which a speaker directly addresses someone (or something) that is not present or... (read more)
Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example of assonance is: "Who gave Newt and Scooter the blue tuna? It was too soon!" (read full assonance explanation with examples) Assonance is a figure of speech in which the same vowel sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are omitted.... (read full asyndeton explanation with examples) An asyndeton (sometimes called asyndetism) is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and", "or", and "but"... (read more)
A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads are typically composed of four-line stanzas that follow an ABCB rhyme scheme. (read full ballad explanation with examples) A ballad is a type of poem that tells a story and was traditionally set to music. English language ballads... (read more)
A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"), and typically have three eight-line stanzas followed by a shorter four-line stanza called an envoi.... (read full ballade explanation with examples) A ballade is a form of lyric poetry that originated in medieval France. Ballades follow a strict rhyme scheme ("ababbcbc"),... (read more)
Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity), with a focus on the trials and misfortunes that affect the character's growth. (read full bildungsroman explanation with examples) Bildungsroman is a genre of novel that shows a young protagonist's journey from childhood to adulthood (or immaturity to maturity),... (read more)
Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is almost always iambic pentameter. Blank verse was particularly popular in English poetry written between the... (read full blank verse explanation with examples) Blank verse is the name given to poetry that lacks rhymes but does follow a specific meter—a meter that is... (read more)
A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of percussive or "explosive" consonants (like T, P, or K) into relatively little space. For instance, the... (read full cacophony explanation with examples) A cacophony is a combination of words that sound harsh or unpleasant together, usually because they pack a lot of... (read more)
A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such as a period, comma, ellipsis, or dash. A caesura doesn't have to be placed in... (read full caesura explanation with examples) A caesura is a pause that occurs within a line of poetry, usually marked by some form of punctuation such... (read more)
Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the Greek kathairein meaning "to cleanse or purge"—to describe the release of emotional tension that he... (read full catharsis explanation with examples) Catharsis is the process of releasing strong or pent-up emotions through art. Aristotle coined the term catharsis—which comes from the... (read more)
Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through direct description, in which the character's qualities are described by a narrator, another character, or... (read full characterization explanation with examples) Characterization is the representation of the traits, motives, and psychology of a character in a narrative. Characterization may occur through... (read more)
Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such that two key concepts from the original phrase reappear in the second phrase in inverted... (read full chiasmus explanation with examples) Chiasmus is a figure of speech in which the grammar of one phrase is inverted in the following phrase, such... (read more)
The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in any type of verse. More recently, cinquain has come to refer to particular types of... (read full cinquain explanation with examples) The word cinquain can refer to two different things. Historically, it referred to any stanza of five lines written in... (read more)
A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling a heartbroken friend that there are "Plenty of fish in the sea" is such a... (read full cliché explanation with examples) A cliché is a phrase that, due to overuse, is seen as lacking in substance or originality. For example, telling... (read more)
Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of importance, as in "Look! Up in the sky! It's a bird! It's a plane! It's... (read full climax (figure of speech) explanation with examples) Climax is a figure of speech in which successive words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are arranged in ascending order of... (read more)
The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot developments have been leading up to. In a traditional "good vs. evil" story (like many superhero movies)... (read full climax (plot) explanation with examples) The climax of a plot is the story's central turning point—the moment of peak tension or conflict—which all the preceding plot... (read more)
Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms, meaning that they are often defined by their use within a dialect, a regionally-defined variant... (read full colloquialism explanation with examples) Colloquialism is the use of informal words or phrases in writing or speech. Colloquialisms are usually defined in geographical terms,... (read more)
Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key traits: it alternates between lines of eight syllables and lines of six syllables, and it... (read full common meter explanation with examples) Common meter is a specific type of meter that is often used in lyric poetry. Common meter has two key... (read more)
A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained comparison is made between two things. A famous example comes from John Donne's poem, "A... (read full conceit explanation with examples) A conceit is a fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely, far-fetched, or strained... (read more)
Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words carry meanings, impressions, or associations apart from or beyond their literal meaning. For example, the... (read full connotation explanation with examples) Connotation is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary definition. Most words... (read more)
Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example of consonance is: "Traffic figures, on July Fourth, to be tough." (read full consonance explanation with examples) Consonance is a figure of speech in which the same consonant sound repeats within a group of words. An example... (read more)
A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form a rhyme, or are separated from other lines by a double line break. (read full couplet explanation with examples) A couplet is a unit of two lines of poetry, especially lines that use the same or similar meter, form... (read more)
A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables. The word “poetry” itself is a great example of a dactyl, with the stressed syllable... (read full dactyl explanation with examples) A dactyl is a three-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by two unstressed syllables.... (read more)
Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is the array of emotions and ideas suggested by a word in addition to its dictionary... (read full denotation explanation with examples) Denotation is the literal meaning, or "dictionary definition," of a word. Denotation is defined in contrast to connotation, which is... (read more)
The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and a sense of resolution is achieved. The shortest and most well known dénouement, it could be... (read full dénouement explanation with examples) The dénouement is the final section of a story's plot, in which loose ends are tied up, lingering questions are answered, and... (read more)
A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by the unexpected appearance of an implausible character, object, action, ability, or event. For example, if... (read full deus ex machina explanation with examples) A deus ex machina is a plot device whereby an unsolvable conflict or point of tension is suddenly resolved by... (read more)
Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening words. The first line of Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy, "Happy families are all alike;... (read full diacope explanation with examples) Diacope is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated with a small number of intervening... (read more)
Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work. In prose writing, lines of dialogue are typically identified by the use of quotation marks... (read full dialogue explanation with examples) Dialogue is the exchange of spoken words between two or more characters in a book, play, or other written work.... (read more)
Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary, use of language to produce a specific tone or atmosphere, and ability to communicate clearly... (read full diction explanation with examples) Diction is a writer's unique style of expression, especially his or her choice and arrangement of words. A writer's vocabulary,... (read more)
Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a character's understanding of a given situation, and that of the audience. More specifically, in dramatic... (read full dramatic irony explanation with examples) Dramatic irony is a plot device often used in theater, literature, film, and television to highlight the difference between a... (read more)
A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change can be extreme or subtle, as long as his or her development is important to... (read full dynamic character explanation with examples) A dynamic character undergoes substantial internal changes as a result of one or more plot developments. The dynamic character's change... (read more)
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined by their subject matter, and don't have to follow any specific form in terms of... (read full elegy explanation with examples) An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, especially one mourning the loss of someone who died. Elegies are defined... (read more)
End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from Dorothy Parker's poem "Interview" use end rhyme: "The ladies men admire, I’ve heard, / Would shudder... (read full end rhyme explanation with examples) End rhyme refers to rhymes that occur in the final words of lines of poetry. For instance, these lines from... (read more)
An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the end of the line. For example, the poet C.P. Cavafy uses end-stopped lines in his... (read full end-stopped line explanation with examples) An end-stopped line is a line of poetry in which a sentence or phrase comes to a conclusion at the... (read more)
Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses enjambment in his poem "The Good-Morrow" when he continues the opening sentence across the line... (read full enjambment explanation with examples) Enjambment is the continuation of a sentence or clause across a line break. For example, the poet John Donne uses... (read more)
An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem or serve as its dedication. The envoi tends to follow the same meter and rhyme... (read full envoi explanation with examples) An envoi is a brief concluding stanza at the end of a poem that can either summarize the preceding poem... (read more)
Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end of that same clause or sentence, with words intervening. The sentence "The king is dead,... (read full epanalepsis explanation with examples) Epanalepsis is a figure of speech in which the beginning of a clause or sentence is repeated at the end... (read more)
An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams typically end with a punchline or a satirical twist. (read full epigram explanation with examples) An epigram is a short and witty statement, usually written in verse, that conveys a single thought or observation. Epigrams... (read more)
An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to encapsulate that work's main themes and to set the tone. For instance, the epigraph of Mary... (read full epigraph explanation with examples) An epigraph is a short quotation, phrase, or poem that is placed at the beginning of another piece of writing to... (read more)
Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences. In his Gettysburg Address, Abraham Lincoln urged the American people to ensure that,... (read full epistrophe explanation with examples) Epistrophe is a figure of speech in which one or more words repeat at the end of successive phrases, clauses,... (read more)
Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening words. In the play Hamlet, when Hamlet responds to a question about what he's reading... (read full epizeuxis explanation with examples) Epizeuxis is a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is repeated in immediate succession, with no intervening... (read more)
Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Ethos is an argument that appeals to the audience by emphasizing the... (read full ethos explanation with examples) Ethos, along with logos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft or muffled sounds (like L, M, N, and R) instead of consonants with harsh, percussive sounds (like... (read full euphony explanation with examples) Euphony is the combining of words that sound pleasant together or are easy to pronounce, usually because they contain lots of consonants with soft... (read more)
Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their relationship to one another, the setting or time and place of events, as well as... (read full exposition explanation with examples) Exposition is the description or explanation of background information within a work of literature. Exposition can cover characters and their... (read more)
An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of multiple interrelated metaphors within an overarching one. So while "life is a highway" is a... (read full extended metaphor explanation with examples) An extended metaphor is a metaphor that unfolds across multiple lines or even paragraphs of a text, making use of... (read more)
An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict drives the action of a plot forward. (read full external conflict explanation with examples) An external conflict is a problem, antagonism, or struggle that takes place between a character and an outside force. External conflict... (read more)
The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict decreases and the story moves toward its conclusion. For instance, the traditional "good... (read full falling action explanation with examples) The falling action of a story is the section of the plot following the climax, in which the tension stemming from... (read more)
Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they often do so in a slightly narrower way. In this narrower definition, figurative language refers... (read full figurative language explanation with examples) Figurative language is language that contains or uses figures of speech. When people use the term "figurative language," however, they... (read more)
A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to produce a stylistic effect. Figures of speech can be broken into two main groups: figures... (read full figure of speech explanation with examples) A figure of speech is a literary device in which language is used in an unusual—or "figured"—way in order to... (read more)
A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily and accurately described using a single word (like "bully") or one short sentence (like "A naive... (read full flat character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "flat" if it is one-dimensional or lacking in complexity. Typically, flat characters can be easily... (read more)
Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the story. Foreshadowing can be achieved directly or indirectly, by making explicit statements or leaving subtle... (read full foreshadowing explanation with examples) Foreshadowing is a literary device in which authors hint at plot developments that don't actually occur until later in the... (read more)
Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables). This two-line poem by Emily Dickinson is formal verse because it rhymes and... (read full formal verse explanation with examples) Formal verse is the name given to rhymed poetry that uses a strict meter (a regular pattern of stressed and... (read more)
Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has no set meter, poems written in free verse can have lines of any length, from... (read full free verse explanation with examples) Free verse is the name given to poetry that doesn’t use any strict meter or rhyme scheme. Because it has... (read more)
Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In the novel Frankenstein, Victor Frankenstein's arrogant conviction that he can usurp the roles of God... (read full hamartia explanation with examples) Hamartia is a literary term that refers to a tragic flaw or error that leads to a character's downfall. In... (read more)
Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to their downfall. In Greek mythology, the legend of Icarus involves an iconic case of hubris:... (read full hubris explanation with examples) Hubris refers to excessive pride or overconfidence, which drives a person to overstep limits in a way that leads to... (read more)
Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements are usually quite obvious exaggerations intended to emphasize a point, rather than be taken literally.... (read full hyperbole explanation with examples) Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which a writer or speaker exaggerates for the sake of emphasis. Hyperbolic statements... (read more)
An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable. The word "define" is an iamb, with the unstressed syllable of "de" followed by the... (read full iamb explanation with examples) An iamb is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which one unstressed syllable is followed by a stressed syllable.... (read more)
An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on a literal interpretation of the words in the phrase. For example, saying that something is... (read full idiom explanation with examples) An idiom is a phrase that conveys a figurative meaning that is difficult or impossible to understand based solely on... (read more)
Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines from Robert Frost's poem "After Apple-Picking" contain imagery that engages the senses of touch, movement,... (read full imagery explanation with examples) Imagery, in any sort of writing, refers to descriptive language that engages the human senses. For instance, the following lines... (read more)
Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines. A single line of poetry can contain internal rhyme (with multiple words in the same... (read full internal rhyme explanation with examples) Internal rhyme is rhyme that occurs in the middle of lines of poetry, instead of at the ends of lines.... (read more)
Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how they actually are. If this seems like a loose definition, don't worry—it is. Irony is a... (read full irony explanation with examples) Irony is a literary device or event in which how things seem to be is in fact very different from how... (read more)
Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images, characters, and actions are all things that can be juxtaposed with one another. For example,... (read full juxtaposition explanation with examples) Juxtaposition occurs when an author places two things side by side as a way of highlighting their differences. Ideas, images,... (read more)
A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression that refers to a person or a thing. For example, "whale-road" is a kenning for... (read full kenning explanation with examples) A kenning is a figure of speech in which two words are combined in order to form a poetic expression... (read more)
A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read full line break explanation with examples) A line break is the termination of one line of poetry, and the beginning of a new line. (read more)
Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating its contrary. For example, saying "It's not the best weather today" during a hurricane would... (read full litotes explanation with examples) Litotes is a figure of speech and a form of understatement in which a sentiment is expressed ironically by negating... (read more)
Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Logos is an argument that appeals to an audience's sense of logic... (read full logos explanation with examples) Logos, along with ethos and pathos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other. The comparison in a metaphor can be stated explicitly, as in the sentence "Love is... (read full metaphor explanation with examples) A metaphor is a figure of speech that compares two different things by saying that one thing is the other.... (read more)
Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns are defined in groupings, called feet, of two or three syllables. A pattern of unstressed-stressed,... (read full meter explanation with examples) Meter is a regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that defines the rhythm of some poetry. These stress patterns... (read more)
Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own name, but instead by the name of something closely associated with it. For example, in... (read full metonymy explanation with examples) Metonymy is a type of figurative language in which an object or concept is referred to not by its own... (read more)
The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes in the reader. Every aspect of a piece of writing can influence its mood, from the... (read full mood explanation with examples) The mood of a piece of writing is its general atmosphere or emotional complexion—in short, the array of feelings the work evokes... (read more)
A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of related symbols, help develop the central themes of a book or play. For example, one... (read full motif explanation with examples) A motif is an element or idea that recurs throughout a work of literature. Motifs, which are often collections of... (read more)
A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives, depending on how they use different narrative elements, such as tone or point of view. For... (read full narrative explanation with examples) A narrative is an account of connected events. Two writers describing the same set of events might craft very different narratives,... (read more)
Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or describe. The “boom” of a firework exploding, the “tick tock” of a clock, and the... (read full onomatopoeia explanation with examples) Onomatopoeia is a figure of speech in which words evoke the actual sound of the thing they refer to or... (read more)
An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to make a point—particularly to reveal a deeper or hidden truth. The most recognizable oxymorons are... (read full oxymoron explanation with examples) An oxymoron is a figure of speech in which two contradictory terms or ideas are intentionally paired in order to... (read more)
A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel of truth or reason. Oscar Wilde's famous declaration that "Life is much too important to be... (read full paradox explanation with examples) A paradox is a figure of speech that seems to contradict itself, but which, upon further examination, contains some kernel... (read more)
Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have the same grammatical structure. These "parallel" elements can be used to intensify the rhythm of... (read full parallelism explanation with examples) Parallelism is a figure of speech in which two or more elements of a sentence (or series of sentences) have... (read more)
Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so that each element is equally important. Parataxis usually involves simple sentences or phrases whose relationships... (read full parataxis explanation with examples) Parataxis is a figure of speech in which words, phrases, clauses, or sentences are set next to each other so... (read more)
A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually for comic effect. Parodies can take many forms, including fiction, poetry, film, visual art, and... (read full parody explanation with examples) A parody is a work that mimics the style of another work, artist, or genre in an exaggerated way, usually... (read more)
Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals. It is often used to make the environment reflect the inner experience of a narrator... (read full pathetic fallacy explanation with examples) Pathetic fallacy occurs when a writer attributes human emotions to things that aren't human, such as objects, weather, or animals.... (read more)
Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective speaking or writing). Pathos is an argument that appeals to an audience's emotions. When a... (read full pathos explanation with examples) Pathos, along with logos and ethos, is one of the three "modes of persuasion" in rhetoric (the art of effective... (read more)
Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the sentence, "The rain poured down on the wedding guests, indifferent to their plans." Describing the... (read full personification explanation with examples) Personification is a type of figurative language in which non-human things are described as having human attributes, as in the... (read more)
Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary work. More than simply an account of what happened, plot reveals the cause-and-effect relationships between... (read full plot explanation with examples) Plot is the sequence of interconnected events within the story of a play, novel, film, epic, or other narrative literary... (read more)
Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The three primary points of view are first person, in which the narrator tells a story from... (read full point of view explanation with examples) Point of view refers to the perspective that the narrator holds in relation to the events of the story. The... (read more)
Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood" and "bleed"). For instance, the question, "Who shall watch the watchmen?" is an example of... (read full polyptoton explanation with examples) Polyptoton is a figure of speech that involves the repetition of words derived from the same root (such as "blood"... (read more)
Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words or clauses in a sentence into relationships of equal importance—are used several times in close... (read full polysyndeton explanation with examples) Polysyndeton is a figure of speech in which coordinating conjunctions—words such as "and," "or," and "but" that join other words... (read more)
The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character tends to be involved in or affected by most of the choices or conflicts that... (read full protagonist explanation with examples) The protagonist of a story is its main character, who has the sympathy and support of the audience. This character... (read more)
A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words that sound similar but mean different things. The comic novelist Douglas Adams uses both types... (read full pun explanation with examples) A pun is a figure of speech that plays with words that have multiple meanings, or that plays with words... (read more)
A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a stand-alone poem of four lines, or it can be a four-line stanza that makes up... (read full quatrain explanation with examples) A quatrain is a four-line stanza of poetry. It can be a single four-line stanza, meaning that it is a... (read more)
A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them to mistakenly expect a particular outcome. Most often, the term red herring is used to refer... (read full red herring explanation with examples) A red herring is a piece of information in a story that distracts readers from an important truth, or leads them... (read more)
In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the end of a stanza in a poem or at the end of a verse in... (read full refrain explanation with examples) In a poem or song, a refrain is a line or group of lines that regularly repeat, usually at the... (read more)
Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in so many different forms that it is usually not thought of as a single figure... (read full repetition explanation with examples) Repetition is a literary device in which a word or phrase is repeated two or more times. Repetition occurs in... (read more)
A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to get an answer—most commonly, it's asked to make a persuasive point. For example, if a... (read full rhetorical question explanation with examples) A rhetorical question is a figure of speech in which a question is asked for a reason other than to... (read more)
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types of poetry, especially at the ends of lines, and is a requirement in formal verse.... (read full rhyme explanation with examples) A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds in two or more words. Rhyming is particularly common in many types... (read more)
A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated in works poetry. Rhyme schemes are described using letters of the alphabet, such that all... (read full rhyme scheme explanation with examples) A rhyme scheme is the pattern according to which end rhymes (rhymes located at the end of lines) are repeated... (read more)
The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming from the story's central conflict grows through successive plot developments. For example, in the story of "Little... (read full rising action explanation with examples) The rising action of a story is the section of the plot leading up to the climax, in which the tension stemming... (read more)
A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and multi-faceted personalities, backgrounds, desires, and motivations. Jay Gatsby in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby... (read full round character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "round" if they are lifelike or complex. Round characters typically have fully fleshed-out and... (read more)
Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians, are often the subject of satire, but satirists can take aim at other targets as... (read full satire explanation with examples) Satire is the use of humor, irony, sarcasm, or ridicule to criticize something or someone. Public figures, such as politicians,... (read more)
A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem, or one that makes up a part of a longer poem. Most commonly, the term... (read full sestet explanation with examples) A sestet is a six-line stanza of poetry. It can be any six-line stanza—one that is, itself, a whole poem,... (read more)
Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the city of New York, or it can be an imagined location, like Middle Earth in... (read full setting explanation with examples) Setting is where and when a story or scene takes place. The where can be a real place like the... (read more)
Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition of "s" sounds. An example of sibilance is: "Sadly, Sam sold seven venomous serpents to Sally and... (read full sibilance explanation with examples) Sibilance is a figure of speech in which a hissing sound is created within a group of words through the repetition... (read more)
A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often use the connecting words "like" or "as," but can also use other words that indicate... (read full simile explanation with examples) A simile is a figure of speech that directly compares two unlike things. To make the comparison, similes most often... (read more)
Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line of poetry themselves end in similar—but not identical—consonant sounds. For instance, the words "pact" and... (read full slant rhyme explanation with examples) Traditionally, slant rhyme referred to a type of rhyme in which two words located at the end of a line... (read more)
A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself, relating his or her innermost thoughts and feelings as if thinking aloud. In some cases,... (read full soliloquy explanation with examples) A soliloquy is a literary device, most often found in dramas, in which a character speaks to him or herself,... (read more)
A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or two quatrains making up a stanza of 8 lines) and a sestet (a stanza of... (read full sonnet explanation with examples) A sonnet is a type of fourteen-line poem. Traditionally, the fourteen lines of a sonnet consist of an octave (or... (read more)
A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a spondee, with the stressed syllable of "down" followed by another stressed syllable, “town”: Down-town. (read full spondee explanation with examples) A spondee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which both syllables are stressed. The word "downtown" is a... (read more)
A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set apart from other lines or stanza within a poem by a double line break or... (read full stanza explanation with examples) A stanza is a group of lines form a smaller unit within a poem. A single stanza is usually set... (read more)
A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of the story's major plot developments. Antagonists are often static characters, but any character in a... (read full static character explanation with examples) A character is said to be "static" if they do not undergo any substantial internal changes as a result of... (read more)
Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's extended thought process, often by incorporating sensory impressions, incomplete ideas, unusual syntax, and rough grammar. (read full stream of consciousness explanation with examples) Stream of consciousness is a style or technique of writing that tries to capture the natural flow of a character's... (read more)
A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at a conclusion. So long as the premises of the syllogism are true and the syllogism... (read full syllogism explanation with examples) A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at... (read more)
Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more abstract. A strong symbol usually shares a set of key characteristics with whatever it is... (read full symbolism explanation with examples) Symbolism is a literary device in which a writer uses one thing—usually a physical object or phenomenon—to represent something more... (read more)
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its whole. For example, "The captain commands one hundred sails" is a synecdoche that uses "sails"... (read full synecdoche explanation with examples) Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which, most often, a part of something is used to refer to its... (read more)
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only... (read full theme explanation with examples) A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary... (read more)
The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical or mournful, praising or critical, and so on. For instance, an editorial in a newspaper... (read full tone explanation with examples) The tone of a piece of writing is its general character or attitude, which might be cheerful or depressive, sarcastic or sincere, comical... (read more)
A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have heroic traits that earn them the sympathy of the audience, but also have flaws or... (read full tragic hero explanation with examples) A tragic hero is a type of character in a tragedy, and is usually the protagonist. Tragic heroes typically have... (read more)
A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable. The word "poet" is a trochee, with the stressed syllable of "po" followed by the... (read full trochee explanation with examples) A trochee is a two-syllable metrical pattern in poetry in which a stressed syllable is followed by an unstressed syllable.... (read more)
Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something is presented as being smaller, worse, or lesser than it really is. Typically, understatement is... (read full understatement explanation with examples) Understatement is a figure of speech in which something is expressed less strongly than would be expected, or in which something... (read more)
Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean. When there's a hurricane raging outside and someone remarks "what lovely weather we're having," this... (read full verbal irony explanation with examples) Verbal irony occurs when the literal meaning of what someone says is different from—and often opposite to—what they actually mean.... (read more)
A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line stanzas) followed by one quatrain (four-line stanza). Villanelles use a specific rhyme scheme of ABA... (read full villanelle explanation with examples) A villanelle is a poem of nineteen lines, and which follows a strict form that consists of five tercets (three-line... (read more)
A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a sentence. Often, the governing word will mean something different when applied to each part, as... (read full zeugma explanation with examples) A zeugma is a figure of speech in which one "governing" word or phrase modifies two distinct parts of a... (read more)

- PDF downloads of each of the 136 Lit Terms we cover
- PDF downloads of 1929 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,694 quotes across 1929 Lit Guides
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play


The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Stylistic Devices – Definition, Types & Tips
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Writing is a form of communication that we cannot live without, whether in business or at home. Stylistic devices are linguistic tools used by writers to enhance the appeal of their writing style, and add layers of meaning, and engage readers by altering language in creative and artistic ways. In this article, you’ll find out everything there is to know about these stylistic devices.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Stylistic devices in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Stylistic Devices
- 3 Functions of Stylistic Devices
- 4 Types of Stylistic Devices
- 5 Impact on literature
- 6 Tips to elevate your writing
Stylistic devices in a nutshell
Writers use stylistic devices as linguistic tools to showcase creative thought and vivid imagery in their works. Applying them in the speech or writing process, makes the listener or reader more engaged in what is being expressed.
Definition: Stylistic Devices
Stylistic devices are typically considered figures of speech , whose key aspect is departing from straightforward or literal language to create depth, emphasize ideas, or convey emotions in a more vivid and imaginative way. These aspects are the factors behind their widespread use in various creative fields, such as academic essays , literature, poetry, speeches, and advertising. In academic writing , they are often used more subtly compared to literary writing.
These stylistic devices encompass a wide range of techniques, such as irony , simile , metaphor , and many others, each serving to achieve specific rhetorical or aesthetic objectives. The variety and complexity of language is enhanced by stylistic devices, enabling writers to convey concepts, express feelings, and shape perceptions with greater clarity and resonance.
Functions of Stylistic Devices
Stylistic devices serve several functions in writing and speech. Below, you will find the most significant ones, along with their respective examples.

Enhancing Clarity
Stylistic devices can help writers convey complex ideas more clearly and effectively by using vivid imagery, comparisons, and other techniques to make abstract concepts more concrete.
Creating Emphasis
Stylistic devices draw attention to key points, or emotions in a text, which helps emphasize their importance and impact on the reader.
Vivid Imagery
Through the use of descriptive language, metaphors, similes, and other stylistic devices, writers can paint vivid mental pictures in the reader’s mind, enhancing the imagery and sensory experience of the writing.
Adding Depth
Figures of speech enhance the quality of writing by adding depth and texture to writing, making it more nuanced and multidimensional by layering different elements of language and meaning.
Types of Stylistic Devices
Stylistic devices can have different categories, e.g., focusing on the sound of words. In this paragraph, we will differentiate between various stylistic tools and give examples for each of them.
Figurative Devices
Sound devices, rhetorical devices.
Figurative devices are techniques used by writers and speakers to convey meaning beyond the literal interpretation of words. These types of stylistic devices add depth and imagery to language, making it more expressive and engaging. Common figurative devices include metaphors, similes, personification, hyperbole, and irony, among others. Each device will be explained below, together with examples.
Metaphor & Simile
By contrasting an item or person with another, prolific writers aid individuals in perceiving the subject from a unique perspective . The sole distinction between a metaphor and a simile is that a metaphor does not draw attention to the fact that it is a comparison , whereas a simile uses one of the comparing terms “like” or “as,” making it easy to recognize.
- He is as strong as an ox. (Simile)
- The world is a stage. (Metaphor)
Personification
Giving human characteristics to non-human entities can make writing come to life. As a result, personification helps the writer express what actual human characters feel by connecting those emotions to their natural world.
- The wind whispered through the trees.
- The flowers danced in the gentle breeze.
Irony can be categorized as either dramatic, verbal, or situational. Verbal irony uses words to express something that contrasts from their literal meaning, while dramatic irony is where the situation is understandable by the audience, but the fictional character is not aware , creating suspense . Situational irony , occurs when there is a discrepancy between what is expected to happen and what actually happens, involving a twist in the story.
- “What a beautiful day,” said sarcastically during a thunderstorm. ( Verbal )
- Unaware character in a horror movie, but the audience knows the danger. ( Dramatic )
- When a firefighter’s house burns down. ( Situational )
A writer who uses hyperbole is using an exaggeration , that is not supposed to be taken literally, but emphasizes the statement. The opposite of hyperbole is litotes , which is an understatement.
- I’m so hungry, I could eat a horse.
- The suitcase weighs a ton !
Euphemism is a device where a milder or less direct word or phrase is used in place of one that is considered harsh or unpleasant, softening the impact . The opposite is dysphemism, which uses a harsh or offensive term for a more neutral or polite one.
- She passed away yesterday. (Died)
- He was let go from the company. (Fired)
The stylistic device allusion refers to a brief and indirect reference to a well-known person, place, event, or another literary work. Allusions are often used in poetry , to add symbolic imagery, or invite readers to engage actively with the poem.
- He’s a real Romeo when it comes to relationships. (Romantic)
- That restaurant is like the Garden of Eden . (Place of beauty & abundance)
Allegory is the use of characters and events to represent ideas. A writer can use this stylistic device to convey hidden meanings , typically moral or political , through symbolic actions, figures, and imagery.
- Animals as political leaders. (Animal Farm, George Orwell)
- Perseverance contrasting with overconfidence (The Tortoise and the Hare)
In the realm of writing, authors employ sound devices as a means of generating auditory effects and rhythm in their work, thereby elevating the text’s remembrance . These types of stylistic devices are especially prominent in poetry , since they play with the sound of words and phrases to evoke specific emotions or enhance the reader’s experience.
Some common sound devices include alliteration, assonance, and onomatopoeia. Each tool will be explained below, together with examples.
Alliteration
Alliteration refers to the use of the same first consonant in a series of words. It can also be the repetition of a single sound at the beginning of several words that follow each other in a sentence. It emphasizes the repeated words and creates a rhythm that makes a piece of text more pleasant to listen to or read.
- S ally s ells s eashells by the s eashore.
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds in a sentence. The use of this stylistic device gives writing rhythm and sound, which may influence the reader’s mood.
- The r ai n in Sp ai n falls m ai nly on the pl ai n.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a sonic device, where words imitate the natural sounds of things they describe. This stylistic device is commonly used in poetry , prose , and other forms of writing.
Rhetorical devices are used to persuade the audience or enhance the rhetorical impact of the text. These tools are focused on the structure and delivery of the message, rather than the content itself. Oftentimes figurative and rhetorical devices, and their meanings both overlap, yet the former specifically conveys a true meaning beyond the literal interpretation.
Parallelism
Parallelism is a rhetorical device, in which a writer or speaker uses similar grammatical structures to create balance and emphasis in their writing. It is commonly used in literature , speeches , and other forms of persuasive writing to enhance clarity and impact.
- Easy come, easy go.
- The sun rises in the east ; it sets in the west .
Repetition can be a powerful tool for prolific writers and speakers to create impact and engage their audience. It helps reinforce the central theme or message of a piece of writing, and make it more memorable to the reader or listener.
While it can certainly contribute to the rhythm of a piece of writing or speech, its primary function is to create emphasis through the repetition of words or phrases. Repetition is an umbrella term for devices, such as epistrophe, anadiplosis, anaphora, chiasmus, and others.
- That is a very, very, very tall hat!
- I have a dream that one day (…) I have a dream that one day (…)
The rhetorical device cataphora is the use of a pronoun or other linguistic unit in an earlier phrase to refer ahead to another word or phrase within a sentence or discourse.
- When he arrived home, John went to sleep.
- She was thirsty. Sarah drank a glass of water, as…
You achieve the rhetorical device climax by arranging words in an order of gradually increasing importance or tension. The opposite of climax is anticlimax , where tension descends as the text progresses.
- When it rains , it pours .
- I came , I saw , I conquered .
The juxtaposition of contrasting words or phrases within a parallel grammatical structure, often used to emphasize contrast, or highlight a point. It’s commonly used in literature, speeches, and debates to underscore a theme or argument by presenting its opposite in a structured and impactful way.
- It was the best of times , it was the worst of times .
- To err is human, to forgive is divine.
Metonymy refers to a figure of speech in which one word or phrase is substituted for another with which it is closely associated .
- The White House issued a statement.
- I’d love to have a glass .
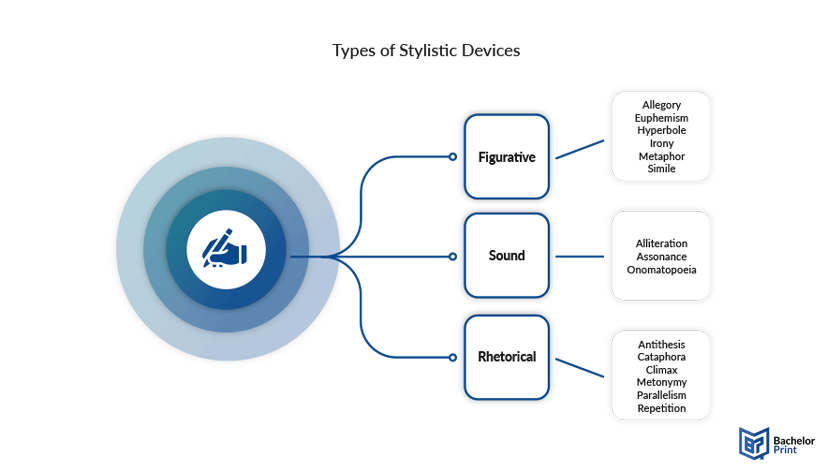
Impact on literature
As mentioned in the examples above, stylistic devices have a significant impact on different genres of literature, influencing the tone of non-fiction and fiction writing. In this paragraph, we’ll break down the effects of their use in various genres, as well as the most popular stylistic devices.
In fiction, stylistic devices are used to develop characters, create vivid setting, and advance the plot. Devices such as imagery , metaphor , and simile can transport readers to imaginary worlds and evoke strong emotional responses from readers.
Dialogue and characterization benefit from techniques like repetition and irony , which add depth and complexity to the store. Flashbacks , foreshadowing , and other structural literary devices enhance narrative flow and engage readers’ interest.
The night was a blanket of darkness , wrapping the city in its embrace. (Metaphor)
Stylistic devices are integral to poetry, where they shape the rhythm and sound patterns of the verse. Incorporation of devices such as rhyme , alliteration , anaphora , and assonance create musicality and enhance the aesthetic appeal of the poem.
Imagery through metaphors and personification evokes powerful sensory experiences and conveys abstract concepts in a condensed form. Poetic devices like parallelism contribute to the poem’s structure and enhance its thematic resonance.
The moonlight danced on the dewy grass. (Personification)
Plays & Speech
Like other forms of literature, plays are crafted with careful attention to language, characterization, plot, and themes. Plays often explore complex human experiences and societal issues, making them an important form of literary expression. Playwrights may use certain motifs or symbols in repetition throughout the play to underscore key themes. A most common tool is dramatic irony , which leads to tension and suspense.
Similarly, speeches are written or spoken compositions, often intended to persuade audiences. Famous speeches, such as Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech or Abraham Lincoln’s “Gettysburg Address,” are frequently studied for their rhetorical techniques. Generally, rhetorical questions are used to engage the audience and encourage active listening. A common stylistic device is repetition , which enhances memorability.
Ask not what your country can do for you, ask what you can do for your country. (Repetition)
Tips to elevate your writing
To round off this article, here’s a list of helpful tips on how you can improve your writing style and its quality.
- Study Examples : Read widely across different genres and pay attention to how authors use stylistic devices to enhance their writing. Analyze the impact of them on tone, mood, and overall effectiveness.
- Practice Regularly : Experiment with incorporating stylistic devices into your writing regularly. Start with simple exercises and gradually work your way up to more complex techniques.
- Consider Context : Choose tools that are appropriate for the genre and audience of your writing. Consider how the devices will resonate with your readers and support your intended message.
- Balance Creativity with Clarity : While they may add flair, avoid overloading your text with too many devices. Strive for a balance between stylistic richness and clarity of expression.
- Embrace Experimentation : Don’t be afraid to experiment with new stylistic devices or unconventional approaches to writing. Push yourself out of your comfort zone and explore different ways of expression.
- Keep Learning : Continuously seek opportunities to expand your knowledge and skills. Attend writing workshops, read craft books, and engage with writing communities to deepen your understanding and hone your craft. Practice makes perfect.
What are stylistic devices and examples?
Stylistic devices are techniques used by prolific writers to enhance their writing and create specific effects. Examples include metaphors, similes, irony, and personification.
Why are stylistic devices important?
Stylistic devices are important in both writing and speech since they add uniqueness to your text by providing clarity, emphasis, and freshness of expression. Reading a text with well-placed stylistic devices is more interesting than reading plain text. Learning how to apply different stylistic devices in your writing will help you elevate your writing from plaintext to addictive pieces of art.
What is the difference between stylistic devices and literary devices?
While these words are used interchangeably, stylistic devices are tricks that make written material enjoyable to read. In contrast, literary devices are tools that create an effect that deepens the reader’s understanding of the issue or insight that the writer is delivering.
Is figurative language the same as stylistic devices?
Figurative language is a subset of stylistic devices. It specifically refers to language that uses figures of speech to convey meanings beyond the literal interpretations of words. Stylistic devices encompass a broader range of techniques used by writers to enhance their writing process, including both literal and figurative elements.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Without such literary device, Literature would be dull and boring (Di Yanni, 2007, p. 779). The analysis of imagery in the Arabic and the English poems on the stylistic level is based on ...
Authored by Hasan Alisoy, a seasoned linguist and educator, this guide delves into the intricacies of stylistic analysis and its practical applications in language pedagogy. The book demystifies ...
The debate among linguists occurs because they have different opinions regarding the nature of literary language, while the debate between linguists and literary scholars arises as literary scholars question the authority of linguistics to study literary writings. Therefore, in this paper I argue that the language of literature is similar to ...
4. To analyze stylistics devices of Keats's poetry through "To Autumn". STYLISTICS Stylistics is the study and interpretation of text from a linguistics perspective. It is branch of applied linguistics concerned with the study of style in texts. Before the 20th century it started to deal with non literary text.
Stylistics, as a discipline based on modern linguistic theories, turns to studying non-literary texts from the perspective of stylistics. The study examines English football news from the three levels of stylistic analysis, namely lexis, syntax and semantics. Compared with other news types, English football news are less attracted to ...
1951. 242. This article explores the translation strategies applied to stylistic devices in literary texts, delving into the complexities of rendering nuanced linguistic and cultural elements. Focused on metaphors, imagery, and wordplay, the study navigates the symbiotic relationship between translation theory and stylistics.
. This article describes that these devices also differ in terms of their effect on the reader or listener. Some devices, such as anaphora and epiphora, create a sense of rhythm and repetition, while others, such as chiasmus and antimetabole, create a sense of balance and symmetry. Some devices, such as epizeuxis and diacope, create a sense of urgency or emphasis, while others, such as ...
Journalists are trained to write according to genre laws (Itule & Anderson, 2006). In news discourse, cognition is supported by a number of simple devices like repetition, but also higher level devices like quotation. Our approach relies on news discourse properties, as described and discussed on theoretical grounds by van Dijk (1988).
The stylistic analysis is a preliminary stage to define the pragmatic potential of the TED Talks texts. The most recurrent literary devices used in the talks are pun, irony, oxymoron, epithet, metaphor, parallel constructions, periphrasis, zeugma, chiasmus, etc. It is assumed that the TED Talks texts are saturated with stylistically coloured verbal means, which ensure the self-sustainability ...
refrained from carrying out stylistic studies and interested more in cultural and mono-linguistic analysis. However, claims supporting the study of stylistics remain robust as critics are still referring to linguistic methods when explaining literary texts (Cureton, 1992). A very essential principle of stylistic study is "foregrounding".
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
The article also deals with the review of the fundamental theories of modern researchers. I.R.Galperin's, Yu.M. Skrebnyov's, V.A.Kukharenko's, Jochen Lüders' classifications are investigated and the relevant conclusions are given. The research advances the idea of classifying the stylistic devices in the circle of language layers.
Vol. 8, No. 5, 2020, pp. 205-215. doi: 10.11648/j.ijll.20200805.13. Abstract: Literary texts have largely been analysed from the perspective of literary criticism, literary stylistics. This paper is a linguistic stylistic analysis of Henrik Ibsen's play, A Doll's House. The principal aim of the paper of the paper is to identify and analyse ...
Teach literary devices - Readers are required to be actively engaged in the process of decoding and comprehending a range of literacy devices, including narrative structure, metaphor and symbolism, point of view, and the use of puns, alliteration, and inferences. Teach the classics- Classic novels that have been adapted to graphic novels ...
This paper discusses stylistic devices in Ben Okris The Famished Road. In the presentation of his story, the novelist makes use of literary devices which enrich the readers' understanding and enjoyment of his subject matter. Satire, register, cliché, pidgin and proverbs are some of the devices. Others include: figurative language, irony and ...
European Journal of Research and Reflection in Educational Sciences Vol. 8 No. 11, 2020 ISSN 2056-5852 Progressive Academic Publishing, UK Page 46 www.idpublications.org spelling or sound in the mother tongue, and general knowledge. Read and identify stylistic devices Nothing much ever happens in our town.
Literary Devices & Terms. Literary devices and terms are the techniques and elements—from figures of speech to narrative devices to poetic meters—that writers use to create narrative literature, poetry, speeches, or any other form of writing. All.
Definition: Stylistic Devices. Stylistic devices are typically considered figures of speech, whose key aspect is departing from straightforward or literal language to create depth, emphasize ideas, or convey emotions in a more vivid and imaginative way. These aspects are the factors behind their widespread use in various creative fields, such as academic essays, literature, poetry, speeches ...
Accurate passenger flow forecasting is crucial in urban areas with growing transit demand. In this paper, we propose a method that combines advanced machine learning with rigorous time series analysis to improve prediction accuracy by integrating different datasets, providing a prescriptive example for passenger flow prediction in urban rail transit systems.
PHONETIC STYLISTIC DEVICES. Shaxzada Sultanbaevna Saymanova. Published in CURRENT RESEARCH JOURNAL OF… 1 October 2021. Linguistics. This article deals with the analysis of phonetic stylistic devices and expressive means in the works of poets. Examples from poetry are given in this research work and they are of great importance for learning ...