47 case interview examples (from McKinsey, BCG, Bain, etc.)

One of the best ways to prepare for case interviews at firms like McKinsey, BCG, or Bain, is by studying case interview examples.
There are a lot of free sample cases out there, but it's really hard to know where to start. So in this article, we have listed all the best free case examples available, in one place.
The below list of resources includes interactive case interview samples provided by consulting firms, video case interview demonstrations, case books, and materials developed by the team here at IGotAnOffer. Let's continue to the list.
- McKinsey examples
- BCG examples
- Bain examples
- Deloitte examples
- Other firms' examples
- Case books from consulting clubs
- Case interview preparation

Click here to practise 1-on-1 with MBB ex-interviewers
1. mckinsey case interview examples.
- Beautify case interview (McKinsey website)
- Diconsa case interview (McKinsey website)
- Electro-light case interview (McKinsey website)
- GlobaPharm case interview (McKinsey website)
- National Education case interview (McKinsey website)
- Talbot Trucks case interview (McKinsey website)
- Shops Corporation case interview (McKinsey website)
- Conservation Forever case interview (McKinsey website)
- McKinsey case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- McKinsey live case interview extract (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
2. BCG case interview examples
- Foods Inc and GenCo case samples (BCG website)
- Chateau Boomerang written case interview (BCG website)
- BCG case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Written cases guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG live case interview with notes (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview with ex-BCG associate director - Public sector case (by IGotAnOffer)
- BCG mock case interview: Revenue problem case (by IGotAnOffer) - See below
3. Bain case interview examples
- CoffeeCo practice case (Bain website)
- FashionCo practice case (Bain website)
- Associate Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Consultant mock interview video (Bain website)
- Written case interview tips (Bain website)
- Bain case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
- Digital transformation case with ex-Bain consultant
- Bain case mock interview with ex-Bain manager (below)
4. Deloitte case interview examples
- Engagement Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Recreation Unlimited practice case (Deloitte website)
- Strategic Vision practice case (Deloitte website)
- Retail Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Finance Strategy practice case (Deloitte website)
- Talent Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Enterprise Resource Management practice case (Deloitte website)
- Footloose written case (by Deloitte)
- Deloitte case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
5. Accenture case interview examples
- Case interview workbook (by Accenture)
- Accenture case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
6. OC&C case interview examples
- Leisure Club case example (by OC&C)
- Imported Spirits case example (by OC&C)
7. Oliver Wyman case interview examples
- Wumbleworld case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Aqualine case sample (Oliver Wyman website)
- Oliver Wyman case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
8. A.T. Kearney case interview examples
- Promotion planning case question (A.T. Kearney website)
- Consulting case book and examples (by A.T. Kearney)
- AT Kearney case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
9. Strategy& / PWC case interview examples
- Presentation overview with sample questions (by Strategy& / PWC)
- Strategy& / PWC case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
10. L.E.K. Consulting case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
- Market sizing case example video walkthrough (L.E.K. website)
11. Roland Berger case interview examples
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- Transit oriented development case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 1 (Roland Berger website)
- 3D printed hip implants case webinar part 2 (Roland Berger website)
- Roland Berger case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. Capital One case interview examples
- Case interview example video walkthrough (Capital One website)
- Capital One case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer)
12. EY Parthenon case interview examples
- Candidate-led case example with feedback (by IGotAnOffer)
14. Consulting clubs case interview examples
- Berkeley case book (2006)
- Columbia case book (2006)
- Darden case book (2012)
- Darden case book (2018)
- Duke case book (2010)
- Duke case book (2014)
- ESADE case book (2011)
- Goizueta case book (2006)
- Illinois case book (2015)
- LBS case book (2006)
- MIT case book (2001)
- Notre Dame case book (2017)
- Ross case book (2010)
- Wharton case book (2010)
Practice with experts
Using case interview examples is a key part of your interview preparation, but it isn’t enough.
At some point you’ll want to practise with friends or family who can give some useful feedback. However, if you really want the best possible preparation for your case interview, you'll also want to work with ex-consultants who have experience running interviews at McKinsey, Bain, BCG, etc.
If you know anyone who fits that description, fantastic! But for most of us, it's tough to find the right connections to make this happen. And it might also be difficult to practice multiple hours with that person unless you know them really well.
Here's the good news. We've already made the connections for you. We’ve created a coaching service where you can do mock case interviews 1-on-1 with ex-interviewers from MBB firms . Start scheduling sessions today!
The IGotAnOffer team
Related articles:


How To Write A Consulting Case Study: Guide, Template, & Examples
When you deliver a successful project, do you publish a consulting case study about it?
A consulting case study is a short story about a successful project that explains…
- The problem your client was dealing with before hiring you;
- your expertise and process for solving that problem;
- and the results your expertise and process created for the client and their business.
In my experience, our consulting case studies are among the most powerful pieces of content we publish. They’re a big reason why people are comfortable signing up for our Clarity Coaching Program .
Because our case studies prove our program helps our clients get results.
I can say that our coaching program is the best on the market until I’m blue in the face.
But it’s much more powerful for consultants to see the results others have experienced for themselves: through our case studies and testimonials.
If you don’t have something of value on your website like a case study — something that actually shows you can achieve results for your clients — then your website will only serve as “confirmational marketing.”
It will confirm what people hear about you. But it won’t help you generate interest and leads.
So, if you want to shift your website beyond mere confirmational marketing to an asset that helps you generate leads and conversions, consider writing consulting case studies using the method below.
In this article, you’ll learn how to write compelling case studies that help you win more consulting clients.
Ready? Let’s dive in…
Your case study is proof that not only can you talk the talk, but you can also walk the walk.
What Is A Consulting Case Study?
When a potential client is deciding on whether they will hire you or not, a big question in their mind is…
“Can this person or company really do what they say they can for my business?”
There are many forms of thought leadership you can use to prove you can deliver results.
The consulting case study is one of them.
A case study, in the context of consulting, is typically a written document that describes…
- the problem a client was facing,
- the actions you took to solve that problem,
- and the outcomes it created for your client.
You write case studies to demonstrate the results and value you created for a past or current client.
What makes them so effective as marketing material?
- They are relatively easy to put together (especially when you use our template below).
- Your potential clients enjoy reading them.
- And they are a highly effective way to demonstrate your authority and expertise in your field.
Next, I’ll walk you through how to write a consulting case study.
In our program, one of the things we teach consultants is how to better understand their clients’ problems and articulate their ability to solve those problems in a way that will attract new clients.
How To Write A Consulting Case Study
Here are the steps to writing your consulting case study. You can follow along with our consulting case study template .
1. Get Permission From The Client
You shouldn’t write a case study that names your client without their permission.
So, before you start writing it, ask them if they’d be OK with you publishing a case study about the project.
Now, I’m not a lawyer, and nothing in this article or anything I write is legal or financial advice. But here’s what we’ve found, through running consulting businesses for over two decades, often works best:
A question we often receive from consultants is “What if I can’t use the name of my client or the company I worked with?” Generally, this isn’t an issue. If your contract says you can’t use the client’s company name, or the client says “No” to your request, all is not lost.
What tends to work extremely well is still writing the case study, but without using the client’s name. Instead, describe the client.
For example, let’s say your client is the automaker Mazda. If you can’t use their name, consider “Working with a top 20 global automaker…”
This gives prospective buyers a good idea of the caliber and type of company you worked with.
When you ask your client for their permission to create a case study that features them, you’ll generally find that 9 times out of 10 they won’t have a problem with you doing so, but make sure you ask before publishing.
2. Introduce The Client’s Business
Once you’ve gotten permission from the client, you’ll begin writing your case study. Follow along using our template .
The first section is the introduction. Set the stage here by introducing your client, their business, and their industry.
This section gives context to the case study. Ideally, your ideal client is intrigued by being in a similar industry or situation as the client in your case study.
3. Describe The Problem Or Challenge
In this section, you outline the problem your client was facing.
Be as specific as you can be.
Simply saying they had marketing issues or a problem with their PR is not enough.
The more detail you include the clearer the picture will become and the more effective your case study copywriting will be.
If your ideal client reads this and has a similar problem as the client in the case study, you can guarantee that their eyes will be glued to the screen, salivating to learn how you solved it.
4. Summarize Your Action Steps
Now that you’ve described the problem your client was up against, you’ll explain what you did to help solve the problem.
In this section, break down each part of the process you used or the steps you took to solve it.
The reader should get the sense that you have a process or system capable of solving the problem and getting results.
This is where you get to demonstrate your know-how and expertise. Get as technical as you can. Show your reader “Hey, this is how I can get YOU results too.”
5. Share The Results
It’s time to demonstrate results.
Write the results that were achieved and how they impacted the business/organization/person.
In many cases, the outcome isn’t just dollars and cents — it can also be less tangible value.
Are they less stressed? Do they have more free time? Are they finding more meaning and enjoyment in their work?
Mention if you’re continuing to work with this client through a retainer . If you’re not, describe how the results will impact their business in the future.
This is also a great place to include a quote or testimonial from your client.
The “Results” section is key because it shows prospective clients that you’ve solved the problems they are facing and have delivered the actual results that they likely desire.
6. Write A Call To Action
At the end of the case study, you should always include a sentence or two inviting the ideal client to reach out.
They’ve just read about the problems you can solve, how you solve them, and the results you can create.
They are primed and ready to reach out to inquire about how you can do it for them.
But if you don’t have a direct call to action for them to do that, many of them will leave without taking action.
So, write a direct, clear call to action that takes them to a page where it’s easy to book a consultation with you or where you provide your contact information.
7. Share It
Marketing for consultants is all about providing value to your ideal clients, being known for something specific, and positioning yourself as an expert and authority that your ideal clients want to work with. So, whenever you publish a piece of valuable content like a case study, your mission is to get as many eyes on the case study as possible.
The best place to publish your case study is on your website or blog.
You can also submit case studies to industry publications. These are a great way to spread the word about you and your client’s business.
Make sure to also share your case study on all social media platforms where your ideal clients hang out online. For consultants, that means LinkedIn.
Work your “marketing muscle” by actively promoting your case study, and you’ll reap the rewards of this powerful piece of authority-building content.
Writing case studies for your consulting business not only helps you land new clients, but it’s also a great way for you to review past projects.
Doing this helps you to find what worked and what didn’t.
And you’ll continue to learn from your experiences and implement your best practices into your next consulting project.
Consulting Case Study Template
Click here to access our Consulting Case Study Template .

This template is designed using a “fill in the blank” style to make it easy for you to put together your case studies.
Save this template for yourself. Use it to follow along with the examples below.
Consulting Case Study Examples
Here are some example case studies from our Clarity Coaching Program clients.
1. Larissa Stoddart
Larissa Stoddart teaches charities and nonprofits how to raise money.
To do that, she provides her clients with a training and coaching program that walks them through twelve modules of content on raising money for their organization, creating a fundraising plan, putting an information management system into place, finding prospects, and asking those prospects for money.

Through her case studies, Larissa provides a comprehensive overview of how she helps her clients build robust fundraising plans and achieve and win more donations.
2. Dan Burgos
Danila “Dan” Burgos is the president and CEO of Alphanova Consulting, which works with US manufacturers to help them increase their profitability through operational improvements.
The goal of Alphanova is to increase their clients’ quality and on-time delivery by 99 percent and help them increase their net profits by over 25 percent.

Through his case studies, Dan lays out the problem, his solution, and the results in a clear simple way.
He makes it very easy for his prospects to envision working with his firm — and then schedule a consultation to make it happen.
3. Vanessa Bennet
Through her company Next Evolution Performance, Vanessa Bennett and her business partner Alex Davides, use neuroscience to help driven business leaders improve their productivity, energy, profitability, and staff retention, while avoiding burnout.

Through her “Clients” page, she provides a list of the specific industries she works with as well as specific case studies from clients within those industries.
She then displays in-depth testimonials that detail the results that her consulting services create for her clients.
These are powerful stories that help Vanessa’s clients see their desired future state — and how her firm is the right choice to help them get there.
As you see, our clients have taken our template and made them work for their unique style, clients, and services.
I encourage you to do the same.
And if you’d benefit from personal, 1-on-1 coaching and support from like-minded consultants, check out our Clarity Coaching Program .
Get Help & Feedback Writing Consulting Case Studies
If writing and demonstrating your authority were easy, then every consultant would be publishing case studies.
But that’s not the case.
Sometimes it helps to have a consulting coach to walk you through each step — and a community of like-minded consultants with whom you can share your work and get feedback from.
That’s why we’ve built the Clarity Coaching Program.
Inside the program, we teach you how to write case studies (among dozens of other critical subjects for consulting business founders).
And we’ve also created a network of coaches and other consultants who are in the trenches — and who are willing to share their hard-fought knowledge with you.
Inside the Clarity Coaching program , we’ve helped over 850 consultants to build a more strategic, profitable, and scalable, consulting business.
Learn More About Clarity Coaching
We’ll work hands-on with you to develop a strategic plan and then dive deep and work through your ideal client clarity, strategic messaging, consulting offers, use an effective and proven consulting pricing strategy, help you to increase your fees, business model optimization, and help you to set up your marketing engine and lead generation system to consistently attract ideal clients.
15 thoughts on “ How To Write A Consulting Case Study: Guide, Template, & Examples ”
This is a great outline and I found it quite helpful. Thanks.
Shana – glad you found this post helpful!
I have used case studies to get new clients and you're right, They work.
Jay – thanks for sharing. I've worked with many clients to implement case studies and have used them in several businesses and have always found them to be great at supporting proof and establishing authority and credibility.
Dumb question: guess you can't charge if you're doing a case study, huh?
Terri – No such thing as a dumb question where I come from. Always good to ask.
You definitely can charge for case studies. Michael Stelzner has a lot more information on writing white papers (and case studies) as projects.
This post was really aimed at using case studies to win more business and attract clients. But you can definitely offer this service to companies and they'll pay handsomely for it.
That was a great question!
Hello,I am really glad I stumbled upon your consulting site. This outline is very helpful and I love the e-mails I recieve as well Thanks!
Happy to hear that
This is a great site for consultants – great information for the team to share with consultants that reach out to us. Thank you!
Thanks Deborah
It is a good steps if we know how we start and control our working.
All I wanted to know about putting together a case study I have got. Thanks so much.
to put together your consulting case study: to put together your consulting case study:
I have used your outline today to write one case. Thank you for sharing.
Hi – This is a great piece, and covers all the core elements of a case study with impact.
Couple of extra points…
1. it’s really powerful to provide a mix of qualitative and quantitative results where possible e.g. ‘we saved the client $500 per month and feedback tells us morale improved’
2. We are seeing more and more consultancies include images and video in their case studies. This obviously depends on the context, so while it’s not necessarily appropriate within the confines of a bid, it is definitely something to think about for those case studies that you want to publish online or in a marketing brochure.
Leave a Comment, Join the Conversation! Cancel reply
Your Email will be kept private and will not be shown publicly.
Privacy Overview
The Ultimate Guide to the Consulting Case Interview – With Examples
This guide, written by a former McKinsey consultant and Wharton MBA, breaks down the management consulting case interview into comprehensible parts with relevant, realistic examples at every turn.

By Tracy V.
Posted March 12, 2024

Table of Contents
While the consulting case study interview may seem daunting at first, most cases follow a typical song-and-dance. Once you get a hang of it, prepping feels much more manageable. The first part of this guide will give a broad overview of the case interview. The second part will break out the typical structure of an interviewee-led case. The last part will dive into each component, with tips and suggestions for preparing. Note that some firms may have their own specific case interview style. Be sure to familiarize yourself with your target firms’ interview processes before the time comes to recruit.
Case interviews involve tackling a business issue or problem faced by a company (the client). These interviews allow consulting firms to gauge candidates’ ability to perform the job. Specifically, firms are testing whether candidates can:
- Think in a structured and creative way
- Analyze and interpret new information
- Communicate persuasively and succinctly
Most firms conduct interviewee-led cases, as outlined in the guide below. In these cases, the candidate is expected to drive the case forward by asking the interviewer for data or information relevant to forming the recommendation. A few firms, most notably McKinsey, are interviewer-led, meaning that the interviewer will be the one guiding the discussion.
Below are a few common types of cases that you can expect to receive. Some cases can be several types all in one (lucky you!):
- Profitability - Determine cause for profit decline and / or ideas for increasing profit; you will rarely get a standalone profitability case – It will usually be rolled up in another case type
- Growth - consider strategies for company growth; could be through sales or market share
- Market Entry / New Business - Assess attractiveness of entering new geography / business / sector and method for entering
- Due Diligence / M&A - Assess attractiveness of purchasing / acquiring a company or business; client can be another company or a financial sponsor
- Competitive Response - Address a competitor’s recent action (e.g., new acquisition, change in pricing strategy)
- Non-Traditional - Similar to the other cases but the client (non-profit, NGO, education-focused entity) has different objectives than a typical corporate company
Case Interview Components
- Prompt: Interviewer reads aloud the case while the interviewee takes notes
- Recap: Interviewee provides a high-level summary of the case and confirms accuracy of information written
- Clarifying Questions: Interviewee asks 2-3 high-level questions
- Structuring (<2 minutes): Interviewee takes a few minutes create a roadmap for approaching the case
- Framework Presentation (2-3 minutes): Interviewee reviews the structure with the interviewer, who may have follow-up questions. Interviewee then moves the case forward by asking for additional information
- Brainstorming: Interviewee is expected to list out several solutions or ideas (e.g., cost drivers for an industry, ways to increase sales)
- Exhibits: Interviewee will be given data in forms such as graphs or charts and expected to provide high-level insights
- Math: Interviewee will be asked to perform a calculation with the new information or using data from the exhibits. Oftentimes, interviewee is not given enough information and must ask for the relevant data
- Synthesis and Recommendation (2-3 minutes) : Interviewee provides the answer first, then supporting facts from the case, and finally risks and next steps
Setup (2-3 minutes)
Prompt : The interviewer may be giving you A LOT of information - don’t write down everything verbatim. Jot down facts and figures, the client name, and the objective(s). If you miss something or don’t remember what a number means, you can ask after your recap.
- Prep: Have a friend read you several different case interview prompts and practice taking down notes. Create your own shorthand and learn how to recognize extraneous pieces of information
Recap : I always reference the client by name and start my recap with the objective(s) first, since this is the most important part of the case. The recap should be summarized, not verbatim, and you should be checking that the figures you wrote down are correct.
- Prep: Practice summarizing your notes out loud instead of repeating the case verbatim. Time yourself to make sure it’s <1 minute.
Clarifying Questions : Very detailed questions should be saved for the case. Clarifying questions are meant to help you with your structure or alleviate any confusion. Keep these at 2-3 questions. I usually ask questions pertaining to:
- Language/terminology - The interviewer won’t expect you to know the nuances of every industry or practice area. It is better you start off the case on the right footing by asking for clarifying definitions
- Goals/objectives - I always ask if there are other goals the company has in mind and, if relevant, specific financial targets or timeframe. Sometimes, the objective given is vague, so I will ask the interviewer to be more specific.
- Business model or geography - Very helpful for cases in niche industries; understanding geography can also prompt you to think about factors like labor cost or global competition
- Scope - To save you time from considering every possibility, you can ask whether the company is leaning towards one option or excluding a set of options completely
- Prep: Have a friend read you case prompts and then practice asking 2-3 clarifying questions on the fly. Try to think of them as you’re taking down notes and giving the recap. Are they helping you with your structuring or are you asking the first thing that pops into your head? Are they broad enough or overly detailed? Are there types of questions you should be asking but keep forgetting?

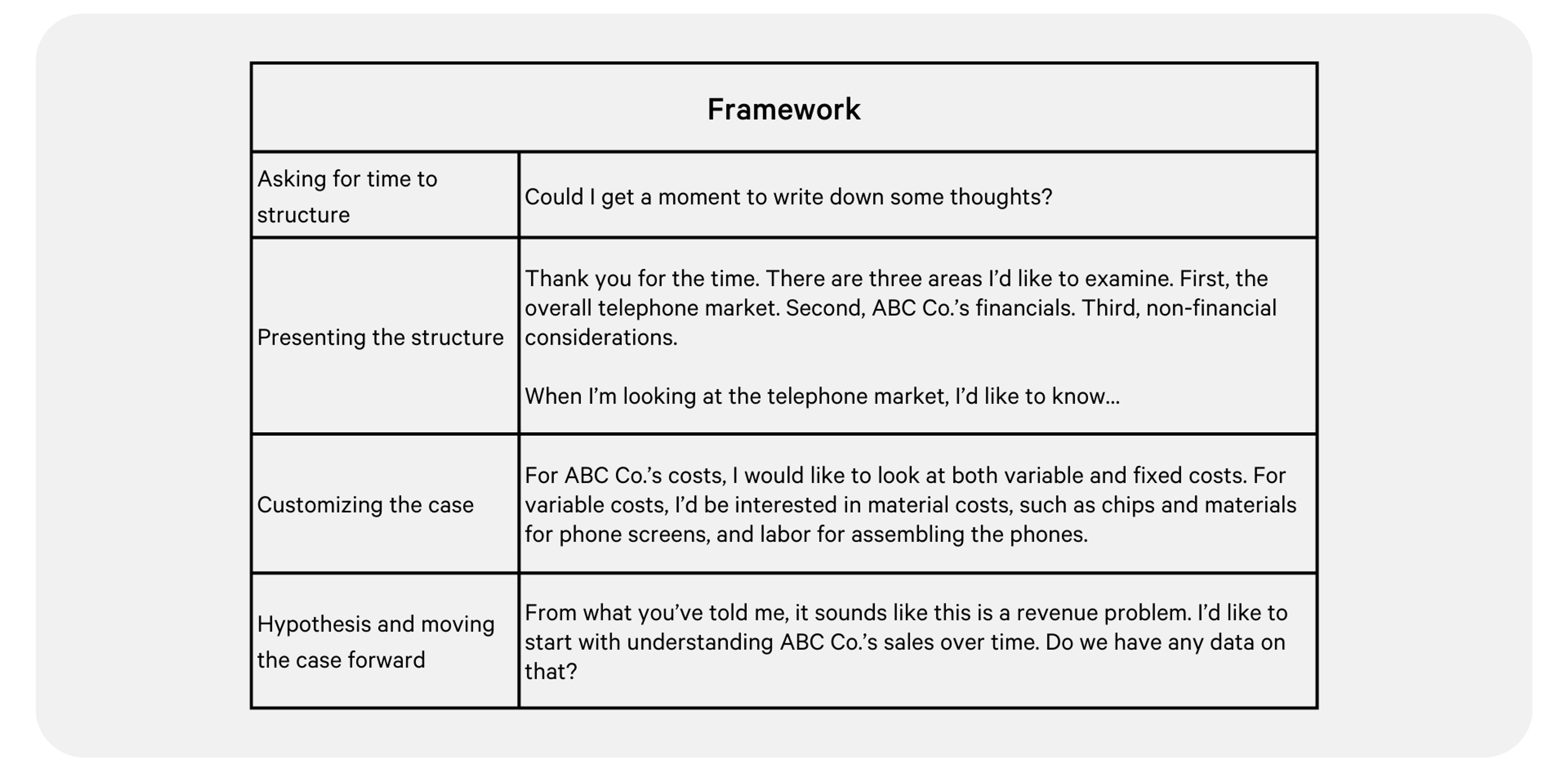
Framework (4-5 minutes)
Structuring (<2 minutes) : Do not use the word “framework” during the interview. I ask if I could have time to “gather my thoughts” when I am structuring. In your structure, you should have at least three but no more than five “buckets.” These are areas that you want to explore in order to solve the case. In each bucket, there should be at least three sub-bullets. Make sure there is no overlap between the buckets.
- Prep: Time yourself structuring your roadmaps. Be comfortable with recalling the different buckets you should be considering for each type of case and brainstorming sub-bullets for those buckets. It’s okay to go over two minutes when you first start, but as you get comfortable, make sure you are becoming more efficient. For example, as you become more familiar with the buckets, you don’t need to write down every example for the sub-bullets, they will become muscle memory as you recite them out loud. Review the suggested frameworks for the case and take note of whether there are vital topics you keep forgetting or whether there are unnecessary buckets you keep adding. There is no one “right” answer, but your roadmap should enable you to uncover the necessary information to make your recommendation.
Presenting: Introduce the high-level buckets first before diving into each one. You will want to “customize” your framework to the specific case you’re working on. This does not mean creating a custom framework for every single case. You can use the same topics for similar types of cases (but ensure that those topics are relevant - some cases sneakily rule out an entire topic to see if you are paying attention), but you need to make sure that you are using case-specific language and examples when you present. This shows that you are thinking about the specific problem, not just recycling a generic framework. After going through the structure, pause and ask if the interviewer has any questions. Then, give your hypothesis and state which bucket you want to start with by asking for data pertaining to that bucket and why you want it.
- Prep: Present your structures out loud and note whether you are rambling or being case-specific in your language. If you find that your presentation is too long, consider cutting down on the examples or explanations. Be succinct and say enough to get your point across. Don’t just move on to the next case if your presentation falls short. Keep practicing until you feel satisfied and make mental notes for the next case.
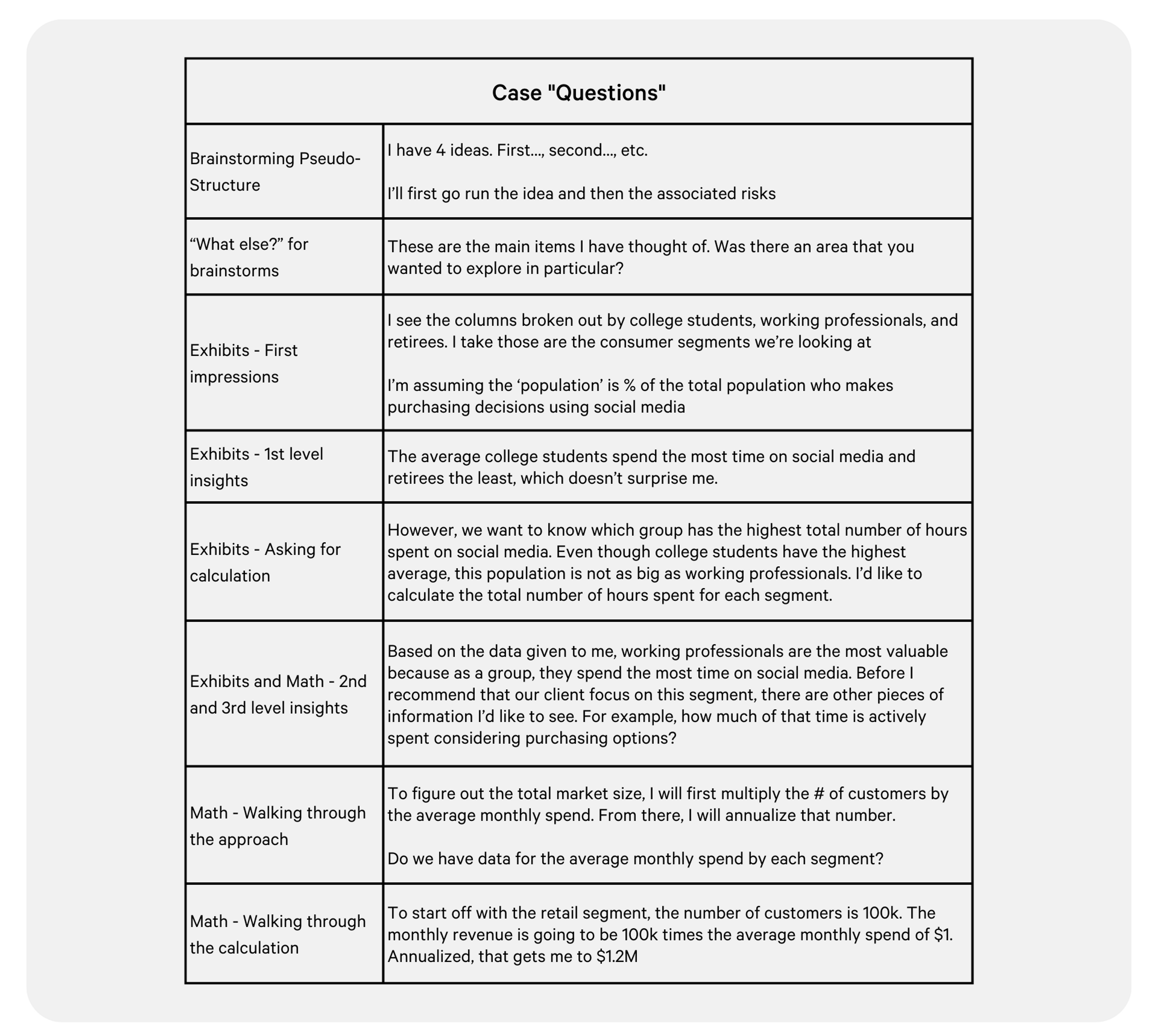
Interview “Questions” (10-20 minutes)
For each type of question, you are going to be doing the same things: answering the question, providing insights, conveying how it impacts your recommendation, and driving the case forward. Every time you have “answered” a question, you want to be thinking, “ What else do I need? What’s the logical path forward ?” The only way you can prepare for this is to run through entire cases! Remember, your framework is your friend. Refer back to it often if you don’t know where to go next.
Brainstorming : You will want to structure your ideas into MECE buckets. They can be fairly simple (financials vs. non-financials, external vs. internal, etc.). Similar to your framework, you will give a preview of the buckets first before going into the details of each and you will need to ensure that it is “custom” for your case. If a structure doesn’t naturally come to you, you can create a pseudo-structure by organizing how you will present your brainstorm. For example, you can state how many ideas you have from the onset or say that you will first go through the ideas first and then the associated risks.
This is a highly debated practice, but I always ask for a few seconds so I can think of a structure (they may say no). Don’t take more than 30 seconds because you can add to your buckets as you are presenting.
For non-technical brainstorms, be creative! For example, when interviewers asked about how to increase sales for a consumer-facing retail company, I would bring up TikTok campaigns and celebrity endorsements as a few ideas. Have fun with it!
Occasionally, interviewers will prod you with, “What else?” This does not always mean you didn’t give enough ideas. Sometimes it’s the opposite – they are looking to challenge you or see how you will react. Just roll with it - if you don’t have anything else, say so.
- Prep: Practice brainstorming for different types of prompts. Collect a bank of general ideas and solutions that can be customized for use across industries. Try to think of as many ideas as you can (four to six at the very least) and exercise that creative muscle. To help you with structuring, have a list of “easy” MECE buckets that you can pull out on the fly.
Exhibits : First, give an overview of the exhibit. As an example, for graphs say what the axes represent, tie it back to the case, and give your interpretation of those axes. This gives the interviewer a chance to course-correct if you misinterpreted the exhibit. Give some insight, even if it is low-hanging fruit, and tie it back to the case. There are three levels of insights for both exhibits and math:
- What the numbers say, patterns/trends (X is smaller than anticipated, Y is the largest driver)
- What the client should do (enter the market, cancel plans, plan for launch)
- What we should do next (reconsider something specific, research more data on X, move on to Y)
Oftentimes, exhibits will tie into a calculation. If you are given an exhibit with data that can be used to calculate more insightful information, tell the interviewer that you would like to make those calculations. The interviewer will lead you down that path regardless but it is more impressive if you call it out.
- Prep: Run through different types of exhibits and see how many insights from each level you can pull out. Practice anticipating what type of data you need next in order to move ahead in the case or whether you can/should calculate anything from the data given. Don’t be too insightful though – you only have a limited amount of time to run through the case.
Math : Before you start calculating anything, it is critical for you to confirm what you are solving for and that the information you wrote down is correct. SUPER IMPORTANT – answer the question that is being asked !! If the interviewer is asking for the incremental profit from a certain strategy, you don’t want to calculate the total profit from the strategy. Active listening is so important!
As you know by now, structure is everything. Again, I always ask for a few seconds to organize my thoughts (the worst thing they can say is no). Set up the problem before you start calculating. This allows you to identify whether there is data missing. Walk the interviewer through your method and ask for missing data. You may need to make your own assumptions or estimates – be sure you can justify them.
If your method is off, the interviewer will usually guide you back to the right path. This saves you from wasting time calculating the incorrect answer. Be sure to pay attention when the interviewer is trying to coach you.
As you are solving the problem, walk the interviewer through each calculation and use math shortcuts as much as possible. Again, if you make a math error, the interviewer can stop you before you go down the entire path. Save time by only calculating what is important for the case and understanding what you can skip.
- Prep: Practice setting up the problem, walking the interviewer through your proposed method, and verbalizing the calculations out loud. On paper, make sure your calculations are being done neatly and not all over the place. Look for different math shortcuts and try them out. Not all of them will fit your style, but you might find new tricks. Track whether you are answering the right questions. Once again, active listening is critical to your candidacy. Once you have correctly solved the problem, make sure you are thinking about the, “So what?” Determine how that number impacts your recommendation and where you should go next.
Synthesis and Recommendation (2-3 minutes)
Again, I always ask for a few seconds to collect your thoughts (<30 secs). If the “CEO is already in the elevator,” they may say no. Have a definitive stance – start with your recommendation and then provide two to three supporting facts using data from the case.
Address risks and next steps (i.e., what is the required analysis/gameplan – this is like real life where the firm is trying to sell additional projects). Your recommendation should be <2 minutes. Frankly, the interviewer has most likely made a decision on your candidacy. Don’t ramble and try to finish strong.
The hardest part of this is pulling out the supporting data in a succinct way. Throughout the case, you should be jotting down notes. I tend to circle what I believe to be relevant supporting data. When you present it, don’t be too specific or granular. You want your recommendation to be punchy.
- Prep: Run through whole cases where you are tracking the relevant supporting data along the way. Time your recommendation and practice verbalizing the information concisely. Don’t forget the risks and next steps. I usually have a list of generic risks (e.g., competitor response, regulation, inaccurate projections) that I can “customize” on the off-chance I’m scrambling to think of some. Your next steps can be collecting additional data to support your recommendation or ways to address those risks.
Free trial!

From 110 top coaches
Access a library of videos, templates, and examples curated by Leland’s top coaches.
Example resumes.

Example Cases
Casing Drills
Mock Interviews

Final Thoughts
- Your approach is more important than the solution – The interviewer is trying to understand how you think. Some cases have data that support recommendations in either direction. The key piece is that you are able to back your stance using the facts and data uncovered during the interview.
- Deadends are okay – There will be times when you make multiple requests for data and the interviewer does not have it. That’s perfectly fine! You can’t read the interviewer’s mind and the case could go in so many directions. Just look back at your framework to see where else you can proceed.
- Be coachable – It’s not the end of the world if your method is wrong or if you misinterpreted an exhibit. The interviewer wants to see that you are actively listening and can take feedback and improve. Don’t freak out! Stay calm! Listen to what the interviewer is trying to tell you.
This guide only scratches the surface of case interviews. The best way to prepare for case interviews is to get your reps in with entire cases. That way, you can identify your areas of weakness and be more precise with the drills. I can give you feedback and additional tips and tricks so that you are performing at your best on interview day. Book a free intro call with me on my Leland profile to discuss how we can personalize your case prep plan!
Preparing for consulting recruiting and/or case interviews? Here are some additional resources to help:
- Top 3 Tactics to Ace Your Case Interview
- A Comprehensive Guide to McKinsey & Co., Bain & Co., and Boston Consulting Group
- From No Offers to Multiple Offers - How to Take Your Casing to the Next Level
- How a Disneyland Churro Helped Me Land a Job at Bain (and 5 Pitfalls to Avoid in Market Sizing Problems)
- Five Tips to Break Into Management Consulting
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.
Browse Related Articles
May 18, 2023
McKinsey Bonus Structure: Understanding the Reward System
Discover how the McKinsey bonus structure works and gain a deeper understanding of the reward system in this comprehensive guide.

Victor Cheng LOMS: Is It the Ultimate Guide to Case Interviews?
Discover the ultimate guide to acing case interviews with Victor Cheng's LOMS program.

June 8, 2023
A Comprehensive Guide to McKinsey Case Interview Preparation
Looking to ace your McKinsey case interview? Our comprehensive guide has got you covered! From understanding the interview process to mastering case frameworks, we provide expert tips and strategies to help you prepare and succeed.

January 2, 2024
The Ultimate Guide to the EY Parthenon Case Interview Process
Are you preparing for the EY Parthenon case interview process? Look no further than our ultimate guide, packed with insider tips and strategies to help you ace the interview and land your dream job.

May 11, 2023
How to Prepare for McKinsey Management Consulting Behavioral Interviews?
If you're preparing for a McKinsey management consulting behavioral interview, this article is a must-read.

How to Prepare for McKinsey Management Consulting Networking Calls?
Learn how to ace your McKinsey management consulting networking calls with these expert tips and strategies.

McKinsey First Year Salary: What to Expect and How to Negotiate
Are you curious about what your first year salary at McKinsey might be? This article provides insights on what to expect and tips on how to negotiate your salary.
Mckinsey Consulting Salary: A Comprehensive Overview
Discover everything you need to know about McKinsey consulting salaries in this comprehensive overview.

Business Analyst McKinsey: A Comprehensive Career Guide
Discover the ins and outs of a career as a Business Analyst at McKinsey with our comprehensive guide.
IQVIA Interview Process: A Comprehensive Guide for Success
Looking to ace your IQVIA interview? Our comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know to succeed, from the application process to common interview questions and tips for impressing your interviewer.

Navigating the Shift from Energy Sector to Management Consulting: An Insider's Guide
Are you considering a career shift from the energy sector to management consulting? Look no further than our insider's guide, filled with tips and insights to help you navigate this exciting transition.

Transportation to Management Consulting: An In-depth Look at How to Make the Transition
Are you considering a career change from transportation to management consulting? Look no further! Our in-depth article provides valuable insights and practical tips on how to successfully make the transition.

The New Equation
Executive leadership hub - What’s important to the C-suite?

Tech Effect

Shared success benefits
Loading Results
No Match Found
PwC case studies
Examples of how a community of solvers brings together the strengths of people and technology to build trust and deliver sustainable outcomes — bringing The New Equation to life.
Featured - 3 items
Reinventing wyndham’s loyalty program technology.
Redesigning the cloud-based ecosystem powering Wyndham Rewards.
Helping the YMCA of GNY meet new community needs
Responding to change and expanding their reach and ability to support.
Baker Hughes is working toward net zero at scale
Learn how PwC helped Baker Hughes accelerate their net zero strategy.
A brighter future for medicine with healthcare technology
A collaboration between OSIC, PwC and Microsoft is helping patients, providers and researchers fight a rare disease.
{{filterContent.facetedTitle}}
- {{v.tagsTitle}}
{{item.title}}
- {{filterContent.dataService.numberHits}} {{filterContent.dataService.numberHits == 1 ? 'result' : 'results'}}
- {{vf.elipsedTagsTitle}}
- 0" ng-click="filterContent.reset()" class="reset-filters"> {{filterContent.resetFiltersLabel}}
{{item.publishDate}}
{{item.text}}
Explore further

Thank you for your interest in PwC
We have received your information. Should you need to refer back to this submission in the future, please use reference number "refID" .
Required fields are marked with an asterisk( * )
Please correct the errors and send your information again.
By submitting your email address, you acknowledge that you have read the Privacy Statement and that you consent to our processing data in accordance with the Privacy Statement (including international transfers). If you change your mind at any time about wishing to receive the information from us, you can send us an email message using the Contact Us page.
© 2017 - 2024 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
- Data Privacy Framework
- Cookie info
- Terms and conditions
- Site provider
- Your Privacy Choices
Career in Consulting

280 Free Case Interview Examples
Do you want to get access to over 280 free case interview examples (with answers)?
If you have interviews planned at McKinsey , The Boston Consulting Group , or any other consulting firm, you are probably looking for case interview examples.
So, to help you prepare, I have compiled a list of 280 free case interview examples:
- Over 30 free case interview examples (+ interview prep tips) from the websites of top consulting firms
- More than 250 free case interview examples from top business school case books
Moreover, you’ll get my take on which case studies you will likely have in interviews.
In short, the resources listed hereafter will be very helpful if you are starting out or have already made good progress in preparing for your case interviews.
One last word : check out this free case-cracking course to learn how to crack the most recent types of case questions consulting firms use in actual interviews.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Get the latest data about salaries in consulting, mckinsey: tips and case interview examples.
McKinsey & Company’s website is definitely one of my favorites.
Because this gives so much insightful information about the role of a consultant and what the hiring process looks like.
Therefore, I highly recommend spending time on their website, even if you are not targeting McKinsey.
In the meantime, here are 8 McKinsey case interview examples
- Electro-light
- GlobaPharma
- National Education
- Talbot trucks
- Shops corporation
- Conservation forever

Check out the McKinsey Hub : A library of 20+ free resources that cover everything you need to secure a job offer at McKinsey.
Besides, here is another McKinsey case interview example.
This case interview question has been recently asked in a real interview:
𝘦𝘊𝘢𝘳𝘊𝘰, 𝘢 𝘑𝘢𝘱𝘢𝘯𝘦𝘴𝘦 𝘭𝘦𝘢𝘥𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘮𝘢𝘯𝘶𝘧𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘳 𝘰𝘧 𝘦𝘭𝘦𝘤𝘵𝘳𝘪𝘤 𝘱𝘢𝘴𝘴𝘦𝘯𝘨𝘦𝘳 𝘷𝘦𝘩𝘪𝘤𝘭𝘦𝘴, 𝘩𝘢𝘴 𝘣𝘦𝘦𝘯 𝘴𝘵𝘳𝘶𝘨𝘨𝘭𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘸𝘪𝘵𝘩 𝘢 𝘭𝘰𝘸 𝘮𝘢𝘳𝘬𝘦𝘵 𝘴𝘩𝘢𝘳𝘦 𝘪𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘉2𝘉 𝘴𝘦𝘨𝘮𝘦𝘯𝘵. 𝘛𝘩𝘦𝘺 𝘦𝘯𝘫𝘰𝘺 𝘴𝘵𝘳𝘰𝘯𝘨 𝘱𝘰𝘴𝘪𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴 𝘪𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘉2𝘊 𝘴𝘱𝘢𝘤𝘦, 𝘣𝘰𝘵𝘩 𝘥𝘰𝘮𝘦𝘴𝘵𝘪𝘤𝘢𝘭𝘭𝘺 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘪𝘯 𝘵𝘩𝘦 𝘪𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘯𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘢𝘭 𝘮𝘢𝘳𝘬𝘦𝘵. 𝘏𝘰𝘸𝘦𝘷𝘦𝘳, 𝘦𝘊𝘢𝘳𝘊𝘰’𝘴 𝘴𝘢𝘭𝘦𝘴 𝘵𝘰 𝘴𝘮𝘢𝘭𝘭 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘮𝘦𝘥𝘪𝘶𝘮 𝘴𝘪𝘻𝘦 𝘣𝘶𝘴𝘪𝘯𝘦𝘴𝘴𝘦𝘴 𝘤𝘰𝘯𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘶𝘦 𝘴𝘵𝘢𝘺𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘧𝘢𝘳 𝘣𝘦𝘭𝘰𝘸 𝘦𝘹𝘱𝘦𝘤𝘵𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴. 𝘛𝘩𝘦 𝘊𝘌𝘖 𝘩𝘢𝘴 𝘪𝘯𝘷𝘪𝘵𝘦𝘥 𝘺𝘰𝘶 𝘵𝘰 𝘩𝘦𝘭𝘱 𝘵𝘩𝘦𝘮 𝘰𝘶𝘵.
How would you approach this business problem?
When ready, check this video below where I present how to approach this problem.
BCG: Tips And Case Interview Examples
The Boston Consulting Group website states something very important: the goal of the hiring process is to get to know you better, which means, in the context of Consulting interviews, understanding how you solve problems .
Remember this: in case interviews, to show how you think is MUCH MORE IMPORTANT than to find an answer to the case .
As a result, you will have case study questions to showcase your problem-solving skills. Likewise, fit interviews have the same purpose: to show what problems you faced and how you resolved them.
- BCG interview prep tips
- BCG’s interactive case tool
- BCG case interview example: climate change challenge
- BCG case interview example: GenCo
- BCG case interview example: FoodCo

Check out the BCG Hub : A library of 20+ free resources that cover everything you need to secure a job offer at BCG.
Bain: Tips And Case Interview Examples
Bain & Company’s website highlights something very important: successful applicants manage to turn a case interview into a conversation between two consultants .
In other words, you don’t want to appear as a candidate but as a consultant !
To do this, you need to master the main problem-solving techniques that consulting firms want to see.
- Bain interview prep tips here and here
- Bain case interview examples: coffee , fashioco
- Bain case interview sample videos: a first video , a second video

Check out the Bain Hub : A library of 20+ free resources that cover everything you need to secure a job offer at Bain & Company.
Deloitte: Tips And Case Interview Examples
As for the BCG’s section above, the Deloitte website clearly states that in case interviews , it is much more important to show how you think and interact with your interviewer than to find the right answer to the case.
- Deloitte interview prep tips
- Deloitte case interview examples: here (more than 15 case interview examples)
- Deloitte case interview example: Federal Agency
- Deloitte case interview example: Recreation Unlimited
- Deloitte case interview example: Federal benefits Provider
- Deloitte case interview example: Federal Civil Cargo protection Bureau
Get 4 Complete Case Interview Courses For Free
You need 4 skills to be successful in all case interviews: Case Structuring, Case Leadership, Case Analytics, and Communication. Join this free training and learn how to ace ANY case questions.
Oliver Wyman: Tips And Case Interview Examples
Like the Deloitte website, Oliver Wyman’s website points out that, above all, you must demonstrate your ability to think in a structured, analytical, and creative way.
In other words, there are no right or wrong answers, but only showing how you solve problems matters.
- Oliver Wyman interview prep tips
- Oliver Wyman case interview examples: here (Aqualine) and here (Wumbleworld)
Kearney: Tips And Case Interview Examples
Now it’s time to tell you something you could have heard a hundred times.
Yet too many candidates do it.
Do NOT force your solution to adapt to a standard framework . As a result, this will only take you to a place you don’t want to go: the pool of rejected candidates .
To learn more about this, check the “What Not To Do” section on the AT Kearney website .
- Kearney interview prep tips
- Kearney case interview examples: here and here
- Kearney case book: here
Strategy&: Interview Prep Tips
Strategy& doesn’t provide case study examples on its website, but it shares insights on career progression, which I recommend reading when you prepare for your fit interviews.
- Strategy& interview prep tips
Roland Berger: Tips And Case Interview Examples
I like the examples of case studies presented on the Roland Berger website .
Because the two examples of case studies are very detailed and illustrate the kind of solutions your interviewers expect during case discussions.
- Roland Berger interview prep tips
- A first Roland Berger case interview example: part 1 and part 2
- A second Roland Berger case interview example: part 1 and part 2
Alix Partners: Interview Prep Tips
Like Strategy&, Alix Partners doesn’t provide case study examples on its website.
However, they give an overview of what they are looking for: they want entrepreneurial, self-starter, and analytical candidates, which are skills that all consulting firms highly appreciate .
- Alix Partners interview prep tips
OC&C: Interview Prep Tips
Here are two case study examples from OC&C:
- Imported spirit
- Leisure clubs
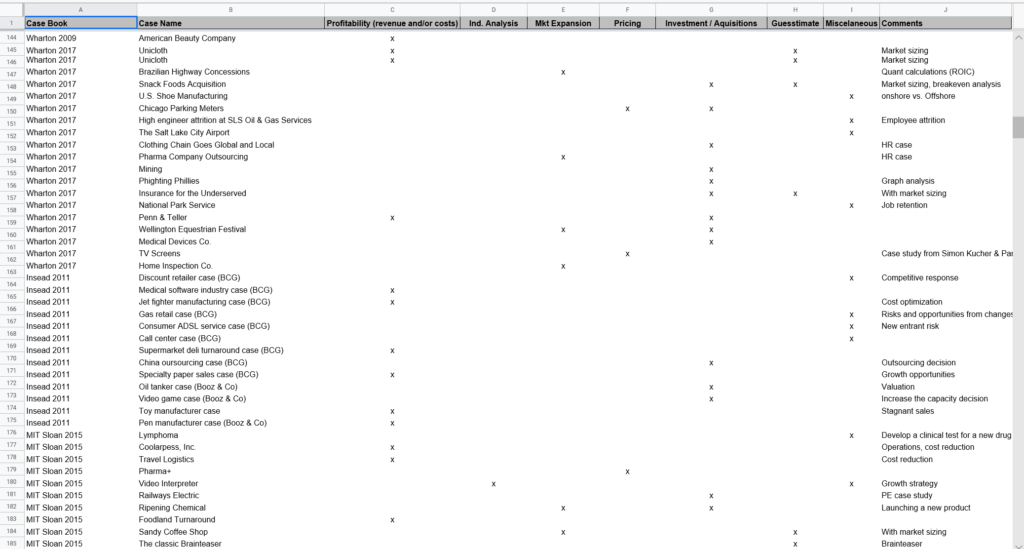
253 Case Studies From Business School Case Books
Most of these 253 case study examples are based on case interviews used by consulting firms in real job interviews .
As a result, you can have a good idea of the case study questions you can have when interviewing at these firms .
The Full List Of 253 Free Case Study Examples
- Chicago business school
- Australian Graduate School of Management
- Columbia business school
- Harvard business school
- Wharton business school (2009)
- Wharton busines school (2017)
- Darden business school
Do you want to practice a specific type of case study? Now you can…
I have sorted this list of 253 case studies by type: profitability, market expansion, industry analysis, pricing, investment or acquisition, and guesstimates (also known as market sizing questions).
Bonus #1: Know The Types Of Cases You Are Likely To have During Your Interviews
- Profitability cases (29% of cases from that list)
- Investment cases (19% of cases from that list)
- Market sizing questions (15% of cases from that list)
As a result, assuming you’ll have 6 interviews (and therefore 6 case interviews) during the recruitment process:
- “Profitability cases are 29%” means that chances to have 2 profitability case studies during your recruitment process are very high
- “Investment cases are 19%” means that chances to have 1 investment case study during your recruitment process are very high.
- “ Guesstimates are 15%” means that chances of having 1 market sizing question during your recruitment process are high.
Bonus #2: The 10 Cases I Recommend You Doing Now
Over 250 examples of case interviews are a great list, and you may not know where to start.
So, I’ve compiled a list of my 10 favorite case studies.
The 5 case studies I recommend doing if you are a BEGINNER
1. stern case book: drinks gone flat (starting at page 24).
This is a good introduction to a common type of case (declining sales here). I liked the solution presented for this case, particularly how it started by isolating declining sales (what range of products? Volumes or prices, or both?).
2. Stern case book: Sport bar (starting at page 46)
This is an investment case (should you invest in a new bar). Even if the solution presented in this case book is not MECE , it covers the most common quantitative questions you might have in such a case. I recommend doing this case.
3. Stern case book: MJ Wineries (starting at page 85)
This is a profitability case. I liked the solution presented in this case because it illustrates how specific good candidates should be. The case concerns wine, so a good candidate should mention the quality of lands and grapes as important factors.
4. AGSM case book: Piano tuners (starting at page 57)
This is a typical market sizing question. How to answer this type of question is a must-know before going to your interviews.
5. Darden case book: National Logistics (starting at page 49)
Again, this is a very common case (how to reduce costs). I liked the broad range of questions asked in this case, covering key skills assessed by consulting firms during case interviews: brainstorming skills (or creativity), quantitative skills, and business sense.
The 5 case studies I recommend if you are more ADVANCED in your preparation
1. stern: the pricing games (starting at page 55).
This case study asks you to help your client assess different business models. I liked this case because the range of issues to tackle is quite broad.
2. Wharton 2017: Engineer attrition at SLS Oil & Gas Services (starting at page 55)
I liked this case study because the case prompt is uncommon: your client has been facing a very high attrition rate among its population of Engineers. As a result, it’s very unlikely that your solution fits a well-known framework, and you’ll have to demonstrate your problem-solving skills by developing a specific solution.
3. Wharton 2017: Pharma Company Goes International, Outsources Benefits, Integrates New Technology (starting at page 95)
This case is about a client considering outsourcing a part of their activity. Even though I don’t know if this type of case study is very common, I had many case studies like this when I passed my interviews a few years ago. And I always found them difficult!
4. Insead: Gas retail case (starting at page 73)
The question in the problem statement is very broad, making this case difficult. So, only good candidates can have a structured case discussion here.
5. Darden: Fire Proof (starting at page 84)
This is a market entry case. Try to solve it by developing a structure as MECE as possible.
CareerInConsulting.com's Free Resources
Access my exclusive free training to help you prepare for your case interviews .
Besides, you can learn my step-by-step guide to answering market sizing questions .
You’ll get my formula to solve all market sizing questions.
Moreover, if you are a beginner, you can read my article on how to solve business cases (+ a 4-week prep plan to get case interview ready).
Also, check these 11 must-know frameworks to ace your case interviews.
Finally, you can read the articles in the blog section of my website.
That’s quite a list.
To complete this list, check this free case interview course , where you’ll find case questions recently asked in actual interviews.
Now, I’d like to hear from you.
Which key insights were new to you?
Or maybe I have missed something.
Either way, let me know by leaving a comment below.
SHARE THIS POST
3 thoughts on “280 Free Case Interview Examples”
Pingback: Market sizing questions: the definite guide (2020) - Career in Consulting
Pingback: Case interview prep: a guide for beginners - Career in Consulting
Pingback: What Does A Management Consultant Do? - Career in Consulting
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
You need 4 skills to be successful in all case interviews: Case Structuring, Case Leadership, Case Analytics, and Communication. Enroll in our 4 free courses and discover the proven systems +300 candidates used to learn these 4 skills and land offers in consulting.
Case Studies

Helping Starbucks design stores that are inclusive for all
Building a next-generation carbon platform to accelerate the path to net zero

How Lufthansa is using data to reduce costs and improve spend and carbon transparency

Banking on innovation: How ING uses generative AI to put people first

From farm to tablet: Building a new business to solve an old challenge

Rewired in action

Partnering on America’s toughest challenges

Made in Africa: Catalyzing stronger, sustainable, and inclusive economies

How a government agency is preparing workers to thrive in the skills-based economy

How a global components manufacturer built an ambitious carbon reduction roadmap

How a major New Zealand retailer reinvented itself around customer satisfaction

Undaunted by global disruption, a logistics company embraces bold transformation

988: Three digits and the nationwide effort to help millions in crisis

An AI power play: Fueling the next wave of innovation in the energy sector

How a manufacturing moonshot was made

Protecting workers through award-winning design

How Telkomsel transformed to reach digital-first consumers

Flying across the sea, propelled by AI

How a steel plant in India tapped the value of data—and won global acclaim

Reimagining the real estate industry for the next normal

Inside a mining company’s AI transformation
New at mckinsey blog.

JobsOhio and the long-term, innovative revitalization of a state’s economy

McKinsey’s new Sustainability Academy helps clients upskill workers for the net-zero transition

Tearing the ‘paper ceiling’: McKinsey supports effort driving upward mobility for millions of workers
28 Case Interview Examples for Consulting Interview Prep (2024)
- Last Updated January, 2024
Rebecca Smith-Allen
Former McKinsey Engagement Manager
How to Use Case Interview Examples
Video Case Interview Example: Questions & Answers
Tips for Acing Your Case
Free Case Interview Examples (Consulting Firms)
Free Case Interview Examples (Consulting Clubs)
Practice is the key to passing your consulting interviews. To practice, you’ll need some examples of case interview questions and answers to work with.
We’ve got links to loads of them below.
In addition, we have:
- Tips on how to use case interview examples to prepare for your consulting interviews,
- A video case interview example with My Consulting Offer founder Davis Nguyen, and
- Insight into the difference between average and exceptional answers to case interview questions.
Get ready to dive deep into structuring your analysis of business problems, identifying the key issues, and recommending solutions!
Keep reading to find out how to use case interview examples to ace your case.
How to Use Case Interview Examples to Ace Your Case
1. start your case interview preparation early..
You’ll need to practice dozens of case interview examples to get good enough to receive an offer from one of the top consulting firms. This is not something you can cram the night before an interview.
Start as soon as possible.
2. Don’t Read Straight through Sample Case Interview Examples or Passively Watch Videos.
Some people think that the best way to improve their chances of passing a case interview is by reading as many cases interview examples as they can.
This is like reading about how to play tennis but never picking up a racket. To get better at tennis, for example, you need to actually pick up a ball and be active. The same applies to your interview preparation.
Stop and think at each step in the case interview question. Come up with your own answer and say it out loud. Practice driving each part of the case interview example yourself.
- How would you structure your analysis of the problem?
- What questions would you ask the interviewer?
- How would you set up the case math problem?
- What recommendation would you make to the client?
After you’ve developed your answer, compare it to the suggested answer for the case.
What did you get right?
How did your answer and the case interview example answer differ?
Are there things you miss consistently across multiple case interview examples?
The answers to these case interview examples can look simple when you just read through them, but it’s not easy to come up with all the key aspects of the solution on your own.
Nail the case & fit interview with strategies from former MBB Interviewers that have helped 89.6% of our clients pass the case interview.
3. Find Partners to Practice Case Interviews with.
Teamwork is an important part of consulting work, so get ready for it now. Find a case interview practice partner, preferably someone else who’s applying to jobs in the management consulting industry because they’ll know more about what recruiters are looking for.
Practicing cases with a partner provides the opportunity to get feedback from someone else on what you’re doing well and what you need to improve. Additionally, you’ll learn a lot by watching how your partner solves sample case studies.
Look for aspects of their approach that are effective as well as what they could do better. Working with a partner will make your consulting interview practice feel more real.
Similar to how you need a tennis partner to feel what is like to play tennis, you need a case partner to experience what a case interview is like.
4. Master the 4 Parts of the Case Interview.
In our article on Case Interview Prep , we discussed the 4 parts of the case interview: the opening, structure, analysis, and conclusion. As you practice with consulting case interview examples, practice each of these 4 parts to ensure you’re strong at them all.
5. Avoid Case Burnout.
A case zombie is someone who’s grown tired of casing from doing too much of it. Their answers feel rehearsed, not conversational.
They may seem bored, not engaged in solving the problem. They’ll be less creative in their solutions. They certainly won’t pass the airport test!
Avoid becoming a case zombie by practicing smarter, not harder.
Video: Case Interview Examples – Questions & Answers
In the following case interview example, Davis Nguyen, founder of My Consulting Offer solves McKinsey’s SuperSoda case. The video is broken into 4 parts of the case interview.
Remember, don’t just watch the video. Stop the video and provide your own answer before listening to Davis’s answer to the case question.
Step 1: Case Interview Example Opening – Ensure you understand the client and the problem you’ll be solving in the case.
Step 2: case interview example structure – break the problem down into smaller parts. make sure you cover all key case issues., step 3: case interview example analysis – ask questions, gathering information from graphs and charts provided by the interviewer, do case math, and provide insight into the client’s business problem based on what you learn., step 4: case interview example recommendation – develop a rational recommendation for the client based on all you’ve learned throughout the case interview., tips for acing your consulting case interviews – the difference between average & exceptional, case interview opening.
The opening is a great point to ask “dumb” questions because, at this point, you’re not expected to know much about the client and their business.
Here your goal is to understand the client, their business, and what a successful project will look like.
Don’t shy away from asking for clarification on things that will help you better understand the business problem and solve it. For example, if you don’t know how life insurance works and the case is about life insurance, then ask.
After ensuring you understand the client and their problem, the next thing to ask about is key metrics of success.
For example, the client may want to find new avenues for growth. Are they looking for a 5% increase in revenue or to double their business?
Finding out what success looks like in the client’s eyes will ensure you work to deliver a solution that meets their expectations, not one that’s underwhelming.
After you find out what success looks like, ask further probing questions to better understand the client, their business, and any constraints on solving the case.
Examples of Relevant Questions to ask Your Interviewer
Examples of relevant questions about the client might include the geography they operate in or the sector of their industry they are strongest in.
Examples of relevant questions about their business might include what products or services are most profitable or most important to their customers.
Examples of relevant questions about the problem might include whether there are any costs that can’t be cut or what the maximum amount the client is able to invest in developing a new product.
Asking these types of questions up front will give you a better context for solving the client’s problem and make it more likely that you will solve the case interview.
Case Interview Structure
You’ll need a framework to make sure your analysis covers all key aspects of the consulting case.
You can use one of the many standard Case Interview Frameworks we’ve outlined , but top interviewees develop their own framework for analyzing the case interview question.
Their frameworks may include pieces of one or more of the standard frameworks but are tailored to the particular business problem they’re discussing.
Good frameworks are hypothesis-driven, that is to say they can be tested similar to the science experiment, so that the answer is either a “yes” or “no.” For example, examining your bank account to see, “if I have $400 for a ticket” is an example.
Second, good frameworks cover all topics relevant to the answer. For example, if the client is opening up a new hotel in a foreign country, checking out the existing competition should be part of the framework.
As you study more about interactive case interviews and practice them you’ll develop a sense for what factors are relevant or not relevant to the case at hand.
Finally, a good structure will be MECE or mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive.
This means the framework will break down the market or population being analyzed into segments that include every part of the whole (collectively exhaustive), and each segment of the market or member of the population will show up in one and only one category without overlap (mutually exclusive).
For example, if you divide the target market for a retail product into segments by age, these segments would be MECE:
- 10-19,
- 40-49, etc.
The categories 15-25, 20-30, 27-35 would not be MECE because people could be counted twice.
Case Interview Analysis
In the analysis phase of your case interview example, you’ll ask questions to get the information you need to solve the client’s business problem. Your questions will likely lead you to one of the 4 types of analysis that are common in consulting interviews: market sizing, brainstorming, quantitative reasoning (case math), or reading exhibits.
No matter which of these types of analysis comes up, there’s a 4-step method that ensures you can crack the case.
This 4-step method is:
- Ask for data,
- Interpret the data,
- Provide insight, and
- Outline next steps.
The data you ask for will depend on the case interview question you’re solving. For example, if the question is about profitability, you’ll need to know about the client’s finances: dig into revenues and costs.
For example, if you find that the client’s revenues are flat while their costs have been rising, you’ll know that the problem is in the cost structure and that you’ll need to examine costs more closely.
Next, provide insight. As you examine costs further, you’ll find out why they’ve grown faster than revenues.
This insight will naturally lead to the next steps. What does the client need to do to get costs under control and fix their profitability problem?
You may need to go through this 4-step method a couple of times, focusing on different aspects of the client’s business problem.
Once you’ve examined and developed insight into all key aspects of the problem, your next step will be to conclude the interview with a recommendation for the client.
Case Interview Conclusion
At this point, you’ve hopefully cracked the case and are ready to present your recommendations to the client (your interviewer).
The best way to do this is to use the 5R approach:
- Recap – restate the business problem you’ve analyzed. In consulting this is done because a CEO might have hired 5 McKinsey teams and can’t remember which one you are on.
- Recommendations – Provide the solution your analysis led to. We lead with the recommendation because it is the most important piece of information. Stating it first and clearly puts everyone on the same page.
- Reasons – Summarize the key facts and insights that lead you to your recommendations.
- Risks – Outline any risks the client should be aware of as they implement your recommendations. No recommendation has a 100% probability of success. Clients need to be aware of business risks in the same way patients need to understand the side effects of drugs.
- Retaining the client – Provide next steps for how you can help the client ensure success. As consultants, we are paid for helping our clients. If there is a natural extension of the work as the client implements the team’s recommendations, we should tell them how we can provide further assistance (and ultimately make money for your firm).
While most candidates will address their recommendations and possibly the reasons for their recommendations, few will hit all these points.
In particular, outlining risks and further ways you can help the client will differentiate you from other candidates and help you to advance to the second round of interviews or get the offer.
Free Online Case Interview Examples from 7 Top Consulting Firms
Now that you’re familiar with how you should use case interview examples and what differentiates an average answer from an exceptional one, you need sample questions to practice with.
Below, we provide links to dozens to help you hone your business problem-solving skills.
1. McKinsey Case Interview Examples
Disconsa – Help a not-for-profit develop better financial-service offerings for remote Mexican communities.
Electro-Light – Help a beverage manufacturer prepare for a new product launch.
GlobalPharm – Help a pharmaceutical industry client manage with its merger and acquisitions strategy.
Transforming a National Education System – Help a country’s education ministry develop a new strategy for educating the country’s children.
2. BCG Case Interview Examples
Climate Challenge – Help a global consumer goods company reduce its environmental impact.
Driving Revenue Growth at a Healthcare Company – Help a medical devices and services company to increase revenues following an acquisition. (The same one that is highlighted above in our example)
3. Bain Case Interview Examples
Coffee Shop Co. – Help a friend decide whether they should open a coffee shop.
F ashionCo. – Help a fashion company understand why its revenues have been going down.
Private Equitas – Help a private equity company maximize its investment in a portfolio company.
4. Deloitte Case Interview Examples
Footloose – Help a footwear company improve their market share in the boots category.
Recreation Unlimited – Help a global apparel and sportswear company improve its digital customer experience and its revenue.
Agency V – Help a large federal agency recover from a front-page scandal that sparked investigations and congressional hearings.
Federal Benefits Provider – Help a federal agency that provides benefits to millions of U.S. citizens prepare for a major expansion of its mandate.
5. AT Kearney Case Interview Examples
Promotion Planning – Help a national grocery and drug store chain improve its product promotion strategy.
6. PWC Case Interview Examples
Modernizing a Hotel’s Loyalty Platform – Help simplify and modernize the platform, providing customers with immediate access to their data.
Green Energy – Help an energy company transition to net zero greenhouse gas emissions.
Nonprofit Impact – Help a community organization respond to client needs during the pandemic.
Love at First Byte – Help a data management client comply with new regulations.
Prioritizing Ethics and Integrity – Help a software company leverage data analytics to comply with regulations.
7. Accenture Case Interview Examples
Sustainability – Help drive sustainability for an auto manufacturer.
IT integration strategy – Driving merger integration by linking technology systems.
We have more on how to Accenture Case Interviews in our article.
8. Capital One Case Interview Examples
Ice Cream Corporation – Help the president of Ice Cream Corporation grow profits.
9. Oliver Wyman Case Interview Examples
Wumbleworld – Help a China-based theme park operator identify the reasons for declining profits and develop options for reversing the trend.
Aqualine – Help a manufacturer of small power boats determine why its sales growth has slowed and identify opportunities to boost sales.
10. LEK Case Interview Examples
Theater chain – Help a large theater chain identify revenue growth opportunities.
Free Online Case Interview Examples from Consulting Clubs
Need more case interview examples? Here are links to MBA case books compiled by INSEAD, Harvard, Wharton, Darden, and several other business schools.
Recent Consulting Case Interview Examples
- Darden School Of Business 2021-2022 Casebook
- NYU Stern MCA 2020-2021 Casebook
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Casebook 2021-2022
- Notre Dame Casebook 2022
- Kellogg Consulting Club 2020 Casebook
- FMS Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- INSEAD Consulting Club Casebook 2021
- IIMC Consulting Casebook 2021-22
- UCLA Case Book 2019 – 2020
- Columbia Business School 2021 Casebook
- IIM Lucknow Casebook 2022
- Cornell MBA Johnson Consulting Club Casebook 2020-2021
- Darden School Of Business 2020-2021 Casebook
Older Consulting Case Interview Examples
- 2019 Berkeley Haas School of Business Consulting Club Interview Preparation Guide and Case Interview Examples
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Casebook 2018-2019
- 2017-2018 McCombs University of Texas at Austin Consulting Case Interview Examples
- Columbia Business School Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples 2017
- Duke Fuqua School of Business MBA Consulting Case Interview Examples 2016-2017
- NYU Stern MBA MCA Case Interview Examples: 2017
- UCLA Anderson School of Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples 2015-2015
- Darden Consulting Club Case Interview Examples: 2014-2015
- Yale Life Sciences Consulting Case Interview Examples 2014
- ESADE MBA Consulting Club Case Interview Examples 2014
- Darden Consulting Case Interview Examples: 2012-2013 Edition
- Kellogg Consulting Club Case Interview Examples and Interview Guide: 2012 Edition
Even More Consulting Case Interview Examples
- The Cornell Consulting Club Interview Interview Examples
- Harvard Business School Management Consulting Club Case Interview Examples
- The MIT Sloan School of Management Consulting Club Case Interview Examples and Interview Guide – October 2001
- The Berkeley MBA Haas Consulting Club 2006 Case Interview Examples
- London Business School – The 2006 Consulting Club Case Interview Examples
- Columbia Business School Management Consulting Association Case Interview Examples – 2006
- Torch the Case – The NYU Stern Consulting Case Interview Examples – 2007 edition
- Michigan – the Ross School of Business Consulting Club 2010 Case Interview Examples
- Wharton Case Interview Examples by the Wharton Consulting Club – December 2010
- The Duke MBA Consulting Club Case Interview Examples – 2010-2011
- Case Interview Examples by the ESADE MBA Consulting Club 2011
- INSEAD Consulting Club Handbook and Case Interview Examples – 2011
Still have questions?
If you still have questions on case interview examples, leave them in the comments below. We’ll ask our My Consulting Offer coaches and get back to you with answers.
We have tons of other articles to help you get an offer from one of the top consulting firms. Check out our pages on:
- Case Interview Math
- Case Interview Types
- Case Interview Formulas
- Market Sizing Questions
Help with Case Study Interview Preparation
Thanks for turning to My Consulting Offer for advice on case study interview prep. My Consulting Offer has helped almost 89.6% of the people we’ve worked with get a job with top management consulting like Bain, BCG and McKinsey . For example, here is how Conor was able to get his BCG offer after previously failing.
If you want a step-by-step solution to land more offers from consulting firms, then grab the free video training series below. It’s been created by former Bain, BCG, and McKinsey Consultants, Managers and Recruiters.
It contains the EXACT solution used by over 700 of our clients to land offers.
The best part?
It’s absolutely free. Just put your name and email address in and you’ll have instant access to the training series.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© My CONSULTING Offer
3 Top Strategies to Master the Case Interview in Under a Week
We are sharing our powerful strategies to pass the case interview even if you have no business background, zero casing experience, or only have a week to prepare.
No thanks, I don't want free strategies to get into consulting.
We are excited to invite you to the online event., where should we send you the calendar invite and login information.
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
Marketing and growth leaders
Cybersecurity and privacy leaders
Risk leaders
EY Center for Board Matters
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
Supply chain and operations
EY Partner Ecosystem
Explore Services
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
MBA and advanced-degree students
Student and entry level programs
Contract workers
EY-Parthenon careers
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
Energy and resources
How data analytics can strengthen supply chain performance
13 Jul 2023 Ben Williams
How Takeda harnessed the power of the metaverse for positive human impact
26 Jun 2023 Edwina Fitzmaurice
Banking and Capital Markets
How cutting back infused higher quality in transaction monitoring
11 Jul 2023 Ron V. Giammarco
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
EY research: Cybersecurity fears on the rise among US workers, with a vast majority concerned about AI in cybersecurity
06 May 2024 Lizzie McWilliams
EY Announces Entrepreneur Of The Year® 2024 Greater Los Angeles Award Finalists
03 May 2024 Victoria Kasper
EY Announces Entrepreneur Of The Year® 2024 Michigan and Northwest Ohio Award Finalists
01 May 2024 Victoria Kasper
No results have been found
Recent Searches

BEPS 2.0: as policies evolve, engagement is key
It remains to be seen whether the US will align its tax law with the OECD/G20’s global BEPS 2.0 rules. MNEs will feel the impact in 2024. Learn more.

How GenAI strategy can transform innovation
Companies considering or investing in a transformative GenAI strategy should tie generative artificial intelligence use cases to revenue, cost and expense. Learn more

Top five private equity trends for 2024
Read about the five key trends private equity firms will emphasize in 2024 as they create value
Select your location
Consulting case studies
Our Consulting teams work with businesses around the world to solve problems , overcome challenges, uncover opportunities and exceed expectations. Our clients’ success stories span all industry sectors — from technology companies to energy providers, financial services to consumer retailers and every strategic function in between.
EY Consulting case studies are a window into how we work alongside our clients to deliver strategic, sustainable growth and success.
- Advanced manufacturing and mobility
- Financial services
- Government and public sector
- Health sciences and wellness
- Technology, media and telecommunications
Direct to your inbox
Stay up to date with the most recent case studies

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
- Legal and privacy
- Accessibility
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.
Case Interview 101: The Online Guidebook
“Case Interview” is the cornerstone of consulting recruitment, playing a decisive role in final results. In 30 minutes, your “consulting” qualities will be tested to the limit as you cruise through a hypothetical “consulting project” with the interviewer.
Yes, this is a BIG topic. The depth of content in this single article is HUGE with various chapters ranging from beginner’s topics to more advanced ones. You would want to bookmark this page and go back often throughout your whole preparation journey.

What is a case interview?
A case interview is a job interview where the candidate is asked to solve a business problem. They are often used by consulting firms, and are among the hardest job interviews, testing both problem-solving skills and “soft” skills. Case interviews often last 30-45 minutes each, and firms can utilize up to 6 case interviews, usually divided into 2 rounds.
Example case questions:
- “We have a restaurant called “In-and-out Burger” with recently falling profits. How can you help?”
- “The CEO of a cement company wants to close one of its plants. Should they do it?”
- “A top 20 bank wants to get in top 5. How can the bank achieve that goal?”
Case interviews are modeled after the course of actions real consultants do in real projects – so success in case interviews is seen by consulting firms as a (partial) indication of a good management consultant.
During the interview, the interviewer will assess your ability to think analytically, probe appropriate questions, and make the most client-friendly pitches. Be noted that the analytical thought process is more important than arriving at correct answers.
Generally, there are 2 styles of conducting cases: Candidate-led and Interviewer-led.

Candidate-led cases
On this end, the interviewer rarely intervenes; the candidate will lead the approach from structuring the problem, drawing frameworks, asking for data, synthesizing findings, to proposing solutions. This format can be difficult for beginners but it provides you with much control over the case.
Interviewer-led cases
On this end, the interviewer controls the process in significant ways. He or she has the candidate work on specific parts of the overall problem and sometimes disregards the natural flow of the case. The game here is not to solve the one big problem, but rather to nail every question, every pitch, every mini-case perfectly. Because the evaluation is done on a question basis, the level of insightfulness required is higher.
Most cases will fall somewhere in the middle section of that spectrum, but for educational purposes, we need to learn case interviews from both extremes ends.
Great details in each and every aspect of the case, as well as tips, techniques and study plans are coming in the chapters below. You may skip straight to Chapter 3 if you have business background and confidence in your own understanding of the terminology used in case interviews.
To better understand or practice candidate-led and interview-led cases, let’s book a personal meeting with our coaches . At MConsultingPrep, you can connect with consulting experts who will help you learn the ins and outs of both cases and the solving approach to each one. Get “real” practice now!
Case interview starter guide for non-business students
All consulting firms claim that all educational backgrounds have equal chances. But no matter what, case interview reflects real-life business problems and you will, therefore, come across business concepts .
Not everybody has the time to go to a full Business Undergraduate program all over. So through this compact Chapter 2, I will provide you, the non-business people, with every business concept you need in case interviews.
Accounting and financial terms – The language of business
Accounting & Financial Terms are often called the language of business, which is used to communicate the firm’s financial and economic information to external parties such as shareholders and creditors.
There are three basic financial statements : Balance Sheet, Income Statement, and Cash Flow Statement.
Balance Sheet
A snapshot of the current stage of the company’s property, debt, and ownership at one given point in time, showing:
- Assets: what the company owns: Building, Equipment, Cash, Inventory, along with some other intangible items.
- Liabilities: what the company owes: Loans, overdrafts, bills to be paid, etc. Debt is like negative assets.
- Equity (Net worth): Calculate by taking Assets subtract Liabilities.
The neat thing about the Balance sheet is that it’s always balanced. Every action, every transaction changes the three components but it’s always in harmony.
Income Statement
A record of the business performance through a period of time , given it a quarter or a year. The Income Statement directly tells you how the company is doing in terms of making money, the heart of any business.
From the top to bottom, the Income Statement shows the Revenues, Costs, and Profits. That’s why often, Profits are referred to as the “bottom line”.
There are a few types of costs to notice – see the two pictures below this table.
One important thing to notice is that even though it may seem like, the Income Statement does NOT necessarily relate to cash. Many times, especially for B2B transactions, the selling happens before the money flow. Therefore, we may have to record revenue without having the cash.
Cash Flow Statement
There’s a famous saying that: Income statement is an opinion, Cash Flow statement is a fact.
The Cash Flow statement just strictly monitors the cash flow in or out, categorized into different sections. Three of them are:
- Operation: illustrates how much cash the company can generate from its products and services.
- Financial: includes the sources of cash from investors or banks and the uses of cash paid to shareholders.
- Investing: includes any sources and uses of cash from a company’s investments.

Upon completion this section, you should be able to read and interpret financial statements for business diagnosis and decision-making.
More importantly, you possess the conceptual base to start solving case interviews on your own. Do not forget that, as with any other language, becoming proficient with accounting and financial terms require constant practice.
Organizational structure – The heart of a company
When it comes to organizational structure, it is important to notice the fine line between the company’s ownership and management .
Technically, at the highest level, there are shareholders . For private companies, the group of shareholders and their shares are not necessarily disclosed and publicly tradable. For public companies, on the other hand, shares are publicly traded on different stock exchanges. One of the most famous is the NYSE, which stands for New York Stock Exchange.

- A company can have one, a few, or millions of individual owners, but being governed by the Board of Directors – a group of people elected by owners, with the President or Chairman being their highest leader.
- The Board usually hires a management team to manage the company. They are led by the Chief Executive Officer – CEO , who makes every decision on day-to-day work. Most of the time, the Board of Directors doesn’t directly intervene in the CEO’s work, but they reserve the right to fire CEOs.
- Besides that, there’s a committee called Supervisors. The supervisor’s job is to independently monitor the CEO and the management team and report to the Board.
Below CEOs, there are two general two ways of structuring the company. One way is through business lines and the other one is through functions. Think of business lines as mini-companies themselves inside the big company.

Within functions, here are a few most typical divisions most companies have:

Business strategy concepts
Even with business students, strategy is a challenging topic – especially with those without a strategy major. These fundamental concepts will get you started.
- Organization: In general, this refers to how a company is organized, what are different components that make up a company
- Governance refers to how a company is managed and directed, how well the leader team runs. The leader team includes the Board of Directors and Board of Managers. A company with good governance has good leadership people, tight control, and effective check & balance processes, etc.
- Process looks like rules and common practices of having a number of processes, entailing every single activity. Process design should include 4 factors: who, what, when, and accompanied tools.
For example, let’s look at Kim’s family picnic process.

- The who part is presented on the y-axis, left-hand side, labeling all departments, a.k.a: family members, involved.
- The what part is presented through the big mid-session with each box represents every single activity.
- The when and tools parts are presented at the bottom
B2B vs B2C : stand for “business-to-business” and “business-to-customer”. These two terms refer to two types of transactions a company typically does: transactions with other companies and transactions with individual customers.
Bottom-up vs Top-down: this refers to two opposite schools of thought or action. Top-down usually encompasses various general branches while bottom-up tends to narrowly focus.
Management consulting terms & concepts
These are the most common consulting terms you may encounter not just in case interviews but also in consulting tasks .
- Lever: Think of this as one or a group of initiatives, actions to perform to meet certain goals. e.g. some levers to help increase customer experience in a hotel are free breakfast, free Wi-Fi, 24/7 support, etc.
- Best practice: Refers to how things should be done, especially if it has been successfully implemented elsewhere.
- Granular: This refers to how specific and detailed a break-down or an issue goes. For example, a not-so-granular breakdown of the NBA is the West and the East conferences. A much more granular is something like this: Leagues, Conferences, Divisions, and Teams.
- MECE: MECE is so important and we explain it in detail in this article. In short, MECE is the standard, per which we can divide things down in a systematic, comprehensive, and non-overlapping way.
There are three parameters the consulting world uses in the categorization of businesses.
- Industry: used to group different companies mostly based on their product (Banking, Construction, Education, Steel Industry, etc.)
- Function: is the categorization mostly based on missions and the type of roles of different parts of a company. We can count some as Human Resource, Finance, Strategy, Operation, Product Development, etc.
- Location: is where things are, geographically.
Normally two consultants ask each other “What do you work on?”, they need to give 3 pieces of information in all of those three parameters, such as “I worked on a Cement project, focusing on Finance, in Southeast Asia”. In fact, all of the McKinsey support networks are organized in this way. During my projects, I would need to speak to some Cement experts, some Finance experts, and some local experts as well.
This chapter is relatively long, yet it is still way shorter than 4 years at business college. I hope this will act as a great prerequisite to your case interview study. Make sure that you have mastered all of these content before really tackling the Case Interview.
Case interview example – The typical flow
In a simplified way, a typical case would go through these phrases (we will talk about exceptions in great detail later):
Case question -> Recap -> Clarification -> Timeout -> Propose issue tree -> Analyze issue tree -> Identify root-causes -> Solutions -> Closing pitch
Problem-solving fundamentals – Candidate-led cases

Though most cases will be conducted in mixed format, let’s dive deep and learn about each extreme end of the spectrum to get the full picture.
Even though this is the harder format, it shows us the foundation of how management consulting works, i.e: the consulting problem-solving logics!
If you were exposed to case interviews, you have probably heard about some of these concepts: framework, issue tree, benchmark, data, root cause, solutions, etc. But how do they all fit into the picture?
It all starts with the PROBLEM
Before getting into anything fancy, the first step is to define and be really clear about the problem.
This sounds easy but can be quite tricky. Here are a few guidelines:
1. What’s the objective?
2. What’s the timeline required?
3. Any quantified or well-described goals?
For example, one client can state a problem as: “I lost my car key”. In normal contexts, this is a perfectly simple and straightforward problem. But a consultant tackling this would go ask clarification questions to achieve even more details:
1. Objective: the client in fact just needs to be able to use the car.
2. Timeline: this is an urgent need. He is happy only if we can help him within the next hour.
3. Specificity: help the client put his car into normal operation like before he lost the key.

Find the ROOT-CAUSE, don’t just fix the symptom
To completely wipe out the problem and create long-lasting impacts, consultants always search and find the root causes.
For example, fixing the symptom is like you breaking the door lock, getting into the ignition electrics behind the wheel, and connecting the wires to start the car.
That does fix the surface symptom: the client can drive the car. But it does NOT create a long-lasting impact because without you there, the car can’t be started. The client will need to rely on you every single time. Plus, more problems even arise (now he needs to fix the broken door lock too).
A much better approach is to find the root cause. What is the bottom-line reason causing the problem? Once we trace, find, and fix it, the problem will be gone for good.
In this example, the root cause is “the lost key”. We need to find its location!

Use ISSUE TREE to isolate potential root-causes into groups
There could be thousands of possible root-causes. How do we make sure every possible one is examined? If we are to list out all thousands and test one by one, there is simply not enough time. On the other hand, if we just list out some of the most “possible” ones, we run a high risk of missing the true root-cause.
This is where we need issue trees ! We would group possible root-causes into big groups. Those big groups will have smaller sub-groups and so on. All is done in the spirit of top-down and MECE. By doing this, we have an organized way to include all possible root-causes.
Continue with the example: A “bottom-up” approach to search for the car key is to go straight to specific places like the microwave’s top, the black jacket pocket, under the master bed, etc. There can be thousands of these possible locations.
The top-down approach is to draw an issue tree, breaking the whole house into groups and examine the whole group one by one. For example: first floor, second floor, and the basement.

Issue Tree only works if it’s MECE
What happens if we break down the search area into the First floor and East wing? The search area would not cover the whole house and there will be some overlapping which creates inefficiencies.
So for an issue tree to work properly, it has to be MECE – Mutually Exclusive and Collectively Exhaustive … which in simple language just mean 2 things: no overlap and no gap

How to draw MECE issue trees? Use FRAMEWORKS!
Each problem requires a unique issue tree. Coming up with MECE and spot-on issue trees for each problem can be really difficult. This is where “framework” helps.
Think of frameworks as “frequently used templates” to draw issue trees in any particular context. Many people use the word “framework” to refer to “issue tree” but this is conceptually incorrect.

We will talk about frameworks in more detail in the below chapters. You can also check out this deep-dive article on Frameworks.
Choosing which branch to go to first? Use HYPOTHESES!
So let’s say you have an issue tree of First floor, Second floor, and Third floor. Now what?
To make the problem-solving process even faster and more efficient, we use hypotheses. In simple language, it’s the educated guess of where the root cause may lie in. So we can prioritize the branch with the highest chance.
So let’s say, the client spends most time on the first floor, it’s where he/she most likely leaves the car key. Any consultant would hypothesize that the root cause is in the first-floor branch and go search there first.
Notice: hypothesis and issue tree always go together. It doesn’t make sense to draw an issue of First, Second, and Third floor and hypothesize that the key is in the East wing. Many times, hypotheses are even the inspiration to draw issue trees.

How to test a branch? Use DATA and compare it with BENCHMARK
Now that we decide to test the branch “First floor”, how do we do that?
We prove or disprove our hypothesis by collecting DATA. That data is then compared with benchmarks to shed more meaning. Two main types of benchmarks are: historical and competitive. For example, let’s say by some magic, the client has a metal detection machine that can measure the metal concentration of any space.
To test the “first-floor” branch, the consultant would come to the first floor, measure the metal concentration and compare it with the data before the car key is lost, a.k.a: historical benchmark.

If a hypothesis is true, drill down; if it’s false, go sideways
What happens when we test a hypothesis?
Assuming that we have access to enough data, it either gets proven TRUE or proven FALSE. How do we proceed from here?
- Proven True: go DOWN the issue tree to sub-branches! Let’s say the metal detector identified the key IS indeed on the first floor. Go deeper. Draw sub-branches of that first-floor branch and repeat the process.
- Proven False: go HORIZONTAL to other big branches! Let’s say the metal detector denies the key presence on the first floor. We then can cross out this branch and go test others, a.k.a: the second and third floor.
Test, Sleep, Test, Repeat … until the ROOT-CAUSE shows up!

Once identified the ROOT-CAUSES, go for SOLUTIONS
With all proven root causes identified, the last step is to come up with solutions to kill the problem … and we are done! There can be multiple solutions to each root cause. These solutions should attack straight to the root cause.

Case interview questions – Interviewer-led cases
While candidate-led cases are all about the logical foundation of problem-solving, interviewer-led cases are more about tackling each individual question itself. The structure of the whole case is relatively loose and flexible.
In this chapter, we touch on some of the most popular ones. You can read in-depth about each in this designated article.
Framework/Issue Tree questions
“Which factors would you consider when tackling this problem?”
This is one of the most popular question types in case interviews, often asked in the beginning. It comes with several shapes and forms, but the real meaning is always: “Give me the bloody issue tree!”
So how do you tackle it? Just like in candidate-led cases. Take a timeout; brainstorm about the problem and how it should be broken down into; plug a few frameworks to see how it looks; and go for the most appropriate issue tree.
Unlike in candidate-led cases where you only present the upper-most layer, here you should walk the interviewer through the whole issue tree, covering at least 2 layers. Interviewer-led cases are much less interactive. It’s more like they ask you a question, and you deliver a comprehensive and big answer. They ask you another one. And so on.
Market-sizing / Guesstimate questions
“How many face masks are being produced in the whole world today?”
This is among the most popular question types and you will likely face a few of them throughout several interview rounds. These questions ask you to “guess” and come up with number estimations in non-conventional contexts. These questions are called “Guesstimate”.
When a guesstimate question asks you to “guess” the size of a market, it’s called a “Market-sizing” question. Though this variation is very popular in consulting, the nature is nothing different from other Guesstimate questions.
It can be intimidating to face a question like this. Where to start? Where to go? What clues to hold on to?
The key is to understand that you don’t have to provide an exact correct answer. In fact, nobody knows or even cares. What matters is HOW you get there. Can you show off consulting traits, using a sound approach to come up with the best “estimate” possible?
Read the designated article on this for great details. Here, let’s walk through the 4-step approach that you can apply to absolutely every market-sizing question.
Step 1: Clarify
Make sure you and the interviewer are on the same page regarding every detail and terminology, so you won’t be answering the wrong question.
Step 2: Break down the problem
Break the item in the question (number of trees in Central Park, market size of pickup trucks) down into smaller, easy-to-estimate pieces.
Step 3: Solve each piece
Estimate each small piece one at a time; each estimation should be backed by facts, figures, or at least observations.
Step 4: Consolidate the pieces
Combine the previous estimations to arrive at a final result; be quick with the math, but don’t rush it if you aren’t confident.
Math questions
“If the factory can lower the clinker factor by 0.2, how much money will they save on production cost?”
Almost all cases involve some math. So you will face math questions for sure. These “questions” can go at you either explicitly and implicitly. Sometimes, the case interviewer will ask out loud a math problem and have you solve. But sometimes, you have to do multiple calculations on the background to push the analysis forward.
Either way, a strong math capability will help you a lot during cases and the future career in consulting. See this Consulting Math article for more details.
Chart insight questions
“What insights can you draw from this chart?”
Consultant works with data and a big chunk of those data are presented by charts. Many times, the interviewer would pull out a sanitized exhibit from an actual project and have you list out insights you can see from it.
There are many types of charts. Getting yourselves familiar with the most popular ones is not a bad idea.
- Bar charts simply compare the values of items that are somewhat parallel in nature.

- Line charts illustrate the continuous nature of a data series, e.g: how my heart rate evolved through time.

- Pie charts illustrate proportions, i.e “parts of a whole” analyses.

- Scatter-plots use data points to visualize how two variables relate to each other. Correlation for example.

Tips on tackling chart-insights questions:
1. Read labels first: from Chart titles, Axis titles, Legend titles, etc. Don’t jump straight to the content of the chart. It takes more time to get lost there and has to go back to read the label. Besides, you may also run a risk of misunderstanding the content.
2. Look for abnormalities: important insights always lie in those unexpected and abnormal data. Look for them!
Value proposition questions
“What factors does a customer consider when deciding which car insurance company to buy from?”
In simple language, this question type asks you: what do the customers want? Understanding exactly this need will put any company in the best position to tailor products/services.
Like any other questions, Value-proposition questions are not only about correctly identifying customer preferences (insights) but also about analyzing and delivering the answer in a structured fashion. Here are a few tips for you to do that:
How to be more insightful:
- It always helps to break customers into groups and provide different substances for each.
- Put yourselves into the customers’ shoes. Think from the first-view perspective and more insights will arrive.
- If there is any data/ information previously provided in the case, definitely use it.
- A library of factors? Safety, speed, convenience, affordability, flexibility, add-on services, durability, fashion, ease of use, location, freshness, etc.
How to appear more structured:
- Follow this structure: Customer group 1, Customer group 2, etc. Under each: Factor A, factor B, factor C.
- Develop your personal script for this question type. Make sure it’s easy to follow and structured in nature.
Information questions
What kind of data do you need to test this hypothesis? How do you get data
Consulting is a data-driven industry. As consultants, we spent most of our time gathering and presenting data to clients ( see the What the heck does a consultant do video ). No surprise information questions are relatively popular in cases.
The best way to tackle this question type is to understand inside out the types of data actual consultants use in real projects. Because almost no candidate knows about this. This is also a very quick way to build rapport. The interviewer will feel like he/she is talking to a real consultant.
Case interview example video – Pandora case
Enough theory! Enough cute little illustrations here and there. Time to get our hands into a serious case interview example.
Notice the following when watching the video:
- How the problem is given and clarified
- How the problem-solving approach is layouted and executed
- How the candidate use wording and frame the pitches
- The dynamic of a case. How energy transfers from one to another person.
Every case is unique in its own way but principles are universal. The more examples you see, the better. This video is extracted from our Case Interview End-to-end Secrets program, where you can find 10 complete examples like this and many other supplement contents.
How to prepare for case interviews
Case Interview preparation is a long and tough process. In an ocean of books, videos, programs, how do we navigate to maximize learning? Most materials floating around are quite good, at least in terms of substance. But the timing and the organization of them can be confusing.
- Too much theory in the beginning can burn brain power very quickly.
- Tackling cases without basics can develop bad habits, which eventually cost more time to unlearn.
- Practicing complicated (or even just normal) cases in the beginning can destroy morale drastically.
So a good study plan is constantly switching between 3 activities: reading theory, watching examples, and practicing, with cases increasing difficulty level. It’s so crucial to start with super easy cases, be patient, and stay on that level until you are ready to move up. There are so many skills, habits, and scripts to develop and these take time.
“The quickest way to do just about everything is … Step by Step”
Even for candidates with cases coming up urgently, I still strongly recommend spending the most valuable time practicing cases that match your level. After all, cases are just the context. What you will be evaluated on is your approach, your skills, your techniques, etc.
So, this is a sample study plan you can adopt for yourselves:
Step 1: Learn the basics of case interview theory
- Read this article thus far
- Watch this Case Interview 101 video
Step 2: Watch a simple case interview example
- Read the sample case flow above.
- Watch this Case Interview Example video
- Go to this list of free case examples and try to select a very simple one. If you can’t follow one, it’s probably not good for you. Just skip it.
- Watch the first example in the End-to-end Program
Step 3: Review the theory of case interview approaches
- Read deeply about the logical foundation of problem-solving in this BCG & Bain Case Interview article.
- Watch intensively the logical foundation of problem-solving in this Candidate-led cases video.
Step 4: Do one mock case interview
- Practice with consultants. They have the insight and knowledge to help you pass the interview. Discover our experienced coaches from McKinsey, BCG and Bain here .
- Find a partner to practice with. Make sure you both watch this Guide on how to conduct a case. A bad coach can do more harm than good.
- Get your hand on another example in the End-to-end Program. But this time, don’t just watch. Actively solve the case as you see it! Try to say out loud your version, then listen to the candidate, then hear the feedback!
Step 5: Start improving your business intuition
Business Intuition is like your natural sense of the business world: how to be insightful and creative in various business contexts, how to feed the “content” into your approach, etc. Think of this as a basketball player trained for muscle strength, agility, or durability. Intuition can be improved gradually through constantly exposing yourselves to a wide range of business situations and contexts.
You can do this by:
- Read consulting publications. One article per day for example. Three wonderful sources are: McKinsey Insights, BCG Perspectives, and Bain Publications
- Train case interview questions individually. By isolating each part of the case, you can focus more on the substance. Hit that link or get more question training on the End-to-end Secret Program .
Step 6: Start training consulting math
- Visit this in-depth consulting math article.
- Train our Mental Math methodology.
Step 7: Practice another mock case interview
At this stage, please still stick to very basic cases. The goal is to see all of the knowledge and skills above in real action. Again, this can be done by either:
- Book a meeting with coaches
- Find another partner to practice with. Just make sure you both watch this Guide on how to conduct a case. A bad coach is always more harmful than not practicing at all.
- See another example in the End-to-end Program. Like the previous one, try actively solving the case as you see it! Say out loud your version, then listen to the candidate, then hear the feedback!
Step 8: Equip yourself with tips, techniques, and advance theory
- Read on! The below chapters of this very article will provide you with more advanced theory and killer tips.
- Watch the whole Tips & Techniques sections of the End-to-end Program. You will find 10 examples with clear walkthroughs of tips and techniques right in the middle of real action.
Step 9: Do further mock cases, review, and improve
Practicing for case interviews is a time consuming process – but as long as you have the right method, you will make it!
- First, brush up on knowledge related to case interviews with the Case Interview End-to-End Secrets Program .
- Second, get personalized practice with ex-consultants. That way, you’ll receive clear and tuned feedback to understand what to improve, building your own proper case approaches. See a list of experienced coaches here .
Stay tuned with us on this website and our Youtube channel for continuously updated information on case interviews and management consulting recruitment; you can also subscribe to the newsletter below for free materials and other insightful content!
Good luck with your case prep!
Case interview tips – With instant results
Imagine a case interview just falls out of the sky and into your lap, scheduled for tomorrow – how can you even prepare?
The answer lies in a few “quick and dirty” tips, which I’ll share with you in a moment.
I am a firm believer in the 80-20 rule – which states that 20% of the causes lead to 80% of the consequences.
In the case interview prep context, 20% of your learning efforts will bring about 80% of the improvements – so the key to instantly and dramatically improving your case performance is to identify and focus on that 20%.

In the next 8 chapters, I’ll tell you the killer tips and tricks that helped me get a McKinsey offer, the majority of which were previously only available in the premium End-to-End Secrets Program , including:
- Chapter 9: Delivering the perfect case opening
- Chapter 10: Remaining absolutely structured throughout the case
- Chapter 11: Taking the best notes
- Chapter 12: Getting out if stuck
- Chapter 13: How to ask for data
- Chapter 14: What to do when receiving data
- Chapter 15: Deliver the most convincing closing pitch
- Chapter 16: Developing your personal scripts
One thing before you proceed: don’t forget to learn the fundamentals, the question types, and the frameworks. Remember, these 20% tips can only get you 80% performance; if you want 100%, there’s no substitute for hard work.
How to deliver the perfect case opening
The result of a case interview is determined the first 3 minutes – and I’m not even exaggerating.
Most people will be put off by this fact – indeed, with all those efforts spent on learning for the later part of the case, and the hiring decision is made when you’re not even properly warmed up yet.
However, putting a spin on it, this is the 20% to focus on – if you nail the opening, you’ll make a better impression than most candidates; it’s also easier to perform well in 3 minutes than in 30 minutes, especially when the case hasn’t gotten tricky. Additionally, you can prepare the opening in a formulaic manner – essentially learning by heart until it becomes natural.
There are 7 steps in the perfect case opening formula:
1. Show appreciation
2. Announce case introduction
5. Announce case approach
7. Ask for a timeout
In this chapter, I’ll walk you through each of those steps.
Step 1: Show appreciation
The quickest way to score the first points with any interviewer is to sincerely compliment them. Everybody loves compliments.
Case interviewers are not dedicated HR staff, but Engagement Managers, Partners, and Directors who conduct interviews ON TOP OF their projects as goodwill for the firm, so you should at least be thankful for the time they spend with you.
Begin your interview with a sincere “thank you” for the interesting case (if you have to fake these words because deep down you don’t like case interviews, you aren’t exactly cut out for the job).
Step 2: Announce case introduction
Announce you’re going to do steps 3, 4, and 5.
This step is related to what I call the “map habit”, which I’ll describe in detail in the next chapter. For now, just understand that it helps the interviewer follow your introduction, and shows you’re a structured person.
Step 3: Recap
What is the key question of the case?
On a side note: one common mistake is to mix up step 3 with step 4 (clarify) – remember, don’t ask anything , just rephrase the case to ensure that you get it right.
Step 4: Clarify
Ask questions to clear up any potential confusion about the details of the case.
Case questions are always very short with a lot of vague details; if you don’t see the need to ask anything, you’re doing it wrong.
Run this checklist through your mind to help you clarify as many unclear points as possible:
- Definitions: are there words you don’t understand or can be interpreted in multiple ways?
- Timeframe: what is the “deadline” for solving this problem?
- Measurement: how are the important variables (performance, revenue, etc.) measured?
Additionally, number your questions so it’s easier for you and the interviewer to keep track.
Step 5: Announce case approach
Roughly sum up how you’ll analyze the problem.
Again, this is related to the map habit, which makes the overall case progress easier to follow.
There are 3 types of cases: (1) problem-solution, (2) should I choose A or B, and (3) how to do C. For each type, there is a different approach. The latter two are discussed in the “Advanced Logic” chapter, for now, we’ll continue with the first type: tell the interviewer you’re going to find the root cause to ensure long-lasting solutions, and to do that you’ll develop an issue tree.
Step 6: Align
Check if the interviewer approves of your case approach.
This is an important habit of real consultants because nobody wants to waste resources going in the wrong direction; interviewers expect candidates to show it in the case interview.
Simply ask “Does this sound like a reasonable approach to you?” – most likely the interviewer will give you the green light, but if you’re lucky he/she may even suggest a better approach.
Step 7: Ask for timeout
After you’ve gone continuously through the 6 steps above, ask the interviewer for timeout to (make this explicit) gather your thoughts and develop the first part of the issue tree.
Make the most of your timeout session, and keep it as short as possible. Any unnecessary silence will damage the impression and hurt your chances (refer to the End-to-End Program example in Chapter 6 to “feel” how awkward a lengthy timeout session is).
Case opening – Example script
Now it’s time to see how you can put all those steps into action!
Thank you for this very interesting case, I am really happy to get a chance to solve it!
The first step in solving any business problem is to make sure we solve the right one, so before diving into the problem, I would like to first recap the case, then ask a few clarification questions to make sure we’re both on the same page, and lastly announce my overall case approach.
So here is my understanding of the case:
- [facts regarding the client and situation]
- [key case question]
Does that correctly summarize the case?
<assume the interview confirms that your playback is correct>
Great, now I’d like to ask my three clarification questions:
- [question 1]
- [question 2]
- [question 3]
<wait for answers>
Thank you for the clarification. Is there anything else I should be aware of?
Thanks for all the insights. It’s great that we all agree on the key details.
For the overall approach to this case, to completely wipe out the problem for a long-lasting impact, we will need to find out the root causes of this problem. To do that I will try to break the problem down into bite-size pieces with issue trees, in order to quickly isolate the root causes inside the branches, then drill down accordingly to gather information until we can draw actionable solutions.
So before I go on to establish my first issue tree, does that approach sound reasonable to you?
<assumes the interviewer agrees with your approach>
It’s great to see that we’re on the same page regarding the key details as well as the overall approach to the case. I do need some time to gather my thoughts, so may I have a short timeout?
Being structured throughout the case
The high stress and large amount of information in case interviews make it easy for even the brightest candidates to derail from the objective or present in an unstructured manner.
I’ll be sharing with you my 3 most impactful tips for keeping the structure in case interview:
1. The map habit
2. Numbering your items
3. Sticking to the big problem
The map habit
It means regularly and explicitly checking where you are, and where you’re doing next.
I call it the map habit because it’s similar to using a map while traveling – pausing every once in a while to check your location, destination, and direction.
This habit gives you a sense of direction and authority while making it easier for the interviewer to follow your case progress. It also makes you sound organized and systematic – a definitive mark of management consultants – and the interviewer will love it!
You’ll see this habit a lot in our Case Interview End-to-End Secrets Program, where candidates would often pause at each key step during the case. Do the same thing in your own case interviews, and you’ll greatly impress the interviewer.
Numbering your items
A very easy and effective way to make your pitches sound structured is to number each item.
The formula is simple: “There are X items that I’m going to say; they are: No.1 … No.2 … No.3 …”
By now you may have noticed that I use this structure many times throughout this guidebook – it’s already quite effective in written language, but it’s even more impactful in spoken communications!
Having this numbering habit will make it very easy for the listener to follow your speech, and it creates an impression of MECE (even if content-wise it’s not MECE).
Sticking to the big problem
There are two ways to keep yourself on track all the time in those high-stress case interviews
1. Occasionally check your position on the issue tree, and quickly get back on track if it seems you’re “derailing”. If this sounds like the previous map habit, you’re right, it is the map habit.
2. Take good notes, with the case question being written big and bold on top of your scratch paper. That way you’ll be reminded every few seconds.
That last point brings us to the next issue: how to take notes.
How to take notes in case interviews
The best notes for case interviews are always clear-cut, structured, and relevant.
Even the smartest candidates suffer from seemingly silly problems in case interviews – forgetting data, messing up the numbers, getting stuck with frameworks, losing sight of the original objective, etc. And in the true management consulting spirit, I set out to find the root causes.
And looking back at hundreds of coaching sessions I did, I found one thing in common – none of those candidates could take good notes.

I’ll tell you precisely how I took notes to get a McKinsey offer; however, I hope that after this chapter, you can install the spirit of the method, not just the method itself.
So here we are, with the 3 groups of sheets laid out for the ideal note-taking:
1. Data sheets
2. Presentation sheets
3. Scratch sheets
Data sheets
Data sheets are used to store and process every piece of incoming data .
Try to draw tables for these sheets, because this not only makes the calculation process easier but also gives the impression that you’re a careful and organized person.
Also, remember to write only the results of calculations on this sheet, to keep it neat and tidy. Most of your calculations should be done mentally (see the article on Consulting Math for more details); if you really need to jot down the calculations, do it on the scratch sheets.
Presentation sheets
Presentation sheets are used to develop and present any “outgoing” content.
Your issue trees should be drawn on these sheets, along with the big-and-bold case question/objective right on top. When delivering your pitches, always turn around the presentation sheets so the interviewer can clearly read what’s on them.
As with the data sheets, avoid any messy “mid-process” drawings. Put them on the scratch sheets instead.
Scratch sheets
Scratch sheets exist to keep other sheets clean.
Ever felt irritated receiving a notebook full of correction marks? That’s exactly how the interviewer feels if you present with untidy notes. You should try your best to hide all the unorganized, messy parts of your thought process.
The scratch sheets provide a sanctuary for that unstructured part of yours – it’s okay to go all over the place for brainstorming, as long as you can organize the incoming resources and present in a systematic manner.
“I took the notes just as you instructed, but I still get stuck in cases. How can I avoid it?” – Well, that’s the subject for our next chapter – “Stuck” situations and how to get out of them.
Stuck in cases – What to do
We’ve all been there – that scarily awkward feeling when you don’t know what to do next in a case interview, that fear of being rejected.
In every “stuck” situation, the most important thing is to remain calm and collected (you’ll lose points if you panic) – then methodically work your way out. I’ll teach you how to get out of those situations, with style.
There are actually 3 different kinds of “stuck”, and for each, I have a different solution:
1. The “Framework” stuck
2. The “Data” stuck
3. The “I-Cannot-Find-The-Problem” stuck
Let’s go through each in detail.
The framework stuck
This situation happens when the candidate does not know which framework to use, and the secret tool for it, is “segmentation”.
Segmentation works just like any framework, and like a Swiss Army knife, it’s usually safe and easy to use. So if you’re unsure how to break things down, say these magic words:
“At this point, I’d like to break down this X item, and one good way is to use the natural segmentation within this line of business. So may I ask how they break this X item in this industry?”
If you get it right, the interviewer will reply with the most industry-relevant way to segment the item.
You may be wondering why I’m not talking about issue trees and frameworks here, after all the theory at the beginning of the guidebook.
The answer is that the textbook and “ideal” solution – learning the problem-solving fundamentals and deep-diving the frameworks to increase your flexibility – takes a lot of time, while the “cliched” solution – learning as many frameworks as possible, usually at the cost of depth – is inherently dangerous.
The data stuck
The “data stuck” happens when the candidate can’t extract relevant insights from the given data. And when this happens, ask for benchmarks.
Comparing with benchmarks is the quickest way to put data into perspective, yielding useful insights. There are 2 kinds of benchmarks – if you remember from the chapter on Candidate-led Cases:
- Historical benchmarks: data on the same entity in the past
- Competitor benchmarks: data on similar/competing entities in the same timeframe
To ask for benchmarks, Just say the following lines:
“For now, I hypothesize that the root cause of the problem comes from the X branch of this issue tree. However, to further break down the problem in a spot-on way, I do need some information on the context of our client’s problem.
One of the quickest ways to grasp that context is to use competitor’s data; so can I have the X figure for our client’s competitors?”
The “I-Cannot-Find-The-Problem” stuck
This is the scariest “stuck” because there’s no obvious reason or solution – you’ve done your math right, your framework is suitable, and you’ve got a lot of interesting insights from data. Why are you still stuck?
From my experience in coaching sessions, there are 2 scenarios where this happens: (1) your issue tree is not MECE, and (2) if your issue tree is MECE, it does not isolate the problem.
You can try to avoid this in the first place by mastering the MECE principle, improving intuition, as well as aligning with the interviewer early and often.
But what if you still get stuck? The answer is to calmly admit you’ve hit a dead-end, and ask for time to fix the problem; be it the first or second scenario, you have to redraw your issue tree.
Literally use the following script:
“My whole analysis seems going towards a dead-end, which means either part of my issue tree is not MECE or my method of breaking down does not isolate the problem. Either way, I would like to take a timeout to have a look at it.”
You likely get stuck when practicing on yourself. That’s the reason why you need personal coaching. Veteran coaches at MConsultingPrep will give insightful feedback, propose actionable steps, and help you significantly enhance your performance. Find my coach !
How to ask for data
Data is the fuel for the case interview engine. Without it , your analysis can’t progress.
The problem is that interviewers don’t simply give out precious data for free. It has to be earned. There are 4 tips you can use to show that “worthiness”, and prompt the interviewer to supply you with the best information:
1. Create a good impression
2. Explain the purpose of the data
3. Explain the method of acquiring the data
4. Ask open-ended questions
Tip 1: Creating a good impression
The interviewer will love you if you think and act like a real consultant – if you can achieve that, he/she will always give you the best pieces of data available.
In this guidebook, there are countless tips to show your consulting characteristics – I even write a whole chapter on how to install consulting culture into your own personality. Generally, you must always be (1) structured , (2) fact-based, and (3) action-oriented.
Additionally, common people skills and interview tips also apply – show your appreciation by thanking for their help, keep a smile on your face to maintain a positive atmosphere, etc.
Tip 2: Explaining the purpose of the data
Say why you need that data, so the interviewer knows you can actually use it.
There are only two purposes for data in case interviews: (1) to test a hypothesis, and (2) to understand the context.
You can use the following scripts to when to reason your data requests:
“For now, I’m hypothesizing that the root cause of this problem comes from the X branch. Since this hypothesis can only be tested with the data on X, may I have those figures?”< testing hypothesis>
“For now, I hypothesize that the root cause of the problem comes from the X branch of this issue tree. However, to further break down the problem in a spot-on way, to better understand the context of our client’s problem, I will ask a few more questions. Does that sound reasonable to you?” < understanding the context>
Tip 3: Explaining the method to acquire the data
By stating how to get the data, you prove its feasibility and reinforce your data request.
In real consulting projects, data is not always available; the interviewer may rely on this logic and refuse to give you any information. So, when you ask for data, make sure your request is realistic, then state the method to acquire it using these words:
“If this was a real project, this information can be acquired from/by X source/method”.
In our Prospective Candidate Starter Pack , there is a sheet listing all the possible sources of information in consulting projects, which you can download for your own use, along with many other free case interview materials.
Accurately explaining the data acquisition method also shows that you’ve done your homework and you know the consulting industry inside-out. Any interviewer will be greatly impressed.
Ask open-ended questions
This prompts the interviewer to give you data you haven’t thought of.
The precise questions mostly depend on specific cases (meaning you need to sharpen your intuition), but there is a Swiss Army knife here: “Is there anything else?” – which is a question real consultants ask several times a day, at the end of their conversations.
Use open-ended questions when you feel you might be missing something – for example, during clarification – and only after a series of well-defined, close-ended questions. Otherwise, you risk appearing lazy and over-reliant.
What to do when receiving data
Suppose the interviewer agrees to give you data. Now what?
Time to shine! If you do these following 3 steps, even just once, in the interviewer’s mind, you already pass:
1. Acknowledge the data and show appreciation
2. Describe the data, especially its notable features
3. State the implications of the data
Let’s dive into each separately.
Step 1: Acknowledging the data
Simply thank the interviewer for the interesting piece of data.
Firstly, it confirms that you have received, and can understand the data.
Secondly, it’s always good to give out modest, subtle compliments to the interviewer. Trust me, conducting case interviews is hard work, and the interviewer does appreciate those little compliments.
Last but not least, it buys you a few seconds to fully absorb the new information and minimize any possible silence.
Step 2: Describing the data
Summarize the most important insights you can extract.
Don’t recite a short essay about the data, there is no time for that. Quickly and mentally calculate all the important points, then state it out loud in 1-2 sentences.
This step has several uses:
It showcases your consulting math skills (chart insights and mental calculation)
It eliminates the silence during your analysis
It helps you quickly memorize the key trends in the data
Step 3: Stating the implications
Concisely explain how the insights from the data related to the issue tree – do they confirm or reject the current hypothesis? Do they open new areas for investigations?
This part is extremely important because it connects to the action-oriented mindset of actual management consultants while laying solid foundations for your next steps (fact-based).
Example – Handling revenue data
Suppose you’re working on a profitability case (how to fix low profits), and you’re trying to dictate whether the root cause comes from the revenue side.
The interviewer gives you this data:
How would you respond? Try to answer it yourself before revealing the sample answer.
Sample Script - Receiving Data
Thank you for the very interesting data. (acknowledging)
It seems that our client’s revenue has been increasing steadily throughout four years – around the mark of 20% annual growth, in fact. (describe the data)
This suggests that the problem may not come from this side of the issue tree. However, in order to fully reject the possibility, I need the figures on the revenue of other companies in this industry around this time. Do we have those numbers? (implications)
Delivering the perfect closing pitch
“You have one minute to summarize all of your findings to the client CEO. What would you say?”
Your answer must be short, to-the-point, action-oriented, and client-friendly.
The closing pitch of the case interview is sometimes called the “elevator pitch” , where you supposedly meet the client CEO inside the elevator and must somehow deliver the results of the project before the elevator arrives at its destination floor (it’s even worded like that sometimes).
Regardless of the wording, the principles remain the same, and your closing pitch must consist of these 4 parts:
1. Introduction / Lead-in
2. Summary of the root causes
3. Summary of the solutions
4. Next step
Part 1: Introduction / Lead-in
Open your pitch in a client-friendly way. Remember, consulting is a service – a premium one, in fact.
There is a simple formula for this part of the pitch:
“Mr. CEO, it has been a great pleasure to be working with you on your company’s X problem.”
Everybody loves a little compliment, don’t they?
Part 2: Summary of the root causes
Don’t go into detail about your analysis – show them the results first.
CEOs are busy people, they have no time for a 15-minute break-down of your issue tree. They only care about the “big picture” – “Why is the problem happening?”.
You need to sum up root causes in a structured manner, with a numbered list – in the case interview context, that’s one characteristic the interviewer looks for, and in real projects, it helps the listener follow your pitch.
“After careful analysis, we have found X root causes for the company’s problem: 1… 2… 3… X”.
Part 3: Summary of the solutions
The solutions are what the clients pay for in the first place, so make sure to deliver them clearly and systematically.
This step must also be structured. Additionally, list the solution in the same order as their corresponding root causes, to imply the connection between them (if the root causes are listed as A, B, C, then the solutions should never be C, B, A).
“To solve the aforementioned issues, we propose the X following solutions: 1… 2… 3… X”.
Part 4: Next step
The ending must lead the customer towards a follow-up project, in a client-friendly way.
This step shows that you have an action-oriented mindset and necessary people skills to represent the firm before the clients.
Moreover, follow-up implementation projects are a major source of revenue for the top consulting firms (such as McKinsey, BCG or Bain), so mentioning them in your case interview ending pitch proves that you did the appropriate research before applying.
So here’s what you’ll say when the elevator reaches the destination:
“We would be more than happy to work with you to implement these solutions”.
Develop personal interview scripts
Every tip I’ve mentioned in the previous 7 chapters is for recurring situations in case interviews, and they can be dealt with using formulaic responses.
What that means for you – the candidate – is that you can make personal scripts and learn them by heart until they all become your second nature. That will save you a lot of brainpower to use on the issue tree. This approach has proven successful with all of my coachees, and it’s also a major part of our Case Interview End-to-End Secrets Program. You will find my own personal script I used back in the day, and I will also personally give feedback to scripts of members of the program.
So open your document tool and start writing now. Once you’ve finished the scripts, learn them by heart one at a time. When you feel comfortable with every one of them, you can move up to a higher level and practice with whole cases.
Inside the case interviewer’s mind – Consulting culture
The best way to impress your consulting interviewer is to act like a consultant. And to do that, you need to know what goes on inside their mind – both the conscious and unconscious – then install it into your own personality.
In this chapter, I’ll guide you through 15 ingredients that make up a consulting mind. However, I won’t tell you how to apply this in case interviews because it will sound fake – what you need is to immerse yourself in a consulting environment, and incorporate these “ingredients” into your own mindset.

Responsibility & proactivity
Everyone talks about responsibility and proactivity these days, but in management consulting, we have a much more powerful word – “ownership” . When you “own” the work, you deeply and sincerely care about it, and you always try to go beyond what is required.
If you ever spend your efforts trying to improve a piece of work that your boss already approved, just because you know it is the right thing to do, because you feel so good seeing a job well-done, you have that “ownership” mindset.
In management consulting, you are expected to possess that mindset. In my early days at McKinsey, I was almost thrown out the window for working on a cement project but not knowing where the aggregate mines were (which was outside my responsibilities, but my boss expected me to know it, since I “owned” that cement project).
If you fail to do your work, don’t ever blame anyone or anything. Your responsibility is to draw up contingency plans for the “worst-case scenarios”:
- Missing the deadline because the client did not send you the data? You should have accounted for it in your schedule.
- Late for work because of a traffic jam? Why didn’t you get up earlier?
- Your pet bite your suit? Any sensible person should have a spare one; even if that one is bitten, aren’t we paying you enough to get a new suit at the store this morning?
In short, if you want to be a consultant, don’t make excuses.
Result-oriented / Can-do attitude
“There’s nothing I can’t do” – that’s the mindset you need to work in management consulting.
The result orientation inside a consulting firm is intense – saying that it’s “Mission Impossible” everyday would not be an exaggeration, but at the end of the day it’s always “Mission Accomplished”.
The boss doesn’t pay much attention to how you do a task, or what resources it takes, as long as you get it done. The firm has enough resources of every kind to help you with that, so there’s no reason you can’t pull it off.
Top-down communication
Communications made by consultants are always short, concise, to-the-point, action-oriented, and structured.
We were all given full-on lectures by our parents back when we were kids, for wasting food or not exercising (or not studying, for Asians like me). If they were management consultants, most of those lectures would be replaced with powerful, action-oriented messages: “Go study. If you don’t get an A+ for the next test, I’ll have to discipline you”.
A consultant seeing something non-MECE is like your mom seeing your messy bedroom. It’s that discomforting.
If you wish to be a consultant, train yourself to be MECE in everything you do. Once you can be MECE effortlessly, and you start spotting the annoying non-MECE-ness in everything around you, you know you’ve got it.

If you’re unstructured, you won’t get into the business.
Being “structured” is a pretty vague concept, but everyone in the consulting industry knows when they see it. It’s about being organized, logical, top-down, MECE, etc.. Basically, if you can approach things the same way as real consultants, you will be deemed “structured”
If you can’t meet the deadline, you’re dead (of course, not literally).
A consulting firm works like the perfect machine, where every part operates as intended. When consultants promise to help you with something, you can be nearly 100% sure that they’ll keep their word. This makes work management that much easier.
Consequently, if you start missing the deadlines, you’ll be out of the game soon enough.
Manager from Day 1
You’ll get the idea right away if you watched this video on the job of management consultants:
In short, even as an entry-level associate, you’ll be managing a multitude of resources (experts, specialists, etc.), contents (reports, client data, expert knowledge,…), and stakeholders (the two most important being your client and your boss).
Pulling all of these together to create impactful results would be an impressive feat, even for the best and brightest new hires.
Client first
Don’t. Ever. Piss off. The client.
Management consulting is a special service industry – besides the usual “don’t disrespect the client” and “don’t leave a bad image of the firm”, there’s also “don’t make them hate you while telling them to do what they probably hate.” (which is a good way to sum up a consultant’s job).
In case interviews and PEIs, the interviewer will be asking himself a big question: “Can I trust this guy to represent me and my firm before the client?” – if the answer is anything below a stellar impression, you won’t be receiving an offer.
Consultants will have valid reasons for everything they do.
In both consulting work and case interviews, you need to be very explicit about the basis of your actions – every conclusion must have backing data, every idea must be explained, and every request must serve a purpose. Don’t ever assume that you’re justified.
Being fact-based is part of the foundation for the trust people place in consulting firms, so people who draw ideas out of thin air and act impulsively will never get into the industry.

Effective time & resources management
Every consultant works hard, so the only way to stand out is to work smart.
Yes, I know it’s a buzzword, and I know it’s cliched, but the 80-20 rule really does apply in this line of work. The best performers are always the ones to identify the most important lever and focus on it.
With the intense workload and up-or-out policy at major consulting firms, this skill is vital. Don’t be surprised if you pull all-nighters and work hard all the time but still get fired, while that one guy who goes home at 5 gets promoted. If you want to survive, learn from him.
Key takeaways & key messages
To a management consultant, everything has a key takeaway.
Consultants are efficient people, they don’t simply waste time, effort, and resources on irrelevant things. Things are only worthy of their attention if they have an interesting, helpful “so what”:
- You tell a story? So what?
- You perform a data analysis? So what are your key insights, and what’s the implication?
- You draw a slide? What’s the key message you’re trying to deliver?
If you already think like this, trust me, the interviewer will love you.
Think on your feet first
You should only ask for leadership assistance only after you’ve thought well about the problem.
Just pause for a second and think: would you be more ready to help someone who really tries their best at the job or someone who does nothing and relies solely on you?
The same thing is true in consulting work, and even in case interviews: the interviewer will assist you if you can deliver well-informed opinions.
With that said, “asking without thinking first” is a very common mistake in case interviews, which you can see in the numerous examples from our End-to-End Secrets Program.
Align early, align often
Always try to reach and maintain a consensus with co-workers and your boss, from the most mundane tasks to the largest projects.
Nobody wants to spend a whole week building a model that the team doesn’t need; it’s a huge waste of time and resources. As such, consultants have this aligning habit very early and often – a little time spent on reaching an agreement now will save a lot of trouble later.
Remember to align in case interviews as well – at the start of the case, and every important step.
Consultants are very action-oriented people who always think about the next step.
Every meeting, phone call, even random catch-up must end with everybody being explicitly and absolutely clear about what to do next.
So what’s YOUR next step, after reading this guidebook?
Scoring in the McKinsey PSG/Digital Assessment
The scoring mechanism in the McKinsey Digital Assessment
Related product
/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/1669783363736_case_interview_end_to_end_secrets_program.png)
Case Interview End-to-End Secrets Program
Elevate your case interview skills with a well-rounded preparation package
Six types of charts in case interview are: Bar/Column chart, Line chart, Percentage chart, Mekko chart, Scatter plot chart, Waterfall chart.
Business knowledge is not a mandatory condition to become a consultant. Nevertheless, it still has specific obligations and advantages for consultants.
There are 9 type of questions that mostly used in actual case interviews. Each type has a different solution, but you can rely on the a 4-step guide to answer

Related Expertise: Culture and Change Management , Business Strategy , Corporate Strategy
Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence
November 03, 2014 By Lars Fæste , Jim Hemerling , Perry Keenan , and Martin Reeves
In a business environment characterized by greater volatility and more frequent disruptions, companies face a clear imperative: they must transform or fall behind. Yet most transformation efforts are highly complex initiatives that take years to implement. As a result, most fall short of their intended targets—in value, timing, or both. Based on client experience, The Boston Consulting Group has developed an approach to transformation that flips the odds in a company’s favor. What does that look like in the real world? Here are five company examples that show successful transformations, across a range of industries and locations.
VF’s Growth Transformation Creates Strong Value for Investors
Value creation is a powerful lens for identifying the initiatives that will have the greatest impact on a company’s transformation agenda and for understanding the potential value of the overall program for shareholders.
VF offers a compelling example of a company using a sharp focus on value creation to chart its transformation course. In the early 2000s, VF was a good company with strong management but limited organic growth. Its “jeanswear” and intimate-apparel businesses, although responsible for 80 percent of the company’s revenues, were mature, low-gross-margin segments. And the company’s cost-cutting initiatives were delivering diminishing returns. VF’s top line was essentially flat, at about $5 billion in annual revenues, with an unclear path to future growth. VF’s value creation had been driven by cost discipline and manufacturing efficiency, yet, to the frustration of management, VF had a lower valuation multiple than most of its peers.
With BCG’s help, VF assessed its options and identified key levers to drive stronger and more-sustainable value creation. The result was a multiyear transformation comprising four components:
- A Strong Commitment to Value Creation as the Company’s Focus. Initially, VF cut back its growth guidance to signal to investors that it would not pursue growth opportunities at the expense of profitability. And as a sign of management’s commitment to balanced value creation, the company increased its dividend by 90 percent.
- Relentless Cost Management. VF built on its long-known operational excellence to develop an operating model focused on leveraging scale and synergies across its businesses through initiatives in sourcing, supply chain processes, and offshoring.
- A Major Transformation of the Portfolio. To help fund its journey, VF divested product lines worth about $1 billion in revenues, including its namesake intimate-apparel business. It used those resources to acquire nearly $2 billion worth of higher-growth, higher-margin brands, such as Vans, Nautica, and Reef. Overall, this shifted the balance of its portfolio from 70 percent low-growth heritage brands to 65 percent higher-growth lifestyle brands.
- The Creation of a High-Performance Culture. VF has created an ownership mind-set in its management ranks. More than 200 managers across all key businesses and regions received training in the underlying principles of value creation, and the performance of every brand and business is assessed in terms of its value contribution. In addition, VF strengthened its management bench through a dedicated talent-management program and selective high-profile hires. (For an illustration of VF’s transformation roadmap, see the exhibit.)
The results of VF’s TSR-led transformation are apparent. 1 1 For a detailed description of the VF journey, see the 2013 Value Creators Report, Unlocking New Sources of Value Creation , BCG report, September 2013. Notes: 1 For a detailed description of the VF journey, see the 2013 Value Creators Report, Unlocking New Sources of Value Creation , BCG report, September 2013. The company’s revenues have grown from $7 billion in 2008 to more than $11 billion in 2013 (and revenues are projected to top $17 billion by 2017). At the same time, profitability has improved substantially, highlighted by a gross margin of 48 percent as of mid-2014. The company’s stock price quadrupled from $15 per share in 2005 to more than $65 per share in September 2014, while paying about 2 percent a year in dividends. As a result, the company has ranked in the top quintile of the S&P 500 in terms of TSR over the past ten years.
A Consumer-Packaged-Goods Company Uses Several Levers to Fund Its Transformation Journey
A leading consumer-packaged-goods (CPG) player was struggling to respond to challenging market dynamics, particularly in the value-based segments and at the price points where it was strongest. The near- and medium-term forecasts looked even worse, with likely contractions in sales volume and potentially even in revenues. A comprehensive transformation effort was needed.
To fund the journey, the company looked at several cost-reduction initiatives, including logistics. Previously, the company had worked with a large number of logistics providers, causing it to miss out on scale efficiencies.
To improve, it bundled all transportation spending, across the entire network (both inbound to production facilities and out-bound to its various distribution channels), and opened it to bidding through a request-for-proposal process. As a result, the company was able to save 10 percent on logistics in the first 12 months—a very fast gain for what is essentially a commodity service.
Similarly, the company addressed its marketing-agency spending. A benchmark analysis revealed that the company had been paying rates well above the market average and getting fewer hours per full-time equivalent each year than the market standard. By getting both rates and hours in line, the company managed to save more than 10 percent on its agency spending—and those savings were immediately reinvested to enable the launch of what became a highly successful brand.
Next, the company pivoted to growth mode in order to win in the medium term. The measure with the biggest impact was pricing. The company operates in a category that is highly segmented across product lines and highly localized. Products that sell well in one region often do poorly in a neighboring state. Accordingly, it sought to de-average its pricing approach across locations, brands, and pack sizes, driving a 2 percent increase in EBIT.
Similarly, it analyzed trade promotion effectiveness by gathering and compiling data on the roughly 150,000 promotions that the company had run across channels, locations, brands, and pack sizes. The result was a 2 terabyte database tracking the historical performance of all promotions.
Using that information, the company could make smarter decisions about which promotions should be scrapped, which should be tweaked, and which should merit a greater push. The result was another 2 percent increase in EBIT. Critically, this was a clear capability that the company built up internally, with the objective of continually strengthening its trade-promotion performance over time, and that has continued to pay annual dividends.
Finally, the company launched a significant initiative in targeted distribution. Before the transformation, the company’s distributors made decisions regarding product stocking in independent retail locations that were largely intuitive. To improve its distribution, the company leveraged big data to analyze historical sales performance for segments, brands, and individual SKUs within a roughly ten-mile radius of that retail location. On the basis of that analysis, the company was able to identify the five SKUs likely to sell best that were currently not in a particular store. The company put this tool on a mobile platform and is in the process of rolling it out to the distributor base. (Currently, approximately 60 percent of distributors, representing about 80 percent of sales volume, are rolling it out.) Without any changes to the product lineup, that measure has driven a 4 percent jump in gross sales.
Throughout the process, management had a strong change-management effort in place. For example, senior leaders communicated the goals of the transformation to employees through town hall meetings. Cognizant of how stressful transformations can be for employees—particularly during the early efforts to fund the journey, which often emphasize cost reductions—the company aggressively talked about how those savings were being reinvested into the business to drive growth (for example, investments into the most effective trade promotions and the brands that showed the greatest sales-growth potential).
In the aggregate, the transformation led to a much stronger EBIT performance, with increases of nearly $100 million in fiscal 2013 and far more anticipated in 2014 and 2015. The company’s premium products now make up a much bigger part of the portfolio. And the company is better positioned to compete in its market.
A Leading Bank Uses a Lean Approach to Transform Its Target Operating Model
A leading bank in Europe is in the process of a multiyear transformation of its operating model. Prior to this effort, a benchmarking analysis found that the bank was lagging behind its peers in several aspects. Branch employees handled fewer customers and sold fewer new products, and back-office processing times for new products were slow. Customer feedback was poor, and rework rates were high, especially at the interface between the front and back offices. Activities that could have been managed centrally were handled at local levels, increasing complexity and cost. Harmonization across borders—albeit a challenge given that the bank operates in many countries—was limited. However, the benchmark also highlighted many strengths that provided a basis for further improvement, such as common platforms and efficient product-administration processes.
To address the gaps, the company set the design principles for a target operating model for its operations and launched a lean program to get there. Using an end-to-end process approach, all the bank’s activities were broken down into roughly 250 processes, covering everything that a customer could potentially experience. Each process was then optimized from end to end using lean tools. This approach breaks down silos and increases collaboration and transparency across both functions and organization layers.
Employees from different functions took an active role in the process improvements, participating in employee workshops in which they analyzed processes from the perspective of the customer. For a mortgage, the process was broken down into discrete steps, from the moment the customer walks into a branch or goes to the company website, until the house has changed owners. In the front office, the system was improved to strengthen management, including clear performance targets, preparation of branch managers for coaching roles, and training in root-cause problem solving. This new way of working and approaching problems has directly boosted both productivity and morale.
The bank is making sizable gains in performance as the program rolls through the organization. For example, front-office processing time for a mortgage has decreased by 33 percent and the bank can get a final answer to customers 36 percent faster. The call centers had a significant increase in first-call resolution. Even more important, customer satisfaction scores are increasing, and rework rates have been halved. For each process the bank revamps, it achieves a consistent 15 to 25 percent increase in productivity.
And the bank isn’t done yet. It is focusing on permanently embedding a change mind-set into the organization so that continuous improvement becomes the norm. This change capability will be essential as the bank continues on its transformation journey.
A German Health Insurer Transforms Itself to Better Serve Customers
Barmer GEK, Germany’s largest public health insurer, has a successful history spanning 130 years and has been named one of the top 100 brands in Germany. When its new CEO, Dr. Christoph Straub, took office in 2011, he quickly realized the need for action despite the company’s relatively good financial health. The company was still dealing with the postmerger integration of Barmer and GEK in 2010 and needed to adapt to a fast-changing and increasingly competitive market. It was losing ground to competitors in both market share and key financial benchmarks. Barmer GEK was suffering from overhead structures that kept it from delivering market-leading customer service and being cost efficient, even as competitors were improving their service offerings in a market where prices are fixed. Facing this fundamental challenge, Barmer GEK decided to launch a major transformation effort.
The goal of the transformation was to fundamentally improve the customer experience, with customer satisfaction as a benchmark of success. At the same time, Barmer GEK needed to improve its cost position and make tough choices to align its operations to better meet customer needs. As part of the first step in the transformation, the company launched a delayering program that streamlined management layers, leading to significant savings and notable side benefits including enhanced accountability, better decision making, and an increased customer focus. Delayering laid the path to win in the medium term through fundamental changes to the company’s business and operating model in order to set up the company for long-term success.
The company launched ambitious efforts to change the way things were traditionally done:
- A Better Client-Service Model. Barmer GEK is reducing the number of its branches by 50 percent, while transitioning to larger and more attractive service centers throughout Germany. More than 90 percent of customers will still be able to reach a service center within 20 minutes. To reach rural areas, mobile branches that can visit homes were created.
- Improved Customer Access. Because Barmer GEK wanted to make it easier for customers to access the company, it invested significantly in online services and full-service call centers. This led to a direct reduction in the number of customers who need to visit branches while maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction.
- Organization Simplification. A pillar of Barmer GEK’s transformation is the centralization and specialization of claim processing. By moving from 80 regional hubs to 40 specialized processing centers, the company is now using specialized administrators—who are more effective and efficient than under the old staffing model—and increased sharing of best practices.
Although Barmer GEK has strategically reduced its workforce in some areas—through proven concepts such as specialization and centralization of core processes—it has invested heavily in areas that are aligned with delivering value to the customer, increasing the number of customer-facing employees across the board. These changes have made Barmer GEK competitive on cost, with expected annual savings exceeding €300 million, as the company continues on its journey to deliver exceptional value to customers. Beyond being described in the German press as a “bold move,” the transformation has laid the groundwork for the successful future of the company.
Nokia’s Leader-Driven Transformation Reinvents the Company (Again)
We all remember Nokia as the company that once dominated the mobile-phone industry but subsequently had to exit that business. What is easily forgotten is that Nokia has radically and successfully reinvented itself several times in its 150-year history. This makes Nokia a prime example of a “serial transformer.”
In 2014, Nokia embarked on perhaps the most radical transformation in its history. During that year, Nokia had to make a radical choice: continue massively investing in its mobile-device business (its largest) or reinvent itself. The device business had been moving toward a difficult stalemate, generating dissatisfactory results and requiring increasing amounts of capital, which Nokia no longer had. At the same time, the company was in a 50-50 joint venture with Siemens—called Nokia Siemens Networks (NSN)—that sold networking equipment. NSN had been undergoing a massive turnaround and cost-reduction program, steadily improving its results.
When Microsoft expressed interest in taking over Nokia’s device business, Nokia chairman Risto Siilasmaa took the initiative. Over the course of six months, he and the executive team evaluated several alternatives and shaped a deal that would radically change Nokia’s trajectory: selling the mobile business to Microsoft. In parallel, Nokia CFO Timo Ihamuotila orchestrated another deal to buy out Siemens from the NSN joint venture, giving Nokia 100 percent control over the unit and forming the cash-generating core of the new Nokia. These deals have proved essential for Nokia to fund the journey. They were well-timed, well-executed moves at the right terms.
Right after these radical announcements, Nokia embarked on a strategy-led design period to win in the medium term with new people and a new organization, with Risto Siilasmaa as chairman and interim CEO. Nokia set up a new portfolio strategy, corporate structure, capital structure, robust business plans, and management team with president and CEO Rajeev Suri in charge. Nokia focused on delivering excellent operational results across its portfolio of three businesses while planning its next move: a leading position in technologies for a world in which everyone and everything will be connected.
Nokia’s share price has steadily climbed. Its enterprise value has grown 12-fold since bottoming out in July 2012. The company has returned billions of dollars of cash to its shareholders and is once again the most valuable company in Finland. The next few years will demonstrate how this chapter in Nokia’s 150-year history of serial transformation will again reinvent the company.

Managing Director & Senior Partner
San Francisco - Bay Area

Managing Director & Senior Partner, Chairman of the BCG Henderson Institute
ABOUT BOSTON CONSULTING GROUP
Boston Consulting Group partners with leaders in business and society to tackle their most important challenges and capture their greatest opportunities. BCG was the pioneer in business strategy when it was founded in 1963. Today, we work closely with clients to embrace a transformational approach aimed at benefiting all stakeholders—empowering organizations to grow, build sustainable competitive advantage, and drive positive societal impact.
Our diverse, global teams bring deep industry and functional expertise and a range of perspectives that question the status quo and spark change. BCG delivers solutions through leading-edge management consulting, technology and design, and corporate and digital ventures. We work in a uniquely collaborative model across the firm and throughout all levels of the client organization, fueled by the goal of helping our clients thrive and enabling them to make the world a better place.
© Boston Consulting Group 2024. All rights reserved.
For information or permission to reprint, please contact BCG at [email protected] . To find the latest BCG content and register to receive e-alerts on this topic or others, please visit bcg.com . Follow Boston Consulting Group on Facebook and X (formerly Twitter) .
Subscribe to our Business Transformation E-Alert.
Practice using our Free Case library
Account not confirmed.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
HBS Case Selections
OpenAI: Idealism Meets Capitalism
- Shikhar Ghosh
- Shweta Bagai
Generative AI and the Future of Work
- Christopher Stanton
- Matt Higgins
Copilot(s): Generative AI at Microsoft and GitHub
- Frank Nagle
- Shane Greenstein
- Maria P. Roche
- Nataliya Langburd Wright
- Sarah Mehta
Innovation at Moog Inc.
- Brian J. Hall
- Ashley V. Whillans
- Davis Heniford
- Dominika Randle
- Caroline Witten
Innovation at Google Ads: The Sales Acceleration and Innovation Labs (SAIL) (A)
- Linda A. Hill
- Emily Tedards
Juan Valdez: Innovation in Caffeination
- Michael I. Norton
- Jeremy Dann
UGG Steps into the Metaverse
- Shunyuan Zhang
- Sharon Joseph
- Sunil Gupta
- Julia Kelley
Metaverse Wars
- David B. Yoffie
Roblox: Virtual Commerce in the Metaverse
- Ayelet Israeli
- Nicole Tempest Keller
Timnit Gebru: "SILENCED No More" on AI Bias and The Harms of Large Language Models
- Tsedal Neeley
- Stefani Ruper
Hugging Face: Serving AI on a Platform
- Kerry Herman
- Sarah Gulick
SmartOne: Building an AI Data Business
- Karim R. Lakhani
- Pippa Tubman Armerding
- Gamze Yucaoglu
- Fares Khrais
Honeywell and the Great Recession (A)
- Sandra J. Sucher
- Susan Winterberg
Target: Responding to the Recession
- Ranjay Gulati
- Catherine Ross
- Richard S. Ruback
- Royce Yudkoff
Hometown Foods: Changing Price Amid Inflation
- Julian De Freitas
- Jeremy Yang
- Das Narayandas
Elon Musk's Big Bets
- Eric Baldwin
Elon Musk: Balancing Purpose and Risk
Tesla's ceo compensation plan.
- Krishna G. Palepu
- John R. Wells
- Gabriel Ellsworth
China Rapid Finance: The Collapse of China's P2P Lending Industry
- William C. Kirby
- Bonnie Yining Cao
- John P. McHugh
Forbidden City: Launching a Craft Beer in China
- Christopher A. Bartlett
- Carole Carlson
Booking.com
- Stefan Thomke
- Daniela Beyersdorfer
Innovation at Uber: The Launch of Express POOL
- Chiara Farronato
- Alan MacCormack
Racial Discrimination on Airbnb (A)
- Michael Luca
- Scott Stern
- Hyunjin Kim
Unilever's Response to the Future of Work
- William R. Kerr
- Emilie Billaud
- Mette Fuglsang Hjortshoej
AT&T, Retraining, and the Workforce of Tomorrow
- Joseph B. Fuller
- Carl Kreitzberg
Leading Change in Talent at L'Oreal
- Lakshmi Ramarajan
- Vincent Dessain
- Emer Moloney
- William W. George
- Andrew N. McLean
Eve Hall: The African American Investment Fund in Milwaukee
- Steven S. Rogers
- Alterrell Mills
United Housing - Otis Gates
- Mercer Cook
The Home Depot: Leadership in Crisis Management
- Herman B. Leonard
- Marc J. Epstein
- Melissa Tritter
The Great East Japan Earthquake (B): Fast Retailing Group's Response
- Hirotaka Takeuchi
- Kenichi Nonomura
- Dena Neuenschwander
- Meghan Ricci
- Kate Schoch
- Sergey Vartanov
Insurer of Last Resort?: The Federal Financial Response to September 11
- David A. Moss
- Sarah Brennan
Under Armour
- Rory McDonald
- Clayton M. Christensen
- Daniel West
- Jonathan E. Palmer
- Tonia Junker
Hunley, Inc.: Casting for Growth
- John A. Quelch
- James T. Kindley
Bitfury: Blockchain for Government
- Mitchell B. Weiss
- Elena Corsi
Deutsche Bank: Pursuing Blockchain Opportunities (A)
- Lynda M. Applegate
- Christoph Muller-Bloch
Maersk: Betting on Blockchain
- Scott Johnson
Yum! Brands
- Jordan Siegel
- Christopher Poliquin
Bharti Airtel in Africa
- Tanya Bijlani
Li & Fung 2012
- F. Warren McFarlan
- Michael Shih-ta Chen
- Keith Chi-ho Wong
Sony and the JK Wedding Dance
- John Deighton
- Leora Kornfeld
United Breaks Guitars
David dao on united airlines.
- Benjamin Edelman
- Jenny Sanford
Marketing Reading: Digital Marketing
- Joseph Davin
Social Strategy at Nike
- Mikolaj Jan Piskorski
- Ryan Johnson
The Tate's Digital Transformation
Social strategy at american express, mellon financial and the bank of new york.
- Carliss Y. Baldwin
- Ryan D. Taliaferro
The Walt Disney Company and Pixar, Inc.: To Acquire or Not to Acquire?
- Juan Alcacer
- David J. Collis
Dow's Bid for Rohm and Haas
- Benjamin C. Esty
Finance Reading: The Mergers and Acquisitions Process
- John Coates
Apple: Privacy vs. Safety? (A)
- Henry W. McGee
- Nien-he Hsieh
- Sarah McAra
Sidewalk Labs: Privacy in a City Built from the Internet Up
- Leslie K. John
Data Breach at Equifax
- Suraj Srinivasan
- Quinn Pitcher
- Jonah S. Goldberg
Apple's Core
- Noam Wasserman
Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple
- Barbara Feinberg
Apple Inc. in 2012
- Penelope Rossano
Iz-Lynn Chan at Far East Organization (Abridged)
- Anthony J. Mayo
- Dana M. Teppert
Barbara Norris: Leading Change in the General Surgery Unit
- Boris Groysberg
- Nitin Nohria
- Deborah Bell
Adobe Systems: Working Towards a "Suite" Release (A)
- David A. Thomas
- Lauren Barley
Home Nursing of North Carolina
Castronics, llc, gemini investors, angie's list: ratings pioneer turns 20.
- Robert J. Dolan
Basecamp: Pricing
- Frank V. Cespedes
- Robb Fitzsimmons
J.C. Penney's "Fair and Square" Pricing Strategy
J.c. penney's 'fair and square' strategy (c): back to the future.
- Jose B. Alvarez
Osaro: Picking the best path
- James Palano
- Bastiane Huang
HubSpot and Motion AI: Chatbot-Enabled CRM
- Thomas Steenburgh
GROW: Using Artificial Intelligence to Screen Human Intelligence
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Paul D. McKinnon
- Paul Yarabe
Arup: Building the Water Cube
- Robert G. Eccles
- Amy C. Edmondson
- Dilyana Karadzhova
(Re)Building a Global Team: Tariq Khan at Tek
Managing a global team: greg james at sun microsystems, inc. (a).
- Thomas J. DeLong
Organizational Behavior Reading: Leading Global Teams
Ron ventura at mitchell memorial hospital.
- Heide Abelli
Anthony Starks at InSiL Therapeutics (A)
- Gary P. Pisano
- Vicki L. Sato
Wolfgang Keller at Konigsbrau-TAK (A)
- John J. Gabarro
Midland Energy Resources, Inc.: Cost of Capital
- Timothy A. Luehrman
- Joel L. Heilprin
Globalizing the Cost of Capital and Capital Budgeting at AES
- Mihir A. Desai
- Doug Schillinger
Cost of Capital at Ameritrade
- Mark Mitchell
- Erik Stafford
Finance Reading: Cost of Capital
David Neeleman: Flight Path of a Servant Leader (A)
- Matthew D. Breitfelder
Coach Hurley at St. Anthony High School
- Scott A. Snook
- Bradley C. Lawrence
Shapiro Global
- Michael Brookshire
- Monica Haugen
- Michelle Kravetz
- Sarah Sommer
Kathryn McNeil (A)
- Joseph L. Badaracco Jr.
- Jerry Useem
Carol Fishman Cohen: Professional Career Reentry (A)
- Myra M. Hart
- Robin J. Ely
- Susan Wojewoda
Alex Montana at ESH Manufacturing Co.
- Michael Kernish
Michelle Levene (A)
- Tiziana Casciaro
- Victoria W. Winston
John and Andrea Rice: Entrepreneurship and Life
- Howard H. Stevenson
- Janet Kraus
- Shirley M. Spence
Partner Center
At home, abroad, working, interning? Wherever you are this summer, contact OCS or make an appointment for a virtual advising session. We are available all summer!
- Undergraduates
- Ph.Ds & Postdocs
- Prospective Students & Guests
- What is a Community?
- Student Athletes
- First Generation and/or Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Veterans
- Exploring Careers
- Advertising, Marketing & PR
- Finance, Insurance & Real Estate
- General Management & Leadership Development Programs
- Law & Legal Services
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelance Work
- Environment, Sustainability & Energy
- Media & Communications
- Policy & Think Tanks
- Engineering
- Healthcare, Biotech & Global Public Health
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Programming & Data Science
- Graduate School
- Health Professions
- Business School
- Meet with OCS
- Student Organizations Workshop Request
- OCS Podcast Series
- Office of Fellowships
- Navigating AI in the Job Search Process
- Cover Letters & Correspondence
- Job Market Insights
- Professional Conduct & Etiquette
- Professional Online Identity
- Interview Preparation
- Resource Database
- Yale Career Link
- Jobs, Internships & Other Experiences
- Gap Year & Short-Term Opportunities
- Planning an International Internship
- Funding Your Experience
- Career Fairs/Networking Events
- On-Campus Recruiting
- Job Offers & Salary Negotiation
- Informational Interviewing
- Peer Networking Lists
- Building Your LinkedIn Profile
- YC First Destinations
- YC Four-Year Out
- GSAS Program Statistics
- Statistics & Reports
- Contact OCS
- OCS Mission & Policies
- Additional Yale Career Offices
Case Interview Study Samples
- Share This: Share Case Interview Study Samples on Facebook Share Case Interview Study Samples on LinkedIn Share Case Interview Study Samples on X
These case studies represent cases across firm styles (McKinsey, Bain, BCG, Deloitte, & more), including interviewer-led and interviewee-led (candidate-led) cases. The video examples demonstrate the nuances of the virtual case interview and include feedback from an MBB coach. The sessions feature consultants or consulting candidates.
Office of Career Strategy
Visiting yale.

Hacking the Case Interview

Case interview frameworks or consulting frameworks are arguably the most critical component of a case interview. Outstanding case frameworks set you up for success for the case while poor frameworks make the case difficult to solve.
Struggling on how to use frameworks in your case interviews? Unsure of which frameworks to use?
Don't worry because we have you covered! We'll teach you step-by-step, how to craft tailored and unique frameworks for any case interview situation.
By the end of this article, you will learn four different strategies on how to create unique and tailored frameworks for any case interview.
Strategy #1: Creating Frameworks from Scratch
- Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 – 10 Broad Business Areas
- Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders
- Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes
- Strategy #5: Two-Part MECE Frameworks
You will apply these strategies to learn how to create case frameworks for the six most common types of case interviews.
Profitability Framework
Market entry framework, merger and acquisition framework, pricing framework, new product framework, market sizing framework.
You will also learn six consulting frameworks that nearly every consultant knows.
Porter’s Five Forces Framework
Swot framework, 4 p’s framework, 3 c’s / business situation framework, bcg 2x2 matrix framework, mckinsey 7s framework.
If you’re looking for a step-by-step shortcut to learn case interviews quickly, enroll in our case interview course . These insider strategies from a former Bain interviewer helped 30,000+ land consulting offers while saving hundreds of hours of prep time.
What is a Case Interview Framework?
A case interview framework is simply a tool that helps you structure and break down complex problems into simpler, smaller components. Think of a framework as brainstorming different ideas and organizing them into different categories.
Let’s look at an example: Coca-Cola is a large manufacturer and retailer of non-alcoholic beverages, such as sodas, juices, sports drinks, and teas. They are looking to grow and are considering entering the beer market in the United States. Should they enter?
In order for you to decide whether Coca-Cola should enter the beer market, you likely have many different questions you’d like to ask:
- Does Coca-Cola know how to produce beer?
- Would people buy beer made by Coca-Cola?
- Where would Coca-Cola sell its beer?
- How much would it cost to enter the beer market?
- Will Coca-Cola be profitable from selling beer?
- How would Coca-Cola outcompete competitors?
- What is the size of the beer market in the United States?
This is not a very structured way of thinking through the case. The questions are listed in no particular order. Additionally, many of the questions are similar to one another and could be grouped together.
A case framework would provide a structure to organize these ideas and questions in a way that is easy to understand.
A framework for this case might look like the following.

Notice that we have simplified the list of questions we had into four main categories. These broad categories are frequently called framework “buckets.” Also notice that we have grouped similar questions together under each framework bucket.
This case framework tells us what areas we need to explore in order to make a recommendation to Coca-Cola. It also clearly shows what questions we need to answer under each area.
This is the power of a case interview framework. It simplifies a complex business problem into smaller and separate components that we can tackle one at a time.
So how do you develop a case framework? The next section will reveal four robust strategies for creating unique and tailored consulting frameworks for any case interview.
Case Interview Framework Strategies
There are four case interview framework strategies you should have in your toolkit:
When given a case interview, you will need to decide which framework strategy you want to use. Some framework strategies will be more effective than others depending on what type of case interview you get.
Therefore, choose the case framework strategy that is easiest for you given the type of case that you get.
This case framework strategy can be used for any type of case. This is the most time-consuming strategy, but yields case frameworks that are the most tailored and unique for the given case interview.
To create a framework from scratch, ask yourself what 3 – 4 statements must be true for you to be 100% confident in your recommendation. These 3 – 4 areas will become the buckets in your framework.
Once you have your framework buckets, brainstorm a few questions for each bucket that you need answers to.
Let’s return to the Coca-Cola case example in which we are asked to determine whether or not they should enter the beer market. What 3 – 4 statements must be true for us to recommend that Coca-Cola should enter the beer market?
The four major statements that must be true are:
- The beer market is an attractive market
- Competitors in the market are weak
- Coca-Cola has the capabilities to produce outstanding beer
- Coca-Cola will be highly profitable from entering the beer market
These will be the major areas or buckets in our framework.

Next, let’s add a few bullet points under each area to add more detail to our case framework.
To determine whether the beer market is attractive, we would need to know the market size, the market growth rate, and the average profit margins in the market.
To assess whether the market is competitive, we would need to know who the competitors are, how much market share they have, and if they have any differentiation or competitive advantages.
To decide whether Coca-Cola has the capabilities to produce beer, we need to know if there are any capability gaps or if there are significant synergies that Coca-Cola can leverage.
Finally, to determine the expected profitability of entering the market, we would need to know what expected revenues are, what expected costs are, and how long it would take Coca-Cola to break even.
This gives us our case framework.

You can repeat this process for any case interview that you get to create an outstanding case framework.
Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 – 10 Broad Business Areas to Make a Framework
Creating case frameworks from scratch can be quite time-consuming. Because of this, many interview candidates make the mistake of using memorized frameworks for case interviews.
Candidates will either use a single memorized framework for every case or memorize a different framework for every type of case interview.
The issue with using memorized frameworks is that they aren’t tailored to the specific case you are solving for. When given an atypical business problem, your framework areas or buckets will not be entirely relevant.
A poor framework makes the case interview significantly more difficult to solve.
Additionally, Interviewers can easily tell that you are regurgitating memorized information and not thinking critically.
Instead of creating frameworks from scratch each time, this second case framework strategy provides a method to speed up the process while still creating frameworks that are unique and tailored to the case. Additionally, you won’t need to memorize multiple different frameworks.
First, memorize a list of 8 - 10 broad business areas, such as the following:

When given a case, mentally run through this list and pick the 3 - 5 areas that are most relevant to the case.
This will be your framework.
If the list does not give you enough areas for your framework, brainstorm and add your own ideas as areas to your framework.
Finally, add a few bullet points under each area to add more detail to your case framework.
This strategy guarantees that your framework elements are relevant to the case. It also demonstrates that you can create unique, tailored frameworks for every business problem.
Let’s return to the Coca-Cola case example in which we are asked to determine whether or not they should enter the beer market.
Running through our list of memorized framework areas, the following six areas would be relevant:
- Market attractiveness : Is the beer market attractive?
- Competitive landscape : How tough is competition?
- Company capabilities : Does Coca-Cola have the capabilities to enter the market?
- Profitability : Will Coca-Cola be profitable from entering the market?
- Risks : What are the risks of entering the market?
- Strategic alternatives : Are there other more attractive markets Coca-Cola should enter?
You can pick 3 – 5 of these areas as the basis for your framework.
This strategy is a shortcut for creating unique and tailored frameworks for every business problem. Even if you and a friend used this same strategy, you both may end up with different frameworks.
That is completely fine. As long as the buckets in your framework are major areas and are relevant to the case, your case framework will be significantly better than most candidates’ frameworks.
You do not need to develop a framework entirely from scratch every time to create outstanding case frameworks. This case framework strategy can be applied to over 90% of case interviews.
For the remaining 10% of case interviews, you will need to learn and use the next two case interview framework strategies.
Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders to Make a Framework
The first two case framework strategies can be applied to over 90% of cases. However, some cases may require you to identify and focus on various stakeholders that are involved in running or operating a business.
For these cases, the primary areas of your case framework will be these major stakeholders.
Let’s take a look at an example: Your client is a non-profit blood bank. They have volunteer nurses that go to schools and companies to collect blood from donors. They then sell this blood to hospitals, which use this blood for emergency situations when a blood transfusion is required. Currently, Hearts4Lives is not profitable because they are not able to collect enough blood to sell to their hospital partners. What can they do to fix this?
This case involves many different stakeholders:
- Volunteer nurses
- Blood donors
- Schools and companies
For cases in which many different stakeholders are involved, it will be useful to look at each stakeholder and determine what each could do to address the problem.
One potential framework could look like the following:
Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes to make a Framework
Similar to the previous case framework strategy, some cases may require you to focus on improving or optimizing a particular process.
For these cases, the primary areas of your case framework will be each major step of the process.
Let’s take a look at an example: Your client is a waste disposal company that manages a fleet of drivers and garbage trucks that go to residential homes, collect garbage, and then dump the garbage in city landfills. They have an obligation to collect each home’s garbage once a week. Recently, they have been failing to meet this requirement and are backed up with garbage disposal requests. What is causing this issue and what should they do to fix it?
For cases involving processes and efficiencies, it can be helpful to look at the different components or steps in the process.
We can think about the process of collecting and disposing of garbage in the following steps:
- Get in a garbage truck
- Drive along a designated route
- Collect garbage at each stop
- Dispose of the garbage in the landfill
Using these steps as the primary areas of our framework, we can create the following case framework:

Once you have systematically listed all of the steps in a process, you can identify the pain points or bottlenecks that are causing the issue and determine ways to improve the process.
Strategy #5: Two-part MECE Frameworks
An easy way to make a 100% MECE framework is to use a two-part MECE framework. For the first step, start with a X and Not X framework. Some examples include:
- Internal / external
- Short-term / long-term
- Economic / non-economic
- Quantitative / qualitative
- Direct / indirect
- Supply-side / demand-side
- Upside / downside
- Benefits / cost
There are probably hundreds more frameworks that follow this pattern.
These frameworks are by definition 100% MECE. Since all of these frameworks are X or Not-X, they are mutually exclusive. There is no redundancy or overlap between X and Not-X.
Together, X and Not-X are also completely exhaustive. They cover the universe of all ideas and possibilities.
The X and Not-X framework by itself is good enough for a lot of the questions you could get asked in a case interview.
If you’re asked to brainstorm ways to decrease costs, you can create a framework consisting of decreasing variable costs and decreasing non-variable costs, also known as fixed costs.
If you’re asked to brainstorm barriers to entry, you can create a framework consisting of economic barriers to entry, such as cash and equipment, and non-economic barriers to entry, such as brand name or distribution channels.
However, to take your framework to the next level and truly impress your interviewer, we have the option of doing step two.
Step two involves adding another layer of X and Not X into your framework. What do we mean by this?
Let’s say you are trying to help a city decide whether they should host the upcoming summer Olympics. You start off with a framework consisting of benefits and costs. You can take this framework to the next level by adding another layer, such as adding in short-term and long-term.
With this additional layer, your framework now has four categories: short-term benefits, long-term benefits, short-term costs, and long-term costs. This is a 100% MECE framework that enables you to think through all possible considerations in deciding whether a city should host the Olympics.
Let’s look at another example. Suppose you are trying to figure out how to reduce a company’s costs. You start with a framework consisting of variable costs and fixed costs. You can take this framework to the next level by adding another layer, such as direct and indirect.
With this additional layer, your framework now has four categories: ways to directly reduce variable costs, ways to indirectly reduce variable costs, ways to directly reduce fixed costs, and ways to indirectly reduce fixed costs. This is another 100% MECE framework.
Case Frameworks: The 6 Most Common Frameworks
There are six common case frameworks in consulting case interviews.
Profitability frameworks are the most common types of frameworks you’ll likely use in consulting first round interviews.
A profitability case might look like this: “An electric car manufacturer has recently been experiencing a decline in profits. What should they do?”
There are two steps to solving a profitability case.
First, you need to understand quantitatively, what is the driver causing the decline in profits?
You should know the following basic profit formulas.

Is the decline in profitability due to a decline in revenue, an increase in costs, or both?
On the revenue side, what is causing the decline? Is it from a decrease in quantity of units sold? If so, is the decrease concentrated in a particular product line, geography, or customer segment?
Or is the decline due to a decrease in price? Are we selling products at a lower price? Is there a sales mix change? In other words, are we selling more low-priced products and fewer high-priced products?
On the cost side, what is causing the increase in costs? Is it from an increase in variable costs? If so, which cost elements have gone up?
Or is the increase in costs due to an increase in fixed costs? If so, which fixed costs have gone up?
Next, you need to understand qualitatively, what factors are driving the decline in profitability that you identified in the previous step.
Looking at customers, have customer needs or preferences changed? Have their purchasing habits or behaviors changed? Have their perceptions of the company changed?
Looking at competitors, have new players entered the market? Have existing competitors made any recent strategic moves? Are competitors also experiencing a decline in profitability?
Looking at the market, are there any market trends that we should be aware of? For example, are there new technology or regulatory changes? How do these trends impact profitability?
Putting all of this together, we get the following profitability framework.

Once you have gone through this profitability framework and understand both quantitatively what is causing the decline in profits and qualitatively why this is happening, you can begin brainstorming ideas to address the profitability issue.
Among the ideas that you brainstorm, you can prioritize which recommendations to focus on based on the level of impact and ease of implementation.
See the video below for an example of how to solve a profitability case using this profitability framework.
Market entry frameworks are the second most common types of frameworks you’ll likely use in consulting first round interviews.
A market entry case might look like this: “Coca-Cola is considering entering the beer market in the United States. Should they enter?”
To create a market entry framework, there are typically four statements that need to be true in order for you to recommend entering the market:
- The market is attractive
- Competition is weak
- The company has the capabilities to enter
- The company will be highly profitable from entering the market
These statements form the foundation of our market entry framework.

Note the logical order of the buckets in the framework.
We first want to determine whether the market is attractive. Then, we need to check if competition is weak and if there is an opportunity to capture meaningful market share.
If these two conditions are true, then we need to confirm that the company actually has the capabilities to enter the market.
Finally, even if the company has the capabilities to enter the market, we need to verify that they will be profitable from entering.
This is a logical progression that your market entry framework will take you through to develop a recommendation for market entry cases.
Merger and acquisition frameworks are also common frameworks you’ll use in consulting interviews.
There are two common business situations.
The first situation is a company looking to acquire another company in order to access a new market, access new customers, or to grow its revenues and profits.
Another situation is a private equity company looking to acquire a company as an investment. Their goal is to then grow the business using their operational expertise and then sell the company years later for a high return on investment. This type of case interview is called a private equity case interview .
In either of these situations, mergers and acquisition cases typically involve acquiring an attractive, successful company.
It is rare to get a case in which a company or private equity firm is looking to acquire a poorly performing company to purchase at a discount. Nevertheless, you can always clarify the goal of the merger or acquisition with the interviewer before beginning the case.
In order to recommend making an acquisition, four statements need to be true.
- The market that the acquisition target is in is attractive
- The acquisition target is an attractive company
- The acquisition generates meaningful synergies
- The acquisition target is at a great price and will generate high returns on investment
These statements become the basis of our merger and acquisition framework.

Synergies is an area that should absolutely be included in any merger or acquisition framework. A merger or acquisition can lead to revenue synergies and cost synergies.
Revenue synergies include:
- Having access to new customer segments
- Having access to new markets
- Having access to new distribution channels
- Cross-selling opportunities
- Up-selling opportunities
Cost synergies include:
- Eliminating cost redundancies
- Consolidating functions or groups
- Increasing buying power with suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retailers
Pricing frameworks are used in cases involving the pricing of a product or service. To develop a pricing framework, you should be familiar with the three different ways to price a product or service.
- Pricing based on costs : set a price by applying a profit margin on the total costs to produce or deliver the product or service
- Pricing based on competition : set a price based on what competitors are charging for products similar to yours
- Pricing based on value added : set a price by quantifying the benefits that the product provides customers
Your answer to pricing cases will likely involve a mix of all three of these pricing strategies.
Your pricing framework will look something like the following.

Pricing based on costs will determine the minimum price you can realistically set. Pricing based on value added will determine the maximum possible price. Pricing based on competition will determine which price in between these two price points you should set.
In order to get customers to purchase your product, the difference between your price point and the customer’s maximum willingness to pay must be greater than or equal to the difference between your competitor’s price point and the customer’s maximum willingness to pay for their product.
New product frameworks are used to help a company decide whether or not to launch a product or service.
New product frameworks share many similarities with market entry frameworks. In order to recommend launching a new product, the following statements would need to be true:
- The product targets an attractive market segment
- The product meets customer needs and is superior to competitor products
- The company has the capabilities to successfully launch the product
- Launching the product will be highly profitable
Expanding on these areas, your new product framework could look like the following:
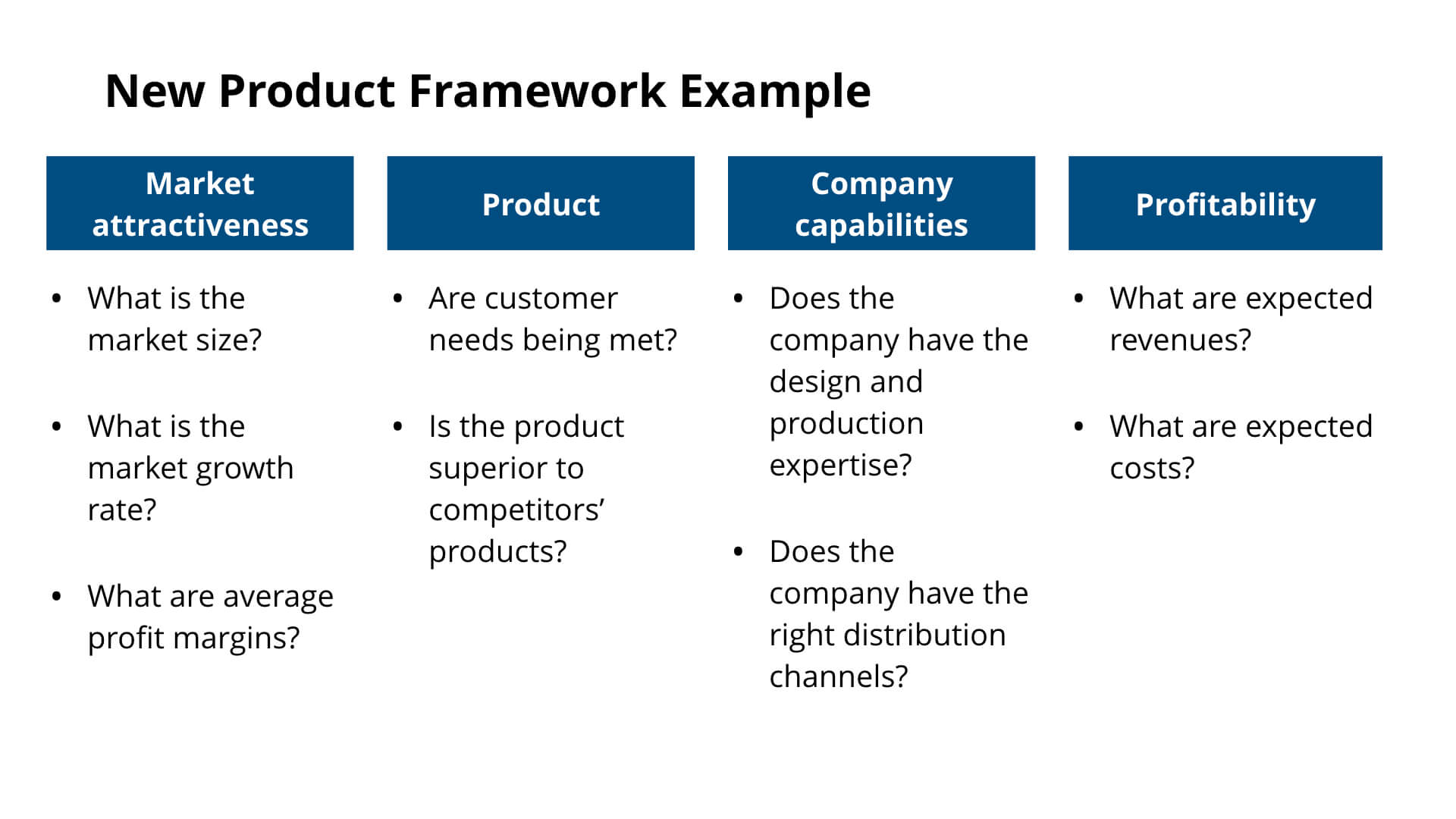
A comprehensive guide to market sizing questions and market sizing frameworks can be found in our comprehensive market sizing article. You can also watch the video below:
As a summary, market sizing or estimation questions ask you to determine the size of a particular market or to estimate a particular figure.
There are two different market sizing frameworks or approaches:
- Top-down approach : start with a large number and then refine and break down the number until you get your answer
- Bottom-up approach : start with a small number and then build up and increase the number until you get your answer
To create your market sizing framework, simply write out in bullet points, the exact steps you would take to calculate the requested market size or estimation figure.
Consulting Frameworks Every Consultant Knows
There are six consulting frameworks that nearly every consultant knows.
I would not recommend using these exact frameworks during a case interview because the interviewer may think you are just regurgitating memorized information instead of thinking critically about the case.
Instead use the four framework strategies that we covered earlier in this article to create tailored and unique frameworks for each case.
Nevertheless, it is helpful to review these common consulting frameworks in order to understand the fundamental concepts and business principles behind them.
Porter’s Five Forces framework was developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter. This framework is used to analyze the attractiveness of a particular industry.
There are five forces that determine whether an industry is attractive or unattractive.

Competitive rivalry: How competitive is the industry?
The more competitive an industry is in terms of number and strength of competitors, the less attractive the industry is. The less competitive an industry is, the more attractive the industry is.
Supplier power: How much power do suppliers have?
Suppliers are companies that provide the raw materials for your company to produce goods or services. The fewer suppliers there are, the more bargaining power suppliers have in setting prices. The more suppliers there are, the weaker bargaining power suppliers have in setting prices.
Therefore, high supplier power makes the industry less attractive while low supplier power makes the industry more attractive.
Buyer power: How much power do buyers have?
Buyers are customers or companies that purchase your company’s product. The more buyers there are, the weaker bargaining power buyers have in setting prices. The fewer buyers there are, the more bargaining power buyers have in setting prices.
Therefore, high buyer power makes the industry less attractive while low buyer power makes the industry more attractive.
Threat of substitution: How difficult is it for customers to find and use substitutes over your product?
The availability of many substitutes makes the industry less attractive while a lack of substitutes makes the industry more attractive
Threat of new entry: How difficult is it for new players to enter the market?
If barriers to entry are high, then it is difficult for new players to enter the market and it is easier for existing players to maintain their market share.
If barriers to entry are low, then it is easy for new players to enter the market and more difficult for existing players to maintain their market share.
A low threat of new entrants makes the market more attractive while a high threat of new entrants makes the market less attractive.
A SWOT framework is used to assess a company’s strategic position. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.

Strengths : What does the company do well? What qualities separate them from competitors?
Weaknesses : What does the company do poorly? What are the things that competitors do better?
Opportunities : Where are the company’s opportunities for growth or improvement?
Threats : Who are the most threatening competitors? What are the major risks to the company’s business?
The 4 P’s framework is used to develop a marketing strategy for a product. The 4 P’s in this framework are: product, place, promotion, and price.

Product : If there are multiple products or different versions of a product, you will need to decide which product to market. To do this, you will need to fully understand the benefits and points of differentiation of each product.
Select the product that best fits customer needs for the customer segment you are focusing on.
Place : You will need to decide where the product will be sold to customers. Different customer segments have different purchasing habits and behaviors. Therefore, some distribution channels will be more effective than others.
Should the product be sold directly to the customer online? Should the product be sold in the company’s stores? Should the product be sold through retail partners instead?
Promotion : You will need to decide how to spread information about the product to customers. Different customer segments have different media consumption habits and preferences. Therefore, some promotional strategies will be more effective than others.
Promotional techniques and strategies include advertising, social media marketing, email marketing, search engine marketing, video marketing, and public relations. Select the strategies and techniques that will be the most effective.
Price : You will need to decide how to price the product. Pricing is important because it determines the profits and the quantity of units sold. Pricing can also communicate information on the quality or value of the product.
If you price the product too high, you may be pricing the product above your customer segment’s willingness to pay. This would lead to lost sales.
If you price the product too low, you may be losing potential profit from customers who were willing to pay a higher price. You may also be losing profits from customers who perceive the product as low-quality due to a low price point.
In deciding on a price, you can consider the costs to produce the product, the prices of other similar products, and the value that you are providing to customers.
The 3 C’s framework is used to develop a business strategy for a company. 3 C’s stands for customers, competition, and company.
The business situation framework was developed by a former McKinsey consultant, Victor Cheng, who added a fourth component to this framework, product.
Both of these frameworks are used to develop a business strategy for a company in a variety of situations, such as market entry, new product launch, and acquisition.

There is another similar framework called the 4C framework that expands upon the 3 C's. The 4C framework stands for customer, competition, capabilities, and cost.
The BCG 2x2 Matrix Framework was developed by BCG founder Bruce Hendersen. It is used to examine all of the different businesses of a company to determine which businesses the company should invest in and focus on.
The BCG 2x2 Matrix has two different dimensions:
- Market growth : How quickly is the market growing?
- Relative market share : How much market share does the company have compared to competitors?
Each business of the company can be assessed on these two dimensions on a scale of low to high. This is what creates the 2x2 Matrix because it creates four different quadrants.
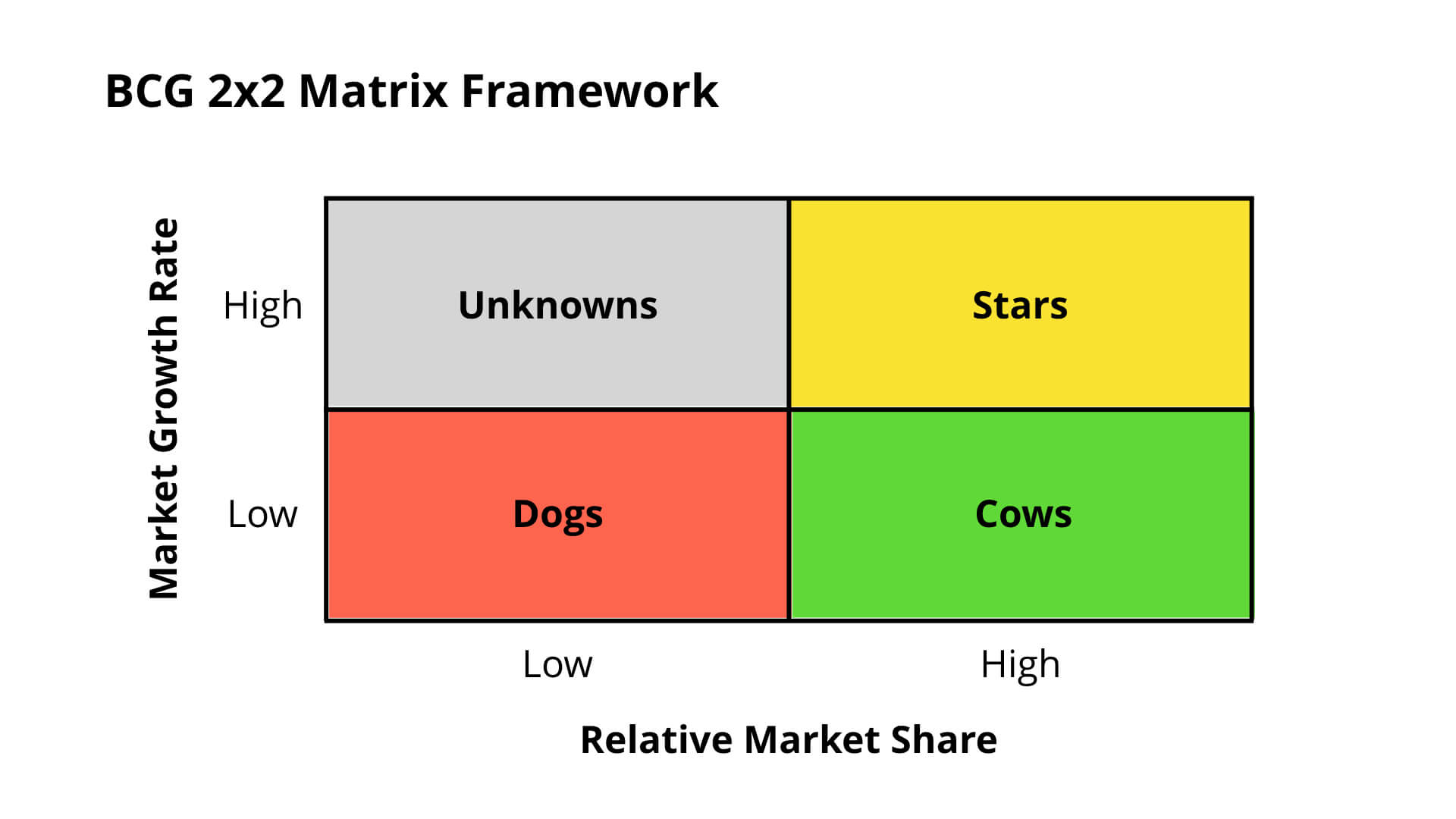
Each quadrant has a recommended strategy.
- Stars : These are businesses that have high market growth rate and high relative market share. These businesses should be heavily invested in so they can continue to grow.
- Cows : These are businesses that have low market growth rate, but high relative market share. These businesses should be maintained since they are stable, profitable businesses.
- Dogs : These are businesses that have low market growth rate and low relative market share. These businesses should not be invested in and should possibly even be divested to free up cash for other businesses.
- Unknown : These are businesses that have high market growth rate and low relative market share. The strategy for these businesses is not clear. With enough investment, these businesses could become stars. However, these businesses could also become dogs if the market growth slows or declines.
The McKinsey 7S Framework was developed by two former McKinsey consultants, Tom Peters and Robert Waterman. The 7S Framework identifies seven elements that a company needs to align on in order to be successful.

These elements are:
- Strategy : The company’s plan to grow and outcompete competitors
- Structure : The organization of the company
- Systems : The company’s daily activities and processes
- Shared values : The core beliefs, values, or mission of the company
- Style : The style of leadership or management used
- Staff : The employees that are hired
- Skills : The capabilities of the company’s employees
Land your Dream Consulting Job
Here are the resources we recommend to learn the most robust, effective case interview strategies in the least time-consuming way:
- Comprehensive Case Interview Course (our #1 recommendation): The only resource you need. Whether you have no business background, rusty math skills, or are short on time, this step-by-step course will transform you into a top 1% caser that lands multiple consulting offers.
- Hacking the Case Interview Book (available on Amazon): Perfect for beginners that are short on time. Transform yourself from a stressed-out case interview newbie to a confident intermediate in under a week. Some readers finish this book in a day and can already tackle tough cases.
- The Ultimate Case Interview Workbook (available on Amazon): Perfect for intermediates struggling with frameworks, case math, or generating business insights. No need to find a case partner – these drills, practice problems, and full-length cases can all be done by yourself.
- Case Interview Coaching : Personalized, one-on-one coaching with former consulting interviewers
- Behavioral & Fit Interview Course : Be prepared for 98% of behavioral and fit questions in just a few hours. We'll teach you exactly how to draft answers that will impress your interviewer
- Resume Review & Editing : Transform your resume into one that will get you multiple interviews
Land Multiple Consulting Offers
Complete, step-by-step case interview course. 30,000+ happy customers.
- All Headlines

Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies of 2021
Two cases about Hertz claimed top spots in 2021's Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies
Two cases on the uses of debt and equity at Hertz claimed top spots in the CRDT’s (Case Research and Development Team) 2021 top 40 review of cases.
Hertz (A) took the top spot. The case details the financial structure of the rental car company through the end of 2019. Hertz (B), which ranked third in CRDT’s list, describes the company’s struggles during the early part of the COVID pandemic and its eventual need to enter Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
The success of the Hertz cases was unprecedented for the top 40 list. Usually, cases take a number of years to gain popularity, but the Hertz cases claimed top spots in their first year of release. Hertz (A) also became the first ‘cooked’ case to top the annual review, as all of the other winners had been web-based ‘raw’ cases.
Besides introducing students to the complicated financing required to maintain an enormous fleet of cars, the Hertz cases also expanded the diversity of case protagonists. Kathyrn Marinello was the CEO of Hertz during this period and the CFO, Jamere Jackson is black.
Sandwiched between the two Hertz cases, Coffee 2016, a perennial best seller, finished second. “Glory, Glory, Man United!” a case about an English football team’s IPO made a surprise move to number four. Cases on search fund boards, the future of malls, Norway’s Sovereign Wealth fund, Prodigy Finance, the Mayo Clinic, and Cadbury rounded out the top ten.
Other year-end data for 2021 showed:
- Online “raw” case usage remained steady as compared to 2020 with over 35K users from 170 countries and all 50 U.S. states interacting with 196 cases.
- Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S..
- The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines.
- Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
- A third of the cases feature a woman protagonist.
- Orders for Yale SOM case studies increased by almost 50% compared to 2020.
- The top 40 cases were supervised by 19 different Yale SOM faculty members, several supervising multiple cases.
CRDT compiled the Top 40 list by combining data from its case store, Google Analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption.
All of this year’s Top 40 cases are available for purchase from the Yale Management Media store .
And the Top 40 cases studies of 2021 are:
1. Hertz Global Holdings (A): Uses of Debt and Equity
2. Coffee 2016
3. Hertz Global Holdings (B): Uses of Debt and Equity 2020
4. Glory, Glory Man United!
5. Search Fund Company Boards: How CEOs Can Build Boards to Help Them Thrive
6. The Future of Malls: Was Decline Inevitable?
7. Strategy for Norway's Pension Fund Global
8. Prodigy Finance
9. Design at Mayo
10. Cadbury
11. City Hospital Emergency Room
13. Volkswagen
14. Marina Bay Sands
15. Shake Shack IPO
16. Mastercard
17. Netflix
18. Ant Financial
19. AXA: Creating the New CR Metrics
20. IBM Corporate Service Corps
21. Business Leadership in South Africa's 1994 Reforms
22. Alternative Meat Industry
23. Children's Premier
24. Khalil Tawil and Umi (A)
25. Palm Oil 2016
26. Teach For All: Designing a Global Network
27. What's Next? Search Fund Entrepreneurs Reflect on Life After Exit
28. Searching for a Search Fund Structure: A Student Takes a Tour of Various Options
30. Project Sammaan
31. Commonfund ESG
32. Polaroid
33. Connecticut Green Bank 2018: After the Raid
34. FieldFresh Foods
35. The Alibaba Group
36. 360 State Street: Real Options
37. Herman Miller
38. AgBiome
39. Nathan Cummings Foundation
40. Toyota 2010

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
12. Capital One case interview examples. Case interview example video walkthrough (Capital One website) Capital One case interview guide (by IGotAnOffer) 12. EY Parthenon case interview examples. Candidate-led case example with feedback (by IGotAnOffer) 14. Consulting clubs case interview examples. Berkeley case book (2006) Columbia case book ...
A case library of 600+ case study examples to get you ready for your case interview! McKinsey, BCG, Bain & 20+ other firm styles represented! ... Welcome to the Case Library, Management Consulted's repository of over 600 cases, organized by firm, difficulty, and subject matter. ... IQVIA Consulting Services: Market Study - Growth: N: 1 ...
10 example cases with 100+ real-time feedbacks on tips and techniques, 50+ exercises on business intuition and 1300+ questions for math practice! Learning 35 case interview examples, 16 casebooks, and a feedback-rich case video help you to best preparing for the management consulting recruitment process.
Follow along using our template. The first section is the introduction. Set the stage here by introducing your client, their business, and their industry. This section gives context to the case study. Ideally, your ideal client is intrigued by being in a similar industry or situation as the client in your case study.
Mental Math for Case Interviews - You were probably better at mental math in 7th grade than you are now. Brush up on your skills to ensure you can ace the interview. Case Interview Examples - See what real consulting applicants experienced during the case interview process. Case Interview Prep - Ordered steps to prepare for your ...
This guide, written by a former McKinsey consultant and Wharton MBA, breaks down the management consulting case interview into comprehensible parts with relevant, realistic examples at every turn. While the consulting case study interview may seem daunting at first, most cases follow a typical song-and-dance. Once you get a hang of it, prepping ...
48 Case Interview Examples: Master List (2024) Updated May 17, 2024. The case interview is the biggest challenge consulting candidates must overcome to receive an offer. Most aspiring consultants are coveting an offer from the likes of McKinsey, Bain, BCG, and Deloitte. Though some are blessed with the innate talent to crack cases, for the vast ...
These case studies represent cases across firm styles (McKinsey, Bain, BCG, Deloitte, & more), including interviewer-led and interviewee-led (candidate-led) cases. The video examples demonstrate the nuances of the virtual case interview and include feedback from an MBB coach. The sessions feature consultants or consulting candidates.
A Case Study Interview is a real-time problem-solving test used to screen candidates for their ability to succeed in consulting. The case is presented as an open-ended question, often a problem that a specific type of business is facing, that an interviewer asks a candidate to solve.
Examples of how PwC US helps clients build value, solve complex business issues, and achieve high performance. ... Asset and wealth management Banking and capital markets Insurance Private Equity. Menu. ... PwC case studies. Examples of how a community of solvers brings together the strengths of people and technology to build trust and deliver ...
Deloitte case interview examples: here (more than 15 case interview examples) Deloitte case interview example: Federal Agency. Deloitte case interview example: Recreation Unlimited. Deloitte case interview example: Federal benefits Provider. Deloitte case interview example: Federal Civil Cargo protection Bureau.
Better business performance for a better world—that's how we think about impact. In practice, that means partnering with our clients every day to set bold strategies, embed technology in everything they do, and create enduring change for their people and their business performance, speeding the transition to sustainable and inclusive growth. From AI transformations to a manufacturing ...
Agency V - Help a large federal agency recover from a front-page scandal that sparked investigations and congressional hearings. Federal Benefits Provider - Help a federal agency that provides benefits to millions of U.S. citizens prepare for a major expansion of its mandate. 5. AT Kearney Case Interview Examples.
EY Consulting case studies are a window into how we work alongside our clients to deliver strategic, sustainable growth and success. Advanced manufacturing and mobility. Consumer. Energy. Financial services. Government and public sector. Health sciences and wellness. Technology, media and telecommunications.
So, this is a sample study plan you can adopt for yourselves: Step 1: Learn the basics of case interview theory. By either: Read this article thus far; Watch this Case Interview 101 video; Step 2: Watch a simple case interview example. By either: Read the sample case flow above. Watch this Case Interview Example video
Five Case Studies of Transformation Excellence. November 03, 2014 By Lars Fæste , Jim Hemerling , Perry Keenan, and Martin Reeves. In a business environment characterized by greater volatility and more frequent disruptions, companies face a clear imperative: they must transform or fall behind. Yet most transformation efforts are highly complex ...
The case interview is the ultimate challenge for most consulting candidates. Whether you're just starting your preparation or you are 30 practice cases in, it's always helpful to familiarize yourself with the most popular case interview frameworks. However, the goal is not to memorize the case study interview frameworks.
Practice using our Free Case library We developed our case library to give you the chance to practice on cases used in real case interviews. You will find cases on a variety of topics such as market sizing, pricing, profitability and growth strategy. The varied difficulty level ensures that both novices and advanced candidates will find their ...
Infuse. Infuse focuses on the operational challenges faced by a biotech company as it prepares the launch of a new Alzheimer's treatment. Explore our consulting case library, where you can download over 100 cases with solutions that you can practice as part of your interview preparations.
Find new ideas and classic advice on strategy, innovation and leadership, for global leaders from the world's best business and management experts.
These case studies represent cases across firm styles (McKinsey, Bain, BCG, Deloitte, & more), including interviewer-led and interviewee-led (candidate-led) cases. The video examples demonstrate the nuances of the virtual case interview and include feedback from an MBB coach. The sessions feature consultants or consulting candidates.
There are hundreds consulting case study examples in the Case Library - this is a Profitability case in the McKinsey firm style. Prompt. A US health care provider suffered a profit decline last year. You are hired to solve this problem. The key revenues come from commissions. H Health signs contracts with patients and provides medical services.
By the end of this article, you will learn four different strategies on how to create unique and tailored frameworks for any case interview. Strategy #1: Creating Frameworks from Scratch. Strategy #2: Memorizing 8 - 10 Broad Business Areas. Strategy #3: Breaking Down Stakeholders. Strategy #4: Breaking Down Processes.
Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S.. The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines. Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.