
UC Berkeley’s Premier Undergraduate Economics Journal

The Hidden Importance of Taxes: More Than Just a Nuisance for Taxpayers

ARDA TUNCTURK – MARCH 6TH, 2024
EDITOR: EVAN FREDERICK DAVIS
Imagine coming home from work. You sit down, grab something to eat and drink, and then turn on the TV. On the screen, you see the same old debate between politicians, normative philosophers, and social scientists: taxes. Should the rich be taxed more? Should the poor be given tax credits to help them survive? Among all of this, you ask a very simple yet profound question: What is the point of arguing over marginal tax rates anyway?
Unless you’re an athlete or very rich, you would arguably be completely right. For many people, the marginal tax rate does not affect their day-to-day lives. While you do have to pay some taxes when purchasing gasoline, many states do not have any taxes for groceries, and, barring economic anomalies such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the income tax rate you face yearly will probably never change. So, with that being said, is wondering about the marginal tax rate completely useless? No.
In economic theory, marginal tax rates are seen as a way of funding public projects and reducing income and wealth inequality, with a new and growing emphasis on the latter. So, rather than just thinking of taxes as the traditional mechanism with which the government amasses revenue that will be used to pay for various social, military, health, and development programs, one could also think of taxes as a way to combat wealth inequality and support the middle and lower classes in a given country. That said, while this article will mainly look into optimum taxes in terms of minimizing wealth inequality, it’s also worth looking at the optimum tax rate in terms of the maximization of government revenue. While minimizing economic inequality is certainly an admirable goal, it would not mean anything if everyone in the country had a low standard of living. In this case, although inequality would be very low since wealth is not unequally concentrated in a certain percentile of the population, since people have a low standard of living, this minimization of inequality is not really doing any good for the general welfare of the people. This is where looking at the maximization of government revenue comes in.
If one were to maximize government revenue, then the government could create more social programs, build more infrastructure, and provide more stimulus than it would under a non-optimum state. While we would not be minimizing economic inequality under this model, we would be increasing the standard of living in the country, which is another incredibly important goal and further highlights how important taxes are as a mechanism that the government can use to improve all facets of the economy.
Economic Growth, Productivity, and International Mobility
Two of the main talking points surrounding tax rates are the effect of increasing taxes on economic growth and productivity. Alinaghi and Reed ( 2020 ) find that a 10% increase in taxes in some cases produced a 0.2% decrease in GDP, and in other cases produced a 0.2% increase in GDP. That is to say that even a significant increase in the tax rates has only a moderate impact on a country’s GDP. In contrast, a paper by Romer and Romer (2010) found that the robust effect of a 1% increase in taxes corresponds to a roughly 2.5% decrease in a country’s GDP. An explanation for the differences in the findings between these two papers is that Alinaghi and Reed fail to account for the type of tax rate increases that are implemented. For example, a higher marginal tax rate (a progressive tax) on top innovators in the United States — who also, for the most part, make up the richest citizens in the United States — could decrease innovation within the United States, which in turn would cause a decrease in GDP.
This idea is exactly what Akcigit & Stantcheva ( 2018 ) found in their paper when analyzing the effects of U.S. state marginal tax rates on patent production. They noted that an increase in the marginal tax rate decreased patent production. Furthermore, Stantcheva ( 2020 ) further corroborated the idea that an increase in marginal tax rates for top earners could reduce innovation since the top earners are also the top innovators.
Along those lines, Akcigit & Stantcheva ( 2018 ) also analyzed the effects of an increase in taxes on international mobility — how investors choose to migrate to different countries based on each country’s given tax level. They analyzed the U.S. 1986 Tax Reform Act under the Reagan administration — which lowered the top tax rate on ordinary income from 50% to 28% — finding that the number of top 1% foreign investors in the U.S. increased after the act passed into law relative to a synthetic counterfactual country. A synthetic counterfactual country is a country that had the same trend in the number of foreign superstars as the U.S before the new tax code implementation in the U.S. This synthetic country is used as a control group in the experiment to see what would have happened to the number of foreign superstars in the U.S. if the tax change was not implemented. The difference between the synthetic country and the U.S. after the implementation is the treatment effect caused by the new law. These findings suggest that it may be beneficial to a country’s economy to decrease taxes if its goal is to increase innovation and economic growth. In terms of policy implications, if the U.S. were recovering from a recent recession, then decreasing taxes — on top of the regular monetary policy response — could lead to a quick recovery, as lower taxes would cause growth and productivity to increase, which would increase GDP.

Photo Credit: Akcigit & Stantcheva ( 2018 )
Taxes and Public Policy
Now that the effects of increasing the taxes have been talked about, what is even the point of increasing taxes in the first place? Over time, there has been a shift in economic discourse regarding social welfare. For many years, economists focused on income inequality as the driving force of evaluating how unequal a country’s economy is, and it, understandably, was a pretty good measure. Financial assets, such as stocks, were far from being the main makeup of a person’s wealth. However, throughout the last decade or so, wealth concentrated in the top 10% has grown a lot faster than income concentrated in the top 10% in the United States, according to the Realtime Inequality database by Thomas Blanchet, Emmanuel Saez, and Gabriel Zucman. This growing wealth inequality inside the United States has led to discussions about progressive policy measures, such as progressive wealth taxes, which are tax rates that increase as one’s wealth increases, with the tax rate depending on the wealth bucket that the economic agent is in.
Even if there is significant discourse about using wealth taxes to curb inequality between America’s rich, the middle class, and the poor, many economists have tried to utilize mathematical economic models to determine the “optimal” tax rate, where the optimal tax rate is defined as the one that maximizes the social welfare of society. This is typically measured in terms of monetary consumer and producer surplus, where consumer surplus is the benefit received by consumers for paying less for a good than what they value it, and producer surplus is profits for firms. This is referred to as the Utilitarian perspective on social welfare and is, for the most part, the most popular way of measuring it. There are also the Libertarian and Rawlsian perspectives. Libertarians reject the concept of measurable utility and instead focus on establishing a regulatory framework promoting free entrepreneurship, and Rawlsians conceive of social wellbeing as the utility of the person who is the worst off in society. Some possible reasons for why these two perspectives are not used in economics are that the Libertarian perspective does not allow for the consideration of public policy in the form of wealth transfers since it does not consider utility to be measurable, and the Rawlsian perspective focuses too much on the poorest individual’s situation at the expense of society as a whole.
With that being said, Piketty, Saez, and Stantcheva ( 2014 ) found a highest marginal tax rate of 83% for top labor incomes. Granted, there might be issues, such as international mobility effects or tax loopholes exploited by the rich, that change the marginal tax rate for behavioral reasons. Nevertheless, this is a significant finding and contributes to the idea that higher marginal tax rates on the top income brackets are in fact a way of reducing income inequality, which is in itself a significant societal and economic goal for any developed country. In addition, while the paper looked at marginal tax rates in the form of optimizing the level of income inequality rather than maximizing societal welfare, in a country like the U.S., which is already pretty rich across the board, the goal should be to minimize inequality between the rich and the poor rather than trying to increase what is already probably a high level of societal welfare.
Interestingly, when Piketty and Saez ( 2013 ) analyzed optimal inheritance taxes (an example of a wealth tax), they found an economically conflicting idea: people in the highest bequest percentiles should receive inheritance subsidies, whereas people in the lowest bequest percentiles should face an average inheritance tax of roughly 50% in the United States and a little more than 55% in France. Additionally, the paper also notes two studies — Chamley ( 1986 ) and Judd ( 1985 ) — that suggest that in an economy with zero stochastic shocks (i.e., random economic events), the optimal inheritance tax is 0% in the long run, since any nonzero tax would distort intertemporal economic choices by economic agents, which would in turn harm economic decision making due to complications in the short term decision-making process.
To note, there is dissent from libertarian-leaning economic think tanks, such as the Cato Institute , who argue that the traditional derived optimal tax formulae produce too generous marginal tax rates (sometimes as high as 83%) due to flawed economic assumptions in producing said mathematical models. They also argue that there is a general lack of empirical substantiation for optimal tax claims, on top of incorrect assumptions that higher marginal tax rates on the top labor income brackets do not affect future taxable capital gains, corporate gains, and GDP.
The increasing concentration of individuals’ wealth — mainly in the form of financial assets, such as stocks — has led to a discussion about an optimal capital gains tax structure that minimizes wealth inequality. While research on this topic is sparse, a Joint Economic Committee study by the U.S. Congress, authored by James D. Gwartney and Randall G. Holcombe, does discuss an optimal (in terms of government revenue) marginal capital gains tax of 20%. While the paper does not analyze the optimum rate for wealth inequality, it does provide some estimate as to what optimum capital gains taxes could look like. Something interesting to note is that the suggested capital gains tax of 20% was actually lower than the tax rate at the time (1997) of 28%, which is consistent with the idea that a tax rate that is too high can decrease innovation and economic growth, which would decrease overall wealth taxable in the future. Thus, a higher tax rate does not necessarily suggest higher government tax revenues. This idea of an optimum tax rate in terms of government revenue maximization shows up in economics in the form of the Laffer curve, which is a curve where government revenue originally increases but later decreases as a function of the tax rate. Therefore, the optimum rate of tax is one that is neither too high nor too low based on the given curve. While the curve is critiqued as “too simple” by some economists, it is nevertheless a good illustration of how a tax rate that is too high disincentivizes innovators, which in turn decreases total taxable wealth.

Photo Credit: Investopedia
With taxes being seen as a “necessary evil” by many people, it can be difficult to remember the profound effects that taxes have on the economy as the whole. To think that taxes exist in an isolated echo chamber where they only affect government revenues would be sorely wrong. Taxes affect economic growth, innovation, and have significant effects on public policy in combating income and wealth inequality, along with bettering the standard of living in a given country. So, while it may be boring for some, it is a “necessary evil” for those bored by the effect of taxes to read up on all of the different outcomes caused by a change in the marginal tax rate, whether it be an inheritance tax, income tax, or something completely different.
Featured Image Source: Patriot Software
Disclaimer: The views published in this journal are those of the individual authors or speakers and do not necessarily reflect the position or policy of Berkeley Economic Review staff, the Undergraduate Economics Association, the UC Berkeley Economics Department and faculty, or the University of California, Berkeley in general.
Share this article:
Related Articles

Presidential Economics: A Series on Presidential Candidates’ Economic Proposals Part 3—Elizabeth Warren

The Pip in the Kiwi: An Analysis of the Automated Delivery Industry

Can you afford kids? The Rising Costs of Children
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
subscribe to our Monthly Newsletter!
- IELTS Scores
- Life Skills Test
- Find a Test Centre
- Alternatives to IELTS
- General Training
- Academic Word List
- Topic Vocabulary
- Collocation
- Phrasal Verbs
- Writing eBooks
- Reading eBook
- All eBooks & Courses
- Sample Essays
Paying Taxes Essay
This is an IELTS Paying Taxes Essay. In nearly all countries people have to pay some kind of taxes.
In this essay you have to decide whether you agree or disagree with the opinion that everyone should be able to keep their money rather than paying money to the government.
Here is the question:
Some people believe that they should be able to keep all the money they earn, and should not have to pay tax to the state.
To what extent do you agree or disagree?
Considering Both Sides
A good answer that looks at all the issues presented in the question would consider the following points:
- Why people may want to keep all the money they earn
- Why people should have to pay money to the state

Those are the two sides, so you should brainstorm some ideas around those two questions/opposing opinions before you start to write.
And of course it is very important to make sure you are very clear what your opinion is .
Now take a look at the paying taxes essay model answer.
You should spend about 40 minutes on this task.
Write about the following topic:
Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own experience or knowledge.
Write at least 250 words.
Model Answer
People work hard and earn money which ideally they would like to retain for themselves. However, a significant portion of this usually has to be given to the state. In my view, it is right that people pay their fair share of taxes.
Money is everything in today’s world. This is because money is used to buy all the necessities such as food, water, and shelter. Money is also used to help a family’s children in the form of school fees and other activities. In addition to this, people do not only need money to cater for their necessities, but also for future investments. The more that people have to invest, the more they believe they can accumulate in the long term. As a result, many are reluctant to lose some of their income through the deduction of tax.
Nevertheless, citizens should be obliged to pay taxes to the government for a number of reasons. They should accept that the taxes they pay help the government offer them the public services all over the country. These public services are things such as the construction of roads, bridges, public hospitals, parks and other public services. The same tax money helps the country’s economy to be stable. Through taxes, the government can also pay off its debts. In short, money received through taxes is a way of ensuring that people have comfortable livelihoods.
In conclusion, even though many people think that they should not pay taxes, that money is useful to the stability of any country. Therefore, people should not avoid paying taxes as it may affect the country’s economy and services that it provides.
(272 Words)
Task Response
- The question is fully addressed so the essay would get a good score for task response.
- The first body paragraph explains the reasons why people may not want to pay tax and the second body paragraph explains why it is important to pay.
- Reasons and examples are given to support the ideas.
- The writer’s opinion is also very clear. It is presented in the thesis statement and repeated in the conclusion. It is explained in body paragraph two.
Coherence and Cohesion
- The paying taxes essay is well organized. Each of the main points is explained in a separate paragraph and a logical argument is presented to support the writer’s opinion.
- Cohesion is also maintained by good uses of linking words to join the ideas and paragraphs.
Lexical Resource
There is some good use of vocabulary and collocations and spelling and word forms are correct.
For example:
- a significant portion of
- necessities
- reluctant to
- deduction of tax
- be obliged to pay
- construction of
- the stability of
Grammatical Range and Accuracy
There is good accuracy in the grammar and a good range of sentence structures. For example:
- People work hard and earn money which ideally they would like to….
- This is because money is used to buy all the necessities such as…
- people do not only need money to cater for their necessities, but also for future investments.
- In conclusion, even though many people think that they should not pay taxes…
<<< Back
Next >>>
More Agree / Disagree Essays:

Extinction of Animals Essay: Should we prevent this from happening?
In this extinction of animals essay for IELTS you have to decide whether you think humans should do what they can to prevent the extinction of animal species.

Human Cloning Essay: Should we be scared of cloning humans?
Human cloning essay - this is on the topic of cloning humans to use their body parts. You are asked if you agree with human cloning to use their body parts, and what reservations (concerns) you have.
IELTS Sample Essay: Is alternative medicine ineffective & dangerous?
IELTS sample essay about alternative and conventional medicine - this shows you how to present a well-balanced argument. When you are asked whether you agree (or disagree), you can look at both sides of the argument if you want.

Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay
Multinational Organisations and Culture Essay: Improve you score for IELTS Essay writing by studying model essays. This Essay is about the extent to which working for a multinational organisation help you to understand other cultures.

Scientific Research Essay: Who should be responsible for its funding?
Scientific research essay model answer for Task 2 of the test. For this essay, you need to discuss whether the funding and controlling of scientific research should be the responsibility of the government or private organizations.

Internet vs Newspaper Essay: Which will be the best source of news?
A recent topic to write about in the IELTS exam was an Internet vs Newspaper Essay. The question was: Although more and more people read news on the internet, newspapers will remain the most important source of news. To what extent do you agree or disagree?
IELTS Internet Essay: Is the internet damaging social interaction?
Internet Essay for IELTS on the topic of the Internet and social interaction. Included is a model answer. The IELTS test usually focuses on topical issues. You have to discuss if you think that the Internet is damaging social interaction.

IELTS Vegetarianism Essay: Should we all be vegetarian to be healthy?
Vegetarianism Essay for IELTS: In this vegetarianism essay, the candidate disagrees with the statement, and is thus arguing that everyone does not need to be a vegetarian.

Free University Education Essay: Should it be paid for or free?
Free university education Model IELTS essay. Learn how to write high-scoring IELTS essays. The issue of free university education is an essay topic that comes up in the IELTS test. This essay therefore provides you with some of the key arguments about this topic.

Return of Historical Objects and Artefacts Essay
This essay discusses the topic of returning historical objects and artefacts to their country of origin. It's an agree/disagree type IELTS question.

Sample IELTS Writing: Is spending on the Arts a waste of money?
Sample IELTS Writing: A common topic in IELTS is whether you think it is a good idea for government money to be spent on the arts. i.e. the visual arts, literary and the performing arts, or whether it should be spent elsewhere, usually on other public services.

Dying Languages Essay: Is a world with fewer languages a good thing?
Dying languages essays have appeared in IELTS on several occasions, an issue related to the spread of globalisation. Check out a sample question and model answer.
Technology Development Essay: Are earlier developments the best?
This technology development essay shows you a complex IELTS essay question that is easily misunderstood. There are tips on how to approach IELTS essay questions

Role of Schools Essay: How should schools help children develop?
This role of schools essay for IELTS is an agree disagree type essay where you have to discuss how schools should help children to develop.

Employing Older People Essay: Is the modern workplace suitable?
Employing Older People Essay. Examine model essays for IELTS Task 2 to improve your score. This essay tackles the issue of whether it it better for employers to hire younger staff rather than those who are older.

Examinations Essay: Formal Examinations or Continual Assessment?
Examinations Essay: This IELTS model essay deals with the issue of whether it is better to have formal examinations to assess student’s performance or continual assessment during term time such as course work and projects.

Essay for IELTS: Are some advertising methods unethical?
This is an agree / disagree type question. Your options are: 1. Agree 100% 2. Disagree 100% 3. Partly agree. In the answer below, the writer agrees 100% with the opinion. There is an analysis of the answer.

Ban Smoking in Public Places Essay: Should the government ban it?
Ban smoking in public places essay: The sample answer shows you how you can present the opposing argument first, that is not your opinion, and then present your opinion in the following paragraph.

Airline Tax Essay: Would taxing air travel reduce pollution?
Airline Tax Essay for IELTS. Practice an agree and disagree essay on the topic of taxing airlines to reduce low-cost air traffic. You are asked to decide if you agree or disagree with taxing airlines in order to reduce the problems caused.

Truthfulness in Relationships Essay: How important is it?
This truthfulness in relationships essay for IELTS is an agree / disagree type essay. You need to decide if it's the most important factor.
Any comments or questions about this page or about IELTS? Post them here. Your email will not be published or shared.
Before you go...
Check out the ielts buddy band 7+ ebooks & courses.

Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
Band 7+ eBooks
"I think these eBooks are FANTASTIC!!! I know that's not academic language, but it's the truth!"
Linda, from Italy, Scored Band 7.5

IELTS Modules:
Other resources:.
- All Lessons
- Band Score Calculator
- Writing Feedback
- Speaking Feedback
- Teacher Resources
- Free Downloads
- Recent Essay Exam Questions
- Books for IELTS Prep
- Useful Links

Recent Articles
Useful Language for IELTS Graphs
May 16, 24 04:44 AM
Taking a Gap Year
May 14, 24 03:00 PM
IELTS Essay: Loving Wildlife and Nature
May 10, 24 02:36 AM
Important pages
IELTS Writing IELTS Speaking IELTS Listening IELTS Reading All Lessons Vocabulary Academic Task 1 Academic Task 2 Practice Tests
Connect with us
Copyright © 2022- IELTSbuddy All Rights Reserved
IELTS is a registered trademark of University of Cambridge, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia.
Why do we pay taxes?
- Why do we pay federal taxes?
- Why do we pay state taxes?
- Why do we pay local taxes?
The bottom line
Why do we pay taxes federal income tax is the biggest source of government funding.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate tax products to write unbiased product reviews.
- The law obliges us to pay taxes, which in turn provide everything from health care and Social Security to education and defense.
- We pay taxes to the federal, state, and local governments, each of which uses the funds for different priorities.
- Taxes support the people and foster economic growth, giving government legitimacy.
- See Personal Finance Insider's picks for the best tax software.

Taxes, though not particularly popular, are key to fostering economic growth and development and to achieving the common goal of a prosperous and functional society.
While we usually think about them around the start of a new year when the federal income-tax season rolls around, we interact with them every day. In addition to our income, we are taxed on the purchases we make and the property we own. It all amounts to trillions of dollars a year in the US and pays for everything from Social Security and the military to trash removal and the upkeep of community greenspaces.
Total US federal spending for fiscal 2021 was about $10.1 trillion, according to data compiled by USAspending.gov . State government general fund spending, meanwhile, was $931.7 billion, according to a report from the National Association of State Budget Officers. All that money has to come from somewhere. That's why we pay taxes: to help fund governments at all levels.
The taxes collected by governments foster economic growth and development, paying for essential goods and services such as infrastructure, health care, and education in order to achieve the common goal of a prosperous, functional, and orderly society, says the World Bank, which provides development finance for collecting public revenue. Taxes are also a key ingredient in the social contract between citizens and the government. How they're collected and spent can determine a government's very legitimacy.
"At their most basic level, taxes address the 'free-rider' problem," says Poppy MacDonald, president at USAFacts , a not-for-profit and nonpartisan civic initiative that makes it easy to access and understand US government data. "If government didn't require citizens to pay for services, those services would be underfunded and, as a result, underprovided."
Each level of government uses the funds it raises in different ways, as each is responsible for different types of services. On the federal level, the government is tasked with large-scale programs, such as defending the country and providing social safety nets in the form of Social Security and Medicare. State spending is focused on things like education, transportation and public housing. Localities spend similarly to states, but tend to put more toward services including fire safety, sanitation, and parks and recreation.
Offers a high-quality user interface and access to experts and is especially valuable for self-employed filers who use QuickBooks integration.
$0 for Free Edition (~37% of filers qualify. Form 1040 and limited credits only), $69 for Deluxe, $129 for Premium
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Can be good for relatively complex tax situations that may require help navigating deductions and forms
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Offers step-by-step guidance
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Ability to upgrade for instant access to an expert
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Not all users will qualify for a $0 filing option
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Most expensive option for many tax situations
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. No brick-and-mortar locations to meet with a tax pro
TurboTax is among the most expensive options for filing taxes online, but offers a high-quality user interface and access to experts. It's especially valuable for self-employed filers who use QuickBooks integration.
- Tell TurboTax about your life and it will guide you step by step. Jumpstart your taxes with last year’s info.
- Snap a photo of your W-2 or 1099-NEC and TurboTax will put your info in the right places.
- CompleteCheck™ scans your return so you can be confident it’s 100% accurate.
- You won’t pay for TurboTax until it’s time to file and you’re fully satisfied.
- TurboTax is committed to getting you your maximum refund, guaranteed.
Why do we pay federal taxes?
The federal government's right to impose taxes is enshrined in the Constitution. Article 1, Section 8, Clause 1, states: "The Congress shall have the Power to lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defense and general Welfare of the United States." However, people are probably more familiar with the specific tax provision established by the 16th Amendment, which was ratified in 1913, and reads: "The Congress shall have the power to lay and collect taxes on income, from whatever source derived, without apportionment among the several States, and without regard to any census or enumeration."
The federal individual income tax is one of the taxes withheld from your paycheck, and is more than likely the biggest item deducted. It's also the federal government's largest single source of revenue.
If you make money — however you make it — it's more than likely that income will be taxed. The federal income tax is progressive, meaning those with larger incomes pay a greater share. Rates range from as little as 10% on the lower end of the scale to as much as 37% on some income at the high end.
The Federal Insurance Contributions Act, better known as FICA, is the law that established the payroll tax that is deducted from each paycheck. It is separate from the federal income tax and helps fund both Social Security and Medicare programs, which provide benefits for retirees, the disabled, and children.
There are more federal taxes as well. For example, corporate income tax is levied on business profits. The estate tax is a tax on your right to transfer property when you die. Excise taxes are imposed on various goods, services and activities and may be imposed on the manufacturer, retailer or consumer, depending on the specific tax. Cigarettes, alcoholic beverages, and gasoline are among those items that are subject to an excise tax. Excise taxes also make up a relatively small and volatile portion of state and local tax collections, according to the non-profit Tax Foundation.
"At tax time, we are hyper focused on our income tax rates and how much income tax we will pay," says Gena Jones, founder and CEO of Jones Tax Group. "These other taxes should also be part of the tax conversation because they can be substantial."
So where does it all go? For fiscal 2021, the largest portion of the US government spending, almost 20%, was in the income security category, which includes programs ranging from unemployment compensation and military retirement to the earned income tax credit and nutrition assistance. Medicare accounted for 13.7%, Social Security was 11.8%, national defense was 11.1%, and health was 10%. The 2021 figures were heavily skewed by massive spending to address the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Fiscal year 2021 federal spending by budget function
Source: USASpending.gov "We won't really appreciate some of the things our tax dollars pay for until our hair turns gray," says Jones. "Look at the bright side, some of the taxes you pay are put into your Social Security savings account, which you can begin to withdraw at retirement age."
Why do we pay state taxes?
As with the federal government, states need their residents to pay taxes in order to fund services. The way in which they do so differs from state to state, with some states choosing not to collect an income tax while others forgo sales tax. All states levy some form of property tax, with state-local tax burdens as of 2019 averaging 10.3% of national income. New Yorkers got hit the hardest at 14.1%, according to data compiled by the Tax Foundation.
Source: Tax Foundation * Does tax certain investment income. "Don't be fooled by states not imposing a certain type of tax. They are going to get the money necessary to operate," notes Jones. Where does the money from state taxes go? Spending on elementary and secondary education constitute the largest share of spending for states, accounting for almost 36% of costs in fiscal 2021, or about $483 billion, according to the National Association of State Budget Officers. Medicaid represented 27% of spending. Public university systems, community colleges, and other higher education institutions account for the third-biggest spending area, around 9%.
Other areas of state spending include transportation, corrections, and other public health programs.
Why do we pay local taxes?
Just like with state taxes, local taxes can vary. They can include taxes on property, sales, income, as well as miscellaneous items like water fees and parking meters. Local governments often get a significant portion of their revenue from sources such as grants from federal and state governments, and from charges for business-like entities that provide services like public utilities, hospitals, and public transit, MacDonald says.
Localities also collect revenue from licenses and sales taxes. Some also tax income or payrolls, such as New York City, which taxes some income at as much as 3.876%, the highest in the country, MacDonald says. Local taxes generally pay for services that people use daily, like K-12 public schools, transportation, police and fire services, and garbage removal.
We pay taxes to fund our federal, state and local governments so they can function properly and provide necessary services. Each particular government has its particular focus, with the big-picture spending on things like defense and Social Security placed in the hands of the federal government. States take on education and health, while local governments pay for things such as your garbage collection and child's school transportation.
- Main content
We sent you SMS, for complete subscription please reply.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Wonder of the Day #194
Why Do You Have To Pay Taxes?

SOCIAL STUDIES — Money
Have You Ever Wondered...
- Why do you have to pay taxes?
- What is the IRS?
- How is tax money used by the government?
- Government ,
- Internal Revenue Service ,
- Social Studies ,
- United States ,
- Legislator ,
- Executive ,
- Percentage ,
- Requirement ,
- Firefighter ,
Today’s Wonder of the Day was inspired by Ainsley from IL. Ainsley Wonders , “ Why do we have to pay taxes? ” Thanks for WONDERing with us, Ainsley!
Every year around April 15, you'll hear adults of all ages groan about “tax day." That's because federal and state income tax forms are due around that time. But have you ever wondered why you have to pay taxes?
In the United States, we have governments at the local, state and national ( federal ) levels. These governments have various parts to them, including legislators (who make laws), executives (who enforce laws), judges , and many others. The money these government workers receive to do their jobs comes from taxes.
Taxes take many forms, too. When you work at a job to make money , you pay income taxes. Depending on how much money you make, a certain percentage (part) of the money you make is withheld (kept out of your paycheck and sent to the government).
When you buy things at a store, you also usually pay sales tax, which is a percentage of the cost of the item charged by the store. If you own property , you also pay property taxes on the value of your property .
Paying your taxes is considered a civic duty , although doing so is also a requirement of the law. If you do not pay your taxes, the government agency that oversees taxes — the Internal Revenue Service or IRS — will require you to pay your taxes or else face penalties, such as fines or going to jail.
The money you pay in taxes goes to many places. In addition to paying the salaries of government workers, your tax dollars also help to support common resources, such as police and firefighters .
Tax money helps to ensure the roads you travel on are safe and well-maintained. Taxes fund public libraries and parks. Taxes are also used to fund many types of government programs that help the poor and less fortunate , as well as many schools!
Each year when “tax day" rolls around, adults of all ages must report their income to the IRS, using special tax forms. There are many, many laws that set forth complicated rules about how much tax is owed and what kinds of special expenses can be used (“written off") to lower the amount of taxes you need to pay.
For the average worker, tax money has been withheld from paychecks throughout the year . On “tax day," each worker reports his or her income and expenses to the IRS.
Employers also report to the IRS how much they paid each worker. The IRS compares all these numbers to make sure that each person pays the correct amount of taxes.
If you haven't had enough tax money withheld from your checks throughout the year to cover the amount of tax you owe, you will have to send more money (“pay in") to the government. If, however, too much tax money was withheld from your paychecks, you will receive a check (get a “ refund ") from the government.
Wonder What's Next?
Tomorrow’s Wonder of the Day features a Japanese icon of breathtaking, but brief, blossoming beauty!
Are you ready to pay up? Be sure to check out the following activities with a friend or family member:
- Although you won't have to worry about paying income taxes until you have a job, there is one tax you're probably already familiar with: sales tax. The next time you head to the store, bring a calculator with you. As you travel the aisles of the store, look at the prices of products. Use the calculator to figure out how much each product would be if you purchased it. For example, if you see a toy truck for $2 and your local tax rate is 6% (six cents for every one dollar), you would multiply $2.00 by 0.06 to get the amount of sales tax you'd pay, which is $0.12. Then you would add $0.12 and $2 to get the total cost of the truck, $2.12. It's important to remember sales tax when you start saving up for an important purchase you want to make. Always remember to calculate how much an item will cost — after tax — so you'll be sure you have enough money when it's time to head to the store!
- Talk with an adult friend or family member about their views on taxes. Do they think they pay too much in taxes? Why or why not? What kinds of things do they think their tax money should be used for? Are there things that governments spend money on that they don't think is worth it? Ask for examples, if so. What kinds of avenues exist for objecting to the way your tax money is spent?
- Ask an adult friend or family member to go with you on a walk or take you for a drive around your hometown. Bring along a piece of paper and a pencil. As you walk or drive around, look for examples of your tax dollars at work. Do you see roads being repaired? Is there a public library in your town? What about police and firefighters? Try to come up with a list of at least 10 examples of your tax dollars at work. You might be surprised at how far your tax dollars go to provide services shared by everyone in your community!
Wonder Sources
- http://life.familyeducation.com/taxation/money-and-kids/47969.html
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tax
Did you get it?
Wonder contributors.
We’d like to thank:
Jeniel , tejashree , diane , reyno and Erica from CT for contributing questions about today’s Wonder topic!
Keep WONDERing with us!
Wonder Words
The people who work for the government get paychecks, just like everyone who works! They also have to pay taxes.
supreet goyal
Great questions for a Wonder Journey--or a read through your textbook!
Great question, Tony. We think you'll find a ton of information at your local library or on the Internet. Enjoy your Wonder Journey!
You can cite Wondreopolis as the author and the date you accessed this Wonder. Thanks for checking!
?? Oh - verrrry clever, A! ?
Taxation IS theft. We pay over 50% of our income to the government in the form of taxes. It's oppressive.
Hi, Kj! Reading through this Wonder will provide you with some general information, but if you want a more detailed outline of the process, there are many tax services that can help!
I wish we never had to pay taxes but at the same time im happy we've had taxes so it's kinda in the middle for me...
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts with us, Alex!
We hope that reading through this Wonder will help answer your question, klk!
julia chungs
Thanks for sharing, julia!
Hi, B! April 15 is "tax day" - hope this helps!! ?
" During the middle decades of the fourteenth-century, the average tax-paying peasant would had to pay the equivalent of 32 grams of silver to the royal treasury. This would represent about 2% of the value of their farm, and if it was delivered as butter, it would be the equivalent of 16 kilograms."
Ref: http://www.medievalists.net/2015/07/how-much-taxes-did-a-medieval-peasant-pay-the-numbers-from-sweden/
Wow! That's some interesting research! Thanks for sharing!
Interesting! Did you already submit it to the Wonder Bank ?
Wenhua Chen
Well, no one likes paying taxes. But if you pay too little, the IRS can ask for more or do what's called an audit. Not fun. Thanks for WONDERing!
trident studios
No, but we CAN give you a new Wonder every day! ?
can u do more wonders about kyrie irving
Here's one: Who Has the Best Handles in the NBA? Answer: Steph Curry. ??
because the gover ment needs to pay police and firefighters and stuff
Well lynnea, most of us don't enjoy paying taxes but the article does explain why it benefits our society to pay them. Thanks for WONDERing with us!
Kaitlyn Galaydick
We're glad you stopped by Wonderopolis and asked, Kaitlyn! The author of this Wonder is Wonderopolis. :)
We just realized we missed this comment, chheee! We're sorry! Wonderopolis was created and is managed by the National Center for Families Learning, which is headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky. :)
i need help for a essay in school give me some reasons why take off taxes
Hi there, josh! We're glad you are WONDERing. We think it would be better if you researched your question rather than us just telling you. We encourage you to keep searching online or at your local library to find the information you need. :)
U have to pay a lot of money
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Peppapig21! We're glad you are WONDERing with us! :)
Howdy, Tyson! We hope that smile means you are really enjoying WONDERing with us! :D
Hi, tyler! We hope this Wonder was helpful and informational! Always keep WONDERing! :)
The Grace Commission found that 0% of the income tax collected in the USA is spend on government services. ( & no, not 10%, 0)
Thank you for sharing, Serge! This article on CNN.com breaks down how income tax is spent. Interesting read!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts about taxes, Jackson! We're glad you're WONDERing! :)
I agree with your comment. I don't believe that everything in this article is facts. Maybe for some tax dollars benefit, but for others, there is no true benefit in paying taxes. The roads are still bad and filled with potholes, the libraries are old and filled with old outdated materials, you have schools that can't even ensure that every student will get a book, and the very people that we pay to protect and serve are killing "tax paying" citizens. How can you take money from someone who barely makes minimum wage to pay people who make twice if not more than them? There's no logic in that.
Thanks for sharing and joining the discussion, Kali!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts and opinions about taxes, Kayarrdee. We're glad you stopped by! :)
But what can we do about it? It comes out of our paychecks, when we buy stuff, etc. Then when the irs gets involved and the court of law. What can we really do?
Thanks for joining the discussion, Aryka! We appreciate you sharing your thoughts about taxes! :)
Loved this answer. Whether or not you know it but you don't even have to be in debt. Our government is so far into a debt spiral that they could triple our taxes and never pay it all back to the Federal Reserve! Matter of fact the could pay them back a dollar a second and it would take 440,000 years to pay it back. They are enslaving our future generations. And guess who pays this debt? It is made on the back of American people. Hence why every dollar bill is actually a promisary note to the Federal Reserve.
Thanks for joining the discussion, Kayarrdee! We appreciate you sharing your beliefs, too. This Wonder represents the common belief of the government behind taxes. If you want to learn more, we encourage you to check out the Wonder Sources where we found the information for this Wonder. :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Branson! We're glad you're WONDERing! :)
Thank YOU for WONDERing with us, Desiree! We're glad you stopped by! :)
We're sorry you didn't like this Wonder. Luckily, there are many more Wonders you can explore on the site! Just click on Explore Wonders at the top of the page! :)
Hi, Wonder Friend! We're glad you liked this Wonder and learning something new! :)
All these can be and have been funded privately, rather than by compulsory taxes (taxation is actually theft)
Thank you for saying this!
Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis, Kayarrdee! Always keep WONDERing! :)
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts, Branson! Thanks for joining the conversation about taxes! :)
Hi, Jett! Thanks for sharing the additional information! You're right that taxes help pay for things in the community! :)
sauske uchiha
Hi, sauske! Thanks for sharing your thoughts and opinion about taxes. We appreciate your comment! :)
Great question, Cameron! We encourage you to keep WONDERing and researching about the history of taxes at your library and online! :)
why are yall not giving answers and just saying great question keep wondering and just leaving us hanging
Hi, alex! Thanks for asking! We like to encourage our Wonder Friends to embark on their own Wonder Journey to keep WONDERing and learning! Sometimes the Wonder of the Day is just the beginning! :)
We're glad you stopped by Wonderopolis to learn more for your project! We're sure you did GREAT! :)
WONDERSheep
Spread the word! The Federal Reserve is enslaving humanity!
We appreciate you sharing your opinion, Kayarrdee. Everyone believes different things and that's okay! :)
Exactly! Taxation is theft!
We appreciate hearing from our Wonder Friends, Branson! Visit again soon! :)
That is a very good point that you make. Maybe the government reads Wonderopolis? Hehe.
Hi, Mc6344! We appreciate you exploring the comments for this Wonder! :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Wonder Friend! Taxes are a heavily debated topic! We're glad you stopped by Wonderopolis! :)
Hi, Wonder Friend! You can use the search box at the top to look for Wonders about all kinds of topics! Always keep WONDERing! :)
Hi, Wonder Friend! Thanks for stopping by Wonderopolis! We're THRILLED you're WONDERing with us! :)
WONDERful, ajmeena! We're glad this Wonder was helpful! Thanks for stopping by! :)
What is the main idea of the passage
Hi, Kaden! It often helps to re-read text so that you understand the information better. Thank you for stopping by Wonderopolis! :)
Hi, andy! You're right, people often have disagreements over taxes. Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
Hi, Wonder Friend! That's right. We encourage you to talk with an accountant for more information. Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
hansy boo boo
Hello there, hansy boo boo! It's true, taxes aren't the most enjoyable way to spend money. If you were in charge, how would you do the tax system differently? If you didn't have taxes, what ways would you produce money to pay for things we all need, like trash removal and clean water? Have fun WONDERing about what you'd do differently! :)
Taxes should be voluntary! Less government less taxes!
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Wonder Friend! We hope you had fun exploring this Wonder! :)
Hey, hannah! It's great that you're WONDERing with us! We hope you are having a nice week! :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion, bradydog22! We appreciate you, Wonder Friend! :)
Wonderopolis
Hi, pooja! Some of the tax money is used to pay for road repairs and upkeep. However, it is hard to keep up with all the roads and city budgets are sometimes another issue to consider. Check out this related WONDER - Wonder #1147: What Is a Pothole? . Have a WONDERful day! :)
Hi monster! Policemen and Firemen are jobs and they need to be paid for their services to the community. They must also pay taxes to the government. Thanks for WONDERing with us and sharing your thoughts! :)
Hi Lucas! There were times in our country's history that the United States rebelled against taxes, such as the Boston Tea Party. Check out Wonder #619: Who Came to the Boston Tea Party? However, as this WONDER about taxes tells us, our taxes help pay for many things we are privileged to have in the United States, such as public education. You can find more information about our country's tax system at the U.S. Department of Treasury website. Always keep WONDERing! :)
Michael Redline
Thank you for sharing your opinion, Michael! By doing a little extra WONDERing, we found that there are different tax brackets so that people who make more money pay a higher tax percentage than those who make less. You can check it out here: http://www.taxact.com/tools/tax-bracket-calculator.asp Thanks for WONDERing with us, Wonder Friend! :)
SuperSmash22
That's a great question, SuperSmash22! Each time an employee gets paid, his or her employer electronically sends a portion of that money to a special accounting office located at their local, state and federal governments. Employers use banks to send money, just like individual people do. :)
Thanks for WONDERing with us, Iver! It's true, we do have to pay taxes - whether at the store, when we purchase things, or at work, when we get paid. It may not be our favorite thing to spend money on, but our dollars go towards helping pay for things we use everyday, like streets, public school, police and water. Paying taxes is pretty important, don't you think? Have a WONDERful day, Iver! :) :)
We are undergoing some spring clearing site maintenance and need to temporarily disable the commenting feature. Thanks for your patience.
Related Wonders for You to Explore

Who Was Lou Castro?

Who Was Dalip Singh Saund?

Who Was the Surfer of the Century?

Who Was Grace Lee Boggs?

How Did the British Save Children From the Nazis?
Drag a word to its definition
Select a Wonder Word:
Match its definition:
Congratulations!
You’ve matched all of the definitions correctly.

Share results
Question 1 of 3
If too much money was withheld from your paychecks throughout the year, what will you receive from the government after you file your taxes?
- a refund Correct!
- b bonus Not Quite!
- c bill Not Quite!
- d summons Not Quite!
Question 2 of 3
What does IRS stand for?
- a Internet Refund Subsidy Not Quite!
- b Illegal Ransom Service Not Quite!
- c Illinois Regulatory System Not Quite!
- d Internal Revenue Service Correct!
Question 3 of 3
When you pay tax on an item you purchase at a store, what type of tax are you paying?
- a property Not Quite!
- b income Not Quite!
- c sales Correct!
- d mercantile Not Quite!
Quiz Results
Share Results
Spread the joy of wonder, get your wonder daily.
Subscribe to Wonderopolis and receive the Wonder of the Day® via email or SMS
Join the Buzz
Don’t miss our special deals, gifts and promotions. Be the first to know!
Share with the World
Tell everybody about Wonderopolis and its wonders.
Share Wonderopolis
Wonderopolis widget.
Interested in sharing Wonderopolis® every day? Want to add a little wonder to your website? Help spread the wonder of families learning together.
You Got It!

http://wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-do-you-have-to-pay-taxes
© National Center for Families Learning (NCFL)
All about Finance » Tax » Why is it important to pay taxes?
Why is it important to pay taxes?

The Federal Income Tax is the largest source of revenue and funding for the U.S. government. It is key to a prosperous and functional society’s economic momentum and common development. But W hy is it important to pay taxes? Easily, so there is a good relationship between citizens and the economy.
Paying taxes allows the country to advance essential services such as health care, infrastructure, and education . How taxes are collected and invested or spent determines the legitimacy of a government.
At larger scales, the federal tax shifts larger tasks to the government, such as providing social safety nets through Social Security and Medicare and defending the country.
Reasons why we should pay taxes
Some consider taxes a large burden that takes up most of their salary. The question of whether it is really important to pay taxes arises when it is unknown where the money that’s collected ends up.
There are several reasons why it is necessary to assume the responsibility of paying taxes. They fall on the common good of the citizens and the country or region where they reside and are divided into two areas.
1. In a society
The government plans social projects, but the development force depends on the citizens. Without taxes, responding to people’s demands is impossible, especially regarding the most necessary public services.
- Education : Undoubtedly, education is one of the areas that most requires attention , and this is achieved with the payment of taxes. It is fundamental to the development of the country and human capital. Public schools are financed, equipped, and cared for thanks to tax money.
- Health : tax collection also helps the health sector . It especially finances health services such as medical research, social security, and social health care.
- Governance : governance is directly linked to the functioning of the country . The government manages the money collected through taxes and uses it profitably for all citizens. The money is also used to pay the police, public services, parliamentarians, postal system, among others.
- Other sectors : environmental protection, security, and scientific research are part of the different sectors necessary for the welfare of citizens. It is important to pay taxes because they allow you to finance projects such as unemployment benefits and pensions. Remember that taxes help stimulate a nation’s economic growth.
2. In business
The prosperity of businesses is linked to roads in excellent condition, good electricity and telephone service, and a good infrastructure. The government develops this infrastructure by collecting taxes while at the same time promoting economic activity.
The government can return the money paid by businesses through taxes to the economy in the form of loans or financing.
As already mentioned, taxes help improve the country’s quality of life. In that sense, consumption will be high as long as the standard of living rises. This favors companies as they will have more internal consumption.
What taxes are important to pay?
All taxes are necessary ; each one guarantees good services and the nation’s economic growth. To understand what taxes exist and why it is important to pay taxes, you need to know about each one.
The U.S. tax system is complex ; understanding the basics of the types of taxes can be valuable for financial planning. Especially for the first month of each year.
1. Income Tax
Income tax can be levied at the federal, state, and local levels . Payments at the national level will depend on several factors, including income and marital status. At the state level, they vary considerably.
Florida does not charge income tax. Some states use a flat income tax rate. While in others, different tax rates apply, depending on income.
2. Sales Taxes
These are taxes on goods and services purchased . They are generally calculated as a percentage of the price already paid. This type of tax varies according to the state or municipality of residence.
Some states do not charge sales taxes at the state or local level. Other states charge substantial amounts. Sales taxes, in some cases, are regressive; low-income households pay a large number of their earnings to cover taxes as opposed to higher-income individuals.
3. Excise taxes
Excise taxes are similar to sales taxes, the difference being that they are levied on specific goods. They are charged for sinful products such as beer, cigarettes, and gasoline.
These taxes are not only intended to raise money but also to discourage certain unhealthy behaviors. Sometimes excise taxes are combined with sales taxes on the same purchase.
4. Payroll taxes
This is made up of two taxes that employees and employers must pay. The Social Security tax is 6.2% of the employee’s salary; the employer matches the amount for 12.4%. The Medicare tax is 2.9%, which equals 1.45% for the employee and the employer to fund the program.
5. Property Taxes
Property taxes are based on the market value of the property . In most cases, it applies to real estate, although it may apply to other property, including a vehicle.
These taxes are generally deductible, but in cases where it is for the public welfare, not for improvements that increase the property’s value. Some people qualify for a mortgage interest deduction.
6. Estate Taxes
The IRS considers the estate tax a tax on the right to transfer property at death. Among the items considered estates are cash, insurance, real estate, securities, and business interests.
The federal government only taxes estates above $5.30 million, so most individuals are exempt from paying federal estate tax. A tax rate is charged, and the highest rate at the national level is 40%.
7. Gift Tax
It is similar to the inheritance tax since it is levied on the transferred wealth. It differs because it involves two living persons. Gifts of more than 14 thousand dollars must pay tax produced by the beneficiary.
It applies not only to cash but also to company shares and vehicles . The highest gift tax rate is 40% on the taxable amount of the gift or donation.
It is essential to know that not all taxes are paid simultaneously. Some taxes are deducted from the paycheck. Three types of taxes are reflected on an employee’s pay stub and are the most widespread: general income taxes, payroll taxes, and state income taxes.
It is important to pay taxes, whether federal, state, or local, to enjoy good public services and quality of life. To see a country’s economic growth, collecting taxes is essential.

For years I have studied American finance regulations. All the information in this blog is sourced from official or contrasted sources from reliable sites.
Salesforce Certified SALES & SERVICE Cloud Consultant in February 2020, Salesforce Certified Administrator (ADM-201), and Master degree in “Business Analytics & Big Data Strategy” with more than 13 years of experience in IT consulting.
- Investor Profile • Why it is so important to know your profile?
- Profit and loss statements why they are so important
- How to pay taxes according to UW Madison?
- 3 important truths about working for a hedge fund
- Are financial industry bloggers important?
- FedEx Hubs • How do they work and which are the most important ones in the USA?
- Employers Incur Operating Costs For Which Payroll Taxes
- When is the deadline to file taxes?
The Importance of Tax in Our Life Essay (Critical Writing)
Introduction, importance of tax.
Bibliography
Tax is one of the ways for authorities in the public sector to raise revenue to run their projects. Public administrations are charged with the development of sufficient revenue to finance programs that benefit the society; hence, they have to either raise the money through investments or apply levies on various commodities to generate the funds. The government can also introduce taxes with the aim of aligning the behavior of various entities with a given policy.
For instance, carbon taxes are used to compel different entities to reduce the impact of their business processes on the environment 1 . In the case under analysis, authorities in Cook County, Chicago, introduced a controversial tax on sweetened beverages in the soft drink field. Taxes are meant to generate revenue or to regulate the behavior of different entities; hence, the actual purpose of a new tax should be communicated to the public.
Lawmakers in the county responded to the pressure from citizens and various lobbying groups that had reviewed the nature and effects of the proposed tax. It is apparent that the tax was meant to reduce the consumption of sweetened soft drinks with the hope that consumers would be discouraged by the increased prices of the products 2 . However, the tax was not effective in attaining the intended health promotion objective because consumers could easily drive to the nearby towns outside the county and shop for the drinks.
A critical view of the tax reveals that its intention was not to boost health outcomes for the citizens of Cook County, but to help the administration in raising about $1.8 billion annually to increase its budget 3 . The government has been facing challenges in raising the required funds for the budget, and it is apparent that the only option it has is the development of new taxes that help in raising the deficit. Economic principles reveal that whenever an administration is facing deficits in its annual budget, there are some options that it may pursue to raise the required money 4 .
Taxes directly involve citizens in contributing to public programs run by the government 5 . However, the government is always limited by various policies when it comes to the introduction of taxes 6 . The policies are meant to ensure that the administration does not introduce laws that exploit the public in an unfair manner. For instance, in Cook County, the local government observes laws that dictate against the development of additional sales taxes on commodities 7 . The associated lawmakers had to introduce the tax at the point of sale, which was quite a bad choice because it would exempt all consumers using food stamps as stipulated by the law.
This case reveals that while taxes are necessary for boosting the capabilities of the government in meeting its obligations and plans, they have to be introduced in a manner that shows legitimacy and appropriate reasoning on the part of the proponents 8 . The tax on sweetened fizzy drinks was banned because its legitimacy was questionable. First, the administration did not have a solid reason for introducing the tax. Secondly, the intentions of the tax were concealed through the claim that the tax was meant to enhance health outcomes for the citizens of Cook County.
The Cook County administration demonstrated that it is always necessary for the authorities to look into introducing legitimate taxes. By introducing the tax, the government intended to raise more money to boost its budget, rather than promote health outcomes as the leaders claimed. Taxes are normally applied to finance government projects by raising revenue or regulating certain behaviors on the part of various entities.
Auerbach, Alan, Raj Chetty, Martin Feldstein, and Emmanuel Saez, eds. Handbook of Public Economics . Vol. 5. Boston: Newnes, 2013.
“ Chicago’s Soda Tax Is Repealed. ” The Economist , 2017. Web.
Lawton, Amy. “Green Taxation Theory in Practice: The 2012 Reform of the Carbon Reduction Commitment.” Environmental Law Review 18, no. 2 (2016): 126-141.
Lu, Xiaobo, and Kenneth Scheve. “Self-Centered Inequity Aversion and the Mass Politics of Taxation.” Comparative Political Studies 49, no. 14 (2016): 1965-1997.
Rood, Deborah K. “The Importance of Tax Quality Control.” Journal of Accountancy 219, no. 4 (2015): 24.
Saad, Natrah. “Tax Knowledge, Tax Complexity and Tax Compliance: Taxpayers’ View.” Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 109, no.1 (2014):1069-1075.
- Amy Lawton, “Green Taxation Theory in Practice: The 2012 Reform of the Carbon Reduction Commitment,” Environmental Law Review 18, no. 2 (2016): 126-141.
- “Chicago’s Soda Tax Is Repealed,” The Economist , 2017. Web.
- “Chicago’s Soda Tax Is Repealed.”
- Natrah Saad, “Tax Knowledge, Tax Complexity and Tax Compliance: Taxpayers’ View,” Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 109, no.1 (2014):1069-1075.
- Alan J. Auerbach et al., eds., Handbook of Public Economics , Vol. 5 (Boston: Newnes, 2013), 4.
- Deborah K. Rood, “The Importance of Tax Quality Control,” Journal of Accountancy 219, no. 4 (2015): 24.
- Xiaobo Lu and Kenneth Scheve, “Self-Centered Inequity Aversion and the Mass Politics of Taxation,” Comparative Political Studies 49, no. 14 (2016): 1965-1997.
- Feminist Perspective Influence on Canadian Laws and Lawmakers
- Childhood Obesity Scientific Studies
- Obesity and Its Challenges Analysis
- Fraud Examiners and the Panama Papers
- "Amazon Laws" and Taxation of Internet Sales
- Personal Income Tax: Arguments For and Against
- Canada Revenue Agency, Its Benefits and Limitations
- Section 179 of the International Revenue Code
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, October 31). The Importance of Tax in Our Life. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-tax-in-our-life/
"The Importance of Tax in Our Life." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-tax-in-our-life/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The Importance of Tax in Our Life'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The Importance of Tax in Our Life." October 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-tax-in-our-life/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Importance of Tax in Our Life." October 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-tax-in-our-life/.
IvyPanda . "The Importance of Tax in Our Life." October 31, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-importance-of-tax-in-our-life/.

Theme 1: Your Role as a Taxpayer Lesson 1: Why Pay Taxes?
Educational Standards
State and National Standards
One to four hours
Curriculum Area(s)
- Civics/Government
- History/Social Studies
To help students understand the basic rationale, nature, and consequences of taxes
Students will be able to
- describe why governments need revenue to provide goods and services.
- identify taxes as an important source of governmental revenue.
- explain how taxes transfer the use of resources from the private sector to the government.
Taxes provide revenue for federal, local, and state governments to fund essential services--defense, highways, police, a justice system--that benefit all citizens, who could not provide such services very effectively for themselves. Taxes also fund programs and services that benefit only certain citizens, such as health, welfare, and social services; job training; schools; and parks.
Article 1 of the United States Constitution grants the U.S. government the power to establish and collect taxes. Congress delegated to the IRS the responsibility of administering and enforcing the Internal Revenue Code.
Taxes reduce taxpayers' income. As a result, taxpayers have less for personal goods and services, savings, and investments. The more services the government provides, the more taxpayers have to pay for them. Whenever new public goods and services are proposed that require new taxes, taxpayers must decide whether the additional benefits are worth the reduction in income.
public goods and services
Benefits that cannot be withheld from those who don't pay for them, and benefits that may be "consumed" by one person without reducing the amount of the product available for others. Examples include national defense, streetlights, and roads and highways. Public services include welfare programs, law enforcement, and monitoring and regulating trade and the economy.
Required payments of money to governments that are used to provide public goods and services for the benefit of the community as a whole.
Opening the Lesson
Ask students whether they know how the government pays for the goods it purchases and the services it provides. Show the Slide Show : Theme 1 Overview: Your Role as a Taxpayer . Then present the information from the background section above.
Developing the Lesson
On the board, list public programs and services such as:
- national defense
- police and fire protection
- public schools
- bank regulation
- job training
- air traffic controllers
- subsidized school lunches
- drug rehabilitation programs
- scientific research
Explain that each is funded by taxes. Ask students:
- Would you rather pay for each of these items with tax dollars or as each service is used? Students should be allowed to voice their opinions freely and differ on the value of specific programs. Try to build a consensus that items on the list are: public goods that benefit and are used by all in such a way that no one uses them up (highways, education, job training, libraries, defense); a public responsibility (nutrition, unemployment benefits, health care); and/or an investment in future productivity and human resources (job training, drug programs, research).
Online Activity
Direct students to Student Lesson: Why Pay Taxes?
Have students complete one or more of the following activities:
Activity 1: Your Federal Government -Check out the vast scope of the federal government.
Activity 2: Public Goods and Services -Get a bird's eye view of a typical community to see how many government services can be found.
Activity 3: Citizen's Guide to the Federal Budget -Learn how the federal government gets and spends its money.
Print Activity
Print and distribute Worksheet: Government Spending .
Worksheet Solutions: Government Spending .
Classroom Activity
Have students meet in small groups to compile a list of activities in which they or their family members have engaged within the last 48 hours. Then have students evaluate the activities to see what public goods or services they used for each activity. Using Info Sheet 1: Taxes Shift Resources , have students identify what resources were shifted from the private sector to the government to provide the public goods and services on their list. For example, students could explain that resources used to produce public education include the building, land, teachers, books, desks, electricity, and students. Have each group share its findings with the class.
To extend the lesson, use Info Sheet 2: Federal Revenues and Spending to show students how their tax dollars are spent. Ask what might happen if the only tax-supported program was national defense. Students should realize that individuals would have more money to spend each year, but none of the services typically provided by the government would be freely available. Ask students what they think might happen in the short term and in the long term. (Most students will probably predict that society in general would suffer.)
Concluding the Lesson
Ask students to think about why people pay taxes. Help students realize that certain functions are better performed collectively than individually.
Online Assessment
Direct students to complete Assessment: Why Pay Taxes? for this lesson.
Assessment Solutions: Why Pay Taxes?
Print Assessment
Print Assessment: Why Pay Taxes? and have students complete it on paper.
tell us what you think!
- Environmental Science
The Importance of Paying Taxes
15 Nov 2022
Format: APA
Academic level: College
Paper type: Essay (Any Type)
Downloads: 0
Electricity is the most used source of energy and with the rapid population and advancement in technology, there is a necessity of producing more electrical energy. Averagely, about $ 300 billion goes to conventional power sources each year. Out of the $300 billion, only thirty percent of it goes to renewable energy each year. This means that every year, 90 billion is spent on renewable energy (Buxbaum, 2014). Two reasons can explain the variance in the amount spent on renewable energy. Firstly, eighty percent of the investment decline came because of the decreasing cost of renewable energy technology, chief among them being solar panels. For instance, the cost of a rooftop solar system that is considered a good national trend barometer is reported to have fallen by almost a third. The other twenty percent was a result of a reduction in actual construction activity. This was influenced by subsidies from the government as well as general sluggishness in economics. With PTC, the cost of energy is significantly reduced. For this reason, businesspersons controlling other non-renewable energy, are using the media to convince people to stop using PTC because they are seeing it as a threat to their business. The majority of the citizens are gradually diverting to PTC products. The PTC is so important to the economy, and thus it must be saved. These tax credits are reported to have benefited many people by playing a significant role in the growth of the America economy, enhancing energy security, and job creation, and providing support to the new manufacturing process in the US among other benefits. Besides, PTC has to increase the production of wind energy which is clean and affordable (Roach, 2015). For proper regulation of energy, it is crucial to have an energy policy. This policy is essential since energy is a basic requirement for most social and economic activities in industrialized nations. The cost of energy has to be regulated because it affects production in industries as well as the living conditions of the citizens.
References
Buxbaum, R. (2014). Driving Renewable Energy Growth Through Effective Public Policy: A Financial and Policy Analysis of Cash Grants, Tax Credits and Pass-Through Tax Structures (MLPs and YieldCos).
Delegate your assignment to our experts and they will do the rest.
Roach, T. (2015). The effect of the production tax credit on wind energy production in deregulated electricity markets. Economics Letters , 127 , 86-88.
- Saudi Arabia to Invest in Nuclear Energy
- Lenticular and Cumulus Clouds
Select style:
StudyBounty. (2023, September 15). The Importance of Paying Taxes . https://studybounty.com/the-importance-of-paying-taxes-essay
Hire an expert to write you a 100% unique paper aligned to your needs.
Related essays
We post free essay examples for college on a regular basis. Stay in the know!
HACCP: A Systematic Approach to Food Safety
Sampling: the selection of a particular sample or group to represent an entire population, gis uses in national wildlife refuge management, factors that least affect the global environment.
Words: 1188
Restoration of the Chesapeake Bay
Hazard analysis techniques for system safety, running out of time .
Entrust your assignment to proficient writers and receive TOP-quality paper before the deadline is over.
Introduction: Why Ethics Matter in Taxation
- First Online: 03 November 2019
Cite this chapter

- Robert F. van Brederode 2
1179 Accesses
This chapter is the introduction to the book and provides an overview of the content of each chapter within the framework of a general, but necessarily short, theoretical treatise on the interaction of morality and taxation, touching topics such as the philosophical justification of taxes, the obligation to pay and the morality of tax avoidance and planning, voluntary compliance, and tax law enforcement and its ethical challenges. It provides context to the individual chapters, places footnotes by positions taken and shows alternative perspectives.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Justice, Equality and Taxation

Ethics of Tax Interpretation

Ethics and Public Policy
This idea goes back to the 19th century German lawyer and philosopher Lorenz von Stein, see Vogel ( 1988 ).
The OECD Average is a weighted average by GDP for all countries excluding the United States.
The story is apocryphal, however. The coined phrase appeared for the first time in the Redland’s Daily Facts on March 15, 1952. Sutton denied in his autobiography ( 1976 , 160) that he ever said it and credits an enterprising journalist.
This is, however, not an argument against progressive taxation per se, but a demonstration of the practical difficulty with implementing such a tax fairly.
That explains why in practice there exists no uniform rate of graduation. The progressive income taxes applied around the world are levied at different rates and use varying income brackets to which these are applied. For example, the U.S. has 7 tax rates for federal personal income tax: 10, 12, 22, 24, 32, 35, and 37% for income over $500,000. In comparison, the Netherlands applies 4 brackets on earned income with the top rate of 51.75% kicking in at income over €68,508; Germany has 3 rates with the top rate of 45% applying to income over €256,304; Australia has 4 rates of 19, 32.5, 37%, and a top rate of 45% which applies to income over AU$180,001.
Tax law could also violate constitutional norms. For the U.S., Vance ( 2013 ) argues that Congress has made the tax code so complex that it violates the due process requirement of the Fifth Amendment that a person of ordinary intelligence must be able to understand how to conform their behavior to the requirements of the law.
See, e.g., Alm et al. ( 1992 ), Alm, and Torgler ( 2006 ), Cummings et al. ( 2005 ), Picur and Riahi-Belkaoui ( 2006 ), Slemrod ( 1992 ), Torgler and Schneider ( 2007 ), Fjeldstad et al. ( 2012 ).
The terminology used to describe unfavorable human actions in the area of reducing tax payments are not neutral but value-based (Sage-Fuller and Lippe 2014 ). The adjective ‘aggressive’ in aggressive tax planning, or the word ‘abuse’ in abuse of law, or ‘harmful’ in harmful tax planning are purposefully used to convey moral condemnation of the action with the intent to steer public opinion towards moral rejection as well. And with notable success as press coverage is also mostly negative towards tax avoidance and arguments defending the practice are generally ignored. The public perception is of course relevant as it determines both the latitude given to companies and individuals in the area of tax planning and the extent and methods available to the state in combatting tax avoidance.
Determining such standards is no sinecure if we take to mind Judith Freedman’s caution (drawing on the work of Onora O’Neill) that increased transparency can actually lower tax morale and the willingness of taxpayers to pay their taxes voluntarily (Freedman 2018 , 130).
IRC v. Duke of Westminster [1936] AC 1 (H.L.) (Eng.).
Ayrshire Pullman Motor Servs. and DM Ritchie v. C.I.R ., [19291 14 T.C. 754, 763/64 (H.L.) (Eng.).
Such sentiments are often attributed to Adam Smith’s canons of taxation. It is however instructive to quote the full sentence on which this view is based: ‘Every tax ought to be so contrived as both to take out and keep out of the pockets of the people as little as possible, over and above what it brings into the public treasury of the state .’ ( The Wealth of Nations Book 5, Chap. 2 [emphasis added]).
Commissioner v. Newman , 159 F.2d 848, 850-51 (C.C.A. 2, 1947).
Compania General De Tabacos De Filipinas v. Collector of Internal Revenue , 275 U.S. 87, 100, dissenting (21 November 1927). This quote is engraved above the entrance to the IRS headquarters at 1111 Constitution Avenue, Washington, DC.
IRC v WT Ramsay Ltd . [1982] AC 300. See Freedman ( 2007 ).
IRC v. Burmah Oil Co. Ltd . (1981) 54 TC 200 (HL).
Supra at 219.
See, e.g., Furniss v. Dawson (1984) 55 TC 324; IRC v. McGuckian [1997] 1 WLR 991; MacNiven v Westmoreland Investments Ltd . [2001] STC 237; Barclays Mercantile Business Finance Ltd . v Mawson [2005] STC 1.
See, Brederode and Krever ( 2017 ).
Alm, James, Gary H. McClelland, and William D. Schulze. 1992. Why do People Pay Taxes? Journal of Public Economics 48 (1): 21–38.
Article Google Scholar
Alm, James, and Benno Torgler. 2006. Culture Differences and Tax Morale in the United States and in Europe. Journal of Economic Psychology 27 (2): 224–246.
Alm, James, and Benno Torgler. 2011. Do Ethics Matter? Tax Compliance and Morality. Journal of Business Ethics 101 (4): 635–651.
Awanis, Sandra, et al. 2017. Asia’s Materialists: Reconciling Collectivism and Materialism. Journal of International Business Studies 48: 964–991.
Bonaham, O. Michael. 1953. Moral and Ethical Considerations in Tax Practice. Marquette Law Review 37 (1): 85.
Google Scholar
Cummings, Ronald G., Jorge Martinez-Vazquez, Michael McKee, and Benno Torgler. 2005. Effects of Tax Morale on Tax Compliance: Experimental and Survey Evidence . CREMA Working Paper no 2005–29. Basel: Centre for Research in Economics, Management and the Arts.
Dworkin, Ronald. 1973. The Original Position. University of Chicago Law Review 40 (4): 500–533.
Filipczyk, Hanna. 2015. Why is Tax Avoidance (Im)Moral? Ethics, Metaethics and Taxes. Toruński Rocznik Podatkowy : 28–48.
Fjeldstad, Odd-Helge, et al. 2012. People’s Views of Taxation in Africa: A Review of Research on Determinants of Tax Compliance . Brighton, UK: ICTD.
Freedman, Judith. 2004. Defining Taxpayer Responsibility: In Support of a General Anti-Avoidance Principle. British Tax Review 4: 331–356.
Freedman, Judith. 2007. Interpreting Tax Statutes: Tax Avoidance and the Intention of Parliament. The Law Quarterly Review 123: 52–90.
Freedman, Judith. 2010. Improving (Not Perfecting) Tax Legislation: Rules and Principles Revisited. British Tax Review 6: 717.
Freedman, Judith. 2018. Restoring Trust in the ‘Fairness’ of Corporate Taxation: Increased Transparency and the Need for Institutional Reform. In Tax and Trust: Institutions, Interactions and Instruments , ed. Goslinga, Sjoerd et al., 121–141. The Netherlands: Eleven International Publishing.
Gribnau, Hans. 2014. Not Argued from but Prayed to: Who’s Afraid of Legal Principles. eJournal of Tax Research 12(1): 185.
Hamill, Susan Pace. 2006. An Evaluation of Federal Tax Policy Based on Judeo-Christian Ethics. Virginia Law Review 25 (3): 671–764.
Hart, H.L.A. 1955. Are There Any Natural Rights? Philosophical Review 64 (2): 175–191.
Johnson, Steve R. 2013. Reforming Federal Tax Litigation: An Agenda. Florida State Law Review 41: 205–273.
McGee, Robert W. (ed.). 2012. The Ethics of Tax Evasion: Perspectives in Theory and Practice . New York: Springer.
OECD. 2015. OECD Tax Statistics. Revenue Statistics: OECD Countries-Comparative Tables.
Picur, Ronald D., and Ahmed Riahi-Belkaoui. 2006. The Impact of Bureaucracy, Corruption and Tax Compliance. Review of Accounting and Finance 5: 174–180.
Prebble, Zoe M., and John Prebble. 2010. The Morality of Tax Avoidance. Creighton Law Review 43 (3): 693–745.
Rawls, John. 1958. Justice and Fairness. Philosophical Review 67: 164–193.
Rawls, John. 1971. A Theory of Justice . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Rousseau, Jean-Jacques. [1762] 1963. Du contrat social ou Principes du droit politique . Paris: Union Général d’Éditions.
Ruppert, Dieter. 1963. Die Beurteilung des deutschen, schweizerischen und französischen Umsatzsteuersystems nach Grundsätzen der allgemeinen Steuerlehre . Frankfurt am Main: Union Druckerei.
Sage-Fuller, Benedicte, and Ferdinand Prinz zur Lippe. 2014. Abuse of Tax Law as Language of Morality of Modern Times: A Comparative Analysis of France, Canada and Ireland. Comparative Law-Engaging Translation : 191.
Slemrod, Joel (ed.). 1992. Why People Pay Taxes: Tax Compliance and Enforcement . Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press.
Smith, Adam. [1776] 1994. An Inquiry Into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations . Modern Library Edition. London: Random House.
Sneed, Joseph T. 1965. The Criteria of Federal Income Tax Policy. Stanford Law Review 17: 567.
Sutton, Willlie, and Edward Linn. 1976. Where the Money Was: The Memoirs of a Bank Robber . New York: Viking Press.
Terra, Ben. 1988. Sales Taxation: The Case of Value Added Tax in the European Community . Deventer-Boston: Kluwer Law International.
Tiebout, Charles. 1956. A Pure Theory of Local Expenditures. Journal of Political Economy 64: 416.
Torgler, Benno, and Friedrich Schneider. 2007. What Shapes Attitudes Toward Paying Taxes? Evidence from Multicultural European Countries. Social Science Quarterly 88 (2): 443–470.
Van Brederode, Robert F. 1996. Ethiek van het Omzetbelastingrecht (Ethics of Turnover Tax Law). Inaugural lecture. Deventer: Kluwer.
Van Brederode, Robert F. 2014. A Normative Evaluation of Tax Law Enforcement: Legislative and Political Responses to Tax Avoidance and Evasion. Intertax 42 (12): 764–783.
Van Brederode, Robert F., and Richard Krever. 2017. Legal Interpretation of Tax Law , 2nd ed. The Netherlands: Kluwer Law International.
Vance, David E. 2013. Is the Federal Income Tax Code Unconstitutionally Vague? Mustang Journal of Law & Legal Studies 5: 47–62.
Vogel, Klaus. 1988. The Justification for Taxation: A Forgotten Question. American Journal of Jurisprudence 33 (1): 19–59.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
BrederodeTax, Lancaster, PA, USA
Robert F. van Brederode
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Robert F. van Brederode .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations, rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
van Brederode, R.F. (2020). Introduction: Why Ethics Matter in Taxation. In: van Brederode, R. (eds) Ethics and Taxation. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0089-3_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0089-3_1
Published : 03 November 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-15-0088-6
Online ISBN : 978-981-15-0089-3
eBook Packages : Law and Criminology Law and Criminology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Paying Taxes
This topic recorded the taxes and mandatory contributions that a medium-size company must have paid or withheld in a given year, as well as the administrative burden of paying taxes and contributions. The most recent round of data collection for the project was completed on May 1, 2019 covering for the Paying Taxes indicator calendar year 2018 (January 1, 2018 – December 31, 2018). See the methodology and video for more information.
To learn more about the results of Paying Taxes in calendar year 2018, see the Paying Taxes 2020 report .
- Doing Business Score
- What is Measured
- Why it Matters
- Good Practices
- Other Resources
Why it matters?
Why do tax rates and tax administration matter?
To foster economic growth and development governments need sustainable sources of funding for social programs and public investments. Programs providing health, education, infrastructure and other services are important to achieve the common goal of a prosperous, functional and orderly society. And they require that governments raise revenues. Taxation not only pays for public goods and services; it is also a key ingredient in the social contract between citizens and the economy. How taxes are raised and spent can determine a government’s very legitimacy. Holding governments accountable encourages the effective administration of tax revenues and, more widely, good public financial management. 1
All governments need revenue, but the challenge is to carefully choose not only the level of tax rates but also the tax base. Governments also need to design a tax compliance system that will not discourage taxpayers from participating. Recent firm survey data for 147 economies show that companies consider tax rates to be among the top five constraints to their operations and tax administration to be among the top 11. 2 Firms in economies that score better on the Doing Business ease of paying taxes indicators tend to perceive both tax rates and tax administration as less of an obstacle to business (figure 1).
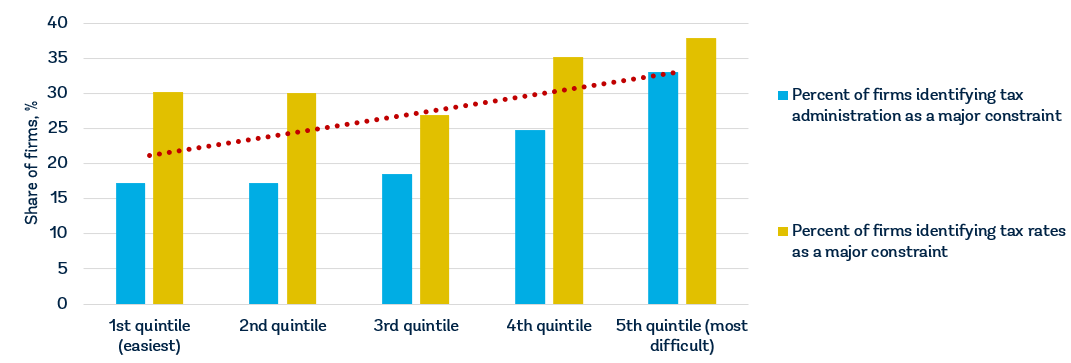
Why tax rates matter?
The amount of the tax cost for businesses matters for investment and growth. Where taxes are high, businesses are more inclined to opt out of the formal sector. A study shows that higher tax rates are associated with fewer formal businesses and lower private investment. A 10-percentage point increase in the effective corporate income tax rate is associated with a reduction in the ratio of investment to GDP of up to 2 percentage points and a decrease in the business entry rate of about 1 percentage point. 3 A tax increase equivalent to 1% of GDP reduces output over the next three years by nearly 3%. 4 Research looking at multinational firms’ decisions on where to invest suggests that a 1-percentage point increase in the statutory corporate income tax rate would reduce the local profits from existing investment by 1.3% on average. 5 A 1-percentage point increase in the effective corporate income tax rate reduces the likelihood of establishing a subsidiary in an economy by 2.9%. 6
Profit taxes are only part of the total business tax cost (around 39% on average). In República Bolivariana de Venezuela, for example, the nominal corporate income tax is based on a progressive scale of 15–34% of net income, but the total business tax bill — even after taking into account deductions and exemptions — is 73.31% of commercial profit owing to a series of other taxes (a profit tax, four labor taxes and contributions, a turnover tax, a property tax and a science, technology and innovation tax).
Keeping tax rates at a reasonable level can encourage the development of the private sector and the formalization of businesses. Modest tax rates are particularly important to small and medium-sizeenterprises, which contribute to economic growth and employment but do not add significantly to tax revenue. 7 Typical distributions of tax revenue by firm size for economies in Sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East and North Africa show that micro, small and medium-size enterprises make up more than 90% of taxpayers but contribute only 25–35% of tax revenue. 8 Imposing high tax costs on businesses of this size might not add much to government tax revenue, but it might cause businesses to move to the informal sector or, even worse, cease operations.
In Brazil, the government created Simples Nacional , a tax regime designed to simplify the collection of taxes for micro and small enterprises. The program reduced overall tax costs by 8% and contributed to an increase of 11.6% in the business licensing rate, a 6.3% increase in the registration of microenterprises and a 7.2% increase in the number of firms registered with the tax authority. Revenue collections rose by 7.4% percent as a result of increased tax payments and social security contributions. Simples Nacional was also credited with increasing the revenue, profit, paid employment and fixed capital of formal-sector firms. 9
Businesses care about what they get for their taxes. Quality infrastructure is critical for the sound functioning of an economy because it plays such a central role in determining the location of economic activity and the kinds of sectors that can develop. A healthy workforce is vital to an economy’s competitiveness and productivity — investing in the provision of health services is essential for both economic and moral reasons. Basic education increases the efficiency of each worker, and good-quality higher education and training allow economies to move up the value chain beyond simple production processes and products.
The efficiency with which tax revenue is converted into public goods and services varies around the world. Recent data from the World Development Indicators and the Human Development Index show that economies such as Ireland and Malaysia — which all have relatively low total tax rates — generate tax revenues efficiently and convert the gains into high-quality public goods and services (figure 2). The data show the opposite for Angola and Afghanistan. Economic development often increases the need for new tax revenue to finance rising public expenditure. At the same, time it requires an economy to be able to meet those needs. More important than the level of taxation, however, is how revenue is used. In developing economies high tax rates and weak tax administration are not the only reasons for low rates of tax collection. The size of the informal sector matters as well; the tax base is much narrower because most workers in the informal sector earn very low wages.
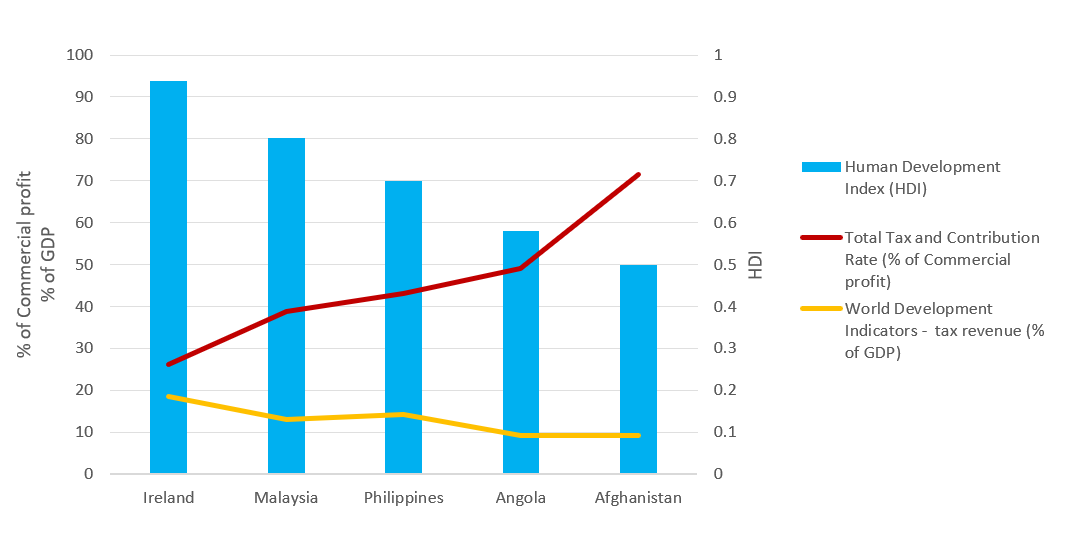
Why tax administration matters
Efficient tax administration can help encourage businesses to become formally registered, thereby expanding the tax base and increasing tax revenues. Tax administration that is unfair and capricious is likely to bring the tax system into disrepute and reduce the government’s legitimacy. In many transition economies in the 1990s, the failure to improve tax administration when new tax systems were introduced resulted in the uneven imposition of taxes, widespread tax evasion and lower-than-expected tax revenue. 10
Compliance with tax laws is important to keep the system working for all and supporting the programs and services that improve lives. One way to encourage compliance is to keep the rules as clear and simple as possible. Overly complicated tax systems are associated with high tax evasion. High tax compliance costs are associated with larger informal sectors, more corruption and less investment. Economies with simple, well-designed tax systems are able to boost businesses activity and, ultimately, investment and employment. 11 New research shows that an important determinant of firm entry is the ease of paying taxes, regardless of the corporate tax rate. A study of 118 economies over six years found that a 10% reduction in the tax administrative burden — as measured by the number of tax payments per year and the time required to pay taxes — led to a 3% increase in annual business entry rates. 12
Tax administration is changing as the ecosystem in which it operates becomes broader and deeper, mostly owing to the vast increase in digital information flows. Tax administrations are responding to these challenges through the introduction of new technology and analytical tools. They must rethink how they operate, offering the prospect of lower costs, increased compliance and incentives for compliant taxpayers. 13 The government of Tajikistan has made tax reform a major priority for the country as it seeks to achieve its development goals. In 2013, Tajikistan launched the Tax Administration Reform Project and, as a result, the country built a more efficient, transparent and service-oriented tax system. The modernization of IT infrastructure and the introduction of a unified tax management system increased efficiency and reduced physical interactions between tax officials and taxpayers. Following the improvement of taxpayer services, the number of active firms and individual taxpayers filing taxes has doubled and revenue collections have risen strongly. A taxpayer in Tajikistan spent 28 days in 2016 complying with all tax-related regulations, compared with 37 days in 2012. 14
A low cost of tax compliance and efficient procedures can make a significant difference for firms. In Hong Kong SAR, China, for example, the standard case study firm would have to make only three payments a year, the lowest number of payments globally. In Qatar and Saudi Arabia, it would have to make four payments, still among the lowest in the world. In Estonia, complying with profit tax, value added tax (VAT) and labor taxes and contributions takes only 50 hours a year, around 6 working days.
Research finds that it takes a Doing Business case study company longer on average to comply with VAT than to comply with corporate income tax. However, the time it takes a company to comply with VAT requirements varies widely. Research shows that this is explained by variations in administrative practices and in how VAT is implemented. Compliance tends to take less time in economies where the same tax authority administers VAT and corporate income tax. The use of online filing and payment also greatly reduces compliance time. Frequency and length of VAT returns also matter; requirements to submit invoices or other documentation with the returns add to compliance time. Streamlining the compliance process and reducing the time needed to comply with the requirements is important for VAT systems to work efficiently. 15
Why do postfiling processes matter?
Filing the tax return with the tax authority does not imply agreement on the final tax liability. Often, the ordeal of taxation starts after the tax return has been filed. Postfiling processes — such as claiming a VAT refund, undergoing a tax audit or appealing a tax assessment — can be the most challenging interaction that a business has with a tax authority. Businesses might have to invest more time and effort into the processes occurring after filing of tax returns than into the regular tax compliance procedures.
Why VAT refund systems matter?
The VAT refund is an integral component of any modern VAT system. In principle, VAT’s statutory incidence is on the final consumer, not on businesses. According to tax policy guidelines set out by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), a VAT system should be neutral and efficient. The absence of an efficient VAT refund system for businesses with an excess input VAT in a given tax period will undermine this goal. VAT could have a distortionary effect on market prices and competition and consequently constrain economic growth. 16
Refund processes can be a major weakness of VAT systems. This view is supported by a study examining VAT administration refund mechanisms in 36 economies worldwide. 17 Even in economies where refund procedures are in place, businesses often find the process complex. The study examined the tax authorities’ treatment of excess VAT credits, size of refund claims, procedures followed by refund claimants and time needed for the tax authorities to process refunds. The study found that statutory time limits for making refunds are crucial but often not applied in practice.
Delays and inefficiencies in the VAT refund systems are often the result of fears that the system might be abused and prone to fraud. 18 Moved by this concern, many economies have established measures to moderate and limit the recourse to the VAT refund system and subject the refund claims to thorough procedural checks. That is also one of the reasons why, in some economies, it is not uncommon for a claim for a VAT refund to automatically trigger a costly audit, undermining the overall effectiveness of the system.
The Doing Business case study company, TaxpayerCo., is a domestic business that does not trade internationally. It performs a general industrial and commercial activity and it is in its second year of operation. TaxpayerCo. meets the VAT threshold for registration and its monthly sales and monthly operating expenses are fixed throughout the year, resulting in a positive output VAT payable within each accounting period. The case study scenario has been expanded to include a capital purchase of a machine in the month of June. This substantial capital expenditure results in input VAT exceeding output VAT in the month of June.
The results show that, in practice, only 107 of the economies covered by Doing Business allow for VAT cash refund in this scenario. This number excludes the 26 economies that do not levy VAT and five economies where the purchase of a machine is exempted from VAT. 19 Some economies restrict the right to receive an immediate cash refund to specific types of taxpayers such as exporters, embassies and non-profit organizations. This is the case in 34 economies including Belarus, Bolivia, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Kazakhstan, Mali and the Philippines.
In other economies businesses are only allowed to claim a cash refund after carrying forward the excess credit for a specified period of time (four example, four months). The net VAT balance is refunded to the business only after this period ends. This is the case in 26 economies of the 190 measured by Doing Business .
The legislation in other economies — typically those with a weaker administrative or financial capacity to handle cash refunds — may not permit refunds outright. Instead, tax authorities require businesses to carry forward a claim and offset an excess amount against future output VAT.
Insofar as procedural checks are concerned, in 77 of the 107 economies which allow for a VAT cash refund in the Doing Business case scenario, a claim for a VAT refund will probably lead to an additional review being conducted before approving the VAT cash refund. Effective audit programs and VAT refund payment systems are inextricably linked. Tax audits (direct and indirect) vary in their scope and complexity, ranging from a full audit — which typically entails a comprehensive examination of all information relevant to the calculation of a taxpayer’s tax liability in a given period — to a limited scope audit that is restricted to specific issues on the tax return or a single-issue audit that is limited to one item.
In Canada, Denmark, Italy and Norway a request for a VAT refund is likely to trigger a correspondence audit, which requires less interaction with the auditor and less paperwork. By contrast, in most economies in Sub-Saharan Africa, where an audit is likely to take place, taxpayers are exposed to a field audit in which the auditor visits the premises of a taxpayer.
As far as the format of the VAT refund request is concerned, in 52 of the 107 economies the VAT refund due is calculated and requested within the standard VAT return submitted in each accounting period. In the other economies, the request procedure varies from filing a separate application, letter or form for a VAT refund to completing a specific section in the VAT return as well as preparing some additional documentation to substantiate the claim. In these economies, businesses spend on average 5.5 hours gathering the required information, calculating the claim and preparing the refund application and other documentation before submitting them to the relevant authority.
Overall, the OECD high-income economies are the most efficient at processing VAT refunds with an average of 14.3 weeks to process reimbursement (including some economies where an audit is likely to be conducted). Economies in Europe and Central Asia also perform well with an average refund processing time of 23.1 weeks. These economies provide refunds in a manner that does not expose businesses to unnecessary administrative costs and detrimental cash flow impacts.
Doing Business data also show a positive correlation between the time to comply with a VAT refund process and the time to comply with filing the standard VAT return and payment of VAT liabilities. This relationship indicates that tax systems that are harder to comply with when filing taxes are more likely to be challenging throughout the process.
Why tax audits matter?
Tax audits play an important role in ensuring tax compliance. Nonetheless, a tax audit is one of the most sensitive interactions between a taxpayer and a tax authority. It imposes a burden on a taxpayer to a greater or lesser extent depending on the number and type of interactions (field visit by the auditor or office visit by the taxpayer) and the level of documentation requested by the auditor. It is therefore essential that the right legal framework is in place to ensure integrity in the way tax authorities carry out audits. 20
A risk-based approach takes into consideration different aspects of a business such as historical compliance, industry and firm-specific characteristics, debt-credit ratios for VAT-registered businesses and the size of a business in order to better assess which businesses are most prone to tax evasion. One study showed that data-mining techniques for auditing, regardless of the technique, captured more noncompliant taxpayers than random audits. 21
In a risk-based approach the exact criteria used to capture noncompliant firms, however, should be concealed to prevent taxpayers from purposefully planning how to avoid detection and to allow for a degree of uncertainty to drive voluntary compliance. 22 23 Most economies have risk assessment systems in place to select companies for tax audits and the basis on which these companies are selected is not disclosed. Despite being a postfiling procedure, audit strategies can have a fundamental impact on the way businesses file and pay taxes. To analyze audits of direct taxes the Doing Business case study scenario was expanded to assume that TaxpayerCo. made a simple error in the calculation of its income tax liability, leading to an incorrect corporate income tax return and consequently an underpayment of the income tax due. TaxpayerCo. detected the error and voluntarily notified the tax authority. In all economies that levy corporate income tax — only 10 out of 190 do not — taxpayers can notify the authorities of the error, submit an amended return and any additional documentation (typically a letter explaining the error and, in some cases, amended financial statements) and pay the difference immediately. Businesses spend 5.7 hours on average preparing the amended return and any additional documents, submitting the files and making payment. In 76 economies the error in the income tax return is likely to be subject to additional review (even following immediate notification by the taxpayer).
In 37 economies this error will lead to a comprehensive review of the income tax return, requiring that additional time be spent by businesses. In the majority of cases the auditor will visit the taxpayer’s premises. On average, it takes about 83 days for the tax authorities to start the comprehensive audit. In these cases, taxpayers will spend 24 hours complying with the requirements of the auditor, going through several rounds of interactions with the auditor during 10.3 weeks and wait 8.1 weeks for the auditor to issue the final decision on the tax assessment. Economies in the OECD high-income group and Central Asian economies have the easiest and simplest processes in place to correct a minor mistake in the income tax return. In 28 economies in the OECD high-income group a mistake in the income tax return does not trigger additional reviews by the tax authorities. Taxpayers are only required to submit an amended return and, in some cases, additional documentation and pay the difference in taxes due. Economies in Latin America and the Caribbean suffer the most from a lengthy process to correct a minor mistake in an income tax return, as in most cases it would involve an audit imposing a waiting time on taxpayers until the final assessment is issued.
---------------
1 FIAS. 2009. “Taxation as State Building: Reforming Tax Systems for Political Stability and Sustainable Economic Growth.” World Bank Group, Washington, DC. 2 World Bank Enterprise Surveys ( http://www.enterprisesurveys.org ). 3 Djankov, Simeon, Tim Ganser, Caralee McLiesh, Rita Ramalho and Andrei Shleifer. 2010. “The Effect of Corporate Taxes on Investment and Entrepreneurship.” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics 2 (3): 31–64. 4 Romer, Christina, and David Romer. 2010. “The Macroeconomic Effects of Tax Changes: Estimates Based on a New Measure of Fiscal Shocks.” American Economic Review 100: 763–801. 5 Huizinga, Harry, and Luc Laeven. 2008. “International Profit Shifting within Multinationals: A Multi-Country Perspective.” Journal of Public Economics 92: 1164–82. 6 Nicodème, Gaëtan. 2008. “Corporate Income Tax and Economic Distortions.” CESifo Working Paper 2477, CESifo Group, Munich. 7 Hibbs, Douglas A., and Violeta Piculescu. 2010. “Tax Toleration and Tax Compliance: How Government Affects the Propensity of Firms to Enter the Unofficial Economy.” American Journal of Political Science 54 (1): 18–33. 8 International Tax Dialogue. 2007. “Taxation of Small and Medium Enterprises.” Background paper for the International Tax Dialogue Conference, Buenos Aires, October. 9 Fajnzylber, Pablo, William F. Maloney and Gabriel V. Montes-Rojas. 2011. “Does Formality Improve Micro-Firm Performance? Evidence from the Brazilian SIMPLES Program.” Journal of Development Economics 94 (2): 262–76. 10 Bird, Richard. 2010. “Smart Tax Administration.” Economic Premise (World Bank) 36: 1–5. 11 Djankov, Simeon, Tim Ganser, Caralee McLiesh, Rita Ramalho and Andrei Shleifer. 2010. “The Effect of Corporate Taxes on Investment and Entrepreneurship.” American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics 2 (3): 31–64. 12 Pontus Braunerhjelm, and Johan E. Eklund. 2014. “Taxes, Tax Administrative Burdens and New Firm Formation.” KYKLOS 67 (February): 1–11. 13 OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development). 2017. Comparative Information on OECD and Other Advanced and Emerging Economies. Paris, France: OECD. 14 IFC (International Finance Corporation). 2018. “Improved Tax Administration Can Increase Private Investment and Boost Economic Development in Tajikistan.” International Finance Corporation, Washington, DC. 15 Symons, Susan, Neville Howlett and Katia Ramirez Alcantara. 2010. The Impact of VAT Compliance on Business . London: PwC. 16 OECD (2014), Consumption Tax Trends 2014: VAT/GST and excise rates, trends and policy issues, OECD Publishing, Paris. 17 Graham Harrison and Russell Krelove 2005, “VAT Refunds: A Review of Country Experience” IMF Working Paper WB/05/218, Washington D.C. 18 Keen M., Smith S., 2007, “VAT Fraud and Evasion: What Do We Know, and What Can be Done?”. IMF Working Paper WP/07/31. 19 It is worth noting that 28 economies analyzed in Doing Business do not levy VAT. 20 OECD (2006), Tax Administration in OECD and Selected Non-OECD Countries: Comparative Information Series (2006), OECD Publishing, Paris. 21 Gupta, M., and V. Nagadevara. 2007. “Audit Selection Strategy for Improving Tax Compliance: Application of Data Mining Techniques.” In Foundations of E-government, eds. A. Agarwal and V. Ramana. Proceedings of the eleventh International Conference on e-Governance, Hyderabad, India, December 28–30. 22 Alm J., and McKee M., 2006, “Tax compliance as a coordination game”, Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization , Vol. 54 (2004) 297–312 23 Khwaja, M. S., R. Awasthi, J. Loeprick, 2011, ”Risk-Based Tax Audits Approaches and Country Experiences”, World Bank, Washington, DC.
Feedback has been successfully submitted.
- Listening Tests
- Reading Tests
- IELTS Writing Checker
- IELTS Writing Samples
- Free IELTS Speaking Test Online
- Speaking Club
- Vocabularying
- 2024 © IELTSing
- free ielts Listening test practice 2024 with answers
- free ielts Reading tests online 2024 with answers
- Free IELTS Writing Checker
- Check IELTS Speaking Test

Some people think paying taxes is enough of a contribution to their society, while others think people have more responsibilities as members of society than only paying taxes. Discuss both views and give your opinion.

IELTS essay Some people think paying taxes is enough of a contribution to their society, while others think people have more responsibilities as members of society than only paying taxes.
- Some people think that schools should be select pupils according to there academic abilities while other believe that is is better to have pupils with different abilities study together discuss both view and give your opinion Even though a lot of academicians suggested that students should sort out based on their academic background but the remaining are against it. However different people have a different mindsets. Nevertheless, from my perspective agree to a large extent that students should not be selected based on t ...
- Some countries are struggling with an increase in the rate of crime. Many people think that having more police on the streets is the only way to reduce these increasing levels of crime. Here and now crime-related statistics are of ever-increasing alarm, noting that the crime rate is mounting relentlessly, therefore numerous countries are struggling hard to confront the problem. Lots of people are suggesting that the sole way to halt the issue is to reinforce the number of law enfor ...
- Sending criminals to prison is not the best method of dealing with them. Education and job training are better ways to help them. Give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge or experience Crime has become one of the most important issues in the society nowadays. While some people think that the best way to solve this problem is placing criminals in jail, others believe that providing education and job training programs for them is more effective. In my opinion, I completely agree wit ...
- Some think that economic progress is completely dependent on the country’s success, while others believe that other factors are also important. What are the different factors contributing to the success of a country? Do you believe that only one factor is important, compared to others? There are different views about the most important goal of a country. While some people think that economic growth is the main purpose of a country, others believe that other factors are key markers in this area. I believe that although the economy has a significant role, other primary aspects contr ...
- The graph below shows the daily consumption of three spreads per person from 1981 to 2007 in a country. The line graph compares 3 type of spreads eaten over a span of 26 years. Overall, the consumption of margarine and butter declined gradually over the given period, whereas low fat and reduced spreads had an upward trend. at the start of the period, butter was the most known spread among other sprea ...
- In many countries, young people are granted certain privileges and responsibilities at the age of sixteen. Clearly, parents have a responsibility to both care for and prepare their children as they approach this important milestone. v. 2 Another problem is social evils. I see a lot of parents due to busy work should pay little attention, care about their children, besides giving them a lot of money. This will lead to the result that children will not perceive right from wrong, there will be no one to teach about the dark sides of ou ...
- Many people believe that the government should spend money on faster public transport. Others think that money should be spent on different aspects of social transportation such as cost reduction and environmental conservation. The question of developing public transport has been widely discussed in recent years. A multitude of individuals suppose that the people in power are advised to invest the budget into more rapid social transportation. Others believe that it is a good idea for finance to be dedicated to various feat ...
- People prefer to watch foreign films rather than locally produced ones. Why do you think this happens? Should government support local film makers financially? In many countries, usually in developed countries, people watch international movies as compared to those, which are produced in their country. there are many reasons of this booming trend and from my point of view, the government should contribute to the progress of local movies. To commence with, ...
- The two floor plans show the renovation of AAA Accountancy's main office. The plans of two floors represent AAA Accountancy’s office before and after renovation. Overall, almost all the offices were removed and on their place one big office was built. Right side of the floor wasn’t changed much. Entrance room with front desk was completely renovated and storage room was ...
- Visitor spend every year from 1996 to 2014 by tourist in 5 countries including Australia, USA, UK, Japan and China. Units are measured in NZ$. v. 2 The line graph illustrates the visitor spend every year from 1996 to 2014 by tourist in 5 countries including Australia, USA, UK, Japan and China. Units are measured in NZ$. Generally, during this period, annual expenditure spend increased in all 5 countries. Among them, Australian spending was by ...
- These days children are surrounded by electronic devices such as personal computers, tablet computers and smart phones, and they learn to use them at a very early age. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this situation? We live in the 21st century which is developing period and people, mostly children use electronic devices from their born’s day. As a result new technologies are the major part our life. Lots of families have computers, tablets and smart phones, and all the latter use they during their day, workday ...
- It is important for children to learn the difference between right and wrong. Punishment is necessary to help them learn this distinction. What sort of punishment should parents and teachers be allowed to use them good behavior The sense of right and wrong should be taught to children at the very beginning stage of their life. It is thought by some that punishment can necessarily help their children to learn this difference. This maybe true to some extent but I do not completely agree with this opinion. Children are very ...

Band 4+: some people think that paying tax is their only duty, while others believed we have more responsibilities toward society. Discuss both views and give your own opinion.
People have different views about whether individuals have only one role and is paying fees or there are other more important duties for them. While covering their taxes are useful, I believe people obligation toward the Earth is more crucial.
On the one hand, citizens by paying their tax can benefit their cities. The government with enough budget can invest more on public facilities in the cities. For instance, they can construct efficient public transportations and there would be enough schools and hospitals for public. Furthermore, when people covering their fees, they may also feel better and see themselves as an effective member of society and this encourage them to participate in more social community’s events.
On the other hand, people have other responsibilities toward community that are more vital that paying tax. One of the most considerable roles is protecting the earth. According to many experts, the statistics of green gas emission arise significantly which is concerning humans and in terms of that individuals will face several problems. Such as global warming and air pollution. People need to find solution for this fundamental issue. Another duty is that try to reduce the among of energy and water consumptions. Statistics that in near future there will be shortage of water storage and that can tend to risk od drought and many other disasters.
In conclusion, I can understand that paying tax are important, but it seem to me protecting our earth are more desirable can reduce many environmental risks in the future.
Check Your Own Essay On This Topic?
Generate a band-9 sample with your idea, overall band score, task response, coherence & cohesion, lexical resource, grammatical range & accuracy, other topics:, many species of animals all around the world are on the verge of extinction. some say that countries and individuals should protect these animals from dying out, while others say that we should concentrate more on the problems of human beings. discuss both viewpoints and give your opinion. give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge or experience..
In this modern era, the extinction of animals has happened more in comparison to previous decades. This essay will discuss whether people around the world should prevent this problem to occur, or whether there are more human related problems need to be focused on. While species of animals’ disappearance can give negative impacts to the […]
More and more students are choosing to study at colleges and universities in a foreign country. Do the benefits of studying abroad outweigh the drawbacks?
It is true that more and more students are preferring to attend universities and colleges abroad. While this trend has some drawbacks, I would argue they are more positive impacts. On the one hand, studying abroad brings many benefits. Firstly, it helps you learn a new language when you study in a country that speaks […]
Many developing countries are currently expanding their tourism industries. Why is this the case? Is it a positive development?
Currently, the tourist industry is extended in developing countries. In this essay, I will attempt to shed light on the two reasons for this situation before giving my perspective. Firstly, the tourist domain brings a large profit for developing countries. They could receive the turnover from not only the domestic visitors but also the foreign […]
It may be a problem for car drivers and cyclists to share the same road. What are the problems and how to improve the situation?
It is clear that sharing the road fifty-fifty between car drivers and cyclists can be a concern. There are a variety of possible problems for this, but steps can definitely be taken to tackle the complications with legitimate initiatives by the government. In my opinion, there are two main problems associated with car drivers and […]
It is clear that go fifty-fifty in certain road can be a concern for car drivers and cyclist. There are a variety of possible problems for this, but steps can be definitely taken to tackle the complications with legitimate initiatives by government. In my opinion, there are two main problems associated with car drivers and […]
In the past, most people lived in small villages where everyone knew everyone else. Nowadays, most people live in large cities where they only know a few people in their area.
In earlier times, people had a tendency to live in tiny villages where everyone knew each other. In modern times, most people live in big cities where they know very few people in surrounded area. In the past, there were both advantages and disadvantages to living in a small community. I believe that there were […]
Plans & Pricing
IELTS Mentor "IELTS Preparation & Sample Answer"
- Skip to content
- Jump to main navigation and login
Nav view search
- IELTS Sample
IELTS Writing Task 2/ Essay Topics with sample answer.
Ielts writing task 2 sample 382 - paying taxes is enough to contribute to the society, ielts writing task 2/ ielts essay:, some people think that paying taxes is enough to contribute to the society. others argue that being a citizen involves more responsibilities., what is your opinion on that, give reasons for your answer and include any relevant examples from your own knowledge and experience..
IELTS Materials
- IELTS Bar Graph
- IELTS Line Graph
- IELTS Table Chart
- IELTS Flow Chart
- IELTS Pie Chart
- IELTS Letter Writing
- IELTS Essay
- Academic Reading
Useful Links
- IELTS Secrets
- Band Score Calculator
- Exam Specific Tips
- Useful Websites
- IELTS Preparation Tips
- Academic Reading Tips
- Academic Writing Tips
- GT Writing Tips
- Listening Tips
- Speaking Tips
- IELTS Grammar Review
- IELTS Vocabulary
- IELTS Cue Cards
- IELTS Life Skills
- Letter Types

- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- HTML Sitemap
Get our daily tax nugget here! Sign up

3 Top Reasons Why We Pay Taxes in the Philippines

The Benefits of Paying Taxes and Why It Matters
In a rapidly developing country like the Philippines, providing essential services and infrastructure to its citizens is a top priority. Taxes play a crucial role in financing these important projects and services and paying the right taxes will surely give our nation benefits.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the significance of tax revenue in funding key government initiatives, such as constructing and maintaining roads and bridges, communication and power facilities, educational and health services, and ensuring peace and order.
We’ll also explore how these investments contribute to the country’s overall growth and development, and how we as responsible tax-paying citizens can take part in shaping a brighter future for the Philippines.
The Importance of Taxes in the in Infrastructure Development
- Roads and Bridges: Paving the Way for Economic Growth

An efficient road network is fundamental for any thriving economy. In the Philippines, taxes are utilized to build, maintain, and repair roads and bridges. These infrastructure projects are essential for connecting urban and rural areas, promoting trade, and providing access to necessary services. Improved road connectivity leads to increased economic activity, job creation, and better living conditions for Filipinos.
Under its “Build, Build, Build” program, the Philippine government has initiated numerous road and bridge projects to accelerate infrastructure development across the country. Some notable projects include the Metro Manila Skyway Stage 3, the North Luzon Expressway (NLEX) Harbor Link, and the Cebu-Cordova Link Expressway. Funded by tax revenue, these projects are expected to significantly reduce traffic congestion, enhance connectivity, and stimulate economic growth.
- Communication and Power Facilities: Empowering the Digital Age
Taxes also contribute to the construction and maintenance of communication and power facilities, which are crucial for the nation’s growth in the digital age.
Communication infrastructure, such as cell towers and fiber-optic networks, allows the Philippines to stay connected with the rest of the world. This connectivity fosters economic growth, encourages innovation, and improves access to information.
The government, through the Department of Information and Communications Technology (DICT), has launched the National Broadband Plan , aiming to provide high-speed internet access to every Filipino household by 2026. This ambitious project, funded by tax revenue, will bridge the digital divide, improve e-governance, and support the growth of the digital economy.
Power facilities, like power plants and electric grids, supply the energy required to power homes, businesses, and industries. Tax revenue is crucial for maintaining and upgrading these facilities to meet the increasing demand for electricity and ensure a stable energy supply for the entire country.
The government has implemented various power sector reforms, such as the Electric Power Industry Reform Act (EPIRA) , to encourage private sector participation and investment in the power sector. These reforms aim to increase power generation capacity, improve the reliability of the power grid, and ensure affordable electricity rates for consumers.
Investing in the Future: Education and Health Services
- Educational Services: Shaping a Brighter Future

A well-educated population is essential for a country’s growth and competitiveness. Taxes enable the Philippine government to invest in educational services, such as building schools, training teachers, and providing scholarships to deserving students. These investments ensure that every Filipino child has access to quality education, empowering them to become productive members of society and contribute to the nation’s progress.
The Department of Education (DepEd) receives a significant portion of the national budget, funded by tax revenues, to implement various educational programs and initiatives. These include the K-12 program, which aims to enhance the basic education curriculum and provide students with a strong foundation for college and future careers. Additionally, the government has been increasing its efforts to strengthen the Alternative Learning System (ALS) to cater to out-of-school youth and adult learners, ensuring that no Filipino is left behind.
Moreover, tax revenue also supports tertiary education through state universities and colleges (SUCs) and the Commission on Higher Education (CHED). The government has implemented the Universal Access to Quality Tertiary Education Act, providing free tuition and other financial assistance to students enrolled in SUCs. This landmark legislation, funded by taxes, has made higher education more accessible to low-income families, helping to break the cycle of poverty and promote social mobility.
- Health Services: Building a Healthy Nation
Health is another crucial aspect of a country’s development. Tax revenue enables the government to invest in health services, such as constructing and maintaining hospitals and health centers, training medical professionals, and providing affordable healthcare to the population. Investing in health services ensures a healthy and productive workforce, which is vital for economic growth and national development.
The Philippine government, through the Department of Health (DOH), allocates a significant portion of the budget to public health programs and initiatives. These include the implementation of the Universal Health Care (UHC) Law, which aims to provide all Filipinos with access to quality and affordable health services. Tax revenue plays a critical role in funding the UHC program, which covers primary care, hospital services, and preventive and promotive health services.
Additionally, taxes support the government’s efforts to improve public health infrastructure, such as the construction of new hospitals, upgrading existing facilities, and providing essential medical equipment. These investments contribute to better healthcare services, improved health outcomes, and ultimately, a healthier population.
Peace and Order: The Backbone of a Thriving Society

Tax revenue also plays a vital role in maintaining peace and order in the Philippines. The government uses taxes to fund the country’s police force, military, and judiciary, ensuring that citizens can live and work in a safe and secure environment. A stable and peaceful society is crucial for attracting investments and fostering economic growth.
The Philippine National Police (PNP), the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP), and the judiciary receive significant funding from tax revenue. These funds are used to train personnel, procure modern equipment, and implement various peace and order programs. Some notable initiatives include the intensified campaign against illegal drugs, the modernization of the AFP, and the strengthening of the judicial system through the construction of new courthouses and the digitization of court records.
Furthermore, taxes also support the government’s efforts to promote peace and development in conflict-affected areas, such as the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). These initiatives aim to address the root causes of conflict, promote social cohesion, and create sustainable development opportunities for marginalized communities.
Conclusion:

In my heart, I truly believe that taxes are a fundamental part of any modern society, and the Philippines is no exception. By understanding the role of taxes in funding essential government projects and services, we can genuinely appreciate the value of our tax contributions.
Paying taxes not only helps build a progressive and sustainable Philippine economy but also allows us to take pride in knowing we have played our part in creating a nation where everyone can enjoy the benefits of well-developed infrastructure, quality education and health services, and a secure and peaceful society.
As responsible citizens, let’s passionately commit ourselves to do our share by paying the correct taxes, and together, we can contribute to a better and brighter future for our beloved country.
Marie is the knowledgeable voice behind Tax Maven Ph, a trusted Philippine blog simplifying tax matters for individuals and businesses. As a Certified Public Accountant with extensive experience at the country's premier tax collecting agency, Marie shares her expertise on various tax topics, demystifying tax laws and helping readers navigate the tax system with confidence. Stay informed and gain valuable insights by connecting with Marie through Tax Maven Ph, your go-to resource for navigating the complexities of the Philippine tax system.
Deadlines can be scary while writing assignments, but with us, you are sure to feel more confident about both the quality of the draft as well as that of meeting the deadline while we write for you.
How Our Essay Service Works

You may be worried that your teacher will know that you took an expert's assistance to write my essay for me, but we assure you that nothing like that will happen with our write essay service. Taking assistance to write from PenMyPaper is both safe and private. We respect your privacy and thus do not ask for credentials like your name, college, location, or your phone number. To pay for the essay writing, you can either use your debit or credit cards to pay via PayPal or use your wallet balance from our website. All we would need is your card details and your email-id. This is our responsibility that your information will be kept all safe. This is what makes our service the best essay writing service to write with.
The shortest time frame in which our writers can complete your order is 6 hours. Length and the complexity of your "write my essay" order are determining factors. If you have a lengthy task, place your order in advance + you get a discount!

Service Is a Study Guide
Our cheap essay writing service aims to help you achieve your desired academic excellence. We know the road to straight A's isn't always smooth, so contact us whenever you feel challenged by any kind of task and have an original assignment done according to your requirements.
Our writers always follow the customers' requirements very carefully

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Two of the main talking points surrounding tax rates are the effect of increasing taxes on economic growth and productivity. Alinaghi and Reed (2020) find that a 10% increase in taxes in some cases produced a 0.2% decrease in GDP, and in other cases produced a 0.2% increase in GDP. That is to say that even a significant increase in the tax ...
Comments. Task Response. The question is fully addressed so the essay would get a good score for task response. The first body paragraph explains the reasons why people may not want to pay tax and the second body paragraph explains why it is important to pay.; Reasons and examples are given to support the ideas.
The law obliges us to pay taxes, which in turn provide everything from health care and Social Security to education and defense. We pay taxes to the federal, state, and local governments, each of ...
3. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite this essay. Download. Taxes can influence many people. The future generations need to know how it can relate to other things we do in life. Gen Z tends to work in a world of technology and rely ...
If you own property, you also pay property taxes on the value of your property. Paying your taxes is considered a civic duty, although doing so is also a requirement of the law. If you do not pay your taxes, the government agency that oversees taxes — the Internal Revenue Service or IRS — will require you to pay your taxes or else face ...
Lesson 1: Why Pay Taxes? The government provides public goods and services for the community as a whole. To pay its bills, the government needs revenue, or a source of income. The money that the federal government uses to pay its bills comes mostly from taxes. Taxes shift resources from private individuals and businesses to the government.
There are several reasons why it is necessary to assume the responsibility of paying taxes. They fall on the common good of the citizens and the country or region where they reside and are divided into two areas. 1. In a society. The government plans social projects, but the development force depends on the citizens.
Importance of Tax. Lawmakers in the county responded to the pressure from citizens and various lobbying groups that had reviewed the nature and effects of the proposed tax. It is apparent that the tax was meant to reduce the consumption of sweetened soft drinks with the hope that consumers would be discouraged by the increased prices of the ...
Article 1 of the United States Constitution grants the U.S. government the power to establish and collect taxes. Congress delegated to the IRS the responsibility of administering and enforcing the Internal Revenue Code. Taxes reduce taxpayers' income. As a result, taxpayers have less for personal goods and services, savings, and investments.
In my opinion, paying taxes greatly helps fund social programs but individuals have little choice but to do more if they also want to think highly of themselves. The main reason that many see taxes as enough are the far reaching impact of tax dollars. Take some well-run European socialist countries such as France for example.
The Importance of Paying Taxes. Electricity is the most used source of energy and with the rapid population and advancement in technology, there is a necessity of producing more electrical energy. Averagely, about $ 300 billion goes to conventional power sources each year.
Obligation to pay. Ethical standards of tax. Tax law enforcement. The word Ethics is derived from the Greek word èthos, which means custom. The word èthos translates in Latin to mos, plural mores, to which the English moral (s) is related. They have the same meaning, that which is related to normative behavior.
The vast majority of utterances providing information about paying income tax do so in a normative way. They often use verbs such as 'must' or 'should', which communicate an obligation (Palmer, 2001) and are used to request compliance with social norms (Edwards, 2006).Other forum members providing information use equivalent normative expressions such as 'you will have to do a self ...
Views. 3848. Paying taxes has become a compulsory obligation of each citizen for a long time but in recent years, there have some heated debates with many people believing that paying taxes is a work expressing adequately their responsibilities with society. While others clam that it is not enough to become a good citizen.
This essay will elaborate on both of the views in detail. To begin with, paying taxes is certainly a big contribution to society as it gives financial resources to the authority for the development of a country. Since the public budget from the taxes is used in all crucial aspects of a nation, paying taxes undoubtedly is vital for each capable ...
The program reduced overall tax costs by 8% and contributed to an increase of 11.6% in the business licensing rate, a 6.3% increase in the registration of microenterprises and a 7.2% increase in the number of firms registered with the tax authority. Revenue collections rose by 7.4% percent as a result of increased tax payments and social ...
This essay will discuss both sides of the argument; in addition, give reasons why I think there are other bonds that are of equal importance as paying taxes. Paying taxes is not only an obligation every single citizen needs to fulfil but also is the way via which they lend their hands to assist the operation of society in general.
On the other hand, people have other responsibilities toward community that are more vital that paying tax. One of the most considerable roles is protecting the earth. According to many experts, the statistics of green gas emission arise significantly which is concerning humans and in terms of that individuals will face several problems.
In particular, to protect their continent against Ebola, a dreadful virus causing thousands of mortality around the world in 2014, many Africans had felt a responsibility to defend their country against this virus. In conclusion, although paying taxes is considered as an important duty of citizens, other responsibilities must not be forgotten.
Essay on the importance and responsibility of paying taxes: The growing government requires money to carry out military activities and oversee the state's running. In fact, this money is collected by state residents in the form of the levy. Therefore, without the levy, the economy is nearly impossible to run.. Every state has its own way to collect taxes from its people.
The Benefits of Paying Taxes and Why It Matters. In a rapidly developing country like the Philippines, providing essential services and infrastructure to its citizens is a top priority. Taxes play a crucial role in financing these important projects and services and paying the right taxes will surely give our nation benefits.
Essay On The Importance And Responsibility Of Paying Taxes - 100% Success rate Testimonials. Bathrooms ... Hire a Writer. Essay On The Importance And Responsibility Of Paying Taxes: Your order is written Before any paper is delivered to you, it first go through our strict checking process in order to ensure top quality.
Essay On The Importance And Responsibility Of Paying Taxes, Como Hacer Un Curriculum Vitae Para Estados Unidos, Research Topic Proposal Examples, Essay Describe A Person Who Has Influenced Your Life, Essay On Mount Everest In English, Heart Touching Essay On Mother In Marathi, Practice And Homework Lesson 1.2 Common Core
صبح 8 بجے کی تمام اہم خبریں - 22 مئی 2024 #BOLNews #Bulletin #ImraKhan #CipherCase #ShahMehmoodQureshi