

Are Business Plans Highly Visual
In today’s business landscape, the role of visual elements in communication and presentation has gained significant prominence, with businesses increasingly recognizing the power of visual storytelling and engaging graphics in conveying complex information.
While traditional business plans have typically been characterized by text-heavy content and detailed financial analyses, the evolution of digital tools and multimedia platforms has paved the way for a more visually dynamic and interactive approach to business plan development. This shift toward visual-centric communication has prompted entrepreneurs and business professionals to explore innovative strategies for integrating visual elements into their business plans, enhancing the overall appeal and accessibility of their strategic vision and operational framework.
The Impact of Visual Communication
Visual communication plays a pivotal role in capturing the attention of stakeholders, investors, and potential business partners, enabling businesses to convey their value proposition and market potential in a compelling and easily digestible format. By incorporating infographics, charts, graphs, and multimedia presentations, businesses can effectively illustrate complex data, market trends, and competitive analyses, fostering a deeper understanding of the business’s key objectives and growth trajectory.
While adding infographics, charts, graphs into your plan can take time, there are AI business plan generators that can do it automatically for you.
Engaging Stakeholders through Visual Storytelling
Visual storytelling serves as a powerful tool for engaging stakeholders and fostering meaningful connections with target audiences. Integrating immersive visuals, dynamic animations, and interactive multimedia components within the business plan enables entrepreneurs to narrate their brand story, showcase product features, and highlight market opportunities in a visually captivating and emotionally resonant manner, fostering a sense of authenticity and brand identity that transcends traditional textual narratives.
Enhancing User Experience and Accessibility
Incorporating visual elements into business plans enhances user experience and accessibility, facilitating seamless navigation and intuitive comprehension of complex business strategies and financial projections. Utilizing user-friendly interfaces, intuitive data visualizations, and interactive design features can empower stakeholders to actively engage with the business plan content, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering a sense of transparency and trust between the business and its key stakeholders.
Balancing Visual Appeal with Content Depth
While visual elements serve as effective tools for enhancing the appeal and accessibility of business plans, striking a balance between visual engagement and substantive content depth is essential for ensuring the comprehensive communication of critical business insights and strategic analyses. The integration of visuals should complement the textual content and financial analyses, providing a comprehensive and holistic overview of the business’s market positioning, competitive advantage, and long-term growth prospects.
Adapting to Evolving Digital Trends
As digital technologies continue to evolve, businesses must adapt to emerging trends and best practices in visual communication to stay relevant and competitive in the contemporary business landscape. Embracing interactive presentations, virtual reality simulations, and augmented reality experiences can foster a dynamic and immersive business plan presentation, enabling stakeholders to actively participate in the strategic vision and experiential journey of the business.
How to Make Your Business Plan Visually Appealing
Crafting a visually appealing business plan is essential for capturing the attention of stakeholders, investors, and potential partners, effectively communicating your business’s value proposition, and showcasing its growth potential. Integrating engaging visuals, dynamic design elements, and intuitive infographics can elevate the aesthetic appeal and overall readability of your business plan, fostering a compelling and memorable narrative that resonates with your target audience. Here are key strategies to make your business plan visually engaging and impactful:
1. Visual Branding and Design Consistency: Infuse your business plan with cohesive visual branding elements, including logos, color schemes, and typography that align with your company’s brand identity. Ensure consistency in design elements throughout the document, reinforcing a strong and unified visual identity that reflects your business’s core values and market positioning.
2. Utilize Infographics and Data Visualizations: Transform complex data sets, market trends, and financial projections into visually compelling infographics and data visualizations. Use charts, graphs, and diagrams to illustrate key metrics and performance indicators, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of your business’s growth trajectory and market potential.
3. Incorporate High-Quality Imagery: Integrate high-resolution images, product photographs, and visual representations of your business operations to enhance the visual appeal of your business plan. Use captivating visuals to showcase your products, services, and unique selling points, providing stakeholders with a vivid and immersive glimpse into your business’s offerings and value proposition.
4. Interactive Multimedia Elements: Leverage interactive multimedia elements, such as videos, animations, and virtual presentations, to create an engaging and immersive business plan experience. Use multimedia content to demonstrate product functionalities, showcase customer testimonials, and articulate your business’s competitive advantage, fostering a dynamic and interactive engagement with your target audience.
5. Clear and Concise Visual Hierarchy: Implement a clear and intuitive visual hierarchy that organizes the content flow and highlights key information within your business plan. Utilize visual cues, bullet points, and section dividers to structure the document effectively, enabling stakeholders to navigate through the business plan seamlessly and access critical insights and analyses with ease.
6. Engage with Professional Design Tools: Leverage professional design software and online tools to create visually polished and professional business plan layouts. Explore design platforms that offer customizable templates, graphic design elements, and intuitive editing features, empowering you to craft visually stunning and industry-standard business plans that reflect a high level of professionalism and sophistication.
7. Incorporate Visual Case Studies and Success Stories: Integrate visual case studies, success stories, and customer testimonials to demonstrate your business’s track record, achievements, and market credibility. Use visually compelling narratives and real-life examples to highlight your business’s impact, success stories, and contributions to the industry, fostering a sense of trust and confidence among stakeholders and potential investors.
8. Responsive Design for Digital Platforms: Ensure that your business plan is optimized for digital platforms and mobile devices, incorporating responsive design elements that adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and resolutions. Prioritize user-friendly interfaces, intuitive navigation, and accessible content formatting to facilitate a seamless and engaging viewing experience for stakeholders accessing the business plan across different devices and platforms.
In conclusion, the integration of visual elements within business plans has become increasingly vital for facilitating effective communication, engaging stakeholders, and fostering a comprehensive understanding of the business’s value proposition and growth potential. By leveraging the power of visual storytelling, businesses can create impactful and immersive business plans that resonate with stakeholders, inspire confidence, and showcase the compelling narrative and strategic vision that underpin their long-term success and market competitiveness.

Diagramming Build diagrams of all kinds from flowcharts to floor plans with intuitive tools and templates.
Whiteboarding collaborate with your team on a seamless workspace no matter where they are., data generate diagrams from data and add data to shapes to enhance your existing visuals., enterprise friendly easy to administer and license your entire organization., security see how we keep your data safe., apps & integrations connect to all the tools you use from microsoft, google workspace, atlassian, and more..
- What's New Read about new features and updates.
Product Management Roadmap features, brainstorm, and report on development, so your team can ship features that users love.
Software engineering design and maintain complex systems collaboratively., information technology visualize system architecture, document processes, and communicate internal policies., sales close bigger deals with reproducible processes that lead to successful onboarding and training..
- Getting Started Learn how to make any type of visual with SmartDraw. Familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
- Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in SmartDraw.
Diagrams Learn about all the types of diagrams you can create with SmartDraw.
Whiteboard learn how to combine free-form brainstorming with diagram blueprints all while collaborating with your team., data visualizers learn how to generate visuals like org charts and class diagrams from data., development platform browse built-in data visualizers and see how you can build your own custom visualization., open api the smartdraw api allows you to skip the drawing process and generate diagrams from data automatically., shape data add data to shapes, import data, export manifests, and create data rules to change dashboards that update..
- Explore SmartDraw Check out useful features that will make your life easier.
- Blog Read articles about best practices, find tips on collaborating, learn to give better presentations and more.
Support Search through SmartDraw's knowledge base, view frequently asked questions, or contact our support team.
Site license site licenses start as low as $2,995 for your entire organization..
- Team License The SmartDraw team License puts you in control with powerful administrative features.
Apps & Integrations Connect to all the tools you use.
- Contact Sales
What's New?

Solutions By Team
Save money, reduce hassle, and get more.
Unleash your team's productivity by combining enterprise-class diagramming, whiteboarding, and data while saving 10x over Visio and Lucidchart!
Getting Started Learn to make visuals, familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in smartdraw., developer resources, additional resources.
Team License The SmartDraw Team License puts you in control with powerful administrative features.
Solutions for your team.
Create a Great Visual Business Plan

Writing a business plan isn't something to be taken lightly. A survey by the University of Oregon's Department of Economics found that companies that complete a business plan are twice as likely to grow and secure investment capital as those that don't.
This may seem like an insurmountable task. But it doesn't need to be.
We've boiled the important elements down to a few diagrams. Complete these and you'll have a great, visual business plan that will take a fraction of the time to complete than a traditional narrative one. It will also be appreciated by readers, who can see and understand the key elements of your plan quickly, without wasting a lot of time.
Step 1. Mission: Explain Why the Business Exists
Too many businesses fail because the entrepreneur(s) weren't in business for the right reason. All too often, the drive is a desire to get rich or leave a job one doesn't like. Unfortunately, emotional motives usually doom a new enterprise.
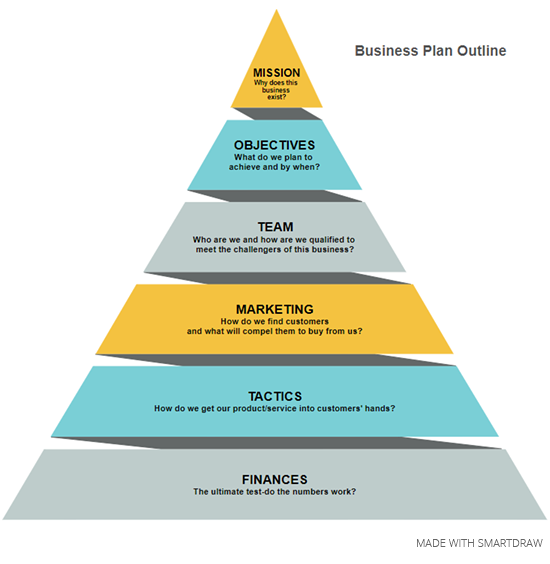
Focus on the "why" of your business—its purpose for existing. Richard Branson believes that a sense of frustration is the key to business success. His first venture, Virgin Records, was launched because he didn't like how a few high-priced London record outlets controlled the market. His company's mission was to ease this frustration by making it easier and cheaper for people to buy music.
A good way to summarize your mission is with a process list diagram. It has five key questions about what your business is, who your customers are, and why it will succeed within its market space. Each answer needs to be brief—no more than a couple of sentences. Keep your thinking very "high level" in this exercise.
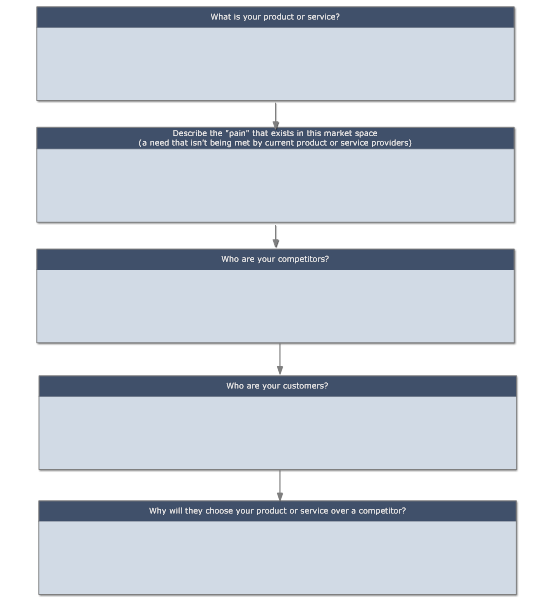
Step 2. Objectives: Create Milestones for Important Events
What are your primary objectives over a specific time period? How long a time period? For most businesses, this timeframe should be long enough to get the business to at least its first major milestone—profitability, an equity event, etc. It should not be less than a year nor should it be longer than five years.
A timeline diagram is a good way to present this.
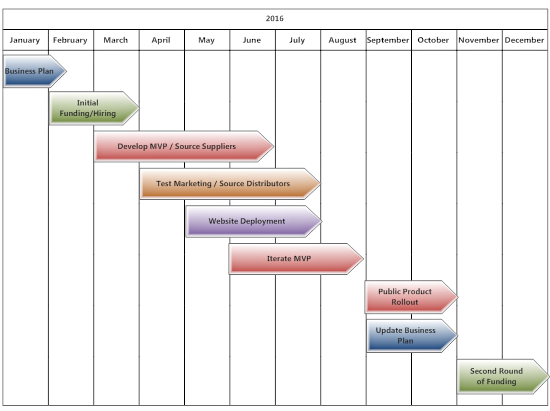
Step 3. Team: Show Them You're the Right People for the Job
Lenders, angel investors, and venture capital firms want to know who comprises the team. Do your backgrounds, qualifications, and experiences fit the mission?
An organizational chart should be included, along with a brief bio of each key individual. Make it clear why each person is the right "fit" for the mission.
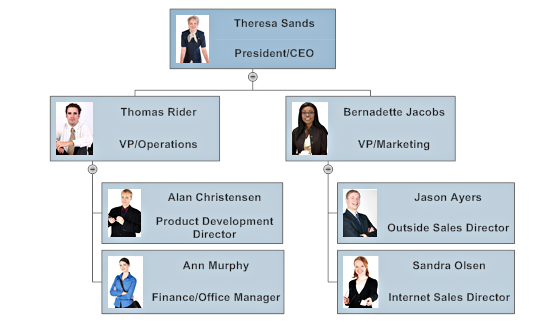
Step 4. Marketing: Show How Your Price, Product, and Promotions will Differ
Getting your product into your customers' hands requires a clear and concise strategy. In today's world, having a well-thought-out marketing plan is essential.
A good starting place for this is a 4Ps diagram. It looks at your product, who the potential buyers are, how to reach them, and at what price point they will buy.
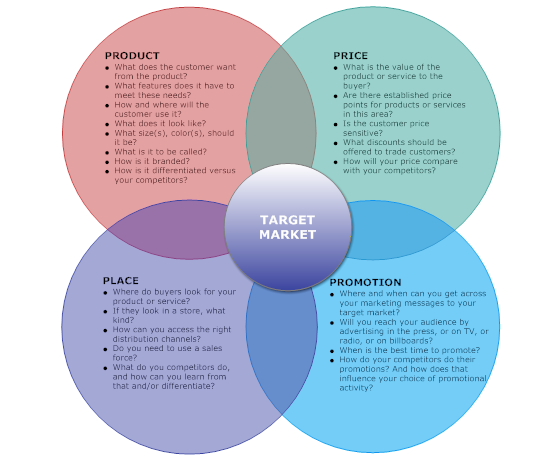
Step 5. Tactics: Show Off Your Process
Here's where you want to show you can deliver on your promises. This means getting the product from concept to customers' hands within a timeframe that meets or exceeds their expectations.
There are a number of ways to present this. For most businesses, a basic flowchart, such as a workflow diagram or business process map will work well.
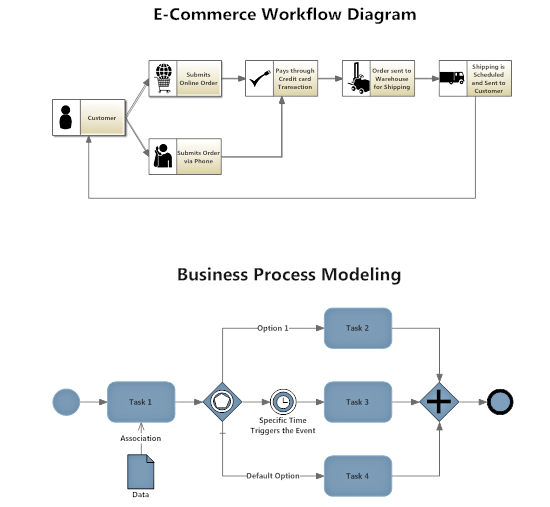
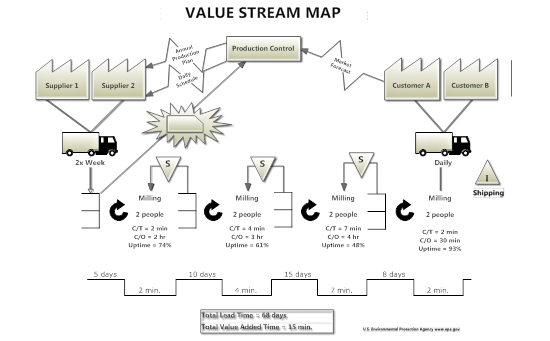
For manufacturing companies, a value stream map is an excellent tool. It not only explains a potentially complicated process succinctly, it also helps your management and production teams to evaluate and streamline operational efficiency.
Step 6. Finances: Presenting the Right Numbers the Right Way is Crucial
What numbers should you present in your business plan? There are many possible answers to this question. It really depends on the purpose of your business plan and who will be receiving it.
For example, say you are writing a business plan for the internal purposes of management. You may not need to document historical data or validate projections to the degree you should, say, for a bank loan.
If you're seeking investment capital, then you need to make sure your forecasts are extremely well thought out, and they show the investor(s) a clear plan for how and when they will be compensated.
Regardless of your intended audience, there are a few financial documents you should include in your business plan.
More Articles
- SmartDraw Blog
- Productivity
- Collaboration
5 Small Business Problems and Solutions
Lean startup: the right strategy or fool's gold.

Six Reasons Why Companies Lose Their Best Employees
Smartdraw makes diagramming easy.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Infographics Business Plan Infographic: Everything You Need to Know [Ideas, Templates & Examples]
Business Plan Infographic: Everything You Need to Know [Ideas, Templates & Examples]
Written by: Victoria Taylor May 13, 2021

Creating a business plan can seem daunting at first but it’s much easier than you think. Your challenge really begins when you want to create a business plan that stands out . Instead of sending over a 50-page document that bores your audience and hardly gets any point across, why not use a business plan infographic?
Using infographics for writing a business plan allows you to visually illustrate your research, pitch, and business structure in an engaging and creative way. Business plan infographics can be used internally or externally with investors or partners who want a quick overview of what your business has to offer.
In this article, you’re going to learn everything you need to create a business plan infographic that will wow your readers and showcase your business at its best.
Not a designer? No problem. Use our professional, fully customizable templates and Infographic Maker to create an engaging infographic today.
START CREATING FOR FREE
Want to learn more about other types of infographics? Read our blog on the 9 main types of infographics or watch the video below:
Click to jump ahead:
What is a business plan infographic, why use business plan infographics, create a goal for your business plan infographic, the best types of business plan infographics, what’s included in a business plan infographic, how to create a traditional business plan infographic, how to create a lean startup business plan infographic, business plan infographic examples, key design elements of a business plan infographic, how to get the most out of your business plan infographic.
- Business plan infographic FAQ
An infographic is a collection of imagery, charts, and minimal text that gives an easy-to-understand overview of a topic.
Being a type of business infographics , the business plan infographic is a collection of text, images, charts and other data visualizations to give an overview of your business plan.
As it’s in the form of an infographic, business plan infographics are normally 1-page documents with visualized data, making them both engaging and easier to skim and scan.
These 1-page business plan infographics can be a reflection of your sales plan , marketing plan, business expansion plan or business stats that you’d like to share with your investors or employees.
Here is an example of a business plan infographic template that presents a 5-step guide to business continuity:
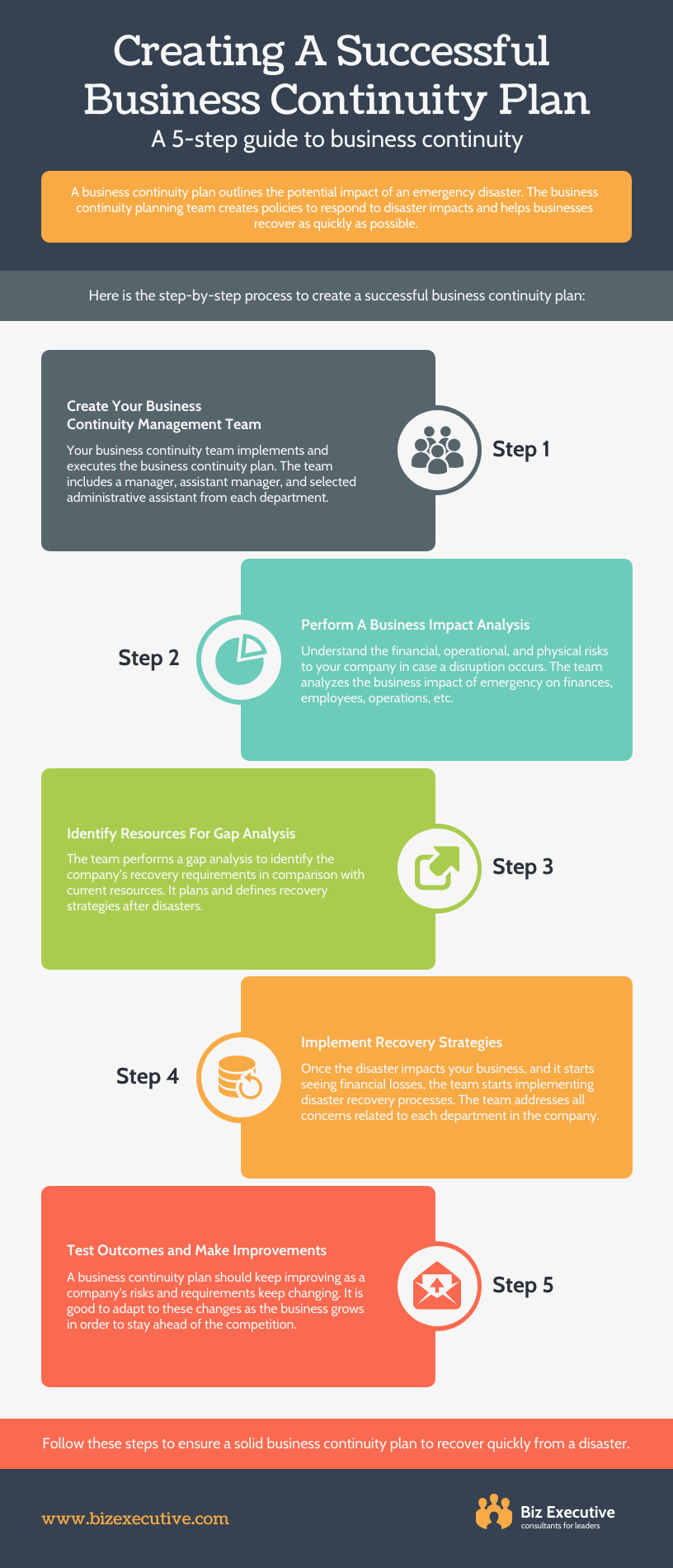
CREATE THIS INFOGRAPHIC TEMPLATE
Return to Table of Contents
Infographics easily allow you to present detailed information in an easy-to-read or simple format so that the viewer can quickly understand and process the information faster than if you had handed them a full-page report.
We live in a fast-paced world where not everyone wants to download a report, view a business plan , or read an entire blog post to get the information they need. Infographics make the whole process a lot easier.
As most humans are visual learners , your business plan infographics will highlight only the essential and important information while being entertaining and eye-catching so readers stay focused.
CREATE THIS PLAN TEMPLATE
Using an infographic for a business plan also makes it easier for stakeholders to understand your ideas and increases the chance of a successful business pitch.
Business plan infographics are also a great way for you to educate investors, employees, or partners about the structure, purpose, and future of your business. It should accomplish three main goals:
- Clarify your project and steps towards growth
- Showcase an exceptional understanding of your financial needs
- Educate investors, bankers, and lenders
Your business plan infographic should have a specific purpose or, rather, a specific topic to avoid confusing readers. For example, does your business plan infographic focus on a specific aspect or educate the reader on your position in a niche market ?
It’s crucial to keep your business plan infographic’s objective to a singular focus.
For example, if you’d like to educate people about how your business helps to optimize email management tools , your business plan infographic should highlight research backing this statement. Stick to the objective and try not to divert to the history of email marketing or how to use emails for your website.
You should also use relevant data for your business plan infographic based on the topic it addresses.
Data storytelling is the best way to use data to create new knowledge, decisions or actions without overloading your infographic with unnecessary information.
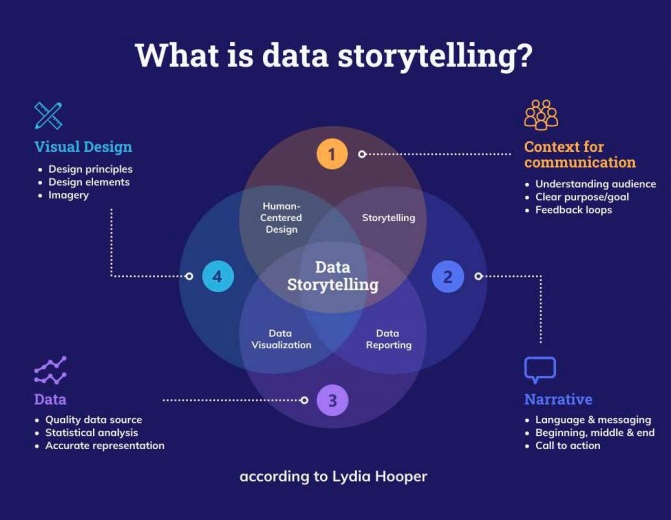
Only focus on the data that matters the most to your readers or industry. But use it in an interesting and educational way that allows the reader to get sucked into your business infographic.
The aim is to cut down the fluff so that readers can consume as much essential information as possible without being bogged down by unwanted data.
There are two types of business plans you can consider using to model your business plan infographic. You can create a traditional or a lean startup business plan infographic. Bplans states the difference between the two mainly has to do with the data that’s presented, as:
A lean startup business plan infographic
This type of plan has a high-level focus, fast to write, and contains key elements only. Some lenders and investors may ask for more information. It’s best to use when presenting a high-level overview with only key information. Most one-page business plan infographics are in this format.
A traditional business plan infographic
This type of plan is very detailed, takes more time to write and is comprehensive. Lenders and investors commonly request this plan. It’s normally in the form of a presentation or a business proposal and includes several business plan infographics altogether.
What you want to include in your business plan infographic might differ depending on the type of business plans you want to create, and we’ll go into more detail on this later. However, there are some common sections that you should consider when gathering information for your business plan infographic. Those include:
- Company profile
- Products & services
- Business model
- Risk management
You want to either include only key information on each of these sections or really elaborate on them depending on the type of business plan infographic you want.
This simple business plan mind map summarizes what you should include in a business plan infographic:
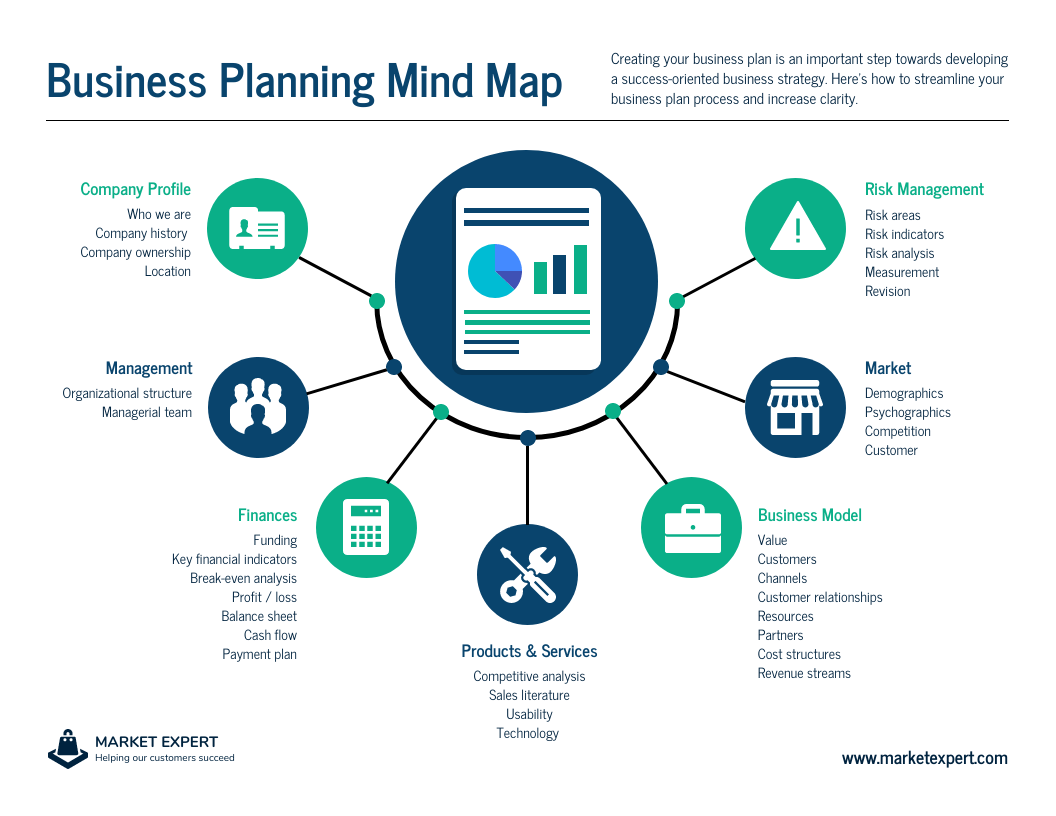
CREATE THIS MIND MAP TEMPLATE
When you’re creating a traditional business plan infographic you need to ensure that you have the following features or data in your infographic based on your objective.
Executive summary
This section should show your reader what your company is all about and why it’s expected to be successful. This means to include your mission statement, values, product or service, company positions, and basic information that will be helpful to know.
Company description
Go in-depth about your company mainly focusing on the problems and solutions your business will provide for your industry, target audience, or niche. In this section, you’ll also have to list out your competitors and how you’ll follow suit on gaining the competitive advantages.
You can include this marketing business plan infographic as part of this section:
CREATE THIS REPORT TEMPLATE
Market analysis
In this section, you’ll show research to show what other businesses are doing and what their strengths are, this means finding trends, stats, reports, themes, and successful breakthroughs that should be considered for your own business and how you can improve upon them.
Related : 20+ Strategy Infographics for Business Planning, Marketing and Branding
Organization & management
Summarize your overall business and legal structure in this section to let investors or bankers know if you’re a C or an S corporation . Take the steps to start an LLC, however, it’s essential to understand the laws and regulations in your state, LLC fees and other aspects that most lawyers recommend. It would also be helpful to add an organizational chart to allow readers to visually see the company hierarchy.
Also, utilizing an LLC Operating Agreement Template can provide a comprehensive framework for defining ownership, management structure, and operational procedures within your limited liability company.
Related : 15+ Company Infographic Templates, Examples & Tips
Service or product
Take the time to give a good first impression about what exactly your service or product does. Showcase the product or service lifecycle with charts and share plans for legal steps surrounding your product or service like copyright or patent filings.
Related : 7 Ways to Show Product Value Using Infographics
Marketing & sales
Outline an overview of your launch marketing strategy and how it will evolve and grow over time to fit your goals and market needs.
Financial projection or Funding request
If you’re sharing this section with an investor then you should focus on convincing them that your business is financially stable to be invested in. This means sharing a prediction of income statements, break-even analysis, return-on-investment calculations, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the coming 2-5 years of your business.
Related : 14+ Finance Infographics to Simplify Financial Information [Templates and Examples]
This Coral Technology Pitch Deck is a perfect example of a comprehensive traditional business plan agency infographic in the form of a presentation that can be used on PowerPoint or Google Slides:
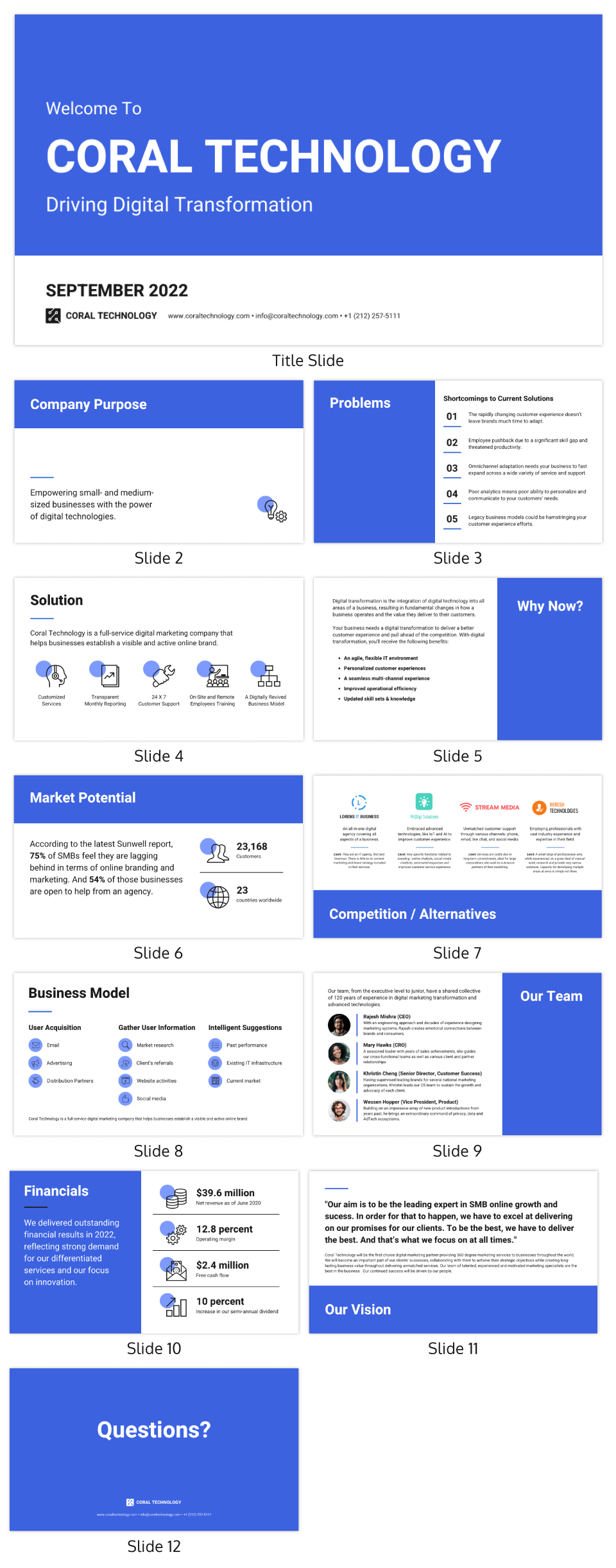
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION TEMPLATE
A lean startup business plan is much “leaner” as the word suggests. This is also shorter than the traditional business plan. A lean startup business plan infographic includes:
Key partnership
In this section state the other businesses or services that you’re working with to run your business’s operations. These could be key suppliers, manufacturers, subcontractors, and partners.
Business activities & resources
List in detail how your business will acquire the upper hand in your industry. Highlight features such as selling directly to consumers or taking advantage of the sharing economy. Run down any assets you’ll use to make an incentive for your customers.
Value proposition
This is a statement that shows the reader what unique value your business offers to your target audience in your niche or industry.
Customer relationships
Create a product or service flow of how consumers will interact with your business. Will this personalized, automated, or specialized based on their needs. You should also list the channels you’ll be using to reach, maintain or optimize for your customers over time.
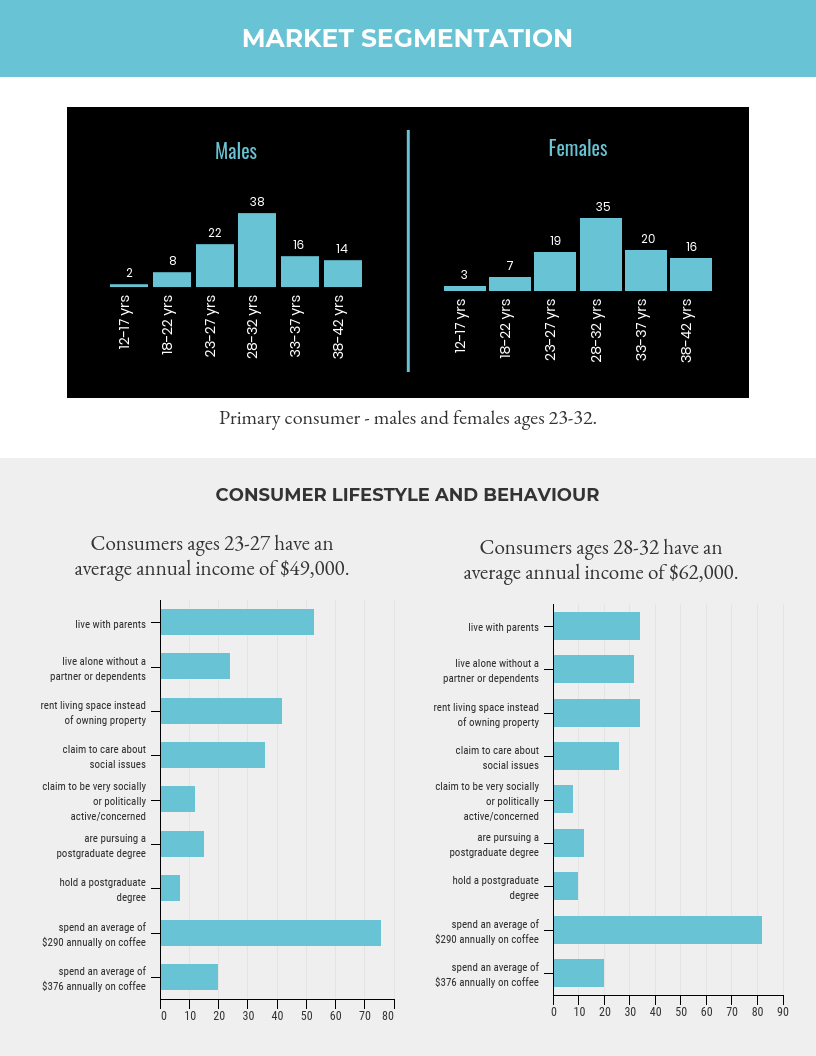
Customer segments
Describe who your ideal customers are in detail. List out who or where your target market will be and how your business will service and connect with them.
Cost structure
This section is similar to the financial projections segment in a traditional business plan, but this also includes how your company will reduce cost or maximize value as you balance significant costs that may challenge your startup.
Revenue streams
Use this section to explain how your startup will become profitable over time and will be used such as membership fees, subscription payments, selling ad space, and obtaining retainer contracts.
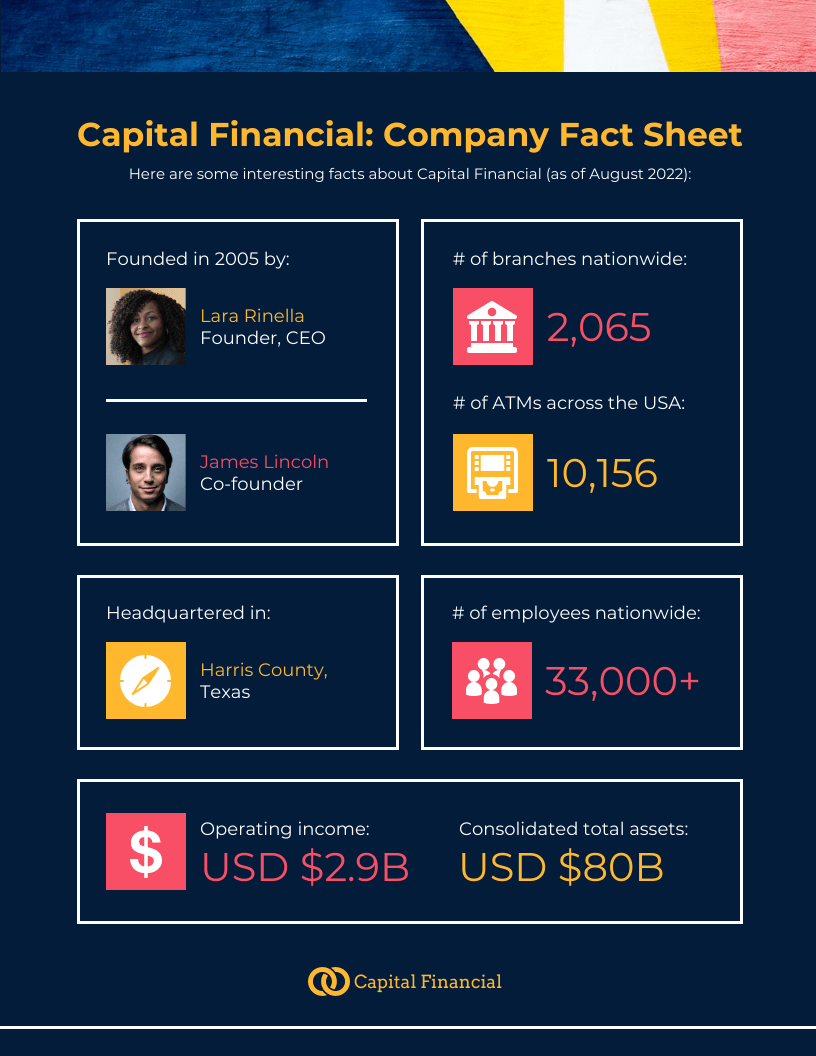
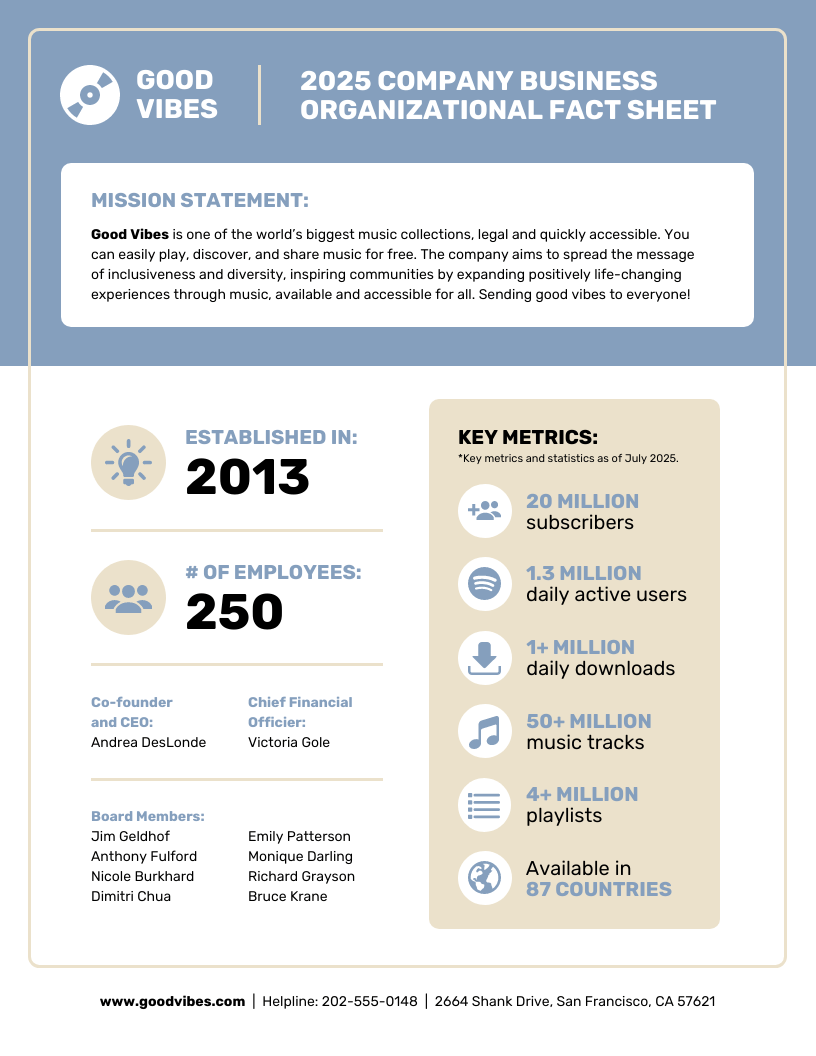
This Financial Company Business Fact Sheet is a good example of a lean startup business plan infographic as it gives an overview of the business with key figures only:
Let’s take a look at some more business plan infographic templates and examples.
Free business plan infographic template
This Light Company Business Fact Sheet is a good example of a free business plan infographic template that belongs to the lean startup type.
Marketing business plan infographic
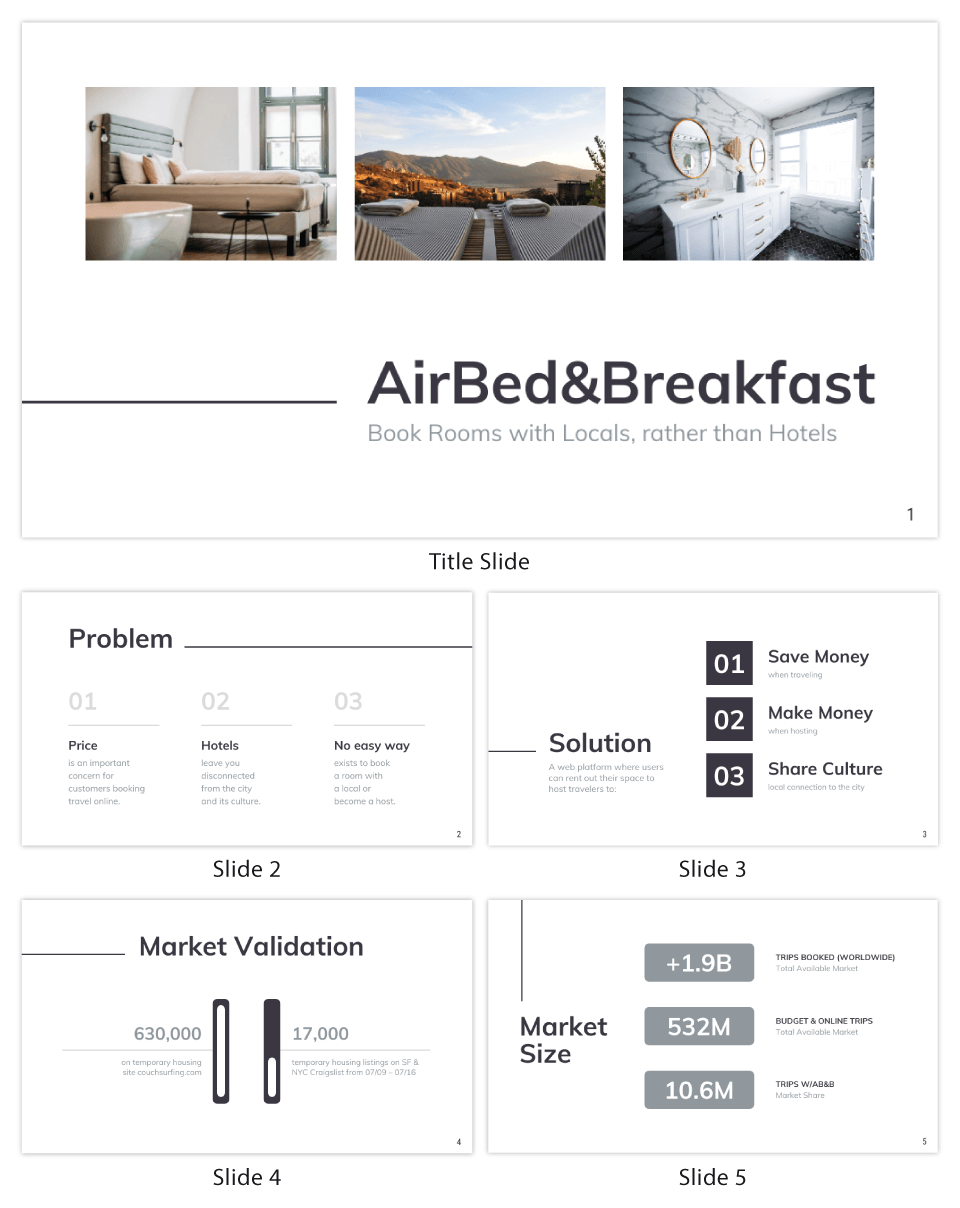
On a different note, this Yellow Marketing Business Plan leans towards the traditional type, being in the form of a comprehensive marketing business proposal that contains multiple infographics.

Real estate commercial business plan infographic
The information in this real estate business plan infographic is broken down in the form of a presentation, making it easy to use in business pitches.
There are three main aspects of a business infographic: visual elements, content elements and data or facts used.
As simple as an infographic may look, putting all three of these elements successfully together can be the difference between good infographics and a cluttered and confusing infographic.
Since we already covered data, let’s dive into the visual and content elements of your infographic.
1. Choose an ideal infographic layout
Infographics come with multiple layout options. Layouts help you to decide how you want to share your story or data with the reader. Layouts also guide your designs and colors. Most layouts are recognized by columns or sections, as shown below:
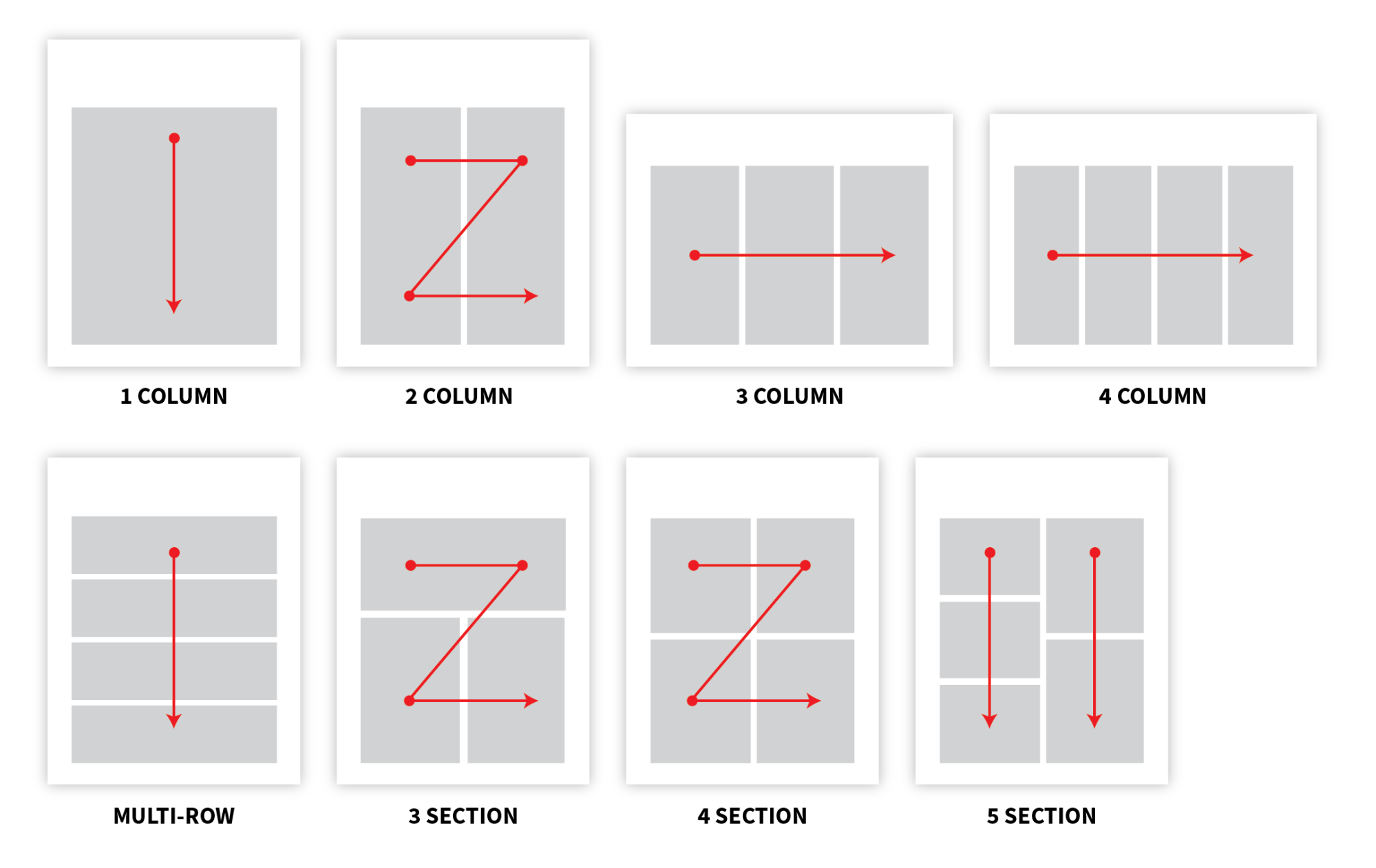
If you’re not someone whose every design is savvy, you don’t need to memorize all these layouts instead, just remember these three main infographic layouts: stacked , comparison , and chronological . For more information, read our blog on how to choose the right infographic layout .
2. Select captivating colors for your infographic
Other than usingy our brand colors, you always want to keep in mind who your audiences are, what action you want them to take and how colors can affect that.
If you need help picking the right colors for your business plan infographic here are two guides that are sure to help you:
- How to Pick Colors to Captivate Readers and Communicate Effectively
- The Do’s And Don’ts of Infographic Color Selection
Or you can watch this short video on color relationship and how that affects your design:
3. Choose the best content elements
Content elements represent the icons or charts you’ll be using to represent your data. Instead of simply dropping numbers and stats you want to give readers a visualization of what the data means and how it’s transitioned through your topic.
For example, if you want to represent the difference between the growing number of brands going wholesale vs retail, you could use a stacked bar chart to compare the two industries.
If you’re not sure about how to select the best chart for your data when you’re putting the final touches on your infographic design, check out our guide on selecting the right charts for your data , or watch the short video below:
The real work starts once you’ve created your business plan infographic. You’ll now need to effectively showcase or share your infographic in a way that allows you to get the most out of it.
If you’re using your business plan infographic for internal purposes then consider:
- Adding it to your onboarding documents
- Using it for presentations
- Sharing it with new or current investors for specific projects
- Showing team roles and hierarchy
Business plan infographics can also be used for external purposes to pitch to potential investors or new clients. They’re normally in presentation or proposal form, as we can see from some of the examples above.
Another thing to consider is to make your infographic mobile-friendly. Not all investors or partners look at documents from a business from a desktop. Having a well-optimized infographic allows the reader to get the full experience from your business plan infographic regardless of what device they may be viewing it on.
Business plan infographic FAQ
1. why should i create a business plan infographic.
A business plan infographic with data visualizations and concise, key information allows stakeholders to take a quick look at the current state the company is in and understand right away. This improves the success rates of your business pitches, whether they’re for investors, clients or senior management.
2. How do I make my business plan infographic look professional?
Make sure you keep in mind your brand guidelines while creating your business plan infographic to ensure consistency and professionalism in all comunications materials. You can also customize one of ours ready-to-use infographics which are designed to be used for businesses.
3. How do I create a business plan infographic?
Start by registering for a free account for Venngage’s Infographic Maker . You can then choose from our wide variety of business plan infographic templates that you can create using our easy-to-use editor, no design skills needed.
In summary: Business plan infographics are great to use for both internal and external purposes
Consider using business plan infographics whenever you need to deliver a sales plan presentation, pitch a new project or present your services to new clients.
Venngage has hundreds of business plan infographic templates you can use to create your business plan infographic with no coding or design experience required.
Need to make an infographic? Start creating in seconds with our professional templates and simple online editor.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How to Write a Business Plan Built for Success (Hint: Visuals)
A business plan is how you put your best foot forward to potential investors, but it can be difficult to understand how to write a business plan that succeeds. We…
Article Last Updated: February 05, 2024

What Needs to Be in a Business Plan Document?
Business plan guide: 8 steps.
A business plan is how you put your best foot forward to potential investors, but it can be difficult to understand how to write a business plan that succeeds. We get it, we’ve been there, and sometimes putting your dream down on paper leads right writer’s block.
Your best tool against this bump is planning. You’ve got to do the heavy lifting of research and reporting before you hit the keyboard, or else things can quickly get muddled and unrealistic. To help, we’ve put together this step-by-step plan for how to write a business plan with thoughts on the information to gather and what to include.
Read on to get started, and don’t forget to start thinking about visuals to include in a business plan so your audience is able to stick with you to the end.
There are a lot of great resources to use when determining how to write a business plan. Read as many of them as possible. Your business is worth it.
One especially useful place for business plans as well as learning about funding, contracting, and paying those taxes when your business gets rolling is the Small Business Administration. It’s experts have a list of elements to include in your business plan that they continually refine and refresh.
Here are a few core pieces from the SBA’s list as well as results from our experience and thoughts that should be included in your business plan documentation:
- Executive summary: This is a short-and-sweet explanation of your company, why you’ll be successful thanks to products or services as well as leadership. Think of it as your Shark Tank pitch.
- Company description and value proposition: Give the highlights of your company, your MVP vs MLP and what makes you valuable. Explain the problems that you solve, general customer info, and
- Market analysis: Discuss your market in both long-term potential as well as your near-term customers.
- Products and/or services: Describe your specific product or service line and what it looks like for you to create and offer those. Discuss any benefits you have, such as IP, patents, copyrights, or other protections.
- Company management: How is your company structured and who will run it? Explain the legal entity of your business and the management structure.
- Partners and providers: Discuss the partnerships your business has already, note if you already have partners like manufacturers, and any resources you have related to these groups.
- Marketing and sales strategies: Describe your broad approach to marketing and sales, including customer retention. Tie it to your market analysis to discuss how you’ll reach that market, because that success will define your financial project.
- The Ask: Here’s where you make your funding request if the reader is a potential investor or lender. Outline funding requirements and needs.
- Financial projections and roadmap: Boost your ask by showing the financial projects and your product roadmap. Explain where you plan to grow over the next five years as well as where you are right now. The more detail you can provide for your first year, the better.
- Supporting documents: A business plan almost always needs an appendix, which is tailored specifically to your audience. In some cases, you’ll want credit histories and letters of reference. Usually, you’ll want product information including photos, licenses, permits, and legal documents.
We’re starting off by thinking about the document itself because that can help you frame all the work you’ll do when creating your plan. Each of the steps outlined below play a vital role in understanding your company, its value, potential market, and how or why someone might fund you.
If you get stuck on a step or aren’t sure if something should be included, look at the pieces of the business plan identified above. When what you’re working on directly correlates to one of those elements or if you think it would boost the argument you make in a section like “The Ask,” then include it.
Now, let’s get to the hard but worthwhile part.
When you’re thinking about how to write a business plan step-by-step, keep the goal and final document in mind. Thankfully, it’s something that you’ll be able to start pulling together when you use this and other business plan guides.
Getting started doesn’t have to be difficult, especially when you follow the steps.
Step 1: Do Your Homework on Your Market
Define your products and services, then research everything about them. You’ll want to look at your products and if they solve the pain points you’ve addressed. Look at competitors and their market opportunity. Learn as much about your customers, competition, and market as possible. Define them as clearly as you can and rank most immediate opportunities and threats.
Look at others’ business plans too. They might show you good market data or products. Pay attention to visual communication! You’ll never truly understand why you must include product visuals in a business plan until you put yourself in the shoes of an investor and look at two similar pitches but only one has visuals.
Step 2: Do You Homework on Your Business
After you look at the market where you can play, it’s time to do some self-reflection. How well is your business poised to enter in that market? How much of an impact can you make? What can derail the whole thing?
Be honest about your company, products, team, and funding. Part of a business plan is to help you identify where and how to grow. If you’re using it to raise funds, you’ll also need to know where you’re weak so you can identify where you’ll spend to help maximize any investor’s return. Using spend management tools can make this process easier once you get your business going.
“Consider spending twice as much time researching, evaluating, and thinking as you spend actually writing the business plan,” is good advice to follow .
Step 2 can be the hardest for many entrepreneurs and startups. Great ideas do start market revolutions. However, that triumph only occurs when customers outside of that company adopt the ideas. Turn to partner, mentors, and people you trust to get an honest evaluation of your business. If you do get criticism, turn that language into positives that show you where to grow and invest.
Step 3: Define Your Plan’s Purpose
Now that you know thy market and self, it’s time to define your document. Business plans can serve a variety of purposes depending on the audience. Do you want to use it to raise venture capital? Are you seeking a traditional business loan? Is this a part of a pitch to a local business Meetup where you want help fleshing out an idea?
Clearly define the purpose of your document so you can understand and address the most important people reading it.
Let’s say you’re using it to share with friends to see if they like the idea of your business. Here, you may want to write it to a general audience who is just learning about your company, without a lot of the specific financial information. Once you have a plan people are excited by, then you can work on adding in broader market analysis so that you have a document you can bring to a loan officer.
Eventually, you’ll likely have multiple variants designed to accomplish different tasks, from gaining funding to exciting customers and planning your roadmap. Each version of your plan always needs a purpose.
Step 4: Tell Your Story
Your company’s mission and purpose are going to play a crucial role in how people perceive you. So, don’t skimp with a basic company profile that is a laundry list-style timeline of your founding. Tell a story about who you are, who the company is, and why you want to serve your specific audience.
Keep focus on the why about creating your company and what it offers. Readers, as individual humans, are going to connect with that why a little more. They’ll be drawn to a product that reduces stress and strain at work by making it easier to perform common tasks than one that reduces back office efficiency by 7% — even if they’re the same product.
Getting people to connect with your mission is a smart business plan guide for attracting talent. If you’re posting this on your site, think about sharing a vision that employees want to connect with too.
Step 5: Turn Homework into Documents
Some steps are more time-consuming than others and this one can be a lengthy process depending on how complex your business is already.
Your readers want proof of what you’re saying. This is especially true of investors looking for a return. So, your mission is to document as much as possible. Source your stats and industry projections, make copies of your contracts and patents, create records of your business expenses, and make it crystal clear what your cashflow is and that no one has their hands in the cookie jar.
Every license, agreement, producer, warehouse provider, and other contractor should be covered by your documents. You can use online tools, such as this digital receipt solution , to make and fill out any documents you’re missing.
Step 6: Build a Timeline
Put everything you have collected and understood about today and your targets together. It shows where you’re at and what you need to become to achieve your goals. Think of it as the first steps in the financial planning and projections that your business plan document will eventually need.
Go back to your competitor and market research to estimate sales and how long new product adoption takes in your area. Look at trends and habits in similarly disruptive situations too. Build your market and financial needs separate from your product/service rollout roadmap.
Bring the two together and try to understand where you need to adjust product to meet market or expansion plan based on the time it takes to code, manufacture, or provide your service. You’ll want to approach this from both a big-picture standpoint as well as very granular.
For example, let’s say it takes your manufacturing partner three months to ramp up for a new product. And, you know your market needs a new product each year. These considerations should give you general guidance as to when your new product would need to be ready and go to your manufacturer so that you and your distribution partners are ready.
You might need to finish R&D in Q1, get it to the manufacturer by the end Q2, create your marketing campaign in Q3 are your manufacturing partner hits inventory levels and ships to you, all for a Q4 launch because your product does its best work right ahead of and during the holiday shopping season.
Surprisingly, getting a timeline and understand that it might take you six months to hit the next big product innovation is a great way to get a handle on how your business should approach pricing structure .
Step 7: Refine Your Targets
The first six steps are all about gathering your data. Now, you’re ready to move into the construction phase of this step-by-step guide for writing a business plan. Your mission is to take the homework and build your story with a specific audience in mind.
Adjust everything based on the goal you have for the person reading your business plan. This potential reader must be specific — employees and VCs prioritize financial statements very differently – and you’ll want to cater to their interests or needs.
The closer you can write the document to speak to the concerns of your audience, the more likely they are to take the step you want. Usually, that’s financing your efforts. While you may want to include certain items or change the tone of some content, don’t adjust firm items like your financial numbers or project roadmap itself. Keep the core data the same.
Step 8: Deliver Big with Visuals
We’ll wrap up with the decisive step of this business plan guide: reviewing everything with an eye for visuals. Listen to the wisdom of authors throughout the ages and show, don’t tell. Visual communication is essential in your business plan because readers demand speed and clarity.
People want to be able to understand who you are and your position, but walls of text won’t do that. Not only do text-only pages fail to “wow,” they can also bore your audience and cause them to mentally checkout.
We’ve all seen Shark Tank where people needed an exciting pitch to win over someone skeptical. Seeing how a product works often was the trick!
New tech means you can show your readers your product or service in action in a variety of ways, no matter where they are or how they’re looking through your plan. Zight (formerly CloudApp) makes it easy for anyone to create videos, screen recordings, image snippets, GIFs, annotated photos, and more. You can even turn elements into videos, such as an explainer in your executive summary that allows people to see your vision right away. You’ll look like a professional without having to pay through the nose.
The brain processes images 60,000x faster than text. Try this free trial here to see if Zight (formerly CloudApp) can make your business plan 60,000x faster to get to “yes!”
Create & share screenshots, screen recordings, and GIFs with Zight
Get Zight for iOS.
How to Improve Your Business Plan Using Visualization
Updated on: 26 August 2021
For the past 20 years, I’ve been helping entrepreneurs and business owners write business plans. In doing so, I’ve learned that the perfect business plan must be both functional and easy to read.
With regards to functional, a business plan should provide a clear roadmap of how you’re going to grow your company. And with regards to “easy to read,” your plan can’t include pages and pages of text sure to make readers cringe.
Rather, you want people to enjoy reading your plan, so they take the action you desire such as funding your business.
Fortunately, when adding Creately to your business plan, you can make your plan both more functional and easier to read.
To confirm this, I used my core business plan template and brainstormed the best places to add Creately diagrams to improve your business plan. Below are five areas I found where Creately can provide significant value.
Company Overview
In the Company Overview section of your business plan, you want to detail what your company has already accomplished to date. This is because past accomplishments are a great indicator of future success.
A Creately chart, like the one below, is a great way to show these accomplishments.

Industry Analysis
It’s very important for readers to understand the size of your marketplace.
And oftentimes your business may compete in more than one market. Using a Venn Diagram within Creately is a great way to quickly explain to readers the markets you’re targeting and their sizes.

A great visualization technique to illustrate your company’s position within the industry is a SWOT analysis.
A SWOT analysis illustrates the strengths and weaknesses that exist within the internal environment of the company and opportunities and threats that exist within the external environment of the organization.
It can help you effectively present the current position and the circumstances of your company within the industry to the reader. Creately has many professionally designed SWOT analysis templates so you can get started instantly.

Key Operational Processes
Your business plan should detail the key day-to-day processes that your company performs to generate sales and profits.
Having a Creately flowchart , like the one below, allows you to easily document your processes and show them to others.

Risk Mitigating Milestones
A “risk mitigating milestone” is a milestone that, once completed, reduces the risk your venture will fail. As such, investors and lenders need to understand your milestones and how they relate to one another.
The Creately Gantt chart below allows the reader to quickly and easily see your company’s milestones. You can even add in times when additional funding might be required.

Management Team
Great ideas are a dime a dozen. Great management teams are not.
The fact is that the quality of your management team is crucial to your company’s success. In your business plan, you should detail who is on your team and your reporting structure.
Also, if you need to hire a key person to improve your team, you should include the title and responsibilities of that person in your plan.
A great way to show your management team in your plan is via a Creately Organization Chart as shown below:

In summary, making your business plan both functional and easy to read will dramatically improve its success, and Creately is a great tool to achieve this most easily.
Dave Lavinsky is a serial entrepreneur and the president and founder of Growthink , which since 1999, has helped hundreds of thousands of entrepreneurs create business plans. Dave is also the founder of BusinessPlanTemplate.com which provides templates for specific niches ranging from restaurants to internet businesses.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

More Related Articles

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Please enter an answer in digits: 18 + 4 =
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning.

Why a Visual Business Game Plan Is Vital and How to Make One
As a business owner, you know that a well-thought-out plan is essential to the success of your business. But what about a visual business plan? Sure, a traditional business plan is important. It gives you a roadmap to follow and helps you track your progress. But a visual business plan is even more important. Why? Because a visual business plan makes your goals and objectives more concrete. It helps you see the big picture and develop a clear strategy for achieving your goals.
Plus, a visual business plan is more likely to capture the attention of potential investors and partners. After all, who doesn’t love a good infographic?
That said, let’s talk about the importance of a visual game plan and how you can create one:
Table of Contents
The Importance of a Visual Business Game Plan
As a business owner, you know that having a plan is essential to success . But what you may not realize is that a visual business plan can be even more helpful in keeping you on track and making sure your business goals are met.
Think about it, a visual business plan can provide a clear overview of your business goals, what you need to do to achieve them, and what your timeline looks like. This can be an invaluable tool for keeping you focused and on track.
Plus, a visual business plan can be a great way to share your vision with others, whether that’s your team, your investors, or your customers. A well-designed plan can help get everyone on the same page and moving in the same direction.
So How Do You Create a Visual Business Plan?
1. Start with a Mind Map
A mind map is a great way to brainstorm ideas and visualize your business plan. Simply create a diagram with your business idea in the center and branch out from there.
2. Use Infographics
Infographics are a powerful way to communicate complex information in a visually appealing way. When creating infographics for your visual business plan, be sure to use simple graphics and easy-to-understand data visualizations.
3. Use Charts and Graphs
Charts and graphs are another great way to communicate complex information visually. When using charts and graphs, be sure to use clear and concise labels.
4. Use Photos and Images
Photos and images can help bring your visual business plan to life. When selecting photos and images, be sure to choose ones that are high quality and relevant to your business.
5. Keep It Simple
When it comes to your visual business plan, less is more. Use simple graphics and concise text to make your point. After all, you want your visual business plan to be easy to understand and easy on the eyes.
By following these tips, you’ll be well on your way to creating a visual business plan that will help you achieve your business goals.
A visual business plan can be a powerful tool for any business owner. By providing a clear overview of your goals and strategies, it can help you stay focused and on track. Plus, it can be a great way to share your vision with others. So, don’t wait! Get started on your visual business plan today!
AMW is a full-service marketing agency that is an expert in music promotion , event management, and so much more. If you are looking for a business promotion firm to work with, reach out to us today!
Home Blog Business How To Craft & Deliver an Effective Business Plan Presentation (Quick Guide)
How To Craft & Deliver an Effective Business Plan Presentation (Quick Guide)
A vital element in today’s highly competitive business landscape is the ability to craft and deliver a business plan presentation. This applies to both entrepreneurs and corporate leaders.
This guide describes essential aspects required to build a business plan presentation and deliver it to stakeholders.
Table of Contents
What is a Business Plan Presentation?
Is a business plan presentation the same as a business presentation, executive summary, justification of the business proposal, swot analysis, the niche of the proposal & actors in the industry, competitors, competitive intensity, trend analysis and critical variables, value chain, market analysis, jobs-to-be-done, value proposition, revenue streams, cost structure, distribution channels, key partnerships for the business model, organizational structure & management, go to market and marketing plan, development plan, qa, and continuous improvement model, distribution plan, inventory management, initial funding and financing structure, projection of income and costs.
- Evaluation of Projected Return vs. Required
Risk Evaluation
Sensitivity to critical variables, how to present bibliographical information in a business plan presentation, how to deliver a business plan presentation.
A business plan presentation is the medium we use to communicate a business plan to an audience.
Presenters commonly ask what is the target length of a business plan presentation in terms of slides. Our expertise in this field tells us it’s advisable to work between 13-20 slides, remaining as concise as possible and using the help of visual aids. Let the graphics speak rather than fill your slides with text blocks.
No. A business plan presentation is used to communicate an identified business opportunity and how it is planned to be served in a way that generates profit. A business presentation is a more generic term, explained in our article about business presentation examples .
How to Create a Business Plan Presentation
This section will list our recommended content for a successful business plan presentation. We broke it down into four stages which help the presenter build the story backing the business: a-. The opportunity and the competitive landscape analyzed, b- the business model designed and tested to serve the opportunity, c- the implementation plan of the business model, and finally, d- the financial and economic projections estimated that show the profitability of the opportunity.
For the purpose of this guide, the slides will refer to a case study of photo editing software. To replicate this slide deck creation process, you can speed up design decisions by working with the SlideModel AI Presentation Maker and tailoring it to your project.
So, how to make a business plan presentation? Let’s see a step by step guide.
Stage 1 – Identifying the Opportunity
After the title slide that defines how to start a presentation , any business plan should proceed by introducing the executive summary in a concise but impactful format.
The purpose of the executive summary is to inform the audience what to expect from the presentation and its conclusion.
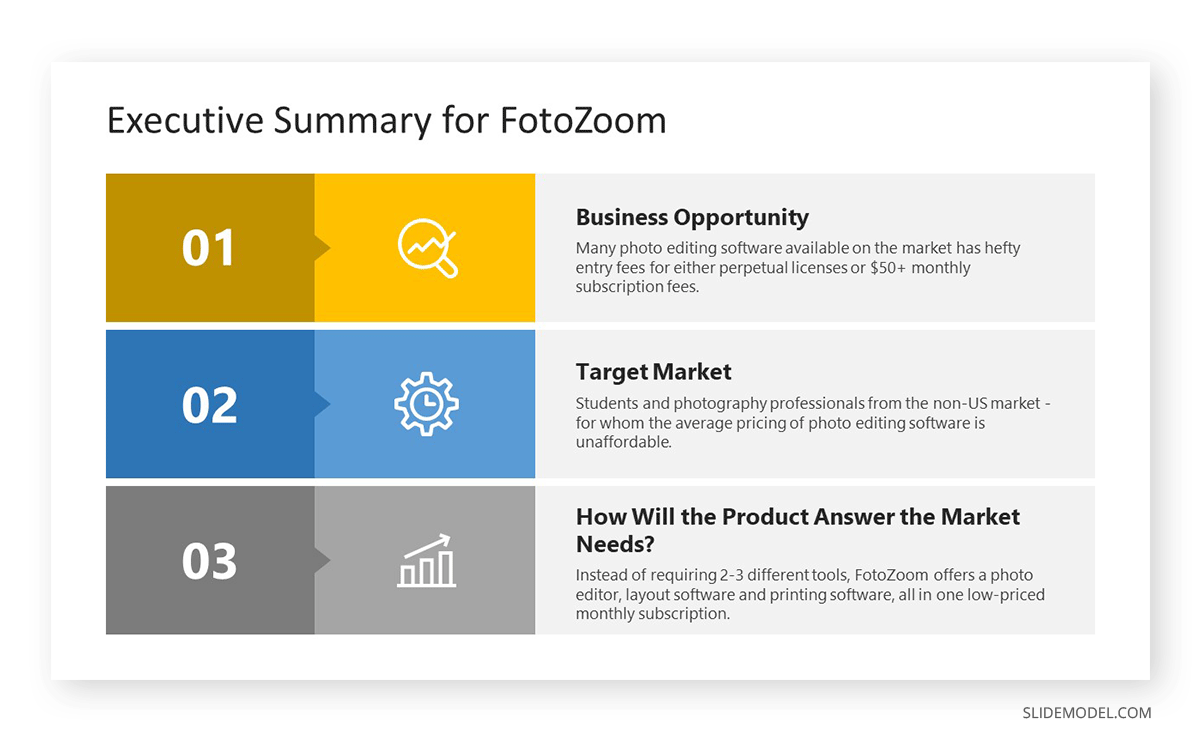
Work with a maximum of two slides for this section, highlighting the key elements through visual cues. Check our guide on how to present an executive summary .
The next slide should disclose all the reasoning behind the business plan proposal, why this plan is being presented at this present moment, and projections of how the plan aligns with the current market trends.
Presenters can share the analysis done by the Market research team as long as it’s made clear which problem is relevant to the current market trends that this business plan aims to solve.
Mention all the references used to arrive at the conclusions expressed so data is backed with meaningful sources.
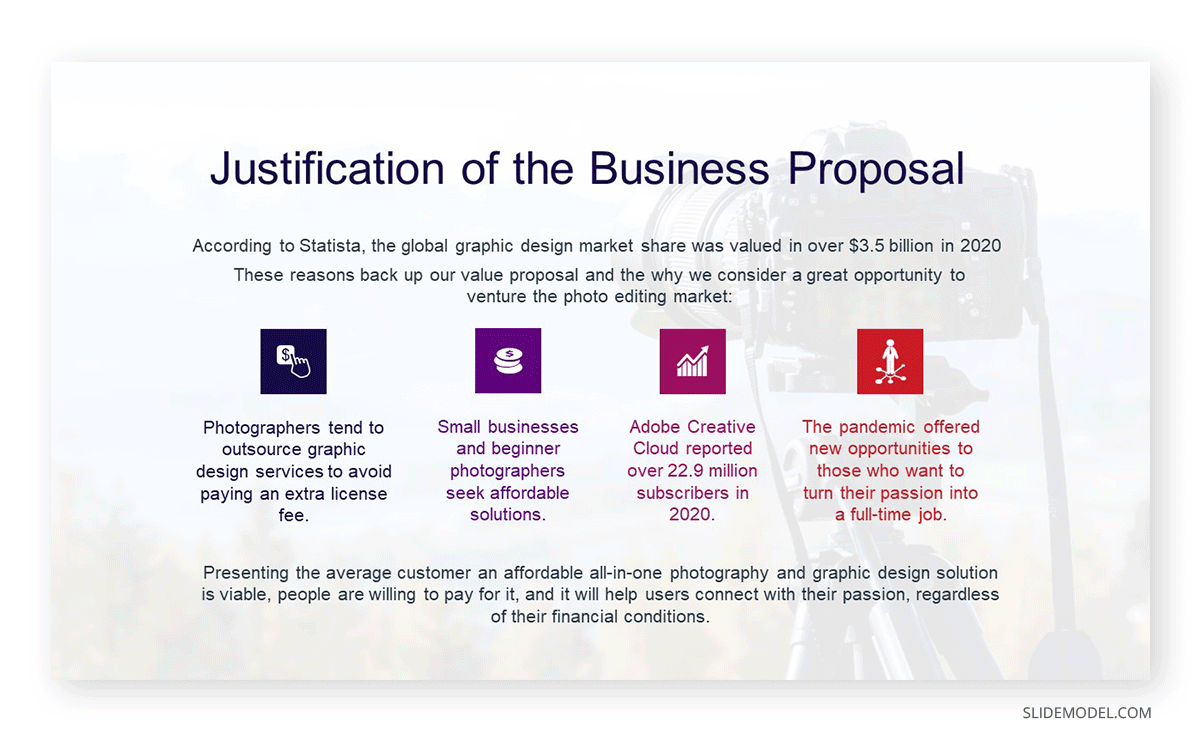
Any corporate PPT template can help you craft this slide, but presenters can also boost their performance through the use of infographics . If your solution for the selected problem involves a complex process, consider using a process flow template to expose the step-by-step justification of this proposal.
Use a SWOT template to showcase the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of this business opportunity.
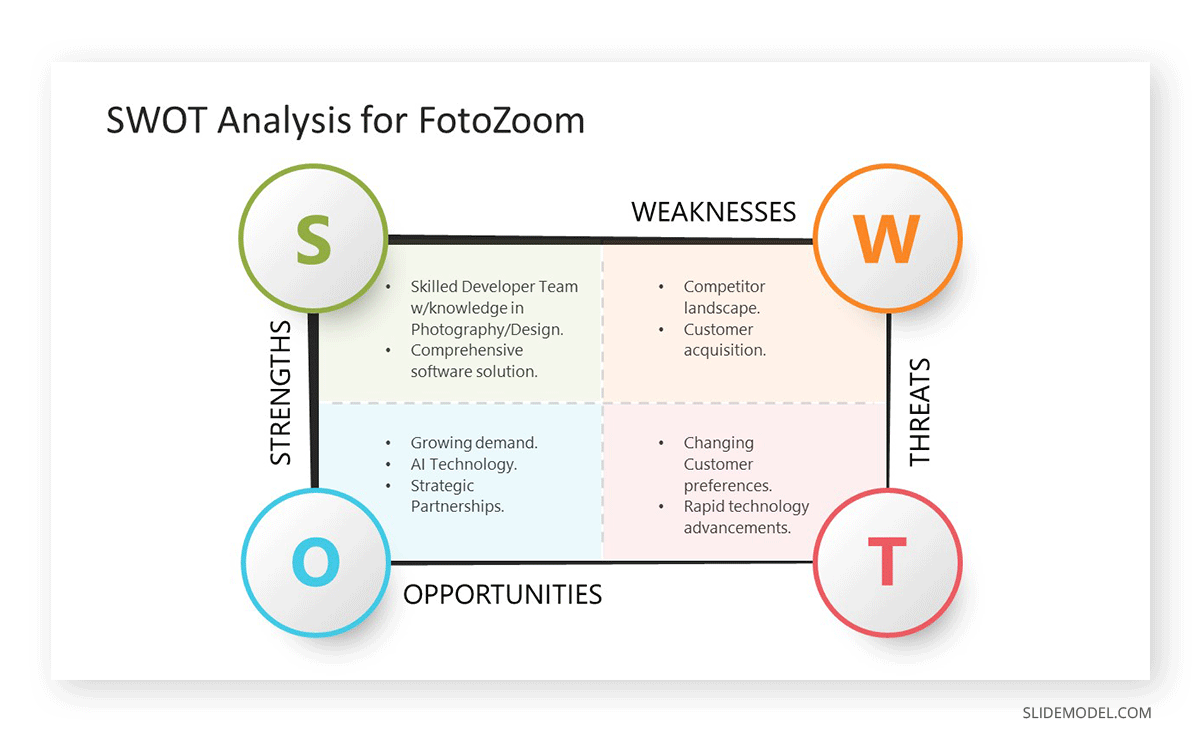
Make sure the SWOT diagram is legible. Work your way to meet the same aesthetic style despite speeding up the process with templates. Mention the tools used for gathering the information for this SWOT Analysis in the footnote and ensure the audience understands which information elements help you reach conclusions in each quadrant. Check our guide on how to create a SWOT analysis and see if your business plan requires a SWOT or SOAR analysis .
Every business plan is scoped under a niche or industry sector. With this slide, describe the sector in which the proposal is immersed. Communicate its value, list the actors involved, and describe their high-level relationships.
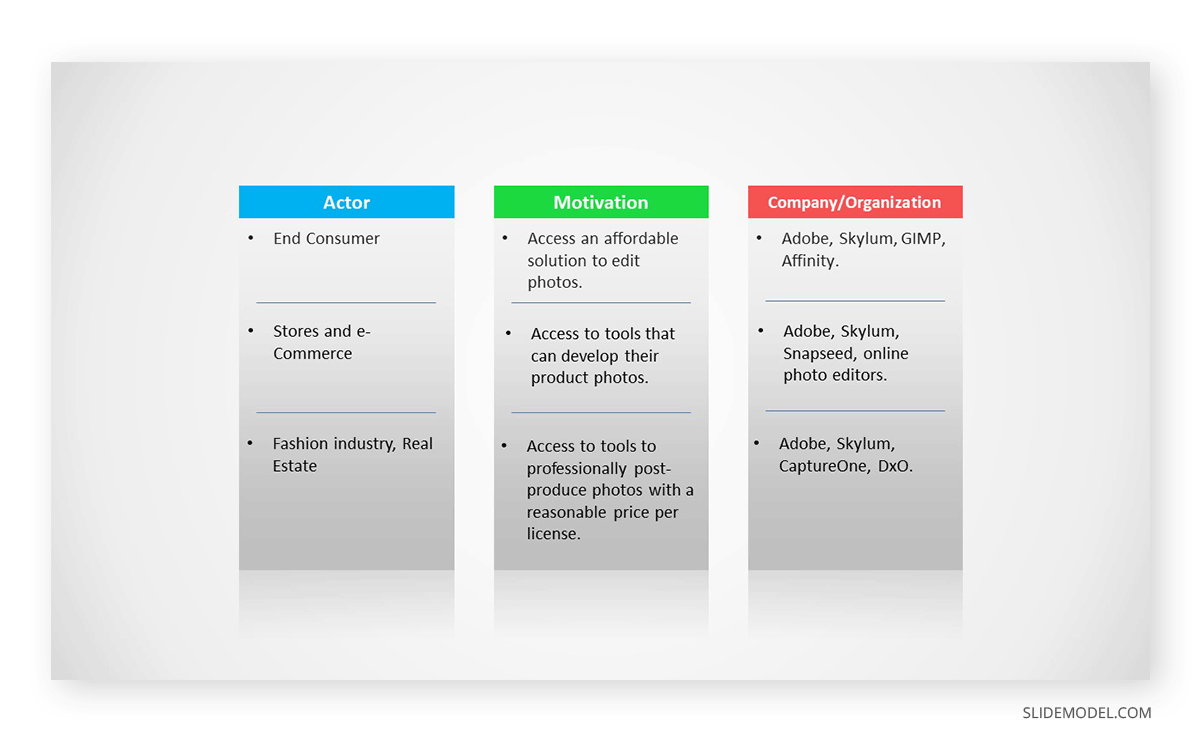
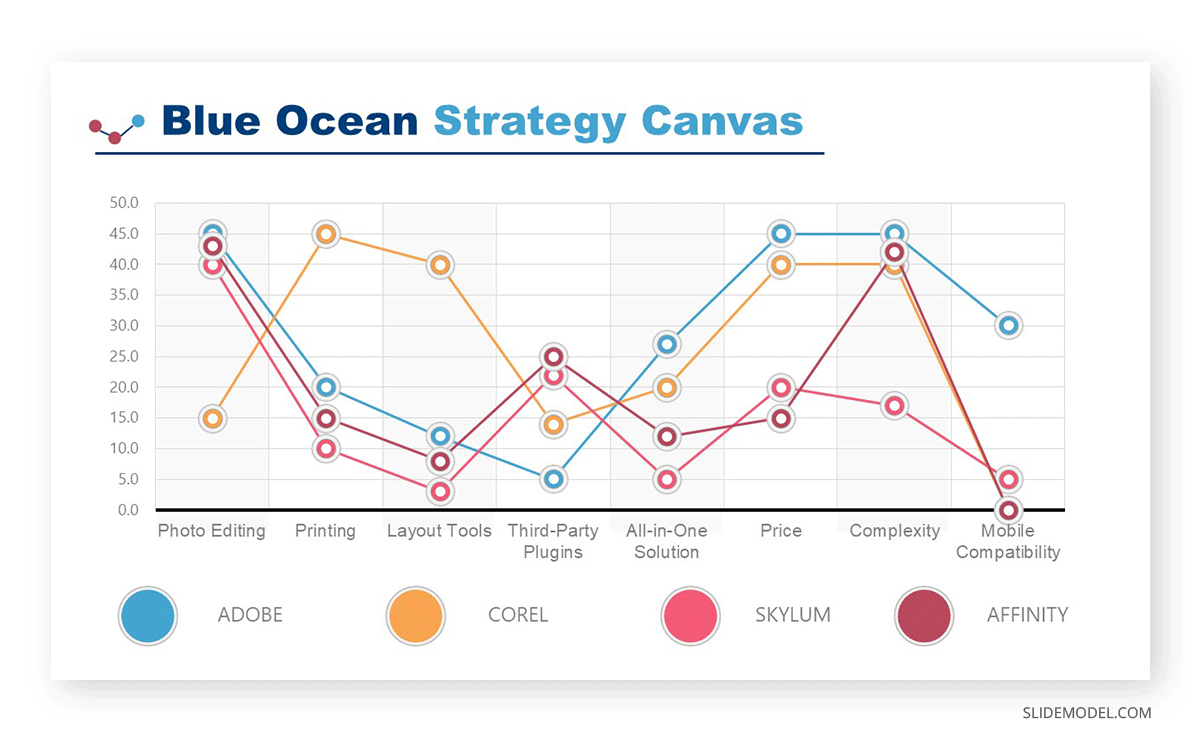
List the analyzed competitors. Communicate their attributes. The competitors’ comparison in business plan presentation can be visually explained using tools from the Blue Ocean Strategy framework, like the Strategy Canvas .
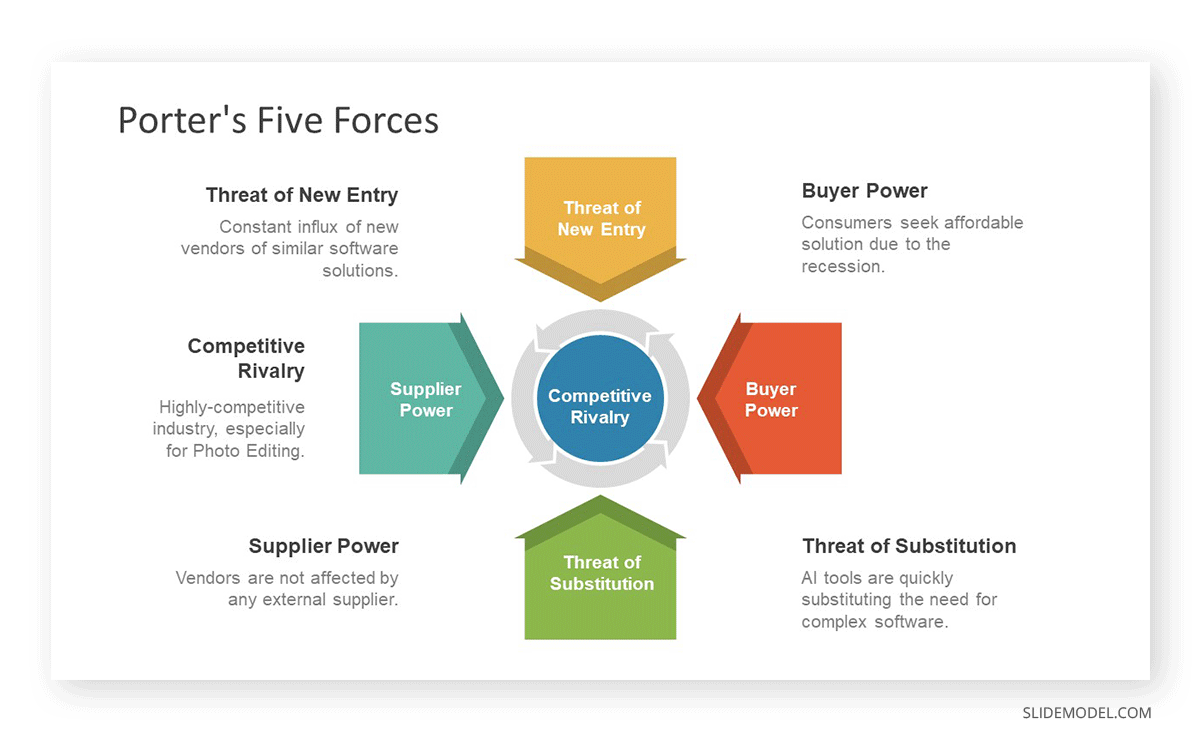
The competitive intensity of an industry sector is studied through the Porter’s 5 Forces model. This intensity expresses how attractive the industry is. Explain the conclusion in each force showcasing the model.
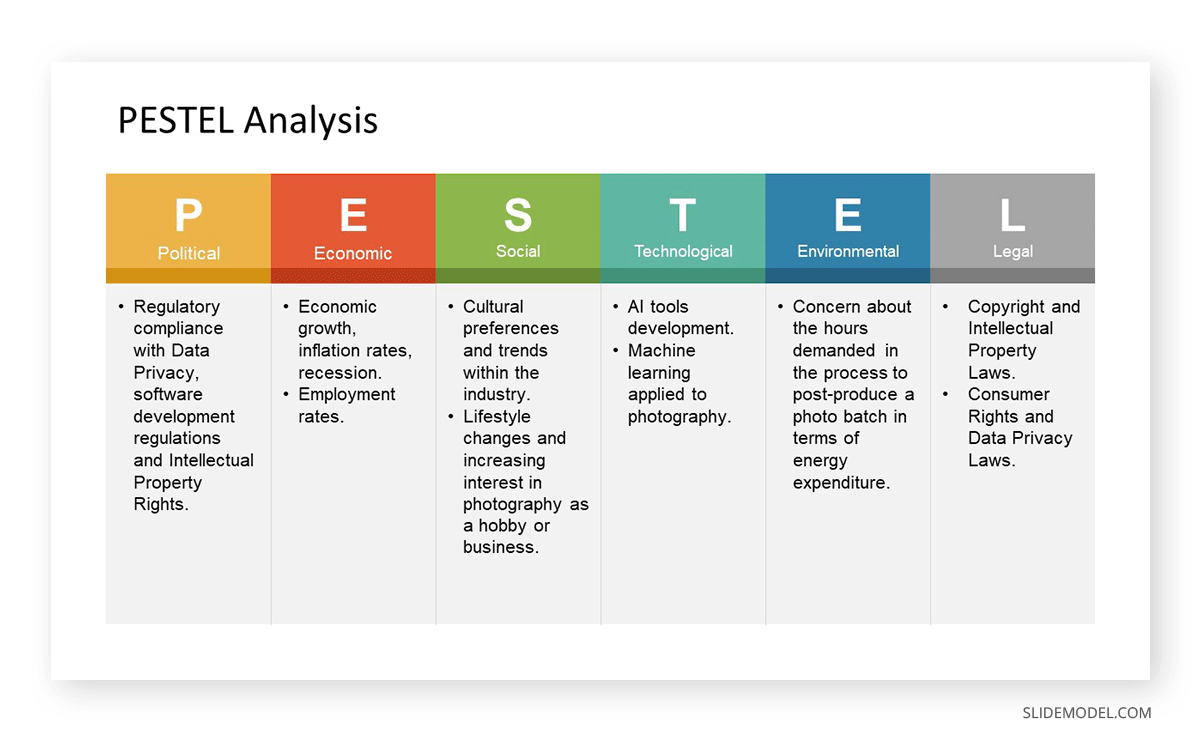
First, introduce the variables identified as important for the industry sector, citing the insight’s source. Secondly, drill down each variable and break down the different trend dimensions ( PESTEL )
- Use a highly visual slide, like a dashboard template , to introduce factual data regarding the trends over a specific time period. Growth rates must be represented in time frames of over 180 days to evaluate the trend accurately.
- List the critical variables (consumers, product, production capability, and financing) briefly.
- Disclose how each variable can affect pricing and your position within the niche for that trend. Presenters can refer to case studies from successful competitor stories on how they responded to trend changes in the niche.
When presenting the value chain, we ought to articulate the sequence of activities the company handles to create value within the business plan. Start by breaking down the value chain into its key components, briefly explaining the stages from inbound logistics all the way through customer service. It is important to highlight the linking point between each stage and express the value of coordinating team activities to enhance overall efficiency.
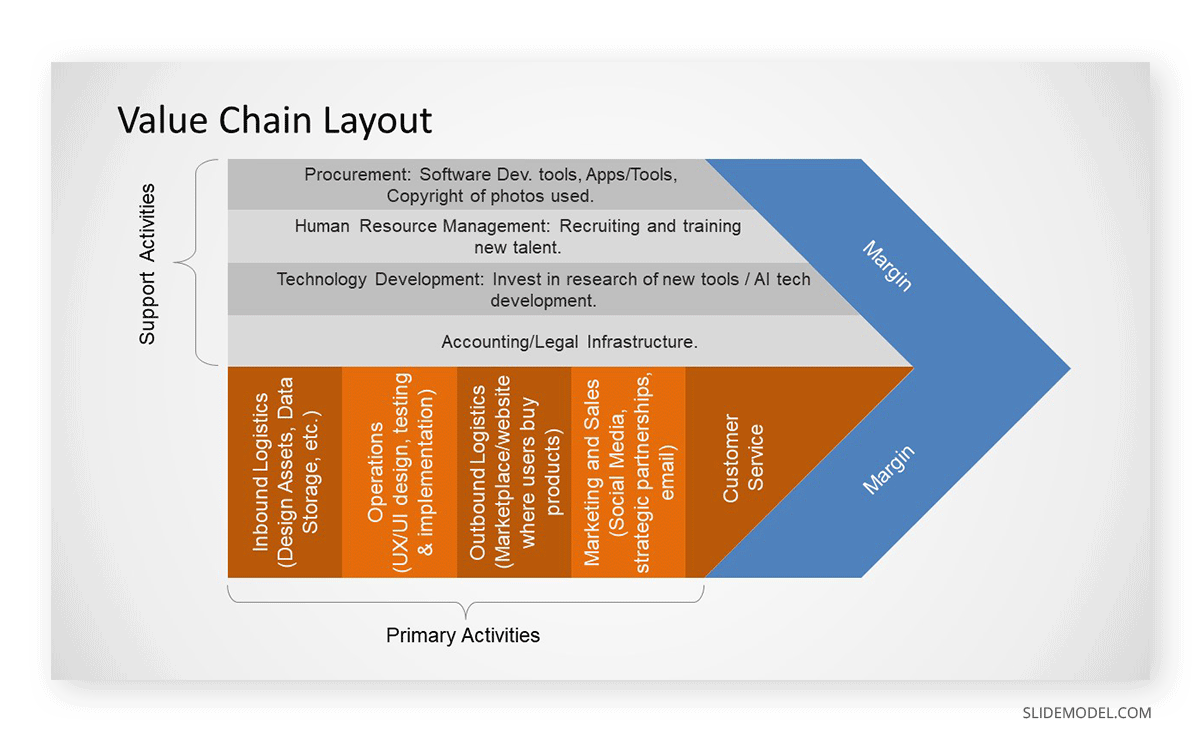
We can use flowchart diagram templates as visual aids for the audience so they can understand the process sequence. Check our guide on how to make a flowchart .
Present the identified Market and its Segments. Continue explaining how conclusions were driven through the analysis and sizing of the market.
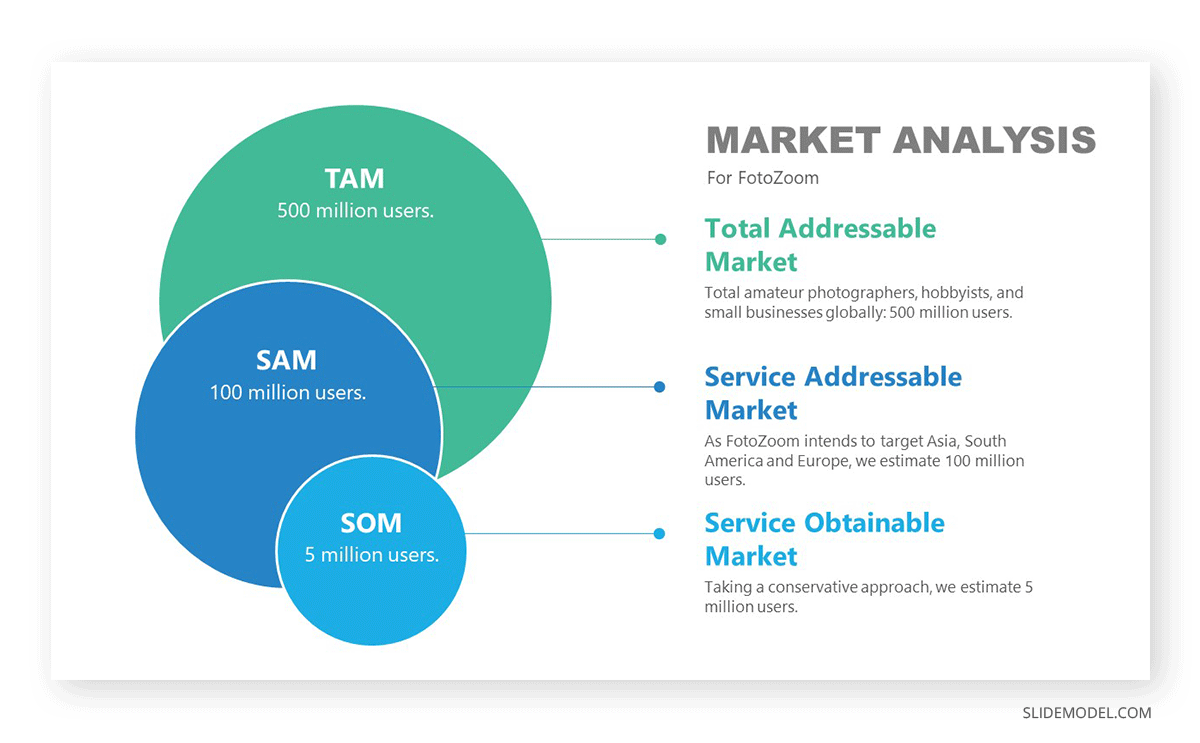
Presenters can use target market analysis templates , market segmentation templates , or TAM SAM SOM templates to compare their target market with the total available market.
We recommend you check our guide on market segmentation for this process.
Then drill down with a Persona definition.
This study can be made by creating ideal customers, describing their demographics and psychological factors that make them prospective candidates to purchase the product or service this business plan presentation refers to.
Here is our guide on creating buyer personas .
The Jobs-to-be-Done theory explains why certain customers are attracted to products and services and how those elements solve core problems in the consumers’ lives.
A Perceptual Map is a tool we can use to measure the consumer perception of different products/services in the same market. This can be particularly useful if our value proposal is to brand ourselves as cheaper alternatives to already existing solutions. Check our guide on perceptual maps for further information.
Check our guide on the Jobs-to-be-Done framework and add suggestions to the business plan presentation.
Stage 2 – Business Model
To describe the Business Model in your Business Plan Presentation, use the business model canvas analysis tool. Display your design in one slide.
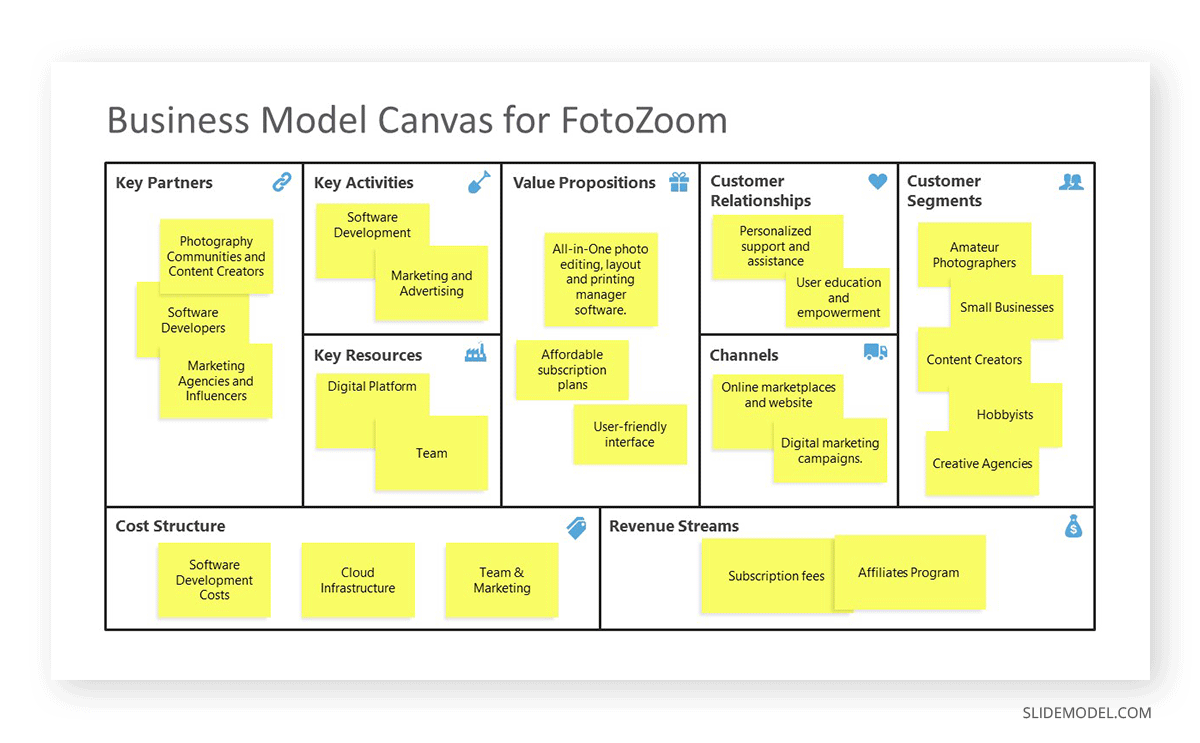
For specific sections of the BMC, you can add slides if you need to drill down for further details. In our experience, the following sections require a deeper level of explanation.
List the Segments targeted in your Business Model. You can include a slide with additional information and segment size. Reference the Market analysis explained earlier to justify the selection or which were the pivots applied.
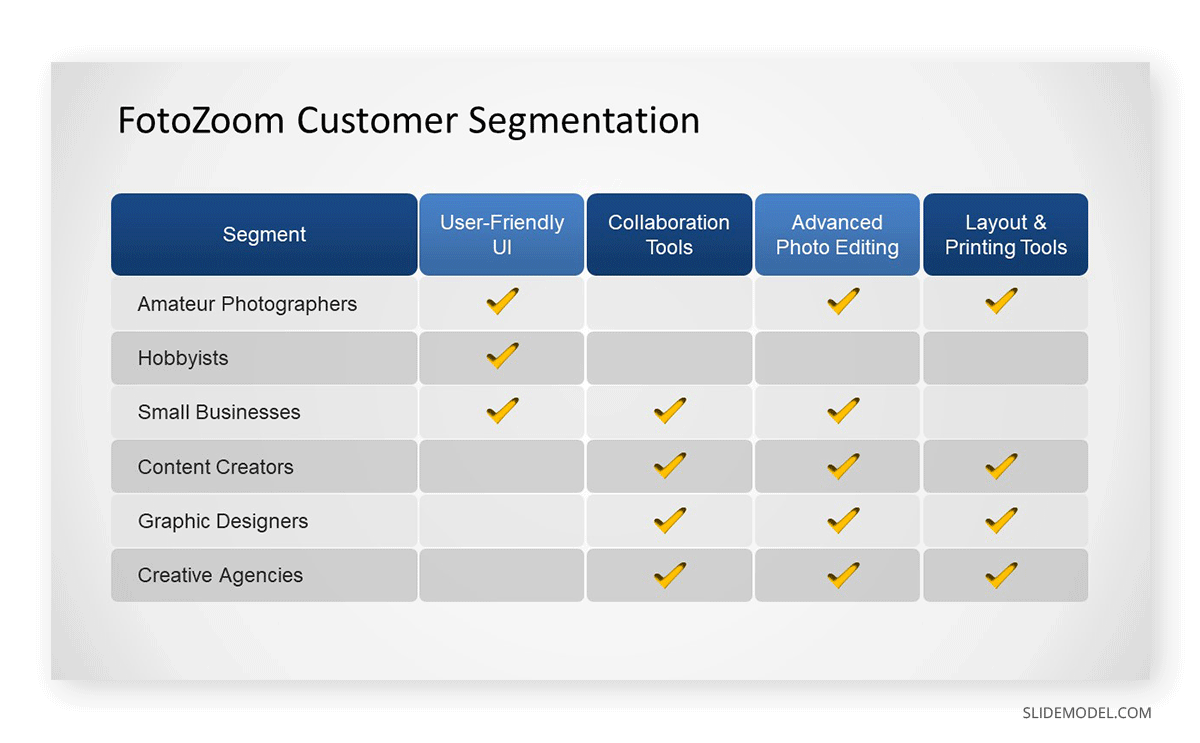
In order to explain the reasoning behind the Value Proposition and how it serves the segments selected, you can use the Value Proposition Canvas tool to explain the logic behind this selection.
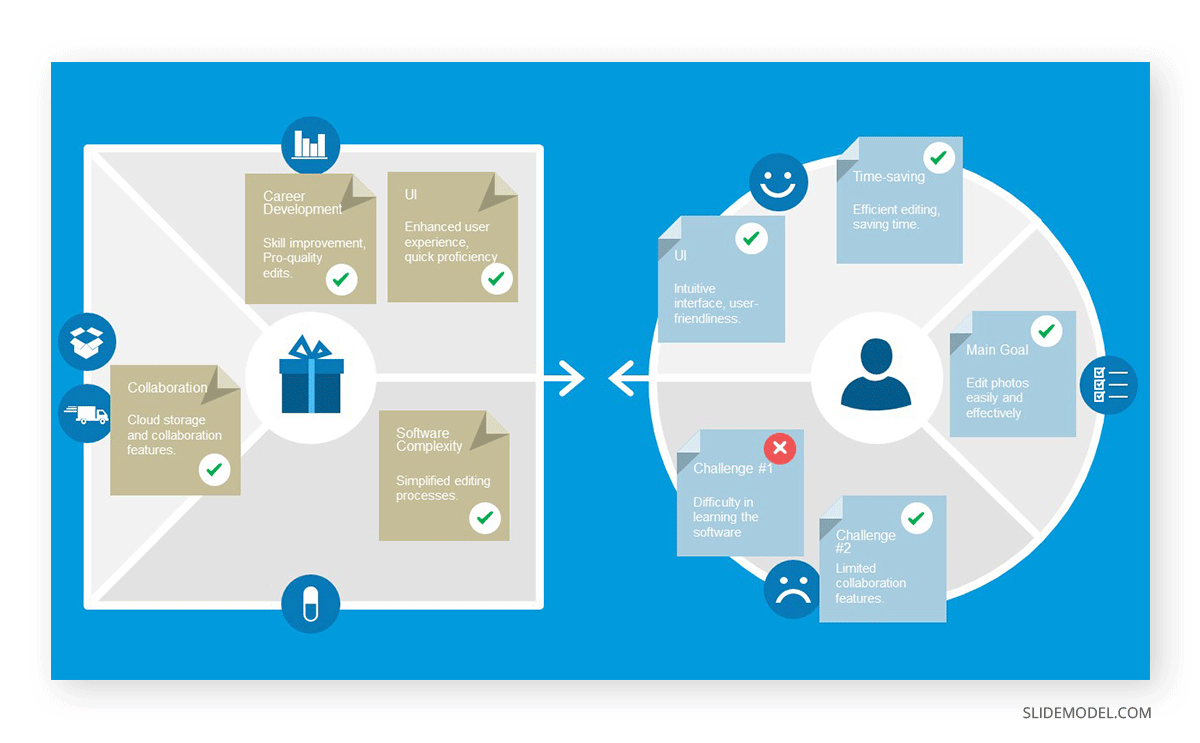
The Value Proposition outlines the unique benefit our product or service offers the market and why customers should choose our offer over potential alternatives. Since we have already analyzed the potential buyers and presented the market, it’s time to deliver that value proposition using our best assets: customer testimonials, report data, surveys, etc.
As testimonials often weigh the most in established brands, be sure to present this information through a narrative that showcases why your product or service had a positive impact on the life of that customer. You can use customer testimonial templates to give an extra boost through visual aids.

Explaining how much the customers will pay for the product/services is critical to understanding the viability and profitability of the business. Showcase for each segment the pricing model and the engagement terms.
The Income Model expresses the sources of revenue for our business plan. This has to be in relationship with the pricing strategy for established businesses. Lean startups can work concerning their minimum viable product (MVP) and then elaborate with projections for future releases or changes in their income stream structure.
At this point, companies need to present the sources of revenue depending on their origin:
- Product Sales
- Subscription Model
- Freemium Model
- Partnerships with other brands in different niches
- Advertising and Sponsorships
- Monetization
Check our guide on pricing strategy models for more information about how to present this point. You can use revenue stream templates to represent this data in style.
Drill down the cost structure categories and relate them to the Value Chain explained earlier. Show a cost breakdown chart to make it easier for the audience to understand their weight in the total costs.
As this step can be a bit complex to articulate, we recommend you check our guide on Cost Structure to see how you can resume all that information in one slide.
At the business model stage, distribution channels should be briefly introduced since they will be mentioned again in the Distribution Plan . In some industries, it is important to highlight which channels are chosen over others for the sake of revenue and faster operation.
Our Distribution Channels PowerPoint Template is a perfect resource for this.
Presenting the strategic partnerships for the business plan is a way to prove the plan’s potential reach and success factor. On this behalf, companies must list which resources they are sharing with their business partners regarding expertise, technology, distribution channels, or capital, as these elements will impact the cost structure.
You can use the Business Partnership PowerPoint Template to present this information in a professional-looking format.
Stage 3 – Implementation
The business plan is designed to offer a product, deliver a service, or combine both. At this stage, the business plan presentation drills down on how the organization will build/deliver the product/service implementing the business model outlined earlier.
Describe how the company operates regarding human capital and its roles. Presenters must describe to the audience the hierarchical structure, responsibilities, and how they play a role within the value chain.
You can use Org Charts to represent the roles and responsibilities in the organization visually. It is also advisable to highlight the expertise and experience of the management team, as it helps to build trust.
The Human Resource Plan must refer to your planned recruitment, training, and employee onboarding. Which talent will be required, and how is it planned to build the different teams of the structure.
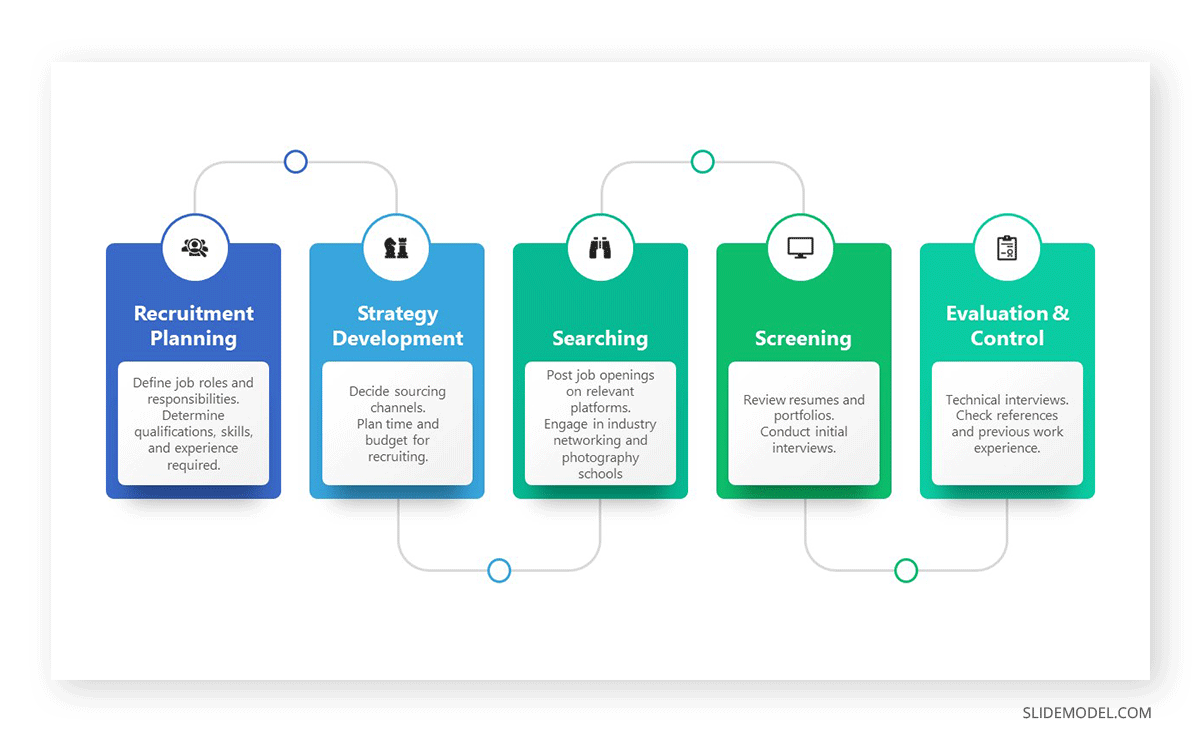
Check the Go To Market Strategy guide and describe how the Business Plan will enter the market and overcome the initial barriers. Continue with the Marketing Plan limited to 1-2 slides resuming the plan’s tactics to increase brand awareness and the selected channels for this strategy.
You can use the Marketing Plan Templates help to speed up the process by focusing on the content to fill rather than the design or creating complex charts from scratch.
Present the sales plan describing the full sales process, lead generation, nurturing customers, and conversion strategies.
Use Sales PowerPoint Templates to visually illustrate your sales process, like the Sales Pipeline Slide Template for PowerPoint , which depicts the process from lead acquisition to a closed deal.
Check our guide on Sales Plan for further information on this topic.
This step refers to presenting the product/service development plan, the Quality Assurance processes behind its validation, and your company’s commitment to a continuous improvement process based on surveyed data or customer feedback.
We can refer to testimonials, user case experiences our team successfully troubleshot, or experiences we learned from competitors in the same niche.
Presenting the distribution plan involves addressing logistics topics, supply chain , and sharing fulfillment strategies. Although we already presented the potential distribution channels, this is the step in which you detail how each will interact and their impact on the estimated revenue.
Present one slide mentioning your company’s approach to these channels, if applicable:
- Direct Sales (either physical store or e-commerce)
- Retail Partnerships
- Wholesalers or Distributors
- E-Commerce marketplaces
This step involves two different approaches depending on the kind of industry we’re in. For traditional business, inventory management in a business plan presentation must highlight how the inventory will be handled to minimize transportation costs or overproduction. Projections must be shown per quarterly period and take into account seasonality if it has a significant impact on the required storage capacity.
On the other hand, e-commerce companies have to present their online infrastructure to secure the product’s availability 24/7, how customer tickets are handled when the customer cannot access the product, server costs, and how we prevent online leaks.
Stage 4 – ROI and Risk Evaluation
This section will outline the Financial Plan of your Business.
Showcase the financial structure, including equity, debt, and potential investors, at the moment of kick-starting this business. It is a good practice to consider the initial funding slide to be a brief summary of those points, with particular emphasis on the funding needs.
Cash Flow Diagrams , Comparison Chart templates , and Timeline templates to showcase when funds help to meet each of the plan’s milestones are good ideas to represent the elements on this slide.
Income and expense projections must be presented over a defined time period by using graphs or charts to clearly visualize the trends supporting each change.
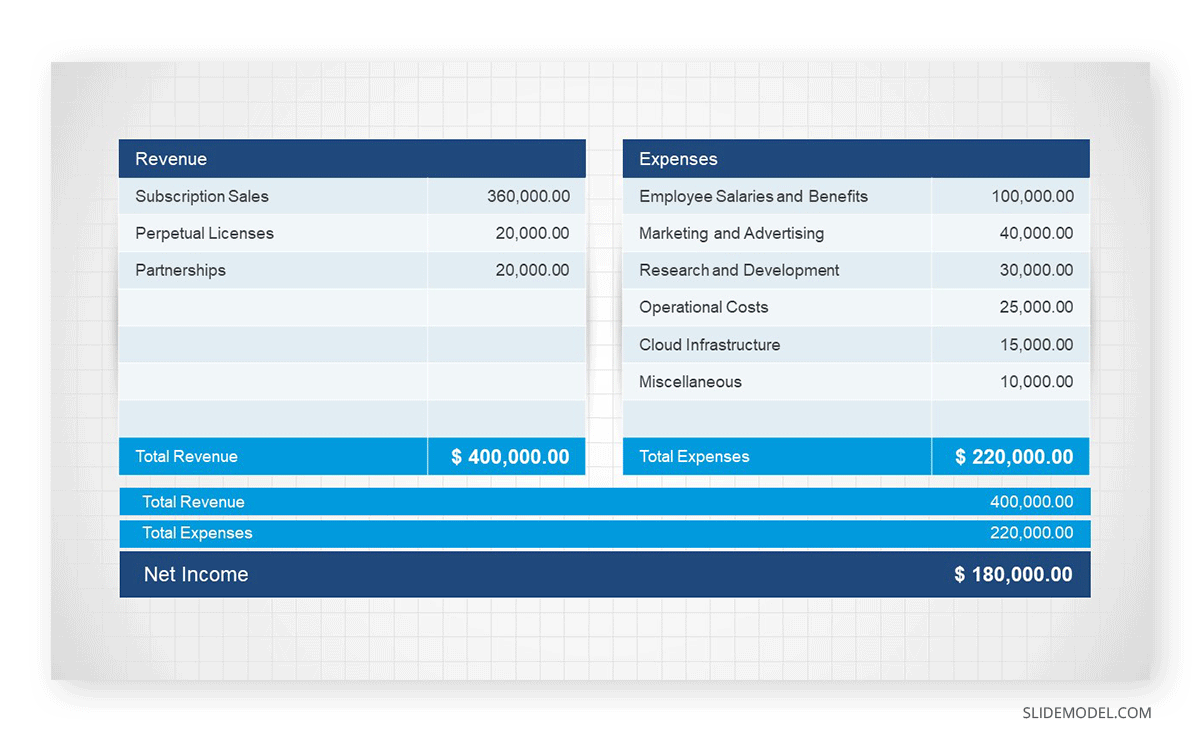
Break down the revenue sources with clear, identifiable icons to showcase: product sales, subscription fees, advertisement, affiliates, etc. Sales estimations have to be realistic and conservative, as they will be contrasted with the production, marketing, administrative, and personnel costs to leave a gross profit margin calculation.
Evaluation of Projected Return vs. Required
Demonstrate the feasibility of your business plan. Start by presenting the profit margins in relation to the projection of income and expenses, then introduce the break-even analysis .
Presenters can make their message more relevant by presenting an ROI calculation and contrasting it with industry benchmarks in the same niche. By following this approach, presenters prove how the ROI offered by this business plan aligns with the investment’s risk projection.
Presenting a risk evaluation analysis in a business plan presentation involves introducing both risks and their mitigation strategies.
Risk Management templates , like the ROAM framework, can help organize potential risk sources by their severity and impact on the organization. A pyramid diagram can be used to demonstrate how risk management can be delegated across the organization to completely eradicate the risk factor depending on its severity.
The elements you should consider presenting are mainly regulatory changes, market changes, competitors (new or existing), and financial crises.
The final point in our business plan presentation involves summarizing how key variables can influence the projected returns in our plan. Examples of these variables can be sudden increases in raw materials (affecting production costs and sales prices), a new pandemic (affecting workforce capacity and shortage of raw materials), geopolitical situations like war, etc.
We highly recommend presenting these critical variables using scenario analysis techniques according to measured data. Introduce best-case, worst-case, and most likely-case to give a full panorama of how your organization is prepared against any contingency.
An often overlooked point in a business plan presentation comes when listing the bibliographical information used to craft the business plan. Follow these steps to ensure a professional outcome for this slide or document.
- Use a title like: “Bibliography,” “Source Credits,” or “References.” If your business plan presentation cites examples from other companies, use a “Works Cited” section.
- References are usually shown in the APA style, but the MLE or Chicago style can be requested depending on your location or situation.
- Maintain a consistent style in terms of reference style used, font, text size, and formatting options across the entire slide deck. Footnotes or in-text citations can be used for important data.
- Verbally acknowledge your sources when required throughout the course of your presentation. This helps to establish credibility and respect for other people’s work rather than just dropping a slide with chunks of text.
This section will cover the most commonly asked questions on delivering a business plan presentation.
How many slides should my business plan presentation list?
This will depend entirely on your niche and the complexity of the business plan. Generally, work with at least 15 slides and no more than 30. It is best to use an extra slide rather than overcrowd an existing slide with tons of information.
What is the best format to present a business plan?
There are different options to present any business plan, so the selected option will mostly consist of the presenter’s preferred style and the audience’s age and interests.
- PowerPoint Presentation : You can start from a blank slide and go all the way through a professionally designed PPT template . PowerPoint documents allow you to present images, text, audio, videos, and any kind of graphic to help you convey the core ideas behind the business plan. They can work with any PC or Mac device, as well as mobile devices.
- PDF Documents: This can be a choice made in a hurry or by preference. Sharing a PDF document can work, but you must include the fonts used in the original document, as some compatibility issues can be present.
- Pitch Deck : Rather than doing a lengthy business plan presentation, a pitch deck consists of a maximum of 15 slides to deliver your proposal concisely. This is the typical approach we can see in TV shows like Shark Tank.
- Video Presentation : In some cases, using a video in a business plan presentation is relevant, especially if we are to introduce an innovative product in the market. You can use videos to showcase features, present services in a live format, introduce your team, and plenty of other options.
Are printables required in business plan presentations?
Although they are not required, using supplementary material in business plan presentations can be useful. You can prepare reference material for investors, especially involving complex data like graphs in an amplified format (and reference the slide in which they appear and vice versa).
Providing a printable to accompany your business plan presentation helps to give an image of professionalism and respect to your proposal.
What are the don’ts of writing a business plan?
The main purpose of this article is to craft and deliver a business plan presentation. Still, we would like to clarify some common errors seen in business plans that typically affect the performance of the presentation.
- Using overcomplicated language : Jargon or unnecessary acronyms may confuse spectators who are not in touch with all the details relevant to a particular industry.
- Ignoring the audience : Not considering the variety of interests among investors, partners, and team members can hinder your presentation.
- Neglecting/underestimating competitors : Any realistic business plan considers the existing competitors in their niche and perhaps potential newcomers. Not doing so will leave you unprepared to present a doable business plan.
- Ignoring Risk Assessment : Omitting the Risk Assessment analysis and mitigation strategies does not respect the value investors and your team have.
How long should the business plan presentation be?
As a general guideline, try to fit your business plan presentation between 20-30 minutes. Some complex plans may require additional time to be presented.
Does the presentation need to be tailored to different audiences?
Using this tactic can be a winning factor for both investors and your team, as you prioritize effective communication for the roles they are relevant. Take these items into consideration for tailoring the presentation for specific needs.
In-Company Presentation
The focus should be on goal accomplishment and the strategies targeted to the team’s roles. Emphasize how teamwork is the pathway to success and how each individual contributes to the bigger picture.
If new technologies or knowledge are required as part of the business plan implementation, then this is the moment to disclose that information and inform the process to coach the team into it.
Board Meeting
Whenever delivering the business plan presentation to a board of directors, focus on the strategic goals, financial projections, and KPIs.
Showcase how this business plan aligns with the company’s core values, mission, vision, and long-term strategy.
Potential Investors
Presenting your unique value proposition, potential ROI, and highlighting the market opportunity is extremely important. Focus on selling your business model and vision with accurate financial projections and growth strategy.
Dedicate some minutes to present your industry’s competitive landscape and answer why your product or service is a better offering than what competitors produce.
As we can see, creating a business plan presentation is a process that can be time-consuming if we lack the required business plan presentation tools to turn data into visually appealing formats.
Remember to work concisely without losing the big picture of what you intend to explain. Your presentation is the entry point into the heart of your business; therefore, by adopting a structured approach, you can deliver an experience that engages, inspires, and builds confidence.
Finally, let’s see some business plan PowerPoint presentation examples & business plan templates that you can use to speed up the presentation design process and save time.
1. Coffee Shop Illustration Business Plan Slides

Create your new business plan presentation with quality vector illustrations for Coffee Shops. Ideal for cafeterias, coffee bars, barista giftshop stores, bookshops and more.
Use This Template
2. Real Estate Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Realtors looking to start their own agencies should take a look at this attractive selection of slides with tailored real estate vector illustrations. These presentation plan slides show the different stages that a prospective buyer may incur, from hiring the services of a Real Estate agent, checking different properties, to finally buying a home. Graphs and charts are included in vivid colors that are fully editable to meet the required branding.
3. Restaurant Business Model PowerPoint Template

As we’ve seen with the previous cases, these vector images depicting typical restaurant activities can help us build a business plan presentation sample to discuss with our team prior to an important meeting. Save time and money by introducing these professional designs into your presentation.
4. One Pager Business Plan PowerPoint

To briefly summarize the objectives of your business plan, work in-team with this one-pager business plan slide. Ideal to take notes, give a general picture of the current status of the business plan and key growth opportunities.
5. Business Plan PowerPoint Templates
If you want to create the best business plan presentation, this slide deck can make that task 100% easier. Containing all the elements described in this guide, introduce your data and prepare to deliver a powerful speech.
6. Flat Bold Business Plan PowerPoint Template
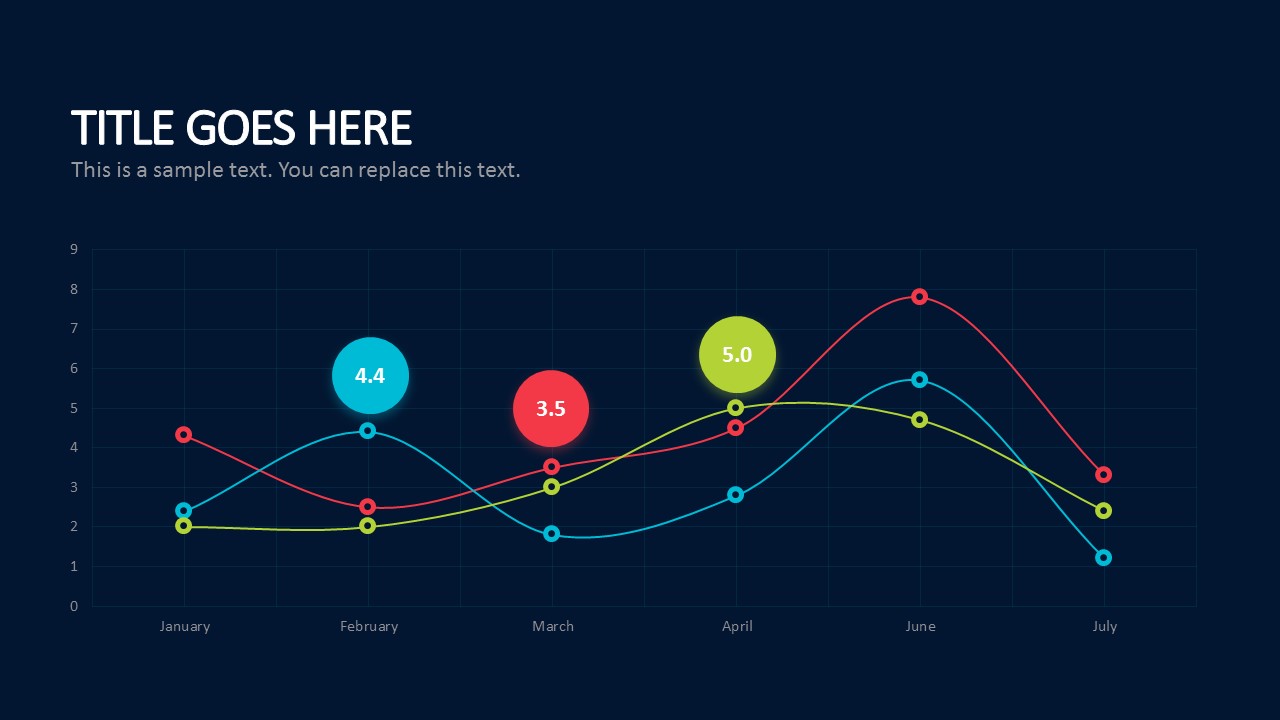
Another slide deck intended for those looking at how to make a business plan presentation that delivers a memorable experience. With a minimalistic design approach, it perfectly balances formal elements and impactful visual cues to help increase your audience’s retention rate.
7. Car Sharing Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Create the next Uber-like car-sharing service with the help of these carpooling vector illustrations perfectly arranged in a cohesive business plan slide deck. Presenters can explain the ins and outs of their business model with highly detailed graphics that grab the attention of potential investors. Check it out now!
8. Beauty Salon Business Plan PowerPoint Template
Business plan presentations don’t have to look formal or boring. This slide deck is geared towards beauty salon businesses, especially for those targeted to women. Chic design, bold color scheme, and extremely useful tools like a pricing list to present an idea like a subscription-based model where consumers see the total value of their investment.
9. CrossFit Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Finally, we list an option filled with tools and gym vector illustrations for those looking to start a gym business or CrossFit academy. These illustrations were crafted with care to express the core idea on every single slide, such as human-shaped graphs to present relevant KPIs.

Like this article? Please share
Business Planning, Business Presentations Filed under Business
Related Articles
Filed under Business • May 17th, 2024
How to Make a Transition Plan Presentation
Make change procedures in your company a successful experience by implementing transition plan presentations. A detailed guide with PPT templates.

Filed under Business • May 8th, 2024
Value Chain Analysis: A Guide for Presenters
Discover how to construct an actionable value chain analysis presentation to showcase to stakeholders with this detailed guide + templates.
Filed under Business • April 22nd, 2024
Setting SMART Goals – A Complete Guide (with Examples + Free Templates)
This guide on SMART goals introduces the concept, explains the definition and its meaning, along the main benefits of using the criteria for a business.
Leave a Reply
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free
8 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
A business plan template can be an excellent tool to simplify the creation of your business plan.
The pre-set structure helps you organize ideas, covers all critical business information, and saves you time and effort on formatting.
The only issue? There are SO many free business plan templates out there.
So, which ones are actually worth using?
To help remove the guesswork, I’ve rounded up some of the best business plan templates you can access right now.
These are listed in no particular order, and each has its benefits and drawbacks.
What to look for in a business plan template
Not all business plan templates are created equal. As you weigh your options and decide which template(s) you’ll use, be sure to review them with the following criteria in mind:
- Easy to edit: A template should save you time. That won’t be the case if you have to fuss around figuring out how to edit the document, or even worse, it doesn’t allow you to edit at all.
- Contains the right sections: A good template should cover all essential sections of a business plan , including the executive summary, product/service description, market/competitive analysis, marketing and sales plan, operations, milestones, and financial projections.
- Provides guidance: You should be able to trust that the information in a template is accurate. That means the organization or person who created the template is highly credible, known for producing useful resources, and ideally has some entrepreneurial experience.
- Software compatibility: Lastly, you want any template to be compatible with the software platforms you use. More than likely, this means it’s available in Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or PDF format at a minimum.
1. Bplans — A plan with expert guidance

Since you’re already on Bplans, I have to first mention the templates that we have available.
Our traditional and one-page templates were created by entrepreneurs and business owners with over 80 years of collective planning experience. We revisit and update them annually to ensure they are approachable, thorough, and aligned with our team’s evolving best practices.
The templates, available in Word, PDF, or Google Doc formats, include in-depth guidance on what to include in each section, expert tips, and links to additional resources.
Plus, we have over 550 real-world sample business plans you can use for guidance when filling out your template.
Download: Traditional lender-ready business plan template or a simple one-page plan template .
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. SBA — Introduction to business plans

The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two different business plan templates along with a short planning guide.
While not incredibly in-depth, it’s enough to help you understand how traditional and lean plans are structured and what information needs to be covered. The templates themselves are more like examples, providing you with a finished product to reference as you write your plan.
The key benefit of using these templates is that they were created by the SBA. While they may provide less guidance, you can be assured that the information and structure meet their expectations.
Explore: The SBA’s planning guide and free templates
3. SCORE — Planning workbook

SCORE’s template is more like a workbook. It includes exercises after each section to help you get your ideas down and turn them into a structured plan.
The market research worksheets are especially useful. They provide a clear framework for identifying your target market and analyzing competitors from multiple angles. Plus, they give you an easy way to document all the information you’re collecting.
You will likely have to remove the exercises in this template to make it investor-ready. But it can be worth it if you’re struggling to get past a blank page and want a more interactive planning method.
Download: SCORE’s business plan template
4. PandaDoc — A template with fillable forms

PandaDoc’s library offers a variety of industry-specific business plan templates that feature a modern design flair and concise instructions.
These templates are designed for sharing. They include fillable fields and sections for non-disclosure agreements, which may be necessary when sending a plan to investors.
But the real benefit is their compatibility with PandaDoc’s platform. Yes, they are free, but if you’re a PandaDoc subscriber, you’ll have far more customization options.
Out of all their templates, the standard business plan template is the most in-depth. The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry.
Explore: PandaDoc’s business plan template library
5. Canva — Pitch with your plan

Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool. It offers a diverse array of templates built by their in-house team and the larger creative community, meaning the number of options constantly grows.
You will need to verify that the information in the template you choose matches the standard structure of a traditional business plan.
You should do this with any template, but it’s especially important with any tool that accepts community submissions. While they are likely reviewed and approved, there may still be errors.
Remember, you can only edit these templates within Canva. Luckily, you only need a free subscription, and you may just miss out on some of the visual assets being used.
To get the most value, it may be best to create a more traditional planning document and transfer that information into Canva.
Explore: Canva’s business plan gallery
6. ClickUp — The collaborative template

Out of all the project management tools that offer free business plan templates, ClickUp’s is the most approachable.
Rather than throwing you into all the features and expecting you to figure it out—ClickUp provides a thorough startup guide with resource links, images, and videos explaining how to write a plan using the tool.
There’s also a completed sample plan (structured like an expanded one-page plan) for you to reference and see how the more traditional document can connect to the product management features. You can set goals, target dates, leave comments, and even assign tasks to someone else on your team.
These features are limited to the ClickUp platform and will not be useful for everyone. They will likely get in the way of writing a plan you can easily share with lenders or investors.
But this is a great option if you’re looking for a template that makes internal collaboration more fluid and keeps all your information in one place.
Sign Up: Get a free trial of ClickUp and explore their template library
7. Smartsheet — A wide variety of templates

I’m including Smartsheet’s library of templates on this list because of the sheer number of options they provide.
They have a simple business plan template, a one-page plan, a fill-in-the-blank template, a plan outline, a plan grading rubric, and even an Excel-built project plan. All are perfectly usable and vary in visual style, depth of instructions, and the available format.
Honestly, the only drawback (which is also the core benefit) is that the amount of templates can be overwhelming. If you’re already uncertain which plan option is right for you, the lengthy list they provide may not provide much clarity.
At the same time, it can be a great resource if you want a one-stop shop to view multiple plan types.
Explore: Smartsheet’s business plan template library
8. ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan

I’m adding ReferralRock’s template to this list due to its specificity.
It’s not your standard business plan template. The plan is tailored with specific sections and guidance around launching an affiliate marketing business.
Most of the template is dedicated to defining how to choose affiliates, set commissions, create legal agreements, and track performance.
So, if you plan on starting an affiliate marketing business or program, this template will provide more specific guidance. Just know that you will likely need to reference additional resources when writing the non-industry sections of your plan.
Download: ReferralRock affiliate marketing business plan template
Does it matter what business plan template you use?
The short answer is no. As long as the structure is correct, it saves you time, and it helps you write your business plan , then any template will work.
What it ultimately comes down to, is what sort of value you hope to get from the template.
- Do you need more guidance?
- A simple way to structure your plan?
- An option that works with a specific tool?
- A way to make your plan more visually interesting?
Hopefully, this list has helped you hone in on an option that meets one (or several) of these needs. Still, it may be worth downloading a few of these templates to determine the right fit.
And really, what matters most is that you spend time writing a business plan . It will help you avoid early mistakes, determine if you have a viable business, and fully consider what it will take to get up and running.
If you need additional guidance, check out our library of planning resources . We cover everything from plan formats , to how to write a business plan, and even how to use it as a management tool .
If you don’t want to waste time researching other templates, you can download our one-page or traditional business plan template and jump right into the planning process.
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.

Table of Contents
- Qualities of a good template
- ReferralRock
- Does the template matter?
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

10 Min. Read
When Should You Write a Business Plan?

3 Min. Read
11 Key Components of a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Home Page | Blog | Managing | Marketing | Planning | Strategy | Sales | Service | Networking | Voice Marketing Inc.
- Privacy Policy
Use a Business Plan Outline
Or business plan layout.
Why do you need a business plan outline ? Because if you need small business startup money, or you want to focus and grow an existing business, you need a business plan. Use an outline, or business plan layout, or examples of business plans to help develop and build your own plan.
Search This Site
This is a comprehensive business plan outline.
Not all small business owners will want (or need) to do a plan as comprehensive and intensive as this one.
But it does help to understand the full range of plan components.
If you are about to startup a business, you will need to do a thorough plan to be able to access small business startup money from banks or financial institutions.
If you are adding new products or services, or looking at a business expansion (maybe through a merger or acquisition), or if you are looking to sell your business, having a comprehensive plan is important to succeeding with your goals.
Using a Business Plan Outline
What's the difference between a business plan outline or a business plan layout? An outline is a usually a full detailed list of the activities needed in the plan; whereas the layout is a higher level overview of what's in the plan.
Review some examples of business plans in your industry (often an industry association will have some sample business plans for review or check out the local community college) to see the type of information you need in your plan.
This business plan outline includes a number of strategic management elements that are not common in all plans but that are useful and necessary if you have a highly active and competitive market, complex products or services, and/or complex buyer behavior.
First, determine why you want to do a business plan:
- Is it to manage and operate your business better?
- Is it to manage fast growth better?
- Is it to manage in a declining market better?
- Is it to manage the impact of your competition better?
- Is it to introduce more products or services (or to consider doing so)? Or to add more locations?
- Is it to change ownership: adding new partners, adding key employees?
- Is it to obtain financing?
- Is it to sell your business?
There are many reasons to write a business plan and how you write your plan depends a lot on why you want to write it.
Here's what I recommend: do the key elements of the plan to start your business or if you haven't done a plan or updated a plan in a long time (key elements will be in italics in the business plan outline below). Then each year when you update your plan, add another element or two. Often the updates will not take as much time as originating the work or the research - and the numbers should be tracked by your system as your business operates.
However if your business is fairly complex, if you have a lot of products or services, if you have a highly active competition, if your life-cycle is in the introductory or the declining phases, do as much of this business plan outline as possible. Outsource some, or all, of the work if necessary: this means do what you can yourself (if you want to) and have a consultant or business plan writer do the sections that you can't do, or don't want to do.
Business Plan Outline:
- Business concept (if a new business) or Business focus (if a plan renewal or update)
- Current Business Environment
- Key Management and/or Ownership
- Key Success Factors
- Key Risk Factors
- Requirements for the plan: managing the business, significant change in the marketplace, selling the business, obtaining bank loans, obtaining grants, obtaining venture capital, going from a private to public enterprise, and more.
- Strategic Vision Statement - set the direction of where your business is going (future)
- Mission Statement - define your business, where it is today
- SWOT Analysis (internal strengths and weaknesses; external opportunities and threats): rank the weaknesses and threats in particular to decide which ones you need to focus on first.
- The Industry
- Market Environment
- Driving Forces in the Industry
- Market Segmentation
- Target Marketing: primary, secondary and tertiary
- Buyer Behavior: characteristics, needs, wants, decisions
- Post purchase buyer/customer behavior
- Conduct a market opportunity analysis which looks at unmet customer needs
- Identifying your competition
- Competition: strengths and weaknesses
- Competition: strategies and objectives
- How does your competition react?
- Primary competitors and their impact
- Competitive Intelligence
- External Opportunities and Threats: impact on competition
- Competive Advantages: Defensive and Offensive Tactics
- Differentiation, Niche, Low-Cost, OR Leader Strategy and Why
- Identify How You Will Implement Your Strategy (What you will do)
- Products or Services List, including features, advantages, and benefits
- Service or Product Differentiation
- Service or Product Positioning
- Your Service or Product Life-Cycle
- Comparison to Competitive Products or Services
- New Services or New Product Development Plan (future)
- demographics
- psychographics
- technological
- political/legal
- Market Research
- Value Chain Analysis
- Price and Pricing Strategy
- Sales tactics, contests, incentives
- Advertising and Media
- Trade shows, Events and Conventions
- Direct Marketing Campaigns, such as Postcard Marketing
- Relationship Marketing
- Personal Selling
- Place or Distribution: Location, Retail and/or Marketing Channels
- Assumptions
- Notes or Comments
- 5 year plan by customer, by sales representative, by geographic market, by product line
- Organization (culture, management team)
- Products or Services List, including production standards, how to produce, and standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Human Resources Plan, including key personnel list
- Capital Expenditures Plan
- Equipment and Asset List
- Customer Service Plan
- Facilities/Location, including future space needs
- Maintenance Plan
- Safety Plan
- Quality Plan
- Environmental Plan
- Management Informations System Plan, including back-up and security
- Financial Plan
- Pro Forma (projected) Balance Sheet
- Pro Form (projected) Income Statement
- Cash Flow Projections
- Financial Ratios
- Business Exit Strategy: yes, you need to plan your exit and your strategy for succession even as you build your business.
- Business Plan Objectives
- Action Plan
- Measure for Success
- Adjust for Improvement Where Necessary
Write a Business Plan: Use Examples of Business Plans
I am often asked how long does it take to write a business plan. The real answer is 'it depends': on how complex your business is, how easy it is to access industry information, how well you know your market, and much more.
But, because I am usually pressed to give a more specific answer, I will assume that the level of complexity is low, industry information is relatively easy to access, and you know your market well. Under those circumstances, to write a simple business plan, if you spend 8 hours a day writing and researching, it can take about 15 business days to do it.
To do a comprehensive business plan, if you spend 8 hours a day writing and researching, it will take you about 30 to 40 business days to do it. Yes, as you can see by this business plan outline, this is a big investment of time.
The Advantages of Outsourcing
Consider outsourcing and hire an outside consultant or business plan writer, it will likely take less time (for either types of plan) because consultants are experienced at writing plans and because they often have other resources (e.g. accountants) that they work with. But they cannot work on producing your plan unless you provide them with the information they need.
Please note, not all business plan writers or consultants will work exclusively for you on your plan so the actual elapsed time might be longer. But negotiate what you want and need up front.
P.S. I am also often asked how much it costs to write a business plan. But the answer to this comes from determining what needs to be done: is this a simple 10 page plan? Is it a basic plan (such as identified in italics in the business plan outline )? Are you wanting part of your plan done or all of it? Are you wanting a comprehensive, strategic plan? Are you wanting your plan edited or reviewed?
There are too many parameters to provide a price here but I can tell you that I have seen pricing range from $500 for an edit and review to over $40,000 for a comprehensive strategic plan that was developed to 'win' a large (multi-million dollar) venture capital investment.
If you need a small business plan writer to build, or help you build, your small business plan, contact us for a quote.
More-For-Small-Business Newsletter:
For more timely and regular monthly information on managing your small business, please subscribe here., additional reading:.
Return from Business Plan Outline to Small Business Plan .
Ensure your Business Financial Plan includes a provision for emergencies.
Your Business Exit Strategy needs to include management succession planning.
Or return to More For Small Business Home Page.
Subscribe to
More Business Resources E-zine
Implement your plan: for results.
Once you've built your plan, you need to implement it.
Developing your strategy (in the plan) is the first, necessary, step. You need to know the direction you want to go, and you need the strategy and the plan to help you get there.
But once you've built the plan, you must execute it.
There is no value in building a plan that just gathers dust.
When building your business plan, make sure that you include an action plan for the strategies, techniques and tactics.
The actions need to include who's responsible for doing what; measurements for success (such as deadlines and timelines, targets and goals, costs, etc.); and why you need to take the action (in some cases, one action needs to be accomplished before subsequent ones can be launched).
As you work through the plan, make sure that you build reporting periods into the implementation: you need to know what's going on and why something is working, or not.
Make sure to communicate progress, or lack of it, throughout the organization. And re-visit the plan when and where necessary.
- Build Your Marketing
Administration
- Advertising
Focus on Your Plan
Plan for the future: lots of business owners want to get, or keep, moving forward. Planning seems to be more of a passive activity.
However, to ensure that your business goes in the right direction and that it optimizes all its opportunities, and manages its challenges, it is important to plan.
Balance your activities against the plan: make sure that you are investing your time, and money, on the elements of your business that will help you succeed.
Measure what works, and what doesn't work, and keep your focus: use your business plan as a map to guide you in the direction you want to go.
Contact
We are located in the Greater Vancouver area of British Columbia, Canada.
You can reach us through our contact page or request a quote for services here .
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Business plan outlines?
- Do you have resources for marketing planning?
- More Questions and Answers
Find the right network for you!
Managing Time | Money | Human Resources | Website Building | FAQs | Privacy Policy | Site Index | About Us | Contact Us | Request Quote
Copyright © 2002 - 2018 Voice Marketing Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Site Policies | Privacy Policy | Disclosure | Advertising
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Business plans: tips for arts, culture and the creative industries
Experts and entrepreneurs offer their insights and top resources for writing a successful business plan
Vikam Modhwadia, programme coordinator, School for Creative Startups
Before you think business plan, think business model A business plan is a smart and sassy document you write for investors, lenders or potential partners to give them an understanding of your business, so they can make a decision to support it. A business model, on the other hand, is the practical understanding of how it will work. The School for Creative Startups has developed some key questions that will help you create your own:
- The proposition: What do you do that people want? How do you know that your product is answering a need or fulfilling a desire?
- The customer and market: Who are your customers and where do you find them? What are their attributes and what are your market segments?
- The competition: Who are you up against and what can you learn from them?
- The industry: What do you have in common with your competition? Which trends are impacting your industry? How can you predict future trends?
- The channel: What are the different routes to finding customers?
- The relationship: What financial relationship do you have with your customers? Do you want to sell your product by subscription, via a payment plan or as a product people buy at a fixed price?
- The pricing model : How much should you charge for your product or service? What are your customers willing to pay? What are the other business costs to factor into your pricing model?
- The key partner: Who is your key partner? How can suppliers, distributors and marketing companies become one? Who can you bring on board to help you deliver your product or service?
- The asset: What is you key asset? What do you have to your advantage, to help you win customers? Is it physical, intellectual, human or financial?
- The key competency: What activities must your business be good at in order to prosper? What skills and experience do you bring to the business?
Pip Jamieson, founder and CEO, The Dots
Collaborate Getting your team excited about the business plan is key to its success. Before getting into the detail, a great first step is to spend an afternoon with the team and key stakeholders to work on the business model canvas : a useful visual collaboration tool that helps teams understand at a much deeper level the business’ relationship with customers, distribution channels, partners, revenue streams, costs and its core value proposition. This will help you consolidate your thinking before diving into the detail of the plan.
Keeping it visual can help My first business plan was a whopping 54-page word document, which was a big mistake. If you can’t articulate your plan over 10 to 15 well-designed presentation slides, you will lose your audience. The key is getting the structure right from the get go, with a slide for each key component of your plan including business overview, target market, unique selling point (USP), market conditions, marketing plan, competitor analysis and so on. Keep text to a minimum and use graphs and visuals to explain some of the trickier bits. A good rule of thumb is that if someone can flick through your business plan in 10 minutes and get it, you’ve done a cracking job.
Andrew Harding, managing director, CIMA
Structure your plan A challenge for anyone who is passionate about their business is to explain it in terms others can understand. A structured way of doing this is to articulate your business model in terms that lead to financial outcomes.
Start with your customers or the market segments you serve. Explain what assets, resources and relationships you have (or need) to serve them. Next, outline the processes and intangibles (specialist knowledge, skills, reputation etc) that enable you to meet customer needs competitively. Finally, you can explain what costs you will have and how you will generate income. Thinking about your business in this way will help you identify how to manage its performance and what strategies you will need to develop your business model. A business plan is simply a means of telling this story.
Sarah Wood, co-founder and COO, Unruly
People power Remember that the point of the plan is to help you and your team focus. It should be an operational plan of action, not a bunch of theoretical concepts, notional market sizes and fanciful financial projections.
The people who you put in the plan are more important than the numbers you submit: who will you hire, when will you hire them and how will their success be measured? What alliances and partnerships beyond employees do you need to succeed? Although it’s good to be ambitious, the most useful business plans don’t look five or three years ahead. Things change too quickly for that to be much use. You want to have an agile, flexible mindset and a business plan to match so you can change direction if necessary.
Stuart Rock, editor-in-chief, Business is GREAT
Sift, aggregate and test Don’t just read one guide to writing a business plan; sift and aggregate the advice from several. None of them will provide you with passion, creativity and vision – that’s down to you – but you’ll have the all-important structure of a valuable business plan. Then test it with that most important constituency: the people who you believe will buy from you. Also, test it with someone who you can trust to be objective. Your plan will rarely survive contact with reality, but it’s a challenging process and an important discipline.
Scott Phillips, founder, Rise Art
Revisit your plan We continue to iterate and improve on our business plan each quarter. I’m constantly looking at the latest research and speaking with our customers to see how we are doing in the real world. Our business plan always changes based on what we’ve seen that has worked and what’s not. We revisit it and modify the assumptions accordingly. Setting the business plan and agreeing regularly on the key indicators with the team also helps keep everyone honest. We know what is working and what is not, and we can measure our success or lack thereof accordingly. We also know where we need to focus our energy.
A really handy way to see if your product resonates with customers is to routinely survey your customers and establish net promoters scores . You’ll see how over time customers view and will recommend your brand.
Bernadine Bröcker, CEO, Vastari
A business model isn’t just a box-ticking exercise It needs to ooze passion, drive, inspiration, as well as ticking the boxes. Make sure you think of all commercial and strategic angles, but also make sure that any potential investor or partner can also read how inspired you are in making this business a reality.
Arts Council England: Starting a business (pdf)
Barclays: Writing a small business plan
Business is GREAT: Writing a business plans
Chartered Global Management Accountant essential tools booklet (pdf)
Creative Industry Finance business planning workshops
Gov.uk: Write a business plan
ICAEW: Writing a business plan (pdf)
Nesta Creative Enterprise Toolkit
Peter Thiel: sample pitch deck
The Prince’s Trust business plan pack (pdf)
RBS online business planner
Join our community of arts, culture and creative professionals by signing up free to the Guardian Culture Pros Network .
- Culture professionals network
- Alternative finance in arts and culture
- Small business
- Entrepreneurs
- sponsored features
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
Business Plans vs. Pitch Decks
As readers of either my Mentor’s Perspective or Mentor’s Journal series will know, one of the most common themes that I come across is that of fundraising in all its guises.
Maybe that is because it is a topic that most businesses will consider at some point in their growth, or maybe it is because it is often the area of running a business that many founders feel most uncomfortable with, or know the least about. I will discuss the art of fundraising in a future article but here I wanted to focus on two of the most important steps that must be taken before setting out to raise any funds – that is writing a business plan and producing a pitch deck.
Indeed, in my opinion, the business plan is such an important document that it is a crucial exercise that should be undertaken for any business, irrespective of whether it wishes to raise funds or not.
For any new business it is an extremely valuable exercise to write a business plan, as this will force you to analyse all of the areas that need to be taken into consideration when deciding upon the focus of your business and your product or service. The process should start with the simplified Business Model Canvas (many examples and templates are available online) as this is a bit more of a brainstorming exercise to try and make sure that you have pulled together all of the areas that need to go into the business plan and then grouped them together sensibly. Once you have spent some time on that exercise you can then start to write the business plan. This does not need to be excessively large or detailed but should go into sufficient detail to cover all aspects of the business.
Business Model Basics
- Your product / service and what differentiates it and you as a company – what are you doing differently and what factors will ensure that your company succeeds?
- Your potential market place and how much of the market you realistically hope to reach – is this just the UK or do you plan to export? How will you develop this and over what time period?
- Your competition and barriers to entry – will you compete with large players and how easy will it be for you to break into the market or indeed for others to break into your market?
- Your management team and what previous experience they have – a previous track record always adds comfort so if you do not have all the experience necessary how will you cover the gaps?
- Your financials – both actuals to date and future forecast (with detailed assumptions based on research). These must be realistic and demonstrably achievable. If they are too optimistic then they will undermine the whole business plan in the eyes of others and also set you wrong targets
- Your manufacturing / distributing / supply chain / route to market – set this out in order to show the complete process and to help the reader put the financials and everything else into perspective
- Your marketing and sales strategy – explain how you will market and sell your product or service and how you plan to grow sales over time. Again, this will help add credibility to the assumptions used in your financial projections
Do not worry if your plan brings out some areas of difficulty as this is to be expected. What is important is that it demonstrates that you know these areas exist and that you have thought about them and found solutions.
There should be a one or two page executive summary at the front that pulls out all of the really important points from the main business plan. Be warned, this summary is extremely important as many readers, especially potential investors, will only read the full plan if you have grabbed their attention sufficiently in the executive summary.
Once the initial plan is written it can be extremely beneficial to discuss it with your Mentor or other trusted advisors as it is likely that they will point out areas that they feel should be included and they should also challenge some of the assumptions made, especially in the financial forecasts. This process ensures that after any revisions that you may decide to make, either to your plan, or indeed your actual business, you have a robust plan and you are able to defend all of the assumptions made.
Once the business plan has been produced it is a very useful document to revise periodically and to update as your business grows and your needs and aspirations change over time. As I mentioned at the beginning of this article, I feel that preparing a business plan should be done simply as a good exercise to clarify your thoughts, but certainly if you are looking to raise funding by way of debt or equity then it becomes a necessity. As such, updating and refining an existing plan is a much easier task then writing one from the start, and because it is not the first attempt it should also be a better document.
If you are looking to raise equity funding then clearly the company needs to have a valuation and the only real way that this can be obtained is by producing a full business plan with financial projections and clear assumptions, together with the future plans of the company. If indeed the company is considering raising equity it is crucial that the management team provides a broad range of experience and any gaps in experience should ideally be filled with non-executive directors and a good advisory board.
Pitch Deck vs. Business plan
The pitch deck complements the business plan and stands alongside it. Just as it is important that the full business plan has a one or two page executive summary which must catch the readers’ imagination and encourage them to read the whole business plan, then the pitch deck can be seen as an alternative form of executive summary but used in a different way.
The business plan is a long, detailed document typically produced in Word, whilst the pitch deck is normally between 10 to 20 pages in length and often produced in PowerPoint, but it is a much more visual document designed entirely to sell the business to potential investors or lenders, or anyone else that reads it. It must grab the reader’s attention immediately and encourage them to want to know more.
It is important to use pictures, graphs, tables and the like, to get as much of the important information over as succinctly as possible and to reduce the number of words required. It needs to tell a story and there is of course a real art to this. Think of it as a trailer to a forthcoming blockbuster film and you start to get the right picture.
The information contained should enable the reader to understand the company’s product or service, the advantages it has over rivals, the size of the market, how much it is raising for what amount of equity and how the money will be spent. It must therefore include projected financials and a pre-money valuation of the company (that is the value of the company before any additional funds are raised). It is also best to include a timeline of significant events in the company’s history.
Producing the bones of a pitch deck is relatively easy once the business plan has been done but given that it effectively acts as the elevator pitch of the company, and first impressions are crucial, I would suggest that it is one thing that is worth spending good money on to ensure that it looks the part and includes all the required information.
Both the business plan and the pitch deck can of course be produced fully in house but I also know of some very good companies out there that can produce extremely professional documents for a modest fee. Like everything, that decision will be dependent upon the in house ability and time available, but do not underestimate the time needed to do either of these properly. Both of these documents could be crucial to securing external investment so they are well worth doing well.
To summarise, all businesses should do a business plan and keep them regularly updated whether they want to raise finance or not. Any company that wishes to raise finance must also produce a first class pitch deck.
Share This Article


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In conclusion, the integration of visual elements within business plans has become increasingly vital for facilitating effective communication, engaging stakeholders, and fostering a comprehensive understanding of the business's value proposition and growth potential. By leveraging the power of visual storytelling, businesses can create ...
Complete these and you'll have a great, visual business plan that will take a fraction of the time to complete than a traditional narrative one. It will also be appreciated by readers, who can see and understand the key elements of your plan quickly, without wasting a lot of time. Step 1. Mission: Explain Why the Business Exists.
These 1-page business plan infographics can be a reflection of your sales plan, marketing plan, business expansion plan or business stats that you'd like to share with your investors or employees. Here is an example of a business plan infographic template that presents a 5-step guide to business continuity: CREATE THIS INFOGRAPHIC TEMPLATE.
We'll wrap up with the decisive step of this business plan guide: reviewing everything with an eye for visuals. Listen to the wisdom of authors throughout the ages and show, don't tell. Visual communication is essential in your business plan because readers demand speed and clarity.
For the past 20 years, I've been helping entrepreneurs and business owners write business plans. In doing so, I've learned that the perfect business plan must be both functional and easy to read.. With regards to functional, a business plan should provide a clear roadmap of how you're going to grow your company. And with regards to "easy to read," your plan can't include pages and ...
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
1. Start with a Mind Map. A mind map is a great way to brainstorm ideas and visualize your business plan. Simply create a diagram with your business idea in the center and branch out from there. 2. Use Infographics. Infographics are a powerful way to communicate complex information in a visually appealing way.
A business plan presentation is the medium we use to communicate a business plan to an audience. ... Use a highly visual slide, like a dashboard template, to introduce factual data regarding the trends over a specific time period. Growth rates must be represented in time frames of over 180 days to evaluate the trend accurately.
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
3. Are business plans highly visual? All plans need not be highly visual. However, adequate data charts, graphs, 3-D models, etc., can make the document look attractive and creates an impression about the effort that has gone into furnishing the plan. It also increases the understandability of the document.
Present your market analysis, timeline, statistics, and more in an engaging and highly visual infographic. The license for this plan is $16 and gives you access to hundreds of editable slides to ...
Highly Visual; Used to Get Investors Attention; THE BUSINESS PLAN. A business plan is a fully researched 10-100 page document. The document is used to store and convey in detail your business' plans for the next 1,3, 5 years. The business plan lays out the research you've done in your industry and competitors.
An outline is a usually a full detailed list of the activities needed in the plan; whereas the layout is a higher level overview of what's in the plan. Review some examples of business plans in your industry (often an industry association will have some sample business plans for review or check out the local community college) to see the type ...
Step 4: Prioritize the ideas and assign a leader to each. After recording your ideas, the next step is to implement a plan to turn these ideas into productive actions, which will provide the best ...
Keeping it visual can help My first business plan was a whopping 54-page word document, which was a big mistake. If you can't articulate your plan over 10 to 15 well-designed presentation slides ...
5. Startup Pitch. This PPT-format business plan sample has a creative tear-away design that's super eye catching and unique. A simple, standout design like this gets their attention but keeps it ...
The business plan is a long, detailed document typically produced in Word, whilst the pitch deck is normally between 10 to 20 pages in length and often produced in PowerPoint, but it is a much more visual document designed entirely to sell the business to potential investors or lenders, or anyone else that reads it.
Here are 10 ways visual thinking skills can help individuals and teams in your organization work through tough problems and communicate more clearly. {1} Explaining Complex Ideas Anytime, Anywhere. The most common way information is exchanged in any organization is one-to-one or in small groups. The most effective way we learn is through ...
The Business Model Canvas tool is an all-in-one resource that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It's a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business. It's a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business—and it's super easy to use!
Select TRUE statements about the components of Business Plans and Pitch Decks. - Business plans are text-based documents - The goal of a pitch deck is to get investors' attention - A pitch deck is a visual slide presentation - Business plans are highly visual - The goal of a business plan is to get investors' to buy-in - A typical pitch deck has between 20-100 slides
Having this context is key for the reader to form a view on whether or not they believe that your plan is achievable and the numbers in your forecast realistic. The written part of a visual effects studio business plan is composed of 7 main sections: The executive summary. The presentation of the company.