- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Enter Today's Teacher Appreciation Giveaway!

46 Unique Phys Ed Games Your Students Will Love
Get your steps in!

There’s nothing kids need more to break up a day spent sitting still and listening than a fun PE class to let off some steam. In the old days, going to gym class probably included playing kickball or dodgeball after running a few laps. Since then, there have been countless reinventions of and variations on old classics as well as completely new games. Although there is no shortage of options, we love that the supplies required remain relatively minimal. You can transport to another galaxy using just a pool noodle or two or create a life-size game of Connect 4 using just Hula-Hoops. You’ll want to make sure to have some staples on hand like balls, beanbags, and parachutes. There are even PE games for kindergartners based on beloved children’s TV shows and party games. Regardless of your students’ athletic abilities, there is something for everyone on our list of elementary PE games!
1. Tic-Tac-Toe Relay

Elementary PE games that not only get students moving but also get them thinking are our favorites. Grab some Hula-Hoops and a few scarves or beanbags and get ready to watch the fun!
Learn more: Tic-Tac-Toe Relay at S&S Blog
2. Blob Tag

Pick two students to start as the Blob, then as they tag other kids, they will become part of the Blob. Be sure to demonstrate safe tagging, stressing the importance of soft touches.
Learn more: Blob Tag at Playworks
3. Cross the River
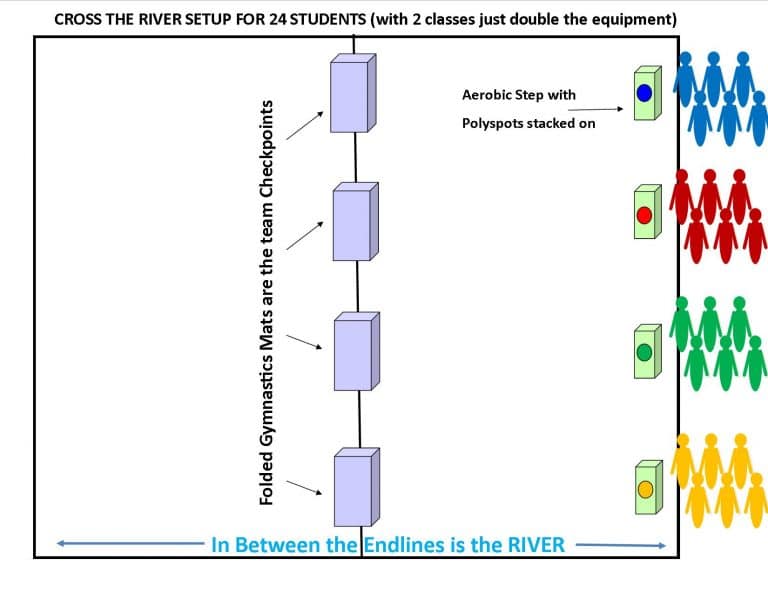
This fun game has multiple levels that students have to work through, including “get to the island,” “cross the river,” and “you lost a rock.”
Learn more: Cross the River at The PE Specialist
4. Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Cones

Line up cones, then have students pair up and stand on either side of a cone. Finally, call out head, shoulders, knees, or cones. If cones is called, students have to race to be the first to pick up their cone before their opponent.
Learn more: Head, Shoulders, Knees & Cones at S&S Blog
5. Spider Ball

Elementary PE games are often variations of dodgeball like this one. One or two players start with the ball and attempt to hit all of the runners as they run across the gym or field. If a player is hit, they can then join in and become a spider themselves.
Learn more: Spider Ball Game at Kid Activities
6. Crab Soccer

We love elementary PE games that require students to act like animals (and we think they will too). Similar to regular soccer, but students will need to play on all fours while maintaining a crab-like position.
Learn more: Crab Soccer at Playworks
7. Halloween Tag

This is the perfect PE game to play in October. It’s similar to tag, but there are witches, wizards, and blobs with no bones!
Learn more: Halloween Tag at The Physical Educator
8. Crazy Caterpillars
We love that this game is not only fun but also works on students’ hand-eye coordination. Students will have fun pushing their balls around the gym with pool noodles while building their caterpillars.
9. Monster Ball
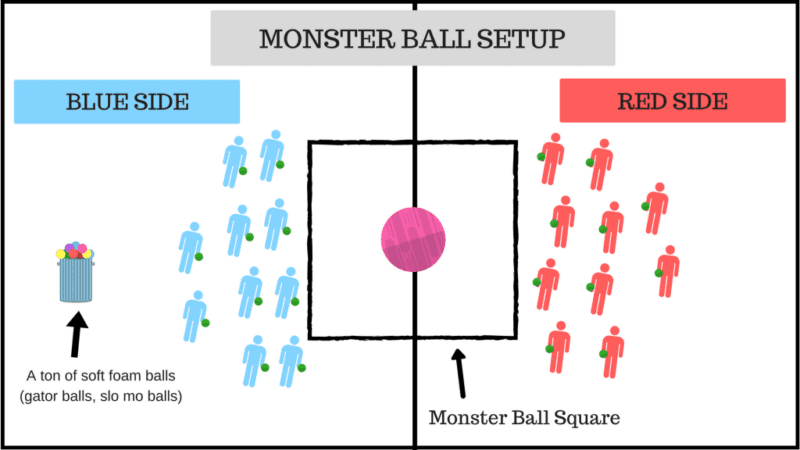
You’ll need a large exercise ball or something similar to act as the monster ball in the middle. Make a square around the monster ball, divide the class into teams on either side of the square, then task the teams with throwing small balls at the monster ball to move it into the other team’s area.
Learn more: Monster Ball at The PE Specialist
10. Striker Ball

Striker ball is an enjoyable game that will keep your students entertained while working on reaction time and strategic planning. We love that there is limited setup required before playing.
Learn more: Striker Ball at S&S Blog
11. Parachute Tug-of-War

What list of elementary PE games would be complete without some parachute fun? So simple yet so fun, all you will need is a large parachute and enough students to create two teams. Have students stand on opposite sides of the parachute, then let them compete to see which side comes out on top.
Learn more: Parachute Tug-of-War at Mom Junction
12. Fleas Off the Parachute
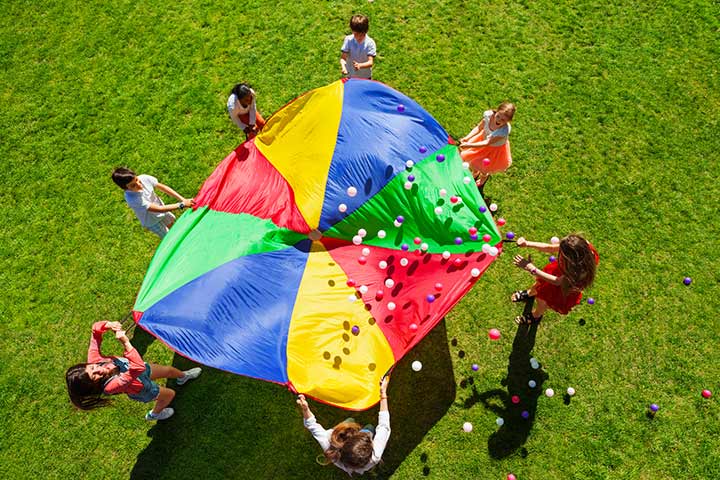

Another fun parachute game where one team needs to try to keep the balls (fleas) on the parachute and the other tries to get them off.
Learn more: Fleas Off the Parachute at Mom Junction
13. Crazy Ball

The setup for this fun game is similar to kickball, with three bases and a home base. Crazy ball really is so crazy as it combines elements of football, Frisbee, and kickball!
Learn more: Crazy Ball at Health Beet
14. Bridge Tag
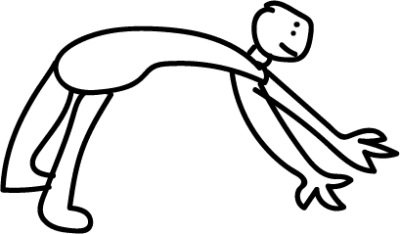
This game starts as simple tag but evolves into something more fun once the tagging begins. Once tagged, kids must form a bridge with their body and they can’t be freed until someone crawls through.
Learn more: Bridge Tag at Great Camp Games
15. Star Wars Tag

Elementary PE games that allow you to be your favorite movie character are just way too much fun! You will need two different-colored pool noodles to stand in for lightsabers. The tagger will have one color pool noodle that they use to tag students while the healer will have the other color that they will use to free their friends.
Learn more: Star Wars Tag at Great Camp Games
16. Rob the Nest
Create an obstacle course that leads to a nest of eggs (balls) and then divide the students into teams. They will have to race relay-style through the obstacles to retrieve eggs and bring them back to their team.
17. Four Corners

We love this classic game since it engages students physically while also working on color recognition for younger students. Have your students stand on a corner, then close their eyes and call out a color. Students standing on that color earn a point.
Learn more: Four Corners at The Many Little Joys
18. Movement Dice
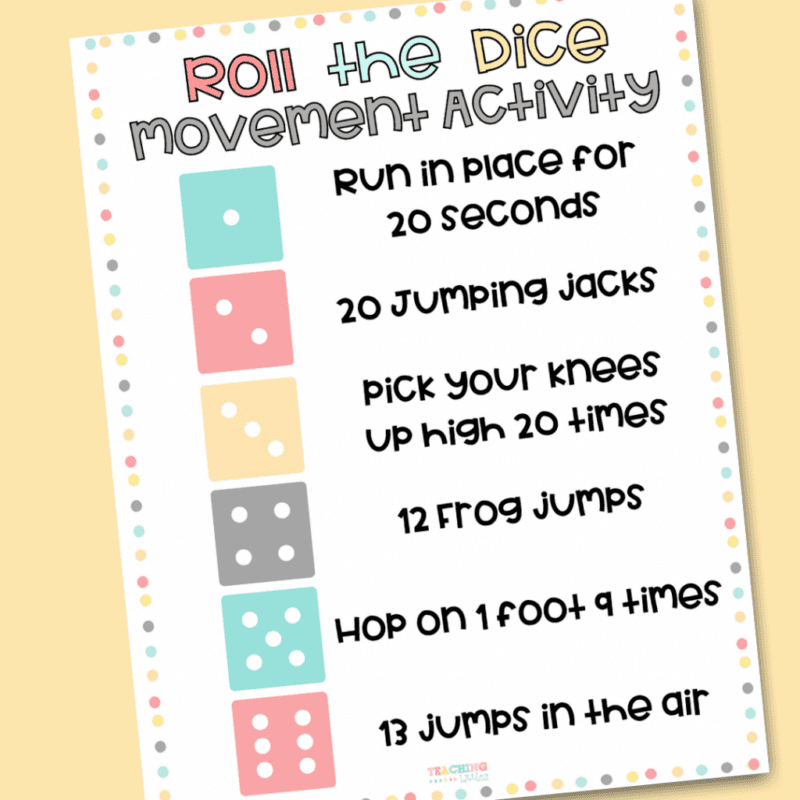
This is a perfect warm-up that requires only a die and a sheet with corresponding exercises.
Learn more: Roll the Dice Movement Break at Teaching Littles
19. Rock, Paper, Scissors Tag

A fun spin on tag, children will tag one another and then play a quick game of Rock, Paper, Scissors to determine who has to sit and who gets to continue playing.
Learn more: Rock, Paper, Scissors Tag at Grade Onederful
20. Cornhole Cardio
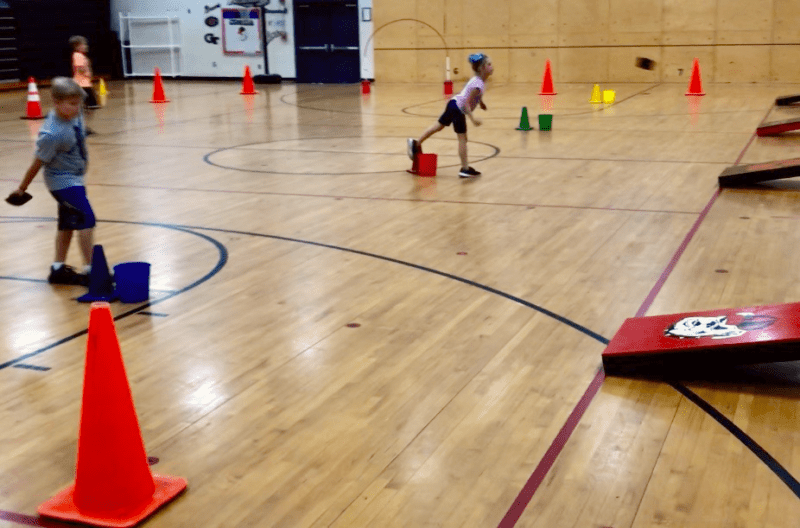

This one is so fun but can be a little bit confusing, so be sure to leave plenty of time for instruction. Kids will be divided into teams before proceeding through a fun house that includes cornhole, running laps, and stacking cups.
Learn more: Cardio Cornhole at S&S Blog
21. Connect 4 Relay
This relay takes the game Connect 4 to a whole new level. Players must connect four dots either horizontally, vertically, or diagonally.
22. Zookeepers
Students will love imitating their favorite animals while playing this fun variation of Four Corners where the taggers are the zookeepers.
23. Racket Whack-It
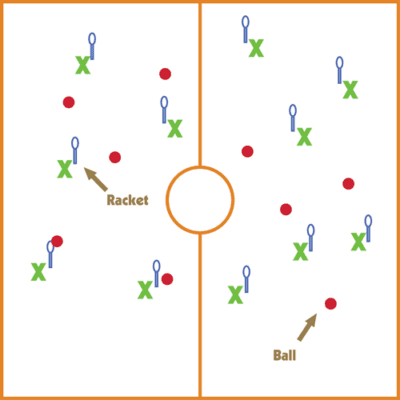
Students stand with rackets in hand while balls are thrown at them—they must either dodge the balls or swat them away.
Learn more: Racket Whack-It via PEgames.org
24. Crazy Moves
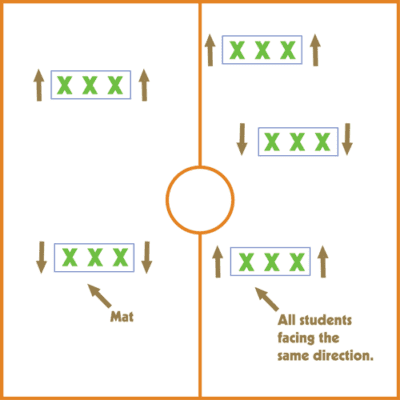
Set mats out around the gym, then yell out a number. Students must race to the mat before it is already filled with the correct number of bodies.
Learn more: Crazy Moves at PEgames.org
25. Wheelbarrow Race
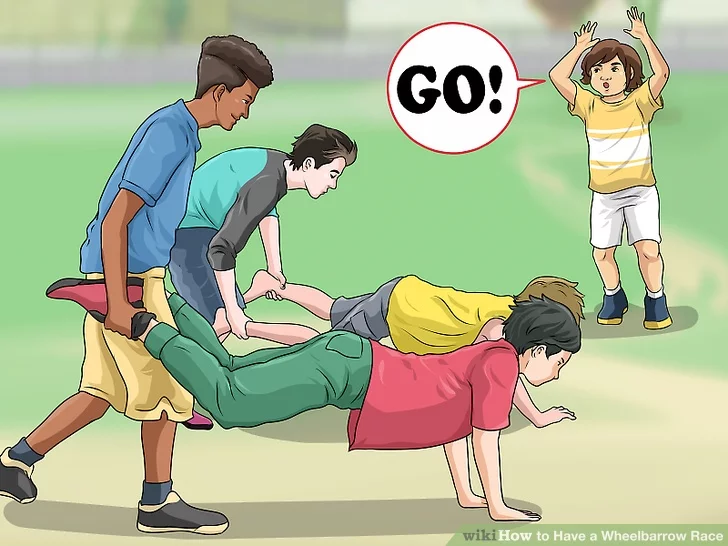
Sometimes the best elementary PE games are the simplest. An oldie but a goodie, wheelbarrow races require no equipment and are guaranteed to be a hit with your students.
Learn more: Wheelbarrow Race at wikiHow
26. Live-Action Pac-Man
Fans of retro video games like Pac-Man will get a kick out of this live-action version where students get to act out the characters.
27. Spaceship Tag
Give each of your students a Hula-Hoop (spaceship), then have them run around trying not to bump into anyone else’s spaceship or get tagged by the teacher (alien). Once your students get really good at it, you can add different levels of complexity.
28. Rock, Paper, Scissors Beanbag Balance
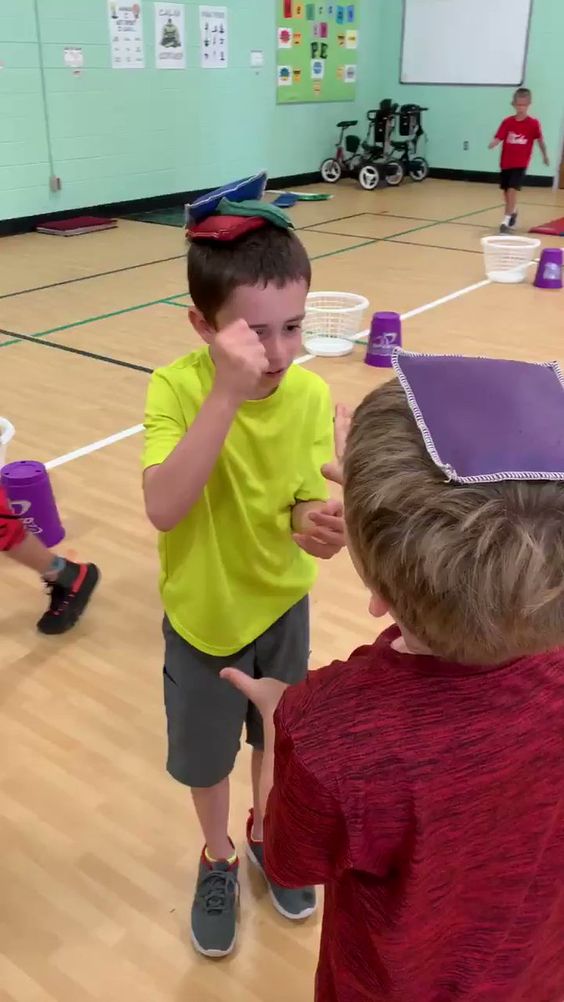

We love this spin on Rock, Paper, Scissors because it works on balance and coordination. Students walk around the gym until they find an opponent, then the winner collects a beanbag, which they must balance on their head!
Learn more: Rock, Paper, Scissors Beanbag Balance at PE Universe
29. Throwing, Catching, and Rolling
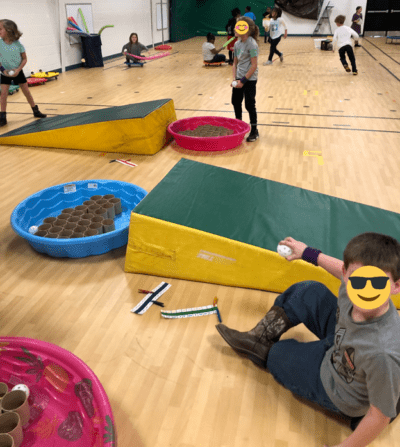

This is a fun activity but it will require a lot of preparation, including asking the school maintenance staff to collect industrial-sized paper towel rolls. We love this activity because it reminds us of the old-school arcade game Skee-Ball!
Learn more: Winter Activity at S&S Blog
30. Jenga Fitness
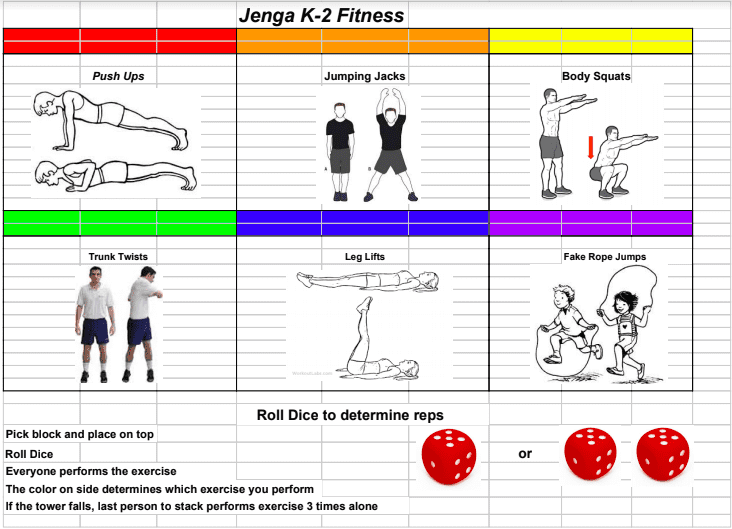
Although Jenga is fun enough on its own, combining it with fun physical challenges is sure to be a winner with young students.
Learn more: Jenga Fitness at S&S Blog
31. Volcanoes and Ice Cream Cones

Divide the class into two teams, then assign one team as volcanoes and the other as ice cream cones. Next, spread cones around the gym, half upside down and half right side up. Finally, have the teams race to flip as many cones as possible to either volcanoes or ice cream cones.
Learn more: Warm-Up Games at Prime Coaching Sport
This fun variation on dodgeball will have your students getting exercise while having a ton of fun! Begin with three balls on a basketball court. If you are hit by a ball, you are out. If you take a step while holding a ball, you are out. There are other rules surrounding getting out and also how to get back in, which can be found in this video.
33. Musical Hula-Hoops
PE games for kindergartners that are similar to party games are some of our favorites! Think musical chairs but with Hula-Hoops! Lay enough Hula-Hoops around the edge of the gym minus five students since they will be in the muscle pot. Once the music starts, students walk around the gym. When the music stops, whoever doesn’t find a Hula-Hoop becomes the new muscle pot!
34. 10-Second Tag
This game is perfect to play at the beginning of the year since it helps with learning names and allows the teacher to get to know the first student in line.
35. The Border
This game is so fun and requires no equipment whatsoever. Divide the gym into two sides. One side can move freely while the other side must avoid letting their feet touch the floor by rolling around, crawling, etc.
36. Freedom Catch
This is a simple throwing, catching, and tag game that will certainly be a hit with your PE class. Captors attempt to tag players so they can send them to jail. You can be freed if someone on your team runs to a freedom cone while throwing a ball to the jailed person. If the ball is caught by the jailed person, they can rejoin the game.
37. Oscar’s Trashcan
As far as PE games for kindergartners goes, this one is a guaranteed winner since it is based on the show Sesame Street . You’ll need two large areas that can be sectioned off to use as trash cans and also a lot of medium-size balls. There are two teams who must compete to fill their opponent’s trash can while emptying their own. Once over, the trash will be counted and the team with the least amount of trash in their trash can wins!
38. 4-Way Frisbee
Divide your class into four separate teams, who will compete for points by catching a Frisbee inside one of the designated goal areas. Defenders are also able to go into the goal areas. There are a number of other rules that can be applied so you can modify the game in a way that’s best for your class.
39. Badminton King’s/Queen’s Court
This one is simple but fun since it is played rapid-fire with kids waiting their turn to take on the King or Queen of the court. Two players start and as soon as a point is earned, the loser swaps places with another player. The goal is to be the player that stays on the court the longest, consistently knocking out new opponents.
40. Jumping and Landing Stations
Kids love stations and they definitely love jumping, so why not combine those things into one super-fun gym class? They’ll have a blast challenging themselves with all the different obstacles presented in this video.
41. Ninja Warrior Obstacle Course
Regardless of whether you’ve ever seen an episode of American Ninja Warrior , you are probably familiar with the concept and so are your students. Plus, you’ll probably have just as much fun as your students setting up the obstacles and testing them out!
42. Balloon Tennis
Since kids love playing keepy-uppy with a balloon, they will love taking it a step further with balloon tag!
43. Indoor Putting Green
If your school can afford to invest in these unique putting green sets, you can introduce the game of golf to kids as young as kindergarten. Who knows, you might just have a future Masters winner in your class!
44. Scooter Activities
Let’s be honest, we all have fond memories of using scooters in gym class. Regardless of whether you do a scooter sleigh or scooter hockey, we think there is something for everyone in this fun video.
45. Pick It Up
This is the perfect PE game to play if you are stuck in a small space with a good-size group. Teams win by making all of their beanbag shots and then collecting all of their dots and stacking them into a nice neat pile.
46. Dodgeball Variations
Since not all kids love having balls thrown at them, why not try a dodgeball alternative that uses gym equipment as targets rather than fellow students? For example, have each student stand in front of a Hula-Hoop with a bowling ball inside of it. Students need to protect their hoop while attempting to knock over their opponents’ pins.
What are your favorite elementary PE games to play with your class? Come and share in our We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out our favorite recess games for the classroom ..

You Might Also Like

38 Old-School Recess Games Your Students Should Be Playing Now
Ready to feel nostalgic? Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

9 Activity Ideas for STEM in Physical Education
- Lauren Chiangpradit
- November 16, 2023
- Reviewed by Sean Barton
- Reviewed by Haley MacLean
Table of Contents
The Synergy of Movement and Learning
Physical education stem activities for elementary school, stem activities for middle school pe students, advanced stem challenges for high school learners, tech, tools, and resources for stem in physical education.
Integrating STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) into Physical Education (PE) classes offers an innovative approach to education. In an era where sports statistics, science, and technology increasingly influence athletics, PE classes are uniquely positioned to blend physical activity with STEM learning and 21st century skills. This article explores how PE educators and facilitators can use STEM learning in their coursework. It also provides a range of curriculum activity ideas to get students at different education and skill levels engaged.
Research indicates that physical activity can significantly bolster cognitive abilities. When students participate in movement-based learning, they benefit physically and experience enhanced concentration, memory, and creativity. This cognitive boost is crucial for comprehending and applying STEM concepts, which often demand high levels of problem-solving and critical thinking. Active learning, where students engage in physical activities while learning STEM concepts, results in more profound understanding and retention of information. Integrating physical and mental challenges not only makes learning more enjoyable, but is more effective, as students apply theoretical concepts in practical settings, leading to better comprehension and recall.
Integrating STEM into elementary physical education presents a fantastic opportunity to lay the foundation for lifelong learning and curiosity in young students. Through these innovative activities, elementary school children can explore and understand key STEM concepts while engaging in fun and physical play. Each activity is designed to be not only educational but highly interactive and suitable for their developmental stage. Here are some engaging activities that blend physical education with STEM learning for elementary students:
- Jump and Measure: Students perform a variety of jumps – like the long jump and high jump – and measure their distances or heights. This activity introduces basic concepts of measurement and physics, encouraging students to understand how force and motion play a role in their physical activities.
- Geometry with Body Movements: In this activity, children use their bodies to create geometric shapes, either individually or in groups. It’s an engaging way for students to learn about basic geometry, spatial awareness, and symmetry. Teachers can challenge students to form complex shapes, enhancing their understanding and teamwork skills.
- STEM Soccer : In a lesson devoted to measuring throw-ins, students collect data in centimeters and convert their data to meters dividing by 100. Students then evaluate measurement systems to decide the best measurement size. This disguised learning, interactive lesson is a great way for physical education teachers to add STEM into their PE classes.
- Weather and Exercise: Students observe and record weather patterns over a week and discuss how different weather conditions affect physical activities. This integrates meteorology into PE, allowing students to see the real-world application of science in their everyday activities.
- Heart Rate Exploration: After engaging in various exercises, students measure their heart rates to learn about the cardiovascular system and the science behind exercise. This activity not only educates them about their bodies, but about the importance of physical fitness in maintaining health.
- Playground Physics: Utilizing playground equipment, this activity allows students to explore concepts like gravity, force, and motion. They can experience firsthand how these physical laws impact their play and movements, turning the playground into a living laboratory.
As students enter middle school, their capacity for more complex and abstract thinking grows significantly. This developmental stage is an ideal time to introduce more intricate STEM concepts through physical education, enhancing their learning experience with practical applications. The following STEM activities are tailored for middle school students, offering a blend of intellectual challenge and physical engagement. These activities are designed to pique students’ curiosity in STEM fields through the familiar and enjoyable medium of sports and physical exercises. By participating in these activities, students not only deepen their understanding of STEM concepts, but learn valuable lessons in teamwork, problem-solving, and the practical application of classroom knowledge to real-world scenarios. Here’s a look at some stimulating and educational STEM activities for middle school PE:
- Sports Statistics Analysis: Students gather and analyze sports statistics from games or physical activities. This teaches them about data collection, interpretation, and the importance of statistics in understanding and improving athletic performance.
- STEM Football: During a lesson in STEM Football, students collect and graph data of a controlled experiment by using a line graph. Students then explain the relationship between kinetic energy and mass by writing a claim evidence supported by evidence-based reasoning from class data. This lesson highlights the strong classroom connection between physical education and STEM learning, and how it can help create tangible examples for students.
- Energy and Movement: This activity focuses on the concept of kinetic and potential energy in the context of sports. Students explore how energy is transferred and transformed during different physical activities, such as running, jumping, or throwing a ball.
- Biomechanics of Sports: Here, students delve into the study of human movement and mechanics in various sports. They learn about the science behind athletic performance, injury prevention , and how athletes optimize their movements for maximum efficiency and safety.
- Mathletics Relay: A relay race where each leg involves solving a math problem before passing the baton. This combines physical fitness with mathematical skills, emphasizing quick thinking and teamwork.
- Technology in Sports Training: Students explore how technology is increasingly used in sports training and performance analysis. They might look at wearable tech, video analysis software, or other tools that help athletes improve their skills and coaches to make informed decisions.
High school students, with their advanced cognitive skills and heightened interests, are well-positioned to tackle complex STEM challenges through physical education. This section of the curriculum is designed to offer high school learners in-depth, hands-on experiences that combine higher-level STEM concepts with physical activities and sports. These advanced activities are not just about physical exertion; they require students to engage in critical thinking, problem-solving, and creative innovation. They provide an opportunity for students to see the real-world applications of the STEM knowledge they acquire in their classrooms, bridging the gap between theoretical learning and practical implementation. By participating in these activities, high school students can gain a deeper understanding of various STEM fields, such as physics, engineering, biotechnology, and environmental science, observing how these disciplines intersect with sports and physical fitness. Here are some challenging and intellectually stimulating STEM activities designed for high school learners:
- Physics of Sports Equipment Design: Students research and discuss the physics principles involved in the design of sports equipment. This can include topics like material science, aerodynamics, and ergonomics, providing insights into how equipment is optimized for performance and safety.
- Engineering a Miniature Golf Course: Students design and construct a miniature golf course, applying concepts of geometry, physics, and design. This project not only involves creativity, but a practical application of STEM principles by creating functional and enjoyable mini-golf holes.
- Sports Analytics Project: Students undertake a project to analyze a sports game using statistical methods and tools. This activity introduces them to data science in sports, teaching them how to interpret and use data to understand game strategies and player performance.
- Biotechnology in Athletics: This topic explores how biotechnology is used in sports, from equipment design to performance enhancement techniques. Students might study material innovations, genetic research in athletics, or the ethical implications of biotechnology in sports.
- Environmental Science in Outdoor Sports: Students analyze how environmental factors impact outdoor sports activities. They can study topics like climate change, pollution, and natural terrain, understanding the interplay between sports and the environment.
- Virtual Reality Sports Training: Students explore how VR technology is being used for skill development, strategy training, and injury rehabilitation in various sports by discussing the emerging role of virtual reality in sports.
Bringing STEM into PE classes effectively requires the right resources, including technology tools, educational kits, and comprehensive guides. Resources like the STEM Sports® kits provide ready-to-use activities that seamlessly blend physical education with STEM learning. These kits offer an invaluable resource for teachers looking to enrich their curriculum and engage K-8 students through a cross-curricular learning approach. For additional resources, tools, and innovative ideas, please visit STEM Sports® .
- +1 (602) 845-0316
- 1601 N. 7th Street Suite 400 Phoenix, AZ 85006

Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
Join Our Mailing List
And get access to exclusive offers and content

Do you wish to stay up-to-date with STEM Sports®?
Sign up below to receive the latest information on our STEM education, curriculum and available resources.

The leader in quality Physical Education, Athletics, and Fitness equipment for 75 years.

Category: Activities
Whether you’re searching for creative PE activities to put a new spin on games, new ideas to become more efficient during assessments, or learn how to add technology to lessons, you have come to the right place! PE professionals share their knowledge to help teachers evolve their activities for students into high-energy and organized curriculum.

Our PE Future is Bright
Still Making Connections…a new passion from a “retired” PE Teacher. Deciding to retire from my district last June came with mixed emotions. I knew it

The Final Push: End-of-Year Reflections and Activities
We are getting close to the end of the school year and the Final Bell is about to ring, which means BRING ON SUMMER BREAK!

Becoming the Teacher your Students Remember
Hooping it up: hula hoop tips and tricks.
If there is one piece of equipment that I would suggest for you to purchase for your PE program, it’s Hula Hoops. They are so

6 Activities to Make Soccer Fun for Young Kids
Are you looking for ways to enhance your soccer unit for students in Kindergarten, 1st and 2nd grade? These games allow students to practice skills
Schooling with Scooters: 6 Great Scooter Games for PE
Kids love scooters because they are fast and fun! Scooter activities provide cardiovascular and muscular endurance opportunities as well as so many other learning experiences.

Challenge Your Students with Parkour
Looking for a challenging content domain to motivate children to learn a broad range of motor skills? Consider parkour! The goal of parkour is to

Flying into Fun: Disc It, the Next Evolution in PE Games
Ah, the humble flying disc – the iconic plastic toy that has been soaring through the skies since its accidental invention in the 1930s. From

Elevate Student Fitness with the Hula Hut Team Challenge
Hula Hut Fitness Team Challenge is an adventure that involves hula hoops, dodgeballs, and Frisbees? Grab your team and gear—6 hula hoops, a foam dodgeball,

It’s Time for Something New: A Journey to Fundraising Success!
*health. moves. minds.® is a fundraising program where 50% of funds raised go back to your school!Get started with your event by completing this short interest form. Describe

JOIN OUR NEWSLETTER
Sign up to receive the latest physical education resources, activities, and more from educational professionals like you straight to your inbox!

- Browse By Category
- View ALL Lessons
- Submit Your Idea
- Shop Lesson Books
- Search our Lessons
- Browse All Assessments
- New Assessments
- Paper & Pencil Assessments
- Alternative Assessments
- Student Assessments
- View Kids Work
- Submit Your Ideas
- Browse All Best Practices
- New Best Practices
- How BPs Work
- Most Popular
- Alphabetical
- Submit Your Best Practice
- Browse All Prof. Dev.
- Online PD Courses
- Onsite Workshops
- Hall of Shame
- Becoming a PE Teacher
- PE Articles
- Defending PE
- Substitute Guidelines
- Online Classes
- PE Research
- Browse All Boards
- Board of the Week
- Submit Your Bulletin Board
- Browse All Class Mngt
- Lesson Ideas
- New Teacher Tips
- Reducing Off-Task Behavior
- Browse All Videos
- Find Grants
- Kids Quote of the Week
- Weekly Activities
- Advertise on PEC
- FREE Newsletter
PE Central has partnered with S&S Discount Sports to provide a full range of sports and PE products for your program.
Get Free Shipping plus 15% OFF on orders over $59! Use offer code B4260. Shop Now!
- Shop Online Courses:
- Classroom Management
- Integrating Literacy & Math
- Grad Credit
- All PE Courses

- Cooperative Fitness Challenge
- Cooperative Skills Challenge
- Log It (Activity Tracker)

- Instant Activities
- Grades 9-12
- Dance of the Month
- Special Events Menu
- Cues/Performance Tips
- College Lessons
- Search All Lessons

- Paper & Pencil Assessments
- Shop Assessment

- How BP's Work

- Shop Bulletin Board Books

- Apps for PE Main Menu
- Submit Your App
- Ask our App Expert
- Active Gaming

- What is Adapted PE
- Ask Our Expert
- Adapting Activities
- IEP Information
- Adapted Web Sites
- Shop Adapted Store

- PreK Lesson Ideas
- PreK Videos
- Homemade PreK PE Equip
- Shop PreK Books

- Shop Class Mngt Products

- Search Jobs
- Interview Questions
- Interview Tips
- Portfolio Development

- Becoming PE Teacher
- Fundraising/Grants

- New Products
- T-Shirts/Accessories
- Class Management
- Middle School
- High School
- Curriculums
- Limited Space

- Search Our Lessons

New Online Courses
- Among Us Fitness Challenge
- Mystery Exercise Box
- The ABC's of Yoga
- Fun Reaction Light Workout
- Virtual Hopscotch
- Red Light, Green Light
- My Name Fitness Challenge
- Holiday Lessons
- Fitness Challenge Calendars
- Field Day Headquarters
- Field Day Online Course
- Star Wars FD
- Power Rangers Field Day
- Superhero FD
- SUPER "FIELD DAY" WORLD
- Nickelodeon FD
- What's New on PEC
- Halloween Station Cards
- Halloween Locomotors
- Thriller Halloween Dance
- Halloween Safety Tips Board
- Spooktacular Diet Board
- Halloween Nutritional Board
- Chicken Dance Drum Fitness
- Mission "Possible" Fitness
- Setting Goals - Fitnessgram
- Muscular Endurance Homework
- Poster Contest-Good Fitness
- Musical Fitness Dots
- FALLing for Fitness
- Fitness Routines
- Free PE Homework Lessons
- K-4 Report Card
- K-2 Progress Report
- Central Cass MS Report Card
- MS Evaluation Tool
- Activity Evaluation Tool
- SLO and Smart Goal Examples
- No Quacks About It-You Can Assess
- Super 6 Fitness Stations
- Throwing at the Moving Ducks
- Basketball Station Team Challenge
- Tennis Stations
- Olympic Volleyball Skills
- Fitness Stations Self Assessment
- Peer Assessment Fitness Checklist
- Where s the Turkey Fitness Game
- Thanksgiving PE Board Game
- Turkey Bowl
- Thanksgiving Extravaganza!
- Twas the Night Before Thanksgiving
- Team Turkey Hunt
- Thanksgiving Healthy Food & Locomotors
- View Spring Schedule
- Curriculum Development in PE
- Assessment in PE
- Methods of Teaching Elem PE
- Methods of Teaching Adapted PE
- Using Technology in PE
- History of PE
- View Self-Paced Courses
- PE for Kids with Severe Disabilities
- Add Int'l Flair to Your Program
- Teaching Yoga in PE
- Classroom Management Tips
- Social & Emotional Learning in PE
- Large Group Games in PE
- Teaching PE In Limited Space
- My Favorite Apps in PE
- See All Courses
- PE Homework Ideas
- Home Activity Visual Packet
- Home Fitness Games
- Activity Calendars
- 10 At Home Learning Activities
- Distance Learning Google Drive
- Log It Activity Log
- Hair UP! Dance
- Jumping Jack Mania Dance
- Shaking it to "Uptown Funk"
- Dynamite Line Dance Routine
- Core Strength w Rhythm Sticks
- Dancing with the Skeletal System
- Team Building and Rhythms Dance
- Back to School Apple Board
- How I Exercised Over the Summer
- Picture Yourself Participating in PE
- Thumbs Up for Learning PE
- Welcome to PE
- Let's Get Moving
- What Makes You a Star
- Do Not Stop Trying!
- Fall Team Buildiing Field Day
- Better When I'm Dancin'
- Locomotor Scavenger Hunt
- Follow My Lead IA
- Pass, Dribble, "D"
- Fitness Concepts Assessment
- Silvia Family Hometown Hero's BB
- See All New Ideas
- Project Based Learning in PE
- Flipped Teaching in PE
- Assessment Strategies
- Technology in PE
- Fitness and FitnessGram
- Curriculum Planning/Mapping
- Call to Book - 678-764-2536
- End of Year PE Poem
- Just Taught My Last Class Blog
- We've Grown so Much Board
- Time Flies Board
- Hanging Out This Summer Board
- How will YOU be ACTIVE? Board
- Staying Active Over Summer Board
- St. Patrick's Day Circuit
- Catch The Leprechaun
- Leprechaun Treasure Hunt
- Irish Jig Tag
- Celebrating St. Patty\92s Day Dance
- LUCKY to have PE Board
- Eat Green for Health Board
- Activity Skills Assessment
- Smart Goal Example
- Understanding Fitness Components
- Cooperation Assessment
- Line Dance Peer Evaluation
- View All Assessments
- Detective Valentine
- Valentine Volley
- Valentine's For the Heart
- Valentine Rescue
- 100 Ways Heart Healthy Board
- Make a Healthy Heart Your Valentine
- Don't Overlook Your Health
- Star Wars Dance Lesson
- Merry Fitmas Bulletin Board
- Welcome to PE Bulletin Board
- Gymnastics Skills Bulletin Board
- Don't Let Being Healthy Puzzle You
- It's Snow Easy to be Active
- Exercise Makes You Bright
- Basketball Lesson
- Bottle Cap Basketball
- Skills Card Warm Up
- Building Dribblers
- Feed the Frogs
- Rings of Fire Dribbling
- All basketball ideas on PEC
- Fall Into Fitness Board
- Turkeys in Training
- Gobbling Up Healthy Snacks
- Gobble If You Love PE
- Don't Gobble 'Til You Wobble
- Hickory Elem is Thankful
- Mr. Gobble Says
- Fall & Rise of PE Part 1
- Fall & Rise of PE Part 2
- PE Teachers Making a Difference
- Leading Enthusiastic Student Groups
- Using Twitter for PE PD
- Two Person Parachute Activity
- Pool Noodle Lessons in PE
- Basketball Shooting Stations
- Thanksgiving Stations
- Sobriety Testing Stations
- Seuss-Perb Stations
- Cooperative Skills Stations
- Cooperative Fitness Stations
Help for HPE at Home Download Free
Pe central online courses learn more, shop the p.e. & sports flash sale now shop now.

Call Sandy ( 800-243-9232 , ext. 2361) at S&S Worldwide for a great equipment deal!
What's New | Search PEC | Teaching Articles | Hall of Shame | Kids Quotes | Shop S&S

What's New Lesson Ideas Newsletter Site Updated: 6-11-15
Great PE Ideas! Superstars of PE
PE Job Center (Job Openings, Sample Interview Questions, Portfolio Guidelines

Inspirational Video! Cerebral Palsy Run--Matt Woodrum Cheered on by PE Teacher, Family and Classmates
New Blog! Physical Educators \96 You Are Making a Difference!
Physical Education teachers are truly amazing! I have believed this ever since I become one back in 1986 and I was reminded of how truly special they are the other day while reviewing 236 responses to a survey that S&S conducted on PE Central. Question number 21 of the survey reads, \93What gets you most excited about your physical education job?\94 Continue to read full blog post


Use LOG IT To Keep Kids Active Over the Summer

We have searched our site and found some fun things to encourage your kids to become physically active over the summer. Check out some of our cool summer bulletin boards and for a great professional development conference we highly recommend the National PE Institute July 27-29 in Asheville, NC.
- LOG IT --walk virtually around the USA. Sign your kids up before they leave school!
- Log It is a Step Towards Fitness (Education World Article)
Best Practices:
- Leadership and Summer Fitness through "Charity Miles"
Bulletin Boards:
- Countdown to Summer
- Hanging Out This Summer
- Summer Plans

New! Dancing with Math Dance Idea of the Month | More New Ideas
FREE Top 10 Field Day Activities eBook Enter $2,500 Giveaway Contest for a chance to win the "Field Day of Your Dreams!" 25% off Field Day equipment! Offer code E4213. (Expires 4/30/15)

Field Day just got easier! We have worked with our partner S&S Discount Sports to come up with the ultimate "Top 10 Field Day Activities" FREE eBook . You can enter their $2,500 Giveaway contest for a chance to win the "Field Day of Your Dreams!" Check it out!

Congrats to Nicki Newman Case and her Student!
Last week, physical education teacher Nicki Newman Case, got her Kids Quote of the Week published. She sent us the picture (below) of the young man who was responsible for the quote! By getting the quote published on PE Central, she has earned a $50 eGift card from our sponsor, S&S Worldwide! Here is her Facebook post on PEC. Thanks for sharing Nicki and congrats to both of you!
Nicki Newman Case, PEC Facebook Post " I wanted to thank PE Central for sending me an email that said I won $50 for a published kid quote. I am going to let the kid who wrote the Valentine help me pick out what he wants from the S&S catalog to use in our gym. I am also going to buy him the "I got Published" t-shirt. THANK YOU! I presented the winner of the Kids Quote of the Week with his T-shirt this morning at assembly! He LOVED it! "

Take the PE Central Survey! Complete and enter to win a $250 S&S Worldwide eGift Card
Stay Connected with PE Central Join the PE Central Facebook Page | Follow PE Central on Twitter

New Dances Waltzing Line Dance (with video) Shake It Senora Dance (with video) McDowell County, WV Happy Dance
Holiday Bulletin Boards | Holiday Lesson Ideas | What's New on PEC

New! Unedited Full Length Video Lessons
New! Valentine's Day Physical Education T-Shirts Order them now! They are awesome!

Share the Cooperative Fitness Challenges! 6 Free Fitness Station Activities
Dance Lesson Ideas of the Month!
Enter for a Chance to Win $100!
Are you teaching The First Tee National School Program in your school? What's working at your school? Send in your best practices and lesson plan ideas for the National School Program. Your roles as physical educators and leaders is vitally important to making a difference in a child\92s life. That\92s why we want to do our part in supporting you and share the great work you are doing. Click here to learn more
Want to bring The First Tee National School Program to your elementary school? To learn more go here
New! Physical Education Report Cards New! Pink PE Women's V-Neck Tee Register for the Cooperative Fitness and Skill Challenges
Featured Article: Using PE Central's \91LOG IT\92 as a Step Toward Fitness (Great way to track summer physical activity-- Log It )
New Teaching Videos Content is King: High School Circuits Lesson Highlights (9-12) Content is King: Food Pond Common Core Lesson Highlights (4th) Content is King: 4 x 4 fitness Lesson Highlights (5th) Basketball Dribbling Full Elementary Lesson
Featured Product! Elements of Dance Poster Set Workbook, Flashcard Set, Value Pack

61 Essential Apps for PE Teachers Book
20% Off Adapted PE Products

Featured Holiday Bulletin Boards
New Boards | View All Boards | Board of the Week | Submit a Board

School Funding Center Find grants for your school and program!
Featured Halloween Bulletin Board Don't Let Fitness Testing Spook You!
New Product Section: eBooks (PDF Downloads) Adapted PE Desk Reference eBook
NEW! Dance Lesson Idea of the Month: Team Building and Rhythms Dance (w/ Video)
Submit Your Ideas Now Published Ideas Earn a $50.00 eGift Card from S&S Worldwide
Sale! Save 20% on Most of Our Products! $3.00 Flat Rate Shipping Rate on ALL Orders
New eBOOKS! TEPE Books: Fitness, PreK, Assessment, PE Homework
Great Back to School Lesson Idea and Product! Behavior Self Check Lesson Idea and Poster Set
This Class Management Lesson idea, featuring 3 vinyl posters should help physical educators when students get a little bit off-task. View the entire lesson idea . Purchase Poster Set

Featured Classroom Management Lesson Idea: Behavior Self-Check Lesson (w/posters)
Check Out Our PE T-shirts
Happy thanksgiving.
Featured Thanksgiving Bulletin Boards

Featured Bulletin Boards ( View All Boards )

PE Central Copyright 1996-2020 All Rights Reserved

PE Central 2516 Blossom Trl W Blacksburg, VA 24060 E-mail : [email protected] Phone : 540-953-1043 Fax : 540-301-0112
Copyright 1996-2016 PE Central® www.pecentral.org All Rights Reserved Web Debut : 08/26/1996

Sign up for our free weekly newsletter and receive
physical education lesson ideas, assessment tips and more!
Your browser does not support iframes.
No thanks, I don't need to stay current on what works in physical education.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Committee on Physical Activity and Physical Education in the School Environment; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine; Kohl HW III, Cook HD, editors. Educating the Student Body: Taking Physical Activity and Physical Education to School. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 Oct 30.

Educating the Student Body: Taking Physical Activity and Physical Education to School.
- Hardcopy Version at National Academies Press
4 Physical Activity, Fitness, and Physical Education: Effects on Academic Performance
Key messages.
- Evidence suggests that increasing physical activity and physical fitness may improve academic performance and that time in the school day dedicated to recess, physical education class, and physical activity in the classroom may also facilitate academic performance.
- Available evidence suggests that mathematics and reading are the academic topics that are most influenced by physical activity. These topics depend on efficient and effective executive function, which has been linked to physical activity and physical fitness.
- Executive function and brain health underlie academic performance. Basic cognitive functions related to attention and memory facilitate learning, and these functions are enhanced by physical activity and higher aerobic fitness.
- Single sessions of and long-term participation in physical activity improve cognitive performance and brain health. Children who participate in vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity benefit the most.
- Given the importance of time on task to learning, students should be provided with frequent physical activity breaks that are developmentally appropriate.
- Although presently understudied, physically active lessons offered in the classroom may increase time on task and attention to task in the classroom setting.
Although academic performance stems from a complex interaction between intellect and contextual variables, health is a vital moderating factor in a child's ability to learn. The idea that healthy children learn better is empirically supported and well accepted ( Basch, 2010 ), and multiple studies have confirmed that health benefits are associated with physical activity, including cardiovascular and muscular fitness, bone health, psychosocial outcomes, and cognitive and brain health ( Strong et al., 2005 ; see Chapter 3 ). The relationship of physical activity and physical fitness to cognitive and brain health and to academic performance is the subject of this chapter.
Given that the brain is responsible for both mental processes and physical actions of the human body, brain health is important across the life span. In adults, brain health, representing absence of disease and optimal structure and function, is measured in terms of quality of life and effective functioning in activities of daily living. In children, brain health can be measured in terms of successful development of attention, on-task behavior, memory, and academic performance in an educational setting. This chapter reviews the findings of recent research regarding the contribution of engagement in physical activity and the attainment of a health-enhancing level of physical fitness to cognitive and brain health in children. Correlational research examining the relationship among academic performance, physical fitness, and physical activity also is described. Because research in older adults has served as a model for understanding the effects of physical activity and fitness on the developing brain during childhood, the adult research is briefly discussed. The short- and long-term cognitive benefits of both a single session of and regular participation in physical activity are summarized.
Before outlining the health benefits of physical activity and fitness, it is important to note that many factors influence academic performance. Among these are socioeconomic status ( Sirin, 2005 ), parental involvement ( Fan and Chen, 2001 ), and a host of other demographic factors. A valuable predictor of student academic performance is a parent having clear expectations for the child's academic success. Attendance is another factor confirmed as having a significant impact on academic performance ( Stanca, 2006 ; Baxter et al., 2011 ). Because children must be present to learn the desired content, attendance should be measured in considering factors related to academic performance.
- PHYSICAL FITNESS AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY: RELATION TO ACADEMIC PERFORMANCE
State-mandated academic achievement testing has had the unintended consequence of reducing opportunities for children to be physically active during the school day and beyond. In addition to a general shifting of time in school away from physical education to allow for more time on academic subjects, some children are withheld from physical education classes or recess to participate in remedial or enriched learning experiences designed to increase academic performance ( Pellegrini and Bohn, 2005 ; see Chapter 5 ). Yet little evidence supports the notion that more time allocated to subject matter will translate into better test scores. Indeed, 11 of 14 correlational studies of physical activity during the school day demonstrate a positive relationship to academic performance ( Rasberry et al., 2011 ). Overall, a rapidly growing body of work suggests that time spent engaged in physical activity is related not only to a healthier body but also to a healthier mind ( Hillman et al., 2008 ).
Children respond faster and with greater accuracy to a variety of cognitive tasks after participating in a session of physical activity ( Tomporowski, 2003 ; Budde et al., 2008 ; Hillman et al., 2009 ; Pesce et al., 2009 ; Ellemberg and St-Louis-Deschênes, 2010 ). A single bout of moderate-intensity physical activity has been found to increase neural and behavioral concomitants associated with the allocation of attention to a specific cognitive task ( Hillman et al., 2009 ; Pontifex et al., 2012 ). And when children who participated in 30 minutes of aerobic physical activity were compared with children who watched television for the same amount of time, the former children cognitively outperformed the latter ( Ellemberg and St-Louis-Desêhenes, 2010 ). Visual task switching data among 69 overweight and inactive children did not show differences between cognitive performance after treadmill walking and sitting ( Tomporowski et al., 2008b ).
When physical activity is used as a break from academic learning time, postengagement effects include better attention ( Grieco et al., 2009 ; Bartholomew and Jowers, 2011 ), increased on-task behaviors ( Mahar et al., 2006 ), and improved academic performance ( Donnelly and Lambourne, 2011 ). Comparisons between 1st-grade students housed in a classroom with stand-sit desks where the child could stand at his/her discretion and in classrooms containing traditional furniture showed that the former children were highly likely to stand, thus expending significantly more energy than those who were seated ( Benden et al., 2011 ). More important, teachers can offer physical activity breaks as part of a supplemental curriculum or simply as a way to reset student attention during a lesson ( Kibbe et al., 2011 ; see Chapter 6 ) and when provided with minimal training can efficaciously produce vigorous or moderate energy expenditure in students ( Stewart et al., 2004 ). Further, after-school physical activity programs have demonstrated the ability to improve cardiovascular endurance, and this increase in aerobic fitness has been shown to mediate improvements in academic performance ( Fredericks et al., 2006 ), as well as the allocation of neural resources underlying performance on a working memory task ( Kamijo et al., 2011 ).
Over the past three decades, several reviews and meta-analyses have described the relationship among physical fitness, physical activity, and cognition (broadly defined as all mental processes). The majority of these reviews have focused on the relationship between academic performance and physical fitness—a physiological trait commonly defined in terms of cardiorespiratory capacity (e.g., maximal oxygen consumption; see Chapter 3 ). More recently, reviews have attempted to describe the effects of an acute or single bout of physical activity, as a behavior, on academic performance. These reviews have focused on brain health in older adults ( Colcombe and Kramer, 2003 ), as well as the effects of acute physical activity on cognition in adults ( Tomporowski, 2003 ). Some have considered age as part of the analysis ( Etnier et al., 1997 , 2006 ). Reviews focusing on research conducted in children ( Sibley and Etnier, 2003 ) have examined the relationship among physical activity, participation in sports, and academic performance ( Trudeau and Shephard, 2008 , 2010 ; Singh et al., 2012 ); physical activity and mental and cognitive health ( Biddle and Asare, 2011 ); and physical activity, nutrition, and academic performance ( Burkhalter and Hillman, 2011 ). The findings of most of these reviews align with the conclusions presented in a meta-analytic review conducted by Fedewa and Ahn (2011) . The studies reviewed by Fedewa and Ahn include experimental/quasi-experimental as well as cross-sectional and correlational designs, with the experimental designs yielding the highest effect sizes. The strongest relationships were found between aerobic fitness and achievement in mathematics, followed by IQ and reading performance. The range of cognitive performance measures, participant characteristics, and types of research design all mediated the relationship among physical activity, fitness, and academic performance. With regard to physical activity interventions, which were carried out both within and beyond the school day, those involving small groups of peers (around 10 youth of a similar age) were associated with the greatest gains in academic performance.
The number of peer-reviewed publications on this topic is growing exponentially. Further evidence of the growth of this line of inquiry is its increased global presence. Positive relationships among physical activity, physical fitness, and academic performance have been found among students from the Netherlands ( Singh et al., 2012 ) and Taiwan ( Chih and Chen, 2011 ). Broadly speaking, however, many of these studies show small to moderate effects and suffer from poor research designs ( Biddle and Asare, 2011 ; Singh et al., 2012 ).
Basch (2010) conducted a comprehensive review of how children's health and health disparities influence academic performance and learning. The author's report draws on empirical evidence suggesting that education reform will be ineffective unless children's health is made a priority. Basch concludes that schools may be the only place where health inequities can be addressed and that, if children's basic health needs are not met, they will struggle to learn regardless of the effectiveness of the instructional materials used. More recently, Efrat (2011) conducted a review of physical activity, fitness, and academic performance to examine the achievement gap. He discovered that only seven studies had included socioeconomic status as a variable, despite its known relationship to education ( Sirin, 2005 ).
Physical Fitness as a Learning Outcome of Physical Education and Its Relation to Academic Performance
Achieving and maintaining a healthy level of aerobic fitness, as defined using criterion-referenced standards from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES; Welk et al., 2011 ), is a desired learning outcome of physical education programming. Regular participation in physical activity also is a national learning standard for physical education, a standard intended to facilitate the establishment of habitual and meaningful engagement in physical activity ( NASPE, 2004 ). Yet although physical fitness and participation in physical activity are established as learning outcomes in all 50 states, there is little evidence to suggest that children actually achieve and maintain these standards (see Chapter 2 ).
Statewide and national datasets containing data on youth physical fitness and academic performance have increased access to student-level data on this subject ( Grissom, 2005 ; Cottrell et al., 2007 ; Carlson et al., 2008 ; Chomitz et al., 2008 ; Wittberg et al., 2010 ; Van Dusen et al., 2011 ). Early research in South Australia focused on quantifying the benefits of physical activity and physical education during the school day; the benefits noted included increased physical fitness, decreased body fat, and reduced risk for cardiovascular disease ( Dwyer et al., 1979 , 1983 ). Even today, Dwyer and colleagues are among the few scholars who regularly include in their research measures of physical activity intensity in the school environment, which is believed to be a key reason why they are able to report differentiated effects of different intensities. A longitudinal study in Trois-Rivières, Québec, Canada, tracked how the academic performance of children from grades 1 through 6 was related to student health, motor skills, and time spent in physical education. The researchers concluded that additional time dedicated to physical education did not inhibit academic performance ( Shephard et al., 1984 ; Shephard, 1986 ; Trudeau and Shephard, 2008 ).
Longitudinal follow-up investigating the long-term benefits of enhanced physical education experiences is encouraging but largely inconclusive. In a study examining the effects of daily physical education during elementary school on physical activity during adulthood, 720 men and women completed the Québec Health Survey ( Trudeau et al., 1999 ). Findings suggest that physical education was associated with physical activity in later life for females but not males ( Trudeau et al., 1999 ); most of the associations were significant but weak ( Trudeau et al., 2004 ). Adult body mass index (BMI) at age 34 was related to childhood BMI at ages 10-12 in females but not males ( Trudeau et al., 2001 ). Longitudinal studies such as those conducted in Sweden and Finland also suggest that physical education experiences may be related to adult engagement in physical activity ( Glenmark, 1994 ; Telama et al., 1997 ). From an academic performance perspective, longitudinal data on men who enlisted for military service imply that cardiovascular fitness at age 18 predicted cognitive performance in later life (Aberg et al., 2009), thereby supporting the idea of offering physical education and physical activity opportunities well into emerging adulthood through secondary and postsecondary education.
Castelli and colleagues (2007) investigated younger children (in 3rd and 5th grades) and the differential contributions of the various subcomponents of the Fitnessgram ® . Specifically, they examined the individual contributions of aerobic capacity, muscle strength, muscle flexibility, and body composition to performance in mathematics and reading on the Illinois Standardized Achievement Test among a sample of 259 children. Their findings corroborate those of the California Department of Education ( Grissom, 2005 ), indicating a general relationship between fitness and achievement test performance. When the individual components of the Fitnessgram were decomposed, the researchers determined that only aerobic capacity was related to test performance. Muscle strength and flexibility showed no relationship, while an inverse association of BMI with test performance was observed, such that higher BMI was associated with lower test performance. Although Baxter and colleagues (2011) confirmed the importance of attending school in relation to academic performance through the use of 4th-grade student recall, correlations with BMI were not significant.
State-mandated implementation of the coordinated school health model requires all schools in Texas to conduct annual fitness testing using the Fitnessgram among students in grades 3-12. In a special issue of Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport (2010), multiple articles describe the current state of physical fitness among children in Texas; confirm the associations among school performance levels, academic achievement, and physical fitness ( Welk et al., 2010 ; Zhu et al., 2010 ); and demonstrate the ability of qualified physical education teachers to administer physical fitness tests ( Zhu et al., 2010 ). Also using data from Texas schools, Van Dusen and colleagues (2011) found that cardiovascular fitness had the strongest association with academic performance, particularly in mathematics over reading. Unlike previous research, which demonstrated a steady decline in fitness by developmental stage ( Duncan et al., 2007 ), this study found that cardiovascular fitness did decrease but not significantly ( Van Dusen et al., 2011 ). Aerobic fitness, then, may be important to academic performance, as there may be a dose-response relationship ( Van Dusen et al., 2011 ).
Using a large sample of students in grades 4-8, Chomitz and colleagues (2008) found that the likelihood of passing both mathematics and English achievement tests increased with the number of fitness tests passed during physical education class, and the odds of passing the mathematics achievement tests were inversely related to higher body weight. Similar to the findings of Castelli and colleagues (2007) , socioeconomic status and demographic factors explained little of the relationship between aerobic fitness and academic performance; however, socioeconomic status may be an explanatory variable for students of low fitness ( London and Castrechini, 2011 ).
In sum, numerous cross-sectional and correlational studies demonstrate small-to-moderate positive or null associations between physical fitness ( Grissom, 2005 ; Cottrell et al., 2007 ; Edwards et al., 2009; Eveland-Sayers et al., 2009 ; Cooper et al., 2010 ; Welk et al., 2010 ; Wittberg et al., 2010 ; Zhu et al., 2010 ; Van Dusen et al., 2011 ), particularly aerobic fitness, and academic performance ( Castelli et al, 2007 ; Chomitz et al., 2008 ; Roberts et al., 2010 ; Welk et al., 2010 ; Chih and Chen, 2011 ; London and Castrechini, 2011 ; Van Dusen et al., 2011 ). Moreover, the findings may support a dose-response association, suggesting that the more components of physical fitness (e.g., cardiovascular endurance, strength, muscle endurance) considered acceptable for the specific age and gender that are present, the greater the likelihood of successful academic performance. From a public health and policy standpoint, the conclusions these findings support are limited by few causal inferences, a lack of data confirmation, and inadequate reliability because the data were often collected by nonresearchers or through self-report methods. It may also be noted that this research includes no known longitudinal studies and few randomized controlled trials (examples are included later in this chapter in the discussion of the developing brain).
Physical Activity, Physical Education, and Academic Performance
In contrast with the correlational data presented above for physical fitness, more information is needed on the direct effects of participation in physical activity programming and physical education classes on academic performance.
In a meta-analysis, Sibley and Etnier (2003) found a positive relationship between physical activity and cognition in school-age youth (aged 4-18), suggesting that physical activity, as well as physical fitness, may be related to cognitive outcomes during development. Participation in physical activity was related to cognitive performance in eight measurement categories (perceptual skills, IQ, achievement, verbal tests, mathematics tests, memory, developmental level/academic readiness, and “other”), with results indicating a beneficial relationship of physical activity to all cognitive outcomes except memory ( Sibley and Etnier, 2003 ). Since that meta-analysis, however, several papers have reported robust relationships between aerobic fitness and different aspects of memory in children (e.g., Chaddock et al., 2010a , 2011 ; Kamijo et al., 2011 ; Monti et al., 2012 ). Regardless, the comprehensive review of Sibley and Etnier (2003) was important because it helped bring attention to an emerging literature suggesting that physical activity may benefit cognitive development even as it also demonstrated the need for further study to better understand the multifaceted relationship between physical activity and cognitive and brain health.
The regular engagement in physical activity achieved during physical education programming can also be related to academic performance, especially when the class is taught by a physical education teacher. The Sports, Play, and Active Recreation for Kids (SPARK) study examined the effects of a 2-year health-related physical education program on academic performance in children ( Sallis et al., 1999 ). In an experimental design, seven elementary schools were randomly assigned to one of three conditions: (1) a specialist condition in which certified physical education teachers delivered the SPARK curriculum, (2) a trained-teacher condition in which classroom teachers implemented the curriculum, and (3) a control condition in which classroom teachers implemented the local physical education curriculum. No significant differences by condition were found for mathematics testing; however, reading scores were significantly higher in the specialist condition relative to the control condition ( Sallis et al., 1999 ), while language scores were significantly lower in the specialist condition than in the other two conditions. The authors conclude that spending time in physical education with a specialist did not have a negative effect on academic performance. Shortcomings of this research include the amount of data loss from pre- to posttest, the use of results of 2nd-grade testing that exceeded the national average in performance as baseline data, and the use of norm-referenced rather than criterion-based testing.
In seminal research conducted by Gabbard and Barton (1979) , six different conditions of physical activity (no activity; 20, 30, 40, and 50 minutes; and posttest no activity) were completed by 106 2nd graders during physical education. Each physical activity session was followed by 5 minutes of rest and the completion of 36 math problems. The authors found a potential threshold effect whereby only the 50-minute condition improved mathematical performance, with no differences by gender.
A longitudinal study of the kindergarten class of 1998–1999, using data from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study, investigated the association between enrollment in physical education and academic achievement ( Carlson et al., 2008 ). Higher amounts of physical education were correlated with better academic performance in mathematics among females, but this finding did not hold true for males.
Ahamed and colleagues (2007) found in a cluster randomized trial that, after 16 months of a classroom-based physical activity intervention, there was no significant difference between the treatment and control groups in performance on the standardized Cognitive Abilities Test, Third Edition (CAT-3). Others have found, however, that coordinative exercise ( Budde et al., 2008 ) or bouts of vigorous physical activity during free time ( Coe et al., 2006 ) contribute to higher levels of academic performance. Specifically, Coe and colleagues examined the association of enrollment in physical education and self-reported vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity outside school with performance in core academic courses and on the Terra Nova Standardized Achievement Test among more than 200 6th-grade students. Their findings indicate that academic performance was unaffected by enrollment in physical education classes, which were found to average only 19 minutes of vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity. When time spent engaged in vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity outside of school was considered, however, a significant positive relation to academic performance emerged, with more time engaged in vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity being related to better grades but not test scores ( Coe et al., 2006 ).
Studies of participation in sports and academic achievement have found positive associations ( Mechanic and Hansell, 1987 ; Dexter, 1999 ; Crosnoe, 2002 ; Eitle and Eitle, 2002 ; Stephens and Schaben, 2002 ; Eitle, 2005 ; Miller et al., 2005 ; Fox et al., 2010 ; Ruiz et al., 2010 ); higher grade point averages (GPAs) in season than out of season ( Silliker and Quirk, 1997 ); a negative association between cheerleading and science performance ( Hanson and Kraus, 1998 ); and weak and negative associations between the amount of time spent participating in sports and performance in English-language class among 13-, 14-, and 16-year-old students ( Daley and Ryan, 2000 ). Other studies, however, have found no association between participation in sports and academic performance ( Fisher et al., 1996 ). The findings of these studies need to be interpreted with caution as many of their designs failed to account for the level of participation by individuals in the sport (e.g., amount of playing time, type and intensity of physical activity engagement by sport). Further, it is unclear whether policies required students to have higher GPAs to be eligible for participation. Offering sports opportunities is well justified regardless of the cognitive benefits, however, given that adolescents may be less likely to engage in risky behaviors when involved in sports or other extracurricular activities ( Page et al., 1998 ; Elder et al., 2000 ; Taliaferro et al., 2010 ), that participation in sports increases physical fitness, and that affiliation with sports enhances school connectedness.
Although a consensus on the relationship of physical activity to academic achievement has not been reached, the vast majority of available evidence suggests the relationship is either positive or neutral. The meta-analytic review by Fedewa and Ahn (2011) suggests that interventions entailing aerobic physical activity have the greatest impact on academic performance; however, all types of physical activity, except those involving flexibility alone, contribute to enhanced academic performance, as do interventions that use small groups (about 10 students) rather than individuals or large groups. Regardless of the strength of the findings, the literature indicates that time spent engaged in physical activity is beneficial to children because it has not been found to detract from academic performance, and in fact can improve overall health and function ( Sallis et al., 1999 ; Hillman et al., 2008 ; Tomporowski et al., 2008a ; Trudeau and Shephard, 2008 ; Rasberry et al., 2011 ).
Single Bouts of Physical Activity
Beyond formal physical education, evidence suggests that multi-component approaches are a viable means of providing physical activity opportunities for children across the school curriculum (see also Chapter 6 ). Although health-related fitness lessons taught by certified physical education teachers result in greater student fitness gains relative to such lessons taught by other teachers ( Sallis et al., 1999 ), non-physical education teachers are capable of providing opportunities to be physically active within the classroom ( Kibbe et al., 2011 ). Single sessions or bouts of physical activity have independent merit, offering immediate benefits that can enhance the learning experience. Studies have found that single bouts of physical activity result in improved attention ( Hillman et al., 2003 , 2009 ; Pontifex et al., 2012 ), better working memory ( Pontifex et al., 2009 ), and increased academic learning time and reduced off-task behaviors ( Mahar et al., 2006 ; Bartholomew and Jowers, 2011 ). Yet single bouts of physical activity have differential effects, as very vigorous exercise has been associated with cognitive fatigue and even cognitive decline in adults ( Tomporowski, 2003 ). As seen in Figure 4-1 , high levels of effort, arousal, or activation can influence perception, decision making, response preparation, and actual response. For discussion of the underlying constructs and differential effects of single bouts of physical activity on cognitive performance, see Tomporowski (2003) .
Information processing: Diagram of a simplified version of Sanders's (1983) cognitive-energetic model of human information processing (adapted from Jones and Hardy, 1989). SOURCE: Tomporowski, 2003. Reprinted with permission.
For children, classrooms are busy places where they must distinguish relevant information from distractions that emerge from many different sources occurring simultaneously. A student must listen to the teacher, adhere to classroom procedures, focus on a specific task, hold and retain information, and make connections between novel information and previous experiences. Hillman and colleagues (2009) demonstrated that a single bout of moderate-intensity walking (60 percent of maximum heart rate) resulted in significant improvements in performance on a task requiring attentional inhibition (e.g., the ability to focus on a single task). These findings were accompanied by changes in neuroelectric measures underlying the allocation of attention (see Figure 4-2 ) and significant improvements on the reading subtest of the Wide Range Achievement Test. No such effects were observed following a similar duration of quiet rest. These findings were later replicated and extended to demonstrate benefits for both mathematics and reading performance in healthy children and those diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ( Pontifex et al., 2013 ). Further replications of these findings demonstrated that a single bout of moderate-intensity exercise using a treadmill improved performance on a task of attention and inhibition, but similar benefits were not derived from moderate-intensity exercise that involved exergaming ( O'Leary et al., 2011 ). It was also found that such benefits were derived following cessation of, but not during, the bout of exercise ( Drollette et al., 2012 ). The applications of such empirical findings within the school setting remain unclear.
Effects of a single session of exercise in preadolescent children. SOURCE: Hillman et al., 2009. Reprinted with permission.
A randomized controlled trial entitled Physical Activity Across the Curriculum (PAAC) used cluster randomization among 24 schools to examine the effects of physically active classroom lessons on BMI and academic achievement ( Donnelly et al., 2009 ). The academically oriented physical activities were intended to be of vigorous or moderate intensity (3–6 metabolic equivalents [METs]) and to last approximately 10 minutes and were specifically designed to supplement content in mathematics, language arts, geography, history, spelling, science, and health. The study followed 665 boys and 677 girls for 3 years as they rose from 2nd or 3rd to 4th or 5th grades. Changes in academic achievement, fitness, and blood screening were considered secondary outcomes. During a 3-year period, students who engaged in physically active lessons, on average, improved their academic achievement by 6 percent, while the control groups exhibited a 1 percent decrease. In students who experienced at least 75 minutes of PAAC lessons per week, BMI remained stable (see Figure 4-3 ).
Change in academic scores from baseline after physically active classroom lessons in elementary schools in northeast Kansas (2003–2006). NOTE: All differences between the Physical Activity Across the Curriculum (PAAC) group ( N = 117) and control (more...)
It is important to note that cognitive tasks completed before, during, and after physical activity show varying effects, but the effects were always positive compared with sedentary behavior. In a study carried out by Drollette and colleagues (2012) , 36 preadolescent children completed two cognitive tasks—a flanker task to assess attention and inhibition and a spatial nback task to assess working memory—before, during, and after seated rest and treadmill walking conditions. The children sat or walked on different days for an average of 19 minutes. The results suggest that the physical activity enhanced cognitive performance for the attention task but not for the task requiring working memory. Accordingly, although more research is needed, the authors suggest that the acute effects of exercise may be selective to certain cognitive processes (i.e., attentional inhibition) while unrelated to others (e.g., working memory). Indeed, data collected using a task-switching paradigm (i.e., a task designed to assess multitasking and requiring the scheduling of attention to multiple aspects of the environment) among 69 overweight and inactive children did not show differences in cognitive performance following acute bouts of treadmill walking or sitting ( Tomporowski et al., 2008b ). Thus, findings to date indicate a robust relationship of acute exercise to transient improvements in attention but appear inconsistent for other aspects of cognition.
Academic Learning Time and On- and Off-Task Behaviors
Excessive time on task, inattention to task, off-task behavior, and delinquency are important considerations in the learning environment given the importance of academic learning time to academic performance. These behaviors are observable and of concern to teachers as they detract from the learning environment. Systematic observation by trained observers may yield important insight regarding the effects of short physical activity breaks on these behaviors. Indeed, systematic observations of student behavior have been used as an alternative means of measuring academic performance ( Mahar et al., 2006 ; Grieco et al., 2009 ).
After the development of classroom-based physical activities, called Energizers, teachers were trained in how to implement such activities in their lessons at least twice per week ( Mahar et al., 2006 ). Measurements of baseline physical activity and on-task behaviors were collected in two 3rd-grade and two 4th-grade classes, using pedometers and direct observation. The intervention included 243 students, while 108 served as controls by not engaging in the activities. A subgroup of 62 3rd and 4th graders was observed for on-task behavior in the classroom following the physical activity. Children who participated in Energizers took more steps during the school day than those who did not; they also increased their on-task behaviors by more than 20 percent over baseline measures.
A systematic review of a similar in-class, academically oriented, physical activity plan—Take 10!—was conducted to identify the effects of its implementation after it had been in use for 10 years ( Kibbe et al., 2011 ). The findings suggest that children who experienced Take 10! in the classroom engaged in moderate to vigorous physical activity (6.16 to 6.42 METs) and had lower BMIs than those who did not. Further, children in the Take 10! classrooms had better fluid intelligence ( Reed et al., 2010 ) and higher academic achievement scores ( Donnelly et al., 2009 ).
Some have expressed concern that introducing physical activity into the classroom setting may be distracting to students. Yet in one study it was sedentary students who demonstrated a decrease in time on task, while active students returned to the same level of on-task behavior after an active learning task ( Grieco et al., 2009 ). Among the 97 3rd-grade students in this study, a small but nonsignificant increase in on-task behaviors was seen immediately following these active lessons. Additionally, these improvements were not mediated by BMI.
In sum, although presently understudied, physically active lessons may increase time on task and attention to task in the classroom setting. Given the complexity of the typical classroom, the strategy of including content-specific lessons that incorporate physical activity may be justified.
It is recommended that every child have 20 minutes of recess each day and that this time be outdoors whenever possible, in a safe activity ( NASPE, 2006 ). Consistent engagement in recess can help students refine social skills, learn social mediation skills surrounding fair play, obtain additional minutes of vigorous- or moderate-intensity physical activity that contribute toward the recommend 60 minutes or more per day, and have an opportunity to express their imagination through free play ( Pellegrini and Bohn, 2005 ; see also Chapter 6 ). When children participate in recess before lunch, additional benefits accrue, such as less food waste, increased incidence of appropriate behavior in the cafeteria during lunch, and greater student readiness to learn upon returning to the classroom after lunch ( Getlinger et al., 1996 ; Wechsler et al., 2001 ).
To examine the effects of engagement in physical activity during recess on classroom behavior, Barros and colleagues (2009) examined data from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study on 10,000 8- to 9-year-old children. Teachers provided the number of minutes of recess as well as a ranking of classroom behavior (ranging from “misbehaves frequently” to “behaves exceptionally well”). Results indicate that children who had at least 15 minutes of recess were more likely to exhibit appropriate behavior in the classroom ( Barros et al., 2009 ). In another study, 43 4th-grade students were randomly assigned to 1 or no days of recess to examine the effects on classroom behavior ( Jarrett et al., 1998 ). The researchers concluded that on-task behavior was better among the children who had recess. A moderate effect size (= 0.51) was observed. In a series of studies examining kindergartners' attention to task following a 20-minute recess, increased time on task was observed during learning centers and story reading ( Pellegrini et al., 1995 ). Despite these positive findings centered on improved attention, it is important to note that few of these studies actually measured the intensity of the physical activity during recess.
From a slightly different perspective, survey data from 547 Virginia elementary school principals suggest that time dedicated to student participation in physical education, art, and music did not negatively influence academic performance ( Wilkins et al., 2003 ). Thus, the strategy of reducing time spent in physical education to increase academic performance may not have the desired effect. The evidence on in-school physical activity supports the provision of physical activity breaks during the school day as a way to increase fluid intelligence, time on task, and attention. However, it remains unclear what portion of these effects can be attributed to a break from academic time and what portion is a direct result of the specific demands/characteristics of the physical activity.
- THE DEVELOPING bRAIN, PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, AND BRAIN HEALTH
The study of brain health has grown beyond simply measuring behavioral outcomes such as task performance and reaction time (e.g., cognitive processing speed). New technology has emerged that has allowed scientists to understand the impact of lifestyle factors on the brain from the body systems level down to the molecular level. A greater understanding of the cognitive components that subserve academic performance and may be amenable to intervention has thereby been gained. Research conducted in both laboratory and field settings has helped define this line of inquiry and identify some preliminary underlying mechanisms.
The Evidence Base on the Relationship of Physical Activity to Brain Health and Cognition in Older Adults
Despite the current focus on the relationship of physical activity to cognitive development, the evidence base is larger on the association of physical activity with brain health and cognition during aging. Much can be learned about how physical activity affects childhood cognition and scholastic achievement through this work. Despite earlier investigations into the relationship of physical activity to cognitive aging (see Etnier et al., 1997 , for a review), the field was shaped by the findings of Kramer and colleagues (1999) , who examined the effects of aerobic fitness training on older adults using a randomized controlled design. Specifically, 124 older adults aged 60 and 75 were randomly assigned to a 6-month intervention of either walking (i.e., aerobic training) or flexibility (i.e., nonaerobic) training. The walking group but not the flexibility group showed improved cognitive performance, measured as a shorter response time to the presented stimulus. Results from a series of tasks that tapped different aspects of cognitive control indicated that engagement in physical activity is a beneficial means of combating cognitive aging ( Kramer et al., 1999 ).
Cognitive control, or executive control, is involved in the selection, scheduling, and coordination of computational processes underlying perception, memory, and goal-directed action. These processes allow for the optimization of behavioral interactions within the environment through flexible modulation of the ability to control attention ( MacDonald et al., 2000 ; Botvinick et al., 2001 ). Core cognitive processes that make up cognitive control or executive control include inhibition, working memory, and cognitive flexibility ( Diamond, 2006 ), processes mediated by networks that involve the prefrontal cortex. Inhibition (or inhibitory control) refers to the ability to override a strong internal or external pull so as to act appropriately within the demands imposed by the environment ( Davidson et al., 2006 ). For example, one exerts inhibitory control when one stops speaking when the teacher begins lecturing. Working memory refers to the ability to represent information mentally, manipulate stored information, and act on the information ( Davidson et al., 2006 ). In solving a difficult mathematical problem, for example, one must often remember the remainder. Finally, cognitive flexibility refers to the ability to switch perspectives, focus attention, and adapt behavior quickly and flexibly for the purposes of goal-directed action ( Blair et al., 2005 ; Davidson et al., 2006 ; Diamond, 2006 ). For example, one must shift attention from the teacher who is teaching a lesson to one's notes to write down information for later study.
Based on their earlier findings on changes in cognitive control induced by aerobic training, Colcombe and Kramer (2003) conducted a meta-analysis to examine the relationship between aerobic training and cognition in older adults aged 55-80 using data from 18 randomized controlled exercise interventions. Their findings suggest that aerobic training is associated with general cognitive benefits that are selectively and disproportionately greater for tasks or task components requiring greater amounts of cognitive control. A second and more recent meta-analysis ( Smith et al., 2010 ) corroborates the findings of Colcombe and Kramer, indicating that aerobic exercise is related to attention, processing speed, memory, and cognitive control; however, it should be noted that smaller effect sizes were observed, likely a result of the studies included in the respective meta-analyses. In older adults, then, aerobic training selectively improves cognition.
Hillman and colleagues (2006) examined the relationship between physical activity and inhibition (one aspect of cognitive control) using a computer-based stimulus-response protocol in 241 individuals aged 15-71. Their results indicate that greater amounts of physical activity are related to decreased response speed across task conditions requiring variable amounts of inhibition, suggesting a generalized relationship between physical activity and response speed. In addition, the authors found physical activity to be related to better accuracy across conditions in older adults, while no such relationship was observed for younger adults. Of interest, this relationship was disproportionately larger for the condition requiring greater amounts of inhibition in the older adults, suggesting that physical activity has both a general and selective association with task performance ( Hillman et al., 2006 ).
With advances in neuroimaging techniques, understanding of the effects of physical activity and aerobic fitness on brain structure and function has advanced rapidly over the past decade. In particular, a series of studies ( Colcombe et al., 2003 , 2004 , 2006 ; Kramer and Erickson, 2007 ; Hillman et al., 2008 ) of older individuals has been conducted to elucidate the relation of aerobic fitness to the brain and cognition. Normal aging results in the loss of brain tissue ( Colcombe et al., 2003 ), with markedly larger loss evidenced in the frontal, temporal, and parietal regions ( Raz, 2000 ). Thus cognitive functions subserved by these brain regions (such as those involved in cognitive control and aspects of memory) are expected to decay more dramatically than other aspects of cognition.
Colcombe and colleagues (2003) investigated the relationship of aerobic fitness to gray and white matter tissue loss using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in 55 healthy older adults aged 55-79. They observed robust age-related decreases in tissue density in the frontal, temporal, and parietal regions using voxel-based morphometry, a technique used to assess brain volume. Reductions in the amount of tissue loss in these regions were observed as a function of fitness. Given that the brain structures most affected by aging also demonstrated the greatest fitness-related sparing, these initial findings provide a biological basis for fitness-related benefits to brain health during aging.
In a second study, Colcombe and colleagues (2006) examined the effects of aerobic fitness training on brain structure using a randomized controlled design with 59 sedentary healthy adults aged 60-79. The treatment group received a 6-month aerobic exercise (i.e., walking) intervention, while the control group received a stretching and toning intervention that did not include aerobic exercise. Results indicated that gray and white matter brain volume increased for those who received the aerobic fitness training intervention. No such results were observed for those assigned to the stretching and toning group. Specifically, those assigned to the aerobic training intervention demonstrated increased gray matter in the frontal lobes, including the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, the supplementary motor area, the middle frontal gyrus, the dorsolateral region of the right inferior frontal gyrus, and the left superior temporal lobe. White matter volume changes also were evidenced following the aerobic fitness intervention, with increases in white matter tracts being observed within the anterior third of the corpus callosum. These brain regions are important for cognition, as they have been implicated in the cognitive control of attention and memory processes. These findings suggest that aerobic training not only spares age-related loss of brain structures but also may in fact enhance the structural health of specific brain regions.
In addition to the structural changes noted above, research has investigated the relationship between aerobic fitness and changes in brain function. That is, aerobic fitness training has also been observed to induce changes in patterns of functional activation. Functional MRI (fMRI) measures, which make it possible to image activity in the brain while an individual is performing a cognitive task, have revealed that aerobic training induces changes in patterns of functional activation. This approach involves inferring changes in neuronal activity from alteration in blood flow or metabolic activity in the brain. In a seminal paper, Colcombe and colleagues (2004) examined the relationship of aerobic fitness to brain function and cognition across two studies with older adults. In the first study, 41 older adult participants (mean age ~66) were divided into higher- and lower-fit groups based on their performance on a maximal exercise test. In the second study, 29 participants (aged 58-77) were recruited and randomly assigned to either a fitness training (i.e., walking) or control (i.e., stretching and toning) intervention. In both studies, participants were given a task requiring variable amounts of attention and inhibition. Results indicated that fitness (study 1) and fitness training (study 2) were related to greater activation in the middle frontal gyrus and superior parietal cortex; these regions of the brain are involved in attentional control and inhibitory functioning, processes entailed in the regulation of attention and action. These changes in neural activation were related to significant improvements in performance on the cognitive control task of attention and inhibition.
Taken together, the findings across studies suggest that an increase in aerobic fitness, derived from physical activity, is related to improvements in the integrity of brain structure and function and may underlie improvements in cognition across tasks requiring cognitive control. Although developmental differences exist, the general paradigm of this research can be applied to early stages of the life span, and some early attempts to do so have been made, as described below. Given the focus of this chapter on childhood cognition, it should be noted that this section has provided only a brief and arguably narrow look at the research on physical activity and cognitive aging. Considerable work has detailed the relationship of physical activity to other aspects of adult cognition using behavioral and neuroimaging tools (e.g., Boecker, 2011 ). The interested reader is referred to a number of review papers and meta-analyses describing the relationship of physical activity to various aspects of cognitive and brain health ( Etnier et al., 1997 ; Colcombe and Kramer, 2003 ; Tomporowski, 2003 ; Thomas et al., 2012 ).
Child Development, Brain Structure, and Function
Certain aspects of development have been linked with experience, indicating an intricate interplay between genetic programming and environmental influences. Gray matter, and the organization of synaptic connections in particular, appears to be at least partially dependent on experience (NRC/IOM, 2000; Taylor, 2006 ), with the brain exhibiting a remarkable ability to reorganize itself in response to input from sensory systems, other cortical systems, or insult ( Huttenlocher and Dabholkar, 1997 ). During typical development, experience shapes the pruning process through the strengthening of neural networks that support relevant thoughts and actions and the elimination of unnecessary or redundant connections. Accordingly, the brain responds to experience in an adaptive or “plastic” manner, resulting in the efficient and effective adoption of thoughts, skills, and actions relevant to one's interactions within one's environmental surroundings. Examples of neural plasticity in response to unique environmental interaction have been demonstrated in human neuroimaging studies of participation in music ( Elbert et al., 1995 ; Chan et al., 1998 ; Münte et al., 2001 ) and sports ( Hatfield and Hillman, 2001 ; Aglioti et al., 2008 ), thus supporting the educational practice of providing music education and opportunities for physical activity to children.
Effects of Regular Engagement in Physical Activity and Physical Fitness on Brain Structure
Recent advances in neuroimaging techniques have rapidly advanced understanding of the role physical activity and aerobic fitness may have in brain structure. In children a growing body of correlational research suggests differential brain structure related to aerobic fitness. Chaddock and colleagues (2010a , b ) showed a relationship among aerobic fitness, brain volume, and aspects of cognition and memory. Specifically, Chaddock and colleagues (2010a) assigned 9- to 10-year-old preadolescent children to lower- and higher-fitness groups as a function of their scores on a maximal oxygen uptake (VO 2 max) test, which is considered the gold-standard measure of aerobic fitness. They observed larger bilateral hippocampal volume in higher-fit children using MRI, as well as better performance on a task of relational memory. It is important to note that relational memory has been shown to be mediated by the hippocampus ( Cohen and Eichenbaum, 1993 ; Cohen et al., 1999 ). Further, no differences emerged for a task condition requiring item memory, which is supported by structures outside the hippocampus, suggesting selectivity among the aspects of memory that benefit from higher amounts of fitness. Lastly, hippocampal volume was positively related to performance on the relational memory task but not the item memory task, and bilateral hippocampal volume was observed to mediate the relationship between fitness and relational memory ( Chaddock et al., 2010a ). Such findings are consistent with behavioral measures of relational memory in children ( Chaddock et al., 2011 ) and neuroimaging findings in older adults ( Erickson et al., 2009 , 2011 ) and support the robust nonhuman animal literature demonstrating the effects of exercise on cell proliferation ( Van Praag et al., 1999 ) and survival ( Neeper et al., 1995 ) in the hippocampus.
In a second investigation ( Chaddock et al., 2010b ), higher- and lower-fit children (aged 9-10) underwent an MRI to determine whether structural differences might be found that relate to performance on a cognitive control task that taps attention and inhibition. The authors observed differential findings in the basal ganglia, a subcortical structure involved in the interplay of cognition and willed action. Specifically, higher-fit children exhibited greater volume in the dorsal striatum (i.e., caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus) relative to lower-fit children, while no differences were observed in the ventral striatum. Such findings are not surprising given the role of the dorsal striatum in cognitive control and response resolution ( Casey et al., 2008 ; Aron et al., 2009 ), as well as the growing body of research in children and adults indicating that higher levels of fitness are associated with better control of attention, memory, and cognition ( Colcombe and Kramer, 2003 ; Hillman et al., 2008 ; Chang and Etnier, 2009 ). Chaddock and colleagues (2010b) further observed that higher-fit children exhibited increased inhibitory control and response resolution and that higher basal ganglia volume was related to better task performance. These findings indicate that the dorsal striatum is involved in these aspects of higher-order cognition and that fitness may influence cognitive control during preadolescent development. It should be noted that both studies described above were correlational in nature, leaving open the possibility that other factors related to fitness and/or the maturation of subcortical structures may account for the observed group differences.
Effects of Regular Engagement in Physical Activity and Physical Fitness on Brain Function
Other research has attempted to characterize fitness-related differences in brain function using fMRI and event-related brain potentials (ERPs), which are neuroelectric indices of functional brain activation in the electro-encephalographic time series. To date, few randomized controlled interventions have been conducted. Notably, Davis and colleagues (2011) conducted one such intervention lasting approximately 14 weeks that randomized 20 sedentary overweight preadolescent children into an after-school physical activity intervention or a nonactivity control group. The fMRI data collected during an antisaccade task, which requires inhibitory control, indicated increased bilateral activation of the prefrontal cortex and decreased bilateral activation of the posterior parietal cortex following the physical activity intervention relative to the control group. Such findings illustrate some of the neural substrates influenced by participation in physical activity. Two additional correlational studies ( Voss et al., 2011 ; Chaddock et al., 2012 ) compared higher- and lower-fit preadolescent children and found differential brain activation and superior task performance as a function of fitness. That is, Chaddock and colleagues (2012) observed increased activation in prefrontal and parietal brain regions during early task blocks and decreased activation during later task blocks in higher-fit relative to lower-fit children. Given that higher-fit children outperformed lower-fit children on the aspects of the task requiring the greatest amount of cognitive control, the authors reason that the higher-fit children were more capable of adapting neural activity to meet the demands imposed by tasks that tapped higher-order cognitive processes such as inhibition and goal maintenance. Voss and colleagues (2011) used a similar task to vary cognitive control requirements and found that higher-fit children outperformed their lower-fit counterparts and that such differences became more pronounced during task conditions requiring the upregulation of control. Further, several differences emerged across various brain regions that together make up the network associated with cognitive control. Collectively, these differences suggest that higher-fit children are more efficient in the allocation of resources in support of cognitive control operations.
Other imaging research has examined the neuroelectric system (i.e., ERPs) to investigate which cognitive processes occurring between stimulus engagement and response execution are influenced by fitness. Several studies ( Hillman et al., 2005 , 2009 ; Pontifex et al., 2011 ) have examined the P3 component of the stimulus-locked ERP and demonstrated that higher-fit children have larger-amplitude and shorter-latency ERPs relative to their lower-fit peers. Classical theory suggests that P3 relates to neuronal activity associated with revision of the mental representation of the previous event within the stimulus environment ( Donchin, 1981 ). P3 amplitude reflects the allocation of attentional resources when working memory is updated ( Donchin and Coles, 1988 ) such that P3 is sensitive to the amount of attentional resources allocated to a stimulus ( Polich, 1997 ; Polich and Heine, 2007 ). P3 latency generally is considered to represent stimulus evaluation and classification speed ( Kutas et al., 1977 ; Duncan-Johnson, 1981 ) and thus may be considered a measure of stimulus detection and evaluation time ( Magliero et al., 1984 ; Ila and Polich, 1999 ). Therefore the above findings suggest that higher-fit children allocate greater attentional resources and have faster cognitive processing speed relative to lower-fit children ( Hillman et al., 2005 , 2009 ), with additional research suggesting that higher-fit children also exhibit greater flexibility in the allocation of attentional resources, as indexed by greater modulation of P3 amplitude across tasks that vary in the amount of cognitive control required ( Pontifex et al., 2011 ). Given that higher-fit children also demonstrate better performance on cognitive control tasks, the P3 component appears to reflect the effectiveness of a subset of cognitive systems that support willed action ( Hillman et al., 2009 ; Pontifex et al., 2011 ).
Two ERP studies ( Hillman et al., 2009 ; Pontifex et al., 2011 ) have focused on aspects of cognition involved in action monitoring. That is, the error-related negativity (ERN) component was investigated in higher- and lower-fit children to determine whether differences in evaluation and regulation of cognitive control operations were influenced by fitness level. The ERN component is observed in response-locked ERP averages. It is often elicited by errors of commission during task performance and is believed to represent either the detection of errors during task performance ( Gehring et al., 1993 ; Holroyd and Coles, 2002 ) or more generally the detection of response conflict ( Botvinick et al., 2001 ; Yeung et al., 2004 ), which may be engendered by errors in response production. Several studies have reported that higher-fit children exhibit smaller ERN amplitude during rapid-response tasks (i.e., instructions emphasizing speed of responding; Hillman et al., 2009 ) and more flexibility in the allocation of these resources during tasks entailing variable cognitive control demands, as evidenced by changes in ERN amplitude for higher-fit children and no modulation of ERN in lower-fit children ( Pontifex et al., 2011 ). Collectively, this pattern of results suggests that children with lower levels of fitness allocate fewer attentional resources during stimulus engagement (P3 amplitude) and exhibit slower cognitive processing speed (P3 latency) but increased activation of neural resources involved in the monitoring of their actions (ERN amplitude). Alternatively, higher-fit children allocate greater resources to environmental stimuli and demonstrate less reliance on action monitoring (increasing resource allocation only to meet the demands of the task). Under more demanding task conditions, the strategy of lower-fit children appears to fail since they perform more poorly under conditions requiring the upregulation of cognitive control.
Finally, only one randomized controlled trial published to date has used ERPs to assess neurocognitive function in children. Kamijo and colleagues (2011) studied performance on a working memory task before and after a 9-month physical activity intervention compared with a wait-list control group. They observed better performance following the physical activity intervention during task conditions that required the upregulation of working memory relative to the task condition requiring lesser amounts of working memory. Further, increased activation of the contingent negative variation (CNV), an ERP component reflecting cognitive and motor preparation, was observed at posttest over frontal scalp sites in the physical activity intervention group. No differences in performance or brain activation were noted for the wait-list control group. These findings suggest an increase in cognitive preparation processes in support of a more effective working memory network resulting from prolonged participation in physical activity. For children in a school setting, regular participation in physical activity as part of an after-school program is particularly beneficial for tasks that require the use of working memory.
Adiposity and Risk for Metabolic Syndrome as It Relates to Cognitive Health
A related and emerging literature that has recently been popularized investigates the relationship of adiposity to cognitive and brain health and academic performance. Several reports ( Datar et al., 2004 ; Datar and Sturm, 2006 ; Judge and Jahns, 2007 ; Gable et al., 2012 ) on this relationship are based on large-scale datasets derived from the Early Child Longitudinal Study. Further, nonhuman animal research has been used to elucidate the relationships between health indices and cognitive and brain health (see Figure 4-4 for an overview of these relationships). Collectively, these studies observed poorer future academic performance among children who entered school overweight or moved from a healthy weight to overweight during the course of development. Corroborating evidence for a negative relationship between adiposity and academic performance may be found in smaller but more tightly controlled studies. As noted above, Castelli and colleagues (2007) observed poorer performance on the mathematics and reading portions of the Illinois Standardized Achievement Test in 3rd- and 5th-grade students as a function of higher BMI, and Donnelly and colleagues (2009) used a cluster randomized trial to demonstrate that physical activity in the classroom decreased BMI and improved academic achievement among pre-adolescent children.
Relationships between health indices and cognitive and brain health. NOTE: AD = Alzheimer's disease; PD = Parkinson's disease. SOURCE: Cotman et al., 2007. Reprinted with permission.
Recently published reports describe the relationship between adiposity and cognitive and brain health to advance understanding of the basic cognitive processes and neural substrates that may underlie the adiposity-achievement relationship. Bolstered by findings in adult populations (e.g., Debette et al., 2010 ; Raji et al., 2010 ; Carnell et al., 2011 ), researchers have begun to publish data on preadolescent populations indicating differences in brain function and cognitive performance related to adiposity (however, see Gunstad et al., 2008 , for an instance in which adiposity was unrelated to cognitive outcomes). Specifically, Kamijo and colleagues (2012a) examined the relationship of weight status to cognitive control and academic achievement in 126 children aged 7-9. The children completed a battery of cognitive control tasks, and their body composition was assessed using dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The authors found that higher BMI and greater amounts of fat mass (particularly in the midsection) were related to poorer performance on cognitive control tasks involving inhibition, as well as lower academic achievement. In follow-up studies, Kamijo and colleagues (2012b) investigated whether neural markers of the relationship between adiposity and cognition may be found through examination of ERP data. These studies compared healthy-weight and obese children and found a differential distribution of the P3 potential (i.e., less frontally distributed) and larger N2 amplitude, as well as smaller ERN magnitude, in obese children during task conditions that required greater amounts of inhibitory control ( Kamijo et al., 2012c ). Taken together, the above results suggest that obesity is associated with less effective neural processes during stimulus capture and response execution. As a result, obese children perform tasks more slowly ( Kamijo et al., 2012a ) and are less accurate ( Kamijo et al., 2012b , c ) in response to tasks requiring variable amounts of cognitive control. Although these data are correlational, they provide a basis for further study using other neuroimaging tools (e.g., MRI, fMRI), as well as a rationale for the design and implementation of randomized controlled studies that would allow for causal interpretation of the relationship of adiposity to cognitive and brain health. The next decade should provide a great deal of information on this relationship.
- LIMITATIONS
Despite the promising findings described in this chapter, it should be noted that the study of the relationship of childhood physical activity, aerobic fitness, and adiposity to cognitive and brain health and academic performance is in its early stages. Accordingly, most studies have used designs that afford correlation rather than causation. To date, in fact, only two randomized controlled trials ( Davis et al., 2011 ; Kamijo et al., 2011 ) on this relationship have been published. However, several others are currently ongoing, and it was necessary to provide evidence through correlational studies before investing the effort, time, and funding required for more demanding causal studies. Given that the evidence base in this area has grown exponentially in the past 10 years through correlational studies and that causal evidence has accumulated through adult and nonhuman animal studies, the next step will be to increase the amount of causal evidence available on school-age children.
Accomplishing this will require further consideration of demographic factors that may moderate the physical activity–cognition relationship. For instance, socioeconomic status has a unique relationship with physical activity ( Estabrooks et al., 2003 ) and cognitive control ( Mezzacappa, 2004 ). Although many studies have attempted to control for socioeconomic status (see Hillman et al., 2009 ; Kamijo et al., 2011 , 2012a , b , c ; Pontifex et al., 2011 ), further inquiry into its relationship with physical activity, adiposity, and cognition is warranted to determine whether it may serve as a potential mediator or moderator for the observed relationships. A second demographic factor that warrants further consideration is gender. Most authors have failed to describe gender differences when reporting on the physical activity–cognition literature. However, studies of adiposity and cognition have suggested that such a relationship may exist (see Datar and Sturm, 2006 ). Additionally, further consideration of age is warranted. Most studies have examined a relatively narrow age range, consisting of a few years. Such an approach often is necessary because of maturation and the need to develop comprehensive assessment tools that suit the various stages of development. However, this approach has yielded little understanding of how the physical activity–cognition relationship may change throughout the course of maturation.
Finally, although a number of studies have described the relationship of physical activity, fitness, and adiposity to standardized measures of academic performance, few attempts have been made to observe the relationship within the context of the educational environment. Standardized tests, although necessary to gauge knowledge, may not be the most sensitive measures for (the process of) learning. Future research will need to do a better job of translating promising laboratory findings to the real world to determine the value of this relationship in ecologically valid settings.
From an authentic and practical to a mechanistic perspective, physically active and aerobically fit children consistently outperform their inactive and unfit peers academically on both a short- and a long-term basis. Time spent engaged in physical activity is related not only to a healthier body but also to enriched cognitive development and lifelong brain health. Collectively, the findings across the body of literature in this area suggest that increases in aerobic fitness, derived from physical activity, are related to improvements in the integrity of brain structure and function that underlie academic performance. The strongest relationships have been found between aerobic fitness and performance in mathematics, reading, and English. For children in a school setting, regular participation in physical activity is particularly beneficial with respect to tasks that require working memory and problem solving. These findings are corroborated by the results of both authentic correlational studies and experimental randomized controlled trials. Overall, the benefits of additional time dedicated to physical education and other physical activity opportunities before, during, and after school outweigh the benefits of exclusive utilization of school time for academic learning, as physical activity opportunities offered across the curriculum do not inhibit academic performance.
Both habitual and single bouts of physical activity contribute to enhanced academic performance. Findings indicate a robust relationship of acute exercise to increased attention, with evidence emerging for a relationship between participation in physical activity and disciplinary behaviors, time on task, and academic performance. Specifically, higher-fit children allocate greater resources to a given task and demonstrate less reliance on environmental cues or teacher prompting.
- Åberg MA, Pedersen NL, Torén K, Svartengren M, Bäckstrand B, Johnsson T, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Åberg ND, Nilsson M, Kuhn HG. Cardiovascular fitness is associated with cognition in young adulthood. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009; 106 (49):20906–20911. [ PMC free article : PMC2785721 ] [ PubMed : 19948959 ]
- Aglioti SM, Cesari P, Romani M, Urgesi C. Action anticipation and motor resonance in elite basketball players. Nature Neuroscience. 2008; 11 (9):1109–1116. [ PubMed : 19160510 ]
- Ahamed Y, Macdonald H, Reed K, Naylor PJ, Liu-Ambrose T, McKay H. School-based physical activity does not compromise children's academic performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2007; 39 (2):371–376. [ PubMed : 17277603 ]
- Aron A, Poldrack R, Wise S. Cognition: Basal ganglia role. Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. 2009; 2 :1069–1077.
- Barros RM, Silver EJ, Stein REK. School recess and group classroom behavior. Pediatrics. 2009; 123 (2):431–436. [ PubMed : 19171606 ]
- Bartholomew JB, Jowers EM. Physically active academic lessons in elementary children. Preventive Medicine. 2011; 52 (Suppl 1):S51–S54. [ PMC free article : PMC3116963 ] [ PubMed : 21281672 ]
- Basch C. Healthier children are better learners: A missing link in school reforms to close the achievement gap. 2010. [October 11, 2011]. http://www .equitycampaign .org/i/a/document /12557_EquityMattersVol6_Web03082010 .pdf . [ PubMed : 21923870 ]
- Baxter SD, Royer JA, Hardin JW, Guinn CH, Devlin CM. The relationship of school absenteeism with body mass index, academic achievement, and socioeconomic status among fourth grade children. Journal of School Health. 2011; 81 (7):417–423. [ PMC free article : PMC3972016 ] [ PubMed : 21668882 ]
- Benden ME, Blake JJ, Wendel ML, Huber JC Jr. The impact of stand-biased desks in classrooms on calorie expenditure in children. American Journal of Public Health. 2011; 101 (8):1433–1436. [ PMC free article : PMC3134494 ] [ PubMed : 21421945 ]
- Biddle SJ, Asare M. Physical activity and mental health in children and adolescents: A review of reviews. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2011; 45 (11):886–895. [ PubMed : 21807669 ]
- Blair C, Zelazo PD, Greenberg MT. The measurement of executive function in early childhood. Developmental Neuropsychology. 2005; 28 (2):561–571. [ PubMed : 16144427 ]
- Boecker H. On the emerging role of neuroimaging in determining functional and structural brain integrity induced by physical exercise: Impact for predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine. EPMA Journal. 2011; 2 (3):277–285. [ PMC free article : PMC3405390 ] [ PubMed : 23199163 ]
- Botvinick MM, Braver TS, Barch DM, Carter CS, Cohen JD. Conflict monitoring and cognitive control. Psychological Review. 2001; 108 (3):624. [ PubMed : 11488380 ]
- Budde H, Voelcker-Rehage C, S-Pietrabyk Kendziorra, Ribeiro P, Tidow G. Acute coordinative exercise improves attentional performance in adolescents. Neuroscience Letters. 2008; 441 (2):219–223. [ PubMed : 18602754 ]
- Burkhalter TM, Hillman CH. A narrative review of physical activity, nutrition, and obesity to cognition and scholastic performance across the human lifespan. Advances in Nutrition. 2011; 2 (2):201S–206S. [ PMC free article : PMC3065760 ] [ PubMed : 22332052 ]
- Carlson SA, Fulton JE, Lee SM, Maynard LM, Brown DR, Kohl HW III, Dietz WH. Physical education and academic achievement in elementary school: Data from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study. American Journal of Public Health. 2008; 98 (4):721–727. [ PMC free article : PMC2377002 ] [ PubMed : 18309127 ]
- Carnell S, Gibson C, Benson L, Ochner C, Geliebter A. Neuroimaging and obesity: Current knowledge and future directions. Obesity Reviews. 2011; 13 (1):43–56. [ PMC free article : PMC3241905 ] [ PubMed : 21902800 ]
- Casey B, Jones RM, Hare TA. The adolescent brain. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2008; 1124 (1):111–126. [ PMC free article : PMC2475802 ] [ PubMed : 18400927 ]
- Castelli DM, Hillman CH, Buck SM, Erwin HE. Physical fitness and academic achievement in third- and fifth-grade students. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology. 2007; 29 (2):239–252. [ PubMed : 17568069 ]
- Chaddock L, Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Kim JS, Voss MW, VanPatter M, Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Konkel A, Hillman CH. A neuroimaging investigation of the association between aerobic fitness, hippocampal volume, and memory performance in preadolescent children. Brain Research. 2010a; 1358 :172–183. [ PMC free article : PMC3953557 ] [ PubMed : 20735996 ]
- Chaddock L, Erickson KI, Prakash RS, VanPatter M, Voss MW, Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Hillman CH, Kramer AF. Basal ganglia volume is associated with aerobic fitness in preadolescent children. Developmental Neuroscience. 2010b; 32 (3):249–256. [ PMC free article : PMC3696376 ] [ PubMed : 20693803 ]
- Chaddock L, Hillman CH, Buck SM, Cohen NJ. Aerobic fitness and executive control of relational memory in preadolescent children. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2011; 43 (2):344. [ PubMed : 20508533 ]
- Chaddock L, Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Voss MW, VanPatter M, Pontifex MB, Hillman CH, Kramer AF. A functional MRI investigation of the association between childhood aerobic fitness and neurocognitive control. Biological Psychology. 2012; 89 (1):260–268. [ PubMed : 22061423 ]
- Chan AS, Ho YC, Cheung MC. Music training improves verbal memory. Nature. 1998; 396 (6707):128. [ PubMed : 9823892 ]
- Chang YK, Etnier JL. Effects of an acute bout of localized resistance exercise on cognitive performance in middle-aged adults: A randomized controlled trial study. Psychology of Sport and Exercise. 2009; 10 (1):19–24.
- Chih CH, Chen JF. The relationship between physical education performance, fitness tests, and academic achievement in elementary school. International Journal of Sport and Society. 2011; 2 (1):65–73.
- Chomitz VR, Slining MM, McGowan RJ, Mitchell SE, Dawson GF, Hacker KA. Is there a relationship between physical fitness and academic achievement? Positive results from public school children in the northeastern United States. Journal of School Health. 2008; 79 (1):30–37. [ PubMed : 19149783 ]
- Coe DP, Pivarnik JM, Womack CJ, Reeves MJ, Malina RM. Effect of physical education and activity levels on academic achievement in children. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2006; 38 (8):1515–1519. [ PubMed : 16888468 ]
- Cohen NJ, Eichenbaum H. Memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal system. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; 1993.
- Cohen NJ, Ryan J, Hunt C, Romine L, Wszalek T, Nash C. Hippocampal system and declarative (relational) memory: Summarizing the data from functional neuroimaging studies. Hippocampus. 1999; 9 (1):83–98. [ PubMed : 10088903 ]
- Colcombe SJ, Kramer AF. Fitness effects on the cognitive function of older adults a meta-analytic study. Psychological Science. 2003; 14 (2):125–130. [ PubMed : 12661673 ]
- Colcombe SJ, Erickson KI, Raz N, Webb AG, Cohen NJ, McAuley E, Kramer AF. Aerobic fitness reduces brain tissue loss in aging humans. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2003; 58 (2):M176–M180. [ PubMed : 12586857 ]
- Colcombe SJ, Kramer AF, Erickson KI, Scalf P, McAuley E, Cohen NJ, Webb A, Jerome GJ, Marquez DX, Elavsky S. Cardiovascular fitness, cortical plasticity, and aging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004; 101 (9):3316–3321. [ PMC free article : PMC373255 ] [ PubMed : 14978288 ]
- Colcombe SJ, Erickson KI, Scalf PE, Kim JS, Prakash R, McAuley E, Elavsky S, Marquez DX, Hu L, Kramer AF. Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2006; 61 (11):1166–1170. [ PubMed : 17167157 ]
- Cooper K, Everett D, Kloster J, Meredith MD, Rathbone M, Read K. Preface: Texas statewide assessment of youth fitness. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 2010; 81 (3):ii. [ PubMed : 21049831 ]
- Cotman CW, Berchtold NC, Christie LA. Exercise builds brain health: Key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends in Neurosciences. 2007; 30 (9):464–472. [ PubMed : 17765329 ]
- Cottrell LA, Northrup K, Wittberg R. The extended relationship between child cardiovascular risks and academic performance measures. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007; 15 (12):3170–3177. [ PubMed : 18198328 ]
- Crosnoe R. Academic and health-related trajectories in high school: The intersection of gender and athletics. Journal of Health and Social Behavior. 2002; 43 :317–335. [ PubMed : 12467256 ]
- Daley AJ, Ryan J. Academic performance and participation in physical activity by secondary school adolescents. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 2000; 91 (2):531–534. [ PubMed : 11065314 ]
- Datar A, Sturm R. Physical education in elementary school and body mass index: Evidence from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study. Journal Information. 2004; 94 (9):1501–1509. [ PMC free article : PMC1448481 ] [ PubMed : 15333302 ]
- Datar A, Sturm R. Childhood overweight and elementary school outcomes. International Journal of Obesity. 2006; 30 (9):1449–1460. [ PubMed : 16534518 ]
- Datar A, Sturm R, Magnabosco JL. Childhood overweight and academic performance: National study of kindergartners and first-graders. Obesity Research. 2004; 12 (1):58–68. [ PubMed : 14742843 ]
- Davidson MC, Amso D, Anderson LC, Diamond A. Development of cognitive control and executive functions from 4 to 13 years: Evidence from manipulations of memory, inhibition, and task switching. Neuropsychologia. 2006; 44 (11):2037. [ PMC free article : PMC1513793 ] [ PubMed : 16580701 ]
- Davis CL, Tomporowski PD, McDowell JE, Austin BP, Miller PH, Yanasak NE, Allison JD, Naglieri JA. Exercise improves executive function and achievement and alters brain activation in overweight children: A randomized, controlled trial. Health Psychology. 2011; 30 (1):91–98. [ PMC free article : PMC3057917 ] [ PubMed : 21299297 ]
- Dawson P, Guare R. Executive skills in children and adolescents: A practical guide to assessment and intervention. New York: Guilford Press; 2004. pp. 2–8.
- Debette S, Beiser A, Hoffmann U, DeCarli C, O'Donnell CJ, Massaro JM, Au R, Himali JJ, Wolf PA, Fox CS, Seshadri S. Visceral fat is associated with lower brain volume in healthy middle-aged adults. Annals of Neurology. 2010; 68 :136–144. [ PMC free article : PMC2933649 ] [ PubMed : 20695006 ]
- Dexter TT. Relationships between sport knowledge, sport performance and academic ability: Empirical evidence from GCSE physical education. Journal of Sports Sciences. 1999; 17 (4):283–295. [ PubMed : 10373038 ]
- Diamond A. The early development of executive functions. In: Bialystok E, Craik FIM, editors. In Lifespan cognition: Mechanisms of change. New York: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 70–95.
- Donchin E. Surprise! … surprise. Psychophysiology. 1981; 18 (5):493–513. [ PubMed : 7280146 ]
- Donchin E, Coles MGH. Is the P300 component a manifestation of context updating. Behavioral and Brain Sciences. 1988; 11 (03):357–374.
- Donnelly JE, Lambourne K. Classroom-based physical activity, cognition, and academic achievement. Preventive Medicine. 2011; 52 (Suppl 1):S36–S42. [ PubMed : 21281666 ]
- Donnelly JE, Greene JL, Gibson CA, Smith BK, Washburn RA, Sullivan DK, DuBose K, Mayo MS, Schmelzle KH, Ryan JJ. Physical Activity Across the Curriculum (PAAC): A randomized controlled trial to promote physical activity and diminish overweight and obesity in elementary school children. Preventive Medicine. 2009; 49 (4):336–341. [ PMC free article : PMC2766439 ] [ PubMed : 19665037 ]
- Drollette ES, Shishido T, Pontifex MB, Hillman CH. Maintenance of cognitive control during and after walking in preadolescent children. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2012; 44 (10):2017–2024. [ PubMed : 22525770 ]
- Duncan SC, Duncan TE, Strycker LA, Chaumeton NR. A cohort-sequential latent growth model of physical activity from ages 12 to 17 years. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2007; 33 (1):80–89. [ PMC free article : PMC2729662 ] [ PubMed : 17291173 ]
- Duncan-Johnson CC. P3 latency: A new metric of information processing. Psychophysiology. 1981; 18 :207–215. [ PubMed : 7291436 ]
- Dwyer T, Coonan W, Worsley A, Leitch D. An assessment of the effects of two physical activity programmes on coronary heart disease risk factors in primary school children. Community Health Studies. 1979; 3 (3):196–202.
- Dwyer T, Coonan WE, Leitch DR, Hetzel BS, Baghurst R. An investigation of the effects of daily physical activity on the health of primary school students in south Australia. International Journal of Epidemiology. 1983; 12 (3):308–313. [ PubMed : 6629620 ]
- Edwards JU, Mauch L, Winkleman MR. Relationship of nutrition and physical activity behaviors and fitness measures to academic performance for sixth graders in a Midwest city school district. Journal of School Health. 2011; 81 :65–73. [ PubMed : 21223273 ]
- Efrat M. The relationship between low-income and minority children's physical activity and academic-related outcomes: A review of the literature. Health Education and Behavior. 2011; 38 (5):441–451. [ PubMed : 21285376 ]
- Eitle TM. Do gender and race matter? Explaining the relationship between sports participation and achievement. Sociological Spectrum. 2005; 25 (2):177–195.
- Eitle TM, Eitle DJ. Sociology of Education. 2002. Race, cultural capital, and the educational effects of participation in sports; pp. 123–146.
- Elbert T, Pantev C, Wienbruch C, Rockstroh B, Taub E. Increased cortical representation of the fingers of the left hand in string players. Science. 1995; 270 (5234):305–307. [ PubMed : 7569982 ]
- Elder C, Leaver-Dunn D, Wang MQ, Nagy S, Green L. Organized group activity as a protective factor against adolescent substance use. American Journal of Health Behavior. 2000; 24 (2):108–113.
- Ellemberg D, St-Louis-Deschênes M. The effect of acute physical exercise on cognitive function during development. Psychology of Sport and Exercise. 2010; 11 (2):122–126.
- Erickson KI, Prakash RS, Voss MW, Chaddock L, Hu L, Morris KS, White SM, Wójcicki TR, McAuley E, Kramer AF. Aerobic fitness is associated with hippocampal volume in elderly humans. Hippocampus. 2009; 19 (10):1030–1039. [ PMC free article : PMC3072565 ] [ PubMed : 19123237 ]
- Erickson KI, Voss MW, Prakash RS, Basak C, Szabo A, Chaddock L, Kim JS, Heo S, Alves H, White SM. Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011; 108 (7):3017–3022. [ PMC free article : PMC3041121 ] [ PubMed : 21282661 ]
- Ericsson KA, Charness N. Expert performance: Its structure and acquisition. American Psychologist. 1994; 49 (8):725.
- Estabrooks AP, Lee RE, Gyurcsik NC. Resources for physical activity participation: Does availability and accessibility differ by neighborhood socioeconomic status. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2003; 25 (2):100–104. [ PubMed : 12704011 ]
- Etnier JL, Salazar W, Landers DM, Petruzzello SJ, Han M, Nowell P. The influence of physical fitness and exercise upon cognitive functioning: A meta-analysis. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology. 1997; 19 (3):249–277.
- Etnier JL, Nowell PM, Landers DM, Sibley BA. A meta-regression to examine the relationship between aerobic fitness and cognitive performance. Brain Research Reviews. 2006; 52 (1):119–130. [ PubMed : 16490256 ]
- Eveland-Sayers BM, Farley RS, Fuller DK, Morgan DW, Caputo JL. Physical fitness and academic achievement in elementary school children. Journal of Physical Activity and Health. 2009; 6 (1):99. [ PubMed : 19211963 ]
- Fan X, Chen M. Parental involvement and students' academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review. 2001; 13 (1):1–22.
- Fedewa AL, Ahn S. The effects of physical activity and physical fitness on children's achievement and cognitive outcomes: A meta-analysis. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 2011; 82 (3):521–535. [ PubMed : 21957711 ]
- Fisher M, Juszczak L, Friedman SB. Sports participation in an urban high school: Academic and psychologic correlates. Journal of Adolescent Health. 1996; 18 (5):329–334. [ PubMed : 9156545 ]
- Fox CK, Barr-Anderson D, D-Neumark Sztainer, Wall M. Physical activity and sports team participation: Associations with academic outcomes in middle school and high school students. Journal of School Health. 2010; 80 (1):31–37. [ PubMed : 20051088 ]
- Fredericks CR, Kokot SJ, Krog S. Using a developmental movement programme to enhance academic skills in grade 1 learners. South African Journal for Research in Sport, Physical Education and Recreation. 2006; 28 (1):29–42.
- Gabbard C, Barton J. Effects of physical activity on mathematical computation among young children. Journal of Psychology. 1979; 103 :287–288.
- Gable S, Krull JL, Chang Y. Boys' and girls' weight status and math performance from kindergarten entry through fifth grade: A mediated analysis. Child Development. 2012; 83 (5):1822–1839. [ PubMed : 22694240 ]
- Gehring WJ, Goss B, Coles MG, Meyer DE, Donchin E. A neural system for error detection and compensation. Psychological Science. 1993; 4 (6):385–390.
- Getlinger MJ, Laughlin V, Bell E, Akre C, Arjmandi BH. Food waste is reduced when elementary-school children have recess before lunch. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 1996; 96 (9):906. [ PubMed : 8784336 ]
- Glenmark B. Skeletal muscle fiber types, physical performance, physical activity and attitude to physical activity in women and men: A follow-up from age 16-27. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica Supplementum. 1994; 623 :1–47. [ PubMed : 7942046 ]
- Grieco LA, Jowers EM, Bartholomew JB. Physically active academic lessons and time on task: The moderating effect of body mass index. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2009; 41 (10):1921–1926. [ PubMed : 19727020 ]
- Grissom JB. Physical fitness and academic achievement. Journal of Exercise Physiology Online. 2005; 8 (1):11–25.
- Gunstad J, Spitznagel MB, Paul RH, Cohen RA, Kohn M, Luyster FS, Clark R, Williams LM, Gordon E. Body mass index and neuropsychological function in healthy children and adolescents. Appetite. 2008; 5 (2):246–51. [ PubMed : 17761359 ]
- Hanson SL, Kraus RS. Women, sports, and science: Do female athletes have an advantage. Sociology of Education. 1998; 71 :93–110.
- Hatfield BD, Hillman CH. The psychophysiology of sport: A mechanistic understanding of the psychology of superior performance. In: Singer RN, Hausenblas HA, Janelle C, editors. In The handbook of research on sport psychology. 2nd. New York: John Wiley; 2001. pp. 362–386.
- Hillman CH, Snook EM, Jerome GJ. Acute cardiovascular exercise and executive control function. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2003; 48 (3):307–314. [ PubMed : 12798990 ]
- Hillman CH, Castelli DM, Buck SM. Aerobic fitness and neurocognitive function in healthy preadolescent children. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2005; 37 (11):1967. [ PubMed : 16286868 ]
- Hillman CH, Motl RW, Pontifex MB, Posthuma D, Stubbe JH, Boomsma DI, De Geus EJC. Physical activity and cognitive function in a cross-section of younger and older community-dwelling individuals. Health Psychology. 2006; 25 (6):678. [ PubMed : 17100496 ]
- Hillman CH, Erickson KI, Kramer AF. Be smart, exercise your heart: Exercise effects on brain and cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2008; 9 (1):58–65. [ PubMed : 18094706 ]
- Hillman CH, Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Castelli DM, Hall EE, Kramer AF. The effect of acute treadmill walking on cognitive control and academic achievement in preadolescent children. Neuroscience. 2009; 159 (3):1044. [ PMC free article : PMC2667807 ] [ PubMed : 19356688 ]
- Holroyd CB, Coles MG. The neural basis of human error processing: Reinforcement learning, dopamine, and the error-related negativity. Psychological Review. 2002; 109 (4):679. [ PubMed : 12374324 ]
- Huttenlocher PR, Dabholkar AS. Regional differences in synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1997; 387 (2):167–178. [ PubMed : 9336221 ]
- Ila AB, Polich J. P300 and response time from a manual Stroop task. Clinical Neurophysiology. 1999; 110 (2):367–373. [ PubMed : 10210626 ]
- Jarrett OS, Maxwell DM, Dickerson C, Hoge P, Davies G, Yetley A. Impact of recess on classroom behavior: Group effects and individual differences. Journal of Educational Research. 1998; 92 (2):121–126.
- Jones JG, Hardy L. Stress and cognitive functioning in sport. Journal of Sports Sciences. 1989; 7 (1):41–63. [ PubMed : 2659817 ]
- Judge S, Jahns L. Association of overweight with academic performance and social and behavioral problems: An update from the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study. Journal of School Health. 2007; 77 :672–678. [ PubMed : 18076412 ]
- Kamijo K, Pontifex MB, O'Leary KC, Scudder MR, Wu CT, Castelli DM, Hillman CH. The effects of an afterschool physical activity program on working memory in preadolescent children. Developmental Science. 2011; 14 (5):1046–1058. [ PMC free article : PMC3177170 ] [ PubMed : 21884320 ]
- Kamijo K, Khan NA, Pontifex MB, Scudder MR, Drollette ES, Raine LB, Evans EM, Castelli DM, Hillman CH. The relation of adiposity to cognitive control and scholastic achievement in preadolescent children. Obesity. 2012a; 20 (12):2406–2411. [ PMC free article : PMC3414677 ] [ PubMed : 22546743 ]
- Kamijo K, Pontifex MB, Khan NA, Raine LB, Scudder MR, Drollette ES, Evans EM, Castelli DM, Hillman CH. The association of childhood obesity to neuroelectric indices of inhibition. Psychophysiology. 2012b; 49 (10):1361–1371. [ PubMed : 22913478 ]
- Kamijo K, Pontifex MB, Khan NA, Raine LB, Scudder MR, Drollette ES, Evans EM, Castelli DM, Hillman CH. Cerebral Cortex. 2012c. [October 4, 2013]. The negative association of childhood obesity to the cognitive control of action monitoring. Epub ahead of print, November 11. cercor .oxfordjournals .org/content/early/2012/11/09/cercor .bhs349.long . [ PMC free article : PMC3920765 ] [ PubMed : 23146965 ]
- Kibbe DL, Hackett J, Hurley M, McFarland A, Schubert KG, Schultz A, Harris S. Ten years of TAKE 10! ® : Integrating physical activity with academic concepts in elementary school classrooms. Preventive Medicine. 2011; 52 (Suppl):S43–S50. [ PubMed : 21281670 ]
- Kramer AF, Erickson KI. Capitalizing on cortical plasticity: Influence of physical activity on cognition and brain function. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2007; 11 (8):342–348. [ PubMed : 17629545 ]
- Kramer AF, Hahn S, Cohen NJ, Banich MT, McAuley E, Harrison CR, Chason J, Vakil E, Bardell L, Boileau RA. Ageing, fitness and neurocognitive function. Nature. 1999; 400 (6743):418–419. [ PubMed : 10440369 ]
- Kutas M, McCarthy G, Donchin E. Augmenting mental chronometry: The P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science. 1977; 197 (4305):792–795. [ PubMed : 887923 ]
- London RA, Castrechini S. A longitudinal examination of the link between youth physical fitness and academic achievement. Journal of School Health. 2011; 81 (7):400–408. [ PubMed : 21668880 ]
- MacDonald AW, Cohen JD, Stenger VA, Carter CS. Dissociating the role of the dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex in cognitive control. Science. 2000; 288 (5472):1835–1838. [ PubMed : 10846167 ]
- Magliero A, Bashore TR, Coles MG, Donchin E. On the dependence of P300 latency on stimulus evaluation processes. Psychophysiology. 1984; 21 (2):171–186. [ PubMed : 6728983 ]
- Mahar MT, Murphy SK, Rowe DA, Golden J, Shields AT, Raedeke TD. Effects of a classroom-based program on physical activity and on-task behavior. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2006; 38 (12):2086. [ PubMed : 17146314 ]
- Mechanic D, Hansell S. Adolescent competence, psychological well-being, and self-assessed physical health. Journal of Health and Social Behavior. 1987; 28 (4):364–374. [ PubMed : 3429806 ]
- Mezzacappa E. Alerting, orienting, and executive attention: Developmental properties and sociodemographic correlates in an epidemiological sample of young, urban children. Child Development. 2004; 75 (5):1373–1386. [ PubMed : 15369520 ]
- Miller KE, Melnick MJ, Barnes GM, Farrell MP, Sabo D. Untangling the links among the athletic involvement, gender, race, and adolescent academic outcomes. Sociology of Sport. 2005; 22 (2):178–193. [ PMC free article : PMC1343519 ] [ PubMed : 16467902 ]
- Monti JM, Hillman CH, Cohen NJ. Aerobic fitness enhances relational memory in preadolescent children: The FITKids randomized control trial. Hippocampus. 2012; 22 (9):1876–1882. [ PMC free article : PMC3404196 ] [ PubMed : 22522428 ]
- Münte TF, Kohlmetz C, Nager W, Altenmüller E. Superior auditory spatial tuning in conductors. Nature. 2001; 409 (6820):580. [ PubMed : 11214309 ]
- NASPE (National Association for Sport and Physical Education). Moving into the future: National Physical Education Content Standards. 2nd. Reston, VA: NASPE; 2004.
- NASPE. Recess for elementary school students. 2006. [December 1, 2012]. http://www .aahperd.org /naspe/standards/upload /recess-for-elementary-school-students-2006.pdf .
- Neeper SA, Gomez-Pinilla F, Choi J, Cotman C. Exercise and brain neuro-trophins. Nature. 1995; 373 (6510):109. [ PubMed : 7816089 ]
- NRC (National Research Council)/IOM (Institute of Medicine). From neurons to neighborhoods: The science of early childhood development. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2000. [ PubMed : 25077268 ]
- O'Leary KC, Pontifex MB, Scudder MR, Brown ML, Hillman CH. The effects of single bouts of aerobic exercise, exergaming, and videogame play on cognitive control. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2011; 122 (8):1518–1525. [ PubMed : 21353635 ]
- Page RM, Hammermeister J, Scanlan A, Gilbert L. Is school sports participation a protective factor against adolescent health risk behaviors. Journal of Health Education. 1998; 29 (3):186–192.
- Pellegrini AD, Bohn CM. The role of recess in children's cognitive performance and school adjustment. Educational Researcher. 2005; 34 (1):13–19.
- Pellegrini AD, Huberty PD, Jones I. The effects of recess timing on children's playground and classroom behaviors. American Educational Research Journal. 1995; 32 (4):845–864.
- Pesce C, Crova C, Cereatti L, Casella R, Bellucci M. Physical activity and mental performance in preadolescents: Effects of acute exercise on free-recall memory. Mental Health and Physical Activity. 2009; 2 (1):16–22.
- Polich J. EEG and ERP assessment of normal aging. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology/Evoked Potentials Section. 1997; 104 (3):244–256. [ PubMed : 9186239 ]
- Polich J, Heine MR. P300 topography and modality effects from a single-stimulus paradigm. Psychophysiology. 2007; 33 (6):747–752. [ PubMed : 8961797 ]
- Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Johnson CR, Chaddock L, Voss MW, Cohen NJ, Kramer AF, Hillman CH. Cardiorespiratory fitness and the flexible modulation of cognitive control in preadolescent children. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2011; 23 (6):1332–1345. [ PubMed : 20521857 ]
- Pontifex MB, Scudder MR, Drollette ES, Hillman CH. Fit and vigilant: The relationship between sedentary behavior and failures in sustained attention during preadolescence. Neuropsychology. 2012; 26 (4):407–413. [ PMC free article : PMC3390762 ] [ PubMed : 22746307 ]
- Pontifex MB, Saliba BJ, Raine LB, Picchietti DL, Hillman CH. Exercise improves behavioral, neurophysiologic, and scholastic performance in children with ADHD. Journal of Pediatrics. 2013; 162 :543–551. [ PMC free article : PMC3556380 ] [ PubMed : 23084704 ]
- Raji CA, Ho AJ, Parikshak NN, Becker JT, Lopez OL, Kuller LH, Hua X, Leow AD, Toga AW, Thompson PM. Brain structure and obesity. Human Brain Mapping. 2010; 31 (3):353–364. [ PMC free article : PMC2826530 ] [ PubMed : 19662657 ]
- Rasberry CN, Lee SM, Robin L, Laris BA, Russell LA, Coyle KK, Nihiser AJ. The association between school-based physical activity, including physical education, and academic performance: A systematic review of the literature. Preventive Medicine. 2011; 52 (Suppl 1):S10–S20. [ PubMed : 21291905 ]
- Raz N. Aging of the brain and its impact on cognitive performance: Integration of structural and functional findings. In: Craik FM, Salthouse TA, editors. In The handbook of aging and cognition. Vol. 2. Mahweh, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2000. pp. 1–90.
- Reed JA, Einstein G, Hahn E, Hooker SP, Gross VP, Kravitz J. Examining the impact of integrating physical activity on fluid intelligence and academic performance in an elementary school setting: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Physical Activity and Health. 2010; 7 (3):343–351. [ PubMed : 20551490 ]
- Ruiz JR, Ortega FB, Castillo R, Martin-Matillas M, Kwak L, Vicente-Rodriguez G, Noriega J, Tercedor P, Sjostrom M, Moreno LA. Journal of Pediatrics. 2010; 157 (6):917–922. [ PubMed : 20673915 ]
- Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Kolody B, Lewis M, Marshall S, Rosengard P. Effects of health-related physical education on academic achievement: Project SPARK. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 1999; 70 (2):127–134. [ PubMed : 10380244 ]
- Sanders A. Towards a model of stress and human performance. Acta Psychologica. 1983; 53 (1):61–97. [ PubMed : 6869047 ]
- Shephard RJ. Habitual physical activity and academic performance. Nutrition Reviews. 1986; 54 (4):S32–S36. [ PubMed : 8700451 ]
- Shephard RJ, Volle M, Lavallee H, LaBarre R, Jequier J, Rajic M. In Children and Sport. Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag; 1984. Required physical activity and academic grades: A controlled study; pp. 58–63.
- Sibley BA, Etnier JL. The relationship between physical activity and cognition in children: A meta-analysis. Pediatric Exercise Science. 2003; 15 :243–256.
- Silliker SA, Quirk JT. The effect of extracurricular activity participation on the academic performance of male and female high school students. School Counselor. 1997; 44 (4):288–293.
- Singh A, Uijtdewilligen L, Twisk JWR, van Mechelen W, Chinapaw MJM. Physical activity and performance at school: A systematic review of the literature including a methodological quality assessment. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 2012; 166 (1):49–55. [ PubMed : 22213750 ]
- Sirin SR. Socioeconomic status and academic achievement: A meta-analytic review of research. Review of Educational Research. 2005; 75 (3):417–453.
- Smith PJ, Blumenthal JA, Hoffman BM, Cooper H, Strauman TA, Welsh-Bohmer K, Browndyke JN, Sherwood A. Aerobic exercise and neuro-cognitive performance: A meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2010; 72 (3):239–252. [ PMC free article : PMC2897704 ] [ PubMed : 20223924 ]
- Stanca L. The effects of attendance on academic performance: Panel data evidence for introductory microeconomics. Journal of Economic Education. 2006; 37 (3):251–266.
- Stephens LJ, Schaben LA. The effect of interscholastic sports participation on academic achievement of middle level school activities. National Association of Secondary School Principals Bulletin. 2002; 86 :34–42.
- Stewart JA, Dennison DA, Kohl HW III, Doyle JA. Exercise level and energy expenditure in the TAKE 10! ® in-class physical activity program. Journal of School Health. 2004; 74 (10):397–400. [ PubMed : 15724566 ]
- Strong WB, Malina RM, Blimkie CJ, Daniels SR, Dishman RK, Gutin B, Hergenroeder AC, Must A, Nixon PA, Pivarnik JM, Rowland T, Trost S, Trudeau F. Evidence based physical activity for school-age youth. Journal of Pediatrics. 2005; 146 (6):732–737. [ PubMed : 15973308 ]
- Taliaferro LA, Rienzo BA, Donovan KA. Relationships between youth sport participation and selected health risk behaviors from 1999 to 2007. Journal of School Health. 2010; 80 (8):399–410. [ PubMed : 20618623 ]
- Taylor MJ. Neural bases of cognitive development. In: Bialystok E, Craik FIM, editors. In Lifespan cognition: Mechanisms of change. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 2006. pp. 15–26.
- Telama R, Yang X, Laakso L, Viikari J. Physical activity in childhood and adolescence as predictor of physical activity in young adulthood. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 1997; 13 (4):317–323. [ PubMed : 9236971 ]
- Thomas AG, Dennis A, Bandettini PA, Johansen-Berg H. The effects of aerobic activity on brain structure. Frontiers in Psychology. 2012; 3 :1–9. [ PMC free article : PMC3311131 ] [ PubMed : 22470361 ]
- Tomporowski PD. Effects of acute bouts of exercise on cognition. Acta Psychologica. 2003; 112 (3):297–324. [ PubMed : 12595152 ]
- Tomporowski PD, Davis CL, Miller PH, Naglieri JA. Exercise and children's intelligence, cognition, and academic achievement. Educational Psychology Review. 2008a; 20 (2):111–131. [ PMC free article : PMC2748863 ] [ PubMed : 19777141 ]
- Tomporowski PD, Davis CL, Lambourne K, Gregoskis M, Tkacz J. Task switching in overweight children: Effects of acute exercise and age. Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology. 2008b; 30 (5):497–511. [ PMC free article : PMC2705951 ] [ PubMed : 18971509 ]
- Trudeau F, Shephard RJ. Physical education, school physical activity, school sports and academic performance. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity. 2008; 5 [ PMC free article : PMC2329661 ] [ PubMed : 18298849 ]
- Trudeau F, Shephard RJ. Relationships of physical activity to brain health and the academic performance of school children. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. 2010; 4 :138–150.
- Trudeau F, Laurencelle L, Tremblay J, Rajic M, Shephard R. Daily primary school physical education: Effects on physical activity during adult life. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1999; 31 (1):111. [ PubMed : 9927018 ]
- Trudeau F, Shephard RJ, Arsenault F, Laurencelle L. Changes in adiposity and body mass index from late childhood to adult life in the Trois-Rivières study. American Journal of Human Biology. 2001; 13 (3):349–355. [ PubMed : 11460900 ]
- Trudeau F, Laurencelle L, Shephard RJ. Tracking of physical activity from childhood to adulthood. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2004; 36 (11):1937. [ PubMed : 15514510 ]
- Van Dusen DP, Kelder SH, Kohl HW III, Ranjit N, Perry CL. Associations of physical fitness and academic performance among schoolchildren. Journal of School Health. 2011; 81 (12):733–740. [ PubMed : 22070504 ]
- Van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nature Neuroscience. 1999; 2 (3):266–270. [ PubMed : 10195220 ]
- Voss MW, Chaddock L, Kim JS, VanPatter M, Pontifex MB, Raine LB, Cohen NJ, Hillman CH, Kramer AF. Aerobic fitness is associated with greater efficiency of the network underlying cognitive control in preadolescent children. Neuroscience. 2011; 199 :166–176. [ PMC free article : PMC3237764 ] [ PubMed : 22027235 ]
- Wechsler H, Brener ND, Kuester S, Miller C. Food service and food and beverage available at school: Results from the School Health Policies and Programs Study. Journal of School Health. 2001; 71 (7):313–324. [ PubMed : 11586874 ]
- Welk GJ, Jackson AW, Morrow J, James R, Haskell WH, Meredith MD, Cooper KH. The association of health-related fitness with indicators of academic performance in Texas schools. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 2010; 81 (Suppl 2):16S–23S. [ PubMed : 21049834 ]
- Welk GJ, Going SB, Morrow JR, Meredith MD. Development of new criterion-referenced fitness standards in the Fitnessgram ® program. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2011; 41 (2):6. [ PubMed : 21961614 ]
- Wilkins J, Graham G, Parker S, Westfall S, Fraser R, Tembo M. Time in the arts and physical education and school achievement. Journal of Curriculum Studies. 2003; 35 (6):721–734.
- Wittberg R, Cottrell LA, Davis CL, Northrup KL. Aerobic fitness thresholds associated with fifth grade academic achievement. American Journal of Health Education. 2010; 41 (5):284–291.
- Yeung N, Botvinick MM, Cohen JD. The neural basis of error detection: Conflict monitoring and the error-related negativity. Psychological Review. 2004; 111 (4):931. [ PubMed : 15482068 ]
- Zhu W, Welk GJ, Meredith MD, Boiarskaia EA. A survey of physical education programs and policies in Texas schools. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport. 2010; 81 (Suppl 2):42S–52S. [ PubMed : 21049837 ]
- Cite this Page Committee on Physical Activity and Physical Education in the School Environment; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine; Kohl HW III, Cook HD, editors. Educating the Student Body: Taking Physical Activity and Physical Education to School. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2013 Oct 30. 4, Physical Activity, Fitness, and Physical Education: Effects on Academic Performance.
- PDF version of this title (4.4M)
In this Page
Related information.
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Recent Activity
- Physical Activity, Fitness, and Physical Education: Effects on Academic Performa... Physical Activity, Fitness, and Physical Education: Effects on Academic Performance - Educating the Student Body
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Guide to Physical Education and Sport
by CoachMePlus | Academy

The Role of Physical Education

P.E. exposes most youth age groups to manipulative, non-manipulative, and locomotor skills. The sequential development of P.E. students is founded on strong pedagogical principles, such as progressions and age-appropriate activities. In addition to independent movement and coordination, later developmental programs include collaboration between students, team activities, and the addition of competitive elements to the curriculum. Eventually, a child develops into a young adult, and priorities change from fundamentals with coordination to lifelong wellness. How many responsibilities exist beyond general exposure to coordination is still unknown, but childhood obesity is evidence that more activity beyond sports is needed. Curriculum development is driven by both research and experience, and instructors are expected to update their approaches to child development internally and with broader organizations outside their school district. Organizing exercises is easy when utilizing workout designing and sharing software
Fundamental Coordination Development
The most vital component of physical education is teaching the student to control their body in time and space. Most of early childhood is grasping simple coordination that serves as a foundation for later stages, specifically sports and fitness. Nearly all of the resources with a curriculum should make coordination development a priority, especially in the area of locomotion. Childhood physical development should also focus on manipulating objects and learning basic activities such as catching, throwing, and other forms of movement skills. As students develop the ability to coordinate their body with simple tasks, the demands are increased through interaction with other students and challenges. In physical education, the progression of a student is gradual, starting with very basic movements in near isolation to more sophisticated coordination with games and sports. As competence is attained with the basics, new priorities such as fitness and performance are introduced.
A common uncertainty about physical education’s role in athletic development is the timing of the inclusion of formal training with sport. Eventually, an athlete needs to play the game, and practices that dedicate more time will be an advantage. The tradeoff of immediate development with specialization occurs early, while the long-term benefit of slower and wider development may be seen much later. The ideal pace with specialization and specific training is when an athlete can reach their potential in one or more sports without negatively affecting their long-term growth or health.
“Most of the empirical evidence is leading experts to believe that specializing too early and for too long leaves most athletes at risk of injury and burnout.”CLICK TO TWEET

Movement Skill Appraisals and Assessment
Connection to games and recreation.

Fitness and Health Promotion Responsibilities
As a student advances to adulthood, the transition from simple recreation to the responsibility of health and fitness begins. Current PE curriculums are now focused on lifelong wellness, as most student-athletes in high school won’t participate in organized sports later in life. Adult leagues and recreational sports attract former athletes, while most fitness and wellness activities are not competitive in nature. Therefore, a focus on lifelong exercise and nutrition is now the new standard with most scholastic curriculums. As a child matures, the focus on sports formally decreases, so the expectations of youth sports should be adjusted as a student gets to high school age. Even in middle school, children start to participate in wellness programs and recreational activities instead of sporting games, so adjustments should be considered with performance programs.
As the curriculum evolves into fitness to ward off childhood obesity, the worry is that the sporting culture will decline. Currently, no evidence or research indicates that a wellness-focused high school curriculum reduces sport participation or success, so a modern health curriculum is not the culprit in school sport performance failure. Other responsibilities of physical education often include community-type programs such as first aid and CPR, as well as a water safety assessment.
Technology use in the classroom is increasing year after year, including in physical education. The adoption of heart rate monitors and other physiological monitoring devices like wearable trackers and pedometers is growing. How physical education evolves in the next decade will be highly dependent on the information collected today. Research on childhood success in the classroom now includes many of the P.E. activities from over a decade ago, and some outcomes look promising. Improvements in emotional and behavior function due to exercise and movement are supported in the research, and many programs are cost-effective since they use existing PE programs to fulfill needs within school districts.
Teaching Physical Literacy and Competence
The primary goal of physical education is to teach essential skills to students and support their health. While athletes may benefit from early coordination and motor skill development, eventually physical education ceases to affect performance as an athlete ages. During later development years, athletes need to be instructed and cultivated with sport-specific training. Those in physical education can benefit from sports performance models, as many of the pedagogical teachings are very parallel to each other. Just as sports performance coaches benefit from actionable and enlightening data , so does the modern physical education teacher. The use of assessments and student evaluations is growing, and the right combination of teaching methodology and testing will be the future of physical education.
Try CoachMePlus Free Today
CoachMePlus is a comprehensive solution for any training environment, ranging from scholastic level to pros, and including both military and private facilities.
Recent Posts
- Reps for Success: Testing
- Reps for Success: Questionnaire
- Reps for Success: Quick Reports
- Reps for Success: Dashboard Builders
- Reps for Success: Nutrition Module
Recent Comments
Privacy overview.
International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport

This Charter is for all. Make it yours!
#sportcharter.
This unique text is the expression of a common vision by all stakeholders whether they are professional or amateur athletes, referees, public authorities, law enforcement, sports organizations, betting operators, owners of sports-related rights, the media, non-governmental organizations, administrators, educators, families, the medical profession or other stakeholders.
The text is available in more than ten languages. Click on "Read".

Adopted at the 20th session of the UNESCO’s General Conference (1978), the original Charter was perceived as innovative at the time - as it was the first rights-based document to state that “the practice of physical education and sport is a fundamental right for all”.
Based on the universal spirit of the original Charter and integrating the significant evolutions in the field of sport since 1978, the revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport was adopted during UNESCO’s 38th session of the General Conference (November 2015). The revised Charter introduces universal principles such as gender equality, non-discrimination and social inclusion in and through sport . It also highlights the benefits of physical activity, the sustainability of sport, the inclusion of persons with disabilities and the protection of children .
The revision of the Charter involved experts and practitioners from governments, sports organizations, academia and NGOs. This new version was carefully examined through sessions of the Intergovernmental Committee for Physical Education and Sport (CIGEPS) and its Permanent Consultative Council (PCC), as well as UNESCO’s Executive Board. It is a follow-up to the Declaration of Berlin that was adopted by 600 participants from 121 countries, as an outcome of the 5th World Conference of Sport Ministers ( MINEPS V ).
The Charter in a glimpse
Access to sport as a fundamental right for all
- Article 1 - The practice of physical education, physical activity and sport is a fundamental right for all
The values and benefits of sport
- Article 2 - Physical education, physical activity and sport can yield a wide range of benefits to individuals, communities and society at large
- Article 11 - Physical education, physical activity and sport can play an important role in the realization of development, peace and post-conflict and post-disaster objectives
Quality and ethical principles
- Article 4 - Physical education, physical activity and sport programmes must inspire lifelong participation
- Article 5 – All stakeholders must ensure that their activities are economically, socially and environmentally sustainable
- Article 6 - Research, evidence and evaluation are indispensable components for the development of physical education, physical activity and sport
- Article 7 - Teaching, coaching and administration of physical education, physical activity and sport must be performed by qualified personnel
- Article 8 - Adequate and safe spaces, facilities and equipment are essential to quality physical education, physical activity and sport
- Article 9 - Safety and the management of risk are necessary conditions of quality provision
- Article 10 - Protection and promotion of the integrity and ethical values of physical education, physical activity and sport must be a constant concern for all
The roles of different stakeholders
- Article 3 – All stakeholders must participate in creating a strategic vision, identifying policy potions and priorities
- Article 12 – International cooperation is a prerequisite for enhancing the scope and impact of physical education, physical activity and sport
Applications of the Charter
Article 12.3 of the Charter indicates its main applications: advocacy; developing/ sharing indicators and other monitoring and evaluation tools; education programmes; exchange of good practice; capacity development.
The Quality Physical Education Policy Project illustrates how principles and recommendations stipulated in the Charter can be translated into action through indicators, benchmarks and other tools.
The present communications toolkit was designed to help all stakeholders promote the revised Sport Charter and to broadcast its application on their domain.

Evolution of the Charter
In 1978, the International Charter of Physical Education and Sport was adopted by UNESCO’s 20th General Conference as a standard-setting instrument.
Resolution 20, View the records of the General Conference English | French | Spanish | Russian | Chinese | Arabic
In 1991, Article 7 of the Charter was amended to avert the dangers and harmful influences which are a threat to sport.
Resolution 26C, View the records of the General Conference English | French | Spanish
In order to integrate the many evolutions in the field of Sports, a thorough revision of the Charter was initiated in 2013.
Revision Timeline
MINEPS V, May 2013 (Berlin, Germany)
Download the Declaration (see paragraph 19): English | French | Spanish | Arabic | Chinese | Russian
First MINEPS V follow-up meeting for Latin America and the Caribbean, October 2013 (Bogota, Colombia)
View the Final Report: English | Spanish
37th session of the UNESCO’s General Conference, November 2013 (UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France)
Resolution 37C/38. View the records of the General Conference English | French | Spanish | Arabic | Chinese | Russian
Ordinary Session of the Intergovernmental Committee for Physical Education and Sport (CIGEPS) and its Permanent Consultative Council (PPC), March 2014 ( UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France)
- 18 Member States take note of the Report on the revision.
Resolution CIGEPS/2014/3, see 2014 Session Report English | French | Spanish
194th session of UNESCO’s Executive Board, March 2014 ( UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France)
- 58 Member States take note of a preliminary study on the desirability to revise the charter.
- They decide that it is necessary to revise the Charter.
Read the Decision 194/EX 9, see Decisions adopted at the 194th session English | French | Spanish | Arabic | Chinese | Russian
Experts Meeting, September 2014 ( Medellin, Colombia )
See report on the Revision of the International Charter, CIGEPS 2015: English | French | Spanish
Circular Letter 4081 from the Director-General of UNESCO, November 2014
Read the Circular Letter (Preliminary Draft of the Revised International Charter of Physical Education and Sport): English | French | Spanish
Extraordinary Session of CIGEPS and its Permanent Consultative Council, January 2015 (International Olympic Committee Headquarters, Lausanne, Switzerland)
- Takes note of comments received from Member States and other stakeholders.
- Discuss and finalize amendments to the Preliminary Draft of the revised Charter.
- Approves a draft revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport, as amended by it.
Resolution CIGEPS/2015/2, See 2015 Session Report: English | French | Spanish
196th session of the UNESCO’s Executive Board, March 2015 ( UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France)
- Takes note of Report on the progress of the revision of the International Charter .
View the Decision 196/9: English | French | Spanish | Arabic | Chinese | Russian
38th session of UNESCO’s General Conference, November 2015 ( UNESCO Headquarters, Paris, France)
- Takes note of the Report on the revision.
- Approves the (revised) International Charter for Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport.
- Invites Member States to implement the principles and recommendations stated in the revised Charter.
- Supports the development of a common framework for the follow-up of both the Declaration of Berlin and the revised Charter.
- Requests the Director-General to ensure a lead role for UNESCO in the follow-up process of the Declaration of Berlin and the revised Charter.
Partners’ Support
UNESCO expresses its gratitude for the support received from the governments of Monaco and Colombia , the International Olympic Committee (IOC) , Play the Game/Danish Institute of Sport Studies , as well as the many experts who have contributed to the revision of the Charter.
Quotes by our partners
“Colombia has supported the whole follow-up process to MINEPS V, the World Conference of Sport Ministers organized in Berlin in 2013. We have invited international experts to my hometown, Medellín, Colombia, to revise the International Charter of Physical Education and Sport. For me, it is a great honor to have contributed to the achievement of this goal. Let us collectively use the revised Charter to leave a legacy to the coming generations through sport.”
Andres Botero Phillipsbourne Colombia National Sports Director, Administrative Department of Sport, Recreation, Physical Activity and the use of leisure time (COLDEPORTES)
“Good sportsmanship is about respect, team spirit, excellence, fair play, friendship solidarity and integrity. With the charter, we wish to promote and protect those values – both for a better sport at all levels and for a free and humane society.”
Bertel Haarder Minister, Ministry of Culture , Denmark
"The updated Charter represents a milestone in the global sporting environment, calling for people with disabilities to be at the table and visible, with a voice, at the center and within physical education, physical activity and sport. People with disabilities can no longer be on the sidelines, no longer objects of charity and pity. The new Charter reflects the paradigm shift as indicated in the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, moving toward empowerment, dignity, universal design and full inclusion."
Eli A. Wolff Director, Inclusive Sports Initiative, Institute for Human Centered Design (IHCD)
“As the voice of persons with disabilities worldwide, more than one billion and rising, the International Disability Alliance fully supports the revised International Charter on Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport. IDA is encouraged by the recognition of the rights of persons with disabilities to participate in all Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport in safe and inclusive environments that are free from discrimination and other harmful practices. We call upon Governments to uphold these rights and invest in policies and systems that expand the scope and quality of opportunities for persons with (…).”
Vladimir Cuk Executive Director, International Disability Alliance (IDA)
“The revised Charter reflects an appreciation of the evolution of the field of physical education, physical activity and sport in recent decades. AIESEP is proud to have modestly contributed to the improvements incorporated in the revised Charter and will fully support the dissemination of the principles it advocates. AIESEP members and friends will be encouraged to introduce and discuss the Charter within their schools, institutions and networks, and to embrace the opportunity it presents for the planning of international research to inform related policy and practice.”
Marc Cloes President, International Association of Physical Education in Higher Education (AIESEP)
“The International Federation of Adapted Physical Activity (IFAPA) is pleased to support the revised Charter. (…) The inclusion of disability in this Charter matches one of our organizations main goals: To encourage international cooperation in the field of physical activity to the benefit of individuals of all abilities. We are particularly pleased that the revised Charter recognizes that inclusive, adapted and safe opportunities to participate in physical education, physical activity and sport must be available to everyone, including persons with disabilities. (…)
Many of our IFAPA members work closely with government and NGOs to create more physical education and sport opportunities for individuals with disabilities in their countries, particularly developing countries in Africa and South America where sport and physical activity for individuals with disabilities is still in its infancy. The revised Charter will provide needed support to help our members work with and push these government and non-government agencies in creating more opportunities for individuals with disabilities."
Martin E. Block President, International Federation of Adapted Physical Activity (IFAPA)
“Physical education and sport are crucial if we are to get the couch potatoes off the couch. Sport has a central role to play in our societies, not just to fight against obesity and non-communicable diseases, prevent sedentary behavior and promote healthy lifestyles. Evidence has shown time and again the positive effects of physical activity on the social and intellectual development of young people and populations at large. In collaboration with UNESCO, we will continue to advocate to governments and other key stakeholders about the benefits of sport and physical education for the mind and the body. Therefore we welcome very much the new International Charter on Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport, a resource which encapsulates the many dimensions of the reality of sport practice today, and shall help all concerned actors at national and international level to develop a strategic vision and implement adequate and sustainable policies and interventions in these fields.”
Thomas Bach President, International Olympic Committee
"(…) Physical education, physical activity and sport contribute significantly to health benefits and outcomes for everyone, particularly individuals with disabilities. The Charter importantly elevates global awareness and recognition for this critical relationship. I would like to commend everyone who worked tirelessly in the drafting process for the revised Charter, and I fully support and encourage its implementation throughout the field of physical medicine and rehabilitation."
Cheri A. Blauwet Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Harvard Medical School Chair, International Paralympic Committee Medical Committee (IPC Medical Committee)
“The FINA welcomes the adoption of the revised Sport Charter. I’ve been working for many years now on these matters – Sport for All – and the adoption of this revised Charter represents a great milestone in promotion of physical education in the five continents. FINA is also committed to this essential effort and has recently launched its ‘ Swimming for All, Swimming for Life’ programme, aimed at reducing the alarming rates of drowning worldwide by getting more and more children acquainted with the practice of Swimming.”
Julio C. Maglione President, International Swimming Federation (FINA)
“The International University Sports Federation (FISU) welcomes the revised International Charter for Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport. FISU believes that the important improvement of the Charter makes it an essential tool on which all partners involved in physical education and sport will rely to improve, extend and overcome the current challenges related to the development of policies and programmes for physical education and sport.
FISU’s approach concerning its sporting and educational events has always focused on the non-tangible values of sport and the integration and cooperation amongst all partners involved, underlining the need of taking advantage of the knowledge and competences developed in education institutions. FISU always favours the fighting spirit rather than pure performance; participation rather than records; meeting and exchange rather than confrontation. This is why FISU is committed to promoting the Charter of Physical Education and Sport adopted by the UNESCO member states amongst its membership and the international educational community, and believes that the International Day of University Sport (IDUS) celebrated on 20 September will be the ideal event where the international university sport community will have an opportunity, on a yearly basis, to reflect on the implementation of the Charter.”
Oleg Matytsin President, International University Sports Federation (FISU)
“The 1978 Charter, of inestimable value in its time, exhibited a neutrality, or linguistic blindness, to the special circumstances that exist as challenges and barriers to progress for specific social groups especially girls and women. The 2015 Revision is gender and culturally aware in many areas that will support efforts to make equitable and productive sport, physical activity, and physical education available globally.”
Carole Oglesby Co-Chair, International Working Group on Women and Sport (IWG) Botswana 2014-2018
“UNESCO’s new Charter is a powerful endorsement of the role of the independent news media sector in relation to sport. As news consumers, citizens and sport participants or observers, we are all in danger of overlooking the unique and important contribution independent news operations and journalism plays. Specialist sports journalist, photographers, news video reporters, editors and their newsrooms play a vital role in acting as the witnesses to events on the field of play and in revealing the truth of how sport is being administered, funded and sadly corrupted in some cases. Major news organisations, which support the work of the NMC, welcome the UNESCO Charter as part of the ongoing debate about how to ensure independent and viable news media operations can continue to provide value to the public, sport movement and sports commercial partners.”
Andrew Moger Executive Director, News Media Coalition (NMC)
“The UNESCO charter offers a unique chance for all nations to make an all-encompassing approach to the growing challenges in modern sport. In fact, it is more than just a chance, it is an essential step for any country that wishes to restore the credibility of sport and secure the well-being of society by offering playful physical activities to all its citizens.”
Jens Sejer Andersen International Director, Play the Game
“Special Olympics pledges its full support of the revised Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport presented to the UNESCO General Assembly. As the largest global movement dedicated to providing year-round sports training and competition to individuals with intellectual disabilities, Special Olympics is committed to ensuring that adapted, safe and high-quality sport is available to all individuals, of all ability levels, regardless of creed, religion or gender. We urge all global actors, and national and regional stakeholders, to adopt the revised Charter so that a more inclusive framework can govern such an important part of the global development community’s work, namely that of development – through-sport for all.”
Timothy Shriver Chairman, Special Olympics International (SOI)
“…I welcome the inclusion of especially Article 11 in the revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport. I have no doubt that this Article will reinforce the potential of sport to serve as a valuable and cost effective tool for peace building, peace keeping, social cohesion and nation building… However, the Charter will have little impact if we and our partners do not ensure that the Articles of the Charter are translated into well-defined action plans. We all need to work hard to achieve the noble, but practical objectives of the Charter and by doing so contributing in building peaceful communities, countries and a better world.”
Gert Oosthuizen Deputy Minister, Ministry of Sport and Recreation , South Africa
"TAFISA welcomes the adoption of the revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport. The Charter places grassroots sport and physical activity at the heart of the individual and social benefits that sport generates. While Charter acknowledges the diversity of physical play, recreation, dance, organized, casual, competitive, traditional and indigenous sports and games, it articulates a unified vision of sport and sets common quality and ethical standards that should be respected by all stakeholders. TAFISA is committed to help translate the principles set forth in the Charter into measurable action."
Ju-Ho Chang President, The Association tor International Sport for All (TAFISA)
“Transparency International’s work to strengthen integrity in sport is founded on the principle of the widest participation, including international cooperation in protecting and promoting sport as a force for good. We believe that UNESCO’s revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport provides a roadmap to move towards public trust in sport.”
Cobus de Swardt Managing Director, Transparency International
“UNICEF welcomes the revised Charter. It is an important framework that can help guide our joint work with governments and a wide range of partners, in particular as we look toward to sport-for-development and physical education as effective strategies for equitable inclusion of all groups of children, adolescents and youth, especially the most vulnerable, thus contributing to the achievement of several of the SDGs.”
Andro Shilakadze Representative to Azerbaijan, United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
“The revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport is a comprehensive reference for all stakeholders in the field of Sport for Development and Peace, perfectly aligned with the sustainable nature of the development goals we are pursuing and responsive to the social, economic and environmental challenges we are facing.
As an advocate for development and peace through sport, I strongly welcome the introduction of Article 11 which positions sport, physical activity and physical education as powerful tools for social transformation and post-conflict recovery.
I welcome the revised Charter as a well-rounded framework not only for guiding policy but also for promoting cooperation and action on the ground for all those of us who strive to put sport, physical activity and education to the best service of humankind.”
Wilfried Lemke Special Adviser to the United Nations Secretary-General on Sport for Development and Peace (UNOSDP)
“The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) welcomes the revised International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport. The fact that anti-doping is specifically referenced in the context of protecting participants from the harmful effects of doping is commendable. And equally important, the inclusion and promotion of values-based prevention programmes is essential to protecting the integrity of sport. WADA was involved from the beginning with the revision work and we acknowledge the hard work, commitment and energy of all involved in bringing it to fruition.”
David Howman Director General, World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA)
“The World Federation of the Sporting Goods Industry (WFSGI) congratulates UNESCO and in particular the driving forces behind the Intergovernmental Committee for Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport (CIGEPS) and its Permanent Consultative Council (PCC) to have achieved a major milestone to increase global physical activity levels. The far-reaching revision of the International Charter gives the right signal and has the potential to create early positive experiences for kids and to propel physical activity levels in schools globally. The revised Charter is a great contribution towards our shared goal to create a world where sports and physical activity are not only highly valued, but an expected and enjoyable part of life. UNESCO as the lead agency for sport and physical education has now set a new standard for global policy makers. We wish to congratulate you on this great achievement and look forward to seeing this revised Charter implemented in Member States across the globe!”
Robbert de Kock Secretary-General, World Federation of the Sporting Goods Industry (WFSGI)
Philipp Müller-Wirth Sport Section Social and Human Sciences Sector - UNESCO 7 place de Fontenoy 75352 Paris 07 SP FRANCE [email protected]
Related items
- Social and human sciences
- Gender equality
- Norms & Standards
- Disabilities
- Discrimination
- Gender discrimination
- Social inequality
- Physical education
- Physically disabled
- Disabled children
- Disadvantaged children
- See more add
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Inclusive School Physical Education and Physical Activity
All students, regardless of ability, should get the recommended 60 minutes or more of daily physical activity . Schools can help all students meet this recommendation by providing equal opportunities for students with disabilities . 1 Creating an inclusive culture for physical education and physical activity helps every student learn to lead a healthy and active lifestyle.
Inclusion means that, “All children, regardless of ability or disability, have the right to be respected and appreciated as valuable members of the school community, fully participate in all school activities, and interact with peers of all ability levels with opportunities to develop friendships.” 2
Inclusive physical education and physical activity:
- Includes students with disabilities in regular physical education classes. Specifically, teaching strategies, equipment, environments, and assessments have been adapted to meet the needs of all students.
- Supports students with disabilities who want to participate in other physical activities before, during, and after school.
- Encourages students with disabilities to have the same roles and experiences as their peers who do not have a disability during physical education and other physical activities.

Download the research brief [PDF - 1 MB] , Inclusion in School Physical Education and Physical Activity .
Federal law requires states, districts, and schools to provide children and adolescents with and without disabilities equal opportunity to participate in physical education and physical activity. 3
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) bans discrimination on the basis of disability. 4 Therefore, schools are required to comply with the accessibility requirements of the ADA and provide appropriate physical education and physical activity opportunities for students with disabilities.
- Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act and Title II of the ADA are federal civil rights laws that prohibit disability discrimination, including in schools. 5
- The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) provides for a “free appropriate public education” in the “least restrictive environment” to all children with a disability. 1 IDEA also states that students with disabilities are to participate in physical education with children without disabilities to the maximum extent appropriate. IDEA includes language for instruction in physical education that may be a part of the special education services prescribed in students’ individualized education program (IEP) , a legally binding document that has been tailored specifically to a child’s educational needs.
Schools are required to have adequate policies and practices that align with the federal policies for inclusion. Schools also need to be aware of any additional policy guidance from their state or school district. At the state level, relevant policy information might be found in the 2016 SHAPE of the Nation report and NASBE’s state policy database . 6,7 At the district level, expectations for inclusion might be found in the local wellness policy. 2 See examples of model wellness policies for inclusion .
Most school districts require schools to meet the physical education needs of students with disabilities by 8 :
- Including accommodations in physical education in 504 plans or IEPs (98%).
- Mainstreaming into regular physical education as appropriate (97%).
- Providing adapted physical education as appropriate (91%).
Among schools that have students with disabilities, 91% include physical education in IEPs or 504 plans for these students. 9
Among schools that have students with disabilities, 62% require students with long-term physical, medical, or cognitive disabilities to participate in physical education. 9
However, 52% of schools exempted students with cognitive disability, and 86% exempted students with long-term physical and medical disability from physical education. Both percentages increased between 2000 and 2014. 9
More information and data can be found in CDC’s research brief, Inclusion in School Physical Education and Physical Activity [PDF – 697 KB] .
Below are six actions state leaders can take to promote inclusion in physical education and physical activity at the district and school levels.
- Share any state laws, policies, and guidance for participation in physical education and physical activity for students with disabilities with district and school staff. This includes policy language around inclusive physical education and physical activities, adapted physical education, professional development for administrators and staff about building a culture of inclusion, and certification of staff working with students with disabilities.
- Share your state-level data about students with disabilities with educational and health leaders. The National Survey of Children’s Health provides an interactive data query site that you can use to identify state estimates about students with disabilities. Starting in 2020, CDC’s School Health Profiles survey will have two questions related to inclusion.
- Identify and reach out to state and district partners that are already leading inclusion efforts and look for opportunities to collaborate. Potential partners include state disability program staff, Special Olympics state affiliates, local university departments working on adapted physical education and inclusion, state Society of Health and Physical Educators (SHAPE) America affiliates, adapted physical education specialists, adapted sport programs or clubs, and allied health–occupational, physical, and speech therapists. CDC funds 19 states under the State Disability and Health Programs .
- Conduct a brief assessment of current activity and needs. This assessment should identify any current activities for inclusion at the state and district levels (e.g., programmatic efforts, built environment improvements, funding, professional development) and any needs at the district and school levels for inclusion. The National Center on Health, Physical Activity, and Disability’s Community Health Inclusion Index is an example of an assessment tool. It is designed to collect information about healthy living resources and the degree to which they are inclusive.
- Provide training to district and school staff on how to create an inclusive Comprehensive School Physical Activity Program (CSPAP) to ensure that physical activity opportunities are accessible and inclusive before, during, and after school.
- Engage partners and university programs to train current and future school leaders, physical education teachers, and classroom teachers on best policies and practices for inclusion. This could include learning about how to make adaptations and accommodations to facilities, rules, equipment, instructions, and assessment.
- Adapted Physical Education Standards
- Adapted Physical Education Resources for Teachers
- Adapted Physical Education/Physical Activity Workshops
- I Can Do It!
- National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability Resources for Educators
- Special Olympics Unified Champion Schools®
- Individuals with Disability Education Act (IDEA), 33 § 1400-1482 (1990).
- National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability. Discover Inclusive School Wellness . Birmingham, AL: National Center on Health, Physical Activity and Disability; 2016. https://www.nchpad.org/fppics/NCHPAD_Discover%20Inclusive%20School%20Wellness(1).pdf [PDF – 4.4 MB] . Accessed December 18, 2019.
- U.S. Department of Education, Office of Special Education and Rehabilitative Services, Office of Special Education Programs. Creating Equal Opportunities for Children and Youth with Disabilities to Participate in Physical Education and Extracurricular Athletics . Washington, DC: US Dept Education; 2011. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED524248 . Accessed December 18, 2019.
- Americans with Disabilities Act, 42 U.S. Code § 12101 12102 (2009).
- Section 504, Rehabilitation Act, 29 U.S.C. § 701, as amended through P.L. 114—95 (2015).
- SHAPE America; American Heart Association. Shape of the Nation. Status of Physical Education in the USA . Reston, VA: SHAPE America—Society of Health and Physical Educators; 2016. https://www.shapeamerica.org/advocacy/son/2016/upload/Shape-of-the-Nation-2016_web.pdf [PDF – 1.4 MB] . Accessed December 18, 2019.
- National Association of State Boards of Education. NASBE State Policy Database. https://statepolicies.nasbe.org/ . Accessed December 18, 2019.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Results from the School Health Policies and Practices Study 2016 . Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2017. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/shpps/pdf/shpps-results_2016.pdf [PDF – 1.5 MB] . Accessed December 18, 2019.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Results from the School Health Policies and Practices Study 2014 . Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/data/shpps/pdf/SHPPS-508-final_101315.pdf [PDF – 1.9 MB] . Accessed December 18, 2019.

Healthy Youth
To receive email updates about this page, enter your email address:
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

ACTIVITIES IN PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND SPORT

Related Papers
Croatian Journal of Education - Hrvatski časopis za odgoj i obrazovanje
prof. dr Nedeljko Rodić
IJMRAP Editor
Analysis of problems in the field of physical education and sports, as well as the elaboration of evidence-based recommendations for the development of this area, as well as showing the importance of higher educational institutions in the training of qualified specialists for physical education and sports. The article used such methods as questioning, a survey of leading experts in our country and abroad, as well as theoretical and methodological studies of the problem of the development strategy of physical education and sports, which made it possible to identify a number of priority areas of modern sports science. The results of the survey, we can see that it is effective to organize sports educational institutions of different status and carry out reforms aimed at their development. In particular, the implementation of reforms aimed at the development of non-state sports educational institutions in the country leads not only to the training of qualified athletes, but also to an increase in the desire and interest of the population to regularly engage in physical culture and sports. It is necessary to organize training and relationships based on modern requirements. Today in our country, research work in the field of physical culture and sports is not organized on the basis of modern scientific standards. The lack of a system that evaluates and puts into practice the results of scientific research, innovative developments in the field of physical culture and sports also has a negative impact on the development of the industry. In this regard, it is important to organize work to promote scientific research in the field of physical culture and sports based on modern scientific standards, to introduce a cluster system for evaluating and putting into practice the results of research activities in this area.
International journal of physical education, sports and health
Madhu Sudan Hazra
It is widely known that education is a mean of all round development of an individual like physical, mental, emotional, social, as well as spiritual aspects. Participation in sports and Physical education, mainly aims at providing sound health, guiding protective measures against diseases, practicing for stamina and fitness, boosting up academic learning, developing self esteem, promoting cooperation, teamwork along with sportsmanship skills and an exclusive art of living with a leadership quality, the objective of this study was to discussion related with the matter that, how sports play significance role in education or in all round development of a person? For fulfill the purpose, author studied several book, journals, periodicals, and gathering the knowledge from several websites. After the study it is descriptively concluded that participation in sports, games physical education influence the overall education of human being.
Fitness & Performance Journal
Estélio H M Dantas
Facta universitatis. Series physical education and sport
Milena Mikalacki
Mihailescu Liliana
Strong influence on the formation of the attitudes of the individual, in the case of the child, his/her primary groups, in particular family and pedagogical staff. In this context, the attitudes of others become formative attitudes of the child, having been filtered through personal experience a considerable influence in shaping the attitudes of the individual exercise and secondary groups, various social and cultural institutions, political organizations, etc. To the extent that the individual can participate in the life and work of these institutions, he forms the right attitudes, according to personal experience. The purpose is to highlight the influences of physical education discipline in the social integration of students in the school environment. The content and forms of organisation-specific, physical education is able to create an appropriate framework for both the formation of moral consciousness and the expression of moral conduct. These effects are possible because phys...
Ivan Anastasovski
Physical culture is a part of the cultural values that are based on motor movements, which are used for training and validation of personality. The term ''physical culture'' down to a sub-culture, or culture of a social group. Physical culture is an activity that is enjoyable and dynamic nature. One of the segments of the school physical education is sports-technical education or adoption of certain number motor forms or techniques of performing certain sports items, etc. motor habits. Creation and development of motor habits is accomplished through the process of exercise, i.e. systematic repetition and development of a specific physical activity. School physical education, his practical course and the results achieved are very complex phenomenon that requires planning and studious study of all its components. Practical work in physical education teacher of great importance is the choice of physical activities, and in particular the sequence of learning them. Physic...
Proceeding book
Jelka Gošnik
Polish Journal of Applied Sciences
igor cieśliński
Physical activity and healthy sports are essential for our health and well being. Appropriate physical activity and sports for everyone constitute one of the major components of a healthy life of a human being and healthy diet, alcohol and tobacoo and other drugs free life and avoidance of other substances harmful to health. Development around the world has made Physical Education and Sports an important part of human life and specially for education of everyone. Hence in recent years due importance to physical education teaching and sports is being given proper attention in our education system. Sports person are considered to be the best ambassadors of the country and the same is also true for a teacher in physical education in Schools and Colleges. In present system our society is facing a very big problem related to health. The present scenario doesn't seem to be encouraging as there is reduced demand for physical education instead of increased risk of life for a common people. In the present research paper the current scenario of physical education and sports in our country. The study also observed the existing status of physical Education and sports development in the country.
RELATED PAPERS
Jefrey I. Kindangen
Ο Άγιος Δημήτριος στο Αετοχώρι (Τούσιανη) Αλμωπίας
Giorgos Skiadaresis
Mikal Håland
Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical
Erica Flapan
The journal of physical chemistry. A
Karel Berka
Jerry Jerry
Hari Sharma Neupane
Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia
Journal of Engineering and Applied Science
Chinedum Mgbemena
Network Modeling Analysis in Health Informatics and Bioinformatics
Experiments in Fluids
Panos Diplas
Brill’s Journal of Afroasiatic Languages and Linguistics 11. 201-225
Shmuel Bolozky
Personal and Ubiquitous Computing
Giuseppe Sansonetti
IEEE Transactions on Appiled Superconductivity
René Flükiger
hajer A B I D I Abidi
Contemporary European History
Jena Gaines
Baldemar Ibarra-Escamilla
Ahmed Ghowel
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Alison Yeates
Revista Española de Cirugía Oral y Maxilofacial
Ludmila Antonelli
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

COMMENTS
Comprehensive physical education. Physical education (PE) is a K-12 academic subject. It provides standards-based curricula to develop students' knowledge and behaviors for physical activity, physical fitness, and motor skills. Schools can develop and carry out comprehensive PE policies for daily physical activity. This will prepare students ...
6. Crab Soccer. Playworks/Crab Soccer via playworks.org. We love elementary PE games that require students to act like animals (and we think they will too). Similar to regular soccer, but students will need to play on all fours while maintaining a crab-like position. Learn more: Crab Soccer at Playworks.
Integrating STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) into Physical Education (PE) classes offers an innovative approach to education. In an era where sports statistics, science, and technology increasingly influence athletics, PE classes are uniquely positioned to blend physical activity with STEM learning and 21st century skills. This article explores how PE educators and ...
Category: Activities. Whether you're searching for creative PE activities to put a new spin on games, new ideas to become more efficient during assessments, or learn how to add technology to lessons, you have come to the right place! PE professionals share their knowledge to help teachers evolve their activities for students into high-energy ...
Practical, proven lesson plans written and submitted by real teachers and approved by our expert editorial team! Helpful online courses and information for the physical education teacher who wants to continue to develop and grow! View all 79 Resources! See what others are doing to improve physical education at their school.
School-based physical activity, including physical education and sports, is designed to increase physical activity while also improving motor skills and development, self-efficacy, and general feelings of competency and engaging children socially (Bailey, 2006).
Physical activity has significant health benefits for hearts, bodies and minds. Physical activity contributes to preventing and managing noncommunicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes. Physical activity reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety. Physical activity enhances thinking, learning, and judgment skills.
Physical education for healthier, happier, longer and more productive living. The time children and adults all over the world spend engaging in physical activity is decreasing with dire consequences on their health, life expectancy, and ability to perform in the classroom, in society and at work. In a new publication, Quality Physical Education ...
2. Definitions of Physical Activity, Exercise, Training, Sport, and Health. Definitions and terms are based on "Physical activity in the prevention and treatment of disease" (FYSS, www.fyss.se [Swedish] []), World Health Organization (WHO) [] and the US Department of Human Services [].The definition of physical activity in FYSS is: "Physical activity is defined purely physiologically, as ...
Although academic performance stems from a complex interaction between intellect and contextual variables, health is a vital moderating factor in a child's ability to learn. The idea that healthy children learn better is empirically supported and well accepted (Basch, 2010), and multiple studies have confirmed that health benefits are associated with physical activity, including cardiovascular ...
Curriculum in Physical Education. A highly effective physical education program aims to develop physical literacy through the acquisition of skills, knowledge, physical fitness, and confidence. Physical education curricula promote healthy development of children, encourage interest in physical activity and sport, improve learning of health and physical education concepts, and accommodate for ...
Outdoor physical education activities like sports require equipment, but you can easily set up and play them in a yard or nearby park. Fun PE games for kids like soccer, kickball, or basketball can be played with just a ball at a nearby park. Games like "H-O-R-S-E" or "around the world" can be played with just two or more players on a ...
Depending on where you're teaching, your students may have a mandated physical education class … then again, maybe not. According to the National Association for Sport and Physical Education, only 22 states require schools to allot a specific amount of time for exercise activities.This leaves a lot of kids with classroom exercises as their only outlet!
A culturally relevant curriculum that includes lifestyle sports, with a focus on mastery and enjoyment through a meaningful experiences approach, is proposed as a viable update to current practice. Keywords: physical education; physical activity; motivation; lifestyle sports; youth culture; meaning-ful experiences. 1. Introduction.
The Role of Physical Education. Physical education (P.E.) is an important component of student development. It should be seen as a small part of athlete development, but not a responsibility for maximizing sports performance. Where physical education ends and athletic development begins is a grey area, but we do know that as an athlete begins ...
The International Charter of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sport is a rights-based reference that orients and supports policy- and decision-making in sport. It promotes inclusive access to sport by all without any form of discrimination. It sets ethical and quality standards for all actors designing, implementing and evaluating sport programmes and policies.
Physical Education and Sport Pedagogy publishes research that reports educational practices in all appropriate contexts including, but not limited to, school physical education, club sport, and active leisure programs. The journal considers papers that discuss a broad range of physical activities, including aquatics, dance, exercise, gymnastics ...
However, 52% of schools exempted students with cognitive disability, and 86% exempted students with long-term physical and medical disability from physical education. Both percentages increased between 2000 and 2014. 9. More information and data can be found in CDC's research brief, Inclusion in School Physical Education and Physical Activity ...
One of the segments of the school physical education is sports-technical education or adoption of certain number motor forms or techniques of performing certain sports items, etc. motor habits. Creation and development of motor habits is accomplished through the process of exercise, i.e. systematic repetition and development of a specific ...
ABSTRACT. Self-advocacy is a critical predictor of actual physical activity participation for children and adolescents with disabilities. Despite its reference within national standards for health and physical education, few practitioners are purported to promote self-advocacy among their students warranting the need for evaluation.
The drop off in physical activity (PA) for children has led to an increased focus on their PA engagement, due to the poor health outcomes often linked to this decline. Subsequently, stakeholders, across a variety of fields, have problematised and intervened in activity settings to address this decline. Many of these studies acknowledge high levels of activity in the primary years and tend to ...
Join us for this afternoon's commencement exercises for our graduating class of 2024. #ForeverToThee24