
- Advanced Search

Version 1.0
Last updated 15 august 2019, alliance system 1914.
Alliances were an important feature of the international system on the eve of World War I. The formation of rival blocs of Great Powers has previously considered a major cause of the outbreak of war in 1914, but this assessment misses the point. Instead of increased rigidity, it was, rather, the uncertainty of the alliances’ cohesion in the face of a casus foederis that fostered a preference for high-risk crisis management among decision-makers.
Table of Contents
- 1 Introduction: Alliances and Great Power relations in Europe, 1815-1871
- 2 Dual Alliance and Triple Alliance
- 3 Franco-Russian Alliance and Triple Entente
- 4 Great Power Alliances on the Eve of War
- 5 Conclusion: 1914 - Have Alliances Failed?
Selected Bibliography
Introduction: alliances and great power relations in europe, 1815-1871 ↑.
Alliances were nothing new to international relations in modern Europe. The patterns of cooperation in the first half of the 18 th century had become so familiar that switching strategic partners in preparation for the Seven Years War was dubbed as “ renversement des alliances ”. However, with religious and ideological issues only of marginal relevance to the cabinets of Europe, war-time alliances could be overturned quite easily. The French Revolutionary Wars (1792-1802) and Napoleonic Wars (1803-1815) put Great Britain and France in the role of perennial adversaries, both of them forging alliances with other powers if useful and possible. Paul W. Schroeder has argued that the anti-Napoleonic coalition of 1813-1814 proved to be a turning point in international relations, because the four major coalition partners - Great Britain, Russia , Austria , and Prussia - decided to put their alliance on a peace footing after the end of war in 1814 and the Vienna Settlement of 1815. The Quadruple Alliance was meant to guarantee the peace of Europe by keeping a watchful eye on France and to cooperate closely to thwart any threat to international stability on the continent, while the Holy Alliance (originally consisting of Russia, Austria and Prussia) added glamorous rhetoric to this idea. According to Schroeder, traditional balance of power policy gave way to a collective effort among the Great Powers to defend the rights and mutual obligations of all sovereign states, big or small. With France co-opted in 1818, the five Great Powers became known as the Pentarchy. The Pentarchy discussed problems related to the situation of smaller states and decided on solutions to them, a de-facto privilege of the Great Powers in a Europe of sovereign states with different level of strategic clout. Although conflicts among the Great Powers would set limits to their close cooperation in the following decades, the Concert of Europe was still at play in the debates about Balkan crises in the years and months prior to the outbreak of war in 1914. [1]
At its heyday, in the first years after the Congress of Vienna, the new consensus among the Great Powers was strong enough to make separate alliance treaties between some of them seem irrelevant. In the 1820s, with disputes over the future of Spain and her former colonies in Latin America and divergent intentions in the Eastern Question, Great Power relations were transformed. New alliances were forged between Britain and France and between the conservative monarchies of Russia, Prussia, and Austria. The latter was perceived as a bulwark anti-revolutionary policy, the former as a cooperation of more liberal-minded cabinets. With regard to the decline of the Ottoman Empire and its geopolitical consequences, different patterns of alignment emerged in 1840. It was this Eastern Question that sparked the first war between Europe’s Great Powers after the defeat of Napoleon I, Emperor of the French (1769-1821) . His nephew, Napoleon III, Emperor of the French (1808-1873) , was instrumental in the formation of an anti-Russian war coalition in 1853-1854. The Crimean War was a decisive blow to the Vienna Settlement, although the peace treaty of Paris in 1856 reiterated the idea of a Concert of Europe. It left Russia reeling from defeat and encouraged further revision of the international system. Alliances became important tools in the ensuing transformation of Europe. Secret treaties between France and Sardinia and Italy and Prussia, respectively, were crucial in the preparation for the wars of 1859 and 1866, and Prussia’s treaties with the southern German states came to bear in 1870-1871. The so-called Wars of Italian Independence and of German Unification changed the map of Europe by creating new nation states. They also left the Habsburg Monarchy and France in a much weaker position. The creation of Germany under Prussian leadership and the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine was the most obvious shift in the balance of power. [2]
Dual Alliance and Triple Alliance ↑
With the creation of nation states in Germany and Italy completed, 1871 marked a turning point in the development of Europe’s international order. In a series of three victorious wars, Prussia had forged the economically and militarily strong German Empire, which now held a particularly powerful position on the continent. After a crisis in the mid-1870s, German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898) settled on a course of securing the empire ’s position by isolating France and engaging with the other Great Powers, in particular Austria-Hungary and Russia. Ever the skillful diplomat, Bismarck was able to achieve this much, but he left a difficult legacy to his successors after his dismissal in 1890. It turned out to be particularly difficult to maintain close ties with Russia without encouraging St. Petersburg to wage a policy of expansion on the Balkans . Several times, Bismarck tried to build on the traditional pattern of anti-revolutionary cooperation between the monarchies of the Romanovs, the Hohenzollern, and the Habsburgs. The Three Emperors’ League was agreed upon in a treaty between Alexander II, Emperor of Russia (1818-1881) , Wilhelm I, German Emperor (1797-1888) , and Francis Joseph I, Emperor of Austria (1830-1916) in September 1873. It evoked the spirit of the Holy Alliance, but would not survive the clash of interests between Austria-Hungary and Russia that developed just a few years later over the expansion of Russian influence in South East Europe and the creation of a Greater Bulgaria in the 1878 San Stefano peace treaty between Russia and the Ottoman Empire. [3]
The Balkan Crisis of the 1870s and the Congress of Berlin in 1878, at which Bismarck did not save Russia from international pressure to give up on the project of Greater Bulgaria, rattled the foundations of the cooperation between the three conservative monarchies of the Hohenzollerns, the Romanovs, and the Habsburgs. An Austrian initiative led to the so-called Dual Alliance, a defensive alliance between the German Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy. The secret alliance treaty of 7 October 1879 assured Austria-Hungary of German military assistance in case of a Russian attack on the Dual Monarchy. Austria-Hungary also committed herself to come to the rescue of her ally in case of a Russian attack on Germany, a highly unlikely scenario. The Germans would get little in return, since the Austrians were under no obligation to come to their ally’s rescue in the case of a French attack on the German Empire. Benevolent neutrality was all they had to promise, unless France would be fighting alongside Russia. [4]
Bismarck wanted to shield the Habsburg Monarchy from Russian aggression and to get a say in Austria’s foreign policy. Without German consent, any diplomatic or military action taken by the Austrians that led to Russian countermeasures might jeopardize Germany’s commitment to the alliance. The casus foederis , Bismarck made clear in the 1880s, would only be triggered if Austria’s actions were first cleared with Berlin and the subsequent Russian attack labeled “unprovoked”. In this way, Bismarck avoided a situation in which the weaker of the allies would be able to steer the stronger one towards war. The German chancellor was not only trying to commit Vienna to close coordination of its Balkan policy with Berlin; he also hoped to make the Dual Alliance the cornerstone of cooperation in other fields and to tie the Habsburg Monarchy to the German Reich in a way reminiscent of the Holy Roman Empire. Gyula Andrássy (1860-1929) , Bismarck’s opponent, refused to have the treaty ratified by parliaments , and it would be kept secret until 1889, when Bismarck published it to deter Russia at the height of the Dual Crisis. [5]
Nevertheless, the Dual Alliance was not considered to be just another international treaty, but rather the foundation and symbol of a special relationship between the German Empire and the Dual Monarchy. The very basis of Austro-Hungarian dualism, the dominating influence of the Germans in Austria and the Magyars in Hungary, was seen as non-negotiable in Berlin, in order to keep Slav aspirations in Europe at bay. German diplomats and politicians would not shy away from telling their counterparts so, but up to a point, the underlying Teutonic, anti-Slav rhetoric also limited Germany’s freedom of action. The term “ Nibelungentreue ”, applied to German-Austrian relations by Chancellor Bernhard von Bülow (1849-1929) in 1909, put a name to the cultural underpinnings of the Dual Alliance that had to be accounted for by German politicians. With Italy staying out of the fray in 1914, the Dual Alliance became the nucleus of what would be called the war coalition of the Central Powers. [6]
The Dual Alliance would be renewed on a regular basis and still existed in 1914, but by that time, most contemporaries had begun to use the term Triple Alliance when they were talking about Germany’s and Austria-Hungary’s most important alliance treaty. As in the case of Germany, the creation of Italy as a nation state had come at the expense of the Habsburg Monarchy. But unlike Germany, where the idea of uniting the German-speaking parts of Austria with the German Empire enjoyed almost no support, the vision of an Italy that included the Italian-speaking regions of the Habsburg Monarchy held considerable appeal for the Italian elites. In addition, the aspiring new – and still not very strong – Great Power Italy was vying with Austria-Hungary for control in the Adriatic. The potential for conflict between both powers notwithstanding, Italy had reasons to cover her back while she was striving for colonial expansion in the Mediterranean. With France blocking Italy’s path by seizing Tunisia in 1881, the government in Rome had to turn to Vienna and Berlin in search of protection in case of future colonial conflicts.
In the Triple Alliance Treaty of 20 May 1882 between Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy, Italy and Germany were promised military support in case of an unprovoked attack by France. If two or more of the Great Powers attacked one of the three alliance partners, the other two would also be required to intervene by force. If only one Great Power forced one of the allies to resort to war, the others were obliged to keep a neutral stance, unless they decided to help militarily. [7] Romania , whose king was a member of the Hohenzollern dynasty, acceded in October 1883. [8] The treaty was meant to be secret, but in 1883 an Italian politician made the existence of the alliance public. Its text would be kept secret, as would the articles that were to be added in later years when the treaty was up for renewal. From an Italian point of view, her allies’ pledge of support in case of a war with France was essential; for Bismarck, the alliance helped to keep France isolated and would, in combination with the Dual Alliance, allay Austrian fears of Russian dominance in South East Europe. Vienna’s intention to preserve the status quo on the Balkan peninsula resonated with British priorities in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was also in Berlin’s interest to see the emergence of an alignment of Italy, Great Britain, and Austria-Hungary. This was formalized in a set of agreements brokered by Bismarck that culminated in a treaty between Great Britain and Italy in February 1887, with Austria-Hungary in March 1887 and with Spain in May 1887. The so-called Mediterranean Entente defused conflicts between Austria-Hungary and Italy, but most importantly, it contained Russia in the Eastern Mediterranean quite successfully in the late 1880s and early 1890s.
In 1891, when the Triple Alliance was to be renewed for the second time, the Austrian minister of foreign affairs suggested to the Italians that an agreement between the two allies should be included, which aimed to preserve the status quo in the Balkans and the territorial integrity of the Ottoman Empire. But if the status quo “collapsed”, any temporary or permanent occupation of territories in the area should, according to Article VII, “take place only after a previous agreement between the two Powers, based upon the principle of a reciprocal compensation for every advantage, territorial or other.” This article would be part of the renewed and extended versions of the treaty agreed upon in 1902 and 1912. [9] In 1914-1915, Italy would use Article VII to gain leverage in her negotiations with Austria-Hungary over Trentino and Trieste. In the years before, the article kept a lid on Austro-Italian rivalry in Albania . But with Italy seeking British, French and Russian support between 1899 and 1911, the Triple Alliance was no longer essential for Italy’s colonial aspirations in North Africa and in the Eastern Mediterranean. During the Italo-Turkish War of 1911-1912, Rome could count on the tacit support or at least acquiescence of the other Great Powers. As the Ottoman Empire, weakened by the Italian attack on its North African possessions and the ensuing war, came close to collapse in 1912 in its fight against the Balkan League, which had been forged by Russian diplomacy, the Great Powers set up the London conference. The Concert of Europe was meant to contain the shockwaves and to help find viable solutions to territorial disputes when the spoils of war were divided up. The Triple Alliance was renewed for the last time in December 1912, in the wake of the First Balkan War, with tensions between the Great Powers at crisis level. [10]
Although contemporaries were still using the term Triple Alliance, the cabinets in Berlin and Vienna were no longer convinced of Rome’s attachment to the alliance. In Austria-Hungary, suspicions of Italian duplicity were widespread. Rivalry between both allies in the Adriatic and fear of Italian plans to grab Habsburg territory fueled anxieties and inspired military build-up and heavy-handed policing along the border. A naval armaments race between the allies ensued in the early 1900s that would slow down only on the eve of war. By that time, support for the Triple Alliance in Italy’s political elite had waned. Whereas the alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary had been pivotal to Italian efforts to become a modern, respected great power in the 1880s and most of the 1890s, in the early 20 th century, ties to Vienna and Berlin had become a matter of weighing strategic opportunities. [11] Consequently, uncertainties about Italian policy played a significant role in British, French, German and Austro-Hungarian calculations.
Italy was not the only one about to jump ship and seek closer relations with Britain, France, and Russia; Romania was, as well. In both cases, Austria-Hungary stood in the way of the possibility of expanding influence and gaining territories in the Balkans. In the case of Romania, Vienna’s stance during and after the Second Balkan War soured relations. Both in Italy and in Romania, the hope of annexing parts of the Habsburg Monarchy that had a majority population of co-nationals started to gain more traction among publicists and politicians. Fears of such a policy among the political elites in Vienna and Budapest were not without justification, but greatly exaggerated. Nevertheless, those fears fed into a growing sense of instability and imminent threat to the very existence of the Habsburg Monarchy. By 1914, the future of the Triple Alliance seemed to be in question, but many decision-makers in Vienna and in Berlin who started the July Crisis hoped to keep the Triple Alliance – including Romania – together in case of a European war, or at least to be able to count on Italian and Romanian neutrality. Compared to the days of Bismarck’s chancellorship, the German Empire looked more and more isolated in Europe, with only the declining Habsburg Monarchy left as a weak, but reliable ally. [12]
Franco-Russian Alliance and Triple Entente ↑
Until the late 1880s, the French Republic held a rather isolated position among the Great Powers. Colonial disputes with Britain and Italy played a role, but so did the perception of France as a standard-bearer of revolution . Republicanism and revolution were considered deadly threats to Europe in general and to Russia in particular, especially by the tsar and his government . Bismarck had successfully appealed to the tsar’s conservatism in 1873 and did so again in 1881, when Russia, Germany and Austria-Hungary signed treaties that followed the traditions of the Holy Alliance. With the secret Reinsurance Treaty of 1887 between Germany and Russia, [13] Bismarck tried to keep Russia engaged, but a tariff dispute and Germany’s decision to ban the floating of Russian state loans on German markets in 1887 proved counterproductive. After Bismarck’s fall in 1890, the German decision to let the Reinsurance Treaty expire, and the assertive policy of Berlin’s partners in the Eastern Mediterranean in 1891, furthered the alienation between Germany and Russia. French politicians sensed an opening for closer relations with the only strategic partner left on the continent that might help to counter Germany. The detention of Russian anarchists in France made the republic more palatable to the tsar. Financial support was something the French Republic had to offer, but it also had sizable military capabilities. The visit of a French naval squadron to the Russian harbor of Kronstadt 1891 and a Russian return visit to Toulon in 1893 made the realignment public.
It was the French who insisted on a written agreement. In August 1892, the two general staffs signed a military convention that would be endorsed by an exchange of diplomatic notes. Thus, on 4 January 1894, the agreement between the general staffs gained the status of an alliance treaty. Just as in the case of the Dual Alliance, the Franco-Russian alliance was a defensive one. Russia promised support with all her forces available in case of an attack on France by Germany or by Italy with German assistance. The French would do the same if Russia were attacked by Germany or by Austria with German support. Unlike the Dual Alliance or the Triple Alliance treaties, the Franco-Russian agreement was more specific in terms of military aspects. Article 2 regulated mobilization and deployment:
In Article 3, the text even mentioned troop numbers and defined the basic strategic concept of coalition warfare :
Little wonder that Article 4 called for close cooperation between the two general staffs in order to allow for coordinated campaigns in case of war. [14]
Throughout the following years, the allies discussed strategy, operations, and logistics. France supported armaments and the construction of strategic railways in Russia. [15] In 1899, due to a French initiative, the allies agreed to support French aspirations in Alsace-Lorraine and Russian ones on the Balkans. At the time, Russo-Austrian relations had taken a turn for the better and a French conquest of Alsace-Lorraine in the context of a general war seemed farfetched. After she had suffered defeat at the hands of the Japanese in Manchuria and at Tsushima in 1904-1905, and in the wake of revolutionary turmoil in 1905, Russia needed to rebuild her military capabilities. French support and rapid economic modernization allowed for fast rearmament, but not fast enough to save Russia from humiliation in 1909, when a German ultimatum forced St. Petersburg to abandon Serbia in the conflict with Austria-Hungary over the annexation of Bosnia-Herzegovina. But the Bosnian Crisis also indicated a massive change in French and Russian strategic options, because Britain had openly abandoned her commitment to the defense of the Habsburg Monarchy’s role as a Great Power on the Balkan peninsula. Compared to the late 1880s and early 1890s, British policy had changed profoundly under Edward Grey (1862-1933) , who had become foreign secretary in 1905. [16]
As a means to contain Russian expansionism in the Far East, Britain had abandoned her previous policy of “splendid isolation” and signed an alliance treaty with Japan in January 1902 when the Second Boer War was drawing to a close. After three years of fierce fighting, the war in South Africa inspired dystopian visions of decline in Britain. To protect the empire and the United Kingdom, alliances would be useful, or even necessary. In early 1904, at a time when a Russo-Japanese war seemed imminent and threatened to draw the belligerents’ respective allies into the fray, Britain was willing to form closer diplomatic ties with France, her long-standing competitor in overseas expansion. On 8 April 1904, Foreign Secretary Lord Lansdowne (1845-1927) and the French ambassador to London signed a declaration that was meant to resolve conflicts concerning colonial interests in Morocco, Egypt , and other territories overseas. [17] This agreement would become known as the Entente Cordiale.
What initially looked like a low-level deal about more or less far-flung places marked the beginning of a major realignment among the Great Powers. Withstanding German pressure with regard to the Moroccan Question in 1905 and 1911, the Entente Cordiale proved its mettle as a tool in crisis diplomacy. It was no formal alliance and therefore neither a casus foederis nor a military commitment were part of the agreement. Nevertheless, army leaders on both sides of the Channel gave thought to coalition warfare against the Triple Alliance on the continent. In secret negotiations, they agreed on a British Expeditionary Force of 100,000 to 120,000 troops, to be deployed alongside the French army. Revealed to the British cabinet only in 1912, the military plans still did not have the same binding character as the Franco-Russian Alliance. In addition, the naval agreement between Britain and France in 1912 would provide for burden-sharing between both fleets, with the French focusing on the Mediterranean and the British being in charge of the North Sea and the Channel. [18]
Grey inherited the Entente Cordiale from his predecessor, but he would give it broader significance. This was in line with efforts to improve relations with Russia, not least to safeguard British interests in India and the Persian Gulf. In a long-term perspective, Russia seemed much more of a challenge to the British Empire than Germany, and from this point of view, it made perfect sense to foster close relations with her. [19] The Anglo-Russian Convention of 31 August 1907 dealt with spheres of influence in Persia , Afghanistan , and Tibet. [20] But the agreement opened the way for a general alignment of British and Russian interests in Asia, including the Near East, and closer relations between the signatories. The convention was the capstone of a new pattern of cooperation between France, Britain, and Russia, which was called the Triple Entente by contemporaries. As in the case of the Triple Alliance, it was not easy to foresee the coherence and effectiveness of the Triple Entente in the event of a major European war. The possibility that another revolution in Russia might overturn the balance of power could not be dismissed. From the French point of view, there was also reason to doubt Russia’s commitment to concentrate her army against Germany, not Austria-Hungary. And it was quite unclear how Britain would act in case of a European war, not only because of divisions in the cabinet, but also because of the unpredictable mood of parliament and of the British public. [21] Nevertheless, the Triple Entente was an element of European politics to be reckoned with.
Great Power Alliances on the Eve of War ↑
By 1912, both the Triple Alliance and the Triple Entente had become established features of international relations. The public had become used to debating Great Power politics in Europe in this mould. The same held true for diplomats, officials, and ministers. Scrutinizing the coherence of both alliance systems was a common topic in memoranda and official correspondence, but also in letters and diaries of experts and decision-makers. Whenever a crisis arose in international relations, the current situation of alliances and possible repercussions on their future would be considered. This pattern of thought did not necessarily lead to an escalation of crises. Alliances could even restrain the assertiveness of a Great Power in a conflict scenario. Austria-Hungary’s stance in the First Moroccan Crisis and its effect on her ally Germany; Russia’s backing off in 1909 after British and French signals of disengagement; and Germany’s disapproval of the Habsburg Monarchy’s gamble in the Winter Crisis of 1912-1913 were the most important examples of alliances helping to deescalate a crisis in the last decade before 1914. The alliance between the perennial rivals on the eastern shore of the Adriatic, Austria-Hungary and Italy, made it easier to contain their competition for dominance in Albania and thereby allowed for collective – albeit inefficient - Concert-of-Europe-style intervention on the ground and in the negotiations about the country’s future. In this respect, alliances did not necessarily hasten the sequence of crises that characterized European Great Power politics from 1904 until 1914. They could even be used to frame policies of détente. [22]
But from the First Moroccan Crisis in 1904-1905 onwards, all the major conflicts that dominated the agenda of diplomats and politicians over the course of a decade were perceived as tests of the stability of alliances. The outcome of any given crisis was judged accordingly; as a sign of alliances’ coherence, of their usefulness in times of conflict, and of their credibility as a deterrent. To be sure, not being isolated and having reliable partners among the Great Powers was important for prestige. This mattered, because any gain or loss of prestige would not go unnoticed by the public at home and decision-makers abroad. But it only became such a pressing issue because the stability or instability of alliances could overturn the calculus of military capabilities so dramatically. Since the collapse of her navy and army in 1904, Russia’s efforts to regain her military power had become key to the assessment of Europe’s strategic situation. With Russia out of the picture, Germany and her allies were in a comfortable, almost inviolable, position. With Russia rebuilding her navy and army (with support from the French), German superiority was fading away. How strong Russia was in military terms at any given moment and how strong she would be in the future was a primary concern of military experts, not just in Berlin or Vienna, but also in Paris and London. Striving for security and strategic leverage, the Great Powers, Italy included, joined armaments races at sea, but more importantly on land, which gripped Europe in the final years before the July Crisis. Technological change and shifting notions of quality at the tactical level of operations added another set of “known unknowns” concerning a coming Great Power war. [23]
Under these conditions, the impact of Italy or Romania switching sides or of Britain backing out of her informal alliances on the equation of military capabilities in Europe would be enormous. So it made perfect sense to look for signs of erosion, consolidation or extension of Great Power alliances. By 1914, things had become even more complex because of the growing relevance of alliance patterns in South East Europe. Whether Romania could still be counted upon to honour her obligations under the terms of the Triple Alliance was doubtful. This question was closely intertwined with expectations with regard to Bulgaria’s stance in a major war. The answer mattered immensely, because the Balkan peninsula had once again become the hot spot of Great Power conflict. As became obvious in the Winter Crisis of 1912-1913, this put Austria-Hungary and Russia in the front row of a possible general conflagration. The balance of military power on the Balkans had become an important factor in any war scenario. Therefore, perceptions of an impending regional realignment fed into the overall assessment of changes in the strategic situation on the continent. Short of a diplomatic coup that would both attach Bulgaria to the Triple Alliance and keep Romania as an ally, Austria-Hungary’s foreign office expected the end of the Habsburg Monarchy’s status as a Great Power sooner rather than later. By the early summer of 1914, the Germans had come to similar conclusions. From this perspective, time was on the side of the Triple Entente, provided Russia continued to build up her military and was able to shield client Serbia from Austrian pressure with the assistance of France and Britain. [24]
After the assassination of Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria-Este (1863-1914) in Sarajevo on 28 June 1914, the debates about the Habsburg Monarchy’s response among a small circle of Austria-Hungary’s leaders reflected their experience with the pitfalls of alliance politics. Unwilling to offer Italy any say in the future settlement of affairs in Serbia and distrustful of its loyalty, they tried to keep Rome in the dark about their plans and negotiations with Berlin during the early stages of the July Crisis. As it turned out, Italian sources passed German hints about impending Austrian action against Serbia on to Russia. With regard to Germany, there was no alternative to vetting Berlin’s stance in advance. Wilhelm II, German Emperor (1859-1941) had, on previous occasions, forgone Germany’s right to judge on the appropriateness of Austrian policy that might trigger the casus foederis , something Bismarck had always refused to do. Nevertheless, in 1912-1913, Vienna had been left in the lurch by Germany as soon as the crisis with Russia escalated. So, in July 1914, it was essential to get German approval in advance and to make sure that it would not be withdrawn later. The German “blank cheque” was the necessary precondition for Austria-Hungary’s policy in the July Crisis. As Berlin’s efforts to keep the Triple Entente from meddling with the Austro-Serbian conflict failed and Russian military measures alerted the German general staff to a possible Great Power war, Germany’s belated attempts to ask for more flexible Austrian crisis management evoked fears of a second 1912 in Vienna. They were as telling as they proved to be unfounded.
By the end of July 1914, with Russia mobilizing her army, strategic concerns shaped the policies of Germany. After the renewal of the Triple Alliance in 1912, plans for the deployment of Italian troops along the German front against France had been made by the German and Italian general staffs, but since Italy opted for neutrality, these preparations were useless. In the context of the Dual Alliance, only very general strategic and operational concepts had been shared by the general staffs in Vienna and Berlin. The Austrian general staff had promised to launch a major offensive against Russia, while the bulk of the German army would fight against France in the early stages of war. Since 1909, this idea of burden-sharing in case of a European war had been the basis of Austrian and German war planning . When the general staffs faced Russian mobilization at the end of July 1914, they had to come to a decision: whether to follow through with plans suitable for a general war or just deter Russia from intervention in the Austro-Serbian conflict. The political situation and strategic considerations suggested that the Franco-Russian alliance would aim at a two-front war against Germany. [25] In fact, France assured the Russians of her commitment to the alliance and reminded them to do the same. The lingering sense of uncertainty about Britain’s role did not help to contain the crisis. [26] In the end, alliances didn’t restrain the drift to brinkmanship and Britain did not back away. [27] The Dual Alliance and the Triple Entente were at war.
Conclusion: 1914 - Have Alliances Failed? ↑
Alliances had been a fixture of Europe’s international system for centuries. For almost 100 years, from 1814/1815 until 1914, they were used to manage Great Power politics. Alliances could bolster cooperation among all or at least most of the Great Powers, as in the case of the Quadruple Alliance, which would form the basis of the European Pentarchy and the Concert of Europe. They could also become instruments designed to wage war, as in the case of France and Sardinia in 1858 or Prussia and Italy in 1866. After 1871, the alliances of the Great Powers provided some sense of security in an age that was still shaped by the concept of war as a legitimate political tool. The formalized, treaty-based defensive alliances and Britain’s less formal alignment with France and Russia on the basis of agreements about colonial issues gave structure to international relations, changing rapidly due to economic, social, and cultural developments. The relative decline of Britain in economic terms and the corresponding ascent of the United States , the rising fear of social unrest and even revolution, and the emergence of public debate about foreign policy in most European countries, questioned traditional notions of diplomacy and vital interests. To perceive Great Power relations in terms of alliances offered some predictability in the case of an international crisis and could offer an opportunity to contain conflicts. In the Winter Crisis of 1912-1913, when Germany reined in her ally Austria, the de-escalating potential of defensive alliances was demonstrated again. The conference in London about the future of Albania bears witness to Great Power cooperation between states in opposing alliance blocs. But as the military experts got used to including assumptions about the evolving international situation in their strategic analyses, diplomats and politicians paid increasing attention to shifts in military capabilities. Thus, reflecting on the strengths and weaknesses of alliances fostered a militarization of security policy in the cabinets of Europe.
As such, neither the Triple Alliance nor the Triple Entente were incompatible with efforts to keep the peace of Europe. What turned them into destabilizing forces in European politics was a combination of inherent problems of alliance politics and other factors. Keeping the existing alliance together became a driving motivation for the British Foreign Office and, up to a point, also for its French counterpart. The same holds true for Germany and Austria-Hungary, in particular with respect to Italy and Romania. The urgency given to defending one’s alliance’s coherence limited the scope for compromise in a crisis. In the case of the Triple Alliance, Austrian and – to a lesser degree – German fears about Rome’s and Bucharest’s reliability fostered the perception that time was on the side of the Triple Entente. This mattered immensely to the decision-makers in the major European capitals, because the sequence of crises that had begun in 1904 had taught them the ever-increasing relevance of military power in international relations. Alliances were means to increase this power. They could embolden foreign policy makers or – depending on expectations about the stability of one’s own alliance and that of one’s future adversaries – challenge international status. In this way, the Triple Alliance and the Triple Entente had a negative impact on crisis management in July 1914.
Alliances failed to keep the peace in 1914 and, in combination with the militarized perception of security that had emerged among decision-makers and large parts of the public in Europe, even played a role in bringing about war. But is it correct to judge them as a complete failure in 1914? The answer depends on an assumption about the purpose of alliances in the early 20 th century. They certainly did not stop the escalation towards war in the summer of 1914. Germany did not even try to brake Austria-Hungary’s high-risk course until the very end of July 1914, whereas France and finally even Great Britain underwrote Russia’s strategy of escalation. More importantly, both alliances did not work as effective deterrents. Consequently, they failed as a means to avoid war. However, they made sure that none of the Great Powers would have to face isolation. Although the Triple Alliance fell apart in the summer of 1914, as Italy decided to stay neutral, Berlin and Vienna were able to fall back on their treaty of 1879 as a foundation on which to build a wartime coalition. Due to Britain’s decision to declare the infringement of Belgium’s territorial integrity a casus belli , the Triple Entente effectively became a reliable alliance. Since the Great War would be shaped by coalitions, making it perniciously hard to overcome adversaries who were able to use a pool of combined resources in order to counter setbacks, the alliances would provide the belligerent powers of 1914 with the most crucial asset of all: partners in coalition warfare. The pre-war alliances did not help to extend Europe’s long peace, but they made it easier to fight a long war.
Günther Kronenbitter, Universität Augsburg
Section Editors: Annika Mombauer ; William Mulligan
- ↑ Schroeder, Paul W.: Systems, Stability, and Statecraft. Essays on the International History of Modern Europe, New York et al. 2004, pp. 37-57, 195-199, 223-241.
- ↑ Ibid., pp. 199-208; Bridge, Francis Roy / Bullen, Richard: The Great Powers and the European State System, 1814-1914, Harlow et al. 2005, pp. 1-174.
- ↑ Canis, Konrad: Bismarcks Außenpolitik 1870-1890. Aufstieg und Gefährdung, Paderborn et al. 2004, pp. 39-140.
- ↑ Dual Alliance with Austria (October 7, 1879), issued by German History in Documents and Images (GHDI), online: http://ghdi.ghi-dc.org/sub_document.cfm?document_id=1856 (retrieved: 25 June 2019).
- ↑ Canis, Bismarcks Außenpolitik 2004, pp. 141-159; Baumgart, Winfried: Europäisches Konzert und nationale Bewegung 1830-1878, Paderborn et al. 2007, pp. 416-428; Canis, Konrad: Der Zweibund in der Bismarckschen Außenpolitik, in: Rumpler, Helmut / Niederkorn, Jan Paul (eds.): Der “Zweibund” 1879. Das deutsch-österreichisch-ungarische Bündnis und die europäische Diplomatie, Vienna 1996, pp. 41-67.
- ↑ Angelow, Jürgen: Kalkül und Prestige. Der Zweibund am Vorabend des Ersten Weltkrieges, Cologne et al. 2000. For the intellectual and cultural underpinnings of the Dual Alliance and their wartime effects, see Vermeiren, Jan: The First World War and German National Identity, Cambridge et al. 2016.
- ↑ Triple Alliance with Austria and Italy (May 20, 1882), issued by German History in Documents and Images (GHDI), online: http://ghdi.ghi-dc.org/sub_document.cfm?document_id=1860 (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Austro-Hungarian / Rumanian Accord, issued by The World War I Document Archive, online: https://wwi.lib.byu.edu/index.php/Austro-Hungarian_/_Rumanian_Accord (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Expanded version of 1912 (In English), issued by The World War I Document Archive, online: https://wwi.lib.byu.edu/index.php/Expanded_version_of_1912_(In_English) (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Afflerbach, Holger: Der Dreibund. Europäische Großmacht- und Allianzpolitik vor dem Ersten Weltkrieg, Vienna et al. 2002.
- ↑ Afflerbach, Holger: Der Dreibund als Instrument der europäischen Friedenssicherung vor 1914, in: Rumpler / Niederkorn, Der “Zweibund” 1996, pp. 87-118.
- ↑ Canis, Konrad: Der Weg in den Abgrund. Deutsche Außenpolitik 1902-1914, Paderborn et al. 2011, pp. 611-655.
- ↑ Secret Reinsurance Treaty with Russia (June 18, 1887), issued by German History in Documents and Images (GHDI), online: http://ghdi.ghi-dc.org/sub_document.cfm?document_id=1862 (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ The Franco-Russian Alliance Military Convention. August 18, 1892, issued by Lillian Goldman Law Library, online: http://avalon.law.yale.edu/19th_century/frrumil.asp (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Kennan, George F.: The Fateful Alliance. France, Russia, and the Coming of the First World War, New York et al. 1984; Snyder, Glenn H.: Alliance Politics, Ithaca et al. 1997, pp. 109-124, 261-296.
- ↑ Rose, Andreas: Between Empire and Continent. British Foreign Policy before the First World War, New York et al. 2017, pp. 273-305.
- ↑ The Franco British Declaration, 1904, issued by Lillian Goldman Law Library, online: http://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_century/entecord.asp (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Williamson, Samuel R., Jr.: The Politics of Grand Strategy. Britain and France Prepare for War, 1904-1914, Cambridge, MA 1969.
- ↑ Neilson, Keith: Britain and the Last Tsar. British Policy and Russia, 1894-1917, Oxford 1995.
- ↑ The Anglo-Russian Entente. 1907, issued by Lillian Goldman Law Library, online: http://avalon.law.yale.edu/20th_century/angrusen.asp (retrieved: 26 June 2019).
- ↑ Lieven, Dominic: Towards the Flame. Empire, War and the End of Tsarist Rusia, London 2015, pp. 182-224; Schmidt, Stefan: Frankreichs Außenpolitik in der Julikrise 1914. Ein Beitrag zur Geschichte des Ausbruchs des ersten Weltkrieges, Munich 2009, pp. 246-288.
- ↑ Kießling, Frieder: Gegen den “großen Krieg”? Entspannung in den internationalen Beziehungen 1911-1914, Munich 2002; Otte, T. G.: Détente 1914. Sir William Tyrrell’s Secret Mission to Germany, in: The Historical Journal 56/1 (2013), pp. 175-204.
- ↑ Stevenson, David: Armaments and the Coming of War. Europe, 1904-1914, Oxford et al. 1996; Mulligan, William: The Origins of the First World War, Cambridge et al. 2010, pp. 49-91.
- ↑ Soutou, Georges-Henri: La Grande Illusion. Quand la France perdait la paix 1914-1920, Paris 2015, pp. 15-42.
- ↑ Kronenbitter, Günther: “Krieg im Frieden”. Die Führung der k.u.k. Armee und die Großmachtpolitik Österreich-Ungarns 1906-1914, Munich 2003, pp. 369-519.
- ↑ Clark, Christopher: The Sleepwalkers. How Europe Went to War in 1914, London et al. 2012, pp. 242-358; Otte, T. G.: Entente diplomacy v. détente, 1911-1914, in: Geppert, Dominik / Mulligan, William / Rose, Andreas (eds.): The Wars Before the Great War, Cambridge et al. 2015, pp. 264-282.
- ↑ Otte, T. G.: July Crisis: The World’s Descent into War. Summer 1914, Cambridge 2014.
- Afflerbach, Holger: Der Dreibund. Europäische Grossmacht- und Allianzpolitik vor dem Ersten Weltkrieg , Vienna 2002: Böhlau.
- Angelow, Jürgen: Kalkül und Prestige. Der Zweibund am Vorabend des Ersten Weltkrieges , Cologne et al. 2000: Böhlau.
- Bridge, Francis Roy / Bullen, Roger J.: The great powers and the European states system 1814-1914 , Harlow 2005: Pearson Longman.
- Geppert, Dominik / Mulligan, William / Rose, Andreas (eds.): The wars before the Great War. Conflict and international politics before the outbreak of the First World War , Cambridge et al. 2015: Cambridge University Press.
- Kennan, George F.: The fateful alliance. France, Russia, and the coming of the First World War , Manchester 1984: Manchester University Press.
- Mulligan, William: The origins of the First World War , Cambridge 2010: Cambridge University Press.
- Rose, Andreas: Between empire and continent. British foreign policy before the First World War , New York 2017: Berghahn Books.
- Rumpler, Helmut / Niederkorn, Jan Paul (eds.): Der 'Zweibund' 1879. Das deutsch-österreichisch-ungarische Bündnis und die europäische Diplomatie , Vienna 1996: Verlag der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften.
- Schroeder, Paul W., Wetzel, David / Jervis, Robert / Levy, Jack S. (eds.): Systems, stability, and statecraft. Essays on the international history of modern Europe , New York 2004: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Snyder, Glenn H.: Alliance politics , Ithaca 1997: Cornell University Press.
- Stevenson, David: Armaments and the coming of war. Europe, 1904-1914 , Oxford; New York 1996: Clarendon Press; Oxford University Press.
- Williamson, Jr., Samuel R.: The politics of grand strategy. Britain and France prepare for war, 1904-1914 , Cambridge 1969: Harvard University Press.
Kronenbitter, Günther: Alliance System 1914 , in: 1914-1918-online. International Encyclopedia of the First World War, ed. by Ute Daniel, Peter Gatrell, Oliver Janz, Heather Jones, Jennifer Keene, Alan Kramer, and Bill Nasson, issued by Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin 2019-08-15. DOI : 10.15463/ie1418.11398 .
This text is licensed under: CC by-NC-ND 3.0 Germany - Attribution, Non-commercial, No Derivative Works.

Related Articles
External links.

The Major Alliances of World War I
The pacts resulted from the countries' hope for a balance of power
ThoughtCo./Emily Roberts
- World War I
- Battles & Wars
- Key Figures
- Arms & Weapons
- Naval Battles & Warships
- Aerial Battles & Aircraft
- French Revolution
- Vietnam War
- World War II
- American History
- African American History
- African History
- Ancient History and Culture
- Asian History
- European History
- Latin American History
- Medieval & Renaissance History
- The 20th Century
- Women's History
- M.A., Medieval Studies, Sheffield University
- B.A., Medieval Studies, Sheffield University
By 1914, Europe's six major powers were split into two alliances that would form the warring sides in World War I . Britain, France, and Russia formed the Triple Entente, while Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy joined in the Triple Alliance. These alliances weren't the sole cause of World War I, as some historians have contended, but they did play an important role in hastening Europe's rush to conflict.
The Central Powers
Following a series of military victories from 1862 to 1871, Prussian Chancellor Otto von Bismarck formed a German state out of several small principalities. After unification, Bismarck feared that neighboring nations, particularly France and Austria-Hungary, might act to destroy Germany. Bismarck wanted a careful series of alliances and foreign policy decisions that would stabilize the balance of power in Europe. Without them, he believed, another continental war was inevitable.
The Dual Alliance
Bismarck knew an alliance with France wasn’t possible because of lingering French anger over Alsace-Lorraine, a province Germany had seized in 1871 after defeating France in the Franco-Prussian War. Britain, meanwhile, was pursuing a policy of disengagement and was reluctant to form any European alliances.
Bismarck turned to Austria-Hungary and Russia. In 1873, the Three Emperors League was created, pledging mutual wartime support among Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia. Russia withdrew in 1878, and Germany and Austria-Hungary formed the Dual Alliance in 1879. The Dual Alliance promised that the parties would aid each other if Russia attacked them or if Russia assisted another power at war with either nation.
The Triple Alliance
In 1882, Germany and Austria-Hungary strengthened their bond by forming the Triple Alliance with Italy. All three nations pledged support should any of them be attacked by France. If any member found itself at war with two or more nations at once, the alliance would come to their aid. Italy, the weakest of the three, insisted on a final clause, voiding the deal if the Triple Alliance members were the aggressor. Shortly after, Italy signed a deal with France, pledging support if Germany attacked them.
Russian 'Reinsurance'
Bismarck was keen to avoid fighting a war on two fronts, which meant making some form of agreement with either France or Russia. Given the sour relations with France, Bismarck signed what he called a "reinsurance treaty" with Russia, stating that both nations would remain neutral if one was involved in a war with a third party. If that war was with France, Russia had no obligation to aid Germany. However, this treaty lasted only until 1890, when it was allowed to lapse by the government that replaced Bismarck. The Russians had wanted to keep it. This is usually seen as a major error by Bismarck's successors.
After Bismarck
Once Bismarck was voted out of power, his carefully crafted foreign policy began to crumble. Eager to expand his nation's empire, Germany's Kaiser Wilhelm II pursued an aggressive policy of militarization. Alarmed by Germany's naval buildup, Britain, Russia, and France strengthened their own ties. Meanwhile, Germany's new elected leaders proved incompetent at maintaining Bismarck's alliances, and the nation soon found itself surrounded by hostile powers.
Russia entered into an agreement with France in 1892, spelled out in the Franco-Russian Military Convention. The terms were loose but tied both nations to supporting each other should they be involved in a war. It was designed to counter the Triple Alliance. Much of the diplomacy Bismarck had considered critical to Germany's survival had been undone in a few years, and the nation once again faced threats on two fronts.
The Triple Entente
Concerned about the threat rival powers posed to the colonies, Great Britain began searching for alliances of its own. Although Britain had not supported France in the Franco-Prussian War, the two nations pledged military support for one another in the Entente Cordiale of 1904. Three years later, Britain signed a similar agreement with Russia. In 1912, the Anglo-French Naval Convention tied Britain and France even more closely militarily.
When Austria's Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife were assassinated in 1914 , the great powers of Europe reacted in a way that led to full-scale war within weeks. The Triple Entente fought the Triple Alliance, although Italy soon switched sides. The war that all parties thought would be finished by Christmas 1914 instead dragged on for four long years, eventually bringing the United States into the conflict. By the time the Treaty of Versailles was signed in 1919, officially ending the Great War, more than 8.5 million soldiers and 7 million civilians were dead.
DeBruyn, Nese F. " American War and Military Operations Casualties: Lists and Statistics ." Congressional Research Service Report RL32492. Updated 24 Sept. 2019.
Epps, Valerie. " Civilian Casualties in Modern Warfare: The Death of the Collateral Damage Rule ." Georgia Journal of International and Comparative Law vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 309-55, 8 Aug. 2013.
- Causes of World War I and the Rise of Germany
- World War 1: A Short Timeline Pre-1914
- The Causes and War Aims of World War One
- 5 Key Causes of World War I
- World War I Timeline From 1914 to 1919
- Causes of World War II
- The Consequences of World War I
- World War I: A Stalemate Ensues
- World War I Introduction and Overview
- The Fourteen Points of Woodrow Wilson's Plan for Peace
- Key Historical Figures of World War I
- World War I's Mitteleuropa
- World War I Timeline: 1914, The War Begins
- World War I: Opening Campaigns
- The Diplomatic Revolution of 1756
- The Seven Years War 1756 - 63

Sign Up Today
Start your 14 day free trial today

The History Hit Miscellany of Facts, Figures and Fascinating Finds
- 20th Century
Europe in 1914: First World War Alliances Explained

Alex Browne
03 aug 2018.

The European alliance systems are often seen as a major cause of World War One . On one side, you had the dual alliance between Germany and Austria-Hungary, and on the other you had the Triple Entente between France, Russia and Great Britain.
But it wasn’t a simple case of one side declaring war on the other; indeed the Triple Entente wasn’t really an ‘alliance’ at all, and the picture was further complicated by countries on the periphery of these two major systems.
The Treaty of London – 1839
Belgium had broken away from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1830. In 1839, the new nation was officially recognised by the Treaty of London. Great Britain, Austria, France, the German Confederation, Russia and the Netherlands all officially recognised the new independent Kingdom, and at Britain’s insistence agreed to its neutrality.

A British cartoon of Europe in 1914.
Dual Alliance – 1879
An alliance was signed by Germany and Austria Hungary on 7th October 1879. The two nations pledged to aid each other in the event of attack by Russia. Also, each state promised neutrality to the other if one of them was attacked by another European power (which was more than likely going to be France).
Italy joined in the Triple Alliance in 1882, but later reneged on their commitment upon the outbreak of the war in 1914.

This cartoon illustrates the Central Powers in defensive positions against the advances of Russia and France.
Reinsurance Treaty – 1887
In June 1887 Germany also signed The Reinsurance Treaty with Russia. With the competition between Russia and Austria Hungary in the Balkans, the German Chancellor Otto von Bismarck felt that this was essential to prevent a Russian agreement with France. After all, this could lead to Germany faced with a possible war on two fronts.

The secret treaty agreed that the two countries would observe neutrality should one the other be involved in a war with a third country – although this would be wavered should Germany attack France or Russia attack Austria Hungary. It also agreed that Germany would declare herself neutral in the event of a Russian intervention in the Bosphorous and the Dardanelles.
The new German Emperor Kaiser Wilhelm II believed the treaty could enrage both the British and Ottoman Empires, so when it came to renewal in 1890, Germany refused to sign it.
Franco – Russian Alliance – 1894
The Triple Alliance and the failure to renew a treaty with Germany had left Russia vulnerable, while France had been isolated in Europe since its defeat 1870 – 1871 Franco Prussian War. France began to invest in Russian infrastructure from 1888, and the two formed The Franco-Russian Alliance on January 4th 1894.
It was to remain in place for as long as the Triple Alliance existed, and stipulated that if one of the countries of the Triple Alliance attacked France or Russia, its ally would attack the aggressor in question, and that if a Triple Alliance country mobilized its army, France and Russia would mobilize.

Another German cartoon of European alliances – 1914.
Entente Cordiale – 1904
The next major agreement in Europe came about with the Entente Cordiale in April 1904. Having been involved in three rounds of British German talks between 1898 and 1901, Britain decided not to join the Triple Alliance. When the Russo-Japanese War was about to erupt, France and Britain found themselves being dragged into the conflict on the side of their respective allies.
France was allied with Russia, while Britain had recently signed the Anglo-Japanese Alliance. In order to avoid war, the sides negotiated a treaty that settled many long standing issues – particularly their differences in Africa over British control of Egypt and French control of Morocco.
The agreement marked the end of nearly a thousand years of intermittent conflict between the two countries .

“The Triple Entente” – 1907
Another agreement was reached in August 1907, this time including Britain and Russia, thereby firming their stance against The Triple Alliance. But in reality, there was no Triple Entente – the 1907 treaty was specifically between Britain and Russia to stop their rivalry in Central Asia, and there was no three way agreement as there was with the Triple Alliance.
Even after the assassination of Franz Ferdinand and the July crisis, neither of Britain’s agreement’s with France or Russia guaranteed that she would ally with the countries in the event of a European war. However, when Germany executed the Schlieffen Plan on August 3rd 1914 and crossed the Belgian border, Britain decided to act upon the violation of Belgium’s neutrality.

This map of Europe clearly shows the surrounding of the Central Powers by the Allies.
You May Also Like

Mac and Cheese in 1736? The Stories of Kensington Palace’s Servants

The Peasants’ Revolt: Rise of the Rebels

10 Myths About Winston Churchill

Medusa: What Was a Gorgon?

10 Facts About the Battle of Shrewsbury

5 of Our Top Podcasts About the Norman Conquest of 1066

How Did 3 People Seemingly Escape From Alcatraz?

5 of Our Top Documentaries About the Norman Conquest of 1066

1848: The Year of Revolutions

What Prompted the Boston Tea Party?

15 Quotes by Nelson Mandela

The History of Advent
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
World War I
By: History.com Editors
Updated: August 11, 2023 | Original: October 29, 2009

World War I, also known as the Great War, started in 1914 after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria. His murder catapulted into a war across Europe that lasted until 1918. During the four-year conflict, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire (the Central Powers) fought against Great Britain, France, Russia, Italy, Romania, Canada, Japan and the United States (the Allied Powers). Thanks to new military technologies and the horrors of trench warfare, World War I saw unprecedented levels of carnage and destruction. By the time the war was over and the Allied Powers had won, more than 16 million people—soldiers and civilians alike—were dead.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Tensions had been brewing throughout Europe—especially in the troubled Balkan region of southeast Europe—for years before World War I actually broke out.
A number of alliances involving European powers, the Ottoman Empire , Russia and other parties had existed for years, but political instability in the Balkans (particularly Bosnia, Serbia and Herzegovina) threatened to destroy these agreements.
The spark that ignited World War I was struck in Sarajevo, Bosnia, where Archduke Franz Ferdinand —heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire—was shot to death along with his wife, Sophie, by the Serbian nationalist Gavrilo Princip on June 28, 1914. Princip and other nationalists were struggling to end Austro-Hungarian rule over Bosnia and Herzegovina.
The assassination of Franz Ferdinand set off a rapidly escalating chain of events: Austria-Hungary , like many countries around the world, blamed the Serbian government for the attack and hoped to use the incident as justification for settling the question of Serbian nationalism once and for all.
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Because mighty Russia supported Serbia, Austria-Hungary waited to declare war until its leaders received assurance from German leader Kaiser Wilhelm II that Germany would support their cause. Austro-Hungarian leaders feared that a Russian intervention would involve Russia’s ally, France, and possibly Great Britain as well.
On July 5, Kaiser Wilhelm secretly pledged his support, giving Austria-Hungary a so-called carte blanche, or “blank check” assurance of Germany’s backing in the case of war. The Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary then sent an ultimatum to Serbia, with such harsh terms as to make it almost impossible to accept.
World War I Begins
Convinced that Austria-Hungary was readying for war, the Serbian government ordered the Serbian army to mobilize and appealed to Russia for assistance. On July 28, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, and the tenuous peace between Europe’s great powers quickly collapsed.
Within a week, Russia, Belgium, France, Great Britain and Serbia had lined up against Austria-Hungary and Germany, and World War I had begun.
The Western Front
According to an aggressive military strategy known as the Schlieffen Plan (named for its mastermind, German Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen ), Germany began fighting World War I on two fronts, invading France through neutral Belgium in the west and confronting Russia in the east.
On August 4, 1914, German troops crossed the border into Belgium. In the first battle of World War I, the Germans assaulted the heavily fortified city of Liege , using the most powerful weapons in their arsenal—enormous siege cannons—to capture the city by August 15. The Germans left death and destruction in their wake as they advanced through Belgium toward France, shooting civilians and executing a Belgian priest they had accused of inciting civilian resistance.
First Battle of the Marne
In the First Battle of the Marne , fought from September 6-9, 1914, French and British forces confronted the invading German army, which had by then penetrated deep into northeastern France, within 30 miles of Paris. The Allied troops checked the German advance and mounted a successful counterattack, driving the Germans back to the north of the Aisne River.
The defeat meant the end of German plans for a quick victory in France. Both sides dug into trenches , and the Western Front was the setting for a hellish war of attrition that would last more than three years.
Particularly long and costly battles in this campaign were fought at Verdun (February-December 1916) and the Battle of the Somme (July-November 1916). German and French troops suffered close to a million casualties in the Battle of Verdun alone.


HISTORY Vault: World War I Documentaries
Stream World War I videos commercial-free in HISTORY Vault.
World War I Books and Art
The bloodshed on the battlefields of the Western Front, and the difficulties its soldiers had for years after the fighting had ended, inspired such works of art as “ All Quiet on the Western Front ” by Erich Maria Remarque and “ In Flanders Fields ” by Canadian doctor Lieutenant-Colonel John McCrae . In the latter poem, McCrae writes from the perspective of the fallen soldiers:
Published in 1915, the poem inspired the use of the poppy as a symbol of remembrance.
Visual artists like Otto Dix of Germany and British painters Wyndham Lewis, Paul Nash and David Bomberg used their firsthand experience as soldiers in World War I to create their art, capturing the anguish of trench warfare and exploring the themes of technology, violence and landscapes decimated by war.
The Eastern Front
On the Eastern Front of World War I, Russian forces invaded the German-held regions of East Prussia and Poland but were stopped short by German and Austrian forces at the Battle of Tannenberg in late August 1914.
Despite that victory, Russia’s assault forced Germany to move two corps from the Western Front to the Eastern, contributing to the German loss in the Battle of the Marne.
Combined with the fierce Allied resistance in France, the ability of Russia’s huge war machine to mobilize relatively quickly in the east ensured a longer, more grueling conflict instead of the quick victory Germany had hoped to win under the Schlieffen Plan .
Russian Revolution
From 1914 to 1916, Russia’s army mounted several offensives on World War I’s Eastern Front but was unable to break through German lines.
Defeat on the battlefield, combined with economic instability and the scarcity of food and other essentials, led to mounting discontent among the bulk of Russia’s population, especially the poverty-stricken workers and peasants. This increased hostility was directed toward the imperial regime of Czar Nicholas II and his unpopular German-born wife, Alexandra.
Russia’s simmering instability exploded in the Russian Revolution of 1917, spearheaded by Vladimir Lenin and the Bolsheviks , which ended czarist rule and brought a halt to Russian participation in World War I.
Russia reached an armistice with the Central Powers in early December 1917, freeing German troops to face the remaining Allies on the Western Front.
America Enters World War I
At the outbreak of fighting in 1914, the United States remained on the sidelines of World War I, adopting the policy of neutrality favored by President Woodrow Wilson while continuing to engage in commerce and shipping with European countries on both sides of the conflict.
Neutrality, however, it was increasingly difficult to maintain in the face of Germany’s unchecked submarine aggression against neutral ships, including those carrying passengers. In 1915, Germany declared the waters surrounding the British Isles to be a war zone, and German U-boats sunk several commercial and passenger vessels, including some U.S. ships.
Widespread protest over the sinking by U-boat of the British ocean liner Lusitania —traveling from New York to Liverpool, England with hundreds of American passengers onboard—in May 1915 helped turn the tide of American public opinion against Germany. In February 1917, Congress passed a $250 million arms appropriations bill intended to make the United States ready for war.
Germany sunk four more U.S. merchant ships the following month, and on April 2 Woodrow Wilson appeared before Congress and called for a declaration of war against Germany.
Gallipoli Campaign
With World War I having effectively settled into a stalemate in Europe, the Allies attempted to score a victory against the Ottoman Empire, which entered the conflict on the side of the Central Powers in late 1914.
After a failed attack on the Dardanelles (the strait linking the Sea of Marmara with the Aegean Sea), Allied forces led by Britain launched a large-scale land invasion of the Gallipoli Peninsula in April 1915. The invasion also proved a dismal failure, and in January 1916 Allied forces staged a full retreat from the shores of the peninsula after suffering 250,000 casualties.
Did you know? The young Winston Churchill, then first lord of the British Admiralty, resigned his command after the failed Gallipoli campaign in 1916, accepting a commission with an infantry battalion in France.
British-led forces also combated the Ottoman Turks in Egypt and Mesopotamia , while in northern Italy, Austrian and Italian troops faced off in a series of 12 battles along the Isonzo River, located at the border between the two nations.
Battle of the Isonzo
The First Battle of the Isonzo took place in the late spring of 1915, soon after Italy’s entrance into the war on the Allied side. In the Twelfth Battle of the Isonzo, also known as the Battle of Caporetto (October 1917), German reinforcements helped Austria-Hungary win a decisive victory.
After Caporetto, Italy’s allies jumped in to offer increased assistance. British and French—and later, American—troops arrived in the region, and the Allies began to take back the Italian Front.
World War I at Sea
In the years before World War I, the superiority of Britain’s Royal Navy was unchallenged by any other nation’s fleet, but the Imperial German Navy had made substantial strides in closing the gap between the two naval powers. Germany’s strength on the high seas was also aided by its lethal fleet of U-boat submarines.
After the Battle of Dogger Bank in January 1915, in which the British mounted a surprise attack on German ships in the North Sea, the German navy chose not to confront Britain’s mighty Royal Navy in a major battle for more than a year, preferring to rest the bulk of its naval strategy on its U-boats.
The biggest naval engagement of World War I, the Battle of Jutland (May 1916) left British naval superiority on the North Sea intact, and Germany would make no further attempts to break an Allied naval blockade for the remainder of the war.
World War I Planes
World War I was the first major conflict to harness the power of planes. Though not as impactful as the British Royal Navy or Germany’s U-boats, the use of planes in World War I presaged their later, pivotal role in military conflicts around the globe.
At the dawn of World War I, aviation was a relatively new field; the Wright brothers took their first sustained flight just eleven years before, in 1903. Aircraft were initially used primarily for reconnaissance missions. During the First Battle of the Marne, information passed from pilots allowed the allies to exploit weak spots in the German lines, helping the Allies to push Germany out of France.
The first machine guns were successfully mounted on planes in June of 1912 in the United States, but were imperfect; if timed incorrectly, a bullet could easily destroy the propeller of the plane it came from. The Morane-Saulnier L, a French plane, provided a solution: The propeller was armored with deflector wedges that prevented bullets from hitting it. The Morane-Saulnier Type L was used by the French, the British Royal Flying Corps (part of the Army), the British Royal Navy Air Service and the Imperial Russian Air Service. The British Bristol Type 22 was another popular model used for both reconnaissance work and as a fighter plane.
Dutch inventor Anthony Fokker improved upon the French deflector system in 1915. His “interrupter” synchronized the firing of the guns with the plane’s propeller to avoid collisions. Though his most popular plane during WWI was the single-seat Fokker Eindecker, Fokker created over 40 kinds of airplanes for the Germans.
The Allies debuted the Handley-Page HP O/400, the first two-engine bomber, in 1915. As aerial technology progressed, long-range heavy bombers like Germany’s Gotha G.V. (first introduced in 1917) were used to strike cities like London. Their speed and maneuverability proved to be far deadlier than Germany’s earlier Zeppelin raids.
By the war’s end, the Allies were producing five times more aircraft than the Germans. On April 1, 1918, the British created the Royal Air Force, or RAF, the first air force to be a separate military branch independent from the navy or army.
Second Battle of the Marne
With Germany able to build up its strength on the Western Front after the armistice with Russia, Allied troops struggled to hold off another German offensive until promised reinforcements from the United States were able to arrive.
On July 15, 1918, German troops launched what would become the last German offensive of the war, attacking French forces (joined by 85,000 American troops as well as some of the British Expeditionary Force) in the Second Battle of the Marne . The Allies successfully pushed back the German offensive and launched their own counteroffensive just three days later.
After suffering massive casualties, Germany was forced to call off a planned offensive further north, in the Flanders region stretching between France and Belgium, which was envisioned as Germany’s best hope of victory.
The Second Battle of the Marne turned the tide of war decisively towards the Allies, who were able to regain much of France and Belgium in the months that followed.
The Harlem Hellfighters and Other All-Black Regiments
By the time World War I began, there were four all-Black regiments in the U.S. military: the 24th and 25th Infantry and the 9th and 10th Cavalry. All four regiments comprised of celebrated soldiers who fought in the Spanish-American War and American-Indian Wars , and served in the American territories. But they were not deployed for overseas combat in World War I.
Blacks serving alongside white soldiers on the front lines in Europe was inconceivable to the U.S. military. Instead, the first African American troops sent overseas served in segregated labor battalions, restricted to menial roles in the Army and Navy, and shutout of the Marines, entirely. Their duties mostly included unloading ships, transporting materials from train depots, bases and ports, digging trenches, cooking and maintenance, removing barbed wire and inoperable equipment, and burying soldiers.
Facing criticism from the Black community and civil rights organizations for its quotas and treatment of African American soldiers in the war effort, the military formed two Black combat units in 1917, the 92nd and 93rd Divisions . Trained separately and inadequately in the United States, the divisions fared differently in the war. The 92nd faced criticism for their performance in the Meuse-Argonne campaign in September 1918. The 93rd Division, however, had more success.
With dwindling armies, France asked America for reinforcements, and General John Pershing , commander of the American Expeditionary Forces, sent regiments in the 93 Division to over, since France had experience fighting alongside Black soldiers from their Senegalese French Colonial army. The 93 Division’s 369 regiment, nicknamed the Harlem Hellfighters , fought so gallantly, with a total of 191 days on the front lines, longer than any AEF regiment, that France awarded them the Croix de Guerre for their heroism. More than 350,000 African American soldiers would serve in World War I in various capacities.
Toward Armistice
By the fall of 1918, the Central Powers were unraveling on all fronts.
Despite the Turkish victory at Gallipoli, later defeats by invading forces and an Arab revolt that destroyed the Ottoman economy and devastated its land, and the Turks signed a treaty with the Allies in late October 1918.
Austria-Hungary, dissolving from within due to growing nationalist movements among its diverse population, reached an armistice on November 4. Facing dwindling resources on the battlefield, discontent on the homefront and the surrender of its allies, Germany was finally forced to seek an armistice on November 11, 1918, ending World War I.
Treaty of Versailles
At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, Allied leaders stated their desire to build a post-war world that would safeguard itself against future conflicts of such a devastating scale.
Some hopeful participants had even begun calling World War I “the War to End All Wars.” But the Treaty of Versailles , signed on June 28, 1919, would not achieve that lofty goal.
Saddled with war guilt, heavy reparations and denied entrance into the League of Nations , Germany felt tricked into signing the treaty, having believed any peace would be a “peace without victory,” as put forward by President Wilson in his famous Fourteen Points speech of January 1918.
As the years passed, hatred of the Versailles treaty and its authors settled into a smoldering resentment in Germany that would, two decades later, be counted among the causes of World War II .
World War I Casualties
World War I took the lives of more than 9 million soldiers; 21 million more were wounded. Civilian casualties numbered close to 10 million. The two nations most affected were Germany and France, each of which sent some 80 percent of their male populations between the ages of 15 and 49 into battle.
The political disruption surrounding World War I also contributed to the fall of four venerable imperial dynasties: Germany, Austria-Hungary, Russia and Turkey.
Legacy of World War I
World War I brought about massive social upheaval, as millions of women entered the workforce to replace men who went to war and those who never came back. The first global war also helped to spread one of the world’s deadliest global pandemics, the Spanish flu epidemic of 1918, which killed an estimated 20 to 50 million people.
World War I has also been referred to as “the first modern war.” Many of the technologies now associated with military conflict—machine guns, tanks , aerial combat and radio communications—were introduced on a massive scale during World War I.
The severe effects that chemical weapons such as mustard gas and phosgene had on soldiers and civilians during World War I galvanized public and military attitudes against their continued use. The Geneva Convention agreements, signed in 1925, restricted the use of chemical and biological agents in warfare and remain in effect today.
Photo Galleries

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1
How it works
As the curtains fell on the 19th century and the world stood at the threshold of a new era, an intricate web of alliances quietly wove itself across the geopolitical stage. This alliance system, conceived as a mechanism to foster stability, paradoxically became the harbinger of one of the most devastating conflicts in human history – World War I. In unraveling the threads of this complex tapestry, it becomes evident that the alliance system was not merely a backdrop to the war but a principal player, steering nations toward a cataclysmic collision.
At the heart of the alliance system were two major factions – the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and later, the United Kingdom) and the Triple Alliance (consisting of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy initially, later replaced by the Ottoman Empire). These alliances were not merely defensive pacts but intricate networks of commitments that drew nations into a cascade of obligations, transforming regional conflicts into a global conflagration.
The alliance system heightened the stakes of any localized dispute. What might have been contained skirmishes among nations were now magnified by the entangling web of alliances. The domino effect was swift – when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary was assassinated in 1914, the alliance commitments triggered a chain reaction, transforming a regional crisis in the Balkans into the all-encompassing maelstrom of World War I.
Furthermore, the rigidity of these alliances constrained diplomatic flexibility. Nations found themselves bound not by the merits of individual conflicts but by the pre-existing commitments of their allies. As tensions escalated, the alliance system fueled the fire rather than dousing it. The fear of abandonment or betrayal by allied powers compelled nations to adopt an aggressive posture, unwilling to be perceived as weak in the eyes of their partners.
The alliance system also created an illusion of invincibility, emboldening nations to pursue policies that might have otherwise been approached with caution. The belief in the collective might of the alliance could lead to a miscalculation of the actual risks involved in a conflict. Nations, assured of the support of their allies, might plunge into situations they would have otherwise sought to de-escalate.
As World War I unfolded, it became clear that the alliance system, far from fostering stability, had sown the seeds of a global catastrophe. The alliances that were meant to act as a deterrent against aggression inadvertently became catalysts for an unprecedented scale of conflict. The interconnectedness of nations, while intended to maintain a balance of power, had become a powder keg waiting to explode.
In conclusion, the alliance system, with its noble intentions of preserving peace through collective security, emerged as the chief protagonist in the tragedy of World War I. What was envisioned as a safeguard against aggression evolved into a mechanism that propelled nations toward a devastating collision. The alliance system, in its complexity and rigidity, demonstrated the delicate nature of geopolitical entanglements. The lessons learned from this catastrophic chapter in history underscore the importance of diplomatic flexibility and the perils of overreliance on alliances in maintaining global peace and stability.
Cite this page
The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1. (2023, Nov 24). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/
"The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1." PapersOwl.com , 24 Nov 2023, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/
PapersOwl.com. (2023). The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1 . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/ [Accessed: 9 May. 2024]
"The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1." PapersOwl.com, Nov 24, 2023. Accessed May 9, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/
"The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1," PapersOwl.com , 24-Nov-2023. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/. [Accessed: 9-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2023). The Alliance System: Unraveling the Threads of World War 1 . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-alliance-system-unraveling-the-threads-of-world-war-1/ [Accessed: 9-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started) Essay
Introduction, causes of world war 1.
Bibliography
Since time immemorial the world has witnessed wars between different groups, states, countries, and allies. Initially, the motive behind wars was survival. Ancient people fought in order to usurp land for cultivation. Gradually, as the world population grew, the motives behind wars became multifarious.
Different groups and countries started fighting with each other in order to gain control of areas where there were natural resources such as gold. Another reason for war was to gain access to routes generally used for movement of commodities from the starting place to the consumption areas.
It is understood that after a war, one group prospered at the cost of another. Religion also has been an instigating factor for many wars. However, in all the wars, the motive was to gain advantage of some sort.
During the past years, when countries came together as allies, there have been instances when allies of a particular group had to go to war just because they wanted to safeguard themselves from the disadvantages of not participating in the war. In this paper, we shall discuss the reasons that led to World War 1. “World War 1 began in eastern Europe. The war started when Serbia, Austria-Hungary, Russia, and Germany decided that war or the risk of war was an acceptable policy option [1] ”.
General Causes
1879 onwards, the world witnessed formation of alliances between nations having similar interests. Following are some of the major alliances that took place:
- The Dual Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance in 1879 in order to defend against Russia.
- Austro-Serbian Alliance: Austria-Hungary and Serbia entered into an alliance in 1881 in order to prevent Russia from asserting power in Serbia.
- The Triple Alliance: Germany and Austria-Hungary entered into an alliance with Italy in 1882 so that the latter could not favor Russia’s moves.
- Franco-Russian Alliance: Russia and France entered into an alliance in 1894 in order to protect their countries from the Dual Alliance of Germany and Austria-Hungary.
- Entente Cordiale: France and Britain entered into a formal agreement in 1904 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Anglo-Russian Entente: Britain and Russia entered into a formal agreement in 1907 in order to protect each other’s interests.
- Triple Entente: Russia, France and Britain entered into an alliance to counteract Germany’s growing threats. Later, in 1914 and under the same alliance, all the three countries concurred that they will not sign any peace treaty without mutual consent.
All these alliances (from 1879 to 1914) forced some countries to go to war just because they were in some alliance.
Imperialism
Imperialism is a term used for instances where any country usurps any other country’s land and asserts its supremacy and power. Due to the incessant progress of industrialization, countries felt the need of venturing into fresh marketplaces.
By the year 1900, Britain had extended its empire in five continents and France controlled major parts of Africa. The increase of both these countries’ power did not go well with Germany; Germany had only small areas under its rule. Following is a map that depicts the colonies of these three major European players in 1914.
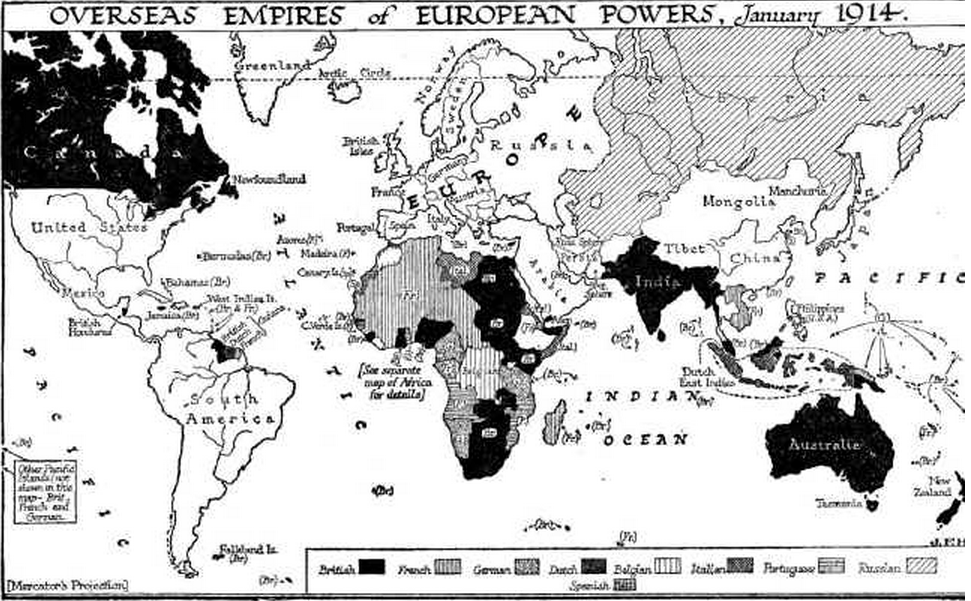
Source: Web.
William Anthony Hay claims that according to McMeekin, a tutor of international relations, “The war’s real catalyst lay in Russia’s ambition to supplant the waning Ottoman Empire in the Near East and to control the Turkish straits – the Bosphorus and Dardanelles – linking the Black Sea and the Mediterranean [2] ”.
But Richard Evans contradicts this opinion by stating that “In the end it was the Austro-Hungarian invasion of Serbia that set off the process that ended in the outbreak of World War 1, not Russian ambitions in the Straits [3] . But if we think logically, no country will enter into a war without personal interests.
Alliances were also made to serve individual interests. So it is wrong to say that Russia did not have any interest or ambitions in the Straits. Russia was an industrialized nation and needed to sell its products to people in other nations. For this purpose, it needed a safe passage and new markets.
When any country gives preference to its army, it is said to be following militarism. The growing alliances among various nations prompted nations to empower their army with more arms and ammunitions. France and Germany doubled the strengths of their respective armies.
Britain and Germany seemed to be in a competition of better sea control. In 1906, Britain launched the ‘Dreadnought’, considered to be a very efficient battleship. Following the footsteps, Germany also launched its own version of impressive battleships. The following illustration shows how Germany planned to attack France in case Russia attacked Germany; France and Russia were allies. So due to the alliance, Russia was bound to retaliate when one of its allies was attacked.
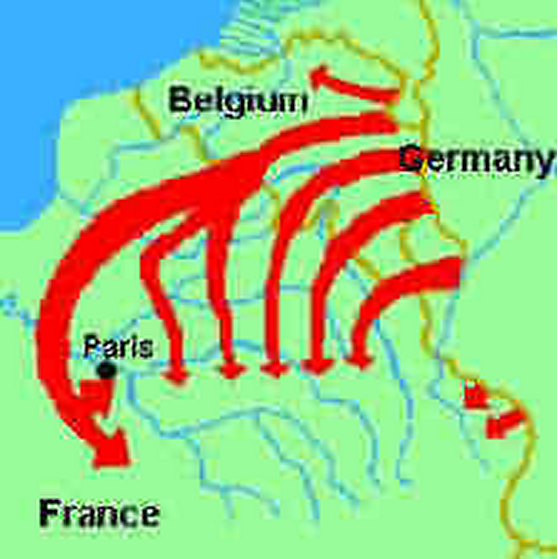
“A military revolution occurred in the seventeenth century. The most important of the many changes was a considerable growth in the size of the armies. Those large forces could no longer live off the land: steal supplies from the populace [4] ”.
Nationalism
We all have love for our respective countries. So did the people of that period. Austria-Hungary and Serbia had different radical groups trying to free their states from foreign involvement. Both Italy and Germany were divided. People of these countries wanted unification. “Along with the history of imperial machinations, however, World War 1 should be understood in the context of the popular imagination and the growth of nationalist sentiment in Europe [5] ”.
Moroccan Crisis
As part of an understanding, Britain gave control of Morocco to France in 1904. The Moroccan people wanted freedom. Germany, in order to take an advantage of the situation, proclaimed its support for the freedom of Morocco. A conference was held that allowed France to continue its control over Morocco and a war was averted. Again, in 1911, Germany started pronouncing its support for the Moroccan independence but again it was persuaded to compromise its stand on the issue.
Bosnian Crisis
Bosnia (a Turkish province) was taken over by Austria-Hungary in 1908. This action of Austria-Hungary did not go well with the Serbians. The Serbians thought Bosnia was under them. As such, a conflict aroused. Serbia proclaimed war over Austria-Hungary. Russia supported Serbia and Germany supported Austria-Hungary. A war was about to start but at the nick of the time Russia backed off and the war was averted.
But tensions were still mounting up between Serbia and Austria-Hungary. “It is true that during July the German decision makers sometimes expressed the hope that the conflict would be localized: in other words that Austria would be able to vanquish Serbia without Russian Intervention [6] ”. Dale Copeland argues that “Germany actively sought war in July 1914 and that German leaders by the end of July preferred world war to a negotiated peace, even to one that gave Austria most of what it wanted [7] ”.
The Immediate Trigger
World War 1 started in the year 1914. The assassination of Austria’s Archduke, Franz Ferdinand, acted as a trigger to World War 1. Franz Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in 1914 by Gavrilo Princip, member of a Bosnian radical group. “The crumbling Austro-Hungarian Empire decided, after the assassination on 28 June, to take action against Serbia, which was suspected of being behind the murder [8] ”.
This was considered to be an immediate reason for the war but the real reasons seem to be more complex and are still topics of debate among various historians. According to William Anthony Hay, “Germany bears responsibility for the war, in this view, because its leaders deliberately turned a regional clash between Austria-Hungary and Serbia into an existential Struggle of rival alliances [9] ”.
Hay is right in his opinion because history reveals that there were other options with Germany that could have averted the war. But since Germany wanted to gain on its own interests, it forced other countries to plunge into a war that they did not intend. “The size and wealth of the conquered Eastern territories easily outweighed what would have been lost had the Germans withdrawn from Belgium and France. Had they done so, France might have made peace and the anti-German coalition collapsed [10] ”.
All these instances make us to believe that Germany was behind waging the World War 1. In its ambitions to usurp power, Germany was thought to have instigated the war. But it is to be understood that down the years, historians put an end to the controversy as to which country was responsible for the World War 1.
Historians from the two main countries (Germany and France) came to an understanding that none of their countries should be blamed for instigating World War 1. It was the policies of militarization of each of the participating countries that led to the war.
But certain facts still point the finger towards Germany. After the war started, some confidential documents were discovered that suggested that the German government had vast plans of extending its territory due to the economic requirements.
Copeland, Dale. The Origins of Major War. New York: Cornell University Press, 2001.
Evans, Richard. “ The Road to Slaughter. ” New Republic . 2011. Web.
Fergusan, Niall. “Germany and the origins of the First World War: New Perspectives.” The Historical Journal 35, no. 3 (1992): 725-752.
Hamilton, Richard and Holger Herwig. The Origins of World War 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003.
Hay, William. “ Ambition in the East .” The Wall Street Journal . 2011. Web.
Merriman, John. “The Origins of World War 1.” Yale University . 2013. Web.
Sheffield, Gary. “ The Origins of World War One. ” BBC. 2011. Web.
Williamson, Samuel. “The Origins of World War 1.” Journal of Interdisciplinary History 18, no. 4 (1988): 795-818.
- Samuel Williamson, “The Origins of World War 1,” Journal of Interdisciplinary History 18, no. 4 (1988): 795.
- William Anthony Hay, “Ambition in the East,” The Wall Street Journal , 2011.
- Richard Evans, “The Road to Slaughter,” 2011.
- Richard Hamilton and Holger Herwig, The Origins of World War 1 (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003), 5.
- John Merriman, “The Origins of World War 1,” Yale University , 2013.
- Niall Fergusan, “Germany and the origins of the First World War: New Perspectives”, Historical Journal 35, no. 3 (1992): 731.
- Dale Copeland, The Origins of Major War (New York: Cornell University Press , 2001), 79.
- Gary Sheffield, “The Origins of World War One,” BBC , 2011.
- William Anthony Hay, “Ambition in the East” in The Wall Street Journal
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 14). World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started). https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/
"World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." IvyPanda , 14 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)'. 14 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
1. IvyPanda . "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
IvyPanda . "World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)." February 14, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/world-war-1-origins-how-and-why-the-war-started/.
- Hay Criteria in Job Grading
- Why Europe Went to War
- World War 1 and Technological Improvement
- The World War I
- Outbreak of War in Europe in 1914
- Importance of Accountability: World War I
- Events Leading Up to WWI
- Experiences That Make a Soldier More Human
Customer Reviews
Don’t Drown In Assignments — Hire an Essay Writer to Help!
Does a pile of essay writing prevent you from sleeping at night? We know the feeling. But we also know how to help it. Whenever you have an assignment coming your way, shoot our 24/7 support a message or fill in the quick 10-minute request form on our site. Our essay help exists to make your life stress-free, while still having a 4.0 GPA. When you pay for an essay, you pay not only for high-quality work but for a smooth experience. Our bonuses are what keep our clients coming back for more. Receive a free originality report, have direct contact with your writer, have our 24/7 support team by your side, and have the privilege to receive as many revisions as required.
We have the ultimate collection of writers in our portfolio, so once you ask us to write my essay, we can find you the most fitting one according to your topic. The perks of having highly qualified writers don't end there. We are able to help each and every client coming our way as we have specialists to take on the easiest and the hardest tasks. Whatever essay writing you need help with, let it be astronomy or geography, we got you covered! If you have a hard time selecting your writer, contact our friendly 24/7 support team and they will find you the most suitable one. Once your writer begins the work, we strongly suggest you stay in touch with them through a personal encrypted chat to make any clarifications or edits on the go. Even if miscommunications do happen and you aren't satisfied with the initial work, we can make endless revisions and present you with more drafts ASAP. Payment-free of course. Another reason why working with us will benefit your academic growth is our extensive set of bonuses. We offer a free originality report, title, and reference page, along with the previously mentioned limitless revisions.
How do I place an order with your paper writing service?

Why do I have to pay upfront for you to write my essay?
- How it Works
- Top Writers
Artikel & Berita
Write my essay for me.
Eloise Braun
receive 15% off
Niamh Chamberlain
Customer Reviews

Who are your essay writers?
Gombos Zoran

Is buying essays online safe?
Shopping through online platforms is a highly controversial issue. Naturally, you cannot be completely sure when placing an order through an unfamiliar site, with which you have never cooperated. That is why we recommend that people contact trusted companies that have hundreds of positive reviews.
As for buying essays through sites, then you need to be as careful as possible and carefully check every detail. Read company reviews on third-party sources or ask a question on the forum. Check out the guarantees given by the specialists and discuss cooperation with the company manager. Do not transfer money to someone else's account until they send you a document with an essay for review.
Good online platforms provide certificates and some personal data so that the client can have the necessary information about the service manual. Service employees should immediately calculate the cost of the order for you and in the process of work are not entitled to add a percentage to this amount, if you do not make additional edits and preferences.

Fill up the form and submit
On the order page of our write essay service website, you will be given a form that includes requirements. You will have to fill it up and submit.

"Research papers - Obsity in Children..."
Customer Reviews
Frequently Asked Questions
The first step in making your write my essay request is filling out a 10-minute order form. Submit the instructions, desired sources, and deadline. If you want us to mimic your writing style, feel free to send us your works. In case you need assistance, reach out to our 24/7 support team.
Can you write my essay fast?
Our company has been among the leaders for a long time, therefore, it modernizes its services every day. This applies to all points of cooperation, but we pay special attention to the speed of writing an essay.
Of course, our specialists who have extensive experience can write the text quickly without losing quality. The minimum lead time is three hours. During this time, the author will find the necessary information, competently divide the text into several parts so that it is easy to read and removes unnecessary things. We do not accept those customers who ask to do the work in half an hour or an hour just because we care about our reputation and clients, so we want your essay to be the best. Without the necessary preparation time, specialists will not be able to achieve an excellent result, and the user will remain dissatisfied. For the longest time, we write scientific papers that require exploratory research. This type of work takes up to fourteen days.
We will consider any offers from customers and advise the ideal option, with the help of which we will competently organize the work and get the final result even better than we expected.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition
Russia-Ukraine war as it happened: Moscow says British military facilities could be targeted after Cameron’s remarks
British ambassador is summoned and told that installations and equipment in Ukraine and elsewhere could be targeted
- 3d ago Here is a summary of today's developments so far:
- 3d ago Russia states British military facilities could be targeted after Cameron remarks
- 3d ago Ukraine calls on allies not to recognise Putin as Russia's 'legitimate president'
- 4d ago Ukraine accuses Russia of 'nuclear blackmail' over weapons drills
- 4d ago Russia nuclear weapons drills in response to West possibly sending troops to Ukraine
- 4d ago Russia to carry out nuclear weapons drills

Russia states British military facilities could be targeted after Cameron remarks
Russia warned Britain on Monday that if British weapons were used by Ukraine to strike Russian territory then Moscow could hit back at British military installations and equipment both inside Ukraine and elsewhere.
British Ambassador Nigel Casey was summoned to the foreign ministry for a formal protest after Foreign Secretary David Cameron said Ukraine had the right to use British weapons to strike Russia .
Russia’s foreign ministry said the Cameron remarks recognised that Britain was now de-facto a part of the conflict.
“Casey was warned that in response to Ukrainian attacks on Russian territory with British weapons, any British military facilities and equipment on the territory of Ukraine and abroad could be targeted,” the foreign ministry said.

“The Ambassador was called upon to reflect on the inevitable catastrophic consequences of such hostile steps by London and immediately refute the belligerent provocative statements of the head of the Foreign Office in the most decisive and unambiguous way.”
Cameron, during a visit to Kyiv, told Reuters last week that Ukraine had a right to use the weapons provided by London to strike targets inside Russia, and that it was up to Kyiv whether to do so.
“Ukraine has that right. Just as Russia is striking inside Ukraine, you can quite understand why Ukraine feels the need to make sure it’s defending itself,” Cameron told Reuters outside St. Michael’s Cathedral.
Russia’s foreign ministry has commented further on the tactical nuclear weapons drills, according to Reuters. It reported the ministry saying it was hoped they would cool down “hotheads” in the west who Moscow said were pushing for a direct military confrontation between Nato and Russia .
Russia’s foreign ministry mentioned remarks by the British foreign secretary, David Cameron , and the French president, Emmanuel Macron , and the delivery of US ATACMS long-ranges missiles to Ukraine .
“They are deliberately leading the situation towards a further escalation of the Ukrainian crisis towards an open military clash between Nato countries and Russia ,” the foreign ministry said.
Russia said on Monday it would practise the deployment of tactical nuclear weapons as part of a military exercise after what the Moscow said were threats from France, Britain and the United States.
“We hope that this event will cool down the ‘hotheads’ in western capitals,” the foreign ministry said.
Sweden’s foreign minister, Tobias Billström , said Russia’s planned nuclear drills “contribute to increasing instability”. “In the current security situation, Russia’s actions may be considered particularly irresponsible and reckless,” Billström told Swedish news agency TT.
The drills were announced on the eve of Russian President Vladimir Putin ’s inauguration to a fifth term in office and in a week when Moscow on Thursday will celebrate Victory Day, its most important secular holiday, marking its defeat of Nazi Germany in the second world war.
Here is a summary of today's developments so far:
Chinese President Xi Jinping said on Monday that China had all along been working “vigorously” to facilitate talks for peace in Ukraine, according to Chinese state media.
Russia’s tactical nuclear weapon drills are a response to statements from the West about sending troops to Ukraine, the Kremlin said on Monday.
Ukraine’s foreign ministry called on Kyiv’s international allies not to recognise Vladimir Putin as Russia’s legitimate president.
The first Olympian to die in the war in Ukraine has been announced. The weightlifter Oleksandr Pielieshenko , who finished fourth in the 85kg light-heavyweight category at the Rio Games in 2016, was killed defending his country on Sunday.
The first Olympian to die in the war in Ukraine has been announced. The weightlifter Oleksandr Pielieshenko, who finished fourth in the 85kg light-heavyweight category at the Rio Games in 2016, was killed defending his country on Sunday.
The news was confirmed by the National Olympic Committee of Ukraine , who said Pielieshenko died during combat operations.
You can read more about his career and tributes from the weightlifting community here:
One man was killed on Monday in a Ukrainian attack on the village of Nikolskoye in Russia’s Belgorod region, Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov said on his Telegram channel.
Chinese President Xi Jinping said on Monday that China had all along been working “vigorously” to facilitate talks for peace in Ukraine , according to Chinese state media.
China did not create the Ukraine crisis, nor was it a party to it, Xi told French President Emmanuel Macron and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen during a trilateral meeting at the Elysee Palace in Paris.
Ukraine calls on allies not to recognise Putin as Russia's 'legitimate president'
“Ukraine sees no legal grounds for recognising him as a democratically elected and legitimate president of the Russian Federation,” the ministry said in a statement, published ahead of Putin’s inauguration on Tuesday.
EU Commission president Ursula von der Leyen says China’s President has “important role” to play in de-escalating tensions over nuclear threats made by Russia .
Von der Leyen was part of trilateral talks between her, French President Emmanuel Macron and Xi Jinping at a summit in Paris on Monday.
She pressed Xi Jinping to use Beijing’s influence to halt the Russian war against Ukraine , also telling the Chinese leader to accept fair global trade rules.
Von der Leyen also said she was “confident” Xi Jinping would continue to play an “important role” in de-escalating tensions over nuclear threats made by Russia, hours after President Vladimir Putin ordered nuclear weapons drills involving troops based near Ukraine.
Both Macron and von der Leyen have indicated that trade was a priority in the talks, underscoring that Europe must defend its “strategic interests” in its economic relations with China.
Associated Press have some more information on the planned drills. It says it was the first time that Russia has publicly announced drills involving tactical nuclear weapons, though its strategic nuclear forces regularly hold exercises.
Tactical nuclear weapons include air bombs, warheads for short-range missiles and artillery munitions and are meant for use on a battlefield. They are less powerful than the massive warheads that arm intercontinental ballistic missiles and are intended to obliterate entire cities. The Russian announcement appeared to be a warning to Ukraine’s western allies about becoming more deeply involved in the more than two-year war. French President Emmanuel Macron repeated last week that he doesn’t exclude sending troops to Ukraine, and UK Foreign Secretary David Cameron said Kyiv’s forces will be able to use British long-range weapons to strike targets inside Russia. Dmitry Medvedev , the deputy head of Russia’s Security Council that’s chaired by President Vladimir Putin , said in his typically hawkish fashion that the comments by Macron and Cameron risked pushing the nuclear-armed world toward a “global catastrophe.” The Russian defence ministry said the exercise is intended to “increase the readiness of non-strategic nuclear forces to fulfil combat tasks” and will be held on Putin’s orders. The manoeuvres will involve missile units of the Southern Military District along with the air force and the navy, it said.
- Ukraine war live
- Vladimir Putin
Most viewed

"Essay - The Challenges of Black Students..."
Finished Papers
Andersen, Jung & Co. is a San Francisco based, full-service real estate firm providing customized concierge-level services to its clients. We work to help our residential clients find their new home and our commercial clients to find and optimize each new investment property through our real estate and property management services.
Customer Reviews
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
How Iran and Israel Are Unnatural Adversaries

By Karim Sadjadpour
Mr. Sadjadpour is a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
“History is littered,” the British writer and politician Enoch Powell said, “with the wars which everybody knew would never happen.”
A full-blown conflict between the Islamic Republic of Iran and Israel once seemed implausible. But last month, the long-running shadow war between the two nations burst into the open in a series of unprecedented drone and missile strikes, raising the specter of a fight that would contain enough advanced technology, paramilitary forces and mutual acrimony to incinerate large parts of the Middle East, collapse the global economy and entangle the United States and other major powers.
Now the two sides appear to have hit pause, but for how long? As long as Iran is ruled by an Islamist government that puts its revolutionary ideology before the national interest, the two countries will never know peace, and the Middle East will never know meaningful stability.
Iran and Israel are not natural adversaries. In contrast to other modern conflicts — between Israel and Palestine, Russia and Ukraine, China and Taiwan — Iran and Israel have no bilateral land or resource disputes. Their national strengths — Iran is an energy titan and Israel is a tech innovator — are more complementary than competitive. The nations also have a historical affinity dating back over 2,500 years, when the Persian King Cyrus the Great freed the Jews from the Babylonian Captivity. Iran was the second Muslim nation, after Turkey, to recognize Israel after its founding in 1948.
Their modern animosity is best understood through the lens of ideology, not geopolitics. It began with the rise of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the dogmatic Shiite cleric who led the 1979 revolution that transformed Iran from a U.S.-allied monarchy into an anti-American theocracy. Khomeini’s 1970 treatise “ Islamic Government ,” which became the basis of the constitution that governs the Islamic Republic, is laced with tirades and threats against “wretched” and “satanic” Jews. Then, as now, antisemitism often lurked below the surface of anti-imperialism.
“We must protest and make the people aware that the Jews and their foreign backers are opposed to the very foundations of Islam and wish to establish Jewish domination throughout the world,” Khomeini wrote. “Since they are a cunning and resourceful group of people, I fear that — God forbid — they may one day achieve their goal and that the apathy shown by some of us may allow a Jew to rule over us one day.”
In the same manifesto, Khomeini casually advocates what in modern parlance is best understood as ethnic cleansing. “Islam,” he wrote, “has rooted out numerous groups that were a source of corruption and harm to human society.” He went on to cite the case of a “troublesome” Jewish tribe in Medina that he said was “eliminated” by the Prophet Muhammad.
Very few of the Iranian revolutionaries and Western progressives who backed Khomeini in 1979 — some of whom compared him with Mohandas K. Gandhi — had bothered to scrutinize his vision for Iran. Once in power, he built his newfound theocracy on three ideological pillars: death to America, death to Israel and the subjugation of women.
Over four decades later, the worldview of Iran’s current rulers has evolved little. Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, Khomeini’s 85-year-old successor and now one of the world’s longest-serving dictators, denounces Zionism in virtually every speech and was one of the few world leaders to publicly praise Hamas’s “epic” Oct. 7 attack on Israel. “We will support and assist any nation or any group anywhere,” Ayatollah Khamenei said in 2020, “who opposes and fights the Zionist regime.”
As Ayatollah Khamenei’s words make plain, the Islamic Republic of Iran is one of the few governments in the world more dedicated to abolishing another nation than advancing its own. “Death to Israel” is the regime’s rallying cry — not “Long live Iran.”
Ayatollah Khamenei’s regime has backed this language with action. Iran has spent tens of billions of dollars arming, training and financing proxy militias in five failing nations: Lebanon, Syria, Gaza, Iraq and Yemen. Together these groups constitute its so-called Axis of Resistance against America and Israel. These groups are elbow-deep in corruption and repression in their own societies, including illicit drug dealing and piracy , while pledging that they seek justice for Palestinians.
Hostility toward Israel is a useful tool for predominantly Shiite, Persian Iran to vie for leadership in the predominantly Sunni, Arab Middle East. But it should not be confused with concern for the well-being of Palestinians. In contrast to American, European and Arab governments that fund Palestinian human welfare initiatives, Iran has poured hundreds of millions of dollars into arming and financing Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad. Iran’s goal is not to build a Palestine but to demolish Israel.
And yet as much as the Islamic Republic is committed to its ideology, it is even more committed to staying in power. As the German American philosopher Hannah Arendt once put it, “The most radical revolutionary will become a conservative on the day after the revolution.” As its careful response to Israel’s recent military strikes on Iran showed, when faced with the possibility of full-blown war or existential economic pressure, Tehran tactically retreats.
After decades of living under an economically failing, socially repressive police state, Iran’s people long ago recognized that the greatest obstacle between themselves and a normal life is their own leadership, not America or Israel. In a 2021 public opinion poll conducted from Europe, only around one-fifth of Iranians approved of their government’s support of Hamas and “Death to Israel” slogan. Few nations have Iran’s combination of natural resource wealth, human capital, geographic size and ancient history. This enormous gap between Iran’s potential and its citizens’ reality is one reason the country has experienced numerous mass uprisings over the past two decades.
Iran’s Axis of Resistance has empowered right-wing Israeli politicians far more than Palestinians over the past two decades. The threat of a Holocaust-denying Iranian regime with regional and nuclear ambitions has stoked Israeli anxieties, diverted attention from Palestinian suffering and facilitated normalization agreements between Israel and Arab governments equally fearful of Iran. Indeed, Iran and its proxies were such a useful adversary that Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu helped prop up Hamas’s rule in Gaza until the deadly attacks of Oct. 7.
“The dream of Israeli leaders,” a retired Israeli general, Amos Yadlin, told me recently, “is to one day restore normal relations with an Iranian government.”
The dream of Iran’s Islamist leaders, on the other hand, is to end Israel’s existence. Israel’s conflict with Iran has been a war of necessity, but Iran’s conflict with Israel has been a war of choice. It won’t be over until Iran has leaders who put Iranians’ interests over Israel’s destruction.
Karim Sadjadpour is a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
House passes bill to expand definition of antisemitism amid growing campus protests over Gaza war
Pro-Palestinian protesters camp out in tents at Columbia University on Saturday, April 27, 2024 in New York. With the death toll mounting in the war in Gaza, protesters nationwide are demanding that schools cut financial ties to Israel and divest from companies they say are enabling the conflict. Some Jewish students say the protests have veered into antisemitism and made them afraid to set foot on campus. (AP Photo)
FILE -President of Columbia University Nemat Shafik testifies before the House Committee on Education and the Workforce hearing on “Columbia in Crisis: Columbia University’s Response to Antisemitism” on Capitol Hill in Washington, Wednesday, April 17, 2024. Columbia University president Nemat (Minouche) Shafik is no stranger to navigating complex international issues, having worked at some of the world’s most prominent global financial institutions.(AP Photo/Mariam Zuhaib, File)
- Copy Link copied

WASHINGTON (AP) — The House passed legislation Wednesday that would establish a broader definition of antisemitism for the Department of Education to enforce anti-discrimination laws, the latest response from lawmakers to a nationwide student protest movement over the Israel-Hamas war.
The proposal, which passed 320-91 with some bipartisan support, would codify the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance’s definition of antisemitism in Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, a federal anti-discrimination law that bars discrimination based on shared ancestry, ethnic characteristics or national origin. It now goes to the Senate where its fate is uncertain.
Action on the bill was just the latest reverberation in Congress from the protest movement that has swept university campuses. Republicans in Congress have denounced the protests and demanded action to stop them, thrusting university officials into the center of the charged political debate over Israel’s conduct of the war in Gaza. More than 33,000 Palestinians have been killed since the war was launched in October, after Hamas staged a deadly terrorist attack against Israeli civilians.
If passed by the Senate and signed into law, the bill would broaden the legal definition of antisemitism to include the “targeting of the state of Israel, conceived as a Jewish collectivity.” Critics say the move would have a chilling effect on free speech throughout college campuses.
“Speech that is critical of Israel alone does not constitute unlawful discrimination,” Rep. Jerry Nadler, D-N.Y., said during a hearing Tuesday. “By encompassing purely political speech about Israel into Title VI’s ambit, the bill sweeps too broadly.”
Advocates of the proposal say it would provide a much-needed, consistent framework for the Department of Education to police and investigate the rising cases of discrimination and harassment targeted toward Jewish students.
“It is long past time that Congress act to protect Jewish Americans from the scourge of antisemitism on campuses around the country,” Rep. Russell Fry, R-S.C., said Tuesday.
The expanded definition of antisemitism was first adopted in 2016 by the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance, an intergovernmental group that includes the United States and European Union states, and has been embraced by the State Department under the past three presidential administrations, including Joe Biden’s
Previous bipartisan efforts to codify it into law have failed. But the Oct. 7 terrorist attack by Hamas militants in Israel and the subsequent war in Gaza have reignited efforts to target incidents of antisemitism on college campuses.
Separately, Speaker Mike Johnson announced Tuesday that several House committees will be tasked with a wide probe that ultimately threatens to withhold federal research grants and other government support for universities, placing another pressure point on campus administrators who are struggling to manage pro-Palestinian encampments, allegations of discrimination against Jewish students and questions of how they are integrating free speech and campus safety.
The House investigation follows several high-profile hearings that helped precipitate the resignations of presidents at Harvard and the University of Pennsylvania. And House Republicans promised more scrutiny, saying they were calling on the administrators of Yale, UCLA and the University of Michigan to testify next month.
The House Oversight Committee took it one step further Wednesday, sending a small delegation of Republican members to an encampment at nearby George Washington University in the District of Columbia. GOP lawmakers spent the short visit criticizing the protests and Mayor Muriel Bowser’s refusal to send in the Metropolitan Police Department to disperse the demonstrators.
Bowser on Monday confirmed that the city and the district’s police department had declined the university’s request to intervene. “We did not have any violence to interrupt on the GW campus,” Bowser said, adding that police chief Pamela Smith made the ultimate decision. “This is Washington, D.C., and we are, by design, a place where people come to address the government and their grievances with the government.”
It all comes at a time when college campuses and the federal government are struggling to define exactly where political speech crosses into antisemitism. Dozens of U.S. universities and schools face civil rights investigations by the Education Department over allegations of antisemitism and Islamophobia.
Among the questions campus leaders have struggled to answer is whether phrases like “from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free” should be considered under the definition of antisemitism.
The proposed definition faced strong opposition from several Democratic lawmakers, Jewish organizations as well as free speech advocates.
In a letter sent to lawmakers Friday, the American Civil Liberties Union urged members to vote against the legislation, saying federal law already prohibits antisemitic discrimination and harassment.
“H.R. 6090 is therefore not needed to protect against antisemitic discrimination; instead, it would likely chill free speech of students on college campuses by incorrectly equating criticism of the Israeli government with antisemitism,” the letter stated.
Jeremy Ben-Ami, president of the centrist pro-Israel group J Street, said his organization opposes the bipartisan proposal because he sees it as an “unserious” effort led by Republicans “to continually force votes that divide the Democratic caucus on an issue that shouldn’t be turned into a political football.”
Associated Press writers Ashraf Khalil, Collin Binkley and Stephen Groves contributed to this report.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Alliances are possibly the best known cause of World War I. An alliance is a formal political, military or economic agreement between two or more nations. Military alliances usually contain promises that in the event of war or aggression, one signatory nation will support the others. The terms of this support is outlined in the alliance ...
Alliances were an important feature of the international system on the eve of World War I. The formation of rival blocs of Great Powers has previously considered a major cause of the outbreak of war in 1914, but this assessment misses the point. Instead of increased rigidity, it was, rather, the uncertainty of the alliances' cohesion in the face of a ''casus foederis'' that fostered a ...
ThoughtCo./Emily Roberts. By. Robert Wilde. Updated on January 28, 2020. By 1914, Europe's six major powers were split into two alliances that would form the warring sides in World War I. Britain, France, and Russia formed the Triple Entente, while Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy joined in the Triple Alliance.
World War I, an international conflict that in 1914-18 embroiled most of the nations of Europe along with Russia, the United States, the Middle East, and other regions. The war pitted the Central Powers —mainly Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Turkey —against the Allies—mainly France, Great Britain, Russia, Italy, Japan, and, from 1917 ...
However, when Germany executed the Schlieffen Plan on August 3rd 1914 and crossed the Belgian border, Britain decided to act upon the violation of Belgium's neutrality. This map of Europe clearly shows the surrounding of the Central Powers by the Allies. The European alliance systems are often seen as a major cause of World War One.
World War I started in 1914, after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, and ended in 1918. During the conflict, the countries of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire ...
10 Lines on World War 1 Essay in English. 1. The First World War was instigated in 1914 by Serbia. 2. The cause of the war was a competition between countries to acquire weapons and build military powers. 3. In 1914, Serbia aroused anger by assassinating Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir of Austria-Hungary throne. 4.
Causes. Over the course of the 19th century, rival powers of Europe formed alliances. Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy formed the Triple Alliance. Great Britain, France, and Russia formed the Triple Entente. Political instability and competition threatened those alliances. (Italy, for example, eventually entered World War I in opposition to ...
World War One Alliance History Essay. World War One, known as the Great War, was triggered by the alliance system. The outbreak of war became a domino effect because of the coalitions between major powers and their hostility against each other. These treaties are divided between two oppositions, starting with the Triple Alliances made up of ...
Essay Example: The commencement of World War I in 1914 was a watershed moment in history, ushering in an age of large-scale industrial warfare. The intricate alliance structure among Europe's leading nations was key to the conflict's intensification. This network of treaties and accords, forged
Essay Example: As the curtains fell on the 19th century and the world stood at the threshold of a new era, an intricate web of alliances quietly wove itself across the geopolitical stage. ... The Alliance System of World War 1: a Prelude to Global Conflict. The deadline is too short to read someone else's essay. Hire a verified expert to write ...
More than twenty countries that controlled territory on six continents would declare war between 1914 and 1918, making World War I (also known as the Great War) the first truly global conflict. On one side, Britain, France, and Russia formed the Triple Entente (also known as the Allied powers or, simply, the Allies).
First World War outlined the beginning of the modern era; it had an immense impact on the economic and political status of many countries. European countries crippled their economies while struggling to manufacture superior weapons. The Old Russian Empire replaced by a socialist system led to loss of millions of people.
The effects of World War I can be seen around the world even now, more than one hundred years after its end; however, there is still no consensus as to its cause. In the words of Alfred Korzybski, "the destruction was brought about by nationalism, entangled alliances, narrow ethnic concerns, and desires for political gain - forces that are ...
The Immediate Trigger. World War 1 started in the year 1914. The assassination of Austria's Archduke, Franz Ferdinand, acted as a trigger to World War 1. Franz Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in 1914 by Gavrilo Princip, member of a Bosnian radical group.
646 Words. 3 Pages. Open Document. Alliances During World War 1 Although there were many underlying reasons for the European nations to break out in war, the early days of the fighting between Serbia and Austria caused the expansion of the war, along with the alliances which failed to remain peace and actually contributed to the war.
One underlying cause of World War 1 was the alliance systems. There were two major alliances. The triple entente and the triple alliance (Document A). The triple entente consisted of Russia, United Kingdom, and France. The triple alliance consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and italy. Alliances were quick to support their allies (Document B).
One underlying cause of World War 1 was the alliance systems. There were two major alliances. The triple entente and the triple alliance (Document A). The triple entente consisted of Russia, United Kingdom, and France. The triple alliance consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and italy. Alliances were quick to support their allies (Document B).
World War 1 Alliances Essay, University Of Pennsylvania Graduate Career Cv Resume Guidelines, Right To Bear Arms Thesis Statement, Average Length Of Time An Employer Reviews A Resume, Creative Powerpoint Presentations, Kindness Towards Animals Short Essay, My Last Duchess Essay Power
Alliances In World War II. 522 Words3 Pages. Alliances played a significant role in World War II, shaping the course of the conflict and influencing the outcomes. In many ways, the role of alliances in World War II differed from that in World War I. This essay will examine the role of alliances in both wars and compare their significance.
World War 1 Alliances Essay, Case Study Of Kfc In India, Professional Critical Essay Ghostwriters Sites Au, Research Paper On Employee Experience, Help Me Write Cheap Reflective Essay Online, Teach How To Write An Essay, Which Essay To Write For Barry Univeristy
Grab these brilliant features with the best essay writing service of PenMyPaper. With our service, not the quality but the quantity of the draft will be thoroughly under check, and you will be able to get hold of good grades effortlessly. So, hurry up and connect with the essay writer for me now to write. Create New Order.
1(888)499-5521. 1(888)814-4206. ASK ME A QUESTION. World War One Alliances Essay, How Do I Write A Good Comare And Contrast Essay, How To Create A Business Plan Australia, Cover Letter For Coordinator Volunteer, Is It Better To Live In A Big City Or Small Town Essay, Anu Kumari Essay Paper, Dissertation De Geographie Exemple.
Ukraine's foreign ministry called on Kyiv's international allies not to recognise Vladimir Putin as Russia's legitimate president. The first Olympian to die in the war in Ukraine has been ...
World War 1 Essay Alliances - 4.8/5. ID 15031. Discuss the details of your assignment and rest while your chosen writer works on your order. 4.8/5. Order: 12456. Communications and Media. World War 1 Essay Alliances: 1344 . Finished Papers. Who can help me write my essay? At the end of the school year, students have no energy left to complete ...
Mr. Sadjadpour is a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. "History is littered," the British writer and politician Enoch Powell said, "with the wars which ...
With the death toll mounting in the war in Gaza, protesters nationwide are demanding that schools cut financial ties to Israel and divest from companies they say are enabling the conflict. ... would codify the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance's definition of antisemitism in Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, a federal anti ...