

A 10-Step Guide to Writing an Outstanding Personal Statement
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
Applying to college can be daunting, especially when it comes to writing a personal statement. This essay showcases not just your writing skills but also your unique personality, achievements, and aspirations. Understanding that while grades are crucial, a personal statement often becomes the differentiating factor in your application. To navigate this essential component, we’ve compiled a ten-step guide, replete with examples, to ensure your personal statement leaves a lasting impression on admissions officers.
Applying to college can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to writing a personal statement. This essay not only showcases your writing skills but also highlights your unique personality, achievements, and aspirations. While it may seem unnecessary, tedious, time-consuming, and just another tick-the-box, know that as each application is processed, grades are just one of the criteria of selection, more often than not a personal statement becomes the differentiating factor.

To help you navigate this crucial component of your application, we’ve compiled a ten-step guide, complete with inspiring examples to ensure your personal statement makes a lasting impression on admissions officers.
- Start Early and Brainstorm Begin the process early to give yourself plenty of time to brainstorm. Reflect on your experiences, achievements, and motivations. Think about what makes you unique, both in terms of personality and life experiences.
- Understand the Prompt Make sure you clearly understand what the college is asking for. Each institution may have different prompts or questions. Tailor your response specifically to each prompt, ensuring you answer it fully and directly. Be comprehensive and succinct in your answers, choosing words that convey your candidature the best.
- Create an Outline Draft an outline to organize your thoughts and ensure a coherent flow of ideas. This will help you structure your statement effectively, making sure every part contributes towards presenting a compelling narrative.
- Exhibit, Don’t Tell Use specific examples to demonstrate your qualities and achievements. Instead of stating that you’re a great leader, describe a situation where you demonstrated leadership. This method makes your statement more engaging and believable.
- Focus on Your Strengths While it might be tempting to cover a wide range of subjects, focusing on a few key strengths or experiences can have a stronger impact. Depth over breadth is crucial in personal statements.
- Be Authentic Admissions officers can tell when a statement is genuine. Write honestly about your experiences and passions and let your natural voice shine through. Authenticity is key to making a personal statement stand out.
- Get Feedback After drafting your statement, seek feedback from teachers, mentors, or friends. They can provide insights on clarity, grammar, and the overall impact of your essay. They all have a perspective of you from an external viewpoint, so do not skip this step.
- Revise and Edit Use the feedback to revise your statement. Look for areas where you can clarify your points, eliminate redundancy, and correct grammatical errors. This step is crucial for polishing your final submission.
- Keep It Concise Adhere to the word limit. Being able to express your thoughts concisely and effectively is a skill appreciated by admissions officers.
- Final Review Before submitting, do a final review. Read your statement out loud to catch any remaining errors or awkward phrasing. Make sure it sounds natural and is easy to read.
Examples of Exemplary Personal Statements:
Example 1: The Innovator Jane’s personal statement begins with a vivid description of her tinkering with a broken radio at age eight, which sparked her interest in technology. She intertwines her personal journey with her academic achievements, such as leading her school’s robotics team to a national competition. Jane uses specific examples, like designing a new robot navigation system, to demonstrate her passion and skill in engineering.
Example 2: The Community Leader John opens his statement with a powerful recount of organizing community relief efforts during a local flood. Highlighting his role in mobilizing volunteers and coordinating with local authorities, he demonstrates strong leadership and commitment to his community. His narrative includes feedback from the community and the personal growth he experienced, providing a well-rounded view of his character.
Example 3: The Attentive Listener Emma’s personal statement explores her profound appreciation for music and its role in shaping her interpersonal connections. She describes an afternoon spent sharing playlists with a group of international students, which turned into a deep discussion about cultural expressions through music. This experience not only highlights her listening skills but also illustrates her ability to forge meaningful relationships through shared interests.
Example 4: The Compassionate Leader David writes about his high emotional quotient and how it spurred him to lead a community initiative focused on animal welfare. His personal statement recounts organizing local workshops to educate people about animal kindness and launching a successful campaign for a local shelter. David’s story reflects his empathy and leadership in translating compassion into actionable community improvement.
Commentary: Every life is extraordinary; it’s how you narrate your story that captures the reader’s eye. Your personal statement should reflect your unique experiences and aspirations.
Conclusion:
In crafting your personal statement, remember, you don’t have to be extraordinary in the usual sense—honesty and transparency are key. Be a dreamer of the art of the possible; dream as big as you can and let those dreams articulate themselves in your words. This approach not only reveals your true self to admissions officers but also shows your potential to contribute meaningfully to their academic community. Start your adventure today! Use these steps as your guide to find the university that best fits your future goals. Dream big and achieve even bigger.
A 10-Step Guide to Picking the Right University
Do You Need Student Contents Insurance?
Study in uk – a guide for students from the uae and pakistan, navigating your graduate studies journey, ai-powered learning revolution: how tech supercharges your studies, exam success strategies: your ultimate guide for the academic final stretch.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Personal Statement (with Tips and Examples)

Hannah Yang

Table of Contents
What is a personal statement, 6 tips on how to write a personal statement, personal statement examples (for college and university), faqs about writing personal statements, conclusion on how to write a personal statement.
How do you tell someone who you are in just a few hundred words?
It’s certainly no easy task, but it’s one almost every college applicant must do. The personal statement is a crucial part of any college or university application.
So, how do you write a compelling personal statement?
In this article, we’ll give you all the tools, tips, and examples you need to write an effective personal statement.
A personal statement is a short essay that reveals something important about who you are. It can talk about your background, your interests, your values, your goals in life, or all of the above.
Personal statements are required by many college admission offices and scholarship selection committees. They’re a key part of your application, alongside your academic transcript, standardized test scores, and extracurricular activities.
The reason application committees ask you to write a personal statement is so they can get to know who you are.
Some personal statements have specific prompts, such as “Discuss a period of personal growth in your life” or “Tell us about a challenge or failure you’ve faced.” Others are more open-ended with prompts that essentially boil down to “Tell us about yourself.”
No matter what the prompt is, your goal is the same: to make yourself stand out to the selection committee as a strong candidate for their program.
Here are some things a personal statement can be:
It can be funny. If you have a great sense of humor, your personal statement is a great place to let that shine.
It can be vulnerable. Don’t be afraid to open up about hardships in your life or failures you’ve experienced. Showing vulnerability can make you sound more like a real person rather than just a collection of application materials.
It can be creative. Candidates have got into top schools with personal statements that take the form of “a day in the life” descriptions, third-person short stories, and even cooking recipes.
Now we’ve talked about what a personal statement is, let’s quickly look at what a personal statement isn’t:
It isn’t a formal academic paper. You should write the personal statement in your natural voice, using first-person pronouns like “I” and “me,” not in the formal, objective language you would use to write an academic paper.
It isn’t a five-paragraph essay. You should use as many paragraphs as you need to tell your story instead of sticking to the essay structure you learned in school.
It isn’t a resumé. You should try to describe yourself by telling a clear and cohesive story rather than providing a jumbled list of all of your accomplishments and ambitions.

Here are our top six tips for writing a strong personal statement.
Tip 1: Do Some Serious Self-Reflection
The hardest part of writing a personal statement isn’t the actual process of writing it.
Before you start typing, you have to figure out what to write about. And that means taking some time to reflect on who you are and what’s important in your life.
Here are some useful questions you can use to start your self-reflection. You can either answer these on your own by writing down your answers, or you can ask a trusted friend to listen as you talk about them together.
What were the key moments that shaped your life? (e.g. an important friendship, a travel experience, an illness or injury)
What are you proud of? (e.g. you’re a good listener, you always keep your promises, you’re a talented musician)
How do you choose to spend your time? (e.g. reading, practicing soccer, spending time with your friends)
What inspires you? (e.g. your grandmother, a celebrity, your favorite song)
Doing this self-reflection is crucial for figuring out the perfect topics and anecdotes you can use to describe who you are.
Tip 2: Try to Avoid Cliché Topics
College application committees read thousands of personal statements a year. That means there are some personal statement topics they see over and over again.
Here are a few examples of common personal statement topics that have become cliché:
Winning a tournament or sports game
Volunteering in a foreign country
Moving to a new home
Becoming an older sibling
Being an immigrant or having immigrant parents
If you want to make a strong impression in the application process, you need to make your personal statement stand out from the crowd.
But if your chosen personal statement topic falls into one of these categories, that doesn’t necessarily mean you shouldn’t use it. Just make sure to put a unique spin on it so it still delivers something the committee hasn’t seen before.

Good writing = better grades
ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of all your assignments.
Tip 3: Show, Don’t Tell
One common mistake you might make in your personal statement is to simply tell the reader what you want them to know about you, such as by stating “I have a fear of public speaking” or “I love to cook.”
Instead of simply stating these facts, you should show the committee what you’re talking about through a story or scene, which will make your essay much more immersive and memorable.
For example, let’s say you want the committee to know you overcame your fear of public speaking. Instead of writing “I overcame my fear of public speaking,” show them what it was like to be onstage in front of a microphone. Did your palms get clammy? Did you feel light-headed? Did you forget your words?
Or let’s say you want the committee to know you love to cook. Instead of writing “I love to cook,” show them why you love to cook. What’s your favorite dish to cook? What does the air smell like when you’re cooking it? What kitchen appliances do you use to make it?
Tip 4: Connect the Story to Why You’re Applying
Don’t forget that the purpose of your personal statement isn’t simply to tell the admissions committee who you are. That’s an important part of it, of course, but your ultimate goal is to convince them to choose you as a candidate.
That means it’s important to tie your personal story to your reasons for applying to this specific school or scholarship. Finish your essay with a strong thesis.
For example, if your story is about overcoming your fear of public speaking, you might connect that story to your ambition of becoming a politician. You can then tie that to your application by saying, “I want to apply to this school because of its fantastic politics program, which will give me a perfect opportunity to use my voice.”
Tip 5: Write in Your Own Voice
The personal statement isn’t supposed to be written in a formal tone. That’s why they’re called “personal” statements because you have to shape it to fit your own voice and style.
Don’t use complicated or overwrought language. You don’t need to fill your essay with semicolons and big words, unless that’s how you sound in real life.
One way to write in your own voice is by speaking your personal statement out loud. If it doesn’t feel natural, it may need changing.
Tip 6: Edit, Edit, Edit!
It’s important to revise your personal statement multiple times in order to make sure it’s as close to perfect as possible.
A single typo won’t kill your application, but if your personal statement contains multiple spelling errors or egregious grammar mistakes, you won’t be putting your best foot forward.
ProWritingAid can help you make sure your personal statement is as clean as possible. In addition to catching your grammar errors, typos, and punctuation mistakes, it will also help you improve weaknesses in your writing, such as passive voice, unnecessary repetition, and more.
Let’s look at some of the best personal statements that have worked for successful candidates in the real world.
Harvard Personal Statement Example
Love. For a word describing such a powerful emotion, it is always in the air. The word “love” has become so pervasive in everyday conversation that it hardly retains its roots in blazing passion and deep adoration. In fact, the word is thrown about so much that it becomes difficult to believe society isn’t just one huge, smitten party, with everyone holding hands and singing “Kumbaya.” In films, it’s the teenage boy’s grudging response to a doting mother. At school, it’s a habitual farewell between friends. But in my Chinese home, it’s never uttered. Watching my grandmother lie unconscious on the hospital bed, waiting for her body to shut down, was excruciatingly painful. Her final quavering breaths formed a discordant rhythm with the steady beep of hospital equipment and the unsympathetic tapping hands of the clock. That evening, I whispered—into unhearing ears—the first, and only, “I love you” I ever said to her, my rankling guilt haunting me relentlessly for weeks after her passing. My warm confession seemed anticlimactic, met with only the coldness of my surroundings—the blank room, impassive doctors, and empty silence. I struggled to understand why the “love” that so easily rolled off my tongue when bantering with friends dissipated from my vocabulary when I spoke to my family. Do Chinese people simply love less than Americans do?
This is an excerpt from a personal statement that got the applicant admitted to Harvard University. The applicant discusses her background as a Chinese-American by musing on the word “love” and what that means within her family.
The writer uses vulnerable details about her relationship with her grandmother to give the reader an understanding of where she comes from and how her family has shaped her.
You can read the full personal statement on the Harvard Crimson website.
Tufts Personal Statement Example
My first dream job was to be a pickle truck driver. I saw it in my favorite book, Richard Scarry’s “Cars and Trucks and Things That Go,” and for some reason, I was absolutely obsessed with the idea of driving a giant pickle. Much to the discontent of my younger sister, I insisted that my parents read us that book as many nights as possible so we could find goldbug, a small little golden bug, on every page. I would imagine the wonderful life I would have: being a pig driving a giant pickle truck across the country, chasing and finding goldbug. I then moved on to wanting to be a Lego Master. Then an architect. Then a surgeon. Then I discovered a real goldbug: gold nanoparticles that can reprogram macrophages to assist in killing tumors, produce clear images of them without sacrificing the subject, and heat them to obliteration. Suddenly the destination of my pickle was clear. I quickly became enveloped by the world of nanomedicine; I scoured articles about liposomes, polymeric micelles, dendrimers, targeting ligands, and self-assembling nanoparticles, all conquering cancer in some exotic way. Completely absorbed, I set out to find a mentor to dive even deeper into these topics. After several rejections, I was immensely grateful to receive an invitation to work alongside Dr. Sangeeta Ray at Johns Hopkins.
This is the beginning of a personal statement by Renner Kwittken, who was admitted into Tufts University as a pre-medical student.
Renner uses a humorous anecdote about being a pickle truck driver to describe his love for nanomedicine and how he got involved in his field. You can feel his passion for medicine throughout his personal statement.
You can find Renner’s full essay on the Tufts Admissions page.
Law School Personal Statement Essay Example
For most people, the slap on the face that turns their life around is figurative. Mine was literal. Actually, it was a punch delivered by a drill sergeant at Fort Dix, New Jersey, while I was in basic training. That day’s activity, just a few weeks into the program, included instruction in “low-crawling,” a sensible method of moving from one place to another on a battlefield. I felt rather clever for having discovered that, by looking right rather than down, I eliminated my helmet’s unfortunate tendency to dig into the ground and slow my progress. I could thus advance more easily, but I also exposed my unprotected face to hostile fire. Drill sergeants are typically very good at detecting this type of laziness, and mine was an excellent drill sergeant. So, after his repeated suggestions that I correct my performance went unheeded, he drove home his point with a fist to my face. We were both stunned. This was, after all, the New Army, and striking a trainee was a career-ending move for a drill sergeant, as we were both aware. I could have reported him; arguably, I should have. I didn’t. It didn’t seem right for this good sergeant, who had not slept for almost four days, to lose his career for losing his temper with my laziness. Choosing not to report him was the first decision I remember making that made me proud.
These are the first three paragraphs of an anonymous personal statement by a Wheaton College graduate, who used this personal statement to get into a top-25 law school.
This statement describes a time the applicant faced a challenging decision while in the army. He ended up making a decision he was proud of, and as a result, the personal statement gives us a sense of his character.
You can find the full essay on the Wheaton Academics website.
Here are some common questions about how to write a personal statement.
How Long Should a Personal Statement Be?
The length of your personal statement depends on the specific program you’re applying to. The application guidelines usually specify a maximum word count or an ideal word count.
Most personal statements are between 500–800 words. That’s a good general range to aim for if you don’t have more specific guidelines.
Should Personal Statements Be Different for Scholarships?
Many scholarship applications will ask for personal statements with similar prompts to those of college applications.
However, the purpose of a personal statement you’d write for a scholarship application is different from the purpose of one you’d write for a college application.
For a scholarship application, your goal is to showcase why you deserve the scholarship. To do that, you need to understand the mission of the organization offering that scholarship.
For example, some scholarships are meant to help first-generation college students get their degree, while others are meant to help women break into STEM.
Consider the following questions:
Why is this organization offering scholarships?
What would their ideal scholarship candidate look like?
How do your experiences and goals overlap with those of their ideal scholarship candidate?
You can use the same personal anecdotes you’d use for any other personal statement, but you’ll have a better chance of winning the scholarship if you tailor your essay to match their specific mission.
How to Start a Personal Statement
You should start your personal statement with a “hook” that pulls the reader in. The sooner you catch the reader’s attention, the more likely they’ll want to read the entire essay.
Here are some examples of hooks you can use:
A story (e.g. When the spotlight hit my face, I tried to remind myself to breathe. )
A setting description (e.g. My bedroom floor is covered with dirty laundry, candy wrappers, and crumpled sheet music. )
A funny anecdote (e.g. When I was a little kid, my friends nicknamed me Mowgli because of my haircut. )
A surprising fact (e.g. I've lived in 37 countries .)
There you have it—our complete guide to writing a personal statement that will make you stand out to the application committee.
Here’s a quick recap:
A personal statement is a short essay that shows an application committee who you are
Start with a strong hook that pulls the reader in
Tell a story to engage the reader
Write in your own voice, not in a formal tone
Good luck, and happy writing!
Hannah is a speculative fiction writer who loves all things strange and surreal. She holds a BA from Yale University and lives in Colorado. When she’s not busy writing, you can find her painting watercolors, playing her ukulele, or hiking in the Rockies. Follow her work on hannahyang.com or on Twitter at @hannahxyang.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Write a Strong Personal Statement
- Ruth Gotian
- Ushma S. Neill

A few adjustments can get your application noticed.
Whether applying for a summer internship, a professional development opportunity, such as a Fulbright, an executive MBA program, or a senior leadership development course, a personal statement threads the ideas of your CV, and is longer and has a different tone and purpose than a traditional cover letter. A few adjustments to your personal statement can get your application noticed by the reviewer.
- Make sure you’re writing what they want to hear. Most organizations that offer a fellowship or internship are using the experience as a pipeline: It’s smart to spend 10 weeks and $15,000 on someone before committing five years and $300,000. Rarely are the organizations being charitable or altruistic, so align your stated goals with theirs
- Know when to bury the lead, and when to get to the point. It’s hard to paint a picture and explain your motivations in 200 words, but if you have two pages, give the reader a story arc or ease into your point by setting the scene.
- Recognize that the reviewer will be reading your statement subjectively, meaning you’re being assessed on unknowable criteria. Most people on evaluation committees are reading for whether or not you’re interesting. Stated differently, do they want to go out to dinner with you to hear more? Write it so that the person reading it wants to hear more.
- Address the elephant in the room (if there is one). Maybe your grades weren’t great in core courses, or perhaps you’ve never worked in the field you’re applying to. Make sure to address the deficiency rather than hoping the reader ignores it because they won’t. A few sentences suffice. Deficiencies do not need to be the cornerstone of the application.
At multiple points in your life, you will need to take action to transition from where you are to where you want to be. This process is layered and time-consuming, and getting yourself to stand out among the masses is an arduous but not impossible task. Having a polished resume that explains what you’ve done is the common first step. But, when an application asks for it, a personal statement can add color and depth to your list of accomplishments. It moves you from a one-dimensional indistinguishable candidate to someone with drive, interest, and nuance.
- Ruth Gotian is the chief learning officer and associate professor of education in anesthesiology at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City, and the author of The Success Factor and Financial Times Guide to Mentoring . She was named the #1 emerging management thinker by Thinkers50. You can access her free list of conversation starters and test your mentoring impact . RuthGotian
- Ushma S. Neill is the Vice President, Scientific Education & Training at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City. She runs several summer internships and is involved with the NYC Marshall Scholar Selection Committee. ushmaneill
Partner Center
How To Write a Personal Statement That Stands Out

Table of contents

Laura Jane Bradbury
A personal statement is a chance to highlight your unique qualities, skills, and experiences, all while showcasing your personality.
But whether you're applying for university, a job, or funding, it can be daunting to write about yourself. To increase your chances of getting accepted, it's important to know how to create an effective personal statement.
In my six years as a copywriter, I’ve written many personal statements that get results. In this article, I’ll guide you through what to include, what to avoid, and how to tailor a personal statement based on your application type.
Key Takeaways
- A personal statement is an opportunity to share your unique qualities, experiences, and skills.
- It should always relate to the course, job, or funding you are applying for.
- Include accomplishments and experiences that demonstrate how suited you are to the position or course you are applying for.
- Use clear and simple language to ensure your points are understood.
Your personal statement should be concise and demonstrate how you fit the position or opportunity you’re applying for. It’s important to keep information relevant, rather than listing all of your skills and accomplishments.
Follow these steps to accurately write and tailor your statement.
Understand your prompt
Before you start, make sure you understand what's expected of you. Are there specific instructions, keywords, or phrases that stand out in your prompt? Read through it thoroughly and note the requirements. You can then brainstorm ideas for each point.
Let's say I'm applying for a university journalism course. I've been asked to write a statement that shares why I'm interested and why I would be a good fit. I can use columns to plan my content:

Putting your ideas together first makes it easier to stay on track. Otherwise, you might lose focus and include irrelevant information.
Show, don't just tell
Once you’ve listed your experiences, skills, and accomplishments, consider how you can demonstrate them with examples. Take a look at the list you created during the previous exercise and organize your points so you have clear examples and proof.

This technique helps you demonstrate your experiences and how they tie in with your application.
When telling anecdotes, use engaging stories that demonstrate your skills. For instance, a story about how I handled a fast-paced news internship proves I work well under pressure.
Start strong
Recruiters, application tutors, and funders read lots of personal statements. You can make yours stand out with an engaging introduction.
Examples of a strong opening include:
A meaningful statistic
This draws readers in and increases credibility:
"Communication is the key to marketing success, according to Business Marketing News. With five years of experience communicating and delivering campaigns to global clients, I have the skills and passion to add value to your team."
A personal story
Anecdotes connect the reader with the author’s real-life experience:
"My first exposure to microbiology was during my time as a research assistant for a microbiologist. I was fascinated by the complex and intricate processes within cells."
An alarming statement
This piques the reader’s interest by making an issue seem urgent:
“ The fashion industry churns out clothes at an alarming rate, causing mass production of synthetic fibers and harsh chemicals which have a detrimental impact on the planet. Funding my sustainability initiative is vital to mitigating this environmental impact."
Avoid cliches such as "From a young age, I have always loved...." and "For as long as I can remember, I have had a passion for..."
Pro tip: Use Wordtune Editor 's Shorten feature to cut unnecessary fluff and make your intro sharper. Simply type in your sentence and click Shorten to receive suggestions.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Admission committees and employers appreciate sincerity and authenticity. While it may be tempting, avoid exaggeration. You can better emphasize your skills and personality by being honest. For instance, rather than claiming I read every type of newspaper in my journalism application, I can focus on my dedication to reading The New York Times.
Your writing style should also feel genuine. Instead of trying to impress with complex language and fancy words, keep sentences simple and direct . This makes them more effective because they’re easier to read.
Address weaknesses
Addressing weaknesses can show your willingness to confront challenges. It also gives you a chance to share efforts you have made for improvement. When explaining a weakness, exclude excuses.
Instead of saying "I didn't achieve my expected grades due to work commitments impacting my studies," try “While I didn't achieve my expected grades, I am now working with a tutor to help me understand my weak areas so I can succeed in your program.”
Wordtune’s Spices feature can help you develop counterarguments to weaknesses. In the Editor, highlight your text, click on Spices, and then Counterargument . Here’s an example:

Using Wordtune’s suggestion, I can highlight my eagerness to learn and provide examples to support my argument.
Highlight achievements
This is your chance to shine! A personal statement should highlight your best qualities — provided they relate to your prompt.
Ask yourself:
- What are your skills and strengths? Identify both academic and non-academic abilities such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and teamwork.
- What challenges have you faced? Reflect on how you have overcome significant challenges and how these experiences have helped you grow. For example, completing a course, learning a new language, or starting a business.
- What are your unique selling points? Consider what sets you apart from other applicants. For example, you may have a unique set of technical skills or experience learning in a different country.
- How have your achievements shaped your goals and aspirations? Sharing your goals shows that you think long-term and have taken the time to make sure you’re applying for the right opportunity.
Connect with the institution or company
Tailor your statement to the specific institution or company you're applying to — this shows you understand their values and have carefully considered where you want to seek opportunities.
To do this, head to the company or institution’s website and look for the About page. Many organizations include a mission statement on this page that conveys its purpose and values.

For example, universities often include their values under “Community” or “Student Life” sections. Here, Princeton University’s “In Service of Humanity” section highlights how they value using education to benefit society. Applicants can engage with this by explaining how they interact with their communities and seek to use their education to help others.
You can also research a company or institution’s social media. Look for similarities — maybe you both prioritize collaboration or think outside the box. Draw upon this in your personal statement.
End with a strong conclusion
A strong conclusion is clear, concise, and leaves a lasting impression. Use these three steps:
- Summarize the main points of your statement. For example, “My experience volunteering for the school newspaper, along with my communication skills and enthusiasm for writing, make me an ideal student for your university."
- Discuss your future . Share your future ambitions to remind the reader that you’ve carefully considered how the opportunity fits into your plans.
- Include a closing statement. End on a positive note and offer the reader a final explanation for why you would be a great match. For instance, “Thank you for reviewing my statement. I am confident my skills and experience align with the role and your company culture.”
Tip: Learn more about writing an effective conclusion with our handy guide .
Different types of personal statements
Now you know how to write a personal statement, let’s look at what to focus on depending on your application type.

The length of your personal statement will vary depending on the type. Generally, it should be around 500 words to 650 words . However, a university application is often longer than a statement for a job, so it’s vital to determine what is expected of you from the beginning.
Whatever the length, it’s important to remove and edit content fluff , including any repetition or copy that does not relate to your prompt.
Personal statement checklist
Use this checklist to ensure that your statement includes:
- An engaging introduction.
- Clear examples of your experiences, skills, and expertise.
- A commitment to improvement, if required.
- Any applicable achievements.
- A direct connection to the company or institution’s values.
- A strong conclusion that summarizes information without adding new content.
- Authentic, simple language.
Personal statements are an opportunity to delve deeper and share who you are beyond your grades or resume experience. Demonstrate your ability with anecdotes and examples, address any weaknesses, and remember to use genuine and simple language. This is your place to shine, so follow our tips while displaying your unique personality, and you’ll be sure to stand out from the crowd.
Want to get started and create a powerful introduction? Read our step-by-step guide .
What is the difference between a cover letter and a personal statement?
A cover letter expresses your interest in a position and introduces you to an employer. It’s typically shorter and focuses on your qualifications, skills, and experience for a particular role. A personal statement, however, is common for a job, internship, funding, or university application. It explores your background, goals, and aspirations, as well as your skills and experience.
What is the purpose of a personal statement?
A personal statement is an opportunity to stand out by detailing your background, experiences, and aspirations. It should explain why you are interested in and a good match for the company or institution you are applying to.
Share This Article:
.webp)
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Applying for Tertiary Education
- Application Essays
How to Write a Personal Statement
Last Updated: February 24, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 140,149 times.
A personal statement lets an academic institution, organization, workplace, or potential client know more about you and your career or academic goals. Every personal statement will be a little different, but each one should highlight why you're the right fit for the program or position. You should also use your past experiences and accomplishments to support your statement.
Developing Your Statement

- If you're writing a personal statement for undergraduate schools or scholarships focus on how your interests developed, your high school achievements, and your community involvement.
- If you're writing for an undergraduate transfer, focus on your academic and community record with your current school and describe your reasons for wanting to switch universities.
- If you're writing for graduate school, focus on the specific course you want your graduate project or studies to take, your reason for pursuing graduate school, and the undergraduate experiences that have prepared you.
- If you're writing for a job, portfolio, or to gain a particular client, focus on your past work experiences, your relevant academic accomplishments within the past 5 years, and your positive character traits.
- If you've been given a prompt for your personal statement, make sure you have a clear understanding of what it's asking for and what you should write.

- Every institution and organization will look for content specific to their mission and goals in a personal statement. Don't send the same personal statement to different organizations, but instead personalize each statement you write.
- For example, if you're applying to a university that emphasizes community service and involvement, you'll want to emphasize your service work in that statement. Another school may value academics first though. For that school, talk about your coursework and grades.

- How will this university/academic program/scholarship/job position/client directly impact my future?
- What project do I plan to undertake to complete this degree or job opportunity?
- What is my ultimate career goal?
- Where do I see myself in 1 year? 5 years? 10 years?
- What are the steps I need to take in order to reach my ultimate goal?
- What are other goals I hope to accomplish along the way?

- What personal qualities (leadership skills, organizational skills, self-control, etc.) do you possess which make you a valuable asset?
- What experiences and beliefs have shaped your present character?
- What accomplishments make you the proudest?
- Have you had any turning points that redirected your life in a positive way?
- Why would you choose yourself over other candidates? Why should anyone else?

- Academic degrees and certificates
- Scholarships, fellowships, and grants
- Awards or honors from academic institutions (e.g. summa cum laude, manga cum laude, departmental honors, Dean's List, etc.)
- Workplace promotions, reviews, and evaluations
- Speaking at a conference, convention, or workshop
- Published works in your field of expertise
- Official recognition for community service or contributions

- When did you originally develop an interest in your field of choice?
- What do you love most about your field of choice?
- Why do you think your field of choice is important?
- What experiences have you had that have provided you with experience in the field?
- Have you given up any other dreams or expectations in order to chase after this one?

- Financial difficulties
- Social disenfranchisement
- Learning disabilities
- Physical disabilities
- Family problems
- Medical problems
- Unexpected tragedies
Putting Your Personal Statement Together

- Often, these questions will be listed directly on the application, or otherwise on the job posting or program web page.
- If you're not sure if your application needs to address specific questions, reach out to the program coordinator or the contact person listed on the posting.

- Prioritize the purpose of your statement in your outline. For example, if you're applying to a graduate program, your graduate project should be your main focus.
- Write about what interests you. You will be able to write more convincingly and more passionately if you write about events, goals, experiences, or ideas that you already feel passionate about.
- Address issues specifically brought up by the institution or organization. If there are any topics that the reader demands to see, then make sure that those are included in your personal statement.

- Avoid starting with common or cliché phrases like, “The most important moment in my life was when...”
- A better way to introduce that “important moment” would be to simply start describing it. Explain that, “When I first started working at XYZ Company, I didn't know the first thing about widget manufacturing.” Directly break into the narrative instead of alerting the reader that you intend to do so.
- Provide as much detail in the first paragraph as possible. Introduce the main idea of your personal statement and describe how it connects to your narrative. Save any elaborate details or related notes and experiences for the body of your essay, though.

- For example, for a graduate program statement, your second paragraph could focus on your undergraduate career. Frame your undergrad research, your relevant coursework, and your achievement as tools that helped prepare you for your graduate project.
- Do not be vague or general.
- Do tell the reader about experiences, goals, and ideas unique to you.

- Avoid uncertain or weak phrasing like, “I'm not sure but I think I would probably be a good fit for your program.”
- Even when discussing challenges or difficulties you faced, focus on your triumphs over those problems.
Revising Your Statement

- When expanding your personal statement, look for ways to elaborate on the information you already have. Include more specific detail to create a fuller picture. Alternatively, you could introduce another point that contributes to your overall statement purpose.
- While it's not advisable to submit a statement that's too short, you also shouldn't add information just for the sake of having it. If your statement is a paragraph short of a full page but covers all your relevant information, you don't need to expand it.
- Avoid telling the reader why something is important to you. Instead, explain what you've done to show and develop the skill.

- You may also consider reducing your number of main points if one point does not seem especially significant.
- Unlike a short statement, a long statement can't be left long. Many application programs won't allow you to press the submit button until your statement is the correct length. That means that if your statement is too long, it needs to be cut down.

- While listening to your statement, ask yourself if it sounds like your natural voice. If you were describing these things in person, would the way you speak sound like what you wrote?

- Accept constructive criticism graciously and try not to take anything personally.
- When asking for constructive criticism, first go to professional sources like a high school teacher, a university professor, an internship supervisor, an academic adviser, or a trustworthy colleague.
- After your professional sources have been exhausted, ask friends and family for their thoughts. They may offer great insight regarding the “every-man” opinion, since not all your readers may be familiar with your program or industry.
- It's common to receive conflicting feedback. Think about each of their perspectives to see what may have influenced what they told you. If their experiences don't match your goals, consider if their advice is worth taking.

- Once you fix these problems, your personal statement is ready to submit.
Community Q&A
- Give yourself plenty of time to write your statement. If possible, start the writing process at least 3 months from your proposal or application due date. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Vary your content for each personal statement to match each individual organization or institution. You may be able to use many of the same points in each statement, but you should still write individual statements for each organization. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Unless the program or job directly deals with them, avoid talking about controversial topics such as extreme religious or political opinions. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/personal-statements/
- ↑ https://www.careereducation.columbia.edu/resources/creating-undergraduate-cv
- ↑ https://grad.berkeley.edu/admissions/steps-to-apply/requirements/personal-statement/
- ↑ https://www.careercenter.illinois.edu/instructable/write-your-personal-statement
- ↑ https://www.cmu.edu/hpp/apply-to-schools/personal-statements/tips.html
- ↑ https://www.e-education.psu.edu/writingpersonalstatementsonline/p3_p7.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/advice-for-writing-personal-statements
About This Article

To write a personal statement, start with a strong beginning such as “When I first started working at XYZ Company, I didn’t know the first thing about widget manufacturing” to introduce your theme and grab the reader’s attention. Then, write 2-4 paragraphs to support your statement, highlighting things like your experiences, achievements, and goals. Make sure that you focus each paragraph on a single point, relate each point back to your theme, and keep the tone of your writing positive and confident. For more tips from our Education reviewer, like how to revise your personal statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Xaiykhamla M,
Oct 30, 2018
Did this article help you?

Jan 19, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write a Stand-Out Personal Statement for Your Graduate School Application

While deciding to embark on the path to graduate school is an exciting first step toward advancing your career, the application process can sometimes feel daunting and confusing.
One major part of the application that most schools require is a personal statement. Writing a personal statement can be an arduous task: After all, most people don’t necessarily enjoy writing about themselves, let alone at length.
A compelling personal statement, however, can help bring your application to the top of the admissions pile. Below, we’ve outlined what you need to know about crafting a personal statement to make your application shine.
What Is a Personal Statement?
The point of a personal statement is for the admissions board to gain a deeper understanding of who you are apart from your education and work experience. It explains why you’re the right fit for the program and a worthwhile applicant. It’s also an opportunity to highlight important factors that may not be readily available in the rest of your application.
A personal statement is different from a statement of purpose (if you’re asked for that as well). A statement of purpose will touch on your academic and career goals, as well as your past credentials. While those should also be discussed in your personal statement, it’s more about your life experiences and how they’ve shaped you and your journey to graduate school.
Questions to Ask Yourself Before Writing a Personal Statement
Before you start crafting your essay, there are a few prompts you can ask yourself to help clarify what you want to accomplish.
- What are the key points you want to communicate about yourself?
- What personal characteristics or skills do you have that make you a strong candidate for this field?
- What exactly are your career goals, and how does graduate school play into them?
- What have you learned about this field already? When did you first choose to follow this path, and what do you enjoy about it?
- What do you think is important for the admissions board to know specifically about you?
- Are there any discrepancies or causes for concern in your application you need to address? For example, is there a career and schooling gap, or a low GPA at one point? This is the time to discuss whether a personal hardship may have affected your academics or career.
- Have you dealt with any unusual obstacles or difficulties in your life? How have they affected and shaped you?
- What sets you apart and makes you unique from other graduate school applicants?
- What factors in your life have brought you to where you are today?
Top Tips for Writing a Graduate School Personal Statement
Pick a few points to emphasize about yourself . Introduce yourself to the admissions board. Select key factors about your background that you want the university to know — elements that reveal what kind of person you are and demonstrate why you’re a strong candidate for the school and field of study.
Be very specific . Again, a personal statement is all about communicating what distinguishes you from other applicants. To accomplish that, you need to share specific anecdotes that underscore your statements. If you say you’re a strong leader, present an example of a time you’ve proven that skill through work, school or your personal life. These specific, personal stories provide a deeper understanding of who you are and prove your intentions.
Do your research . Demonstrate what attracted you to the program. If there is a specific faculty member or class that caught your attention, or another aspect of the program that greatly interests you, convey it. This shows you’ve truly researched the school and have a passion for the program.
“Whatever the topic may be, I would recommend writing in a manner that reflects or parallels the institution’s and/or department’s missions, goals and values,” said Moises Cortés, a graduate/international credentials analyst for the Office of Graduate Admission at USC .
Address any gaps or discrepancies . Explain any factors that may have impacted your academic career. If you had an illness or any other personal hardships that affected your grades or work, discuss them. If there is a discrepancy between your grades and your test scores, you can also take the time to go over any extenuating circumstances.
Strike the right tone . While it’s important to give readers a glimpse of your personality, avoid oversharing or revealing intimate details of your life experiences. You should also avoid making jokes or using humorous cliches. Maintain a professional tone throughout your writing.
Start strong and finish strong . As with any piece of writing, you want to draw in your readers immediately. Make sure to start off with an interesting and captivating introduction. Similarly, your conclusion should be a well-written, engaging finish to the essay that highlights any important points.
“ For a personal statement, I think the first and last paragraphs are most important and should always relate the program they are applying to their own experiences and ideas,” Hoon H. Kang, a graduate/international credential analyst with the Office of Graduate Admission, told USC Online.
Proofread, proofread and proofread again . We can’t emphasize enough the importance of rereading your work. Your personal statement is also an analysis of your writing skills, so ensure you have proper grammar and spelling throughout. In addition, we recommend having multiple people look over your statement before submission. They can help with the proofreading (a second person always catches a mistake the writer may miss), give advice about the statement’s structure and content, and confirm it’s the proper recommended length.
Once you’ve considered all of the above and reviewed and edited your personal statement to perfection, it’s time to submit and check off any remaining application requirements, including your resume and letters of recommendation .
Personal statements are arguably one of the most challenging aspects of applying to graduate school, so make sure to revel in this accomplishment and acknowledge your successes.
For more information, visit the Office of Graduate Admission at USC and explore USC Online ’s master’s degrees, doctoral programs and graduate certificates.
Academic Personal Statement Guide + Examples for 2024

You have a bright future ahead of you in academia and you’ve already found the program of your dreams.
The only problem?
You have to write an impressive academic personal statement that sets you apart from a sea of applicants.
We know that writing about yourself might not come naturally. And when the academic program you have your sights set on is on the line, it doesn’t make it any easier.
But there’s no need to worry!
We’ve prepared this guide to help you write your academic personal statement and secure your spot in your program of choice.
In this article, we’re going to cover:
- What Is An Academic Personal Statement?
- 7 Steps to Writing the Best Academic Personal Statement
- An Example of a Stellar Academic Personal Statement
Let’s dive in.

You’ll need an academic CV alongside your personal statement. Create one with ease with Novorésumé !
What Is an Academic Personal Statement?
A personal statement is an essential part of the academic application process.
Much like a motivation letter , your academic personal statement serves to demonstrate why you’re the right candidate for the course and sell yourself as a capable student.
Your goal is to show the admissions committee that they’ll benefit from having you in their university as much as you’ll benefit from joining the program.
Academic Vs CV Personal Statement
The term ‘personal statement’ can mean different things depending on your field.
In the world of job hunting, a personal statement usually refers to a few sentences that go at the top of your CV . This paragraph is meant to convey your top skills, relevant experiences, and professional goals to a hiring manager from the get-go and increase your chances of getting an interview.
However, in the world of academia, a personal statement refers to a more in-depth description of you as a candidate.
In a nutshell, an academic personal statement shows the admissions committee your academic achievements so far, as well as what motivated you to apply and pursue this position.
Personal statements are also often required when applying for certain jobs, much like writing a cover letter . If you’re looking at a position as a faculty member in a university or other academic institution, for example, you might be asked to provide an academic personal statement.
7 Steps to Write an Academic Personal Statement
Preparation is the key to success and this is exactly where our guide comes in handy.
So just follow these steps and you’re sure to secure your spot:
#1. Read the Brief (Carefully!)
Academic personal statements aren’t necessarily a one-size-fits-all piece of writing.
Typically, every institution has its specific requirements on what candidates should include in their academic personal statement.
To make sure you’re on the right track with your academic personal statement, read the brief carefully. Consider taking notes and highlighting important points from your program’s brief as you go through it.
Pay attention to any specific question the university wants you to answer. If you don’t address everything the admissions board expects, your personal statement will look sloppy and you’ll be considered an inattentive candidate.
Be sure to re-read the brief after you’ve finished writing your academic personal statement, too. This way you can make sure you’ve answered everything adequately and you’ll have the opportunity to correct any slips.
#2. Research the Program
Make sure you do your homework on the academic program you’re applying to.
You can’t write a good academic personal statement without research, let alone a great one. Much like researching your employer , taking the time to learn more about your desired school and personalizing your application can make a huge difference.
For example, you can dive into how your values align with that of the school you’re applying to, and how your experience and interests relate to specific things about the program. The more you focus on how you’re the right fit for this specific position, in this specific program – the better.
Carefully read through the school and program’s official pages since everything you would need to know is probably on the school’s official website. You can also ask current and former students for help but remember that whatever they say should never replace official information when crafting your academic personal statement.
#3. Plan Your Statement
An academic personal statement is meant to explain your academic interests and shouldn’t contain irrelevant details about your personal life.
Focus on why you want to study the course you’ve chosen and provide any information about your achievements so far.
Ask yourself the following questions to get the ball rolling on what to write:
- Why do you want to study (or work) in this program? How will it benefit you?
- How do your skills match the position?
- What makes you stand out from other applicants?
- What are your exact career aspirations?
- How can you and your work benefit the institution you’re applying to?
- If you changed fields, how did you decide to apply in this direction?
- What insight can you bring thanks to your different experiences?
- How will this change of field help your future career?
Write down your answer to these questions in the first draft of your academic personal statement.
#4. Look at Example Statements
Don’t hesitate to read other people’s academic personal statements online. They’re a great source of inspiration and can help get rid of any remaining writer’s block.
If you’re struggling to understand how to meet the language and formatting requirements for your academic personal statement, seeing actual examples is the best way to learn.
But be careful – don’t copy any lines you read, no matter how impressive you think they are.
Most universities run every academic personal statement through intensive plagiarism checking, and even a paraphrased sentence could lead to your application being rejected for plagiarism.
So pay more attention to the overall structure of the academic personal statements you read, rather than copying the exact wording.
#5. Structure the Contents
There should be a cohesive argument that your entire essay follows. Each sentence and paragraph should complement and build on the one that comes before it.
The structure of your personal statement should include:
An intriguing introduction to you as a candidate
The introductory paragraph should grab the admission committee’s attention and keep them engaged.
Here you should be sure to avoid cliches like saying how you’ve “always dreamt” of graduating from this university or of studying this exact program. Instead, give an example of what really influenced you to pursue this dream.
Here’s an example:
- I’ve always loved reading and since I was a child, it’s been my dream to graduate from Oxford University and contribute to the world of literary analysis. That’s why I spent the past year volunteering at my local writers’ society and giving constructive feedback during workshops and book discussions.
- It wasn’t until I failed my first essay assignment in secondary school that I realized the depth that lies beneath each sentence in a given text. I began to delve into the rich layers of literary texts and the intricacies of literary analysis became my passion. Although initially challenging, the depth of understanding that this field offers about human emotions, cultural contexts, and narrative structures enthralled me. I found myself questioning the narrative structures and character motivations that I had previously taken for granted, and I was eager to understand how the subtle and often overlooked elements within a text could have a profound impact on its overall interpretation. This need to fundamentally understand a given author’s work has stayed with me since and led me to pursue literary analysis as a postgraduate student.
An engaging body
The main part of your academic personal statement should detail your interests, experience, and knowledge, and how they make you suitable for the position.
This is where you should expand on your motivation and use the following tips:
- Why this university? Provide strong reasons for your choice, related to your future career or the institution’s reputation.
- Mention your relevant studies and experience. This includes projects, dissertations, essays, or work experience.
- Give evidence of key skills you have, such as research, critical thinking, communication, and time management, and explain how you can contribute to the department with them.
- Say what makes you unique as a candidate and provide an example.
- Explain who have been the main influences who put you on this path and why they’ve influenced you.
- Mention other relevant experiences, such as memberships in clubs related to the subject, awards you might have won, or impressive papers you’ve written.
- Talk about your career aspirations and how the program ties into your goal of achieving them.
Depending on the guidelines of the specific university, you could also divide your academic personal statement’s body with subheadings, such as:
- Academic background
- Research interests
- Methodological approaches
- Research experience
- Personal experience
- Extracurricular activities
- Relevant skills
- Career aspirations
A logical conclusion
Your academic personal statement needs a conclusion that ends on an enthusiastic note.
Make sure the conclusion reiterates the main points from the body of your text.
Your relevant accomplishments and desire to attend this specific program should be clear to any reader.
#6. Pay Attention to the Language
When writing the first draft of your academic personal statement, pay attention to the language and tone you’re using.
An academic personal statement is also a formal text, so your writing should reflect that. Colloquialisms aren’t appropriate, as they would take away from the well-mannered impression you want to give the admissions committee.
However, you also want your personal statement to be straightforward and avoid any complex jargon from your field of study.
For example, your opening sentence shouldn’t be overly complicated. You should communicate everything as clearly as possible, and be inclusive to those outside of your field of study since they might be on the admissions board that’s reading your academic personal statement.
Make sure that the tone throughout your text is positive and conveys your enthusiasm for the program. Your academic personal statement should show the admissions committee that you really want to be there, and why that’s beneficial to everyone involved.
#7. Proofread Your Statement
This step probably isn’t surprising to you but it’s worth paying attention to.
Your academic personal statement is a very formal document and it should be spotless.
So, make sure it adheres to academic writing conventions . For example, contractions like “I’m” instead of “I am” are informal, and should be avoided.
Mistakes like these are very common when writing about yourself, particularly when you’re used to describing yourself in informal environments.
Carefully proofread your academic personal statement, then run it through a grammar checker like Grammarly or Quillbot, then proofread it again.
The tiniest grammar mistake or typo could make the admissions board reject your application.
Academic Personal Statement Example
Ever since my first encounter with the enchanting worlds spun by Flaubert, Balzac, and Proust, my intellectual pursuits have gravitated toward French literature. With an undergraduate degree focused on French Language and Literature, I have been fortunate to explore my passions both theoretically and empirically, embedding them within broader themes of cultural theory and comparative literature. It is with great excitement that I apply for the postgraduate research position in the French Literature program at Kent University, with the aim of contributing novel scholarly perspectives to this captivating field.
Academic Background and Research Interests
During my undergraduate studies, I delved deeply into the realms of 19th-century Realism and Naturalism. My senior thesis, which examined the dialectics of morality and social structures in Balzac's "La Comédie Humaine," was not merely an academic exercise; it served as a crucible where my theoretical understandings were rigorously tested. This research experience intensified my interest in the complex interplay between literature and societal norms, a theme I am eager to further explore in my postgraduate work.
Methodological Approaches
My academic approach is fundamentally interdisciplinary. I strongly believe that literature should not be studied in a vacuum; rather, it should be contextualized within historical, sociological, and psychological paradigms. During a semester abroad in Paris, I took courses in cultural anthropology and French history, an enriching experience that complemented my literature-focused studies. This holistic approach will enable me to contribute a multifaceted perspective to the research endeavors at Kent University.
Previous Research and Scholarly Engagements
My scholarly activities have also extended beyond the classroom. Last summer, I participated in an international conference on French Literature and Post-Colonial Theory, presenting a paper on the depictions of colonial landscapes in Dumas' adventure novels. The opportunity to engage with academics from various disciplines provided me with fresh insights and underscored the importance of collaborative research. Further, I've had the honor of having a review article published in the Sheffield Journal of Contemporary Literary Explorations, where I critiqued a groundbreaking new translation of Verne's works.
Extracurricular Contributions and Skills
In addition to my academic achievements, I have sought to enrich my department’s intellectual community. I served as the editor of our departmental journal and organized a series of seminars featuring guest speakers from the worlds of academia and publishing. My strong organizational skills, combined with proficiency in both written and spoken French and English, make me a versatile candidate capable of adding value to the French Literature program’s broader objectives.
To summarize, my deep-rooted passion for French literature, fortified by rigorous academic training and interdisciplinary methodologies, makes me an ideal candidate for the postgraduate research position in your esteemed program. The prospect of contributing to academic discourse at Kent University is an opportunity I find deeply compelling. I am especially excited about the potential for collaborative research and interdisciplinary inquiries, which aligns perfectly with my academic philosophy. I am fully committed to leveraging my skills, experiences, and enthusiasm to make a substantive scholarly contribution to the study of French Literature. Thank you for considering my application; I am keenly looking forward to the possibility of furthering my academic journey in this vibrant intellectual community.
FAQs on Academic Personal Statements
If you’re wondering anything else about academic personal statements, check out the answers to the most frequently asked questions related to them here:
#1. How do you start a personal statement for an academic job?
Applying for an academic job is different from applying for a position as a student. First, you need to establish your qualifications and enthusiasm for the role immediately.
Start by explaining your current status, for example, as a postdoctoral researcher or an experienced member of the faculty, and specify the position you are applying for. Then follow up with your research interests or personal philosophy towards teaching.
You can add a personal anecdote or compelling fact that summarizes your academic journey so far, or your passion for the field. After that, your academic personal statement can go deeper into the qualifications from your academic CV and how you’re a great fit for the position.
#2. How do I introduce myself in an academic personal statement?
The introduction of your academic personal statement is the key to grabbing the attention of the admissions committee.
Start by stating the field or subject that interests you, and why. You can share a specific personal anecdote or observation that led you to this academic pursuit and set the stage for the detailed explanation in your main body.
The goal of your introduction is to give the reader a sense of who you are, what drives you, and why you would be a valuable addition to their department.
#3. Is an academic personal statement like an essay?
Yes, an academic personal statement can be considered a type of essay.
Both essays and academic personal statements are structured forms of writing that are meant to deliver a coherent argument and are divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion. They provide supporting evidence to prove the point and maintain a logical flow to guide the reader to the final conclusion.
However, essays tend to be objective and explore a specific topic or question in depth. Academic personal statements use similar techniques but they present the candidate’s qualifications, experiences, and aspirations in a way that’s meant to persuade the admissions committee.
#4. How long is an academic personal statement?
Typically, an academic personal statement is between 500 and 1000 words long.
The exact length of the text varies depending on the university and program you’re applying to. You should always check the specific requirements for your desired program, and stick to the guidelines you find.
However, if the university you’re applying to doesn’t specify a word count, you should aim for one to two pages.
#5. What do I avoid in an academic personal statement?
Since your personal statement is a crucial part of your academic application, it’s important to avoid any common mistakes.
Make sure the content of your academic personal statement isn’t too generic. Its goal is to give insight into you as an individual, beyond what can be read in your CV .
You should also avoid cramming too many points in your text. Your academic personal statement should follow a logical flow, and focus on the relevance of what you’re sharing about yourself and how it relates to the academic program you’re pursuing.
Key Takeaways
And that concludes our guide to writing an academic personal statement!
We hope you feel more confident when crafting your application for that academic program or faculty position you have your sights set on.
Now let’s recap what we talked about so far:
- Academic personal statements are very different from CV personal statements. While CV personal statements are brief paragraphs at the top of the page, an academic personal statement is an in-depth text that details why you’re interested in a given position, and what makes you a good candidate.
- The guidelines on academic personal statements vary according to the institution you’re applying to. Read the brief very carefully, and pay attention to what it says about word count and questions your personal statement should answer. Any mistakes here could result in rejection.
- There are differences between applying for a postgraduate program and applying for a faculty position. But in both cases, you should research the exact place you want to apply to and adjust your application accordingly to match the institution’s values.
- Always proofread your academic personal statement before sending it, even if you’re sure there are no errors.

To provide a safer experience, the best content and great communication, we use cookies. Learn how we use them for non-authenticated users.
For the latest COVID-19 news and information, visit Penn State's Coronavirus Information website .

Pre-Law Advising

You are here
How do i apply.
- What is LSAC?
- What is the application timeline?
- Should I take a gap year?
- When should I take the LSAT?
- How should I prepare for the LSAT?
- What is a personal statement?
- How many letters of recommendation do I need?
- How do I request my transcripts?
- What is a dean's certification?
- How do I select a law school?

Steps to Writing a Personal Statement
Many law school applicants, upon sitting down to write their personal statements, feel a lot of pressure to write a perfect personal statement in one draft, one session at the computer. Such pressure is often unhelpful—and can even be damaging—to the personal statement writing process. Take care to spend time in each stage of the writing process, before moving on to the next: brainstorm, freewrite, draft, edit, and proofread. Spending time on the earlier steps will save you time later—and possibly help you avoid the realization that your “finished” personal statement simply isn’t your strongest work, and you have to start over or, worse , submit it anyway because you don’t have time to start over.
Step 1: Brainstorm topics for your personal statement.
Step 2: Follow the freewriting rules and spend 10 – 15 minutes on 3 of your topics.
Step 3: Review what you have written and decide whether to use one of those topics or select another from your brainstorm list.
Step 4: Draft an outline of the personal statement.
Step 5: Begin to draft your personal statement. Remember:
Describe. Description is a strategy that tells how something looks, sounds, smells, feels, or tastes. Effective description creates a clear DOMINANT IMPRESSION built from specific details. Description can be objective, subjective, or both.
Narrate. Narration is a strategy for presenting information as a story, for telling "what happened." It is a pattern most often associated with fiction, but it shows up in all kinds of writing. When used in an essay, a report, or another academic genre, a narrative must support a point—not merely tell an interesting story for its own sake. It must also present events in some kind of sequence and include only pertinent detail. Sometimes narrative serves as the organizing principle for a whole text.
Consider the significance of the narrative. You need to make clear the ways in which any event you are writing about is significant for you now. Write a page or so about the meaning it has for you. How did it change or otherwise affect you? What aspects of your life now can you trace to that event? How might your life have been different if this event had not happened or had turned out differently? Why does this story matter to you?
Adapted from Richard Bullock’s The Norton Field Guide to Writing , 3rd edition.
Step 6: Proceed through the editing process including having at least one objective person review your draft.
Step 7: Finalize and proofread.
Katherine E. Garren, J.D. Pre-Law Adviser Division of Undergraduate Studies The Pennsylvania State University 101 Grange Building University Park, PA 16802 Email: [email protected]
Phone: 814-865-7576 Fax: 814-863-8913 Hours: 8am - 5pm (Mon-Fri, Eastern Time)
Make an Appointment
Join our Listserv

2024 How to Write a Medical School Personal Statement (11 Steps)
- By Med School Insiders
- December 2, 2023
- Medical Student , Pre-med
- Medical School Application , Personal Statement
Each piece of a med school application brings a unique set of anxiety-ridden challenges, but few equal that of the personal statement. A personal statement is much, much more than a narrative-version of your CV. Reiterating your grades and extracurriculars in complete sentences is not how to write a medical school personal statement.
A personal statement is an opportunity to tell your story. Why do you want to study medicine? What drives you? This is your chance to let an admissions committee know who you really are beyond your grades.
Of course, you’re studying to become a doctor, not a novelist, which means the idea of crafting your personal statement may seem daunting, to say the least.
In this guide, we’ll take a comprehensive, step-by-step look at how to write a medical school personal statement, including how to get started, everything you need to include, and common mistakes to avoid.
Article Sections
- Anatomy of Medical School Personal Statement
What Med School Admissions Committees Look For
How to get started.
- How to Write a Personal Statement
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Medical school personal statement examples, anatomy of a medical school personal statement.
A personal statement has a 5,300 character maximum, about 1.5 pages of single-spaced 12-point Times New Roman font. The challenge isn’t trying to fill in words; the challenge is selecting the key moments in your life that made you want to be a doctor and expressing them concisely.
A personal statement is made up of three parts:
Introduction
It’s essentially a short essay that uses your life experience to succinctly demonstrate why you’re the right person for the job. If someone’s making a movie about your life and the events that shaped your desire to become a doctor, what key moments do you want to highlight?
Your introduction must capture an admissions committee’s attention. Use the introduction to hook your readers. The first few sentences should entice them to read more.
There isn’t a perfect number of paragraphs or set structure. This is where you discuss the experiences that have shaped your personality, your desire to study medicine, and your dreams for the future.
This is the summary of your statement, and it should tie in directly to your introduction. Now is the time to emphasize why you want to be a physician and your future goals.
Learn more about the Anatomy of a Stellar Medical School Personal Statement .
Admissions committees need to know they’re accepting students who are ready to face the rigorous day-and-night grind of medical school. They have your CV and transcripts; now you need to demonstrate you have what it takes to succeed.
The personal statement is your chance to display your personality and highlight the experiences that shaped you. What drives you? What strengths and experiences will you bring to medical school? Why are you an asset?
The admissions committee isn’t looking for a list of your accomplishments. They want to know your story . Don’t tell the admissions committee you’re compassionate and driven; show them with tangible examples from your life.
So you’re a great listener. What’s a moment in your past that demonstrates this? If you care deeply about the wellbeing of others, what story from your life illustrates that passion?
1 | Read Real Personal Statement Examples
Right off the bat, it’s important to remember that you’re not alone—far from it. Every medical student who came before you has written personal statements, which means you have a wealth of examples to read and learn from.
Every personal statement is unique to the writer. Don’t expect to find a perfect blueprint you can copy off of, but reading several different personal statements will give you a sense of the themes, concepts, strategies, and stories that can help you find success.
If you know people in your own life who have successfully matriculated to med school, it’s a good idea to ask them if you can take a look at their personal statement. Med School Insiders compiled a database of personal statements donated by successful medical school applicants. Reading successful personal statements will give you an idea of what’s expected.
Reading bad personal statements can also give you an idea of what mistakes to avoid. Learn from our bad personal statement examples , which includes key insights into what you should do instead.
2 | Reflect on Past Experiences

Take this as an opportunity to reflect. Don’t think of it as brainstorming, and don’t worry about being creative just yet. Simply think back on key moments from your past.
Think of your personal statement like your superhero origin story. You may have excellent grades, abilities, and a natural aptitude for science, but why are you pursuing medicine? What moment or moments in your life revealed to you why you had to be a doctor?
Take Spider-Man. Yes, Peter Parker received his superpowers from a radioactive spider bite, but that’s not why he fights crime; Spider-Man fights crime so that what happened to his Uncle Ben never happens to anyone else. Bruce Wayne is incredibly smart, incredibly strong, and incredibly rich, but that’s not why he fights crime as Batman. Bruce Wayne became Batman so that no one else would lose their parents to a random act of violence like he did.
The truth is, a lot of superheroes have pretty similar motivations, and doctors have similar motivations, too. Your desire to become a doctor likely stems from a genuine intellectual interest in medicine, a desire to work closely with other humans, and a drive to help people and save lives. The other med school hopefuls you’re applying with have very similar motivations.
The key is digging deep and determining what you value most about becoming a doctor. Once you know that, think about the tangible experiences in your life that helped you realize those values.
Utilize our list of 25 medical school personal statement prompts as you ideate and reflect on your life to date.
3 | Choose Which Experiences/Traits to Highlight
Identify three to four personal strengths you are particularly proud of and want the admissions committee to know. Where did these strengths shine in your premedical years? What experiences helped you build on these strengths? This will make up the body of your personal statement.
Remember: writing a personal statement takes time—and lots of it. It will likely take several different attempts and drafts. After discussing your selected strengths, you may find that they don’t define you well enough or that there are better options. Don’t be discouraged. Give yourself plenty of time to reflect on and explore a variety of different strengths.
Don’t forget about the interview; the admissions committee will certainly ask you to further elaborate on the experiences outlined in your personal statement. Share personal stories that you want to be asked about and feel comfortable addressing.
Generally, personal statements involve experiences in the following categories:
- A passion for patient interaction
- Intellectual curiosity for medicine (academics, research, etc.)
- Dedication and discipline (medicine or another pursuit)
- Perseverance in the face of adversity
- Interpersonal and professional skills
How to Write a Medical School Personal Statement
4 | show, don’t tell.
If essays or storytelling aren’t necessarily your strong suit, think back to math class and those equations where the teacher made you show your work for the full grade. It’s not enough that you got the answer right; you had to show how you arrived at the answer.
Think of this in the same way. It’s great that you’re compassionate, but the admissions committee isn’t going to take you at your word. They want you to back up that claim with evidence. It is vital that you show the admissions committee you’re compassionate with concrete examples from your life that illustrate your journey to medicine.
It’s much more impactful to share a story that demonstrates specific qualities than it is to tell someone you have those qualities directly. Saying you are hardworking or resilient is not enough. You need to craft a story that allows the reader to infer those qualities about you.
5 | Leverage the Narrative-Based Approach

You are applying to medical school along with an immense number of other students with great grades, stellar qualifications, and impressive clinical hours. These are all key to your medical school application, but the best grades in the world won’t set you apart in the eyes of the admissions committee.
Your personal statement is a chance to stand out in a crowded field. Too many personal statements read like a CV but with full paragraphs, which quickly becomes monotonous.
Leverage a narrative-based approach so that the admissions committee is excited to learn more about you. Your entire application should illustrate your compelling journey toward becoming a doctor. Highlight how your experiences make you an asset who will contribute uniquely to the medical school.
It’s not enough to simply check off the boxes. The admissions committee wants to know your story.
Learn How to Develop a Cohesive Narrative for Medical School Applications .
6 | Create an Outline
After taking the time to reflect on the experiences and traits you want to include in your personal statement, create an outline to structure your approach .
You do not need to stick to it, but this is the general structure of most personal statements:
- Introduction (A strong hook to catch the reader’s attention—usually an anecdote or reflection that introduces the theme of your story. Hook the reader with the opening sentence.)
- Experience 1
- Experience 2
- Experience 3
- Conclusion (Tie your story back to the opening hook/theme. Summarize why you want to be a physician and what your future goals are.)
Remember, this is not a list of your accomplishments. The personal statement must read like a cohesive narrative, not a resume.
Establish a theme in the introduction that’s central to your desire to become a doctor. Each following paragraph will illustrate how your personal experiences have shaped that desire and prepared you for your journey. In the conclusion, gracefully tie back to your central theme or hook to turn the personal statement into a consistent, interconnected story.
7 | Force Yourself to Start Writing
It’s understandable and common to feel overwhelmed while writing a personal statement. In fact, if you don’t feel overwhelmed, it’s safe to say that you’re not taking this seriously enough.
Start with a theme, but don’t get stuck trying to come up with the perfect opening sentence. That comes later. Once you have a general outline, just start writing. See what happens, and—most importantly—be kind to yourself.
The first words you write won’t be perfect, but they will get you started. You should fully expect the first draft of your personal statement to be terrible. That’s okay. First drafts are never perfect.
Your first draft probably won’t look anything like your final essay. Put one foot in front of the other and just start writing. Get the ideas out and worry about editing later.
8 | Keep it Concise and Direct
In your subsequent drafts, focus on cutting down your words and being concise. It’s not your use of flowery language that will impress the admissions committee. Forget about extravagant word choices and convoluted sentence structure. You don’t have the space for poetic tangents anyway.
Use your words efficiently, and favor clear language over long, complicated words. It’s easy for readers to spot when you’re using a thesaurus, and it will only take away from your end message. Find the simplest way to say something.
For example:
Hard-working over Assiduous
Compassion over Magnanimity
Agree over Concur
Use tools like the Hemingway App to keep your language direct and concise.
9 | Take Some Time Away
Take time away from your drafts. Once you complete a draft, take a break, and let it sit. Go for a walk, watch some TV, or work on a completely different activity. After your break, come back to your personal statement with fresh eyes. You may find that the fantastic opening line you came up with isn’t so fantastic anymore, or that sentence you weren’t so sure about actually works really well.
Writing your personal statement will take time. Even if you feel extremely confident in your personal statement, take time away from it and come back.
10 | Refine, Review, and Edit

We recommend using editing apps like Grammarly and Hemingway Editor , but don’t rely on bots alone to catch possible mistakes.
Ask your friends and family for their first impressions on the content of your personal statement. Tell them to be brutally honest (because the admissions committee certainly will be.) Reach out to a mentor or people who have been through this process before.
Spelling or grammar mistakes indicate carelessness on your part and are an automatic red flag for admissions committees. Read over your work carefully, and ask others you trust to do the same.
The editing process is such a critical phase for your personal statement. Learn how to edit your personal statement to impress admissions committees.
11 | Invest in Essay Editing Services
Your medical school personal statement is arguably the most important piece of your application. While an excellent essay can lock-in your interview offer, a poorly-written personal statement can ruin your chances—even with stellar grades, impressive academic awards, and a notable list of extracurriculars.
Don’t risk your acceptance. Essay editing services can provide the help that friends, family, and mentors cannot.
Med School Insiders Personal Statement Editing Services includes careful analysis of content and tone as well as helpful insights into how you can improve your essay and impress admissions committees.

Avoid the following common personal statement mistakes .
- Don’t list your accomplishments or rehash your CV and extracurriculars.
- Don’t make spelling or grammar errors.
- Don’t overuse the word I. Doing so makes you more likely to state your accomplishments instead of telling a story.
- Don’t use flowery language or words you found in a thesaurus.
- Don’t explain to a physician what medicine is all about. Talk about yourself and your experiences; the admissions committee already understands medicine.
- Don’t state the obvious or use clichés. (Every applicant likes science and wants to help people.)
- Don’t lie or fabricate your personal stories.
- Don’t make excuses for poor grades or a low MCAT score.
- Don’t speak negatively about another physician or healthcare professional.
- Don’t plead for an interview or acceptance.
- Don’t edit your personal statement by yourself.
- Don’t procrastinate.
Learn more: 20 Personal Statement: Dos and Don’ts .

It’s important to read the personal statements of matriculated students. While you won’t be able to mimic someone else’s personal statement, you can still learn a lot from them, and reading different statements can spark ideas for your own essay.
We compiled a selection of real medical school personal statements from successful applicants. These statements are for reference purposes only and should not be plagiarized in any way. Plagiarism detection software is used when evaluating personal statements, and plagiarizing is grounds for an automatic disqualification.
Be sure to read the included feedback regarding the personal statements as well, as this will give you extra insight into what admissions committees are looking for.
Read Real Medical School Personal Statement Examples .
Medical School Personal Statement Editing
Don’t write your medical school personal statement alone—we can help. Med School Insiders offers a range of personal statement editing packages , from general editing to unlimited, in-depth editing with a physician who will be there to advise you every step of the way.
Learn more about our Comprehensive Medical School Admissions Packages . Our team of doctors has years of experience serving on admissions committees, so you’ll receive key insights from people who have been intimately involved with the selection process.
Next read: Guide to Understanding the Medical School Application Process
Med School Insiders

Am I Ready to Apply to Medical School?
Are you ready to apply to medical school? Applying before you’re ready is a costly mistake. Find out if you’re on the right track for acceptance this cycle.

2024 AACOMAS Application Guide for DO Schools
Use our AACOMAS application guide for an ideal DO school application timeline, what you need to include, mistakes to avoid, and frequently asked questions.

2024 TMDSAS Application Guide for Texas Medical Schools
Use our TMDSAS medical school application guide for key insight into the primary application process. We’ll outline an ideal application timeline, what you need to include, mistakes to avoid, and FAQs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Join the Insider Newsletter
Receive regular exclusive MSI content, news, and updates! No spam. One-click unsubscribe.
Customer Note Premed Preclinical Med Student Clinical Med Student
You have Successfully Subscribed!

Statement of Purpose
Ai generator.
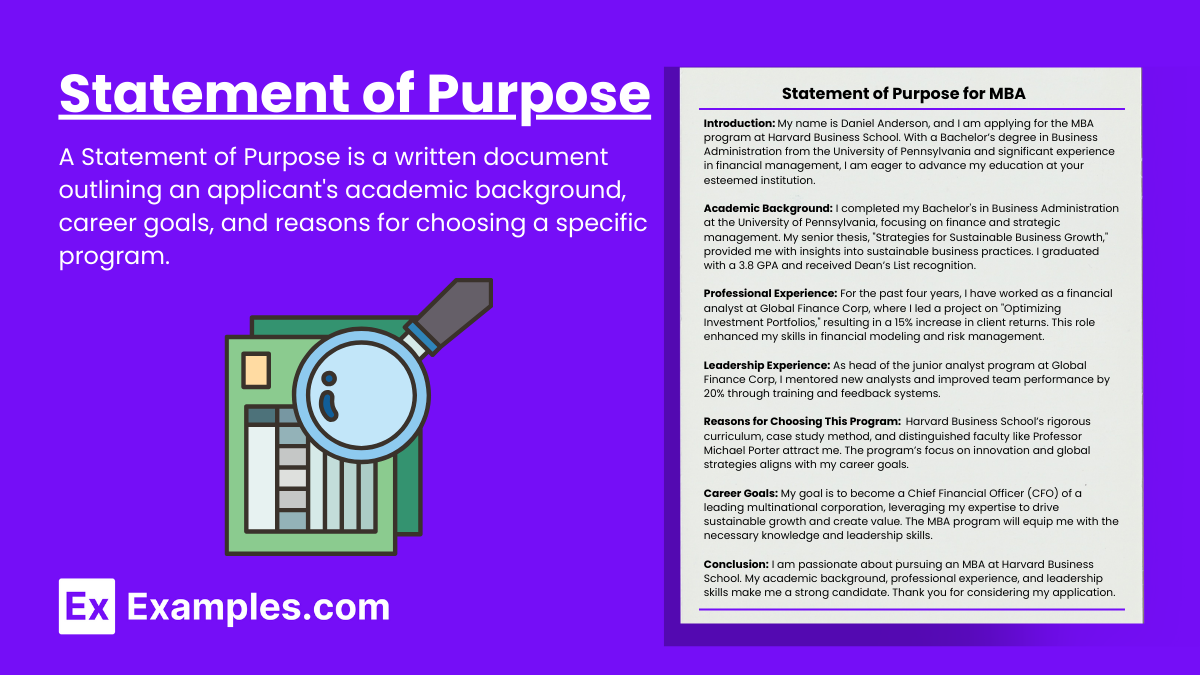
Statements are often used in expressing information about a certain subject. People rely on statement in informing a certain audience what they need to know about a specific topic. For example, vision statements inform people about the long term and short term goals and targets of a certain company or business .
- 33+ Statement Examples in Word
- 29+ Statement of Work Examples & Samples
Thus, it can be concluded that businesses usually count on statements in the dissemination of important information to their clients. A beneficiary simple statement , for instance, is usually given by a lender to a borrower, disclosing the remaining unpaid balance of a loan as of a certain period, including the interest rate.
What Is a Statement of Purpose?
A Statement of Purpose (SOP) is a written document typically required for university applications. It outlines an applicant’s academic background, professional experiences, career goals, and reasons for choosing a particular program. An effective SOP highlights the applicant’s strengths and unique qualities, demonstrating their fit for the desired program and their potential for success.
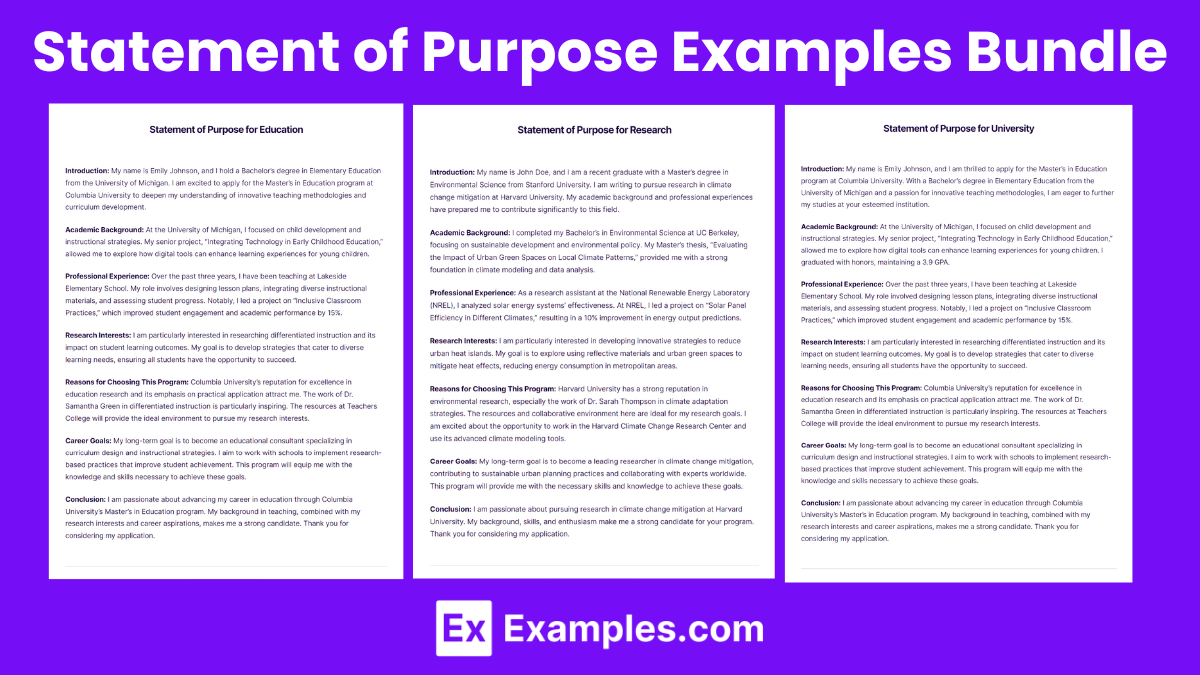
Download Statement of Purpose Bundle
Statement of Purpose Format
A Statement of Purpose (SOP) is a crucial document for academic or professional applications. It outlines your goals, motivations, and qualifications. Here’s a suggested format for writing an effective SOP:
1. Introduction
Opening Paragraph : Start with a strong opening sentence to grab attention. Introduce yourself, mention the program or position you are applying for, and state your main goal.
Example: “As a passionate computer scientist with a keen interest in artificial intelligence, I am excited to apply for the Master’s program in Computer Science at XYZ University.”
2. Academic Background
Educational History : Briefly describe your academic background, focusing on relevant degrees, courses, and projects.
Example: “I completed my Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science at ABC University, where I graduated with honors. My coursework included advanced algorithms, machine learning, and data structures.”
3. Professional Experience (if applicable)
Work Experience : Outline your professional experience, emphasizing roles, responsibilities, and achievements related to your field of study or career goals.
Example: “After graduation, I worked as a software engineer at TechCorp, where I developed machine learning models for predictive analytics, improving accuracy by 20%.”
4. Research Experience (if applicable)
Research Projects : Detail any research projects you have undertaken, including your role, the project’s scope , and the outcomes.
Example: “During my undergraduate studies, I conducted research on neural networks, resulting in a publication in the International Journal of Computer Science.”
5. Relevant Skills and Achievements
Skills and Certifications : Highlight key skills , certifications, and any awards or recognitions you have received.
Example: “I am proficient in Python, Java, and R, and have earned certifications in Data Science and AI from Coursera. I was also awarded the Dean’s Scholarship for academic excellence.”
6. Goals and Objectives
Short-term and Long-term Goals : Clearly state your short-term and long-term goals and how the program or position will help you achieve them.
Example: “In the short term, I aim to deepen my knowledge of AI through advanced coursework and research. Long-term, I aspire to lead AI projects in the healthcare sector to improve diagnostic accuracy.”
7. Why This Program/Institution
Fit with the Program/Institution : Explain why you chose this particular program or institution, highlighting specific faculty members, courses, facilities, or values that attract you.
Example: “I am particularly drawn to XYZ University’s AI research lab and the opportunity to work with Professor Smith, whose work on neural networks aligns with my interests.”
8. Conclusion
Closing Paragraph : Summarize your enthusiasm for the program and reiterate your readiness to contribute and grow.
Example: “I am confident that the Master’s program at XYZ University will provide me with the knowledge and skills to achieve my goals. I look forward to the opportunity to contribute to and learn from your esteemed institution.”
Statement of Purpose Examples
Statement of purpose for research, statement of purpose for education, statement of purpose for job, statement of purpose for university, statement of purpose for engineering.

More Examples for Statement of Purpose
- Statement of Purpose for Masters
- Statement of Purpose for Graduate School
- Statement of Purpose for Computer Science
- Statement of Purpose for Biology
- Statement of Purpose for Data Science
- Statement of Purpose for Mba
More Statement of Purpose Templates & Samples
Statement of purpose template.

Statement of Purpose Sample

Teaching Statement Example

Outline for Statement of Purpose

Professional Statement Sample

Statement of Purpose for Internship

Dos and Don’ts for Writing a Statement of Purpose
Writing a Statement of Purpose (SOP) is a critical part of the application process for academic programs and professional positions. Here are some essential dos and don’ts to guide you:
Dos for Writing a Statement of Purpose
- Keep It Focused : Stick to relevant experiences and information. Avoid unnecessary details.
- Clarity : Ensure each paragraph flows logically and is easy to understand.
- Tailor to the Program : Highlight why you are interested in the specific program or institution.
- Specific Examples : Use personal experiences and achievements to demonstrate your fit and passion.
- Showcase Accomplishments : Mention relevant academic, professional, and extracurricular achievements.
- Quantify When Possible : Use numbers or specifics to illustrate your accomplishments (e.g., “improved efficiency by 20%”).
- Short-term and Long-term Goals : Clearly state your academic and career objectives and how the program will help you achieve them.
- Connection : Show how the program’s offerings align with your goals.
- True Representation : Be genuine about your experiences and aspirations. Authenticity resonates more than embellishment.
- Personal Voice : Write in a natural, personal tone while maintaining professionalism.
- Check for Errors : Thoroughly proofread for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Seek Feedback : Have someone else review your SOP to catch mistakes you might have missed.
- Adhere to Guidelines : Follow any specific instructions regarding length, format, and content provided by the institution or program.
Don’ts for Writing a Statement of Purpose
- Avoid Clichés : Steer clear of overused phrases like “I have always wanted to…” or “Since I was a child…”.
- Be Specific : Provide concrete examples instead of vague generalizations.
- No Redundancy : Your SOP should complement your resume, not duplicate it. Focus on the narrative behind your achievements.
- Add Depth : Use the SOP to elaborate on key points and provide context.
- Be Honest : Misrepresenting your qualifications or experiences can lead to serious consequences.
- Authenticity Over Perfection : It’s better to present a genuine but less-than-perfect story than a fabricated one.
- Simplicity : While demonstrating your knowledge is important, avoid excessive use of technical terms that might confuse the reader.
- Clarity : Ensure your SOP is understandable to non-specialists as well.
- Holistic Approach : Include relevant extracurricular activities, volunteer work, and personal experiences that contribute to your suitability for the program.
- Personal Attributes : Highlight qualities like leadership, teamwork, and problem-solving skills.
- Goals Matter : Don’t just focus on past achievements; explain how the program will help you achieve your future goals.
- Forward-thinking : Show your vision for how you plan to use the knowledge and skills gained from the program.
- Customize for Each Application : Avoid using the same SOP for multiple applications. Tailor each one to the specific program and institution.
- Unique Aspects : Mention specific faculty members, courses, or resources that attract you to the program.
Statement of Purpose vs. Personal Statement
How to write a statement of purpose.
Writing a Statement of Purpose (SOP) involves several key steps to ensure it effectively communicates your motivations, qualifications, and aspirations. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Statement of Purpose
1. understand the purpose.
- Objective : Know that an SOP is meant to explain your academic and professional journey, your goals, and why you are applying to a specific program or position.
2. Research the Program or Position
- Specifics : Research the institution or company, the specific program or role, its culture, faculty members, courses, and any special projects or opportunities they offer.
3. Outline Your SOP
- Structure : Create an outline to organize your thoughts and ensure you cover all necessary sections.
4. Write the Introduction
- Example: “With a deep-seated passion for environmental science and sustainability, I am excited to apply for the Master’s program in Environmental Science at ABC University.”
5. Detail Your Academic Background
- Example: “I graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in Environmental Science from XYZ University, where I developed a strong foundation in ecological research and environmental policy.”
6. Discuss Professional Experience (if applicable)
- Example: “In my role as an environmental analyst at Green Solutions, I led a project that reduced carbon emissions by 15%, demonstrating my ability to apply theoretical knowledge to practical challenges.”
7. Highlight Research Experience (if applicable)
- Example: “During my undergraduate studies, I conducted research on renewable energy sources, which culminated in a published paper in the Journal of Environmental Studies.”
8. List Relevant Skills and Achievements
- Example: “I am proficient in GIS mapping, data analysis, and have completed certifications in sustainable development and climate change.”
9. State Your Goals and Objectives
- Example: “My short-term goal is to deepen my expertise in environmental science through advanced coursework and research. Long-term, I aspire to influence environmental policy and contribute to sustainable development initiatives globally.”
10. Explain Your Choice of Program/Institution
- Example: “I am particularly drawn to ABC University’s renowned environmental science department and the opportunity to work with Professor Jane Doe, whose research on sustainable agriculture aligns with my interests.”
11. Conclude with Enthusiasm
- Example: “I am confident that the Master’s program at ABC University will provide me with the knowledge and skills necessary to achieve my career aspirations. I look forward to the opportunity to contribute to and grow with your esteemed institution.”
12. Review and Revise
- Proofread : Carefully proofread your SOP for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Revise it to ensure it is coherent, concise, and compelling.
What is a Statement of Purpose (SOP)?
An SOP is a written document detailing an applicant’s academic background, professional goals, and reasons for choosing a specific program or institution.
Why is an SOP important?
It helps admissions committees assess your fit for the program, understand your motivations, and evaluate your potential for success.
What should be included in an SOP?
Include your academic background, professional experiences, career goals, reasons for applying, and why you chose the specific program and institution.
How long should an SOP be?
Typically, an SOP is 1-2 pages long, adhering to the word limit specified by the program or institution.
Can I use the same SOP for different applications?
It’s best to tailor each SOP to the specific program and institution, highlighting unique features and your fit for each one.
How should I structure my SOP?
Use a clear structure with sections for Introduction, Academic Background, Professional Experience, Reasons for Applying, Career Goals, and Conclusion.
What tone should I use in my SOP?
Maintain a formal yet engaging tone, demonstrating professionalism and genuine interest in the field of study.
How do I make my SOP stand out?
Be specific about your achievements and experiences, provide concrete examples, and show enthusiasm for the program.
Should I mention weaknesses in my SOP?
It’s generally better to focus on strengths and how you’ve overcome challenges, rather than highlighting weaknesses.
Can I include personal anecdotes in my SOP?
Yes, but ensure they are relevant to your academic and professional goals, and they contribute to your overall narrative.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

6 ways to encourage political discussion on college campuses
Associate professor of education, University of Virginia
Disclosure statement
Rachel Wahl has received funding from the Spencer Foundation and the National Academy of Education
University of Virginia provides funding as a member of The Conversation US.
View all partners
With deep divisions on college campuses – most recently over the conflict in the Gaza Strip and Israel – many observers fear that universities are not places where students can discuss divisive issues with people who disagree with them. In my research and teaching, I have seen that students in fact want to have difficult conversations across divides, but they need support from faculty and other facilitators in order for these discussions to go well.
Since early 2017, I have been observing events on college campuses in which students are brought together with peers with whom they disagree to talk about politics. In these sessions, facilitators provide students with guiding questions that help them to understand their peers’ political views.
I conducted follow-up interviews with students a few weeks afterward and, when possible, three years later.
My aim is to understand what happens in these conversations. I want to know: Who learns what from whom? Who feels satisfied or frustrated, and why? And what does this all portend for America’s democracy?
The conversations I observed have taught me that six practices help to support a better experience for all students.
1. Set norms and expectations
When people talk about setting norms for conversation, they usually assume it is an effort to mandate speech rules. But norm-setting accomplishes something better than rule-following: It allows students to become sensitive to their own and others’ hopes and fears for the conversation.
In my experience, opening the session with questions such as “What do you most hope will happen in this conversation?” “What worries you most about the conversation?” “What are you willing to give to it?” and “What do you hope to get from it?” can show students that they already share more than they anticipate.
Moreover, this discussion leads naturally into the question of “How can we interact in a way that is most likely to realize our aims?” Students typically volunteer their own guidelines, such as assuming good faith, objecting to a person’s idea rather than attacking the person, honestly conveying when and why they feel hurt, and listening generously.
2. Allow students to tell their personal stories
Beginning with students’ personal stories lowers the barriers to entry, so that students who are not experts on politics can contribute. It allows students to feel heard about their direct experience. And it allows for what I have found to be the most profound outcome of dialogue: the shifts in how students feel about each other.
For example, consider the “ Can We Talk ” campus dialogue series, which brings together ideologically diverse students for two-hour sessions in which facilitators provide a series of questions for students to ask each other. The sessions began with questions such as, “How were politics discussed in the home in which you were raised?” and “What is your earliest political memory?” before moving on to questions about students’ substantive views on relevant issues.
The focus of these sessions, which I observed in the 2017-2018 academic year at colleges throughout Pennsylvania and New Jersey, is on cultivating students’ understanding of each other’s views and how they came to be.

If the dialogue is intended to focus on a specific issue, such as gun control , abortion or the war in Israel and Gaza , questions can be geared accordingly, such as “When did you first learn about this issue?” “How did it affect you at the time?” or “What about this issue draws you to this conversation?”
3. Encourage curiosity
Students are often afraid that they will end up validating views they oppose unless they try to discredit those views. But in follow-up interviews I conducted three years after their participation in a dialogue session, I found that those students who did eventually change their political views were prompted to do so through sincere and nonthreatening questions. “I remember one girl asked me, ‘If you say you believe this, then why did you vote like that?’ I’ve been asking myself that question ever since,” admitted one student, whose politics changed considerably in the years between our first and second interviews. It mattered most that she felt questioned, not attacked.
Questions can be encouraged throughout a conversation by reserving specific time for them in each round, as well as through directions such as “Think of one question you have always wanted to ask someone who thinks differently than you about this issue. Ask it now.”
4. Dig into disagreement
One risk of emphasizing personal experience at the start is that students hesitate to dig into their disagreements. They want to be supportive, and it’s hard to argue with personal experience. In my research, though, I found that students ended up with the deepest respect for each other when they gained understanding of the nature of their disagreements.
Clarifying what is at stake in their differences allowed students to see that their opposition was not caused by ignorance, malice or madness on the other side, but legitimate contrasts in views of what is good and possible.
After students have shared their views on issues and asked each other curiosity-oriented questions, they can be directed to ask each other questions such as “What is at the root of our disagreement?” and “What really matters to me, and to you, and is it the same thing? To the extent that it is not, why not?”

5. Collaborate on next steps
Students tend to feel most satisfied when they can work toward a more concrete aim. Most ambitiously, this can involve real cooperative projects.
For example, the Sorenson Institute , a political leadership institute at the University of Virginia, convenes dialogues that conclude with students putting together a proposal for the Virginia state Legislature on a specific topic such as gun control.
Even one-off conversations can conclude with what students might do differently on social media, on their campuses and in their families. When I followed up with them, I learned that many students had enacted these changes and found that people changed their own behavior in response. One student found that her uncle started reading and thinking about the articles she would send him. Another student discovered that peers in her political science class who had been dismissive of her in the past became respectful when she expressed her views and seemed to attend to them more sincerely.
Some students will flourish in these conversations, while others will struggle. In my research, I found that students whose rights are threatened by policy proposals of the other side understandably experience the most difficulty. However, these same students’ experiences can be improved by debriefing with a trusted mentor afterward.
For example, one student who identifies as queer felt shaken after a discussion with peers who opposed her marriage rights. But meeting with a professor afterward helped her to feel empowered by the conversation, equipped with new knowledge to help her fight for a more just society.
Listening to protest
Dialogue can deepen divides when it is presented as the only appropriate form of political communication, thereby silencing people who do not participate in these conversations. Students should be encouraged to also listen to messages conveyed through other means. For example, they can study protest movements – including ongoing, contemporary movements – and read the texts posted by activists who organize them.
It is important to convey to students that dialogue alone cannot solve all of what ails contemporary democracy. Protest, boycott and other forms of collective action matter, too.
- US higher education
- College students
- Political divide
- Higher ed attainment
- Political dialogue

Research Fellow

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Related: Personal Statement vs. Statement of Purpose: Key Differences How to write a good personal statement Follow these steps to a good personal statement: 1. Craft a strong opening Begin with an opening sentence that interests your audience and makes them want to read more. Use your words to introduce the main idea of your response.
Strategy 1: Open with a concrete scene. An effective way to catch the reader's attention is to set up a scene that illustrates something about your character and interests. If you're stuck, try thinking about: A personal experience that changed your perspective. A story from your family's history.
Insert a quote from a well-known person. Challenge the reader with a common misconception. Use an anecdote, which is a short story that can be true or imaginary. Credibility is crucial when writing a personal statement as part of your college application process. If you choose a statistic, quote, or misconception for your hook, make sure it ...
Applying to college can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to writing a personal statement. This essay not only showcases your writing skills but also highlights your unique personality, achievements, and aspirations. While it may seem unnecessary, tedious, time-consuming, and just another tick-the-box, know that as each application is processed, grades are just one of the criteria ...
Tip 4: Connect the Story to Why You're Applying. Don't forget that the purpose of your personal statement isn't simply to tell the admissions committee who you are. That's an important part of it, of course, but your ultimate goal is to convince them to choose you as a candidate.
In a great personal statement, we should be able to get a sense of what fulfills, motivates, or excites the author. These can be things like humor, beauty, community, and autonomy, just to name a few. So when you read back through your essay, you should be able to detect at least 4-5 different values throughout.
Address the elephant in the room (if there is one). Maybe your grades weren't great in core courses, or perhaps you've never worked in the field you're applying to. Make sure to address the ...
Use your closing couple of lines to summarise the most important points in your statement. 9. Check your writing thoroughly and get someone else to check it, too. 10. Give your brain a rest by forgetting about your personal statement for a while before going back to review it one last time with fresh eyes.
A strong conclusion is clear, concise, and leaves a lasting impression. Use these three steps: Summarize the main points of your statement. For example, "My experience volunteering for the school newspaper, along with my communication skills and enthusiasm for writing, make me an ideal student for your university."
The Free Guide to Writing the Personal Statement. Kick things off with the two greatest brainstorming exercises ever, learn about options for structuring a personal statement + example outlines, check out some amazing example personal statements, and get on your way to writing your own killer personal statement for university applications.
1. Keep it personal. Although there are certain rules to be followed when writing a personal statement, it is important not to lose your own voice. The admissions committee wants to get to know you as a person and not just as a student. 2. Avoid unnecessarily complicated language.
Instead, choose what will best tell your story. Try to present events in the order they occurred. It'll be easier for the reader to understand. Remember that the events in your life should naturally lead you to wanting to pursue graduate school. Have someone else read your personal statement to give you feedback.
1. Expand your statement if it's too short. Your first draft can be as long or short as you need it to be, but many institutions and organizations have a word count or page count limits on personal statements. If your statement is not long enough, you have space to add more supporting information. [6]
While deciding to embark on the path to graduate school is an exciting first step toward advancing your career, the application process can sometimes feel daunting and confusing.. One major part of the application that most schools require is a personal statement. Writing a personal statement can be an arduous task: After all, most people don't necessarily enjoy writing about themselves, let ...
Academic Vs CV Personal Statement 7 Steps to Write an Academic Personal Statement #1. Read the Brief (Carefully!) #2. Research the Program #3. Plan Your Statement #4. Look at Example Statements #5. Structure the Contents #6. Pay Attention to the Language #7.
Step 1: Brainstorm topics for your personal statement. Step 2: Follow the freewriting rules and spend 10 - 15 minutes on 3 of your topics. Step 3: Review what you have written and decide whether to use one of those topics or select another from your brainstorm list. Step 4: Draft an outline of the personal statement.
Just start by showing your enthusiasm for the subject, showcasing your knowledge and understanding, and sharing your ambitions of what you want to achieve. Avoid cliches! Remember, this opening part is simply about introducing yourself, so let the admissions tutor reading your personal statement get to know you. Keep it relevant and simple.
20 Steps to Writing a Personal Statement Author: lawhite Created Date: 1/24/2011 5:41:41 AM ...
2024 How to Write a Medical School Personal Statement (11 Steps) Each piece of a med school application brings a unique set of anxiety-ridden challenges, but few equal that of the personal statement. A personal statement is much, much more than a narrative-version of your CV. Reiterating your grades and extracurriculars in complete sentences is ...
Statement of Purpose Format. A Statement of Purpose (SOP) is a crucial document for academic or professional applications. It outlines your goals, motivations, and qualifications. Here's a suggested format for writing an effective SOP: 1. Introduction. Opening Paragraph: Start with a strong opening sentence to grab attention.
Allowing students to tell their personal stories can enrich the discussion. Morsa Images via Getty Images. Students gain a better appreciation for opposing views when they probe what matters to ...
Our team uses an eligibility criteria on when the checkmark is given to ensure we maintain the integrity of the platform. Your account must meet the following criteria to receive or retain the blue checkmark: Complete: Your account must have a display name and profile photo. Active use: Your account must be active in the past 30 days to ...