Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Research Highlight
- Published: 26 July 2021
SILICON PHOTONICS

Co-packaged transceivers speed up
- Christiana Varnava 1
Nature Electronics volume 4 , page 455 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
285 Accesses
Metrics details
- Engineering
- Optical techniques
In Proc. 2021 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology (in the press); https://go.nature.com/3hL2gsH
Integrated optical input–output technologies are promising for high-speed communications because of their scaling and bandwidth advantages compared with electrical alternatives. Optical transceivers based on microring modulators can, for example, achieve high-throughput transmission using wavelength-division multiplexing. However, such transceivers have so far only demonstrated capacity up to 50 Gbit s –1 in the O-band (1,260 nm to 1,360 nm). Jahnavi Sharma, Hao Li and colleagues at Intel Corporation now show that a hybrid integrated transceiver based on photonic and electronic circuits can achieve a capacity up to 112 Gbit s –1 in the O-band with a pulse-amplitude modulation four-level scheme.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
111,21 € per year
only 9,27 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nature Electronics https://www.nature.com/natelectron
Christiana Varnava
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christiana Varnava .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Varnava, C. Co-packaged transceivers speed up. Nat Electron 4 , 455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00628-3
Download citation
Published : 26 July 2021
Issue Date : July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00628-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
A Comprehensive Analysis in Recent Advances in 3D VLSI Floorplan Representations
- Conference paper
- First Online: 01 December 2022
- Cite this conference paper

- Rohin Gupta 41 &
- Sandeep Singh Gill 42
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering ((LNEE,volume 962))
378 Accesses
Floorplan is one of the most critical steps of the physical design of VLSI Design flow. Decreasing size, interconnects, power consumption, and chip leakage are always on the top priority list for consumers and researchers. This article presents the latest advancements in one of the hot research topics in VLSI Physical Design: 3D Floorplanning. A lot of research articles have been studied for this article, and only major research points from some chosen relevant to 3D architecture articles have been incorporated in this paper. The 3D VLSI floorplan field is quite vast than the 2D VLSI floorplan and is comparatively less explored. This article reviews various aspects of floorplanning that cover floorplanning based on volume, tiers, vias, TSVs, and other representations of 3D VLSI Floorplan. These techniques, when applied as algorithms, help in simplifying the problem. These algorithms help optimize results that increase the chip’s overall performance. Some of the central representations have been incorporated in Sect. 5 . Conclusion with research gap and future scope is described in the end.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

VLSI Floorplan Area Optimisation Technique

A new representation in 3D VLSI floorplan: 3D O-Tree

G-NSVF: A Greedy Algorithm for Non-Slicing VLSI Floorplanning
Bernstein, K., Andry, P., Cann, J., Emma, P., Greenberg, D., Haensch, W., Ignatowski, M., Koester, S., Magerlein, J., Puri, R., & Young, A. (2007). Interconnects in the third dimension: Design challenges for 3D ICs. In 44th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference (pp. 562–567). San Diego, CA, USA.
Google Scholar
Sheng, S., Chandrakasan, A., & Brodersen, R. W. (1992). A portable multimedia terminal. IEEE Communications Magazine, 30 (12), 64–75.
Article Google Scholar
Salewski, S., & Barke, E. (2002). An upper bound for 3D slicing floorplans. In Proceedings of ASP-DAC/VLSI Design 2002. 7th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference and 15h International Conference on VLSI Design (pp. 567–572). India.
Yuh, P.-H., Yang, C.-L., Chang, Y.-W., & Chen, H.-L. (2004). Temporal floorplanning using 3D-subTCG. In ASP-DAC 2004: Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (pp. 725–730). Yokohama, Japan.
Yuh, P.-H., Yang, C.-L., Chang, Y.-W., & Chen, H.-L. (2004). Temporal floorplanning using the T-tree formulation. In: IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design, 2004. ICCAD-2004 (pp. 300–305). San Jose, CA, USA.
Cong, J., Wei, J., & Zhang, Y. (2004). A thermal-driven floorplanning algorithm for 3D ICs. In IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design , ICCAD-2004 (pp. 306–313). San Jose, CA, USA.
Ma, Y., Hong, X., Dong, S., & Cheng, C. K. (2005). 3D CBL: An efficient algorithm for general 3D packing problems. In: 48th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (pp. 1079–1082). Covington, KY, USA.
Hong, X., Huang, G., Cai, Y., Gu, J., Dong, S., Cheng, C.-K., & Gu, J. (2000). Corner block list: an effective and efficient topological representation of non-slicing floorplan. In IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design. ICCAD 2000 . IEEE/ACM Digest of Technical Papers (pp. 8–12). San Jose, CA, USA
Cheng, L., Deng, L., & Wong, M. D. F. (2005). Floorplanning for 3-D VLSI design. In Proceedings of the ASP-DAC 2005. Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (pp. 405–411). Shanghai, China.
Dong, S., Wang, R., Guo, F., Yuan, J., & Hong, X. (2006). Floorplanning by a revised 3-D corner block list with sub-C+-tree. In 9th Joint International Conference on Information Sciences (JCIS-06) (pp. 429–432). Atlantis Press.
Wong, E., Minz, J., & Lim, S. K. (2006). Multi-objective module placement for 3-D system-on-package. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 14 (5), 553–557.
Zhang, L., Dong, S., Hong, X., & Ma, Y. (2007). A fast 3D-BSG algorithm for 3D packing problem. In 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (pp. 2044–2047). New Orleans, LA, USA.
Li, Z., Hong, X., Zhou, Q., Zeng, S., Bian, J., Yu, W., Yang, H. H., Pitchumani, V., & Cheng, C.-K. (2007). Efficient thermal via planning approach and its application in 3-D floorplanning. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 26 (4), 645–658.
Falkenstern, P., Xie, Y., Chang, Y.-W., & Wang, Y.: Three-dimensional integrated circuits (3D IC) floorplan and power/ground network co-synthesis. In 2010 15th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC) (pp. 169–174). Taipei, Taiwan.
Frantz, F., Labrak, L., & O’Connor, I. (2011). 3D-IC floorplanning: Applying meta-optimization to improve performance. In 2011 IEEE/IFIP 19th International Conference on VLSI and System-on-Chip (pp. 404–409). Hong Kong, China.
Nain, R. K., & Chrzanowska-Jeske, M. (2011). Fast placement-aware 3-D floorplanning using vertical constraints on sequence pairs. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 19 (9), 1667–1650.
Li, C., Mak, W., & Wang, T. (2013). Fast fixed-outline 3-D IC floorplanning with TSV co-placement. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 21 (3), 523–532.
Wen, C., Chen, Y., & Ruan, S. (2013). Cluster-based thermal-aware 3D-floorplanning technique with post-floorplan TTSV insertion at via-channels. In Fifth Asia Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ASQED 2013) (pp. 200–207). Penang, Malaysia.
Khan, A. K., Vatsa, R., Roy, S., & Das, B. (2014). A new efficient topological structure for floorplanning in 3D VLSI physical design. In 2014 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference (IACC) (pp. 696–701). Gurgaon, India.
Chen, Y., & Ruan, S. (2015). A cluster-based reliability- and thermal-aware 3D floorplanning using redundant STSVs. In 2015 IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC) (pp. 349–354). Daejeon, Korea (South).
Quiring, A., Olbrich, M., & Barke, E. (2015). Fast global interconnnect driven 3D floorplanning. In 2015 IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC) (pp. 313–318). Daejeon, Korea (South).
Song, T., Panth, S., Chae, Y.-J., & Lim, S.K. (2015) Three-tier 3D ICs for more power reduction: Strategies in CAD, design, and bonding selection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD ’15) (pp. 752–757). Austin, TX, USA: IEEE Press.
Chan, W. J., Kahng, A. B., & Li, J. (2016). Revisiting 3DIC benefit with multiple tiers. In Proceedings of ASP-DAC/VLSI Design 2002. 2016 ACM/IEEE International Workshop on System Level Interconnect Prediction (SLIP) (pp. 1–8). Austin, TX, USA.
Wang, R., Young, E. F. Y., & Cheng, C. (2009). Representing topological structures for 3-D floorplanning. In 2009 International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems (pp. 1098–1102). Milpitas, CA, USA.
Alpert, C. J. (1998). The ISPD98 circuit benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 1998 International Symposium on Physical Design (ISPD ’98) (pp. 80–85). NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery.
Tsai, M., Wang, T., & Hwang, T. (2011). Through-silicon via planning in 3-D floorplanning. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 19 (8), 1448–1457.
Li, J. X., Liu, W., Du, H., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., & Yang, H. (2013). Whitespace-aware TSV arrangement in 3D clock tree synthesis. In 2013 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI (ISVLSI) (pp. 115–120). Natal, Brazil.
Wilkerson, P., Raman, A., & Turowski, M. (2004). Fast, automated thermal simulation of three-dimensional integrated circuits. In The Ninth Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems (pp. 706–713). Las Vegas, NV, USA.
Cong, J., Luo, G., Wei, J., & Zhang, Y. (2007). Thermal-aware 3D IC placement via transformation. In 2007 Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (pp. 780–785). Yokohama, Japan.
Ma, Y., Dong, S., Hong, X., Cai, Y., Cheng, C.-K., & Gu, J. (2001). VLSI floorplanning with boundary constraints based on corner block list. In Proceedings of the ASP-DAC 2001. Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (pp. 509–514). Yokohama, Japan.
Young, F. Y., & Wong, D. F. (1999). Slicing floorplans with boundary constraint. In Proceedings of the ASP-DAC ’99 Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (pp. 17–20). Hong Kong, China.
Nakatake, S., Fujiyoshi, K., Murata, H., & Kajitani, Y. (1996). Module placement on BSG-structure and IC layout applications. In Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Aided Design (pp. 484–491). San Jose, CA, USA.
Chang, Y.-C., Chang, Y.-W., Wu, G.-M., & Wu, S.-W. (2000). B*-trees: a new representation for non-slicing floorplans. In Proceedings 37th Design Automation Conference (pp. 458–463). Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Download references
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by I.K. Gujral Punjab Technical University, Kapurthala, India. The authors would like to extend their gratitude to the university for all the support.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Research Scholar, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, I.K. Gujral Punjab Technical University, Kapurthala, Punjab, 144603, India
Rohin Gupta
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, National Institute of Technical Teachers Training and Research, Chandigarh, 160019, India
Sandeep Singh Gill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rohin Gupta .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Electronics Engineering, Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, Surat, Gujarat, India
Anand D. Darji
Deepak Joshi
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Department of Computer Science, Edge Hill University, Ormskirk, Lancashire, UK
Ray Sheriff
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Gupta, R., Gill, S.S. (2023). A Comprehensive Analysis in Recent Advances in 3D VLSI Floorplan Representations. In: Darji, A.D., Joshi, D., Joshi, A., Sheriff, R. (eds) Advances in VLSI and Embedded Systems. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 962. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6780-1_20
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-6780-1_20
Published : 01 December 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-6779-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-6780-1
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Search form

Robust Low Power VLSI
Search This Site
- Body Sensor Networks
- Energy Efficient Circuit Design
- Energy Harvesting and Power Management Unit
- System-on-Chip
- Design Automation
- Wake-Up Receiver
- Chip Gallery
- Photo Gallery
The Robust Low Power VLSI Group, led by Professor Ben Calhoun, investigates research topics related to modern VLSI design. Among the many challenges facing circuit designers in deep sub-micron technologies, power and variation are perhaps the most critical. Our group's focus is to confront these problems in a range of applications and different regions of the design space. Our specific research interests include low power digital circuit design, sub-threshold digital circuits, SRAM design for end-of-the-roadmap silicon, variation tolerant circuit design methodologies, and medical applications for low energy electronics. The group is engaged in projects related to each of these topics.
Featured Projects
View more projects
| In this project, a low power wireless ECG sensor is implemented using commercial off the shelf (COTS) components. The resulting system can acquire and process ECG data and send it wirelessly to a basestation such as a handheld device. The picture shows the ECG sensor in operation, with the PDA plotting the real time ECG signal. |
This work explores reconfigurable circuits operating at low voltages. While the existing FPGAs are too high power to meet the requirements of IoT applications, we designed and optimized new circuit typologies of CLBs and global interconnect in near/sun-threshold region. We also developed custom tool flow to support full chip configuration. A 90nm chip implements the FPGA with 1134 LUTs, which is 2.7X smaller, 14X faster, and 4.7X less energy than a sub-threshold FPGA using conventional circuits and 22X less energy than an equivalent FPGA at full VDD. We are currently working towards dynamic voltage scaling and measurements using real-life applications.
| The artificial seal whisker project is a joint effort with the University of Virginia’s Mechanical Engineering Department and the University of California Santa Cruz to detect and track underwater wakes using an array of bio-inspired sensors. Previous biological work found harbor seals are able to track wakes using only their whiskers. In this project, the seal whisker team is focused on understanding how seals sense wakes using their whiskers, designing a capacitance based whisker-like sensor, and designing the electrical backend printed circuit board for sensing, storing, and transmitting data. The biologically inspired sensor’s design is based on seal whiskers and previous effort in the field involving spider hairs and fish lateral lines. All components will be integrated in the Wake Information Detection and Tracking System (WIDTS) to be carried by a trained harbor seal for testing. |
Featured Chips
View more chips in the Chip Gallery

Emerging VLSI Trends in 2023
- by Maven Silicon
- July 19, 2023
- 3 minutes read
Looking for the latest VLSI trends and VLSI jobs in 2023? Maven Silicon, a leading VLSI training institute, is here to guide you. VLSI is revolutionizing industries with its ability to integrate millions of transistors onto a single chip. In this blog post, we’ll explore the emerging VLSI trends in 2023 that are shaping the future and highlight the exciting job openings in this field. Discover the benefits of pursuing a career in VLSI and how Maven Silicon can help you kick-start your journey.
VLSI Application & Trends in 2023
The applications of VLSI span across various industries, including telecommunications, automotive, healthcare, and artificial intelligence. As we move into 2023, several VLSI trends are making waves:
AI-driven VLSI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has merged with VLSI, opening up endless possibilities. AI-driven VLSI solutions have gained significant traction in industries like autonomous vehicles, robotics, smart homes, and beyond. The integration of AI algorithms directly into VLSI chips allows for the real-time processing of massive amounts of data, leading to intelligent decision-making and unprecedented levels of efficiency. This trend empowers autonomous vehicles to analyze complex surroundings, robots to navigate dynamically changing environments, and smart homes to adapt to residents’ preferences seamlessly. The synergy between AI and VLSI has propelled us toward a new era of intelligent and responsive technologies.
IoT and VLSI
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution is in full swing, and VLSI plays a pivotal role in shaping this interconnected ecosystem. Emerging trends in VLSI focus on designing chips optimized for IoT-enabled devices, ensuring efficient data communication, low power consumption, and enhanced security. These specialized VLSI chips enable IoT devices to communicate seamlessly over the internet, exchanging data with other devices and cloud services. Moreover, with advancements in low-power design techniques, IoT devices can operate for extended periods on battery power, making them more practical and environmentally friendly. VLSI’s contribution to IoT is driving the proliferation of smart homes, smart cities, and industrial automation, transforming the way we interact with our surroundings.
Edge Computing and VLSI
Edge computing has emerged as a game-changer in handling real-time data processing and analysis. VLSI’s role in this trend is crucial, as it enables the development of high-performance, energy-efficient chips tailored for edge devices. By processing data locally at the edge, these VLSI chips significantly reduce latency and response times, making them ideal for applications that demand immediate results. Edge devices, such as sensors and cameras, benefit from low-power VLSI solutions that allow for prolonged operation without compromising performance. The combination of edge computing and VLSI has unlocked a new realm of possibilities, from responsive AI applications to smart infrastructure like traffic management and environmental monitoring.
Benefits of VLSI
Exciting and challenging work.
The field of VLSI indeed provides a dynamic and intellectually stimulating work environment for engineers and professionals. As a VLSI engineer, you get the opportunity to be at the forefront of designing complex integrated circuits that power a wide range of electronic devices, from smartphones and computers to IoT devices and automotive electronics.
Also read: Why VLSI is Used?
Lucrative Job Opportunities
The demand for VLSI professionals is on the rise, making it a highly sought-after field with numerous job opportunities across various industries. As technology continues to advance and electronic devices become an integral part of our lives, the need for skilled VLSI engineers has grown significantly.
Positions such as VLSI Design Engineer, Verification Engineer, and Physical Design Engineer are in high demand. VLSI Design Engineers are responsible for designing and architecting integrated circuits, while Verification Engineers focus on validating and testing chip designs. Physical Design Engineers, on the other hand, play a crucial role in implementing the circuit layout to optimize performance and power consumption.
Also read: Skills required to become a VLSI engineer?
Job Openings
If you’re eager to embark on a VLSI career, numerous job openings await you. Maven Silicon is renowned for its VLSI training with 100% placement assistance. Explore exciting roles like VLSI Design Engineer, Verification Engineer, Physical Design Engineer, FPGA Engineer, and Analog/Mixed-Signal Design Engineer.
Also read: Salary of VLSI Engineers in India
As we step into 2023, the world of VLSI presents abundant opportunities. Stay updated with the latest VLSI trends, leverage the benefits of this field, and secure a rewarding career in VLSI. Maven Silicon can equip you with the necessary skills to excel in the ever-evolving VLSI landscape. Start your journey towards a successful VLSI career today with our job-oriented courses .
Share This Post:
[…] Discover the emerging VLSI trends in 2023, from groundbreaking innovations to cutting-edge advancements. Stay ahead in the world of technology. […]
Comments are closed.
Related Post
VLSI Design: Future of Wireless Communication
Growth of Semiconductor Industry in 2024
ASIC Verification Best Practices
Refer your friends to Maven, you'll get 20% off once they enroll in out course.
Your friends name
Your friends email id
Have Doubts?
Why should i do vlsi training.
All the Integrated Chips we use in mobiles, TVs, computers, satellites, and automobiles, etc. are designed with VLSI technology. Hence, there is a huge scope and growth in the VLSI Industry and it is full of job opportunities. Since there is a huge gap between what the college education offers and the industry expectation, it is recommended to go for the VLSI training which bridges that gap and gives you a great hands-on experience.
What is chip designing?
Steps involved in Chip design Chip’s architecture: Create circuit designs, Run simulations, Supervise layout, Tape out the chip to the foundry and Evaluate the prototype once the chip comes back from the laboratory. Chip designers work to make faster, cheaper and more innovative chips that can automate parts or the entire function of electronic devices. A chip design engineer’s job involves architecture, logic design, circuit design and physical design of the chip, testing, and verification of the final product.
Is VLSI a good career?
VLSI is a very good domain to build a career with a huge number of opportunities. There is a demand for chips in every sector, be it automobiles, consumer electronics or high-end servers. You should have good command on Verilog, SystemVerilog, and UVM to start your career as VLSI Design or VLSI Verification Engineer
What is the eligibility for VLSI Chip Designing Courses?
The undergraduates, graduates, or postgraduates from below streams can take up VLSI Chip Design Course and make a career in VLSI Industry. BE/BTech in EEE/ECE/TE or ME/MTech/MS in Electronics/MSc Electronics
To join the industry as a VLSI verification engineer, you must have hands-on experience of below topics: SystemVerilog, Universal Verification Methodologies UVM, Assertion based Verification SVA
Maven Silicon provides the best quality VLSI training through a variety of design and verification courses to suit your need and demand. We offer online VLSI courses, Job-oriented fulltime and Blended VLSI courses, Internship programs, part time courses and corporate training.Explore our offerings at https://www.maven-silicon.com/
Every course has a different admission procedure: 1. For Advanced VLSI Design and Verification course at Maven Silicon, you can apply while you are in the final semester, graduation or post-graduation. 2. For the Internship program, you can apply in your pre-final/final year. Advise you to book your seats in advance, pertaining to limited admissions and increased demand. 3. You can subscribe to our online courses directly from our elearn portal https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ You can apply for our Online, Job-oriented, Part-time and Corporate courses on https://www.maven-silicon.com/application
We do have an entrance exam for our job-oriented courses VLSI RN and VLSI VM. After you meet the eligibility criteria you have to undergo an Online Entrance Test which would check you on the concepts of Basic Electronics and Digital Electronics. Post scoring 60% in this test, you are processed for the technical interview with our technical experts. Based on your performance during the interview, you will be selected for the Advanced VLSI Design and Verification course. For our online VLSI courses, we do not have any entrance exams. You can directly subscribe the courses from our elearn portal https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/
Yes, we do provide the scholarship on our job-oriented courses VLSI RN and VLSI VM based on your performance in the technical interview. To excel in the Online entrance test and the technical interview, we suggest you take our Online Digital electronics course at https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/digital-electronics This online Digital electronics course will help you to learn and refresh the complete fundamentals of digital electronics, highly needed for any VLSI course. Contact us for more details.
We provide 100% placement assistance with our job-oriented course until you get placed. You can refer the link for the placement updates and know more about our hiring partners: https://www.maven-silicon.com/placement
VLSI Frontend course imparts training in the Design and Verification of a chip which mostly includes RTL(Register Transfer Level) coding using either VHDL/Verilog/SystemVerilog and the verification of the DUT(can be an IP or SOC) by building verification Environment or Testbench using SystemVerilog/UVM/.You also learn to meet the timing constraints of the chip using STA(Static Timing Analysis) and Synthesizing the design using synthesizable constructs. The maximum number of VLSI job opportunities are available in the Verification segment. Backend courses mostly deal with the physical design part of the chip which includes Floorplan, Map, Place and route and DFT and ATPG scan insertion and checks for the flip flops. It also includes the physical verification part of the chip, memory characterization, analog layout, and design.
Yes. VLSI is a high growth domain with huge job opportunities. Electronics is the basic knowledge required to get into the VLSI industry. Engineers with Electronics background can enter into VLSI Industry easily. The VLSI Course is helpful for ECE/EEE students to learn and build up the skill set as per the Industry requirement to enter the Chip/IC Design and Verification Domain.
Inexpensive courses with the utmost quality are our unique selling points. You can explore our courses at https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/
We help you with support material to enhance your basic knowledge of Digital electronics and perform your best. Our online Digital electronics course will help you to learn and refresh the complete fundamentals of digital electronics, which are highly needed for any VLSI course. Contact us for more details.
We do have online VLSI courses for engineers like you. You can start learning with our hands-on online VLSI courses which comes with labs, project, reference material. We also connect with live Q&A, doubt clarification sessions and Whatsapp support group. Click here to explore and subscribe https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ . If you are looking for online VLSI course with Placement support, then you refer our Blended VLSI learning program at https://www.maven-silicon.com/blended-vlsi-design-asic-verification
We always encourage you to join the course along with friends because it motivates you to learn and finish the course at a fast pace. Contact us to know about group discount options.
Yes. It is good to start early. You can explore and subscribe to our online VLSI design methodologies course or our Internship Program. It is a front-end VLSI course that imparts the VLSI Design Flow, Digital Design and RTL programming using Verilog HDL. After completing the online VLSI DM course/Internship Program, you can easily crack college campus interviews or you can also take up our Advanced ASIC Verification course with 100% placement assistance and can avail up to 100% scholarship based on your grades in our Online VLSI Design Course and the scores of technical interview with our experts.
Yes, we have part-time/Weekend VLSI courses for working professionals. They are specially designed to help you strike a balance between your job and learning. Explore VLSI DM and VM part-time course under Part-time VLSI course in Program offerings at our website https://www.maven-silicon.com/systemverilog-uvm-functional-verification-course
Our Job oriented VLSI courses are highly effective and rigorous programs and follow a continuous evaluation scheme. Candidates are evaluated in the courses through lab reports, project reports, practice tests, assignments, technical presentations, and mock interviews. We also have an evaluation program in our Online VLSI courses through quizzes, tests, and assignments.
You do not need to pay extra for the requisite learning material. We do provide free library access and free online VLSI Courses to our trainees enrolled for job oriented courses for reference and support.
Once you complete your online VLSI course you can upgrade to job oriented VLSI Courses with a very good scholarship. We provide 100% placement assistance for the job oriented VLSI Courses. Advanced VLSI Design and Verification [VLSI – RN ] and Advanced ASIC Verification [ VLSI-VM ] are the job oriented VLSI Courses.
Maven Silicon offers customized in-house and onsite corporate VLSI training courses. This program is specially designed for engineers keeping in view the ever-changing demands of the industry. The participants are equipped with the latest tools, techniques, and skills needed to excel as Verification Engineers. Some of our Corporate training VLSI Courses are SystemVerilog HVL, Verilog HDL, Universal Verification Methodology and Assertion based Verification. Click here for more details: https://www.maven-silicon.com/corporate-training
Yes. Our courses will be very useful. We have had many students taking up our course before going to foreign universities for their Master’s program in VLSI. The practical approach of the courses could help them get campus job opportunities and assistantships..
You can opt for online or offline course but you must choose the right mode considering the time you can spend and the flexibility you need. The online course also provides you Live Q&A, doubt clarification, handy technical support and reference material. So, it is a great offering with best of both worlds. You can learn on the go along with your college studies/ regular office hours and upskill yourself. With Maven Silicon’s Online Verification course, you can master VLSI even if you stay in a remote corner of the world.
Steps involved in Chip design Chip’s architecture: Create circuit designs, Run simulations, Supervise layout, Tape out the chip to the foundry and Evaluate the prototype once the chip comes back from the laboratory. Chip designers work to make faster, cheaper and more innovative chips that can automate parts or the entire function of electronic devices. A chip design engineer’s job involves architecture, logic design, circuit design and physical design of the chip, testing, and verification of the final product.
We do have online VLSI courses for engineers like you. You can start learning with our hands-on online VLSI courses which comes with labs, project, reference material. We also connect with live Q&A, doubt clarification sessions and Whatsapp support group. Click here to explore and subscribe https://elearn.maven-silicon.com/ . If you are looking for online VLSI course with Placement support, then you refer our Blended VLSI learning program at https://www.maven-silicon.com/blended-vlsi-design-asic-verification
Once you complete your online VLSI course you can upgrade to job oriented VLSI Courses with a very good scholarship. We provide 100% placement assistance for the job oriented VLSI Courses. Advanced VLSI Design and Verification [VLSI – RN ] and Advanced ASIC Verification [ VLSI-VM ] are the job oriented VLSI Courses.
You can opt for online or offline course but you must choose the right mode considering the time you can spend and the flexibility you need. The online course also provides you Live Q&A, doubt clarification, handy technical support and reference material. So, it is a great offering with best of both worlds. You can learn on the go along with your college studies/ regular office hours and upskill yourself. With Maven Silicon’s Online Verification course, you can master VLSI even if you stay in a remote corner of the world.
- Why Maven Silicon
- Success Stories
- Training Calender
- Advanced VLSI Design and Verification Course – [VLSI RN]
- Advanced ASIC Verification Course – [VLSI VM]
- Advanced VLSI Design and DFT Course – [VLSI DFT]
- Advanced Physical Design Course – [VLSI PD] NEW
- Online VLSI Design Course
- Online VLSI Verification Course
- Advanced ASIC Verification Course – [VLSI VM-PT]
- VLSI Design Course – [VLSI DM-PT]
- Free VLSI Courses
- VLSI jobs for freshers
- Free VLSI Projects
- Free VLSI Workshop
- Maven Podcast
- Hire Talent
- Corporate Training
Download the Maven Learning App
South Taluk, 21/1A, III Floor, MS Plaza, Gottigere Uttarahalli Hobli, Bannerghatta Main Rd, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560076
© Copyright 2023 Maven Silicon, All Rights Reserved. Privacy and Terms
- Physical Design Interview Questions
- Physical Design Course
- VLSI Physical Design Flow
- VLSI Training Institute in Hyderabad
- SystemVerilog Assertions
- Verilog Interview Questions
- DFT interview question
- VLSI interview questions
- SystemVerilog Interview Questions
- SystemVerilog Course
- VLSI courses online
- ASIC Verification
- UVM Verification
- Systemverilog Tutorial
- Internship in electronics
- VLSI Design
- VLSI projects
- VLSI System Design
- VLSI Internship in Bangalore
vlsi testing Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
Embedded Radiation sensor with OBIST structure for applications in mixed signal systems
Oscillation based testing (OBT) has proven to be a simple and effective test strategy for numerous kind of circuits. In this work, OBT is applied to a radiation sensor to be used as a VLSI cell in embedded applications, implementing an oscillation built-in self-test (OBIST) structure. The oscillation condition is achieved by means of a minimally intrusive switched feedback loop and the response evaluation circuit can be included in a very simple way, minimizing the hardware overhead. The fault simulation indicates a fault coverage of 100% for the circuit under test.Keywords: fault simulation, mixed signal testing, OBIST, oscillation-based test, VLSI testing.
Implementation of a Parallel Fault Simulation System using PODEM in a Hardware Accelerator using Python
VLSI Testing is one of the essential domains in recent times. With the channel length of the transistor decreasing continually, the number of transistors in a chip increases, thus increasing the probability of defects or faults. Automatic Test Pattern Generator is one way to find such input test vectors to the circuit, which will help identify the faults if present. PODEM algorithm is one such algorithm used in this regard. This paper helps in reducing the runtime of this algorithm by the parallelism approach. Different stuck-at faults in the gate level circuit are simulated parallelly.
AI-Powered Terahertz VLSI Testing Technology for Ensuring Hardware Security and Reliability
A low-power true single phase clock scan cell design for vlsi testing, ai powered thz vlsi testing technology, methods of automated test solutions design for vlsi testing, covert gates: protecting integrated circuits with undetectable camouflaging.
Integrated circuit (IC) camouflaging has emerged as a promising solution for protecting semiconductor intellectual property (IP) against reverse engineering. Existing methods of camouflaging are based on standard cells that can assume one of many Boolean functions, either through variation of transistor threshold voltage or contact configurations. Unfortunately, such methods lead to high area, delay and power overheads, and are vulnerable to invasive as well as non-invasive attacks based on Boolean satisfiability/VLSI testing. In this paper, we propose, fabricate, and demonstrate a new cell camouflaging strategy, termed as ‘covert gate’ that leverages doping and dummy contacts to create camouflaged cells that are indistinguishable from regular standard cells under modern imaging techniques. We perform a comprehensive security analysis of covert gate, and show that it achieves high resiliency against SAT and test-based attacks at very low overheads. We also derive models to characterize the covert cells, and develop measures to incorporate them into a gate-level design. Simulation results of overheads and attacks are presented on benchmark circuits.
A heuristic fault based optimization approach to reduce test vectors count in VLSI testing
A comprehensive review on applications of don’t care bit filling techniques for test power reduction in digital vlsi systems.
Massive power consumption during VLSI testing is a serious threat to reliability concerns of ubiquitous silicon industry. A significant amount of low-power methodologies are proposed in the relevant literature to address this issue of test mode power consumption and don’t care bit(X) filling approaches are one of them in this fraternity. These don’t care(X) bit filling techniques have drawn the significant attention of industry and academia for its higher compatibility with existing design flow as neither modification of the CUT is required nor they need to rerun the time-consuming ATPG process. This paper presents an empirical survey of those X-bit filling techniques, applied to mitigate prime two types of dynamic power dissipation namely shift power and capture power, occurred during full scan testing.
VLSI Testing
Export citation format, share document.


- Advanced Search

A Remote FPGA-based Experimental Teaching System Design Supporting Single-board Multi-user and Multi-board Single-user Operations in MOOCs
Southwest Jiaotong University, China
School of Information Science and Technology, Southwest Jiaotong University, China
SWJTU-LEEDS JOINT SCHOOL, Southwest Jiaotong University, China
New Citation Alert added!
This alert has been successfully added and will be sent to:
You will be notified whenever a record that you have chosen has been cited.
To manage your alert preferences, click on the button below.
New Citation Alert!
Please log in to your account
- Publisher Site
GLSVLSI '24: Proceedings of the Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2024

Unlike traditional offline courses, where the enrollment number is generally fixed, massive open online courses (MOOCs) often exhibit significant disparities in the enrollment number across different sections. Namely, this number can vary by several or even hundreds of times depending on the MOOC sections. To this end, this study proposes a remote FPGA-based experimental teaching system with two main innovations. First, a software-hardware co-work framework is designed to divide a single physical FPGA into multiple independently virtual FPGAs, allowing for multiple users to use the same physical FPGA concurrently. Second, an "X86 CPU+Multi-PYNQ" collaborative computing system supporting up to 16 PYNQs for parallel computing is designed. This system uses an X86 CPU as a main processor to distribute computing tasks to the PYNQ-cluster for scheduling FPGA parallel computations, which enables a single user to use multiple FPGAs concurrently. Therefore, the proposed system can effectively address the problem of underutilized boards in MOOCs where the enrollment number is smaller than the number of available FPGA boards. In summary, the system proposed in this paper can effectively mitigate the conflict between the number of students and the number of FPGA boards in MOOCs.
Index Terms
Applied computing
Distance learning
Learning management systems
Integrated circuits
Reconfigurable logic and FPGAs
Reconfigurable logic applications
Recommendations
Asic design principle course with combination of online-mooc and offline-inexpensive fpga board.
ASIC Design Principle (ASICDP) is a compulsory course for undergraduate majors in microelectronics and integrated circuits, and the focus of this paper is the teaching methods of online theoretical teaching and offline experimental teaching of this ...
A Multi-Paradigm Approach to Teaching Students Embedded Systems Design using FPGAs and CPLDs
To create optimal embedded electronic systems, it is essential to ensure all implementation options are considered, and students of electronics and computer engineering must be educated in hardware, software and firmware.
We begin by reviewing in an ...
Design and evaluation of a hardware/software FPGA-based system for fast image processing
We evaluate the performance of a hardware/software architecture designed to perform a wide range of fast image processing tasks. The system architecture is based on hardware featuring a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) co-processor and a host ...
Login options
Check if you have access through your login credentials or your institution to get full access on this article.
Full Access
- Information
- Contributors
Published in

University of Illinois Chicago, USA
University of South Florida, USA
Tulane University, USA
McGill University, Canada
University of Texas at Dallas, USA
Copyright © 2024 ACM
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work for personal or classroom use is granted without fee provided that copies are not made or distributed for profit or commercial advantage and that copies bear this notice and the full citation on the first page. Copyrights for components of this work owned by others than the author(s) must be honored. Abstracting with credit is permitted. To copy otherwise, or republish, to post on servers or to redistribute to lists, requires prior specific permission and/or a fee. Request permissions from [email protected] .
In-Cooperation
Association for Computing Machinery
New York, NY, United States
Publication History
- Published: 12 June 2024
Permissions
Request permissions about this article.
Check for updates
Author tags.
- Online Education
- research-article
- Refereed limited
Acceptance Rates
Upcoming conference, funding sources, other metrics.
- Bibliometrics
- Citations 0
Article Metrics
- 0 Total Citations View Citations
- 0 Total Downloads
- Downloads (Last 12 months) 0
- Downloads (Last 6 weeks) 0
This publication has not been cited yet
Digital Edition
View this article in digital edition.
Share this Publication link
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3649476.3658762
Share on Social Media
- 0 References
Export Citations
- Please download or close your previous search result export first before starting a new bulk export. Preview is not available. By clicking download, a status dialog will open to start the export process. The process may take a few minutes but once it finishes a file will be downloadable from your browser. You may continue to browse the DL while the export process is in progress. Download
- Download citation
- Copy citation
We are preparing your search results for download ...
We will inform you here when the file is ready.
Your file of search results citations is now ready.
Your search export query has expired. Please try again.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Journal Menu
- Electronics Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
- arrow_forward_ios Forthcoming issue arrow_forward_ios Current issue
- Vol. 13 (2024)
- Vol. 12 (2023)
- Vol. 11 (2022)
- Vol. 10 (2021)
- Vol. 9 (2020)
- Vol. 8 (2019)
- Vol. 7 (2018)
- Vol. 6 (2017)
- Vol. 5 (2016)
- Vol. 4 (2015)
- Vol. 3 (2014)
- Vol. 2 (2013)
- Vol. 1 (2012)
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
VLSI Architectures for Wireless Communications and Digital Signal Processing
- Print Special Issue Flyer
Special Issue Editors
Special issue information.
- Published Papers
A special issue of Electronics (ISSN 2079-9292). This special issue belongs to the section " Circuit and Signal Processing ".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (31 August 2022) | Viewed by 16492
Share This Special Issue

Dear Colleagues,
Due to the relentless growth of computational complexity, state-of-the-art technologies cannot be realized unless they are accelerated by very-large-scale-integration (VLSI) circuits. For instance, 5G telecommunications necessitate application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) to achieve data rates over tens of gigabits per second. The Internet-of-Things (IoT) systems connecting a massive number of edge devices also demand highly efficient hardware to accommodate data transfer within a few milliseconds under a limited power budget. Computer-vision applications based on deep neural networks are so computationally intensive that they incur orders-of-magnitude more operations than ever before. To facilitate the realization of such cutting-edge technologies, considerable attention should be paid to the development of efficient VLSI architectures.
This Special Issue solicits original and unpublished papers on high-performance and low-power VLSI architectures and the relevant algorithmic optimizations in the field of wireless communications and digital signal processing.
The topics of interest include but are not limited to:
- VLSI architectures for 5G and 6G telecommunications;
- FPGA and ASIC implementations of signal-processing systems;
- Baseband signal processing for communication systems;
- Circuits and systems for the Internet-of-Things (IoT);
- VLSI architectures for machine learning and artificial intelligence;
- Application-specific instruction-set processors for digital signal processing;
- Hardware-friendly algorithms and optimization techniques;
- Embedded systems on chip (SoCs) for signal-processing applications.
Prof. Dr. Byeong Yong Kong Prof. Dr. Hoyoung Yoo Guest Editors
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website . Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form . Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Electronics is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (4 papers)
Further Information
Mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Recent Trends in VLSI Design & its research issues in Industry Compliance

Recent Trends in VLSI Design & its research issues in Industry Compliance its consist of the following 1. Over View - VLSI 2. Research Methodology 3. Recent Research 4. Industrial Need 5. Industrial requirement 6. ULSI 7. Research Area- Funding Agencies in India
Related Papers
mes.tu-darmstadt.de
Mladen Berekovic , R. Goettsche
IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology
KARTHIKEYAN DEVARAJ
Dr.R. Manikandan
Partitioning and placement are the significant areas of VLSI Physical design. In this paper, we have elaborated four main design issues in VLSI circuit partitioning and placement. The objective of study in VLSI physical design is to optimize the chip area and to maintain chip performance
VLSI Circuit Design Methodology Demystified
Raushan Sharma
In this document we also give the overview of vlsi and also write some programs with the help of vhdl language.
Gaurav Soni
IEEE Transactions on Education
Kenneth Pocek
Lynn Conway
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Technologies
- Privacy Policy
Latest Research topics in vlsi design
Latest research topics in vlsi design.
If we narrow down our discussion to research in areas like electronics, electrical, computer science, artificial intelligence , wireless communication and related fields, which are the base of everything in this high-tech world. In these fields researchers have developed applications (aided with technology) for every field ranging from biomedical to aerospace and construction, which were nowhere related to electronics or even current.
As the research fields we are talking about are providing base to the developing world and providing it with reliable technologies which are being used in real time, the work of researcher becomes more wide starting with an idea to the realization of the idea in the real world in form of application or product.
To make a reliable and working model the idea of the VLSI design project ( i.e speech processing application, biomedical monitoring system etc) needs to be implemented and re-implemented, re-tested and improvised. The there are many development cycles and techniques available which eases up the implementation like:
- Behavioral simulation
- Software based model
- Hardware Implementation (ASIC)
- Programmable hardware (FPGA)
- Co-simulation
Behavioral simulation is used at initial phase and it is not appropriate for testing the real time behavior of the system in actual environment as it is more close to systems behavior in ideal environment.
We can simulate the actual environment by using different software models (more like software models of channels used to test communication systems) but its capabilities are also limited to human capability to model the environmental conditions in mathematical equations and models.
All of us are familiar with ASIC, their high performance and hardwired implementation. These are good for final implementation but not for intermediate stages of implementation and testing. Nothing is better than ASIC for real time testing of analog VLSI circuits. But for digital circuits and DSP applications we have a better option of FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array).
The hardware co-simulation is a good idea to test and monitor systems in real time. To get more details about PhD thesis in VLSI you can do online research or contact us.
latest Low power research topics in vlsi design
The Research Support Centre provides expert advice and support across the whole Engineering and Technical research lifecycle, from discovery through exploitation of technical and translational research. The centre has two primary functions:
- i) to facilitate the delivery of the Engineering Sciences research strategy and to build partnerships andii) to bring together all the technical research management and support services for Students.
To achieve these goals the centre is made up of two inter-relating components. The Academic Research Support Centre consists of the Research Coordination Office, Platform Technologies team and a Translational Research Office. The Technical Research Support Centre is made up of the Joint Research Office.
The Research Support Centre encompasses a wide range of expertise and facilities. By coordinating these resources, we can provide researchers with a package of support that is integrated, high quality and streamlined – and clearly accountable.
Once a researcher has a proposal for high quality research that will benefit, they can access all the help and resources they need through one gateway. This includes support with the approval process and funding applications and help setting up technical trials.
VLSI PHD Projects
Our research interests cover low power processor architectures, low power circuit design techniques, analog and mixed signal circuit design, rapid prototyping of digital systems, reconfigurable processors, Digital arithmetic, advanced processor architectures, vlsi implementation of signal and image processing algorithms, testing verification, memory design, Embedded vlsi and asynchronous circuits.
Organization engaged with embedded commodity development and serving various business solutions such as
- Embedded System Product Development,
- Software services,
- Android development,
- Web development.
Description for “Ph.d guidance with project assitance” Ph.d/ M.Phil PROJECT ASSISTANCE We look forward to welcoming you to one of our “Research and Development Division” for all Ph.D., Research scholars. We will arrange you the following details for completing your Ph.d Degree
- Any University Admission- We provides a step-to-step guide to completing the application form, and will help make the process as straight forward as possible.
- Guide Arrangement
- Survey Paper Preparation
- Problem Identification –Problem Identification of Existing System.
- Implementation in all domains
- Mobile Ad hoc Networks
- Wireless Networks
- Image Processing
- Grid Computing
- Distributed Computing
- Natural Language Processing
- Cloud Computing
- Soft Computing
- Data Mining
- Wireless Senor Networks
Delivering effective support on your Ph. D work:
Companies represents a simple and practical advice on the problems of getting started, getting organized with the working on Ph.D projects.
We make you understand the practicalities of surviving the ordeal. We just make you divide the huge task into less challenging pieces. The training includes a suggested structure and a guide to what should go in each section.
We afford complete support with real-time exposure in your Ph.D works in the field of VLSI. Our Mission drives us in the way of delivering applications as well as products with complete integrity, innovative & interesting ideas with 100% accuracy.
- Assistance in ALL Stages of your PhD Research in VLSI from Topic Selection to Thesis Submission.
- Creating 100% confident in submitting your thesis work.
- Our experienced professionals support you in your research works.
- Providing complete solutions for the Research Scholars in many advanced domains.
Technologies used in VLSI:
- Modelsim 6.5b Simulator
- Xilinx ISE 10.1 System generator
III. Quartus 11.1
- Tanner v7 EDA tool
iii. W-Edit
- Microwind & DSCH v2
VII. P-spice
VIII. LT-spice
. Spartan IIIe
- Hardware Description Language
. Verilog HDL
CORE AREA OF GUIDANCE:
- Digital signal processing Vlsi
- Image processing Vlsi
III. Wireless Vlsi
- Communication Vlsi
- Testing Vlsi
- Digital cmos Vlsi
VII. low power Vlsi
VIII. Core Vlsi
- Memory Designs
PROJECT SUPPORT:
- Confirmation Letter
- Attendance Certificate
III. Completion Certificate
Preprocessing Work:
- Paper Selection
Identifying the problem:
- Screenshots
III. Simulation Report
- Synthesize Report
Report Materials:
- Block Diagrams
- Review Details
III. Relevant Materials
- Presentation
- Supporting Documents
- Software E-Books
VII. Software Development Standards & Procedure – E-Book
Learning Exposure:
VIII. Programming classes
- Practical training
- Project Design & Implementation
Publishing Support:
XII. Conference Support
XIII. Journal Support
XIV. Guide Arrangements
Vlsi based projects like image processing projects, low power projects, matlab with vlsi projects , cryptography projects, OFDM projects, SDR projects, communication projects, zigbee projects, digital signal processing projects, and also protocol interfacing projects like uart ,i2c,spi projects.
Signal and Image processing projects can be simulated by using Modelsim 6.5b and synthesized by Xilinx 10.1 using Spartan IIIe fpga and by Quartus 11.1using altera de2 fpga. In image processing projects, the input image or video can be converted to coefficients using Matlab. Low power projects can be designed using Tanner, Microwind and spice tools.
We spotlights on imparting an overall exposure to the concept and design methodologies of all major aspects of vlsi engineering relevant to industry needs and ground-breaking thoughts with 100% pure accuracy.
latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design low power testing bist latest research topics in vlsi design latest latest research topics in vlsi design area latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design latest research topics in vlsi design

IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Research details method to get efficient, environmentally friendly lithium
June 7, 2024
By Sarah C.P. Williams
Related content
- Finding a better path to lithium
- Chong Liu wins prestigious Sloan Fellowship
- To boost supply chains, scientists are looking at ways to recover valuable materials from water
As the electric vehicle market booms, the demand for lithium — the mineral required for lithium-ion batteries — has also soared. Global lithium production has more than tripled in the last decade. But current methods of extracting lithium from rock ores or brines are slow and come with high energy demands and environmental costs. They also require sources of lithium which are incredibly concentrated to begin with and are only found in a few countries.
Now, researchers at the University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) have optimized a new method for extracting lithium from more dilute — and widespread — sources of the mineral, including seawater, groundwater, and “flowback water” left behind from fracking and offshore oil drilling.
“Right now there is a gap between the demand for lithium and the production,” said Chong Liu, Neubauer Family Assistant Professor of Molecular Engineering and senior author of the new work, published in Nature Communications . “Our method allows the efficient extraction of the mineral from very dilute liquids, which can greatly broaden the potential sources of lithium.”
In the new research, Liu and her colleagues showed how certain particles of iron phosphate can most efficiently pull lithium out of dilute liquids. Their new findings could hasten an era of faster, greener lithium extraction.
Lithium at a cost
Today, most lithium used in lithium batteries comes from two basic extraction processes. Lithium rock ores can be mined, smashed up with heavy machinery, and then treated with acid to isolate the lithium. Lithium brine pools, on the other hand, use massive amounts of water pumped to the earth’s surface and then evaporated away — over the course of more than a year — to yield dried lithium.
“These methods aren’t particularly environmentally friendly to begin with, and if you start trying to work with less concentrated sources of lithium, they’re going to become even less efficient,” said Liu. “If you have a brine that is 10 times more dilute, you need 10 times more briny water to get the same amount of lithium.”
In recent years, Liu’s team has spearheaded a completely different method to get lithium out of dilute liquids. Their approach isolates lithium based on its electrochemical properties, using crystal lattices of olivine iron phosphate. Because of its size, charge and reactivity, lithium is drawn into the spaces in the olivine iron phosphate columns — like water being soaked into the holes in a sponge. But, if the column is designed perfectly, sodium ions, also present in briny liquids, are left out or enter the iron phosphate at a much lower level.
In the new work, Liu and her colleagues, including first author of the new paper Gangbin Yan, a PME graduate student, tested how variation in olivine iron phosphate particles impacted their ability to selectively isolate lithium over sodium.
“When you produce iron phosphate, you can get particles that are drastically different sizes and shapes,” explains Yan. “In order to figure out the best synthesis method, we need to know which of those particles are most efficient at selecting lithium over sodium.”
Not too big, not too small
The research team synthesized olivine iron phosphate particles using different methods, resulting in a range of particle sizes spanning 20 to 6,000 nanometers. Then, they divided those particles into groups based on their size and used them to build electrodes that could extract lithium from a weak solution.
When iron phosphate particles were too large or too small, they discovered, they tended to let more sodium into their structures. That led to less pure extractions of lithium.
“It turned out that there was this sweet spot in the middle where both the kinetics and the thermodynamics favor lithium over sodium,” said Liu.
The findings are vital to moving electrochemical lithium extraction toward commercial use. They suggest that researchers should focus on not just producing olivine iron phosphate, but producing olivine iron phosphate at the ideal particle size.
“We have to keep this desired particle size in mind as we pick synthesis methods to scale up,” Liu said. “But if we can do this, we think we can develop a method that reduces the environmental impact of lithium production and secures the lithium supply in this country.”
Other authors on the paper are Emory Apodaca, Suin Choi, Peter J. Eng, Joanne E. Stubbs, Yu Han, Siqi Zou, Mrinal K. Bera and Ronghui Wu of University of Chicago; Jialiang Wei and Wei Chen of Illinois Institute of Technology; and Evguenia Karapetrova and Hua Zhou of Argonne National Laboratory.
Citation: “Identifying critical features of iron phosphate particle for lithium preference,” Yan et al, Nature Communications , June 7, 2024. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49191-3
Funding: This work was supported by the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy Office of Science.
People often overestimate their resilience following failure, research suggests

The myth that failure is always a good teacher may need an update.
People tend to overestimate the likelihood of success following failure, which may make us less willing to help others who are struggling, according to a new study.
A team of researchers from the business schools of Northwestern, Cornell, Yale and Columbia universities analyzed data from different online surveys including over 1,800 adults in the United States mostly between the ages of 29 to 49. One survey involved oncology nurses attending a virtual conference.
“We wanted to see if people think about resilience wrong,” lead author Lauren Eskreis-Winkler, assistant professor of management and organizations at Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois, told NBC News in an email.
The study was published online Monday by the American Psychological Association in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
The researchers looked at how people predicted the resilience of professionals such as lawyers, teachers and nurses, as well as people with substance use disorders and heart problems.
“People thought that tens of thousands of professionals who failed standardized tests would go on to pass (who don’t), that tens of thousands of people with drug addiction would get sober (who don’t), and that tens of thousands of individuals with heart failure would make major lifestyle changes to improve their health,” Eskreis-Winkler wrote.
When people believe that others who have experienced setbacks will grow from their failure on their own, they are less motivated to help those in need because they believe these problems will “self-correct,” the report said.
The researchers also found that participants wrongly assumed people focus on their mistakes and learn from them after failure.
In one of the findings, people who exaggerated the benefits of failure were less interested in channeling taxpayer dollars to support people with drug addiction and formerly incarcerated people.
However, when the researchers corrected exaggerated beliefs about the benefits of failure, the same participants increased their motivation to help.
“The main finding is that people systematically — blissfully — overestimate the likelihood of resilience following failure,” according to the researchers.
This “pollyannish” perception allows people to take more chances despite erroneously believing that failure fuels success, Eskreis-Winkler said in the email. “But from a helping perspective, exaggerating the benefits of failure is disastrous.”
In reality, it’s difficult to learn from a bad experience because failure is “demotivating and ego-threatening,” the report found.
The findings highlight how our outside perspective tends to focus on what can be learned from a failure, overlooking that people living through a setback may not perceive it as a learning opportunity.
It’s a painful ego lesson, said Dr. Ryan Sultan , director of the Mental Health Informatics Lab at Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
“If you have failed at something, just retrying is likely not sufficient to change your outcome,” Sultan said.
Sultan recommends re-evaluating the situation by asking:
- What new strategies could be adopted?
- What resources or support systems could we engage with that would improve our chances of success in the future?
Dr. Lama Bazzi, a psychiatrist in private practice in New York City, advocates patience, despite the desire to quickly move forward. Achieving a goal often means tolerating the discomfort of failing in order to “grow” as a person.
“In order to change course, you must feel uncomfortable, analyze where you went wrong, and make a conscious effort to approach similar future challenges mindfully and differently,” said Bazzi, who was not part of the study.
The study findings don’t mean that if you fail at something, you can’t ever succeed.
People need to be mindful of the path that led to these outcomes and re-evaluate it with a critical eye, Sultan noted.
“As my father, who is also a psychiatrist, told me in my youth: When you fail, Ryan, you must ask yourself the hard questions of what you did to contribute to that failure so you can grow and learn from that experience,” Sultan said.
Although the researchers analyzed different populations in the U.S., including students, professionals and medical patients, more research is needed to generalize the study’s findings to non-Western cultures, which have different perceptions, interpretations and reactions to failure, the study said.
Shiv Sudhakar, M.D., is an infectious disease specialist and health contributor to NBC News Health. He works in addiction medicine, so is very passionate about decreasing substance abuse, combating homelessness and improving mental health.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Cultural Issues and the 2024 Election
4. Gender, family, reproductive issues and the 2024 election
Table of contents.
- Voters’ views about race and society, the impact of the legacy of slavery
- Most voters, but not all, view the nation’s diversity as a strength
- How should the country handle undocumented immigrants currently in the U.S.?
- Attitudes toward hearing other languages in public places
- Biden and Trump supporters’ views about discussing America’s historical successes, failures
- How does the U.S. compare with other countries?
- Views of women’s progress
- How much of a priority should marriage and children be?
- Abortion, IVF access and birth control
- Views of gender identity
- Voters’ attitudes toward use of gender-neutral pronouns
- Societal impact of more social acceptance of lesbian, gay, bisexual people
- Religion and government policy
- How much influence should the Bible have on the nation’s laws, if any?
- Views on the federal government’s role in promoting Christian values
- Most voters say it is not necessary to believe in God to be moral
- Is the justice system too tough on criminals, or not tough enough?
- Policing and law enforcement
- How Trump, Biden supporters view gun rights and ownership
- Views on the increasing number of guns in the U.S.
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
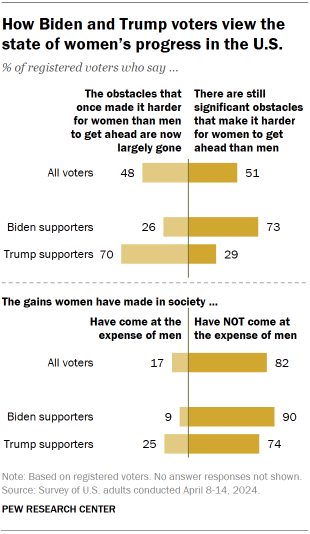
Biden and Trump voters differ sharply over the state of women’s progress in the U.S., as well as over whether society should prioritize marriage and children.
Yet majorities of both candidates’ supporters say that the gains women have made in society have not come at the expense of men.
Nearly two years after the Supreme Court overturned the Roe v. Wade decision that guaranteed a right to abortion, the issue continues to divide the two coalitions: Biden supporters overwhelmingly say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while a narrower majority of Trump backers say it should not.
But the two groups generally share the view that birth control and access to in vitro fertilization (IVF) should be widely available. Majorities of both Biden and Trump supporters view the broad availability of birth control as a good thing and say the same about access to IVF.
Supporters of Joe Biden and Donald Trump have mirror-image views on whether women face obstacles to getting ahead in society that men do not.
- About three-quarters of Biden supporters (73%) say there are still significant obstacles making it harder for women than men to get ahead. About a quarter (26%) say these obstacles are now largely gone.
- In contrast, seven-in-ten Trump supporters say the obstacles that once made it harder for women than men to get ahead are now largely gone. About three-in-ten (29%) say women still face significant obstacles.
There were also wide gaps in these opinions during the 2016 and 2020 presidential campaigns .
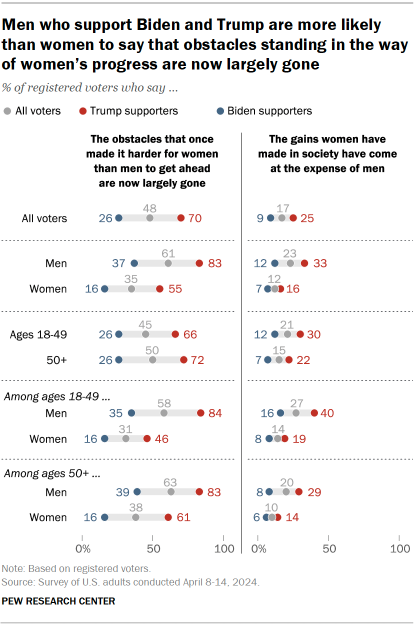
Differences between Biden and Trump voters are much more modest when it comes to views of whether women’s gains have come at the expense of men. Sizable majorities of both Biden (90%) and Trump supporters (74%) reject this idea.
Among both Biden supporters and Trump supporters, men are more likely than women to say the obstacles that once made it harder for women than men to get ahead are now largely gone.
Among Trump supporters, 83% of men say this, compared with 55% of women.
Almost four-in-ten men who back Biden (37%) say women’s obstacles to progress are now largely gone. Just 16% of women who back Biden say the same.
While most voters across age groups and genders say that gains women have made have not come at the expense of men, a third of men who support Trump do think women’s gains have cost men. This share increases to 40% among men under age 50 who support Trump. About 20% of women or fewer – regardless of age or which candidate they support – say that women’s gains come at the expense of men.
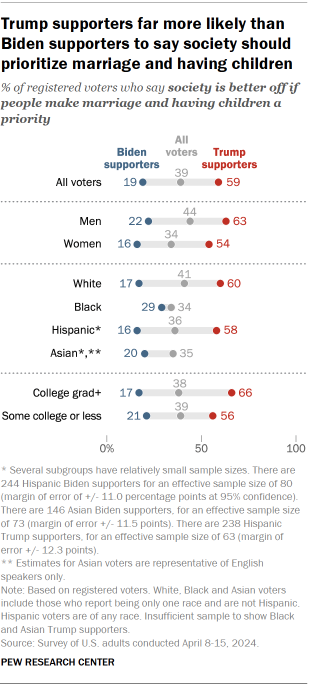
Roughly four-in-ten registered voters (39%) say society is better off if people make marriage and having children a priority, while a majority (59%) say society is just as well off if people have priorities other than family and children.
- Trump supporters (59%) are much more likely than Biden supporters (19%) to say that it is better if people prioritize marriage and children.
There are modest differences between men and women in whether focusing on marriage and children makes society better.
- About six-in-ten men who support Trump (63%) say this, compared with 54% of Trump-supporting women. There is a similar gender gap among Biden supporters (22% of men vs. 16% of women).
Black voters who support Biden (29%) are more likely than White (17%) and Hispanic (16%) Biden supporters to say an emphasis on marriage and family makes society better off. Two-in-ten Asian voters who back Biden say this.
Marriage and children
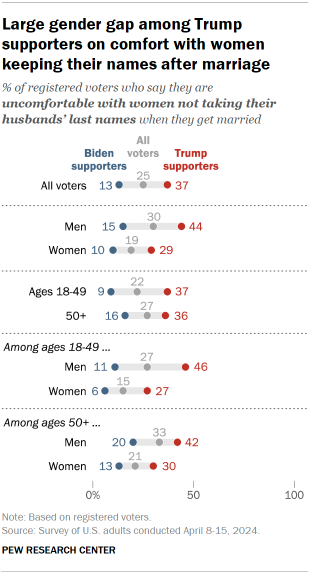
Three-quarters of registered voters say they are comfortable with women not taking their husbands’ last names when they get married. Just a quarter are uncomfortable with this.
However, Trump supporters (37%) are much more likely than Biden supporters (13%) to express discomfort with married women not taking their husbands’ last names.
And men who support Trump (44%) are more likely than women who support him (29%) to say they are uncomfortable with the practice of women not taking their husbands’ last names.
Related: About 8 in 10 women in opposite-sex marriages say they took their husband’s last name
The nation’s fertility rate, which has been declining for years, is now at its lowest point in more than a century, according to a recent study by the Centers for Disease Control. About four-in-ten voters (43%) say it is neither good nor bad for society that people are having fewer children; 35% view this trend negatively, while 22% say it is good for society.
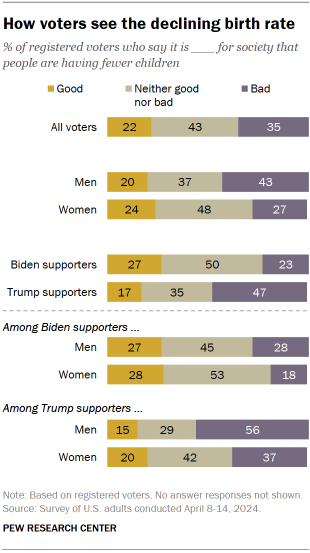
Biden supporters have mixed views of the fact that people are having fewer children. Half say this is neither good nor bad, 27% view this as good for society, and 23% say it is bad.
Trump supporters – especially men who back Trump – view this trend more negatively.
- Nearly half of Trump supporters (47%), including a 56% majority of men who support Trump, say it is bad for society that people are having fewer children. Roughly four-in-ten women who support Trump (37%) see this trend as a bad thing.
Abortion deeply divides supporters of Biden and Trump. About nine-in-ten Biden supporters (88%) say abortion should be legal in most (46%) or all (42%) cases. Just 11% of Biden supporters say abortion should be illegal in all or most cases.
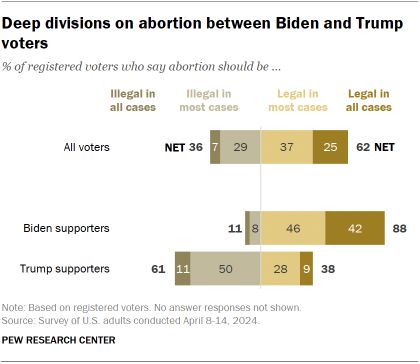
Conversely, about six-in-ten Trump supporters (61%) say abortion should be illegal in all (11%) or most (50%) cases. A significant minority of Trump supporters say abortion should be legal in most or all cases (38%).
Related: Broad Public Support for Legal Abortion Persists 2 Years After Dobbs
Age, gender differences among Trump supporters – but not Biden supporters – on abortion

About half of Trump supporters ages 18 to 34 (51%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, a substantially higher share than among older Trump supporters (35% of those 35 and older).
Among Biden supporters, nearly nine-in-ten across all age groups say abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
Both women and men who back Trump are more likely to say abortion should be illegal than to say it should be legal. However, more women who support Trump (41%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, compared with 34% of men who support Trump.
There is no difference in these views between women and men who support Biden.
By contrast, 73% of all voters – including majorities of Biden (83%) and Trump supporters (64%) – say access to in vitro fertilization (IVF) is a good thing.
Related: Americans overwhelmingly say access to IVF is a good thing
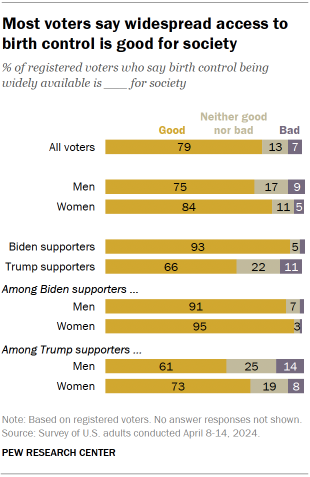
Voters overwhelmingly express positive views of birth control, condoms and other forms of contraception being widely available in the United States. Nearly eight-in-ten (79%) say this is very or somewhat good for society, 13% view it as neither good nor bad, and 7% say it is bad.
- 93% of Biden supporters and 66% of Trump supporters say it’s good for society that birth control is widely available.
- Men who support Trump (61%) are less likely than women who back the former president (73%) to say that birth control being widely available is good for society. There is no meaningful gender gap on this question among Biden supporters.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Criminal Justice
- Discrimination & Prejudice
- Donald Trump
- Election 2024
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Identity
- Immigration & Language Adoption
- LGBTQ Attitudes & Experiences
- Marriage & Divorce
- Partisanship & Issues
- Political Issues
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
- Religion & Government
- Religion & Politics
- Unauthorized Immigration
More than half of Americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out
Americans have mixed views about how the news media cover biden’s, trump’s ages, an early look at black voters’ views on biden, trump and election 2024, voters’ views of trump and biden differ sharply by religion, in tight presidential race, voters are broadly critical of both biden and trump, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The current research in VLSI explores emerging trends and novel ideas and concepts covering a broad range of topics in the area of VLSI: from VLSI circuits, systems, and design methods, to system-level design and systemon- chip issues, to bringing VLSI methods to new areas and technologies such as nano and molecular devices, MEMS, and quantum computing. Future design methodologies are also key ...
The VLSI industry has grown a lot for several decades. The Packing density of integrated circuits has been increased without compromising the functionality. Scaling of semiconductor devices, improvements in process technology and the development of new device designs are the key to this. Starting from the planar MOSFETs to novel multigate transistors, semiconductor devices have a history of ...
Intel researchers will present their latest research on breakthroughs in power efficiencies enabled by new materials and circuits in silicon at the VLSI Circuits Symposium. Intel will join leaders in the semiconductor industry during this year's 2021 Symposia on VLSI Technology and Circuits, held online from June 13-19, to discuss the latest ...
The development of complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology brought about a new paradigm for low-power circuit design. For the implementation of digital circuits with very large-scale integration, CMOS design styles are frequently employed in VLSI. There are billions of transistors on a single die in today's IC devices.
Highlights: The 2022 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits will run from June 13-17th in Honolulu, HI, and offer limited access to conference content on-demand. Researchers present 13 papers, including results of a new advanced CMOS FinFET technology, Intel 4, demonstrating more than 20% performance gain at iso-power over Intel 7.
Co-packaged transceivers speed up. Integrated optical input-output technologies are promising for high-speed communications because of their scaling and bandwidth advantages compared with ...
Through a critical examination of recent research and advancements, this review article aims to offer insights into the promising role of ML in revolutionizing VLSI testing methodologies, ultimately contributing to more efficient and reliable semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Recently, a brief review of recent machine learning and deep learning techniques incorporated in analog and digital VLSI, including physical design, is discussed in [31]. VLSI Computer-Aided Design at different abstraction levels from a machine-learning perspective is presented in [32] .
The focus of this Special Issue is on the research challenges related to the design of emerging microelectronics and VLSI circuits and systems that meet the demanding specifications of innovative applications. This Special Issue considers challenges in the fields of low power consumption, small integration area, testing and security, without ...
Placement is essential in very large-scale integration (VLSI) physical design, as it directly affects the design cycle. Despite extensive prior research on placement, achieving fast and efficient placement remains challenging because of the increasing design complexity. In this paper, we comprehensively review the progress of placement optimization from the perspective of accelerating VLSI ...
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on VLSI TECHNOLOGY. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on VLSI ...
The performance and efficiency of the integrated circuit are impacted by power optimization, making it a crucial component in VLSI design. The operational expenses, battery life, and environmental effect of electronic devices are all impacted by power consumption, which is a crucial factor in VLSI design. The majority of recent research concentrate on simulations or laboratory trials, which ...
The focus of this Special Issue is on the research challenges related to the design of emerging microelectronics and VLSI circuits and related systems that meet the demanding specifications of innovative applications. This Special Issue considers challenges in the fields of low power consumption, small integration areas, testing and security ...
The use of ML in predicting power is a new paradigm. It needs previous knowledge of power dissipated by the circuits. ... Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image, ... Ren, Q., H. Cheng, and H. Han. (2017, March). Research on machine learning framework based on random forest algorithm. In AIP conference proceedings (Vol. 1820 ...
D Amuru et al.: PagePreprint submitted to Elsevier 1 of 41 AI/ML Algorithms and Applications in VLSI Design and Technology Deepthi Amurua,∗, aHarsha V. Vudumula , aPavan K Cherupallya, Sushanth R Gurram , Amir Ahmadb, Andleeb Zahraa and Zia Abbasa aCenter for VLSI and Embedded Systems Technology (CVEST), International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad (IIIT-H),
Abstract. Floorplan is one of the most critical steps of the physical design of VLSI Design flow. Decreasing size, interconnects, power consumption, and chip leakage are always on the top priority list for consumers and researchers. This article presents the latest advancements in one of the hot research topics in VLSI Physical Design: 3D ...
The Robust Low Power VLSI Group, led by Professor Ben Calhoun, investigates research topics related to modern VLSI design. Among the many challenges facing circuit designers in deep sub-micron technologies, power and variation are perhaps the most critical. Our group's focus is to confront these problems in a range of applications and different ...
Emerging trends in VLSI focus on designing chips optimized for IoT-enabled devices, ensuring efficient data communication, low power consumption, and enhanced security. These specialized VLSI chips enable IoT devices to communicate seamlessly over the internet, exchanging data with other devices and cloud services.
VLSI Testing is one of the essential domains in recent times. With the channel length of the transistor decreasing continually, the number of transistors in a chip increases, thus increasing the probability of defects or faults. Automatic Test Pattern Generator is one way to find such input test vectors to the circuit, which will help identify ...
Association for Computing Machinery. New York. NY. United States. Conference: GLSVLSI '24: Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2024 Clearwater FL USA June 12 - 14, 2024. ISBN: 979-8-4007-0605-9.
Heterogeneous chiplets have been proposed for accelerating high-performance computing tasks. Integrated inside one package, CPU and GPU chiplets can share a common interconnection network that can be implemented through the interposer.
Towards systems education for artificial intelligence: a course practice in intelligent computing architectures. In Proceedings of the 2020 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI. 567-572. Google Scholar Digital Library; Qian Yue and Yang Jiqiong. 2020. Research on Online and Offline Blended Teaching Mode Based on "MOOC+ SPOC+ flipped class".
This Special Issue solicits original and unpublished papers on high-performance and low-power VLSI architectures and the relevant algorithmic optimizations in the field of wireless communications and digital signal processing. The topics of interest include but are not limited to: VLSI architectures for 5G and 6G telecommunications;
Recent Trends in VLSI Design & its research issues in Industry Compliance its consist of the following 1. Over View - VLSI 2. Research Methodology 3. Recent Research 4. Industrial Need 5. Industrial requirement 6. ULSI 7. Research Area- Funding
latest research topics in vlsi design. latest research topics in vlsi design - Doctor of philosophy is the final degree in any area. It requires a lot of efforts and hard work to achieve this.It starts with selection of a topic which should be recent and lies in your area of interest. If we talk specifically about research in technology then ...
Need Help? US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333 Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060 Contact & Support
The Nuclear Research Foundation School Certificate Integrated, Volume 1. Book • 1966. ... A Global, Case Study-Based Assessment of Current Experience, Cross-sectorial Effects, and Socioeconomic Transformations. Book • 2019. Accelerator Health Physics. Book • 1973.
In the new research, Liu and her colleagues showed how certain particles of iron phosphate can most efficiently pull lithium out of dilute liquids. Their new findings could hasten an era of faster, greener lithium extraction. ... The research team synthesized olivine iron phosphate particles using different methods, resulting in a range of ...
People tend to overestimate the likelihood of success following failure, which may make us less willing to help others who are struggling, according to a new study. A team of researchers from the ...
The nation's fertility rate, which has been declining for years, is now at its lowest point in more than a century, according to a recent study by the Centers for Disease Control. About four-in-ten voters (43%) say it is neither good nor bad for society that people are having fewer children; 35% view this trend negatively, while 22% say it is ...