Essay Papers Writing Online
Ultimate guide on writing an effective evaluation essay – tips, examples, and guidelines.

Are you puzzled when it comes to writing an evaluation essay? In this guide, we will provide you with all the essential information you need to master the art of crafting a compelling appraisal composition. Whether you are new to this type of writing or just looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive manual will equip you with the necessary tools and techniques to excel. From understanding the purpose and structure of an evaluation essay to exploring various tips and examples, this guide has got you covered.
An evaluation essay is a piece of writing that aims to assess the value or quality of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves analyzing a topic, presenting your judgment or opinion on it, and providing evidence or examples to support your claims. This type of essay requires critical thinking, research, and effective communication skills to present a well-balanced evaluation.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the nitty-gritty of writing an evaluation essay. We will start by discussing the key elements that make up a successful evaluation essay, such as establishing clear criteria, conducting thorough research, and adopting a structured approach. Additionally, we will explore practical tips and strategies to help you gather relevant information, organize your thoughts, and present a persuasive argument. To illustrate these concepts, we will provide you with a range of examples covering various topics and subjects.

Tips for Writing a Top-Notch Evaluation Essay
When it comes to crafting a high-quality evaluation essay, there are several key tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your essay stands out and effectively evaluates the subject matter at hand.
1. Be objective and unbiased: A top-notch evaluation essay should approach the topic with an unbiased and objective perspective. Avoid personal bias or overly emotional language, and instead focus on presenting an honest and well-balanced evaluation of the subject.
2. Provide clear criteria: To effectively evaluate something, it’s important to establish clear criteria or standards by which to assess it. Clearly define the criteria you will be using and explain why these specific factors are essential in evaluating the subject. This will help provide structure to your essay and ensure that your evaluation is thorough and comprehensive.
3. Support your evaluation with evidence: In order to make a convincing argument, it’s crucial to support your evaluation with solid evidence. This can include examples, statistics, expert opinions, or any other relevant information that strengthens your claims. By providing strong evidence, you can enhance the credibility of your evaluation and make it more persuasive.
4. Consider multiple perspectives: A well-rounded evaluation takes into account multiple perspectives on the subject matter. Acknowledge and address counterarguments or differing opinions, and provide thoughtful analysis and reasoning for your stance. This demonstrates critical thinking and a comprehensive evaluation of the topic.
5. Use clear and concise language: Clarity is vital in an evaluation essay. Use clear and concise language to express your thoughts and ideas, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary. Your essay should be accessible to a wide audience and easy to understand, allowing your evaluation to be conveyed effectively.
6. Revise and edit: Don’t neglect the importance of revising and editing your essay. Take the time to review your work and ensure that your evaluation is well-structured, coherent, and error-free. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation, as these details can greatly impact the overall quality of your essay.
7. Conclude with a strong summary: For a top-notch evaluation essay, it’s important to conclude with a strong and concise summary of your evaluation. Restate your main points and findings, providing a clear and memorable conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
By following these tips, you can enhance your writing skills and create a top-notch evaluation essay that effectively assesses and evaluates the subject matter at hand.
Choose a Relevant and Engaging Topic
When it comes to writing an evaluation essay, one of the most important aspects is selecting a topic that is both relevant and engaging. The topic you choose will determine the focus of your essay and greatly impact the overall quality of your writing. It is crucial to choose a topic that not only interests you but also captivates your audience.
When selecting a topic, consider the subject matter that you are knowledgeable or passionate about. This will enable you to provide a well-informed evaluation and maintain your readers’ interest throughout your essay. Additionally, choose a topic that is relevant in today’s society or has a direct impact on your target audience. This will ensure that your evaluation essay has a practical and meaningful purpose.
Furthermore, it is essential to select a topic that is controversial or debatable. This will allow you to present different perspectives and arguments to support your evaluation. By choosing a topic that sparks discussions and debates, you can engage your readers and encourage them to think critically about the subject matter.
In conclusion, choosing a relevant and engaging topic is crucial for writing an effective evaluation essay. By selecting a topic that interests you, appeals to your readers, and is relevant to society, you can ensure that your essay is engaging and impactful. Remember to choose a topic that is controversial or debatable to provide a comprehensive evaluation and encourage critical thinking among your audience.
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement

Crafting an impactful thesis statement is an essential aspect of writing an evaluation essay. The thesis statement serves as the main argument or claim that you will be supporting throughout your essay. It encapsulates the central idea and sets the tone for the rest of the paper.
When developing your thesis statement, it is crucial to be clear, concise, and specific. It should provide a clear indication of your stance on the subject matter being evaluated while also highlighting the main criteria and evidence that will be discussed in the body paragraphs. A strong thesis statement should be thought-provoking and hook the reader’s attention, compelling them to continue reading.
To build a strong thesis statement, you need to engage in a careful analysis of the topic or subject being evaluated. Consider the various aspects that you will be assessing and select the most significant ones to include in your argument. Your thesis statement should be focused and arguable, allowing for a clear position on the matter.
Additionally, it is crucial to avoid vague or general statements in your thesis. Instead, aim for specificity and clarity. By clearly stating your evaluation criteria, you provide a roadmap for the reader to understand what aspects you will be analyzing and what conclusions you intend to make.
Furthermore, a strong thesis statement should be supported by evidence and examples. You should be able to provide concrete support for your evaluation through relevant facts, statistics, or expert opinions. This strengthens the credibility and persuasiveness of your argument, making your thesis statement more compelling.
In summary, developing a strong thesis statement is a critical step in writing an evaluation essay. It sets the foundation for your argument, guiding your analysis and providing a clear direction for the reader. By being clear, concise, specific, and well-supported, your thesis statement helps you create a persuasive and impactful evaluation essay.
Provide Clear and Concise Criteria for Evaluation
One of the most important aspects of writing an evaluation essay is providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation. In order to effectively evaluate a subject or topic, it is essential to establish specific standards or benchmarks that will be used to assess its performance or quality.
When establishing criteria for evaluation, it is crucial to be thorough yet succinct. Clear criteria enable the reader to understand the basis upon which the evaluation is made, while concise criteria ensure that the evaluation remains focused and impactful.
There are several strategies you can employ to provide clear and concise criteria for evaluation. One approach is to define specific attributes or characteristics that are relevant to the subject being evaluated. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, you might establish criteria such as the quality of the food, the level of service, and the ambience of the establishment.
Another strategy is to utilize a scoring system or rating scale to assess the subject. This can help provide a more quantitative evaluation by assigning numerical values to different aspects of the subject. For instance, a movie review might use a rating scale of 1 to 5 to evaluate the acting, plot, and cinematography of the film.
In addition to defining specific attributes or using a scoring system, it is important to provide examples or evidence to support your evaluation. This can help make your criteria more concrete and relatable to the reader. For instance, if you are evaluating a car, you could provide examples of its fuel efficiency, handling performance, and safety features.
By providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation, you can effectively communicate your assessment to the reader and support your conclusions. This will help ensure that your evaluation essay is well-structured, informative, and persuasive.
Support Your Evaluation with Solid Evidence

When writing an evaluation essay, it is crucial to support your evaluations with solid evidence. Without proper evidence, your evaluation may appear weak and unsubstantiated. By providing strong evidence, you can convince your readers of the validity of your evaluation and make a compelling argument.
One effective way to support your evaluation is by using concrete examples. These examples can be specific instances or cases that illustrate the strengths or weaknesses of the subject being evaluated. By presenting real-life examples, you can provide tangible evidence and make your evaluation more persuasive.
Another way to support your evaluation is by referring to expert opinions or research studies. These external sources can add credibility to your evaluation and demonstrate that your assessment is based on sound knowledge and expertise. Citing respected experts or referencing reputable studies can enhance the validity of your evaluation and make it more convincing.
In addition to concrete examples and expert opinions, statistical data can also be a powerful tool for supporting your evaluation. Numbers and statistics can provide objective evidence and strengthen your evaluation by adding a quantitative dimension to your argument. By citing relevant statistics, you can add weight to your evaluations and demonstrate the magnitude of the subject’s strengths or weaknesses.
Furthermore, it is important to consider counterarguments and address them in your evaluation. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and addressing them effectively, you can strengthen your own evaluation and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject. This approach shows that you have considered different perspectives and have arrived at a well-rounded evaluation.
In conclusion, supporting your evaluation with solid evidence is essential to writing a persuasive evaluation essay. By using concrete examples, expert opinions, statistical data, and addressing counterarguments, you can bolster the validity and strength of your evaluation. Remember to present your evidence clearly and logically, making your evaluation more compelling and convincing to your readers.
Use a Structured Format to Organize Your Essay
When writing an evaluation essay, it is important to use a structured format to organize your thoughts and arguments. This will help you present your ideas in a clear and logical manner, making it easier for your reader to follow along and understand your points. By using a structured format, you can ensure that your essay flows smoothly and effectively communicates your evaluation.
One effective way to structure your evaluation essay is to use a table format. This allows you to present your evaluation criteria and supporting evidence in a concise and organized manner. By using a table, you can easily compare and contrast different aspects of the subject being evaluated, making it easier for your reader to grasp the overall evaluation.
In addition to using a table format, you should also follow a logical structure within each section of your essay. Start with a clear introduction, where you introduce the subject you are evaluating and provide some background information. Then, present your evaluation criteria and explain why these criteria are important for assessing the subject. Next, provide specific examples and evidence to support your evaluation, using the table format as a guide. Finally, end your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your evaluation and reinforces your main points.
By using a structured format, you can effectively organize your evaluation essay and present your ideas in a clear and concise manner. This will make your essay more engaging and persuasive, and help your reader understand and appreciate your evaluation.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.
7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)
In this ultimate guide, I will explain to you exactly how to write an evaluation essay.
1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
An evaluation essay should provide a critical analysis of something.
You’re literally ‘evaluating’ the thing you’re looking up.
Here’s a couple of quick definitions of what we mean by ‘evaluate’:
- Merriam-Webster defines evaluation as: “to determine the significance, worth, or condition of usually by careful appraisal and study”
- Collins Dictionary says: “If you evaluate something or someone, you consider them in order to make a judgment about them, for example about how good or bad they are.”
Here’s some synonyms for ‘evaluate’:
So, we could say that an evaluation essay should carefully examine the ‘thing’ and provide an overall judgement of it.
Here’s some common things you may be asked to write an evaluation essay on:
This is by no means an exhaustive list. Really, you can evaluate just about anything!
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
2. How to write an Evaluation Essay
There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria.
Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument
Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
The evaluation argument will show your reader what you have decided is the final value of the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating.
But in order to convince your reader that your evaluative argument is sound, you need to do some leg work.
The aim will be to show that you have provided a balanced and fair assessment before coming to your conclusion.
In order to appear balanced you should:
- Discuss both the pros and cons of the thing
- Discuss both the strengths and weaknesses of the thing
- Look at the thing from multiple different perspectives
- Be both positive and critical. Don’t make it look like you’re biased towards one perspective.
In other words, give every perspective a fair hearing.
You don’t want to sound like a propagandist. You want to be seen as a fair and balanced adjudicator.
Use an Evaluation Criteria
One way to appear balanced is to use an evaluation criteria.
An evaluation criteria helps to show that you have assessed the ‘thing’ based on an objective measure.
Here’s some examples of evaluation criteria:
- Strength under pressure
- Longevity (ability to survive for a long time)
- Ease of use
- Ability to get the job done
- Friendliness
- Punctuality
- Ability to predict my needs
- Calmness under pressure
- Attentiveness
A Bed and Breakfast
- Breakfast options
- Taste of food
- Comfort of bed
- Local attractions
- Service from owner
- Cleanliness
We can use evaluation criteria to frame out ability to conduct the analysis fairly.
This is especially true for if you have to evaluate multiple different ‘things’. For example, if you’re evaluating three novels, you want to be able to show that you applied the same ‘test’ on all three books!
This will show that you gave each ‘thing’ a fair chance and looked at the same elements for each.
3. How to come up with an Evaluation Argument
After you have:
- Looked at both good and bad elements of the ‘thing’, and
- Used an evaluation criteria
You’ll then need to develop an evaluative argument. This argument shows your own overall perspective on the ‘thing’.
Remember, you will need to show your final evaluative argument is backed by objective analysis. You need to do it in order!
Analyze first. Evaluate second.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say you’re evaluating the quality of a meal.
You might say:
- A strength of the meal was its presentation. It was well presented and looked enticing to eat.
- A weakness of the meal was that it was overcooked. This decreased its flavor.
- The meal was given a low rating on ‘cost’ because it was more expensive than the other comparative meals on the menu.
- The meal was given a high rating on ‘creativity’. It was a meal that involved a thoughtful and inventive mix of ingredients.
Now that you’ve looked at some pros and cons and measured the meal based on a few criteria points (like cost and creativity), you’ll be able to come up with a final argument:
- Overall, the meal was good enough for a middle-tier restaurant but would not be considered a high-class meal. There is a lot of room for improvement if the chef wants to win any local cooking awards.
Evaluative terms that you might want to use for this final evaluation argument might include:
- All things considered
- With all key points in mind
4. Evaluation Essay Outline (with Examples)
Okay, so now you know what to do, let’s have a go at creating an outline for your evaluation essay!
Here’s what I recommend:
4.1 How to Write your Introduction
In the introduction, feel free to use my 5-Step INTRO method . It’ll be an introduction just like any other essay introduction .
And yes, feel free to explain what the final evaluation will be.
So, here it is laid out nice and simple.
Write one sentence for each point to make a 5-sentence introduction:
- Interest: Make a statement about the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating that you think will be of interest to the reader. Make it a catchy, engaging point that draws the reader in!
- Notify: Notify the reader of any background info on the thing you’re evaluating. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge. What is a historical fact about the ‘thing’?
- Translate: Re-state the essay question. For an evaluative essay, you can re-state it something like: “This essay evaluates the book/ product/ article/ etc. by looking at its strengths and weaknesses and compares it against a marking criteria”.
- Report: Say what your final evaluation will be. For example you can say “While there are some weaknesses in this book, overall this evaluative essay will show that it helps progress knowledge about Dinosaurs.”
- Outline: Simply give a clear overview of what will be discussed. For example, you can say: “Firstly, the essay will evaluate the product based on an objective criteria. This criteria will include its value for money, fit for purpose and ease of use. Next, the essay will show the main strengths and weaknesses of the product. Lastly, the essay will provide a final evaluative statement about the product’s overall value and worth.”
If you want more depth on how to use the INTRO method, you’ll need to go and check out our blog post on writing quality introductions.
4.2 Example Introduction
This example introduction is for the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society.
“Facebook is the third most visited website in the world. It was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg in his college dorm. This essay evaluates the impact of Facebook on society and makes an objective judgement on its value. The essay will argue that Facebook has changed the world both for the better and worse. Firstly, it will give an overview of what Facebook is and its history. Then, it will examine Facebook on the criteria of: impact on social interactions, impact on the media landscape, and impact on politics.”
You’ll notice that each sentence in this introduction follows my 5-Step INTRO formula to create a clear, coherent 5-Step introduction.
4.3 How to Write your Body Paragraphs
The first body paragraph should give an overview of the ‘thing’ being evaluated.
Then, you should evaluate the pros and cons of the ‘thing’ being evaluated based upon the criteria you have developed for evaluating it.
Let’s take a look below.
4.4 First Body Paragraph: Overview of your Subject
This first paragraph should provide objective overview of your subject’s properties and history. You should not be doing any evaluating just yet.
The goal for this first paragraph is to ensure your reader knows what it is you’re evaluating. Secondarily, it should show your marker that you have developed some good knowledge about it.
If you need to use more than one paragraph to give an overview of the subject, that’s fine.
Similarly, if your essay word length needs to be quite long, feel free to spend several paragraphs exploring the subject’s background and objective details to show off your depth of knowledge for the marker.
4.5 First Body Paragraph Example
Sticking with the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society , this might be your paragraph:
“Facebook has been one of the most successful websites of all time. It is the website that dominated the ‘Web 2.0’ revolution, which was characterized by user two-way interaction with the web. Facebook allowed users to create their own personal profiles and invite their friends to follow along. Since 2004, Facebook has attracted more than one billion people to create profiles in order to share their opinions and keep in touch with their friends.”
Notice here that I haven’t yet made any evaluations of Facebook’s merits?
This first paragraph (or, if need be, several of them) should be all about showing the reader exactly what your subject is – no more, no less.
4.6 Evaluation Paragraphs: Second, Third, Forth and Fifth Body Paragraphs
Once you’re confident your reader will know what the subject that you’re evaluating is, you’ll need to move on to the actual evaluation.
For this step, you’ll need to dig up that evaluation criteria we talked about in Point 2.
For example, let’s say you’re evaluating a President of the United States.
Your evaluation criteria might be:
- Impact on world history
- Ability to pass legislation
- Popularity with voters
- Morals and ethics
- Ability to change lives for the better
Really, you could make up any evaluation criteria you want!
Once you’ve made up the evaluation criteria, you’ve got your evaluation paragraph ideas!
Simply turn each point in your evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
How do you do this?
Well, start with a topic sentence.
For the criteria point ‘Impact on world history’ you can say something like: “Barack Obama’s impact on world history is mixed.”
This topic sentence will show that you’ll evaluate both pros and cons of Obama’s impact on world history in the paragraph.
Then, follow it up with explanations.
“While Obama campaigned to withdraw troops from Iraq and Afghanistan, he was unable to completely achieve this objective. This is an obvious negative for his impact on the world. However, as the first black man to lead the most powerful nation on earth, he will forever be remembered as a living milestone for civil rights and progress.”
Keep going, turning each evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
4.7 Evaluation Paragraph Example
Let’s go back to our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
I’ve decided to use the evaluation criteria below:
- impact on social interactions;
- impact on the media landscape;
- impact on politics
Naturally, I’m going to write one paragraph for each point.
If you’re expected to write a longer piece, you could write two paragraphs on each point (one for pros and one for cons).
Here’s what my first evaluation paragraph might look like:
“Facebook has had a profound impact on social interactions. It has helped people to stay in touch with one another from long distances and after they have left school and college. This is obviously a great positive. However, it can also be seen as having a negative impact. For example, people may be less likely to interact face-to-face because they are ‘hanging out’ online instead. This can have negative impact on genuine one-to-one relationships.”
You might notice that this paragraph has a topic sentence, explanations and examples. It follows my perfect paragraph formula which you’re more than welcome to check out!
4.8 How to write your Conclusion
To conclude, you’ll need to come up with one final evaluative argument.
This evaluation argument provides an overall assessment. You can start with “Overall, Facebook has been…” and continue by saying that (all things considered) he was a good or bad president!
Remember, you can only come up with an overall evaluation after you’ve looked at the subject’s pros and cons based upon your evaluation criteria.
In the example below, I’m going to use my 5 C’s conclusion paragraph method . This will make sure my conclusion covers all the things a good conclusion should cover!
Like the INTRO method, the 5 C’s conclusion method should have one sentence for each point to create a 5 sentence conclusion paragraph.
The 5 C’s conclusion method is:
- Close the loop: Return to a statement you made in the introduction.
- Conclude: Show what your final position is.
- Clarify: Clarify how your final position is relevant to the Essay Question.
- Concern: Explain who should be concerned by your findings.
- Consequences: End by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance. The ‘concern’ and ‘consequences’ sentences can be combined
4.9 Concluding Argument Example Paragraph
Here’s a possible concluding argument for our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
“The introduction of this essay highlighted that Facebook has had a profound impact on society. This evaluation essay has shown that this impact has been both positive and negative. Thus, it is too soon to say whether Facebook has been an overall positive or negative for society. However, people should pay close attention to this issue because it is possible that Facebook is contributing to the undermining of truth in media and positive interpersonal relationships.”
Note here that I’ve followed the 5 C’s conclusion method for my concluding evaluative argument paragraph.
5. Evaluation Essay Example Template
Below is a template you can use for your evaluation essay , based upon the advice I gave in Section 4:
6. 23+ Good Evaluation Essay Topics
Okay now that you know how to write an evaluation essay, let’s look at a few examples.
For each example I’m going to give you an evaluation essay title idea, plus a list of criteria you might want to use in your evaluation essay.
6.1 Evaluation of Impact
- Evaluate the impact of global warming on the great barrier reef. Recommended evaluation criteria: Level of bleaching; Impact on tourism; Economic impact; Impact on lifestyles; Impact on sealife
- Evaluate the impact of the Global Financial Crisis on poverty. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on jobs; Impact on childhood poverty; Impact on mental health rates; Impact on economic growth; Impact on the wealthy; Global impact
- Evaluate the impact of having children on your lifestyle. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on spare time; Impact on finances; Impact on happiness; Impact on sense of wellbeing
- Evaluate the impact of the internet on the world. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on connectedness; Impact on dating; Impact on business integration; Impact on globalization; Impact on media
- Evaluate the impact of public transportation on cities. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on cost of living; Impact on congestion; Impact on quality of life; Impact on health; Impact on economy
- Evaluate the impact of universal healthcare on quality of life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on reducing disease rates; Impact on the poorest in society; Impact on life expectancy; Impact on happiness
- Evaluate the impact of getting a college degree on a person’s life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on debt levels; Impact on career prospects; Impact on life perspectives; Impact on relationships
6.2 Evaluation of a Scholarly Text or Theory
- Evaluate a Textbook. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of explanations; relevance to a course; value for money; practical advice; depth and detail; breadth of information
- Evaluate a Lecture Series, Podcast or Guest Lecture. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of speaker; engagement of attendees; appropriateness of content; value for monet
- Evaluate a journal article. Recommended evaluation criteria: length; clarity; quality of methodology; quality of literature review ; relevance of findings for real life
- Evaluate a Famous Scientists. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to scientific knowledge; impact on health and prosperity of humankind; controversies and disagreements with other scientists.
- Evaluate a Theory. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to knowledge; reliability or accuracy; impact on the lives of ordinary people; controversies and contradictions with other theories.
6.3 Evaluation of Art and Literature
- Evaluate a Novel. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Play. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Film. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate an Artwork. Recommended evaluation criteria: impact on art theory; moral or social message; complexity or quality of composition
6.4 Evaluation of a Product or Service
- Evaluate a Hotel or Bed and Breakfast. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; flexibility of check-in and check-out times; cleanliness; location; value for money; wi-fi strength; noise levels at night; quality of meals; value for money
- Evaluate a Restaurant. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; menu choices; cleanliness; atmosphere; taste; value for money.
- Evaluate a Car. Recommended evaluation criteria: fuel efficiency; value for money; build quality; likelihood to break down; comfort.
- Evaluate a House. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; build quality; roominess; location; access to public transport; quality of neighbourhood
- Evaluate a Doctor. Recommended evaluation criteria: Quality of service; knowledge; quality of equipment; reputation; value for money.
- Evaluate a Course. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; practical advice; quality of teaching; quality of resources provided.
7. Concluding Advice

Evaluation essays are common in high school, college and university.
The trick for getting good marks in an evaluation essay is to show you have looked at both the pros and cons before making a final evaluation analysis statement.
You don’t want to look biased.
That’s why it’s a good idea to use an objective evaluation criteria, and to be generous in looking at both positives and negatives of your subject.
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
I recommend you use the evaluation template provided in this post to write your evaluation essay. However, if your teacher has given you a template, of course use theirs instead! You always want to follow your teacher’s advice because they’re the person who will be marking your work.
Good luck with your evaluation essay!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
2 thoughts on “7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)”
What an amazing article. I am returning to studying after several years and was struggling with how to present an evaluative essay. This article has simplified the process and provided me with the confidence to tackle my subject (theoretical approaches to development and management of teams).
I just wanted to ask whether the evaluation criteria has to be supported by evidence or can it just be a list of criteria that you think of yourself to objectively measure?
Many many thanks for writing this!

Usually we would want to see evidence, but ask your teacher for what they’re looking for as they may allow you, depending on the situation.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

19 Evaluation Essays
Evaluative arguments center around the question of quality. Is something good? Bad? Honest? Dishonest? Evaluative judgments are also about values—what the writer thinks is important. Sometimes the writer’s values are not the same as his/her readers’ values, so he/she has to bridge the gap by showing respect for the audience’s opinions and clarifying the points that they do and don’t agree upon.
An important first step in writing an evaluation is to consider the appropriate standards/criteria for evaluating the subject. If a writer is evaluating a car, for example, the writer might consider standard criteria like fuel economy, price, crash ratings. But the writer also might consider style, warranty, color, special options, like sound systems. Even though all people might not base their choice of a car on these secondary criteria, they are still considered acceptable or standard criteria.
To be taken seriously, a writer must have valid reasons for his evaluation. These reasons are based on criteria. Imagine choosing your attire for a job interview at a very prestigious law firm. You look at the jeans and t-shirts in your closet and immediately decide to go shopping. Why? Because the clothes in your closet don’t meet the criteria for the interview.
The Purpose of Evaluative Writing
Writers evaluate arguments in order to present an informed and well-reasoned judgment about a subject. While the evaluation will be based on their opinion, it should not seem opinionated. Instead, it should aim to be reasonable and unbiased. This is achieved through developing a solid judgment, selecting appropriate criteria to evaluate the subject, and providing clear evidence to support the criteria.
Evaluation is a type of writing that has many real-world applications. Anything can be evaluated. For example, evaluations of movies, restaurants, books, and technology ourselves are all real-world evaluations.
Five Characteristics of an Evaluative Essay
by Dr. Karen Palmer
1. Presenting the subject.
Presenting the subject is an often misunderstood aspect of an evaluative essay. Either writers give too little information or too much. Presenting the subject occurs in two different places in the essay.
First, the writer should give a brief introduction of the subject in the introduction of the evaluation. This introduction occurs in the second part of the introduction–the intro to the topic. At this point, the writer should simply name the subject and give a very brief description. For example, a restaurant review should include at a minimum the name and location of the restaurant. An evaluation of a vehicle might include the make, model, and year of the vehicle and any important features.
Second, the writer should give a more detailed description of the subject following the introduction in the background section of the paper. Here the writer could give a more detailed overview of the restaurant (the type of decor, type of food, owners, history), describe the vehicle in detail, etc. Striking a balance between giving the reader the necessary information to understand the evaluation and telling readers everything is important. The amount of detail necessary depends on the topic. If you are reviewing a brand new technology or a machine, specific to your line of work, for example, you will need to give readers more information than if you are simply reviewing a restaurant or a doctor’s office.
The language used in your description can be evaluative. For example, a writer can use descriptive adjectives and adverbs to convey a certain impression of the subject, even before the claim is made.
2. Asserting an overall judgment.
The main point/thesis should be located at the end of the paper’s introduction. It should be definitive—certain, clear, and decisive. Asking a question does not pose a definitive claim. Giving several different perspectives also does not give a definitive claim. It is ok to balance your claim, though, acknowledging weaknesses (or strengths) even as you evaluate a subject positively: “While the Suburban is a gas guzzler, it is the perfect car for a large family….”
Providing a map of your reasons/criteria within the thesis is a great technique for creating organization and focus for your essay. For example, “While the Suburban is a gas guzzler, it is the perfect car for a large family because it can seat up to 9, it has a high safety rating, and it has the best in class towing capacity.” Not only does this example give a clear, balanced claim, but it also lays out the writer’s reasons upfront, creating a map in the reader’s mind that will help him follow the reasoning in the essay.
3. Giving Reasons and Support
After presenting the subject and providing readers with a clear claim, the writer must explain and justify his/her evaluation using reasons that are recognized by readers as appropriate. This occurs in the argument section of the paper and should be the most extensive part of the paper. Reasons should reflect values or standards typical for the subject. If a writer uses criteria that is not typical for the subject, he/she must be prepared to defend that decision in the essay. For example, “Buying local may not always be at the forefront of a buyer’s mind when shopping for eggs, but…” Each reason should be clearly stated as a topic sentence that both states the reason and refers back to the main claim. Going back to the suburban example, a body paragraph/section might begin with the following topic sentence: “One of the obvious reasons a suburban is great for large families is its capacity for holding that large family and all of their necessary traveling items.”
Following the topic sentence, a writer must include relevant examples, quotes, facts, statistics, or personal anecdotes to support the reason. Depending on what the subject is, the support might be different. To support a claim about a book/film, for example, a writer might include a description of a pivotal scene or quotes from the book/film. In contrast, to support a claim about gas mileage, a writer would probably simply give the information from the vehicle specifications. Support can come from a writer’s own knowledge and experience, or from published sources.
4. Counterarguing:
Counterarguing means responding to readers’ objections and questions. In order to effectively counterargue, a writer must have a clear conception of his/her audience. What does the audience already know or believe about the subject? Effective counterarguing builds credibility in the eyes of the audience because it creates a sense that the writer is listening to the reader’s questions and concerns.
Counterarguments can occur at the end of the essay, after the writer has made his/her point, or throughout the essay as the writer anticipates questions or objections. Writers can respond to readers’ objections in two ways. First, a writer can acknowledge an objection and immediately provide a counter-argument, explaining why the objection is not valid. Second, a writer can concede the point, and allow that, the subject does have a flaw. In either case, it is important to be respectful of opposing positions, while still remaining firm to the original claim.
5. Establishing credibility and authority:
A writer’s credibility and authority lead to readers’ confidence in your judgment and their willingness to recognize and acknowledge that credibility and authority. An author can gain credibility by showing that he/she knows a lot about the subject. In addition, the writer shows that his/her judgment is based on valid values and standards.
The writer’s authority is in large part based upon the background of the author—education, etc. Is the author qualified to make a judgment? For some subjects, like a film review, simply watching the film might be enough. In other instances, like evaluating the quality of newly constructed cabinets or the engine of a new car, more experience might be necessary.
The Structure of an Evaluation Essay
Evaluation essays are structured as follows.
First, the essay will present the subject . What is being evaluated? Why? The essay begins with the writer giving any details needed about the subject.
Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria.
The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for evaluating the subject under consideration. Appropriate criteria will help to keep the essay from seeming biased or unreasonable. If authors evaluated the quality of a movie based on the snacks sold at the snack bar, that would make them seem unreasonable, and their evaluation may be disregarded because of it.
The evidence of an evaluation essay consists of the supporting details authors provide based on their judgment of the criteria.
For example, if the subject of an evaluation is a restaurant, a judgment could be “Kay’s Bistro provides an unrivaled experience in fine dining.” Some authors evaluate fine dining restaurants by identifying appropriate criteria in order to rate the establishment’s food quality, service, and atmosphere. The examples are evidence.
Another example of evaluation is literary analysis; judgments may be made about a character in the story based on the character’s actions, characteristics, and past history within the story. The scenes in the story are evidence for why readers have a certain opinion of the character.
Job applications and interviews are more examples of evaluations. Based on certain criteria, management and hiring committees determine which applicants will be considered for an interview and which applicant will be hired.
Example Outline
Thesis: McAdoo’s is a fantastic family restaurant, offering young and old alike a great atmosphere, wonderful customer service, and a fantastic menu.
- Introduction
- Location–New Braunfels, TX
- History–old post office, restored
- Type of food
- Walking up to the restaurant–cool exterior
- Lobby–original post office doors, etc
- Tables–great decor–memorabilia from NB history
- prompt, courteous service
- refills, bread
- taking care of complaints–all you can eat lobster out–so price reduced
- land lovers
- Conclusion…If you’re ever in NB, I highly suggest stopping in at McAdoo’s and absorbing some of the great old world charm with some delicious food.
Possible “Get Started” Idea
- Evaluate a restaurant. What do you expect in a good restaurant? What criteria determine whether a restaurant is good?
- List three criteria that you will use to evaluate a restaurant. Then dine there. Afterward, explain whether or not the restaurant meets each criterion, and include evidence (qualities from the restaurant) that backs your evaluation.
- Give the restaurant a star rating. (5 Stars: Excellent, 4 Stars: Very Good, 3 Stars: Good, 2 Stars: Fair, 1 Star: Poor). Explain why the restaurant earned this star rating.
Time to Write
In this essay, you will evaluate potential obstacles to learning. Think about the health and wellness of a college student during an international pandemic. What do you need to be successful? Do you have access to resources? Are the GCC resources adequate to support the community and its students during the pandemic?
You will evaluate at least three campus resources. Your recommendation should clearly state which of the resources should be maintained, which should be improved, and which might be eliminated, if any.
Purpose: This assignment will demonstrate the understanding of how to do a thorough evaluation of an approved topic. Students will review the complex elements of the topic they have chosen. Evaluative essays call for the writer to assess a subject in light of specific and explicit criteria and to make a judgment based on the assessment.
Task: This assignment evaluates a campus resource.
Write an Evaluation Essay. For this essay, you will choose a clear topic, give a reason for the evaluation, use description and categorization, create evaluation criteria, use concrete evidence and demonstrate the “why” of your position.
Possible Topics
Some topics to consider are listed here:
- Center for Learning
- Writing Center
- Math Solutions
- High Tech 1
- High Tech 2
- GCC Counseling and Career Services
- Fitness Center
Key Features of an Evaluation:
- Describe the particular phenomenon or work in a way that the rhetorical audience will understand and value.
- Present the criteria on which the phenomenon or work is to be evaluated clearly, persuasively, authoritatively, and often in an order indicating importance. Criteria can be categorized into three groups: necessary (crucial but not enough to meet your overall assessment), sufficient (meeting all of your minimum standards, including the necessary ones), and accidental (unnecessary but an added bonus to the necessary and sufficient criteria).
- Include concrete evidence and relevant examples from your personal experience and research illustrate the ways (usually in the form of assertions) the phenomenon does or does not meet each evaluative criterion. These fair and balanced assertions support the thesis statement.
- At least three (3) sources on the Works Cited; these could be from your personal experience, college web pages, public health information, or sources related to quality college resources.
- Articulate a clear argument (usually in the form of a thesis statement) about whether or not the object or phenomenon meets the criteria on which it is being evaluated.
- Demonstrate an ethical approach to the process.
Key Grading Considerations
- A clear reason for the evaluation
- Use of description
- Categorizing
- Clear evaluation criteria
- Concrete evidence & Examples
- A clear argument presented (Thesis)
- The establishment of ethos (balanced argument)
- Secure closure to the argument (conclusion)
- Three (3) sources minimum
- Key Features are included
- One inch margins
- Typed and double-spaced
- The heading is double-spaced on the left side of the page (includes name, my name, class, date)
- Upper right-hand corner has last name and page number (EX: Dewey 1)
- The font is Times New Roman, size 12
- The title is original and is centered one line under the heading
- Works Cited page lists outside sources in MLA format
- Descriptive Language
- Correct, appropriate, and varied integration of textual examples, including in-text citations
- Limited errors in spelling, grammar, word order, word usage, sentence structure, and punctuation
- Good use of academic English
- Demonstrates cohesion and flow
- Works Cited page has hanging indents and is in alphabetical order by author’s last name
Attribution
- Content Adapted from “Five Characteristics of an Evaluative Essay” from The Worry-Free Writer by Dr. Karen Palmer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
- Content Adapted from Susan Wood, “Evaluation Essay,” Leeward CC ENG 100 OER, licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- Original Content contributed by Christine Jones “Time to Write” licensed under Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication.
English 101: Journey Into Open Copyright © 2021 by Christine Jones is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
📕 Studying HQ
The ultimate guide to writing an evaluation essay, carla johnson.
- June 14, 2023
- Essay Topics and Ideas , How to Guides
Evaluation essays are a common type of writing assignment in school. They ask students to evaluate and analyze the quality or value of something like a book, movie, product, or service. In this article, we’ll give you the most complete guide to writing an evaluation essay. We’ll talk about everything from an evaluation essay’s purpose and importance to the steps you need to take to write a good one.
An evaluation essay is a type of writing that tries to give an unbiased opinion about a topic based on a set of criteria. It’s not just a summary of the topic; it’s a critical analysis of what’s good and bad about it . The writer should give a fair assessment of the topic by pointing out both its strengths and weaknesses.
The point of an evaluation essay is to give a critical analysis of a topic so that the reader can form a well-informed opinion about it. For this kind of essay , the writer needs to know a lot about the subject, including its background, history, and effects. It is a good activity for students to do because it helps them learn how to think critically , do research, and write well.
Evaluation essays are also important in academic writing because they help students show that they can think critically and explain their ideas clearly. Because of this, evaluation essays are often given in many different classes, such as literature, film studies, business, and marketing. By learning how to write an evaluation essay, students can do better in school and improve their chances of getting jobs in their chosen fields.
An evaluation essay is a type of academic writing that asks students to give a critical analysis of a certain topic based on a set of criteria. The point of writing an evaluation essay is to give the reader an unbiased look at the topic so that they can form an opinion about it.
Lastly, evaluation essays are an important part of academic writing because they help students improve their critical thinking, research, and writing skills, all of which are important for academic success and moving up in a career. In the sections that follow, we’ll talk more about the steps you need to take to write a good evaluation essay.
What You'll Learn
Choosing a Topic for an Evaluation Essay
Choosing the right topic is crucial when it comes to writing an effective evaluation essay. A well-chosen topic will not only make the writing process easier but will also ensure that the essay is engaging and relevant to the reader. Here are some tips for selecting an evaluation essay topic:
– Choose a topic that you are interested in: It is essential to choose a topic that you are passionate about and have some knowledge of. This will make the writing process more enjoyable and will also result in a more engaging and informative essay .
– Select a topic that is relevant: Choose a subject that is current and relevant to the reader. This will ensure that your essay is informative and interesting to read.
– Narrow down your topic: It is important to select a topic that is specific and narrow. This will enable you to focus on a particular aspect of the subject and provide a more detailed evaluation.
– Consider both sides of the argument: Choose a topic that allows you to evaluate both the strengths and weaknesses of the subject. This will ensure that your essay is balanced and provides a fair evaluation .
– Use credible sources: Ensure that your topic is backed by credible sources, such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
Here is a list of 50 evaluation essay topics:
1. The impact of social media on modern relationships
2. The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning
3. The portrayal of mental health in popular media4. The impact of technology on our daily lives
5. The effectiveness of government policies on climate change
6. The quality of customer service in the hospitality industry
7. The effectiveness of performance-enhancing drugs in sports
8. The portrayal of women in the media
9. The impact of smartphones on communication skills
10. The effectiveness of gun control laws in reducing gun violence
11. The quality of healthcare services in rural areas
12. The impact of video games on children’s behavior
13. The effectiveness of alternative medicine in treating chronic illnesses
14. The portrayal of minorities in the media
15. The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem
16. The effectiveness of online dating in finding a partner
17. The quality of fast food restaurants
18. The impact of globalization on cultural diversity
19. The effectiveness of police body cameras in reducing police brutality
20. The portrayal of mental illness in popular media
21. The impact of artificial intelligence on job opportunities
22. The effectiveness of vaccination programs in preventing diseases
23. The quality of public transportation in urban areas
24. The impact of social media on political campaigns
25. The effectiveness of rehabilitation programs for prisoners
26. The portrayal of LGBTQ+ individuals in the media
27. The impact of technology on education
28. The effectiveness of animal testing in developing new drugs
29. The quality of public schools in low-income areas
30. The impact of social media onteenagers’ mental health
31. The effectiveness of renewable energy sources in reducing carbon emissions
32. The portrayal of disability in the media
33. The impact of celebrity culture on society
34. The effectiveness of anti-bullying programs in schools
35. The quality of public parks and recreation areas
36. The impact of social media on political polarization
37. The effectiveness of online therapy in treating mental illness
38. The portrayal of aging in the media
39. The impact of automation on job security
40. The effectiveness of recycling programs in reducing waste
41. The quality of public libraries
42. The impact of social media on privacy
43. The effectiveness of parenting classes in improving child behavior
44. The portrayal of mental health in the workplace
45. The impact of technology on the music industry
46. The effectiveness of drug rehabilitation programs
47. The quality of public restrooms
48. The impact of social media on activism
49. The effectiveness of sex education programs in schools
50. The portrayal of race in the media.
Understanding the Structure of an Evaluation Essay
A basic structure for an evaluation essay is an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The purpose of the introduction is to give background information about the subject and explain how it will be judged. Based on the criteria set out in the introduction, the body paragraphs should give a detailed analysis of the topic. In the end, the conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and give a final opinion on the subject.
Here is a breakdown of each section of an evaluation essay:
1. Introduction: The introduction should begin with an attention-grabbing hook that draws the reader in and provides some background information on the subject. This should be followed by a clear thesis statement that outlines the criteria that will be used to evaluate the subject.
2. Body Paragraphs: Each of the body paragraphs should look at a different part of the topic and judge it based on the criteria set out in the introduction. Every paragraph should start with a topic sentence that makes it clear what is being evaluated and how. The evaluation should then be backed up with evidence , such as examples, statistics, and quotes from reliable sources.
3. Conclusion: The conclusion should provide a summary of the main points made in the essay and restate the thesis statement . The writer should then provide a final evaluation of the subject based on the evidence presented in the body paragraphs. This evaluation should be balanced and fair, taking into account both the strengths and weaknesses of the subject.
An evaluation essay outline can be helpful in organizing and structuring the essay. Here is an example of an evaluation essay outline:
I. Introduction
– Hook
– Background information
– Thesis statement
II. Body Paragraphs
– Aspect 1
– Criteria
– Evidence
– Aspect 2
– Aspect 3
-Criteria
III. Conclusion
– Summary of main points
– Restate thesis statement
– Final evaluation
Understanding the structure of an evaluation essay and choosing the right topic are both critical to writing an effective evaluation essay. By following the tips provided for selecting a topic and using an evaluation essay outline, you can create a well-organized and engaging essay that provides a fair assessment of the subject.
Writing an Effective Evaluation Essay
Writing an effective evaluation essay requires careful planning and execution. Here are some tips to help you write a powerful evaluation essay:
1. Developing a thesis statement for an evaluation essay: A strong thesis statement should clearly state the criteria that will be used to evaluate the subject. It should also provide a clear indication of the writer’s stance on the subject, whether it is positive, negative, or neutral.
2. Tips for writing a powerful evaluation essay:
– Use specific criteria: Provide clear and specific criteria for evaluating the subject, and use evidence to support your evaluation.
– Use credible sources: Use credible sources to support your evaluation, such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites.
– Be objective: Provide a balanced evaluation of the subject, highlighting both its strengths and weaknesses.
– Use clear and concise language: Use clear and concise language to make your evaluation easy to understand and engaging to read.
– Use transitions: Use transitions to connect your ideas and ensure that the essay flows smoothly.
3. Common mistakes to avoid when writing an evaluation essay:
– Being too subjective: Avoid being too subjective and provide a balanced evaluation of the subject.
– Failing to provide evidence: Use evidence to support your evaluation, and avoid making unsupported claims.
– Focusing too much on summary: Avoid simply summarizing the subject and focus on providing a critical analysis of its merits and demerits.
– Failing to use credible sources: Use credible sources to support your evaluation andavoid relying solely on personal opinions or unsupported claims.
Examples of Evaluation Essays
To help you get a better understanding of how to write an effective evaluation essay, here are 10 inspiring evaluation essay examples from different fields:
1. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine rollout strategy in the United States
2. Evaluation of the impact of the #MeToo movement on workplace culture
3. Evaluation of the nutritional value of plant-based diets compared to meat-based diets
4. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the Paris Climate Agreement in reducing global carbon emissions
5. Evaluation of the impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior
6. Evaluation of the effectiveness of mindfulness meditation in reducing stress and anxiety
7. Evaluation of the quality of customer service provided by leading airlines
8. Evaluation of the portrayal of mental illness in popular TV shows
9. Evaluation of the effectiveness of online therapy in treating depression and anxiety
10. Evaluation of the impact of video games on children’s cognitive development
Writing an effective evaluation essay involves selecting the right topic, understanding the structure of the essay, and following the tips provided to develop a powerful evaluation essay. By avoiding common mistakes and using credible sources, you can create an engaging and informative evaluation essay that provides a balanced assessment of the subject. The examples provided can also serve as a guide to help you craft a compelling evaluation essay in any field.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is an evaluation essay.
An evaluation essay is a type of academic writing that asks students to evaluate and analyze the quality or value of something like a book, movie, product, or service. The writer should give a fair assessment of the topic by pointing out both its strengths and weaknesses.
2. What are the elements of an evaluation essay?
An evaluation essay has three parts: an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. In the introduction, you should give some background information about the topic and explain how it will be judged. Based on the criteria set out in the introduction, the body paragraphs should give a detailed analysis of the topic. In the end, the conclusion should summarize the main points of the essay and give a final opinion on the topic .
3. How do I choose a topic for an evaluation essay?
To pick a topic for an evaluation essay, think about something you are interested in and know a little bit about. It’s also important to choose a topic that is relevant and specific. Think about both sides of the argument and back up your opinion with information from reliable sources.
4. What is the difference between an evaluation essay and a review?
The main difference between an evaluation essay and a review is that an evaluation essay has a different focus and goal. An evaluation essay tries to give a critical analysis of the subject based on a set of criteria, while a review gives a summary of the subject and often includes personal opinions.
In conclusion, writing an effective evaluation essay is an essential skill for students to master, as it helps to develop critical thinking , research, and writing abilities. To write an effective evaluation essay, it is important to choose the right topic, understand the structure of the essay, and follow the tips provided in this guide. It is also important to avoid common mistakes and use credible sources to support your evaluation.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Have a subject expert write for you now, have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, popular topics.
Business StudyingHq Essay Topics and Ideas How to Guides Samples
- Nursing Solutions
- Study Guides
- Free Study Database for Essays
- Privacy Policy
- Writing Service
- Discounts / Offers
Study Hub:
- Studying Blog
- Topic Ideas
- How to Guides
- Business Studying
- Nursing Studying
- Literature and English Studying
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Maker
- Research Title Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Summarizing Tool
- Terms and Conditions
- Confidentiality Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Refund and Revision Policy
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
Contact Us:
📞 +15512677917
2012-2024 © studyinghq.com. All rights reserved
Academic Language: Language for evaluating
- Academic Vocabulary
- Cautious Language
- Language for evaluating
- Sentence structure
- Word families & Collocation
Academic language for evaluating
In academic writing we have to show that we do not accept without questioning the ideas or concepts in the texts we read, but that we evaluate points or ideas in these texts.
Evaluation in academic writing requires us to analyse the points, ideas or topics in academic texts and to discuss their relevance, effectiveness or application to the topic/s we are writing about. Evaluation is key to critical writing because it allows us to show that we question, understand and analyse what we read.
We can evaluate an issue or idea by interpreting it and commenting on its relevance, effectiveness, significance, limitations, implications, etc.
On this page you will find;
Types of evaluative language
- Help on bringing your own voice
- Effectiveness
- Limitation or weakness
- Significance of evidence
We can evaluate the effectiveness of an argument or intervention using phrases such as:
- the approach has been successful in...
- the intervention has proven effective in...
- the results demonstrate the efficacy of the intervention
- the approach has potential to improve...
“Truth is demoted to current understandings of the world, based on the available evidence and resources we possess. This view, which problematises uncritical acceptance of truths and current understandings, is helpful when we consider the impact of changes to social life.”
“Also relevant to changing student populations is Harris and Brampton’s (2003) suggestion that postmodern paradigms are important for an understanding of the debates about language, ethnicity and race because they highlight tensions in the way different people experience the world.”
We can show how strongly our views are aligned with or against an idea using phrases such as:
- strong evidence suggests that...
- there is substantial evidence to support...
- the evidence is convincing
- the data is consistent with...
- the results are statistically significant
“In his analysis of students in French HE institutions, Bourdieu (1997) convincingly argued that working-class students were less successful (Thomas 2002) not because they were of inferior intelligence or not gifted, but because the curriculum was `biased in favour of those things with which middle-class students were already familiar’ (Robbins 1993, p. 153).”
“One of the most serious effects of deficit thinking is that it strengthens stereotypes in the minds and thought of educators, policy makers and students themselves.”
“In essence, deficit thinking allows generalisations about student ability to be made, and supports a laziness to grapple with the complex issues around student difficulties. In the process, people who are already disenfranchised are labelled and further stigmatised.”
“In highlighting the political meaning and historical relevance of absences or silences, Cooper offers an astute revision of historical memory and an insightful analysis of France’s fundamental political and philosophical paradoxes.”
We can evaluate limitations or weaknesses in the evidence or arguments using phrases such as:
- one limitation of this study is...
- this argument is weakened by...
- the evidence presented is limited by...
- there are inconsistencies in the data
- the methodology used in this study has limitations
“Media coverage of this phenomenon, readers’ heated responses to media coverage, and existing research literature around Chinese students’ experiences tend to centre around challenges students face in the USA without adequate exploration of how external sociocultural contexts and histories shaped students’ experiences (Abelmann and Kang 2014). This creates an incomplete understanding of Chinese students’ experiences in the USA and inadvertently perpetuates a stereotype that the students are incompetent and deficient.”
“One problem with this binary view of good-bad language or good-bad writing is that a variety of ‘problems’ within an educational setting are sometimes misdiagnosed as language problems, whereas I found issues affecting the practice of writing to be more complex.”
“This deficit position tends to view literacy practices as neutral and objective, and one further consequence of this perspective is that there has been a focus on what is referred to as "strong text" conceptions of literacy characteristics (Meacham 2000, p.181) which rarely acknowledge a reliance on culture or diversity in terms of sociolinguistic, historical or political context.”
We can evaluate the significance of the evidence or argument by using phrases such as:
- this is a significant finding because...
- this study contributes to the field by...
- this evidence has important implications for...
- this result is consistent with previous research on the topic
“In seeking to use crisis as a term of analysis, Hay (1999, p.318) argued for the concept to be re-defined, indeed more closely defined, in order to differentiate between ‘a punctuated or step-wise periodisation’ in accounting for socio-political change and the ‘more incremental and evolutionary understandings of the process’ (ibid.). This understanding is critical; for in setting the conceptual parameters for the periodisation of crisis it thus becomes possible to define the opening and closing of the crisis period, and to contain the analysis of federal dynamics within a time frame."
“E. H. Carr profoundly adds to the debate on the immanence of crisis in International Relations theory at the world analysis level, and also reflects his knowledge and understanding of the Marxist approach to International Political Economy in his analysis of the sources of crisis and conflict.”
“In the seminal ‘Twenty years’ Crisis’, Carr challenges the utopian direction of International Relations in the interwar years from a realist perspective, grounded in critical thought.”
“Of more direct salience to the thesis’s conceptualising of crisis is their link of the ‘scope and nature of the crisis’ (ibid.p.18) and their focus on ‘accountability and learning processes’ (ibid.).”
We can evaluate and compare different arguments or pieces of evidence using phrases such as:
- in comparison to...
- on the other hand...
- when compared to...
- in contrast...
- conversely...
- there is a significant difference between...
“Our conceptualisation of racial macroaggressions is different from many other scholars who define racial macroaggressions as the overt, ‘large scale’ (i.e. state) acts of racism experienced by People of Color (Gildersleeve, Croom, and Vasquez 2011; Smith et al., 2007a).” “We argue that the terms ‘micro’ and ‘macro’ should not define acts of racism as subtle or blatant. In fact, Pierce (1974) makes a similar argument about the limitations of terminology when he stated, ‘[t]hese problems are only micro in name, since their very number requires a total effort that is incalculable’.”
“We concur with Pierce that we are limited by the terms we use to describe the complexities of racism and the harm they can cause. We certainly do not intend to depreciate everyday racism by using the term micro. To the contrary, we would agree with scholars like Dumas (2014) who argue that microaggressions are in fact a form of ‘everyday suffering’ that have become socially and systemically normalised and effectively minimised.”
“National cultural labels are sometimes applied less critically by some from the field of intercultural communication and management (see Hampden-Turner and Trompenaars 1993; Hofstede 1980). Indeed, for this reason, Norton (2000) prefers to avoid definitions of cultural identity framed by a sense of a shared group or language because of the tendency for this to become fixed and the potential for it to become essentialist. This is an important point and Norton concedes the term can and ought to be understood in a more flexible way.”
Bringing our own voice
- Expressing your own voice
- Ways to express our voice
We can show our position towards ideas discussed in our writing by replacing the over-used ‘according to’ in our writing with a range of evaluative adjectives and adverbs that indicate what we think of other writers’ views.
Example 1: “Atkinson is misguided when he inaccurately claims that students need . . .”
We can show our position with regard to the points of view or evidence that we have presented by using a combination of precise verbs, hedging and other evaluative language .
Example 2: “Furthermore, it appears that Friedman may have overlooked some key data when he raises the possibility that . . .”
We can show how confident – or not – we are with regard to our position through the use of hedging / cautious language , such as may, might or could
Example 3: “The investigations to date may indicate a fundamental flaw in this approach."
You can be more confident through the use of intensifying language as certainly, definitely or must.
Example 4: “The findings certainly show a need for more research on this topic . . .”
Evaluation in academic writing allows us to show our voice (our view on the topic). Voice can be expressed through:
- Presenting a position
- Presenting a position and developing/defending/supporting it.
- Presenting counter evidence and making an argument against it.
- Identifying a gap.
- Hedging/more assertive language (show your contribution by commenting on the strength or weakness of a point).
- Avoiding overuse of according to, strengthening your argument with an adjective/adverb that indicates your position.
- Using active verbs.
- Giving your opinion/evaluation of what other writers claim - showing confidence in your own position.
- Relating one text to another.
- Critically commenting/concluding.
Further Reading
- << Previous: Cautious Language
- Next: Sentence structure >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 3:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uos.ac.uk/academic-language
➔ About the Library
➔ Meet the Team
➔ Customer Service Charter
➔ Library Policies & Regulations
➔ Privacy & Data Protection
Essential Links
➔ A-Z of eResources
➔ Frequently Asked Questions
➔Discover the Library
➔Referencing Help
➔ Print & Copy Services
➔ Service Updates
Library & Learning Services, University of Suffolk, Library Building, Long Street, Ipswich, IP4 1QJ
✉ Email Us: [email protected]
✆ Call Us: +44 (0)1473 3 38700
How to Write an Evaluation Essay – A Complete Guide

Introduction
Welcome to The Knowledge Nest's complete guide on how to write an evaluation essay. If you're looking to enhance your writing skills and learn the art of evaluating different subjects or objects effectively, you've come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps of crafting an evaluation essay, offer valuable tips, and provide examples to support your understanding. So let's dive in!
Understanding the Purpose
Before we dive into the specifics, it's crucial to understand the purpose of an evaluation essay. An evaluation essay aims to assess the quality, significance, or value of a particular subject or object. It goes beyond mere description and requires you to provide an informed judgment based on specific criteria and evidence.
Key Components of an Evaluation Essay
When writing an evaluation essay, keep in mind the following key components:
- Subject: Clearly define the subject you will be evaluating. It could be a book, movie, restaurant, product, or any other topic.
- Criteria: Establish the criteria on which you will base your evaluation. These criteria should be relevant and objective.
- Evidence: Provide evidence to support your judgment. This can include facts, statistics, expert opinions, or examples.
- Analysis: Examine and analyze the subject thoroughly, considering different perspectives and angles.
- Conclusion: Summarize your evaluation and restate your overall judgment.
Step-by-Step Guide
Now that you have a basic understanding of what an evaluation essay entails, let's explore the step-by-step process of crafting an impressive evaluation essay:
Step 1: Choosing a Subject
The first step in writing an evaluation essay is selecting a subject that you can assess and analyze effectively. Choose a topic that you are familiar with and have enough knowledge or experience to make an informed judgment.
Step 2: Establishing Criteria
Once you have chosen your subject, it is essential to establish the criteria on which you will evaluate it. Consider the qualities or attributes that are relevant to the subject and define specific criteria accordingly.
Step 3: Gathering Evidence
Before you can begin evaluating your subject, you need substantial evidence to support your analysis. Conduct thorough research, gather relevant data, and find reliable sources to back up your claims.
Step 4: Structuring Your Essay
A well-structured evaluation essay enhances readability and ensures your points are effectively communicated. Consider the following structure:
- Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the subject and state your evaluation's purpose and significance.
- Main Body: Break your evaluation into logical paragraphs, each focusing on a specific aspect of the subject. Provide evidence, present your analysis, and relate everything back to the established criteria.
- Conclusion: Summarize your evaluation, restate your judgment, and offer final thoughts or recommendations.
Step 5: Writing and Revising
Once you have gathered all the necessary information and structured your essay, it's time to start writing. Begin with a strong introduction, develop coherent paragraphs, and ensure your arguments flow logically. After completing your initial draft, revise and edit it for clarity, coherence, and grammatical accuracy.
Step 6: Providing Examples
Support your evaluation with relevant examples that illustrate specific points or highlight the strengths and weaknesses of the subject. These examples will add depth and credibility to your essay.
Let's explore a couple of examples to solidify your understanding of how to write an evaluation essay:
Example 1: Evaluating a Movie
Subject: "Inception" directed by Christopher Nolan
- Plot structure
- Character development
- Cinematography
Begin describing your evaluation here, providing evidence and analysis for each criterion. Remember to support your claims with specific examples from the movie.
Example 2: Evaluating a Restaurant
Subject: "The Taste Haven"
- Quality of food
Start your evaluation by discussing the selected restaurant. Evaluate each criterion individually, citing specific instances and experiences to back up your assessment.
Congratulations! You've now completed The Knowledge Nest's complete guide on how to write an evaluation essay. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can master the art of crafting well-structured and compelling evaluation essays. Remember to choose your subject wisely, establish objective criteria, gather sufficient evidence, and structure your essay effectively. Don't forget to revise and provide examples to support your evaluation. Happy writing!


Psychology Case Study: Guide to Follow

Dissertation Abstract Help - Studybay

Write My Term Paper for Me - Studybay

6 Essential Classes to Take in College

Healthy Community Essay - Creative Writing Example

Writing Samples Case Studies Quickly And Efficiently

About Geometry Homework Help - The Knowledge Nest

Hiring a Literature Review Writing Service - Studybay

Oliver Twist Essay Topics and Writing Tips - Studybay

Ideal Hamlet Essay Topic Ideas To Choose From - Studybay
Definition and Examples of Evaluation Essays
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
An evaluation essay is a composition that offers value judgments about a particular subject according to a set of criteria. Also called evaluative writing , evaluative essay or report , and critical evaluation essay .
An evaluation essay or report is a type of argument that provides evidence to justify a writer's opinions about a subject.
"Any kind of review is essentially a piece of evaluative writing," says Allen S. Goose. "This type of writing calls for the critical thinking skills of analysis, synthesis, and evaluation" ( 8 Kinds of Writing , 2001).
Observations
- "Without good reasons for liking or disliking certain things, students can never get beyond being passive receivers of marketing, fickle consumers without a basis for their opinions. Writing evaluation papers asks them to question why they feel the way they do." (Allison D. Smith, et al., Teaching in the Pop Culture Zone: Using Popular Culture in the Composition Classroom . Wadsworth, 2009)
How to Evaluate
- "If you are evaluating a piece of writing, then you are going to need to thoroughly read the work. While you read the work, keep in mind the criteria you are using to evaluate. The evaluative aspects may be: grammar, sentence structure, spelling, content, usage of sources, style, or many other things. Other things to consider when evaluating a piece of writing is whether the writing appealed to its target audience . Was there an emotional appeal? Did the author engage the audience, or was the piece lacking something? ..."If you are evaluating anything else, use your head. You need to try, use, or test whatever thing you are evaluating. That means you should not evaluate a 2005 Chevrolet Corvette unless you have the $45,000 (or more) to buy one, or the money to rent one. You also need the know-how of driving a car of that power and a base of knowledge of other cars that you have tested to compare it to." (Joe Torres, Rhetoric and Composition Study Guide . Global Media, 2007)
Identifying Criteria for an Evaluation
- " Make a list of prominent, widely recognized standards for judging your subject. If you do not know the standards usually used to evaluate your subject, you could do some research . For example, if you are reviewing a film, you could read a few recent film reviews online or in the library, noting the standards that reviewers typically use and the reasons that they assert for liking or disliking a film. If you are evaluating a soccer team or one winning (or losing) game, you could read a book on coaching soccer or talk to an experienced soccer coach to learn about what makes an excellent soccer team or winning game." (Rise B. Axelrod and Charles R. Cooper, Axelrod & Cooper's Concise Guide to Writing , 4th ed. Bedford/St. Martin's, 2006)
Ways of Organizing an Evaluation Essay
- "One way to organize an evaluation essay is point-by-point: describe one element of the subject and then evaluate it; present the next element and evaluate it; and so on. Comparison/contrast could be an organizing structure as well, in which you evaluate something by comparing (or contrasting) it to a known item. Culinary and music reviews often use this strategy. Chronological organization can be used for evaluating an event (either current or historical). Sequential organization can be used when describing how something works and evaluating the effectiveness of the process, procedure, or mechanism. Spatial organization can be used for evaluating art or architecture in which you describe and evaluate one element of the artifact and then move spatially to the next major element to be described and evaluated." (David S. Hogsette, Writing That Makes Sense: Critical Thinking in College Composition . Wipf and Stock, 2009)
- Questions for Each Level of Bloom's Taxonomy
- Holistic Grading (Composition)
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- What Is a Critique in Composition?
- Critical Thinking in Reading and Composition
- Self-Evaluation of Essays
- Research in Essays and Reports
- Topical Organization Essay
- What Is Composition? Definition, Types, and Examples
- Sample Essay Rubric for Elementary Teachers
- Moving Past the Five Paragraph Essay
- Who Should You Ask for a Recommendation Letter?
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Peer Response (Composition)
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- Definition Examples of Collage Essays

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
53 Introduction to Evaluative Writing
Amy Minervini
by Amy Minervini
Evaluation is the process of using specific criteria in an effort to ‘judge’ the quality or effectiveness of something. We use evaluation skills every day when we decide which grocery store to shop, which restaurant to eat, which movie to go see or stream, and which product to buy off Amazon. We may even use others’ evaluations of places or products in order to make decisions. This is why review sites and apps are so popular and why people rely on reviews when buying things.
But evaluation is more akin to analysis than merely giving a preference. For example, if you wanted to know about a new restaurant that just opened in town, someone saying ‘I just didn’t like it’ is not the most helpful or effective advice. Of course, you would want to know why this person didn’t like it. Was it the quality of the food, service, portion size, temperature, or atmosphere? If the person says they didn’t like the decor, well, that might be a personal preference that is valid but it isn’t a criterion that necessarily carries weight with regard to the food or service the new restaurant provides. In other words, you want a detailed judgment or evaluation based on specific criteria, criteria that is universally meaningful to most patrons.
Evaluation can occur with many types of mediums, making it a popular mode for both informal and formal writing. The things that can be evaluated include: books, chapters, articles, films, TV shows, music, restaurants, products, speeches, poetry, plays, commercials, advertisements, and even procedures, just to name a few.
Key Characteristics
Evaluative writing generally exhibits the following:
- Puts the writer in the position as expert or trusted evaluator
- Makes a judgment about something using facts and evidence rather than feelings
- Uses specific criteria that are relevant, common, or somewhat universal
- Organizes the analysis based on specified criteria; avoids irrelevant, unnecessary, or unhelpful criteria
- Avoids being overly biased; executes evaluation with some balance
Essay Types within this Chapter
- Classification
- Comparison-Contrast
Introduction to Evaluative Writing Copyright © 2020 by Amy Minervini is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

14.3: Structure of the Evaluative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 50425

- Chris Manning, Sally Pierce, & Melissa Lucken
- Lansing Community College
13.3.1 Introduction
In the introduction of your evaluative essay, you should clearly state the following: – what you are evaluating (the subject – like Citizen Kane or National Lampoon’s Christmas Vacation ) – the purpose of your evaluation – what criteria you are evaluating your subject on (plot, characterization, cinematography etc.) For example, you should not just write that you are judging the acting in the film. You should explain that you are judging the individual performances of actor, the plot of the screenplay, and cinematography. Give the reader background on the subject including the “who, what, when, where, and why” elements of the subject.
13.3.2 Body
Be sure to be very descriptive and thorough when evaluating your subject. The more you leave out of the essay, the more unanswered questions your readers are left with. Your goal should be to cover all aspects of the subject and to tell the audience how good or bad it is. Consider, for example, not only what quality the subject possesses, but what is missing. Good evaluations measure the quality or value of a subject by considering what it has and what it lacks.
13.3.3 Conclusion
The conclusion for an evaluative essay is pretty straightforward. Simply go over the main points from the body of your essay. After that, make an overall evaluation of the subject. Tell the audience if they should buy it, eat it, use it, wear it, etc. and why. After that is done, your essay is finished.
The conclusion of a review is also an opportunity for some flourish. Think about how you can sum up the best or worst of the experience to send your audience marching toward or away from the subject of your evaluation. Good job!

Mark Roberts Teach
Thoughts and ideas about words, stories and what works best in the classroom and beyond.

Evaluative verbs – adding sophistication to analysis
Recently, I wrote an article for TES about how an unexpected number of pupils at my school achieved grade 9s in GCSE English. It was popular and I received lots of feedback. One area that interested many people was the discussion about the evaluative verbs that top students tended to use in their writing. Traditionally, teachers of GCSE English have encouraged pupils to use analytical verbs, often pushing them for a synonym for ‘suggests’ or ‘shows’. I have an example list of my own that I’ve used for some time:
With the advent of the evaluation question on GCSE English language specifications, teachers have now placed a greater onus on ensuring their pupils use the language of evaluation to ensure that examiners can tell they are attempting to sum up the quality of a piece of writing or the technique that the writer has deployed. Often this takes the form of the ubiquitous adverb ‘effectively’ and adjective ‘effective’. For example ‘Orwell effectively portrays the unpleasant conditions for miners through his personification of the ‘roaring…machines’…’ Or ‘This is effective because ‘roaring’ implies the lethal nature of these giant machines and gives a sense of the deafening volume…’
What I find, however, is that the most successful pupils evaluate consistently, whether or not the question prompts them. In the literature exams, our highest attainers wrote about how a writer ‘ridicules’, ‘trivialises’, ‘demonises’ or how a character ‘coerces’, ‘sentimentalises’ or ‘derides’ another. I’ve tried to put together a list of the evaluative verbs pupils might typically use in their writing. This is far from definitive. And some of the verbs are only evaluative if used in a particular context. But it’s a good place to start if you wish to really stretch your top pupils:
- Criticises – rebukes, admonishes, chastises, lambasts, castigates, demonises, condemns
- Questions – queries, disputes, casts doubt upon, refutes, interrogates, examines, challenges, exposes, provokes
- Ridicules – mocks, trivialises, satirises, lampoons, derides, pillories, parodies, caricatures
- Celebrates – commemorates, honours, salutes, recognises, acknowledges, memorialises, lionises, fetishises, idealises, eulogises, elevates, glorifies, sentimentalises, romanticises, beautifies, deifies
- Subverts – undermines, overturns, alters, modifies, corrupts
- Accepts – welcomes, embraces, affirms, reaffirms
- internalises, externalises
- Technical terms – anthropomorphises, zoomorphises
Here are some examples of how evaluative verbs might elevate responses to a sophisticated understanding of the writer’s intention:
- Stephenson portrays Jekyll as a duplicitous character. (simple statement)
- Stephenson insinuates that Jekyll has repressed his transgressive desires, leading a conflicted dual nature. (analytical statement)
- Through his portrayal of Jekyll’s conflicted dual nature caused by his repressed transgressive desires, Stevenson ridicules hypocritical Victorian attitudes towards sin. (evaluative statement)
Thanks for reading,
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

IOE Writing Centre

IOE Writing Centre Online
Self-access resources for Academic Writing in Education Studies.
Access our Resources for academic reading and writing

Evaluation Essay
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
13 min read

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Are you unsure about what it takes to evaluate things from your perspective in an evaluation essay?
If you’re having a hard time understanding how to present a balanced assessment of the subject, worry not! We are here to help you get through the evaluation essay writing process.
In this blog, you will learn all about evaluation essays. From the definition, writing process, topics, tips, and a lot more, you’ll learn how to write an evaluation essay effortlessly!
Continue reading to get a better idea.
- 1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
- 2. Evaluation Essay Structure
- 3. How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
- 4. How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
- 5. How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
- 6. Evaluation Essay Examples
- 7. Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
- 8. Evaluation Essay vs. Review
What is an Evaluation Essay?
Let’s first understand the evaluation essay meaning, here is the standard definition:
An evaluation essay offers a value judgment or an opinion of something. It presents an overall view of a particular subject’s quality. Moreover, it provides a critical analysis and a complete evaluation of something.
What is the Purpose of an Evaluation Essay?
The main purpose of an evaluation essay is to present an opinion and evaluate a topic critically. This type of writing determines the condition, worth, or significance by careful appraisal and study.
This essay features the writer’s opinion, but when done correctly, it does not sound opinionated. Instead, it provides the facts and evidence to justify the opinions about the essay’s subject.
To write a good evaluation essay, you need to master critical evaluation and present the evaluation in an unbiased manner. You may also discuss both the pros and cons of the subject.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job
Evaluation Essay Structure
The four different ways to format and organize the evaluation essay are as follows.
1. Chronological Structure
It is a sequential organization that could be used for evaluating historical or current events. It tells how something works and assesses the effectiveness of a mechanism, procedure, or process.
2. Spatial Structure
The spatial organization structure is used for evaluating or describing art or architecture. Here, you will define one element of the artifact and spatially move to the next.
3. Compare and Contrast Structure
The compare and contrast structure is used to evaluate or review the culinary or music genre. Here the writer evaluates a subject by comprising and contrasting it with the known subject.
4. Point-by-Point Structure
The point-by-point structure is also used for culinary and music reviews. But, in this structure, you describe one element and then evaluate it, describe the second element and evaluate it, and so on.
After setting the criteria and collecting evidence for strengthening your judgment, you’ll start your evaluation essay. Let’s see what are the steps involved in starting an evaluation essay.
How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
When you start writing an evaluation essay, grabbing the reader’s attention is essential. For this, hook the reader from the beginning until the end to ensure that your essay’s opening follows an engaging tone.
Step 1. Choose an Interesting Topic
Deciding the topic and evaluation essay criteria is important. Make sure it's not just compelling and interesting, but also informative so that you can find enough material for a detailed evaluation.
Step 2. Set the Evaluation Essay Criteria
For an evaluation essay, you have to set the criteria for evaluation first. Criteria are the standards or measures by which someone assesses the quality or value of the subject.
Some key points to establish the criteria are:
- Identifying relevant aspects that relate to the subject
- Defining the criteria clearly so that it is specific and understandable for readers
- Your criteria should be directly relevant to the nature of the subject
- Always consider the audience’s expectations and standards while setting the criteria
- Your thesis statement should always align with your evaluation criteria
Step 3. Collect Evidence for Your Judgment
The author’s judgment of the subject states whether the subject is good or bad. It is an overall assessment or the opinion supported by the evidence. The judgment corresponds to the benchmarks set by the author in the essay criteria.
The evidence is a combination of supporting data and facts. Using the evidence, the author demonstrates how well the subject meets the judgment. The evidence serves as the foundation of your evaluation.
Without providing strong and accurate evidence, you will not be able to convince the readers of your judgment.
Step 4. Decide the Essay Structure
After that, decide on the structure that you want to follow. It can be a chronological or point-by-point structure
Step 5. Craft the Essay Outline
When you create an essay outline , evaluate what should be added and removed. If you skip this step before writing, you may lose track of what to include in your essay while you write.
So, writing an outline for your evaluation essay is a critical step that eases your writing journey.
Here is a sample evaluation essay outline:
Step 6. Declare Your Thesis Statement
For an evaluation essay that keeps the reader hooked from the start, opt for a catchy thesis statement . The thesis should state the main point of the evaluation.
In the thesis statement, you should always express your stance on the subject clearly. In doing so, the readers will have a clear idea about the purpose and direction of your essay.
Now, understand how to write an evaluation essay by following the detailed procedure mentioned below.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
Here is a step-by-step guide for you to write an evaluation essay.
Step 1. Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first impression your readers will have of you, so it's crucial to make a good one. It should capture attention and excite readers, drawing them into what you have to say about this topic.
The following are the elements that you should consider while writing the introduction:
- Start with an interesting hook statement so that you can get the reader’s attention.
- Provide background information about the topic for the reader to understand the subject
- Establish the evaluation essay thesis statement. It sets out the overall purpose of the evaluation, so make sure it is apparent and to the point
Read this evaluation essay introduction example, and you’ll understand exactly what to pen down in yours:
Step 2. Draft the Body Section
The body of the essay consists of three paragraphs. Each paragraph holds different ideas related to one another and flows smoothly from start to finish, just like how a good story should be told.
Here are the important points that must be included in the body paragraphs.
- Start with the topic sentence that presents your judgment about the topic
- Present the supporting evidence to back up the topic sentence and your viewpoint.
- Present a balanced evaluative argument to show impartiality
- Compare and contrast the subject to another subject to show the strengths and weaknesses
- Present the evaluation from multiple perspectives, while being both positive and critical
- Always use transition words between your paragraphs to ensure a smooth and coherent flow for the reader.
Step 3. Write the Conclusion
It is the final chance to convince your reader to agree with your point of view. You’re supposed to summarize and conclude the essay. In the conclusion , you present your final evaluation of the essay.
Keep in mind the following aspects while writing a closing paragraph of an evaluation essay.
- Summarize the points and evaluative arguments that you made in the body section.
- Justify your thesis statement.
- Provide a concrete and secure conclusion to your argument by ultimately leaving the reader convinced by your evaluation.
Step 4. Proofread, Revise, and Edit
The final step is proofreading and editing. Always spend enough time reading your essay carefully. It will help you catch the unintentional mistakes you have made and recover them. If needed, you can also revise your essay 2–3 times.
How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
For formatting your evaluation essay, follow the standard academic writing guidelines. You can opt for different formatting styles like APA, MLA, or Chicago.
In general, you should stick to the below formatting guidelines:
Font and Size:
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman or Arial.
- Choose a standard font size, often 12-point.
- Set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, and body paragraphs.
- Create a title for your essay that reflects the subject and purpose of the evaluation.
- Center the title on the page.
- Use title case (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Include a header with your last name and page number in the top right corner.
- Follow the format “Last Name Page Number” (e.g., “Smith 1”).
Citations (if applicable):
- Include citations for any sources used in your evaluation.
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor or the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago).
Counterargument (if included):
- Clearly label and present any counterargument.
- Provide a well-reasoned response to the counterargument.
References or Works Cited Page (if applicable):
- Include a separate page for references or a works cited page if your essay includes citations.
- List all sources in the appropriate citation style.
Well, the time has come to look at some great evaluation essay examples. Getting help from sample essays is always a great way to perfect your evaluation papers.
Evaluation Essay Examples
Evaluation can be written on any topic, i.e., book, movie, music, etc. Below, we have given some evaluation essay examples for students:
Evaluation Essay Sample PDF
Movie Evaluation Essay Example
Critical evaluation Essay Example PDF
Product Evaluation Essay PDF
Source Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Employee Self-Evaluation Essay Example
How to Start A Self-Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
For writing an amazing evaluation essay, the first thing that you require is an essay topic. Here are some incredible topic ideas for college students. You can use or mold them according to your preference.
- Artificial intelligence's impact on society: A double-edged sword?
- Evaluate the online teaching and on-campus teaching styles
- Analyze and evaluate the Real Madrid football team and their performance
- Is media a threat to cultural cohesion or a source of enrichment?
- Compare and evaluate recorded music and live performance
- Evaluate how a university's football team impacts students' personalities
- Critically evaluate a remake of an original movie you have watched recently
- Analyze how the roles of females and males changed in recent romantic movies
- Evaluate your favorite restaurant, its food, aroma, and everything
- Critically evaluate gender disparities in college majors and career choices.
Evaluation Essay vs. Review
At first glance, an evaluation essay might look like a review. But, there are some notable differences between them. See this table to see how both pieces of writing differ from each other.
To conclude,
After reading the step-by-step guide and examples, you must have learned the art of writing a good evaluation essay. We’re confident that you’re now able to provide a balanced and effective evaluation of the topics you choose for your essay.
But writing a perfect essay is not that simple; you require a lot of practice and experience to become a good writer. That is why we are here to help you write any type of academic essay.
MyPerfectWords.com is a writing service that offers help for all academic writing assignments. We have a team of professional writers who are experts in writing all types of essays and evaluation papers.
So what are you waiting for? Buy custom essay online and have a sigh of relief!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what are the four components of an evaluation essay.
The four components of an evaluation essay are:
- Introduction
- Background information
2. What are the 4 types of evaluation?
The four types of evaluation are:

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
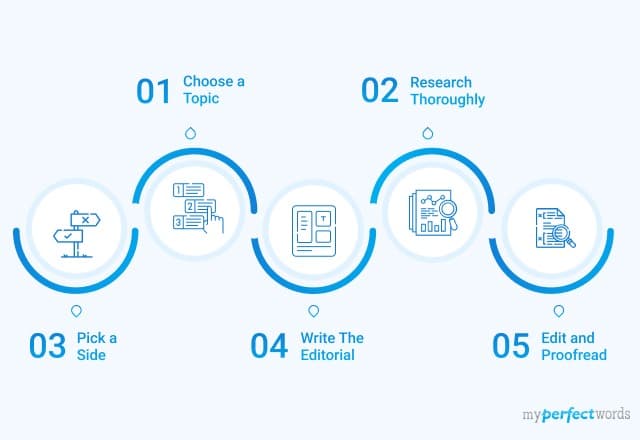
Jun 29, 2023
Evaluation Essay Examples: Master the Art of Critical Assessment with Examples and Techniques
Want to turn good evaluation essays into great ones? We've got you covered with the guidance and insights you need. Join us as we delve into the art of critical assessment!
An evaluation paper's main purpose is to assess entities like a book, movie, restaurant, or product and provide constructive criticism. This writing style can be approached with serious objectivity or with humor and sarcasm. Reviewing is a common form of academic writing that serves to assess something and is often used in various fields as a research method. For example, research papers might include literature reviews or case studies, using evaluation as an analytical tool.
Evaluation reports can also take the form of analyses and critiques. A critique of a scientific study would look at its methodology and findings, while an analysis of a novel would focus on its themes, characters, and writing style. It's essential to consider your audience and your purpose before starting an evaluation document.
Evaluation papers are a versatile and meaningful writing form that can both educate and entertain audiences. Regardless of whether the tone is serious or humorous, objective or subjective, a well-written review can engage and educate.
To understand everything about evaluation essays, from their definition and purpose to potential topics and writing tips, read on.
What are Evaluation Essays?
An evaluation essay allows the author to make a claim and offer a verdict on a topic. This essay type can be used to identify the best option among several alternatives, or to analyze a specific method, product, or situation. It is a common academic task across all levels. Evaluation essays come in different forms, from online product reviews to business cases prepared by management professionals.
In contrast to a descriptive essay, an evaluation essay aims to express the author's judgment. However, this essay type is defined by an objective tone. The author's judgment should be based on careful examination of the available evidence. This differs from a persuasive essay, which seeks to convince the reader to adopt the author's point of view. An evaluation essay starts with the facts and forms conclusions based on these facts.
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
To write an effective evaluation essay, follow these essential writing tips:
1. Select a Topic
The essay topic is crucial. It should be both educational and interesting, providing enough information to fill an entire essay.
2. Draft an Evaluation Essay Outline
Professional writers always advise creating an evaluation essay outline before writing the essay itself. This aids in writing and ensures content coherence. An outline is also easier to modify than a complete essay. Think about what should be included and excluded when designing your essay's outline. However, skipping this step and diving straight into the essay writing can create extra work later, as it can mean editing and revising the entire piece.
The general components of an evaluation essay outline include:
a. Introduction
The introduction is vital as it forms the readers' first impression. It should engage readers and arouse their interest in the topic. The aspects to consider when writing the introduction are as follows:
Begin with a compelling hook statement to capture the reader's interest.
Provide background information on the topic for better understanding.
Formulate a clear and concise thesis statement, outlining the main objective of the evaluation.
b. Body Section
The body of the essay consists of three paragraphs. Each paragraph should deliver several related ideas and flow seamlessly from start to finish. The key ideas to cover in the body paragraphs include:
Start with a sentence that presents your view on the topic.
Provide arguments that support the topic sentence and your stance.
Present a well-rounded argument to show impartiality.
Compare the subject to a different topic to showcase its strengths and weaknesses.
Present the evaluation from various angles, applying both approving and critical thinking.
c. Conclusion
This is your final chance to convince the reader of your viewpoint. The conclusion should summarize the essay and present the overall evaluation and final assessment. When composing an evaluation essay's conclusion, keep the following points in mind:
Restate your main points and arguments from the essay body.
Present evidence to support your thesis.
Conclude your argument convincingly, ultimately persuading the reader of your assessment.
3. Review, Edit, and Proofread
The final steps after writing the essay are editing and proofreading. Carefully reading your essay will help identify and correct any unintentional errors. If necessary, review your draft multiple times to ensure no mistakes are present.
Structure of an Evaluation Essay
An evaluation essay, like any good piece of writing, follows a basic structure: an introduction, body, and conclusion. But to make your evaluation essay standout, it's crucial to distinctly outline every segment and explain the process that led you to your final verdict. Here's how to do it:
Introduction
Start strong. Your introduction needs to captivate your readers and compel them to read further. To accomplish this, begin with a clear declaration of purpose. Provide a brief background of the work being evaluated to showcase your expertise on the topic.
Next, rephrase the essay prompt, stating the purpose of your piece. For example, "This essay will critically assess X, utilizing Y standards, and analyzing its pros and cons." This presents your comprehension of the task at hand.
Wrap up your introduction with a thesis statement that clearly outlines the topics to be discussed in the body. This way, you set the stage for the essay's content and direction, sparking curiosity for the main body of the work.
Body of the Essay
Dive deep, but not without preparation. Before delving into the assessment, offer an unbiased overview of the topic being evaluated. This reaffirms your understanding and familiarity with the subject.
Each paragraph of the body should focus on one evaluation criterion, presenting either support or criticism for the point. This structured approach ensures clarity while presenting evidence to substantiate each point. For instance, discussing the benefits of a product, you can outline each advantage and back it up with supporting evidence like customer reviews or scientific studies.
Ensure a smooth flow of thoughts by linking paragraphs with transitional phrases like "in addition," "moreover," and "furthermore." Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence, explanation, and supporting evidence or examples for easy understanding.
Your conclusion is where you make your final, compelling argument. It should focus on summarizing the points made according to your evaluation criteria. This isn't the place for new information but rather a concise summary of your work.
To conclude effectively, revisit your thesis and check whether it holds up or falls short based on your analysis. This completes the narrative arc and provides a solid stance on the topic. A thoughtful conclusion should consider the potential impact and outcomes of your evaluation, illustrating that your findings are based on the available data and recognizing the potential need for further exploration.
Evaluation Essay Examples
Now that we've covered the structure, let's take a look at some examples. Remember, an evaluation essay is just one type of essay that can be generated using tools like Jenni.ai. This AI-powered software can produce high-quality essays on any topic at impressive speeds. Here are some ideas to kickstart your assessment essay writing journey.
Evaluation Essay: Online Teaching vs. On-campus Teaching
In the face of technological evolution, education has seen a shift in teaching styles, with online learning platforms providing an alternative to traditional on-campus teaching. This essay will evaluate and compare the effectiveness of these two teaching styles, delving into various factors that contribute to their strengths and weaknesses.
The landscape of education has transformed significantly with the advent of online learning. This essay will scrutinize and juxtapose the effectiveness of online teaching against traditional on-campus teaching. The evaluation will take into account numerous factors that contribute to the success of each teaching style, focusing on their individual benefits and drawbacks.
On-campus Teaching
On-campus teaching, the time-tested method of education, has proven its effectiveness repeatedly. The physical classroom setting provides students direct access to their teachers, promoting immediate feedback and real-time interaction. Moreover, the hands-on learning, group discussions, and collaborative projects intrinsic to on-campus teaching cultivate crucial soft skills like communication and teamwork.
A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research reveals that students attending on-campus classes show higher academic performance and are more likely to complete their degrees compared to those in online classes (Bettinger & Loeb, 2017). However, on-campus teaching isn't without its challenges. It offers limited flexibility in scheduling and requires physical attendance, which can be inconvenient for students residing far from campus or those with mobility constraints.
Online Teaching
Online teaching, propelled by technological advancements and digital learning platforms, offers a compelling alternative. The most significant benefit of online teaching is its scheduling flexibility. Students can access classes and course materials from anywhere, at any time, providing a superior balance for work, family, and other commitments.
Online teaching democratizes education by enabling access for students in remote areas or with mobility challenges. The use of innovative teaching methods like interactive multimedia and gamification enhances engagement and enjoyment in learning.
Despite its numerous advantages, online teaching presents its own set of challenges. A major drawback is the lack of direct interaction with teachers and peers, potentially leading to delayed feedback and feelings of isolation. Furthermore, online classes demand a higher degree of self-motivation and discipline, which may be challenging for some students.
Both online teaching and on-campus teaching present their unique benefits and drawbacks. While on-campus teaching fosters direct interaction and immediate feedback, online teaching provides unmatched flexibility and accessibility. The choice between the two often depends on factors such as the course content, learning objectives, and student preferences.
A study by the University of Massachusetts reports that the academic performance of students in online classes is on par with those attending on-campus classes (Allen & Seaman, 2017). Furthermore, online classes are more cost-effective, eliminating the need for physical classrooms and related resources.
In conclusion, while both teaching styles have their merits, the effectiveness of each is heavily dependent on the subject matter, learning objectives, and the individual needs and preferences of students.
Citations: Allen, I. E., & Seaman, J. (2017). Digital learning compass: Distance education enrollment report 2017. Babson Survey Research Group. Bettinger, E., & Loeb, S. (2017). Promises and pitfalls of online education. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity, Spring 2017, 347-384.
Evaluation essay: Analyze how the roles of females and males changed in recent romantic movies
Romantic movies have long been a popular genre, offering a glimpse into the complex and varied world of relationships. Over the years, the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies has evolved significantly. This essay aims to evaluate and analyze how the roles of females and males have changed in recent romantic movies.
Historical Context of Gender Roles in Romantic Movies:
Gender roles have played a significant role in shaping the portrayal of romantic relationships in movies. In the past, traditional gender roles were often reinforced, with women playing the role of the damsel in distress, and men playing the role of the protector and provider.
However, over the years, the feminist movement and other social changes have led to a more nuanced portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies. Women are no longer just passive objects of desire, and men are not just dominant figures. Instead, both genders are portrayed as complex and multifaceted individuals with their desires, needs, and struggles.
Analysis of Recent Romantic Movies:
In recent years, romantic movies have become more diverse and inclusive, featuring a wider range of gender identities, sexual orientations, and cultural backgrounds. As a result, the portrayal of gender roles in these movies has also become more nuanced and complex.
One significant trend in recent romantic movies is the portrayal of female characters as strong, independent, and empowered. Female characters are no longer just passive objects of desire, waiting for the male lead to sweep them off their feet. Instead, they are shown to be capable of taking charge of their own lives, pursuing their goals, and making their own decisions.
For example, in the movie "Crazy Rich Asians," the female lead, Rachel, is portrayed as a strong and independent woman who stands up for herself and refuses to be intimidated by the wealthy and powerful people around her. Similarly, in the movie "The Shape of Water," the female lead, Elisa, is portrayed as a determined and resourceful woman who takes action to rescue the creature she has fallen in love with.
Another trend in recent romantic movies is the portrayal of male characters as vulnerable and emotionally expressive. Male characters are no longer just stoic and unemotional but are shown to have their insecurities, fears, and vulnerabilities.
For example, in the movie "Call Me By Your Name," the male lead, Elio, is shown to be sensitive and emotional, struggling with his feelings for another man. Similarly, in the movie "Moonlight," the male lead, Chiron, is shown to be vulnerable and emotionally expressive, struggling with his identity and his relationships with those around him.
However, while there have been significant changes in the portrayal of gender roles in recent romantic movies, there are still some aspects that remain problematic. For example, female characters are still often portrayed as objects of desire, with their value determined by their physical appearance and sexual appeal. Male characters are still often portrayed as dominant and aggressive, with their masculinity tied to their ability to assert control over others.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the portrayal of gender roles in recent romantic movies has evolved significantly, with female characters being portrayed as strong, independent, and empowered, and male characters being portrayed as vulnerable and emotionally expressive. These changes reflect the shifting social norms and values of our society and offer a more nuanced and complex portrayal of romantic relationships.
However, there are still some problematic aspects of the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies, such as the objectification of female characters and the perpetuation of toxic masculinity. Filmmakers and audiences need to continue to push for greater diversity, inclusivity, and nuance in the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies so that everyone can see themselves reflected in these stories.
"Crazy Rich Asians" Directed by Jon M. Chu, performances by Constance Wu, Henry Golding, and Michelle
Final Thoughts
The step-by-step guide and examples provided should have equipped you with the skills necessary to write a successful evaluation essay. However, crafting the perfect essay isn't a simple task; it demands practice, patience, and experience.
Incorporate Jenni.ai into your academic journey to revolutionize your writing experience. This advanced AI writing tool is designed to assist with a range of academic writing projects. With Jenni.ai, you can confidently tackle essays on any topic, easing your writing tasks considerably. Don't hesitate to register with Jenni.ai today ! Discover a world of writing opportunities and take your essay writing skills to new heights!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back
- Architecture and Design
- Asian and Pacific Studies
- Business and Economics
- Classical and Ancient Near Eastern Studies
- Computer Sciences
- Cultural Studies
- Engineering
- General Interest
- Geosciences
- Industrial Chemistry
- Islamic and Middle Eastern Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Library and Information Science, Book Studies
- Life Sciences
- Linguistics and Semiotics
- Literary Studies
- Materials Sciences
- Mathematics
- Social Sciences
- Sports and Recreation
- Theology and Religion
- Publish your article
- The role of authors
- Promoting your article
- Abstracting & indexing
- Publishing Ethics
- Why publish with De Gruyter
- How to publish with De Gruyter
- Our book series
- Our subject areas
- Your digital product at De Gruyter
- Contribute to our reference works
- Product information
- Tools & resources
- Product Information
- Promotional Materials
- Orders and Inquiries
- FAQ for Library Suppliers and Book Sellers
- Repository Policy
- Free access policy
- Open Access agreements
- Database portals
- For Authors
- Customer service
- People + Culture
- Journal Management
- How to join us
- Working at De Gruyter
- Mission & Vision
- De Gruyter Foundation
- De Gruyter Ebound
- Our Responsibility
- Partner publishers

Your purchase has been completed. Your documents are now available to view.
Evaluative language in undergraduate academic writing: expressions of attitude as sources of text effectiveness in English as a Foreign Language
The purpose of this paper is to explore whether the use of attitudinal language stands as a potential source of effectiveness in undergraduate academic writing in English as a Foreign Language (EFL). In order to achieve this purpose, interpersonal features of a corpus of essays written by Mexican undergraduate students of English Language and Literature were analyzed. The model of appraisal (Martin, James R. & Peter R. R. White. 2005. The language of evaluation: Appraisal systems in English . Basingtoke: Palgrave Macmillan) was used to trace and contrast attitude resources of affect, judgement and appreciation in academic essays in relation to the grades they were granted by university professors at different levels of instruction. The results of the study confirm a significant relation between the use of resources of attitude and the perceived (in)effectiveness of the analyzed texts, as well as factors which potentially determine the nature of such relation and pose relevant implications for academic writing instruction in EFL in the context of the analyzed corpus.
1 Introduction
Writing academically in English as a Foreign Language (EFL) is widely recognized as central to undergraduate education due to its role as the main means of production and dissemination of knowledge in international contexts ( Nesi and Gardner 2012 ). Academic writing is also considered as an activity which involves complex sets of skills that even expert writers keep on improving after continued experience ( Chazal 2014 ). As part of such complexity, the appropriate expression of interpersonal meanings has been found to be one of the most challenging components when learning how to write academically ( Hood 2010 ), mainly because of the pedagogical challenges involved in an appropriate induction of learners into the linguistic conventions developed by specialized discourse communities to produce interpersonal meanings.
Different from skills and competencies related to the communication of factual information and conventional paradigms of textual organization, construing interpersonal meanings involves the use of linguistic resources to express interaction among speakers, as well as the communication of the feelings and points of view they intend to share ( Moss 2011 ). Interpersonal meanings also convey social roles and evaluations ( Hyland 2005 ), as well as the speakers’ expression of a subjective reality, which conveys social relations, personal values, and different kinds of opinions they want to share with other speakers ( Perales et al. 2012 ). Additionally, the expression of interpersonal meanings relates to authorial presence, also known as stance, in academic texts; “how writers present themselves and express their own views and judgements” in relation to others ( Candarli et al. 2015 : 193). Because of their discourse semantic nature, the workings of these dynamics and their rhetorical effects might make it harder for learners of EFL academic writing to acquire, observe, and evaluate than grammatical and organizational features, as attested by observations like Lancaster’s (2014) , who has referred to interpersonal dynamics as recurring patterns of language use that are difficult to notice from casual scanning.
As explained by Ken Hyland, research has shown that fundamental challenges in teaching and learning interpersonal conventions in writing are found in two main sources of difficulties. For one thing, despite its actual social nature, academic writing may still be regarded as objective, rational and impersonal, which results in a neglection of the fact that academic, disciplinary practices involve variations in systems “of appropriate social engagement with one’s material and one’s colleagues” ( Hyland 2004 : 11). Additionally, cultural factors that shape students’ expectations, strategies, beliefs and, in general, schemas of knowledge and the whole process of learning also present learners with important challenges; besides the acquisition of grammatical structures, lexical resources, and notions of textual organization, learners writing in EFL have to deal with differences between diverse cultural conceptualizations of knowledge construction and communication. While certain cultures tend to favor “an analytical, questioning, and evaluative stance to knowledge”, others “have a very different perspective that favors conserving and reproducing existing knowledge” ( Hyland 2003 : 38).
Hyland’s considerations coincide with Chitez and Kruse’s (2012) observations about what they call writing cultures , which result from the fact that “each educational system creates its unique mixture of educational genres, writing/learning practices, assessment procedures, instructional materials, expectations towards writing, and required writing competencies, in varied relationships with the genres and practices of professional or scientific domains” (p. 153). An imminent consequence of this is that communities of learners and individual writers carry particular writing dynamics acquired from their various experiences, many of which differ significantly from each other. Thus, students learning how to write in EFL face the challenge to adjust – to lesser or greater degrees – to generalized conventions according to which they are expected to demonstrate their knowledge by voicing their judgements and putting their opinions forward in certain ways. Adjusting appropriately to such conventions may result in effective writing, which has been defined by Vega (2015) as the instantiation of argumentation which appropriately accommodates to the audience’s framework of attitudes and beliefs, gaining force in its adhesion to the speaker’s proposals.
Based on the consideration that the expression of interpersonal meanings plays an important role in the production of successful written academic texts and, as a result, may represent a significant source of (in)effectiveness in academic writing, several works have analyzed the use of interpersonal resources by undergraduate students in EFL in diverse international contexts. Some of such works have explored this dimension of academic writing from the perspective of Hyland’s (2005) metadiscourse model ( Candarli et al. 2015 ; Crosthwaite and Jiang 2017 ; Lee and Deakin 2016 ), while others have adopted the systemic-functional perspective of the appraisal model ( Martin and White 2005 ) as their theoretical and methodological basis ( Derewianka 2007 ; Lee 2008 , 2015 ; Mei 2006 , 2007 ; Ryshina-Pankova 2014 ).
Despite the abundant production of research this subject has seen around the globe, the exploration of the relationship between interpersonal resources and effectiveness in academic EFL writing has not received much attention in Mexico and Latin America, where most related research has focused on academic writing in Spanish L1 ( Castro 2013 ; Castro and Sánchez 2013 ; González 2011 ; Ignatieva 2021 ; Navarro 2014 ; Valerdi 2021 ; Zamudio 2016 ). It is also worth noticing that, as it will be shown in further sections of this paper, most previous works beyond Latin American contexts have explored the interpersonal discourse of EFL writers from disciplines which require effective communication in English, but not the professional mastery or depth that is expected from future professionals of the English Language and Literature at different levels of linguistic and disciplinary instruction. Such potential mastery and depth in knowledge represent the need to analyze the workings of interpersonal language considering as many realizational variables as possible. Stemming from this, the objective of this paper is to use qualitative and quantitative research methods to analyze the use of interpersonal resources in a corpus of academic essays written in EFL by Mexican undergraduate students of English Language and Literature at a public university in Central Mexico. This exploration is developed within the framework of Martin and White’s (2005) model of appraisal with specific focus on the system of attitude and the instantiation variables of attitudinal category, realization, explicitness, trigger, and authorship. In this work, I compare the features of attitudinal realizations in low-, middle-, and high-graded essays in order to understand the relationship between the use of attitudinal language and the perceived effectiveness of the essays where it is instantiated. Additionally, the features of the evaluative language in the corpus are observed in relation to the instructional and linguistic experience of the undergraduate authors of the texts, which were classified as basic, intermediate, and advanced.
In the following section, a brief account of the system of attitude is presented with particular focus on the categories that have been analyzed in this research. This is followed by an account of previous works that have explored the relationship between attitudinal language and the (in)effectiveness of academic writing by undergraduate EFL learners from different linguistic and cultural backgrounds. Then, a description of the mixed methodological approach which was applied in this research is presented. Finally, I report the most significant findings of this work in order to discuss their implications to teaching academic writing in EFL in the Mexican context.
2 The appraisal model and the system of attitude
Martin and White (2005) developed the appraisal model as an extension of the analysis of the interpersonal metafunction proposed in Halliday’s Systemic Functional Grammar (1985 , 2004 . While Halliday describes this metafunction at the lexicogrammar stratum in terms of the clause as an exchange through the system of mood , the appraisal model approaches the expression of feelings, points of view and social relations at the stratum of discourse semantics through the systems of attitude , engagement , and graduation . The first one involves the discursive negotiation of emotion-related meanings (feelings, moral/ethical judgements, and aesthetic responses), while the second one relates to the speaker’s positioning in relation to other voices. The system of graduation has to do with the resources deployed to intensify and attenuate realizations of attitude and engagement ( Martin and White 2005 ).
This paper is concerned with the system of attitude , which encompasses the linguistic expression of emotions and their institutionalization as opinions related to the notions of ethics and aesthetics. The ultimate objective of using these resources is to share subjective points of view for the audience to consider them and, if the discourse is successful, adhere to them. In this sense, the expression of attitude is central for speakers’ argumentation of their positions and the representations of the world they communicate since “it is possible to adhere oneself not only to a thesis, but also to ways of thinking, seeing, and feeling” ( Amossy 2009 : 67–68). Thus, considering Vega’s definition of effectiveness (2015) as argumentation which accommodates to the audience’s attitudes and beliefs in order to increase its adhesion to the speaker’s proposals, the rhetorical effects of communicating one’s propositions accompanied by attitudinal evaluations may have the potential to enhance the effectiveness of the produced text beyond the scope of its objective contents.
In the model of appraisal , expressions of attitude are analyzed in terms of three sub-systems: affect , judgement , and appreciation . Affect relates to the linguistic realization of feelings, considered as the most basic forms of personal reaction in human linguistic development ( Martin 2000 ; Painter 2003 ; Torr 1997 ). These expressions are usually classified into the categories of +/− happiness [“affairs of the heart” ( Martin and White 2005 : 49)], +/− security (related to ecosocial well-being and sensations of anxiety and confidence), +/− satisfaction (linked to the satisfaction of personal needs and goals) and +/− desire (involving the willingness or attraction towards entities and processes). Prototypically, instances of affect are lexically realized in the form of qualities (attributes and epithets), mental and behavioral processes, and modal adjuncts. Table 1 illustrates examples of affect analyzed in the corpus of this study. The two columns on the right present information about the variables of realization – the lexico-grammatical form – and category – attitudinal sub-type – of each example.
Instances of the four categories of affect .
All the examples presented on this and other tables and figures are instances of evaluative language analyzed in the corpus of this research, except for *, which has been adapted from Martin and White (2005 : 46).
Resources from the judgement and appreciation sub-systems are the result of the modelling and sophistication of affectivity according to social norms and aesthetic parameters produced by social conventions, hence their status as institutionalizations of affect . These institutionalizations represent moral/ethic judgements about people, their actions, and the consequences of their actions, as well as personal considerations about the aesthetic properties of things, processes, and people. Following Martin and White’s (2005) description, expressions of judgement are classified into the categories of +/− normality (how special or unique someone is), +/− capacity (how able a person is), +/− tenacity (how resolute someone is), +/− veracity (related to people’s honesty) and +/− propriety (linked to people’s integrity). Judgement is typically realized through qualities and modal adjuncts ( Table 2 ).
Instances of the five categories of judgement.
Expressions of appreciation encode aesthetic evaluations of speakers in terms of three categories: +/− reaction (emotional responses provoked by things and processes), +/− composition (perceptions of the balance, regularity, and order of things), and +/− valuation (opinions about the aesthetic and practical value of things). Prototypical realizations of appreciation take the form of qualities and circumstances ( Table 3 ).
Instances of the three categories of appreciation.
The examples of attitude presented up to this point correspond to inscribed realizations; expressions that encode attitude overtly or explicitly. Affect , judgement , and appreciation can also be indirectly invoked . The particularity of invoked realizations of attitude is that they demand a special effort from the audience or interlocutor to identify and process the type of evaluation the speaker is doing. Another peculiarity of this type of realization is that it involves the selection of resources pertaining to the ideational metafunction, which “gives structure to experience, and helps to determine our way of looking at things, so that it requires some intellectual effort to see them in any other way than that which our language suggests to us” ( Halliday 2002 : 175). Hence observations by Hood and Martin (2005) and Hood (2010) of processes and participants as efficient attitudinal invokers: ideational meanings are seldom neutral, and speakers choose non-inherently evaluative resources for their invoking potential.
attitude is prototypically invoked through lexical metaphors, processes, nominal participants, and nominalizations of processes and qualities. A notorious exception to these invoked realizations is the case of affect , which can be inscribed through mental and behavioral processes. Table 4 illustrates invoked realizations of attitude analyzed in the corpus of this work.
Invoked realizations of attitude.
An additional remark on attitudinal invocation relates to potential double coding ( Martin and White 2005 ) resulting from indirect realizations of attitude where a given evaluation from one category may be invoked by means of the inscription of another category as in (1) below. In this example, the author expresses a negative evaluation of a reviewer’s knowledge ( appreciation > −composition), which indirectly realizes a negative evaluation about his abilities as a literary analyst ( judgement > −capacity). The possibility of finding such types of invoked realizations in discourse represents the need to make methodological decisions regarding the labelling of attitudinal realizations in an analysis, as was the case in this work. Pertinent observations are made later in the Section 4 .
For the purposes of this research, additionally to the variables of realization, category and explicitness, the variable of trigger is particularly relevant. This variable indicates the stimulus that motivates an evaluation. For the nature of the essays studied in this work – i.e., essays on literary works from English Literature – triggers of attitude were related to characters, other components of the literary works commented by the authors of the corpus (atmosphere, style, plot, etc.), and entities external to the literary works about which they write in their essays (literary concepts, periods, genres, currents, other works, different authors, etc.). Table 5 illustrates instantiations of attitude with labels of their realization, category, explicitness, and trigger.
Instantiations of attitude with realization variables.
3 Research on attitudinal meanings in undergraduate EFL academic writing
The study of the linguistic expression of attitude and its relationship with successful EFL academic writing has received considerable attention in international contexts. Jalilifar and Hemmati (2013) analyzed a corpus of argumentative essays written by postgraduate Kurdish-speaking Iranian students of TEFL to explore whether appraisal resources can be used as a reference to evaluate argumentative writing in low- and high-graded essays. These authors found that higher proportions of attitude were characteristic of more successful texts, although both groups of texts were similar in a tendency to use more judgement and appreciation than affect . Additionally, high-graded essays displayed significantly more invoked affect through nominalizations and more inscribed valuation than low-graded texts, which tended to inscribe affect through mental processes and to invoke valuation . In terms of judgement , the main contrast between both sub-corpora lied in the selection of sub-categories, with high-graded essays mainly displaying resources of capacity and low-graded texts mainly instantiating normality . Jalilifar and Hemmati (2013) conclude that, although clear tendencies showed that more successful essays tend to display more attitude , punctual instantiations suggested that “in assessing the essays as high- or low-graded, more important than the number of appraisal markers exploited in essays was how these resources were employed” (p. 75). This conclusion coincides with observations by Hunston (2011) , Hunston and Su (2019) , and Valerdi (2021) , who have pointed at the centrality of lexico-grammatical patterns and the strategic use of evaluative language in argumentative structures over low or high proportions of appraisal resources in texts.
Reaching similar conclusions, Myskow and Ono (2018) studied how Japanese undergraduate students of Law and Political Science used resources of affect, judgement and appreciation as part of their arguments’ justifying evidence in a corpus of 62 biographical essays. Having rated the texts as either high or low on the basis of a self-designed rubric, these authors found that both low- and high-rated essays displayed similar proportions of general attitudinal appraisal , with judgement as the most prevalent type of evaluation. Here, the relevant contrasts took place in terms of the most frequently used sub-systems in each group of texts, with high-rated essays displaying higher proportions of appreciation and judgement , and low-rated texts displaying more resources of affect . Additionally, for these researchers, what students found challenging was not the selection of particular attitudinal categories, but finding appropriate grammatical constructions for them to support their arguments; they noticed students relied heavily on attributes to inscribe conclusive evaluations about people. Myskow and Ono (2018) suggest writing teachers should not encourage learners to adopt critical perspectives through heavily polarized inscriptions, but to integrate evaluations with evidence in support of their conclusions through particular grammatical constructions.
In a work that explores the relationship between undergraduate students’ lack of critical voice and limitations in the management of evaluative language, Lee (2015) compared high- and low-graded persuasive essays written by native (Australian) and non-native (South Korean, Japanese, and Taiwanese) undergraduate EAP students to identify how evaluative language contributes to academic writing success. In that study, native and non-native writers deployed judgement and appreciation ten times more frequently than affect . When focusing on appreciation resources, the author found that valuation was predominantly more used over expressions of composition and reaction , which they interpretated as a subject-specific particularity. When contrasting low- and high-graded essays, Lee found that less successful texts displayed affect-related reaction twelve times more frequently than successful essays. Additionally, she found that high-graded essays by both native and non-native writers displayed similar tendencies, with frequent use of judgement -invoking valuations . In 2008, Lee had reported very similar tendencies in a study based on a remarkably similar corpus, with high-graded essays deploying significantly more varied attitudinal resources – mainly invoked evaluations of judgment – and depersonalized attitude – in the form of nominalizations – than low-graded texts. For Lee (2015) , shaping an appropriate use of evaluative language is key in EAP instruction, where “students’ exposure to the appraisal system helps them to acquire the relevant English Language skills including grammar and vocabulary most effectively in a context-appropriate manner” (p. 73).
In a work which supports Lee’s (2015) position, Bahmani et al. (2021) propose the model of appraisal as a pedagogical tool to help EAP writers show their critical stance in their texts. To support their claim, the authors developed an experimental study at an Iranian university, comparing the writing successfulness of an experimental group of 30 postgraduate students of English Language Teaching to that of a control group with the same number of students. The experimental group received writing instruction with explicit explanations and analyses of attitude and graduation . On the basis of standardized pre-tests and post-tests applied to both groups, Bahmani et al. concluded that explicit instruction on the use of evaluative language enabled the experimental group to perform more successfully in contrast with the control group, which did not improve its performance significantly.
Besides research based on appraisal analysis, the role of attitudes in academic writing in EFL has seen remarkable contributions developed through applications of Hyland’s (2005) metadiscourse model. Despite general differences between metadiscourse and appraisal , both models have been found to share remarkable similarities in their conceptualization of linguistic attitudes (Du et al. 2023) : linguistic resources that “indicate the writer’s affective […] attitude to propositions” via markers of surprise, agreement, frustration, importance, etc. ( Hyland 2005 : 53). In this paper, key metadiscourse works are worth mentioning for their special focus on contrasting less or more effective texts on the basis of their attitudinal features.
One of such works is that by Crosthwaite and Jiang (2017) , who support the idea that successful attitudinal conventions can stem from instruction in academic writing. They explored how explicit instruction on the use of attitudinal metadiscourse affects the development of stance features in essays and reports. The authors investigated the development of attitude markers and other metadiscoursal resources during one semester of EAP instruction to undergraduate students from various disciplines in Hong Kong. After analyzing written samples before, during, and after explicit instruction, Crosthwaite and Jiang (2017) found that undergraduate authors had reduced their use of attitudinal markers significantly in their texts. Additionally, when they graded the same written samples, they found that interpersonal features developed through instruction were more likely to have a positive impact on evaluators. For these authors, “the ability to express a relevant and plausible stance is a crucial indicator of writing quality and development” (p. 94). As challenging as this has been proved to be, such ability can be trained in undergraduate students, who enter university writing privileging their attitudes about their claims and their positions, but may be instructed to develop a new academic voice, “gaining control over the rhetorical and linguistic aspects of academic discourse via the use of a more careful, narrower, less polarising and less personal range of expressions with which to convey their attitudes on a given topic” (p. 102).
Lee and Deakin (2016) looked more closely at the role of attitudinal metadiscourse markers in the effectiveness of undergraduate writing in EFL by analyzing essays written by Chinese learners enrolled in their first or second writing course at a university in the United States. The essays had been rated through a standardized grading rubric either as low or high. Lee and Deakin (2016) found that authors of successful essays had a tendency to include significantly more attitudinal markers than less successful essays. Additionally, these authors observed that attitudinal resources in high-rated texts displayed more varied lexico-grammatical realizations. In these authors’ corpus, the expression of authorial stance through attitude seems to be an important factor of success. Nevertheless, compared to other types of stance markers – namely hedges, boosters, self-mention, and engagement markers –, they observe that attitudinal resources are among the least used expressions of interpersonal meanings in both low- and high-rated essays. These findings can be related to those by Crosthwaite and Jiang (2017) in that not only do linguistic realizations of attitude seem to be modulated by EFL writers when writing in English, but they also appear to stem from effective instruction that results in the acquisition of rhetorical conventions of academic EFL writing. Adhering to or neglecting such conventions affects the impression of (in)effectiveness of undergraduate academic texts.
These works have explored and confirmed, to varying degrees and from interrelated perspectives, the possibility to link the use of evaluative attitudinal language to effectiveness in academic EFL writing in different international contexts. The following section presents a description of the methodological approach that was applied in this research in order to explore such relationship in the Mexican context. This will be followed by a report of the results obtained.
4 Methodology
The purpose of this paper is to analyze realizations of attitude in undergraduate academic essays in EFL in order to determine if their attitudinal features represent a potential source of text (in)effectiveness beyond lexicogrammatical and structural considerations. This is done through a mixed qualitative and quantitative methodology, comparing the deployment of resources from the three attitude sub-systems in essays written by Mexican undergraduate students from different instructional levels of the major on English Language and Literature at a public university in Central Mexico.
The major in English Language and Literature consists of eight consecutive semesters. Students entering the first semester must provide evidence of having completed three years of EFL instruction during their high school studies. Additionally, they must pass an exam that determines whether they possess competencies equivalent to band B2 from the Common European Framework. As part of their studies in the major, they study four 16-week language courses during the first four semesters (one course per semester). From the fifth to the eight semesters, their training in the language takes place through specialized content subjects that are taught in English. These subjects include advanced English Literature courses where essay writing is a regular instructional and evaluative practice.
4.1 The corpus
The corpus of this work includes 41 essays that were written as final assignments in 16-week English Literature courses by students from different instructional levels: it comprises 15 essays written by students from 1st through 3rd semester – labeled as ‘basic’–, 15 essays from 4th through 6th semester – classified as ‘intermediate’ –, and 11 essays from 7th through 8th semester – considered as ‘advanced’ –. The texts were written under the general instruction to analyze one of the literary works studied during one semester, identify its most remarkable literary features, and justify observations about the chosen work. Each essay was evaluated by the teacher of the English Literature course where it was collected and was granted a grade from 5 to 10. During the recollection of the corpus, teachers in charge of the courses reported to have evaluated the essays on the basis of appropriate analysis of literary concepts and features, as well as cohesion, coherence, and grammatical accuracy. No standardized or specially-designed rubric was used, so the results of evaluation resulted from the expert view of teachers according to the academic liberty policy of the university.
For the purposes of this study, the texts were further divided into three sub-categories according to the grade they were granted by course teachers: low-graded (essays with notes from 5 to 6), middle-graded (notes from 7 to 8), and high-graded (notes from 9 to 10). Table 6 illustrates the composition and distribution of the corpus.
Composition and distribution of the corpus and sub-corpora.
4.2 The analysis
All realizations of attitude in the corpus were recorded and analyzed taking into account the variables of category, realization, explicitness, and trigger. For the trigger variable, five subject-specific labels were established due to the nature of the analyzed discourse: Author 1 (A1) is marked when the writer evaluates him or herself; Author 2 (A2), when the writer evaluates the author of the literary work he or she discusses in the essay; Character (CH), when the evaluated entity is a character or narrator from the literary work discussed in the essay; Text (TXT), when the writer evaluates elements of the literary work he or she analyzes in the essay, such as atmosphere, style, plot, etc.; and Other (OTH), when the evaluated entity is external to the literary work under analysis, such as literary periods, genres, other works, different authors, etc. Additionally, the authorship of attitudinal evaluation was identified through the variable of appraiser ( Martin and White 2005 ). This variable distinguishes between authorial (the writer is the one who evaluates attitudinally) and non-authorial (the writer attributes an attitudinal evaluation to someone else) realizations of attitude .
Besides tracking attitude types in the corpus, the purpose of observing all these realizational variables was to avoid misleading recordings due to potential double coding – i.e., invoked realizations of one attitudinal category instantiated by inscribed realizations of a different one. Because a delicate analysis of this type of invoked attitude is beyond the scope and purpose of this work, when examples of this were identified in the corpus, the inscribed interpretations were considered for the analysis on the basis of prototypical realizations and variables described earlier in Section 2 .
Table 7 illustrates attitudinal instantiations from the corpus with the labels of all the variables observed, including an instance of invoked judgement which was recorded as inscribed appreciation (**). In this example, inscribed appreciation ( +valuation ) is used to evaluate human +veracity indirectly.
Instantiations of attitude with labels of five realizational variables.
All instances of attitude were recorded and quantified in dynamic tables. Proportions of expression of each type of attitude were calculated by dividing the number of occurrences of each attitudinal paradigm by the total number of clauses in each text and sub-corpus (# of attitude instantiations/# of clauses). When focus was on attitude sub-types and realizational variables, proportions were calculated by dividing the number of the corresponding attitudinal paradigm by the total number of attitude instantiations in each text and sub-corpus. As in previous work on appraisal ( Lee 2008 ; Mei 2007 ; Valerdi 2016 ), Chi-squared tests were performed in order to confirm the statistical significance of the findings. This type of test is used to “examine the distribution of data across the categories of our analysis” and “the extent to which the distribution of your observed data varies from the distribution that would be expected if the independent variable had no effect on the dependent variable” ( Levon 2010 : 78). The students’ instructional level (basic, intermediate, and advanced) and perceived effectiveness (low, middle, and high) are independent variables in this study while the expression of attitude and its variables are dependent variables.
In linguistic studies involving categorical dependent variables, chi-square tests with a resulting p value of <0.05 indicate there is a relationship between the variables ( Rasinger 2013 ). In other words, such tests “tell you that there is at least a 95 % chance that the independent variable does in fact have an effect on the dependent variable” ( Levon 2010 : 81). The following section presents the results of the study and indicate p values obtained by the chi-square tests.
5.1 Attitude in the general corpus and by instructional level
As a general feature, there is a significantly reduced proportion of evaluative language in the whole corpus, with only 18.02 % of the clauses expressing attitude. This is reflected in each of the instructional level sub-corpora: 19 % in basic essays, 16 % in intermediate essays, and 20 % in advanced essays. Additionally, these sub-corpora display appreciation as the most recurrent type of attitudinal positioning, while affect is the least frequent attitudinal paradigm in the corpus. The proportions of the different types of attitude are statistically significant in all the instructional levels of the texts ( Table 8 ).
Proportions of realization per attitude sub-system by instructional level.
a When a p value is too long to be contained in a single cell, Excel, the program used for quantitative explorations in this work, reports the result with the suffix ‘E’ followed by an entire number. Such coding means that, for an exact reading of the p value, the decimal point in the result must be moved as many places to the left as indicated by the number following ‘E’. In this case, the value of p is statistically significant, as the full result (0.0000000000000000108249) is meaningfully bellow conventional 0.05.
When considering the variable of explicitness, the corpus features a progressive reduction of evaluative inscription, which is predominant in basic essays and reduces by 21 % in advanced texts ( Table 9 ). The differences in explicitness among the sub-corpora are highly statistically significant.
Proportions of inscribed and invoked attitude by instructional level.
Further careful analysis of the explicitness variable reveals that evaluations of affect and appreciation are mainly inscribed in the three groups of texts while resources of judgement tend to be invoked ( Table 10 ). This corresponds directly to the most representative lexical realizations of attitude in the corpus: attributes, epithets, and mental processes for affect; attributes and epithets for appreciation; and processes, nouns and nominalizations for judgement. The proportions of explicitness were found statistically significant for judgement and appreciation only.
Proportions of invocation and inscription of attitude types by instructional level. Predominant tendencies are highlighted.
Regarding the realizational variable of triggers, authors of intermediate and advanced essays have literary characters, literary features, and external entities related to the works they analyze in their essays as stimuli for evaluative expressions, in that order of saliency and in almost identical proportions. Writers of basic essays, on the other hand, focus primarily on the authors of the works they discuss when positioning themselves attitudinally, but coincide with their intermediate and advanced counterparts in focusing on literary features of their analyzed works secondly, and thirdly on external entities ( Table 11 ).
Triggers of attitudinal evaluations by instructional level. The three most representative types of triggers in each sub-corpus are highlighted.
5.2 Attitude by perceived effectiveness
The corpus displays meaningful contrasts in the evaluative features of the essays when their perceived effectiveness is taken into consideration. In Table 12 , we can see there is an increasing presence of attitudinal evaluation that progresses from low-graded to middle-graded essays in the basic and intermediate sub-corpora. Such progression, however, does not continue in essays from the advanced sub-corpus, where the distribution of attitudinal realizations contrasts with the other texts and was found to be not statistically significant.
Proportions of attitude in relation to grades granted by university teachers.
A ppreciation resources are the most recurrent attitude type in all low-, middle-, and high-graded essays, followed by judgement and, in much lower proportions, by affect . Additionally, as illustrated in Table 13 , proportions of judgement and affect are close in representativeness to each other in all groups of texts, which indicates an interesting regularity related to the degree of effectiveness attributed to the essays by university teachers.
Proportions of attitude types in relation to grades granted by university teachers.
The explicitness variable does not seem to affect the tendencies in the corpus when related to perceived effectiveness ( Table 14 ). Inscribed appreciation and invoked judgement are the most representative choices in low-, middle-, and high-graded essays. Realizations of affect are significantly inscribed with two exceptions to this tendency. First, intermediate middle-graded essays display invoked affect over inscribed realizations by a difference of 20 %. Secondly, advanced low-graded essays are radically different from middle- and high-graded texts from the same instructional level with 100 % of affective realizations being invoked. Despite the clarity of these tendencies, differences in explicitness were not found statistically significant in relation to perceived effectiveness.
Proportions of invocation and inscription of attitude types in relation to grades granted by university teachers. Predominant tendencies are highlighted.
Table 15 shows remarkable regularities in the types of triggers that undergraduate writers of two sub-corpora have in mind when expressing attitudinal evaluation of different types. In the intermediate and advanced sub-corpora, all low-, middle-, and high-graded essays display evaluative focus on characters, textual literary features, external elements, the authors of their analyzed works, and the very authors of the essays, in that order of predominance. Interestingly, essays from the basic instructional level differ in every single proportion of trigger choice from the others, with textual literary features as the main attitudinal trigger in all low-, middle, and high-graded essays. The second most representative triggers in low- and middle-graded essays are external elements and characters, respectively, while high-graded essays prioritize authors of their analyzed woks. Finally, low- and middle-graded texts coincide in privileging the attitudinal evaluation of the authors of the works they study in the third place. High-graded essays, on the other hand, prioritize their attitudinal stance regarding elements external to their analyzed literary works. These results were found to be highly statistically significant for the basic essays of the corpus, slightly non-significant for the intermediate texts, and markedly non-significant for advanced essays.
Triggers of attitudinal evaluation in all sub-corpora in relation to grades granted by university teachers. The three most representative types of triggers in each sub-corpus are highlighted.
6 Discussion
The results of this research show a meaningful relationship between the use of attitudinal evaluation in undergraduate academic EFL writing and the production of effective texts in the context of the analyzed corpus. In this section, this is shown by discussing the results from general to particular starting with a global scenario of the corpus, then looking at attitudinal features of the texts according to their instructional levels, and finally discussing attitude in relation to the essays’ perceived effectiveness. Following this order, it will be easier to relate the findings to attitudinal features in general undergraduate academic writing and then observe specific features where perceived effectiveness in the texts plays a distinctive role in the corpus of this work.
6.1 Attitude in the general corpus
The first relevant observation is the reduced presence of expressions of attitude in the global corpus, which is a general regularity that previous studies from various contexts have found as a significant feature of academic writing. The low occurrence of attitudinal evaluations in this sort of discourse can be understood in terms of argumentative pertinence. As Hunston states ( 1999 ), in academic discourse, only certain things get linguistically evaluated and they do it in specific ways when it is worth it. Additionally, looking back at Petty and Cacioppo’s (1986) observations on the effects of subjective language in discourse, the appeal to the affective responses of an audience usually takes place at strategic points where an objective argumentation may lack the necessary persuasive potential. Thus, in discourses where objectivity is highly appreciated, attitudinal evaluations are used in limited proportions and forms, leading to a strategic management of evaluative resources.
Such strategic nature in the use of attitudinal evaluations has been previously explored in academic discourse in Spanish and in EFL academic writing. Valerdi (2021) found that attitude resources occurred in limited proportions due to their usefulness in certain specific types of argument components in postgraduate academic discourses in Spanish. The corpus of this study seems to conform to this strategic management of attitudinal expression. Within the area of EFL academic writing, Jalilifar and Hemmati (2013) concluded that particular dynamics of attitudinal deployment in texts are more determinant than large global amounts of attitudinal language in texts. In line with this, Crosthwaite and Jiang (2017) concluded that effective writing displays limited and careful expression of attitudinal meanings. Considering these antecedents, the general features of evaluative expressions in the corpus of this work seem to respond to academic writing conventions that learners have associated to their use of their target language and, in turn, reflect a general tendency that has been identified as a feature of effective writing in academic contexts.
6.1.1 Attitude types
A second feature the corpus shares with general effective writing is the predominance of realizations of appreciation in more than 50 % of evaluative resources. Such predominance prevails when breaking the corpus into smaller sub-corpora of basic, intermediate and advanced instructional levels. This leaves little room for affective evaluations, which occur in no more than 9 % of attitudinal realizations in all sub-corpora. As mentioned before, only certain things are evaluated in academic texts, and they are in certain ways only. This is confirmed when comparing these findings with those of previous works on appraisal in different contexts. Zhang and Cheung (2018) , for instance, found appreciation as the most realized type of attitude in articles on Second Language Writing, which they see as the result of a strategic evaluation which focuses on the value of things in order to objectify observations that are subjective in nature. Lee (2015) observes similar tendencies in undergraduate essays and emphasizes the importance of evaluating things related to the subject matter in the production of academic texts. According to these interpretations, prioritizing the appraisal of discipline-related things is central in academic arguments, where evaluation tends to be more objective than it would were it based on observations about human behavior or emotional responses of writers.
6.1.2 Attitudinal explicitness
The inscription and invocation of attitudinal meanings display one more regularity of the corpus that remains constant in the basic, intermediate, and advanced sub-corpora. From a general perspective, attitudinal evaluations are predominantly inscribed, making their attitudinal stance accessible in terms of the effort their identification and interpretation demand from the reader ( Halliday 2002 ). Nonetheless, such inscribing tendency changes when looking at each attitudinal category; realizations of judgement tend to be invoked in more than 65 % of occurrences.
These features carry interesting implications in terms of the degrees of explicitness with which EFL academic undergraduate authors deploy their evaluations. First, the global tendency to inscribe evaluations coincides with Hood and Martin’s (2005) observation that academic writers do not usually invoke attitude when constructing arguments around their work. The features of the corpus of this work confirm the validity of that observation in EFL academic writing. Regarding the contrasting realizations of judgement , previous research has shown how evaluations focused on people and their behavior tend to be managed more carefully in academic contexts than those triggered by things, taking the form of invoked attitudinal resources ( Hood and Martin 2005 ; Valerdi 2016 ). Apparently, the authors of the corpus behave more freely or confidently when evaluating things related to the subject matter of their work and their own personal impressions through appreciation and affect than when dealing with human – or humanized – triggers, in which case they tend to proceed more cautiously. It seems plausible to say these features correspond to generally effective evaluative dynamics in academic writing. Even though proportional differences between inscribed and invoked affect are not statistically significant ( Table 10 ), the regularity of their plain contrast and the significance of differences in judgement and appreciation stand as a remarkable feature of the corpus.
6.1.3 Triggers of attitudinal evaluation
The tendencies of the most recurrent triggers of attitudinal evaluation in the corpus are another area of significant regularity across instructional levels. The vast majority of attitude realizations is triggered by elements inherently associated to the literary works the authors analyzed in their essays; in the overall corpus, the most recurrent triggers are literary characters, followed by textual features from the realm of literary studies, and entities and concepts external to literary works in second and third place, respectively. These results seem to be a direct consequence of the instructions authors were given to analyze a literary work by identifying its most remarkable features as instances of literary genres and to justify their observations. Here, the notion of justification is key; since the authors were expected to justify their observations about literary features, it would seem natural to expect arguments founded on argumentative conclusions and supporting ideas focused on such things as characters, textual features and the contexts around literary works. Such was the case of the corpus of academic essays analyzed by Myskow and Ono (2018) , who found that attitudinal resources were used as part of the two central components of arguments, namely conclusions and supporting ideas, connected to subject matter-related triggers. Taking into consideration Myskow and Ono’s experience, together with Valerdi (2016) findings on the realizations of attitudinal evaluations directly connected to specific argument components, the statistically significant features of the triggers variable in this corpus confirm the centrality of attitudinal evaluation on the elaboration of academic arguments.
6.2 Attitude by instructional level
The corpus displays significant variations if the results are seen from the perspective of the three levels of instruction of the authors of the texts. There is a clear tendency for uses of affect and appreciation to decrease progressively from basic through advanced essays, while realizations of judgement increase from 13 % to 40 % ( Table 8 ). This could be interpreted as the direct consequence of the authors’ choice to evaluate characters from the works they studied and, as a result, it further supports the strategic nature of evaluative choices in the corpus; if any type of attitude was to remain present at different instructional levels, it was the one triggered by human-like entities. Additionally, despite the general reduction of inscribed evaluations in all three sub-corpora ( Table 9 ), expressions of judgement developed on the opposite direction, reducing their invoked realizations significantly ( Table 10 ). These observations suggest interesting evaluative dynamics on the corpus; while there is a general caution on the part of authors to evaluate human and human-like entities in their texts, there also seems to be certain development of a notion of discursive authority ( Poynton 1985 , as cited in Valerdi 2016 ) allowing writers to express their stance regarding human triggers in more open terms through inscribed judgmental evaluations as they gain more linguistic and disciplinary experience.
The relationship between evaluative language and disciplinary experience can also be seen in the triggers on which authors focus their attitude realizations. Writers of basic essays contrast with writers of intermediate and advanced texts in their evaluative focus on authors of literary works as the third most relevant triggers ( Table 11 ). Clearly, the interpretation of writers of basic essays regarding what elements are central in literary analysis is particular. Considering previous observations about the relevance of prioritizing arguments around the value of things to objectify evaluations ( Zhang and Cheung 2018 ), it seems plausible to conclude that, in intermediate and advanced texts, the less central consideration of human elements different from literary characters is the result of the development of a more specialized selection of elements worthy of literary discussion. These findings further support what has been observed by Candarli et al. (2015) , Lee and Deakin (2016) and Crosthwaite and Jiang (2017) ; attitudinal choices seem to be modulated by EFL writers when writing in English and, in parallel with this, they stem from disciplinary instruction which leads to the acquisition of academic EFL writing rhetorical conventions. On the grounds of these observations, it is clear how previously discussed general features of effective writing develop in the corpus as essays progress towards more experienced writing.
6.3 Attitude in relation to perceived effectiveness
The results of the analysis evidence a tendency in high-graded essays to display significantly greater proportions of attitude than texts graded as low and middle ( Table 12 ). The fact that the advanced sub-corpus displays an irregular distribution – with middle-graded essays presenting the most attitude – could be explained by the acquisition of more regularly applied conventions by advanced writers resulting in closer proportions between these groups of texts. Further explorations of advanced essays in this and similar contexts are needed to confirm this. Still, even though the p value of 0.11234221 indicates results might be different for this sub-corpus if this research were replicated, in the actuality of these results low-graded essays display the least instances of attitudinal evaluation.
It is remarkable to notice the significant predominance of appreciation over judgement and affect stands when effectiveness is considered. This indicates the development of attitude -related interpersonal conventions along basic, intermediate, and advanced instructional levels has been shaped by pedagogical dynamics that favor the observed tendencies via both instruction and academic evaluation: what teachers disseminate and evaluate as effective motivates what learners use to shape their discourse in this type of writing as they move towards more specialized levels of literary analysis. It is worth remembering that, according to what they reported, teachers who assessed the essays did not consider attitudinal expressions in their evaluation criteria. Then, in line with Lee’s analysis (2008), we can conclude that teachers might have perceived the management of evaluative language, which directly relates to writers’ stance and voice, as part of the appropriate analysis of literary components and features they sought; attitude is central to effectiveness in the corpus of this work.
Similar findings in previous research indicate the latter interpretation may also apply to other contexts; Jalilifar and Hemmati (2013) found successful EFL texts by Iranian writers displayed significantly more frequent instances of appreciation than judgement and affect , just as Myskow and Ono (2018) did in their essays by Japanese students. Moreover, similarly to this research, patterns of attitudinal inscription and invocation in the corpora analyzed by those authors can be significantly related to degrees of (in)effectiveness. In the corpus of this work, inscription of affect and appreciation contrasts with invocation of judgement in low-, middle-, and high-graded essays – save for minor variations in affect , the least representative category, in the basic and intermediate sub-corpora. Although these contrasts may require further exploration to confirm statistical significance, their plain tendencies and their consistency with the significant dynamics by instructional level confirm the role of attitudinal meanings in the shaping of undergraduate writers’ positioning and, most importantly, a positive relationship between realizations of attitude and the effectiveness of undergraduate EFL academic writing instantiated by the corpus.
Such relationship is further evidenced by the development of attitudinal triggers selection patterns. As it was previously described, in both intermediate and advanced essays, characters, textual features and external literary elements are the most representative triggers in low-, middle-, and high-graded essays. In the basic sub-corpus, however, the very authors of the essays figure as either the second (low- and middle-graded texts) or first (high-graded-texts) choices. The contrast this represents can be explained, once more, on the basis of instruction and academic evaluation; although attitudinal stance focused on the very authors of the essays conflicts with the general features of the corpus, the fact that the other two main trigger types in basic essays remain within what can be seen as disciplinarily central in the general scenario may have allowed for certain tolerance on the part of teachers. Although having access to feedback received by the writers of the basic essays would be the only way to confirm this, it should be enough to notice that trigger selection in relation to text effectiveness takes a clear orientation in the rest of the corpus, thus corroborating the role of attitudinal evaluations in undergraduate academic writing instantiated by the corpus.
In the light of these results, a positive relationship between the expression of attitudinal meanings and academic texts (in)effectiveness has been confirmed. What is more, the writing conventions followed by the authors of the corpus of this work suggest that attitudinal features privileged by university teachers in basic levels of instruction determine the conventions adopted in effective texts at more advanced levels, even when attitudinal dynamics do not seem to have been explicitly prioritized. Apparently, attitudinal dynamics in the context of the corpus have developed from complex influences which go beyond mere linguistic and disciplinary instruction. These observations relate to Chitez and Kruse’s (2012) considerations about writing cultures: further extra disciplinary features related to writing cultures shape what could be considered as effective or successful in writing academically. These include learners’ class experience before and during university education, contact with diverse curricular arrangements, university-specific organizational structures, national writing cultures, and differences among languages. As evidenced by the findings of this work, these factors represent important aspects to consider in the design of academic writing programs and discipline-specific writing courses as these may have to take into consideration the features of their participants’ target audiences, including potential expectations determined by their own linguistic, cultural, and even institutional backgrounds.
All these considerations have a particular centrality in programs focused on training future professionals in English Language and Literature for, as it has been shown, even when interpersonal dynamics involving attitude conform to similar general tendencies in the whole corpus of this study, they vary significantly at more delicate degrees of analysis such as instructional levels and realizational variables. Additionally, exploring such delicacy in variation, which can only be done by analyzing the academic discourse of speakers from different instructional levels within the same undergraduate community, may also serve as a valuable source of information for pedagogical actions aiming to guide undergraduate writers in the production of effective texts in other disciplines.
7 Conclusions
As the findings of this work have shown, the construction of interpersonal relationships through the use of linguistic resources of attitude plays an important role in the perceived effectiveness of undergraduate EFL academic writing at different levels of experience and disciplinary instruction, which indicates the importance of broadening assessment criteria of academic writing beyond the constraints of lexicogrammatical accuracy and text structure, as well as pertinent observations about attitudinal positioning in instructional processes, in favor of deeper interpersonal metalinguistic awareness in both students and writing instructors. In order to face these instructional challenges, it is important to emphasize the results also show that the influence of attitudinal language in the (in)effectiveness of academic texts is furtherly determined by a complex series of contextual factors including discursive authority, writing experience, discipline-specific focus objects, and the multi-faceted writing-related cultural background of writers.
These conclusions are supported by six main findings that have been reported in this paper: 1) In adherence to general academic writing, the corpus displays a significantly low occurrence of attitude resources, which results from a strategic deployment of interpersonal resources by writers as to what is evaluated in their texts and in what ways; 2) General attitudinal features in the corpus privilege appreciation as the most frequent type of attitude and position affect as the least deployed evaluative resource, which reflects the writers’ prioritizing of evaluations of discipline-related things to project an objective-like positioning; 3) Realizations of judgement throughout the corpus are mainly invoked, signaling the adoption of particular evaluation strategies around human or human-like triggers; 4) Basic essays feature greater use of attitudinal resources than intermediate and advanced essays, suggesting a progressive development of objective-like writing dynamics; 5) Overall, high-graded essays display more frequent expressions of attitude than middle- and low-graded essays, suggesting that the expression of attitude is not simply reduced in learners’ discourse as they move forward in their academic training, but according to conventions that favor certain types of strategic attitudinal positioning in texts; 6) In general, the realizational variables of attitude category, explicitness and trigger selection show significantly matching tendencies in high-graded essays in the basic, intermediate and advanced sub-corpora, confirming the central role of the strategic use of affect , judgement and appreciation resources in terms of their realizational variables in the production of effective texts, even when writing conventions develop towards reduced proportions of attitude . Those findings which were not found to be statistically significant might need further exploration, perhaps on the basis of a larger corpus, in order to refine their implications from a statistical perspective. Still, it is worth remembering statistical interpretations, either descriptive or inferential, always leave room for open possibilities.
Regarding the latter point, interpretations of the reported results need to take into consideration that a relevant limitation of this study is the size of its corpus. Although the results of the analysis demonstrate consistent and mostly statistically significant features, their full implications apply to the context of the academic community where the essays were collected. In order to obtain more generalizable findings with more predictive potential in relation to the Mexican context, future work might need to replicate the study on the basis of a larger and more varied corpus.
While the scope of the results of this work is limited to the boundaries of the context of this research, the implications of its findings represent meaningful contributions that complement previous research on the workings of appraisal resources of attitude in EFL academic writing. Most importantly, this work contributes to further understanding of the workings of evaluative language in academic instruction in the context of Mexico, where pedagogical developments from the systemic functional perspective of appraisal theory are still in their early stages. It is ideal that the focus of future work seek to implement research findings in the development of concrete instructional tools which improve the scenario of effective interpersonal positioning for undergraduate authors seeking to take part in international disciplinary dialogue through academic English.
Amossy, Ruth. 2009. Argumentación y análisis del discurso: Perspectivas teóricas y recortes disciplinarios. En Luisa A. Puig (ed.), El discurso y sus espejos , 67–98. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Search in Google Scholar
Bahmani, Mona, Azizeh Chalak & Hossein H. Tabrizi. 2021. The effect of evaluative language on high- and low- graded post-graduate students’ academic writing ability across gender. Cogent Education 8. 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2021.1905229 . Search in Google Scholar
Candarli, Duygu, Yasemin Bayyurt & Leyla Marti. 2015. Authorial presence in L1 and L2 novice academic writing: Crosslinguistic and cross-cultural perspectives. Journal of English for Academic Purposes 20. 192–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2015.10.001 . Search in Google Scholar
Castro, María. 2013. Posicionamiento discursivo en el ensayo de opinión escrito por estudiantes universitarios. Lenguas en contexto 10. 98–107. Search in Google Scholar
Castro, María & Martín Sánchez. 2013. La expresión de opinión en textos académicos escritos por estudiantes universitarios. Revista Mexicana de Investigación Educativa 18(57). 483–506. Search in Google Scholar
Chazal, Edward de. 2014. English for academic purposes . Oxford: Oxford University Press. Search in Google Scholar
Chitez, Madalina & Otto Kruse. 2012. Writing cultures and genres in European higher education. In Montserrat Castelló & Christiane Donahue (eds.), University writing: Selves and texts in academic societies , 151–175. United Kingdom: Emerald. 10.1163/9781780523873_010 Search in Google Scholar
Crosthwaite, Peter & Kevin Jiang. 2017. Does EAP affect written L2 academic stance? Longitudinal learner corpus study. System 69. 92–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2017.06.010 Search in Google Scholar
Derewianka, Beverly. 2007. Using Appraisal Theory to track interpersonal development in adolescent academic writing. In Rachael Whittaker, Mike O’Donell & Anne McCabe (eds.), Advances in language and education , 142–165. London: Continuum. Search in Google Scholar
Du, Jianying, Hao Yuan & Qiong Li. 2023. Read between the lines: Evaluative patterns and paces in engineering research article introductions. English for Specific Purposes 71. 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2023.02.002 . Search in Google Scholar
González, María. 2011. La expresión lingüística de la actitud en el género de opinión: El modelo de la Valoración. Revista de lingüística teórica y aplicada 49(1). 109–141. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-48832011000100006 . Search in Google Scholar
Halliday, Michael A. K. 1985. An introduction to functional grammar . London: Arnold. Search in Google Scholar
Halliday, Michael A. K. 2002. Language structure and language function. In Jonathan Webster (ed.), On Grammar. Vol. 1 in the collected works of M. A. K. Halliday , 173–195. London: Continuum. Search in Google Scholar
Halliday, Michael A. K. 2004. An introduction to functional grammar , 3rd edn. Revised by Christian M. I. M. Matthiessen. London: Arnold. Search in Google Scholar
Hyland, Ken. 2003. Second language writing . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/CBO9780511667251 Search in Google Scholar
Hyland, Ken. 2004. Disciplinary discourses: Social interactions in academic writing . Michigan: The University of Michigan Press. Search in Google Scholar
Hyland, Ken. 2005. Metadiscourse: Exploring interaction in writing . London: Continuum. Search in Google Scholar
Hood, Susan. 2010. Appraising research: Evaluation in academic language . Basingtoke: Palgrave McMillan. 10.1057/9780230274662 Search in Google Scholar
Hood, Susan. & James R. Martin. 2005. Invoking attitude: The play of graduation in appraising discourse. Signos 38(58). 195–220. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-09342005000200004 . Search in Google Scholar
Hunston, Susan. 1999. Evaluation in the planes of discourse: Status and value in persuasive texts. In Susan Hunston & Geoff Thompson (eds.), Evaluation in text: Authorial stance and the construction of discourse , 176–206. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 10.1093/oso/9780198238546.003.0009 Search in Google Scholar
Hunston, Susan. 2011. Corpus approaches to evaluation: Phraseology and evaluative language . New York: Routledge. 10.4324/9780203841686 Search in Google Scholar
Hunston, Susan & Hang Su. 2019. Patterns, constructions, and local grammar: A case study of evaluation. Applied Linguistics 40(4). 567–593. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/amx046 . Search in Google Scholar
Ignatieva, Natalia. 2021. Análisis ideacional e interpersonal de escritos estudiantiles de historia en español dentro del marco sistémico. Signos 54(105). 169–190. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-09342021000100169 . Search in Google Scholar
Jalilifar, Alireza & Ali Hemmati. 2013. Constructions of evaluative meanings by Kurdish-speaking learners of English: A comparison of high- and low-graded argumentative essays. Issues in Language Teaching 2(2). 57–84. Search in Google Scholar
Lancaster, Zak. 2014. Tracking interpersonal style: The use of functional language analysis in college writing instruction. In Mike Duncan & Star M. Vanguri (eds.), The centrality of style , 191–212. Colorado: Parlor Press. 10.37514/PER-B.2013.0476.2.13 Search in Google Scholar
Lee, Sook H. 2008. Attitude in undergraduate persuasive essays. Prospect: An Australian Journal of TESOL 23. 43–58. Search in Google Scholar
Lee, Sook H. 2015. Evaluative stances in persuasive essays by undergraduate students: Focusing on appreciation resources. Text & Talk 35(1). 49–76. https://doi.org/10.1515/text-2014-0029 . Search in Google Scholar
Lee, Joseph J. & Lydia Deakin. 2016. Interactions in L1 and L2 undergraduate student writing: Interactional metadiscourse in successful and less-successful argumentative essays. Journal of Second Language Writing 33. 21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2016.06.004 . Search in Google Scholar
Levon, Erez. 2010. Organizing and processing your data: The nuts and bolts of quantitative analysis. In Lia Litosseliti (ed.), Research methods in linguistics , 68–92. London: Continuum. Search in Google Scholar
Martin, James R. 2000. Beyond exchange: Appraisal systems in English. In Susan Hunston & Geoff Thompson (eds.), Evaluation in text: Authorial stance and the construction of discourse , 142–175. Oxford: Oxford University Press. 10.1093/oso/9780198238546.003.0008 Search in Google Scholar
Martin, James R. & Peter R. R. White. 2005. The language of evaluation: Appraisal systems in English . Basingtoke: Palgrave Macmillan. Search in Google Scholar
Mei, Wu S. 2006. Creating a contrastive rhetorical stance: Investigating the strategy of problematization in students’ argumentation. RELC Journal: Journal of Language Teaching and Research 37(3). 329–353. https://doi.org/10.1177/0033688206071316 . Search in Google Scholar
Mei, Wu S. 2007. The use of engagement resources in high- and low-rated undergraduate geography essays. Journal of English for Academic Purposes 6. 254–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2007.09.006 . Search in Google Scholar
Moss, Gillian. 2011. La negación: Un diálogo exigente. In Norma Barleta & Diana Chamorro (eds.), El texto escolar y el aprendizaje: Enredos y desenredos , 181–194. Barranquilla: Universidad del Norte. Search in Google Scholar
Myskow, Gordon & Masumi Ono. 2018. A matter of facts: L2 writers’ use of evidence and evaluation in biographical essays. Journal of Second Language Writing 41. 55–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2018.08.002 . Search in Google Scholar
Navarro, Fernando. 2014. Gradación y compromiso en escritura académica estudiantil de humanidades. Análisis contrastivo desde la Teoría de la Valoración. Estudios de Linguistica Aplicada 32(60). 9–33. https://doi.org/10.22201/enallt.01852647p.2014.60.1 . Search in Google Scholar
Nesi, Hilary & Sheena Gardner. 2012. Genres across the disciplines: Student writing in higher education . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/9781009030199 Search in Google Scholar
Painter, Clare. 2003. Developing attitude: An ontogenetic perspective on appraisal. Text 23(2). 183–209. https://doi.org/10.1515/text.2003.008 . Search in Google Scholar
Petty, Richard E. & John T. Cacioppo. 1986. The elaboration likelihood model of persuasion. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology 19. 123–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60214-2 . Search in Google Scholar
Perales, Moisés D., Eyder G. Sima & Sandra Valdez. 2012. Movimientos retóricos en las conclusiones de tesis de licenciatura en antropología social: Un estudio sistémico-funcional. Escritos: Revista del Centro de Ciencias del Lenguaje 45. 33–60. Search in Google Scholar
Poynton, Cate. 1985. Language and gender: Making the difference . Geelong, Vic.: Deakin University Press. Search in Google Scholar
Rasinger, Sebastian M. 2013. Quantitative research in linguistics: An introduction , 2nd edn. London: Bloomsbury 10.5040/9781350284883 Search in Google Scholar
Ryshina-Pankova, Marianna. 2014. Exploring academic argumentation in course-related blogs through engagement. In Geoff Thompson & Laura Alba-Juez (eds.), Evaluation in context , 281-302. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. 10.1075/pbns.242.14rys Search in Google Scholar
Torr, Jane. 1997. From child language to mother tongue: A case study of language development in the first two and a half years . Nottingham: University of Nottingham. Search in Google Scholar
Valerdi, Julio. 2016. La heteroglosia en la redacción académica en inglés: una exploración de la propiedad lingüística en el ensayo académico universitario. In Natalia Ignatieva & Daniel Rodríguez-Vergara (eds.), Lingüística sistémico funcional en México: aplicaciones e implicaciones , 147–176. Ciudad de México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. Search in Google Scholar
Valerdi, Julio. 2021. Exploring new perspectives and degrees of delicacy in appraisal studies: An analysis of engagement resources in academic discourse in Spanish. In María Brisk & Schleppegrell Mary (eds.), Language in action: SFL theory across contexts , 119–148. Sheffield: Equinox. Search in Google Scholar
Vega, Luis. 2015. Introducción a la teoría de la argumentación. Problemas y perspectivas . Lima: Palestra. Search in Google Scholar
Zamudio, Victoria. 2016. La expresión de opiniones y puntos de vista en textos académicos estudiantiles sobre literatura. Lenguaje 44(1). 35–39. https://doi.org/10.25100/lenguaje.v44i1.4629 . Search in Google Scholar
Zhang, Weiyu & Yin L. Cheung. 2018. The construction of authorial voice in writing research articles: A corpus-based study from an appraisal theory perspective. International Journal of English Studies 18(2). 53–75. https://doi.org/10.6018/ijes/2018/2/320261 . Search in Google Scholar
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- X / Twitter
Supplementary Materials
Please login or register with De Gruyter to order this product.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use clear and concise language: Clarity is vital in an evaluation essay. Use clear and concise language to express your thoughts and ideas, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary. Your essay should be accessible to a wide audience and easy to understand, allowing your evaluation to be conveyed effectively. 6.
Evaluative language. Evaluative language includes positive, negative or neutral words and expressions that convey a judgement or an appraisal. The use of such language indicates your considered attitude to the particular topic - that is, your critical position.
How to write an Evaluation Essay. There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria. Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument. Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
Evaluation is a type of writing that has many real-world applications. Anything can be evaluated. For example, evaluations of movies, restaurants, books, and technology ourselves are all real-world evaluations. Five Characteristics of an Evaluative Essay. by Dr. Karen Palmer 1. Presenting the subject.
Examples of Evaluation Essays. To help you get a better understanding of how to write an effective evaluation essay, here are 10 inspiring evaluation essay examples from different fields: 1. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine rollout strategy in the United States. 2. Evaluation of the impact of the #MeToo movement on ...
Example 1: "Atkinson is misguided when he inaccurately claims that students need . . ." We can show our position with regard to the points of view or evidence that we have presented by using a combination of precise verbs, hedging and other evaluative language. Example 2:
Step 4: Structuring Your Essay. A well-structured evaluation essay enhances readability and ensures your points are effectively communicated. Consider the following structure: Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the subject and state your evaluation's purpose and significance. Main Body: Break your evaluation into logical paragraphs, each ...
An evaluation essay is a composition that offers value judgments about a particular subject according to a set of criteria. Also called evaluative writing, evaluative essay or report, and critical evaluation essay . An evaluation essay or report is a type of argument that provides evidence to justify a writer's opinions about a subject.
Key Characteristics. Evaluative writing generally exhibits the following: Puts the writer in the position as expert or trusted evaluator. Makes a judgment about something using facts and evidence rather than feelings. Uses specific criteria that are relevant, common, or somewhat universal. Organizes the analysis based on specified criteria ...
Learn about the evaluation essay and how it's written with an evaluative essay example. Review an evaluative thesis and other parts of the evaluation essay. Updated: 11/21/2023
An evaluation argument based on moral criteria will claim that something is right or wrong. It will need to appeal to shared values or make a case for a particular value that serves as criteria. Some values are nearly universal, such as honesty, reasonableness, and fairness, as we will discuss in 9.6: Moral Character.
An evaluation essay is a type of essay that requires you to judge the quality of a subject based on some ideal criteria that act as a point of comparison. We guide you through writing one with examples.
13.3.1 Introduction. In the introduction of your evaluative essay, you should clearly state the following: - what you are evaluating (the subject - like Citizen Kane or National Lampoon's Christmas Vacation) - the purpose of your evaluation - what criteria you are evaluating your subject on (plot, characterization, cinematography etc.)For example, you should not just write that you ...
To identify language resources for writing an academic argument. To demonstrate how evaluative vocabulary, modality, endorsement, attribution, comparison and concession can be effective resources for building an argument in an essay. In English there are many language resources which allow writers and speakers to effectively present an argument.
Have a strong opinion—positive or negative—about this topic. Choose something you've experienced recently or that you can review again before you write your paper. Know a lot about this type of experience. Use the following list of categories to brainstorm ideas for what you might want to evaluate. Use this list of categories to brainstorm ...
Here are some examples of how evaluative verbs might elevate responses to a sophisticated understanding of the writer's intention: Stephenson portrays Jekyll as a duplicitous character. (simple statement) Stephenson insinuates that Jekyll has repressed his transgressive desires, leading a conflicted dual nature. (analytical statement)
Example of Descriptive, Analytical, Critical/Evaluative, and Reflective Writing . Descriptive Writing Analytical Writing Critical/Evaluative Writing Reflective Writing "The early childhood -school relationship has been researched largely from three positions" (Henderson, 2012, p. 20). "Learning how to 'fit in' seemed to
Writing a Critique. A critique (or critical review) is not to be mistaken for a literature review. A 'critical review', or 'critique', is a complete type of text (or genre), discussing one particular article or book in detail. In some instances, you may be asked to write a critique of two or three articles (e.g. a comparative critical review).
Here is a step-by-step guide for you to write an evaluation essay. Step 1. Write the Introduction. The introduction is the first impression your readers will have of you, so it's crucial to make a good one. It should capture attention and excite readers, drawing them into what you have to say about this topic.
When composing an evaluation essay's conclusion, keep the following points in mind: Restate your main points and arguments from the essay body. Present evidence to support your thesis. Conclude your argument convincingly, ultimately persuading the reader of your assessment. 3.
The purpose of this paper is to explore whether the use of attitudinal language stands as a potential source of effectiveness in undergraduate academic writing in English as a Foreign Language (EFL). In order to achieve this purpose, interpersonal features of a corpus of essays written by Mexican undergraduate students of English Language and Literature were analyzed. The model of appraisal ...
conveyed through the use of explicitly evaluative language, particularly adjectives, suchasbeautiful,terrifying,ordespicable,butisoftenconveyedimplicitly,triggered in context, and merged with referential meaning, as seen in the examples of the Victorianpropertyandsilkyhair.Asmentionedabove,theexpressivestrategiesthat
1. X endeavours to show/prove, put forth. Panova endeavours to show that although Holden is not a very likeable character on the surface, one comes to like him in the end. 2. Expresses a view....to the effect that. Panova expresses a view to the effect that although Holden is not a very likeable character on the surface, one comes to like him ...