Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.

How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Qualitative case study data analysis: an example from practice
Affiliation.
- 1 School of Nursing and Midwifery, National University of Ireland, Galway, Republic of Ireland.
- PMID: 25976531
- DOI: 10.7748/nr.22.5.8.e1307
Aim: To illustrate an approach to data analysis in qualitative case study methodology.
Background: There is often little detail in case study research about how data were analysed. However, it is important that comprehensive analysis procedures are used because there are often large sets of data from multiple sources of evidence. Furthermore, the ability to describe in detail how the analysis was conducted ensures rigour in reporting qualitative research.
Data sources: The research example used is a multiple case study that explored the role of the clinical skills laboratory in preparing students for the real world of practice. Data analysis was conducted using a framework guided by the four stages of analysis outlined by Morse ( 1994 ): comprehending, synthesising, theorising and recontextualising. The specific strategies for analysis in these stages centred on the work of Miles and Huberman ( 1994 ), which has been successfully used in case study research. The data were managed using NVivo software.
Review methods: Literature examining qualitative data analysis was reviewed and strategies illustrated by the case study example provided. Discussion Each stage of the analysis framework is described with illustration from the research example for the purpose of highlighting the benefits of a systematic approach to handling large data sets from multiple sources.
Conclusion: By providing an example of how each stage of the analysis was conducted, it is hoped that researchers will be able to consider the benefits of such an approach to their own case study analysis.
Implications for research/practice: This paper illustrates specific strategies that can be employed when conducting data analysis in case study research and other qualitative research designs.
Keywords: Case study data analysis; case study research methodology; clinical skills research; qualitative case study methodology; qualitative data analysis; qualitative research.
- Case-Control Studies*
- Data Interpretation, Statistical*
- Nursing Research / methods*
- Qualitative Research*
- Research Design
A Guide To The Methods, Benefits & Problems of The Interpretation of Data

Table of Contents
1) What Is Data Interpretation?
2) How To Interpret Data?
3) Why Data Interpretation Is Important?
4) Data Interpretation Skills
5) Data Analysis & Interpretation Problems
6) Data Interpretation Techniques & Methods
7) The Use of Dashboards For Data Interpretation
8) Business Data Interpretation Examples
Data analysis and interpretation have now taken center stage with the advent of the digital age… and the sheer amount of data can be frightening. In fact, a Digital Universe study found that the total data supply in 2012 was 2.8 trillion gigabytes! Based on that amount of data alone, it is clear the calling card of any successful enterprise in today’s global world will be the ability to analyze complex data, produce actionable insights, and adapt to new market needs… all at the speed of thought.
Business dashboards are the digital age tools for big data. Capable of displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) for both quantitative and qualitative data analyses, they are ideal for making the fast-paced and data-driven market decisions that push today’s industry leaders to sustainable success. Through the art of streamlined visual communication, data dashboards permit businesses to engage in real-time and informed decision-making and are key instruments in data interpretation. First of all, let’s find a definition to understand what lies behind this practice.
What Is Data Interpretation?
Data interpretation refers to the process of using diverse analytical methods to review data and arrive at relevant conclusions. The interpretation of data helps researchers to categorize, manipulate, and summarize the information in order to answer critical questions.
The importance of data interpretation is evident, and this is why it needs to be done properly. Data is very likely to arrive from multiple sources and has a tendency to enter the analysis process with haphazard ordering. Data analysis tends to be extremely subjective. That is to say, the nature and goal of interpretation will vary from business to business, likely correlating to the type of data being analyzed. While there are several types of processes that are implemented based on the nature of individual data, the two broadest and most common categories are “quantitative and qualitative analysis.”
Yet, before any serious data interpretation inquiry can begin, it should be understood that visual presentations of data findings are irrelevant unless a sound decision is made regarding measurement scales. Before any serious data analysis can begin, the measurement scale must be decided for the data as this will have a long-term impact on data interpretation ROI. The varying scales include:
- Nominal Scale: non-numeric categories that cannot be ranked or compared quantitatively. Variables are exclusive and exhaustive.
- Ordinal Scale: exclusive categories that are exclusive and exhaustive but with a logical order. Quality ratings and agreement ratings are examples of ordinal scales (i.e., good, very good, fair, etc., OR agree, strongly agree, disagree, etc.).
- Interval: a measurement scale where data is grouped into categories with orderly and equal distances between the categories. There is always an arbitrary zero point.
- Ratio: contains features of all three.
For a more in-depth review of scales of measurement, read our article on data analysis questions . Once measurement scales have been selected, it is time to select which of the two broad interpretation processes will best suit your data needs. Let’s take a closer look at those specific methods and possible data interpretation problems.
How To Interpret Data? Top Methods & Techniques

When interpreting data, an analyst must try to discern the differences between correlation, causation, and coincidences, as well as many other biases – but he also has to consider all the factors involved that may have led to a result. There are various data interpretation types and methods one can use to achieve this.
The interpretation of data is designed to help people make sense of numerical data that has been collected, analyzed, and presented. Having a baseline method for interpreting data will provide your analyst teams with a structure and consistent foundation. Indeed, if several departments have different approaches to interpreting the same data while sharing the same goals, some mismatched objectives can result. Disparate methods will lead to duplicated efforts, inconsistent solutions, wasted energy, and inevitably – time and money. In this part, we will look at the two main methods of interpretation of data: qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Qualitative Data Interpretation
Qualitative data analysis can be summed up in one word – categorical. With this type of analysis, data is not described through numerical values or patterns but through the use of descriptive context (i.e., text). Typically, narrative data is gathered by employing a wide variety of person-to-person techniques. These techniques include:
- Observations: detailing behavioral patterns that occur within an observation group. These patterns could be the amount of time spent in an activity, the type of activity, and the method of communication employed.
- Focus groups: Group people and ask them relevant questions to generate a collaborative discussion about a research topic.
- Secondary Research: much like how patterns of behavior can be observed, various types of documentation resources can be coded and divided based on the type of material they contain.
- Interviews: one of the best collection methods for narrative data. Inquiry responses can be grouped by theme, topic, or category. The interview approach allows for highly focused data segmentation.
A key difference between qualitative and quantitative analysis is clearly noticeable in the interpretation stage. The first one is widely open to interpretation and must be “coded” so as to facilitate the grouping and labeling of data into identifiable themes. As person-to-person data collection techniques can often result in disputes pertaining to proper analysis, qualitative data analysis is often summarized through three basic principles: notice things, collect things, and think about things.
After qualitative data has been collected through transcripts, questionnaires, audio and video recordings, or the researcher’s notes, it is time to interpret it. For that purpose, there are some common methods used by researchers and analysts.
- Content analysis : As its name suggests, this is a research method used to identify frequencies and recurring words, subjects, and concepts in image, video, or audio content. It transforms qualitative information into quantitative data to help discover trends and conclusions that will later support important research or business decisions. This method is often used by marketers to understand brand sentiment from the mouths of customers themselves. Through that, they can extract valuable information to improve their products and services. It is recommended to use content analytics tools for this method as manually performing it is very time-consuming and can lead to human error or subjectivity issues. Having a clear goal in mind before diving into it is another great practice for avoiding getting lost in the fog.
- Thematic analysis: This method focuses on analyzing qualitative data, such as interview transcripts, survey questions, and others, to identify common patterns and separate the data into different groups according to found similarities or themes. For example, imagine you want to analyze what customers think about your restaurant. For this purpose, you do a thematic analysis on 1000 reviews and find common themes such as “fresh food”, “cold food”, “small portions”, “friendly staff”, etc. With those recurring themes in hand, you can extract conclusions about what could be improved or enhanced based on your customer’s experiences. Since this technique is more exploratory, be open to changing your research questions or goals as you go.
- Narrative analysis: A bit more specific and complicated than the two previous methods, it is used to analyze stories and discover their meaning. These stories can be extracted from testimonials, case studies, and interviews, as these formats give people more space to tell their experiences. Given that collecting this kind of data is harder and more time-consuming, sample sizes for narrative analysis are usually smaller, which makes it harder to reproduce its findings. However, it is still a valuable technique for understanding customers' preferences and mindsets.
- Discourse analysis : This method is used to draw the meaning of any type of visual, written, or symbolic language in relation to a social, political, cultural, or historical context. It is used to understand how context can affect how language is carried out and understood. For example, if you are doing research on power dynamics, using discourse analysis to analyze a conversation between a janitor and a CEO and draw conclusions about their responses based on the context and your research questions is a great use case for this technique. That said, like all methods in this section, discourse analytics is time-consuming as the data needs to be analyzed until no new insights emerge.
- Grounded theory analysis : The grounded theory approach aims to create or discover a new theory by carefully testing and evaluating the data available. Unlike all other qualitative approaches on this list, grounded theory helps extract conclusions and hypotheses from the data instead of going into the analysis with a defined hypothesis. This method is very popular amongst researchers, analysts, and marketers as the results are completely data-backed, providing a factual explanation of any scenario. It is often used when researching a completely new topic or with little knowledge as this space to start from the ground up.
Quantitative Data Interpretation
If quantitative data interpretation could be summed up in one word (and it really can’t), that word would be “numerical.” There are few certainties when it comes to data analysis, but you can be sure that if the research you are engaging in has no numbers involved, it is not quantitative research, as this analysis refers to a set of processes by which numerical data is analyzed. More often than not, it involves the use of statistical modeling such as standard deviation, mean, and median. Let’s quickly review the most common statistical terms:
- Mean: A mean represents a numerical average for a set of responses. When dealing with a data set (or multiple data sets), a mean will represent the central value of a specific set of numbers. It is the sum of the values divided by the number of values within the data set. Other terms that can be used to describe the concept are arithmetic mean, average, and mathematical expectation.
- Standard deviation: This is another statistical term commonly used in quantitative analysis. Standard deviation reveals the distribution of the responses around the mean. It describes the degree of consistency within the responses; together with the mean, it provides insight into data sets.
- Frequency distribution: This is a measurement gauging the rate of a response appearance within a data set. When using a survey, for example, frequency distribution, it can determine the number of times a specific ordinal scale response appears (i.e., agree, strongly agree, disagree, etc.). Frequency distribution is extremely keen in determining the degree of consensus among data points.
Typically, quantitative data is measured by visually presenting correlation tests between two or more variables of significance. Different processes can be used together or separately, and comparisons can be made to ultimately arrive at a conclusion. Other signature interpretation processes of quantitative data include:
- Regression analysis: Essentially, it uses historical data to understand the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Knowing which variables are related and how they developed in the past allows you to anticipate possible outcomes and make better decisions going forward. For example, if you want to predict your sales for next month, you can use regression to understand what factors will affect them, such as products on sale and the launch of a new campaign, among many others.
- Cohort analysis: This method identifies groups of users who share common characteristics during a particular time period. In a business scenario, cohort analysis is commonly used to understand customer behaviors. For example, a cohort could be all users who have signed up for a free trial on a given day. An analysis would be carried out to see how these users behave, what actions they carry out, and how their behavior differs from other user groups.
- Predictive analysis: As its name suggests, the predictive method aims to predict future developments by analyzing historical and current data. Powered by technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, predictive analytics practices enable businesses to identify patterns or potential issues and plan informed strategies in advance.
- Prescriptive analysis: Also powered by predictions, the prescriptive method uses techniques such as graph analysis, complex event processing, and neural networks, among others, to try to unravel the effect that future decisions will have in order to adjust them before they are actually made. This helps businesses to develop responsive, practical business strategies.
- Conjoint analysis: Typically applied to survey analysis, the conjoint approach is used to analyze how individuals value different attributes of a product or service. This helps researchers and businesses to define pricing, product features, packaging, and many other attributes. A common use is menu-based conjoint analysis, in which individuals are given a “menu” of options from which they can build their ideal concept or product. Through this, analysts can understand which attributes they would pick above others and drive conclusions.
- Cluster analysis: Last but not least, the cluster is a method used to group objects into categories. Since there is no target variable when using cluster analysis, it is a useful method to find hidden trends and patterns in the data. In a business context, clustering is used for audience segmentation to create targeted experiences. In market research, it is often used to identify age groups, geographical information, and earnings, among others.
Now that we have seen how to interpret data, let's move on and ask ourselves some questions: What are some of the benefits of data interpretation? Why do all industries engage in data research and analysis? These are basic questions, but they often don’t receive adequate attention.
Your Chance: Want to test a powerful data analysis software? Use our 14-days free trial & start extracting insights from your data!
Why Data Interpretation Is Important

The purpose of collection and interpretation is to acquire useful and usable information and to make the most informed decisions possible. From businesses to newlyweds researching their first home, data collection and interpretation provide limitless benefits for a wide range of institutions and individuals.
Data analysis and interpretation, regardless of the method and qualitative/quantitative status, may include the following characteristics:
- Data identification and explanation
- Comparing and contrasting data
- Identification of data outliers
- Future predictions
Data analysis and interpretation, in the end, help improve processes and identify problems. It is difficult to grow and make dependable improvements without, at the very least, minimal data collection and interpretation. What is the keyword? Dependable. Vague ideas regarding performance enhancement exist within all institutions and industries. Yet, without proper research and analysis, an idea is likely to remain in a stagnant state forever (i.e., minimal growth). So… what are a few of the business benefits of digital age data analysis and interpretation? Let’s take a look!
1) Informed decision-making: A decision is only as good as the knowledge that formed it. Informed data decision-making can potentially set industry leaders apart from the rest of the market pack. Studies have shown that companies in the top third of their industries are, on average, 5% more productive and 6% more profitable when implementing informed data decision-making processes. Most decisive actions will arise only after a problem has been identified or a goal defined. Data analysis should include identification, thesis development, and data collection, followed by data communication.
If institutions only follow that simple order, one that we should all be familiar with from grade school science fairs, then they will be able to solve issues as they emerge in real-time. Informed decision-making has a tendency to be cyclical. This means there is really no end, and eventually, new questions and conditions arise within the process that need to be studied further. The monitoring of data results will inevitably return the process to the start with new data and sights.
2) Anticipating needs with trends identification: data insights provide knowledge, and knowledge is power. The insights obtained from market and consumer data analyses have the ability to set trends for peers within similar market segments. A perfect example of how data analytics can impact trend prediction is evidenced in the music identification application Shazam . The application allows users to upload an audio clip of a song they like but can’t seem to identify. Users make 15 million song identifications a day. With this data, Shazam has been instrumental in predicting future popular artists.
When industry trends are identified, they can then serve a greater industry purpose. For example, the insights from Shazam’s monitoring benefits not only Shazam in understanding how to meet consumer needs but also grant music executives and record label companies an insight into the pop-culture scene of the day. Data gathering and interpretation processes can allow for industry-wide climate prediction and result in greater revenue streams across the market. For this reason, all institutions should follow the basic data cycle of collection, interpretation, decision-making, and monitoring.
3) Cost efficiency: Proper implementation of analytics processes can provide businesses with profound cost advantages within their industries. A recent data study performed by Deloitte vividly demonstrates this in finding that data analysis ROI is driven by efficient cost reductions. Often, this benefit is overlooked because making money is typically viewed as “sexier” than saving money. Yet, sound data analyses have the ability to alert management to cost-reduction opportunities without any significant exertion of effort on the part of human capital.
A great example of the potential for cost efficiency through data analysis is Intel. Prior to 2012, Intel would conduct over 19,000 manufacturing function tests on their chips before they could be deemed acceptable for release. To cut costs and reduce test time, Intel implemented predictive data analyses. By using historical and current data, Intel now avoids testing each chip 19,000 times by focusing on specific and individual chip tests. After its implementation in 2012, Intel saved over $3 million in manufacturing costs. Cost reduction may not be as “sexy” as data profit, but as Intel proves, it is a benefit of data analysis that should not be neglected.
4) Clear foresight: companies that collect and analyze their data gain better knowledge about themselves, their processes, and their performance. They can identify performance challenges when they arise and take action to overcome them. Data interpretation through visual representations lets them process their findings faster and make better-informed decisions on the company's future.
Key Data Interpretation Skills You Should Have
Just like any other process, data interpretation and analysis require researchers or analysts to have some key skills to be able to perform successfully. It is not enough just to apply some methods and tools to the data; the person who is managing it needs to be objective and have a data-driven mind, among other skills.
It is a common misconception to think that the required skills are mostly number-related. While data interpretation is heavily analytically driven, it also requires communication and narrative skills, as the results of the analysis need to be presented in a way that is easy to understand for all types of audiences.
Luckily, with the rise of self-service tools and AI-driven technologies, data interpretation is no longer segregated for analysts only. However, the topic still remains a big challenge for businesses that make big investments in data and tools to support it, as the interpretation skills required are still lacking. It is worthless to put massive amounts of money into extracting information if you are not going to be able to interpret what that information is telling you. For that reason, below we list the top 5 data interpretation skills your employees or researchers should have to extract the maximum potential from the data.
- Data Literacy: The first and most important skill to have is data literacy. This means having the ability to understand, work, and communicate with data. It involves knowing the types of data sources, methods, and ethical implications of using them. In research, this skill is often a given. However, in a business context, there might be many employees who are not comfortable with data. The issue is the interpretation of data can not be solely responsible for the data team, as it is not sustainable in the long run. Experts advise business leaders to carefully assess the literacy level across their workforce and implement training instances to ensure everyone can interpret their data.
- Data Tools: The data interpretation and analysis process involves using various tools to collect, clean, store, and analyze the data. The complexity of the tools varies depending on the type of data and the analysis goals. Going from simple ones like Excel to more complex ones like databases, such as SQL, or programming languages, such as R or Python. It also involves visual analytics tools to bring the data to life through the use of graphs and charts. Managing these tools is a fundamental skill as they make the process faster and more efficient. As mentioned before, most modern solutions are now self-service, enabling less technical users to use them without problem.
- Critical Thinking: Another very important skill is to have critical thinking. Data hides a range of conclusions, trends, and patterns that must be discovered. It is not just about comparing numbers; it is about putting a story together based on multiple factors that will lead to a conclusion. Therefore, having the ability to look further from what is right in front of you is an invaluable skill for data interpretation.
- Data Ethics: In the information age, being aware of the legal and ethical responsibilities that come with the use of data is of utmost importance. In short, data ethics involves respecting the privacy and confidentiality of data subjects, as well as ensuring accuracy and transparency for data usage. It requires the analyzer or researcher to be completely objective with its interpretation to avoid any biases or discrimination. Many countries have already implemented regulations regarding the use of data, including the GDPR or the ACM Code Of Ethics. Awareness of these regulations and responsibilities is a fundamental skill that anyone working in data interpretation should have.
- Domain Knowledge: Another skill that is considered important when interpreting data is to have domain knowledge. As mentioned before, data hides valuable insights that need to be uncovered. To do so, the analyst needs to know about the industry or domain from which the information is coming and use that knowledge to explore it and put it into a broader context. This is especially valuable in a business context, where most departments are now analyzing data independently with the help of a live dashboard instead of relying on the IT department, which can often overlook some aspects due to a lack of expertise in the topic.
Common Data Analysis And Interpretation Problems

The oft-repeated mantra of those who fear data advancements in the digital age is “big data equals big trouble.” While that statement is not accurate, it is safe to say that certain data interpretation problems or “pitfalls” exist and can occur when analyzing data, especially at the speed of thought. Let’s identify some of the most common data misinterpretation risks and shed some light on how they can be avoided:
1) Correlation mistaken for causation: our first misinterpretation of data refers to the tendency of data analysts to mix the cause of a phenomenon with correlation. It is the assumption that because two actions occurred together, one caused the other. This is inaccurate, as actions can occur together, absent a cause-and-effect relationship.
- Digital age example: assuming that increased revenue results from increased social media followers… there might be a definitive correlation between the two, especially with today’s multi-channel purchasing experiences. But that does not mean an increase in followers is the direct cause of increased revenue. There could be both a common cause and an indirect causality.
- Remedy: attempt to eliminate the variable you believe to be causing the phenomenon.
2) Confirmation bias: our second problem is data interpretation bias. It occurs when you have a theory or hypothesis in mind but are intent on only discovering data patterns that support it while rejecting those that do not.
- Digital age example: your boss asks you to analyze the success of a recent multi-platform social media marketing campaign. While analyzing the potential data variables from the campaign (one that you ran and believe performed well), you see that the share rate for Facebook posts was great, while the share rate for Twitter Tweets was not. Using only Facebook posts to prove your hypothesis that the campaign was successful would be a perfect manifestation of confirmation bias.
- Remedy: as this pitfall is often based on subjective desires, one remedy would be to analyze data with a team of objective individuals. If this is not possible, another solution is to resist the urge to make a conclusion before data exploration has been completed. Remember to always try to disprove a hypothesis, not prove it.
3) Irrelevant data: the third data misinterpretation pitfall is especially important in the digital age. As large data is no longer centrally stored and as it continues to be analyzed at the speed of thought, it is inevitable that analysts will focus on data that is irrelevant to the problem they are trying to correct.
- Digital age example: in attempting to gauge the success of an email lead generation campaign, you notice that the number of homepage views directly resulting from the campaign increased, but the number of monthly newsletter subscribers did not. Based on the number of homepage views, you decide the campaign was a success when really it generated zero leads.
- Remedy: proactively and clearly frame any data analysis variables and KPIs prior to engaging in a data review. If the metric you use to measure the success of a lead generation campaign is newsletter subscribers, there is no need to review the number of homepage visits. Be sure to focus on the data variable that answers your question or solves your problem and not on irrelevant data.
4) Truncating an Axes: When creating a graph to start interpreting the results of your analysis, it is important to keep the axes truthful and avoid generating misleading visualizations. Starting the axes in a value that doesn’t portray the actual truth about the data can lead to false conclusions.
- Digital age example: In the image below, we can see a graph from Fox News in which the Y-axes start at 34%, making it seem that the difference between 35% and 39.6% is way higher than it actually is. This could lead to a misinterpretation of the tax rate changes.
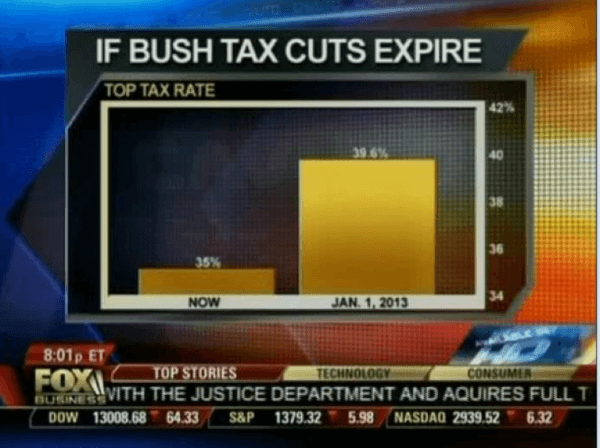
* Source : www.venngage.com *
- Remedy: Be careful with how your data is visualized. Be respectful and realistic with axes to avoid misinterpretation of your data. See below how the Fox News chart looks when using the correct axis values. This chart was created with datapine's modern online data visualization tool.
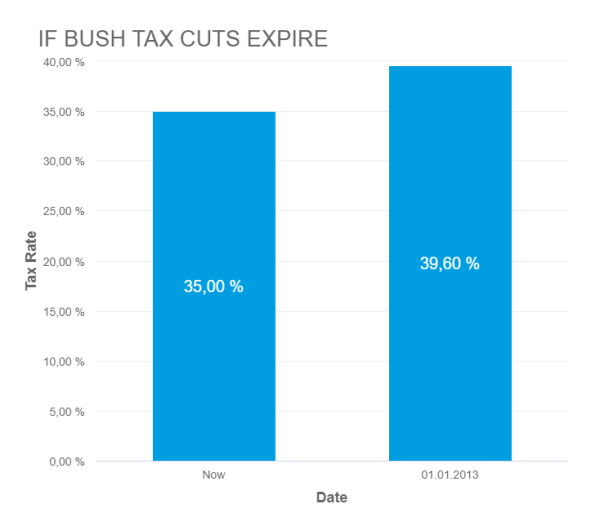
5) (Small) sample size: Another common problem is using a small sample size. Logically, the bigger the sample size, the more accurate and reliable the results. However, this also depends on the size of the effect of the study. For example, the sample size in a survey about the quality of education will not be the same as for one about people doing outdoor sports in a specific area.
- Digital age example: Imagine you ask 30 people a question, and 29 answer “yes,” resulting in 95% of the total. Now imagine you ask the same question to 1000, and 950 of them answer “yes,” which is again 95%. While these percentages might look the same, they certainly do not mean the same thing, as a 30-person sample size is not a significant number to establish a truthful conclusion.
- Remedy: Researchers say that in order to determine the correct sample size to get truthful and meaningful results, it is necessary to define a margin of error that will represent the maximum amount they want the results to deviate from the statistical mean. Paired with this, they need to define a confidence level that should be between 90 and 99%. With these two values in hand, researchers can calculate an accurate sample size for their studies.
6) Reliability, subjectivity, and generalizability : When performing qualitative analysis, researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations when interpreting the data. In some cases, this type of research can be considered unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that might or might not affect the results. This is paired with the fact that the researcher has a primary role in the interpretation process, meaning he or she decides what is relevant and what is not, and as we know, interpretations can be very subjective.
Generalizability is also an issue that researchers face when dealing with qualitative analysis. As mentioned in the point about having a small sample size, it is difficult to draw conclusions that are 100% representative because the results might be biased or unrepresentative of a wider population.
While these factors are mostly present in qualitative research, they can also affect the quantitative analysis. For example, when choosing which KPIs to portray and how to portray them, analysts can also be biased and represent them in a way that benefits their analysis.
- Digital age example: Biased questions in a survey are a great example of reliability and subjectivity issues. Imagine you are sending a survey to your clients to see how satisfied they are with your customer service with this question: “How amazing was your experience with our customer service team?”. Here, we can see that this question clearly influences the response of the individual by putting the word “amazing” on it.
- Remedy: A solution to avoid these issues is to keep your research honest and neutral. Keep the wording of the questions as objective as possible. For example: “On a scale of 1-10, how satisfied were you with our customer service team?”. This does not lead the respondent to any specific answer, meaning the results of your survey will be reliable.

Data Interpretation Best Practices & Tips
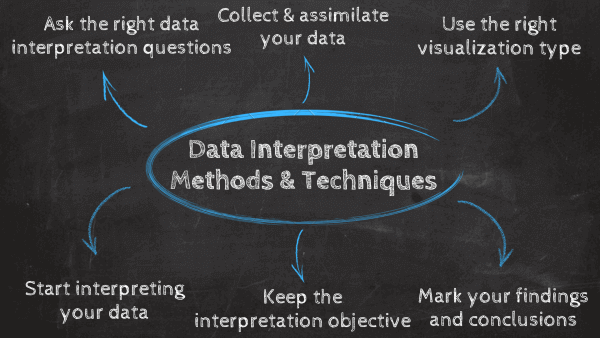
Data analysis and interpretation are critical to developing sound conclusions and making better-informed decisions. As we have seen with this article, there is an art and science to the interpretation of data. To help you with this purpose, we will list a few relevant techniques, methods, and tricks you can implement for a successful data management process.
As mentioned at the beginning of this post, the first step to interpreting data in a successful way is to identify the type of analysis you will perform and apply the methods respectively. Clearly differentiate between qualitative (observe, document, and interview notice, collect and think about things) and quantitative analysis (you lead research with a lot of numerical data to be analyzed through various statistical methods).
1) Ask the right data interpretation questions
The first data interpretation technique is to define a clear baseline for your work. This can be done by answering some critical questions that will serve as a useful guideline to start. Some of them include: what are the goals and objectives of my analysis? What type of data interpretation method will I use? Who will use this data in the future? And most importantly, what general question am I trying to answer?
Once all this information has been defined, you will be ready for the next step: collecting your data.
2) Collect and assimilate your data
Now that a clear baseline has been established, it is time to collect the information you will use. Always remember that your methods for data collection will vary depending on what type of analysis method you use, which can be qualitative or quantitative. Based on that, relying on professional online data analysis tools to facilitate the process is a great practice in this regard, as manually collecting and assessing raw data is not only very time-consuming and expensive but is also at risk of errors and subjectivity.
Once your data is collected, you need to carefully assess it to understand if the quality is appropriate to be used during a study. This means, is the sample size big enough? Were the procedures used to collect the data implemented correctly? Is the date range from the data correct? If coming from an external source, is it a trusted and objective one?
With all the needed information in hand, you are ready to start the interpretation process, but first, you need to visualize your data.
3) Use the right data visualization type
Data visualizations such as business graphs , charts, and tables are fundamental to successfully interpreting data. This is because data visualization via interactive charts and graphs makes the information more understandable and accessible. As you might be aware, there are different types of visualizations you can use, but not all of them are suitable for any analysis purpose. Using the wrong graph can lead to misinterpretation of your data, so it’s very important to carefully pick the right visual for it. Let’s look at some use cases of common data visualizations.
- Bar chart: One of the most used chart types, the bar chart uses rectangular bars to show the relationship between 2 or more variables. There are different types of bar charts for different interpretations, including the horizontal bar chart, column bar chart, and stacked bar chart.
- Line chart: Most commonly used to show trends, acceleration or decelerations, and volatility, the line chart aims to show how data changes over a period of time, for example, sales over a year. A few tips to keep this chart ready for interpretation are not using many variables that can overcrowd the graph and keeping your axis scale close to the highest data point to avoid making the information hard to read.
- Pie chart: Although it doesn’t do a lot in terms of analysis due to its uncomplex nature, pie charts are widely used to show the proportional composition of a variable. Visually speaking, showing a percentage in a bar chart is way more complicated than showing it in a pie chart. However, this also depends on the number of variables you are comparing. If your pie chart needs to be divided into 10 portions, then it is better to use a bar chart instead.
- Tables: While they are not a specific type of chart, tables are widely used when interpreting data. Tables are especially useful when you want to portray data in its raw format. They give you the freedom to easily look up or compare individual values while also displaying grand totals.
With the use of data visualizations becoming more and more critical for businesses’ analytical success, many tools have emerged to help users visualize their data in a cohesive and interactive way. One of the most popular ones is the use of BI dashboards . These visual tools provide a centralized view of various graphs and charts that paint a bigger picture of a topic. We will discuss the power of dashboards for an efficient data interpretation practice in the next portion of this post. If you want to learn more about different types of graphs and charts , take a look at our complete guide on the topic.
4) Start interpreting
After the tedious preparation part, you can start extracting conclusions from your data. As mentioned many times throughout the post, the way you decide to interpret the data will solely depend on the methods you initially decided to use. If you had initial research questions or hypotheses, then you should look for ways to prove their validity. If you are going into the data with no defined hypothesis, then start looking for relationships and patterns that will allow you to extract valuable conclusions from the information.
During the process of interpretation, stay curious and creative, dig into the data, and determine if there are any other critical questions that should be asked. If any new questions arise, you need to assess if you have the necessary information to answer them. Being able to identify if you need to dedicate more time and resources to the research is a very important step. No matter if you are studying customer behaviors or a new cancer treatment, the findings from your analysis may dictate important decisions in the future. Therefore, taking the time to really assess the information is key. For that purpose, data interpretation software proves to be very useful.
5) Keep your interpretation objective
As mentioned above, objectivity is one of the most important data interpretation skills but also one of the hardest. Being the person closest to the investigation, it is easy to become subjective when looking for answers in the data. A good way to stay objective is to show the information related to the study to other people, for example, research partners or even the people who will use your findings once they are done. This can help avoid confirmation bias and any reliability issues with your interpretation.
Remember, using a visualization tool such as a modern dashboard will make the interpretation process way easier and more efficient as the data can be navigated and manipulated in an easy and organized way. And not just that, using a dashboard tool to present your findings to a specific audience will make the information easier to understand and the presentation way more engaging thanks to the visual nature of these tools.
6) Mark your findings and draw conclusions
Findings are the observations you extracted from your data. They are the facts that will help you drive deeper conclusions about your research. For example, findings can be trends and patterns you found during your interpretation process. To put your findings into perspective, you can compare them with other resources that use similar methods and use them as benchmarks.
Reflect on your own thinking and reasoning and be aware of the many pitfalls data analysis and interpretation carry—correlation versus causation, subjective bias, false information, inaccurate data, etc. Once you are comfortable with interpreting the data, you will be ready to develop conclusions, see if your initial questions were answered, and suggest recommendations based on them.
Interpretation of Data: The Use of Dashboards Bridging The Gap
As we have seen, quantitative and qualitative methods are distinct types of data interpretation and analysis. Both offer a varying degree of return on investment (ROI) regarding data investigation, testing, and decision-making. But how do you mix the two and prevent a data disconnect? The answer is professional data dashboards.
For a few years now, dashboards have become invaluable tools to visualize and interpret data. These tools offer a centralized and interactive view of data and provide the perfect environment for exploration and extracting valuable conclusions. They bridge the quantitative and qualitative information gap by unifying all the data in one place with the help of stunning visuals.
Not only that, but these powerful tools offer a large list of benefits, and we will discuss some of them below.
1) Connecting and blending data. With today’s pace of innovation, it is no longer feasible (nor desirable) to have bulk data centrally located. As businesses continue to globalize and borders continue to dissolve, it will become increasingly important for businesses to possess the capability to run diverse data analyses absent the limitations of location. Data dashboards decentralize data without compromising on the necessary speed of thought while blending both quantitative and qualitative data. Whether you want to measure customer trends or organizational performance, you now have the capability to do both without the need for a singular selection.
2) Mobile Data. Related to the notion of “connected and blended data” is that of mobile data. In today’s digital world, employees are spending less time at their desks and simultaneously increasing production. This is made possible because mobile solutions for analytical tools are no longer standalone. Today, mobile analysis applications seamlessly integrate with everyday business tools. In turn, both quantitative and qualitative data are now available on-demand where they’re needed, when they’re needed, and how they’re needed via interactive online dashboards .
3) Visualization. Data dashboards merge the data gap between qualitative and quantitative data interpretation methods through the science of visualization. Dashboard solutions come “out of the box” and are well-equipped to create easy-to-understand data demonstrations. Modern online data visualization tools provide a variety of color and filter patterns, encourage user interaction, and are engineered to help enhance future trend predictability. All of these visual characteristics make for an easy transition among data methods – you only need to find the right types of data visualization to tell your data story the best way possible.
4) Collaboration. Whether in a business environment or a research project, collaboration is key in data interpretation and analysis. Dashboards are online tools that can be easily shared through a password-protected URL or automated email. Through them, users can collaborate and communicate through the data in an efficient way. Eliminating the need for infinite files with lost updates. Tools such as datapine offer real-time updates, meaning your dashboards will update on their own as soon as new information is available.
Examples Of Data Interpretation In Business
To give you an idea of how a dashboard can fulfill the need to bridge quantitative and qualitative analysis and help in understanding how to interpret data in research thanks to visualization, below, we will discuss three valuable examples to put their value into perspective.
1. Customer Satisfaction Dashboard
This market research dashboard brings together both qualitative and quantitative data that are knowledgeably analyzed and visualized in a meaningful way that everyone can understand, thus empowering any viewer to interpret it. Let’s explore it below.
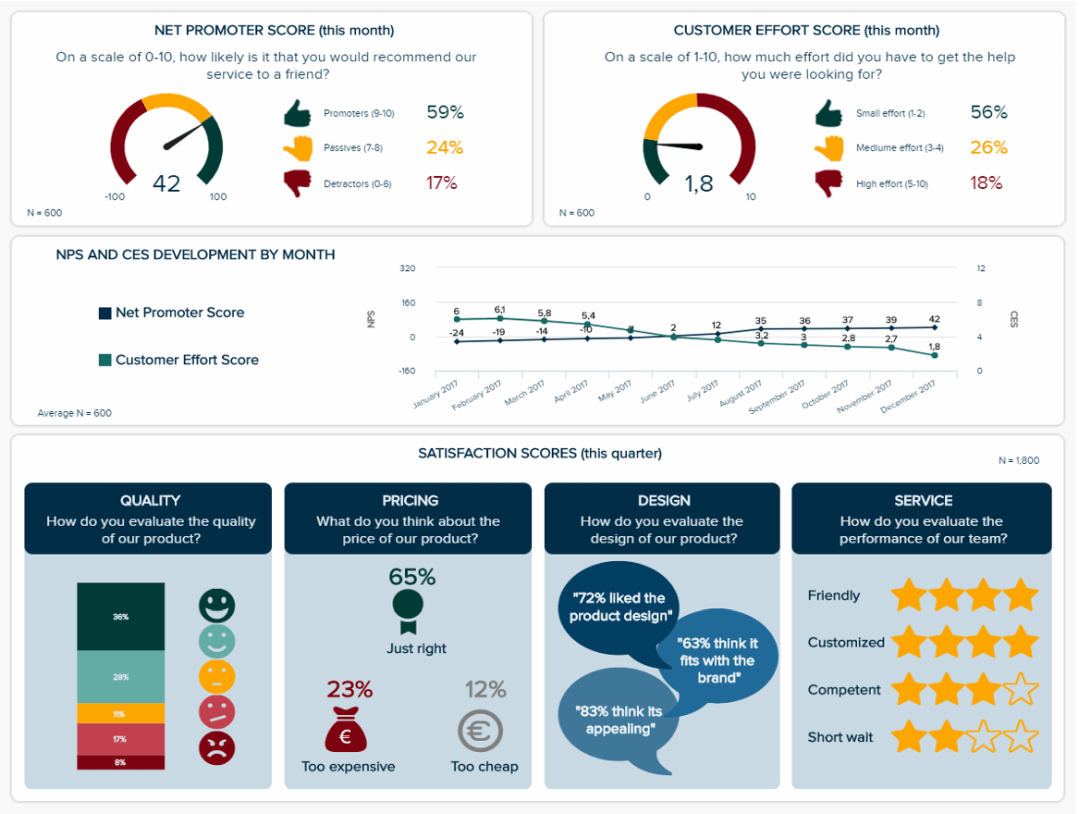
**click to enlarge**
The value of this template lies in its highly visual nature. As mentioned earlier, visuals make the interpretation process way easier and more efficient. Having critical pieces of data represented with colorful and interactive icons and graphs makes it possible to uncover insights at a glance. For example, the colors green, yellow, and red on the charts for the NPS and the customer effort score allow us to conclude that most respondents are satisfied with this brand with a short glance. A further dive into the line chart below can help us dive deeper into this conclusion, as we can see both metrics developed positively in the past 6 months.
The bottom part of the template provides visually stunning representations of different satisfaction scores for quality, pricing, design, and service. By looking at these, we can conclude that, overall, customers are satisfied with this company in most areas.
2. Brand Analysis Dashboard
Next, in our list of data interpretation examples, we have a template that shows the answers to a survey on awareness for Brand D. The sample size is listed on top to get a perspective of the data, which is represented using interactive charts and graphs.
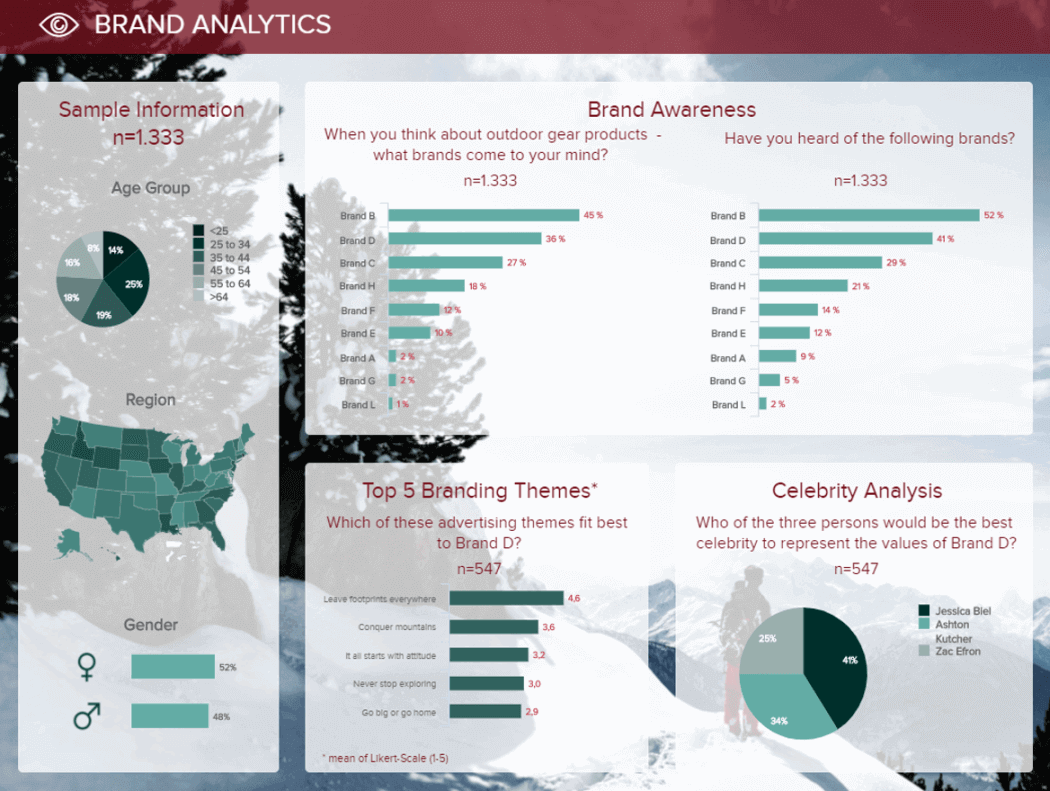
When interpreting information, context is key to understanding it correctly. For that reason, the dashboard starts by offering insights into the demographics of the surveyed audience. In general, we can see ages and gender are diverse. Therefore, we can conclude these brands are not targeting customers from a specified demographic, an important aspect to put the surveyed answers into perspective.
Looking at the awareness portion, we can see that brand B is the most popular one, with brand D coming second on both questions. This means brand D is not doing wrong, but there is still room for improvement compared to brand B. To see where brand D could improve, the researcher could go into the bottom part of the dashboard and consult the answers for branding themes and celebrity analysis. These are important as they give clear insight into what people and messages the audience associates with brand D. This is an opportunity to exploit these topics in different ways and achieve growth and success.
3. Product Innovation Dashboard
Our third and last dashboard example shows the answers to a survey on product innovation for a technology company. Just like the previous templates, the interactive and visual nature of the dashboard makes it the perfect tool to interpret data efficiently and effectively.
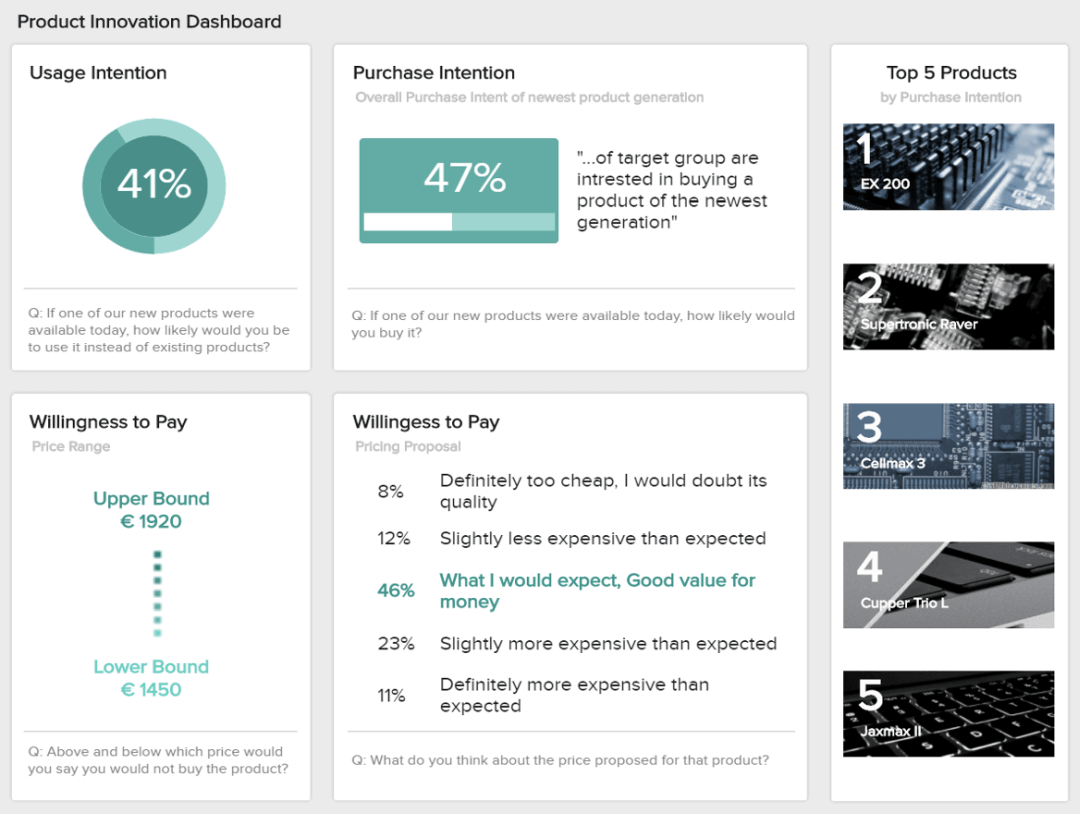
Starting from right to left, we first get a list of the top 5 products by purchase intention. This information lets us understand if the product being evaluated resembles what the audience already intends to purchase. It is a great starting point to see how customers would respond to the new product. This information can be complemented with other key metrics displayed in the dashboard. For example, the usage and purchase intention track how the market would receive the product and if they would purchase it, respectively. Interpreting these values as positive or negative will depend on the company and its expectations regarding the survey.
Complementing these metrics, we have the willingness to pay. Arguably, one of the most important metrics to define pricing strategies. Here, we can see that most respondents think the suggested price is a good value for money. Therefore, we can interpret that the product would sell for that price.
To see more data analysis and interpretation examples for different industries and functions, visit our library of business dashboards .
To Conclude…
As we reach the end of this insightful post about data interpretation and analysis, we hope you have a clear understanding of the topic. We've covered the definition and given some examples and methods to perform a successful interpretation process.
The importance of data interpretation is undeniable. Dashboards not only bridge the information gap between traditional data interpretation methods and technology, but they can help remedy and prevent the major pitfalls of the process. As a digital age solution, they combine the best of the past and the present to allow for informed decision-making with maximum data interpretation ROI.
To start visualizing your insights in a meaningful and actionable way, test our online reporting software for free with our 14-day trial !
10 Real World Data Science Case Studies Projects with Example
Top 10 Data Science Case Studies Projects with Examples and Solutions in Python to inspire your data science learning in 2023.

BelData science has been a trending buzzword in recent times. With wide applications in various sectors like healthcare , education, retail, transportation, media, and banking -data science applications are at the core of pretty much every industry out there. The possibilities are endless: analysis of frauds in the finance sector or the personalization of recommendations on eCommerce businesses. We have developed ten exciting data science case studies to explain how data science is leveraged across various industries to make smarter decisions and develop innovative personalized products tailored to specific customers.

Walmart Sales Forecasting Data Science Project
Downloadable solution code | Explanatory videos | Tech Support
Table of Contents
Data science case studies in retail , data science case study examples in entertainment industry , data analytics case study examples in travel industry , case studies for data analytics in social media , real world data science projects in healthcare, data analytics case studies in oil and gas, what is a case study in data science, how do you prepare a data science case study, 10 most interesting data science case studies with examples.

So, without much ado, let's get started with data science business case studies !
With humble beginnings as a simple discount retailer, today, Walmart operates in 10,500 stores and clubs in 24 countries and eCommerce websites, employing around 2.2 million people around the globe. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2021, Walmart's total revenue was $559 billion showing a growth of $35 billion with the expansion of the eCommerce sector. Walmart is a data-driven company that works on the principle of 'Everyday low cost' for its consumers. To achieve this goal, they heavily depend on the advances of their data science and analytics department for research and development, also known as Walmart Labs. Walmart is home to the world's largest private cloud, which can manage 2.5 petabytes of data every hour! To analyze this humongous amount of data, Walmart has created 'Data Café,' a state-of-the-art analytics hub located within its Bentonville, Arkansas headquarters. The Walmart Labs team heavily invests in building and managing technologies like cloud, data, DevOps , infrastructure, and security.

Walmart is experiencing massive digital growth as the world's largest retailer . Walmart has been leveraging Big data and advances in data science to build solutions to enhance, optimize and customize the shopping experience and serve their customers in a better way. At Walmart Labs, data scientists are focused on creating data-driven solutions that power the efficiency and effectiveness of complex supply chain management processes. Here are some of the applications of data science at Walmart:
i) Personalized Customer Shopping Experience
Walmart analyses customer preferences and shopping patterns to optimize the stocking and displaying of merchandise in their stores. Analysis of Big data also helps them understand new item sales, make decisions on discontinuing products, and the performance of brands.
ii) Order Sourcing and On-Time Delivery Promise
Millions of customers view items on Walmart.com, and Walmart provides each customer a real-time estimated delivery date for the items purchased. Walmart runs a backend algorithm that estimates this based on the distance between the customer and the fulfillment center, inventory levels, and shipping methods available. The supply chain management system determines the optimum fulfillment center based on distance and inventory levels for every order. It also has to decide on the shipping method to minimize transportation costs while meeting the promised delivery date.
Here's what valued users are saying about ProjectPro

Director Data Analytics at EY / EY Tech

Tech Leader | Stanford / Yale University
Not sure what you are looking for?
iii) Packing Optimization
Also known as Box recommendation is a daily occurrence in the shipping of items in retail and eCommerce business. When items of an order or multiple orders for the same customer are ready for packing, Walmart has developed a recommender system that picks the best-sized box which holds all the ordered items with the least in-box space wastage within a fixed amount of time. This Bin Packing problem is a classic NP-Hard problem familiar to data scientists .
Whenever items of an order or multiple orders placed by the same customer are picked from the shelf and are ready for packing, the box recommendation system determines the best-sized box to hold all the ordered items with a minimum of in-box space wasted. This problem is known as the Bin Packing Problem, another classic NP-Hard problem familiar to data scientists.
Here is a link to a sales prediction data science case study to help you understand the applications of Data Science in the real world. Walmart Sales Forecasting Project uses historical sales data for 45 Walmart stores located in different regions. Each store contains many departments, and you must build a model to project the sales for each department in each store. This data science case study aims to create a predictive model to predict the sales of each product. You can also try your hands-on Inventory Demand Forecasting Data Science Project to develop a machine learning model to forecast inventory demand accurately based on historical sales data.
Get Closer To Your Dream of Becoming a Data Scientist with 70+ Solved End-to-End ML Projects
Amazon is an American multinational technology-based company based in Seattle, USA. It started as an online bookseller, but today it focuses on eCommerce, cloud computing , digital streaming, and artificial intelligence . It hosts an estimate of 1,000,000,000 gigabytes of data across more than 1,400,000 servers. Through its constant innovation in data science and big data Amazon is always ahead in understanding its customers. Here are a few data analytics case study examples at Amazon:
i) Recommendation Systems
Data science models help amazon understand the customers' needs and recommend them to them before the customer searches for a product; this model uses collaborative filtering. Amazon uses 152 million customer purchases data to help users to decide on products to be purchased. The company generates 35% of its annual sales using the Recommendation based systems (RBS) method.
Here is a Recommender System Project to help you build a recommendation system using collaborative filtering.
ii) Retail Price Optimization
Amazon product prices are optimized based on a predictive model that determines the best price so that the users do not refuse to buy it based on price. The model carefully determines the optimal prices considering the customers' likelihood of purchasing the product and thinks the price will affect the customers' future buying patterns. Price for a product is determined according to your activity on the website, competitors' pricing, product availability, item preferences, order history, expected profit margin, and other factors.
Check Out this Retail Price Optimization Project to build a Dynamic Pricing Model.
iii) Fraud Detection
Being a significant eCommerce business, Amazon remains at high risk of retail fraud. As a preemptive measure, the company collects historical and real-time data for every order. It uses Machine learning algorithms to find transactions with a higher probability of being fraudulent. This proactive measure has helped the company restrict clients with an excessive number of returns of products.
You can look at this Credit Card Fraud Detection Project to implement a fraud detection model to classify fraudulent credit card transactions.
New Projects
Let us explore data analytics case study examples in the entertainment indusry.
Ace Your Next Job Interview with Mock Interviews from Experts to Improve Your Skills and Boost Confidence!
Netflix started as a DVD rental service in 1997 and then has expanded into the streaming business. Headquartered in Los Gatos, California, Netflix is the largest content streaming company in the world. Currently, Netflix has over 208 million paid subscribers worldwide, and with thousands of smart devices which are presently streaming supported, Netflix has around 3 billion hours watched every month. The secret to this massive growth and popularity of Netflix is its advanced use of data analytics and recommendation systems to provide personalized and relevant content recommendations to its users. The data is collected over 100 billion events every day. Here are a few examples of data analysis case studies applied at Netflix :
i) Personalized Recommendation System
Netflix uses over 1300 recommendation clusters based on consumer viewing preferences to provide a personalized experience. Some of the data that Netflix collects from its users include Viewing time, platform searches for keywords, Metadata related to content abandonment, such as content pause time, rewind, rewatched. Using this data, Netflix can predict what a viewer is likely to watch and give a personalized watchlist to a user. Some of the algorithms used by the Netflix recommendation system are Personalized video Ranking, Trending now ranker, and the Continue watching now ranker.
ii) Content Development using Data Analytics
Netflix uses data science to analyze the behavior and patterns of its user to recognize themes and categories that the masses prefer to watch. This data is used to produce shows like The umbrella academy, and Orange Is the New Black, and the Queen's Gambit. These shows seem like a huge risk but are significantly based on data analytics using parameters, which assured Netflix that they would succeed with its audience. Data analytics is helping Netflix come up with content that their viewers want to watch even before they know they want to watch it.
iii) Marketing Analytics for Campaigns
Netflix uses data analytics to find the right time to launch shows and ad campaigns to have maximum impact on the target audience. Marketing analytics helps come up with different trailers and thumbnails for other groups of viewers. For example, the House of Cards Season 5 trailer with a giant American flag was launched during the American presidential elections, as it would resonate well with the audience.
Here is a Customer Segmentation Project using association rule mining to understand the primary grouping of customers based on various parameters.
Get FREE Access to Machine Learning Example Codes for Data Cleaning , Data Munging, and Data Visualization
In a world where Purchasing music is a thing of the past and streaming music is a current trend, Spotify has emerged as one of the most popular streaming platforms. With 320 million monthly users, around 4 billion playlists, and approximately 2 million podcasts, Spotify leads the pack among well-known streaming platforms like Apple Music, Wynk, Songza, amazon music, etc. The success of Spotify has mainly depended on data analytics. By analyzing massive volumes of listener data, Spotify provides real-time and personalized services to its listeners. Most of Spotify's revenue comes from paid premium subscriptions. Here are some of the examples of case study on data analytics used by Spotify to provide enhanced services to its listeners:
i) Personalization of Content using Recommendation Systems
Spotify uses Bart or Bayesian Additive Regression Trees to generate music recommendations to its listeners in real-time. Bart ignores any song a user listens to for less than 30 seconds. The model is retrained every day to provide updated recommendations. A new Patent granted to Spotify for an AI application is used to identify a user's musical tastes based on audio signals, gender, age, accent to make better music recommendations.
Spotify creates daily playlists for its listeners, based on the taste profiles called 'Daily Mixes,' which have songs the user has added to their playlists or created by the artists that the user has included in their playlists. It also includes new artists and songs that the user might be unfamiliar with but might improve the playlist. Similar to it is the weekly 'Release Radar' playlists that have newly released artists' songs that the listener follows or has liked before.
ii) Targetted marketing through Customer Segmentation
With user data for enhancing personalized song recommendations, Spotify uses this massive dataset for targeted ad campaigns and personalized service recommendations for its users. Spotify uses ML models to analyze the listener's behavior and group them based on music preferences, age, gender, ethnicity, etc. These insights help them create ad campaigns for a specific target audience. One of their well-known ad campaigns was the meme-inspired ads for potential target customers, which was a huge success globally.
iii) CNN's for Classification of Songs and Audio Tracks
Spotify builds audio models to evaluate the songs and tracks, which helps develop better playlists and recommendations for its users. These allow Spotify to filter new tracks based on their lyrics and rhythms and recommend them to users like similar tracks ( collaborative filtering). Spotify also uses NLP ( Natural language processing) to scan articles and blogs to analyze the words used to describe songs and artists. These analytical insights can help group and identify similar artists and songs and leverage them to build playlists.
Here is a Music Recommender System Project for you to start learning. We have listed another music recommendations dataset for you to use for your projects: Dataset1 . You can use this dataset of Spotify metadata to classify songs based on artists, mood, liveliness. Plot histograms, heatmaps to get a better understanding of the dataset. Use classification algorithms like logistic regression, SVM, and Principal component analysis to generate valuable insights from the dataset.
Explore Categories
Below you will find case studies for data analytics in the travel and tourism industry.
Airbnb was born in 2007 in San Francisco and has since grown to 4 million Hosts and 5.6 million listings worldwide who have welcomed more than 1 billion guest arrivals in almost every country across the globe. Airbnb is active in every country on the planet except for Iran, Sudan, Syria, and North Korea. That is around 97.95% of the world. Using data as a voice of their customers, Airbnb uses the large volume of customer reviews, host inputs to understand trends across communities, rate user experiences, and uses these analytics to make informed decisions to build a better business model. The data scientists at Airbnb are developing exciting new solutions to boost the business and find the best mapping for its customers and hosts. Airbnb data servers serve approximately 10 million requests a day and process around one million search queries. Data is the voice of customers at AirBnB and offers personalized services by creating a perfect match between the guests and hosts for a supreme customer experience.
i) Recommendation Systems and Search Ranking Algorithms
Airbnb helps people find 'local experiences' in a place with the help of search algorithms that make searches and listings precise. Airbnb uses a 'listing quality score' to find homes based on the proximity to the searched location and uses previous guest reviews. Airbnb uses deep neural networks to build models that take the guest's earlier stays into account and area information to find a perfect match. The search algorithms are optimized based on guest and host preferences, rankings, pricing, and availability to understand users’ needs and provide the best match possible.
ii) Natural Language Processing for Review Analysis
Airbnb characterizes data as the voice of its customers. The customer and host reviews give a direct insight into the experience. The star ratings alone cannot be an excellent way to understand it quantitatively. Hence Airbnb uses natural language processing to understand reviews and the sentiments behind them. The NLP models are developed using Convolutional neural networks .
Practice this Sentiment Analysis Project for analyzing product reviews to understand the basic concepts of natural language processing.
iii) Smart Pricing using Predictive Analytics
The Airbnb hosts community uses the service as a supplementary income. The vacation homes and guest houses rented to customers provide for rising local community earnings as Airbnb guests stay 2.4 times longer and spend approximately 2.3 times the money compared to a hotel guest. The profits are a significant positive impact on the local neighborhood community. Airbnb uses predictive analytics to predict the prices of the listings and help the hosts set a competitive and optimal price. The overall profitability of the Airbnb host depends on factors like the time invested by the host and responsiveness to changing demands for different seasons. The factors that impact the real-time smart pricing are the location of the listing, proximity to transport options, season, and amenities available in the neighborhood of the listing.
Here is a Price Prediction Project to help you understand the concept of predictive analysis which is widely common in case studies for data analytics.
Uber is the biggest global taxi service provider. As of December 2018, Uber has 91 million monthly active consumers and 3.8 million drivers. Uber completes 14 million trips each day. Uber uses data analytics and big data-driven technologies to optimize their business processes and provide enhanced customer service. The Data Science team at uber has been exploring futuristic technologies to provide better service constantly. Machine learning and data analytics help Uber make data-driven decisions that enable benefits like ride-sharing, dynamic price surges, better customer support, and demand forecasting. Here are some of the real world data science projects used by uber:
i) Dynamic Pricing for Price Surges and Demand Forecasting
Uber prices change at peak hours based on demand. Uber uses surge pricing to encourage more cab drivers to sign up with the company, to meet the demand from the passengers. When the prices increase, the driver and the passenger are both informed about the surge in price. Uber uses a predictive model for price surging called the 'Geosurge' ( patented). It is based on the demand for the ride and the location.
ii) One-Click Chat
Uber has developed a Machine learning and natural language processing solution called one-click chat or OCC for coordination between drivers and users. This feature anticipates responses for commonly asked questions, making it easy for the drivers to respond to customer messages. Drivers can reply with the clock of just one button. One-Click chat is developed on Uber's machine learning platform Michelangelo to perform NLP on rider chat messages and generate appropriate responses to them.
iii) Customer Retention
Failure to meet the customer demand for cabs could lead to users opting for other services. Uber uses machine learning models to bridge this demand-supply gap. By using prediction models to predict the demand in any location, uber retains its customers. Uber also uses a tier-based reward system, which segments customers into different levels based on usage. The higher level the user achieves, the better are the perks. Uber also provides personalized destination suggestions based on the history of the user and their frequently traveled destinations.
You can take a look at this Python Chatbot Project and build a simple chatbot application to understand better the techniques used for natural language processing. You can also practice the working of a demand forecasting model with this project using time series analysis. You can look at this project which uses time series forecasting and clustering on a dataset containing geospatial data for forecasting customer demand for ola rides.
Explore More Data Science and Machine Learning Projects for Practice. Fast-Track Your Career Transition with ProjectPro
7) LinkedIn
LinkedIn is the largest professional social networking site with nearly 800 million members in more than 200 countries worldwide. Almost 40% of the users access LinkedIn daily, clocking around 1 billion interactions per month. The data science team at LinkedIn works with this massive pool of data to generate insights to build strategies, apply algorithms and statistical inferences to optimize engineering solutions, and help the company achieve its goals. Here are some of the real world data science projects at LinkedIn:
i) LinkedIn Recruiter Implement Search Algorithms and Recommendation Systems
LinkedIn Recruiter helps recruiters build and manage a talent pool to optimize the chances of hiring candidates successfully. This sophisticated product works on search and recommendation engines. The LinkedIn recruiter handles complex queries and filters on a constantly growing large dataset. The results delivered have to be relevant and specific. The initial search model was based on linear regression but was eventually upgraded to Gradient Boosted decision trees to include non-linear correlations in the dataset. In addition to these models, the LinkedIn recruiter also uses the Generalized Linear Mix model to improve the results of prediction problems to give personalized results.
ii) Recommendation Systems Personalized for News Feed
The LinkedIn news feed is the heart and soul of the professional community. A member's newsfeed is a place to discover conversations among connections, career news, posts, suggestions, photos, and videos. Every time a member visits LinkedIn, machine learning algorithms identify the best exchanges to be displayed on the feed by sorting through posts and ranking the most relevant results on top. The algorithms help LinkedIn understand member preferences and help provide personalized news feeds. The algorithms used include logistic regression, gradient boosted decision trees and neural networks for recommendation systems.
iii) CNN's to Detect Inappropriate Content
To provide a professional space where people can trust and express themselves professionally in a safe community has been a critical goal at LinkedIn. LinkedIn has heavily invested in building solutions to detect fake accounts and abusive behavior on their platform. Any form of spam, harassment, inappropriate content is immediately flagged and taken down. These can range from profanity to advertisements for illegal services. LinkedIn uses a Convolutional neural networks based machine learning model. This classifier trains on a training dataset containing accounts labeled as either "inappropriate" or "appropriate." The inappropriate list consists of accounts having content from "blocklisted" phrases or words and a small portion of manually reviewed accounts reported by the user community.
Here is a Text Classification Project to help you understand NLP basics for text classification. You can find a news recommendation system dataset to help you build a personalized news recommender system. You can also use this dataset to build a classifier using logistic regression, Naive Bayes, or Neural networks to classify toxic comments.
Get confident to build end-to-end projects
Access to a curated library of 250+ end-to-end industry projects with solution code, videos and tech support.
Pfizer is a multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in New York, USA. One of the largest pharmaceutical companies globally known for developing a wide range of medicines and vaccines in disciplines like immunology, oncology, cardiology, and neurology. Pfizer became a household name in 2010 when it was the first to have a COVID-19 vaccine with FDA. In early November 2021, The CDC has approved the Pfizer vaccine for kids aged 5 to 11. Pfizer has been using machine learning and artificial intelligence to develop drugs and streamline trials, which played a massive role in developing and deploying the COVID-19 vaccine. Here are a few data analytics case studies by Pfizer :
i) Identifying Patients for Clinical Trials
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are used to streamline and optimize clinical trials to increase their efficiency. Natural language processing and exploratory data analysis of patient records can help identify suitable patients for clinical trials. These can help identify patients with distinct symptoms. These can help examine interactions of potential trial members' specific biomarkers, predict drug interactions and side effects which can help avoid complications. Pfizer's AI implementation helped rapidly identify signals within the noise of millions of data points across their 44,000-candidate COVID-19 clinical trial.
ii) Supply Chain and Manufacturing
Data science and machine learning techniques help pharmaceutical companies better forecast demand for vaccines and drugs and distribute them efficiently. Machine learning models can help identify efficient supply systems by automating and optimizing the production steps. These will help supply drugs customized to small pools of patients in specific gene pools. Pfizer uses Machine learning to predict the maintenance cost of equipment used. Predictive maintenance using AI is the next big step for Pharmaceutical companies to reduce costs.
iii) Drug Development
Computer simulations of proteins, and tests of their interactions, and yield analysis help researchers develop and test drugs more efficiently. In 2016 Watson Health and Pfizer announced a collaboration to utilize IBM Watson for Drug Discovery to help accelerate Pfizer's research in immuno-oncology, an approach to cancer treatment that uses the body's immune system to help fight cancer. Deep learning models have been used recently for bioactivity and synthesis prediction for drugs and vaccines in addition to molecular design. Deep learning has been a revolutionary technique for drug discovery as it factors everything from new applications of medications to possible toxic reactions which can save millions in drug trials.
You can create a Machine learning model to predict molecular activity to help design medicine using this dataset . You may build a CNN or a Deep neural network for this data analyst case study project.
Access Data Science and Machine Learning Project Code Examples
9) Shell Data Analyst Case Study Project
Shell is a global group of energy and petrochemical companies with over 80,000 employees in around 70 countries. Shell uses advanced technologies and innovations to help build a sustainable energy future. Shell is going through a significant transition as the world needs more and cleaner energy solutions to be a clean energy company by 2050. It requires substantial changes in the way in which energy is used. Digital technologies, including AI and Machine Learning, play an essential role in this transformation. These include efficient exploration and energy production, more reliable manufacturing, more nimble trading, and a personalized customer experience. Using AI in various phases of the organization will help achieve this goal and stay competitive in the market. Here are a few data analytics case studies in the petrochemical industry:
i) Precision Drilling
Shell is involved in the processing mining oil and gas supply, ranging from mining hydrocarbons to refining the fuel to retailing them to customers. Recently Shell has included reinforcement learning to control the drilling equipment used in mining. Reinforcement learning works on a reward-based system based on the outcome of the AI model. The algorithm is designed to guide the drills as they move through the surface, based on the historical data from drilling records. It includes information such as the size of drill bits, temperatures, pressures, and knowledge of the seismic activity. This model helps the human operator understand the environment better, leading to better and faster results will minor damage to machinery used.
ii) Efficient Charging Terminals
Due to climate changes, governments have encouraged people to switch to electric vehicles to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. However, the lack of public charging terminals has deterred people from switching to electric cars. Shell uses AI to monitor and predict the demand for terminals to provide efficient supply. Multiple vehicles charging from a single terminal may create a considerable grid load, and predictions on demand can help make this process more efficient.
iii) Monitoring Service and Charging Stations
Another Shell initiative trialed in Thailand and Singapore is the use of computer vision cameras, which can think and understand to watch out for potentially hazardous activities like lighting cigarettes in the vicinity of the pumps while refueling. The model is built to process the content of the captured images and label and classify it. The algorithm can then alert the staff and hence reduce the risk of fires. You can further train the model to detect rash driving or thefts in the future.
Here is a project to help you understand multiclass image classification. You can use the Hourly Energy Consumption Dataset to build an energy consumption prediction model. You can use time series with XGBoost to develop your model.
10) Zomato Case Study on Data Analytics
Zomato was founded in 2010 and is currently one of the most well-known food tech companies. Zomato offers services like restaurant discovery, home delivery, online table reservation, online payments for dining, etc. Zomato partners with restaurants to provide tools to acquire more customers while also providing delivery services and easy procurement of ingredients and kitchen supplies. Currently, Zomato has over 2 lakh restaurant partners and around 1 lakh delivery partners. Zomato has closed over ten crore delivery orders as of date. Zomato uses ML and AI to boost their business growth, with the massive amount of data collected over the years from food orders and user consumption patterns. Here are a few examples of data analyst case study project developed by the data scientists at Zomato:
i) Personalized Recommendation System for Homepage
Zomato uses data analytics to create personalized homepages for its users. Zomato uses data science to provide order personalization, like giving recommendations to the customers for specific cuisines, locations, prices, brands, etc. Restaurant recommendations are made based on a customer's past purchases, browsing history, and what other similar customers in the vicinity are ordering. This personalized recommendation system has led to a 15% improvement in order conversions and click-through rates for Zomato.
You can use the Restaurant Recommendation Dataset to build a restaurant recommendation system to predict what restaurants customers are most likely to order from, given the customer location, restaurant information, and customer order history.
ii) Analyzing Customer Sentiment
Zomato uses Natural language processing and Machine learning to understand customer sentiments using social media posts and customer reviews. These help the company gauge the inclination of its customer base towards the brand. Deep learning models analyze the sentiments of various brand mentions on social networking sites like Twitter, Instagram, Linked In, and Facebook. These analytics give insights to the company, which helps build the brand and understand the target audience.
iii) Predicting Food Preparation Time (FPT)
Food delivery time is an essential variable in the estimated delivery time of the order placed by the customer using Zomato. The food preparation time depends on numerous factors like the number of dishes ordered, time of the day, footfall in the restaurant, day of the week, etc. Accurate prediction of the food preparation time can help make a better prediction of the Estimated delivery time, which will help delivery partners less likely to breach it. Zomato uses a Bidirectional LSTM-based deep learning model that considers all these features and provides food preparation time for each order in real-time.
Data scientists are companies' secret weapons when analyzing customer sentiments and behavior and leveraging it to drive conversion, loyalty, and profits. These 10 data science case studies projects with examples and solutions show you how various organizations use data science technologies to succeed and be at the top of their field! To summarize, Data Science has not only accelerated the performance of companies but has also made it possible to manage & sustain their performance with ease.
FAQs on Data Analysis Case Studies
A case study in data science is an in-depth analysis of a real-world problem using data-driven approaches. It involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to extract insights and solve challenges, offering practical insights into how data science techniques can address complex issues across various industries.
To create a data science case study, identify a relevant problem, define objectives, and gather suitable data. Clean and preprocess data, perform exploratory data analysis, and apply appropriate algorithms for analysis. Summarize findings, visualize results, and provide actionable recommendations, showcasing the problem-solving potential of data science techniques.

About the Author

ProjectPro is the only online platform designed to help professionals gain practical, hands-on experience in big data, data engineering, data science, and machine learning related technologies. Having over 270+ reusable project templates in data science and big data with step-by-step walkthroughs,
© 2024
© 2024 Iconiq Inc.
Privacy policy
User policy
Write for ProjectPro

Data Analytics Case Study: Complete Guide in 2024
What are data analytics case study interviews.
When you’re trying to land a data analyst job, the last thing to stand in your way is the data analytics case study interview.
One reason they’re so challenging is that case studies don’t typically have a right or wrong answer.
Instead, case study interviews require you to come up with a hypothesis for an analytics question and then produce data to support or validate your hypothesis. In other words, it’s not just about your technical skills; you’re also being tested on creative problem-solving and your ability to communicate with stakeholders.
This article provides an overview of how to answer data analytics case study interview questions. You can find an in-depth course in the data analytics learning path .
How to Solve Data Analytics Case Questions
Check out our video below on How to solve a Data Analytics case study problem:
With data analyst case questions, you will need to answer two key questions:
- What metrics should I propose?
- How do I write a SQL query to get the metrics I need?
In short, to ace a data analytics case interview, you not only need to brush up on case questions, but you also should be adept at writing all types of SQL queries and have strong data sense.
These questions are especially challenging to answer if you don’t have a framework or know how to answer them. To help you prepare, we created this step-by-step guide to answering data analytics case questions.
We show you how to use a framework to answer case questions, provide example analytics questions, and help you understand the difference between analytics case studies and product metrics case studies .
Data Analytics Cases vs Product Metrics Questions
Product case questions sometimes get lumped in with data analytics cases.
Ultimately, the type of case question you are asked will depend on the role. For example, product analysts will likely face more product-oriented questions.
Product metrics cases tend to focus on a hypothetical situation. You might be asked to:
Investigate Metrics - One of the most common types will ask you to investigate a metric, usually one that’s going up or down. For example, “Why are Facebook friend requests falling by 10 percent?”
Measure Product/Feature Success - A lot of analytics cases revolve around the measurement of product success and feature changes. For example, “We want to add X feature to product Y. What metrics would you track to make sure that’s a good idea?”
With product data cases, the key difference is that you may or may not be required to write the SQL query to find the metric.
Instead, these interviews are more theoretical and are designed to assess your product sense and ability to think about analytics problems from a product perspective. Product metrics questions may also show up in the data analyst interview , but likely only for product data analyst roles.

TRY CHECKING: Marketing Analytics Case Study Guide
Data Analytics Case Study Question: Sample Solution
Let’s start with an example data analytics case question :
You’re given a table that represents search results from searches on Facebook. The query column is the search term, the position column represents each position the search result came in, and the rating column represents the human rating from 1 to 5, where 5 is high relevance, and 1 is low relevance.
Each row in the search_events table represents a single search, with the has_clicked column representing if a user clicked on a result or not. We have a hypothesis that the CTR is dependent on the search result rating.
Write a query to return data to support or disprove this hypothesis.
search_results table:
search_events table
Step 1: With Data Analytics Case Studies, Start by Making Assumptions
Hint: Start by making assumptions and thinking out loud. With this question, focus on coming up with a metric to support the hypothesis. If the question is unclear or if you think you need more information, be sure to ask.
Answer. The hypothesis is that CTR is dependent on search result rating. Therefore, we want to focus on the CTR metric, and we can assume:
- If CTR is high when search result ratings are high, and CTR is low when the search result ratings are low, then the hypothesis is correct.
- If CTR is low when the search ratings are high, or there is no proven correlation between the two, then our hypothesis is not proven.
Step 2: Provide a Solution for the Case Question
Hint: Walk the interviewer through your reasoning. Talking about the decisions you make and why you’re making them shows off your problem-solving approach.
Answer. One way we can investigate the hypothesis is to look at the results split into different search rating buckets. For example, if we measure the CTR for results rated at 1, then those rated at 2, and so on, we can identify if an increase in rating is correlated with an increase in CTR.
First, I’d write a query to get the number of results for each query in each bucket. We want to look at the distribution of results that are less than a rating threshold, which will help us see the relationship between search rating and CTR.
This CTE aggregates the number of results that are less than a certain rating threshold. Later, we can use this to see the percentage that are in each bucket. If we re-join to the search_events table, we can calculate the CTR by then grouping by each bucket.
Step 3: Use Analysis to Backup Your Solution
Hint: Be prepared to justify your solution. Interviewers will follow up with questions about your reasoning, and ask why you make certain assumptions.
Answer. By using the CASE WHEN statement, I calculated each ratings bucket by checking to see if all the search results were less than 1, 2, or 3 by subtracting the total from the number within the bucket and seeing if it equates to 0.
I did that to get away from averages in our bucketing system. Outliers would make it more difficult to measure the effect of bad ratings. For example, if a query had a 1 rating and another had a 5 rating, that would equate to an average of 3. Whereas in my solution, a query with all of the results under 1, 2, or 3 lets us know that it actually has bad ratings.
Product Data Case Question: Sample Solution

In product metrics interviews, you’ll likely be asked about analytics, but the discussion will be more theoretical. You’ll propose a solution to a problem, and supply the metrics you’ll use to investigate or solve it. You may or may not be required to write a SQL query to get those metrics.
We’ll start with an example product metrics case study question :
Let’s say you work for a social media company that has just done a launch in a new city. Looking at weekly metrics, you see a slow decrease in the average number of comments per user from January to March in this city.
The company has been consistently growing new users in the city from January to March.
What are some reasons why the average number of comments per user would be decreasing and what metrics would you look into?
Step 1: Ask Clarifying Questions Specific to the Case
Hint: This question is very vague. It’s all hypothetical, so we don’t know very much about users, what the product is, and how people might be interacting. Be sure you ask questions upfront about the product.
Answer: Before I jump into an answer, I’d like to ask a few questions:
- Who uses this social network? How do they interact with each other?
- Has there been any performance issues that might be causing the problem?
- What are the goals of this particular launch?
- Has there been any changes to the comment features in recent weeks?
For the sake of this example, let’s say we learn that it’s a social network similar to Facebook with a young audience, and the goals of the launch are to grow the user base. Also, there have been no performance issues and the commenting feature hasn’t been changed since launch.
Step 2: Use the Case Question to Make Assumptions
Hint: Look for clues in the question. For example, this case gives you a metric, “average number of comments per user.” Consider if the clue might be helpful in your solution. But be careful, sometimes questions are designed to throw you off track.
Answer: From the question, we can hypothesize a little bit. For example, we know that user count is increasing linearly. That means two things:
- The decreasing comments issue isn’t a result of a declining user base.
- The cause isn’t loss of platform.
We can also model out the data to help us get a better picture of the average number of comments per user metric:
- January: 10000 users, 30000 comments, 3 comments/user
- February: 20000 users, 50000 comments, 2.5 comments/user
- March: 30000 users, 60000 comments, 2 comments/user
One thing to note: Although this is an interesting metric, I’m not sure if it will help us solve this question. For one, average comments per user doesn’t account for churn. We might assume that during the three-month period users are churning off the platform. Let’s say the churn rate is 25% in January, 20% in February and 15% in March.
Step 3: Make a Hypothesis About the Data
Hint: Don’t worry too much about making a correct hypothesis. Instead, interviewers want to get a sense of your product initiation and that you’re on the right track. Also, be prepared to measure your hypothesis.
Answer. I would say that average comments per user isn’t a great metric to use, because it doesn’t reveal insights into what’s really causing this issue.
That’s because it doesn’t account for active users, which are the users who are actually commenting. A better metric to investigate would be retained users and monthly active users.
What I suspect is causing the issue is that active users are commenting frequently and are responsible for the increase in comments month-to-month. New users, on the other hand, aren’t as engaged and aren’t commenting as often.
Step 4: Provide Metrics and Data Analysis
Hint: Within your solution, include key metrics that you’d like to investigate that will help you measure success.
Answer: I’d say there are a few ways we could investigate the cause of this problem, but the one I’d be most interested in would be the engagement of monthly active users.
If the growth in comments is coming from active users, that would help us understand how we’re doing at retaining users. Plus, it will also show if new users are less engaged and commenting less frequently.
One way that we could dig into this would be to segment users by their onboarding date, which would help us to visualize engagement and see how engaged some of our longest-retained users are.
If engagement of new users is the issue, that will give us some options in terms of strategies for addressing the problem. For example, we could test new onboarding or commenting features designed to generate engagement.
Step 5: Propose a Solution for the Case Question
Hint: In the majority of cases, your initial assumptions might be incorrect, or the interviewer might throw you a curveball. Be prepared to make new hypotheses or discuss the pitfalls of your analysis.
Answer. If the cause wasn’t due to a lack of engagement among new users, then I’d want to investigate active users. One potential cause would be active users commenting less. In that case, we’d know that our earliest users were churning out, and that engagement among new users was potentially growing.
Again, I think we’d want to focus on user engagement since the onboarding date. That would help us understand if we were seeing higher levels of churn among active users, and we could start to identify some solutions there.
Tip: Use a Framework to Solve Data Analytics Case Questions
Analytics case questions can be challenging, but they’re much more challenging if you don’t use a framework. Without a framework, it’s easier to get lost in your answer, to get stuck, and really lose the confidence of your interviewer. Find helpful frameworks for data analytics questions in our data analytics learning path and our product metrics learning path .
Once you have the framework down, what’s the best way to practice? Mock interviews with our coaches are very effective, as you’ll get feedback and helpful tips as you answer. You can also learn a lot by practicing P2P mock interviews with other Interview Query students. No data analytics background? Check out how to become a data analyst without a degree .
Finally, if you’re looking for sample data analytics case questions and other types of interview questions, see our guide on the top data analyst interview questions .
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
Credit Exploratory Data Analysis Case Study - March - 2022
Coder0071/EDA-Sourabh-Upgrad
Folders and files, repository files navigation.
EDA-Sourabh-S H
Credit Exploratory Data Analysis Case Study - March - 2022 Submitted By: Sourabh S Hubballi Dated: 28/03/2022
Objective's are mentioned Below: 1.0 Problem Statement - I Introduction: This assignment aims to give you an idea of applying EDA in a real business scenario. In this assignment, apart from applying the techniques that you have learnt in the EDA module, you will also develop a basic understanding of risk analytics in banking and financial services and understand how data is used to minimise the risk of losing money while lending to customers. Business Understanding: The loan providing companies find it hard to give loans to the people due to their insufficient or non-existent credithistory. Because of that, some consumers use it as their advantage by becoming a defaulter. Suppose you work for a consumer finance company which specialises in lending various types of loans to urban customers. You have to use EDA to analyse the patterns present in the data. This will ensure that the applicants capable of repaying the loan are not rejected. When the company receives a loan application, the company has to decide for loan approval based on the applicant’s profile.Two types of risks are associated with the bank’s decision: If the applicant is likely to repay the loan, then not approving the loan results in a loss of business to the company If the applicant is not likely to repay the loan, i.e. he/she is likely to default, then approving the loan may lead toa financial loss for the company. The data given below contains the information about the loan application at the time of applying for the loan. It contains two types of scenarios: The client with payment difficulties: he/she had late payment more than X days on at least one of the first Y stalments of the loan in our sample, All other cases: All other cases when the payment is paid on time. When a client applies for a loan, there are four types of decisions that could be taken by the client/company):1. Approved: The Company has approved loan Application. Cancelled: The client cancelled the application sometime during approval. Either the client changed her/his mind about the loan or in some cases due to a higher risk of the client he received worse pricing which he did not want. Refused: The company had rejected the loan (because the client does not meet their requirements etc.). Unused offer: Loan has been cancelled by the client but on different stages of the process. In this case study, you will use EDA to understand how consumer attributes and loan attributes influence the tendency of default.
Business Objectives: This case study aims to identify patterns which indicate if a client has difficulty paying their installments which may be used for taking actions such as denying the loan, reducing the amount of loan, lending (to risky applicants) at a higher interest rate, etc.This will ensure that the consumers capable of repaying the loan are not rejected. Identification of such applicants using EDA is the aim of this case study.
In other words, the company wants to understand the driving factors (or driver variables) behind loan default, i.e. the variables which are strong indicators of default.The company can utilise this knowledge for its portfolio and risk assessment. To develop your understanding of the domain, you are advised to independently research a little about risk analytics - understanding the types of variables and their significance should be enough).
Data Understanding: This dataset has 3 files as explained below:
'application_data.csv' contains all the information of the client at the time of application.The data is about whether a client has payment difficulties. 'previous_application.csv' contains information about the client’s previous loan data. It contains the data whether the previous application had been Approved, Cancelled, Refused or Unused offer. columns_description.csv' is data dictionary which describes the meaning of the variables. 2.0 Problem Statement - II: Results Expected by Learners: Present the overall approach of the analysis in a presentation. Mention the problem statement and the analysis approach briefly. Identify the missing data and use appropriate method to deal with it. (Remove columns/or replace it with an appropriate value) Hint: Note that in EDA, since it is not necessary to replace the missing value, but if you have to replace the missing value, what should be the approach. Clearly mention the approach.
Identify if there are outliers in the dataset. Also, mention why do you think it is an outlier. Again, remember that for this exercise, it is not necessary to remove any data points. Identify if there is data imbalance in the data. Find the ratio of data imbalance. Hint: How will you analyse the data in case of data imbalance? You can plot more than one type of plot to analyse the different aspects due to data imbalance. For example, you can choose your own scale for the graphs, i.e. one can plot in terms of percentage or absolute value. Do this analysis for the ‘Target variable’ in the dataset ( clients with payment difficulties and all other cases). Use a mix of univariate and bivariate analysis etc.
Hint: Since there are a lot of columns, you can run your analysis in loops for the appropriate columns and find the insights.
Explain the results of univariate, segmented univariate, bivariate analysis, etc. in business terms. Find the top 10 correlation for the Client with payment difficulties and all other cases (Target variable). Note that you have to find the top correlation by segmenting the data frame w.r.t to the target variable and then find the top correlation for each of the segmented data and find if any insight is there. Say, there are 5+1(target) variables in a dataset: Var1, Var2, Var3, Var4, Var5, Target. And if you have to find top 3 correlation, it can be: Var1 & Var2, Var2 & Var3, Var1 & Var3. Target variable will not feature in this correlation as it is a categorical variable and not a continuous variable which is increasing or decreasing. Include visualisations and summarise the most important results in the presentation. You are free to choose the graphs which explain the numerical/categorical variables. Insights should explain why the variable is important for differentiating the clients with payment difficulties with all other cases.
- Jupyter Notebook 100.0%
4 Case Study Questions for Interviewing Data Analysts at a Startup
A good data analyst is one who has an absolute passion for data, he/she has a strong understanding of the business/product you are running, and will be always seeking meaningful insights to help the team make better decisions.
Jan 22, 2019 . 4 min read
- If you're an aspiring data professionals wanting to learn more about how the underlying data world works, check out: The Analytics Setup Guidebook
- Doing a case study as part of analytics interview? Check out: Nailing An Analytics Interview Case Study: 10 Practical Tips
At Holistics, we understand the value of data in making business decisions as a Business Intelligence (BI) platform, and hiring the right data team is one of the key elements to get you there.
To get hired for a tech product startup, we all know just doing reporting alone won't distinguish a potential data analyst, a good data analyst is one who has an absolute passion for data. He/she has a strong understanding of the business/product you are running, and will be always seeking meaningful insights to help the team make better decisions.
That's the reason why we usually look for these characteristics below when interviewing data analyst candidates:
- Ability to adapt to a new domain quickly
- Ability to work independently to investigate and mine for interesting insights
- Product and business growth Mindset Technical skills
In this article, I'll be sharing with you some of our case studies that reveal the potential of data analyst candidates we've hired in the last few months.
For a list of questions to ask, you can refer to this link: How to interview a data analyst candidate
1. Analyze a Dataset
- Give us top 5–10 interesting insights you could find from this dataset
Give them a dataset, and let them use your tool or any tools they are familiar with to analyze it.
Expectations
- Communication: The first thing they should do is ask the interviewers to clarify the dataset and the problems to be solved, instead of just jumping into answering the question right away.
- Strong industry knowledge, or an indication of how quickly they can adapt to a new domain.
- The insights here should not only be about charts, but also the explanation behind what we should investigate more of, or make decisions on.
Let's take a look at some insights from our data analyst's work exploring an e-commerce dataset.
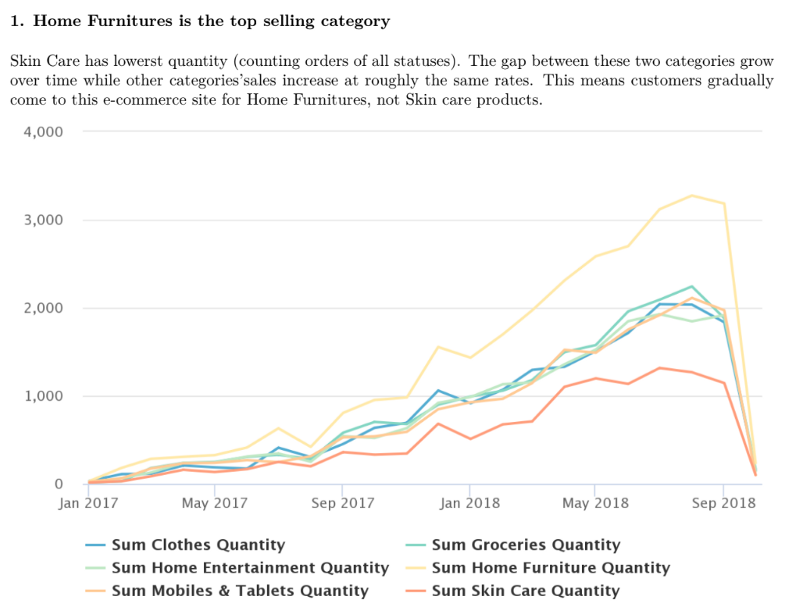
2. Product Mindset
In a product startup, the data analyst must also have the ability to understand the product as well as measure the success of the product.
- How would you improve our feature X (Search/Login/Dashboard…) using data?
- Show effort for independent research, and declaring some assumptions on what makes a feature good/bad.
- Ask/create a user flow for the feature, listing down all the possible steps that users should take to achieve that result. Let them assume they can get all the data they want, and ask what they would measure and how they will make decisions from there.
- Provide data and current insights to understand how often users actually use the feature and assess how they evaluate if it's still worth working on.
3. Business Sense
Data analysts need to be responsible for not only Product, but also Sales, Marketing, Financial analyses and more as well. Hence, they must be able to quickly adapt to any business model or distribution strategy.
- How would you increase our conversion rate?
- How would you know if a customer will upgrade or churn?
- The candidate should ask the interviewer to clarify the information, e.g. How the company defines conversion rate?
- Identify data sources and stages of the funnels, what are the data sources we have and what others we need, how to collect and consolidate the data?
- Ability to extract the data into meaningful insights that can inform business decisions, the insights would differ depending on the business model (B2B, B2C, etc.) e.g. able to list down all the factors that could affect users subscriptions (B2B).
- Able to compare and benchmark performance with industry insights e.g able to tell what is the average conversion rate of e-commerce companies.
4. Metric-driven
- Top 3 metrics to define the success of this product, what, why and how would you choose?
- To answer this question, the candidates need to have basic domain knowledge of the industry or product as well as the understanding of the product's core value propositions.
- A good candidate would also ask for information on company strategy and vision.
- Depending on each product and industry, the key metrics would be different, e.g. Facebook - Daily active users (DAU), Number of users adding 7 friends in the first 10 days; Holistics - Number of reports created and viewed, Number of users invited during the trial period; Uber - Weekly Rides, First ride/passenger …
According to my experience, there are a lot of data analysts who are just familiar with doing reporting from requirements, while talented analysts are eager to understand the data deeply and produce meaningful insights to help their team make better decisions, and they are definitely the players you want to have in your A+ team.
Finding a great data analyst is not easy, technical skill is essential, however, mindset is even more important. Therefore, list down all you need from a data analyst, trust your gut and hiring the right person will be a super advantage for your startup.
What's happening in the BI world?
Join 30k+ people to get insights from BI practitioners around the globe. In your inbox. Every week. Learn more
No spam, ever. We respect your email privacy. Unsubscribe anytime.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case study is unbounded and relies on gathering external information; case analysis is a self-contained subject of analysis. The scope of a case study chosen as a method of research is bounded. However, the researcher is free to gather whatever information and data is necessary to investigate its relevance to understanding the research problem.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case study protocol is a formal document capturing the entire set of procedures involved in the collection of empirical material . It extends direction to researchers for gathering evidences, empirical material analysis, and case study reporting . This section includes a step-by-step guide that is used for the execution of the actual study.
Cumulative case study, frequently employed in qualitative research, gathers data from diverse sources multiple times. This assignment serves as a means of data analysis, minimizing the need for redundant investigations. Critical instance case study, discerning the causes and consequences of specific events. It is employed to scrutinize cases of ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a real-life phenomenon or situation. Learn how to write a case study for your social sciences research assignments with this helpful guide from USC Library. Find out how to define the case, select the data sources, analyze the evidence, and report the results.
2 CASE STUDY ASSIGNMENT C ASE S TUDY: D ATA I NTERPRETATIONS A NALYZING D ATA G UIDE Using the information from the case study and graphs/charts documents for Ethan Smith (Case Study: Data Interpretations), analyze the data and write your answers directly in this document. The candidate will answer the following questions in complete sentences/paragraphs to demonstrate an understanding of data ...
A case study analysis requires you to investigate a business problem, examine the alternative solutions, and propose the most effective solution using supporting evidence. ... but these may differ depending on your assignment directions or your specific case study: Introduction. Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate ...
propose an approach to the analysis of case study data by logically linking the data to a series of propositions and then interpreting the subsequent information. Like the Yin (1994) strategy, the Miles and Huberman (1994) process of analysis of case study data, although quite detailed, may still be insufficient to guide the novice researcher.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
Data sources: The research example used is a multiple case study that explored the role of the clinical skills laboratory in preparing students for the real world of practice. Data analysis was conducted using a framework guided by the four stages of analysis outlined by Morse ( 1994 ): comprehending, synthesising, theorising and recontextualising.
7) The Use of Dashboards For Data Interpretation. 8) Business Data Interpretation Examples. Data analysis and interpretation have now taken center stage with the advent of the digital age… and the sheer amount of data can be frightening. In fact, a Digital Universe study found that the total data supply in 2012 was 2.8 trillion gigabytes!
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
A case study in data science is an in-depth analysis of a real-world problem using data-driven approaches. It involves collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to extract insights and solve challenges, offering practical insights into how data science techniques can address complex issues across various industries.
A case study is a detailed analysis of a specific topic in a real-world context. It can pertain to a person, place, event, group, or phenomenon, among others. The purpose is to derive generalizations about the topic, as well as other insights. Case studies find application in academic, business, political, or scientific research.
EDUC 622-B03: CASE STUDY PART I Page 2 of 7 2 C ASE S TUDY: D ATA I NTERPRETATIONS - A NALYZING D ATA G UIDE Using the information from the case study and graphs/charts documents for Ethan Smith (Case Study Part 1), analyze the data and write your answers directly in this document. The candidate will answer the following questions in complete sentences/paragraphs to demonstrate an ...
Step 1: With Data Analytics Case Studies, Start by Making Assumptions. Hint: Start by making assumptions and thinking out loud. With this question, focus on coming up with a metric to support the hypothesis. If the question is unclear or if you think you need more information, be sure to ask.
EDUC 622 CASE STUDY PART 1 - ANALYZING DATA GUIDE Using the information from the case study and graphs/charts documents. ... Submit this assignment by 11:59 p.m. (ET) on Sunday of Module/Week 4. ... Analysis (Vowels, Consonants, Beginning, Middle, ...
Feb 21, 2021. --. 1. Solving a Data Science case study means analyzing and solving a problem statement intensively. Solving case studies will help you show unique and amazing data science use ...
Advantages of Using Case Studies for Data Analysts. Problem-solving (PS) - PS plays an important role for DS ( data scientists )/DA (data analyst)/BA (business analyst). The magnitude of efforts used on PS can vary across organizations and projects, with some teams working mainly on PS about 80% of the time, while others work 20% of the time.
RISK FACTORS COMPARISON IN MEN AND WOMEN (INTERPRETATION) • Based off the data given, I was able to calculate differences between men and women when looking at the different characteristics used in the study. The data collected shows that the mean age for both men and women during the study is around 50 years of age. The Systolic blood pressure is very close; however, it is higher among women.
Credit Exploratory Data Analysis Case Study - March - 2022 Submitted By: Sourabh S Hubballi Dated: 28/03/2022. Objective's are mentioned Below: 1.0 Problem Statement - I Introduction: This assignment aims to give you an idea of applying EDA in a real business scenario. In this assignment, apart from applying the techniques that you have learnt ...
Let's take a look at some insights from our data analyst's work exploring an e-commerce dataset. 2. Product Mindset. In a product startup, the data analyst must also have the ability to understand the product as well as measure the success of the product.